Page 1

Contents
Before driving
Introduction 2
Instrumentation 4
Controls and features 16
Seating and safety restraints 37
Starting and driving
Starting 59
Driving 64
Roadside emergencies 93
Servicing
Maintenance and care 110
Capacities and specifications 147
Reporting safety defects 155
Index 156
All rights reserved. Reproduction by any means, electronic or mechanical
including photocopying, recording or by any information storage and retrieval
system or translation in whole or part is not permitted without written
authorization from Ford Motor Company.
Copyrightr1997 Ford Motor Company
1
Page 2
Introduction
ICONS
Indicates a warning. Read the
following section on Warnings for a
full explanation.
Indicates vehicle information related
to recycling and other
environmental concerns will follow.
Correct vehicle usage and the
authorized disposal of waste
cleaning and lubrication materials are significant steps towards
protecting the environment.
WARNINGS
Warnings provide information which may reduce the risk of personal
injury and prevent possible damage to others, your vehicle and its
equipment.
BREAKING-IN YOUR VEHICLE
There are no particular breaking-in rules for your vehicle. During the
first 1 600 km (1 000 miles) of driving, vary speeds frequently. This is
necessary to give the moving parts a chance to break in.
If possible, you should avoid full use of the brakes for the first 1 600 km
(1 000 miles).
INFORMATION ABOUT THIS GUIDE
The information found in this guide was in effect at the time of printing.
Ford may change the contents without notice and without incurring
obligation.
SPECIAL NOTICES
Notice to owners of utility type vehicles
Before you drive your vehicle, please read this Owner’s Guide carefully.
Your vehicle is not a passenger car. As with other vehicles of this type,
failure to operate this vehicle correctly may result in loss of control or an
accident.
2
Page 3

Introduction
Be sure to read Driving off road in the Driving chapter as well as the
“Four Wheeling” supplement included with 4WD and utility type vehicles.
Using your vehicle as a snowplow
Do not use this vehicle for snowplowing.
Using your vehicle as an ambulance
Do not use this vehicle as an ambulance.
Your vehicle is not equipped with the Ford Ambulance Preparation
package.
Electric vehicles
For information on operating your Electric Vehicle, also refer to the
Electric Vehicle Owner’s Guide Supplement.
3
Page 4
S
L
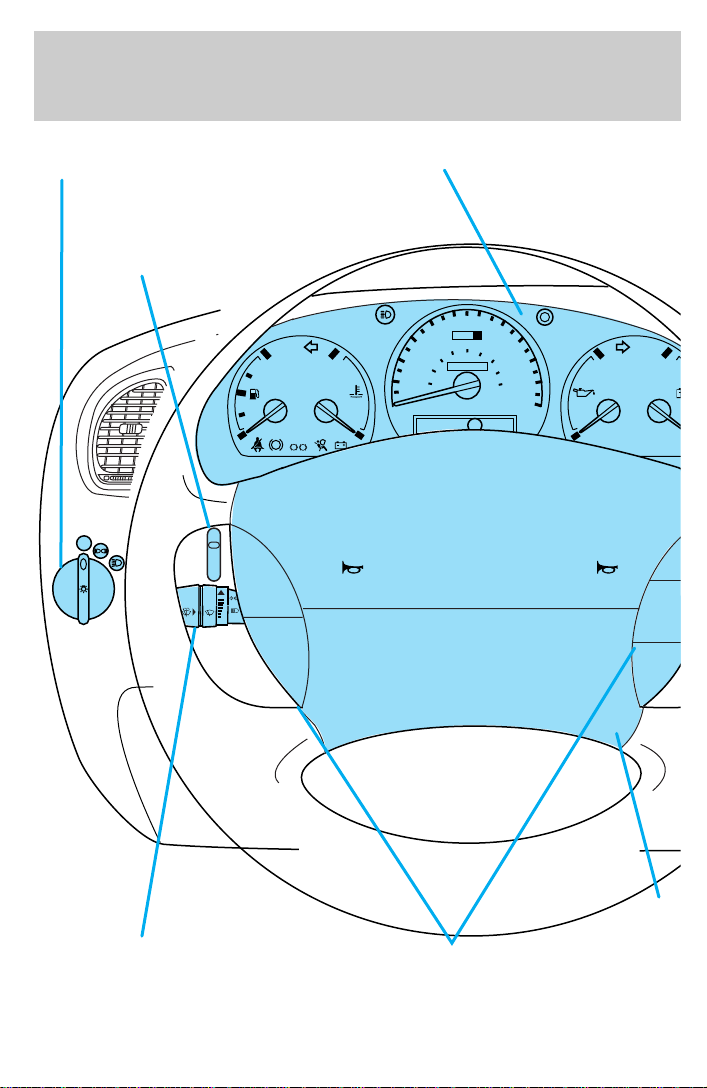
Instrumentation
Headlamp control
(pg. 16)
Instrument panel
dimmer switch
(pg. 17)
OFF
Instrument cluster
(pg. 6)
60
70
CHECK
ENGINE
F
H
EL
BRAKE
ABS
!
P
50
40
30
40
20
20
10
MPH
P
0 0 0
100
80
120
60
0 0 0 0 0 0
RND21
80
140
km/h
90
00
1
160
180
1
ON
OFF
SRS
H
H
101
20
L
SPEED
O/D
CONT
OFF
R
SET
ACC
COAST
Turn signal and wiper/washer control
(pg. 24, 29)
4
Speed control
(pg. 24)
Driver side
air bag
(pg. 47)
Page 5

L
Instrumentation
Electronic sound system;
refer to Audio Guide
Auxiliary power point
(pg. 23)
(pg. 24)
SEEK
M
1
2
34AM-FM
TUNE
OFF
A/C
MAX
A/C
ON
OFF
OFF
PASSENGER AIRBAG
Passenger air bag deactivate
switch
(pg. 51)
Climate control systems
(pg. 17)
5
Page 6

Instrumentation
STANDARD INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
60
70
50
30
20
40
40
20
MPH
P
6
P
60
0 0 0
100
80
0 0 0 0 0 0
RND21
DOOR
AJAR
40
30
20
20
10
RND21
CHECK
ENGINE
H
F
10
<FUEL DOOR
EL
!
ABS
BRAKE
OPTIONAL INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
CHECK
FUEL
RESET
CHECK
ENGINE
GAGE
H
C
1
F
E
0
ABS
BRAKE
5
4
RPMx1000
3
2
!
120
50
40
MPH
80
140
km/h
60
90
00
1
160
180
1
60
0 0 0
100
80
0 0 0 0 0 0
DOOR
AJAR
H
H
101
20
LL
SPEED
THEFT
70
80
90
120
140
00
1
160
180
101
20
1
km/h
THEFT
O/D
CONT
OFF
H
SPEED
CONT
L
4WD
HIGH
4WD
H
LOW
L
O/D
OFF
Check engine
Your vehicle is equipped with a
computer that monitors the engine’s
emission control system. This
system is commonly known as the
CHECK
ENGINE
On Board Diagnostics System
(OBD II). This OBD II system protects the environment by ensuring that
your vehicle continues to meet government emission standards. The OBD
II system also assists the service technician in properly servicing your
vehicle.
6
Page 7

Instrumentation
The Check Engine indicator light illuminates when the ignition is first
turned to the ON position to check the bulb. If it comes on after the
engine is started, one of the engine’s emission control systems may be
malfunctioning. The light may illuminate without a driveability concern
being noted. The vehicle will usually be drivable and will not require
towing.
What you should do if the check engine light illuminates
Light turns on solid:
This means that the OBD II system has detected a malfunction.
Temporary malfunctions may cause your Check Engine light to
illuminate. Examples are:
1. The vehicle has run out of fuel.
(The engine may misfire or run poorly.)
2. Poor fuel quality or water in the fuel.
3. The fuel cap may not have been properly installed and securely
tightened.
These temporary malfunctions can be corrected by filling the fuel tank
with good quality fuel and/or properly installing and securely tightening
the gas cap. After three driving cycles without these or any other
temporary malfunctions present, the Check Engine light should turn off.
(A driving cycle consists of a cold engine startup followed by mixed
city/highway driving.) No additional vehicle service is required.
If the Check Engine light remains on, have your vehicle serviced at the
first available opportunity.
Light is blinking:
Engine misfire is occurring which could damage your catalytic converter.
You should drive in a moderate fashion (avoid heavy acceleration and
deceleration) and have your vehicle serviced at the first available
opportunity.
Under engine misfire conditions, excessive exhaust temperatures
could damage the catalytic converter, the fuel system, interior
floor coverings or other vehicle components, possibly causing a fire.
7
Page 8
Instrumentation
Fuel reset (if equipped)
Illuminates when the ignition key is
turned to the ON position and the
fuel pump shut-off switch has been
triggered. For more information,
refer to Fuel pump shut-off switch
in the Roadside emergencies chapter.
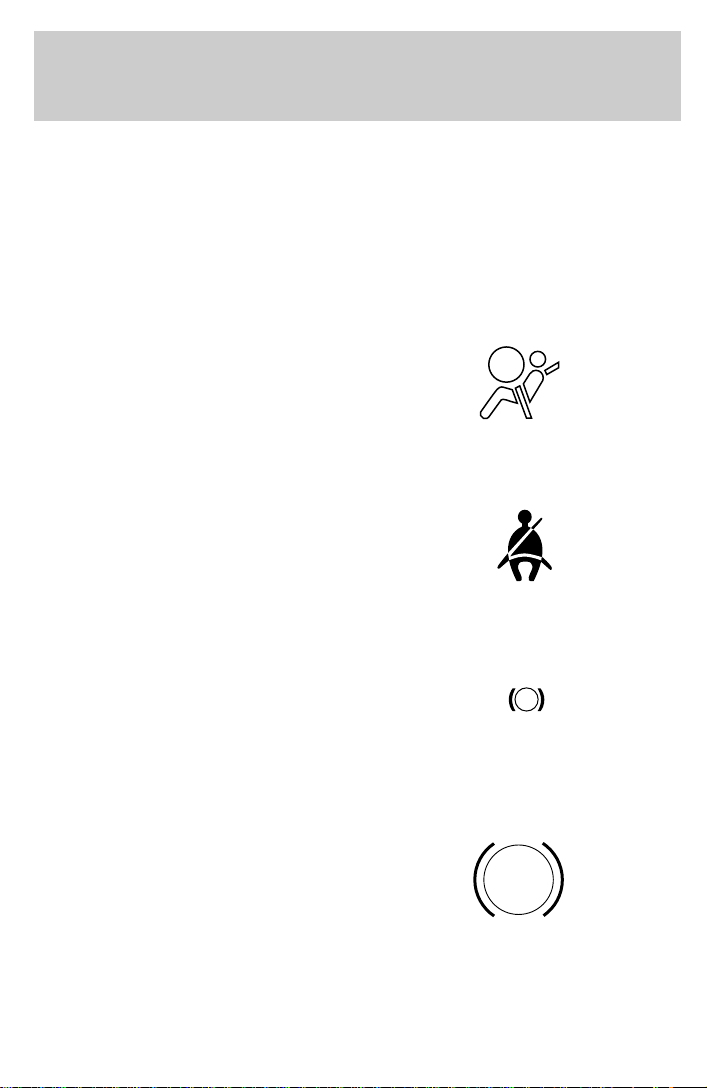
Air bag readiness
Momentarily illuminates when the
ignition is turned ON. If the light
fails to illuminate, continues to flash
or remains on, have the system
serviced immediately.
Safety belt
Momentarily illuminates when the
ignition is turned to the ON position
to remind you to fasten your safety
belts. For more information, refer to
the Seating and safety restraints
chapter.
Brake system warning
Momentarily illuminates when the
ignition is turned to the ON position
and the engine is off. Also
illuminates when the parking brake
is engaged. Illumination after
releasing the parking brake indicates low brake fluid level.
FUEL
RESET
!
BRAKE
Anti-lock brake system (ABS)
Momentarily illuminates when the
ignition is turned to the ON position
and the engine is off. If the light
remains on, continues to flash or
fails to illuminate, have the system
serviced immediately.
8
ABS
Page 9

Instrumentation
Turn signal
Illuminates when the left or right
turn signal or the hazard lights are
turned on. If one or both of the
indicators stay on continuously,
check for a burned-out turn signal
bulb. Refer to Exterior bulbs in the Maintenance and care chapter.
High beams
Illuminates when the high beam
headlamps are turned on.
Alarm system (if equipped)
Illuminates when the alarm system
is pre-arming and flashes when the
alarm system is active. Refer to
Perimeter alarm system in the
Controls and features chapter.
Charging system
Illuminates when the ignition is
turned to the ON position and the
engine is off. The light also
illuminates when the battery is not
charging properly, requiring
electrical system service.
THEFT
O/D off (if equipped)
Illuminates when the transmission
control switch has been pushed.
When the light is on, the
transmission does not shift into
overdrive. If the light does not come
on when the transmission control switch is depressed or if the light
flashes when you are driving, have your vehicle serviced.
O/D
OFF
9
Page 10

Instrumentation
Check gage (if equipped)
Illuminates when the key is in the
ON position and the engine coolant
temperature is high, the engine oil
pressure is low or the fuel level is
near empty. Refer to Engine coolant temperature gauge, Engine oil
pressure gauge or Fuel gauge in this chapter for more information.
Four wheel drive low (if equipped)
Illuminates when four-wheel drive
low is engaged.
CHECK
GAGE
4WD
LOW
Four wheel drive high (if equipped)
Illuminates when four-wheel drive
high is engaged.
4WD
HIGH
Door ajar
Illuminates when the ignition is in
the ON or START position and any
door is open.
DOOR
AJAR
Speed control (if equipped)
This light comes on when either the
SET/ACCEL or RESUME controls
are pressed. It turns off when the
speed control OFF control is
pressed, the brake is applied or the ignition is turned to the OFF
position.
10
SPEED
CONT
Page 11
Instrumentation
Safety belt warning chime
Chimes to remind you to fasten your safety belts.
For information on the safety belt warning chime, refer to the Seating
and safety restraints chapter.
Supplemental restraint system (SRS) warning chime
For information on the SRS warning chime, refer to the Seating and
safety restraints chapter.
Key-in-ignition warning chime
Sounds when the key is left in the ignition in the OFF/LOCK or ACC
position and either front door is opened.
Headlamps on warning chime
Sounds when the headlamps or parking lamps are on, the ignition is off
(and the key is not in the ignition) and the driver’s door is opened.
STANDARD INSTRUMENT CLUSTER GAUGES
60
70
CHECK
ENGINE
F
<FUEL DOOR
EL
H
!
ABS
BRAKE
50
40
60
30
40
20
20
10
MPH
P
80
0 0 0
100
80
120
140
0 0 0 0 0 0
km/h
RND21
90
00
1
160
180
101
20
1
DOOR
H
H
AJAR
L
SPEED
THEFT
CONT
O/D
OFF
L
11
Page 12

Instrumentation
OPTIONAL INSTRUMENT CLUSTER GAUGES
DOOR
CHECK
GAGE
4
RPMx1000
3
2
1
0
ABS
!
BRAKE
FUEL
RESET
CHECK
ENGINE
H
C
F
E
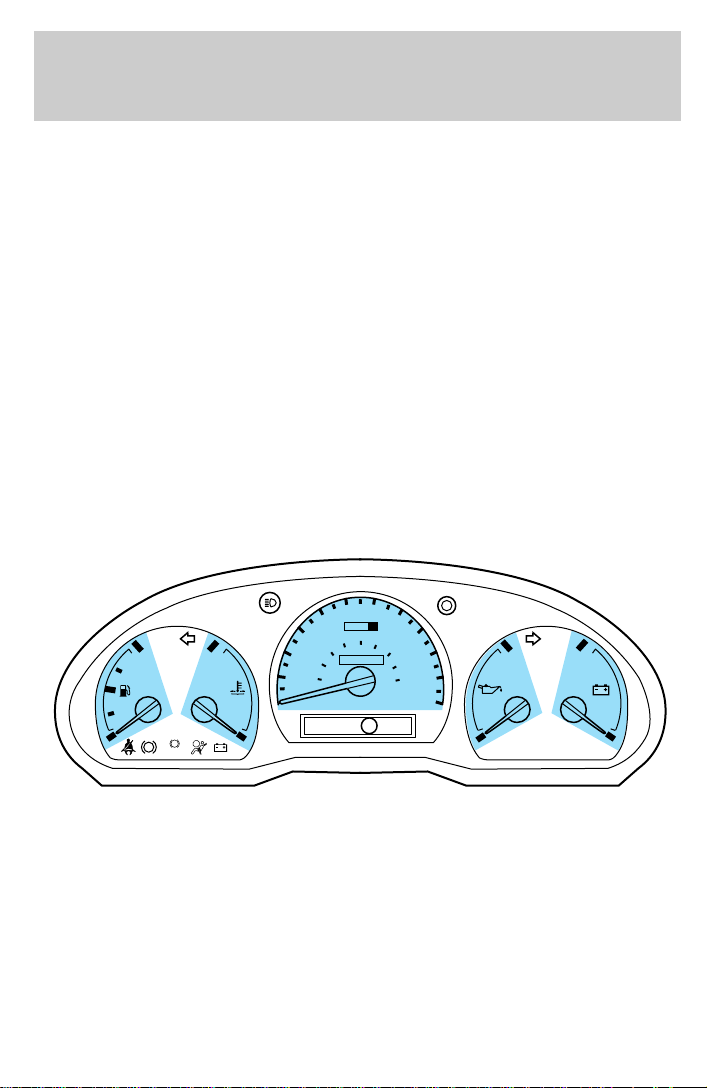
Fuel gauge
Displays approximately how much
fuel is in the fuel tank (when the
key is in the ON position). The fuel
gauge may vary slightly when the
vehicle is in motion. The ignition
should be in the OFF position while
the vehicle is being refueled. When
the gauge first indicates empty,
there is a small amount of reserve
fuel in the tank. When refueling the
vehicle from empty indication, the
amount of fuel that can be added will be less than the advertised
capacity due to the reserve fuel.
The FUEL DOOR icon and arrow indicates which side of the vehicle the
fuel filler door is located.
AJAR
60
5
6
40
30
20
10
RND21
P
50
40
20
MPH
60
0 0 0
100
80
0 0 0 0 0 0
70
80
90
120
140
km/h
THEFT
160
180
H
00
1
101
20
1
SPEED
CONT
L
4WD
HIGH
4WD
H
LOW
L
O/D
OFF
F
E
12
Page 13
Instrumentation
Engine coolant temperature gauge
Indicates the temperature of the
engine coolant. At normal operating
temperature, the needle remains
within the normal area (the area
between the “H” and “C”). If it
enters the red section, the engine is
overheating. Stop the vehicle as
soon as safely possible, switch off
the engine immediately and let the
C
engine cool. Refer to Engine
coolant in the Maintenance and
care chapter.
Never remove the coolant recovery cap while the engine is
running or hot.
This gauge indicates the temperature of the engine coolant, not the
coolant level. If the coolant is not at its proper level the gauge indication
will not be accurate.
Tachometer (if equipped)
Indicates the engine speed in
revolutions per minute.
4
3
2
H
5
RPMx1000
6
1
0
13
Page 14
Instrumentation
Speedometer
Indicates the current vehicle speed.
Odometer
Registers the total kilometers
(miles) of the vehicle.
Trip odometer
Registers the kilometers (miles) of
individual journeys. To reset,
depress the control.
10
20
30
20
10
10
40
30
30
20
40
20
MPH
50
40
20
40
60
50
60
40
MPH
50
40
20
MPH
60
0 0 0
80
0 0 0 0 0 0
80
60
100
60
70
0 0 0
100
0 0 0 0 0 0
60
0 0 0
100
80
0 0 0 0 0 0
70
80
120
140
km/h
70
160
120
km/h
120
km/h
90
1
180
80
00
1
140
80
140
101
20
90
00
1
160
180
101
20
1
90
00
1
160
180
101
20
1
14
Page 15

Engine oil pressure gauge
This shows the engine oil pressure
in the system. Sufficient pressure
exists as long as the needle remains
in the normal range (the area
between the “H” and “L”).
If the gauge indicates low pressure,
stop the vehicle as soon as safely
possible and switch off the engine
immediately. Check the oil level.
Add oil if needed (refer to
Checking and adding engine oil in
the Maintenance and care
chapter). If the oil level is correct,
have your vehicle checked at your
dealership or by a qualified
technician.
Battery voltage gauge
This gauge shows the battery
voltage when the ignition is in the
ON position. If the pointer moves
and stays outside the normal
operating range (as indicated), have
the vehicle’s electrical system
checked as soon as possible.
Instrumentation
H
L
H
L
H
L
15
Page 16
Controls and features
HEADLAMP CONTROL
Rotate the headlamp control to the
first position to turn on the parking
lamps only. Rotate to the second
position to also turn on the
headlamps.
Foglamp control (if equipped)
Turn on the low-beam headlamps
and press the foglamp control to
activate the foglamps. The foglamp
control will illuminate when the
foglamps are on.
Press the foglamp control a second time to deactivate the foglamps.
Daytime running lamps (DRL) (if equipped)
Turns the highbeam headlamps on with a reduced output. To activate:
• the engine must be running and
• the headlamp control is in the OFF or Parking lamps position.
OFF
The Daytime Running Light (DRL) system will not illuminate the
tail lamps and parking lamps. Turn on your headlamps at dusk.
Failure to do so may result in a collision.
High beams
Push forward to activate.
16
Page 17
Flash to pass
Pull toward you to activate and
release to deactivate.
PANEL DIMMER CONTROL
Use to adjust the brightness of the
instrument panel during headlamp
and parklamp operation.
• Rotate up to brighten.
• Rotate down to dim.
CLIMATE CONTROL SYSTEM
Heater only system (if equipped)
Controls and features
DIM
Fan speed control
Controls the volume of air circulated
in the vehicle.
OFF
17
Page 18

Controls and features
Temperature control knob
Controls the temperature of the
airflow inside the vehicle. On
heater-only systems, the air cannot
be cooled below the outside
temperature.
Mode selector control
Controls the direction of the airflow
to the inside of the vehicle.
OFF
•
(Vent)-Distributes outside air through the instrument panel
registers.
• (Panel and floor)-Distributes outside air through the instrument
panel registers and the floor ducts.
• OFF-Outside air is shut out and the fan will not operate.
•
(Floor)-Allows for maximum heating. Distributes outside air
through the floor ducts.
• (Floor and defrost)-Distributes outside air through the floor
ducts and the windshield defroster ducts.
•
-Distributes outside air through the windshield defroster ducts.
It can be used to clear ice or fog from the windshield.
Operating tips
• In humid weather, select before driving. This will help to prevent
your windshield from fogging. After a few minutes, select any desired
position.
• To prevent humidity buildup inside the vehicle, don’t drive with the
climate control system in the OFF position.
• Don’t put objects under the front seat that will interfere with the
airflow to the jumper seats (if equipped).
18
Page 19

Controls and features
• Remove any snow, ice or leaves
from the air intake area (at the
bottom of the windshield under
the hood).
• When placing objects on top of your instrument panel, be careful to
not place them over the defroster outlets. These objects can block
airflow and reduce your ability to see through your windshield. Also,
avoid placing small objects on top of your instrument panel. These
objects can fall down into the defroster outlets and block airflow and
possibly damage your climate control system.
Manual heating and air conditioning system (if equipped)
OFF
A/C
MAX
A/C
Fan speed control
Controls the volume of air circulated
in the vehicle.
Temperature control knob
Controls the temperature of the
airflow inside the vehicle.
19
Page 20

Controls and features
Mode selector control
Controls the direction of the airflow
to the inside of the vehicle.
OFF
A/C
MAX
A/C
The air conditioning compressor will operate in all modes except
and
. However, the air conditioning will only function if the outside
temperature is about 10°C (50°F) or above.
Since the air conditioner removes considerable moisture from the air
during operation, it is normal if clear water drips on the ground under
the air conditioner drain while the system is working and even after you
have stopped the vehicle.
Under normal conditions, your vehicle’s climate control system should be
left in any position other than MAX A/C or OFF when the vehicle is
parked. This allows the vehicle to “breathe” through the outside air inlet
duct.
• MAX A/C-Uses recirculated air to cool the vehicle. MAX A/C is noisier
than A/C but more economical and will cool the inside of the vehicle
faster. Airflow will be from the instrument panel registers. This mode
can also be used to prevent undesirable odors from entering the
vehicle.
• A/C-Uses outside air to cool the vehicle. It is quieter than MAX A/C
but not as economical. Airflow will be from the instrument panel
registers.
•
(Vent)-Distributes outside air through the instrument panel
registers. However, the air will not be cooled below the outside
temperature because the air conditioning does not operate in this
mode.
• OFF-Outside air is shut out and the fan will not operate. For short
periods of time only, use this mode to prevent undesirable odors from
entering the vehicle.
•
(Panel and floor)-Distributes outside air through the instrument
panel registers and the floor ducts. Heating and air conditioning
capabilities are provided in this mode. For added customer comfort,
when the temperature control knob is anywhere in between the full
hot and full cold positions, the air distributed through the floor ducts
will be slightly warmer than the air sent to the instrument panel
registers.
20
Page 21

Controls and features
• (Floor)-Allows for maximum heating by distributing outside air
through the floor ducts. However, the air will not be cooled below the
outside temperature because the air conditioning does not operate in
this mode.
•
•
Operating tips
• In humid weather, select before driving. This will prevent your
• To prevent humidity buildup inside the vehicle, don’t drive with the
• Don’t put objects under the front seat that will interfere with the
• Remove any snow, ice or leaves
(Floor and defrost)-Distributes outside air through the
windshield defroster ducts and the floor ducts. Heating and air
conditioning capabilities are provided in this mode. For added
customer comfort, when the temperature control knob is anywhere in
between the full hot and full cold positions, the air distributed through
the floor ducts will be slightly warmer than the air sent to the
instrument panel registers. If the temperature is about 10°C (50°F) or
higher, the air conditioner will automatically dehumidify the air to
prevent fogging.
-Distributes outside air through the windshield defroster ducts.
It can be used to clear ice or fog from the windshield. If the
temperature is about 10°C (50°F) or higher, the air conditioner will
automatically dehumidify the air to prevent fogging.
windshield from fogging. After a few minutes, select any desired
position.
climate control system in the OFF position.
airflow to the back seats (if equipped).
from the air intake area (at the
bottom of the windshield under
the hood).
• If your vehicle has been parked with the windows closed during hot
weather, the air conditioner will do a much faster job of cooling if you
drive for two or three minutes with the windows open. This will force
most of the hot, stale air out of the vehicle. Then operate your air
conditioner as you would normally.
21
Page 22
Controls and features
• When placing objects on top of your instrument panel, be careful to
not place them over the defroster outlets. These objects can block
airflow and reduce your ability to see through your windshield. Also,
avoid placing small objects on top of your instrument panel. These
objects can fall down into the defroster outlets and block airflow and
possibly damage your climate control system.
4WD CONTROL (IF EQUIPPED)
This control operates the 4WD.
Refer to the Driving chapter for
more information.
2WD
4X4
HIGH
4X4
LOW
22
Page 23

AUXILIARY POWER POINT
Controls and features
SEEK
TUNE
1
2
34AM-FM
OFF
A/C
MAX
A/C
The auxiliary power point is located on the instrument panel. This outlet
should be used in place of the cigarette lighter for optional electrical
accessories.
PASSENGER AIR BAG DEACTIVATE SWITCH
This switch must be used to
deactivate the passenger air bag
whenever a child seat is used in the
ON
OFF
right front or center front passenger
seat position. Refer to Passenger
OFF
air bag deactivate switch in the
Seating and safety restraints
chapter.
PASSENGER AIRBAG
23
Page 24
Controls and features
AUDIO SYSTEM
Refer to the “Audio Guide” in your owner portfolio.
TURN SIGNAL CONTROL
• Push down to activate the left
turn signal.
• Push up to activate the right turn
signal.
SPEED CONTROL (IF EQUIPPED)
To turn speed control on
• Press ON.
Vehicle speed cannot be controlled
until the vehicle is traveling at or
above 48 km/h (30 mph).
ON
OFF
24
Do not use the speed control in heavy traffic or on roads that
are winding, slippery, or unpaved.
Do not shift the gearshift lever into N (Neutral) with the speed
control on.
Page 25
Controls and features
To turn speed control off
• Press OFF or
• Turn off the vehicle ignition.
ON
OFF
Once speed control is switched off, the previously programmed set speed
will be erased.
To set a speed
• Press SET ACC/SET ACCEL. For
speed control to operate, the
speed control must be ON and
the vehicle speed must be greater
than 48 km/h (30 mph).
SET
ACC
COAST
RSM
If you drive up or down a steep hill, your vehicle speed may vary
momentarily slower or faster than the set speed. This is normal.
Speed control cannot reduce the vehicle speed if it increases above the
set speed on a downhill. If your vehicle speed is faster than the set
speed while driving on a downhill, you may want to shift to the next
lower gear or apply the brakes to reduce your vehicle speed.
If your vehicle slows down more than 16 km/h (10 mph) below your set
speed on an uphill, your speed control will disengage. This is normal.
Pressing RES/RSM/RESUME will re-engage it.
Do not use the speed control in heavy traffic or on roads that
are winding, slippery, or unpaved.
25
Page 26
Controls and features
To set a higher set speed
• Press and hold SET ACC/SET
ACCEL. Release the control when
the desired vehicle speed is
reached or
• Press and release SET ACC/SET
ACCEL. Each press will increase
the set speed by 1.6 km/h
(1 mph) or
• Accelerate with your accelerator
pedal, then press and release SET
ACC/SET ACCEL.
You can accelerate with the accelerator pedal at any time during speed
control usage. Releasing the accelerator pedal will return your vehicle to
the previously programmed set speed.
To set a lower set speed
• Press and hold CST/COAST.
Release the control when the
desired speed is reached or
• Press and release CST/COAST.
Each press will decrease the set
speed by 1.6 km/h (1 mph) or
SET
ACC
COAST
SET
ACC
COAST
RSM
RSM
• Depress the brake pedal. When
the desired vehicle speed is
reached, press SET ACC/SET
ACCEL.
26
SET
ACC
COAST
RSM
Page 27
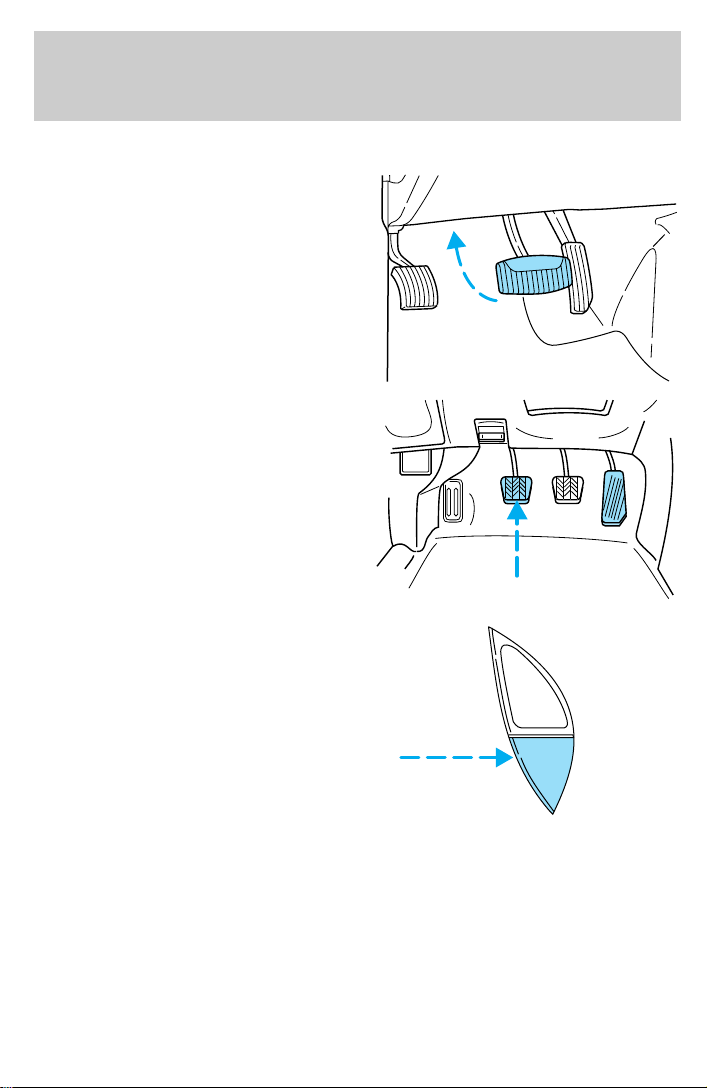
To disengage speed control
• Depress the brake pedal or
• Depress the clutch pedal
(if equipped).
Disengaging the speed control will
not erase the previously
programmed set speed.
Pressing OFF will erase the
previously programmed set speed.
Controls and features
ON
OFF
27
Page 28
Controls and features
To return to a previously set speed
• Press RES/RSM/RESUME. For
RES/RSM/RESUME to operate,
the vehicle speed must be faster
than 48 km/h (30 mph).
Indicator light (if equipped)
This light comes on when either the
SET ACC/SET ACCEL or
RES/RSM/RESUME controls are
pressed. It turns off when the speed
control OFF control is pressed, the brake is applied or the ignition is
turned to the OFF position.
OVERDRIVE CONTROL
Activating overdrive
(Overdrive) is the normal drive position for the best fuel economy.
The overdrive function allows automatic upshifts to second, third and
fourth gear.
Deactivating overdrive
Press the Transmission Control
Switch (TCS) located on the end of
the gearshift lever. The
Transmission Control Indicator Light
(TCIL) will illuminate on the
instrument cluster.
The transmission will operate in
gears one through three. To return
to normal overdrive mode, press the
Transmission Control Switch again.
The TCIL will no longer be
illuminated.
When you shut off and re-start your vehicle, the transmission will
automatically return to normal
(Overdrive) mode.
RSM
SET
ACC
COAST
SPEED
CONT
O/D
ON/OFF
O/D
ON/OFF
28
Page 29
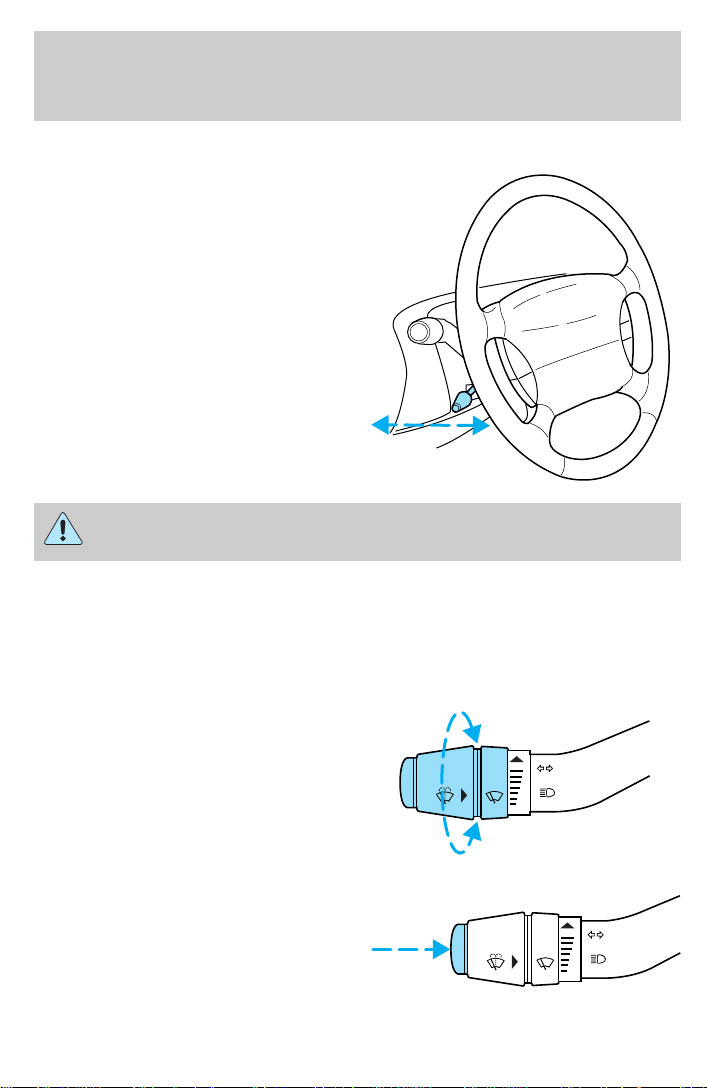
Controls and features
TILT STEERING (IF EQUIPPED)
Push the steering control away from
you to move the steering wheel up
or down. Tip the steering wheel to
the desired position, then pull the
control back into place to lock the
steering wheel in position.
Never adjust the steering wheel when the vehicle is moving.
HAZARD FLASHER
For information on the hazard flasher control, refer to Hazard lights
control in the Roadside emergencies chapter.
WINDSHIELD WIPER/WASHER CONTROLS
Rotate the windshield wiper control
to the desired interval, low or high
speed position.
The bars of varying length are for
intermittent wipers. When in this
position rotate the control upward
for fast intervals and downward for
slow intervals.
Push the control on the end of the
stalk to activate washer. Push and
hold for a longer wash cycle.
29
Page 30
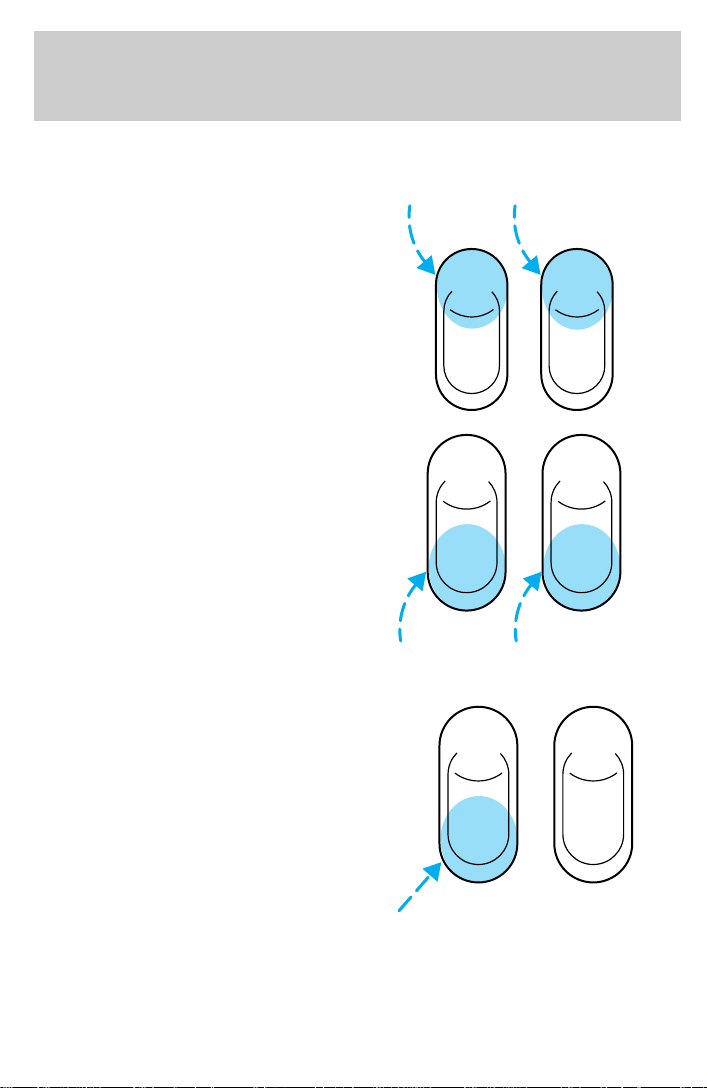
Controls and features
POWER WINDOWS (IF EQUIPPED)
Press and hold the rocker switches to open and close windows.
• Press the top portion of the
rocker switch to close.
AUTO
• Press the bottom portion of the
rocker switch to open.
AUTO
One touch down
• Press AUTO completely down and
release quickly. The window will
open fully. Depress again to stop
window operation.
30
AUTO
Page 31

Controls and features
POWER DOOR LOCKS (IF EQUIPPED)
Press the top of the control to
unlock all doors and the bottom to
lock all doors.
POWER SIDE VIEW MIRRORS (IF EQUIPPED)
To adjust your mirrors:
1. Select
2. Move the control in the direction
you wish to tilt the mirror.
to adjust the left mirror or to adjust the right mirror.
UNLOCK
LOCK
3. Return to the center position to lock mirrors in place.
CENTER CONSOLE (IF EQUIPPED)
Your vehicle may be equipped with a
variety of console features. These
include:
• utility compartment with
cassette/compact disc storage
• auxiliary power point
• cupholders
• coin holder slots
• ashtray
• flip up armrest
31
Page 32

Controls and features
Use only soft cups in the cupholder. Hard objects can injure you
in a collision.
REMOTE ENTRY SYSTEM (IF EQUIPPED)
The remote entry system allows you to lock or unlock all vehicle doors
without a key.
The remote entry features only operate with the ignition in the OFF
position.
Unlocking the doors
Press this control to unlock the
driver door. The interior lamps will
illuminate.
Press the control a second time
within five seconds to unlock all
doors.
Locking the doors
Press this control to lock all doors.
To confirm all doors are closed and
locked, press the control a second
time within five seconds. The doors
will lock again, the horn will chirp
and the lamps will flash.
If any of the doors are ajar, the horn
will make two quick chirps,
reminding you to properly close all
doors.
32
Page 33

Controls and features
Sounding a panic alarm
Press this control to activate the alarm.
To deactivate the alarm, press the
control again or turn the ignition to
ACC or ON.
This device complies with part 15 of
the FCC rules and with RS-210 of
Industry Canada. Operation is
subject to the following two
conditions: (1) This device may not
cause harmful interference, and (2)
This device must accept any interference received, including interference
that may cause undesired operation.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to
operate the equipment.
Replacing the battery
The transmitter is powered by one coin type three-volt lithium battery
CR2032 or equivalent. Typical operating range will allow you to be up to
10 meters (33 feet) away from your vehicle. A decrease in operating
range can be caused by:
• battery weakness due to time and use
• weather conditions
• nearby radio towers
• structures around the vehicle
• other vehicles parked next to the vehicle
To replace the battery:
1. Twist a thin coin between the two halves of the transmitter near the
key ring. DO NOT TAKE THE FRONT PART OF THE TRANSMITTER
APART.
2. Place the positive (+) side of new battery in the same orientation.
Refer to the diagram inside the transmitter unit.
3. Snap the two halves back together.
33
Page 34

Controls and features
Replacing lost transmitters
Take all your vehicle’s transmitters
to your dealer for reprogramming if:
• a transmitter is lost or
• you want to purchase additional
transmitters (up to four may be
programmed).
Reprogramming transmitters
To reprogram all transmitters, place the key in the ignition and switch
from OFF to ON eight times in a row (within 10 seconds). After doors
lock/unlock, press any button on all transmitters (up to four). When
completed, switch the ignition to OFF.
All transmitters must be reprogrammed at the same time.
Illuminated entry
The interior lamps illuminate when the remote entry system is used to
unlock the door(s) or sound the personal alarm.
The system automatically turns off after 25 seconds or when the ignition
is turned to the START or ACC position. The dome lamp switch
(if equipped) must not be set to the OFF position for the illuminated
entry system to operate.
The inside lights will not turn off if:
• they have been turned on with the dimmer control or
• any door is open.
The battery saver will shut off the interior lamps 40 minutes after the
ignition has been turned to the OFF position.
34
Page 35

Controls and features
PERIMETER ALARM SYSTEM
Arming the system
When armed, this system will help protect your vehicle from
unauthorized entry. When unauthorized entry occurs, the system will
flash the parking lamps and the theft indicator lamp, and chirp the horn.
The system is ready to arm whenever the ignition is turned OFF. Any of
the following actions will prearm the alarm system:
• Press the remote entry lock
control
• Open a door and press the power
door lock control to lock the
doors
If a door is open, the system is prearmed and is waiting for the door to
close. The theft indicator in the instrument panel will be lit continuously
when the system is prearmed.
Once the doors are closed, the system will arm in 30 seconds.
When you press the lock control
twice within 5 seconds, the horn will
chirp once to let you know that the
system is armed.
If the doors are not closed and you press the remote entry transmitter
twice to confirm the doors are locked, the horn will chirp twice to warn
you that the system is not arming.
35
Page 36

Controls and features
Disarming the system
You can disarm the system by any of the following actions:
• Unlock the doors by using your
remote entry transmitter.
• Unlock the doors with a key. Turn
the key full travel (toward the
front of the vehicle) to make sure
the alarm disarms.
• Turn ignition to ACC or ON.
• Press the panic control on the
remote entry transmitter. This
will disarm the system only if the
alarm is sounding.
36
Page 37

Seating and safety restraints
SEATING
Front seats
Never adjust the driver’s seat or seatback when the vehicle is
moving.
Do not pile cargo higher than the seatbacks to avoid injuring
people in a collision or sudden stop.
Always drive and ride with your seatback upright and the lap
belt snug and low across the hips.
Lift handle to move seat forward or
backward.
37
Page 38

Seating and safety restraints
Pull lever up to adjust seatback.
Using the manual lumbar support
Turn the lumbar support control
clockwise to increase firmness.
Turn the lumbar support control
counterclockwise to increase
softness.
REAR SEATS
Center facing jump seat (2 door SuperCab) (if equipped)
To open, pull inboard and down on the seat handle.
To stow the seat, pull seat bottom back to the fully upright position.
Do not install a child seat in a center facing jump seat.
38
Page 39

Seating and safety restraints
Center facing jump seat (4 door SuperCab)(if equipped)
To open, lift handle and pull seat
assembly down, then raise seatback.
To stow the seat, fold seat back
down and raise seat assembly to the
fully upright position.
Do not install a child seat in
a center facing jump seat.
SAFETY RESTRAINTS
Safety restraints precautions
Always drive and ride with your seatback upright and the lap
belt snug and low across the hips.
To prevent the risk of injury, make sure children sit where they
can be properly restrained.
Never let a passenger hold a child on his or her lap while the
vehicle is moving. The passenger cannot protect the child from
injury in a collision.
All occupants of the vehicle, including the driver, should always
wear their safety belts.
It is extremely dangerous to ride in a cargo area, inside or
outside of a vehicle. In a collision, people riding in these areas
are more likely to be seriously injured or killed. Do not allow people to
ride in any area of your vehicle that is not equipped with seats and
safety belts. Be sure everyone in your vehicle is in a seat and using a
safety belt properly.
39
Page 40

Seating and safety restraints
Each seating position in your vehicle has a specific safety belt
assembly which is made up of one buckle and one tongue that
are designed to be used as a pair. 1) Use the shoulder belt on the
outside shoulder only. Never wear the shoulder belt under the arm.
2) Never swing it around your neck over the inside shoulder. 3) Never
use a single belt for more than one person.
On four-door SuperCab vehicles, do not open the rear door when
the rear seat belt is still buckled.
Combination lap and shoulder belts
1. To fasten, insert the tongue into
the slot in the buckle.
2. To unfasten, push the red release
button and remove the tongue from
the buckle.
The front outboard safety restraints in the vehicle are combination lap
and shoulder belts. The front passenger outboard safety belt has two
types of locking modes described below:
40
Page 41

Seating and safety restraints
Vehicle sensitive mode
The vehicle sensitive mode is the normal retractor mode, allowing free
shoulder belt length adjustment to your movements and locking in
response to vehicle movement. For example, if the driver brakes
suddenly or turns a corner sharply, or the vehicle receives an impact of
8 km/h (5 mph) or more, the combination safety belts will lock to help
reduce forward movement of the driver and passengers.
In this mode, the shoulder belt is automatically pre-locked. The belt will
still retract to remove any slack in the shoulder belt.
The automatic locking mode is not available on the driver safety belt.
When to use the automatic locking mode
• When a tight lap/shoulder fit is desired.
• Anytime a child safety seat is installed in the vehicle. Refer to Safety
Restraints for Children or Safety Seats for Children later in this
chapter.
How to use the automatic locking mode
• Buckle the combination lap and
shoulder belt.
41
Page 42

Seating and safety restraints
• Grasp the shoulder portion and
pull downward until the entire
belt is extracted.
• Allow the belt to retract. As the belt retracts, you will hear a clicking
sound. This indicates the safety belt is now in the automatic locking
mode.
How to disengage the automatic locking mode
Disconnect the combination lap/shoulder belt and allow it to retract
completely to disengage the automatic locking mode and activate the
vehicle sensitive (emergency) locking mode.
Front safety belt height adjustment
Your vehicle has safety belt height adjustments for the driver and front
passenger. Adjust the height of the shoulder belt so the belt rests across
the middle of your shoulder.
• Regular Cab
42
Page 43

• 2–door SuperCab
• 4–door SuperCab
Seating and safety restraints
To lower the shoulder belt height, push the button and slide the height
control down. To raise the height of the shoulder belt, slide the height
adjuster up. Pull down on the height adjustment assembly to make sure
it is locked in place.
Position the shoulder belt height adjuster so that the belt rests
across the middle of your shoulder. Failure to adjust the safety
belt properly could reduce the effectiveness of the safety belt and
increase the risk of injury in a collision.
43
Page 44

Seating and safety restraints
Lap belts
Adjusting the front center seat lap belt (if equipped)
The lap belt does not adjust automatically. Adjust to fit snugly and as low
as possible around your hips. Do not wear the lap belt around your waist.
Insert the tongue into the correct
buckle. To lengthen the belt, turn
the tongue at a right angle to the
belt and pull across your lap until it
reaches the buckle. To tighten the
belt, pull the loose end of the belt
through the tongue until it fits
snugly across the hips.
Shorten and fasten the belt when
not in use.
44
Page 45

Seating and safety restraints
Adjusting the rear center facing jump seat lap belt (if equipped)
The lap belts for rear center facing jump seat occupants have automatic
retractors for the belt tongue and a fixed position buckle.
To fasten the belt, pull the belt all
the way across your hips and insert
the tongue into the buckle on your
rear door until you hear a snap and
feel it latch. Make sure the buckle is
securely fastened by pulling on the tongue.
• Position the belt so that it fits snugly and as low as possible around
the hips.
• If you need to lengthen the belt, unfasten it and repeat the procedure
above.
To unfasten the belt, push in the release button prior to opening the rear
door.
Safety belt extension assembly
If the safety belt assembly is too short, even when fully extended, 20 cm
(8 inches) can be added to the safety belt assembly by adding a safety
belt extension assembly (part number 611C22). Safety belt extension
assemblies can be obtained from your dealer at no cost.
Use only extensions manufactured by the same supplier as the safety
belt. Manufacturer identification is located at the end of the webbing on
the label. Also, use the safety belt extension only if the safety belt is too
short for you when fully extended. Do not use extensions to change the
fit of the shoulder belt across the torso.
Safety belt warning light and indicator chime
The seat belt warning light illuminates in the instrument cluster and a
chime sounds to remind the occupants to fasten their safety belts.
45
Page 46

Seating and safety restraints
Conditions of operation
If... Then...
The driver’s safety belt is not
buckled before the ignition switch
is turned to the ON position...
The driver’s safety belt is buckled
while the indicator light is
illuminated and the warning chime
is sounding...
The driver’s safety belt is buckled
before the ignition switch is turned
to the ON position...
Safety belt maintenance
Check the safety belt systems periodically to make sure they work
properly and are not damaged. Check the safety belts to make sure there
are no nicks, wears or cuts. All safety belt assemblies, including
retractors, buckles, front seat belt buckle assemblies (slide bar)
(if equipped), shoulder belt height adjusters (if equipped), child safety
seat tether bracket assemblies (if equipped), and attaching hardware,
should be inspected after a collision. Ford recommends that all safety
belt assemblies used in vehicles involved in a collision be replaced.
However, if the collision was minor and a qualified technician finds that
the belts do not show damage and continue to operate properly, they do
not need to be replaced. Safety belt assemblies not in use during a
collision should also be inspected and replaced if either damage or
improper operation is noted.
The safety belt warning light
illuminates for one to two minutes
and the warning chime sounds for
four to eight seconds.
The safety belt warning light and
warning chime turn off.
The safety belt warning light and
indicator chime remain off.
Failure to replace the safety belt assembly under the above
conditions could result in severe personal injuries in the event of
a collision.
Refer to Cleaning and maintaining the safety belts in the
Maintenance and care section.
46
Page 47

Seating and safety restraints
AIR BAG SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM (SRS)
60
70
50
80
0 0 0
CHECK
40
100
80
90
ENGINE
F
EL
BRAKE
ABS
OFF
ON
OFF
Important supplemental restraint system (SRS) precautions
The supplemental restraint system
is designed to work with the safety
belt to help protect the driver and
right front passenger from certain
upper body injuries.
Air bags DO NOT inflate slowly or
gently and the risk of injury from a
deploying air bag is greatest close to
the trim covering the air bag
module.
120
60
140
H
30
H
20
10
!
P
H
00
1
0 0 0 0 0 0
40
160
180
20
101
20
1
km/h
MPH
RND21
P
SRS
L
L
SPEED
O/D
CONT
OFF
SEEK
COAST
RSM
SET
ACC
1
ON
PASSENGER AIRBAG
OFF
OFF
2
34AM-FM
A/C
MAX
A/C
TUNE
OFF
All occupants of the vehicle including the driver should always
properly wear their safety belts even when air bag SRS is
provided.
Always transport children 12 years old and under in the back
seat and always use appropriate child restraints.
NHTSA recommends a minimum distance of at least ten (10)
inches between an occupant’s chest and the air bag module.
47
Page 48

Seating and safety restraints
The right front passenger air bag is not designed to restrain
occupants in the center front seating position.
Do not put anything on or over the air bag module. Placing
objects on or over the air inflation area may cause those objects
to be propelled by the air bag into your face and torso causing serious
injury.
Do not attempt to service, repair, or modify the Air Bag
Supplemental Restraint System or its fuses. See your Ford or
Lincoln-Mercury dealer.
Children and air bags
For additional important safety information, read all information on
safety restraints in this guide.
Children must always be properly restrained. Failure to follow these
instructions may increase the risk of injury in a collision.
Air bags can kill or injure a child in a child seat. Child seats
should never be placed in the front seats, unless passenger air
bag switch is turned off. See Passenger air bag deactivate switch.
How does the air bag supplemental restraint system work?
The air bag SRS is designed to
activate when the vehicle sustains
sufficient longitudinal deceleration.
The fact that the air bags did not
inflate in a collision does not mean
that something is wrong with the
system. Rather, it means the forces
were not of the type sufficient to
cause activation. Air bags are
designed to inflate in frontal and
near-frontal collisions, not rollover,
side-impact, or rear-impacts.
48
Page 49

Seating and safety restraints
The air bags inflate and deflate
rapidly upon activation. After air bag
deployment, it is normal to notice a
smoke-like, powdery residue or
smell the burnt propellant. This may
consist of cornstarch, talcum
powder (to lubricate the bag) or
sodium compounds (e.g., baking
soda) that result from the
combustion process that inflates the
air bag. Small amounts of sodium
hydroxide may be present which
may irritate the skin and eyes, but
none of the residue is toxic.
While the system is designed to help
reduce serious injuries, it may also
cause minor burns, abrasions, swelling or temporary hearing loss.
Because air bags must inflate rapidly and with considerable force, there
is the risk of death or serious injuries such as fractures, facial and eye
injuries or internal injuries, particularly to occupants who are not
properly restrained or are otherwise out of position at the time of air bag
deployment. Thus, it is extremely important that occupants be properly
restrained as far away from the air bag module as possible while
maintaining vehicle control.
Several air bag system components get hot after inflation. Do not
touch them after inflation.
If the air bag is inflated, the air bag will not function again
and must be replaced immediately. If the air bag is not
replaced, the unrepaired area will increase the risk of injury in a
collision.
49
Page 50

Seating and safety restraints
The SRS consists of:
• driver and passenger air bag modules
(which include the inflators and air bags)
• one or more impact and safing sensors, passenger air bag deactivation
switch and diagnostic monitor (RCM)
• a readiness light and tone
• and the electrical wiring which connects the components.
The RCM (restraints control module) monitors its own internal circuits
and the supplemental air bag electrical system warning (including the
passenger air bag deactivation switch, the impact sensors, the system
wiring, the air bag system readiness light, the air bag back up power and
the air bag ignitors).
Determining if the system is operational
The SRS uses readiness lights in the instrument cluster and the
passenger air bag deactivate switch or a tone to indicate the condition of
the system. Refer to the Air bag readiness section in the
Instrumentation chapter or Passenger air bag deactivate switch
section in this chapter. Routine maintenance of the air bag is not
required.
A difficulty with the system is indicated by one or more of the following:
• The readiness lights will either
flash or stay lit.
• The readiness lights will not
illuminate immediately after
ignition is turned on.
• A series of five beeps will be heard. The tone pattern will repeat
periodically until the problem and light are repaired.
If any of these things happen, even intermittently, have the SRS serviced
at your dealership or by a qualified technician immediately. Unless
serviced, the system may not function properly in the event of a
collision.
Disposal of air bags and air bag equipped vehicles
For disposal of air bags or air bag equipped vehicles, see your local
dealership or qualified technician. Air bags MUST BE disposed of by
qualified personnel.
50
Page 51

Seating and safety restraints
Passenger air bag deactivate switch
Your vehicle has a passenger air bag
deactivate switch. This switch MUST
be used to activate or deactivate the
passenger air bag whenever a child
seat is used in the right front or
center front passenger seat position.
PASSENGER AIRBAG
Keep the passenger air bag turned on unless there is a child seat
installed in the front seat. When the passenger air bag switch is
turned off, the passenger air bag will not inflate in a collision.
If the passenger air bag switch is turned off, it increases the likelihood of
injury to forward facing occupants in the passenger seat.
Turning the passenger air bag off
1. Insert the ignition key, turn the
switch to OFF and remove the key.
2. When the ignition is turned to the
ON position the OFF light
illuminates briefly, momentarily
shuts off and then turns back on.
This indicates that the passenger air
bag is deactivated.
PASSENGER AIRBAG
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
If the light fails to illuminate when the passenger air bag switch
is in the OFF position and the ignition switch is in ON, have the
passenger air bag switch serviced at your Ford or Lincoln-Mercury
dealer immediately.
In order to avoid inadvertent deployment of the passenger air
bag, always remove the ignition key from the passenger air bag
deactivate switch.
51
Page 52

Seating and safety restraints
Turning the passenger air bag back on
The passenger air bag remains OFF until you turn it back ON.
1. Insert the ignition key and turn
the switch to ON.
2. The OFF light will briefly
illuminate when the ignition is
turned to On. This indicates that the
passenger air bag is operational.
PASSENGER AIRBAG
If the light is illuminated when the passenger air bag switch is in
the ON position and the ignition switch is in ON, have the
passenger air bag switch serviced at your Ford or Lincoln-Mercury
dealer immediately.
Keep the passenger air bag turned on unless there is a child seat
installed in the front seat. When the passenger air bag switch is
turned off, the passenger air bag will not inflate in a collision.
CHILDREN AND SAFETY BELTS
Children who are too large for child safety seats (as specified by your
child safety seat manufacturer) should always wear safety belts.
Follow all the important safety restraint and air bag precautions that
apply to adult passengers in your vehicle.
If the shoulder belt portion of a combination lap and shoulder belt can
be positioned so it does not cross or rest in front of the child’s face or
neck, the child should wear the lap and shoulder belt. Moving the child
closer to the center of the vehicle may help provide a good shoulder belt
fit.
If the shoulder belt cannot be properly positioned:
• move the child to one of the seats with a lap belt only (if equipped) or
• if the child is the proper size, restrain the child in a safety seat.
ON
OFF
OFF
52
Page 53

Seating and safety restraints
Do not leave children, unreliable adults, or pets unattended in
your vehicle.
To improve the fit of lap and shoulder belts on children who have
outgrown child safety seats, Ford recommends use of a belt-positioning
booster seat that is labelled as conforming to all Federal motor vehicle
safety standards. Belt-positioning booster seats raise the child and
provide a shorter, firmer seating cushion that encourages safer seating
posture and better fit of lap and shoulder belts on the child.
A belt-positioning booster should be used if the shoulder belt rests in
front of the child’s face or neck, or if the lap belt does not fit snugly on
both thighs, or if the thighs are too short to let the child sit all the way
back on the seat cushion when the lower legs hang over the edge of the
seat cushion. You may wish to discuss the special needs of your child
with your pediatrician.
Important child restraint precautions
You are required by law to use safety restraints for children in the U.S.
and Canada. If small children ride in your vehicle (generally children who
are four years old or younger and who weigh 18 kg [40 lbs] or less), you
must put them in safety seats made especially for children. Check your
local and state or provincial laws for specific requirements regarding the
safety of children in your vehicle.
Never let a passenger hold a child on his or her lap while the
vehicle is moving. The passenger cannot protect the child from
injury in a collision.
Always follow the instructions and warnings that come with any infant or
child restraint you might use.
When possible, place children in the rear seat of your vehicle. Accident
statistics suggest that children are safer when properly restrained in the
rear seating positions than in the front seating position.
Do not install a child seat in a center facing jump seat.
53
Page 54

Seating and safety restraints
SAFETY SEATS FOR CHILDREN
Child and infant or child safety seats
Use a safety seat that is recommended for the size and weight of the
child. Carefully follow all of the manufacturer’s instructions with the
safety seat you put in your vehicle. If you do not install and use the
safety seat properly, the child may be injured in a sudden stop or
collision.
When installing a child safety seat:
• Use the correct safety belt buckle
for that seating position.
• Make sure the tongue is securely
fastened in the buckle.
• Keep the buckle release button
pointing up and away from the
safety seat, with the tongue
between the child seat and the
release button, to prevent
accidental unbuckling.
• Place seat back in upright position.
• Put the safety belt in the automatic locking mode. Refer to Automatic
locking mode.
Ford recommends the use of a child safety seat having a top tether
strap. Install the child safety seat in a seating position which is capable
of providing a tether anchorage. For more information on top tether
straps, refer to Attaching safety seats with tether straps.
Carefully follow all of the manufacturer’s instructions included
with the safety seat you put in your vehicle. If you do not install
and use the safety seat properly, the child may be injured in a sudden
stop or collision.
54
Page 55

Seating and safety restraints
1. Position the child safety seat in a
seat with a combination lap and
shoulder belt.
Air bag can kill or injure a child in a child seat. If you must use a
forward-facing child seat in the front seat, move seat all the way
back.
Air bag can kill or injure a child in a child seat. Child seats
should be never be placed in the front seats, unless passenger
air bag switch is turned off. See Passenger air bag deactivation
switch.
2. Pull down on the shoulder belt
and then grasp the shoulder belt
and lap belt together.
55
Page 56

Seating and safety restraints
3. While holding the shoulder and
lap belt portions together, route the
tongue through the child seat
according to the child seat
manufacturer’s instructions. Be sure
the belt webbing is not twisted.
4. Insert the belt tongue into the
proper buckle for that seating
position until you hear and feel the
latch engage. Make sure the tongue
is latched securely by pulling on it.
5. To put the retractor in the
automatic locking mode, grasp the
shoulder portion of the belt and pull
downward until all of the belt is
extracted and a click is heard.
6. Allow the belt to retract. The belt will click as it retracts to indicate it
is in the automatic locking mode.
56
Page 57

Seating and safety restraints
7. Pull the lap belt portion across
the child seat toward the buckle and
pull up on the shoulder belt while
pushing down with knee on the
child seat.
8. Allow the safety belt to retract to
remove any slack in the belt.
9. Before placing the child in the
seat, forcibly tilt the seat forward
and back to make sure the seat is
securely held in place.
10. Try to pull the belt out of the retractor to make sure the retractor is
in the automatic locking mode (you should not be able to pull more belt
out). If the retractor is not locked, unbuckle the belt and repeat steps
two through nine.
Check to make sure the child seat is properly secured before each use.
Attaching safety seats with tether straps
Some manufacturers make safety seats that include a tether strap that
goes over the back of the vehicle seat and attaches to an anchoring
point. Other manufacturers offer the tether strap as an accessory.
Contact the manufacturer of your child safety seat for information about
ordering a tether strap.
In SuperCabs equipped with Center Facing Jump Seats, the tether strap
anchor bracket should be installed only at the center of the cab’s back
panel with the child seat in the front center seating position. Installing
an anchor bracket at the right rear of the cab may increase risk of injury
to an occupant of the right rear center facing jump seat in the event of a
collision or a sudden stop. If a tether child seat is installed in the right
57
Page 58

Seating and safety restraints
front seating position, secure the tether strap to the webbing of the
buckled right rear lap belt.
You can attach a tether strap anchor bracket to the cab inner back panel
by using a tether anchor kit (613D74) available at no charge from any
Ford dealer.
Do not install a child seat in a center facing jump seat.
Tether anchorage hardware
Tether anchorage hardware kits (part number 613D74) including
instructions, may be obtained at no charge from any Ford or
Lincoln-Mercury dealer.
Tighten the anchor according to specifications. Otherwise, the
safety seat may not be properly secured and the child may be
injured in a sudden stop or collision.
58
Page 59

Starting
PREPARING TO START YOUR VEHICLE
Engine starting is controlled by the ignition system. This system meets
all Canadian Interference-Causing Equipment standard requirements
regulating the impulse electrical field strength of radio noise.
When starting a fuel-injected engine, avoid pressing the accelerator
before or during starting. Only use the accelerator when you have
difficulty starting the engine. For more information on starting the
vehicle, refer to Starting the engine in this chapter.
Extended idling at high engine speeds can produce very high
temperatures in the engine and exhaust system, creating the risk
of fire or other damage.
Do not park, idle, or drive your vehicle in dry grass or other dry
ground cover. The emission system heats up the engine
compartment and exhaust system, which can start a fire.
Do not start your vehicle in a closed garage or in other enclosed
areas. Exhaust fumes can be toxic. Always open the garage door
before you start the engine. See Guarding against exhaust fumes in
this chapter for more instructions.
If you smell exhaust fumes inside your vehicle, have your dealer
inspect your vehicle immediately. Do not drive if you smell
exhaust fumes.
Important safety precautions
A computer system controls the engine’s idle revolutions per minute
(RPM). When the engine starts, the idle RPM runs faster to warm the
engine. If the engine idle speed does not slow down automatically, have
the vehicle checked. Do not allow the vehicle to idle for more than ten
minutes.
Before starting the vehicle:
1. Make sure all vehicle occupants have buckled their safety belts. For
more information on safety belts and their proper usage, refer to the
Seating and safety restraints chapter.
59
Page 60

Starting
2. Make sure the headlamps and vehicle accessories are off.
If starting a vehicle with an automatic transmission:
• Make sure the parking brake is
set.
• Make sure the gearshift is in P (Park).
If starting a vehicle with a manual transmission:
• Make sure the parking brake is set.
• Push the clutch pedal to the
floor.
3. Turn the key to 4 (ON) without
turning the key to 5 (START).
60
3
4
5
2
1
Page 61

60
30
20
10
5
RPMx1000
40
40
20
MPH
P
6
P
50
60
80
0 0 0 0 0 0
RND21
DOOR
AJAR
20
10
RND21
CHECK
ENGINE
H
F
EL
!
ABS
BRAKE
CHECK
GAGE
4
3
2
1
0
ABS
!
BRAKE
FUEL
RESET
CHECK
ENGINE
<FUEL DOOR
H
C
F
E
0 0 0
30
Starting
70
80
100
90
120
40
50
40
20
MPH
140
km/h
60
1
160
180
60
0 0 0
100
80
0 0 0 0 0 0
00
101
20
1
LL
70
80
90
120
140
00
1
160
180
101
20
1
km/h
THEFT
H
H
SPEED
O/D
CONT
OFF
H
SPEED
CONT
L
4WD
HIGH
4WD
H
LOW
L
O/D
OFF
Make sure the corresponding lights illuminate briefly. If a light fails to
illuminate, have the vehicle serviced.
• If the driver’s safety belt is fastened, the light ( ) will not illuminate.
STARTING THE ENGINE
1. Turn the key to 5 (START)
without pressing the accelerator
pedal and release as soon as the
engine starts. The key will return
to 4 (ON).
3
4
5
2
1
61
Page 62

Starting
2. If the engine does not start within five seconds, wait ten seconds and
try again.
3. If the engine does not start in two attempts or if the temperature is
below -12°C (10°F), depress the accelerator and start the engine while
holding the accelerator down. Release the accelerator when the engine
starts.
4. After idling for a few seconds, apply the brake and release the parking
brake.
Using the engine block heater (if equipped)
An engine block heater warms the engine coolant, which improves
starting, warms up the engine faster and allows the heater-defroster
system to respond quickly. Use of an engine block heater is strongly
recommended if you live in a region where temperatures reach -23°C
(-10°F) or below. Your engine block heater also comes with a battery
warmer. The battery warmer wraps around the battery and keeps the
battery warm when the engine block heater is plugged in.
For best results, plug the heater in at least three hours before starting
the vehicle. Using the heater for longer than three hours will not harm
the engine, so the heater can be plugged in the night before starting the
vehicle.
To prevent electrical shock, do not use your heater with
ungrounded electrical systems or two-pronged (cheater)
adapters.
62
Page 63

Starting
Guarding against exhaust fumes
Although odorless and colorless, carbon monoxide is present in exhaust
fumes. Take precautions to avoid its dangerous effects.
If you ever smell exhaust fumes of any kind inside your vehicle,
have your dealer inspect and fix your vehicle immediately. Do
not drive if you smell exhaust fumes. These fumes are harmful and
could kill you.
Have the exhaust and body ventilation systems checked whenever:
• the vehicle is raised for service.
• the sound of the exhaust system changes.
• the vehicle has been damaged in a collision.
Important ventilating information
If the engine is idling while the vehicle is stopped in an open area for
long periods of time, open the windows at least 2.5 cm (one inch).
Adjust the heating or air conditioning (if equipped) to bring in fresh air.
Improve vehicle ventilation by
keeping all air inlet vents clear of
snow, leaves and other debris.
63
Page 64

Driving
BRAKES
Your brakes are self-adjusting. Refer to the “Service Guide” for scheduled
maintenance.
Occasional brake noise is normal and often does not indicate a
performance concern with the vehicle’s brake system. In normal
operation, automotive brake systems may emit occasional or intermittent
squeal or groan noises when the brakes are applied. Such noises are
usually heard during the first few brake applications in the morning;
however, they may be heard at any time while braking and can be
aggravated by environmental conditions such as cold, heat, moisture,
road dust, salt or mud. If a “metal-to-metal,” “continuous grinding” or
“continuous squeal” sound is present while braking, the brake linings
may be worn-out and should be inspected by a qualified service
technician.
Rear anti-lock brake system (RABS)
Rear Anti-lock Brake System (RABS) is standard equipment on this
vehicle. RABS is designed to help you maintain directional stability in
emergency stopping situations. With RABS, the rear brakes are kept from
locking during panic stops; however, the front wheels can lock because
they are not controlled by RABS. You should apply the brakes with
steadily increasing force, as if “squeezing” the brakes. If you feel the
front wheels begin to lock, momentarily release the pedal and repeat the
“squeeze” technique. Whenever the front wheels lock, the vehicle cannot
be steered.
A clicking noise and slight pedal pulsation during RABS braking events
indicates the RABS is functioning. Pedal pulsation coupled with clicking
noise while braking under panic conditions on loose gravel, wet or snowy
roads is normal and indicates proper functioning of the vehicle’s RABS. If
the vehicle has continuous vibration or shudder while braking, felt mainly
in the steering wheel, the vehicle most likely needs service.
The RABS operates by detecting the onset of rear wheel lockup during
brake applications and compensating for this tendency.
64
Page 65

Driving
RABS warning lamp
ABS
The
fault is detected. Have your vehicle serviced as soon as possible.
Normal braking is still effective
unless the BRAKE warning lamp is
also illuminated.
Using RABS
• In an emergency, applying full pressure may cause the front wheels to
lock. If the front brakes lock, the vehicle cannot be steered. You
should apply the brakes with steadily increasing force, as if
“squeezing” the brakes. If you feel the front wheels begin to lock,
momentarily release the pedal and repeat the “squeeze” technique.
• We recommend that you familiarize yourself with how the RABS
performs. However, avoid unnecessary risks.
Four-wheel anti-lock brake system (ABS) (if equipped)
On vehicles equipped with an anti-lock braking system (ABS), a noise
from the hydraulic pump motor and pulsation in the pedal may be
observed during ABS braking events. Pedal pulsation coupled with noise
while braking under panic conditions or on loose gravel, bumps, wet or
snowy roads is normal and indicates proper functioning of the vehicle’s
anti-lock brake system. If the vehicle has continuous vibration or shudder
while braking, felt mainly in the steering wheel, the vehicle most likely
needs service.
The ABS operates by detecting the
onset of wheel lock up during brake
applications and compensating for
this tendency. The wheels are
prevented from locking even when
the brakes are firmly applied. The
accompanying illustration depicts
the advantage of an ABS equipped
vehicle (on bottom) to a non-ABS
equipped vehicle (on top) during
hard braking.
warning lamp in the instrument cluster illuminates if a RABS
!
BRAKE
65
Page 66

Driving
ABS warning lamp
ABS
The
five seconds when starting the vehicle. If an ABS fault is detected, the
light will remain on and your vehicle should be serviced as soon as
possible.
Normal braking is still effective
unless the BRAKE warning lamp is
also illuminated.
Using ABS
• In an emergency or when maximum efficiency from the ABS is
required, apply continuous full force on the brake. The ABS will be
activated immediately, thus allowing you to retain full steering control
of your vehicle and, providing there is sufficient space, will enable you
to avoid obstacles and bring the vehicle to a controlled stop.
• We recommend that you familiarize yourself with this braking
technique. However, avoid taking any unnecessary risks.
Parking brake
Apply the parking brake whenever
the vehicle is parked. To set the
parking brake, press the parking
brake pedal down until the pedal
stops.
warning lamp in the instrument cluster illuminates for about
!
BRAKE
The BRAKE warning lamp in the
instrument cluster illuminates and
remains illuminated (when the
ignition is turned ON) until the
parking brake is released.
66
!
BRAKE
Page 67

Driving
Always set the parking brake fully and make sure that the
gearshift is securely latched in P (Park) (automatic
transmission) or in 1 (First) (manual transmission).
The parking brake is not designed to stop a moving vehicle. However, if
the normal brakes fail, the parking brake can be used to stop your
vehicle in an emergency. Since the parking brake applies only the rear
brakes, the vehicle’s stopping distance will be adversely affected.
Pull the release lever to release the
brake. Driving with the parking
brake on will cause the brakes to
wear out quickly and reduce fuel
economy.
TRANSMISSION OPERATION
Automatic transmission operation
Brake-shift interlock
This vehicle is equipped with a brake-shift interlock feature that prevents
the gearshift from being moved from P (Park) unless the brake pedal is
depressed.
If you cannot move the gearshift out of P (Park) with the brake pedal
depressed:
1. Apply the parking brake, turn ignition key to LOCK, then remove the
key.
2. Insert the key and turn it to OFF. Apply the brake pedal and shift to N
(Neutral).
3. Start the vehicle.
If it is necessary to use the above procedure to move the gearshift, it is
possible that a fuse has blown. Refer to Fuses and relays in the
Roadside emergencies chapter.
67
Page 68

Driving
Do not drive your vehicle until you verify that the brakelamps
are working.
If your vehicle gets stuck in mud or snow it may be rocked out by
shifting between forward and reverse gears in a steady pattern. Press
lightly on the accelerator in each gear.
Do not rock the vehicle for more than a few minutes. The
transmission and tires may be damaged or the engine may
overheat.
Always set the parking brake fully and make sure the gearshift is
latched in P (Park). Turn off the ignition whenever you leave
your vehicle.
Driving with a 4–speed automatic transmission
(2.5L and 3.0L engines only)
Understanding gearshift positions
Pull the gearshift lever towards you and downward to move the
automatic gearshift.
Hold the brake pedal down while you move the gearshift lever
from position to position. If you do not hold the brake pedal
down, your vehicle may move unexpectedly and injure someone.
P (Park)
Always come to a complete stop
before shifting into P (Park). Make
sure the gearshift is securely latched
in P (Park).
R (Reverse)
With the gearshift in R (Reverse),
the vehicle will move backward.
Always come to a complete stop
before shifting into and out of R
(Reverse).
68
Page 69

Driving
N (Neutral)
With the gearshift in N (Neutral),
the vehicle can be started and is
free to roll. Hold the brake pedal
down while in this gear.
(Overdrive)
The normal driving position for the
best fuel economy. Transmission
operates in gears one through four.
(Overdrive) can be deactivated
by pressing the transmission control
switch on the end of the gearshift
lever.
The transmission control indicator
light (TCIL) will illuminate on the
instrument cluster.
Drive – Not shown on the display. Activate by pressing the transmission
control switch on the end of the gearshift lever with the gearshift in the
position. The TCIL will illuminate on the instrument cluster.
Transmission operates in gears one through three.
more engine braking than
• driving with a heavy load
• towing a trailer up or down steep hills
• additional engine braking is desired. If towing a trailer, refer to
Driving while you tow in the Towing a trailer chapter.
To return to
The TCIL will no longer be illuminated.
Each time the vehicle is started, the transmission will automatically
return to normal overdrive mode.
Every time the vehicle is shut off and restarted, you must press the
transmission control switch to cancel overdrive operation if driving in
overdrive is not desired.
(Overdrive) mode, press the transmission control switch.
(Overdrive) and is useful when:
O/D
ON/OFF
O/D
OFF
(Drive) provides
69
Page 70

Driving
2 (Second)
Use 2 (Second) to start-up on
slippery roads or to provide
additional engine braking on
downgrades.
1 (First)
Use 1 (Low) to provide maximum
engine braking on steep
downgrades. Upshifts can be made
by shifting to 2 (Second) or to
(Overdrive). Selecting 1 (Low)
at higher speeds causes the transmission to shift to a lower gear, and will
shift to 1 (Low) after vehicle decelerates to the proper speed.
Driving with a 5–speed automatic transmission (4.0L engines only)
Understanding gearshift positions
Hold the brake pedal down while you move the gearshift lever
from position to position. If you do not hold the brake pedal
down, your vehicle may move unexpectedly and injure someone.
Pull the gearshift lever towards you and downward to move the
automatic gearshift.
P (Park)
Always come to a complete stop
before shifting into or out of P
(Park). Make sure the gearshift is
securely latched in P (Park).
R (Reverse)
With the gearshift in R (Reverse),
the vehicle will move backward.
Always come to a complete stop
before shifting into and out of R
(Reverse).
70
Page 71

Driving
N (Neutral)
With the gearshift in N (Neutral),
the vehicle can be started and is
free to roll. Hold the brake pedal
down while in this gear.
(Overdrive)
The normal driving position for the
best fuel economy. Transmission
operates in gears one through five.
(Overdrive) can be deactivated
by pressing the transmission control
switch on the end of the gearshift
lever.
The transmission control indicator
light (TCIL) will illuminate on the
instrument cluster.
Drive – Not shown on the display. Activate by pressing the transmission
control switch on the end of the gearshift lever with the gearshift in the
position. The TCIL will illuminate on the instrument cluster.
Transmission operates in gears one through four.
more engine braking than
conditions (i.e., city traffic, hilly terrain, etc.) cause the transmission to
excessively shift between
(Overdrive) when:
• driving with a heavy load
• towing a trailer up or down steep hills
• additional engine braking is desired.
To return to
The TCIL will no longer be illuminated.
Each time the vehicle is started, the transmission will automatically
return to normal overdrive mode.
(Overdrive) mode, press the transmission control switch.
(Overdrive) and is useful whenever driving
(Overdrive) and (Drive). Also deactivate
O/D
ON/OFF
O/D
OFF
(Drive) provides
71
Page 72

Driving
2 (Second)
Use 2 (Second) to start-up on
slippery roads or to provide
additional engine braking on
downgrades. Transmission operates
in third gear.
1 (First)
Use 1 (First) to provide maximum
engine braking on steep
downgrades. Upshifts can be made
by shifting to 2 (Second) or to
(Overdrive). Selecting 1 (Low)
at higher speeds causes the transmission to shift to a lower gear and will
shift to 1 (First) after the vehicle decelerates to the proper vehicle
speed.
Driving a manual transmission (if equipped)
Using the clutch
Vehicles equipped with a manual
transmission have a starter interlock
that prevents cranking the engine
unless the clutch pedal is fully
depressed.
When starting a vehicle with a
manual transmission:
1. Hold down the brake pedal.
2. Depress the clutch pedal.
3. Put the gearshift lever in N
(Neutral).
4. Crank the engine and let it idle for a few seconds.
• Put the gearshift in 1 (First) or R (Reverse).
5. Release the clutch slowly while pressing gradually down on the
accelerator pedal.
• Do not drive with your foot resting on the clutch pedal. Do not use
the clutch to hold your vehicle at a standstill while waiting on a hill.
These actions may reduce clutch life.
72
Page 73

Driving
Recommended shift speeds
Upshifts when accelerating (for best fuel economy)
Shift from:
1 - 2 14 km/h (10 mph) 5 km/h (4 mph)
2 - 3 32 km/h (22 mph) 11 km/h (9 mph)
3 - 4 50 km/h (33 mph) 19 km/h (13 mph)
4 - 5 (Overdrive) 71 km/h (41 mph) 27 km/h (17 mph)
Upshifts when cruising (recommended for best fuel economy)
Shift from:
1 - 2 16 km/h (10 mph) 6 km/h (4 mph)
2 - 3 26 km/h (19 mph) 10 km/h (8 mph)
3 - 4 43 km/h (28 mph) 16 km/h (12 mph)
4 - 5 (Overdrive) 68 km/h (40 mph) 26 km/h (16 mph)
Maximum downshift speeds
Shift from:
5 (Overdrive) - 4 88 km/h (55 mph) 34 km/h (22 mph)
4 - 3 72 km/h (45 mph) 34 km/h (18 mph)
3 - 2 56 km/h (35 mph) 21 km/h (14 mph)
2 - 1 32 km/h (20 mph) 11 km/h (8 mph)
Transfer case position (if equipped)
4H 4L
Transfer case position (if equipped)
4H 4L
Transfer case position (if equipped)
4H 4L
Parking
1. Apply the brake and shift into N
(Neutral).
73
Page 74

Driving
2. Engage the parking brake.
3. Shift into 1 (First).
4. Turn the ignition to Off.
Do not park your vehicle in Neutral, it may move unexpectedly
and injure someone. Use 1 (First) gear and set the parking brake
fully.
Reverse
Ensure that the vehicle is at a complete stop before shifting into R
(Reverse). Failure to do so may damage the transmission.
Put the gearshift into N and wait at least several seconds before shifting
into R.
You can shift into R (Reverse) only by moving the gearshift from left of
3 (Third) and 4 (Fourth) gears before you shift into R (Reverse). This is
a special lockout feature that protects you from accidentally shifting into
R (Reverse) when you downshift from 5 (Overdrive).
FOUR-WHEEL DRIVE (4WD) OPERATION (IF EQUIPPED)
When Four–wheel drive (4WD) is engaged, power is supplied to all four
wheels through a transfer case. 4WD power can be selected when
additional driving power is desired.
All utility-type vehicles and 4WD vehicles have special design and
equipment features to make them capable of performing in a wide
variety of off-road applications. Specific design characteristics give them
higher centers of gravity than ordinary passenger cars.
74
Page 75

Driving
Utility and four-wheel drive vehicles are not designed for
cornering at speeds as high as passenger cars any more than
low-slung sports cars are designed to perform satisfactorily under
off-road conditions. Avoid sharp turns or abrupt maneuvers in these
vehicles.
4WD operation is not recommended on dry pavement. Doing so could
result in difficult disengagement of the transfer case, increased tire wear
and decreased fuel economy.
4WD system indicator lights
The 4WD system indicator lights illuminate only under the following
conditions. If these lights illuminate during normal driving, have your
vehicle serviced.
• 4WD HIGH – illuminates when
the ignition is turned on or when
4H (4WD High) is selected.
4WD
HIGH
• 4WD LOW – illuminates when
the ignition is turned on and 4L
(4WD Low) is selected.
4WD
LOW
Using the electronic shift 4WD system (if equipped)
Positions of the electronic shift system
2WD (2WD High) – Power to rear axle only.
4X4 HIGH (4WD High) – Power delivered to front and rear axles for
increased traction.
4X4 LOW (4WD Low) – Power to front and rear axles at low speeds.
75
Page 76

Driving
Shifting from 2WD (2WD high) to 4X4 HIGH (4WD High)
Move the 4WD control to the 4X4
HIGH.
At temperatures below 0°C (32°F),
shifts from 2WD to 4X4 HIGH
should not be performed above
72 km/h (45 mph).
• Do not shift into 4X4 HIGH with
the rear wheels slipping.
Shifting from 4X4 HIGH (4WD high) to 2WD (2WD high)
Move the 4WD control to 2WD at
any forward speed. You do not need
to put the gearshift in R (Reverse)
to disengage your front hubs.
Shifting between 4X4 HIGH (4WD high) and 4X4 LOW (4WD low)
1. Bring the vehicle to a stop.
2. Depress the brake.
3. Place the gearshift in N (Neutral) (automatic transmission) or depress
the clutch (manual transmission).
4. Move the 4WD control to the 4X4
HIGH or 4X4 LOW position.
2WD
2WD
2WD
4X4
HIGH
4X4
HIGH
4X4
HIGH
4X4
LOW
4X4
LOW
4X4
LOW
76
Page 77

Driving
Driving off-road with 4WD
Your vehicle is specially equipped for driving on sand, snow, mud and
rough terrain and has operating characteristics that are somewhat
different from conventional vehicles, both on and off the road.
Maintain steering wheel control at all times, especially in rough terrain.
Since sudden changes in terrain can result in abrupt steering wheel
motion, make sure you grip the steering wheel from the outside. Do not
grip the spokes.
Drive cautiously to avoid vehicle damage from concealed objects such as
rocks and stumps.
You should either know the terrain or examine maps of the area before
driving. Map out your route before driving in the area. For more
information on driving off-road, read the “Four Wheeling” supplement in
your owner’s portfolio.
If your vehicle gets stuck
If the vehicle is stuck, shift the transmission in a steady motion between
forward and reverse gears. Allow the transmission to engage, then press
lightly on the accelerator.
Do not rock the vehicle for more than a few minutes. The
transmission and tires may be damaged or the engine can
overheat.
Do not spin the wheels at over 56 km/h (35 mph). The tires may
fail and injure a passenger or bystander.
Sand
When driving over sand, try to keep all four wheels on the most solid
area of the trail. Do not reduce the tire pressures but shift to a lower
gear and drive steadily through the terrain. Apply the accelerator slowly
and avoid spinning the wheels.
77
Page 78

Driving
Mud and water
If you must drive through high water, drive slowly. Traction or brake
capability may be limited.
When driving through water, determine the depth; avoid water higher
than the bottom of the hubs (if possible) and proceed slowly. If the
ignition system gets wet, the vehicle may stall.
Once through water, always try the brakes. Wet brakes do not stop the
vehicle as effectively as dry brakes. Drying can be improved by moving
your vehicle slowly while applying light pressure on the brake pedal.
After driving through mud, clean off residue stuck to rotating driveshafts
and tires. Excess mud stuck on tires and rotating driveshafts causes an
imbalance that could damage drive components.
If the transmission and transfer case are submerged in water, their fluids
should be checked and changed, if necessary.
Water intrusion into the transmission may damage the
transmission.
If the rear axle is submerged in water, the rear axle lubricant should be
checked and changed, if necessary. The rear axle is filled with a
synthetic lubricant and does not normally require a lubricant change for
the life of the vehicle. Rear axle lubricant quantities should not need to
be checked unless a leak is suspected.
Driving on hilly or sloping terrain
When driving on a hill, avoid driving crosswise or turning on steep
slopes. You could lose traction and slip sideways. Drive straight up,
straight down or avoid the hill completely. Know the conditions on the
other side of a hill before driving over the crest.
When climbing a steep hill, start in a lower gear rather than downshifting
to a lower gear from a higher gear once the ascent has started. This
reduces strain on the engine and the possibility of stalling.
When descending a steep hill, avoid sudden braking. Rapid pumping of
the brake pedal will help slow the vehicle and still maintain steering
control.
When speed control is on and you are driving uphill, your vehicle speed
may drop considerably, especially if you are carrying a heavy load.
If vehicle speed drops more than 16 km/h (10 mph), the speed control
will cancel automatically. Resume speed with accelerator pedal.
78
Page 79

Driving
If speed control cancels after climbing the hill, reset speed by pressing
and holding the SET ACCEL button to resume speeds over 50 km/h
(30 mph).
Automatic transmissions may shift frequently while driving up steep
grades. Eliminate frequent shifting by shifting out of
D (Drive).
Driving on snow and ice
A 4WD vehicle has advantages over 2WD vehicles in snow and ice but
can skid like any other vehicle.
Avoid sudden applications of power and quick changes of direction on
snow and ice. Apply the accelerator slowly and steadily when starting
from a full stop.
When braking, apply the brakes as you normally would. In order to allow
the anti-lock brake system (ABS) to operate properly, keep steady
pressure on the brake pedal.
Allow more stopping distance and drive slower than usual. Consider
using one of the lower gears.
TRACTION-LOK AXLE (IF EQUIPPED)
This axle provides added traction on slippery surfaces, particularly when
one wheel is on a poor traction surface. Under normal conditions, the
Traction-Lok axle functions like a standard rear axle.
Extended use of other than the manufacturer’s specified size tires on a
Traction-Lok rear axle could result in a permanent reduction in
effectiveness. This loss of effectiveness does not affect normal driving
and should not be noticeable to the driver.
(Overdrive) into
To avoid injury, never run the engine with one wheel off the
ground, such as when changing a tire.
VEHICLE LOADING
Before loading a vehicle, familiarize yourself with the following terms:
• Base Curb Weight : Weight of the vehicle including any standard
equipment, fluids, lubricants, etc. It does not include passengers or
aftermarket equipment.
79
Page 80

Driving
• Payload : Combined maximum allowable weight of cargo, passengers
and optional equipment. The payload equals the gross vehicle weight
rating minus base curb weight.
• GVW (Gross Vehicle Weight) : Base curb weight plus payload
weight. The GVW is not a limit or a specification.
• GVWR (Gross Vehicle Weight Rating) : Maximum total weight of
the base vehicle, passengers, optional equipment and cargo. The
GVWR is specific to each vehicle and is listed on the Safety
Compliance Label on the driver’s door pillar.
• GAWR (Gross Axle Weight Rating) : Carrying capacity for each
axle system. The GAWR is specific to each vehicle and is listed on the
Safety Compliance Label on the driver’s door pillar.
• GCWR (Gross Combined Weight Rating) : Maximum combined
weight of towing vehicle (including passengers and cargo) and the
trailer. The GCWR indicates the maximum loaded weight that the
vehicle is allowed to tow.
• Maximum Trailer Weight Rating : Maximum weight of a trailer the
vehicle is permitted to tow. The maximum trailer weight rating is
determined by subtracting the vehicle curb weight for each
engine/transmission combination, any required option weight for trailer
towing and the weight of the driver from the GCWR for the towing
vehicle.
• Maximum Trailer Weight : maximum weight of a trailer the loaded
vehicle (including passengers and cargo) is permitted to tow. It is
determined by subtracting the weight of the loaded trailer towing
vehicle from the GCWR for the towing vehicle.
• Trailer Weight Range : Specified weight range that the trailer must
fall within that ranges from zero to the maximum trailer weight rating.
Remember to figure in the tongue load of your loaded trailer when
figuring the total weight.
Do not exceed the GVWR or the GAWR specified on the Safety
Compliance Certification Label.
Do not use replacement tires with lower weight capacities than the
originals because they may lower the vehicle’s GVWR and GAWR
limitations. Replacement tires with a higher weight limit than the
originals do not increase the GVWR and GAWR limitations.
80
Page 81

Driving
Calculating the load your vehicle can carry/tow
1. Use the Safety Compliance Certification Label to find the axle code
number and engine type for your vehicle.
2. Use the appropriate maximum gross combined weight rating (GCWR)
chart to find the maximum GCWR for your type engine and rear axle
ratio.
3. Weigh your vehicle as you customarily operate the vehicle without
cargo. To obtain correct weights, try taking your vehicle to a shipping
company or an inspection station for trucks.
4. Subtract your loaded vehicle weight from the maximum GCWR on the
following charts. This is the maximum trailer weight your vehicle can tow
and must fall below the maximum shown under maximum trailer weight
on the chart.
DRIVING THROUGH WATER
Do not drive quickly through standing water, especially if the depth is
unknown. Traction or brake capability may be limited and if the ignition
system gets wet, your engine may stall. Water may also enter your
engine’s air intake and severely damage your engine.
If driving through deep or standing water is unavoidable, proceed very
slowly. Never drive through water that is higher than the bottom of the
hubs (truck)/wheel rims (car).
Once through the water, always try the brakes. Wet brakes do not stop
the vehicle as effectively as dry brakes. Drying can be improved by
moving your vehicle slowly while applying light pressure on the brake
pedal.
TRAILER TOWING
Your vehicle may tow a class I, II or III trailer provided the maximum
trailer weight is less than or equal to the maximum trailer weight listed
for your engine and rear axle ratio on the following charts.
Your vehicle’s load capacity is designated by weight, not by volume, so
you cannot necessarily use all available space when loading a vehicle.
Towing a trailer places an additional load on your vehicle’s engine,
transmission, axle, brakes, tires and suspension. Inspect these
components carefully after any towing operation.
81
Page 82

Driving
Trailer towing table (4x2 manual transmission)
Engine Rear
axle
ratio
2.5L 3.45 Not recommended for trailer towing
2.5L 3.73 2 177
3.0L 3.45 2 267
3.0L 3.73 2 721
4.0L 3.08 2 267
4.0L 3.55 3 175 (7 000) 0-1 651 (0-3 640) 4.64 (50)
Regular Cab 4x2 (Splash or Special Suspension)
2.5L 3.73 2 177
3.0L 3.73 2 449
4.0L 3.08 2 267
4.0L 3.55 2 495
2.5L 3.73 2 177
3.0L 3.45 2 267
3.0L 3.73 2 271 (6 000) 0-1 133 (0-2 500) 4.64 (50)
4.0L 3.08 2 267
4.0L 3.55 3 175 (7 000) 0-1 542 (0-3 400) 4.64 (50)
Maximum
GCWR-kg
(lbs.)
Regular Cab 4x2
(4 800)
(5 000)
(6 000)
(5 000)
(4 800)
(5 400)
(5 000)
(5 500)
(4 800)
(5 000)
(5 000)
Maximum
trailer
weight-kg (lbs.)
(0-maximum)
0-717
(0-1 580)
0-789
(0-1 740)
0-1 225
(0-2 700)
0-753
(0-1 660)
0-680
(0-1 500)
0-907
(0-2 000)*
0-717
(0-1 580)
0-907
(0-2 000)*
SuperCab 4x2
0-626
(0-1 380)
0-698
(0-1 540)
0-635
(0-1 400)
Maximum frontal
area of trailer-m
(ft2)
Equal to frontal
area of base vehicle
Equal to frontal
area of base vehicle
4.64 (50)
Equal to frontal
area of base vehicle
Equal to frontal
area of base vehicle
Equal to frontal
area of base vehicle
Equal to frontal
area of base vehicle
Equal to frontal
area of base vehicle
Equal to frontal
area of base vehicle
Equal to frontal
area of base vehicle
Equal to frontal
area of base vehicle
2
82
Page 83

Driving
Trailer towing table (4x2 manual transmission)
SuperCab 4x2 (Splash or Special Suspension)
3.0L 3.73 2 540
(5 600)
4.0L 3.08 2 267
(5 000)
4.0L 3.55 2 540
(5 600)
*Optional payload is not available on 4x2 Splash or Special Suspension,
therefore maximum trailer weight is 907 kg. (2 000 lbs.).
For high altitude operation, reduce GCW by 2% per 300 meters
(1 000 ft.) elevation.
For definition of terms used in this table see Vehicle Loading earlier
in this chapter.
To determine maximum trailer weight designed for your particular
vehicle, see Calculating the load earlier in this chapter.
Maximum trailer weight is shown. The combined weight of the
completed towing vehicle (including hitch, passengers and cargo) and
the loaded trailer must not exceed the Gross Combined Weight Rating
(GCWR).
0-907
(0-2 000)*
0-635
(0-1 400)
0-907
(0-2 000)*
Equal to frontal
area of base vehicle
Equal to frontal
area of base vehicle
Equal to frontal
area of base vehicle
Trailer tow table (4x4 manual transmission)
Engine Rear
axle
ratio
Maximum
GCWR-kg
(lbs.)
Maximum
trailer
weight-kg (lbs.)
Maximum
frontal area of
trailer-m
2
Regular Cab
3.0L 3.73 2 721 (6 000) 0-1 080 (0-2 380) Equal to frontal
area of base
vehicle.
4.0L 3.27 2 721 (6 000) 0-907 (0-2 000) Equal to frontal
area of base
vehicle.
4.0L 3.73 3 175 (7 000) 0-1 515 (0-3 340) Equal to frontal
area of base
vehicle.
(ft2)
83
Page 84

Driving
Trailer tow table (4x4 manual transmission)
Regular Cab (Splash)
3.0L 3.73 2 721 (6 000) 0-1 070 (0-2 360) 4.64 (50)
4.0L 3.27 2 721 (6 000) 0-907 (0-2 000) 4.64 (50)
4.0L 3.73 3 175 (7 000) 0-1 497 (0-3 300) 4.64 (50)
SuperCab
3.0L 3.73 2 721 (6 000) 0-1 007 (0-2 220) 4.64 (50)
4.0L 3.27 2 721 (6 000) 0-907 (0-2 000) 4.64 (50)
4.0L 3.73 3 175 (7 000) 0-1 442 (0-3 180) 4.64 (50)
SuperCab (Splash)
3.0L 3.73 2 721 (6 000) 0-998 (0-2 200) 4.64 (50)
4.0L 3.27 2 721 (6 000) 0-907 (0-2 000) 4.64 (50)
4.0L 3.73 3 175 (7 000) 0-1 424 (0-3 140) 4.64 (50)
For high altitude operation, reduce GCW by 2% per 300 meters
(1 000 ft.) of elevation.
For definition of terms used in this table, see Vehicle loading earlier
in this chapter.
To determine maximum trailer weight designed for your vehicle, see
Calculating the load earlier in this chapter.
Maximum trailer weight is shown. The combined weight of the
completed towing vehicle (including hitch, passengers and cargo) and
the loaded trailer must not exceed the Gross Combined Weight Rating
(GCWR).
Trailer towing table (4x2 automatic transmission)
Engine Rear
axle
ratio
Maximum
GCWR-kg
(lbs.)
Maximum trailer
weight-kg (lbs.)
(0-maximum)
Maximum frontal
area of trailer-m
(ft2)
Regular Cab 4x2
2.5L 4.10 2 494 (5 500) 0-1 007 (2 220) Equal to frontal
area of base vehicle
3.0L 3.45 3 175 (7 000) 0-1 660 (0-3 660) 4.64 (50)
3.0L 3.73 3 401 (7 500) 0-1 814 (0-4 000) 4.64 (50)
4.0L 3.08 2 721 (6 000) 0-1 179 (0-2 600) 4.64 (50)
4.0L 3.55 4 309 (9 500) 0-2 721 (0-6 000) 4.64 (50)
84
2
Page 85

Driving
Trailer towing table (4x2 automatic transmission)
Regular Cab 4x2 (Splash or Special Suspension)
2.5L 3.73 2 449 (5 400) 0-907 (0-2 000)* Equal to frontal
area of base vehicle
3.0L 3.73 2 449 (5 400) 0-907 (0-2 000)* Equal to frontal
area of base vehicle
4.0L 3.08 2 495 (5 500) 0-907 (0-2 000)* Equal to frontal
area of base vehicle
4.0L 3.55 2 495 (5 500) 0-907 (0-2 000)* Equal to frontal
area of base vehicle
SuperCab 4x2
3.0L 3.73 3 401 (7 500) 0-1 796 (0-3 960) 4.64 (50)
4.0L 3.08 2 721 (6 000) 0-1 080 (0-2 380) 4.64 (50)
4.0L 3.55 4 309 (9 500) 0-2 676 (0-5 900) 4.64 (50)
SuperCab 4x2 (Splash or Special Suspension)
3.0L 3.73 2 540 (5 600) 0-907 (0-2 000)* Equal to frontal
area of base vehicle
4.0L 3.08 2 586 (5 700) 0-907 (0-2 000)* Equal to frontal
area of base vehicle
4.0L 3.55 2 586 (5 700) 0-907 (0-2 000) Equal to frontal
area of base vehicle
*Optional payload is not available on 4x2 Splash or Special Suspension,
therefore maximum trailer weight is 907 kg. (2 000 lbs.).
For high altitude operation, reduce GCW by 2% per 300 meters
(1 000 ft.) elevation.
For definition of terms used in this table see Vehicle Loading earlier
in this chapter.
To determine maximum trailer weight designed for your particular
vehicle, see Calculating the load earlier in this chapter.
Maximum trailer weight is shown. The combined weight of the
completed towing vehicle (including hitch, passengers and cargo) and
the loaded trailer must not exceed the Gross Combined Weight Rating
(GCWR).
85
Page 86

Driving
Trailer tow table (4x4 automatic transmission)
Engine Rear
axle
ratio
3.0L 3.73 3 401 (7 500) 0-1 741 (0-3 840) 4.64 (50)
3.0L 4.10 3 628 (8 000) 0-1 969 (0-4 340) 4.64 (50)
4.0L 3.27 3 401 (7 500) 0-1 724 (0-3 800) 4.64 (50)
4.0L 3.73 4 309 (9 500) 0-2 631 (0-5 800) 4.64 (50)
3.0L 3.73 3 401 (7 500) 0-1 733 (0-3 820) 4.64 (50)
3.0L 4.10 3 628 (8 000) 0-1 960 (0-4 320) 4.64 (50)
4.0L 3.27 3 401 (7 500) 0-1 706 (0-3 760) 4.64 (50)
4.0L 3.73 4 309 (9 500) 0-2 613 (0-5 760) 4.64 (50)
3.0L 3.73 3 401 (7 500) 0-1 669 (0-3 680) 4.64 (50)
3.0L 4.10 3 628 (8 000) 0-1 896 (0-4 180) 4.64 (50)
4.0L 3.27 3 401 (7 500) 0-1 651 (3 640) 4.64 (50)
4.0L 3.73 4 309 (9 500) 0-2 558 (0-5 640) 4.64 (50)
3.0L 3.73 3 401 (7 500) 0-1 660 (0-3 660) 4.64 (50)
3.0L 4.10 3 628 (8 000) 0-1 887 (0-4 160) 4.64 (50)
4.0L 3.27 3 401 (7 500) 0-1 633 (0-3 600) 4.64 (50)
4.0L 3.73 4 309 (9 500) 0-2 540 (0-5 600) 4.64 (50)
For high altitude operation, reduce GCW by 2% per 300 meters
(1 000 ft.) of elevation.
For definition of terms used in this table, see Vehicle loading earlier
in this chapter.
To determine maximum trailer weight designed for your vehicle, see
Calculating the load earlier in this chapter.
Maximum trailer weight is shown. The combined weight of the
completed towing vehicle (including hitch, passengers and cargo) and
the loaded trailer must not exceed the Gross Combined Weight Rating
(GCWR).
Maximum
Maximum
GCWR-kg
(lbs.)
weight-kg (lbs.)
Regular Cab
Regular Cab (Splash)
SuperCab
SuperCab (Splash)
trailer
Maximum
frontal area of
trailer-m
2
(ft2)
86
Page 87

Driving
Do not exceed the GVWR or the GAWR specified on the Safety
Compliance Certification Label.
Towing trailers beyond the maximum recommended gross trailer
weight could result in engine damage, transmission/axle damage,
structural damage, loss of control, and personal injury.
Preparing to tow
Use the proper equipment for towing a trailer, and make sure it is
properly attached to your vehicle. See your dealer or a reliable trailer
dealer if you require assistance.
Hitches
For towing trailers up to 907 kg (2 000 lb), use a weight carrying hitch
and ball which uniformly distributes the trailer tongue loads through the
underbody structure. Use a frame-mounted weight distrubuting hitch for
trailers over 907 kg (2 000 lb).
Do not install a single or multi-clamp type bumper hitch, or a hitch
which attaches to the axle. Underbody mounted hitches are acceptable if
they are installed properly. Follow the towing instructions of a reputable
rental agency.
Whenever a trailer hitch and hardware are removed, make sure all
mounting holes in the underbody are properly sealed to prevent noxious
gases or water from entering.
Safety chains
Always connect the trailer’s safety chains to the vehicle. To connect the
trailer’s safety chains, cross the chains under the trailer tongue and allow
slack for turning corners.
If you use a rental trailer, follow the instructions that the rental agency
gives to you.
Trailer brakes
Electric brakes and manual, automatic or surge-type brakes are safe if
installed properly and adjusted to the manufacturer’s specifications. The
trailer brakes must meet local and Federal regulations.
87
Page 88

Driving
Do not connect a trailer’s hydraulic brake system directly to your
vehicle’s brake system. Your vehicle may not have enough
braking power and your chances of having a collision greatly increase.
The braking system of the tow vehicle is rated for operation at the
GVWR not GCWR.
Trailer lamps
Trailer lamps are required on most towed vehicles. Make sure your
trailer lamps conform to local and Federal regulations. See your dealer or
trailer rental agency for proper instructions and equipment for hooking
up trailer lamps.
Using a step bumper
The optional step bumper is equipped with an integral hitch and requires
only a ball with a 19 mm (3/4 inch) shank diameter. The bumper has a
907 kg (2 000 lb.) trailer weight and 91 kg (200 lb.) tongue weight
capability.
The rated capcities (as shown in this guide) for trailer towing with the
factory bumper are only valid when the trailer hitch ball is installed
directly into the ball hole in the bumper. Addition of bracketry to either
lower the ball hitch position or extend the ball hitch rearward will
significantly increase the loads on the bumper and its attachments. This
can result in the failure of the bumper or the bumper attachments. Use
of any type of hitch extensions should be considered abuse.
Driving while you tow
Do not drive faster than 88 km/h (55 mph) when towing a trailer.
Speed control may shut off if you are towing on long, steep grades.
When towing a trailer:
• Use a lower gear when towing up or down steep hills. This will
eliminate excessive downshifting and upshifting for optimum fuel
economy and transmission cooling.
• Anticipate stops and brake gradually.
Servicing after towing
If you tow a trailer for long distances, your vehicle will require more
frequent service intervals. Refer to the Severe Duty Schedule in your
“Service Guide” for more information.
88
Page 89

Driving
Trailer towing tips
• Practice turning, stopping and backing up in an area before starting on
a trip to get the feel of the vehicle trailer combination. When turning,
make wider turns so the trailer wheels will clear curbs and other
obstacles.
• Allow more distance for stopping with a trailer attached.
• The trailer tongue weight should be 10–15% of the loaded trailer
weight.
• After you have traveled 80 km (50 miles), thoroughly check your
hitch, electrical connections and trailer wheel lug nuts.
• When stopped in traffic for long periods of time in hot weather, place
the gearshift in P (Park) (automatic transmissions) or 1 (First)
(manual transmissions) and increase idle speed. This aids engine
cooling and air conditioner efficiency.
• Vehicles with trailers should not be parked on a grade. If you must
park on a grade, place wheel chocks under the trailer’s wheels.
Launching or retrieving a boat
When backing down a ramp during boat launching or retrieval,
• Do not allow the static water level to rise above the bottom edge of
the rear bumper and
• Do not allow waves to break higher than 15 cm (six inches) above the
bottom edge of the rear bumper.
Exceeding these limits may allow water to enter critical vehicle
components, adversely affecting driveability, emissions and reliability.
If the rear axle is submerged in water, the rear axle lubricant should be
changed. Axle lubricant quantities are not to be checked unless a leak is
suspected.
Recreational towing (all wheels on the ground)
Follow these guidelines for your specific powertrain combination to tow
your vehicle with all four wheels on the ground (such as behind a
recreational vehicle).
These guidelines are designed to ensure that your transmission is not
damaged due to insufficient lubrication.
89
Page 90

Driving
2WD (automatic transmissions)
• Release the parking brake and place the transmission in N (Neutral).
• Maximum speed is 56 km/h (35 mph).
• Maximum distance is 80 km (50 miles).
If a distance of 80 km (50 miles) or a speed of 56 km/h (35 mph) must
be exceeded, you must disconnect the driveshaft. Mark the driveshaft
and axle flanges to ensure proper position when reconnecting the
driveshaft. Refer to the “Workshop Manual” for proper fastener torque
specifications.
When disconnecting/installing the driveshaft, the parking brake
must be set and the wheels blocked to ensure the vehicle does
not roll.
With the driveshaft disconnected, the maximum speed is 88 km/h
(55 mph) and there are no mileage restrictions.
See your dealer for help with disconnecting the driveshaft.
2WD (manual transmissions)
• Release the parking brake and place the transmission in the neutral
position.
• Maximum speed is 56 km/h (35 mph).
• Maximum distance is limited by towing equipment manufacturer’s
recommendation, unlimited distance.
4WD – Electronic shift transfer case
• Release the parking brake and place transmission in the neutral
position.
• Shift the transfer case to 2H (2WD high).
Both the 4WD HIGH and 4WD LOW indicator lights in the instrument
cluster will be off when the 4WD control is in 2WD.
For automatic transmissions, maximum speed is 56 km/h (35 mph)
and maximum distance is 80 km (50 miles).
• If you must exceed the distance or 80 km (50 miles) and/or speed of
56 km/h (35 mph), you must remove the rear driveshaft. Mark the
90
Page 91

Driving
driveshaft and axle flanges to ensure proper position when
reconnecting the driveshaft. Refer to the “Workshop Manual” for
proper fastener torque specifications.
When disconnecting/installing the driveshaft, the parking brake
must be set and the wheels blocked to ensure the vehicle does
not roll.
• When the driveshaft is disconnected, the maximum speed is 88 km/h
(55 mph) and the distance is unlimited.
• If you must exceed the distance or 80 km (50 miles) and/or speed of
56 km/h (35 mph), you must remove the rear driveshaft. Mark the
driveshaft and axle flanges to ensure proper position when
reconnecting the driveshaft. Refer to the “Workshop Manual” for
proper fastener torque specifications.
For manual transmissions, maximum speed is 88 km/h (55 mph) and
distance is unlimited.
Limited vehicle operation, such as driving the vehicle at a campsite, can
be accomplished with the rear driveshaft removed by using the front
drive to propel the vehicle. To operate the vehicle in this condition, you
must follow these guidelines:
• Place the transfer case in 4WD by rotating the 4WD control to 4WD
HIGH.
• Drive the vehicle only on good surface roads to avoid excessive loads
on the front-wheel drive system.
• Maximum speed is 56 km/h (35 mph).
• Maximum distance is 80 km (50 miles).
• Avoid quick acceleration and steep grades.
To return the vehicle to a towable condition, you must place the transfer
case in 2WD by rotating the 4WD control to 2WD. Both the 4WD HIGH
and 4WD LOW indicator lights in the instrument cluster will be off when
the 4WD control is in 2WD.
In addition, it is recommended that you follow the instruction provided
by the manufacturer of the towing apparatus.
91
Page 92

Driving
CAMPER BODIES
Your Ranger Pickup is not recommended for slide–in camper bodies.
FUEL CONSUMPTION
Fuel economy can be improved by avoiding:
• lack of regular, scheduled maintenance.
• excessive speed.
• rapid acceleration.
• extended idle.
92
Page 93

Roadside emergencies
HAZARD LIGHTS CONTROL
Use only in an emergency to warn traffic of vehicle breakdown,
approaching danger, etc. The hazard flashers can be operated when the
ignition is off.
• The hazard lights control is
located on top of the steering
column.
• Depress hazard lights control to
activate all hazard flashers
simultaneously.
• Depress control again to turn the
flashers off.
FUEL PUMP SHUT-OFF SWITCH (GASOLINE ENGINES ONLY)
If the engine cranks but does not start after a collision, the fuel pump
shut-off switch may have been activated. A “Fuel Reset” indicator light
may illuminate in the instrument cluster. The shut-off switch is a device
intended to stop the electric fuel pump when your vehicle has been
involved in a substantial jolt.
1. Turn the ignition to the OFF position.
2. Check the fuel system for leaks.
3. If no fuel leak is apparent, reset the fuel pump shut-off switch by
pushing in the button on the switch.
4. Turn the ignition to the ON position. Pause for a few seconds and
return the key to the OFF position.
5. Make a further check for leaks in the fuel system.
93
Page 94

Roadside emergencies
The fuel pump shut-off switch is
located in the passenger’s foot well,
behind the kick panel.
FUSES AND RELAYS
Fuses
If electrical components in the
vehicle are not working, a fuse may
have blown. Blown fuses are
identified by a broken wire within
the fuse. Check the appropriate
fuses before replacing any electrical
components.
15 15
Always replace a fuse with one that has the specified amperage
rating. Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating can cause
severe wire damage and could start a fire.
94
Page 95

Roadside emergencies
Standard fuse amperage rating and color
Fuse rating Color
5 amp Tan
7.5 amp Brown
10 amp Red
15 amp Light blue
20 amp Yellow
20 amp fuse link Light blue
25 amp Natural
30 amp Light green
30 amp fuse link Pink
40 amp fuse link Green
50 amp fuse link Red
60 amp fuse link Yellow
80 amp fuse link Black
100 amp fuse link Dark blue
Passenger compartment fuse panel
The fuse panel is located on the left
hand side of the instrument panel
facing the driver’s side door. Pull the
panel cover outward to access the
fuses.
To remove a fuse use the fuse puller tool provided on the fuse panel
cover.
95
Page 96

Roadside emergencies
36
1234
5678
9 101112
13 14 15 16
17 18 19 20
21 22 23 24
27 28
25 26
29 30
35
32
31
34
33
The fuses are coded as follows:
Fuse/
Relay
Location
Fuse
Amp
Rating
Description
1 7.5A Power Mirror Switch
2 7.5A Blower Motor Relay, PAD Module, Air Bag
Diagnostic Monitor
3 7.5A Left Stop/Turn Trailer Tow Connector
4 10A Left Headlamp
5 10A Data Link Connector (DLC)
6 - NOT USED
7 7.5A Right Stop/Turn Trailer Tow Connector
8 10A Right Headlamp, Fog Lamp Relay
9 7.5A Brake Pedal Position Switch
10 7.5A Speed Control Servo/Amplifier Assembly, Generic
Electronic Module (GEM), Shift Lock Actuator,
Blend Door Actuator, A/C-Heater Assembly, Turn
Signals
96
Page 97

Roadside emergencies
Fuse/
Relay
Location
11 7.5A Instrument Cluster, Daytime Running Lights
12 - NOT USED
13 20A Brake Pedal Position Switch
14 20A or
15 7.5A Instrument Cluster
16 30A Windshield Wiper Motor, Wiper Hi-Lo Relay,
17 25A Cigar Lighter
18 15A Driver’s Unlock Relay, All-Unlock Relay, All-Lock
19 25A PCM Power Diode
20 7.5A RAP Module, Generic Electronic Module (GEM),
21 15A Flasher (Hazard)
22 20A Auxiliary Power Socket
23 — Not Used
24 7.5A Clutch Pedal Position (CPP) switch, Starter
25 7.5A Generic Electronic Module (GEM), Instrument
26 10A Battery Saver Relay, Electronic Shift Relay,
27 15A Electric Shift, Backup Lamps, Daytime Running
28 7.5A Generic Electronic Module (GEM), Radio
Fuse
Amp
Rating
10A
Description
(DRL), RABS Resistor
20A: If equipped with Rear Anti-Lock Brake
System (RABS) Module. 10A: If equipped with
4 Wheel Anti-Lock Brake System (4WABS)
Module, 4WABS Main Relay
Wiper Run/Park Relay
Relay
Radio
Interrupt Relay, Anti-Theft
Cluster
Interior Lamp Relay, Power Window Relay,
Electronic Shift Control Module, Dome/Map
Lamp, GEM
Lamps (DRL), Transmission Control Switch
97
Page 98

Roadside emergencies
Fuse/
Relay
Location
29 15A Radio
30 15A Park Lamp/Trailer Tow Relay
31 — Not Used
32 — Not Used
33 15A Headlamps, Daytime Running Lamps (DRL)
34 — Not Used
35 10A RABS Test Connector
36 — Not Used
Power distribution box
The power distribution box is
located in the engine compartment
near the battery. The power
distribution box contains
high-current fuses that protect your
vehicle’s main electrical systems
from overloads.
Fuse
Amp
Rating
Description
Module, Instrument Cluster
98
Always disconnect the battery before servicing high current
fuses.
Always replace the cover to the Power Distribution Box before
reconnecting the battery or refilling fluid reservoirs.
Page 99

Roadside emergencies
175
MEGAFUSE
11
13
23
1415 13
12
14
54321
12 11 10 9
8765
4321
The high-current fuses are coded as follows:
1
211
4
6
7
5
9
10
8
Fuse/Relay
Location
Fuse Amp
Rating
Description
1 50A** I/P Fuse Panel
2 40A** Blower Motor Relay
3 50A** 4 Wheel Anti-Lock Brake System (4WABS)
Module
4 20A** Power Windows
5 50A Ignition Switch, Starter Relay
1 10A* A/C Relay
2 20A* Auxiliary Power Point
3 20A* Electronic Shift Relay and Electronic Shift
Control Module
4 15A* Fog Lamp and Daytime Running Lamps
5 10A* Air Bag Diagnostic Monitor
6 10A* Powertrain Control Module
7 30A* 4 Wheel Anti-lock Brake System (4WABS)
Module
99
Page 100

Roadside emergencies
Fuse/Relay
Location
8 30A* PCM Relay
9 20A* Fuel Pump Relay and RAP Module
10 15A* Horn Relay
11 15A* Parklamps Relay and Main Light Switch
12 30A* Main Light Switch and Multifunction Switch
13 15A* Heated Oxygen Sensor, EGR Vacuum
14 30A* Generator Voltage Regulator
15 - NOT USED
1 - Wiper Park Relay
2 - A/C Relay
3 - Wiper Hi/Lo Relay
4 - PCM Power Relay
5 - Fuel Pump Relay
6 - Starter Relay
7 - Horn Relay
8 - Washer Pump Relay
9 - Blower Motor Relay
10 - Foglamp Relay
11 - Not Used
12 - Not Used
13 - Park Lamp/Trailer Tow Relay
14 - Not Used
1 - RABS Resistor
1 - RABS Diode
2 - Electronic Engine Controls Diode
* Mini Fuses ** Maxi Fuses
Fuse Amp
Rating
Description
Regulator, EVR Solenoid, Camshaft Position
Sensor (CMP), Canister Vent Solenoid
100
 Loading...
Loading...