Page 1

A6700sc/A6750sc
User’s Manual
This document is controlled to FLIR Technology Level 2. The information contained in this document
pertains to a dual use product controlled for export by the Export Administration Regulations
(EAR). Diversion contrary to US law is prohibited. US Department of Commerce authorization is not
required prior to export or transfer to foreign persons or parties unless otherwise prohibited.
Document Number: 29249-000
Version: 5
Issue Date: February 2, 2015
Page 2

FLIR Systems, Inc.
9 Townsend West,
Nashua, NH 03063
Support: 1-800-GO-INFR A (800-464-6372)
http://flir.custhelp.com
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
Service: 1-866-FLIR-911
www.flir.com
©2015 FLIR Systems, Inc.
2
Page 3

Table of Contents
1 REVISION HISTORY ...................................................................................................................................... 6
2 INTRODUCTION ............................................................................................................................................. 7
2.1 Camera System Components .......................................................................................... 7
2.2 System Overview............................................................................................................. 7
2.3 Key features of the A6700sc/A6750sc cameras .............................................................. 8
3 WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS ...................................................................................................................... 10
4 INSTALLATION ............................................................................................................................................ 11
4.1 Basic Connections ......................................................................................................... 11
4.1.1 Power ......................................................................................................................................... 12
4.1.2 Analog Video .............................................................................................................................. 12
4.1.3 GigE Digital Vi deo ...................................................................................................................... 12
5 CAMERA CONTROLLER ............................................................................................................................. 13
5.1 ResearchIR Mini Controller ............................................................................................ 13
5.1.1 Single Preset Mode .................................................................................................................... 13
5.1.2 Superframing Mode [A675xsc only] ........................................................................................... 13
5.2 Menu Bar ....................................................................................................................... 14
5.2.1 Tools Menu ................................................................................................................................. 14
Advanced Time Controls .................................................................................................................................... 14
5.2.2 Help Menu .................................................................................................................................. 15
5.2.3 Status Page ................................................................................................................................ 15
5.2.4 Setup Page ................................................................................................................................. 16
5.2.4.1 Setup Tab ................................................................................................................................... 16
5.2.4.2 Sync Tab [A6750sc only] ............................................................................................................ 17
5.2.4.2.1 Sync Mode .......................................................................................................................................... 17
5.2.4.2.2 Sync Source ........................................................................................................................................ 20
5.2.4.2.3 Sync Options ....................................................................................................................................... 21
5.2.4.2.4 Sync Out ............................................................................................................................................. 22
5.2.5 Correction Page .......................................................................................................................... 22
NUC Information ................................................................................................................................................. 24
Manage NUCs .................................................................................................................................................... 24
Load NUC Options .............................................................................................................................................. 24
Performing a NUC .............................................................................................................................................. 25
What is a Non-Uniformity Correction (NUC)? ..................................................................................................... 27
5.2.5.1.1 One-Point Correction Process............................................................................................................. 28
5.2.5.1.2 Two-Point Correction Process............................................................................................................. 28
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
3
Page 4

5.2.5.1.3 Offset Update ...................................................................................................................................... 29
5.2.5.1.4 Bad Pixel Correction ........................................................................................................................... 29
5.2.6 Video Page ................................................................................................................................. 31
6 INTERFACES ................................................................................................................................................ 34
6.1 Mechanical (dimensions in inches) ................................................................................ 34
6.1.1 Status Lights ............................................................................................................................... 36
6.1.2 Power Interface .......................................................................................................................... 36
6.1.3 Other Interfaces .......................................................................................................................... 37
6.1.3.1 Gigabit Ethernet .......................................................................................................................... 37
6.1.3.2 Sync In ........................................................................................................................................ 37
6.1.3.3 Video .......................................................................................................................................... 37
6.1.3.4 AUX Connector [A6750sc only] .................................................................................................. 37
7 SPECIFICATIONS ........................................................................................................................................ 39
7.1 Interface ........................................................................................................................ 39
7.2 Windowing Capacity ...................................................................................................... 39
7.3 Acquisition Modes and Features .................................................................................... 39
7.4 Analog Video ................................................................................................................. 40
7.5 Performance Characteristics ......................................................................................... 40
7.6 Non Uniformity Correction ............................................................................................. 41
7.7 Detector/FPA ................................................................................................................. 41
7.8 General Characteristics ................................................................................................. 42
8 MAINTENANCE ............................................................................................................................................ 43
8.1 Camera and Lens Cleaning ........................................................................................... 43
8.1.1 Camera Body, Cables and Accessories ..................................................................................... 43
8.1.2 Lenses ........................................................................................................................................ 43
9 INFRARED PRIMER ..................................................................................................................................... 45
9.1 History of Infrared .......................................................................................................... 45
9.2 Theory of Thermography ............................................................................................... 48
9.2.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................................. 48
9.2.2 The Electromagnetic Spectrum .................................................................................................. 48
9.2.3 Blackbody Radiation ................................................................................................................... 48
Planck’s Law ....................................................................................................................................................... 49
Wien’s Displacement Law ................................................................................................................................... 50
Stefan-Boltzmann's Law ..................................................................................................................................... 51
Non-Blackbody Emitters ..................................................................................................................................... 52
9.2.4 Infrared Semi-Transparent Materials .......................................................................................... 54
9.3 The Measurement Formula ........................................................................................... 55
9.4 Emissivity tables ............................................................................................................ 58
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
4
Page 5

A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
5
Page 6
1 Revision History
Version
Date
Initials
Changes
2
08/27/13
RM
Added 2D drawings, corrections
1 08/26/13 RM Initial Release
3 11/21/13 RM Corrections to specifications section
4 11/05/14 RM Removed ITAR control statement.
5 02/02/15 RM Added A6750sc GigE
1 – Revision History
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
6
Page 7
2 – Introduction
2 Introduction
2.1 Camera System Components
The A6700sc infrared camera and its accessories are delivered in a box which typically contains the
items below. There may also be additional items that you have ordered such as lenses, software,
CDs, etc.
Description FLIR Part Number
A67xxsc Camera 29350-2xx
Power supply, 24V, 4A 24123-000
AC line cord 24124-000
Gigabit Ethernet Cat-6 cable, 2m length 23700-000
Bayonet mount plug 23901-000
BNC cable 26393-000
ResearchIR Max download/activation card T199013
AUX connector breakout cable [A6750sc only] 29402-500
Laboratory calibration plate 261-0005-00
Water-resistant transit case 24043-000
Documentation CD 24048-050
2.2 System Overview
The A6700sc infrared camera system has been developed by FLIR Advanced Thermal Solutions
(ATS) to meet the needs of the commercial R&D user. The camera makes use of FLIR’s advanced
ISC0403 4-channel readout integrated circuit (ROIC), mated to an Indium Antimonide (InSb) detector
to cover the midwave infrared band. The A6700sc camera utilizes a large format, 640 x 512 array
with 15μm pixel pitch.
The A6700sc is a stand-alone imaging camera that interfaces to host PC using Gigabit Ethernet. An
SDK is available, which makes it possible for t he system designer to write their own camera cont roller
and acquire image data with their own custom application.
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
7
Page 8

2.3 Key features of the A6700sc/A6750sc cameras
Fully GEV/GenICam compliant
The image stream protocol is GigE Vision 2.0 compliant and the camera is fully controllable
by GenICam.
Improved Linearity to Zero Well-Fill
Typical direct injection ROIC designs exhibit a non-linear response when the signal drops
below 10% of well-fill. The ISC0403 ROIC provides a linear response even at very low signal
levels. This results in an increased linear dynamic range, much better NUC performance at
low signal levels and makes it easier to perform a user calibration of the camera.
14-Bit Digital Image Data
The A6700sc camera system is built around high performance 14-bit A/D converters,
preserving the full dynamic range of the FPA.
Windowing Capability
Higher frame rates are available by windowing down at the Focal Plane Array (FPA) level.
The A6700sc has three available window sizes with a max frame rate of 480Hz. The
A6750sc has flexible window sizes with frame rates up to 4kHz.
2 – Introduction
Presets
Up to four presets and their associated parameters such as integration time, frame rate,
window size and window location, are available for instant selection with a single command.
Superframing [A6750sc only]
Up to four presets can be cycled continuously. This can be used in conjunction with the
Dynamic Range Extension (DRX) algorithm to provide a single movie with increased dynamic
range.
Independently Adjustable Frame Rates
Frame rate is user selectable from 0.0015 Hz up to the maximum allowed for the select ed
window size.
External Sync
The A6700sc camera provides a SYNC input that can be used to control the camera frame
rate using an external LVCMOS input (can handle 5.5V Max) .
External Trigger [A6750sc only]
An external trigger input can be used to signal ResearchIR to start rec ording or to precisely
start the image stream relative to an external event.
Multiple Video Outputs
The A6700sc camera features multiple independent and simultaneous video:
▫ Digital – Gigabit Ethernet
▫ Analog – Composite video (NTSC or PAL)
Analog Video Color Palettes
The A6700sc camera supports a selection of standard and user-defined color palettes f or th e
analog video output.
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
8
Page 9

2 – Introduction
Digital Detail Enhancement (DDE)
DDE is an analog video AGC mode that provides a significant improvement to scene detail
and contrast.
On-Camera NUCs with Auto Update
NUCs can be stored in camera memory and can be applied independently to the digital and
analog video outputs. The camera can be configured to automatically update the NUC using
the internal flag based on a change of an internal temperature sensor and/or a timer.
Standard Lens Interface
The A6700sc camera uses th e same bayonet-mount as other SCx000 series cameras.
However, even though the mount is the same, due to differences in the opto-mechanical
layout, lenses for the SC6000/4000 are not an optimal solution for the A6700sc. The SC6000
lenses will provide fairly good imagery but some vignetting in the corners may be visible. For
best performance the user should use lenses designed for the A6700sc. Lenses for the
SC8000 will not work on the A6700sc.
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
9
Page 10

3 – Warnings and Cautions
3 Warnings and Cautions
For best results and user safety, the following warnings and precautions should be followed when
handling and operating the camera.
Warnings and Cautions:
Do not open the camera body for any reason. Disassembly of the camera (including
removal of the cover) can cause permanent damage and will void the warranty.
Great care should be exercised with your camera optics. Refer to Chapter 7 for lens
cleaning.
Operating the camera outside of the specified input voltage range or the specified
operating temperature range can cause permanent damage.
The camera is not completely sealed. Avoid exposure to dust and moisture and replace
the lens cap when not in use.
Do not image extremely high intensity radiation sources, such as the sun, lasers, arc
welders, etc.
The camera is a precision optical instrument and should not be exposed to excessive
shock and/or vibration. Refer to the Chapter 6 for detailed environmental requirements.
The camera contains static-sensitive electronics and should be handled appropriately.
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
10
Page 11
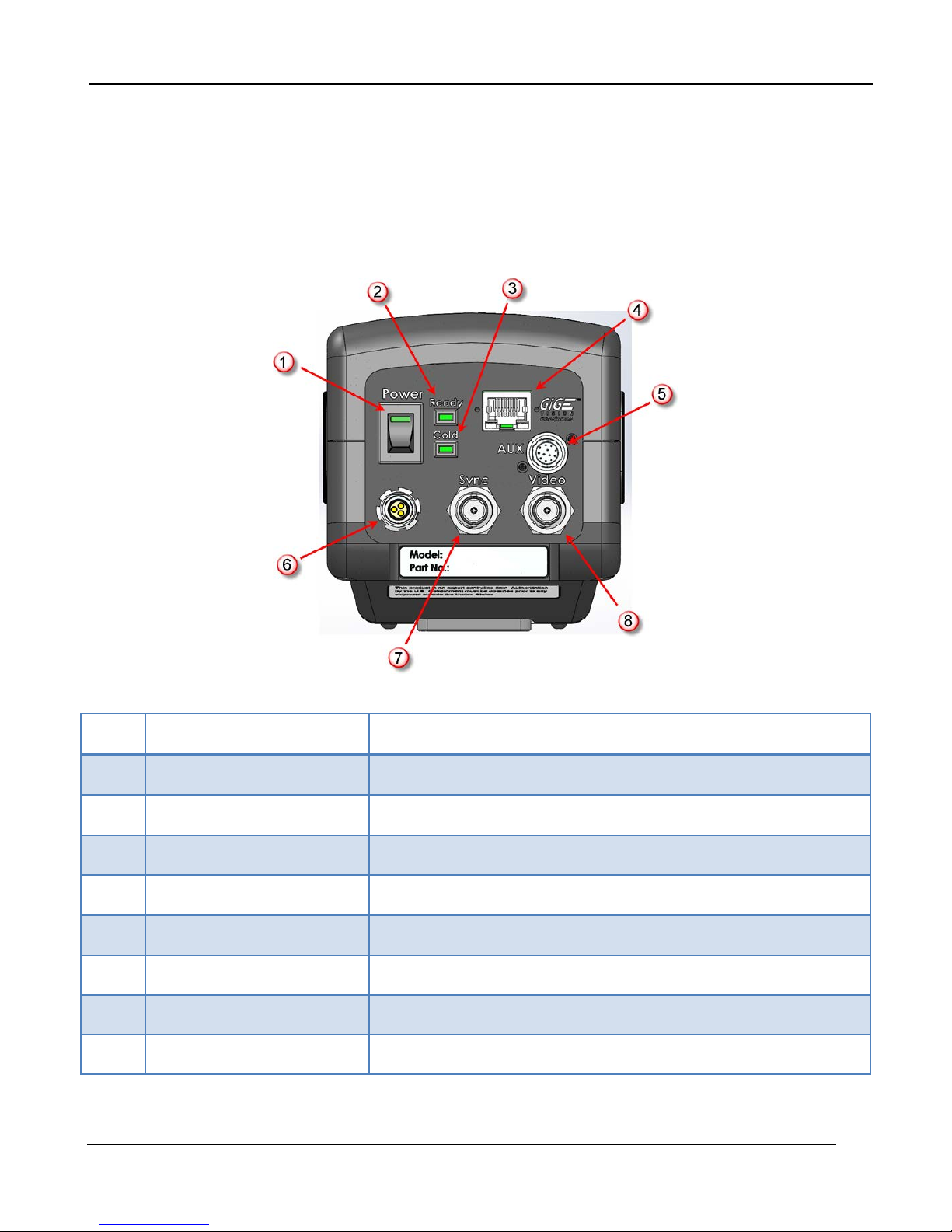
4 Installation
4.1 Basic Connections
All connections to the A6700sc are located on the Back Panel.
4 – Installation
Item Name Description
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Power Switch LED will light when power is ON
Ready Light LED will turn on when camera is booted
Cold LED LED will light when FPA temp is <80K
Gigabit Ethernet (RJ45) Connect to a PC for digital IR image data
AUX Connector A675xsc only. (See Section 6.1.3.4 for details)
DC Power Input 24VDC
Sync Input External Frame Sync
Video Out NTSC or PAL, selectable in camera controller
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
11
Page 12

4 – Installation
4.1.1 Power
Plug in the AC power supply to a standard 120V outlet. Connect the DC power cable between the
power supply and the power connector located on the rear panel of the A6700sc camera. Turn on
the imaging head by pressing the power button on the rear panel. The green power LED will
illuminate to indicate that the unit is ON.
4.1.2 Analog Video
The camera will automatically boot up into the last saved state. The boot process takes about 30
seconds. To see the Composite video on a monitor, connect the provided BNC cable from the VIDEO
port to your monitor. If you are powering up the camera for the first time, the camera should produce
a 640x480 image with Non-Unifority Correction (NUC), ba d pixel replacement enabled.
4.1.3 GigE Digital Video
If you have a PC data system running ResearchIR (or your own custom application based on the BHP
SDK) you can view the 14-bit digital video over Gigabit Ethernet.
The A6700sc has a Gigabit Ethernet interface that is GigE Vision (GEV) and GenICam compliant Use
a regular CAT5e or CAT6 Ethernet patch cable. If a crossover cable is used, the camera interface will
automatically detect and configure itself to work with this kind of cable.
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
12
Page 13
5 –Camera Controller
5 Camera Controller
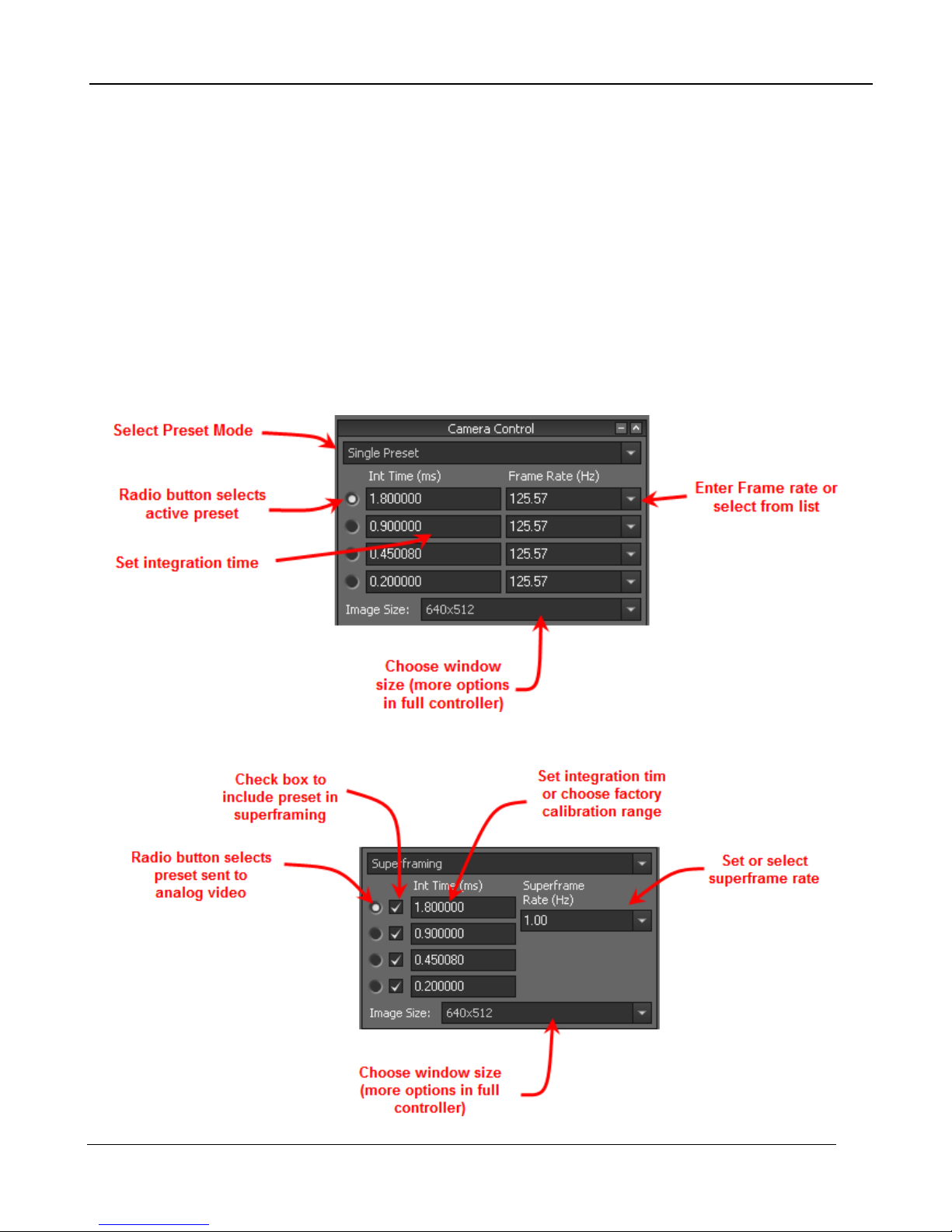
5.1 ResearchIR Mini Controller
The Camera Controller (also called the Graphical User Interface or GUI) can be accessed from within
the ResearchIR software. Once you are connected to the camera, a mini controller will be visible in
the left pane. This controller will have basic controls for the most commonly used settings, like
integration time, frame rate, preset selection, and window size. Choosing the Camera>>Control menu
option will display the full camera controller. The rest of this chapter will describe the full camera
controller features in detail.
5.1.1 Single Preset Mode
5.1.2 Superframing Mode [A675xsc only]
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
13
Page 14
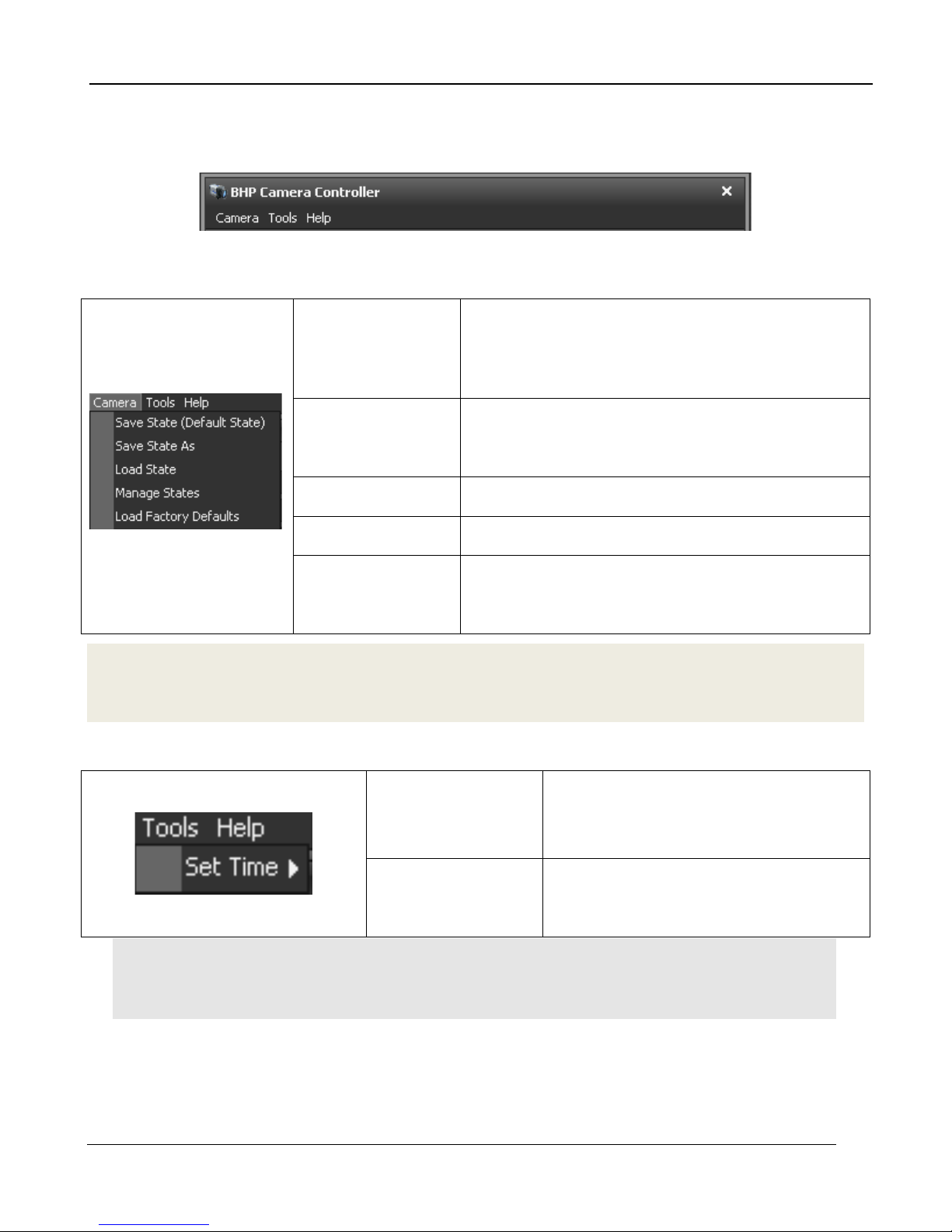
5.2 Menu Bar
The menu bar is the same for both Basic and Advanced User Modes .
Saves the camera state to the current (name). This
Save State (name)
Save State As
Load State Load a state from flash memory.
Manage States Rename or delete states from camera memory.
state will be reloaded at power up. Stored in flash
memory.
Saves the current camera state to a name chosen
by the user. State names other than (name) my be
loaded manually. Stored in flash memory
5 –Camera Controller
Load Factory
Defaults
Loads factory defaults for all camera Settings and
NUCs. The factory defaults cannot be modified by
the user.
NOTE: Camera states contain information about all configurable camera parameters. They do not
contain the NUC data, but contain the filenames of the currently loaded NUCs. These NUCs will be
reloaded with the state, however, if the NUCs are changed, deleted, or renamed, the state may not be
able to load the NUCs.
5.2.1 Tools Menu
Set Camera Time to
PC Time
NOTE: The A6700sc has two internal clocks: a Real Time Clock (RTC) and a timestamp clock. The RTC is a low
resolution clock used to keep system time. The RTC has a battery backup and will retain time while the camera is
off. The timestamp clock is a high resolution clock (1us). This clock does not have a battery backup but at power
up the timestamp clock is initialized to the current RTC time and will free-wheel until the camera is power cycled.
Advanced…
Sets the camera RTC clock to the time
from the PC clock.
Allows user to manually set the IRIG and
RTC clocks in the camera. See Section
4.2.2.1
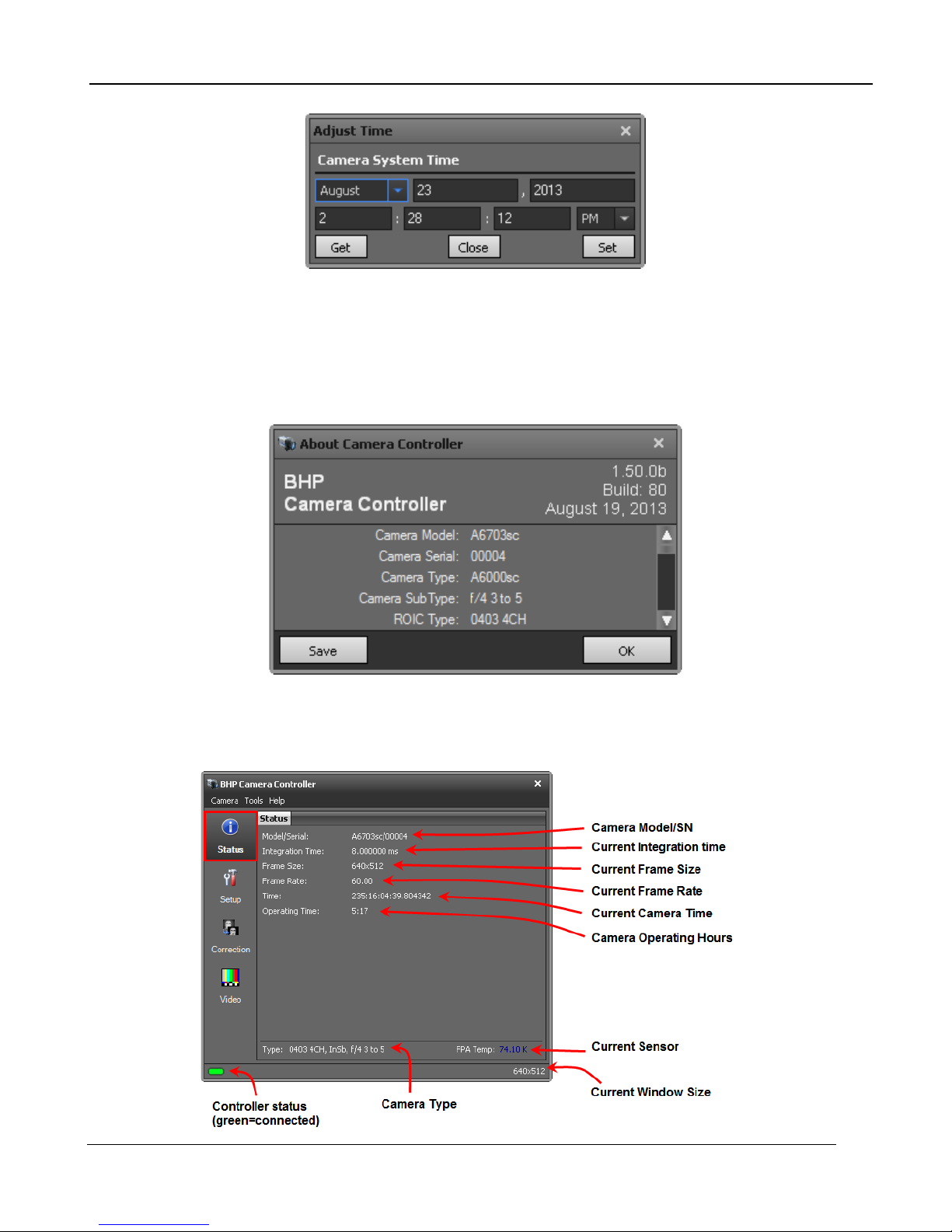
Advanced Time Controls
This dialog is accessed using the Tools>>Set Time>>Advanced menu options. This allows the user
to directly set the cameras system time. The Get button will pull time from the PC clock. The Set
button will set the camera RTC clock using the manually entered time.
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
14
Page 15
5 –Camera Controller
Figure 4-1 Advanced Time Controls
5.2.2 Help Menu
The “About” menu item shows a dialog indicating the current controller version number. If the
controller is connected to a camera a list will be displayed that shows all versions of software and
firmware in the camera. The “Save” button allows the user to create a text file with this version
information.
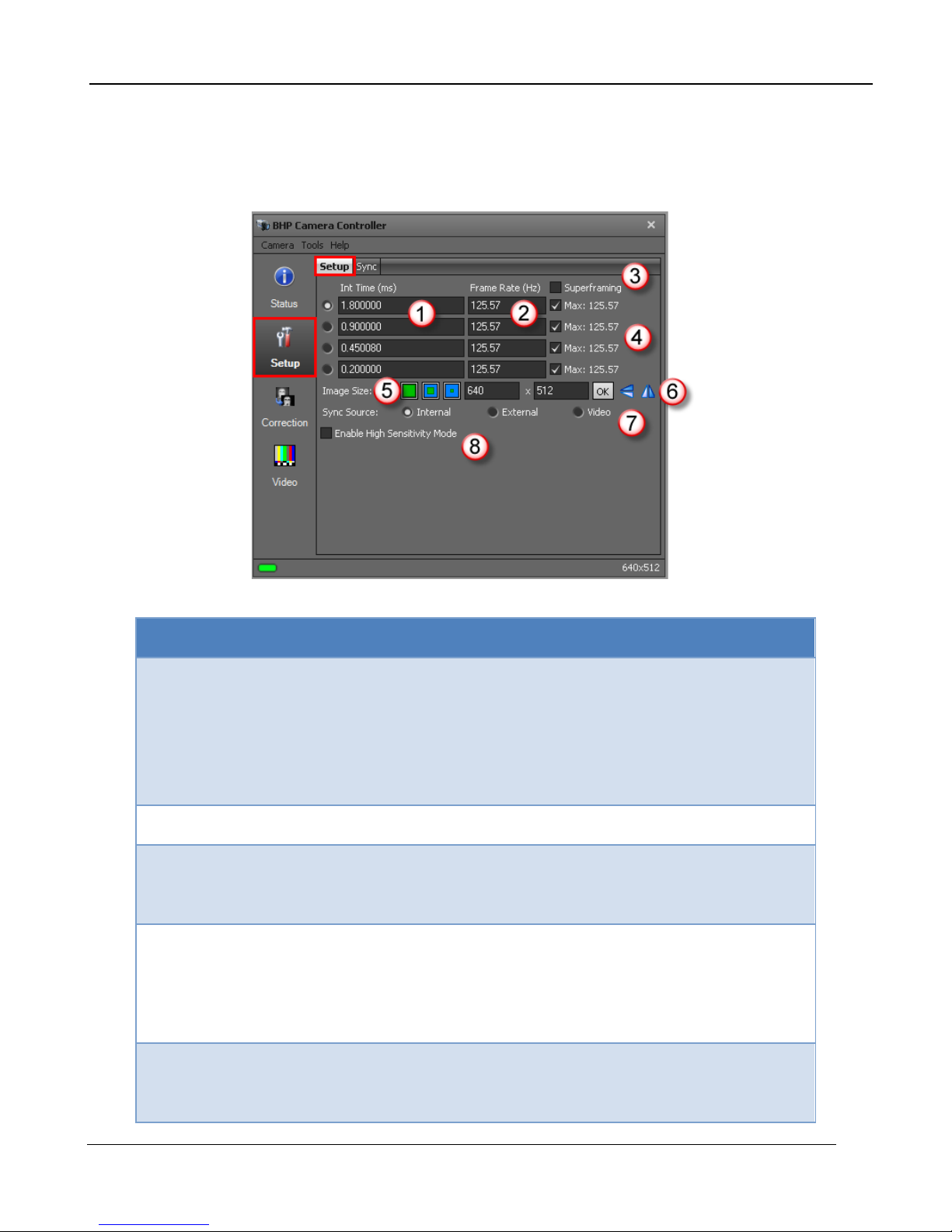
5.2.3 Status Page
The Status Page gives general information about the camera state including camera type, camera
time, integration time, frame size, and frame rate.
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
15
Page 16
5 –Camera Controller
5.2.4 Setup Page
The Setup page allows the user to set integration time, frame rate, frame size, and Sync source.
5.2.4.1 Setup Tab
Item Name Description
1
Integration Time No factory calibration: Enter desired integration
time in milliseconds.
With factory calibration: The box will have a
dropdown list with the available ranges. To
manually enter integration time scroll to bottom of
list and select “no factory calibration”.
2
3
Frame Rate Enter the desired frame rate in Hz.
Superframing
[A6750sc only]. When this is enabled the user
can then select the presets to include and set the
burst rate.
4
Max Frame Rate This indicates the max possible frame rate based
on the current window size and integration time.
Checking the box will automatically keep the
camera at max frame rate as these parameters
change.
5
Image size A6700sc: This control will be simply a dropdown
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
list with the three window size options available
(Full, ½, ¼).
16
Page 17
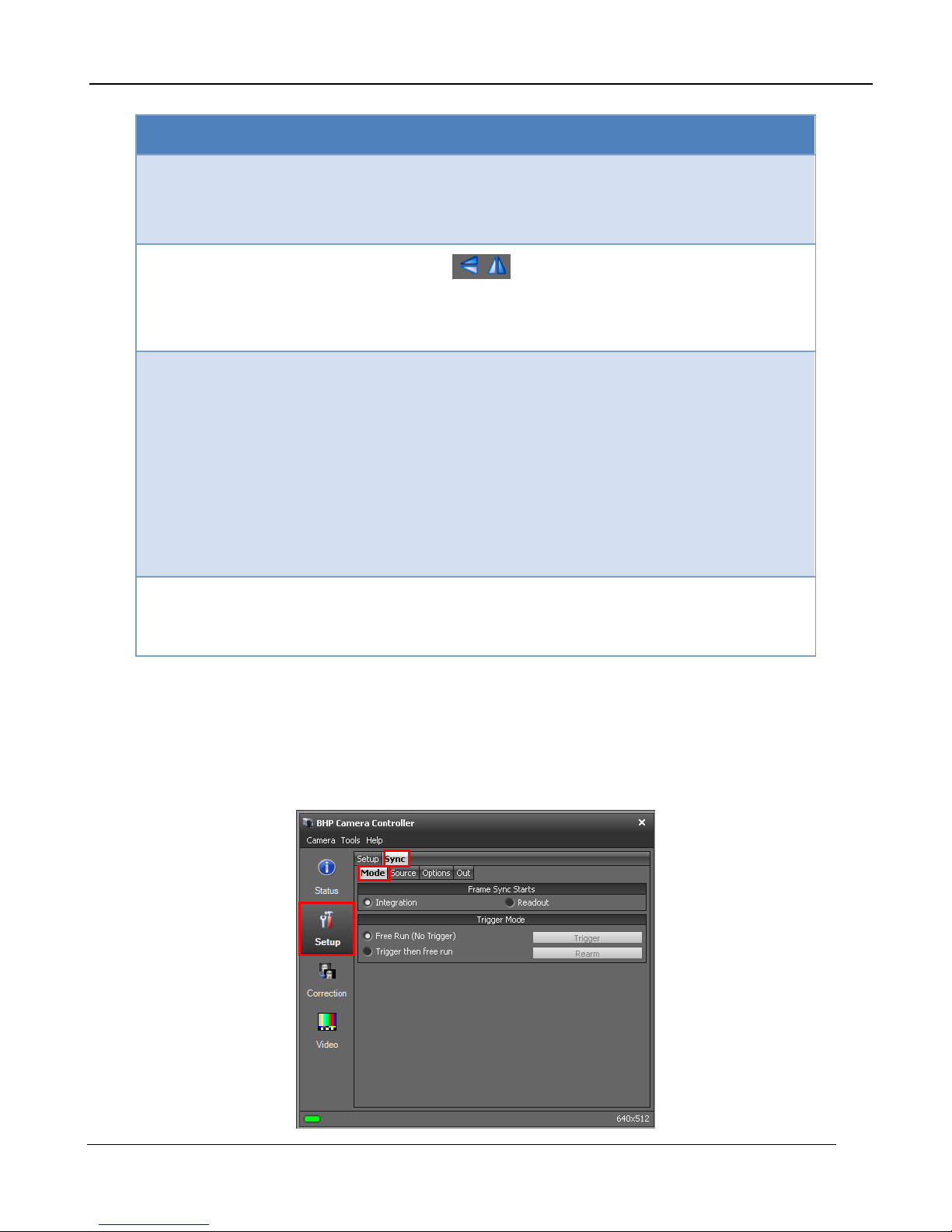
Item Name Description
A6750sc: There are buttons to select Full, ½, ¼
windows as well as boxes to enter other sizes.
Click “OK” to set a size. The box will turn red if the
size is not valid.
5 –Camera Controller
6
Image Flipping
The icons control horizontal and vertical
image flipping. With these controls, the flipping is
done in the camera so both the digital and analog
video are affected.
7
Sync Source Select internal, external, or video.
Internal: The frame sync is generated internally to
run at the frequency set by the user
External: The frame sync is generated externally
through the Sync In connect on the camer a rear
chassis.
Video: The FPA frame sync is generated from the
internal video encoder , locking the digital and
analog clocks together
8
High Sensitivity Mode
(HSM)
HSM is a FLIR-patented algorithm first introduced
in the Gas FindIR cameras that allows the user to
see small temperature changes in the scene.
5.2.4.2 Sync Tab [A6750sc only]
The sync tab allows the user to control function for Syncs, and triggers. All of these sync features
apply only to the A6750sc.
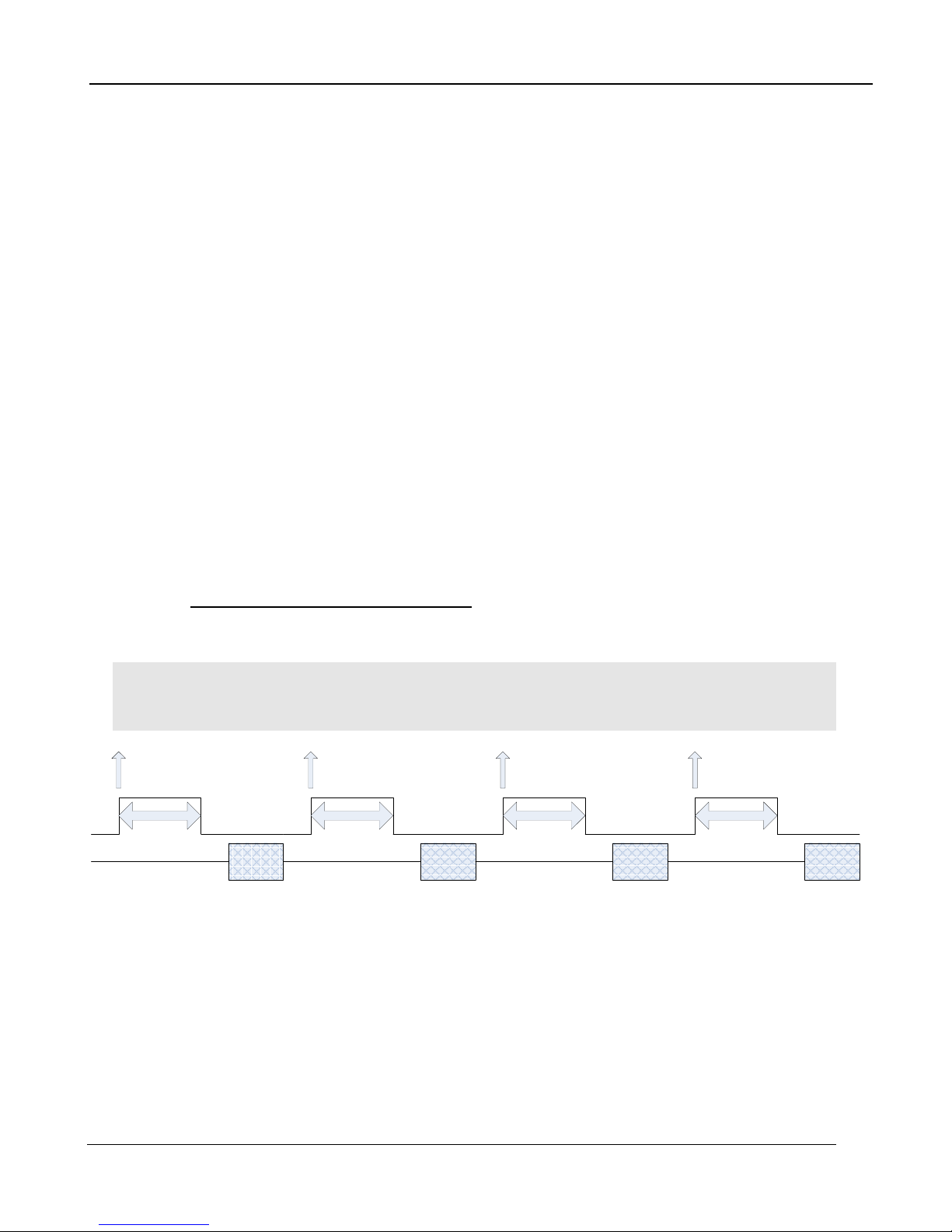
5.2.4.2.1 Sync Mode
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
17
Page 18
5 –Camera Controller
Preset 0
Data
Frame Sync
Preset 1
Data
Preset 2
Data
Preset 3
Data
Frame Sync Frame Sync Frame Sync
Preset 3
Integration
Preset 2
Integration
Preset 1
Integration
Preset 0
Integration
5.2.4.2.1.1 Frame Sync Starts
The A6750sc makes use of frame syncs and triggers to control the generation of image data. Frame
syncs control the start of individual frames whereas triggers start sequences of frames.
The generation of a frame consists of two phases: integration and data readout. Depending on the
timing between these two events, you can have two basic integration modes: Integrate Then Read
(ITR), and Integrate While Read (IWR). In ITR, integration and data readout occur sequentially. The
complete frame time is the combined total of the integration time plus readout time. In IWR, the
integration phase of the current frame occurs during the readout phase of the previous fra me. In
other words, ITR and IWR terms refer to whether or not the camera will overlap the data readout and
integration periods. In ITR, the data is not overlapped which means lower frame rates but provides a
less noisy image. IWR can achieve much faster frame rates with a slight increase in noise. The
A6750sc does not require the user to explicitly choose whether to operate in ITR or IWR modes. The
camera will automatically select the integration mode based on the integration time, frame rate, and
frame sync mode.
The A6750sc supports two Frame Sync Modes: Frame Sync Starts Integration (FSSI), and Frame
Sync Starts Readout (FSSR). FSSI and FSSR determine which phase of the frame generation
process (integration or data readout) is synchronized to the frame sync. FSSI starts the integration
period when a frame sync occurs (i.e. “take a picture now”). The camera automatically calculates
when to start data readout. FSSR starts the data readout (for the previous frame) when a frame sync
occurs (i.e. “give me data now”). The camera automatically calculates when to start integration for the
current frame. In FSSI mode, the camera could be in either ITR or IWR mode. In FSSR mode, the
camera is always in IWR mode.
5.2.4.2.1.1.1 Frame Sync Starts Integration (FSSI)
Upon frame sync, the camera immediately integrates followed by data read out. Based on integration
time, frame size, and frame rate, the camera will automatically choose ITR or IWR mode.
NOTE: When using an external frame sync and superframing, the external frame sy nc should be set
to comply with ITR frame rate limits. If the exte rnal syn c rate is to o fast, the camera w ill ignore syncs
that come before the camera is ready
Figure 4-2: Frame Sync Starts Integration, ITR
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
18
Page 19
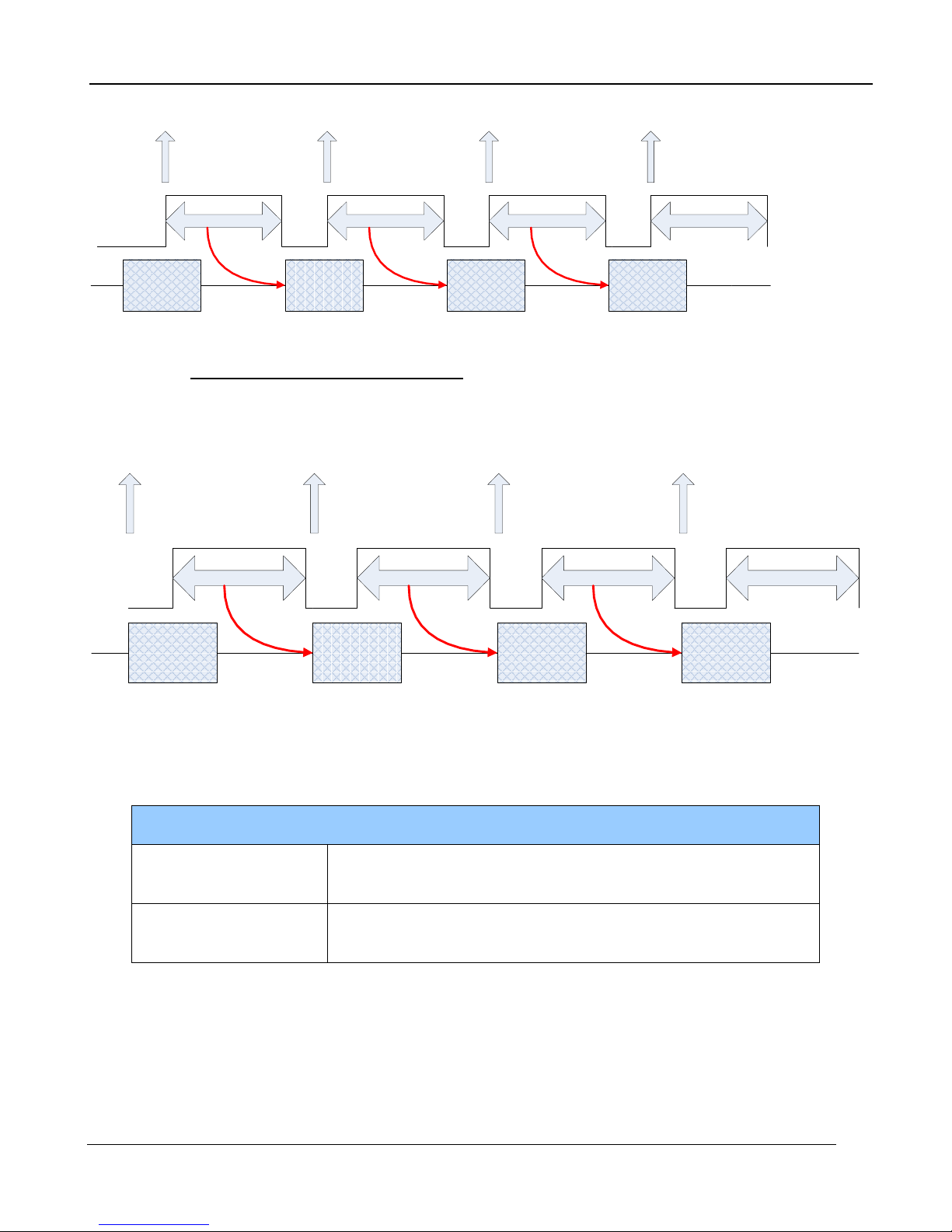
5 –Camera Controller
Frame
1 Data
Frame 1 Integration
Frame 2 Integration
Frame Sync
Frame Sync
Frame 2 Data
Frame 3 Integration
Frame Sync
Frame 3 Data
Frame 4 Integration
Frame Sync
Frame 1
Data
Frame 1 Integration
Frame 2 Integration
Frame Sync
Frame Sync
Frame 2 Data
Frame 3 Integration
Frame Sync
Frame 3 Data
Frame 4 Integration
Frame Sync
Figure 4-3: Frame Sync Starts Integration, IWR
5.2.4.2.1.1.2 Frame Sync Starts Readout (FSSR)
Upon frame sync, the camera immediately transmits the data from the previous frame. The
integration period is then placed to meet ROIC requirements. This mode always operates in IWR
mode. This mode can be used with either internal or external frame sync at full frame rates.
Figure 4-4: Frame Sync Starts Readout
5.2.4.2.1.2 Trigger Mode
When the camera is placed in a triggered mode, the image stream will stop until the trigger is
received.
Trigger Modes
Free Run (No Trigger)
Trigger then free run
In free run the camera cycles through frames/sequences
continuously.
Upon receiving a trigger (external or software) the camera will
start to generate sequences continuously.
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
19
Page 20
5 –Camera Controller
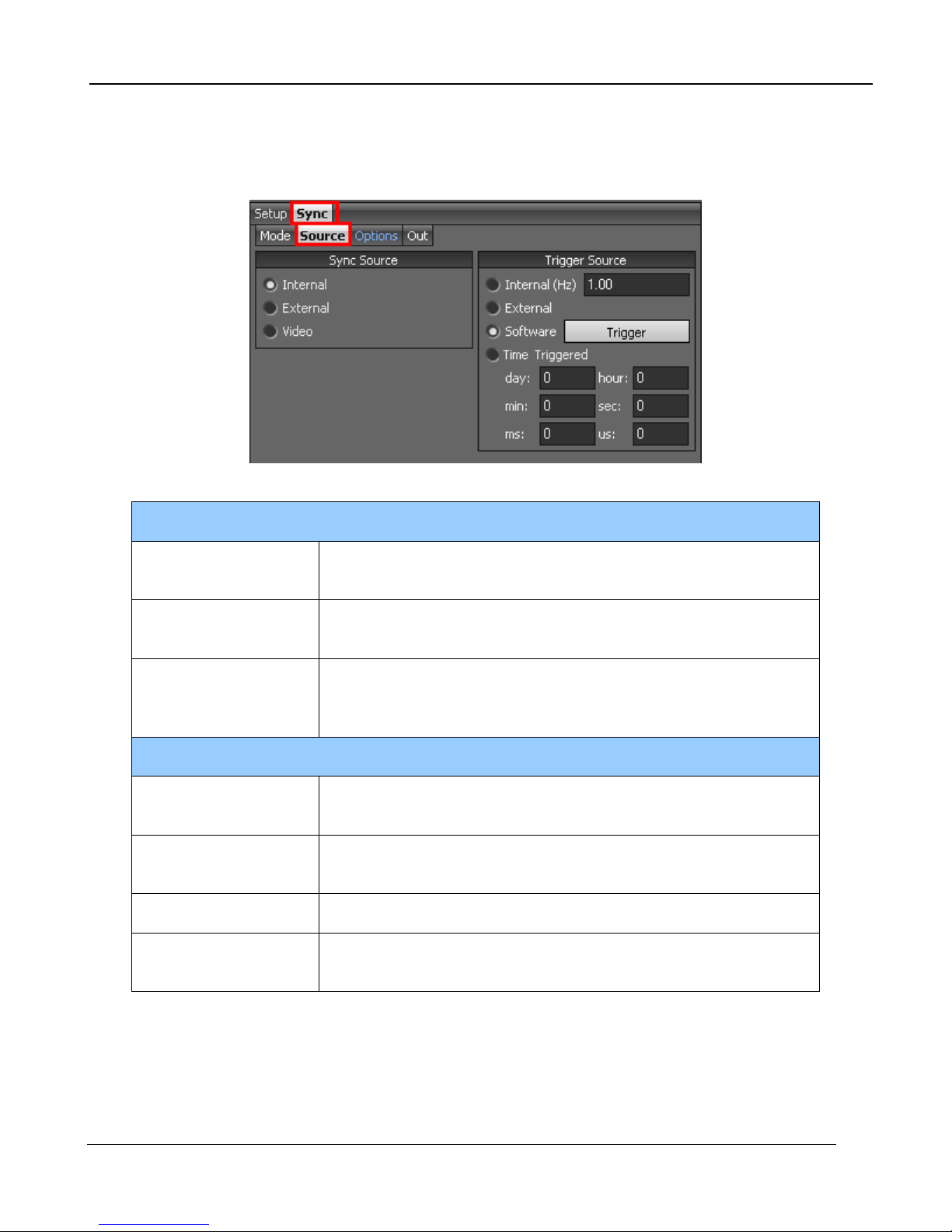
5.2.4.2.2 Sync Source
The Source options page allows the user to select the source for Syncs and Triggers.
Sync Sources
Internal
External
The frame sync is generated internally to run at the frequency
set by the user
The frame sync is generated externally through the Sync In
connect on the camera rear chassis.
The frame sync is generated from a external video source
Video
connected to the Gen Lock In connector on the camera rear
chassis.
Trigger Sources
Internal
External
The tri gger is gener ated internally to run at the frequency set by
the user (Hz).
The trigger is generated externally through the Trigger In
connector on the camera rear chassis. (3.3V LVCMOS)
Software The trigger is generated via a software button (Trigger button)
Time Triggered
Camera generates an internal trigger when the internal
timestamp clock reaches a specified time.
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
20
Page 21
5 –Camera Controller
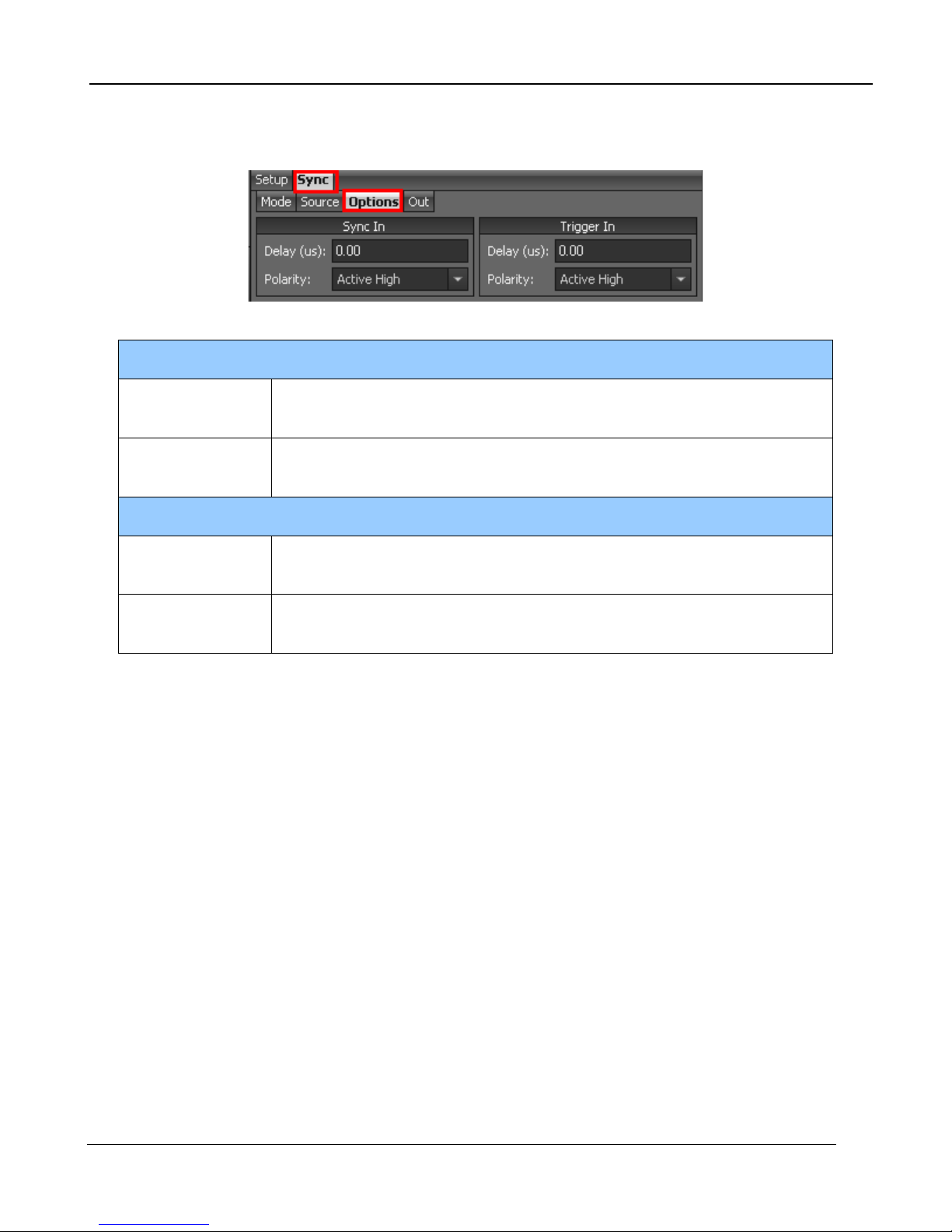
5.2.4.2.3 Sync Options
The Sync Options page allows the user to set delays and polarities for the Sync and Trigger In.
Sync In
Delay
Polarity
Delay
Polarity
Allows for the user to set a delay (µsec) for the external sync. See
timing diagrams below.
The sync is edge triggered. Allows for the camera to use the rising or
falling edge.
Allows for the user to set a delay (µsec) for the external trigger. See
timing diagrams below.
Trigger is edge triggered. Allows for the camera to use the rising or
falling edge.
Trigger In
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
21
Page 22
5 –Camera Controller
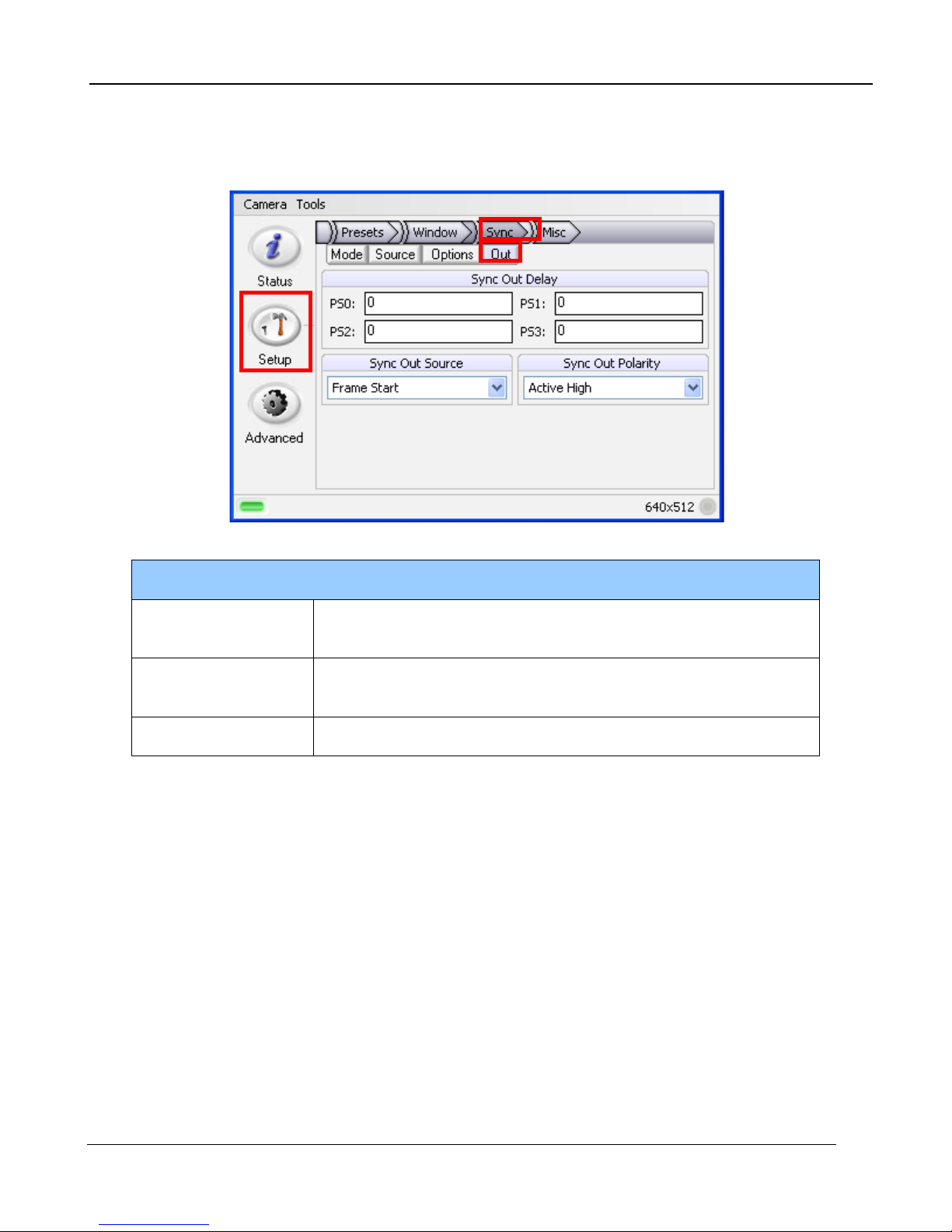
5.2.4.2.4 Sync Out
The Sync Out options allow the user to set a delay for the sync out pulse as well as the sync delay
reference and polarity. The Sync Out signal always has a jitter of ±1 clock (160nsec).
Sync Out Options
Sync Out Delay Allows for the user to set a delay for the sync out on a preset
basis.
Sync Out Source Allows for the sync out to be referenced to the star t of frame or
start of integration.
Sync Out Polarity Allows for the sync out to be active high or low.
5.2.5 Correction Page
The Correction Tab contains all the controls needed to manage the on-camera NUCs. On-camera
NUCs are stored in two types of memory:
RAM memory. This type of memory is used to store NUCs that will be applied to live image data.
There is enough RAM memory for one NUC to be loaded for each Preset. This memory is volatile
and is lost when then camera is turned off. If a NUC was loaded into RAM, the camera will reload that
NUC from flash automatically when the camera is turned on if a Save State was performed.
Flash Memory. This type of memory is used as nonvolatile NUC storage. There is about 2GB of
flash memory available for storing NUCs. This is enough space to store hundreds of full frame NUCs.
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
22
Page 23
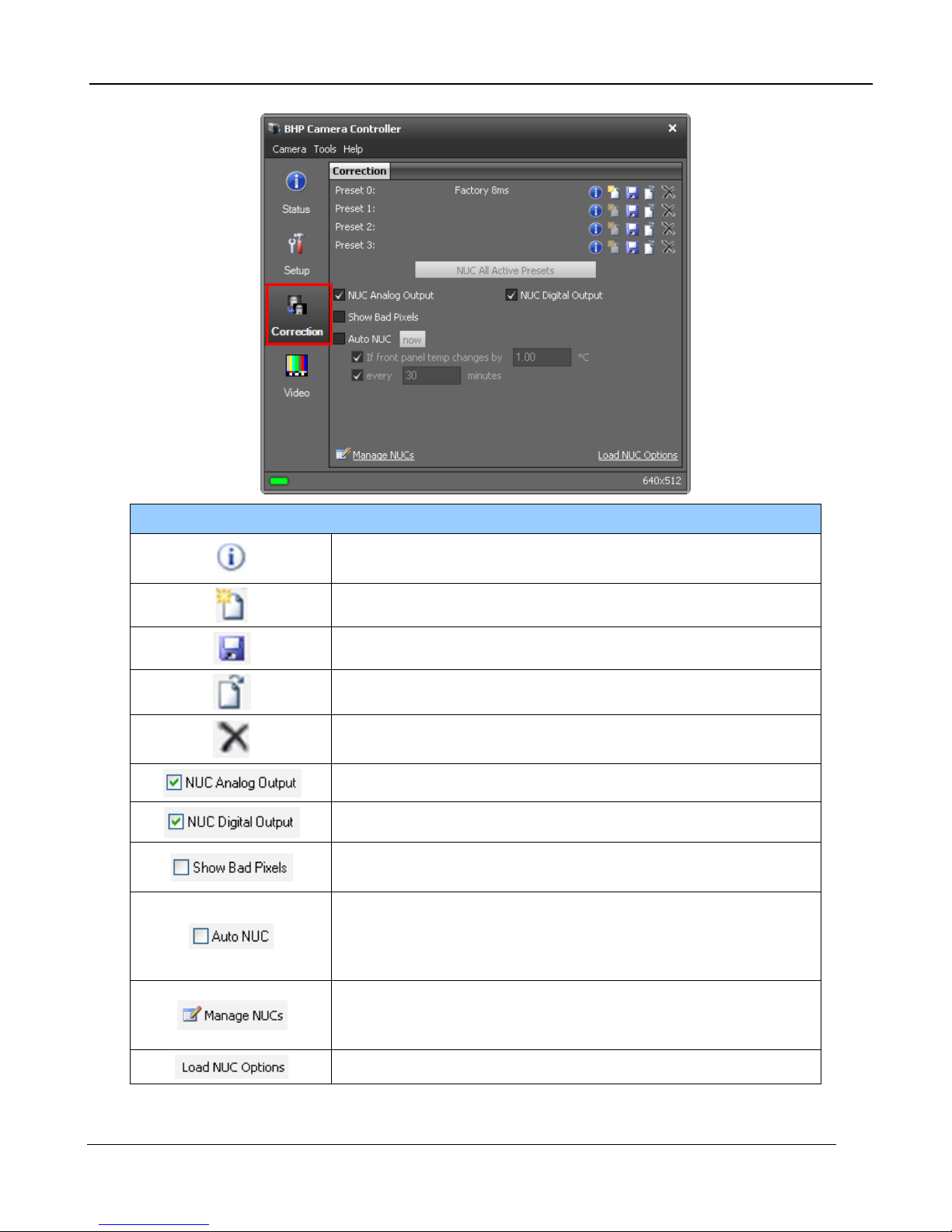
5 –Camera Controller
flag and perform a NUC Offset Update when selected criteria
Displays a list of NUCs stored in flash memory. User can
NUC Controls
NUC Info. Displays camera parameters and statistics related
to the selected NUC
Perform NUC. Starts the NUC Wizar d.
Updates the current NUC to flash memory
Load a NUC from flash to RAM memory.
Unload NUC from RAM mem ory. No on-camera NUC will be
applied to the data.
Apply NUC to Analog video data
Apply NUC to Digital output (Gig E, CameraLink)
Displays all pixels marked as “bad” as white dots on both the
analog and digital outputs.
When enabled, the camera will automatically drop the internal
are met. The NUC update can be triggered on demand, by a
change in the internal temperature sensor or by a ti mer
delete NUCs from flash memory as well as upload/download
NUCs (.NPK files) from the host PC.
Displays options for loading NUCs.
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
23
Page 24
5 –Camera Controller
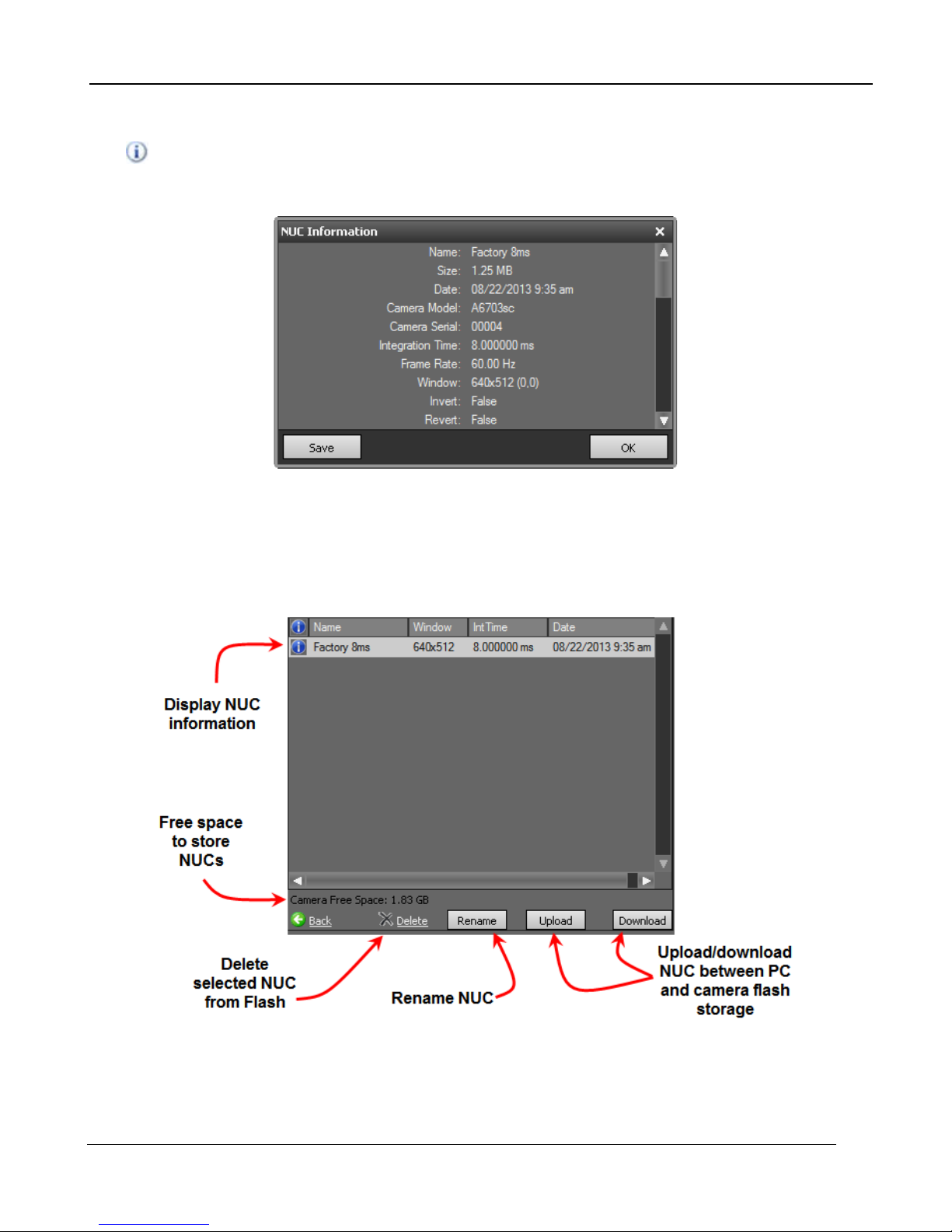
NUC Information
The button displays a list of camera parameters that are saved as part of the NUC as well as bad
pixel statistics. Note that there is a scroll bar that can be used to see the whole list. The Save button
allows the user to dump this list to a text file.
Manage NUCs
This dialog box allows the user to manage NUCs stored in non-volatile flash memory. Changes here
will persists through a camera power cycle. For example, if you rename a NUC here and do not
update the NUC loaded into RAM and the camera state, the camera will not be able to reload the
NUC after a power cycle.
Load NUC Options
Typically, all of the camera configuration parameters are derived from the current Camera State.
When the camera is powered up, it loads the last saved camera state. The names of the NUCs are
stored as part of the state. Normally the NUC is performed with the settings that are eventually going
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
24
Page 25
5 –Camera Controller
to be part of the state. If a NUC is loaded that has a setting that differs from the camera state, the
state will override the NUC. If the user wants the NUC setting to override the state then “Load NUC
Options” can be set.
The default setting is to “Load Table Only”, in which case only the NUC coefficients are used from a
NUC file. When the user selects “Load Table and the Following Settings”, the user can select which
parameters from the NUC will override the current state. The option will not affect NUCs that are
currently loaded into RAM, only those NUCs that are subsequently loaded from Flash memory.
Unless a new state is saved, these override settings will not be remembered after a power cycle.
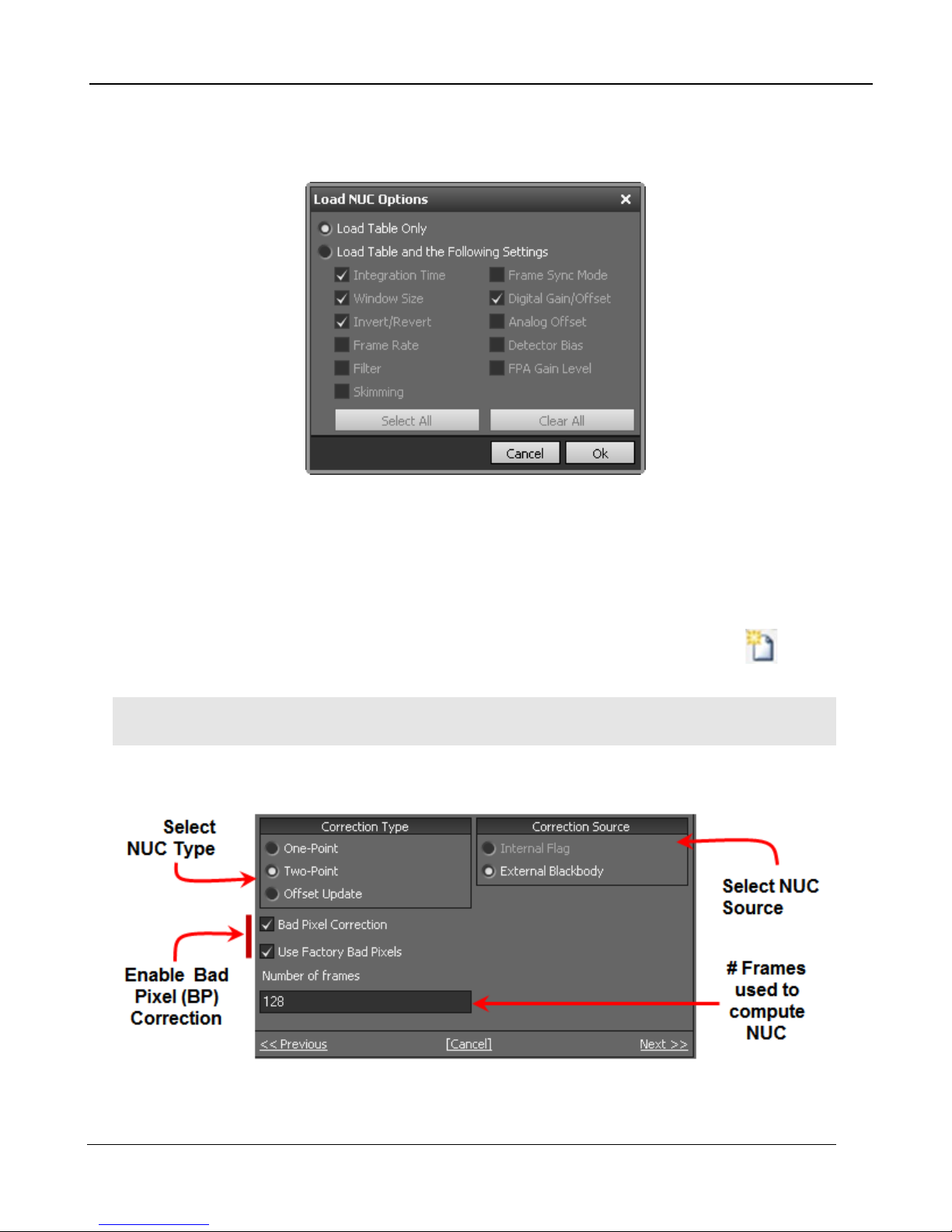
Performing a NUC
To build a NUC table using the camera electronics, select the Perform Correction icon to start
the NUC Wizard for the desired preset.
NOTE: Due to differences in camera electronics and FP A timi ngs i t is i mpo rtant to p erform the NUC
with the camera operatin g modes confi gured as it w ill be used w hen imaging.
After selecting the Perform Correction a second window comes up to allow the user to select
correction parameters. When all selections have been made, click Next>> to continue.
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
25
Page 26

One Point
5 –Camera Controller
Correction (NUC) Types
Sets the gain terms to “1” and computes the offset terms.
Uses a single NUC source. Does not compute a BP
correction.
Two Point
Sets both the gain and offset terms. Uses two NUC
sources. Computes a bad pixel correction.
Retains the current NUC gain terms and updates the offset
Offset Update
terms. Uses a single NUC source. Retains the current bad
pixel (BP) correction.
Correction Sources
Use the internal flag as the NUC source. Because the flag
Internal Flag
is not temperature controlled, it can only be used for 1-point
and Offset Update NUC functions
Use an external blackbody as the NUC source. Program
External Blackbody
will prompt the user to place each source in front of the
camera. NUC source needs to fill the entire field of view.
Set the number of to average when computing NUC
Number of frames
coefficients. 16 frames is the default and works well for
most scenarios. The value can be to be 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64,
or 128.
After configuring the correction parameters and selecting Next>> the next window allows the user to
set up the parameters used for the Bad Pixel Detection. Once the parameters are set, select Next>>
to continue.
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
26
Page 27

5 –Camera Controller
The next window allows the user to name the NUC. Simply type in the name for the table in the text
box or select a previously saved file to replace it. Select Next>> to continue.
The next two screens will collect data from the NUC sources. If using the internal flag you will only
see a few status messages. If using external blackbodies you will be prompted. After each step, click
Next>> to continue.
The last screen gives a report of the bad pixels found. The dialog shows how many pixels failed in
each category. If the result is satisfactory, click Accept to save the NUC. The NUC table will be
stored to flash memory and loaded into RAM memory for that preset. If the NUC is poor and you want
to abort, click[Discard].
NOTE: It is possible for a bad pixel to fail more than one category , so the total bad pixels may be less
than the sum of each category. “Fac tory” bad pixels are those that were deter mined to be bad during
camera production testing.
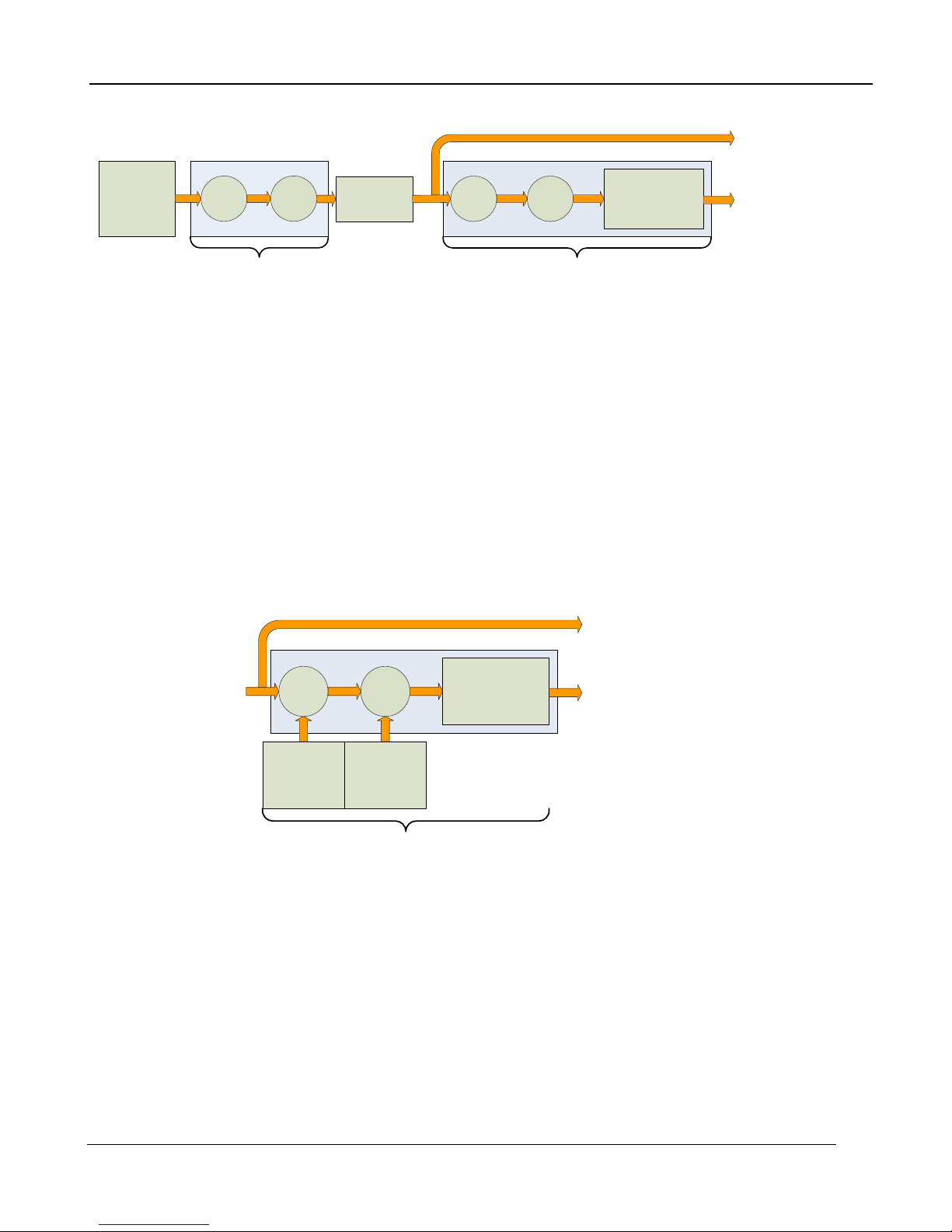
What is a Non-Uniformity Correction (NUC)?
Non-Uniformity Correction (NUC) refers the process by which the camera electronics correct for the
differences in the pixel-to-pixel response for each individual pixel in the detector array. The camera
can create (or allow for the user to load) a Non-Uniformity Correction (NUC) table which consists of a
unique gain and offset coefficient and a bad pixel indicator for each pixel. The table is then applied in
the digital processing pipeline as shown in Figure 4-12. The result is corrected data where each pixel
responds consistently across the detector input range creating a uniform image.
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
27
Page 28
5 –Camera Controller
Detector
14
-bit A/D
x +
NUC Table
Bad Pixel
Replacement
Algorithm
Corrected Data
Uncorrected Data
x
+
Analog
Gain/Offset
x
+
NUC Table
Bad Pixel
Replacement
Algorithm
Corrected Data
Uncorrected Data
“
1”
Offset
Coefficients
Figure 4-12: Digital Process Showing NUC Table Application
To create the NUC table, the camera images either one or two uniform temperature sources. The
source can be an external source provided by the user or the camera’s internal NUC flag which is
basically a shutter the camera places in front of the detector. If the source is external it should be
uniform and large enough to overfill the cameras field-of-view (FOV). By analyzing the pixel data from
these constant sources, the non-uniformity of the pixels can be determined and corrected. There are
three types of processes which are used to create the NUC table; One-Point, Two-Point, and Offset
Update.
5.2.5.1.1 One-Point Correction Process
A One-Point Correction Process requires one uniform source, which is typically in the middle of the
usable range. The One-Point Correction replaces all gain coefficients in the NUC table with a value of
one (“1”) as seen in Figure 4-13. The offset coefficients are computed uniquely for each pixel.
5.2.5.1.2 Two-Point Correction Process
The Two-Point Correction Process builds a NUC table that contains an individually computed gain
and offset coefficient for each pixel as seen in Figure 4-14. Two uniform sources are required for this
correction. One source at the low end and a second source at the upper end of the usable detector
input range. Because of the use of two images at either end of the input range, the Two-Point
Correction yields better correction results verses the One-Point process. A 2-point correct will also
work better over a wider range of scene temperatures than a 1-point correction.
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
Figure 4-13: One-Point Correction
28
Page 29

5 –Camera Controller
x
+
NUC Table
Bad Pixel
Replacement
Algorithm
Corrected Data
Uncorrected Data
Gain
Coefficients
Offset
Coefficients
x
+
NUC Table
Bad Pixel
Replacement
Algorithm
Corrected Data
Uncorrected Data
Bad Pixel
Indicator
Figure 4-14: Two-Point Correction
5.2.5.1.3 Offset Update
Often times during the normal operation of a camera the electronics and/or optics will heat up or cool
down which changes the uniformity of the camera image. This change requires a new NUC.
However, this change is mainly in the offset response of the image while the gain component stays
constant. An Offset Update simply computes a new offset coefficient using the existing gain
coefficient and corrects the image non-uniformity. Offsets Update are typically performed when a
Two-Point NUC table is being used.
An Offset Update requires only one uniform source, usually set at a temperature on the lower edge of
the operational range.
5.2.5.1.4 Bad Pixel Correction
Within the NUC table there is an indication as to whether or not a pixel has been determined to be
bad as seen in Figure 4-15. There are two methods the A6700sc uses to determine bad pixels.
First, the NUC table gain coefficients are compared to a user defined acceptance boundary,
Responsivity Limit Low/High (%). The responsivity of a pixel can be thought of as the gain of that
pixel. The gain coefficient in the NUC Table is a computed value that attempts to correct the
individual pixel gain, or responsivity, to a normalized value across the array. Since the responsivity
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
Figure 4-15: Bad Pixel Correction
29
Page 30

5 –Camera Controller
value directly relates to the gain coefficient in the NUC table, the A6700sc can scan the NUC table
gain coefficients and use them to determine if a pixel’s responsivity exceeds the limits as set by the
user.
The second method of determining bad pixels is to search for twinklers. Twinklers are pixels that
have responsivity values within normal tolerances, but still exhibit large swings for small input
changes. These pixels are on the “verge” of being bad and often appear to be noisy. To find these
types of pixels the camera collects N number of frames and records the maximum and minimum
values across that sample set for each pixel. If the delta between max and min exceeds the Twinkler
max pixel value delta then the pixel is determined to be bad.
Since the responsivity test requires a gain coefficient, it is useless on NUC tables determine by the
One-Point Correction because those tables have a value of one (“1”) as the gain coefficients. The
Twinkler test can be done on either correction process.
The A6700sc uses two algorithms for bad pixel replacement: 2-point Gradient, and Nearest Neighbor.
The 2-point gradient algorithm is the default bad pixel correction method. With this algorithm, the two
pairs of pixels above and below and to the left and right of the bad pixel are evaluated. The algorithm
compares the differences between the pixels and chooses the pair with smallest gradient (difference).
It then averages the two adjacent pixels and uses that value for the replacement value. This
algorithm is better at handling bad pixels near a high contrast edge and is the default method. If the
algorithm encounters a situation is cannot solve (for example, an edge or corner) it will fall back on the
nearest neighbor algorithm.
Nearest neighbor uses a simple replacement using an adjacent pixel. The adjacent pixel is picked
using the pattern depicted below. When a bad pixel is near an edge, those search positions are
skipped.
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
30
Page 31

5 –Camera Controller
5.2.6 Video Page
The A6700sc camera has a 14-bit digital output. However, the analog output is only 8-bit. An
Automatic Gain Control (AGC) algorithm is used to map the 14-bit digital to the 8-bit analog data. The
Video Tab provides controls related to optimizing the Analog video output. These controls affect
only the analog video. Figure 4-16 shows a flow chart of the analog video process and how the
parameters of this screen are used.
Analog Video Setup Options
NTSC: 640x480, 30Hz interlaced, color based on Palette selection,
(Note: top and bottom 16 lines are truncated when full images are
displayed. The Analog window can be adjusted +/- 16 rows using the
Format
Overlay Enables the analog video overlay.
Filter Rate Rate at which AGC is com puted (1 to 20 Hz)
Dampening
Setup>>Window Tab)
PAL: 640x480, 25Hz interlaced, color based on Palette selection
Note: When camera frame size is smaller than video frame size, black
borders are added to maintain standard video output sizes
Rate at which AGC is allowed to change. This will keep the AGC from
responding rapidly to fast tridents changes. Specified as a fraction from
0 to 1. This fraction is used as a weighting factor for the current AGC vs.
the newly computed AGC.
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
31
Page 32

AGC Mode
Corrected Data
Uncorrected Data
Mux
Plateau
Scalar
Linear
Scalar
GUI: Plateau P
GUI: Bounds
Mux
GUI
: AGC Mode
Video
Encoder
GUI: Format
GUI: Position
GUI: Brightness
GUI: Contrast
Overlay
GUI: Overlay
GUI: NUC’d
Analog Video
Pallete
Scalar
GUI: Palette
5 –Camera Controller
Analog Video Setup Options
Plateau: Uses a plateau equalization (PE) algorithm to scale the image
data for video display
DDE: Digital Detail Enhancement.
Manual Linear: Scales the im age data to a windowed s ec tion of data range
as set by the user
Auto Linear: Same as Manual Linear except camera analyzes image and
sets limits at ~1% and 98% of the histogram.
Plateau P
Bounds
DDE Sharpness
Scaling factor for the Plateau Equalization function
Note: Plateau P is only visible when AGC Mode>> Plat eau is select ed
Sets the lower and upper data range to be scaled to on the video data.
Note: Bounds is only visible when AGC Mode>>Manual Linear is selected
Only visible when AGC is set to DDE. Selects the amount of enhancement
processing.
Palette Allows user to select the color scheme to use on the analog video channel.
Allows user to set brightness and contrast on the video encoder. As shown
Brightness and
Contrast
in Figure 4-16, this occurs after the digital data has been scaled and
converted to analog. These controls don’t tend to have as much effect as
the controls that are applied to the digital side (before the video encoder).
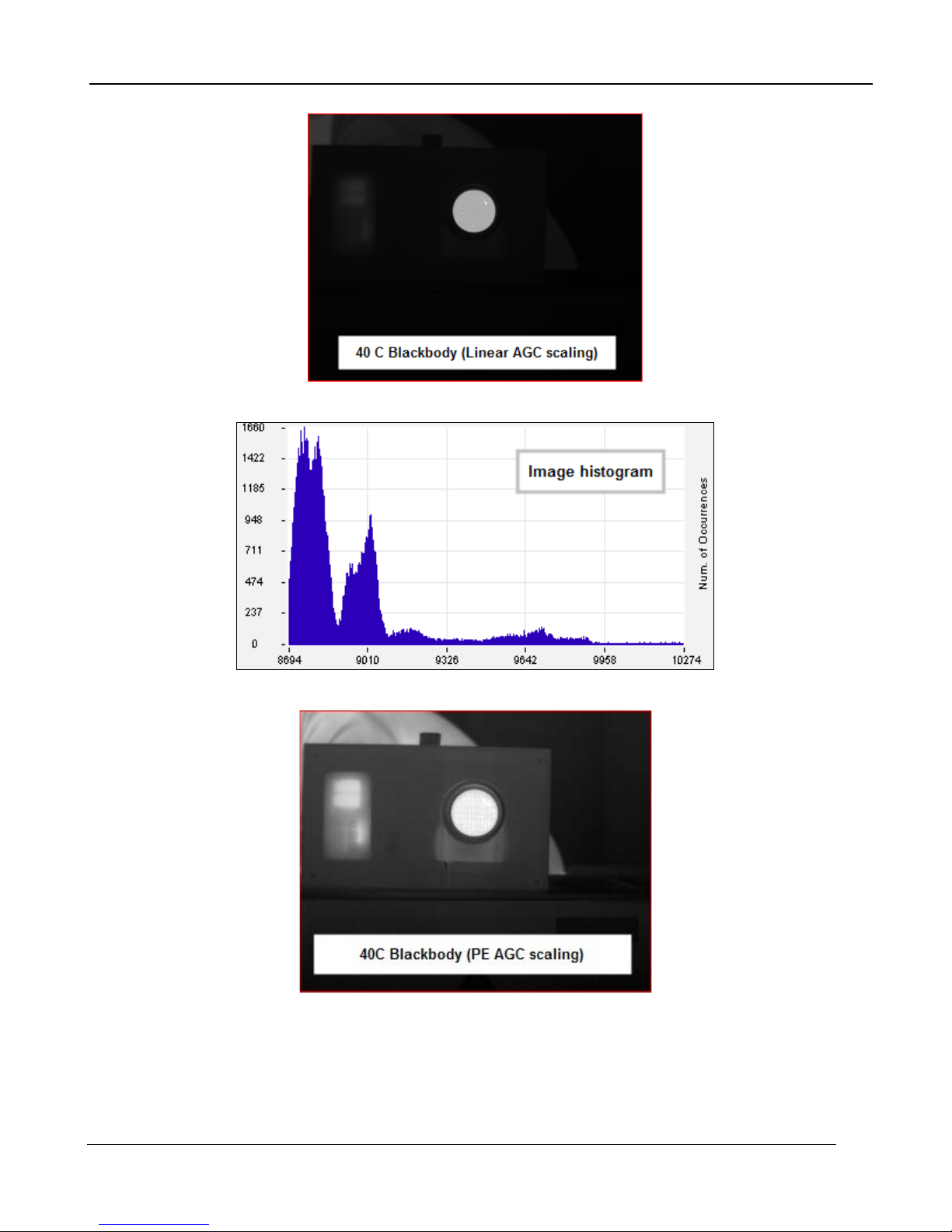
The Manual Linear algorithm evenly distributes the grayscale values over the digital values. This
works fairly well if the image dynamic range is fairly evenly distributed but in general does not produce
high contrast imagery, but it also does not saturate or clip the hot and cold regions either. The
Plateau Equalization algorithm (also called PE) is a nonlinear AGC algorithm that uses the image
histogram to optimally map the 256 gray scales. This algorithm works well for most scenes but it
works best when the scene has a “bi-modal” distribution (two clumps). It usually the most popular
because algorithm because it produces high contrast (but more saturated) video. The following
pictures illustrate the differences in AGC algorithms. (The data was captured from the digital output
but the effect is similar for the analog side.)
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
Figure 4-5: Analog Video Flow
32
Page 33
5 –Camera Controller
One final note about the PE algorithm. It is very aggressive. It can pull detail out of very low contrast
imagery. It can also pull out some very low-level NUC and FPA artifacts and noise if the contrast is
low enough. This does not necessarily mean there is a problem with the camera, or NUC.
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
33
Page 34

6 Interfaces
6.1 Mechanical (dimensions in inches)
6 – Interfaces
Figure 6-1: Front view of A6700sc
Figure 6-2: Side view of A6700sc with 50mm lens
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
34
Page 35
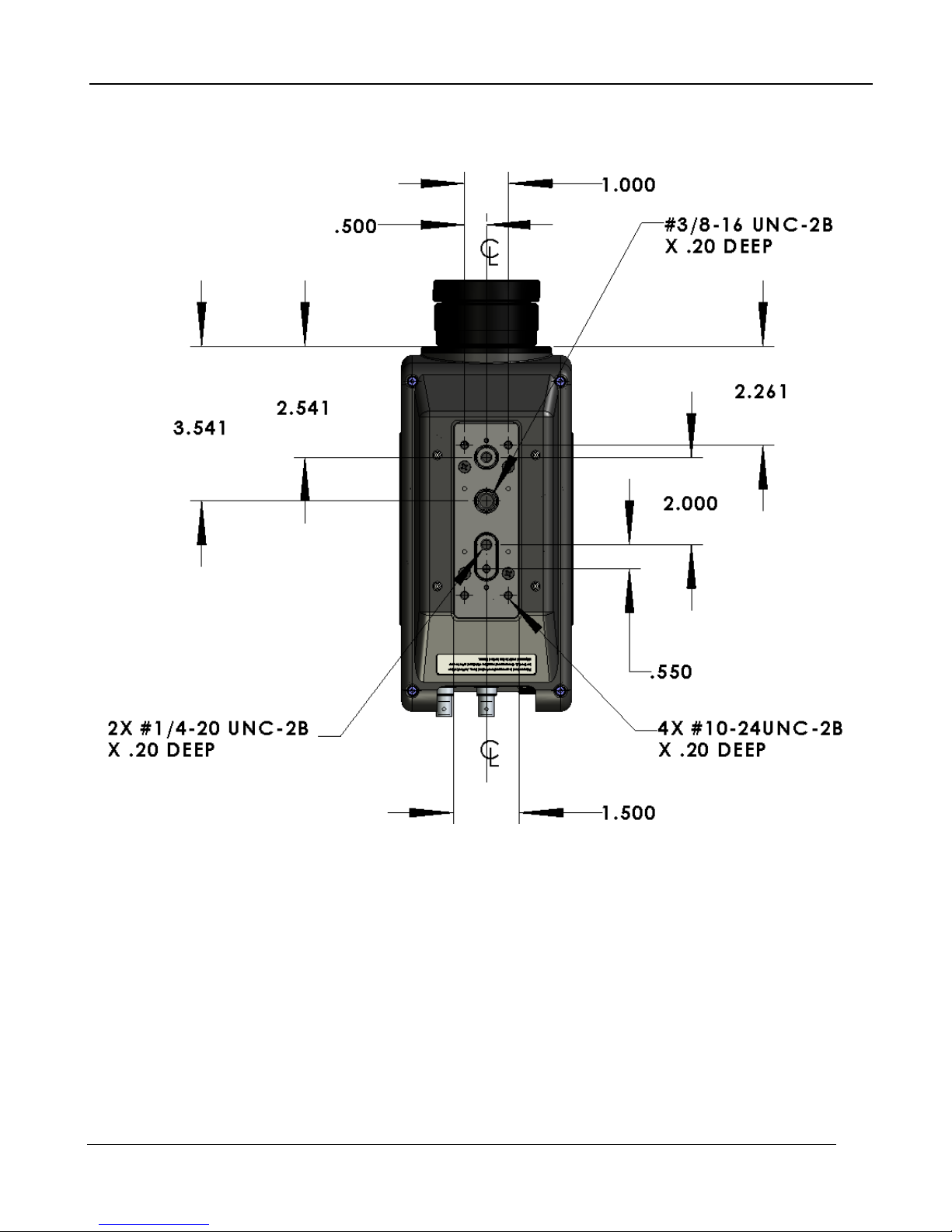
6 – Interfaces
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
Figure 6-1: Bottom view of A6700sc
35
Page 36

6 – Interfaces
6.1.1 Status Light s
The A6700sc provides a set of status indicators on the back panel to give the user some visual
feedback on the camera operating state.
POWER (on power switch): Indicates that the camera is ON.
READY: Camera electronics have completed boot up. Camera is
ready to accept commands.
COLD: Indicates that the FPA has reached operating tem perature
(<80K).
6.1.2 Power Interface
24V DC nominal, external AC-DC power converter is provided with the A6700sc camera system as a
standard accessory. Power supply specifications are:
Input voltage range: 100-250VAC 50/60Hz
Current draw: 24 VDC at up to 4.0 amps input to the camera
Converter dimensions: 6.25 inches x 3.5 inches x 2.75 inch (L x W x H)
Converter weight: approximately 1 lb
The power input pinouts are shown in Figure 6-4.
Figure 6-4: A6700sc Power Input Pinouts
When using your own DC power supply, you should take note of the following information:
Output voltage: 24 VDC
Current draw: 1.4 amps nominal steady state, 2.6 amps peak (during cooldown)
A6700sc power dissipation is <50 Watts steady state at nominal ambient temperature.
Mating Connector: Fisher Connectors, S103A052-130+E31 103.1/5.7 +B. (FLIR PN 26399-000).
The power cable should be 20AWG (stranded 10/30), 3 conductor, no shield, max diameter of 0.223
inches. (Example: Alphawire PN 882003)
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
36
Page 37

6 – Interfaces
6.1.3 Other Interfaces
6.1.3.1 Gigabit Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet (GigE) is a common interface found in most PC’s. The GigE interface can be used
for image acquisition and/or camera control. The GigE interface is GigE Vision compliant (for the
image stream, but does not support Genicam for camera control).
6.1.3.2 Sync In
The Sync In can be selected, by the user, to operate as an external clock It is a rising edge LV-CMOS
signal (5.5V max). The minimum width is 160nS.
6.1.3.3 Video
Composite video out (BNC connector). User selectable to be NTSC standard (640x480, 30Hz
interlaced) or PAL standard (640x512, 25Hz interlaced). Video supports user selectable color
palettes.
6.1.3.4 AUX Connector [A6750sc only]
The AUX connector provides access to additional signals. The diagram below shows a closeup view
of the rear panel connector.
A breakout cable is provided with all A6750sc cameras.
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
37
Page 38

6 – Interfaces
The provided breakout cable has numerical markings on the BNC overmolding that are described in
the table below.
Pin Name Breakout
Type Description
Connector
1
NC
2
NC
3
RECORD
START
4
SYNC OUT BNC 4 OUTPUT 160ns wide pulse at start of integration
5
GROUND
6
GPIO IN BNC 6 INPUT Sets bits in image header. Updated at ~1Hz rate.
7
Reserved BNC 7
8
TRIGGER BNC 8 INPUT External trigger. Can be used by ResearchIR to start
BNC 3 INPUT Sets bit in image header. Can be used by
ResearchIR to start recording.
recording.
9
Reserved BNC 9
10
SYNC IN BNC 10 INPUT Duplicate of rear panel input. Do not use both at the
same time.
11
RS-232 TX DB9 Male OUTPUT For camera control
12
RS-232 RX DB9 Male INPUT For camera control
Inputs are all LV-CMOS. High>2V, Low<0.2V. Max is 5.5V
If you wish to make your own breakout cable, there are three variants of the Hirose mating connector
that will work: HR10A-10P-12S(73), HR10-10P-12S(73) or HR10A-10P-12SC(73).
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
38
Page 39

7.1 Interface
7 – Specifications
7 Specifications
AC Power
Control
Analog Video Out
Frame Sync In
Digital Video Out
Optical Interface
Thermal Interface
Mechanical Interface
7.2 Windowing Capacity
Window Sizes
90-230VAC, 50-60 Hz (using FLIR 24123-000 power supply)
Genicam over Gigabit Ethernet (10/100/1000)
Selectable
• NTSC/PAL selectable, BNC, 75Ω, 1V pk-pk
LVCMOS singled ended, BNC, selectable polarity, >160ns pulse
width
14-bit Gigabit Ethernet (GigE Vision 2.0)
Bayonet
Semi-sealed enclosure with integral forced air heat exchanger
2 (two) ¼-20 tripod screws; 1 (one) 3/8-16 professional tripod
screw; 4 (four) 10-24 mount holes
640x512, 320x256, 160x120, [flexible for A6750sc]
Windowing Step Size
Window Offset Step Size
16 columns, 4 rows (A6750sc)
No offset, FPA centered
7.3 Acquisition Modes and Features
Frame Rate :
Max at Full Window
Max w/ Windowing
Max @ Min Window
Minimum
Resolution
Pixel Rate (burst)
Integration Width
Maximum
60 Hz for A6700, 125Hz for A6750sc
240 Hz @ ½ window, 480 Hz @ ¼ window (A6700sc)
406 Hz @ ½ window, 1063 Hz @ ¼ window (A6750sc)
4175 Hz @ 16x4 (A6750sc)
1.45mHz
160nS
50 MHz
98% selected frame time (1/frame rate)
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
39
Page 40
7 – Specifications
Minimum
480 nS
Resolution
Preset Sequencing
Digital Video Output
7.4 Analog Video
Video Output
Data Output
AGC
160 nS
• N/A
Selectable:
• Raw digital video (14-bits)
• Gain and offset (NUC) corrected (14-bits)
• NUC with bad pixel replaced (14-bits)
• NTSC or PAL composite
Selectable
• Raw, uncorrected
• Corrected
Selectable
• DDE
• Plateau based equalization
• Linear equalization
User controlled damping factor
AGC Filter
User controlled update rate
Overlay
Available on analog output
Selectable
Palettes
• Grayscale
• Various color palettes
Auto-selected
Zoom (Analog video)
• x1 for 640x512
• x2 for 320x256 and 160x120 window sizes
Brightness and Contrast
(analog video)
User controlled to increase or decrease
7.5 Performance Characteristics
Power Consumption
FLIR PWR Supply @ 120V
Continuous Cool Down: 50 VA
AC
Continuous Normal: 41 VA
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
40
Page 41

7 – Specifications
Power Consumption
Camera DC Power @ 24V
Cool-down Ti me
Sensitivity (w/o optics)
NEΔT
1) NE∆T is at 50% nominal bucket fill, 298K background, + 5oC signal
Continuous Cool Down: 24 Watts
DC
Continuous Normal: 21.25 Watts
≈7 minutes to reach operating temperature
1
18 mK typ .
7.6 Non Uniformity Correcti on
One Point (offset value with unity gain)
NUC Types
NUC Source
Bad Pixel Replacement
Two Point (offset and gain values) non-volatile
Two Point w/Bad Pixel Detection/Replacement
Update Offset (recalculates offset using current gain)
Internal: Ambient flag (for 1-pt and offset update only)
External: Any user supplied source which covers entire FOV
Two-Point Gradient and neares t neighbor (autoselected)
Number of NUC’s
NUC Time
NUC Performance
7.7 Detector/FPA
Spectral Response
Detector Type
f/#
Integration Mode
Format (HxV)
Operability
Charge Handling
Capacity
Detector Pitch
1
4 active NUC’s in preset selectable form
>100 NUCs in on-board flash
< 15 seconds
0.1%
3-5um (1-5um for broadband models)
InSb
f/2.5 or f/4
Snapshot
640 x 512
>99.8%, 99.95% typical
7.2 x106 e-
15 microns
Detector Cooling
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
Rotary Cryo Cooler
41
Page 42

7.8 General Characteristics
7 – Specifications
Size
Length
Width
Height
Weight
Temperature
Operating
Storage
Shock
Vibration
Humidity
Altitude
Operating Orientation
8.5 inches
4.0 inches
4.3 inches
(not including lens or lens cover)
5 lbs (not including lens or lens cover)
-40C to +50C
-55C to +80C
40 g’s, 11 msec half sine pulse
4.3 g's RMS random vibration, all three axes
<95% relative humidity, non-condensing
0 to 10,000 feet operational, 0 to 70,000 feet non-operational
No restriction in orientation
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
42
Page 43

8 – Maintenance
8 Maintenance
8.1 Camera and Lens Cleaning
8.1.1 Camera Body, Cables and Accessories
The camera body, cables and accessories may be cleaned by wiping with a soft cloth. To remove
stains, wipe with a soft cloth moistened with a mild detergent solution and wrung dry, then wipe with a
dry soft cloth.
Do not use benzene, thinner, or any other chemical product on the camera, the cables or the
accessories, as this may cause deterioration.
8.1.2 Lenses
It is recommends that all optics be handled with care and the need for cleaning is eliminated or at
least reduced. If however,cleaning is deemed necessary, the methods herein are accepted industry
standards and should yield good results.
Before you BEGIN,
Identify the type of optic to be cleaned.
▫ Is it hard or soft material?
▫ Is it coated & with what?
How is it contaminated?
▫ Particulate or film or both.
Set a standard of cleanliness.
▫ What is clean enough?
▫ Establish & document a standard.
Know your solvent.
▫ Read the MSDS
▫ See recommended solvents
Assemble your supplies:
▫ Latex gloves
▫ Clean, well-lit work area
▫ Inspection light
▫ Lens tissue or cloth
▫ Dust bulb or filtered air
▫ Proper solvent
▫ Solvent dispenser
The Drag Wipe Method:
Set-up a clean area to work from with an anti-roll barrier around the edge to prevent anything from
leaving the table.
Use a clean, lint free cloth or lens tissue.
Wear latex gloves - clean them with alcohol or detergent before handling optic.
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
43
Page 44
8 – Maintenance
NEVER touch the face of the optic.
Cover the optic and store in a dry - dust free area immediately after cleaning.
1. Blow or brush loose particles from surface. Don’t let them contaminate your work area. Use
air from a can or a filtered source.
2. Apply solvent directly to your cloth. Use slow, even, light pressure working from edge to edge
across the optic.
Recommended Solvents
Material Solvent
Fused Silica 1,2,3,4 Zinc Selenide 1,2,4
BK-7 1,2,3,4 Zinc Sulfide 1,2,4
Optical Crown Glass 1,2,3,4 Sapphire 1,2,3,4
Zerodur 1,2,3,4
Calcium Fluoride 1,2,4 Coated Optics
Magnesium Fluoride 1,2,4 Dielectric coating 1,2,3,4
Sodium Chloride Nitrogen Interference filters 3
Potassium Chloride Nitrogen Soft metallic coating Air only
Potassium Bromide Nitrogen Hard/Protected metallic 1,2,3,4
Thallium Bromoiodide Nitrogen
1] Water free Acetone
2] Ethanol
3] Methanol
4] Isopropanol
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
44
Page 45

9 – Infrared Primer
9 Infrared Primer
9.1 History of Infrared
Less than 200 years ago the existence of the infrared portion of the electromagnetic spectrum wasn't
even suspected. The original significance of the infrared spectrum, or simply ‘the infrared’ as it is often
called, as a form of heat radiation is perhaps less obvious today than it was at the time of its discovery
by Herschel in 1800.
Figure 8-1: Sir William Herschel (1738–1822)
The discovery was made accidentally during the search for a new optical material. Sir William
Herschel – Royal Astronom er to King George III of England, and already famous for his discovery of
the planet Uranus – was searching for an optical filter material to reduce the brightness of the sun’s
image in telescopes during solar observations. While testing different samples of colored glass which
gave similar reductions in brightness he was intrigued to find that some of the samples passed very
little of t he sun’s heat, while others passed so much heat that he risked eye damage aft er only a few
seconds’ observation.
Herschel was soon convinced of the necessity of setting up a systematic experiment, with the
objective of finding a single material that would give the desired reduction in brig htness as well as the
maximum reduction in heat. He began the experiment by actually repeating Newton’s prism
experiment, but looking for the heating effect rather than the visual distribution of intensity in the
spectrum. He first blackened the bulb of a sensitive mercury-in-glass thermometer with ink, and with
this as his radiation detector he proceeded to test the heating effect of the various colors of the
spectrum formed on the top of a table by passing sunlight t hrough a g lass prism. Other thermometers,
placed outside the sun’s rays, served as controls.
As the blackened thermometer was moved slowly along the colors of the spectrum, the temperature
readings showed a steady increase from the violet end to the red end. This was not entirely
unexpected, since the Italian researcher, Landriani, in a similar experiment in 1777 had observed
much the same effect. It was Herschel, however, who was the f irst to recognize that there must be a
point where the heating effect reaches a maximum, and those measurements confined to the visible
portion of the spectrum failed to locate this point.
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
45
Page 46

9 – Infrared Primer
Figure 8-2: Marsilio Landriani (1746–1815)
Moving the thermometer into the dark region beyond the red end of the spectrum, Her s c h el c onfirmed
that the heating continued to increase. The maximum point, when he found it, lay well beyond the red
end – in what is known today as the ‘infrared wavelengths’.
When Herschel revealed his discovery, he referred to this new portion of the electromagnetic
spectrum as the ‘thermometrical spectrum’. The radiation itself he sometimes referred to as ‘dark
heat’, or simply ‘the invisible rays’. Ironically, and contrary to popular opinion, it wasn't Herschel who
originated the term ‘infrared’. The word only began to appear in print around 75 years later, and it is
still unclear who should receive credit as the originator.
Herschel’s use of glass in the prism of his original experiment led to some early controversies with his
contemporaries about the actual existence of the infrared wavelengths. Different investigators, in
attempting to confirm his work, used various types of glass indiscriminately, having different
transparencies in the infrared. Through his later experiments, Herschel was aware of the limited
transparency of glass to the newly-discovered thermal radiation, and he was forced to conclude that
optics for the infrared would probably be doomed to the use of reflective elements exclusively (i.e.
plane and curved mirrors). Fortunately, this proved to be true only until 1830, when the Italian
investigator, Melloni, made his great disc overy that naturally occurring rock salt (NaCl) – whic h was
available in large enough natural crystals to be made into lenses and prisms – is remarkably
transparent to the infrared. The result was that rock salt became the principal infrared optical material,
and remained so for the next hundred years, until the art of synthetic crystal growing was mastered in
the 1930’s.
Figure 8-3: Macedonio Melloni (1798–1854)
Thermometers, as radiation detectors, remained unchallenged until 1829, the year Nobili invented the
thermocouple. (Herschel’s own thermometer could be read to 0.2 °C (0.036 °F), and later models
were able to be read to 0.05 °C (0.09 °F)). Then a breakthrough occurred; Melloni connected a
number of thermocouples in series to form the first thermopile. The new device was at least 40 times
as sensitive as the best thermometer of the day for detecting heat radiation – capable of detecting the
heat from a person standing three meters away.
The first so-called ‘heat-picture’ became possible in 1840, the result of work by Sir John Herschel, son
of the discoverer of the infrared and a famous astronomer in his own right. Based upon the differential
evaporation of a thin film of oil when exposed to a heat pattern focused upon it, the thermal image
could be seen by reflected light where the interference effects of the oil film made the image visible to
the eye. Sir John also m anaged to obtain a primitive record of the thermal image on paper, which he
called a ‘thermograph’.
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
46
Page 47

9 – Infrared Primer
Figure 8-4: Samuel P. Langley (1834–1906)
The improvement of infrared-detector sensitivity progressed slowly. Another major breakthrough,
made by Langley in 1880, was the invention of the bolometer. This consisted of a thin blackened strip
of platinum connected in one arm of a Wheatstone bridge circuit upon which the infrared radiation was
focused and to which a sensitive galvanometer responded. This instrument is said to have been able
to detect the heat from a cow at a distance of 400 meters.
An English scientist, Sir James Dewar, first introduced the use of liquefied gases as cooling agents
(such as liquid nitrogen with a temperature of -196 °C (-320. 8 °F)) in low temperature research. In
1892 he invented a unique vacuum insulating container in which it is possible to store liquefied gases
for entire days. The common ‘thermos bottle’, used for storing hot and c old drinks, is based upon his
invention.
Between the years 1900 and 1920, the inventors of the world ‘discovered’ the infrared. Many patents
were issued for devices to detect personnel, artillery, aircraft, ships – and even icebergs. The first
operating systems, in the modern sense, began to be developed during the 1914–18 war, when both
sides had research programs devoted to the military exploitation of the infrared. These programs
included experimental systems for enemy intrusion/detection, remote temperature sensing, secure
communications, and ‘flying torpedo’ guidance. An infrared search system tested during this period
was able to detect an approaching airplane at a distance of 1.5 km (0.94 miles), or a person more
than 300 meters (984 ft.) away.
The most sensitive systems up to this time were all based upon variations of the bolometer idea, but
the period between the two wars saw the development of two revolutionary new infrared detectors:
the image converter and the photon detector. At first, the image converter received the greatest
attention by the military, because it enabled an observer for the first time in history to literally ‘see in
the dark’. However, the sensitivity of the image converter was limited to the near infrared
wavelengths, and the most inter esting military targets (i.e. enemy soldiers) had to be illuminated by
infrared search beams. Since this involved the risk of giving away the observer’s position to a
similarly-equipped enemy observer, it is underst andable that military interest in the imag e converter
eventually faded.
The tactical military disadvantages of so-called 'active’ (i.e. search beam-equipped) thermal imaging
systems provided impetus following the 1939–45 war for extensive secret military infrared-research
programs into the possibilities of developing ‘passive’ (no search beam) systems around the
extremely sensitive photon detector. During this period, military secrecy regulations completely
prevented disclosure of the status of infrare d -imaging technology. This secrecy only began to be lifted
in the middle of the 1950’s, and from that time adequate thermal-imaging devices finally began to be
available to civilian science and industry.
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
47
Page 48

9 – Infrared Primer
9.2 Theory of Thermography
9.2.1 Introduction
The subjects of infrared radiation and the related technique of thermography are still new to many
who will use an infrared camera. In this section the theory behind thermography will be given.
9.2.2 The Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is divided arbitrarily into a number of wavelength regions, called bands,
distinguished by the methods used to produce and detect the radiation. There is no fundamental
difference between radiation in the different bands of the electromagnetic spectrum. They are all
governed by the same laws and the only differences are those due to differences in wavelength.
Figure 8-5 The Electromagnetic Spectrum
1: X-ray; 2: UV; 3: Visible; 4: IR; 5: Microwaves; 6: Radiowaves.
Thermography makes use of the infrared spectral band. At the short -wavelength end the boundary
lies at the limit of visual perception, in the deep red. At the longwavelength end it merges with the
microwave radio wavelengths, in the millimeter range.
The infrared band is often further subdivided into four smaller bands, the boundaries of which are also
arbitrarily chosen. They include: the near infrared (0.75–3 μm), the middle infrared (3–6 μm), t he far
infrared (6–15 μm) and the extreme infrared (15–100 μm). Although the wavelengths are given in μm
(micrometers), other units are often still used to measure wavelength in this spectral region, e.g.
nanometer (nm) and Ångström (Å). The relationships between the different wavelength
measurements is:
9.2.3 Blackbod y Radiation
A blackbody is defined as an object which absorbs all radiation that impinges on it at any wavelength.
The apparent misnomer black relating to an object emitting radiation is explained by Kirchhoff’s Law
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
48
Page 49

9 – Infrared Primer
(after Gustav Robert Kirchhoff, 1824–1887), which states that a body capable of absorbing all
radiation at any wavelength is equally capable in the emission of radiation.
Figure 8-6: Gustav Robert Kirchhoff (1824–1887)
The construction of a blackbody source is, in principle, very simple. The radiation characteristics of an
aperture in an isotherm cavity made of an opaque absorbing material represents almost exactly the
properties of a blackbody. A practical application of the principle to the construction of a perfect
absorber of radiation consists of a box that is light tight except for an aperture in one of the sides. Any
radiation which then enters the hole is scattered and absorbed by repeated reflections so only an
infinitesimal fraction can possibly escape. The blackness which is obtained at the aperture is nearly
equal to a blackbody and almost perfect for all wavelengths.
By providing such an isothermal cavity with a suitable heater it becomes what is termed a cavity
radiator. An isothermal cavity heated to a uniform temperature generates blackbody radiation, the
characteristics of which are determined solely by the temperature of the cavity. Such cavity radiators
are commonly used as sources of radiation in temperature reference standards in the laboratory for
calibrating thermographic instruments, such as a FLIR Systems camera for example.
If the temperature of blackbody radiation increases to more than 525 °C (977 °F), the source begins to
be visible so that it appears to the eye no longer black. This is the incipient red heat temperature of
the radiator, which then becomes orange or yellow as the temperature increases further. In fact, the
definition of the so-called color temperature of an object is the temperature to which a blackbody
would have to be heated to have the same appearance. Now consider three expressions that
describe the radiation emitted from a blackbody.
Planck’s Law
Figure 8-7: Max Planck (1858–1947)
Max Planck (1858–1947) was able to describe the spectral distribution of the radiation from a
blackbody by means of the following formula:
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
49
Page 50
9 – Infrared Primer
Where:
Wλb = Blackbody spectral radiant emittance at wavelength λ.
c = Velocity of light = 3 × 108 m/s
h = Planck’s constant = 6.6 × 10-34 Joule sec.
k = Boltzmann’s constant = 1.4 × 10-23 Joule/K.
T = Absolute temperature (K) of a blackbody.
λ = Wavelength (μm).
Note
The factor 10-6 is used since spectral emittance in the curves is expressed in Watt/m2 m. If the
factor is excluded, the dim ension w ill be Watt/m2μm.
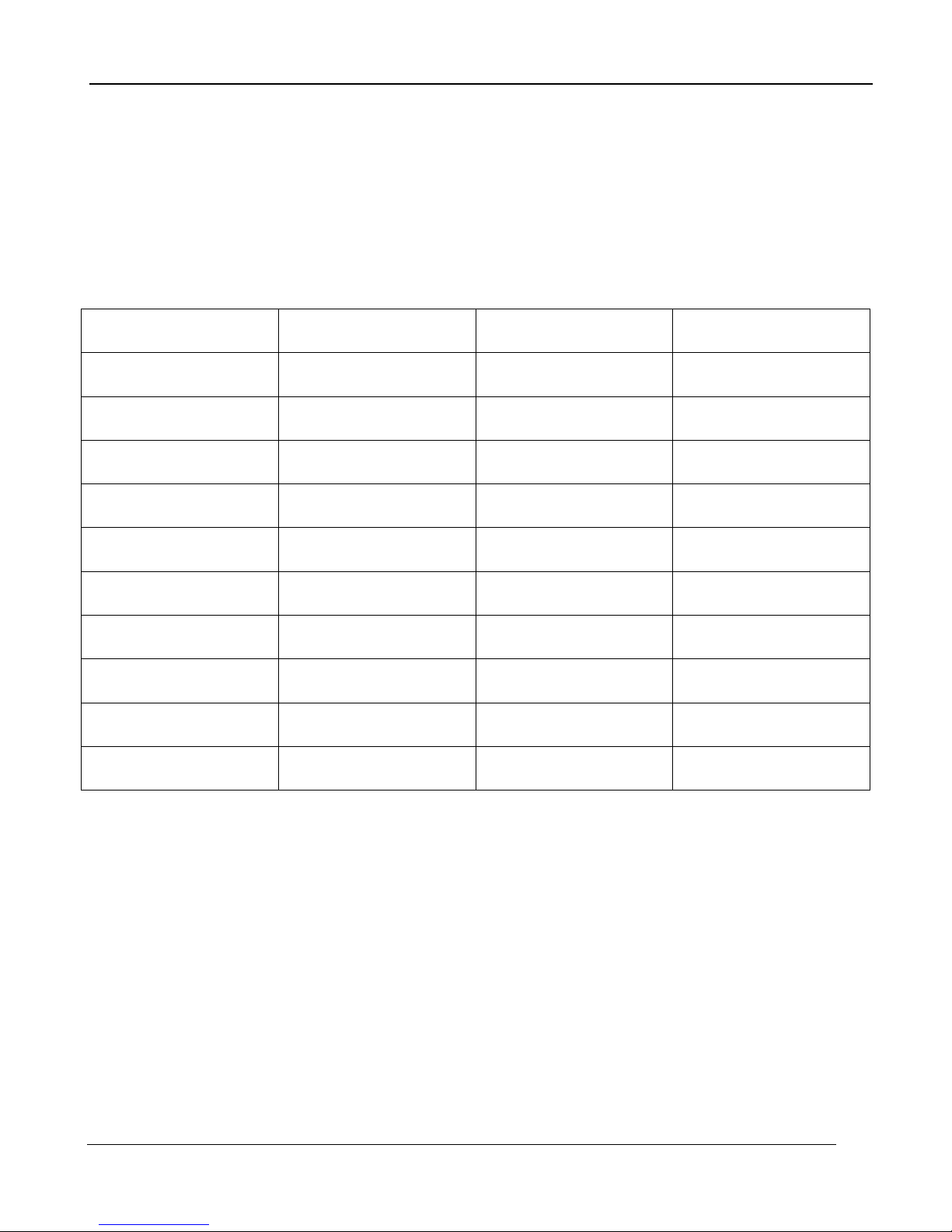
Planck’s formula, when plotted graphically for various temperatures, produces a family of curves.
Following any particular Planck curve, the spectral emittance is zero at λ = 0, then increases r apidly to
a maximum at a wavelength λmax and after passing it approaches zero again at very long
wavelengths. The higher the temperature, the shorter the wavelength at which maximum occurs.
Figure 8-8: Blackbody spectral radiant emittance according to Planck’s law, plotted for various
absolute temperatures. 1: Spectral radiant emittance (W/cm2 × 103(μm)); 2: Wavelength (μm)
Wien’s Displacement Law
By differentiating Planck’s formula with respect to λ, and finding the maximum, we have:
This is Wien’s formula (after Wilhelm Wien, 1864–1928), which expresses mathematically the
common observation that colors vary from red to orange or yellow as the temperature of a thermal
radiator increases. The wavelength of the color is the same as the wavelength calculated for λmax. A
good approximation of the value of λma x for a g iven blackbody temperature is obtained by applying
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
50
Page 51

9 – Infrared Primer
the rule-of-thumb 3 000/T μm. Thus, a very hot star such as Sirius (11 000 K), em itting bluish-white
light, radiates with the peak of spectral radiant emittance occurring within the invisible ultraviolet
spectrum, at wavelength 0.27 μm.
Figure 8-9: Wilhelm Wien (1864–1928)
The sun (approx. 6 000 K) emits yellow light, peaking at about 0.5 μm in the middle of the visible light
spectrum.
At room temperature (300 K) the peak of radiant emittance lies at 9.7 μm, in the f ar infrared, while at
the temperature of liquid nitrogen (77 K) the maximum of the almost insignificant amount of radiant
emittance occurs at 38 μm, in the extreme infrared wavelengths.
Figure 8-10: Planckian curves plotted on semi-log scales from 100 K to 1000 K. The dotted line
represents the locus of maximum radiant emittance at each temperature as described by
Wien's displacement law. 1: Spectral radiant emittance (W/cm2 (μm)); 2: Wavelength (μm).
Stefan-Boltzmann's Law
By integrating Planck’s form ula from λ = 0 to λ = ∞, we obtain the total r adiant emittance (Wb) of a
blackbody:
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
51
Page 52

9 – Infrared Primer
This is the Stefan-Boltzmann formula (after Josef Stefan, 1835–1893, and Ludwig Boltzmann, 1844–
1906), which states that the total emissive power of a blackbody is proportional to the fourth power of
its absolute temperature. Graphically, Wb represents the area below the Planck curve for a particular
temperature. It can be shown that the radiant emittance in the interval λ = 0 t o λmax is only 25 % of
the total, which represents about the amount of the sun’s radiation which lies inside the visible light
spectrum.
Figure 8-11: Josef Stefan (1835–1893), and Ludwig Boltzmann (1844–1906)
Using the Stefan-Boltzmann formula to calculate the power radiated by the human body, at a
temperature of 300 K and an external surface area of approx. 2 m2, we obtain 1 kW. This power loss
could not be sustained if it were not for the compensating absorption of radiation from surrounding
surfaces, at room temperatures which do not vary too drastically from the temperature of the body –
or, of course, the addition of clothing.
Non-Blackbody Emitters
So far, only blackbody radiators and blackbody radiation have been discussed. However, real objects
almost never comply with these laws over an extended wavelength region – although they may
approach the blackbody behavior in certain spectral intervals. For example, a certain type of white
paint may appear perfectly white in the visible light spectrum, but becomes distinctly gray at about 2 μ
m, and beyond 3 μm it is almost black.
There are three processes which can occur that prevent a real object from acting like a blackbody: a
fraction of the incident radiation α may be absorbed, a fraction ρ may be reflected, and a fraction τ
may be transmitted. Since all of these factors are more or less wavelength dependent, the subscript λ
is used to imply the spectral dependence of their definitions. Thus:
The spectral absorptance αλ= the ratio of the spectral radiant power absorbed by an object to that
incident upon it.
The spectral reflectance ρλ = the ratio of the spectral radiant power reflected by an object to that
incident upon it.
The spectral transmittance τλ = the ratio of the spectral radiant power transmitted thr o ug h an o b j ec t to
that incident upon it.
The sum of these three factors must always add up to the whole at any wavelength, so we have the
relation:
For opaque materials τ
λ = 0 and the relation simplifies to:
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
52
Page 53

9 – Infrared Primer
Another factor, called the emissivity, is required to describe the fraction ε of the radiant emittance of a
blackbody produced by an object at a specific temperature. Thus, we have the definition: The spectral
emissivity ε
λ= the ratio of the spectral radiant power from an object to that from a blackbody at the
same temperature and wavelength. Expressed mathematically, this can be written as the ratio of the
spectral emittance of the object to that of a blackbody as follows:
Generally speaking, there are three types of radiat ion source, distinguished by the ways in which the
spectral emittance of each varies with wavelength.
A blackbody, for which ελ = ε = 1
A graybody, for which ελ = ε = constant less than 1
A selective radiator, for which ε varies with wavelength
According to Kirchhoff’s law, for any material the spectral emissivity and spectral absorptance of a
body are equal at any specified temperature and wavelength. That is:
From this we obtain, for an opaque material (since α
λ + ρλ = 1):
For highly polished materials ε
λ approaches zero, so that for a perfectly reflecting material (i.e. a
perfect mirror) we have:
For a graybody radiator, the Stefan-Boltzmann formula becomes:
This states that the total emissive power of a graybody is the same as a blackbody at the same
temperature reduced in proportion to the value of ε from the graybody.
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
53
Page 54
9 – Infrared Primer
Figure 8-12: Spectral radiant emittance of three types of radiators. 1: Spectral radiant
emittance; 2: avelength; 3: Blackbody; 4: Selective radiator; 5: Graybody.
Figure 8-13: Spectral emissivity of three types of radiators. 1: Spectral emissivity; 2:
Wavelength; 3: blackbody; 4: Graybody; 5: Selective radiator.
9.2.4 Infrared Semi-Transparent Materials
Consider now a non-metallic, semi-transparent body – let us say, in the form of a thick flat plate of
plastic material. When the plate is heated, radiation generated within its volume must work its way
toward the surfaces through the material in which it is partially absorbed. Moreover, when it arrives at
the surface, some of it is reflected back into the interior. The back-reflected radiation is again partially
absorbed, but some of it arrives at the other surface, through which most of it escapes; part of it is
reflected back again. Although the progressive reflections become weaker and weaker they must all
be added up when the total emittance of the plate is sought. W hen the resulting geometrical series is
summed, the ef fecti ve emissivity of a semi-transparent plate is obtained as:
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
54
Page 55

9 – Infrared Primer
When the plate becomes opaque this formula is reduced to the single formula:
This last relation is a particularly convenient one, because it is often easier to measure reflectance
than to measure emissivity directly.
9.3 The Measurement Formula
As already mentioned, when viewing an object, the camera receives radiation not only from the object
itself. It also collects radiation from the surroundings reflected via the object surface. Both these
radiation contributions become attenuated to some extent by the atmosphere in the measurement
path. To this comes a third radiation contribution from the atmosphere itself.
This description of the measurement situation, as illustrated in the figure below, is so far a fairly true
description of the real conditions. What has been neglected could for instance be sun lig ht scattering
in the atmosphere or stray radiation from intense radiation sources outside the field of view. Such
disturbances are difficult to quantify, however, in most cases they are fortunately small enough to be
neglected. In case they are not negligible, the measurement configuration is likely to be such that the
risk for disturbance is obvious, at least to a tr ained operator. It is then his r esponsibility to modify the
measurement situation to avoid the disturbance e.g. by changing the viewing direction, shielding off
intense radiation sources etc.
Accepting the description above, we can use the figure below to derive a formula for the calculation of
the object temperature from the calibrated camera output.
Figure 8-14: A schematic representation of the general thermographic measurement
situation.1: Surroundings; 2: Object; 3: Atmosphere; 4: Camera
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
55
Page 56

9 – Infrared Primer
Assume that the received radiation power W from a blackbody source of temperature Tsource on short
distance generates a camera output signal U
source that is proportional to the power input (power linear
camera). We can then write (Equation 1):
Where C i s a const ant.
Should the source be a graybody with emittance ε, the received radiation would consequently be ε
W
source.
We are now ready to write the three collected radiation power terms:
1. Emission from the object = ετWobj, where ε is the emittance of the object and τ is the
transmittance of the atmosphere. The object temperature is Tobj.
2. Reflected emission from am bient sources = (1 – ε)τWrefl, where (1 – ε) is the reflectance of
the object. The ambient sources have the temperature Trefl.
It has here been assumed that the temperature T
refl is the same for all emitting surfaces within the
halfsphere seen from a point on the object surface. This is of course sometimes a simplif ication of the
true situation. It is, however, a necessary simplification in order to derive a workable formula, and T
refl
can – at least theoretically – be given a value that represents an efficient temperature of a complex
surrounding.
Note also that we have assumed that the emittance for the surroundings = 1. This is correct in
accordance with Kirchhoff’s law: All radiation impinging on the surrounding surfaces will eventually be
absorbed by the same surfaces. Thus the emittance = 1.
Note
Though that the latest discussion requires the complete sphere around theobject to be
considered.
3. Emission from the atmosphere = (1 – τ)τWatm, where (1 – τ) is the emittance of the
atmosphere. The temperature of the atmosphere is Tatm.
The total received radiation power can now be written (Equation 2):
We multiply each term by the constant C of Equation 1 and replace the CW products by the
corresponding U according to the same equation, and get (Equation 3):
Solve Equation 3 for U
obj (Equation 4):
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
56
Page 57

9 – Infrared Primer
This is the general measurement formula used in all the FLIR Systems thermographic equipment. The
voltages of the formula are:
Uobj = Calculated camera output voltage for a blackbody of temperature T obj i. e. a voltag e that ca n
be directly converted into true requested object temperature.
Utot = Measured camera output voltage for the actual case.
Urefl = Theoretical camera output voltage for a blackbody of temperature Trefl according to the
calibration.
Uatm = Theoretical camera output voltage for a blackbody of temperature Tatm according to the
calibration.
The operator has to supply a number of parameter values for the calculation:
The object emittance ε,
The relative humidity,
Tatm
Object distance (Dobj)
The (effective) temperature of the object surroundings, or the reflected ambient temperature Trefl, and
The temperature of the atmosphere Tatm
This task could sometimes be a heavy burden for the operator since there are normally no easy ways
to find accurate values of emittance and atmospheric transmittance for the actual case. The two
temperatures are normally less of a problem provided the surroundings do not contain large and
intense radiation sources.
A natural question in this connection is: How important is it to know the right values of these
parameters? It could though be of interest to get a feeling for this problem already here by looking into
some different measurement cases and compare the relative magnitudes of the three radiation terms.
This will give indications about when it is important to use correct values of which parameters.
The figures below illustrates the relative magnitudes of the three radiation contributions for three
different object temperatures, two emittances, and two spectral ranges: SW and LW. Remaining
parameters have the following fixed values:
τ = 0.88
Trefl = +20 °C (+68 °F)
Trefl = +20 °C (+68 °F)
It is obvious that measurement of low object temperatures are more critical than measuring high
temperatures since the ‘disturbing’ radiation sources are relatively much stronger in the first case.
Should also the object emittance be low, the situation would be still more difficult.
We have finally to answer a question about the importance of being allowed to use the calibration
curve above the highest calibration point, what we call extrapolation. Imagine that we in a certain case
measure U
value unknown to the operator. Thus, even if the object happened to be a blackbody, i.e. U
tot = 4.5 volts. The highest calibrat ion point for the camera was in the order of 4.1 volts, a
obj = Utot,
we are actually performing extrapolation of the calibration curve when converting 4.5 volts into
temperature.
Let us now assume that the object is not black, it has an emittance of 0.75, and the transmittance is
0.92. We also assume that the two second terms of Equation 4 amount to 0.5 volts together.
Computation of U
obj by means of Equation 4 then results in Uobj = 4.5 / 0.75 / 0.92 – 0.5 = 6.0. This is a
rather extreme extrapolation, particularly when considering that the video amplifier might limit the
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
57
Page 58

9 – Infrared Primer
output to 5 volts! Note, though, that the application of the calibration curve is a theoretical procedure
where no electronic or other limitations exist. W e trust that if there had been no signal limitations in
the camera, and if it had been calibrated far beyond 5 volts, the resulting curve would have been very
much the same as our real curve extrapolated beyond 4.1 volts, provided t he calibration algorithm is
based on radiation physics, like the FLIR Systems algorithm. Of course there must be a limit to such
extrapolations.
Figure 8-15: Relative magnitudes of radiation sources under varying measurement conditions
(SW camera).1: Object temperature; 2: Emittance; RED: Object radiation; BLUE: Reflected
radiation; GREEN: atmosphere radiation. Fixed parameters: τ = 0.88; Trefl = 20 °C (+68 °F);
Tatm = 20 °C (+68 °F).
9.4 Emissivity tables
This section presents a compilation of emissivity data from the infrared literature and FLIR Systems
own measurements.
Table 8-1: T: Total spectrum; SW: 2–5 µm; LW: 8–14 µm, LLW: 6.5–20 µm; 1: Material; 2:
Specification; 3: Temperature in °C; 4: Spectrum; 5: Emissivity: 6: Reference
1. Mikael A. Bramson: Infrared Radiation, A Handbook for Applications, Plenum press, N.Y.
2. William L. Wolfe, George J. Zissis: The Infrared Handbook, Office of Naval Research,
Department of Navy, Washington, D.C.
3. Madding, R. P.: Thermographic Instruments and systems. Madison, Wisconsin: University of
Wisconsin–Extension, Department of Engineering and Applied Science.
4. William L. Wolfe: Handbook of Military Infrared Technology, Office of Naval Research,
Department of Navy, Washington, D.C.
5. Jones, Smith, Probert: External thermography of buildings..., Proc. of the Society of PhotoOptical Instrumentation Engineers, vol.110, Industrial and Civil Applications of Infrared
Technology, June 1977, London.
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
58
Page 59

9 – Infrared Primer
6. Paljak, Pettersson: Thermography of Buildings, Swedish Building Research Institute,
Stockholm 1972.
7. Vlcek, J: Determination of emissivity with imaging radiometers and some emissivities at l ~ 5
mm. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing.
8. Kern: Evaluation of infrared emission of clouds and gr ound as measured by weather satellites,
Defence Documentation Center, AD 617 417.
9. Ohman, Claes: Emittansmatningar med AGEMA E-Box. Teknisk rapport, AGEMA 1999.
(Emittance measurements using AGEMA E-Box. Technical report, AGEMA 1999.)
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
59
Page 60
9 – Infrared Primer
1
2
3 4 5
6
Aluminum
anodized, black, dull
70
LW
0.95
9
Aluminum
anodized, black, dull
70
SW
0.67
9
Aluminum
anodized, light gray, dull
70 T 0.97
9
Aluminum
anodized, light gray, dull
70 T 0.61
9
Aluminum
anodized sheet
100 T 0.55
2
Aluminum
as received, plate
100 T 0.09
4
Aluminum
as received, sheet
100 T 0.09
2
Aluminum
cast, blast cleaned
70
LW
0.46
9
Aluminum
cast, blast cleaned
70
SW
0.47
9
Aluminum
dipped in HNO3, plate
100 T 0.09
4
Aluminum
Foil
27
3 µm
0.09
3
Aluminum
Foil
27
10 µm
0.04
3
Aluminum
oxidized, strongly
50-100
T
0.2-0.3
1
Aluminum
polished
50-100
T
0.04-0.06
1
Aluminum
polished, sheet
100 T 0.05
2
Aluminum
polished plate
100 T 0.05
4
Aluminum
roughened
27
3 µm
0.28
3
Aluminum
roughened
27
10 µm
0.18
3
Aluminum
rough surface
20-50
T
0.06-0.07
1
Aluminum
Sheet, 4 samples differently
70
LW
0.03-0.06
9
Aluminum
Sheet, 4 samples differently
70
SW
0.05-0.08
9
Aluminum
vacuum deposited
20 T 0.04
2
Aluminum
weathered, heavily
17
SW
0.83-0.94
5
Aluminum bronze
20 T 0.60
1
Aluminum hydroxide
powder
T 0.28
1
Aluminum oxide
activated, powder
T 0.46
1
Aluminum oxide
pure, powder alumina
T 0.16
1
Asbestos
Board
20 T 0.96
1
Asbestos
Fabric
T 0.78
7
Asbestos
floor tile
35
SW
0.94
1
Asbestos
Paper
40-400
T
0.93-0.95
1
Asbestos
Powder
T 0.40-0.60
1
Asbestos
Slate
20 T 0.96
8
scratched
scratched
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
60
Page 61

9 – Infrared Primer
Asphalt paving
4 LLW
0.967
1
Brass
dull, tarnished
20-350
T
0.22
9
Brass
oxidized
70
SW
0.04-0.09
9
Brass
oxidized
70
LW
0.03-0.07
2
Brass
oxidized
100 T 0.61
1
Brass
oxidized at 600 °C
200-600
T
0.59-0.61
1
Brass
polished
200 T 0.03
2
Brass
polished, highly
100 T 0.03
2
Brass
rubbed with 80- grit emery
20 T 0.20
1
Brass
Sheet, rolled
20 T 0.06
1
Brass
Sheet, worked with emer y
20 T 0.2 5 Brick
Alumina
17
SW
0.68
5
Brick
common
17
SW
0.86-0.81
5
Brick
Dinas silica, glazed, rough
1100
T
0.85
1
Brick
Dinas silica, refractory
1000
T
0.66
1
Brick
Dinas silica, unglazed, rough
1000
T
0.80
1
Brick
firebrick
17
SW
0.68
5
Brick
Fireclay
20 T 0.85
1
Brick
fireclay
1000
T
0.75
1
Brick
fireclay
1200
T
0.59
1
Brick
masonry
35
SW
0.94
7
Brick
masonry,
20 T 0.94
1
Brick
red, common
20 T 0.93
2
Brick
red, rough
20 T 0.88-0.93
1
Brick
refractory, corundum
1000
T
0.46
1
Brick
refractory, magnesite
1000-1300
T
0.38
1
Brick
refractory, strongly radiating
500-1000
T
0.8-0.9
1
Brick
refractory, weakly radiating
500-1000
T
0.65-0.75
1
Brick
Silica, 95 % SiO2
1230
T
0.66
1
Brick
sillimanite, 33 % SiO2, 64 %
1500
T
0.29
1
Brick
waterproof
17
SW
0.87
5
Bronze
phosphor bronze
70
LW
0.06
9
Bronze
phosphor bronze
70
SW
0.08
9
Bronze
polished
50 T 0.1
1
plastered
Al2O3
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
61
Page 62

9 – Infrared Primer
Bronze
porous, rough
50-150
T
0.55
1
Bronze
Powder
T 0.76-0.80
1
Carbon
candle soot
20 T 0.95
2
Carbon
charcoal powder
T 0.96
1
Carbon
graphite, filed surface
20 T 0.98
2
Carbon
graphite powder
T 0.97
1
Carbon
lampblack
20-400
T
0.95-0.97
1
Chipboard
untreated
20
SW
0.90
6
Chromium
polished
50 T 0.10
1
Chromium
Polished
500-1000
T
0.28-0.38
1
Clay
Fired
70 T 0.91
1
Cloth
Black
20 T 0.98
1
Concrete
20
SW
0.92
2
Concrete
Dry
36
SW
0.95
7
Concrete
Rough
17
LLW
0.97
5
Concrete
Walkway
5 T 0.974
8
Copper
commercial, burnished
20 T 0.07
1
Copper
electrolytic, carefully polished
80 T 0.018
1
Copper
electrolytic, polished
-34 T 0.006
4
Copper
Molten
1100-1300
T
0.13-0.15
1
Copper
Oxidized
50 T 0.6-0.7
1
Copper
oxidized, black
27 T 0.78
4
Copper
oxidized, heavily
20 T Copper
oxidized to blackness
T 0.88
1
Copper
Polished
50-100
T
0.02
1
Copper
Polished
100 T 0.03
2
Copper
polished, commercial
27 T 0.03
4
Copper
polished, mechanical
22 T 0.015
4
Copper
pure, carefully prepared surface
22 T 0.008
4
Copper
Scraped
27 T 0.07
4
Copper dioxide
Powder
T 0.84
1
Copper oxide
red, powder
T 0.70
1
Ebonite
T
0.89
1
Emery
Coarse
80 T 0.85
1
Enamel
20 T 0.9
1
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
62
Page 63

9 – Infrared Primer
Enamel
Lacquer
20 T 0.85-0.95
1
Fiber board
hard, untreated
20
SW
0.85
6
Fiber board
Masonite
70
LW
0.88
9
Fiber board
Masonite
70
SW
0.75
9
Fiber board
particle board
70
LW
0.89
9
Fiber board
particle board
70
SW
0.77
9
Fiber board
porous, untreated
20
SW
0.85
6
Gold
Polished
130 T 0.018
1
Gold
polished, carefully
200-600
T
0.02-0.03
1
Gold
polished, highly
100 T 0.02
2
Granite
Polished
20
LLW
0.849
8
Granite
Rough
21
LLW
0.879
8
Granite
rough, 4 different samples
70
LW
0.77-0.87
9
Granite
rough, 4 different samples
70
SW
0.95-0.97
9
Gypsum
20 T 0.8-0.9
1
Ice: See Water
T
Iron, cast
Casting
50 T 0.81
1
Iron, cast
Ingots
1000
T
0.95
1
Iron, cast
Liquid
1300
T
0.28
1
Iron, cast
Machined
800-1000
T
0.60-0.70
1
Iron, cast
Oxidized
38 T 0.63
4
Iron, cast
Oxidized
100 T 0.64
2
Iron, cast
Oxidized
260 T 0.66
4
Iron, cast
Oxidized
538 T 0.76
4
Iron, cast
oxidized at 600°C
200-600
T
0.64-0.78
1
Iron, cast
Polished
38 T 0.21
4
Iron, cast
Polished
40 T 0.21
2
Iron, cast
Polished
200 T 0.21
1
Iron, cast
Unworked
900-1100
T
0.87-0.95
1
Iron and steel
cold rolled
70
LW
0.09
9
Iron and steel
cold rolled
70
SW
0.20
9
Iron and steel
covered with red rust
20 T 0.61-0.85
1
Iron and steel
Electrolytic
22 T 0.05
4
Iron and steel
Electrolytic
100 T 0.05
4
Iron and steel
Electrolytic
260 T 0.07
4
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
63
Page 64

9 – Infrared Primer
Iron and steel
electrolytic, carefully polished
175-225
T
0.05-0.06
1
Iron and steel
freshly worked with emer y
20 T 0.24
1
Iron and steel
ground sheet
950-1100
T
0.55-0.61
1
Iron and steel
heavily rusted sheet
20 T 0.69
2
Iron and steel
hot rolled
20 T 0.77
1
Iron and steel
hot rolled
130 T 0.60
1
Iron and steel
Oxidized
100 T 0.74
1
Iron and steel
Oxidized
100 T 0.74
4
Iron and steel
Oxidized
125-525
T
0.78-0.82
1
Iron and steel
Oxidized
200 T 0.79
2
Iron and steel
Oxidized
1227
T
0.89
4
Iron and steel
Oxidized
200-600
T
0.80
1
Iron and steel
oxidized strongly
50 T 0.88
1
Iron and steel
oxidized strongly
500 T 0.98
1
Iron and steel
Polished
100 T 0.07
2
Iron and steel
Polished
400-1000
T
0.14-0.38
1
Iron and steel
polished sheet
750-1050
T
0.52-0.56
1
Iron and steel
rolled, freshly
20 T 0.24
1
Iron and steel
rolled sheet
50 T 0.56
1
Iron and steel
rough, plane surface
50 T 0.95-0.98
1
Iron and steel
rusted, heavily
17
SW
0.96
5
Iron and steel
rusted red, sheet
22 T 0.69
4
Iron and steel
rusty, red
20 T 0.69
1
Iron and steel
shiny, etched
150 T 0.16
1
Iron and steel
Shiny oxide layer, sheet
20 T 0.82
1
Iron and steel
Wrought, carefully polished
40-250
T
0.28
1
Iron galvanized
heavily oxidized
70
LW
0.85
9
Iron galvanized
heavily oxidized
70
SW
0.64
9
Iron galvanized
Sheet
92 T 0.07
4
Iron galvanized
sheet, burnished
30 T 0.23
1
Iron galvanized
sheet, oxidized
20 T 0.28
1
Iron tinned
Sheet
24 T 0.064
4
Lacquer
3 colors sprayed on Aluminum
70
LW
0.92-0.94
9
Lacquer
3 colors sprayed on Aluminum
70
SW
0.50-0.53
9
Lacquer
Aluminum on rough surface
20 T 0.4
1
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
64
Page 65

9 – Infrared Primer
Lacquer
Bakelite
80 T 0.83
1
Lacquer
black, dull
40-100
T
0.96-0.98
1
Lacquer
black, matte
100 T 0.97
2
Lacquer
black, shiny, sprayed on iron
20 T 0.87
1
Lacquer
heat–resistant
100 T 0.92
1
Lacquer
White
40-100
T
0.8-0.95
1
Lacquer
White
100 T 0.92
2
Lead
oxidized, gray
20 T 0.28
1
Lead
oxidized, gray
22 T 0.28
4
Lead
oxidized at 200 °C
200 T 0.63
1
Lead
Shiny
250 T 0.08
1
Lead
unoxidized, polished
100 T 0.05
4
Lead red
100 T 0.93
4
Lead red, powder
100 T 0.93
1
Leather
Tanned
T 0.75-0.80
1
Lime
T
0.3-0.4
1
Magnesium
22 T 0.07
4
Magnesium
260 T 0.13
4
Magnesium
538 T 0.18
4
Magnesium
Polished
20 T 0.07
2
Magnesium
T
0.86
1
Molybdenum
600-1000
T
0.08-0.13
1
Molybdenum
1500-2200
T
0.19-0.26
1
Molybdenum
Filament
700-2500
T
0.1-0.3
1
Mortar
17
SW
0.87
5
Mortar
Dry
36
SW
0.94
7
Nichrome
Rolled
700 T 0.25
1
Nichrome
Sandblasted
700 T 0.70
1
Nichrome
wire, clean
50 T 0.65
1
Nichrome
wire, clean
500-1000
T
0.71-0.79
1
Nichrome
wire, oxidized
50-500
T
0.95-0.98
1
Nickel
bright matte
122 T 0.041
4
Nickel
Commercially pure, polished
100 T 0.045
1
Nickel
Commercially pure, polished
200-400
T
0.07-0.09
1
powder
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
65
Page 66

9 – Infrared Primer
Nickel
Electrolytic
22 T 0.04
4
Nickel
Electrolytic
38 T 0.06
4
Nickel
Electrolytic
260 T 0.07
4
Nickel
Electrolytic
538 T 0.10
4
Nickel
electroplated, polished
20 T 0.05
2
Nickel
Electroplated on iron, polished
22 T 0.045
4
Nickel
electroplated on iron,
20 T 0.11-0.40
1
Nickel
electroplated on iron,
22 T 0.11
4
Nickel
Oxidized
200 T 0.37
2
Nickel
Oxidized
227 T 0.37
4
Nickel
Oxidized
1227
T
0.85
4
Nickel
oxidized at 600 °C
200-600
T
0.37-0.48
1
Nickel
Polished
122 T 0.045
4
Nickel
Wire
200-1000
T
0.1-0.2
1
Nickel oxide
500-650
T
0.52-0.59
1
Nickel oxide
1000-1250
T
0.75-0.86
1
Oil, lubricating
0.025 mm film
20 T 0.27
2
Oil, lubricati ng
0.050 mm film
20 T 0.46
2
Oil, lubricati ng
0.125 mm film
20 T 0.72
2
Oil, lubricati ng
film on Ni base: Ni base only
20 T 0.05
2
Oil, lubricati ng
thick coating
20 T 0.82
2
Paint
8 different colors and qualities
70
LW
0.92-0.94
9
Paint
8 different colors and qualities
70
SW
0.88-0.96
9
Paint
Aluminum, various ages
50-100
T
0.27-0.67
1
Paint
cadmium yellow
T 0.28-0.33
1
Paint
chrome green
T 0.65-0.70
1
Paint
cobalt blue
T 0.7-0.8
1
Paint
Oil
17
SW
0.87
5
Paint
oil, black flat
20
SW
0.94
6
Paint
oil, black gloss
20
SW
0.92
6
Paint
oil, gray flat
20
SW
0.97
6
Paint
oil, gray gloss
20
SW
0.96
6
Paint
oil, various colors
100 T 0.92-0.96
1
Paint
oil based, average of 16 colors
100 T 0.94
2
unpolished
unpolished
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
66
Page 67

9 – Infrared Primer
Paint
plastic, black
20
SW
0.95
6
Paint
plastic, white
20
SW
0.84
6
Paper
4 different colors
70
LW
0.92-0.94
9
Paper
4 different colors
70
SW
0.68-0.74
9
Paper
Black
T 0.90
1
Paper
black, dull
T 0.94
1
Paper
black, dull
70
LW
0.89
9
Paper
black, dull
70
SW
0.86
9
Paper
blue, dark
T 0.84
1
Paper
coated with black lacquer
T 0.93
1
Paper
Green
T 0.85
1
Paper
Red
T 0.76
1
Paper
White
20 T 0.7-0.9
1
Paper
white, 3 different glosses
70
LW
0.88-0.90
9
Paper
white, 3 different glosses
70
SW
0.76-0.78
9
Paper
white bond
20 T 0.93
2
Paper
Yellow
T 0.72
1
Plaster
17
SW
0.86
5
Plaster
plasterboard, untreated
20
SW
0.90
6
Plaster
rough coat
20 T 0.91
2
Plastic
glass fibre laminate (printed
70
LW
0.91
9
Plastic
glass fibre laminate (printed
70
SW
0.94
9
Plastic
Polyurethane isolation boar d
70
LW
0.55
9
Plastic
Polyurethane isolation boar d
70
SW
0.29
9
Plastic
PVC, plastic floor, dull,
70
LW
0.93
9
Plastic
PVC, plastic for, dull, structured
70
SW
0.94
9
Platinum
17 T 0.016
4
Platinum
22 T 0.03
4
Platinum
100 T 0.05
4
Platinum
260 T 0.06
4
Platinum
538 T 0.10
4
Platinum
1000-1500
T
0.14-0.18
1
Platinum
1094
T
0.18
4
circ. board)
circ. board)
structured
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
67
Page 68
9 – Infrared Primer
Platinum
pure, polished
200-600
T
0.05-0.10
1
Platinum
Ribbon
900-1100
T
0.12-0.17
1
Platinum
Wire
50-200
T
0.06-0.07
1
Platinum
Wire
500-1000
T
0.10-0.16
1
Platinum
Wire
1400
T
0.18
1
Porcelain
Glazed
20 0.92
1
Porcelain
white, shiny
T 0.70-0.75
1
Rubber
Hard
20 T 0.95
1
Rubber
soft, gray, rough
20 T 0.95
1
Sand
T
0.60
1
Sand
20 T 0.90
2
Sandstone
Polished
19
LLW
0.909
8
Sandstone
Rough
19
LLW
0.935
8
Silver
Polished
100 T 0.03
2
Silver
pure, polished
200-600
T
0.02-0.03
1
Skin
Human
32 T 0.98
2
Slag
Boiler
0-100
T
0.97-0.93
1
Slag
Boiler
200-500
T
0.89-0.78
1
Slag
Boiler
600-1200
T
0.76-0.70
1
Slag
Boiler
1400-1800
T
0.69-0.67
1
Snow: See Water
Soil
Dry
20 T 0.92
2
Soil
saturated with water
20 T 0.95
2
Stainless steel
alloy, 8 % Ni, 18 % Cr
500 T 0.35
1
Stainless steel
Rolled
700 T 0.45
1
Stainless steel
Sandblasted
700 T 0.70
1
Stainless steel
sheet, polished
70
LW
0.14
9
Stainless steel
sheet, polished
70
SW
0.18
9
Stainless steel
sheet, untreated, somewhat
70
LW
0.28
9
Stainless steel
sheet, untreated, somewhat
70
SW
0.30
9
Stainless steel
type 18-8, buffed
20 T 0.16
2
Stainless steel
type 18-8, oxidized at 800 °C
60 T 0.85
2
Stucco
rough, lime
10-90
T
0.91
1
Styrofoam
Insulation
37
SW
0.60
7
scratched
scratched
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
68
Page 69
9 – Infrared Primer
Tar T 0.79-0.84
1
Tar
Paper
20 T 0.91-0.93
1
Tile
Glazed
17
SW
0.94
5
Tin
Burnished
20-50
T
0.04-0.06
1
Tin
tin–plated sheet iron
100 T 0.07
2
Titanium
Oxidized at 540 °C
200 T 0.40
1
Titanium
Oxidized at 540 °C
500 T 0.50
1
Titanium
Oxidized at 540 °C
1000
T
0.60
1
Titanium
Polished
200 T 0.15
1
Titanium
Polished
500 T 0.20
1
Titanium
Polished
1000
T
0.36
1
Tungsten
200 T 0.05
1
Tungsten
600-1000
T
0.1-0.16
1
Tungsten
1500-2200
T
0.24-0.31
1
Tungsten
Filament
3300
T
0.39
1
Varnish
Flat
20
SW
0.93
6
Varnish
on oak parquet floor
70
LW
0.90-0.93
9
Varnish
on oak parquet floor
70
SW
0.90
9
Wallpaper
slight pattern, light gray
20
SW
0.85
6
Wallpaper
slight pattern, red
20
SW
0.90
6
Water
Distilled
20 T 0.96
2
Water
frost crystals
-10 T 0.98
2
Water
ice, covered with heavy frost
0 T 0.98
1
Water
ice, smooth
-10 T 0.96
2
Water
ice, smooth
0 T 0.97
1
Water
layer >0.1 mm thick
0-100
T
0.95-0.98
1
Water
Snow
T 0.8 1 Water
Snow
-10 T 0.85
2
Wood
17
SW
0.98
5
Wood
19
LLW
0.962
8
Wood
Ground
T 0.5-0.7
1
Wood
pine, 4 different samples
70
LW
0.81-0.89
9
Wood
pine, 4 different samples
70
SW
0.67-0.75
9
Wood
Planed
20 T 0.8-0.9
1
Wood
planed oak
20 T 0.90
2
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
69
Page 70
9 – Infrared Primer
Wood
planed oak
70
LW
0.88
9
Wood
planed oak
70
SW
0.77
9
Wood
plywood, smooth, dry
36
SW
0.82
7
Wood
plywood, untreated
20
SW
0.83
6
Wood
white, damp
20 T 0.7-0.8
1
Zinc
oxidized at 400 °C
400 T 0.11
1
Zinc
oxidized surface
100-1200
T
0.50-0.60
1
Zinc
Polished
200-300
T
0.04-0.05
1
Zinc
Sheet
50 T 0.20
1
A6700sc/A6750sc User’s Manual
70
 Loading...
Loading...