Fortinet FortiGate FortiGate-1000A, FortiGate FortiGate-1000AFA2, FortiGate 1000A, FortiGate 1000AFA2 Administration Manual
Page 1

FortiGate 1000A
FortiGate 1000AFA2
Administration Guide
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide
Version 2.80 MR11
15 November 2005
01-28011-0254-20051115
CONSOLE
USB
A2A1
Page 2

© Copyright 2005 Fortinet Inc. All rights reserved.
No part of this publication including text, examples, diagrams or illustrations may be reproduced,
transmitted, or translated in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, manual, optical or
otherwise, for any purpose, without prior written permission of Fortinet Inc.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide
Version 2.80 MR11
15 November 2005
01-28011-0254-20051115
Trademarks
Products mentioned in this document are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
holders.
Regulatory Compliance
FCC Class A Part 15 CSA/CUS
CAUTION: RISK OF EXPLOSION IF BATTERY IS REPLACED BY AN INCORRECT TYPE.
DISPOSE OF USED BATTERIES ACCORDING TO THE INSTRUCTIONS.
For technical support, please visit http://www.fortinet.com.
Send information about errors or omissions in this document or any Fortinet technical documentation to
techdoc@fortinet.com.
Page 3

Table of Contents
Introduction.......................................................................................................... 13
About FortiGate Antivirus Firewalls................................................................................... 13
Antivirus protection ....................................................................................................... 14
Web content filtering ..................................................................................................... 15
Spam filtering ................................................................................................................ 15
Firewall.......................................................................................................................... 16
VLANs and virtual domains........................................................................................... 17
Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)................................................................................ 17
VPN............................................................................................................................... 17
High availability ............................................................................................................. 18
Secure installation, configuration, and management .................................................... 19
About the FortiOS International and US Domestic distributions ....................................... 20
US Domestic distribution changes ................................................................................ 20
Document conventions ..................................................................................................... 22
Fortinet documentation .................................................................................................... 23
Fortinet Knowledge Center .......................................................................................... 24
Comments on Fortinet technical documentation .......................................................... 24
Customer service and technical support........................................................................... 24
Contents
Web-based manager............................................................................................ 25
Button bar features ........................................................................................................... 26
Contact Customer Support ........................................................................................... 26
Online Help ................................................................................................................... 27
Easy Setup Wizard ....................................................................................................... 27
Console Access ............................................................................................................ 28
Logout ........................................................................................................................... 28
Web-based manager pages.............................................................................................. 29
Web-based manager menu .......................................................................................... 29
Lists............................................................................................................................... 30
Icons ............................................................................................................................. 30
Status bar...................................................................................................................... 31
Organization of this manual .............................................................................................. 32
System Status ...................................................................................................... 33
Status................................................................................................................................ 33
Viewing system status .................................................................................................. 34
Changing unit information ............................................................................................. 38
Session list........................................................................................................................ 40
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 3
Page 4

Contents
Changing the FortiGate firmware...................................................................................... 41
Upgrading to a new firmware version ........................................................................... 42
Reverting to a previous firmware version...................................................................... 44
Installing firmware images from a system reboot using the CLI ................................... 47
Testing a new firmware image before installing it ......................................................... 50
Installing and using a backup firmware image .............................................................. 52
System Network................................................................................................... 55
Interface............................................................................................................................ 55
Interface settings........................................................................................................... 56
Configuring interfaces ................................................................................................... 62
Zone.................................................................................................................................. 66
Zone settings ................................................................................................................ 67
Management..................................................................................................................... 68
DNS .................................................................................................................................. 69
Routing table (Transparent Mode).................................................................................... 70
Routing table list ........................................................................................................... 70
Transparent mode route settings .................................................................................. 70
VLAN overview ................................................................................................................. 71
FortiGate units and VLANs ........................................................................................... 72
VLANs in NAT/Route mode .............................................................................................. 72
Rules for VLAN IDs....................................................................................................... 72
Rules for VLAN IP addresses ....................................................................................... 72
Adding VLAN subinterfaces .......................................................................................... 73
VLANs in Transparent mode............................................................................................. 74
Rules for VLAN IDs....................................................................................................... 76
Transparent mode virtual domains and VLANs ............................................................ 76
Transparent mode VLAN list......................................................................................... 77
Transparent mode VLAN settings................................................................................. 77
FortiGate IPv6 support...................................................................................................... 79
System DHCP ....................................................................................................... 81
Service.............................................................................................................................. 81
DHCP service settings .................................................................................................. 82
Server ............................................................................................................................... 83
DHCP server settings ................................................................................................... 84
Exclude range................................................................................................................... 85
DHCP exclude range settings....................................................................................... 86
IP/MAC binding................................................................................................................. 86
DHCP IP/MAC binding settings .................................................................................... 87
Dynamic IP........................................................................................................................ 87
System Config...................................................................................................... 89
System time ...................................................................................................................... 89
4 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 5

Options.............................................................................................................................. 90
HA..................................................................................................................................... 92
HA overview.................................................................................................................. 92
HA configuration ........................................................................................................... 95
Configuring an HA cluster ........................................................................................... 101
Managing an HA cluster.............................................................................................. 105
SNMP.............................................................................................................................. 108
Configuring SNMP ...................................................................................................... 108
SNMP community ....................................................................................................... 109
FortiGate MIBs............................................................................................................ 112
FortiGate traps ............................................................................................................ 112
Fortinet MIB fields ....................................................................................................... 114
Replacement messages ................................................................................................. 117
Replacement messages list ........................................................................................ 118
Changing replacement messages .............................................................................. 119
FortiManager................................................................................................................... 120
System Admin .................................................................................................... 123
Contents
Administrators................................................................................................................. 125
Administrators list........................................................................................................ 125
Administrators options ................................................................................................ 125
Access profiles................................................................................................................ 127
Access profile list ........................................................................................................ 127
Access profile options ................................................................................................. 128
System Maintenance ......................................................................................... 129
Backup and restore......................................................................................................... 129
Backing up and Restoring........................................................................................... 130
Update center ................................................................................................................. 132
Updating antivirus and attack definitions .................................................................... 134
Enabling push updates ............................................................................................... 137
Support ........................................................................................................................... 140
Sending a bug report .................................................................................................. 140
Registering a FortiGate unit ........................................................................................ 141
Shutdown........................................................................................................................ 143
System Virtual Domain...................................................................................... 145
Virtual domain properties................................................................................................ 146
Exclusive virtual domain properties ............................................................................ 146
Shared configuration settings ..................................................................................... 147
Administration and management ................................................................................ 148
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 5
Page 6

Contents
Virtual domains ............................................................................................................... 148
Adding a virtual domain .............................................................................................. 149
Selecting a virtual domain........................................................................................... 149
Selecting a management virtual domain..................................................................... 149
Configuring virtual domains ............................................................................................ 150
Adding interfaces, VLAN subinterfaces, and zones to a virtual domain ..................... 150
Configuring routing for a virtual domain ...................................................................... 152
Configuring firewall policies for a virtual domain......................................................... 152
Configuring IPSec VPN for a virtual domain ............................................................... 154
Router ................................................................................................................. 155
Static............................................................................................................................... 155
Static route list ............................................................................................................ 157
Static route options ..................................................................................................... 158
Policy .............................................................................................................................. 159
Policy route list............................................................................................................ 159
Policy route options..................................................................................................... 160
RIP.................................................................................................................................. 160
General ....................................................................................................................... 161
Networks list................................................................................................................ 162
Networks options ........................................................................................................ 163
Interface list................................................................................................................. 163
Interface options ......................................................................................................... 164
Distribute list ............................................................................................................... 165
Distribute list options................................................................................................... 166
Offset list ..................................................................................................................... 167
Offset list options ........................................................................................................ 167
Router objects................................................................................................................. 168
Access list ................................................................................................................... 168
New access list ........................................................................................................... 169
New access list entry .................................................................................................. 169
Prefix list ..................................................................................................................... 170
New Prefix list ............................................................................................................. 170
New prefix list entry..................................................................................................... 171
Route-map list............................................................................................................. 171
New Route-map .......................................................................................................... 172
Route-map list entry.................................................................................................... 173
Key chain list............................................................................................................... 174
New key chain............................................................................................................. 174
Key chain list entry...................................................................................................... 175
Monitor............................................................................................................................ 176
Routing monitor list ..................................................................................................... 176
6 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 7

CLI configuration............................................................................................................. 177
get router info ospf ...................................................................................................... 177
get router info protocols .............................................................................................. 177
get router info rip......................................................................................................... 178
config router ospf ....................................................................................................... 178
config router static6..................................................................................................... 201
Firewall................................................................................................................ 203
Policy .............................................................................................................................. 204
How policy matching works......................................................................................... 204
Policy list ..................................................................................................................... 204
Policy options.............................................................................................................. 205
Advanced policy options ............................................................................................. 208
Configuring firewall policies ........................................................................................ 211
Policy CLI configuration .............................................................................................. 212
Address........................................................................................................................... 213
Address list ................................................................................................................. 214
Address options .......................................................................................................... 214
Configuring addresses ................................................................................................ 215
Address group list ....................................................................................................... 216
Address group options ................................................................................................ 216
Configuring address groups........................................................................................ 217
Service............................................................................................................................ 218
Predefined service list................................................................................................. 218
Custom service list...................................................................................................... 221
Custom service options............................................................................................... 222
Configuring custom services....................................................................................... 223
Service group list ........................................................................................................ 224
Service group options ................................................................................................. 225
Configuring service groups ......................................................................................... 225
Schedule......................................................................................................................... 226
One-time schedule list ................................................................................................ 226
One-time schedule options ......................................................................................... 227
Configuring one-time schedules ................................................................................. 227
Recurring schedule list................................................................................................ 228
Recurring schedule options ........................................................................................ 229
Configuring recurring schedules ................................................................................. 229
Virtual IP ......................................................................................................................... 230
Virtual IP list ................................................................................................................ 230
Virtual IP options......................................................................................................... 231
Configuring virtual IPs................................................................................................. 232
Contents
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 7
Page 8

Contents
IP pool............................................................................................................................. 234
IP pool list ................................................................................................................... 235
IP pool options ............................................................................................................ 236
Configuring IP pools.................................................................................................... 236
IP Pools for firewall policies that use fixed ports ......................................................... 237
IP pools and dynamic NAT ......................................................................................... 237
Protection profile............................................................................................................. 237
Protection profile list.................................................................................................... 238
Default protection profiles ........................................................................................... 238
Protection profile options ............................................................................................ 239
Configuring protection profiles .................................................................................... 244
Profile CLI configuration.............................................................................................. 245
User..................................................................................................................... 249
Setting authentication timeout......................................................................................... 250
Local ............................................................................................................................... 250
Local user list .............................................................................................................. 250
Local user options....................................................................................................... 250
RADIUS .......................................................................................................................... 251
RADIUS server list ...................................................................................................... 251
RADIUS server options............................................................................................... 252
LDAP............................................................................................................................... 252
LDAP server list .......................................................................................................... 253
LDAP server options ................................................................................................... 253
User group ...................................................................................................................... 255
User group list............................................................................................................. 255
User group options...................................................................................................... 256
CLI configuration............................................................................................................. 257
peer............................................................................................................................. 257
peergrp........................................................................................................................ 258
VPN...................................................................................................................... 261
Phase 1........................................................................................................................... 262
Phase 1 list ................................................................................................................. 262
Phase 1 basic settings ................................................................................................ 263
Phase 1 advanced settings......................................................................................... 265
Phase 2........................................................................................................................... 266
Phase 2 list ................................................................................................................. 267
Phase 2 basic settings ................................................................................................ 268
Phase 2 advanced options.......................................................................................... 268
Manual key...................................................................................................................... 270
Manual key list ............................................................................................................ 271
Manual key options ..................................................................................................... 271
8 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 9

Concentrator ................................................................................................................... 272
Concentrator list.......................................................................................................... 273
Concentrator options................................................................................................... 273
Ping Generator................................................................................................................ 274
Ping generator options................................................................................................ 275
Monitor............................................................................................................................ 275
Dialup monitor............................................................................................................. 275
Static IP and dynamic DNS monitor............................................................................ 277
PPTP............................................................................................................................... 277
PPTP range ................................................................................................................ 278
L2TP .............................................................................................................................. 278
L2TP range ................................................................................................................. 278
Certificates...................................................................................................................... 279
Local certificate list...................................................................................................... 279
Certificate request....................................................................................................... 280
Importing signed certificates ...................................................................................... 281
CA certificate list ......................................................................................................... 282
Importing CA certificates............................................................................................. 282
VPN configuration procedures........................................................................................ 283
IPSec configuration procedures.................................................................................. 283
PPTP configuration procedures .................................................................................. 285
L2TP configuration procedures................................................................................... 285
CLI configuration............................................................................................................. 286
ipsec phase1............................................................................................................... 286
ipsec phase2............................................................................................................... 288
ipsec vip ...................................................................................................................... 289
Contents
IPS ....................................................................................................................... 293
Signature......................................................................................................................... 294
Predefined signatures ................................................................................................. 295
Predefined signature list ............................................................................................. 295
Configuring predefined signatures .............................................................................. 296
Configuring parameters for dissector signatures ........................................................ 298
Custom signatures ...................................................................................................... 298
Custom signature list .................................................................................................. 299
Adding custom signatures........................................................................................... 300
Backing up and restoring custom signature files ........................................................ 300
Anomaly.......................................................................................................................... 300
Anomaly list................................................................................................................. 301
Configuring an anomaly .............................................................................................. 301
IPS CLI configuration...................................................................................................... 303
Configuring system settings........................................................................................ 304
Configuring anomaly settings...................................................................................... 305
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 9
Page 10

Contents
Antivirus ............................................................................................................. 307
File block......................................................................................................................... 308
File block list ............................................................................................................... 309
Configuring the file block list ....................................................................................... 310
Quarantine ...................................................................................................................... 310
Quarantined files list ................................................................................................... 310
Quarantined files list options....................................................................................... 311
AutoSubmit list ............................................................................................................ 312
AutoSubmit list options ............................................................................................... 312
Configuring the AutoSubmit list................................................................................... 312
Config.......................................................................................................................... 313
Config.............................................................................................................................. 314
Virus list ...................................................................................................................... 314
Config.......................................................................................................................... 314
Grayware .................................................................................................................... 315
Grayware options........................................................................................................ 315
CLI configuration............................................................................................................. 317
system global av_failopen........................................................................................... 317
system global optimize................................................................................................ 318
config antivirus heuristic.............................................................................................. 319
config antivirus quarantine .......................................................................................... 320
config antivirus service http......................................................................................... 320
config antivirus service ftp........................................................................................... 322
config antivirus service pop3....................................................................................... 324
config antivirus service imap....................................................................................... 325
config antivirus service smtp....................................................................................... 327
Web filter............................................................................................................. 329
Content block.................................................................................................................. 331
Web content block list ................................................................................................. 331
Web content block options.......................................................................................... 331
Configuring the web content block list ........................................................................ 332
URL block ....................................................................................................................... 332
Web URL block list...................................................................................................... 333
Web URL block options .............................................................................................. 333
Configuring the web URL block list ............................................................................. 334
Web pattern block list.................................................................................................. 334
Web pattern block options .......................................................................................... 335
Configuring web pattern block .................................................................................... 335
URL exempt.................................................................................................................... 335
URL exempt list........................................................................................................... 336
URL exempt list options .............................................................................................. 336
Configuring URL exempt............................................................................................. 336
10 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 11

Category block................................................................................................................ 337
FortiGuard-Web Filtering service ................................................................................ 337
Category block configuration options.......................................................................... 338
Configuring web category block.................................................................................. 339
Category block reports................................................................................................ 339
Category block reports options ................................................................................... 340
Generating a category block report............................................................................. 340
Category block CLI configuration................................................................................ 340
Script filter....................................................................................................................... 341
Web script filter options............................................................................................... 342
Spam filter .......................................................................................................... 343
Order of spam filter operations ....................................................................................... 345
FortiGuard-Antispam Service.......................................................................................... 346
FortiGuard-Antispam Service Spam filtering............................................................... 346
FortiGuard-Antispam Service options ......................................................................... 347
Configuring the FortiGuard-Antispam Service ............................................................ 348
FortiGuard-Antispam Service CLI configuration ......................................................... 349
IP address....................................................................................................................... 350
IP address list ............................................................................................................. 350
IP address options ...................................................................................................... 350
Configuring the IP address list .................................................................................... 350
DNSBL & ORDBL ........................................................................................................... 351
DNSBL & ORDBL list.................................................................................................. 352
DNSBL & ORDBL options........................................................................................... 352
Configuring the DNSBL & ORDBL list ........................................................................ 352
Email address ................................................................................................................. 353
Email address list........................................................................................................ 353
Email address options................................................................................................. 353
Configuring the email address list............................................................................... 353
MIME headers................................................................................................................. 354
MIME headers list ....................................................................................................... 355
MIME headers options ................................................................................................ 355
Configuring the MIME headers list.............................................................................. 355
Banned word................................................................................................................... 356
Banned word list ......................................................................................................... 356
Banned word options .................................................................................................. 357
Configuring the banned word list ................................................................................ 357
Using Perl regular expressions....................................................................................... 358
Contents
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 11
Page 12

Contents
Log & Report ...................................................................................................... 361
Log config ....................................................................................................................... 362
Log Setting options ..................................................................................................... 362
Alert E-mail options..................................................................................................... 366
Log filter options.......................................................................................................... 367
Configuring log filters .................................................................................................. 370
Enabling traffic logging................................................................................................ 370
High Availability cluster logging ...................................................................................... 371
Log access...................................................................................................................... 371
Disk log file access ..................................................................................................... 371
Viewing log messages ................................................................................................ 373
Searching log messages............................................................................................. 375
CLI configuration............................................................................................................. 376
fortilog setting.............................................................................................................. 376
syslogd setting ............................................................................................................ 377
FortiGuard categories ....................................................................................... 381
Glossary ............................................................................................................. 387
Index .................................................................................................................... 393
12 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 13

FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide Version 2.80 MR11
Introduction
FortiGate Antivirus Firewalls support network-based deployment of application-level
services, including antivirus protection and full-scan content filtering. FortiGate
Antivirus Firewalls improve network security, reduce network misuse and abuse, and
help you use communications resources more efficiently without compromising the
performance of your network. FortiGate Antivirus Firewalls are ICSA-certified for
firewall, IPSec, and antivirus services.
This chapter introduces you to FortiGate Antivirus Firewalls and the following topics:
• About FortiGate Antivirus Firewalls
• About the FortiOS International and US Domestic distributions
• Document conventions
• Fortinet documentation
• Customer service and technical support
About FortiGate Antivirus Firewalls
The FortiGate Antivirus Firewall is a dedicated easily managed security device that
delivers a full suite of capabilities that include:
• application-level services such as virus protection and content filtering,
• network-level services such as firewall, intrusion detection, VPN, and traffic
shaping.
The FortiGate Antivirus Firewall uses Fortinet’s Accelerated Behavior and Content
Analysis System (ABACAS™) technology, which leverages breakthroughs in chip
design, networking, security, and content analysis. The unique ASIC-based
architecture analyzes content and behavior in real-time, enabling key applications to
be deployed right at the network edge, where they are most effective at protecting
your networks. The FortiGate series complements existing solutions, such as hostbased antivirus protection, and enables new applications and services while greatly
lowering costs for equipment, administration, and maintenance.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 13
Page 14

About FortiGate Antivirus Firewalls Introduction
Figure 1: FortiGate-1000A (top) and FortiGate-1000AFA2 (bottom)
CONSOLE
USB
A2A1
The FortiGate-1000A is a high performance solution that delivers gigabit throughput
with exceptional reliability for the most demanding large enterprise and service
provider environments. The FortiGate-1000AFA2 optionally provides 2 ports featuring
FortiAccel technology enhancing small packet performance. All FortiGate-1000A
products deploy easily in existing networks and can be used for antivirus and content
filtering only or can be deployed as a complete network protection solution. High
Availability (HA) operation and redundant hot-swappable power supplies ensure nonstop operation in mission-critical applications. The FortiGate-1000A is kept up to date
automatically by Fortinet’s FortiGuard network, which provides continuous updates for
FortiGuard Subscription Services that ensure protection against the latest viruses,
worms, trojans and other threats around the clock.
Antivirus protection
FortiGate ICSA-certified antivirus protection scans web (HTTP), file transfer (FTP),
and email (SMTP, POP3, and IMAP) content as it passes through the FortiGate unit.
FortiGate antivirus protection uses pattern matching and heuristics to find viruses. If a
virus is found, antivirus protection removes the file containing the virus from the
content stream and forwards a replacement message to the intended recipient.
For extra protection, you can configure antivirus protection to block specified file types
from passing through the FortiGate unit. You can use the feature to stop files that
might contain new viruses.
FortiGate antivirus protection can also identify and remove known grayware
programs. Grayware programs are usually unsolicited commercial software programs
that get installed on PCs, often without the user’s consent or knowledge. Grayware
programs are generally considered an annoyance, but these programs can cause
system performance problems or be used for malicious means.
14 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 15

Introduction About FortiGate Antivirus Firewalls
If the FortiGate unit contains a hard disk, infected or blocked files and grayware files
can be quarantined. The FortiGate administrator can download quarantined files so
that they can be virus scanned, cleaned, and forwarded to the intended recipient. You
can also configure the FortiGate unit to automatically delete quarantined files after a
specified time.
The FortiGate unit can send email alerts to system administrators when it detects and
removes a virus from a content stream. The web and email content can be in normal
network traffic or encrypted IPSec VPN traffic.
ICSA Labs has certified that FortiGate Antivirus Firewalls:
• detect 100% of the viruses listed in the current In The Wild List (www.wildlist.org),
• detect viruses in compressed files using the PKZip format,
• detect viruses in email that has been encoded using uuencode format,
• detect viruses in email that has been encoded using MIME encoding,
• log all actions taken while scanning.
Web content filtering
FortiGate web content filtering can scan all HTTP content protocol streams for URLs,
URL patterns, and web page content. If there is a match between a URL on the URL
block list, or a web page contains a word or phrase that is in the content block list, the
FortiGate unit blocks the web page. The blocked web page is replaced with a
message that you can edit using the FortiGate web-based manager.
FortiGate web content filtering also supports FortiGuard web category blocking. Using
web category blocking you can restrict or allow access to web pages based on
content ratings of web pages.
You can configure URL blocking to block all or some of the pages on a web site. Using
this feature, you can deny access to parts of a web site without denying access to it
completely.
To prevent unintentionally blocking legitimate web pages, you can add URLs to an
exempt list that overrides the URL blocking and content blocking lists. The exempt list
also exempts web traffic this address from virus scanning.
Web content filtering also includes a script filter feature that can block unsecure web
content such as Java applets, cookies, and ActiveX.
Spam filtering
FortiGate spam filtering can scan all POP3, SMTP, and IMAP email content for spam.
You can configure spam filtering to filter mail according to IP address, email address,
mime headers, and content. Mail messages can be identified as spam or clear.
FortiShield is an antispam system from Fortinet that includes an IP address black list,
a URL black list, and spam filtering tools. The IP address black list contains IP
addresses of email servers known to be used to generate Spam. The URL black list
contains URLs of website found in Spam email.
You can also add the names of known third-party DNS-based Blackhole List (DNSBL)
and Open Relay Database List (ORDBL) servers. These services contain lists of
known spam sources.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 15
Page 16

About FortiGate Antivirus Firewalls Introduction
If an email message is found to be spam, the FortiGate unit adds an email tag to the
subject line of the email. The recipient can use their mail client software to filter
messages based on the email tag. Spam filtering can also be configured to delete
SMTP email messages identified as spam.
Firewall
The FortiGate ICSA-certified firewall protects your computer networks from Internet
threats. ICSA has granted FortiGate firewalls version 4.0 firewall certification,
providing assurance that FortiGate firewalls successfully screen and secure corporate
networks against a range of threats from public or other untrusted networks.
After basic installation of the FortiGate unit, the firewall allows users on the protected
network to access the Internet while blocking Internet access to internal networks.
You can configure the firewall to put controls on access to the Internet from the
protected networks and to allow controlled access to internal networks.
FortiGate policies include a range of options that:
• control all incoming and outgoing network traffic,
• control encrypted VPN traffic,
• apply antivirus protection and web content filtering,
• block or allow access for all policy options,
• control when individual policies are in effect,
• accept or deny traffic to and from individual addresses,
• control standard and user defined network services individually or in groups,
• require users to authenticate before gaining access,
• include traffic shaping to set access priorities and guarantee or limit bandwidth for
each policy,
• include logging to track connections for individual policies,
• include Network Address Translation (NAT) mode and Route mode policies,
• include mixed NAT and Route mode policies.
The FortiGate firewall can operate in NAT/Route mode or Transparent mode.
NAT/Route mode
In NAT/Route mode, the FortiGate unit is a Layer 3 device. This means that each of its
interfaces is associated with a different IP subnet and that it appears to other devices
as a router. This is how a firewall is normally deployed.
In NAT/Route mode, you can create NAT mode policies and Route mode policies.
• NAT mode policies use network address translation to hide the addresses in a
more secure network from users in a less secure network.
• Route mode policies accept or deny connections between networks without
performing address translation.
16 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 17

Introduction About FortiGate Antivirus Firewalls
Transparent mode
In Transparent mode, the FortiGate unit does not change the Layer 3 topology. This
means that all of its interfaces are on the same IP subnet and that it appears to other
devices as a bridge. Typically, the FortiGate unit is deployed in Transparent mode to
provide antivirus and content filtering behind an existing firewall solution.
Transparent mode provides the same basic firewall protection as NAT mode. The
FortiGate unit passes or blocks the packets it receives according to firewall policies.
The FortiGate unit can be inserted in the network at any point without having to make
changes to your network or its components. However, some advanced firewall
features are available only in NAT/Route mode.
VLANs and virtual domains
Fortigate Antivirus Firewalls support IEEE 802.1Q-compliant virtual LAN (VLAN) tags.
Using VLAN technology, a single FortiGate unit can provide security services to, and
control connections between, multiple security domains according to the VLAN IDs
added to VLAN packets. The FortiGate unit can recognize VLAN IDs and apply
security policies to secure network and IPSec VPN traffic between each security
domain. The FortiGate unit can also apply authentication, content filtering, and
antivirus protection to VLAN-tagged network and VPN traffic.
The FortiGate unit supports VLANs in NAT/Route and Transparent mode. In
NAT/Route mode, you enter VLAN subinterfaces to receive and send VLAN packets.
FortiGate virtual domains provide multiple logical firewalls and routers in a single
FortiGate unit. Using virtual domains, one FortiGate unit can provide exclusive firewall
and routing services to multiple networks so that traffic from each network is
effectively separated from every other network.
You can develop and manage interfaces, VLAN subinterfaces, zones, firewall policies,
routing, and VPN configuration for each virtual domain separately. For these
configuration settings, each virtual domain is functionally similar to a single FortiGate
unit. This separation simplifies configuration because you do not have to manage as
many routes or firewall policies at one time.
Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)
The FortiGate Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) combines signature and anomaly
based intrusion detection and prevention. The FortiGate unit can record suspicious
traffic in logs, can send alert email to system administrators, and can log, pass, drop,
reset, or clear suspicious packets or sessions. Both the IPS predefined signatures and
the IPS engine are upgradeable through the FortiProtect Distribution Network (FDN).
You can also create custom signatures.
VPN
Using FortiGate virtual private networking (VPN), you can provide a secure
connection between widely separated office networks or securely link telecommuters
or travellers to an office network.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 17
Page 18

About FortiGate Antivirus Firewalls Introduction
FortiGate VPN features include the following:
• Industry standard and ICSA-certified IPSec VPN, including:
• IPSec VPN in NAT/Route and Transparent mode,
• IPSec, ESP security in tunnel mode,
• DES, 3DES (triple-DES), and AES hardware accelerated encryption,
• HMAC MD5 and HMAC SHA1 authentication and data integrity,
• AutoIKE key based on pre-shared key tunnels,
• IPSec VPN using local or CA certificates,
• Manual Keys tunnels,
• Diffie-Hellman groups 1, 2, and 5,
• Aggressive and Main Mode,
• Replay Detection,
• Perfect Forward Secrecy,
• XAuth authentication,
• Dead peer detection,
• DHCP over IPSec,
• Secure Internet browsing.
• PPTP for easy connectivity with the VPN standard supported by the most popular
operating systems.
• L2TP for easy connectivity with a more secure VPN standard, also supported by
many popular operating systems.
• Firewall policy based control of IPSec VPN traffic.
• IPSec NAT traversal so that remote IPSec VPN gateways or clients behind a NAT
can connect to an IPSec VPN tunnel.
• VPN hub and spoke using a VPN concentrator to allow VPN traffic to pass from
one tunnel to another through the FortiGate unit.
• IPSec Redundancy to create a redundant AutoIKE key IPSec VPN connection to a
remote network.
High availability
Fortinet achieves high availability (HA) using redundant hardware and the FortiGate
Clustering Protocol (FGCP). Each FortiGate unit in an HA cluster enforces the same
overall security policy and shares the same configuration settings. You can add up to
32 FortiGate units to an HA cluster. Each FortiGate unit in an HA cluster must be the
same model and must be running the same FortiOS firmware image.
FortiGate HA supports link redundancy and device redundancy.
FortiGate units can be configured to operate in active-passive (A-P) or active-active
(A-A) HA mode. Active-active and active-passive clusters can run in either NAT/Route
or Transparent mode.
An active-passive (A-P) HA cluster, also referred to as hot standby HA, consists of a
primary FortiGate unit that processes traffic, and one or more subordinate FortiGate
units. The subordinate FortiGate units are connected to the network and to the
primary FortiGate unit but do not process traffic.
18 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 19

Introduction About FortiGate Antivirus Firewalls
Active-active (A-A) HA load balances virus scanning among all the FortiGate units in
the cluster. An active-active HA cluster consists of a primary FortiGate unit that
processes traffic and one or more secondary units that also process traffic. The
primary FortiGate unit uses a load balancing algorithm to distribute virus scanning to
all the FortiGate units in the HA cluster.
Secure installation, configuration, and management
The first time you power on the FortiGate unit, it is already configured with default IP
addresses and security policies. Connect to the web-based manager, set the
operating mode, and use the Setup wizard to customize FortiGate IP addresses for
your network, and the FortiGate unit is ready to protect your network. You can then
use the web-based manager to customize advanced FortiGate features.
You can also create a basic configuration using the FortiGate front panel control
buttons and LCD.
Web-based manager
Using HTTP or a secure HTTPS connection from any computer running Internet
Explorer, you can configure and manage the FortiGate unit. The web-based manager
supports multiple languages. You can configure the FortiGate unit for HTTP and
HTTPS administration from any FortiGate interface.
You can use the web-based manager to configure most FortiGate settings. You can
also use the web-based manager to monitor the status of the FortiGate unit.
Configuration changes made using the web-based manager are effective immediately
without resetting the firewall or interrupting service. Once you are satisfied with a
configuration, you can download and save it. The saved configuration can be restored
at any time.
Command line interface
You can access the FortiGate command line interface (CLI) by connecting a
management computer serial port to the FortiGate RS-232 serial console connector.
You can also use Telnet or a secure SSH connection to connect to the CLI from any
network that is connected to the FortiGate unit, including the Internet.
The CLI supports the same configuration and monitoring functionality as the
web-based manager. In addition, you can use the CLI for advanced configuration
options that are not available from the web-based manager.
This Administration Guide contains information about basic and advanced CLI
commands. For a more complete description about connecting to and using the
FortiGate CLI, see the FortiGate CLI Reference Guide.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 19
Page 20

About the FortiOS International and US Domestic distributions Introduction
Logging and reporting
The FortiGate unit supports logging for various categories of traffic and configuration
changes. You can configure logging to:
• report traffic that connects to the firewall,
• report network services used,
• report traffic that was permitted by firewall policies,
• report traffic that was denied by firewall policies,
• report events such as configuration changes and other management events,
IPSec tunnel negotiation, virus detection, attacks, and web page blocking,
• report attacks detected by the IPS,
• send alert email to system administrators to report virus incidents, intrusions, and
firewall or VPN events or violations.
Logs can be sent to a remote syslog server or a WebTrends NetIQ Security Reporting
Center and Firewall Suite server using the WebTrends enhanced log format. Some
models can also save logs to an optional internal hard drive. If a hard drive is not
installed, you can configure most FortiGate units to log the most recent events and
attacks detected by the IPS to the system memory.
About the FortiOS International and US Domestic distributions
Fortinet produces two distributions of FortiOS v3.0, an International distribution and a
US Domestic distribution. The International distribution is available to users outside of
the United States and the US Domestic distribution is available to all users, including
users in the United States.
The main difference between the US Domestic and International distributions of
FortiOS is the Antivirus engine. The US Domestic Antivirus engine processes SMTP
traffic in streaming mode with object based scanning. The US Domestic Antivirus
engine also uses a new hot list antivirus scanning technique for all protocols (HTTP,
FTP, IMAP, POP3, SMTP, and IM). Streaming mode is also called splice mode.
US Domestic distribution changes
If you are operating your FortiGate unit with the US Domestic distribution, on the
web-based manager System Status page unit Unit Information, Distribution is set to
US Domestic (see “System Status” on page 33). In addition the US Domestic
distribution firmware has the following changes:
• SMTP virus scanning only operates in streaming mode
• Spam filter email tagging for SMTP is not supported
• SMTP quarantine file name system generated
• The default mail virus replacement message (splice mode) is changed
20 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 21

Introduction About the FortiOS International and US Domestic distributions
SMTP virus scanning only operates in streaming mode
SMTP virus scanning operates in streaming in mode (also called splice mode) only. In
streaming mode the FortiGate unit simultaneously scans an email and sends it to the
SMTP server. If the FortiGate unit detects a virus, the FortiGate unit terminates the
server connection and returns an error message to the sender, listing the virus name
and system generated quarantine file name. If SMTP quarantine is not enabled, the
quarantine filename is blank. The SMTP server is not able to deliver the email if it was
sent with an infected attachment. An error message is returned to the sender if an
attachment is infected. The receiver does not receive the email or the attachment.
Spam filter email tagging for SMTP is not supported
Because SMTP virus scanning operates in streaming mode the FortiGate unit
discards spam email and immediately drops the connection. In the US Domestic
distribution, spam filter email tagging is not supported.
SMTP quarantine file name system generated
When the FortiGate unit quarantines files from an SMTP email the file name of the
quarantined file is changed to a system generated file name. The system generated
file name consists of the name of the of the sender email address and the name of the
receiver email address separated with an underscore. The system generated file
name does not include a file name extension.
For example, if the file test.doc was quarantined in an email being sent from
user@address.com to info@fortinet.com the file name of the quarantined file would be
user_info.
The default mail virus replacement message (splice mode) is
changed
The default mail virus message (splice mode) replacement message is changed from:
The file %%FILE%% has been infected with the virus %%VIRUS%% File quarantined
as %%QUARFILENAME%%
to
An email has been infected with the virus %%VIRUS%% File quarantined as
%%QUARFILENAME%%
This change removes the name of the infected file from the replacement message.
The replacement message now only contains the name of the virus that the file is
infected with, and the quarantine filename.
For SMTP email, %%QUARFILENAME%% is the system-generated quarantine file
name. For other email protocols %%QUARFILENAME%% is the original file name. If
quarantine is not enabled for the email protocol, %%QUARFILENAME%% will be
blank.
The %%FILE%% variable is still available. If you add %%FILE%% to the mail virus
message (splice mode) replacement message, %%FILE%% will always add
<no filename> to replacement messages generated for viruses found in SMTP email.
For other email protocols, %%FILE%% adds the name of the infected file to the
replacement message.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 21
Page 22

Document conventions Introduction
Document conventions
This guide uses the following conventions to describe CLI command syntax.
• Angle brackets < > to indicate variables.
For example:
execute restore config <filename_str>
You enter:
execute restore config myfile.bak
<xxx_str> indicates an ASCII string that does not contain new-lines or carriage
returns.
<xxx_integer> indicates an integer string that is a decimal (base 10) number.
<xxx_octet> indicates a hexadecimal string that uses the digits 0-9 and letters
A-F.
<xxx_ipv4> indicates a dotted decimal IPv4 address.
<xxx_v4mask> indicates a dotted decimal IPv4 netmask.
<xxx_ipv4mask> indicates a dotted decimal IPv4 address followed by a dotted
decimal IPv4 netmask.
<xxx_ipv6> indicates a dotted decimal IPv6 address.
<xxx_v6mask> indicates a dotted decimal IPv6 netmask.
<xxx_ipv6mask> indicates a dotted decimal IPv6 address followed by a dotted
decimal IPv6 netmask.
• Vertical bar and curly brackets {|} to separate alternative, mutually exclusive
required keywords.
For example:
set opmode {nat | transparent}
You can enter set opmode nat or set opmode transparent.
• Square brackets [ ] to indicate that a keyword or variable is optional.
For example:
show system interface [<name_str>]
To show the settings for all interfaces, you can enter show system interface.
To show the settings for the internal interface, you can enter show system
interface internal.
• A space to separate options that can be entered in any combination and must be
separated by spaces.
For example:
set allowaccess {ping https ssh snmp http telnet}
You can enter any of the following:
set allowaccess ping
set allowaccess ping https ssh
set allowaccess https ping ssh
22 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 23

Introduction Fortinet documentation
set allowaccess snmp
In most cases to make changes to lists that contain options separated by spaces,
you need to retype the whole list including all the options you want to apply and
excluding all the options you want to remove.
Fortinet documentation
The most up-to-date publications and previous releases of Fortinet product
documentation are available from the Fortinet Technical Documentation web site at
http://docs.forticare.com.
The following FortiGate product documentation is available:
• FortiGate QuickStart Guide
Provides basic information about connecting and installing a FortiGate unit.
• FortiGate Installation Guide
Describes how to install a FortiGate unit. Includes a hardware reference, default
configuration information, installation procedures, connection procedures, and
basic configuration procedures. Choose the guide for your product model number.
• FortiGate Administration Guide
Provides basic information about how to configure a FortiGate unit, including how
to define FortiGate protection profiles and firewall policies; how to apply intrusion
prevention, antivirus protection, web content filtering, and spam filtering; and how
to configure a VPN.
• FortiGate online help
Provides a context-sensitive and searchable version of the Administration Guide in
HTML format. You can access online help from the web-based manager as you
work.
• FortiGate CLI Reference
Describes how to use the FortiGate CLI and contains a reference to all FortiGate
CLI commands.
• FortiGate Log Message Reference
Available exclusively from the Fortinet Knowledge Center, the FortiGate Log
Message Reference describes the structure of FortiGate log messages and
provides information about the log messages that are generated by FortiGate
units.
• FortiGate High Availability User Guide
Contains in-depth information about the FortiGate high availability feature and the
FortiGate clustering protocol.
• FortiGate IPS User Guide
Describes how to configure the FortiGate Intrusion Prevention System settings and
how the FortiGate IPS deals with some common attacks.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 23
Page 24

Customer service and technical support Introduction
• FortiGate IPSec VPN User Guide
Provides step-by-step instructions for configuring IPSec VPNs using the webbased manager.
• FortiGate SSL VPN User Guide
Compares FortiGate IPSec VPN and FortiGate SSL VPN technology, and
describes how to configure web-only mode and tunnel-mode SSL VPN access for
remote users through the web-based manager.
• FortiGate PPTP VPN User Guide
Explains how to configure a PPTP VPN using the web-based manager.
• FortiGate Certificate Management User Guide
Contains procedures for managing digital certificates including generating
certificate requests, installing signed certificates, importing CA root certificates and
certificate revocation lists, and backing up and restoring installed certificates and
private keys.
• FortiGate VLANs and VDOMs User Guide
Describes how to configure VLANs and VDOMS in both NAT/Route and
Transparent mode. Includes detailed examples.
Fortinet Knowledge Center
Additional Fortinet technical documentation is available from the Fortinet Knowledge
Center. The knowledge center contains troubleshooting and how-to articles, FAQs,
technical notes, and more. Visit the Fortinet Knowledge Center at
http://kc.forticare.com.
Comments on Fortinet technical documentation
Please send information about any errors or omissions in this document, or any
Fortinet technical documentation, to techdoc@fortinet.com.
Customer service and technical support
Fortinet Technical Support provides services designed to make sure that your Fortinet
systems install quickly, configure easily, and operate reliably in your network.
Please visit the Fortinet Technical Support web site at http://support.fortinet.com to
learn about the technical support services that Fortinet provides.
24 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 25
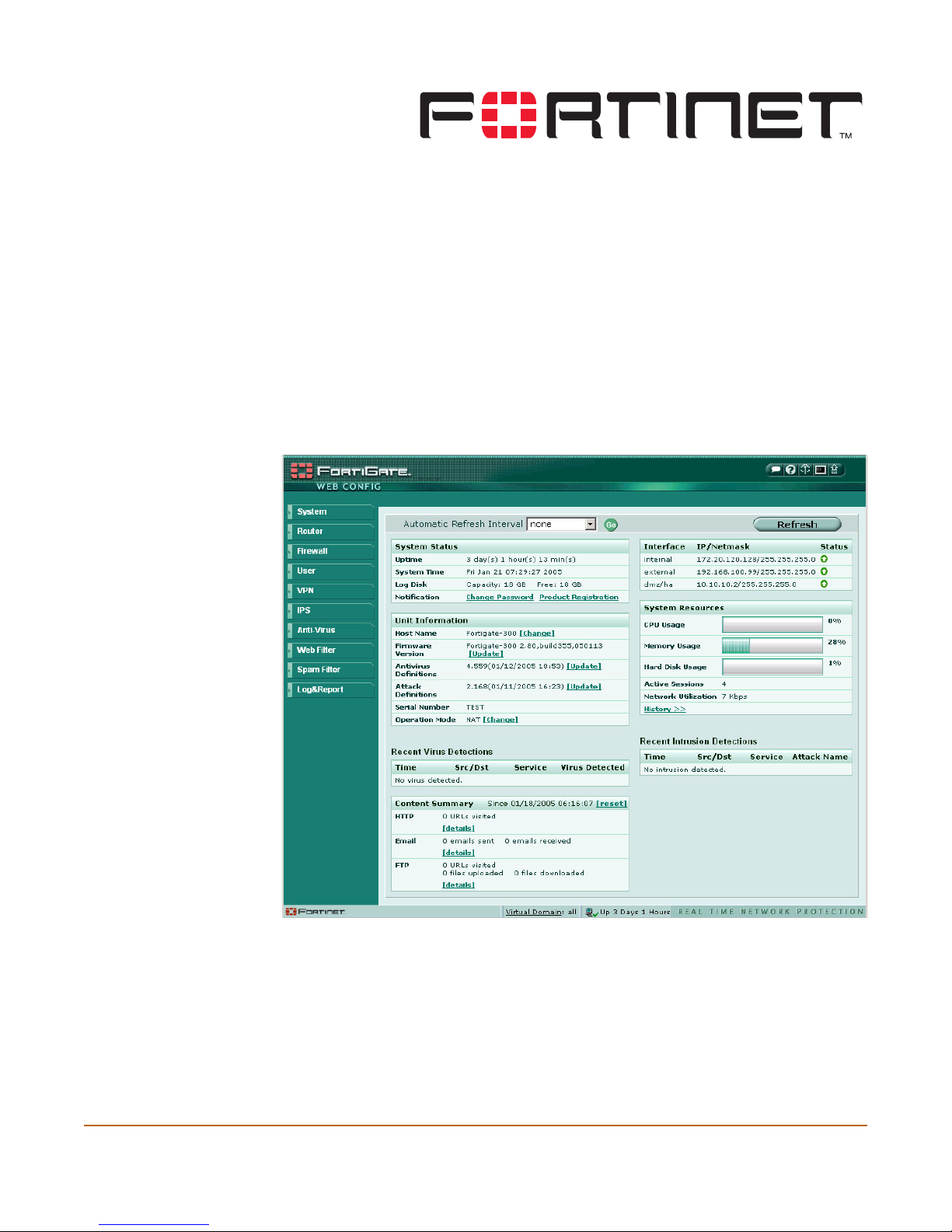
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide Version 2.80 MR11
Web-based manager
Using HTTP or a secure HTTPS connection from any computer running a web
browser, you can configure and manage the FortiGate unit. The web-based manager
supports multiple languages. You can configure the FortiGate unit for HTTP and
HTTPS administration from any FortiGate interface.
Figure 1: Web-based manager screen
You can use the web-based manager to configure most FortiGate settings. You can
also use the web-based manager to monitor the status of the FortiGate unit.
Configuration changes made using the web-based manager are effective immediately
without resetting the firewall or interrupting service. Once you are satisfied with a
configuration, you can back it up. The saved configuration can be restored at any
time.
For information about connecting to the web-based manager, see “Connecting to the
web-based manager” in the Installation Guide for your unit.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 25
Page 26

Button bar features Web-based manager
This chapter includes:
• Button bar features
• Web-based manager pages
Button bar features
The button bar in the upper right corner of the web-based manager provides access to
several important FortiGate features.
Figure 2: Web-based manager button bar
Contact Customer Support
Online Help
Easy Setup Wizard
Contact Customer Support
The Contact Customer Support button opens the Fortinet support web page in a new
browser window. From this page you can
• Register your FortiGate unit (Product Registration). Fortinet will email you your
username and password to log in to the customer support center.
• Log in to the Customer Support Center.
• Visit the FortiProtect Center.
• Download virus and attack definition updates.
• Find out about training and certification programs.
• Read about Fortinet and its products.
Console Access
Logout
26 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 27
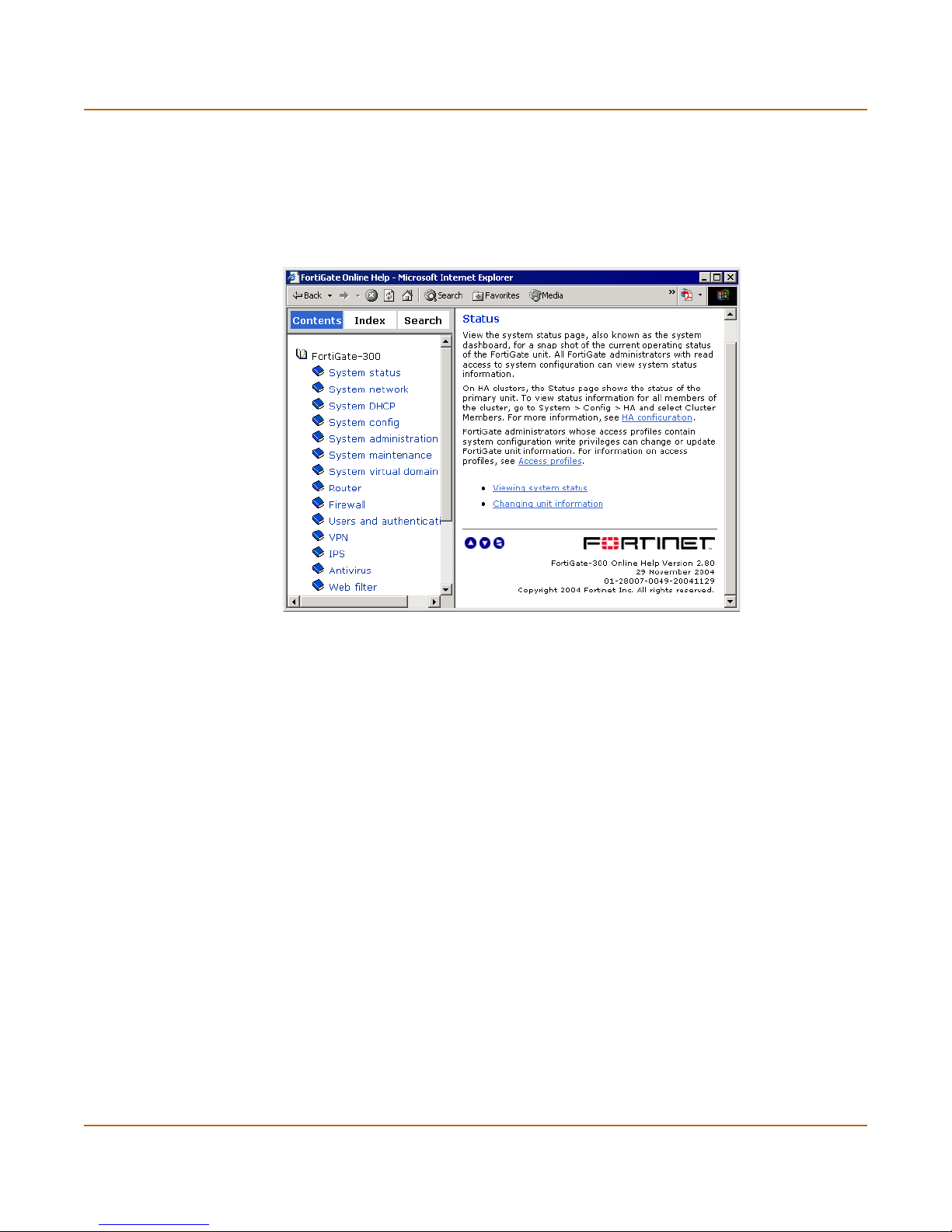
Web-based manager Button bar features
Online Help
The Online Help button opens web-based help for the current web-based manager
page. There are hyperlinks to related topics and procedures related to the controls on
the current web-based manager page.
Figure 3: Online Help window
You can view other parts of the help system as you like. The help system includes a
navigation pane with table of contents, index and a text search function.
Easy Setup Wizard
The FortiGate setup wizard provides an easy way to configure basic initial settings for
the FortiGate unit. The wizard walks through the configuration of a new administrator
password, FortiGate interfaces, DHCP server settings, internal servers (web, FTP,
etc.), and basic antivirus settings. For detailed instructions on the initial setup of your
FortiGate unit, see the Installation Guide for your unit.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 27
Page 28
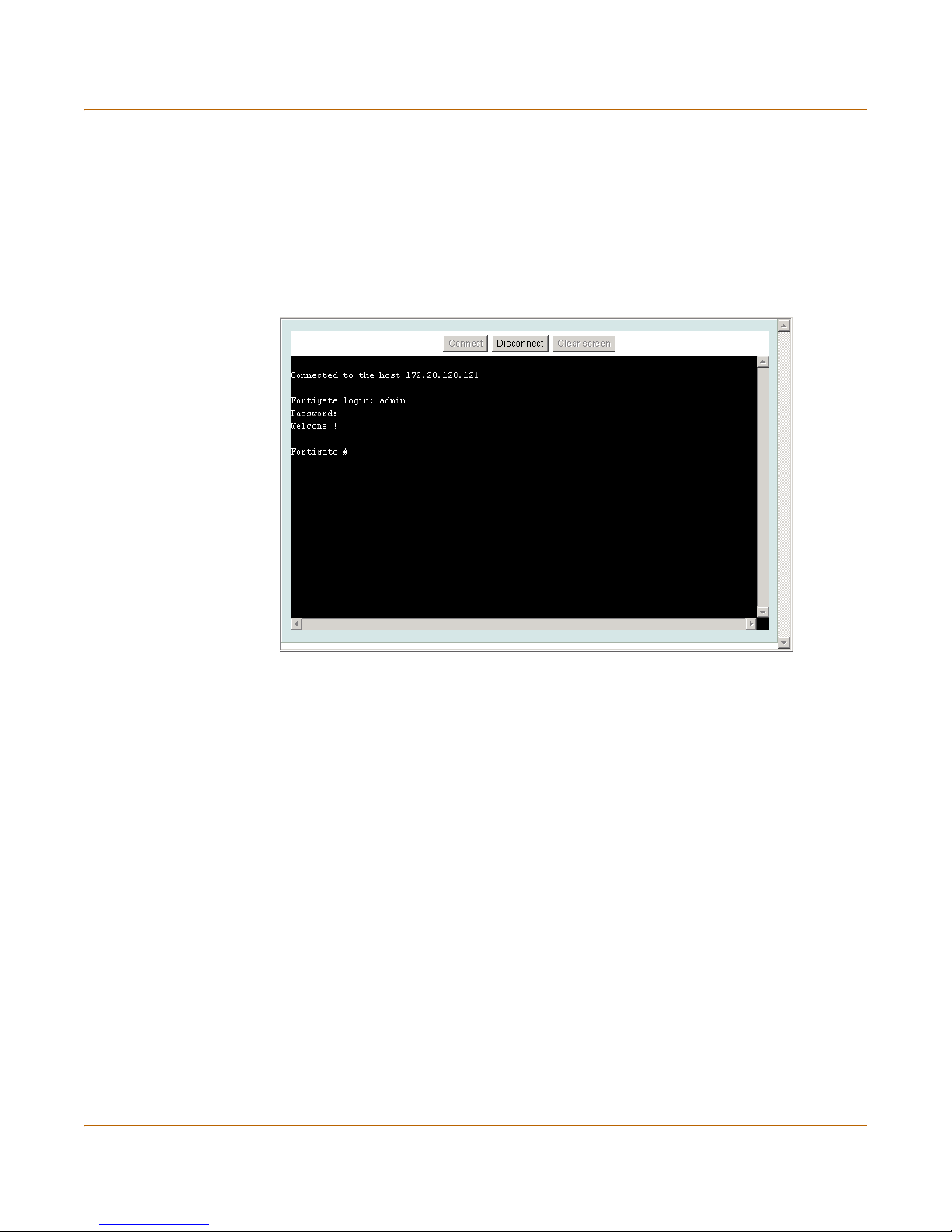
Button bar features Web-based manager
Console Access
An alternative to the web-based manager user interface is the text-based command
line interface (CLI). There are some options that are configurable only from the CLI.
The Console Access button opens a Java-based terminal application. The
management computer must have Java version 1.3 or higher installed.
For information on how to use the CLI, see the FortiGate CLI Reference Guide.
Figure 4: Console access
Logout
Connect Connect to the FortiGate unit using the CLI.
Disconnect Disconnect from the FortiGate unit.
Clear screen Clear the screen.
The Logout button immediately logs you out of the web-based manager. Log out
before you close the browser window. If you simply close the browser or leave the
web-based manager, you remain logged-in until the idle timeout (default 5 minutes)
expires.
28 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 29
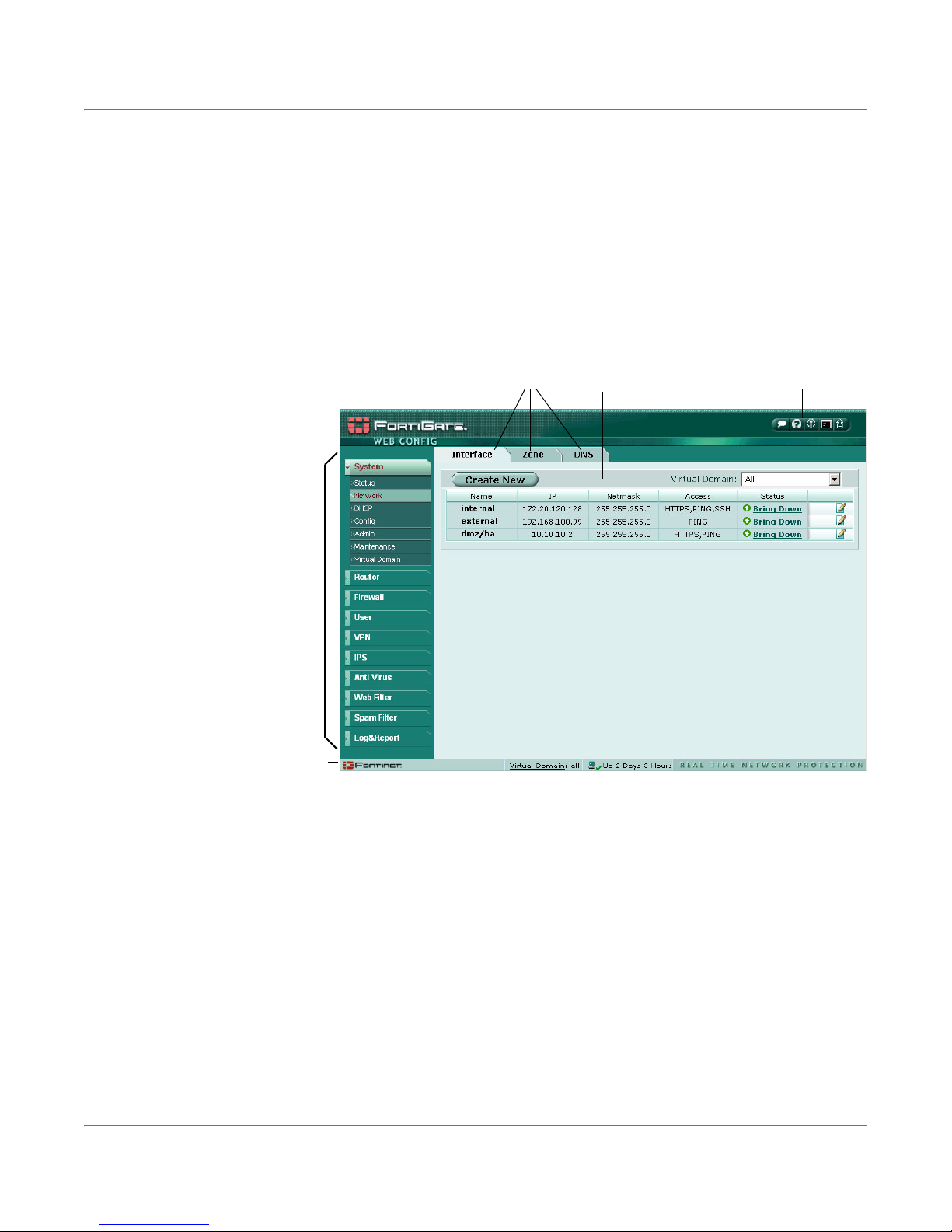
Web-based manager Web-based manager pages
Web-based manager pages
The web-based manager interface consists of a menu and pages, many of which have
multiple tabs. When you select a menu item, such as System, it expands to reveal a
submenu. When you select one of the submenu items, the associated page opens at
its first tab. To view a different tab, select the tab.
The procedures in this manual direct you to a page by specifying the menu item, the
submenu item and the tab, like this:
1 Go to System > Network > Interface.
Figure 5: Parts of the web-based manager
Menu
Status
bar
Ta bs
Page Button bar
Web-based manager menu
The menu provides access to configuration options for all major features of the
FortiGate unit.
System Configure system facilities, such as network interfaces, virtual domains,
Router Configure the router.
Firewall Configure firewall policies and protection profiles that apply the network
User Configure user accounts for use with firewall policies that require user
VPN Configure virtual private networks.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 29
DHCP services, time and set system options.
protection features. Also configure virtual IP addresses and IP pools.
authentication. Also configure external authentication servers.
Page 30

Web-based manager pages Web-based manager
IPS Configure the intrusion prevention system.
Antivirus Configure antivirus protection.
Web Filter Configure web filtering.
Spam Filter Configure email spam filtering.
Log & Report Configure logging. View log messages.
Lists
Many of the web-based manager pages are lists. There are lists of network interfaces,
firewall policies, administrators, users, and so on.
Figure 6: Example of a web-based manager list
Delete
Edit
Icons
The list shows some information about each item and the icons in the rightmost
column enable you to take action on the item. In this example, you can select Delete
to remove the item or select Edit to modify the item.
To add another item to the list, you select Create New. This opens a dialog box in
which you define the new item. The dialog box for creating a new item is similar to the
one for editing an existing item.
The web-based manager has icons in addition to buttons to enable you to interact with
the system. There are tooltips to assist you in understanding the function of the icon.
Pause the mouse pointer over the icon to view the tooltip. The following table
describes the icons that you will see in the web-based manager.
Icon Name Description
Change
Password
Clear Clear a log file.
Column
Settings
Change the administrator password. This icon appears in the
Administrators list if your access profile enables write permission
on Admin Users.
Select log columns to display.
30 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Delete Delete an item. This icon appears in lists where the item is
deletable and you have write permission on the page.
Page 31

Web-based manager Web-based manager pages
Download
or Backup
Edit Edit a configuration. This icon appears in lists where you have
Go Do a search.
Insert Policy
before
Move to Move item in list.
Next page View next page of list.
Previous
page
Restore Restore a configuration from a file.
View View a configuration. This icon appears in lists instead of the
Download a log file or back up a configuration file.
write permission on the page.
Create a new policy to precede the current one.
View previous page of list.
Edit icon when you do not have write permission on that page.
Status bar
The status bar is at the bottom of the web-based manager screen.
Figure 7: Status bar
The status bar shows
• how long the FortiGate unit has been operating since the last time it was restarted
• the virtual domain to which the current page applies
Virtual domain information is not shown if there is only one virtual domain. For
information about virtual domains, see “System Virtual Domain” on page 145.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 31
Page 32

Organization of this manual Web-based manager
Organization of this manual
This manual describes the web-based manager pages in the same order as the webbased manager menu. There is a chapter for each item in the System menu, followed
by a chapter for each of the remaining top-level menu items.
System Status
System Network
System DHCP
System Config
System Admin
System Maintenance
System Virtual Domain
Router
Firewall
User
VPN
IPS
Antivirus
Web filter
Spam filter
Log & Report
FortiGuard categories
32 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 33

FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide Version 2.80 MR11
System Status
You can connect to the web-based manager and view the current system status of the
FortiGate unit. The status information that is displayed includes the system status, unit
information, system resources, and session log.
This chapter includes:
• Status
• Session list
• Changing the FortiGate firmware
Status
View the system status page, also known as the system dashboard, for a snap shot of
the current operating status of the FortiGate unit. All FortiGate administrators with
read access to system configuration can view system status information.
On HA clusters, the Status page shows the status of the primary unit. To view status
information for all members of the cluster, go to System > Config > HA and select
Cluster Members. For more information, see “HA configuration” on page 95.
FortiGate administrators whose access profiles contain system configuration write
privileges can change or update FortiGate unit information. For information on access
profiles, see “Access profiles” on page 127.
• Viewing system status
• Changing unit information
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 33
Page 34

Status System Status
Viewing system status
Figure 8: System status (FortiGate-1000A)
Automatic Refresh
Interval
Go Select to set the selected automatic refresh interval.
Refresh Select to manually update the system status display.
Select to control how often the web-based manager updates the system
status display.
Alert Message Console
You can read alert messages about
• system restarts
• firmware upgrades
• Antivirus or IPS fail-open conditions
If there is insufficient space for all of the messages, you can scroll to view the rest of
them.
The following types of messages can appear in the Alert Message Console:
System restart The system restarted. The restart could be due to
Firmware upgraded by
<admin_name>
operator action or power off/on cycling.
The named administrator upgraded the firmware on
either the active or non-active partition.
34 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 35

System Status Status
Firmware downgraded by
<admin_name>
Fortigate has reached connection
limit for <n> seconds
The named administrator downgraded the firmware
on either the active or non-active partition.
The antivirus engine was low on memory for the
duration of time shown. Depending on model and
configuration, content can be blocked or pass
unscanned under these conditions.
Each message shows the date and time that it was posted. If there is insufficient
space for all of the messages, you can select Show All to view the rest of them.
Figure 9: System status (FortiGate-1000AFA2)
System status
UP Time The time in days, hours, and minutes since the FortiGate unit was last
System Time The current time according to the FortiGate unit internal clock.
Log Disk Displays hard disk capacity and free space if the FortiGate unit contains a
Notification Contains reminders such as “Change Password” or “Product Registration”.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 35
started.
hard disk or Not Available if no hard disk is installed. The FortiGate unit uses
the hard disk to store log messages and quarantine files infected with a virus
or blocked by antivirus file blocking.
Select the reminder to see the detailed reminder message.
Page 36

Status System Status
Unit Information
Admin users and administrators whose access profiles contain system configuration
read and write privileges can change or update the unit information. For information
on access profiles, see “Access profiles” on page 127.
Host Name The host name of the current FortiGate unit.
Firmware Version The version of the firmware installed on the current FortiGate unit.
Distribution The distribution of the firmware installed on the FortiGate unit.
FortiGuard - AV
Definitions
FortiGuard Intrusion Definitions
Serial Number The serial number of the current FortiGate unit.
Distribution can be US Domestic and only appears in the US Domestic
distribution.
The current installed version of the FortiGuard - AV Definitions.
The current installed version of the FortiGuard - Intrusion Definitions
used by the Intrusion Prevention System (IPS).
The serial number is
specific to the FortiGate unit and does not change with firmware
upgrades.
Operation Mode The operation mode of the current FortiGate unit.
Recent Virus Detections
Time The time at which the recent virus was detected.
Src / Dst The source and destination addresses of the virus.
Service The service from which the virus was delivered; HTTP, FTP, IMAP,
Virus Detected The name of the virus detected.
POP3, or SMTP.
Content Summary
The Content Summary shows information about Content Archiving, configured in
firewall protection profiles. The Details pages provide a link to either the FortiLog unit
or to the Log & Report > Log Config > Log Setting page where you can configure
logging to a FortiLog unit.
Reset Select to reset the count values in the table to zero.
HTTP The number of URLs visited. Select Details to see the list of URLs, the
Email The number of email sent and received. Select Details to see the date
FTP The number of URLs visited and the number of files uploaded and
time they were accessed and the IP address of the host that accessed
them.
and time, the sender, the recipient and the subject of each email.
downloaded. Select Details to see the FTP site URL, date, time, user
and lists of files uploaded and downloaded.
Interface Status
All interfaces in the FortiGate unit are listed in the table.
Interface The name of the interface.
36 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 37

System Status Status
IP / Netmask The IP address and netmask of the interface (NAT/Route mode only).
Status The status of the interface; either up (green up arrow) or down (red
down arrow).
System Resources
CPU Usage The current CPU status. The web-based manager displays CPU usage
Memory Usage The current memory status. The web-based manager displays memory
Hard Disk Usage The current hard disk (local disk) status, if the unit has a hard disk. The
Active Sessions The number of communications sessions being processed by the
Network Utilization The total network bandwidth being used through all FortiGate interfaces
History Select History to view a graphical representation of the last minute of
Figure 10: Sample system resources history
for core processes only. CPU usage for management processes (for
example, for HTTPS connections to the web-based manager) is
excluded.
usage for core processes only. Memory usage for management
processes (for example, for HTTPS connections to the web-based
manager) is excluded.
web-based manager displays hard disk usage for core processes only.
Hard disk usage for management processes (for example, for HTTPS
connections to the web-based manager) is excluded.
FortiGate unit.
and the percentage of the maximum network bandwidth that can be
processed by the FortiGate unit.
CPU, memory, sessions, and network usage. This page also shows the
virus and intrusion detections over the last 20 hours.
History
The history page displays 6 graphs representing the following system resources and
protection:
CPU Usage History CPU usage for the previous minute.
Memory Usage History Memory usage for the previous minute.
Session History Session history for the previous minute.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 37
Page 38

Status System Status
Network Utilization
History
Virus History The virus detection history over the last 20 hours.
Intrusion History The intrusion detection history over the last 20 hours.
Recent Intrusion Detections
Time The time at which the recent intrusion was detected.
Src / Dst The source and destination addresses of the attack.
Service The service from which the attack was delivered; HTTP, FTP, IMAP,
Attack Name The name of the attack.
Changing unit information
Administrators with system configuration write access can use the unit information
area of the System Status page:
• To change FortiGate host name
• To update the firmware version
• To update the antivirus definitions manually
• To update the attack definitions manually
• To change to Transparent mode
• To change to NAT/Route mode
Network utilization for the previous minute.
POP3, or SMTP.
To change FortiGate host name
The FortiGate host name appears on the Status page and in the FortiGate CLI
prompt. The host name is also used as the SNMP system name. For information
about the SNMP system name, see “SNMP” on page 108.
The default host name is FortiGate-1000A.
Note: If the FortiGate unit is part of an HA cluster, you should set a unique name to distinguish
the unit from others in the cluster.
1 Go to System > Status > Status.
2 In the Host Name field of the Unit Information section, select Change.
3 In the New Name field, type a new host name.
4 Select OK.
The new host name is displayed in the Host Name field, and in the CLI prompt, and is
added to the SNMP System Name.
To update the firmware version
For information on updating the firmware, see “Changing the FortiGate firmware” on
page 41.
38 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 39

System Status Status
To update the antivirus definitions manually
Note: For information about configuring the FortiGate unit for automatic antivirus definitions
updates, see “Update center” on page 132.
1 Download the latest antivirus definitions update file from Fortinet and copy it to the
computer that you use to connect to the web-based manager.
2 Start the web-based manager and go to System > Status > Status.
3 In the Antivirus Definitions field of the Unit Information section, select Update.
4 In the Update File field, type the path and filename for the antivirus definitions update
file, or select Browse and locate the antivirus definitions update file.
5 Select OK to copy the antivirus definitions update file to the FortiGate unit.
The FortiGate unit updates the antivirus definitions. This takes about 1 minute.
6 Go to System > Status to confirm that the Antivirus Definitions Version information
has updated.
To update the attack definitions manually
Note: For information about configuring the FortiGate unit for automatic attack definitions
updates, see “Update center” on page 132.
1 Download the latest attack definitions update file from Fortinet and copy it to the
computer that you use to connect to the web-based manager.
2 Start the web-based manager and go to System > Status > Status.
3 In the Attack Definitions field of the Unit Information section, select Update.
The Intrusion Detection System Definitions Update dialog box appears.
4 In the Update File field, type the path and filename for the attack definitions update
file, or select Browse and locate the attack definitions update file.
5 Select OK to copy the attack definitions update file to the FortiGate unit.
The FortiGate unit updates the attack definitions. This takes about 1 minute.
6 Go to System > Status > Status to confirm that the Attack Definitions Version
information has updated.
To change to Transparent mode
After you change the FortiGate unit from the NAT/Route mode to Transparent mode,
most of the configuration resets to Transparent mode factory defaults, except for HA
settings (see “HA” on page 92).
To change to Transparent mode:
1 Go to System > Status > Status.
2 In the Operation Mode field of the Unit Information section, select Change.
3 In the Operation Mode field, select Transparent.
4 Select OK.
The FortiGate unit changes operation mode.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 39
Page 40

Session list System Status
5 To reconnect to the web-based manager, connect to the interface configured for
Transparent mode management access and browse to https:// followed by the
Transparent mode management IP address.
By default in Transparent mode, you can connect to port1. The default Transparent
mode management IP address is 10.10.10.1.
Note: If the web-based manager IP address was on a different subnet in NAT/Route mode, you
may have to change the IP address of your computer to the same subnet as the management
IP address.
To change to NAT/Route mode
After you change the FortiGate unit from the NAT/Route mode to Transparent mode,
most of the configuration resets to Transparent mode factory defaults, except for HA
settings (see “HA” on page 92).
To change to NAT/Route mode:
1 Go to System > Status > Status.
2 In the Operation Mode field of the Unit Information section, select Change.
3 In the Operation Mode field, select NAT/Route.
4 Select OK.
The FortiGate unit changes operation mode.
5 To reconnect to the web-based manager, you must connect to the interface configured
by default for management access.
By default in NAT/Route mode, you can connect to port1. The default port1 IP address
is 192.168.1.99.
Session list
Note: If the management IP address was on a different subnet in Transparent mode, you may
have to change the IP address of your computer to the same subnet as the interface configured
for management access.
The session list displays information about the communications sessions currently
being processed by the FortiGate unit. You can use the session list to view current
sessions.
Figure 11: Sample session list
From IP Set source IP address for list filtering
From Port Set source port for list filtering
40 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 41

System Status Changing the FortiGate firmware
To IP Set destination IP address for list filtering
To Port Set destination port for list filtering
Apply Filter Select to filter session list
Virtual Domain Select a virtual domain to list the sessions being processed by that virtual
Total Sessions Total number of sessions currently being conducted through the FortiGate
Protocol The service protocol of the connection, for example, udp, tcp, or icmp.
From IP The source IP address of the connection.
From Port The source port of the connection.
To IP The destination IP address of the connection.
To Port The destination port of the connection.
Expire The time, in seconds, before the connection expires.
Policy ID The number of the firewall policy allowing this session or blank if the session
domain. Select All to view sessions being processed by all virtual domains.
unit.
Refresh icon. Select to update the session list
Page up icon. Select to view previous page in the session list
Page down icon. Select to view the next page in the session list.
involves only one FortiGate interface (admin session, for example).
Delete icon. Select to stop an active communication session.
To view the session list
1 Go to System > Status > Session.
The web-based manager displays the total number of active sessions in the FortiGate
unit session table and lists the top 16.
2 To navigate the list of sessions, select Page Up or Page Down.
3 Select Refresh to update the session list.
4 If you are logged in as an administrative user with read and write privileges or as the
admin user, you can select Delete to stop an active session.
Changing the FortiGate firmware
FortiGate administrators whose access profiles contain system configuration read and
write privileges and the FortiGate admin user can change the FortiGate firmware.
After you download a FortiGate firmware image from Fortinet, you can use the
procedures listed in Tab le 1 to install the firmware image on your FortiGate unit.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 41
Page 42

Changing the FortiGate firmware System Status
Table 1: Firmware upgrade procedures
Procedure Description
Upgrading to a new
firmware version
Reverting to a
previous firmware
version
Installing firmware
images from a system
reboot using the CLI
Testing a new
firmware image before
installing it
Installing and using a
backup firmware
image
Use the web-based manager or CLI procedure to upgrade to a new
FortiOS firmware version or to a more recent build of the same
firmware version.
Use the web-based manager or CLI procedure to revert to a
previous firmware version. This procedure reverts the FortiGate
unit to its factory default configuration.
Use this procedure to install a new firmware version or revert to a
previous firmware version. To use this procedure you must connect
to the CLI using the FortiGate console port and a null-modem
cable. This procedure reverts the FortiGate unit to its factory
default configuration.
Use this procedure to test a new firmware image before installing it.
To use this procedure you must connect to the CLI using the
FortiGate console port and a null-modem cable. This procedure
temporarily installs a new firmware image using your current
configuration. You can test the firmware image before installing it
permanently. If the firmware image works correctly you can use
one of the other procedures listed in this table to install it
permanently.
If the FortiGate unit is running BIOS version v3.x, you can install a
backup firmware image. Once the backup firmware image is
installed you can switch to this backup image when required.
Upgrading to a new firmware version
Use the following procedures to upgrade the FortiGate unit to a newer firmware
version.
Upgrading the firmware using the web-based manager
Note: Installing firmware replaces the current antivirus and attack definitions with the definitions
included with the firmware release that you are installing. After you install new firmware, use the
procedure “To update antivirus and attack definitions” on page 135 to make sure that antivirus
and attack definitions are up to date.
To upgrade the firmware using the web-based manager
1 Copy the firmware image file to your management computer.
2 Log into the web-based manager as the admin administrative user.
Note: To use this procedure you must login using the admin administrator account, or an
administrator account that has system configuration read and write privileges.
3 Go to System > Status.
4 Under Unit Information > Firmware Version, select Update.
5 Type the path and filename of the firmware image file, or select Browse and locate the
file.
42 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 43

System Status Changing the FortiGate firmware
6 Select OK.
The FortiGate unit uploads the firmware image file, upgrades to the new firmware
version, restarts, and displays the FortiGate login. This process takes a few minutes.
7 Log into the web-based manager.
8 Go to System > Status and check the Firmware Version to confirm that the firmware
upgrade is successfully installed.
9 Update antivirus and attack definitions. For information about updating antivirus and
attack definitions, see “Update center” on page 132.
Upgrading the firmware using the CLI
To use the following procedure you must have a TFTP server that the FortiGate unit
can connect to.
Note: Installing firmware replaces your current antivirus and attack definitions with the
definitions included with the firmware release that you are installing. After you install new
firmware, use the procedure “To update antivirus and attack definitions” on page 135 to make
sure that antivirus and attack definitions are up to date. You can also use the CLI command
execute update_now to update the antivirus and attack definitions.
To upgrade the firmware using the CLI
1 Make sure that the TFTP server is running.
2 Copy the new firmware image file to the root directory of the TFTP server.
3 Log into the CLI.
Note: To use this procedure you must login using the admin administrator account, or an
administrator account that has system configuration read and write privileges.
4 Make sure the FortiGate unit can connect to the TFTP server.
You can use the following command to ping the computer running the TFTP server.
For example, if the IP address of the TFTP server is 192.168.1.168:
execute ping 192.168.1.168
5 Enter the following command to copy the firmware image from the TFTP server to the
FortiGate unit:
execute restore image <name_str> <tftp_ipv4>
Where <name_str> is the name of the firmware image file and <tftp_ip> is the IP
address of the TFTP server. For example, if the firmware image file name is
FGT_300-v280-build183-FORTINET.out and the IP address of the TFTP server
is 192.168.1.168, enter:
execute restore image FGT_300-v280-build183-FORTINET.out
192.168.1.168
The FortiGate unit responds with the message:
This operation will replace the current firmware version!
Do you want to continue? (y/n)
6 Type y.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 43
Page 44

Changing the FortiGate firmware System Status
The FortiGate unit uploads the firmware image file, upgrades to the new firmware
version, and restarts. This process takes a few minutes.
7 Reconnect to the CLI.
8 To confirm that the new firmware image is successfully installed, enter:
get system status
9 Use the procedure “To update antivirus and attack definitions” on page 135 to update
antivirus and attack definitions, or from the CLI, enter:
execute update_now
Reverting to a previous firmware version
Use the following procedures to revert your FortiGate unit to a previous firmware
version.
Reverting to a previous firmware version using the web-based
manager
The following procedures revert the FortiGate unit to its factory default configuration
and deletes IPS custom signatures, web content lists, email filtering lists, and changes
to replacement messages.
Before beginning this procedure you can:
• Back up the FortiGate unit configuration.
• Back up the IPS custom signatures.
• Back up web content and email filtering lists.
For information, see “Backing up and Restoring” on page 130.
If you are reverting to a previous FortiOS version (for example, reverting from FortiOS
v2.80 to FortiOS v2.50), you might not be able to restore the previous configuration
from the backup configuration file.
Note: Installing firmware replaces the current antivirus and attack definitions with the definitions
included with the firmware release that you are installing. After you install new firmware, use the
procedure “To update antivirus and attack definitions” on page 135 to make sure that antivirus
and attack definitions are up to date.
44 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 45

System Status Changing the FortiGate firmware
To revert to a previous firmware version using the web-based manager
1 Copy the firmware image file to the management computer.
2 Log into the FortiGate web-based manager.
Note: To use this procedure you must login using the admin administrator account, or an
administrator account that has system configuration read and write privileges.
3 Go to System > Status.
4 Under Unit Information > Firmware Version, select Update.
5 Type the path and filename of the firmware image file, or select Browse and locate the
file.
6 Select OK.
The FortiGate unit uploads the firmware image file, reverts to the old firmware version,
resets the configuration, restarts, and displays the FortiGate login. This process takes
a few minutes.
7 Log into the web-based manager.
8 Go to System > Status and check the Firmware Version to confirm that the firmware
is successfully installed.
9 Restore your configuration.
For information about restoring your configuration, see “Backup and restore” on
page 129.
10 Update antivirus and attack definitions.
For information about antivirus and attack definitions, see “To update antivirus and
attack definitions” on page 135.
Reverting to a previous firmware version using the CLI
This procedure reverts the FortiGate unit to its factory default configuration and
deletes IPS custom signatures, web content lists, email filtering lists, and changes to
replacement messages.
Before beginning this procedure you can:
• Back up the FortiGate unit system configuration using the command execute
backup config.
• Back up the IPS custom signatures using the command execute backup
ipsuserdefsig
• Back up web content and email filtering lists.
For information, see “Backing up and Restoring” on page 130.
If you are reverting to a previous FortiOS version (for example, reverting from FortiOS
v2.80 to FortiOS v2.50), you might not be able to restore your previous configuration
from the backup configuration file.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 45
Page 46

Changing the FortiGate firmware System Status
Note: Installing firmware replaces the current antivirus and attack definitions with the definitions
included with the firmware release that you are installing. After you install new firmware, use the
procedure “To update antivirus and attack definitions” on page 135 to make sure that antivirus
and attack definitions are up to date. You can also use the CLI command execute
update_now
to update the antivirus and attack definitions.
To use the following procedure you must have a TFTP server that the FortiGate unit
can connect to.
To revert to a previous firmware version using the CLI
1 Make sure that the TFTP server is running.
2 Copy the firmware image file to the root directory of the TFTP server.
3 Log into the FortiGate CLI.
Note: To use this procedure you must login using the admin administrator account, or an
administrator account that has system configuration read and write privileges.
4 Make sure the FortiGate unit can connect to the TFTP server.
You can use the following command to ping the computer running the TFTP server.
For example, if the TFTP server's IP address is 192.168.1.168:
execute ping 192.168.1.168
5 Enter the following command to copy the firmware image from the TFTP server to the
FortiGate unit:
execute restore image <name_str> <tftp_ipv4>
Where <name_str> is the name of the firmware image file and <tftp_ip> is the IP
address of the TFTP server. For example, if the firmware image file name is
FGT_300-v280-build158-FORTINET.out and the IP address of the TFTP server
is 192.168.1.168, enter:
execute restore image FGT_300-v280-build158-FORTINET.out
192.168.1.168
The FortiGate unit responds with the message:
This operation will replace the current firmware version!
Do you want to continue? (y/n)
6 Type y.
The FortiGate unit uploads the firmware image file. After the file uploads, a message
similar to the following is displayed:
Get image from tftp server OK.
Check image OK.
This operation will downgrade the current firmware version!
Do you want to continue? (y/n)
7 Type y.
The FortiGate unit reverts to the old firmware version, resets the configuration to
factory defaults, and restarts. This process takes a few minutes.
8 Reconnect to the CLI.
46 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 47

System Status Changing the FortiGate firmware
9 To confirm that the new firmware image has been loaded, enter:
get system status
10 To restore your previous configuration if needed, use the command:
execute restore config <name_str> <tftp_ipv4>
11 Update antivirus and attack definitions.
For information, see “To update antivirus and attack definitions” on page 135, or from
the CLI, enter:
execute update_now
Installing firmware images from a system reboot using the CLI
This procedure installs a specified firmware image and resets the FortiGate unit to
default settings. You can use this procedure to upgrade to a new firmware version,
revert to an older firmware version, or re-install the current firmware version.
Note: This procedure varies for different FortiGate BIOS versions. These variations are
explained in the procedure steps that are affected. The version of the BIOS running on the
FortiGate unit is displayed when you restart the FortiGate unit using the CLI through a console
connection.
For this procedure you:
• access the CLI by connecting to the FortiGate console port using a null-modem
cable,
• install a TFTP server that you can connect to from port1. The TFTP server should
be on the same subnet as port3.
Before beginning this procedure you can:
• Back up the FortiGate unit configuration.
For information, see “Backing up and Restoring” on page 130.
• Back up the IPS custom signatures.
For information, see “Backing up and restoring custom signature files” on
page 300.
• Back up web content and email filtering lists.
For information, see “Web filter” on page 329 and “Spam filter” on page 343.
If you are reverting to a previous FortiOS version (for example, reverting from FortiOS
v2.80 to FortiOS v2.50), you might not be able to restore your previous configuration
from the backup configuration file.
Note: Installing firmware replaces the current antivirus and attack definitions with the definitions
included with the firmware release that you are installing. After you install new firmware, use the
procedure “To update antivirus and attack definitions” on page 135 to make sure that antivirus
and attack definitions are up to date.
To install firmware from a system reboot
1 Connect to the CLI using the null-modem cable and FortiGate console port.
2 Make sure that the TFTP server is running.
3 Copy the new firmware image file to the root directory of the TFTP server.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 47
Page 48

Changing the FortiGate firmware System Status
4 Make sure that port1 is connected to the same network as the TFTP server.
5 To confirm that the FortiGate unit can connect to the TFTP server, use the following
command to ping the computer running the TFTP server. For example, if the IP
address of the TFTP server is 192.168.1.168, enter:
execute ping 192.168.1.168
6 Enter the following command to restart the FortiGate unit:
execute reboot
The FortiGate unit responds with the following message:
This operation will reboot the system !
Do you want to continue? (y/n)
7 Type y.
As the FortiGate units starts, a series of system startup messages is displayed.
When one of the following messages appears:
• FortiGate unit running v2.x BIOS
Press Any Key To Download Boot Image.
...
• FortiGate unit running v3.x BIOS
Press any key to display configuration menu.....
......
Immediately press any key to interrupt the system startup.
Note: You have only 3 seconds to press any key. If you do not press a key soon enough, the
FortiGate unit reboots and you must log in and repeat the execute reboot command.
If you successfully interrupt the startup process, one of the following messages
appears:
• FortiGate unit running v2.x BIOS
Enter TFTP Server Address [192.168.1.168]:
Go to step 9.
• FortiGate unit running v3.x BIOS
[G]: Get firmware image from TFTP server.
[F]: Format boot device.
[B]: Boot with backup firmware and set as default.
[Q]: Quit menu and continue to boot with default firmware.
[H]: Display this list of options.
Enter G,F,B,Q,or H:
8 Type G to get the new firmware image from the TFTP server.
The following message appears:
Enter TFTP server address [192.168.1.168]:
9 Type the address of the TFTP server and press Enter.
The following message appears:
Enter Local Address [192.168.1.188]:
48 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 49

System Status Changing the FortiGate firmware
10 Type an IP address that the FortiGate unit can use to connect to the TFTP server.
The IP address can be any IP address that is valid for the network that the interface is
connected to. Make sure you do not enter the IP address of another device on this
network.
The following message appears:
Enter File Name [image.out]:
11 Enter the firmware image filename and press Enter.
The TFTP server uploads the firmware image file to the FortiGate unit and messages
similar to the following are displayed:
• FortiGate unit running v2.x BIOS
Do You Want To Save The Image? [Y/n]
Type Y.
• FortiGate unit running v3.x BIOS
Save as Default firmware/Run image without saving:[D/R]
or
Save as Default firmware/Backup firmware/Run image without
saving:[D/B/R]
12 Type D.
The FortiGate unit installs the new firmware image and restarts. The installation might
take a few minutes to complete.
Restoring the previous configuration
Change the internal interface address if required. You can do this from the CLI using
the command:
config system interface
edit internal
set ip <address_ipv4mask>
set allowaccess {ping https ssh telnet http}
end
After changing the interface address, you can access the FortiGate unit from the
web-based manager and restore the configuration.
• To restore the FortiGate unit configuration, see “Backup and restore” on page 129.
• To restore IPS custom signatures, see “Backing up and restoring custom signature
files” on page 300.
• To restore web content filtering lists, see “Backup and restore” on page 129.
• To restore email filtering lists, see “Backup and restore” on page 129.
• To update the virus and attack definitions to the most recent version, see “Updating
antivirus and attack definitions” on page 134.
If you are reverting to a previous firmware version (for example, reverting from
FortiOS v2.80 to FortiOS v2.50), you might not be able to restore your previous
configuration from the backup up configuration file.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 49
Page 50

Changing the FortiGate firmware System Status
Testing a new firmware image before installing it
You can test a new firmware image by installing the firmware image from a system
reboot and saving it to system memory. After completing this procedure the FortiGate
unit operates using the new firmware image with the current configuration. This new
firmware image is not permanently installed. The next time the FortiGate unit restarts,
it operates with the originally installed firmware image using the current configuration.
If the new firmware image operates successfully, you can install it permanently using
the procedure “Upgrading to a new firmware version” on page 42.
For this procedure you:
• access the CLI by connecting to the FortiGate console port using a null-modem
cable,
• install a TFTP server that you can connect to from port1. The TFTP server should
be on the same subnet as port3.
To test a new firmware image
1 Connect to the CLI using a null-modem cable and FortiGate console port.
2 Make sure the TFTP server is running.
3 Copy the new firmware image file to the root directory of the TFTP server.
4 Make sure that port1 is connected to the same network as the TFTP server.
You can use the following command to ping the computer running the TFTP server.
For example, if the TFTP server's IP address is 192.168.1.168:
execute ping 192.168.1.168
5 Enter the following command to restart the FortiGate unit:
execute reboot
6 As the FortiGate unit reboots, press any key to interrupt the system startup.
As the FortiGate units starts, a series of system startup messages are displayed.
When one of the following messages appears:
• FortiGate unit running v2.x BIOS
Press Any Key To Download Boot Image.
...
• FortiGate unit running v3.x BIOS
Press any key to display configuration menu.....
......
7 Immediately press any key to interrupt the system startup.
Note: You have only 3 seconds to press any key. If you do not press a key soon enough, the
FortiGate unit reboots and you must log in and repeat the
50 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
execute reboot command.
Page 51

System Status Changing the FortiGate firmware
If you successfully interrupt the startup process, one of the following messages
appears:
• FortiGate unit running v2.x BIOS
Enter TFTP Server Address [192.168.1.168]:
Go to step 9.
• FortiGate unit running v3.x BIOS
[G]: Get firmware image from TFTP server.
[F]: Format boot device.
[Q]: Quit menu and continue to boot with default firmware.
[H]: Display this list of options.
Enter G,F,Q,or H:
8 Type G to get the new firmware image from the TFTP server.
The following message appears:
Enter TFTP server address [192.168.1.168]:
9 Type the address of the TFTP server and press Enter.
The following message appears:
Enter Local Address [192.168.1.188]:
10 Type an IP address that can be used by the FortiGate unit to connect to the FTP
server.
The IP address must be on the same network as the TFTP server, but make sure you
do not use the IP address of another device on this network.
The following message appears:
Enter File Name [image.out]:
11 Enter the firmware image file name and press Enter.
The TFTP server uploads the firmware image file to the FortiGate unit and messages
similar to the following appear.
• FortiGate unit running v2.x BIOS
Do You Want To Save The Image? [Y/n]
Type N.
• FortiGate unit running v3.x BIOS
Save as Default firmware/Run image without saving:[D/R]
or
Save as Default firmware/Backup firmware/Run image without
saving:[D/B/R]
12 Type R.
The FortiGate image is installed to system memory and the FortiGate unit starts
running the new firmware image but with its current configuration.
13 You can log into the CLI or the web-based manager using any administrative account.
14 To confirm that the new firmware image has been loaded, from the CLI enter:
get system status
You can test the new firmware image as required.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 51
Page 52

Changing the FortiGate firmware System Status
Installing and using a backup firmware image
If the FortiGate unit is running BIOS version v3.x, you can install a backup firmware
image. Once the backup firmware image is installed you can switch to this backup
image when required.
• Installing a backup firmware image
• Switching to the backup firmware image
• Switching back to the default firmware image
Installing a backup firmware image
To run this procedure you:
• access the CLI by connecting to the FortiGate console port using a null-modem
cable,
• install a TFTP server that you can connect to from the FortiGate as described in
the procedure “Installing firmware images from a system reboot using the CLI” on
page 47.
To install a backup firmware image
1 Connect to the CLI using the null-modem cable and FortiGate console port.
2 Make sure that the TFTP server is running.
3 Copy the new firmware image file to the root directory of your TFTP server.
4 To confirm that the FortiGate unit can connect to the TFTP server, use the following
command to ping the computer running the TFTP server. For example, if the IP
address of the TFTP server is 192.168.1.168:
execute ping 192.168.1.168
5 Enter the following command to restart the FortiGate unit:
execute reboot
As the FortiGate unit starts, a series of system startup messages are displayed.
When of the following message appears:
Press any key to enter configuration menu.....
......
6 Immediately press any key to interrupt the system startup.
Note: You have only 3 seconds to press any key. If you do not press a key soon enough, the
FortiGate unit reboots and you must log in and repeat the execute reboot command.
If you successfully interrupt the startup process, the following message appears:
[G]: Get firmware image from TFTP server.
[F]: Format boot device.
[B]: Boot with backup firmware and set as default.
[Q]: Quit menu and continue to boot with default firmware.
[H]: Display this list of options.
Enter G,F,B,Q,or H:
52 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 53

System Status Changing the FortiGate firmware
7 Type G to get the new firmware image from the TFTP server.
The following message appears:
Enter TFTP server address [192.168.1.168]:
8 Type the address of the TFTP server and press Enter.
The following message appears:
Enter Local Address [192.168.1.188]:
9 Type an IP address that can be used by the FortiGate unit to connect to the FTP
server.
The IP address can be any IP address that is valid for the network that the interface is
connected to. Make sure you do not enter the IP address of another device on this
network.
The following message appears:
Enter File Name [image.out]:
10 Enter the firmware image file name and press Enter.
The TFTP server uploads the firmware image file to the FortiGate unit and the
following message is displayed.
Save as Default firmware/Backup firmware/Run image without
saving:[D/B/R]
11 Type B.
The FortiGate unit saves the backup firmware image and restarts. When the FortiGate
unit restarts it is running the previously installed firmware version.
Switching to the backup firmware image
Use this procedure to switch the FortiGate unit to operating with a backup firmware
image that you previously installed. When you switch the FortiGate unit to the backup
firmware image, the FortiGate unit operates using the configuration that was saved
with that firmware image.
If you install a new backup image from a reboot, the configuration saved with this
firmware image is the factory default configuration. If you use the procedure
“Switching back to the default firmware image” on page 54 to switch to a backup
firmware image that was previously running as the default firmware image, the
configuration saved with this firmware image is restored.
To switch to the backup firmware image
1 Connect to the CLI using the null-modem cable and FortiGate console port.
2 Enter the following command to restart the FortiGate unit:
execute reboot
As the FortiGate units starts, a series of system startup messages are displayed.
When the following message appears:
Press any key to enter configuration menu.....
......
3 Immediately press any key to interrupt the system startup.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 53
Page 54

Changing the FortiGate firmware System Status
Note: You have only 3 seconds to press any key. If you do not press a key soon enough, the
FortiGate unit reboots and you must log in and repeat the
execute reboot command.
If you successfully interrupt the startup process, the following message appears:
[G]: Get firmware image from TFTP server.
[F]: Format boot device.
[B]: Boot with backup firmware and set as default.
[Q]: Quit menu and continue to boot with default firmware.
[H]: Display this list of options.
Enter G,F,B,Q,or H:
4 Type B to load the backup firmware image.
The FortiGate unit loads the backup firmware image and restarts. When the FortiGate
unit restarts, it is running the backup firmware version and the configuration is set to
factory default.
Switching back to the default firmware image
Use this procedure to switch the FortiGate unit to operating with the backup firmware
image that had been running as the default firmware image. When you switch to this
backup firmware image, the configuration saved with this firmware image is restored.
To switch back to the default firmware image
1 Connect to the CLI using the null-modem cable and FortiGate console port.
2 Enter the following command to restart the FortiGate unit:
execute reboot
As the FortiGate units starts, a series of system startup messages are displayed.
When the following message appears:
Press any key to enter configuration menu.....
......
3 Immediately press any key to interrupt the system startup.
Note: You have only 3 seconds to press any key. If you do not press a key soon enough, the
FortiGate unit reboots and you must log in and repeat the
execute reboot command.
If you successfully interrupt the startup process, the following message appears:
[G]: Get firmware image from TFTP server.
[F]: Format boot device.
[B]: Boot with backup firmware and set as default.
[Q]: Quit menu and continue to boot with default firmware.
[H]: Display this list of options.
Enter G,F,B,Q,or H:
4 Type B to load the backup firmware image.
The FortiGate unit loads the backup firmware image and restarts. When the FortiGate
unit restarts it is running the backup firmware version with a restored configuration.
54 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 55

FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide Version 2.80 MR11
System Network
System network settings control how the FortiGate unit connects to and interacts with
your network. Basic network settings start with configuring FortiGate interfaces to
connect to your network and configuring the FortiGate DNS settings.
More advanced network settings include adding VLAN subinterfaces and zones to the
FortiGate network configuration.
• Interface
• Zone
• Management
• DNS
• Routing table (Transparent Mode)
• VLAN overview
• VLANs in NAT/Route mode
• VLANs in Transparent mode
• FortiGate IPv6 support
Interface
In NAT/Route mode, go to System > Network > Interface to configure FortiGate
interfaces and to add and configure VLAN subinterfaces.
Note: Unless stated otherwise, in this section the term interface can refer to a physical
FortiGate interface or to a FortiGate VLAN subinterface.
• For information about VLANs in NAT/Route mode, see “VLANs in NAT/Route
mode” on page 72.
• For information about VLANs in Transparent mode, see “VLANs in Transparent
mode” on page 74.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 55
Page 56

Interface System Network
Figure 12: Interface list (FortiGate-1000A)
Create New Select Create New to create a VLAN.
Virtual Domain Select a virtual domain to display the interfaces added to this virtual domain.
Name The names of the physical interfaces available to your FortiGate unit.
IP The current IP address of the interface.
Netmask The netmask of the interface.
Access The administrative access configuration for the interface.
Status The administrative status for the interface.
Only available if you have added a virtual domain.
• Interface names indicate the default function of the interface (for
example, internal and external)
• Interface names indicate that the interface can be connected to any
network (for example, port1, port2, and portx)
If you have added VLAN subinterfaces, they also appear in the name list,
below the physical interface that they have been added to. See “VLAN
overview” on page 71.
See “To control administrative access to an interface” on page 65 for
information about administrative access options.
If the administrative status is a green arrow, the interface is up and can
accept network traffic. If the administrative status is a red arrow, the
interface is administratively down and cannot accept traffic. To change the
administrative status, select Bring Down or Bring Up. For more information,
see “To bring down an interface that is administratively up” on page 62 and
“To start up an interface that is administratively down” on page 62.
Delete, edit, and view icons.
Interface settings
Interface settings displays the current configuration of a selected FortiGate interface
or VLAN subinterface. Use interface settings to configure a new VLAN subinterface or
to change the configuration of a FortiGate interface or VLAN subinterface.
You cannot change the name, interface or VLAN ID of an existing interface.
56 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 57

System Network Interface
Figure 13: Interface settings
See the following procedures for configuring interfaces:
• To bring down an interface that is administratively up
• To start up an interface that is administratively down
• To add interfaces to a zone
• To add an interface to a virtual domain
• To change the static IP address of an interface
• To configure an interface for DHCP
• To configure an interface for PPPoE
• To configure support for dynamic DNS services
• To add a secondary IP address
• To add a ping server to an interface
• To control administrative access to an interface
• To change the MTU size of the packets leaving an interface
• To configure traffic logging for connections to an interface
Name
The name of the Interface.
Interface
Select the name of the physical interface to add the VLAN subinterface to. All VLAN
subinterfaces must be associated with a physical interface. Once created, the VLAN is
listed below its physical interface in the Interface list.
VLAN ID
Enter the VLAN ID that matches the VLAN ID of the packets to be received by this
VLAN subinterface. You cannot change the VLAN ID of an existing VLAN
subinterface.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 57
Page 58

Interface System Network
The VLAN ID can be any number between 1 and 4096 and must match the VLAN ID
added by the IEEE 802.1Q-compliant router or switch connected to the VLAN
subinterface.
For more information on VLANs, see “VLAN overview” on page 71.
Virtual Domain
Select a virtual domain to add the interface or VLAN subinterface to this virtual
domain. Virtual domain is only available if you have added a virtual domain.
For more information on virtual domains, see “System Virtual Domain” on page 145.
Addressing mode
Select Manual, DHCP, or PPPoE to set the addressing mode for this interface.
Manual
Select Manual and enter an IP address and netmask for the interface. The IP address
of the interface must be on the same subnet as the network the interface is connecting
to.
Note: Where you can enter both an IP address and a netmask in the same field, you can use
the short form of the netmask. For example, 192.168.1.100/255.255.255.0 can also be entered
as 192.168.1.100/24.
Two interfaces cannot have the same IP address and cannot have IP addresses on
the same subnet.
DHCP
If you configure the interface to use DHCP, the FortiGate unit automatically broadcasts
a DHCP request. You can disable Connect to server if you are configuring the
FortiGate unit offline and you do not want the FortiGate unit to send the DHCP
request.
Distance Enter the administrative distance for the default gateway retrieved from
Retrieve default
gateway from server
Override internal DNS Enable Override internal DNS to use the DNS addresses retrieved
Connect to server Enable Connect to Server so that the interface automatically attempts
Status Displays DHCP status messages as the FortiGate unit connects to the
the DHCP server. The administrative distance, an integer from 1-255,
specifies the relative priority of a route when there are multiple routes
to the same destination. A lower administrative distance indicates a
more preferred route. The default distance for the default gateway is 1.
Enable Retrieve default gateway from server to retrieve a default
gateway IP address from the DHCP server. The default gateway is
added to the static routing table.
from the DHCP server instead of the DNS server IP addresses on the
DNS page.
to connect to a DHCP server. Disable this option if you are configuring
the interface offline.
DHCP server and gets addressing information. Select Status to refresh
the addressing mode status message.
58 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 59

System Network Interface
initializing No activity.
connecting The interface is attempting to connect to the DHCP server.
connected The interface retrieves an IP address, netmask, and other settings
failed The interface was unable to retrieve an IP address and other
from the DHCP server.
information from the DHCP server.
PPPoE
If you configure the interface to use PPPoE, the FortiGate unit automatically
broadcasts a PPPoE request. You can disable connect to server if you are configuring
the FortiGate unit offline and you do not want the FortiGate unit to send the PPPoE
request.
FortiGate units support many of the PPPoE RFC features (RFC 2516) including
unnumbered IPs, initial discovery timeout that times and PPPoE Active Discovery
Terminate (PADT).
Figure 14: PPPoE settings
User Name The PPPoE account user name.
Password The PPPoE account password.
Unnumbered IP Specify the IP address for the interface. If your ISP has assigned you a
Initial Disc
Timeout
Initial PADT
timeout
Distance Enter the administrative distance for the default gateway retrieved from the
Retrieve default
gateway from
server
Override internal
DNS
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 59
block of IP addresses, use one of them. Otherwise, this IP address can be
the same as the IP address of another interface or can be any IP address.
Initial discovery timeout. The time to wait before retrying to start a PPPoE
discovery. Set Initial Disc to 0 to disable.
Initial PPPoE Active Discovery Terminate (PADT) timeout in seconds. Use
this timeout to shut down the PPPoE session if it is idle for this number of
seconds. PADT must be supported by your ISP. Set initial PADT timeout to
0 to disable.
PPPoE server. The administrative distance, an integer from 1-255,
specifies the relative priority of a route when there are multiple routes to the
same destination. A lower administrative distance indicates a more
preferred route. The default distance for the default gateway is 1.
Enable Retrieve default gateway from server to retrieve a default gateway
IP address from a PPPoE server. The default gateway is added to the static
routing table.
Enable Override internal DNS to replace the DNS server IP addresses on
the DNS page with the DNS addresses retrieved from the PPPoE server.
Page 60

Interface System Network
Connect to server Enable Connect to Server so that the interface automatically attempts to
Status Displays PPPoE status messages as the FortiGate unit connects to the
initializing No activity.
connecting The interface is attempting to connect to the PPPoE server.
connected The interface retrieves an IP address, netmask, and other settings from the
failed The interface was unable to retrieve an IP address and other information
connect to a PPPoE server. Disable this option if you are configuring the
interface offline.
PPPoE server and gets addressing information. Select Status to refresh the
addressing mode status message.
PPPoE server.
from the PPPoE server.
DDNS
Enable or disable updates to a Dynamic DNS (DDNS) service. When the FortiGate
unit has a static domain name and a dynamic public IP address, select DDNS Enable
to force the unit to update the DDNS server each time the address changes. In turn,
the DDNS service updates Internet DNS servers with the new IP address for the
domain.
Dynamic DNS is available only in NAT/Route mode.
Server Select a DDNS server to use. The client software for these services is built into the
Domain The domain name to use for the DDNS service.
Username The user name to use when connecting to the DDNS server.
Password The password to use when connecting to the DDNS server.
FortiGate firmware. The FortiGate unit can only connect automatically to a DDNS
server for the supported clients.
Ping server
Add a ping server to an interface if you want the FortiGate unit to confirm connectivity
with the next hop router on the network connected to the interface. Adding a ping
server is required for routing failover. See “To add a ping server to an interface” on
page 65.
The FortiGate unit uses dead gateway detection to ping the Ping Server IP address to
make sure that the FortiGate unit can connect to this IP address. To configure dead
gateway detection, see “To modify the dead gateway detection settings” on page 92.
Administrative access
Configure administrative access to an interface to control how administrators access
the FortiGate unit and the FortiGate interfaces to which administrators can connect.
You can select the following administrative access options:
HTTPS To allow secure HTTPS connections to the web-based manager through this
PING If you want this interface to respond to pings. Use this setting to verify your
interface.
installation and for testing.
60 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 61

System Network Interface
HTTP To allow HTTP connections to the web-based manager through this interface.
SSH To allow SSH connections to the CLI through this interface.
SNMP To allow a remote SNMP manager to request SNMP information by connecting to
TELNET To allow Telnet connections to the CLI through this interface. Telnet connections
HTTP connections are not secure and can be intercepted by a third party.
this interface. See “Configuring SNMP” on page 108.
are not secure and can be intercepted by a third party.
MTU
To improve network performance, you can change the maximum transmission unit
(MTU) of the packets that the FortiGate unit transmits from any physical interface.
Ideally, this MTU should be the same as the smallest MTU of all the networks between
the FortiGate unit and the destination of the packets. If the packets that the FortiGate
unit sends are larger, they are broken up or fragmented, which slows down
transmission. Experiment by lowering the MTU to find an MTU size for best network
performance.
To change the MTU, select Override default MTU value (1500) and enter the
maximum packet size. For manual and DHCP addressing mode the MTU size can be
from 576 to 1500 bytes. For PPPoE addressing mode the MTU size can be from 576
to 1492 bytes.
Note: In Transparent mode, if you change the MTU of an interface, you must change the MTU
of all interfaces to match the new MTU.
Log
Select Log to record logs for any traffic to or from the interface. To record logs you
must also enable traffic log for a logging location and set the logging severity level to
Notification or lower. Go to Log & Report > Log Config to configure logging locations
and types. For information about logging see “Log & Report” on page 361.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 61
Page 62

Interface System Network
Configuring interfaces
Use the following procedures to configure FortiGate interfaces and VLAN
subinterfaces.
• To bring down an interface that is administratively up
• To add interfaces to a zone
• To add an interface to a virtual domain
• To change the static IP address of an interface
• To configure an interface for DHCP
• To configure an interface for PPPoE
• To add a secondary IP address
• To configure support for dynamic DNS services
• To add a ping server to an interface
• To control administrative access to an interface
• To change the MTU size of the packets leaving an interface
• To configure traffic logging for connections to an interface
To add a VLAN subinterface
See “To add a VLAN subinterface in NAT/Route mode” on page 73.
To bring down an interface that is administratively up
You can bring down physical interfaces or VLAN subinterfaces. Bringing down a
physical interface also brings down the VLAN subinterfaces associated with it.
1 Go to System > Network > Interface.
The interface list is displayed.
2 Select Bring Down for the interface that you want to stop.
To start up an interface that is administratively down
You can start up physical interfaces and VLAN subinterfaces. Starting a physical
interface does not start the VLAN subinterfaces added to it.
1 Go to System > Network > Interface.
The interface list is displayed.
2 Select Bring Up for the interface that you want to start.
To add interfaces to a zone
If you have added zones to the FortiGate unit, you can use this procedure to add
interfaces or VLAN subinterfaces to the zone. To add a zone, see “To add a zone” on
page 67. You cannot add an interface to a zone if you have added firewall policies for
the interface. Delete firewall policies for the interface and then add the interface to the
zone.
1 Go to System > Network > Zone.
2 Choose the zone to add the interface or VLAN subinterface to and select Edit.
3 Select the names of the interfaces or VLAN subinterfaces to add to the zone.
62 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 63

System Network Interface
4 Select OK to save the changes.
To add an interface to a virtual domain
If you have added virtual domains to the FortiGate unit, you can use this procedure to
add an interface or VLAN subinterface to a virtual domain. To add a virtual domain,
see “To add a virtual domain” on page 149. You cannot add an interface to a virtual
domain if you have added firewall policies for the interface. Delete firewall policies for
the interface and then add the interface to the virtual domain.
1 Go to System > Network > Interface.
2 Choose the interface or VLAN subinterface to add to a virtual domain and select Edit.
3 From the Virtual Domain list, select the virtual domain that you want to add the
interface to.
4 Select OK to save the changes.
5 Repeat these steps to add more interfaces or VLAN subinterfaces to virtual domains.
To change the static IP address of an interface
You can change the static IP address of any FortiGate interface.
1 Go to System > Network > Interface.
2 Choose an interface and select Edit.
3 Set Addressing Mode to Manual.
4 Change the IP address and Netmask as required.
5 Select OK to save your changes.
If you changed the IP address of the interface to which you are connecting to manage
the FortiGate unit, you must reconnect to the web-based manager using the new
interface IP address.
To configure an interface for DHCP
You can configure any FortiGate interface to use DHCP.
1 Go to System > Network > Interface.
2 Choose an interface and select Edit.
3 In the Addressing Mode section, select DHCP.
4 Select the Retrieve default gateway and DNS from server check box if you want the
FortiGate unit to obtain a default gateway IP address and DNS server IP addresses
from the DHCP server.
5 Select the Connect to Server check box if you want the FortiGate unit to connect to
the DHCP server.
6 Select Apply.
The FortiGate unit attempts to contact the DHCP server from the interface to set the
IP address, netmask, and optionally the default gateway IP address, and DNS server
IP addresses.
7 Select Status to refresh the addressing mode status message.
8 Select OK.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 63
Page 64

Interface System Network
To configure an interface for PPPoE
Use this procedure to configure any FortiGate interface to use PPPoE. See “PPPoE”
on page 59 for information on PPPoE settings.
1 Go to System > Network > Interface.
2 Choose an interface and select Edit.
3 In the Addressing Mode section, select PPPoE.
4 Enter your PPPoE account User Name and Password.
5 Enter an Unnumbered IP if required by your PPPoE service.
6 Set the Initial Disc Timeout and Initial PADT Timeout if supported by your ISP.
7 Select the Retrieve default gateway from server check box if you want the FortiGate
unit to obtain a default gateway IP address from the PPPoE server.
8 Select the Override Internal DNS check box if you want the FortiGate unit to obtain a
DNS server IP address from the PPPoE server.
9 Select the Connect to Server check box if you want the FortiGate unit to connect to
the PPPoE server.
10 Select Apply.
The FortiGate unit attempts to contact the PPPoE server from the interface to set the
IP address, netmask, and optionally default gateway IP address and DNS server IP
addresses.
11 Select Status to refresh the addressing mode status message.
12 Select OK.
To add a secondary IP address
You can use the CLI to add a secondary IP address to any FortiGate interface. The
secondary IP address cannot be on the same subnet as the primary interface, any
other interface or any other secondary IP address.
From the FortiGate CLI, enter the following commands:
config system interface
edit <intf_str>
config secondaryip
edit 0
set ip <second_ip> <netmask_ip>
Optionally, you can also configure management access and add a ping server to the
secondary IP address:
set allowaccess ping https ssh snmp http telnet
set gwdetect enable
Save the changes:
end
64 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 65

System Network Interface
To configure support for dynamic DNS services
1 Go to System > Network > Interface.
2 Select the interface to the Internet and then select Edit.
3 Select DDNS Enable.
4 From the Server list, select one of the supported dynamic DNS services.
5 In the Domain field, type the fully qualified domain name of the FortiGate unit.
6 In the Username field, type the user name that the FortiGate unit must send when it
connects to the dynamic DNS server.
7 In the Password field, type the associated password.
8 Select OK.
To add a ping server to an interface
1 Go to System > Network > Interface.
2 Choose an interface and select Edit.
3 Set Ping Server to the IP address of the next hop router on the network connected to
the interface.
4 Select the Enable check box.
5 Select OK to save the changes.
To control administrative access to an interface
For a FortiGate unit running in NAT/Route mode, you can control administrative
access to an interface to control how administrators access the FortiGate unit and the
FortiGate interfaces to which administrators can connect.
Controlling administrative access for an interface connected to the Internet allows
remote administration of the FortiGate unit from any location on the Internet. However,
allowing remote administration from the Internet could compromise the security of
your FortiGate unit. You should avoid allowing administrative access for an interface
connected to the Internet unless this is required for your configuration. To improve the
security of a FortiGate unit that allows remote administration from the Internet:
• Use secure administrative user passwords,
• Change these passwords regularly,
• Enable secure administrative access to this interface using only HTTPS or SSH,
• Do not change the system idle timeout from the default value of 5 minutes (see “To
set the system idle timeout” on page 91).
To configure administrative access in Transparent mode, see “To configure the
management interface” on page 68.
1 Go to System > Network > Interface.
2 Choose an interface and select Edit.
3 Select the Administrative Access methods for the interface.
4 Select OK to save the changes.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 65
Page 66

Zone System Network
To change the MTU size of the packets leaving an interface
1 Go to System > Network > Interface.
2 Choose an interface and select Edit.
3 Select Override default MTU value (1500).
4 Set the MTU size.
Note: You cannot set the MTU of a VLAN. It always has the same MTU as its physical interface.
To configure traffic logging for connections to an interface
1 Go to System > Network > Interface.
2 Choose an interface and select Edit.
3 Select the Log check box to record log messages whenever a firewall policy accepts a
connection to this interface.
4 Select OK to save the changes.
Zone
You can use zones to group related interfaces and VLAN subinterfaces. Grouping
interfaces and VLAN subinterfaces into zones simplifies policy creation. If you group
interfaces and VLAN subinterfaces into a zone, you can configure policies for
connections to and from this zone, rather than to and from each interface and VLAN
subinterface.
You can add zones, rename and edit zones, and delete zones from the zone list.
When you add a zone, you select the names of the interfaces and VLAN subinterfaces
to add to the zone.
Zones are added to virtual domains. If you have added multiple virtual domains to
your FortiGate configuration, make sure you are configuring the correct virtual domain
before adding or editing zones.
Figure 15: Zone list
Create New Select Create New to create a zone.
Name The names of the zones that you have added.
Block intra-zone
traffic
Interface Members The names of the interfaces added to the zone.
Displays Yes if traffic between interfaces in the same zone is blocked and
No if traffic between interfaces in the same zone is not blocked.
Edit/View icons. Select to edit or view a zone.
Delete icon. Select to remove a zone.
66 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 67

System Network Zone
Zone settings
Figure 16: Zone options
Name Enter the name to identify the zone.
Block intra-zone
traffic
Interface members Enable check boxes to select the interfaces that are part of this zone.
To add a zone
1 If you have added a virtual domain, go to System > Virtual Domain > Current Virtual
Domain and select the virtual domain to which you want to add the zone.
2 Go to System > Network > Zone.
Select Block intra-zone traffic to block traffic between interfaces or VLAN
subinterfaces in the same zone.
3 Select Create New.
4 In the New Zone dialog box, type a name for the zone.
5 Select the Block intra-zone traffic check box if you want to block traffic between
interfaces or VLAN subinterfaces in the same zone.
6 Select the names of the interfaces or VLAN subinterfaces to add to the zone.
7 Select OK.
To delete a zone
You can only delete zones that have the Delete icon beside them in the zone list.
1 If you have added a virtual domain, go to System > Virtual Domain > Current Virtual
Domain and select the virtual domain from which to delete the zone.
2 Go to System > Network > Zone.
3 Select Delete to remove a zone from the list.
4 Select OK to delete the zone.
To edit a zone
1 If you have added a virtual domain, go to System > Virtual Domain > Current Virtual
Domain and select the virtual domain in which to edit the zone.
2 Go to System > Network > Zone.
3 Select Edit to modify a zone.
4 Select or deselect Block intra-zone traffic.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 67
Page 68

Management System Network
5 Select the names of the interfaces or VLAN subinterfaces to add to the zone.
6 Clear the check box for the names of the interfaces or VLAN subinterfaces to remove
from the zone.
7 Select OK.
Management
Configure the management interface in Transparent mode to set the management IP
address of the FortiGate unit. Administrators connect to this IP address to administer
the FortiGate unit. The FortiGate also uses this IP address to connect to the FDN for
virus and attack updates (see “Update center” on page 132).
You can also configure interfaces to control how administrators connect to the
FortiGate unit for administration. See “To control administrative access to an interface”
on page 65.
Controlling administrative access to a FortiGate interface connected to the Internet
allows remote administration of the FortiGate unit from any location on the Internet.
However, allowing remote administration from the Internet could compromise the
security of the FortiGate unit. You should avoid allowing administrative access for an
interface connected to the Internet unless this is required for your configuration. To
improve the security of a FortiGate unit that allows remote administration from the
Internet:
• Use secure administrative user passwords,
• Change these passwords regularly,
• Enable secure administrative access to this interface using only HTTPS or SSH,
• Do not change the system idle timeout from the default value of 5 minutes (see “To
set the system idle timeout” on page 91).
Figure 17: Management
Management
IP/Netmask
Default
Gateway
Management
Virtual Domain
Enter the management IP address and netmask. This must be a valid IP
address for the network that you want to manage the FortiGate unit
from.
Enter the default gateway address.
Select the virtual domain from which you want to perform system
management.
To configure the management interface
1 Go to System > Network > Management.
2 Enter the Management IP/Netmask.
68 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 69

System Network DNS
3 Enter the Default Gateway.
4 Select the Management Virtual Domain.
5 Select Apply.
The FortiGate unit displays the following message:
Management IP address was changed. Click here to redirect.
6 Click on the message to connect to the new Management IP.
DNS
Several FortiGate functions, including Alert E-mail and URL blocking, use DNS. You
can add the IP addresses of the DNS servers to which your FortiGate unit can
connect. DNS server IP addresses are usually supplied by your ISP.
Figure 18: DNS
Primary DNS Server Enter the primary DNS server IP address.
Secondary DNS Server Enter the secondary DNS server IP address.
To add DNS server IP addresses
1 Go to System > Network > DNS.
2 Change the primary and secondary DNS server IP addresses as required.
3 Select Apply to save the changes.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 69
Page 70

Routing table (Transparent Mode) System Network
Routing table (Transparent Mode)
In Transparent mode, you can configure routing to add static routes from the FortiGate
unit to local routers.
Routing table list
Figure 19: Routing table
Create New Select Create New to add a new route.
# Route number.
IP The destination IP address for this route.
Mask The netmask for this route.
Gateway The IP address of the next hop router to which this route directs traffic.
Distance The the relative preferability of this route. 1 is most preferred.
Delete icon. Select to remove a route.
View/edit icon. Select to view or edit a route.
Move To icon. Select to change the order of a route in the list.
Transparent mode route settings
Figure 20: Transparent mode route options
Destination IP
/Mask
Gateway Enter the IP address of the next hop router to which this route directs traffic
Distance The the relative preferability of this route. 1 is most preferred.
To add a Transparent mode route
1 Go to System > Network > Routing Table.
2 Select Create New to add a new route.
3 Set the Destination IP and Mask to 0.0.0.0.
For the default route, set the Destination IP and Mask to 0.0.0.0.
Note: Only one default route can be active at a time. If two default routes are added to the
routing table, only the default route closest to the top of the routing table is active.
Enter the destination IP address and netmask for this route.
70 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 71

System Network VLAN overview
4 Set Gateway to the IP address of the next hop routing gateway.
For an Internet connection, the next hop routing gateway routes traffic to the Internet.
5 Select OK to save the route.
VLAN overview
A VLAN is group of PCs, servers, and other network devices that communicate as if
they were on the same LAN segment, even though they may not be. For example, the
workstations and servers for an accounting department could be scattered throughout
an office, connected to numerous network segments, but they can still belong to the
same VLAN.
A VLAN segregates devices logically instead of physically. Each VLAN is treated as a
broadcast domain. Devices in VLAN 1 can connect with other devices in VLAN 1, but
cannot connect with devices in other VLANs. The communication among devices on a
VLAN is independent of the physical network.
A VLAN segregates devices by adding 802.1Q VLAN tags to all of the packets sent
and received by the devices in the VLAN. VLAN tags are 4-byte frame extensions that
contain a VLAN identifier as well as other information.
VLANs allow highly flexible, efficient network segmentation, enabling users and
resources to be grouped logically, regardless of physical locations.
Figure 21: Basic VLAN topology
Internet
Untagged
packets
Esc Enter
VLAN trunk
VLAN 1
VLAN 2
POWER
VLAN 1
VLAN 1 network VLAN 2 network
Firewall or
Router
VLAN Switch or router
VLAN 2
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 71
Page 72

VLANs in NAT/Route mode System Network
FortiGate units and VLANs
In a typical VLAN configuration, 802.1Q-compliant VLAN layer-2 switches or layer-3
routers or firewalls add VLAN tags to packets. Packets passing between devices in
the same VLAN can be handled by layer 2 switches. Packets passing between
devices in different VLANs must be handled by a layer 3 device such as router,
firewall, or layer 3 switch.
Using VLANs, a single FortiGate unit can provide security services and control
connections between multiple security domains. Traffic from each security domain is
given a different VLAN ID. The FortiGate unit can recognize VLAN IDs and apply
security policies to secure network and IPSec VPN traffic between security domains.
The FortiGate unit can also apply authentication, protection profiles, and other firewall
policy features for network and VPN traffic that is allowed to pass between security
domains.
VLANs in NAT/Route mode
Operating in NAT/Route mode, the FortiGate unit functions as a layer 3 device to
control the flow of packets between VLANs. The FortiGate unit can also remove VLAN
tags from incoming VLAN packets and forward untagged packets to other networks,
such as the Internet.
In NAT/Route mode, the FortiGate units support VLANs for constructing VLAN trunks
between an IEEE 802.1Q-compliant switch (or router) and the FortiGate unit. Normally
the FortiGate unit internal interface connects to a VLAN trunk on an internal switch,
and the external interface connects to an upstream Internet router untagged. The
FortiGate unit can then apply different policies for traffic on each VLAN that connects
to the internal interface.
In this configuration, you add VLAN subinterfaces to the FortiGate internal interface
that have VLAN IDs that match the VLAN IDs of packets in the VLAN trunk. The
FortiGate unit directs packets with VLAN IDs, to subinterfaces with matching VLAN
IDs.
You can also define VLAN subinterfaces on all FortiGate interfaces. The FortiGate unit
can add VLAN tags to packets leaving a VLAN subinterface or remove VLAN tags
from incoming packets and add a different VLAN tags to outgoing packets.
Rules for VLAN IDs
In NAT/Route mode, two VLAN subinterfaces added to the same physical interface
cannot have the same VLAN ID. However, you can add two or more VLAN
subinterfaces with the same VLAN IDs to different physical interfaces. There is no
internal connection or link between two VLAN subinterfaces with same VLAN ID. Their
relationship is the same as the relationship between any two FortiGate network
interfaces.
Rules for VLAN IP addresses
IP addresses of all FortiGate interfaces cannot overlap. That is, the IP addresses of all
interfaces must be on different subnets. This rule applies to both physical interfaces
and to VLAN subinterfaces.
72 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 73

System Network VLANs in NAT/Route mode
Note: If you are unable to change your existing configurations to prevent IP overlap, enter the
CLI command config system global and set ip-overlap enable to allow IP address
overlap. If you enter this command, multiple VLAN interfaces can have an IP address that is
part of a subnet used by another interface. This command is recommended for advanced users
only.
Figure 22 shows a simplified NAT/Route mode VLAN configuration. In this example,
FortiGate internal interface connects to a VLAN switch using an 802.1Q trunk and is
configured with two VLAN subinterfaces (VLAN 100 and VLAN 200). The external
interface connects to the Internet. The external interface is not configured with VLAN
subinterfaces.
When the VLAN switch receives packets from VLAN 100 and VLAN 200, it applies
VLAN tags and forwards the packets to local ports and across the trunk to the
FortiGate unit. The FortiGate unit is configured with policies that allow traffic to flow
between the VLANs and from the VLANs to the external network.
Figure 22: FortiGate unit in Nat/Route mode
POWER
Fa0/3 Fa0/9 Fa0/24
VLAN switch
802.1Q Trunk
FortiGate
Esc Enter
Internal
192.168.110.126
External
172.16.21.2
VLAN 100 VLAN 200
VLAN 100 network
10.1.1.0
10.1.1.2
Adding VLAN subinterfaces
The VLAN ID of each VLAN subinterface must match the VLAN ID added by the IEEE
802.1Q-compliant router. The VLAN ID can be any number between 1 and 4096.
Each VLAN subinterface must also be configured with its own IP address and
netmask.
Note: A VLAN must not have the same name as a virtual domain or zone.
You add VLAN subinterfaces to the physical interface that receives VLAN-tagged
packets.
To add a VLAN subinterface in NAT/Route mode
1 Go to System > Network > Interface.
2 Select Create New to add a VLAN subinterface.
3 Enter a Name to identify the VLAN subinterface.
VLAN 200 network
10.1.2.0
10.1.2.2
Internet
4 Select the physical interface that receives the VLAN packets intended for this VLAN
subinterface.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 73
Page 74

VLANs in Transparent mode System Network
5 Enter the VLAN ID that matches the VLAN ID of the packets to be received by this
VLAN subinterface.
6 Select the virtual domain to which to add this VLAN subinterface.
See “System Virtual Domain” on page 145 for information about virtual domains.
7 Select the name of a zone if you want this VLAN subinterface to belong to a zone.
You can only select a zone that has been added to the virtual domain selected in the
previous step. See “Zone” on page 66 for information about zones.
8 Configure the VLAN subinterface settings as you would for any FortiGate interface.
See “Interface settings” on page 56.
9 Select OK to save your changes.
The FortiGate unit adds the new VLAN subinterface to the interface that you selected
in step 4.
To add firewall policies for VLAN subinterfaces
Once you have added VLAN subinterfaces you can add firewall policies for
connections between VLAN subinterfaces or from a VLAN subinterface to a physical
interface.
1 Go to Firewall > Address.
2 Select Create New to add firewall addresses that match the source and destination IP
addresses of VLAN packets.
See “Address” on page 213.
3 Go to Firewall > Policy.
4 Add firewall policies as required.
VLANs in Transparent mode
In Transparent mode, the FortiGate unit can apply firewall policies and services, such
as authentication, protection profiles, and other firewall features, to traffic on an IEEE
802.1 VLAN trunk. You can insert the FortiGate unit operating in Transparent mode
into the trunk without making changes to your network. In a typical configuration, the
FortiGate internal interface accepts VLAN packets on a VLAN trunk from a VLAN
switch or router connected to internal VLANs. The FortiGate external interface
forwards tagged packets through the trunk to an external VLAN switch or router which
could be connected to the Internet. The FortiGate unit can be configured to apply
different policies for traffic on each VLAN in the trunk.
For VLAN traffic to be able to pass between the FortiGate Internal and external
interface you would add a VLAN subinterface to the internal interface and another
VLAN subinterface to the external interface. If these VLAN subinterfaces have the
same VLAN IDs, the FortiGate unit applies firewall policies to the traffic on this VLAN.
If these VLAN subinterfaces have different VLAN IDs, or if you add more than two
VLAN subinterfaces, you can also use firewall policies to control connections between
VLANs.
74 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 75

System Network VLANs in Transparent mode
If the network uses IEEE 802.1 VLAN tags to segment your network traffic, you can
configure a FortiGate unit operating in Transparent mode to provide security for
network traffic passing between different VLANs. To support VLAN traffic in
Transparent mode, you add virtual domains to the FortiGate unit configuration. A
virtual domain consists of two or more VLAN subinterfaces or zones. In a virtual
domain, a zone can contain one or more VLAN subinterfaces.
When the FortiGate unit receives a VLAN tagged packet at an interface, the packet is
directed to the VLAN subinterface with matching VLAN ID. The VLAN subinterface
removes the VLAN tag and assigns a destination interface to the packet based on its
destination MAC address. The firewall policies for this source and destination VLAN
subinterface pair are applied to the packet. If the packet is accepted by the firewall,
the FortiGate unit forwards the packet to the destination VLAN subinterface. The
destination VLAN ID is added to the packet by the FortiGate unit and the packet is
sent to the VLAN trunk.
Figure 23: FortiGate unit with two virtual domains in Transparent mode
VLAN Switch or router
FortiGate unit
VLAN1
External
VLAN trunk
VLAN1
VLAN2
VLAN3
VLAN Switch
or router
Internet
VLAN2
Internal
VLAN1
VLAN2
VLAN3
VLAN trunk
root virtual domain
VLAN1
New virtual domain
VLAN2
VLAN3
VLAN1
VLAN2
VLAN3
VLAN3
Figure 24 shows a FortiGate unit operating in Transparent mode and configured with
three VLAN subinterfaces. In this configuration the FortiGate unit could be added to
this network to provide virus scanning, web content filtering, and other services to
each VLAN.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 75
Page 76

VLANs in Transparent mode System Network
Figure 24: FortiGate unit in Transparent mode
VLAN 1
VLAN ID = 100
FortiGate unit
operating in
Transparent mode
VLAN
switch
VLAN 2
VLAN ID = 200
POWER
Esc Enter
VLAN
switch
POWER
VLAN
Trunk
Internal
External
VLAN 1
VLAN 2
VLAN 3
VLAN
Trunk
Untagged
packets
Router
VLAN 3
VLAN ID = 300
VLAN 1
VLAN 2
VLAN 3
Internet
Rules for VLAN IDs
In Transparent mode two VLAN subinterfaces added to the same physical interface
cannot have the same VLAN ID. However, you can add two or more VLAN
subinterfaces with the same VLAN IDs to different physical interfaces. There is no
internal connection or link between two VLAN subinterfaces with same VLAN ID. Their
relationship is the same as the relationship between any two FortiGate network
interfaces.
Transparent mode virtual domains and VLANs
VLAN subinterfaces are added to and associated with virtual domains. By default the
FortiGate configuration includes one virtual domain, named root, and you can add as
many VLAN subinterfaces as you require to this virtual domain.
You can add more virtual domains if you want to separate groups of VLAN
subinterfaces into virtual domains. For information on adding and configuring virtual
domains, see “System Virtual Domain” on page 145
76 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 77

System Network VLANs in Transparent mode
Transparent mode VLAN list
In Transparent mode, go to System > Network > Interface to add VLAN
subinterfaces.
Figure 25: Sample Transparent mode VLAN list
Create New Select Create New to add a VLAN subinterface to a FortiGate interface.
Virtual Domain Select a virtual domain to display the VLAN interfaces added to this virtual
Name The name of the interface or VLAN subinterface.
Access The administrative access configuration for the interface. See “To control
Status The administrative status for the interface.
domain.
administrative access to an interface” on page 65 for information about
administrative access options.
If the administrative status is a green arrow, the interface is up and can accept
network traffic. If the administrative status is a red arrow, the interface is
administratively down and cannot accept traffic. To change the administrative
status, see “To bring down an interface that is administratively up” on page 62
and “To start up an interface that is administratively down” on page 62.
Delete icon. Select to delete a VLAN subinterface.
View/Edit icon. Select to view or edit an interface or VLAN subinterface.
Transparent mode VLAN settings
VLAN settings displays the current configuration of a selected FortiGate interface or
VLAN subinterface. Use VLAN settings to configure a new VLAN subinterface or to
change the configuration of a FortiGate interface or VLAN subinterface.
Figure 26: VLAN settings
See “Interface settings” on page 56 for descriptions of all VLAN settings.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 77
Page 78

VLANs in Transparent mode System Network
To add a VLAN subinterface in Transparent mode
The VLAN ID of each VLAN subinterface must match the VLAN ID added by the IEEE
802.1Q-compliant router or switch. The VLAN ID can be any number between 1 and
4096. You add VLAN subinterfaces to the physical interface that receives VLAN-
tagged packets.
Note: A VLAN must not have the same name as a virtual domain or zone.
1 Go to System > Network > Interface.
2 Select Create New to add a VLAN subinterface.
3 Enter a Name to identify the VLAN subinterface.
4 Select the physical interface that receives the VLAN packets intended for this VLAN
subinterface.
5 Enter the VLAN ID that matches the VLAN ID of the packets to be received by this
VLAN subinterface.
6 Select the virtual domain to which to add this VLAN subinterface.
See “System Virtual Domain” on page 145 for information about virtual domains.
7 Enable or disable using a Dynamic DNS service (DDNS). If the FortiGate unit uses a
dynamic IP address, you can arrange with a DDNS service provider to use a domain
name to provide redirection of traffic to your network whenever the IP address
changes.
8 Configure the administrative access and log settings as you would for any FortiGate
interface.
See “Interface settings” on page 56 for more descriptions of these settings.
9 Select OK to save your changes.
The FortiGate unit adds the new subinterface to the interface that you selected.
10 Select Bring up to start the VLAN subinterface.
To add firewall policies for VLAN subinterfaces
Once you have added VLAN subinterfaces you can add firewall policies for
connections between VLAN subinterfaces or from a VLAN subinterface to a physical
interface.
1 Go to Firewall > Address.
2 Select Create New to add firewall addresses that match the source and destination IP
addresses of VLAN packets.
See “Address” on page 213.
3 Go to Firewall > Policy.
4 Add firewall policies as required.
78 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 79

System Network FortiGate IPv6 support
FortiGate IPv6 support
You can assign both an IPv4 and an IPv6 address to any interface on a FortiGate unit.
The interface functions as two interfaces, one for IPv4-addressed packets and
another for IPv6-addressed packets.
FortiGate units support static routing, periodic router advertisements, and tunneling of
IPv6-addressed traffic over an IPv4-addressed network. All of these features must be
configured through the Command Line Interface (CLI). See the FortiGate CLI
Reference Guide for information on the following commands:
Table 2: IPv6 CLI commands
Feature CLI Command
Interface configuration, including periodic
router advertisements
Static routing config router static6
IPv6 tunneling config system ipv6_tunnel
config system interface
See the keywords beginning with “ip6”.
config ip6-prefix-list
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 79
Page 80

FortiGate IPv6 support System Network
80 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 81

FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide Version 2.80 MR11
System DHCP
You can configure DHCP server or DHCP relay agent functionality on any FortiGate
interface or VLAN subinterface.
A FortiGate interface can act as either a DHCP server or as a DHCP relay agent. An
interface cannot provide both functions at the same time.
Note: To configure DHCP server or DHCP relay functionality on an interface, the FortiGate unit
must be in NAT/Route mode and the interface must have a static IP address.
This section describes:
• Service
• Server
• Exclude range
• IP/MAC binding
• Dynamic IP
Service
Go to System > DHCP > Service to configure the DHCP service provided by each
FortiGate interface. You can configure each interface to be a DHCP relay or a DHCP
server or you can turn off DHCP services.
Figure 27: DHCP service list
Interface List of FortiGate interfaces.
Service The DHCP service provided by the interface (none, DHCP Relay, or DHCP
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 81
Server).
Edit/View icon. Select to view or modify the DHCP service configuration for
an interface.
Page 82

Service System DHCP
DHCP service settings
Go to System > DHCP > Service and select an edit or view icon to view to modify the
DHCP service configuration for an interface.
Figure 28: View or edit DHCP service settings for an interface
Interface The name of the interface.
None No DHCP services provided by the interface.
DHCP Relay Agent Select to configure the interface to be a DHCP relay agent.
Type Select the type of DHCP relay agent.
Regular Configure the interface to be a DHCP relay agent for computers on the
IPSEC Configure the interface to be a DHCP relay agent only for remote VPN
DHCP Server IP If you select DHCP Relay Agent, enter the IP address of the DHCP server
DHCP Server Select DHCP Server if you want the FortiGate unit to be the DHCP server.
network connected to this interface. See “To configure an interface as a
regular DHCP relay agent” on page 82.
clients with an IPSec VPN connection to this interface that uses DHCP
over IPSec.
used by the computers on the network connected to the interface.
See “To configure an interface to be a DHCP server” on page 83.
To configure an interface as a regular DHCP relay agent
In a DHCP relay configuration, the FortiGate interface configured for DHCP relay
forwards DHCP requests from DHCP clients through the FortiGate unit to a DHCP
server. The FortiGate unit also returns responses from the DHCP server to the DHCP
clients. The DHCP server must have a route to the FortiGate unit that is configured as
the DHCP relay so that the packets sent by the DHCP server to the DHCP client arrive
at the FortiGate performing DHCP relay.
1 Go to System > DHCP > Service.
2 Select Edit for the interface that you want to be a DHCP relay agent.
3 Select DHCP Relay Agent.
4 Set type to Regular.
5 Enter the DHCP Server IP address.
6 Select OK.
82 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 83

System DHCP Server
To configure an interface to be a DHCP server
You can configure a DHCP server for any FortiGate interface. As a DHCP server, the
interface dynamically assigns IP addresses to hosts on the network connected to the
interface. You can also configure a DHCP server for more than one FortiGate
interface.
1 Go to System > DHCP > Service.
2 Select Edit beside the interface to which you want to add a DHCP server.
3 Select DHCP Server.
4 Select OK.
5 Add a DHCP server configuration for this interface.
See “To configure a DHCP server for an interface” on page 85.
Server
You can configure one or more DHCP servers for any FortiGate interface. As a DHCP
server, the interface dynamically assigns IP addresses to hosts on a network
connected to the interface.
You can add more than one DHCP server to a single interface to be able to provide
DHCP services to multiple networks. For more information, see “To configure multiple
DHCP servers for an interface” on page 85.
Figure 29: DHCP Server list
Create New Add a new DHCP server.
Name Name of the DHCP server.
Interface The interface for which the DHCP server is configured.
Default Gateway The DHCP server configuration default gateway
Delete Delete a DHCP server configuration.
Edit/View icon View or modify a DHCP server configuration.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 83
Page 84

Server System DHCP
DHCP server settings
Figure 30: Server options
Name Enter a name for the DHCP server configuration.
Interface Select the interface for which to configure the DHCP server.
Domain Enter the domain that the DHCP server assigns to DHCP clients.
Default Gateway Enter the IP address of the default gateway that the DHCP server
IP Range Enter the starting IP and ending IP for the range of IP addresses that this
Network Mask Enter the netmask that the DHCP server assigns to DHCP clients.
Lease Time Select Unlimited for an unlimited lease time or enter the interval in days,
DNS Server Enter the IP addresses of up to 3 DNS servers that the DHCP server
WINS Server Add the IP addresses of one or two WINS servers that the DHCP server
Option Up to three custom DHCP options that can be sent by the DHCP server.
assigns to DHCP clients.
DHCP server assigns to DHCP clients.
hours, and minutes after which a DHCP client must ask the DHCP server
for new settings. The lease time can range from 5 minutes to 100 days.
assigns to DHCP clients.
assigns to DHCP clients.
Code is the DHCP option code in the range 1 to 255. Option is an even
number of hexadecimal characters and is not required for some option
codes. For detailed information about DHCP options, see RFC 2132,
DHCP Options and BOOTP Vendor Extensions.
84 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 85

System DHCP Exclude range
To configure a DHCP server for an interface
After configuring an interface to be a DHCP server (using the procedure “To configure
an interface to be a DHCP server” on page 83), you must configure a DHCP server for
the interface.
1 Go to System > DHCP > Server.
2 Select Create New.
3 Add a name for the DHCP server.
4 Select the interface
5 Configure the DHCP server.
The IP range must match the subnet address of the network from which the DHCP
request was received. Usually this would be the subnet connected to the interface for
which you are added the DHCP server.
6 Select OK to save the DHCP server configuration.
To configure multiple DHCP servers for an interface
If an interface is connected to a network that includes routers connected to different
subnets, you can:
1 Configure computers on the subnets to get their IP configuration using DHCP.
The IP range of each DHCP server must match the subnet addresses.
2 Configure the routers for DHCP relay.
3 Add multiple DHCP servers to the interface, one for each subnet.
Exclude range
When a computer on one of the connected subnets sends a DHCP request it is
relayed to the FortiGate interface by the router, using DHCP relay. The FortiGate unit
selects the DHCP server configuration with an IP range that matches the subnet
address from which the DHCP request was received and uses this DHCP server to
assign an IP configuration to the computer that made the DHCP request. The DHCP
configuration packets are sent back to the router and the router relays them to the
DHCP client.
Add up to 16 exclude ranges of IP addresses that FortiGate DHCP servers cannot
assign to DHCP clients. Exclude ranges apply to all FortiGate DHCP servers.
Figure 31: Exclude range list
Create New Select Create New to add an exclude range.
# The ID number of each exclude range. ID numbers are assigned
sequentially by the web-based manager. When you add or edit exclude
ranges from the CLI you must specify the ID number.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 85
Page 86

IP/MAC binding System DHCP
Starting IP The starting IP of the exclude range.
Ending IP The ending IP of the exclude range.
Delete Delete an exclude range.
Edit/View icon View or modify an exclude range.
DHCP exclude range settings
The range cannot exceed 65536 IP addresses.
Figure 32: Exclude range settings
Starting IP Enter the starting IP of an exclude range.
Ending IP Enter the ending IP of an exclude range.
To add an exclusion range
1 Go to System > DHCP > Exclude Range.
2 Select Create New.
3 Add the starting IP and ending IP.
4 Select OK to save the exclusion range.
IP/MAC binding
If you have added DHCP servers, you can use DHCP IP/MAC binding to reserve an
IP address for a particular device on the network according to the MAC address of the
device. When you add the MAC address and an IP address to the IP/MAC binding list,
the DHCP server always assigns this IP address to the MAC address. IP/MAC binding
pairs apply to all FortiGate DHCP servers.
Figure 33: IP/MAC binding list
Create New Select Create New to add a DHCP IP/MAC binding pair.
Name The name for the IP and MAC address pair.
IP Address The IP address for the IP and MAC address pair. The IP address must be
within the configured IP range.
MAC Address The MAC address of the device.
86 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 87

System DHCP Dynamic IP
Delete icon. Delete an IP/MAC binding pair.
Edit/View icon. View or modify an IP/MAC binding pair.
DHCP IP/MAC binding settings
Figure 34: IP/MAC binding options
Name Enter a name for the IP/MAC address pair.
IP Address Enter the IP address for the IP and MAC address pair. The IP address must
MAC Address Enter the MAC address of the device.
To add a DHCP IP/MAC binding pair
1 Go to System > DHCP > IP/MAC Binding.
2 Select Create New.
be within the configured IP range.
Dynamic IP
3 Add a name for the IP/MAC pair.
4 Add the IP address and MAC address.
5 Select OK to save the IP/MAC pair.
You can view the list of IP addresses that the DHCP server has assigned, their
corresponding MAC addresses, and the expiry time and date for these addresses.
Interface Select to display its dynamic IP list.
IP The IP addresses that the DHCP server has assigned.
MAC The corresponding MAC addresses for the dynamic IP addresses.
Expire The expiry time and date for the dynamic IP addresses and their corresponding
MAC addresses.
To view the dynamic IP list
1 Go to System > DHCP > Dynamic IP.
2 Select the interface for which you want to view the list.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 87
Page 88

Dynamic IP System DHCP
88 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 89

FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide Version 2.80 MR11
System Config
Use the System Config page to make any of the following changes to the FortiGate
system configuration:
• System time
• Options
• HA
• SNMP
• Replacement messages
• FortiManager
System time
Go to System > Config > Time to set the FortiGate system time.
For effective scheduling and logging, the FortiGate system time must be accurate.
You can either manually set the FortiGate system time or you can configure the
FortiGate unit to automatically keep its system time correct by synchronizing with a
Network Time Protocol (NTP) server.
Figure 35: System time
System Time The current FortiGate system date and time.
Refresh Select Refresh to update the display of the current FortiGate system date
Time Zone Select the current FortiGate system time zone.
and time.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 89
Page 90

Options System Config
Automatically
adjust clock for
daylight saving
changes
Set Time Select Set Time to set the FortiGate system date and time to the correct
Synchronize with
NTP Server
Server Enter the IP address or domain name of the NTP server that the
Syn Interval Specify how often the FortiGate unit should synchronize its time with the
Select the Automatically adjust clock for daylight saving changes check
box if you want the FortiGate system clock to be adjusted automatically
when your time zone changes to daylight saving time and back to
standard time.
date and time.
Select Synchronize with NTP Server to configure the FortiGate unit to
use NTP to automatically set the system date and time. For more
information about NTP and to find the IP address of an NTP server that
you can use, see http://www.ntp.org.
FortiGate unit can use to set its time and date.
NTP server. A typical Syn Interval would be 1440 minutes for the
FortiGate unit to synchronize its time once a day.
To manually set the FortiGate date and time
1 Go to System > Config > Time.
2 Select Refresh to display the current FortiGate system date and time.
3 Select your Time Zone from the list.
4 Optionally, select Automatically adjust clock for daylight saving changes check box.
5 Select Set Time and set the FortiGate system date and time.
6 Set the hour, minute, second, month, day, and year as required.
7 Select Apply.
Options
To use NTP to set the FortiGate date and time
1 Go to System > Config > Time.
2 Select Synchronize with NTP Server to configure the FortiGate unit to use NTP to
automatically set the system time and date.
3 Enter the IP address or domain name of the NTP server that the FortiGate unit can
use to set its time and date.
4 Specify how often the FortiGate unit should synchronize its time with the NTP server.
5 Select Apply.
Go to System > Config > Options to set the following options:
• Timeout settings including the idle timeout and authentication timeout
• The language displayed by the web-based manager
• Front control buttons and LCD PIN protection
• Dead gateway detection interval and failover detection
90 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 91

System Config Options
Figure 36: System config options
Idle Timeout Set the idle time out to control the amount of inactive time before the
Auth Timeout Set the firewall user authentication timeout to control how long an
Language Select a language for the web-based manager to use. Choose from
LCD Panel Select the PIN Protection check box and type a 6-digit PIN.
Detection Interval Set the dead gateway detection failover interval. Enter a number in
Fail-over Detection Set the ping server dead gateway detection failover number. Enter the
administrator must log in again. The maximum admintimeout is 480
minutes (8 hours). To improve security keep the idle timeout at the
default value of 5 minutes.
authenticated connection can be idle before the user must authenticate
again. The maximum authtimeout is 480 minutes (8 hours). The
default Auth Timeout is 15 minutes.
For more information, see “Setting authentication timeout” on page 250.
English, Simplified Chinese, Japanese, Korean, or French.
Administrators must enter the PIN to use the control buttons and LCD.
See “To set PIN protection for the LCD panel” on page 92.
seconds to specify how often the FortiGate unit pings the target.
number of times that ping fails before the FortiGate unit assumes that the
gateway is no longer functioning.
To set the system idle timeout
1 Go to System > Config > Options.
2 For Idle Timeout, type a number in minutes.
3 Select Apply.
To set the Auth timeout
1 Go to System > Config > Options.
2 For Auth Timeout, type a number in minutes.
3 Select Apply.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 91
Page 92

HA System Config
To select a language for the web-based manager
1 Go to System > Config > Options.
2 From the Languages list, select a language for the web-based manager to use.
3 Select Apply.
Note: You should select the language that the management computer operating system uses.
To set PIN protection for the LCD panel
1 Go to System > Config > Options.
2 In the LCD Panel section, select the PIN Protection check box.
3 Type a 6-digit PIN.
4 Select Apply.
To modify the dead gateway detection settings
Modify dead gateway detection to control how the FortiGate unit confirms connectivity
with a ping server added to an interface configuration. For information about adding a
ping server to an interface, see “To add a ping server to an interface” on page 65.
HA
1 Go to System > Config > Options.
2 For Detection Interval, type a number in seconds to specify how often the FortiGate
unit tests the connection to the ping target.
3 For Fail-over Detection, type a number of times that the connection test fails before
the FortiGate unit assumes that the gateway is no longer functioning.
4 Select Apply.
Go to System > Config > HA to configure the FortiGate unit for High Availability (HA)
mode operation.
• HA overview
• HA configuration
• Configuring an HA cluster
• Managing an HA cluster
HA overview
FortiGate HA consists of two or more FortiGate units operating as an HA cluster. To
the network, the HA cluster appears to function as a single FortiGate unit, processing
network traffic and providing normal security services such as firewalling, VPN, IPS,
virus scanning, web filtering, and spam filtering services.
92 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 93

System Config HA
Inside the cluster the individual FortiGate units are called cluster units. These cluster
units share state and configuration information. If one cluster unit fails, the other units
in the cluster automatically replace that unit, taking over the work that the failed unit
was doing. The cluster continues to process network traffic and provide normal
FortiGate services with virtually no interruption.
Every cluster contains one primary cluster unit (also called primary units) and one or
more subordinate cluster units (also called subordinate units). The primary unit
controls how the cluster operates. The roles that the primary and subordinate units
play in the cluster depend on the mode in which the cluster operates. See “HA modes”
on page 94.
The ability of an HA cluster to continue providing firewall services after a failure, is
called failover. FortiGate HA failover means that your network does not have to rely on
one FortiGate unit to continue functioning. You can install additional units and form an
HA cluster. Other units in the cluster will take over if one of the units fails.
A second HA feature, called load balancing, can be used to increase firewall
performance. A cluster of FortiGate units can increase overall network performance
by sharing the load of processing network traffic and providing security services. The
cluster appears to your network to be a single device, adding increased performance
without changing your network configuration.
The FortiGate Clustering Protocol (FGCP)
Fortinet achieves high availability (HA) using redundant hardware and the FortiGate
Clustering Protocol (FGCP). Each FortiGate unit in an HA cluster enforces the same
overall security policy and shares the same configuration settings. You can add up to
32 FortiGate units to an HA cluster. Each FortiGate unit in an HA cluster must be the
same model and must be running the same FortiOS firmware image.
The FortiGate units in the cluster use ethernet interfaces to communicate cluster
session information, synchronize the cluster configuration, synchronize the cluster
routing table, and report individual cluster member status. In the cluster, these
ethernet interfaces are called heartbeat devices and the communication between
cluster units is called the HA heartbeat. Using the HA heartbeat, cluster units are
constantly communicating HA status information to make sure that the cluster is
operating properly.
FortiGate HA and the FGCP support link failover, device failover, and HA heartbeat
failover.
Link failover If one of the links to a FortiGate unit in an HA cluster fails, all functions, all
Device failover If one of the FortiGate units in an HA cluster fails, all functions, all established
HA heartbeat
failover
established firewall connections, and all IPSec VPN sessionsa are maintained
by the other FortiGate units in the HA cluster. For information about link
failover, see “Monitor priorities” on page 100.
firewall connections, and all IPSec VPN sessions are maintained by the other
FortiGate units in the HA cluster.
You can configure multiple interfaces to be HA heartbeat devices. If an
interface functioning as an HA heartbeat device fails, the HA heartbeat is
transferred to another interface also configured as an HA heartbeat device.
a.HA does not provide session failover for PPPoE, DHCP, PPTP, and L2TP services.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 93
Page 94

HA System Config
HA modes
FortiGate units can be configured to operate in active-passive (A-P) or active-active
(A-A) HA mode. Active-active and active-passive clusters can run in either NAT/Route
or Transparent mode.
An active-passive (A-P) HA cluster, also referred to as failover HA, consists of a
primary unit that processes traffic, and one or more subordinate units. The
subordinate units are connected to the network and to the primary unit but do not
process traffic.
When a cluster is operating in active-passive mode, in addition to the operating mode
(NAT or Transparent) the front panel LCD of all cluster units displays (a-p). On the
primary unit the LCD displays primary. One the subordinate units, the LCD displays
slave <priority_id>. The priority_id is the priority that the subordinate unit
has in the cluster. If there are three units in the Cluster the LCD displays are:
• primary (a-p)
• slave 1 (a-p)
• slave 2 (a-p)
Active-active (A-A) HA load balances network traffic to all of the cluster units. An
active-active HA cluster consists of a primary unit that processes traffic and one or
more subordinate units that also process traffic. The primary unit uses a load
balancing algorithm to distribute processing to all of the cluster units in the HA cluster.
By default a FortiGate HA active-active cluster load balances virus scanning sessions
among all cluster units. All other traffic is processed by the primary unit. Using the CLI,
you can configure the cluster to load balance TCP traffic and virus scanning traffic
among all cluster units. See “To configure load balancing TCP and virus scanning
traffic” on page 104.
When a cluster is operating in active-active mode, in addition to the operating mode
(NAT or Transparent) the front panel LCD of all cluster units displays (a-a). On the
primary unit the LCD displays primary. One the subordinate units, the LCD displays
slave <priority_id>. The priority_id is the priority that the subordinate unit
has in the cluster. If there are three units in the Cluster the LCD displays are:
• primary (a-a)
• slave 1 (a-a)
• slave 2 (a-a)
For more information about FortiGate HA and the FGCP, see the FortiGate High
Availability Guide and the Fortinet Knowledge Center.
FortiGate HA compatibility with DHCP and PPPoE
FortiGate HA is not compatible with PPP protocols such as DHCP or PPPoE. If one or
more FortiGate unit interfaces is dynamically configured using DHCP or PPPoE you
cannot switch to operating in HA mode. Also, if you are operating a FortiGate HA
cluster, you cannot change a FortiGate interface in the cluster to be configured
dynamically using DHCP or PPPoE.
Configuring a FortiGate interface to be a DHCP server or a DHCP relay agent is not
affect by HA operation. For information about DHCP server and relay, see “System
DHCP” on page 81.
94 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 95

System Config HA
PPTP and L2TP are supported in HA mode. You can configure PPTP and L2TP
settings (see “PPTP range” on page 278 and “L2TP range” on page 278) you can also
add firewall policies to allow PPTP and L2TP pass through. However, during an HA
failover event, any active PPTP and L2TP sessions are lost and must be restarted
after the failover.
HA configuration
Go to System > Config > HA and use the options described below to configure HA.
• Standalone Mode
• High Availability
• Cluster Members
• Mode
• Group ID
• Unit Priority
• Override Master
• Password
• Schedule
• Priorities of Heartbeat Device
• Heartbeat device IP addresses
• Monitor priorities
Figure 37: HA configuration (FortiGate-1000A)
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 95
Page 96

HA System Config
Standalone Mode
Standalone mode is the default operation mode. If Standalone mode is selected the
FortiGate unit is not operating in HA mode.
Select Standalone Mode if you want to stop a cluster unit from operating in HA mode.
High Availability
Select High Availability to operate the FortiGate unit in HA mode. After selecting High
Availability, complete the remainder of the HA configuration.
Cluster Members
When the cluster is operating, you can select Cluster Members to view the status of all
FortiGate units in the cluster. Status information includes the cluster ID, status, up
time, weight, and monitor information. For more information, see “To view the status of
each cluster member” on page 105.
Mode
All members of the HA cluster must be set to the same HA mode.
Active-Active Load balancing and failover HA. Each cluster unit actively processes
Active-Passive Failover HA. The primary unit processes all connections. All other cluster units
connections and monitors the status of the other cluster units. The primary unit
controls load balancing among all of the cluster units.
passively monitor the cluster status and remain synchronized with the primary
unit.
For more information about HA mode, see “HA modes” on page 94.
Group ID
The group ID range is from 0 to 63. All cluster units must have the same group ID.
When the FortiGate units are switched to HA mode, all of the interfaces of all of the
cluster units acquire the same virtual MAC address. This virtual MAC address is set
according to the group ID. Table 3 lists the virtual MAC address set for each group ID.
Table 3: HA group ID and MAC address
Group ID MAC Address
0 00-09-0f-06-ff-00
1 00-09-0f-06-ff-01
2 00-09-0f-06-ff-02
3 00-09-0f-06-ff-03
… ...
63 00-09-0f-06-ff-3f
If you have more than one HA cluster on the same network, each cluster should have
a different group ID. If two clusters on the same network have the same group ID, the
duplicate MAC addresses can cause addressing conflicts on the network.
96 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 97

System Config HA
Unit Priority
Optionally set the unit priority of the cluster unit. Each cluster unit can have a different
unit priority. The unit priority is not synchronized among cluster members. During HA
negotiation, the unit with the highest unit priority becomes the primary unit. The unit
priority range is 0 to 255. The default unit priority is 128.
You can use the unit priority to control the order in which cluster units become the
primary unit when a cluster unit fails. For example, if you have three FortiGate units in
a cluster you can set the unit priorities as shown in Table 4. Cluster unit A will always
be the primary unit because it has the highest priority. If cluster unit A fails, cluster
unit B becomes the primary unit because cluster unit B has a higher unit priority than
cluster unit C.
Table 4: Example unit priorities for a cluster of three cluster units
Cluster unit Unit priority
A200
B100
C50
In a functioning cluster, if you change the unit priority of the current primary unit to a
lower priority, when the cluster renegotiates a different cluster unit becomes the
primary unit.
Override Master
Configure a cluster unit to always override the current primary unit and become the
primary unit. Enable override master for the cluster unit that you have given the
highest unit priority. Enabling override master means that this cluster unit always
becomes the primary unit.
In a typical FortiGate cluster configuration, the primary unit is selected automatically.
In some situations, you might want to control which unit becomes the primary unit. You
can configure a FortiGate unit as the permanent primary unit by setting a high unit
priority and by selecting override master. With this configuration, the same cluster unit
always becomes the primary unit.
If override master is enabled and the primary unit fails, another cluster unit becomes
the primary unit. When the cluster unit with override master enabled rejoins the cluster
it overrides the current primary unit and becomes the new primary unit. When this
override occurs, all communication sessions through the cluster are lost and must be
re-established.
Override master is not synchronized to all cluster units.
In a functioning cluster, if you select override master for a cluster unit the cluster re-
negotiates and may select a new primary cluster unit.
Password
Enter a password for the HA cluster. The password must be the same for all cluster
units. The maximum password length is 15 characters.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 97
Page 98

HA System Config
If you have more than one FortiGate HA cluster on the same network, each cluster
must have a different password.
Schedule
If you are configuring an active-active cluster, select a load balancing schedule.
None No load balancing. Select None when the cluster interfaces are connected
Hub Load balancing if the cluster interfaces are connected to a hub. Traffic is
Least-
Connection
Round-Robin Round robin load balancing. If the cluster units are connected using
Weighted
Round-Robin
Random Random load balancing. If the cluster units are connected using switches,
IP Load balancing according to IP address. If the cluster units are connected
IP Port Load balancing according to IP address and port. If the cluster units are
to load balancing switches.
distributed to cluster units based on the Source IP and Destination IP of
each packet processed by the cluster.
Least connection load balancing. If the cluster units are connected using
switches, select Least Connection to distribute network traffic to the cluster
unit currently processing the fewest connections.
switches, select Round-Robin to distribute network traffic to the next
available cluster unit.
Weighted round robin load balancing. Similar to round robin, but weighted
values are assigned to each of the units in a cluster based on their capacity
and on how many connections they are currently processing. For example,
the primary unit should have a lower weighted value because it handles
scheduling and forwards traffic. Weighted round robin distributes traffic
more evenly because units that are not processing traffic will be more likely
to receive new connections than units that are very busy. To configure
weighted round robin weights, see “To configure weighted-round-robin
weights” on page 103.
select Random to randomly distribute traffic to cluster units.
using switches, select IP to distribute traffic to cluster units based on the
Source IP and Destination IP of the packet.
connected using switches, select IP Port to distribute traffic to cluster units
based on the source IP, source port, destination IP, and destination port of
the packet.
By default a FortiGate HA active-active cluster load balances virus scanning sessions
among all cluster units. All other traffic is processed by the primary unit. Using the CLI,
you can configure the cluster to load balance all network traffic among all cluster units.
See “To configure load balancing TCP and virus scanning traffic” on page 104.
Priorities of Heartbeat Device
Enable or disable HA heartbeat communication and set the heartbeat priority for each
interface in the cluster.
By default, HA heartbeat communication is set for two interfaces. You can disable the
HA heartbeat for either of these interfaces or enable HA heartbeat for other interfaces.
In most cases you can maintain the default heartbeat device configuration as long as
you can connect the heartbeat device interfaces together.
The heartbeat priority must be set for at least one cluster interface. If heartbeat
communication is interrupted the cluster stops processing traffic.
98 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 99

System Config HA
To enable HA heartbeat communication for an interface, enter a priority for the
interface. To disable HA heartbeat communication for an interface, delete the priority
for the interface.
The HA heartbeat priority range is 0 to 512. The interface with the highest priority
handles all HA heartbeat traffic. If this interface fails or becomes disconnected, the
interface with the next highest priority handles all HA heartbeat traffic.
The cluster units use the ethernet interfaces configured with HA heartbeat priorities for
HA heartbeat communication. The HA heartbeat communicates cluster session
information, synchronizes the cluster configuration, synchronizes the cluster routing
table, and reports individual cluster member status. The HA heartbeat constantly
communicates HA status information to make sure that the cluster is operating
properly.
You can enable heartbeat communications for physical interfaces, but not for VLAN
subinterfaces.
Enabling the HA heartbeat for more interfaces increases reliability. If an interface fails,
the HA heartbeat can be diverted to another interface.
HA heartbeat traffic can use a considerable amount of network bandwidth. If possible,
enable HA heartbeat traffic on interfaces only used for HA heartbeat traffic or on
interfaces connected to less busy networks.
Table 5: Default heartbeat device configuration
FortiGate model Default heartbeat device Default priority
FortiGate-1000A and
FortiGate-1000AFA2
Port 3 50
Port 4 100
Change the heartbeat device priorities as required to control the interface that is used
for heartbeat traffic and the interface to which heartbeat traffic reverts if the interface
with the highest heartbeat priority fails or is disconnected.
Setting the heartbeat priority for more interfaces increases the reliability of the cluster.
To optimize bandwidth use, you can route most heartbeat traffic to interfaces that
handle less network traffic. You can also create a failover path by setting heartbeat
priorities so that you can control the order in which interfaces are used for heartbeat
traffic.
Heartbeat device IP addresses
You do not need to assign IP addresses to heartbeat device interfaces for them to be
able to process heartbeat packets. The cluster assigns virtual IP addresses to the
heartbeat device interfaces. The primary cluster unit heartbeat device interface is
assigned the IP address 10.0.0.1 and the subordinate unit heartbeat device interface
is assigned the IP address 10.0.0.2. A third cluster unit would be assigned the IP
address 10.0.0.3 and so on.
FortiGate-1000A/FA2 Administration Guide 01-28011-0254-20051115 99
Page 100

HA System Config
For best results, isolate each heartbeat device on its own network. Heartbeat packets
contain sensitive information about the cluster configuration. Also, heartbeat packets
may use a considerable amount of network bandwidth and it is preferable to isolate
this traffic from your user networks. The extra bandwidth used by heartbeat packets
could also reduce the capacity of the interface to process network traffic.
For most FortiGate models if you do not change the heartbeat device configuration,
you would isolate the HA interfaces of all of the cluster units by connecting them all to
the same switch. If the cluster consists of two FortiGate units you can connect the
heartbeat device interfaces directly using a crossover cable.
HA heartbeat and data traffic are supported on the same FortiGate interface. In
NAT/Route mode, if you decide to use the heartbeat device interfaces for processing
network traffic or for a management connection, you can assign the interface any IP
address. This IP address does not affect the heartbeat traffic.
In Transparent mode, you can connect the interface to your network and enable
management access. You would then establish a management connection to the
interface using the Transparent mode management IP address.
Monitor priorities
Enable or disable monitoring a FortiGate interface to verify that the interface is
functioning properly and connected to its network. If a monitored interface fails or is
disconnected from its network the interface leaves the cluster. The cluster reroutes the
traffic being processed by that interface to the same interface of another cluster unit
that still has a connection to the network. This other cluster unit becomes the new
primary cluster unit.
If you can re-establish traffic flow through the interface (for example, if you re-connect
a disconnected network cable) the interface rejoins the cluster. If Override Master is
enabled for this FortiGate unit (see “Override Master” on page 97), this FortiGate unit
becomes the primary unit in the cluster again.
Note: Only monitor interfaces that are connected to networks.
Note: You can monitor physical interfaces, but not VLAN subinterfaces.
Increase the priority of interfaces connected to higher priority networks or networks
with more traffic. The monitor priority range is 0 to 512.
If a high priority interface on the primary unit fails, one of the other cluster units
becomes the new primary unit to provide better service to the high priority network.
If a low priority interface fails on one cluster unit and a high priority interface fails on
another cluster unit, a unit in the cluster with a working connection to the high priority
interface would, if it becomes necessary to negotiate a new primary unit, be selected
instead of a unit with a working connection to the low priority interface.
• Configuring an HA cluster
• Managing an HA cluster
100 01-28011-0254-20051115 Fortinet Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...