Page 1

FortiGate 60R
Installation and
Configuration Guide
FortiGate User Manual Volume 1
INTERNAL
PWR STATUS
LINK 100 LINK 100 LINK 100 LINK 100 LINK 100 LINK 100 LINK 100
Version 2.50 MR2
18 August 2003
DMZ4321
WAN1 WAN2
Page 2

© Copyright 2003 Fortinet Inc. All rights reserved.
No part of this publication including text, examples, diagrams or illustrations may be reproduced,
transmitted, or translated in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, manual, optical or
otherwise, for any purpose, without prior written permission of Fortinet Inc.
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide
Version 2.50 MR2
18 August 2003
Trademarks
Products mentioned in this document are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
holders.
Regulatory Compliance
FCC Class A Part 15 CSA/CUS
For technical support, please visit http://www.fortinet.com.
Send information about errors or omissions in this document or any Fortinet technical documentation to
techdoc@fortinet.com.
Page 3

Table of Contents
Introduction .......................................................................................................... 13
Antivirus protection ........................................................................................................... 13
Web content filtering ......................................................................................................... 14
Email filtering .................................................................................................................... 14
Firewall.............................................................................................................................. 15
NAT/Route mode .......................................................................................................... 15
Transparent mode......................................................................................................... 16
Network intrusion detection............................................................................................... 16
VPN................................................................................................................................... 16
Secure installation, configuration, and management ........................................................ 17
Web-based manager .................................................................................................... 17
Command line interface ................................................................................................ 18
Logging and reporting ................................................................................................... 19
What’s new in Version 2.50 .............................................................................................. 19
System administration................................................................................................... 19
Firewall.......................................................................................................................... 20
Users and authentication .............................................................................................. 20
VPN............................................................................................................................... 20
NIDS ............................................................................................................................. 21
Antivirus ........................................................................................................................ 21
Web Filter...................................................................................................................... 21
Email filter ..................................................................................................................... 21
Logging and Reporting.................................................................................................. 21
About this document ......................................................................................................... 22
Document conventions ..................................................................................................... 23
Fortinet documentation ..................................................................................................... 24
Comments on Fortinet technical documentation........................................................... 24
Customer service and technical support........................................................................... 25
Contents
Getting started ..................................................................................................... 27
Package contents ............................................................................................................. 28
Mounting ........................................................................................................................... 28
Powering on...................................................................................................................... 29
Connecting to the web-based manager............................................................................ 30
Connecting to the command line interface (CLI)............................................................... 31
Factory default FortiGate configuration settings ............................................................... 31
Factory Default DHCP configuration............................................................................. 32
Factory default NAT/Route mode network configuration .............................................. 33
Factory default Transparent mode network configuration............................................. 33
Factory default firewall configuration ............................................................................ 34
Factory default content profiles..................................................................................... 35
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 3
Page 4

Contents
Planning your FortiGate configuration .............................................................................. 37
NAT/Route mode .......................................................................................................... 37
Transparent mode......................................................................................................... 38
Configuration options .................................................................................................... 39
FortiGate model maximum values matrix ......................................................................... 40
Next steps......................................................................................................................... 41
NAT/Route mode installation.............................................................................. 43
Installing the FortiGate unit using the default configuration .............................................. 43
Changing the default configuration ............................................................................... 44
Preparing to configure NAT/Route mode.......................................................................... 44
Advanced NAT/Route mode settings............................................................................ 45
DMZ interface ............................................................................................................... 45
Using the setup wizard...................................................................................................... 46
Starting the setup wizard .............................................................................................. 46
Reconnecting to the web-based manager .................................................................... 46
Using the command line interface..................................................................................... 46
Configuring the FortiGate unit to operate in NAT/Route mode ..................................... 46
Connecting the FortiGate unit to your networks................................................................ 48
Configuring your networks ................................................................................................ 49
Completing the configuration ............................................................................................ 50
Configuring the DMZ interface ...................................................................................... 50
Configuring the WAN2 interface ................................................................................... 50
Setting the date and time .............................................................................................. 50
Changing antivirus protection ....................................................................................... 50
Registering your FortiGate............................................................................................ 51
Configuring virus and attack definition updates ............................................................ 51
Configuration example: Multiple connections to the Internet ............................................ 51
Configuring Ping servers............................................................................................... 52
Destination based routing examples............................................................................. 53
Policy routing examples ................................................................................................ 56
Firewall policy example................................................................................................. 57
Transparent mode installation............................................................................ 59
Preparing to configure Transparent mode ........................................................................ 59
Using the setup wizard...................................................................................................... 60
Changing to Transparent mode .................................................................................... 60
Starting the setup wizard .............................................................................................. 60
Reconnecting to the web-based manager .................................................................... 60
Using the command line interface..................................................................................... 61
Changing to Transparent mode .................................................................................... 61
Configuring the Transparent mode management IP address ....................................... 61
Configure the Transparent mode default gateway........................................................ 61
Connecting the FortiGate unit to your networks................................................................ 62
4 Fortinet Inc.
Page 5

Completing the configuration ............................................................................................ 63
Setting the date and time .............................................................................................. 63
Enabling antivirus protection......................................................................................... 63
Registering your FortiGate............................................................................................ 63
Configuring virus and attack definition updates ............................................................ 64
Transparent mode configuration examples....................................................................... 64
Default routes and static routes .................................................................................... 64
Example default route to an external network............................................................... 65
Example static route to an external destination ............................................................ 66
Example static route to an internal destination ............................................................. 69
System status....................................................................................................... 71
Changing the FortiGate host name................................................................................... 72
Changing the FortiGate firmware...................................................................................... 72
Upgrade to a new firmware version .............................................................................. 73
Revert to a previous firmware version .......................................................................... 74
Install a firmware image from a system reboot using the CLI ....................................... 77
Test a new firmware image before installing it .............................................................. 79
Manual virus definition updates ........................................................................................ 81
Manual attack definition updates ...................................................................................... 82
Displaying the FortiGate serial number............................................................................. 82
Displaying the FortiGate up time....................................................................................... 82
Backing up system settings .............................................................................................. 82
Restoring system settings................................................................................................. 83
Restoring system settings to factory defaults ................................................................... 83
Changing to Transparent mode ........................................................................................ 83
Changing to NAT/Route mode.......................................................................................... 84
Restarting the FortiGate unit............................................................................................. 84
Shutting down the FortiGate unit ...................................................................................... 84
System status ................................................................................................................... 85
Viewing CPU and memory status ................................................................................. 85
Viewing sessions and network status ........................................................................... 86
Viewing virus and intrusions status............................................................................... 87
Session list........................................................................................................................ 88
Contents
Virus and attack definitions updates and registration ..................................... 89
Updating antivirus and attack definitions .......................................................................... 89
Connecting to the FortiResponse Distribution Network ................................................ 90
Configuring scheduled updates .................................................................................... 91
Configuring update logging ........................................................................................... 92
Adding an override server............................................................................................. 93
Manually updating antivirus and attack definitions........................................................ 93
Configuring push updates ............................................................................................. 93
Push updates through a NAT device ............................................................................ 94
Scheduled updates through a proxy server .................................................................. 98
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 5
Page 6

Contents
Registering FortiGate units ............................................................................................... 99
FortiCare Service Contracts.......................................................................................... 99
Registering the FortiGate unit ..................................................................................... 100
Updating registration information .................................................................................... 102
Recovering a lost Fortinet support password.............................................................. 102
Viewing the list of registered FortiGate units .............................................................. 102
Registering a new FortiGate unit ................................................................................ 103
Adding or changing a FortiCare Support Contract number......................................... 103
Changing your Fortinet support password .................................................................. 104
Changing your contact information or security question ............................................. 104
Downloading virus and attack definitions updates ...................................................... 104
Registering a FortiGate unit after an RMA...................................................................... 105
Network configuration....................................................................................... 107
Configuring interfaces ..................................................................................................... 107
Viewing the interface list ............................................................................................. 108
Bringing up an interface .............................................................................................. 108
Changing an interface static IP address ..................................................................... 108
Adding a secondary IP address to an interface .......................................................... 108
Adding a ping server to an interface ........................................................................... 109
Controlling management access to an interface ......................................................... 109
Configuring traffic logging for connections to an interface .......................................... 110
Configuring the wan1 and wan2 interfaces with a static IP address........................... 110
Configuring the wan1 or wan2 interfaces for DHCP ................................................... 110
Configuring the wan1 and wan2 interfaces for PPPoE ............................................... 111
Changing the wan1 and wan2 interface MTU size to improve network performance. 111
Configuring the management interface (Transparent mode) ...................................... 112
Adding DNS server IP addresses ................................................................................... 113
Configuring routing.......................................................................................................... 113
Adding a default route................................................................................................. 114
Adding destination-based routes to the routing table.................................................. 114
Adding routes in Transparent mode............................................................................ 115
Configuring the routing table....................................................................................... 116
Policy routing .............................................................................................................. 116
Providing DHCP services to your internal network ......................................................... 117
RIP configuration ............................................................................................... 119
RIP settings..................................................................................................................... 120
Configuring RIP for FortiGate interfaces......................................................................... 122
Adding RIP neighbors..................................................................................................... 123
6 Fortinet Inc.
Page 7

Adding RIP filters ............................................................................................................ 124
Adding a single RIP filter............................................................................................. 124
Adding a RIP filter list.................................................................................................. 125
Adding a neighbors filter ............................................................................................. 126
Adding a routes filter ................................................................................................... 126
System configuration ........................................................................................ 127
Setting system date and time.......................................................................................... 127
Changing web-based manager options .......................................................................... 128
Adding and editing administrator accounts..................................................................... 130
Adding new administrator accounts ............................................................................ 130
Editing administrator accounts.................................................................................... 131
Configuring SNMP .......................................................................................................... 132
Configuring the FortiGate unit for SNMP monitoring .................................................. 132
Configuring FortiGate SNMP support ......................................................................... 132
FortiGate MIBs............................................................................................................ 133
FortiGate traps ............................................................................................................ 134
Customizing replacement messages.............................................................................. 134
Customizing replacement messages .......................................................................... 135
Customizing alert emails............................................................................................. 136
Contents
Firewall configuration........................................................................................ 139
Default firewall configuration........................................................................................... 140
Interfaces .................................................................................................................... 140
Addresses ................................................................................................................... 140
Services ...................................................................................................................... 141
Schedules ................................................................................................................... 141
Content profiles........................................................................................................... 141
Adding firewall policies.................................................................................................... 142
Firewall policy options................................................................................................. 143
Configuring policy lists .................................................................................................... 147
Policy matching in detail ............................................................................................. 147
Changing the order of policies in a policy list.............................................................. 147
Enabling and disabling policies................................................................................... 148
Addresses ....................................................................................................................... 148
Adding addresses ....................................................................................................... 149
Editing addresses ....................................................................................................... 150
Deleting addresses ..................................................................................................... 150
Organizing addresses into address groups ................................................................ 150
Services .......................................................................................................................... 151
Predefined services .................................................................................................... 151
Providing access to custom services .......................................................................... 154
Grouping services ....................................................................................................... 154
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 7
Page 8

Contents
Schedules ....................................................................................................................... 155
Creating one-time schedules ...................................................................................... 155
Creating recurring schedules ...................................................................................... 156
Adding a schedule to a policy ..................................................................................... 157
Virtual IPs........................................................................................................................ 158
Adding static NAT virtual IPs ...................................................................................... 158
Adding port forwarding virtual IPs ............................................................................... 159
Adding policies with virtual IPs.................................................................................... 161
IP pools........................................................................................................................... 162
Adding an IP pool........................................................................................................ 162
IP Pools for firewall policies that use fixed ports ......................................................... 163
IP pools and dynamic NAT ......................................................................................... 163
IP/MAC binding ............................................................................................................... 164
Configuring IP/MAC binding for packets going through the firewall ............................ 164
Configuring IP/MAC binding for packets going to the firewall ..................................... 165
Adding IP/MAC addresses.......................................................................................... 165
Viewing the dynamic IP/MAC list ................................................................................ 166
Enabling IP/MAC binding ............................................................................................ 166
Content profiles............................................................................................................... 167
Default content profiles ............................................................................................... 168
Adding a content profile .............................................................................................. 168
Adding a content profile to a policy ............................................................................. 169
Users and authentication .................................................................................. 171
Setting authentication timeout......................................................................................... 172
Adding user names and configuring authentication ........................................................ 172
Adding user names and configuring authentication .................................................... 172
Deleting user names from the internal database ........................................................ 173
Configuring RADIUS support .......................................................................................... 174
Adding RADIUS servers ............................................................................................. 174
Deleting RADIUS servers ........................................................................................... 174
Configuring LDAP support .............................................................................................. 175
Adding LDAP servers.................................................................................................. 175
Deleting LDAP servers................................................................................................ 176
Configuring user groups.................................................................................................. 177
Adding user groups..................................................................................................... 177
Deleting user groups................................................................................................... 178
IPSec VPN........................................................................................................... 179
Key management............................................................................................................ 180
Manual Keys ............................................................................................................... 180
Automatic Internet Key Exchange (AutoIKE) with pre-shared keys or certificates ..... 180
8 Fortinet Inc.
Page 9

Manual key IPSec VPNs................................................................................................. 181
General configuration steps for a manual key VPN .................................................... 181
Adding a manual key VPN tunnel ............................................................................... 181
AutoIKE IPSec VPNs ...................................................................................................... 183
General configuration steps for an AutoIKE VPN ....................................................... 183
Adding a phase 1 configuration for an AutoIKE VPN.................................................. 183
Adding a phase 2 configuration for an AutoIKE VPN.................................................. 187
Managing digital certificates............................................................................................ 189
Obtaining a signed local certificate ............................................................................. 189
Obtaining a CA certificate ........................................................................................... 193
Configuring encrypt policies............................................................................................ 194
Adding a source address ............................................................................................ 195
Adding a destination address...................................................................................... 195
Adding an encrypt policy............................................................................................. 195
IPSec VPN concentrators ............................................................................................... 197
VPN concentrator (hub) general configuration steps .................................................. 197
Adding a VPN concentrator ........................................................................................ 199
VPN spoke general configuration steps...................................................................... 200
Redundant IPSec VPNs.................................................................................................. 201
Configuring redundant IPSec VPN ............................................................................. 201
Monitoring and Troubleshooting VPNs ........................................................................... 203
Viewing VPN tunnel status.......................................................................................... 203
Viewing dialup VPN connection status ....................................................................... 203
Testing a VPN............................................................................................................. 204
Contents
PPTP and L2TP VPN .......................................................................................... 205
Configuring PPTP ........................................................................................................... 205
Configuring the FortiGate unit as a PPTP gateway .................................................... 206
Configuring a Windows 98 client for PPTP ................................................................. 208
Configuring a Windows 2000 client for PPTP ............................................................. 209
Configuring a Windows XP client for PPTP ................................................................ 210
Configuring L2TP............................................................................................................ 211
Configuring the FortiGate unit as a L2TP gateway ..................................................... 212
Configuring a Windows 2000 client for L2TP.............................................................. 215
Configuring a Windows XP client for L2TP ................................................................. 216
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 9
Page 10

Contents
Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS) ................................................... 219
Detecting attacks ............................................................................................................ 219
Selecting the interfaces to monitor.............................................................................. 220
Disabling the NIDS...................................................................................................... 220
Configuring checksum verification .............................................................................. 220
Viewing the signature list ............................................................................................ 221
Viewing attack descriptions......................................................................................... 221
Enabling and disabling NIDS attack signatures .......................................................... 222
Adding user-defined signatures .................................................................................. 222
Preventing attacks .......................................................................................................... 223
Enabling NIDS attack prevention ................................................................................ 223
Enabling NIDS attack prevention signatures .............................................................. 224
Setting signature threshold values.............................................................................. 224
Configuring synflood signature values ........................................................................ 226
Logging attacks............................................................................................................... 226
Logging attack messages to the attack log................................................................. 226
Reducing the number of NIDS attack log and email messages.................................. 227
Antivirus protection........................................................................................... 229
General configuration steps............................................................................................ 229
Antivirus scanning........................................................................................................... 230
File blocking.................................................................................................................... 231
Blocking files in firewall traffic ..................................................................................... 231
Adding file patterns to block........................................................................................ 231
Blocking oversized files and emails ................................................................................ 232
Configuring limits for oversized files and email........................................................... 232
Exempting fragmented email from blocking.................................................................... 232
Viewing the virus list ....................................................................................................... 232
Web filtering ....................................................................................................... 233
General configuration steps............................................................................................ 233
Content blocking ............................................................................................................. 234
Adding words and phrases to the banned word list .................................................... 234
URL blocking................................................................................................................... 235
Using the FortiGate web filter ..................................................................................... 235
Using the Cerberian web filter..................................................................................... 238
Script filtering .................................................................................................................. 240
Enabling the script filter............................................................................................... 240
Selecting script filter options ....................................................................................... 240
Exempt URL list .............................................................................................................. 241
Adding URLs to the exempt URL list .......................................................................... 241
Email filter........................................................................................................... 243
General configuration steps............................................................................................ 243
10 Fortinet Inc.
Page 11

Email banned word list.................................................................................................... 244
Adding words and phrases to the banned word list .................................................... 244
Email block list ................................................................................................................ 245
Adding address patterns to the email block list........................................................... 245
Email exempt list............................................................................................................. 245
Adding address patterns to the email exempt list ....................................................... 246
Adding a subject tag ....................................................................................................... 246
Logging and reporting....................................................................................... 247
Recording logs................................................................................................................ 247
Recording logs on a remote computer ........................................................................ 248
Recording logs on a NetIQ WebTrends server ........................................................... 248
Recording logs in system memory.............................................................................. 249
Filtering log messages .................................................................................................... 249
Configuring traffic logging ............................................................................................... 251
Enabling traffic logging................................................................................................ 251
Configuring traffic filter settings................................................................................... 252
Adding traffic filter entries ........................................................................................... 252
Viewing logs saved to memory ....................................................................................... 253
Viewing logs................................................................................................................ 253
Searching logs ............................................................................................................ 254
Configuring alert email .................................................................................................... 254
Adding alert email addresses...................................................................................... 254
Testing alert email....................................................................................................... 255
Enabling alert email .................................................................................................... 255
Contents
Glossary ............................................................................................................. 257
Index .................................................................................................................... 261
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 11
Page 12

Contents
12 Fortinet Inc.
Page 13

FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide Version 2.50 MR2
Introduction
The FortiGate Antivirus Firewall supports network-based deployment of
application-level services—including antivirus protection and full-scan content filtering.
FortiGate Antivirus Firewalls improve network security, reduce network misuse and
abuse, and help you use communications resources more efficiently without
compromising the performance of your network. FortiGate Antivirus Firewalls are
ICSA-certified for firewall, IPSec and antivirus services.
Your FortiGate Antivirus Firewall is a dedicated easily managed security device that
delivers a full suite of capabilities that include:
• application-level services such as virus protection and content filtering,
• network-level services such as firewall, intrusion detection, VPN, and traffic
shaping.
Your FortiGate Antivirus Firewall employs Fortinet’s Accelerated Behavior and
Content Analysis System (ABACAS™) technology, which leverages breakthroughs in
chip design, networking, security, and content analysis. The unique ASIC-based
architecture analyzes content and behavior in real-time, enabling key applications to
be deployed right at the network edge where they are most effective at protecting your
networks. The FortiGate series complements existing solutions, such as host-based
antivirus protection, and enables new applications and services while greatly lowering
costs for equipment, administration and maintenance.
The FortiGate-60 model is ideally suited
for small businesses, remote offices, retail
stores, and broadband telecommuter
sites. The FortiGate-60 Antivirus Firewall
features dual WAN link support for
redundant internet connections, and an integrated 4-port switch that eliminates the
need for an external hub or switch. Networked devices connect directly to the
FortiGate-60 unit.
The FortiGate-60R is limited to a maximum of 12 users.
Antivirus protection
FortiGate ICSA-certified antivirus protection virus scans web (HTTP), file transfer
(FTP), and email (SMTP, POP3, and IMAP) content as it passes through the
FortiGate. If a virus is found, antivirus protection removes the file containing the virus
from the content stream and forwards an replacement message to the intended
recipient.
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 13
Page 14

Web content filtering Introduction
For extra protection, you also configure antivirus protection to block files of specified
file types from passing through the FortiGate unit. You can use the feature to stop files
that may contain new viruses.
If the FortiGate unit contains a hard disk, infected or blocked files can be quarantined.
The FortiGate administrator can download quarantined files, so that they can be virus
scanned, cleaned, and forwarded to the intended recipient. You can also configure the
FortiGate unit to automatically delete quarantined files after a specified time period.
The FortiGate unit can send email alerts to system administrators when it detects and
removes a virus from a content stream. The web and email content can be in normal
network traffic or in encrypted IPSec VPN traffic.
ICSA Labs has certified that FortiGate Antivirus Firewalls:
• detect 100% of the viruses listed in the current In The Wild List (www.wildlist.org),
• detect viruses in compressed files using the PKZip format,
• detect viruses in e-mail that has been encoded using uuencode format,
• detect viruses in e-mail that has been encoded using MIME encoding,
• log all actions taken while scanning.
Web content filtering
FortiGate web content filtering can be configured to scan all HTTP content protocol
streams for URLs or for web page content. If a match is found between a URL on the
URL block list, or if a web page is found to contain a word or phrase in the content
block list, the FortiGate blocks the web page. The blocked web page is replaced with a
message that you can edit using the FortiGate web-based manager.
You can configure URL blocking to block all or just some of the pages on a web site.
Using this feature you can deny access to parts of a web site without denying access
to it completely.
To prevent unintentional blocking of legitimate web pages, you can add URLs to an
Exempt List that overrides the URL blocking and content blocking lists.
Web content filtering also includes a script filter feature that can be configured to block
unsecure web content such as Java Applets, Cookies, and ActiveX.
You can also use the Cerberian URL blocking to block unwanted URLs.
Email filtering
FortiGate Email filtering can be configured to scan all IMAP and POP3 email content
for unwanted senders or for unwanted content. If a match is found between a sender
address pattern on the Email block list, or if an email is found to contain a word or
phrase in the banned word list, the FortiGate adds a Email tag to subject line of the
email. Receivers can then use their mail client software to filter messages based on
the Email tag.
14 Fortinet Inc.
Page 15

Introduction Firewall
You can configure Email blocking to tag email from all or some senders within
organizations that are known to send spam email. To prevent unintentional tagging of
email from legitimate senders, you can add sender address patterns to an exempt list
that overrides the email block and banned word lists.
Firewall
The FortiGate ICSA-certified firewall protects your computer networks from the hostile
environment of the Internet. ICSA has granted FortiGate firewalls version 4.0 firewall
certification, providing assurance that FortiGate firewalls successfully screen for and
secure corporate networks against a wide range of threats from public or other
untrusted networks.
After basic installation of the FortiGate unit, the firewall allows users on the protected
network to access the Internet while blocking Internet access to internal networks. You
can modify this firewall configuration to place controls on access to the Internet from
the protected networks and to allow controlled access to internal networks.
FortiGate policies include a complete range of options that:
• control all incoming and outgoing network traffic,
• control encrypted VPN traffic,
• apply antivirus protection and web content filtering,
• block or allow access for all policy options,
• control when individual policies are in effect,
• accept or deny traffic to and from individual addresses,
• control standard and user defined network services individually or in groups,
• require users to authenticate before gaining access,
• include traffic shaping to set access priorities and guarantee or limit bandwidth for
each policy,
• include logging to track connections for individual policies,
• include Network address translation (NAT) mode and Route mode policies,
• include Mixed NAT and Route mode policies.
The FortiGate firewall can operate in NAT/Route mode or Transparent mode.
NAT/Route mode
In NAT/Route mode, you can create NAT mode policies and Route mode policies.
• NAT mode policies use network address translation to hide the addresses in a
more secure network from users in a less secure network.
• Route mode policies accept or deny connections between networks without
performing address translation.
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 15
Page 16

Network intrusion detection Introduction
Transparent mode
Transparent mode provides the same basic firewall protection as NAT mode. Packets
received by the FortiGate unit are intelligently forwarded or blocked according to
firewall policies. The FortiGate unit can be inserted in your network at any point
without the need to make changes to your network or any of its components.
However, VPN and some advanced firewall features are only available in NAT/Route
mode.
Network intrusion detection
The FortiGate Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS) is a real-time network
intrusion detection sensor that detects and prevents a wide variety of suspicious
network activity. NIDS detection uses attack signatures to identify over 1000 attacks.
You can enable and disable the attacks that the NIDS detects. You can also write your
own user-defined detection attack signatures.
NIDS prevention detects and prevents many common denial of service and packetbased attacks. You can enable and disable prevention attack signatures and
customize attack signature thresholds and other parameters.
To notify system administrators of the attack, the NIDS records the attack and any
suspicious traffic to the attack log and can be configured to send alert emails.
VPN
Fortinet updates NIDS attack definitions periodically. You can download and install
updated attack definitions manually, or you can configure the FortiGate to
automatically check for and download attack definition updates.
Using FortiGate virtual private networking (VPN), you can provide a secure
connection between widely separated office networks or securely link telecommuters
or travellers to an office network.
FortiGate VPN features include the following:
• Industry standard and ICSA-certified IPSec VPN including:
• IPSec, ESP security in tunnel mode,
• DES, 3DES (triple-DES), and AES hardware accelerated encryption,
• HMAC MD5 and HMAC SHA1 authentication and data integrity,
• AutoIKE key based on pre-shared key tunnels,
• IPSec VPN using local or CA certificates,
• Manual Keys tunnels,
• Diffie-Hellman groups 1, 2, and 5,
• Aggressive and Main Mode,
• Replay Detection,
• Perfect Forward Secrecy,
• XAuth authentication,
• Dead peer detection.
16 Fortinet Inc.
Page 17

Introduction Secure installation, configuration, and management
• PPTP for easy connectivity with the VPN standard supported by the most popular
operating systems.
• L2TP for easy connectivity with a more secure VPN standard also supported by
many popular operating systems.
• Firewall policy based control of IPSec VPN traffic.
• IPSec NAT traversal so that remote IPSec VPN gateways or clients behind a NAT
can connect to an IPSec VPN tunnel.
• VPN hub and spoke using a VPN concentrator to allow VPN traffic to pass from
one tunnel to another tunnel through the FortiGate unit.
• IPSec Redundancy to create a redundant AutoIKE key IPSec VPN connection to a
remote network.
Secure installation, configuration, and management
Installation is quick and simple. The first time you turn on the FortiGate unit, it is
already configured with default IP addresses and security policies. Connect to the
web-based manager, set the operating mode, and use the setup wizard to customize
FortiGate IP addresses for your network, and the FortiGate unit is set to protect your
network. You can then use the web-based manager to customize advanced FortiGate
features to meet your needs.
You can also create a basic configuration using the FortiGate command line interface
(CLI).
Web-based manager
Using HTTP or a secure HTTPS connection from any computer running Internet
Explorer, you can configure and manage the FortiGate unit. The web-based manager
supports multiple languages. You can configure the FortiGate unit for HTTP and
HTTPs administration from any FortiGate interface.
You can use the web-based manager for most FortiGate configuration settings. You
can also use the web-based manager to monitor the status of the FortiGate unit.
Configuration changes made with the web-based manager are effective immediately
without the need to reset the firewall or interrupt service. Once a satisfactory
configuration has been established, it can be downloaded and saved. The saved
configuration can be restored at any time.
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 17
Page 18
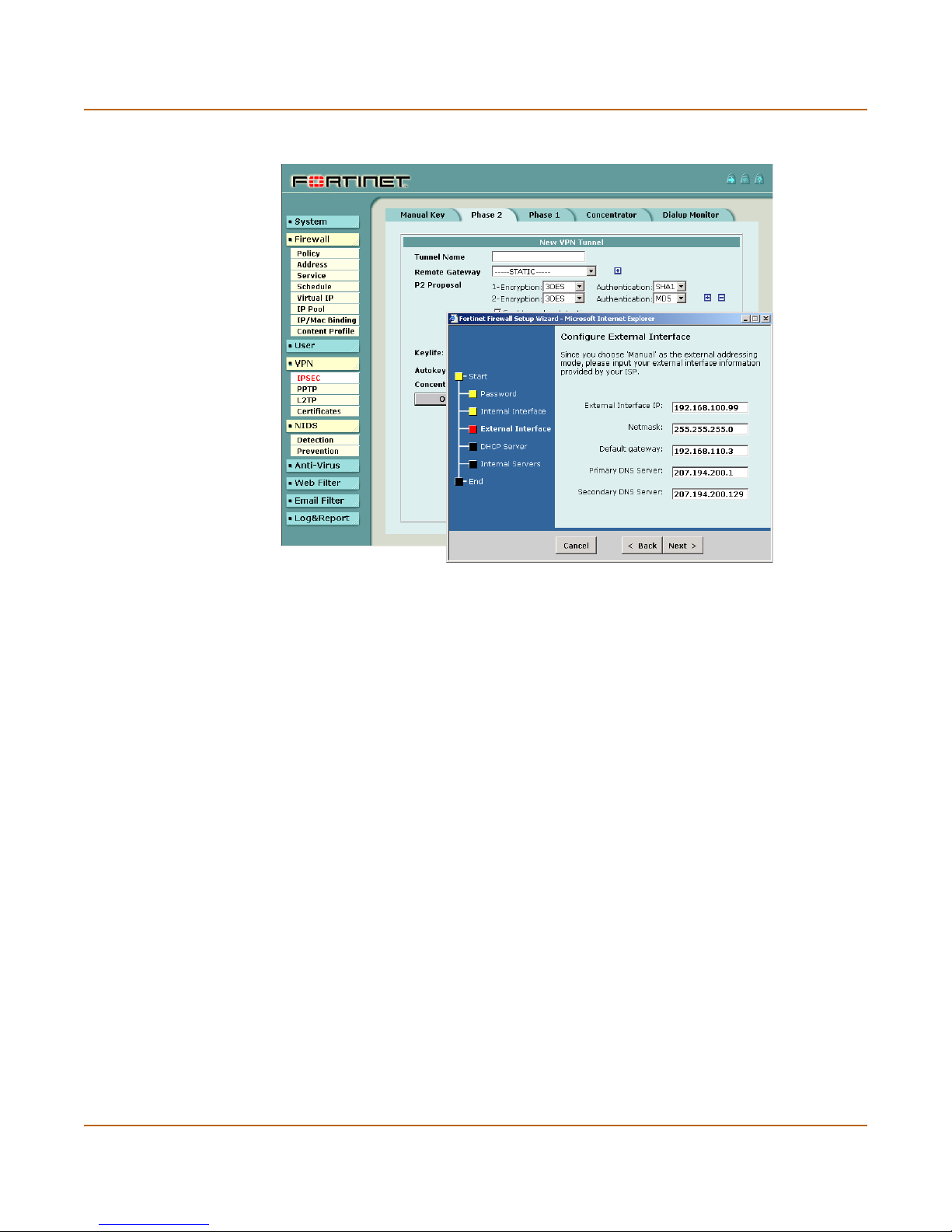
Secure installation, configuration, and management Introduction
Figure 1: The FortiGate web-based manager and setup wizard
Command line interface
You can access the FortiGate command line interface (CLI) by connecting a
management computer serial port to the FortiGate RS-232 serial Console connector.
You can also use Telnet or a secure SSH connection to connect to the CLI from any
network connected to the FortiGate, including the Internet.
The CLI supports the same configuration and monitoring functionality as the
web-based manager. In addition, you can use the CLI for advanced configuration
options not available from the web-based manager. This Installation and
Configuration Guide contains information about basic and advanced CLI commands.
You can find a more complete description of connecting to and using the FortiGate CLI
in the FortiGate CLI Reference Guide.
18 Fortinet Inc.
Page 19

Introduction What’s new in Version 2.50
Logging and reporting
The FortiGate supports logging of various categories of traffic and of configuration
changes. You can configure logging to:
• report traffic that connects to the firewall,
• report network services used,
• report traffic permitted by firewall policies,
• report traffic that was denied by firewall policies,
• report events such as configuration changes and other management events, IPSec
tunnel negotiation, virus detection, attacks, and web page blocking,
• report attacks detected by the NIDS,
• send alert email to system administrators to report virus incidents, intrusions, and
firewall or VPN events or violations.
Logs can be sent to a remote syslog server or to a WebTrends NetIQ Security
Reporting Center and Firewall Suite server using the WebTrends enhanced log
format. Some models can also save logs to an optional internal hard drive. If a hard
drive is not installed, you can configure most FortiGates to log the most recent events
and attacks detected by the NIDS to shared system memory.
What’s new in Version 2.50
This section presents a brief summary of some of the new features in FortiOS v2.50:
System administration
• Improved graphical FortiGate system health monitoring that includes CPU and
memory usage, session number and network bandwidth usage, and the number of
viruses and intrusions detected. See “System status” on page 85.
• Revised antivirus and attack definition update functionality that connects to a new
version of the FortiResponse Distribution network. Updates can now be scheduled
hourly and the System > Update page displays more information about the current
update status. See “Updating antivirus and attack definitions” on page 89.
• Direct connection to the Fortinet tech support web page from the web-based
manager. You can register your FortiGate unit and get access to other technical
support resources. See “Registering FortiGate units” on page 99.
Network configuration
• New interface configuration options. See “Configuring interfaces” on page 107.
• Ping server and dead gateway detection for all interfaces.
• HTTP and Telnet administrative access to any interface.
• Secondary IP addresses for all FortiGate interfaces.
Routing
• Simplified direction-based routing configuration.
• Advanced policy routing (CLI only).
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 19
Page 20

What’s new in Version 2.50 Introduction
DHCP server
• Addition of a WINS server to DHCP configuration.
• Reserve IP/MAC pair combinations for DHCP servers (CLI only).
RIP
• New RIP v1 and v2 functionality. See “RIP configuration” on page 119.
SNMP
• SNMP v1 and v2 support.
• Support for RFC 1213 and RFC 2665
• Monitoring of all FortiGate configuration and functionality
•See “Configuring SNMP” on page 132
Replacement messages
You can customize messages sent by the FortiGate unit:
• When a virus is detected,
• When a file is blocked,
• When a fragmented email is blocked
• When an alert email is sent
See “Customizing replacement messages” on page 134.
Firewall
• The firewall default configuration has changed. See “Default firewall configuration”
on page 140.
• Add virtual IPs to all interfaces. See “Virtual IPs” on page 158.
• Add content profiles to firewall policies to configure blocking, scanning, quarantine,
web content blocking, and email filtering. See “Content profiles” on page 167.
Users and authentication
• LDAP authentication. See “Configuring LDAP support” on page 175.
VPN
See the FortiGate VPN Guide for a complete description of FortiGate VPN
functionality. New features include:
•Phase 1
• AES encryption
• Certificates
• Advanced options including Dialup Group, Peer, XAUTH, NAT Traversal, DPD
•Phase 2
• AES encryption
• Encryption policies select service
• Generate and import local certificates
• Import CA certificates
20 Fortinet Inc.
Page 21

Introduction What’s new in Version 2.50
NIDS
See the FortiGate NIDS Guide for a complete description of FortiGate NIDS
functionality. New features include:
• Attack detection signature groups
• User-configuration attack prevention
• Monitor multiple interfaces for attacks
• User-defined attack detection signatures
Antivirus
See the FortiGate Content Protection Guide for a complete description of FortiGate
antivirus functionality. New features include:
• Content profiles
• Blocking oversized files
Web Filter
See the FortiGate Content Protection Guide for a complete description of FortiGate
web filtering functionality. New features include:
• Cerberian URL Filtering
Email filter
See the FortiGate Content Protection Guide for a complete description of FortiGate
email filtering functionality.
Logging and Reporting
See the FortiGate Logging and Message Reference Guide for a complete description
of FortiGate logging.
• Log to remote host CSV format
• Log message levels: Emergency, Alert, critical, error, Warning, notification,
information
• Log level policies
• Traffic log filter
• New antivirus, web filter, and email filter logs
• Alert email supports authentication
• Suppress email flooding
• Extended WebTrends support for graphing activity
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 21
Page 22

About this document Introduction
About this document
This installation and configuration guide describes how to install and configure the
FortiGate-60. This document contains the following information:
• Getting started describes unpacking, mounting, and powering on the FortiGate.
• NAT/Route mode installation describes how to install the FortiGate if you are
planning on running it in NAT/Route mode.
• Transparent mode installation describes how to install the FortiGate if you are
planning on running it in Transparent mode.
• System status describes how to view the current status of your FortiGate unit and
related status procedures including installing updated FortiGate firmware, backing
up and restoring system settings, and switching between Transparent and
NAT/Route mode.
• Virus and attack definitions updates and registration describes configuring
automatic virus and attack definition updates. This chapter also contains
procedures for connecting to the FortiGate tech support webs site and for
registering your FortiGate unit.
• Network configuration describes configuring interfaces, configuring routing, and
configuring the FortiGate as a DHCP server for your internal network.
• RIP configuration describes the FortiGate RIP2 implementation and how to
configure RIP settings.
• System configuration describes system administration tasks available from the
System > Config web-based manager pages. This chapter describes setting
system time, adding and changed administrative users, configuring SNMP, and
editing replacement messages.
• Firewall configuration describes how to configure firewall policies to control traffic
through the FortiGate unit and apply content protection profiles to content traffic.
• Users and authentication describes how to add user names to the FortiGate user
database and how to configure the FortiGate to connect to a RADIUS server to
authenticate users.
• IPSec VPN describes how to configure FortiGate IPSec VPN.
• PPTP and L2TP VPN describes how to configure PPTP and L2TP VPNs between
the FortiGate and a windows client.
• Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS) describes how to configure the
FortiGate NIDS to detect and prevent network attacks.
• Antivirus protection describes how use the FortiGate to protect your network from
viruses and worms.
• Web filtering describes how to configure web content filtering to prevent unwanted
Web content from passing through the FortiGate.
• Email filter describes how to configure email filtering to screen unwanted email
content.
• Logging and reporting describes how to configure logging and alert email to track
activity through the FortiGate.
•The Glossary defines many of the terms used in this document.
22 Fortinet Inc.
Page 23

Introduction Document conventions
Document conventions
This guide uses the following conventions to describe CLI command syntax.
• angle brackets < > to indicate variable keywords
For example:
execute restore config <filename_str>
You enter restore config myfile.bak
<xxx_str> indicates an ASCII string variable keyword.
<xxx_integer> indicates an integer variable keyword.
<xxx_ip> indicates an IP address variable keyword.
• vertical bar and curly brackets {|} to separate alternative, mutually exclusive
required keywords
For example:
set system opmode {nat | transparent}
You can enter set system opmode nat or set system opmode
transparent
• square brackets [ ] to indicate that a keyword is optional
For example:
get firewall ipmacbinding [dhcpipmac]
You can enter get firewall ipmacbinding or
get firewall ipmacbinding dhcpipmac
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 23
Page 24

Fortinet documentation Introduction
Fortinet documentation
Information about FortiGate products is available from the following FortiGate User
Manual volumes:
• Volume 1: FortiGate Installation and Configuration Guide
Describes installation and basic configuration for the FortiGate unit. Also describes
how to use FortiGate firewall policies to control traffic flow through the FortiGate
unit and how to use firewall policies to apply antivirus protection, web content
filtering, and email filtering to HTTP, FTP and email content passing through the
FortiGate unit.
• Volume 2: FortiGate VPN Guide
Contains in-depth information about FortiGate IPSec VPN using certificates, preshared keys and manual keys for encryption. Also contains basic configuration
information for the Fortinet Remote VPN Client, detailed configuration information
for FortiGate PPTP and L2TP VPN, and VPN configuration examples.
• Volume 3: FortiGate Content Protection Guide
Describes how to configure antivirus protection, web content filtering, and email
filtering to protect content as it passes through the FortiGate unit.
• Volume 4: FortiGate NIDS Guide
Describes how to configure the FortiGate NIDS to detect and protect the FortiGate
unit from network-based attacks.
• Volume 5: FortiGate Logging and Message Reference Guide
Describes how to configure FortiGate logging and alert email. Also contains the
FortiGate log message reference.
• Volume 6: FortiGate CLI Reference Guide
Describes the FortiGate CLI and contains a reference to all FortiGate CLI
commands.
The FortiGate online help also contains procedures for using the FortiGate web-based
manager to configure and manage your FortiGate unit.
Comments on Fortinet technical documentation
You can send information about errors or omissions in this document or any Fortinet
technical documentation to techdoc@fortinet.com.
24 Fortinet Inc.
Page 25

Introduction Customer service and technical support
Customer service and technical support
For antivirus and attack definition updates, firmware updates, updated product
documentation, technical support information, and other resources, please visit the
Fortinet technical support web site at http://support.fortinet.com.
You can also register FortiGate Antivirus Firewalls from http://support.fortinet.com and
modify your registration information at any time.
Fortinet email support is available from the following addresses:
amer_support@fortinet.com For customers in the United States, Canada, Mexico, Latin
apac_support@fortinet.com For customers in Japan, Korea, China, Hong Kong, Singapore,
eu_support@fortinet.com For customers in the United Kingdom, Scandinavia, Mainland
America and South America.
Malaysia, all other Asian countries, and Australia.
Europe, Africa, and the Middle East.
For information on Fortinet telephone support, see http://support.fortinet.com.
When requesting technical support, please provide the following information:
• Your name
• Company name
•Location
• Email address
• Telephone number
• FortiGate unit serial number
• FortiGate model
• FortiGate FortiOS firmware version
• Detailed description of the problem
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 25
Page 26

Customer service and technical support Introduction
26 Fortinet Inc.
Page 27

FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide Version 2.50 MR2
Getting started
This chapter describes unpacking, setting up, and powering on your FortiGate
Antivirus Firewall. When you have completed the procedures in this chapter, you can
proceed to one of the following:
• If you are going to operate the FortiGate unit in NAT/Route mode, go to
“NAT/Route mode installation” on page 43.
• If you are going to operate the FortiGate unit in Transparent mode, go to
“Transparent mode installation” on page 59.
This chapter describes:
• Package contents
• Mounting
• Powering on
• Connecting to the web-based manager
• Connecting to the command line interface (CLI)
• Factory default FortiGate configuration settings
• Planning your FortiGate configuration
• FortiGate model maximum values matrix
• Next steps
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 27
Page 28

Package contents Getting started
Package contents
The FortiGate-60 package contains the following items:
• FortiGate-60 Antivirus Firewall
• one orange crossover ethernet cable
• one gray regular ethernet cable
• one null modem cable
• FortiGate-60 Quick Start Guide
• CD containing the FortiGate user documentation
• one power cable and AC adapter
Figure 2: FortiGate-60 package contents
Front
Mounting
Ethernet Cables:
Orange - Crossover
Grey - Straight-through
Null-Modem Cable
(RS-232)
PWR STATUS
Power
LED
INTERNAL
LINK 100 LINK 100 LINK 100 LINK 100 LINK 100 LINK 100 LINK 100
Status
LED
Internal
Interface
DMZ
Interface
DMZ4321
WAN1 WAN2
WAN 1,2
Interface
Back
Power Cable Power Supply
FortiGate-60
INTERNAL
DMZ4321
WAN1 WAN2
PWR STATUS
USER MANUAL
LINK 100 LINK 100 LINK 100 LINK 100 LINK 100 LINK 100 LINK 100
QuickStart Guide
Copyright 2003 Fortinet Incorporated. All rights reserved.
Trademarks
Products mentioned in this document are trademarks.
Documentation
DC+12V
Power
Connection
RS-232 Serial
Connection
Console
USB
USB
(future)
WAN2 WAN1 DMZ
WAN2
WAN1
DMZ
1234
Internal
Internal Interface,
switch connectors
1,2,3,4
The FortiGate-60 unit can be installed on any stable surface. Make sure that the
appliance has at least 1.5 in. (3.75 cm) of clearance on each side to allow for
adequate air flow and cooling.
Dimensions
• 8.63 x 6.13 x 1.38 in. (21.9 x 15.6 x 3.5 cm)
Weight
• 1.5 lb. (0.68 kg)
28 Fortinet Inc.
Page 29
Getting started Powering on
Power requirements
• DC input voltage: 12 V
• DC input current: 3 A
Environmental specifications
• Operating temperature: 32 to 104°F (0 to 40°C)
• Storage temperature: -13 to 158°F (-25 to 70°C)
• Humidity: 5 to 95% non-condensing
Powering on
To power on the FortiGate-60 unit:
1 Connect the AC adapter to the power connection at the back of the FortiGate-60 unit.
2 Connect the AC adapter to the power cable.
3 Connect the power cable to a power outlet.
The FortiGate-60 unit starts up. The Power and Status lights light.
Table 1: FortiGate-60 LED indicators
LED State Description
Power Green The FortiGate unit is powered on.
Off The FortiGate unit is powered off.
Status Red The FortiGate unit is starting up.
Off The FortiGate unit is running normally.
Off The FortiGate unit is powered off.
Link
(Internal
DMZ
WAN1
WAN2)
100
(Internal
DMZ
WAN1
WAN2)
Green The correct cable is in use and the connected
equipment has power.
Flashing Green Network activity at this interface.
Off No link established.
Green The interface is connected at 100 Mbps.
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 29
Page 30
Connecting to the web-based manager Getting started
Connecting to the web-based manager
Use the following procedure to connect to the web-based manager for the first time.
Configuration changes made with the web-based manager are effective immediately
without the need to reset the firewall or interrupt service.
To connect to the web-based manager, you need:
• a computer with an ethernet connection,
• Internet Explorer version 4.0 or higher,
• an ethernet cable.
• a crossover cable or an ethernet hub and two ethernet cables.
Note: You can use the web-based manager with recent versions of most popular web browsers.
The web-based manager is fully supported for Internet Explorer version 4.0 or higher.
Connecting to the web-based manager
1 Set the IP address of the computer with an ethernet connection to the static IP
address 192.168.1.2 and a netmask of 255.255.255.0.
You can also configure the management computer to obtain an IP address
automatically using DHCP. The FortiGate DHCP server assigns the management
computer an IP address in the range 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.254.
2 Using the ethernet cable, connect the Internal interface of the FortiGate unit to the
computer ethernet connection.
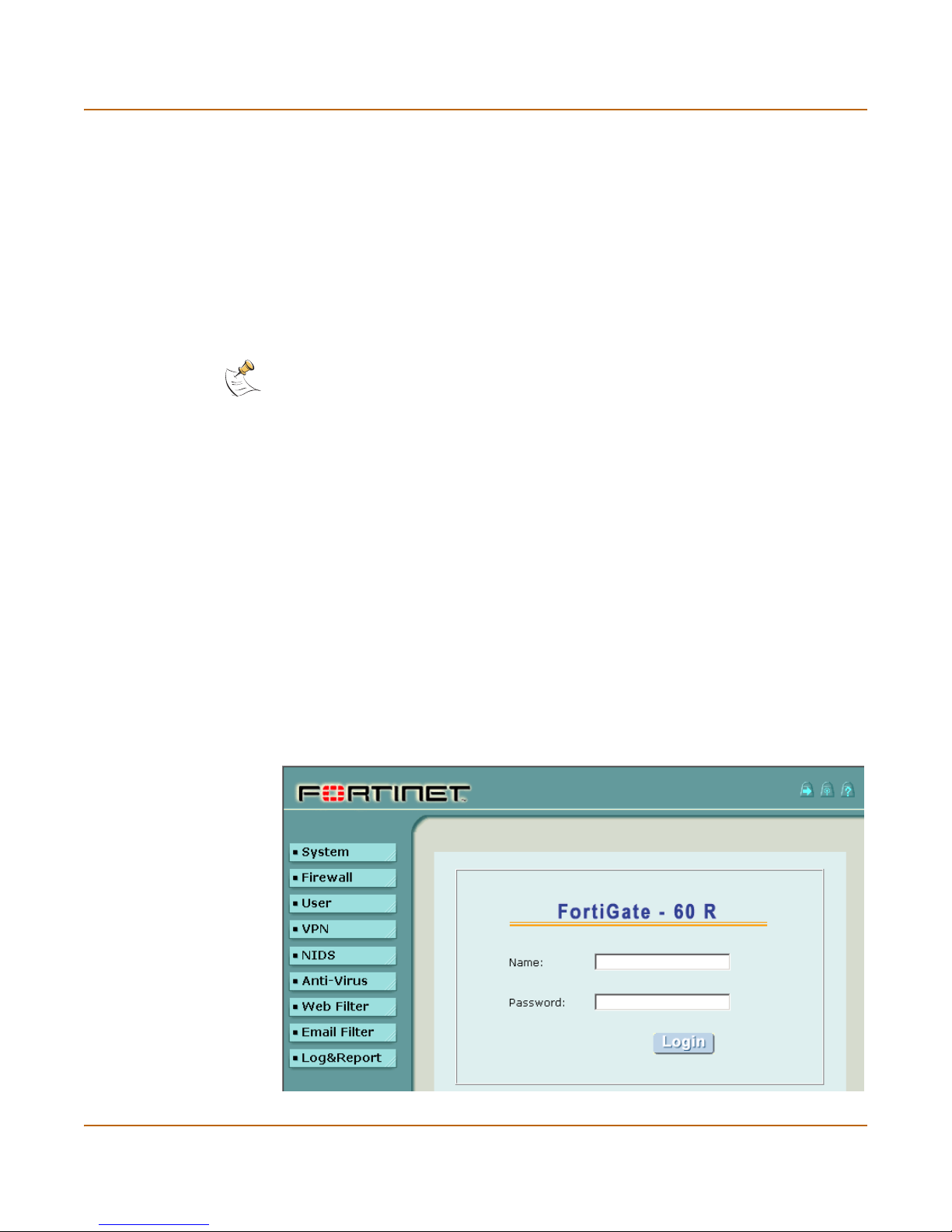
3 Start Internet Explorer and browse to the address https://192.168.1.99 (remember to
include the “s” in https://).
The FortiGate login is displayed.
4 Type admin in the Name field and select Login.
The Register Now window is displayed. Use the information on this window to register
your FortiGate unit so that Fortinet can contact you for firmware updates. You must
also register to receive updates to the FortiGate virus and attack definitions.
Figure 3: FortiGate login
30 Fortinet Inc.
Page 31

Getting started Connecting to the command line interface (CLI)
Connecting to the command line interface (CLI)
As an alternative to the web-based manager, you can install and configure the
FortiGate unit using the CLI. Configuration changes made with the CLI are effective
immediately without the need to reset the firewall or interrupt service.
To connect to the FortiGate CLI, you need:
• a computer with an available communications port,
• the null modem cable included in your FortiGate package,
• terminal emulation software such as HyperTerminal for Windows.
Note: The following procedure describes how to connect to the CLI using Windows
HyperTerminal software. You can use any terminal emulation program.
To connect to the CLI:
1 Connect the null modem cable to the communications port of your computer and to
the FortiGate Console port.
2 Make sure that the FortiGate unit is powered on.
3 Start HyperTerminal, enter a name for the connection, and select OK.
4 Configure HyperTerminal to connect directly to the communications port on the
computer to which you have connected the null modem cable and select OK.
5 Select the following port settings and select OK.
Bits per second 9600
Data bits 8
Parity None
Stop bits 1
Flow control None
6 Press Enter to connect to the FortiGate CLI.
The following prompt appears:
FortiGate-60 login:
7 Type admin and press Enter twice.
The following prompt appears:
Type ? for a list of commands.
For information on how to use the CLI, see the FortiGate CLI Reference Guide.
Factory default FortiGate configuration settings
The FortiGate unit is shipped with a factory default configuration. This default
configuration allows you to connect to and use the FortiGate web-based manager to
configure the FortiGate unit onto your network. To configure the FortiGate unit onto
your network you add an administrator password, change network interface IP
addresses, add DNS server IP addresses, and configuring routing if required.
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 31
Page 32

Factory default FortiGate configuration settings Getting started
If you are planning on operating the FortiGate unit in Transparent mode, you can
switch to transparent mode from the factory default configuration and then configure
the FortiGate unit onto your network in Transparent mode.
Once the network configuration is complete, you can perform additional configuration
tasks such as setting system time, configuring virus and attack definition updates, and
registering the FortiGate unit.
The factory default firewall configuration includes a single network address translation
(NAT) policy that allows users on your internal network to connect to the external
network, and stops users on the external network from connecting to the internal
network. You can add more policies to provide more control of the network traffic
passing through the FortiGate unit.
The factory default content profiles can be used to quickly apply different levels of
antivirus protection, web content filtering, and email filtering to the network traffic
controlled by firewall policies.
• Factory Default DHCP configuration
• Factory default NAT/Route mode network configuration
• Factory default Transparent mode network configuration
• Factory default firewall configuration
• Factory default content profiles
Factory Default DHCP configuration
When the FortiGate unit is first powered on, the WAN1 interface is configured to
receive its IP address by connecting to a DHCP server. If your ISP provides IP
addresses using DHCP, no other configuration is required for this interface.
The FortiGate unit can also function as a DHCP server for your internal network. You
can configure the TCP/IP settings of the computers on your internal network to obtain
an IP address automatically from the FortiGate unit DHCP server. For more
information about the FortiGate DHCP server, see “Providing DHCP services to your
internal network” on page 117.
Table 2: FortiGate DHCP Server default configuration
Enable DHCP ;
Starting IP 192.168.1.1
Ending IP 192.168.1.254
Netmask 255.255.255.0
Lease Duration 604800 seconds
Default Route 192.168.1.99
Exclusion Range 192.168.1.99 - 192.168.1.99
32 Fortinet Inc.
Page 33

Getting started Factory default FortiGate configuration settings
Factory default NAT/Route mode network configuration
When the FortiGate unit is first powered on, it is running in NAT/Route mode and has
the basic network configuration listed in Ta bl e 3. This configuration allows you to
connect to the FortiGate unit web-based manager and establish the configuration
required to connect the FortiGate unit to your network. In Table 3 HTTPS
management access means you can connect to the web-based manager using this
interface. Ping management access means this interface responds to ping requests.
Table 3: Factory default NAT/Route mode network configuration
Administrator
account
Internal interface
WAN1 interface
WAN2 interface
DMZ interface
User name: admin
Password: (none)
IP: 192.168.1.99
Netmask: 255.255.255.0
Management Access: HTTPS, Ping
Addressing Mode: DHCP
Management Access: Ping
IP: 192.168.101.99
Netmask: 255.255.255.0
Management Access: Ping
IP: 10.10.10.1
Netmask: 255.255.255.0
Management Access: HTTPS, Ping
Factory default Transparent mode network configuration
If you switch the FortiGate unit to Transparent mode, it has the default network
configuration listed in Ta bl e 4 .
Table 4: Factory default Transparent mode network configuration
Administrator
account
Management IP
DNS
Management access
User name: admin
Password: (none)
IP: 10.10.10.1
Netmask: 255.255.255.0
Primary DNS Server: 207.194.200.1
Secondary DNS Server: 207.194.200.129
Internal HTTPS, Ping
WAN1 Ping
WAN2 Ping
DMZ HTTPS, Ping
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 33
Page 34

Factory default FortiGate configuration settings Getting started
Factory default firewall configuration
The factory default firewall configuration is the same in NAT/Route and Transparent
mode.
Table 5: Factory default firewall configuration
Internal
Address
WAN1
Address
DMZ
Address
Recurring
Schedule
Firewall
Policy
Internal_All
WAN1_All
DMZ_All
Always The schedule is valid at all times. This means that
Internal->WAN1 Firewall policy for connections from the internal
Source Internal_All The policy source address. Internal_All means that
Destination WAN1_All The policy destination address. WAN1_All means
Schedule Always The policy schedule. Always means that the policy
Service ANY The policy service. ANY means that this policy
Action ACCEPT The policy action. ACCEPT means that the policy
; NAT NAT is selected for the NAT/Route mode default
Traffic Shaping Traffic shaping is not selected. The policy does not
Authentication Authentication is not selected. Users do not have to
; Antivirus & Web Filter Antivirus & Web Filter is selected.
Content
Profile
Log Traffic Log Traffic is not selected. This policy does not
IP: 0.0.0.0 Represents all of the IP addresses on the internal
Mask: 0.0.0.0
IP: 0.0.0.0 Represents all of the IP addresses on the network
Mask: 0.0.0.0
IP: 0.0.0.0 Represents all of the IP addresses on the network
Mask: 0.0.0.0
Scan The scan content profile is selected. The policy
network.
connected to the WAN1 interface.
connected to the DMZ interface.
the firewall policy is valid at all times.
network to the external network.
the policy accepts connections from any internal IP
address.
that the policy accepts connections with a
destination address to any IP address on the
external (WAN1) network.
is valid at any time.
processes connections for all services.
allows connections.
policy so that the policy applies network address
translation to the traffic processed by the policy.
NAT is not available for Transparent mode policies.
apply traffic shaping to the traffic controlled by the
policy. You can select this option to control the
maximum or minimum amount of bandwidth
available to traffic processed by the policy.
authenticate with the firewall before connecting to
their destination address. You can configure user
groups and select this option to require users to
authenticate with the firewall before they can
connect through the firewall.
scans all HTTP, FTP, SMTP, POP3, and IMAP
traffic for viruses. See “Scan content profile” on
page 36 for more information about the scan
content profile. You can select one of the other
content profiles to apply different levels of content
protection to traffic processed by this policy.
record messages to the traffic log for the traffic
processed by this policy. You can configure
FortiGate logging and select Log Traffic to record all
connections through the firewall that are accepted
by this policy.
34 Fortinet Inc.
Page 35

Getting started Factory default FortiGate configuration settings
Factory default content profiles
You can use content profiles to apply different protection settings for content traffic
controlled by firewall policies. You can use content profiles for:
• Antivirus protection of HTTP, FTP, IMAP, POP3, and SMTP network traffic
• Web content filtering for HTTP network traffic
• Email filtering for IMAP and POP3 network traffic
• Oversized file and email blocking for HTTP, FTP, POP3, SMTP, and IMAP network
traffic
• Passing fragmented emails in IMAP, POP3, and SMTP email traffic
Using content profiles you can build up protection configurations that can be easily
applied to different types of Firewall policies. This allows you to customize different
types and different levels of protection for different firewall policies.
For example, while traffic between internal and external addresses might need strict
protection, traffic between trusted internal addresses might need moderate protection.
You can configure policies for different traffic services to use the same or different
content profiles.
Content profiles can be added to NAT/Route mode and Transparent mode policies.
Strict content profile
Use the strict content profile to apply maximum content protection to HTTP, FTP,
IMAP, POP3, and SMTP content traffic. You would not use the strict content profile
under normal circumstances, but it is available if you are having extreme problems
with viruses and require maximum content screening protection.
Table 6: Strict content profile
Options HTTP FTP IMAP POP3 SMTP
Antivirus Scan ;;;;;
File Block ;;;;;
Web URL Block ;
Web Content Block ;
Web Script Filter ;
Web Exempt List ;
Email Block List ;;
Email Exempt List ;;
Email Content Block ;;
Oversized File/Email Block block block block block block
Pass Fragmented Emails
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 35
Page 36

Factory default FortiGate configuration settings Getting started
Scan content profile
Use the scan content profile to apply antivirus scanning to HTTP, FTP, IMAP, POP3,
and SMTP content traffic.
Table 7: Scan content profile
Options HTTP FTP IMAP POP3 SMTP
Antivirus Scan ;;;;;
File Block
Web URL Block
Web Content Block
Web Script Filter
Web Exempt List
Email Block List
Email Exempt List
Email Content Block
Oversized File/Email Block pass pass pass pass pass
Pass Fragmented Emails
Web content profile
Use the web content profile to apply antivirus scanning and Web content blocking to
HTTP content traffic. You can add this content profile to firewall policies that control
HTTP traffic.
Table 8: Web content profile
Options HTTP FTP IMAP POP3 SMTP
Antivirus Scan ;
File Block
Web URL Block ;
Web Content Block ;
Web Script Filter
Web Exempt List
Email Block List
Email Exempt List
Email Content Block
Oversized File/Email Block pass pass pass pass pass
Pass Fragmented Emails
36 Fortinet Inc.
Page 37

Getting started Planning your FortiGate configuration
Unfiltered content profile
Use the unfiltered content profile if you do not want to apply any content protection to
content traffic. You can add this content profile to firewall policies for connections
between highly trusted or highly secure networks where content does not need to be
protected.
Table 9: Unfiltered content profile
Options HTTP FTP IMAP POP3 SMTP
Antivirus Scan
File Block
Web URL Block
Web Content Block
Web Script Filter
Web Exempt List ;
Email Block List
Email Exempt List ;;
Email Content Block
Oversized File/Email Block pass pass pass pass pass
Pass Fragmented Emails ;;;
Planning your FortiGate configuration
Before beginning to configure the FortiGate unit, you need to plan how to integrate the
unit into your network. Among other things, you have to decide whether or not the unit
will be visible to the network, which firewall functions it will provide, and how it will
control the traffic flowing between its interfaces.
Your configuration plan is dependent upon the operating mode that you select. The
FortiGate unit can be configured in either of two modes: NAT/Route mode (the default)
or Transparent mode.
NAT/Route mode
In NAT/Route mode, the unit is visible to the network. Like a router, all of its interfaces
are on different subnets. The following interfaces are available in NAT/Route mode:
• WAN1 is the default interface to the external network (usually the Internet).
• WAN2 is the redundant interface to the external network.
• Internal is the interface to the internal network.
• DMZ is the interface to the DMZ network.
You must configure routing to support the redundant WAN1 and WAN2 internet
connections. Routing can be used to automatically re-direct connections from an
interface if its connection to the external network fails.
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 37
Page 38

Planning your FortiGate configuration Getting started
You can add security policies to control whether communications through the
FortiGate unit operate in NAT mode or in route mode. Security policies control the flow
of traffic based on each packet’s source address, destination address and service. In
NAT mode, the FortiGate performs network address translation before the packet is
sent to the destination network. In route mode, no translation takes place.
By default, the FortiGate unit has a NAT mode security policy that allows users on the
internal network to securely download content from the external network. No other
traffic is possible until you have configured more security policies.
You would typically use NAT/Route mode when the FortiGate unit is used as a
gateway between private and public networks. In this configuration, you would create
NAT mode policies to control traffic flowing between the internal, private network and
the external, public network (usually the Internet).
If you have multiple internal networks, such as a DMZ network in addition to the
internal, private network, you could create route mode policies for traffic flowing
between them.
Figure 4: Example NAT/Route mode network configuration
Transparent mode
In Transparent mode, the FortiGate unit is invisible to the network. Similar to a
network bridge, all of FortiGate interfaces must be on the same subnet. You only have
to configure a management IP address so that you can make configuration changes.
The management IP address is also used for antivirus and attack definition updates.
You would typically use the FortiGate unit in Transparent mode on a private network
behind an existing firewall or behind a router. The FortiGate unit performs firewalling
as well as antivirus and content scanning but not VPN.
38 Fortinet Inc.
Page 39

Getting started Planning your FortiGate configuration
Figure 5: Example Transparent mode network configuration
You can connect up to four network segments to the FortiGate unit to control traffic
between these network segments.
• WAN1 can connect to the external firewall or router.
• Internal can connect to the internal network.
• DMZ and WAN2 can connect to other network segments.
Configuration options
Once you have selected Transparent or NAT/Route mode operation, you can
complete your configuration plan, and begin configuring the FortiGate unit.
You can use the web-based manager setup wizard or the command line interface
(CLI) for the basic configuration of the FortiGate unit.
Setup Wizard
If you are configuring the FortiGate unit to operate in NAT/Route mode (the default),
the Setup Wizard prompts you to add the administration password and the internal
interface address. The Setup Wizard also prompts you to choose either a manual
(static) or a dynamic (DHCP or PPPoE) address for the WAN1 interface. Using the
wizard, you can also add DNS server IP addresses and a default route for the WAN1
interface.
In NAT/Route mode you can also change the configuration of the FortiGate DHCP
server to supply IP addresses for the computers on your internal network. You can
also configure the FortiGate to allow Internet access to your internal Web, FTP, or
email servers.
If you are configuring the FortiGate unit to operate in Transparent mode, you can
switch to Transparent mode from the web-based manager and then use the Setup
Wizard to add the administration password, the management IP address and
gateway, and the DNS server addresses.
CLI
If you are configuring the FortiGate unit to operate in NAT/Route mode, you can add
the administration password and all interface addresses. You can also use the CLI to
configure the WAN1 interface for either a manual (static) or a dynamic (DHCP or
PPPoE) address. Using the CLI, you can also add DNS server IP addresses and a
default route for the WAN1 interface.
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 39
Page 40

FortiGate model maximum values matrix Getting started
In NAT/Route mode you can also change the configuration of the FortiGate DHCP
server to supply IP addresses for the computers on your internal network.
If you are configuring the FortiGate unit to operate in Transparent mode, you can use
the CLI to switch to Transparent mode, Then you can add the administration
password, the management IP address and gateway, and the DNS server addresses.
FortiGate model maximum values matrix
Table 10: FortiGate maximum values matrix
FortiGate model
50 60 100 200 300 400 500 1000 2000 3000 3600
Policy 200 500 1000 2000 5000 5000 20000 50000 50000 50000 50000
Address 500 500 500 500 3000 3000 6000 10000 10000 10000 10000
Address group 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500
Service 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500
Service group 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500
Recurring schedule 256 256 256 256 256 256 256 256 256 256 256
Onetime schedule 256 256 256 256 256 256 256 256 256 256 256
User 20 500 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000
User group 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100
Group members 300 300 300 300 300 300 300 300 300 300 300
Virtual IPs 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500
IP/MAC binding 50 100 1000 1000 2000 2000 2000 5000 5000 5000 5000
Route 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500
Policy route gateway 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500
Admin user 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500
IPsec Phase 1 20 50 80 200 1500 1500 3000 5000 5000 5000 5000
VPN concentrator 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500
VLAN subinterface N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A 1024* 1024* 2048* 2048* 8192* 8192*
Zone N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A 100 100 200 200 300 500
IP pool 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50
RADIUS server 66666666666
File pattern 56 56 56 56 56 56 56 56 56 56 56
PPTP user 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500
L2TP user 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500
URL block no limit no limit no limit no limit no limit no limit no limit no limit no limit no limit no limit
Content block no limit no limit no limit no limit no limit no limit no limit no limit no limit no limit no limit
Exempt URL no limit no limit no limit no limit no limit no limit no limit no limit no limit no limit no limit
40 Fortinet Inc.
Page 41

Getting started Next steps
Next steps
Now that your FortiGate unit is operating, you can proceed to configure it to connect to
networks:
• If you are going to operate the FortiGate unit in NAT/Route mode, go to
“NAT/Route mode installation” on page 43.
• If you are going to operate the FortiGate unit in Transparent mode, go to
“Transparent mode installation” on page 59.
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 41
Page 42

Next steps Getting started
42 Fortinet Inc.
Page 43

FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide Version 2.50 MR2
NAT/Route mode installation
This chapter describes how to install the FortiGate unit in NAT/Route mode. To install
the FortiGate unit in Transparent mode, see “Transparent mode installation” on
page 59.
This chapter describes:
• Installing the FortiGate unit using the default configuration
• Preparing to configure NAT/Route mode
• Using the setup wizard
• Using the command line interface
• Connecting the FortiGate unit to your networks
• Configuring your networks
• Completing the configuration
• Configuration example: Multiple connections to the Internet
Installing the FortiGate unit using the default configuration
Depending on your requirements, you may be able to deploy the FortiGate unit
without changing its factory default configuration. If the factory default settings in
Ta bl e 11 are compatible with your requirements, all you need to do is configure your
internal network and then connect the FortiGate unit.
Table 11: FortiGate unit factory default configuration
Operating Mode NAT/Route mode.
Firewall Policy One NAT mode policy that allows users on the internal network to access
WAN1 interface The WAN1 interface receives its IP address by DHCP from your Internet
DHCP Server
on internal
network
any Internet service. No other traffic is allowed. All web and email traffic
is scanned for viruses.
Service Provider (ISP).
The FortiGate unit functions as a DHCP server for your internal network.
If you configure the computers on your internal network to obtain an IP
address automatically using DHCP, the FortiGate unit automatically sets
the IP addresses of the computers in this range:
Starting IP: 192.168.1.1
Ending IP: 192.168.1.254
One IP address is reserved for the FortiGate internal interface:
192.168.1.99.
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 43
Page 44

Preparing to configure NAT/Route mode NAT/Route mode installation
To use the factory default configuration, follow these steps to install the FortiGate unit:
1 Configure the TCP/IP settings of the computers on your internal network to obtain an
IP address automatically using DHCP. Refer to your computer documentation for
assistance.
2 Complete the procedure in the section “Connecting the FortiGate unit to your
networks” on page 48.
Changing the default configuration
You can use the procedures in this chapter to change the default configuration. For
example, if your ISP assigns IP addresses using PPPoE instead of DHCP, you only
need to change the configuration of the WAN1 interface. Use the information in the
rest of this chapter to change the default configuration as required.
Preparing to configure NAT/Route mode
Use Tab le 12 to gather the information that you need to customize NAT/Route mode
settings.
Table 12: NAT/Route mode settings
Administrator password:
Internal
interface
WAN1 interface
WAN2 interface
Internal servers
If you provide access from the Internet to a web server, mail server, IMAP
server, or FTP server installed on an internal network, add the IP
addresses of the servers here.
IP: _____._____._____._____
Netmask: _____._____._____._____
IP: _____._____._____._____
Netmask: _____._____._____._____
Default Gateway: _____._____._____._____
Primary DNS Server: _____._____._____._____
Secondary DNS Server: _____._____._____._____
IP: _____._____._____._____
Netmask: _____._____._____._____
Web Server: _____._____._____._____
SMTP Server: _____._____._____._____
POP3 Server: _____._____._____._____
IMAP Server: _____._____._____._____
FTP Server: _____._____._____._____
44 Fortinet Inc.
Page 45

NAT/Route mode installation Preparing to configure NAT/Route mode
Advanced NAT/Route mode settings
Use Tab le 13 to gather the information that you need to customize advanced
FortiGate NAT/Route mode settings.
Table 13: Advanced FortiGate NAT/Route mode settings
WAN1 interface
WAN2 interface
DHCP server
DHCP:
PPPoE:
If your ISP supplies you with an IP address using PPPoE, record your
PPPoE user name and password.
DHCP:
PPPoE:
If your ISP supplies you with an IP address using PPPoE, record your
PPPoE user name and password.
The FortiGate unit contains a DHCP server that you can configure to
automatically set the addresses of the computers on your internal network.
If your Internet Service Provider (ISP) supplies you with
an IP address using DHCP, no further information is
required.
User name:
Password:
If your Internet Service Provider (ISP) supplies you with
an IP address using DHCP, no further information is
required.
User name:
Password:
Starting IP: _____._____._____._____
Ending IP: _____._____._____._____
Netmask: _____._____._____._____
Default Route: _____._____._____._____
DNS IP: _____._____._____._____
DMZ interface
Use Tab le 14 to record the IP address and netmask of the FortiGate DMZ interface if
you are configuring it during installation.
.
Table 14: DMZ interface (Optional)
DMZ IP: _____._____._____._____ Netmask: _____._____._____._____
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 45
Page 46

Using the setup wizard NAT/Route mode installation
Using the setup wizard
From the web-based manager, you can use the setup wizard to create the initial
configuration of your FortiGate unit. To connect to the web-based manager, see
“Connecting to the web-based manager” on page 30.
Starting the setup wizard
1 Select Easy Setup Wizard (the middle button in the upper-right corner of the
web-based manager).
2 Use the information that you gathered in Table 12 on page 44 to fill in the wizard fields.
Select the Next button to step through the wizard pages.
3 Confirm your configuration settings and then select Finish and Close.
Note: If you use the setup wizard to configure internal server settings, the FortiGate unit adds
port forwarding virtual IPs and firewall policies for each server. For each server located on your
internal network the FortiGate unit adds a WAN1->Internal policy. For each server located on
your DMZ network, the FortiGate unit adds a WAN1->DMZ policy.
Reconnecting to the web-based manager
If you used the setup wizard to change the IP address of the internal interface, you
must reconnect to the web-based manager using a new IP address. Browse to https://
followed by the new IP address of the internal interface. Otherwise, you can reconnect
to the web-based manager by browsing to https://192.168.1.99.
You have now completed the initial configuration of your FortiGate unit, and you can
proceed to “Connecting the FortiGate unit to your networks” on page 48.
Using the command line interface
As an alternative to using the setup wizard, you can configure the FortiGate unit using
the command line interface (CLI). To connect to the CLI, see “Connecting to the
command line interface (CLI)” on page 31.
Configuring the FortiGate unit to operate in NAT/Route mode
Use the information that you gathered in Table 12 on page 44 to complete the
following procedures.
Configuring NAT/Route mode IP addresses
1 Log into the CLI if you are not already logged in.
2 Set the IP address and netmask of the internal interface to the internal IP address and
netmask that you recorded in Table 12 on page 44. Enter:
set system interface internal mode static ip <IP address>
<netmask>
Example
set system interface internal mode static ip 192.168.1.1
255.255.255.0
46 Fortinet Inc.
Page 47

NAT/Route mode installation Using the command line interface
3 Set the IP address and netmask of the WAN1 interface to the IP address and netmask
that you recorded in Table 12 on page 44.
To set the manual IP address and netmask, enter:
set system interface wan1 mode static ip <IP address> <netmask>
Example
set system interface wan1 mode
static
ip 204.23.1.5 255.255.255.0
To set the WAN1 interface to use DHCP, enter:
set system interface wan1 mode dhcp connection enable
To set the WAN1 interface to use PPPoE, enter:
set system interface wan1 mode pppoe
password
<password>
connection
enable
username
<user name>
Example
set system interface wan1 mode pppoe username user@domain.com
password mypass connection enable
4 Optionally set the IP address and netmask of the WAN2 interface to the IP address
and netmask that you recorded in Table 12 on page 44.
To set the manual IP address and netmask, enter:
set system interface wan2 mode static ip <IP address> <netmask>
Example
set system interface wan2 mode
static
ip 34.3.21.35 255.255.255.0
To set the WAN2 interface to use DHCP, enter:
set system interface wan2 mode dhcp connection enable
To set the WAN2 interface to use PPPoE, enter:
set system interface wan2 mode pppoe
password
<password>
connection
enable
username
<user name>
Example
set system interface wan2 mode pppoe username user@domain.com
password mypass connection enable
5 Optionally set the IP address and netmask of the DMZ interface to the DMZ IP
address and netmask that you recorded in Table 14 on page 45. Enter:
set system interface dmz mode static ip <IP address> <netmask>
Example
set system interface dmz mode static ip 10.10.10.2
255.255.255.0
6 Confirm that the addresses are correct. Enter:
get system interface
The CLI lists the IP address, netmask and other settings for each of the FortiGate
interfaces.
7 Set the primary DNS server IP addresses. Enter
set system dns primary <IP address>
Example
set system dns primary 293.44.75.21
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 47
Page 48

Connecting the FortiGate unit to your networks NAT/Route mode installation
8 Optionally, set the secondary DNS server IP addresses. Enter
set system dns secondary <IP address>
Example
set system dns secondary 293.44.75.22
9 Set the default route to the Default Gateway IP address (not required for DHCP and
PPPoE).
set system route number <route_no> dst 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 gw1
<gateway_ip>
Example
set system route number 0 dst 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 gw1 204.23.1.2
Connecting the FortiGate unit to your networks
When you have completed the initial configuration, you can connect the FortiGate unit
between your internal network and the Internet.
There are seven 10/100 BaseTX connectors on the back of the FortiGate-60 unit:
• Four Internal ports for connecting to your internal network,
• One WAN1 port for connecting to your public switch or router and the Internet,
• One WAN 2 port for connecting to a second public switch or router and the Internet
for a redundant Internet connection,
• One DMZ port for connecting to a DMZ network.
Note: You can also connect the WAN1 and WAN2 interfaces to different Internet connections to
provide a redundant connection to the Internet.
To connect the FortiGate unit:
1 Connect the Internal interface connectors to PCs and other network devices in your
internal network.
The Internal interface functions as a switch, allowing up to four devices to be
connected to the internal network and the internal interface.
2 Connect the WAN1 interface to the Internet.
Connect to the public switch or router provided by your Internet Service Provider. If
you are a DSL or cable subscriber, connect the WAN1 interface to the internal or LAN
connection of your DSL or cable modem.
3 Optionally connect the WAN2 interface to the Internet.
Connect to the public switch or router, usually provided by a different Internet Service
Provider. If you are a DSL or cable subscriber, connect the WAN2 interface to the
internal or LAN connection of your DSL or cable modem.
4 Optionally, connect the DMZ interface to your DMZ network.
You can use a DMZ network to provide access from the Internet to a web server or
other server without installing the servers on your internal network.
48 Fortinet Inc.
Page 49

NAT/Route mode installation Configuring your networks
Figure 6: FortiGate-60 NAT/Route mode connections
Configuring your networks
If you are operating the FortiGate unit in NAT/Route mode, your networks must be
configured to route all Internet traffic to the IP address of the FortiGate interface to
which they are connected. For your internal network, change the default gateway
address of all computers and routers connected directly to your internal network to the
IP address of the FortiGate internal interface. For your DMZ network, change the
default gateway address of all computers and routers connected directly to your DMZ
network to the IP address of the FortiGate DMZ interface. For the external network,
route all packets to the FortiGate WAN1 or WAN 2 interface.
If you are using the FortiGate unit as the DHCP server for your internal network,
configure the computers on your internal network for DHCP.
Make sure that the connected FortiGate unit is functioning properly by connecting to
the Internet from a computer on your internal network. You should be able to connect
to any Internet address.
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 49
Page 50

Completing the configuration NAT/Route mode installation
Completing the configuration
Use the information in this section to complete the initial configuration of the FortiGate
unit.
Configuring the DMZ interface
If you are planning to configure a DMZ network, you might want to change the IP
address of the DMZ interface. Use the following procedure to configure the DMZ
interface using the web-based manager.
1 Log into the web-based manager.
2 Go to System > Network > Interface.
3 For the dmz interface, select Modify .
4 Change the IP address and Netmask as required.
5 Select Apply.
Configuring the WAN2 interface
If you are planning to configure a second internet connection using the WAN2
interface, you might want to change the IP address of the WAN2 interface. Use the
following procedure to configure the WAN2 interface using the web-based manager.
1 Log into the web-based manager.
2 Go to System > Network > Interface.
3 For the wan2 interface, select Modify .
4 Change the IP address and Netmask as required.
5 Select Apply.
Setting the date and time
For effective scheduling and logging, the FortiGate system date and time should be
accurate. You can either manually set the system date and time or you can configure
the FortiGate unit to automatically keep its time correct by synchronizing with a
Network Time Protocol (NTP) server.
To set the FortiGate system date and time, see “Setting system date and time” on
page 127.
Changing antivirus protection
By default, the FortiGate unit scans all web and email content for viruses. You can use
the following procedure to change the antivirus configuration. To change the antivirus
configuration:
1 Go to Firewall > Policy > Internal->WAN1.
2 Select Edit to edit this policy.
3 For Anti-Virus & Web Filter you can select a different Content Profile.
See “Factory default content profiles” on page 35 for descriptions of the default
content profiles.
50 Fortinet Inc.
Page 51

NAT/Route mode installation Configuration example: Multiple connections to the Internet
4 Select OK to save your changes.
You can also add you own content profiles. See “Adding a content profile” on
page 168.
Registering your FortiGate
After purchasing and installing a new FortiGate unit, you can register the unit by going
to System > Update > Support, or using a web browser to connect to
http://support.fortinet.com and selecting Product Registration.
Registration consists of entering your contact information and the serial numbers of
the FortiGate units you or your organization have purchased. Registration is quick and
easy. You can register multiple FortiGate units in a single session without re-entering
your contact information.
For more information about registration, see “Registering FortiGate units” on page 99.
Configuring virus and attack definition updates
You can go to System > Update to configure the FortiGate unit to automatically check
to see if new versions of the virus definitions and attack definitions are available. If it
finds new versions, the FortiGate unit automatically downloads and installs the
updated definitions.
The FortiGate unit uses HTTPS on port 8890 to check for updates. The FortiGate
WAN1 interface must have a path to the FortiResponse Distribution Network (FDN)
using port 8890.
To configure automatic virus and attack updates, see “Updating antivirus and attack
definitions” on page 89.
Configuration example: Multiple connections to the Internet
This section describes some basic routing and firewall policy configuration examples
for a FortiGate unit with multiple connections to the Internet (see Figure 7). In this
topology, the organization operating the FortiGate unit uses two Internet service
providers to connect to the Internet. The FortiGate unit is connected to the Internet
using the WAN1 and WAN2 interfaces. The WAN1 interface connects to gateway 1,
operated by ISP1 and the WAN2 interface connects to gateway 2, operated by ISP2.
By adding ping servers to interfaces, and by configuring routing you can control how
traffic uses each Internet connection. With this routing configuration is place you can
proceed to create firewall policies to support multiple internet connections.
This section provides some examples of routing and firewall configurations to
configure the FortiGate unit for multiple internet connections. To use the information in
this section you should be familiar with FortiGate routing (see “Configuring routing” on
page 113) and FortiGate firewall configuration (see “Firewall configuration” on
page 139).
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 51
Page 52

Configuration example: Multiple connections to the Internet NAT/Route mode installation
The examples below show how to configure destination-based routing and policy
routing to control different traffic patterns.
• Configuring Ping servers
• Destination based routing examples
• Policy routing examples
• Firewall policy example
Figure 7: Example multiple Internet connection configuration
Configuring Ping servers
Use the following procedure to make Gateway 1 the ping server for the WAN1
interface and Gateway 2 the ping server for the WAN2 interface.
1 Go to System > Network > Interface.
52 Fortinet Inc.
Page 53

NAT/Route mode installation Configuration example: Multiple connections to the Internet
2 For the WAN1 interface, select Modify .
• Ping Server: 1.1.1.1
• Select Enable Ping Server
•Select OK
3 For the WAN2 interface, select Modify .
• Ping Server: 2.2.2.1
• Select Enable Ping Server
•Select OK
Using the CLI
1 Add a ping server to the WAN1 interface.
set system interface wan1 config detectserver 1.1.1.1 gwdetect
enable
2 Add a ping server to the WAN2 interface.
set system interface wan2 config detectserver 2.2.2.1 gwdetect
enable
Destination based routing examples
This section describes the following destination-based routing examples:
• Primary and backup links to the Internet
• Load sharing
• Load sharing and primary and secondary connections
Primary and backup links to the Internet
Use the following procedure to add a default destination-based route that directs all
outgoing traffic to Gateway 1. If Gateway 1 fails, all connections are re-directed to
Gateway 2. Gateway 1 is the primary link to the Internet and Gateway 2 is the backup
link.
1 Go to System > Network > Routing Table.
2 Select New.
• Destination IP: 0.0.0.0
• Mask: 0.0.0.0
• Gateway #1: 1.1.1.1
• Gateway #2: 2.2.2.1
• Device #1: wan1
• Device #2: wan2
•Select OK.
Using the CLI
1 Add the route to the routing table.
set system route number 0 dst 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 gw1 1.1.1.1
dev1 wan1 gw2 2.2.2.1 dev2 wan2
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 53
Page 54

Configuration example: Multiple connections to the Internet NAT/Route mode installation
Table 15: Route for primary and backup links
Destination IP‘ Mask Gateway #1 Device #1 Gateway #2 Device #2
0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 1.1.1.1 wan1 2.2.2.1 wan2
Load sharing
You can also configure destination routing to direct traffic through both gateways at
the same time. If users on your internal network connect to the networks of ISP1 and
ISP2, you can add routes for each of these destinations. Each route can include a
backup destination to the network of the other ISP.
Table 16: Load sharing routes
Destination IP‘ Mask Gateway #1 Device #1 Gateway #2 Device #2
100.100.100.0 255.255.255.0 1.1.1.1 wan1 2.2.2.1 wan2
200.200.200.0 255.255.255.0 2.2.2.1 wan2 1.1.1.1 wan1
The first route directs all traffic destined for the 100.100.100.0 network to gateway 1
with the IP address 1.1.1.1. If this router is down, traffic destined for the 100.100.100.0
network is re-directed to gateway 2 with the IP address 2.2.2.1.
Load sharing and primary and secondary connections
You can combine these routes into a more complete multiple internet connection
configuration. In the topology shown in Figure 7 on page 52, users on the Internal
network would connect to the Internet to access web pages and other Internet
resources. However, they may also connect to services, such as email, provided by
their ISPs. You can combine the routes described in the previous examples to provide
users with a primary and backup connection to the Internet, while at the same time
routing traffic to each ISP network as required.
The routing described below allows a user on the internal network to connect to the
Internet through gateway 1 and ISP1. At the same time, this user can also connect
through the DMZ interface to gateway 2 to access a mail server maintained by ISP2.
Adding the routes using the web-based manager
1 Go to System > Network > Routing Table.
2 Select New to add the default route for primary and backup links to the Internet.
• Destination IP: 0.0.0.0
• Mask: 0.0.0.0
• Gateway #1: 1.1.1.1
• Gateway #2: 2.2.2.1
• Device #1: wan1
• Device #2: wan2
•Select OK.
54 Fortinet Inc.
Page 55

NAT/Route mode installation Configuration example: Multiple connections to the Internet
3 Select New to add a route for connections to the network of ISP1.
• Destination IP: 100.100.100.0
• Mask: 255.255.255.0
• Gateway #1: 1.1.1.1
• Gateway #2: 2.2.2.1
• Device #1: wan1
• Device #2: wan2
4 Select New to add a route for connections to the network of ISP2.
• Destination IP: 200.200.200.0
• Mask: 255.255.255.0
• Gateway #1: 2.2.2.1
• Gateway #2: 1.1.1.1
• Device #1: wan1
• Device #2: wan2
•Select OK.
5 Change the order of the routes in the routing table to move the default route below the
other two routes.
• For the default route select Move to .
• Type a number in the Move to field to move this route to the bottom of the list.
If there are only 3 routes, type 3.
•Select OK.
Adding the routes using the CLI
1 Add the route for connections to the network of ISP2.
set system route number 1 dst 100.100.100.0 255.255.255.0 gw1
1.1.1.1 dev1 wan1 gw2 2.2.2.1 dev2 wan2
1 Add the route for connections to the network of ISP1.
set system route number 2 dst 200.200.200.0 255.255.255.0 gw1
2.2.2.1 dev1 wan2 gw2 1.1.1.1 dev2 wan1
2 Add the default route for primary and backup links to the Internet.
set system route number 3 dst 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 gw1 1.1.1.1
dev1 wan1 gw2 2.2.2.1 dev2 wan2
The routing table should have routes arranged as shown in Tab le 1 7.
Table 17: Example combined routing table
Destination IP‘ Mask Gateway #1 Device #1 Gateway #2 Device #2
100.100.100.0 255.255.255.0 1.1.1.1 wan1 2.2.2.1 wan2
200.200.200.0 255.255.255.0 2.2.2.1 wan2 1.1.1.1 wan1
0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 1.1.1.1 wan1 2.2.2.1 wan2
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 55
Page 56

Configuration example: Multiple connections to the Internet NAT/Route mode installation
Policy routing examples
Policy routing can be added to increase the control you have over how packets are
routed. Policy routing works on top of destination-based routing. This means you
should configure destination-based routing first and then build policy routing on top to
increase the control provided by destination-based routing.
For example, if you have used destination-based routing to configure routing for dual
internet connections, you can use policy routing to apply more control to which traffic
is sent to which destination route. This section describes the following policy routing
examples, based on topology similar to that shown in Figure 7 on page 52.
Differences are noted in each example.
The policy routes described in these examples only work if you have already defined
destination routes similar to those described in the previous section.
• Routing traffic from internal subnets to different external networks
• Routing a service to an external network
For more information about policy routing, see “Policy routing” on page 116.
Routing traffic from internal subnets to different external networks
If the FortiGate unit provides internet access for multiple internal subnets, you can use
policy routing to control the route that traffic from each network takes to the Internet.
For example, if the internal network includes the subnets 192.168.10.0 and
192.168.20.0 you can enter the following policy routes:
1 Enter the following command to route traffic from the 192.168.10.0 subnet to the
100.100.100.0 external network:
set system route policy 1 src 192.168.10.0 255.255.255.0 dst
100.100.100.0 255.255.255.0 gw 1.1.1.1
2 Enter the following command to route traffic from the 192.168.20.0 subnet to the
200.200.200.0 external network:
set system route policy 2 src 192.168.20.0 255.255.255.0 dst
200.200.200.0 255.255.255.0 gw 2.2.2.1
Routing a service to an external network
You can use the following policy routes to direct all HTTP traffic (using port 80) to one
external network and all other traffic to the other external network.
1 Enter the following command to route all HTTP traffic using port 80 to the next hop
gateway with IP address 1.1.1.1.
set system route policy 1 src 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 dst 0.0.0.0
0.0.0.0 protocol 6 port 1 1000 gw 1.1.1.1
2 Enter the following command to route all other traffic to the next hop gateway with IP
address 2.2.2.1.
Set system route policy 2 src 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 dst 0.0.0.0
0.0.0.0 gw 2.2.2.1
56 Fortinet Inc.
Page 57

NAT/Route mode installation Configuration example: Multiple connections to the Internet
Firewall policy example
Firewall policies control how traffic flows through the FortiGate unit. Once routing for
multiple internet connections has been configured you must create firewall policies to
control which traffic is allowed through the FortiGate unit and the interfaces through
which this traffic can connect.
For traffic originating on the Internal network to be able to connect to the Internet
through both Internet connections, you must add redundant policies from the internal
interface to each interface that connects to the Internet. Once these policies have
been added, the routing configuration controls which internet connection is actually
used.
Adding a redundant default policy
Figure 7 on page 52 shows a FortiGate unit connected to the Internet using its internal
and DMZ interfaces. The default policy allows all traffic from the internal network to
connect to the Internet through the WAN1 interface. If you add a similar policy to the
internal to WAN2 policy list, this policy will allow all traffic from the internal network to
connect to the Internet through the WAN2 interface. With both of these policies added
to the firewall configuration, the routing configuration will determine which Internet
connection the traffic from the internal network actually uses. For more information
about the default policy, see “Default firewall configuration” on page 140.
To add a redundant default policy
1 Go to Firewall > Policy > Int->WAN2.
2 Select New.
3 Configure the policy to match the default policy.
Source Internal_All
Destination WAN2_All
Schedule Always
Service ANY
Action Accept
NAT Select NAT.
4 Select OK to save your changes.
Adding more firewall policies
In most cases your firewall configuration includes more than just the default policy.
However, the basic premise of creating redundant policies applies even as the firewall
configuration becomes more complex. To configure the FortiGate unit to use multiple
Internet connections you must add duplicate policies for connections between the
internal network and both interfaces connected to the Internet. As well, as you add
redundant policies, you must arrange them in both policy lists in the same order.
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 57
Page 58

Configuration example: Multiple connections to the Internet NAT/Route mode installation
Restricting access to a single Internet connection
In some cases you might want to limit some traffic to only being able to use one
Internet connection. For example, in the topology shown in Figure 7 on page 52 the
organization might want its mail server to only be able to connect to the SMTP mail
server of ISP1. To do this, you add a single Internal->WAN1 firewall policy for SMTP
connections. Because redundant policies have not been added, SMTP traffic from the
Internet network is always connected to ISP1. If the connection to ISP1 fails the SMTP
connection is not available.
58 Fortinet Inc.
Page 59

FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide Version 2.50 MR2
Transparent mode installation
This chapter describes how to install your FortiGate unit in Transparent mode. If you
want to install the FortiGate unit in NAT/Route mode, see “NAT/Route mode
installation” on page 43.
This chapter describes:
• Preparing to configure Transparent mode
• Using the setup wizard
• Using the command line interface
• Connecting the FortiGate unit to your networks
• Completing the configuration
• Transparent mode configuration examples
Preparing to configure Transparent mode
Use Ta bl e 1 8 to gather the information that you need to customize Transparent mode
settings.
Table 18: Transparent mode settings
Administrator Password:
IP: _____._____._____._____
Netmask: _____._____._____._____
Management IP
The management IP address and netmask must be valid for the network
from which you will manage the FortiGate unit. Add a default gateway if the
FortiGate unit must connect to a router to reach the management
computer.
DNS Settings
Default Gateway: _____._____._____._____
Primary DNS Server: _____._____._____._____
Secondary DNS Server: _____._____._____._____
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 59
Page 60

Using the setup wizard Transparent mode installation
Using the setup wizard
From the web-based manager, you can use the setup wizard to create the initial
configuration of your FortiGate unit. To connect to the web-based manager, see
“Connecting to the web-based manager” on page 30.
Changing to Transparent mode
The first time that you connect to the FortiGate unit, it is configured to run in
NAT/Route mode. To switch to Transparent mode using the web-based manager:
1 Go to System > Status.
2 Select Change to Transparent Mode.
3 Select Transparent in the Operation Mode list.
4 Select OK.
The FortiGate unit changes to Transparent mode.
To reconnect to the web-based manager, change the IP address of your management
computer to 10.10.10.2. Connect to the internal or DMZ interface and browse to
https:// followed by the Transparent mode management IP address. The default
FortiGate Transparent mode management IP address is 10.10.10.1.
Starting the setup wizard
1 Select Easy Setup Wizard (the middle button in upper-right corner of the web-based
manager).
2 Use the information that you gathered in Table 18 on page 59 to fill in the wizard fields.
Select the Next button to step through the wizard pages.
3 Confirm your configuration settings and then select Finish and Close.
Reconnecting to the web-based manager
If you changed the IP address of the management interface while you were using the
setup wizard, you must reconnect to the web-based manager using the new IP
address. Browse to https:// followed by the new IP address of the management
interface. Otherwise, you can reconnect to the web-based manager by browsing to
https://10.10.10.1. If you connect to the management interface through a router, make
sure that you have added a default gateway for that router to the management IP
default gateway field.
60 Fortinet Inc.
Page 61

Transparent mode installation Using the command line interface
Using the command line interface
As an alternative to the setup wizard, you can configure the FortiGate unit using the
command line interface (CLI). To connect to the CLI, see “Connecting to the command
line interface (CLI)” on page 31. Use the information that you gathered in Table 18 on
page 59 to complete the following procedures.
Changing to Transparent mode
1 Log into the CLI if you are not already logged in.
2 Switch to Transparent mode. Enter:
set system opmode transparent
After a few seconds, the login prompt appears.
3 Type admin and press Enter.
The following prompt appears:
Type ? for a list of commands.
4 Confirm that the FortiGate unit has switched to Transparent mode. Enter:
get system status
The CLI displays the status of the FortiGate unit. The last line shows the current
operation mode.
Operation mode: Transparent
Configuring the Transparent mode management IP address
1 Log into the CLI if you are not already logged in.
2 Set the management IP address and netmask to the IP address and netmask that you
recorded in Table 18 on page 59. Enter:
set system management ip <IP address> <netmask>
Example
set system management ip 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.0
3 Confirm that the address is correct. Enter:
get system management
The CLI lists the management IP address and netmask.
Configure the Transparent mode default gateway
1 Log into the CLI if you are not already logged in.
2 Set the default route to the default gateway that you recorded in Table 18 on page 59.
Enter:
set system route number <number> gateway <IP address>
Example
set system route
You have now completed the initial configuration of the FortiGate unit.
number 1 gw1
204.23.1.2
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 61
Page 62

Connecting the FortiGate unit to your networks Transparent mode installation
Connecting the FortiGate unit to your networks
When you have completed the initial configuration, you can connect the FortiGate unit
between your internal network and the Internet using the Internal and WAN1
interfaces. You can also connect networks to the DMZ interface and the WAN2
interface.
There are seven 10/100Base-TX connectors on the FortiGate-60:
• Four Internal ports for connecting to your internal network,
• WAN1 for connecting to the Internet,
• DMZ and WAN2 which can be connected to networks.
To connect the FortiGate unit running in Transparent mode:
1 Connect the Internal interface connectors to PCs and other network devices in your
internal network.
The Internal interface functions as a switch, allowing up to four devices to be
connected to the internal network and the internal interface.
2 Connect the WAN1 interface to the Internet.
Connect to the public switch or router provided by your Internet Service Provider. If
you are a DSL or cable subscriber, connect the WAN1 interface to the internal or LAN
connection of your DSL or cable modem.
3 Optionally connect the WAN2 and DMZ interfaces to other networks.
Figure 8: FortiGate-60 Transparent mode connections
62 Fortinet Inc.
Page 63

Transparent mode installation Completing the configuration
In Transparent mode, the FortiGate unit does not change the layer 3 topology. This
means that all of its interfaces are on the same IP subnet and that it appears to other
devices as a bridge. Typically, the FortiGate unit would be deployed in Transparent
mode when it is intended to provide antivirus and content scanning behind an existing
firewall solution.
A FortiGate unit in Transparent mode can also perform firewalling. Even though it
takes no part in the layer 3 topology, it can examine layer 3 header information and
make decisions on whether to block or pass traffic.
Completing the configuration
Use the information in this section to complete the initial configuration of the FortiGate
unit.
Setting the date and time
For effective scheduling and logging, the FortiGate system date and time should be
accurate. You can either manually set the date and time or you can configure the
FortiGate unit to automatically keep its date and time correct by synchronizing with a
Network Time Protocol (NTP) server.
To set the FortiGate system date and time, see “Setting system date and time” on
page 127.
Enabling antivirus protection
To enable antivirus protection to protect users on your internal network from
downloading a virus from the Internet:
1 Go to Firewall > Policy > Internal->WAN1.
2 Select Edit to edit this policy.
3 Select Anti-Virus & Web filter to enable antivirus protection for this policy.
4 Select the Scan Content Profile.
5 Select OK to save your changes.
Registering your FortiGate
After purchasing and installing a new FortiGate unit, you can register the unit by going
to System > Update > Support, or using a web browser to connect to
http://support.fortinet.com and selecting Product Registration.
Registration consists of entering your contact information and the serial numbers of
the FortiGate units you or your organization have purchased. Registration is quick and
easy. You can register multiple FortiGate units in a single session without re-entering
your contact information.
For more information about registration, see “Registering FortiGate units” on page 99.
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 63
Page 64

Transparent mode configuration examples Transparent mode installation
Configuring virus and attack definition updates
You can configure the FortiGate unit to automatically check to see if new versions of
the virus definitions and attack definitions are available. If it finds new versions, the
FortiGate unit automatically downloads and installs the updated definitions.
The FortiGate unit uses HTTPS on port 8890 to check for updates. The FortiGate
WAN1 interface must have a path to the FortiResponse Distribution Network (FDN)
using port 8890.
To configure automatic virus and attack updates, see “Updating antivirus and attack
definitions” on page 89.
Transparent mode configuration examples
A FortiGate unit operating in Transparent mode still requires a basic configuration to
operate as a node on the IP network. As a minimum, the FortiGate unit must be
configured with an IP address and subnet mask. These are used for management
access and to allow the unit to receive antivirus and definitions updates. Also, the unit
must have sufficient route information to reach:
• the management computer,
• The FortiResponse Distribution Network (FDN),
• a DNS server.
A route is required whenever the FortiGate unit connects to a router to reach a
destination. If all of the destinations are located on the external network, you may be
required to enter only a single default route. If, however, the network topology is more
complex, you may be required to enter one or more static routes in addition to the
default route.
This section describes:
• Default routes and static routes
• Example default route to an external network
• Example static route to an external destination
• Example static route to an internal destination
Default routes and static routes
To create a route to a destination, you need to define an IP prefix which consists of an
IP network address and a corresponding netmask value. A default route matches any
prefix and forwards traffic to the next hop router (otherwise known as the default
gateway). A static route matches a more specific prefix and forwards traffic to the next
hop router.
Default route example:
IP Prefix 0.0.0.0 (IP address)
0.0.0.0 (Netmask)
Next Hop 192.168.1.2
64 Fortinet Inc.
Page 65

Transparent mode installation Transparent mode configuration examples
Static Route example:
IP Prefix 172.100.100.0 (IP address)
255.255.255.0 (Netmask)
Next Hop 192.168.1.2
Note: When adding routes to the FortiGate unit, add the default route last so that it
appears on the bottom of the route list. This ensures that the unit will attempt to match
more specific routes before selecting the default route.
Example default route to an external network
Figure 9 shows a FortiGate unit where all destinations, including the management
computer, are located on the external network. To reach these destinations, the
FortiGate unit must connect to the “upstream” router leading to the external network.
To facilitate this connection, you must enter a single default route that points to the
upstream router as the next hop/default gateway.
Figure 9: Default route to an external network
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 65
Page 66

Transparent mode configuration examples Transparent mode installation
General configuration steps
1 Set the FortiGate unit to operate in Transparent mode.
2 Configure the Management IP address and Netmask of the FortiGate unit.
3 Configure the default route to the external network.
Web-based manager example configuration steps
To configure basic Transparent mode settings and a default route using the
web-based manager:
1 Go to System > Status.
• Select Change to Transparent Mode.
• Select Transparent in the Operation Mode list.
•Select OK.
The FortiGate unit changes to Transparent mode.
2 Go to System > Network > Management.
• Change the Management IP and Netmask:
IP: 192.168.1.1
Mask: 255.255.255.0
• Select Apply.
3 Go to System > Network > Routing.
• Select New to add the default route to the external network.
Destination IP: 0.0.0.0
Mask: 0.0.0.0
Gateway: 192.168.1.2
•Select OK.
CLI configuration steps
To configure the Fortinet basic settings and a default route using the CLI:
1 Change the system to operate in Transparent Mode.
set system opmode transparent
2 Add the Management IP address and Netmask.
set system management ip 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
3 Add the default route to the external network.
set system route number 1 gw1 192.168.1.2
Example static route to an external destination
Figure 10 shows a FortiGate unit that requires routes to the FDN located on the
external network. The Fortigate unit does not require routes to the DNS servers or
management computer because they are located on the internal network.
66 Fortinet Inc.
Page 67

Transparent mode installation Transparent mode configuration examples
To connect to the FDN, you would typically enter a single default route to the external
network. However, to provide an extra degree of security, you could enter static routes
to a specific FortiResponse server in addition to a default route to the external
network. If the static route becomes unavailable (perhaps because the IP address of
the FortiResponse server changes) the FortiGate unit will still be able to receive
antivirus and NIDS updates from the FDN using the default route.
Note: This is an example configuration only. To configure a static route, you require a
destination IP address.
Figure 10: Static route to an external destination
General configuration steps
1 Set the FortiGate unit to operate in Transparent mode.
2 Configure the Management IP address and Netmask of the FortiGate unit.
3 Configure the static route to the FortiResponse server.
4 Configure the default route to the external network.
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 67
Page 68

Transparent mode configuration examples Transparent mode installation
Web-based manager example configuration steps
To configure the basic FortiGate settings and a static route using the web-based
manager:
1 Go to System > Status.
• Select Change to Transparent Mode.
• Select Transparent in the Operation Mode list.
•Select OK.
The FortiGate unit changes to Transparent mode.
2 Go to System > Network > Management.
• Change the Management IP and Netmask:
IP: 192.168.1.1
Mask: 255.255.255.0
• Select Apply.
3 Go to System > Network > Routing.
• Select New to add the static route to the FortiResponse server.
Destination IP: 24.102.233.5
Mask: 255.255.255.0
Gateway: 192.168.1.2
•Select OK.
• Select New to add the default route to the external network.
Destination IP: 0.0.0.0
Mask: 0.0.0.0
Gateway: 192.168.1.2
•Select OK.
CLI configuration steps
To configure the Fortinet basic settings and a static route using the CLI:
1 Set the system to operate in Transparent Mode.
set system opmode transparent
2 Add the Management IP address and Netmask.
set system management ip 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
3 Add the static route to the primary FortiResponse server.
set system route number 1 dst 24.102.233.5 255.255.255.0 gw1
192.168.1.2
4 Add the default route to the external network.
set system route number 2 gw1 192.168.1.2
68 Fortinet Inc.
Page 69

Transparent mode installation Transparent mode configuration examples
Example static route to an internal destination
Figure 11 shows a FortiGate unit where the FDN is located on an external subnet and
the management computer is located on a remote, internal subnet. To reach the FDN,
you need to enter a single default route that points to the upstream router as the next
hop/default gateway. To reach the management computer, you need to enter a single
static route that leads directly to it. This route will point to the internal router as the
next hop. (No route is required for the DNS servers because they are on the same
layer 3 subnet as the FortiGate unit.)
Figure 11: Static route to an internal destination
General configuration steps
1 Set the unit to operate in Transparent mode.
2 Configure the Management IP address and Netmask of the FortiGate unit.
3 Configure the static route to the management computer on the internal network.
4 Configure the default route to the external network.
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 69
Page 70

Transparent mode configuration examples Transparent mode installation
Web-based manager example configuration steps
To configure the FortiGate basic settings, a static route, and a default route using the
web-based manager:
1 Go to System > Status.
• Select Change to Transparent Mode.
• Select Transparent in the Operation Mode list.
•Select OK.
The FortiGate unit changes to Transparent mode.
2 Go to System > Network > Management.
• Change the Management IP and Netmask:
IP: 192.168.1.1
Mask: 255.255.255.0
• Select Apply.
3 Go to System > Network > Routing.
• Select New to add the static route to the management computer.
Destination IP: 172.16.1.11
Mask: 255.255.255.0
Gateway: 192.168.1.3
•Select OK.
• Select New to add the default route to the external network.
Destination IP: 0.0.0.0
Mask: 0.0.0.0
Gateway: 192.168.1.2
•Select OK.
CLI configuration steps
To configure the FortiGate basic settings, a static route, and a default route using the
CLI:
1 Set the system to operate in Transparent Mode.
set system opmode transparent
2 Add the Management IP address and Netmask.
set system management ip 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
3 Add the static route to the management computer.
set system route number 1 dst 172.16.1.11 255.255.255.0 gw1
192.168.1.3
4 Add the default route to the external network.
set system route number 2 gw1 192.168.1.2
70 Fortinet Inc.
Page 71

FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide Version 2.50 MR2
System status
You can connect to the web-based manager and go to System > Status to view the
current status of your FortiGate unit. The status information that is displayed includes
the current firmware version, the current virus and attack definitions, and the FortiGate
unit serial number.
If you have logged into the web-based manager using the admin administrator
account, you can use System Status to make any of the following changes to the
FortiGate system settings:
• Changing the FortiGate host name
• Changing the FortiGate firmware
• Manual virus definition updates
• Manual attack definition updates
• Backing up system settings
• Restoring system settings
• Restoring system settings to factory defaults
• Changing to Transparent mode
• Changing to NAT/Route mode
• Restarting the FortiGate unit
• Shutting down the FortiGate unit
If you log into the web-based manager with any other administrator account, you can
go to System > Status to view the system settings including:
• Displaying the FortiGate serial number
• Displaying the FortiGate up time
All administrative users can also go to System > Status > Monitor and view
FortiGate system status. System status displays FortiGate health monitoring
information including CPU and memory status, Session and network status.
• System status
All administrative users can also go to System > Status > Session and view the
active communication sessions to and through the FortiGate unit.
• Session list
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 71
Page 72

Changing the FortiGate host name System status
Changing the FortiGate host name
The FortiGate host name appears on the System > Status page and on the FortiGate
CLI prompt. The host name is also used as the SNMP System Name (see
“Configuring SNMP” on page 132).
The default host name is FortiGate-60.
To change the FortiGate host name:
1 Go to System > Status.
2 Select Edit Host Name .
3 Enter a new host name.
4 Select OK.
The new host name appears on the System Status page and is added to the SNMP
System Name.
Changing the FortiGate firmware
After you download a FortiGate firmware image from Fortinet, you can use the
procedures in Tab le 1 to install the firmware image on your FortiGate unit.
Table 1: Firmware upgrade procedures
Procedure Description
Upgrade to a new
firmware version
Revert to a previous
firmware version
Install a firmware
image from a system
reboot using the CLI
Test a new firmware
image before
installing it
Commonly-used web-based manager and CLI procedures to
upgrade to a new FortiOS firmware version or to a more recent
build of the same firmware version.
Use the web-based manager or CLI procedure to revert to a
previous firmware version. This procedure reverts your FortiGate
unit to its factory default configuration.
Use this procedure to install a new firmware version or revert to a
previous firmware version. You must run this procedure by
connecting to the CLI using the FortiGate console port and a nullmodem cable. This procedure reverts your FortiGate unit to its
factory default configuration.
Use this procedure to test a new firmware image before installing it.
You must run this procedure by connecting to the CLI using the
FortiGate console port and a null-modem cable. This procedure
temporarily installs a new firmware image using your current
configuration. You can test the firmware image before installing it
permanently. If the firmware image works correctly you can use
one of the other procedures listed in this table to install it
permanently.
72 Fortinet Inc.
Page 73

System status Changing the FortiGate firmware
Upgrade to a new firmware version
Use the following procedures to upgrade your FortiGate to a newer firmware version.
Upgrading the firmware using the web-based manager
Note: Installing firmware replaces your current antivirus and attack definitions with the
definitions included with the firmware release that you are installing. When you have installed
new firmware, use the procedure “Manually updating antivirus and attack definitions” on
page 93 to make sure that antivirus and attack definitions are up-to-date.
1 Copy the firmware image file to your management computer.
2 Login to the FortiGate web-based manager as the admin administrative user.
3 Go to System > Status.
4 Select Firmware Upgrade .
5 Enter the path and filename of the firmware image file, or select Browse and locate the
file.
6 Select OK.
The FortiGate unit uploads the firmware image file, upgrades to the new firmware
version, restarts, and displays the FortiGate login. This process takes a few minutes.
7 Login to the web-based manager.
8 Go to System > Status and check the Firmware Version to confirm that the firmware
upgrade has been installed successfully.
9 Use the procedure “Manually updating antivirus and attack definitions” on page 93 to
update antivirus and attack definitions.
Upgrading the firmware using the CLI
To use the following procedure you must have a TFTP server that you can connect to
from the FortiGate unit.
Note: Installing firmware replaces your current antivirus and attack definitions with the
definitions included with the firmware release that you are installing. When you have installed
new firmware, use the procedure “Manually updating antivirus and attack definitions” on
page 93 to make sure that antivirus and attack definitions are up-to-date. You can also use the
CLI command
definitions.
1 Make sure that the TFTP server is running.
2 Copy the new firmware image file to the root directory of the TFTP server.
3 Log into the CLI as the admin administrative user.
4 Make sure the FortiGate unit can connect to the TFTP server.
You can use the following command to ping the computer running the TFTP server.
For example, if the TFTP server's IP address is 192.168.1.168:
execute ping 192.168.1.168
execute updatecenter updatenow to update the antivirus and attack
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 73
Page 74

Changing the FortiGate firmware System status
5 Enter the following command to copy the firmware image from the TFTP server to the
FortiGate:
execute restore image <name_str> <tftp_ip>
Where <name_str> is the name of the firmware image file on the TFTP server and
<tftp_ip> is the IP address of the TFTP server. For example, if the firmware image
file name is FGT_300-v250-build045-FORTINET.out and the IP address of the
TFTP server is 192.168.1.168, enter:
execute restore image FGT_300-v250-build045-FORTINET.out
192.168.1.168
The FortiGate unit uploads the firmware image file, upgrades to the new firmware
version, and restarts. This process takes a few minutes.
6 Reconnect to the CLI.
7 To confirm that the new firmware image has been loaded, enter:
get system status
8 Use the procedure “Manually updating antivirus and attack definitions” on page 93 to
update antivirus and attack definitions, or from the CLI, enter:
execute updatecenter updatenow
9 To confirm that the antivirus and attack definitions have been updated, enter the
following command to display the antivirus engine, virus and attack definitions version,
contract expiry, and last update attempt information.
get system objver
Revert to a previous firmware version
Use the following procedures to revert your FortiGate unit to a previous firmware
version.
Reverting to a previous firmware version using the web-based
manager
The following procedures return your FortiGate unit to its factory default configuration
and delete NIDS user-defined signatures, web content lists, email filtering lists, and
changes to replacement messages.
Before running this procedure you can:
• Backup the FortiGate unit configuration, use the procedure “Backing up system
settings” on page 82.
• Backup the NIDS user defined signatures, see the FortiGate NIDS Guide
• Backup web content and email filtering lists, see the FortiGate Content Protection
Guide.
If you are reverting to a previous FortiOS version (for example, reverting from FortiOS
v2.50 to FortiOS v2.36) you may not be able to restore your previous configuration
from the backup configuration file.
1 Copy the firmware image file to your management computer.
2 Login to the FortiGate web-based manager as the admin administrative user.
74 Fortinet Inc.
Page 75

System status Changing the FortiGate firmware
Note: Installing firmware replaces your current antivirus and attack definitions with the
definitions included with the firmware release that you are installing. When you have installed
new firmware, use the procedure “Manually updating antivirus and attack definitions” on
page 93 to make sure that antivirus and attack definitions are up-to-date.
3 Go to System > Status.
4 Select Firmware Upgrade .
5 Enter the path and filename of the previous firmware image file, or select Browse and
locate the file.
6 Select OK.
The FortiGate unit uploads the firmware image file, reverts to the old firmware version,
resets the configuration, restarts, and displays the FortiGate login. This process takes
a few minutes.
7 Login to the web-based manager.
For information about logging into the web-based manager when the FortiGate unit is
set to factory defaults, see “Connecting to the web-based manager” on page 30.
8 Go to System > Status and check the Firmware Version to confirm that the firmware
has been installed successfully.
9 Restore your configuration.
See “Restoring system settings” on page 83 to restore your previous configuration.
10 Use the procedure “Manually updating antivirus and attack definitions” on page 93 to
update antivirus and attack definitions.
Reverting to a previous firmware version using the CLI
This procedure reverts your FortiGate unit to its factory default configuration and
deletes NIDS user-defined signatures, web content lists, email filtering lists, and
changes to replacement messages.
Before running this procedure you can:
• Backup the FortiGate unit configuration using the command execute backup
config.
• Backup the NIDS user defined signatures using the command execute backup
nidsuserdefsig
• Backup web content and email filtering lists, see the FortiGate Content Protection
Guide.
If you are reverting to a previous FortiOS version (for example, reverting from FortiOS
v2.50 to FortiOS v2.36) you may not be able to restore your previous configuration
from the backup configuration file.
Note: Installing firmware replaces your current antivirus and attack definitions with the
definitions included with the firmware release that you are installing. When you have installed
new firmware, use the procedure “Manually updating antivirus and attack definitions” on
page 93 to make sure that antivirus and attack definitions are up-to-date. You can also use the
CLI command execute updatecenter updatenow to update the antivirus and attack
definitions.
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 75
Page 76

Changing the FortiGate firmware System status
To use the following procedure you must have a TFTP server that you can connect to
from the FortiGate unit.
1 Make sure that the TFTP server is running.
2 Copy the new firmware image file to the root directory of the TFTP server.
3 Login to the FortiGate CLI as the admin administrative user.
4 Make sure the FortiGate unit can connect to the TFTP server.
You can use the following command to ping the computer running the TFTP server.
For example, if the TFTP server's IP address is 192.168.1.168:
execute ping 192.168.1.168
5 Enter the following command to copy the firmware image from the TFTP server to the
FortiGate unit:
execute restore image <name_str> <tftp_ip>
Where <name_str> is the name of the firmware image file on the TFTP server and
<tftp_ip> is the IP address of the TFTP server. For example, if the firmware image
file name is FGT_300-v250-build045-FORTINET.out and the IP address of the
TFTP server is 192.168.1.168, enter:
execute restore image FGT_300-v250-build045-FORTINET.out
192.168.1.168
The FortiGate unit uploads the firmware image file. Once the file has been uploaded a
message similar to the following is displayed:
Get image from tftp server OK.
This operation will downgarde the current firmware version!
Do you want to continue? (y/n)
6 Type Y
7 The FortiGate unit reverts to the old firmware version, resets the configuration to
factory defaults, and restarts. This process takes a few minutes.
8 Reconnect to the CLI.
For information about logging into the web-based manager when the FortiGate unit is
set to factory defaults, see “Connecting to the command line interface (CLI)” on
page 31.
9 To confirm that the new firmware image has been loaded, enter:
get system status
10 Restore your previous configuration. Use the following command:
execute restore config
11 Use the procedure “Manually updating antivirus and attack definitions” on page 93 to
update antivirus and attack definitions, or from the CLI, enter:
execute updatecenter updatenow
12 To confirm that the antivirus and attack definitions have been updated, enter the
following command to display the antivirus engine, virus and attack definitions version,
contract expiry, and last update attempt information.
get system objver
76 Fortinet Inc.
Page 77

System status Changing the FortiGate firmware
Install a firmware image from a system reboot using the CLI
This procedure installs a specified firmware image and resets the FortiGate unit to
default settings. You can use this procedure to upgrade to a new firmware version,
revert to an older firmware version, or to re-install the current firmware.
Note: There are a few variations on this procedure for different FortiGate BIOS versions. These
variations are explained in the procedure steps that are affected. The version of the BIOS
running on your FortiGate unit is displayed when you restart the FortiGate unit while accessing
the CLI by connecting to the FortiGate console port using a null-modem cable.
To run this procedure you:
• access the CLI by connecting to the FortiGate console port using a null-modem
cable,
• install a TFTP server that you can connect to from the FortiGate internal interface.
The TFTP server should be on the same subnet as the internal interface.
Before running this procedure you can:
• Backup the FortiGate unit configuration, use the procedure “Backing up system
settings” on page 82.
• Backup the NIDS user defined signatures, see the FortiGate NIDS Guide
• Backup web content and email filtering lists, see the FortiGate Content Protection
Guide.
If you are reverting to a previous FortiOS version (for example, reverting from FortiOS
v2.50 to FortiOS v2.36) you may not be able to restore your previous configuration
from the backup configuration file.
Note: Installing firmware replaces your current antivirus and attack definitions with the
definitions included with the firmware release that you are installing. When you have installed
new firmware, use the procedure “Manually updating antivirus and attack definitions” on
page 93 to make sure that antivirus and attack definitions are up-to-date.
To install firmware from a system reboot
1 Connect to the CLI using the null modem cable and FortiGate console port.
2 Make sure that the TFTP server is running.
3 Copy the new firmware image file to the root directory of your TFTP server.
4 To confirm that the FortiGate unit can connect to the TFTP server, use the following
command to ping the computer running the TFTP server. For example, if the TFTP
server’s IP address is 192.168.1.168:
execute ping 192.168.1.168
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 77
Page 78

Changing the FortiGate firmware System status
5 Enter the following command to restart the FortiGate unit:
execute reboot
As the FortiGate units starts, a series of system startup messages are displayed.
When one of the following messages appears:
• FortiGate unit running v2.x BIOS
Press Any Key To Download Boot Image.
...
• FortiGate unit running v3.x BIOS
Press any key to enter configuration menu.....
......
6 Immediately press any key to interrupt the system startup.
I
Note: You only have 3 seconds to press any key. If you do not press any key soon enough, the
FortiGate unit reboots and you must log in and repeat the
execute reboot command.
If you successfully interrupt the startup process, one of the following messages
appears:
• FortiGate unit running v2.x BIOS
Enter TFTP Server Address [192.168.1.168]:
Go to step 8.
• FortiGate unit running v3.x BIOS
[G]: Get firmware image from TFTP server.
[F]: Format boot device.
[B]: Boot with backup firmware and set as default.
[Q]: Quit menu and continue to boot with default firmware.
[H]: Display this list of options.
Enter G,F,B,Q,or H:
7 Type G to get the new firmware image from the TFTP server.
8 Type the address of the TFTP server and press Enter.
The following message appears:
Enter Local Address [192.168.1.188]:
9 Type the address of the internal interface of the FortiGate unit and press Enter.
Note: The local IP address is only used to download the firmware image. After the firmware is
installed the address of this interface is changed back to the default IP address for this interface.
The following message appears:
Enter File Name [image.out]:
78 Fortinet Inc.
Page 79

System status Changing the FortiGate firmware
10 Enter the firmware image file name and press Enter.
The TFTP server uploads the firmware image file to the FortiGate unit and messages
similar to the following appear.
• FortiGate unit running v2.x BIOS
Do You Want To Save The Image? [Y/n]
Type Y.
• FortiGate unit running v3.x BIOS
Save as Default firmware/Run image without saving:[D/R]
Save as Default firmware/Backup firmware/Run image without
saving:[D/B/R]
Type D.
The FortiGate unit installs the new firmware image and restarts. The installation might
take a few minutes to complete.
Restoring your previous configuration
You can then restore your previous configuration. Begin by changing the interface
addresses if required. You can do this from the CLI using the command:
set system interface
After changing the interface addresses, you can access the FortiGate unit from the
web-based manager and restore your configuration.
To restore your FortiGate unit configuration, see “Restoring system settings” on
page 83. To restore NIDS user defined signatures, see the FortiGate NIDS Guide. To
restore web content and email filtering lists, see the FortiGate Content Protection
Guide.
If you are reverting to a previous firmware version (for example, reverting from
FortiOS v2.50 to FortiOS v2.36) you may not be able to restore your previous
configuration from the backup up configuration file.
11 Update the virus and attack definitions to the most recent version, see “Manually
updating antivirus and attack definitions” on page 93.
Test a new firmware image before installing it
You can test a new firmware image by installing the firmware image from a system
reboot and saving it to system memory. After completing this procedure the FortiGate
unit operates using the new firmware image with the current configuration. This new
firmware image is not permanently installed. The next time the FortiGate unit restarts
it will be operating with the originally installed firmware image using the current
configuration. If the new firmware image operates successfully, you can install it
permanently using the procedure “Upgrade to a new firmware version” on page 73.
To run this procedure you:
• access the CLI by connecting to the FortiGate console port using a null-modem
cable,
• install a TFTP server that you can connect to from the FortiGate internal interface.
The TFTP server should be on the same subnet as the internal interface.
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 79
Page 80

Changing the FortiGate firmware System status
To test a new firmware image:
1 Connect to the CLI using a null modem cable and FortiGate console port.
2 Make sure the TFTP server is running.
3 Copy the new firmware image file to the root directory of the TFTP server.
You can use the following command to ping the computer running the TFTP server.
For example, if the TFTP server's IP address is 192.168.1.168:
execute ping 192.168.1.168
4 Enter the following command to restart the FortiGate unit:
execute reboot
5 As the FortiGate unit reboots, press any key to interrupt the system startup.
As the FortiGate units starts, a series of system startup messages are displayed.
When one of the following messages appears:
• FortiGate unit running v2.x BIOS
Press Any Key To Download Boot Image.
...
• FortiGate unit running v3.x BIOS
Press any key to enter configuration menu.....
......
6 Immediately press any key to interrupt the system startup.
I
Note: You only have 3 seconds to press any key. If you do not press any key soon enough, the
FortiGate unit reboots and you must log in and repeat the
execute reboot command.
If you successfully interrupt the startup process, one of the following messages
appears:
• FortiGate unit running v2.x BIOS
Enter TFTP Server Address [192.168.1.168]:
Go to step 8.
• FortiGate unit running v3.x BIOS
[G]: Get firmware image from TFTP server.
[F]: Format boot device.
[Q]: Quit menu and continue to boot with default firmware.
[H]: Display this list of options.
Enter G,F,Q,or H:
7 Type G to get the new firmware image from the TFTP server.
8 Type the address of the TFTP server and press Enter.
The following message appears:
Enter Local Address [192.168.1.188]:
9 Type the address of the internal interface of the FortiGate unit and press Enter.
80 Fortinet Inc.
Page 81

System status Manual virus definition updates
Note: The local IP address is only used to download the firmware image. After the firmware is
installed the address of this interface is changed back to the default IP address for this interface.
The following message appears:
Enter File Name [image.out]:
10 Enter the firmware image file name and press Enter.
The TFTP server uploads the firmware image file to the FortiGate unit and messages
similar to the following appear.
• FortiGate unit running v2.x BIOS
Do You Want To Save The Image? [Y/n]
Type N.
• FortiGate unit running v3.x BIOS
Save as Default firmware/Run image without saving:[D/R]
Type R.
The FortiGate image is installed to system memory and the FortiGate starts running
the new firmware image but with its current configuration.
11 You can login to the CLI or the web-based manager using any administrative account.
12 To confirm that the new firmware image has been loaded, from the CLI enter:
get system status
You can test the new firmware image as required.
Manual virus definition updates
The System > Status page of the FortiGate web-based manager displays the current
installed versions of the FortiGate Antivirus Definitions. You can use the following
procedure to update the antivirus definitions manually.
Note: To configure the FortiGate unit for automatic antivirus definitions updates, see “Virus and
attack definitions updates and registration” on page 89. You can also manually initiate an
antivirus definitions update by going to System > Update and selecting Update Now.
1 Download the latest antivirus definitions update file from Fortinet and copy it to the
computer that you use to connect to the web-based manager.
2 Start the web-based manager and go to System > Status.
3 To the right of the Antivirus Definitions Version, select Definitions Update .
4 Enter the path and filename for the antivirus definitions update file, or select Browse
and locate the antivirus definitions update file.
5 Select OK to copy the antivirus definitions update file to the FortiGate unit.
The FortiGate unit updates the antivirus definitions. This takes about 1 minute.
6 Go to System > Status to confirm that the Antivirus Definitions Version information
has been updated.
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 81
Page 82

Manual attack definition updates System status
Manual attack definition updates
The System > Status page of the FortiGate web-based manager displays the current
installed versions of the FortiGate Attack Definitions used by the Network Intrusion
Detection System (NIDS). You can use the following procedure to update the attack
definitions manually.
Note: To configure the FortiGate unit for automatic attack definitions updates, see “Virus and
attack definitions updates and registration” on page 89. You can also manually initiate an attack
definitions update by going to System > Update and selecting Update Now.
1 Download the latest attack definitions update file from Fortinet and copy it to the
computer that you use to connect to the web-based manager.
2 Start the web-based manager and go to System > Status.
3 To the right of the Attack Definitions Version, select Definitions Update .
4 Enter the path and filename for the attack definitions update file, or select Browse and
locate the attack definitions update file.
5 Select OK to copy the attack definitions update file to the FortiGate unit.
The FortiGate unit updates the attack definitions. This takes about 1 minute.
6 Go to System > Status to confirm that the Attack Definitions Version information has
been updated.
Displaying the FortiGate serial number
1 Go to System > Status.
The serial number is displayed in the System Status page of the web-based manager.
The serial number is specific to the FortiGate unit and does not change with firmware
upgrades.
Displaying the FortiGate up time
1 Go to System > Status.
The FortiGate up time displays the time in days, hours, and minutes since the
FortiGate unit was last started.
Backing up system settings
You can back up system settings by downloading them to a text file on the
management computer:
1 Go to System > Status.
2 Select System Settings Backup.
3 Select Backup System Settings.
4 Type a name and location for the file.
The system settings file is backed up to the management computer.
5 Select Return to go back to the Status page.
82 Fortinet Inc.
Page 83

System status Restoring system settings
!
Restoring system settings
You can restore system settings by uploading a previously downloaded system
settings text file:
1 Go to System > Status.
2 Select System Settings Restore.
3 Enter the path and filename of the system settings file, or select Browse and locate
the file.
4 Select OK to restore the system settings file to the FortiGate unit.
The FortiGate unit restarts, loading the new system settings.
5 Reconnect to the web-based manager and review your configuration to confirm that
the uploaded system settings have taken effect.
Restoring system settings to factory defaults
Use the following procedure to restore system settings to the values set at the factory.
This procedure does not change the firmware version or the antivirus or attack
definitions.
Caution: This procedure deletes all changes that you have made to the FortiGate configuration
and reverts the system to its original configuration, including resetting interface addresses.
1 Go to System > Status.
2 Select Restore Factory Defaults.
3 Select OK to confirm.
The FortiGate unit restarts with the configuration that it had when it was first powered
on.
4 Reconnect to the web-based manager and review the system configuration to confirm
that it has been reset to the default settings.
To restore your system settings, see “Restoring system settings” on page 83.
Changing to Transparent mode
Use the following procedure to switch the FortiGate unit from NAT/Route mode to
Transparent mode. When the FortiGate unit has changed to Transparent mode its
configuration resets to Transparent mode factory defaults.
1 Go to System > Status.
2 Select Change to Transparent Mode.
3 Select Transparent in the operation mode list.
4 Select OK.
The FortiGate unit changes operation mode.
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 83
Page 84

Changing to NAT/Route mode System status
5 To reconnect to the web-based manager, connect to the interface configured for
Transparent mode management access and browse to https:// followed by the
Transparent mode management IP address.
By default in Transparent mode, you can connect to the internal or DMZ interface. The
default Transparent mode management IP address is 10.10.10.1.
Changing to NAT/Route mode
Use the following procedure to switch the FortiGate unit from Transparent mode to
NAT/Route mode. When the FortiGate unit has changed to NAT/Route mode its
configuration resets to NAT/Route mode factory defaults.
1 Go to System > Status.
2 Select Change to NAT Mode.
3 Select NAT/Route in the operation mode list.
4 Select OK.
The FortiGate unit changes operation mode.
5 To reconnect to the web-based manager you must connect to the interface configured
by default for management access.
By default in NAT/Route mode, you can connect to the internal or DMZ interface. The
default Transparent mode management IP address is 192.168.1.99.
See “Connecting to the web-based manager” on page 30 or “Connecting to the
command line interface (CLI)” on page 31.
Restarting the FortiGate unit
1 Go to System > Status.
2 Select Restart.
The FortiGate unit restarts.
Shutting down the FortiGate unit
1 Go to System > Status.
2 Select Shutdown.
The FortiGate unit shuts down and all traffic flow stops.
The FortiGate unit can only be restarted after shutdown by turning the power off, then
on.
84 Fortinet Inc.
Page 85

System status System status
System status
You can use the system status monitor to display FortiGate system health information.
The system health information includes memory usage, the number of active
communication sessions, and the amount of network bandwidth currently in use. The
web-based manager displays current statistics as well as statistics for the previous
minute.
You can also view current virus and intrusion status. The web-based manager
displays the current number of viruses and attacks as well as a graph of virus and
attack levels over the previous 20 hours.
In each case you can set an automatic refresh interval that updates the display every
5 to 30 seconds. You can also refresh the display manually.
• Viewing CPU and memory status
• Viewing sessions and network status
• Viewing virus and intrusions status
Viewing CPU and memory status
Current CPU and memory status indicates how close the FortiGate unit is to running
at full capacity. The web-based manager displays CPU and memory usage for core
processes only. CPU and memory use for management processes (for example, for
HTTPS connections to the web-based manager) is excluded.
If CPU and memory use is low, the FortiGate unit is able to process much more
network traffic than is currently running. If CPU and memory use is high, the FortiGate
unit is performing near its full capacity. Placing additional demands on the system
could lead to traffic processing delays.
Figure 1: CPU and memory status monitor
CPU and memory intensive processes such as encrypting and decrypting IPSec VPN
traffic, virus scanning, and processing high levels of network traffic containing small
packets will increase CPU and memory usage.
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 85
Page 86

System status System status
1 Go to System > Status > Monitor.
CPU & Memory status is displayed. The display includes bar graphs of current CPU
and memory usage as well as line graphs of CPU and memory usage for the last
minute.
2 Set the automatic refresh interval and select Go to control how often the web-based
manager updates the display.
More frequent updates use system resources and increase network traffic. However,
this only occurs when you are viewing the display using the web-based manager.
3 Select Refresh to manually update the information displayed.
Viewing sessions and network status
Use the session and network status display to track how many network sessions the
FortiGate unit is processing and to see what effect the number of sessions has on the
available network bandwidth. Also, by comparing CPU and memory usage with
session and network status you can see how much demand network traffic is placing
on system resources.
Sessions displays the total number of sessions being processed by the FortiGate unit
on all interfaces. Sessions also displays the sessions as a percentage of the
maximum number of sessions that the FortiGate unit is designed to support.
Network utilization displays the total network bandwidth being used through all
FortiGate interfaces. Network utilization also displays network utilization as a
percentage of the maximum network bandwidth that can be processed by the
FortiGate unit.
1 Go to System > Status > Monitor.
2 Select Sessions & Network.
Sessions and network status is displayed. The display includes bar graphs of the
current number of sessions and current network utilization as well as line graphs of
session and network utilization usage for the last minute. The line graph scales are
shown in the upper left corner of the graph.
Figure 2: Sessions and network status monitor
86 Fortinet Inc.
Page 87

System status System status
3 Set the automatic refresh interval and select Go to control how often the web-based
manager updates the display.
More frequent updates use system resources and increase network traffic. However,
this only occurs when you are viewing the display using the web-based manager.
4 Select Refresh to manually update the information displayed.
Viewing virus and intrusions status
Use the virus and intrusions status display to track when viruses are found by the
FortiGate antivirus system and to track when the NIDS detects a network-based
attack.
1 Go to System > Status > Monitor.
2 Select Virus & Intrusions.
Virus and intrusions status is displayed. The display includes bar graphs of the
number viruses and intrusions detected per hour as well as line graphs of the number
of viruses and intrusions detected for the last 20 hours.
Figure 3: Sessions and network status monitor
3 Set the automatic refresh interval and select Go to control how often the web-based
manager updates the display.
More frequent updates use system resources and increase network traffic. However,
this only occurs when you are viewing the display using the web-based manager. The
line graph scales are shown on the upper right corner of the graph.
4 Select Refresh to manually update the information displayed.
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 87
Page 88

Session list System status
Session list
The session list displays information about the communications sessions currently
being processed by the FortiGate unit. You can use the session list to view current
sessions. FortiGate administrators with read and write permission, and the FortiGate
admin user can also stop active communication sessions.
Viewing the session list
1 Go to System > Status > Session.
The web-based manager displays the total number of active sessions in the FortiGate
unit session table and lists the top 16.
2 To page through the list of sessions, select Page Up or Page Down .
3 Select Refresh to update the session list.
4 If you have logged in as an administrative user with read and write privileges or as the
admin user, you can select Clear to stop any active session.
Each line of the session list displays the following information:
Protocol The service protocol of the connection, for example, udp, tcp, or icmp.
From IP The source IP address of the connection.
From Port The source port of the connection.
To IP The destination IP address of the connection.
To Po r t The destination port of the connection.
Expire The time, in seconds, before the connection expires.
Clear Stop an active communication session.
Figure 4: Example session list
88 Fortinet Inc.
Page 89

FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide Version 2.50 MR2
Virus and attack definitions updates
and registration
You can configure the FortiGate unit to connect to the FortiResponse Distribution
Network (FDN) to update the antivirus and attack definitions and antivirus engine. You
have the following update options:
• Request updates from the FDN manually,
• Schedule updates to automatically request the latest versions hourly, daily, or
weekly
• Push updates so that the FDN contacts your FortiGate unit when a new update is
available.
To receive scheduled updates and push updates, you must register the FortiGate unit
on the Fortinet Support web page.
This chapter describes:
• Updating antivirus and attack definitions
• Registering FortiGate units
• Updating registration information
• Registering a FortiGate unit after an RMA
Updating antivirus and attack definitions
You can configure the FortiGate unit to connect to the FortiResponse Distribution
Network (FDN) to automatically receive the latest antivirus and attack definitions and
antivirus engine updates. The FortiGate unit supports the following antivirus and
attack definition update features:
• User-initiated manual updates from the FDN,
• Hourly, daily, or weekly scheduled antivirus and attack definition and antivirus
engine updates from the FDN,
• Push updates from the FDN,
• View the update status including version numbers, expiry dates, and update dates
and times,
• Push updates through a NAT device.
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 89
Page 90

Updating antivirus and attack definitions Virus and attack definitions updates and registration
The System > Update page web-based manager displays the following antivirus and
attack definition update information:
Version Displays the current antivirus engine, virus definition, and attack definition
Expiry date Displays the expiry date of your license for antivirus engine, virus definition,
Last update
attempt
Last update
status
version numbers.
and attack definition updates.
Displays the date and time on which the FortiGate unit last attempted to
download antivirus engine, virus definition, and attack definition updates.
Displays the success or failure of the last update attempt. No updates means
the last update attempt was successful but no new updates are available.
Update succeeded or similar messages mean the last update attempt was
successful and new updates were installed. Other messages can indicate
that the FortiGate was not able to connect to the FDN and other error
conditions.
This section describes:
• Connecting to the FortiResponse Distribution Network
• Configuring scheduled updates
• Configuring update logging
• Adding an override server
• Manually updating antivirus and attack definitions
• Configuring push updates
• Push updates through a NAT device
• Scheduled updates through a proxy server
Connecting to the FortiResponse Distribution Network
Before the FortiGate unit can receive antivirus and attack updates, it must be able to
connect to the FortiResponse Distribution Network (FDN). The FortiGate unit uses
HTTPS on port 8890 to connect to the FDN. The FortiGate WAN1 interface must have
a path to the internet using port 8890. To configure scheduled updates, see
“Configuring scheduled updates” on page 91.
You can also configure the FortiGate unit to allow push updates. Push updates are
provided to the FortiGate unit from the FDN using HTTPS on UDP port 9443. To
receive push updates, the FDN must have a path to the FortiGate WAN1 interface
using UDP port 9443. To configure push updates, see “Configuring push updates” on
page 93.
The FDN is a world-wide network of FortiResponse Distribution Servers (FDSs).
When your FortiGate unit connects to the FDN it actually connects to the nearest
FDS. To do this, all FortiGate units are programmed with a list of FDS addresses
sorted by nearest time zone according to the time zone configured for the FortiGate
unit. To make sure the FortiGate unit receives updates from the nearest FDS, go to
System > Config > Time and make sure you have selected the correct time zone for
your area.
90 Fortinet Inc.
Page 91

Virus and attack definitions updates and registration Updating antivirus and attack definitions
To make sure the FortiGate unit can connect to the FDN:
1 Go to System > Config > Time and make sure the time zone is set to the correct time
zone for your area.
2 Go to System > Update.
3 Select Refresh.
The FortiGate unit tests its connection to the FDN. The test results are displayed at
the top of the System Update page.
Table 1: Connections to the FDN
Connections Status Comments
Available The FortiGate unit can connect to the FDN. You can
Not available The FortiGate unit cannot connect to the FDN. You
FortiResponse
Distribution
Network
Available The FDN can connect to the FortiGate unit to send
Not available The FDN cannot connect to the FortiGate unit to send
Push Update
configure the FortiGate unit for scheduled updates.
See “Configuring scheduled updates” on page 91.
must configure your FortiGate unit and your network so
that the FortiGate unit can connect to the Internet and
to the FDN. For example, you may need to add routes
to the FortiGate routing table or configure your network
to allow the FortiGate unit to use HTTPS on port 8890
to connect to the Internet.
You may also have to connect to an override
FortiResponse server to receive updates. See
“Configuring update logging” on page 92.
push updates. You can configure the FortiGate unit to
receive push updates. See “Configuring push updates”
on page 93.
push updates. Push updates may not be available if
you have not registered the FortiGate unit (see
“Registering the FortiGate unit” on page 100), if there is
a NAT device installed between the FortiGate unit and
the FDN (see “Push updates through a NAT device” on
page 94), or if your FortiGate unit connects to the
Internet using a proxy server (see “Scheduled updates
through a proxy server” on page 98).
Configuring scheduled updates
You can configure the FortiGate unit to check for and download updated definitions
hourly, daily, or weekly according to the schedule you specify.
1 Go to System > Update.
2 Select Scheduled Update.
3 Select whether to check for and download updates hourly, daily, or weekly:
Hourly Once every 1 to 23 hours. Select the number of hours and minutes between
Daily Once a day. You can specify the time of day to check for updates.
Weekly Once a week. You can specify the day of the week and the time of day to check
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 91
each update request.
for updates.
Page 92

Updating antivirus and attack definitions Virus and attack definitions updates and registration
4 Select Apply.
The FortiGate unit starts the next scheduled update according to the new update
schedule.
Whenever a scheduled update is run, the event is recorded in the FortiGate event log.
Figure 1: Configuring automatic antivirus and attack definitions updates
Configuring update logging
Use the following procedure to configure FortiGate logging to record log messages
when the FortiGate unit updates antivirus and attack definitions. Update log messages
are recorded on the FortiGate Event log.
1 Go to Log&Report > Log Setting.
2 Select Config Policy for the type of logs that the FortiGate unit is configured to record.
See “Recording logs” on page 247.
3 Select Update to record log messages when the FortiGate unit updates antivirus and
attack definitions.
4 Select the following update log options:
Failed Update The FortiGate unit records a log message whenever and update attempt
Successful
Update
FDN error The FortiGate unit records a log messages whenever it cannot connect to
fails.
The Fortigate unit records a log message whenever an update attempt is
successful.
the FDN or whenever it receives an error message from the FDN.
5 Select OK.
92 Fortinet Inc.
Page 93

Virus and attack definitions updates and registration Updating antivirus and attack definitions
Adding an override server
If you cannot connect to the FDN or if your organization provides antivirus and attack
updates using their own FortiResponse server, you can use the following procedure to
add the IP address of an override FortiResponse server.
1 Go to System > Update.
2 Select Use override server address and add the IP address of a FortiResponse
server.
3 Select Apply.
The FortiGate unit tests the connection to the override server.
If the FortiResponse Distribution Network setting changes to available, the FortiGate
unit has successfully connected to the override server.
If the FortiResponse Distribution Network stays set to not available, the FortiGate unit
cannot connect to the override server. Check the FortiGate configuration and the
network configuration to make sure you can connect to the override FortiResponse
server from the FortiGate unit.
Manually updating antivirus and attack definitions
You can use the following procedure to update the antivirus and attack definitions at
any time. To run this procedure the FortiGate unit must be able to connect to the FDN
or to an override FortiResponse server.
1 Go to System > Update.
2 Select Update Now to update the antivirus and attack definitions.
If the connection to the FDN or override server is successful, the web-based manager
displays a message similar to the following:
Your update request has been sent. Your database will be updated
in a few minutes. Please check your update page for the status
of the update.
After a few minutes, if an update is available, the System Update page lists new
version information for antivirus definitions, the antivirus engine, or for attack
definitions. The System Status page will also displays new dates and version numbers
for antivirus and attack definitions. Messages are recorded to the event log indicating
whether the update was successful or not.
Configuring push updates
The FDN can push updates to FortiGate units to provide the fastest possible response
to critical situations. You must register the FortiGate unit before it can receive push
updates. See “Registering the FortiGate unit” on page 100.
If the FDN must connect to the FortiGate unit through a NAT device, see “Push
updates through a NAT device” on page 94.
Push updates are not supported if the FortiGate unit must use a proxy server to
connect to the FDN. See “Scheduled updates through a proxy server” on page 98 for
more information.
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 93
Page 94

Updating antivirus and attack definitions Virus and attack definitions updates and registration
To enable push updates
1 Go to System > Update.
2 Select Allow Push Update.
3 Select Apply.
About push updates
When you configure a FortiGate unit to allow push updates, the FortiGate unit sends a
SETUP message to the FDN. The next time a new antivirus engine, new antivirus
definitions, or new attack definitions are released, the FDN notifies all FortiGate units
configured for push updates that a new update is available. Within 60 seconds of
receiving a push notification, the FortiGate unit attempts to request an update from the
FDN.
If available for your network configuration, configuring push updates is recommended
in addition to configuring scheduled updates. Push updates mean that on average the
FortiGate unit receives new updates sooner than if the FortiGate just receives
scheduled updates. However, scheduled updates make sure that the FortiGate unit
does eventually receives the latest updates.
Enabling push updates is not recommended as the only method for obtaining updates.
The push notification may not be received by the FortiGate unit. Also, when the
FortiGate unit receives a push notification it will only make one attempt to connect to
the FDN and download updates.
Push updates and WAN1 dynamic IP addresses
If the WAN1 interface of the FortiGate unit is configured with a dynamic IP address
(using PPPoE or DHCP), whenever the IP address of the WAN1 interface changes, a
SETUP message is sent to the FDN to notify it of the change. As long as this SETUP
message is sent, the FDN will have the most up-to-date IP address and the next push
notification is sent to this IP address.
Push updates through a NAT device
If the FDN can only connect to the FortiGate unit through a NAT device, you must
configure port forwarding on the NAT device and add the port forwarding information
to the push update configuration. Using port forwarding, the FDN connects to the
FortiGate unit using either port 9443 or an override push port that you assign.
Note: You cannot receive push updates through a NAT device if the external IP address of the
NAT device is dynamic (for example, set using PPPoE or DHCP).
94 Fortinet Inc.
Page 95

Virus and attack definitions updates and registration Updating antivirus and attack definitions
Example: push updates through a NAT device
This example describes how to configure a FortiGate NAT device to forward push
updates to a FortiGate unit installed on its internal network. For the FortiGate unit on
the internal network to receive push updates, the FortiGate NAT device must be
configured with a port forwarding virtual IP. This virtual IP maps the IP address of the
external interface of the FortiGate NAT device and a custom port to the IP address of
the FortiGate unit on the internal network. This IP address can either be the external
IP address of the FortiGate unit if it is operating in NAT/Route mode or the
Management IP address of the FortiGate unit if it is operating in Transparent mode.
Note: This example describes the configuration for a FortiGate NAT device. However, any NAT
device with a static external IP address that can be configured for port forwarding can be used.
Figure 2: Example network topology: Push updates through a NAT device
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 95
Page 96

Updating antivirus and attack definitions Virus and attack definitions updates and registration
General procedure
Use the following steps to configure the FortiGate NAT device and the FortiGate unit
on the Internal network so that the FortiGate unit on the Internal network can receive
push updates:
1 Add a port forwarding virtual IP to the FortiGate NAT device.
2 Add a firewall policy to the FortiGate NAT device that includes the port forwarding
virtual IP.
3 Configure the FortiGate unit on the internal network with an override push IP and port.
Note: Before completing the following procedure you should register the FortiGate unit on the
internal network so that it can receive push updates.
Adding a port forwarding virtual IP to the FortiGate NAT device
Use the following procedure to configure a FortiGate NAT device to use port
forwarding to forward push update connections from the FDN to a FortiGate unit on
the internal network.
To configure the FortiGate NAT device:
1 Go to Firewall > Virtual IP.
2 Select New.
3 Add a name for the virtual IP.
4 Select the External interface that the FDN connects to.
For the example topology, select the external interface.
5 Select Port Forwarding.
6 Enter the External IP address that the FDN connects to.
For the example topology, enter 64.230.123.149.
7 Enter the External Service Port that the FDN connects to.
For the example topology, enter 45001.
8 Set Map to IP to the IP address of the FortiGate unit on the internal network.
If the FortiGate unit is operating in NAT/Route mode, enter the IP address of the
external interface.
If the FortiGate unit is operating in Transparent mode, enter the management IP
address.
For the example topology, enter 192.168.1.99.
9 Set the Map to Port to 9443.
10 Set Protocol to UDP.
11 Select OK.
96 Fortinet Inc.
Page 97

Virus and attack definitions updates and registration Updating antivirus and attack definitions
Figure 3: Push update port forwarding virtual IP
Adding a firewall policy for the port forwarding virtual IP
To configure the FortiGate NAT device:
1 Add a new external to internal firewall policy.
2 Configure the policy with the following settings:
Source External_All
Destination The virtual IP added above.
Schedule Always
Service ANY
Action Accept
NAT Selected.
3 Select OK.
Configure the FortiGate unit with an override push IP and port
To configure the FortiGate unit on the internal network:
1 Go to System > Update.
2 Select Allow Push Update.
3 Select Use override push.
4 Set IP to the External IP Address added to the virtual IP.
For the example topology, enter 64.230.123.149.
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 97
Page 98

Updating antivirus and attack definitions Virus and attack definitions updates and registration
5 Set Port to the External Service Port added to the virtual IP.
For the example topology, enter 45001.
6 Select Apply.
The FortiGate unit sends the override push IP address and Port to the FDN. The FDN
will now use this IP address and port for push updates to the FortiGate unit on the
internal network.
If the External IP Address or External Service Port change, add the changes to the
Use override push configuration and select Apply to update the push information on
the FDN.
Figure 4: Example push update configuration
7 Select Apply.
8 You can select Refresh to make sure that push updates work.
Push Update should change to Available.
Scheduled updates through a proxy server
If your FortiGate unit must connect to the Internet through a proxy server, you can use
the set system autoupdate tunneling command to allow the FortiGate unit to
connect (or tunnel) to the FDN using the proxy server. Using the command you can
specify the IP address and port of the proxy server. As well, if the proxy server
requires authentication, you can add the user name and password required for the
proxy server to the autoupdate configuration. The full syntax for enabling updates
through a proxy server is:
set system autouopdate tunneling enable [address
<proxy-address_ip> [port <proxy-port> [username <username_str>
[password <password_str>]]]]
For example, if the IP address of the proxy server is 64.23.6.89 and its port is 8080,
enter the following command:
set system autouopdate tunneling enable address 64.23.6.89
port 8080
For more information about the set system autoupdate command, see Volume 6,
FortiGate CLI Reference Guide.
The FortiGate unit connects to the proxy server using the HTTP CONNECT method,
as described in RFC 2616. The FortiGate unit sends an HTTP CONNECT request to
the proxy server (optionally with authentication information) specifying the IP address
and port required to connect to the FDN. The proxy server establishes the connection
to the FDN and passes information between the FortiGate unit and the FDN.
The CONNECT method is used mostly for tunneling SSL traffic. Some proxy servers
won't allow the CONNECT to connect to just any port; they restrict the allowed ports to
the well known ports for HTTPS and perhaps some other similar services. Because
FortiGate autoupdates use HTTPS on port 8890 to connect to the FDN, your proxy
server may have to be configured to allow connections on this port.
98 Fortinet Inc.
Page 99

Virus and attack definitions updates and registration Registering FortiGate units
There are no special tunneling requirements if you have configured an override server
address to connect to the FDN.
Push updates are not supported if the FortiGate must connect to the Internet through
a proxy server.
Registering FortiGate units
After purchasing and installing a new FortiGate unit, you can register the unit using
the web-based manager by going to System > Update > Support, or by using a web
browser to connect to http://support.fortinet.com and selecting Product Registration.
Registration consists of entering your contact information and the serial numbers of
the FortiGate units you or your organization have purchased. Registration is quick and
easy. You can register multiple FortiGate units in a single session without re-entering
your contact information.
Once registration is completed, Fortinet sends a Support Login user name and
password to your email address. You can use this user name and password to log on
to the Fortinet support web site to:
• View your list of registered FortiGate units
• Register additional FortiGate units
• Add or change FortiCare Support Contract numbers for each FortiGate unit
• View and change registration information
• Download virus and attack definitions updates
• Download firmware upgrades
• Modify registration information after an RMA
Soon you will also be able to:
• Access Fortinet user documentation
• Access the Fortinet knowledge base
All registration information is stored in the Fortinet Customer Support database. This
information is used to make sure that your registered FortiGate units can be kept up to
date. All information is strictly confidential. Fortinet does not share this information
with any third party organizations for any reason.
This section describes:
• FortiCare Service Contracts
• Registering the FortiGate unit
FortiCare Service Contracts
Owners of a new FortiGate unit are entitled to 90 days of technical support services.
To continue receiving support services after the 90 day expiry date, you must
purchase a FortiCare Support Contract from an authorized Fortinet reseller or
distributor. Different levels of service are available so you can purchase the support
that you need. For maximum network protection, Fortinet strongly recommends that
all customers purchase a service contract that covers antivirus and attack definition
updates. See your Fortinet reseller or distributor for details of packages and pricing.
FortiGate-60R Installation and Configuration Guide 99
Page 100

Registering FortiGate units Virus and attack definitions updates and registration
To activate the FortiCare Support Contract, you must register the FortiGate unit and
add the FortiCare Support Contract number to the registration information. You can
also register the FortiGate unit without purchasing a FortiCare Support Contract. In
this case, when you do purchase a FortiCare Support Contract you can update the
registration information to add the support contract number.
A single FortiCare Support Contract can cover multiple FortiGate units. You must
enter the same service contract number for each of the FortiGate models covered by
the service contract.
Registering the FortiGate unit
Before registering a FortiGate unit, you require the following information:
• Your contact information including:
• First and last name
• Company name
• Email address (Your Fortinet support login user name and password will be
sent to this email address.)
•Address
• Contact phone number
• A security question and an answer to the security question.
This information is used for password recovery. The security question should be a
simple question that only you know the answer to. The answer should not be easy
to guess.
• The product model and serial number for each FortiGate unit to be registered.
The serial number is located on a label on the bottom of the FortiGate unit.
You can view the Serial number from the web-based manager by going to
System > Status.
The serial number is also available from the CLI using the get system status
command.
• FortiCare Support Contract numbers if you have purchased FortiCare Support
Contracts for the FortiGate units to be registered.
To register one or more FortiGate units
1 Go to System > Update > Support.
2 Enter your contact information into the product registration form.
100 Fortinet Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...