Page 1
OWNERS GUIDE TO
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION
4” — 35-85 GPM and
6” — 50-250 GPM
8” — 325-400 GPM
SUBMERSIBLE PUMPS
WARNING
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
RULES FOR SAFE INSTALLATION AND OPERATION
FW1184
0314
Supersedes
0611
1. Read these warnings and instructions carefully.
Failure to follow them could cause serious bodily
injury and/or property damage.
2. Follow all local electrical and safety codes as well
as the National Electrical Code (NEC) and the
Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA).
3. The power supply should be a separate circuit,
independent of all other circuits. Be sure it is
equipped with a fuse and disconnect box of ample
capacity.
4. For fire protection, the power supply should be free
of any building, preferably on a direct line from the
transformer. In the event of fire, the wires will not be
destroyed and the water supply not cut-off.
5. Always disconnect power source before performing
any work on or near the motor or its connected load.
If the power disconnect point is out-of-sight, lock it in
the open position and tag it to prevent unexpected
application of power. Failure to do so could result in
fatal electrical shock.
6. DO NOT handle pump with wet hands or when
standing in water as fatal electrical shock could occur.
Disconnect main power supply before handling pump
for any reason.
7. Shut off power source when voltage drops 10% below
the rated voltage of the motor.
8. Protect the power cable from coming in contact with
sharp objects, oil, grease, hot surfaces or chemicals.
DO NOT kink the power cable. If damaged replace
immediately.
9. NEVER leave the control box, fused disconnect
switch, or covers open (either partially or completely)
when not being worked on by a competent electrician
or repairman.
10. Always use caution when operating electrical controls
in damp areas. If possible, avoid all contact with
electrical equipment during thunderstorms or extreme
damp conditions.
11. Install all electrical equipment in protected area to
prevent mechanical damage which could produce
serious electrical shock and/or equipment failure.
12. Pump is designed to pump cold ground water that is
free of air or gases. Decreased pump performance
and life expectancy can occur if the ground water is
not cold (86F/30C) or contains air or gases.
13. Pump and controls must be securely and adequately
grounded as specified in section 250-43 item (A) of
the U.S.A. National Electric Code (NEC) and Section
26-954 Canadian Electrical Code. Failure to do so
could result in a fatal injury.
14. DO NOT use this pump to pump flammable liquids
such as gasoline, fuel oil, kerosene, etc. Failure to
follow the above warning could result in property
damage and/or personal injury.
WARNING: The pump is intended for use in a well. Motor
frame must be connected to power supply ground or fatal
electrical shock may result. Do not use this pump in
swimming pools.
NOTE: Pumps with the “CSA” mark are tested to UL
standard UL778 and certified to CSA standard C22.2 No.
108.
130582
Copyright © 2014. All rights reserved • 95 North Oak St. • Kendallville, IN 46755
1
Page 2
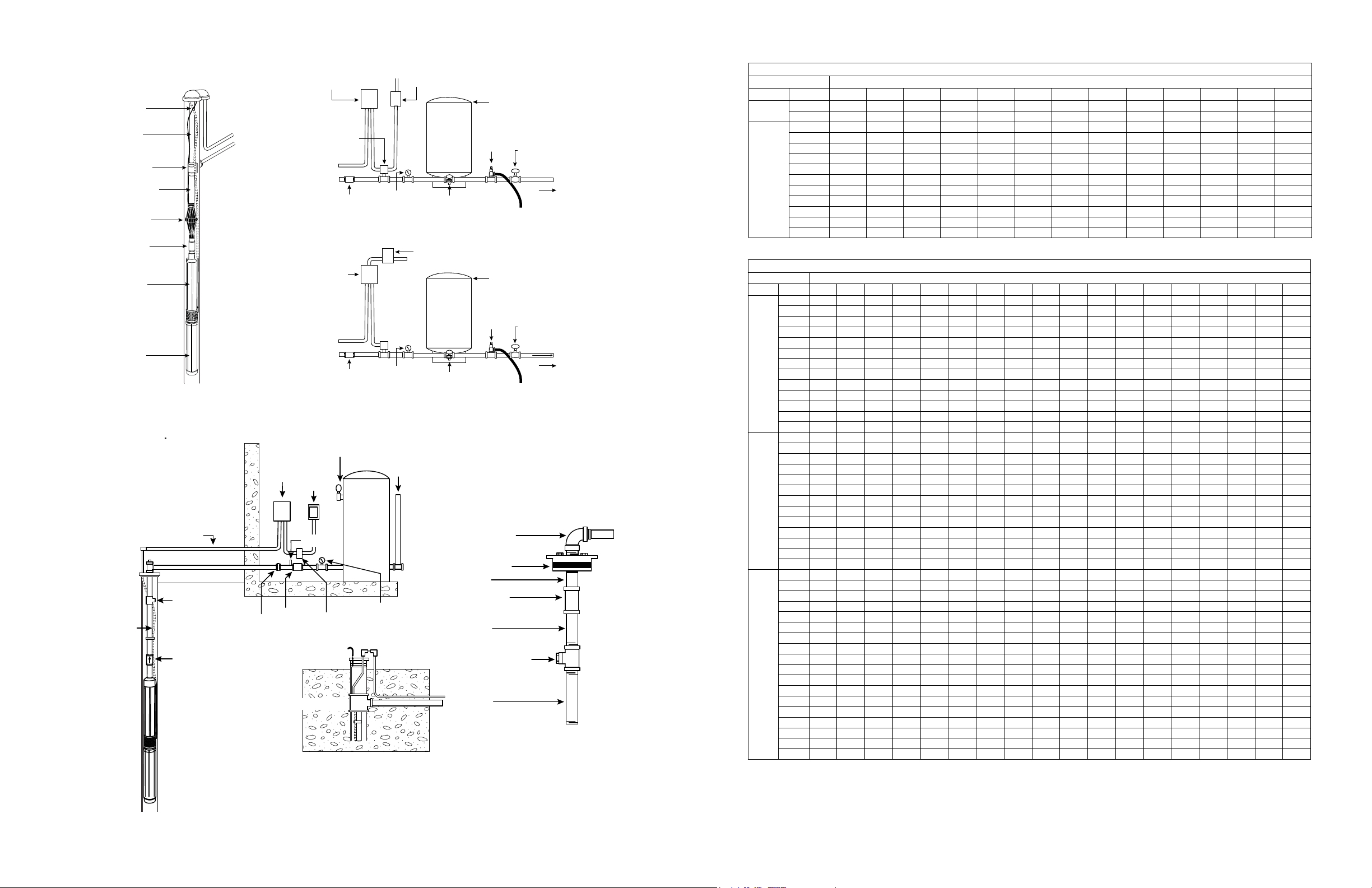
Typical Installation
Submersible
Cable
Riser
Pipe
Pitless
Adapter
Plastic or
Steel Pipe
Torque
Arrestor
Check
Valve
Submersible
Pump
Submersible
Motor
Figure 1 — Typical Installation with Pre-Charged Tank
Submersible Power
Cable to Pump
Bleeder Orifice
Power Cable
Taped
to Pipe
Check Valve
Figure 2 — Typical Installation with Standard Pneumatic Tank
Copyright © 2014. All rights reserved • 95 North Oak St. • Kendallville, IN 46755
Conduit
IL0092
Union
Control
Box
Check
Valve
Magnetic
Starter
Fused
Switch
Box
Snifter
Pressure
Switch
Pitless Unit
Control
Box
Pressure
Switch
Check
Valve
Single Phase Tank/Controls Installation
Check
Valve
Three Phase Tank/Controls Installation
Air Release and
Pressure Gauge
Tank
Relief Valve
2
Fuse Disconnect
Box
Pressure
Gauge
Fuse Disconnect
Box
Pressure
Gauge
Outlet to Service
Drain
Valve
Drain
Valve
Pre-Charged
Pressure
Tank
Pressure
Relief
Valve
Gate
Valve
To Drain
Pre-Charged
Pressure
Tank
Pressure
Relief
Valve
Gate
Valve
To Drain
90º Elbow
Well Seal
Pipe
Coupling
Pipe
Bleeder Valve
Rubber Orifice
Pipe
To
Service
To
Service
IL0093A
CABLE SELECTION
Single Phase, 2-Wire or 3-Wire Cable, 60 Hz (Service Entrance to Motor)
Motor Rating Copper Wire Size
Volts HP 14
115
230
1 foot = .3048 meters
1/3 130 210 340 540 840 1300 1610 1960 2390 2910 3540 4210 5060
1/2 100 160 250 390 620 960 1190 1460 1780 2160 2630 3140 3770
1/3 550 880 1390 2190 3400 5250 6520 7960 9690 11770
1/2 400 650 1020 1610 2510 3880 4810 5880 7170 8720
3/4 300 480 760 1200 1870 2890 3580 4370 5330 6470 7870
1 250 400 630 990 1540 2380 2960 3610 4410 5360 6520
1-1/2 190 310 480 770 1200 1870 2320 2850 3500 4280 5240
2 150 250 390 620 970 1530 1910 2360 2930 3620 4480
3 120* 190 300 470 750 1190 1490 1850 2320 2890 3610
5 0 0 180* 280 450 710 890 1110 1390 1740 2170 2680
7-1/2 0 0 0 200* 310 490 610 750 930 1140 1410 1720
10 0 0 0 0 250 390 490 600 750 930 1160 1430 1760
15 0 0 0 0 170* 270* 340 430 530 660 820 1020 1260
Three Phase, 3-Wire, 60 Hz, 200 and 230 Volts (Service Entrance to Motor)
Motor Rating Copper Wire Size
Volts HP 14 12 10 8 6 4 3 2 1 0 00 000 0000 250 300 350 400 500
200V
60Hz 3
Phase
3 Wire
230V
60Hz 3
Phase
3 Wire
460V
Phase
3 Wire
CAUTION: Use of wire size smaller than listed will void warranty.
(*) Meet the U.S. National Electrical Code ampacity only for individual conductor 60ºC cable. Only the lengths without * meet the code for jacketed 60ºC cable. Local code
Maximum lengths shown maintain motor voltage at 95% of service entrance voltage, running at maximum nameplate amperes. If service entrance voltage will be at least motor nameplate
voltage under normal load conditions, 50% additional length is permissible for all sizes.
This table is based on copper wire. If aluminum wire is used it must be two (2) sizes larger. Example: When the table calls for #12 copper wire you would use #10 aluminum wire.
Single phase control boxes may be connected at any point of the total cable length.
Cables #14 to #0000 are AWG sizes.
1/2 710 1140 1800 2840 4420
3/4 510 810 1280 2030 3160
1 430 690 1080 1710 2670 4140 5140
1-1/2 310 500 790 1260 1960 3050 3780
2 240 390 610 970 1520 2360 2940 3610 4430 5420
3 180 290 470 740 1160 1810 2250 2760 3390 4130
5 110* 170 280 440 690 1080 1350 1660 2040 2490 3050 3670 4440 5030
7-1/2 0 0 200 310 490 770 960 1180 1450 1770 2170 2600 3150 3560
10 0 0 0 230* 370 570 720 880 1090 1330 1640 1970 2390 2720 3100 3480 3800 4420
15 0 0 0 160* 250* 390 490 600 740 910 111 0 1340 1630 1850 2100 2350 2570 2980
20 0 0 0 0 190* 300* 380 460 570 700 860 1050 1270 1440 1650 1850 2020 2360
25 0 0 0 0 0 240* 300* 370* 460 570 700 840 1030 1170 1330 1500 1640 1900
30 0 0 0 0 0 0 250* 310* 380* 470 580 700 850 970 111 0 1250 1360 1590
1/2 930 1490 2350 3700 5760 8910
3/4 670 1080 1700 2580 4190 6490 8060 9860
1 560 910 1430 2260 3520 5460 6780 8290
1-1/2 420 670 1060 1670 2610 4050 5030 6160 7530 9170
2 320 510 810 1280 2010 3130 3890 4770 5860 7170 8780
3 240 390 620 990 1540 2400 2980 3660 4480 5470 6690 8020 9680
5 140* 230 370 590 920 1430 1790 2190 2690 3290 4030 4850 5870 6650 7560 8460 9220
7-1/2 0 160* 260 420 650 1020 1270 1560 1920 2340 2870 3440 4160 4710 5340 5970 6500 7510
10 0 0 190* 310 490 760 950 1170 1440 1760 2160 2610 3160 3590 4100 4600 5020 5840
15 0 0 0 210* 330 520 650 800 980 1200 1470 1780 2150 2440 2780 3110 3400 3940
20 0 0 0 0 250* 400 500 610 760 930 1140 1380 1680 1910 2180 2450 2680 3120
25 0 0 0 0 0 320* 400 500 610 750 920 1120 1360 1540 1760 1980 2160 2520
30 0 0 0 0 0 260* 330* 410* 510 620 760 930 1130 1280 1470 1650 1800 2110
1/2 3770 6020 9460
3/4 2730 4350 6850
1 2300 3670 5770 9070
1-1/2 1700 2710 4270 6730
2 1300 2070 3270 5150 8050
3 1000 1600 2520 3970 6200
5 590 950 1500 2360 3700 5750
7-1/2 420 680 1070 1690 2640 4100 5100 6260 7680
60
Hz 3
10 310 500 790 1250 1960 3050 3800 4680 5750 7050
15 0 340* 540 850 1340 2090 2600 3200 3930 4810 5900 7110
20 0 0 410* 650 1030 1610 2000 2470 3040 3730 4580 5530
25 0 0 0 530* 830 1300 1620 1990 2450 3010 3700 4470 5430
30 0 0 0 430* 680 1070 1330 1640 2030 2490 3060 3700 4500 5130 5860
40 0 0 0 0 500* 790 980 1210 1490 1830 2250 2710 3290 3730 4250
50 0 0 0 0 0 640* 800 980 1210 1480 1810 2190 2650 3010 3420 3830 4180 4850
60 0 0 0 0 0 540* 670* 830* 1020 1250 1540 1850 2240 2540 2890 3240 3540 4100
75 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 680* 840* 1030 1260 1520 1850 2100 2400 2700 2950 3440
100 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 620* 760* 940* 1130 1380 1560 1790 2010 2190 2550
requirements may vary.
12 10 8 6 4 3 2 1 0 00 000 0000
3
Copyright © 2014. All rights reserved • 95 North Oak St. • Kendallville, IN 46755
Page 3
ell Screen
IL0096
Pump on.
Water enters
the reservoir
System Filled.
Pump Off
READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS COMPLETELY BEFORE INSTALLATION
ASSEMBLY
CAUTION: Be sure pump size corresponds with
horsepower size of motor. If pump size exceeds
recommended motor, overloading of motor and damage to
the motor could result.
1. If not yet assembled, check that the pump and motor
mounting faces are free from dirt.
2. Assemble the pump liquid end and motor together
so that mounting faces are in contact. Then tighten
assembly bolts evenly.
NOTE: Apply non-toxic FDA approved waterproof grease
such as Mobile 102, Texaco CYGNUS2661 or equivalent
to the coupling before assembly of pump coupling to
motor shaft. This will prolong spline life and prevent
abrasives from entering the spline area.
3. Check for free rotation of the pump and motor. A
slight drag is permissible.
4. Assemble the pump lead guard over the motor leads.
CAUTION: Do not cut or pinch lead wire during assembly.
5. Assemble suction screen to pump mounting ring.
Lead Wire
Liquid
End
IL0094B
Figure 3
PRE-INSTALLATION
To save possible added expense and extra trips, observe
and complete as many as possible of the following
precautions and pre-installation procedures before going
to the job site or beginning the installation.
IMPORTANT PRECAUTIONS
1. Prior to installation, inspect the pump for damage.
Check for free pump and motor rotation. A slight
drag is permissible.
2. Check to make certain that the voltage of the motor
end and control agree with the available phase and
voltage. Check power source. Check electrical
supply for correct fusing, correct wire size, and
adequate grounding and transformer size.
Guard
Motor
WARNING: Since most submersible pump problems are
electrical, it is very important that all electrical work be
done properly. Therefore, all electrical hook-up work
or electrical service work should be done by a qualified
electrician or service man only!
3. Throughout installation, take care not to damage
the insulation of the electrical cable or motor leads.
Never support the weight of the unit by electrical
cable or motor leads.
4. Before the pump is installed, the well should be
pumped free of sand and other foreign matter with
a test pump. The warranty is void if it is used to
clean the well.
5. Follow wiring directions in the control box and make
momentary tests to see that motor runs. (It is normal
to hear some noise from the pump when you are
momentarily testing it). Do not run pump dry for
more than three (3) seconds.
MAJOR WELL COMPONENTS (see Figures 1 & 2)
1. Submersible Pump — A submersible pump is a multistage centrifugal. Each stage consists of an impeller
and diffuser. Water pressure increases in equal
amounts as it passes from stage to stage. The more
stages, the higher the pressure the pump will develop.
2. Submersible Motor — Submersible pumps can
be powered by either single phase or three phase
motors. Make certain that the motor corresponds
with the horsepower required by the pump. Failure
to do so, could result in overloading of the motor and
motor damage.
3. Control Box — Single phase submersible motors
require the use of an above ground control box for
starting. Operation of these motors without control
boxes or with incorrect boxes can result in failure of
motors which will void the warranty.
4. Magnetic Starters and Overload Protection —
Three phase submersible motors require the use
of an above ground magnetic starter and overload
protection. Operation of these motors without or
incorrect starters and protectors will result in the
failure of motor which will void the warranty. See
Magnetic Starter Chart for the correct selection of
magnetic starters and ambient compensated quick
trip protectors.
5. The Well — The well should be sand free and have
a sufficient flow of water to supply the pump. Clear
well of sand and any other foreign matter with a test
pump before installing the new submersible pump.
CAUTION: Using the submersible pump to clean the well
will void the warranty.
6. When drilling a new well in an area where sand is a
problem, a sand screen should be installed to protect
the pump and motor.
7. The well should be straight so damage during
installation does not occur to the pump or motor by
becoming lodged in a crooked well casing.
8. The complete pump and motor should be submerged
at least twenty feet below the draw down level of the
well, and the motor should be a minimum of ten feet
off the bottom of the well (Figure 4).
Drawdown
Water Level
20 Ft.
Top of W
10 Ft. Min.
Figure 4
Bottom of Well
9. The Piping — Install the pump with pipe of the same
diameter as the discharge port of the pump or larger.
NOTE: Use of pipe smaller that the discharge port of the
pump will restrict the capacity of the pump and lower its
operating performance.
10. Check Valve — A check valve is required on all
submersible installations. This valve maintains water
within the pipe when the pump is running. A line check
should be installed within 25 feet of the pump and
below the draw down level of the water supply.
a. For well depths exceeding 200 feet, it is suggested
that an additional check valve be installed every
100 feet.
b. An additional check valve should be installed in the
horizontal line between the well top and the pressure
tank (See Figures 1 & 2).
CAUTION: Make certain that the check valve is pointing in
the right direction, arrow pointing towards the tank.
11. Torque Arrester — To center the pump as it is
being lowered into the well, a torque arrester is
recommended. This will also minimize the pump
whipping due to the starting torque of the motor (See
Figure 2).
NOTE: On plastic pipe installations a torque arrester
must be installed. Cable guards should also be installed.
12. Pressure Tank — The purpose of the pressure tank
is to allow an amount of water to be drawn before the
pressure drops enough to cause the pump to start.
Without a pressure tank, the pump would start and
stop continuously when water is drawn. There are
two types of pressure tanks, the standard tank that
requires an air volume control and the pre-charged
tank.
a. On a standard pneumatic tank system, air is
introduced to compensate for that which is
absorbed by the water. Each time the pump
cycles air is added to the tank through a bleeder
and snifter valve. The excess air is released by
a float assembly (air volume control) in the upper
side tapping of the tank (See Figure 2).
b. In a pre-charged tank, a flexible diaphragm or
bladder separates the air and water areas of the
tank. The air chamber is pre-charged by means of
a tire valve with pressure 2 PSI less than the cuton pressure of the pump. Because the air is not
in contact with the water, it cannot be absorbed by
the water. Therefore, the original charge of air is
never lost.
13. In pre-charged tank systems, none of the fittings for
air introduction or air level control are required (Figure
1). The piping in the well is also different for the two
systems. The pre-charged tank system does not
require a bleeder orifice assembly, which simplifies
the installation.
Figure 5
14. The tank size should be selected to keep the pump
starts per day as low as practical for maximum life.
Excessive motor cycling accelerates motor bearing
and spline wear, pump wear and contact erosion.
Use as a guide, 100 starts per day (24 hours) on
single phase motors and 300 starts per day on three
phase units.
15. Pressure Switch — The pressure switch provides
for automatic operation. The pump starts when the
pressure drops to the switch cut-in setting and stops
when the pressure reaches the switch cut-out setting.
The pressure switch must be installed as close to the
tank as possible (Figures 1 & 2).
16. Pressure Relief Valve — A properly sized pressure
relief valve must be installed on any installation where
the pump pressure can exceed the pressure tank’s
maximum working pressure or on systems where
the discharge line can be shut off or obstructed. The
relief valve drain port should be piped to a drain
(Figures 1 & 2).
WARNING: Not providing a relief valve can cause extreme
over pressure, which could result in personal and/or
property damage.
Copyright © 2014. All rights reserved • 95 North Oak St. • Kendallville, IN 46755
4
Copyright © 2014. All rights reserved • 95 North Oak St. • Kendallville, IN 46755
5
Page 4

IL0099
IL0097
Staked Connector
Rubber Tape
PVC Electrical Tape
2” 2”
2” 2”
17. Pitless Adapter — A pitless adapter provides below
grade discharge while maintaining above grade
access to the well. Placed below the frost line they
are frost proof and also prevent well contamination
by providing a water tight seal between the vertical
drop pipe and the horizontal service pipe connection
(Figure 1).
18. Well Seal — On well seal installations the piping in
the well projects above the well and is connected
above ground to the system piping by means of a
tee or elbow. Since the plumbing is above ground, it
must be protected from freezing (Figure 2).
19. Submersible Cable — Submersible power cable
must be UL listed for submersible pump application.
Selecting the proper cable size is important.
Undersized cable results in a too low voltage supply to
the pump motor and ultimate motor failure. Oversized
cable is costly and not necessary. Refer to cable
selection chart for proper cable selection. Cable is
selected for the maximum pump setting plus the offset
distance to the service entrance.
20. Ground Wire — The National Electric Code (NEC 250-
43) requires a separate ground wire be run down the
well to the submersible pump and to be connected to
all exposed metal parts of the pump and motor. Refer
to the most recent National Electric Code (NEC) for
additional grounding information. All wiring should be
done by a competent electrician.
INSTALLATION
SUBMERSIBLE CABLE INSTALLATION
1. Check power source. Check electrical supply for
correct fusing, correct wire size, and adequate
grounding and transformer size.
WARNING: Since most submersible pump problems are
electrical, it is very important that all electrical work be
done properly. Therefore, all electrical hook-up work
or electrical service work should be done ny a qualified
electrician or serviceman only!
2. Follow wiring directions in the control box and make
momentary tests to see that the motor runs. Do not
run pump dry for more than three (3) seconds. If
test is satisfactory, proceed to Step 3 (cable splice).
3. First check cable size against the Submersible
Wire Size Chart. Use extreme care; this is a very
important step. If required length falls between
two wire sizes, use the larger of the two wire sizes
(smaller number).
IMPORTANT: Use of wire sizes smaller than those
specified in the charts will cause low starting voltage,
may cause early pump failure and will void the warranty.
Larger wire sizes may always be used for better operating
economy.
4. Splice motor leads to submersible cable with
commercially available potting, heat shrink splicing
kits or by careful tape splicing. Tape splicing should
use the following procedure.
a) Strip individual conductor of insulation only as far
as necessary to provide room for a stake type
Copyright © 2014. All rights reserved • 95 North Oak St. • Kendallville, IN 46755
connector. Tubular connectors of the staked type
are preferred. If connector O.D. is not as large as
cable insulation, build-up with rubber electrical tape.
b) Tape individual joints with rubber electrical tape,
using two layers; the first extending two inches
beyond each end of the conductor insulation end,
the second layer two inches beyond the ends of
the first layer. Wrap tightly, eliminating air spaces
as much as possible.
c) Tape over the rubber electrical tape with #33
Scotch electrical tape, (Minnesota Mining Co.)
or equivalent, using two layers as in step “B”
and making each layer overlap the end of the
preceding layer at least two inches.
5. In the case of a cable with three conductors encased
in a single outer sheath, tape individual conductors as
described, staggering joints. Total thickness of tape
should be less than the thickness of the conductor
insulation.
GROUND WIRE INSTALLATION
WARNING: Motor frame must be connected to power
supply ground or fatal electrical shock may result.
Figure 6
NOTE: All electrical wiring should be done by a
competent electrician.
1. Grounding the submersible pump is accomplished
by running a copper grounding wire from the pump
motor to the main electrical system ground.
2. The ground wire to be used must be of the same
size as the submersible power cable. It may be
insulated or bare. If insulated, it must be green, with
or without yellow stripe(s). The ground wire may be
part of, or separate from, the supply cable. It may be
continuous or spliced above the pump along with the
supply cable.
3. The motor lead wire assembly includes a green
insulated ground lead. Splice the ground wire to the
green insulated lead as shown in Figure 6.
4. The other end of the ground wire will be connected to
the power supply grounding terminal or to the control
panel ground bar if it is connected to the power
supply ground.
NOTE: See section entitled Grounding for detailed
grounding instructions.
6
INSULATION AND CONTINUITY TEST
1. It is recommended that this test be done when the
splicing is complete and pump is being test run in
a tank of water. This test can be repeated after
installation in well but before the final electrical hookup is made to the control box or pressure switch (see
Figures 7 & 8).
Figure 7
Figure 8
2.
Zero the ohmmeter by clipping the leads together and
adjusting the zero ohm knob until the needle indicates
zero. Zero the ohmmeter before each use or every time
selector switch is changed.
3. Clip one ohmmeter lead to bare cable end.
4. Clip the other lead to edge of steel tank in which
pump and cable are submerged. If pump is already
in the well, clip lead to discharge pipe metal well
casing or bare ground wire.
5. A reading of less that 1,000,000 ohms indicates that
cable or splice is grounded. Slowly raise cable from
the water at the ohmmeter end. When trouble spot
moves clear of the water, needle will move toward
infinity reading. In an old installation with the pump in
the well, a reading of 20,000 ohms or less indicates
Copyright © 2014. All rights reserved • 95 North Oak St. • Kendallville, IN 46755
a breakdown in the insulation; in this case pull the
pump.
PUMP INSTALLATION
1. The following pump installation instructions use
Schedule 80 PVC pipe or galvanized pipe. If either
of these two types are used, a foot clamp or vise will
be required to hold the PVC or galvanized pipe when
connecting the next pipe length.
2. Install the pump in a well which is sand-free, straight,
and has sufficient flow of water to supply the pump.
Clear well of sand and any other foreign matter with a
test pump before installing the submersible pump.
NOTE: Using the submersible pump to clean the well
will void the warranty. When drilling a new well in an
area where sand is a problem, a sand screen must be
installed to protect the pump and motor.
3. Chlorinate the well first. Drop 24 to 48 HTH (chlorine)
tablets into the well before lowering the pump into the
well. This will prevent contamination and the growth
of iron bacteria which could later plug the well and the
pump. The chlorinated water will be pumped out of
the system when testing the pump flow.
4. BE SURE the top edge of the well casing is perfectly
smooth; sharp or jagged edges can cut or scrape the
cable and cause a short.
5. Install a line check valve within 25 feet of the pump
and below the draw down level of the water supply.
The check valve should be the same size as the
discharge outlet of the pump or larger.
NOTE: Use of pipe smaller that the discharge tapping of
the pump will restrict the capacity of the pump and lower
its operating performance.
6. When connecting the first length of pipe and
placing the pump in the well casing, care should be
maintained to center the pump in the well. It is easier
to handle the pump if a short piece of pipe is installed
first, rather than a long piece. Install the check valve
at the end of the first piece of pipe prior to lowering
the pump into the well. Maintain alignment as the
pump is placed and lowered into the well, a torque
arrester is recommended. Position the torque arrestor
to within 6” of the pump discharge and clamp arrestor
to pipe. Wrap the pipe with enough tape at top and
bottom of torque arrestor to keep it from sliding up the
pipe while the pump is being lowered into the well.
7. If not already done, splice the electrical cable to the
motor leads. The cable and ground wire should be
taped to the discharge pipe. Tape the cable about 5
feet above the discharge and every 20 feet thereafter.
Install cable guards if required to eliminate rubbing
against the well casing. Do not let the cable drag
over the edge of the well casing. Never allow the
weight of the pump to hang on the cable alone.
7
Page 5

IL0100
Fused Disconnect
Switch
Ground
Pressure
Switch
Ground
L1 L2
R Y B
Control Box
To Motor
Ground
Red
Yellow
Black
Lightning
Arrestor
SW
IL0102
Pressure
Switch
3
2
L1 L2 L3
Fused Disconnect
Switch
Lightning
Arrestors
V
M
W
T1
T2
X2
T3
Motor
Ground
T3
T1
Fused Disconnect
Switch
Ground
Pressure Switch
Ground
L1 L2
R Y B
Control Box
To Motor
Ground
Red
Yellow
Black
Lightning
Arrestor
IL0100
8. Lower the pump into the well slowly without forcing.
Use a vise or foot clamp to hold the pipe while
connecting the next length. A boom, tripod or
pump setting rig is recommended. Lower pump to
approximately 10 feet below maximum draw down
of the water if possible and keep approximately 10
feet from the bottom. DO NOT set pump on bottom
of well. Before each new length of pipe is added,
attach the coupling to the top of the pipe length. This
will provide a stop for the foot clamp to hold while the
next section of pipe is being installed.
9. On a standard tank with an air volume control a
bleeder orifice is required. Install the bleeder orifice
in the discharge pipe 5 feet or more below the snifter
valve. See Figure 2 and the table below.
Distance Table
Tank Size
Gallons
42
82
120
220
315
525
Depth From Horizontal Check
Valve To Bleeder Orifice
5
10
15
15
20
20-35
Installations that use a pre-charged pressure tank
do not require a bleeder orifice.
WELL SEAL/PITLESS ADAPTER INSTALLATION
1. All installations should have a well seal. Make sure
the seal is seated and tighten the bolts evenly.
NOTE: Be sure to assemble the tee to the pipe above
the well seal to prevent dropping the pipe and pump
down the well as you lower it.
IMPORTANT: Well seal and piping must be protected
from freezing.
2. On a pitless adapter installation, the connection to the
system supply line is made below ground. Install the
pitless adapter following the instructions included with
particular brand or design being used in the installation.
NOTE: Follow ALL applicable state and local plumbing
codes.
PRELIMINARY TEST RUN
1. When pump is at desired depth, install throttle valve
for preliminary test run. Wire single phase motors
through the control box, following instructions in box
regarding color coding of wires, etc. Wire 3-phase
motors through a magnetic starter. Test cable for
continuity with an ohmmeter.
2. With pump discharge throttled, run pump until water
is clear of sand or any other impurities. Gradually
open discharge.
CAUTION: Be sure you do not stop pump before water
runs clear. This may take several hours. If pump stops
with sand in it, it will lock.
3. If pump lowers water in the well far enough to lose
prime, either lower pump in the well (if possible) or
throttle discharge to capacity of the well.
4. If well is low capacity, use a low water level control.
5. On 3-phase units, establish correct motor rotation
by running in both directions. Change rotation by
exchanging any two of the three motor leads. The
rotation that gives the most water flow is always the
correct rotation.
PRESSURE TANK INSTALLATION
1. On a new installation, install the pressure tank along
with the pressure switch, pressure gauge, pressure
relief valve, check valve, gate valves and unions as
shown in Figures 1 & 2.
2. On replacement pump installations be sure that the
tank system is in good operating condition, as a
water logged tank may cause pump failure.
ELECTRICAL HOOK-UP
WARNING: Since most submersible pump problems are
electrical, it is very important that all electrical work be
done properly. Therefore, all electrical hook-up work
or electrical service work should be done by a qualified
electrician or serviceman only!
WARNING: Always disconnect power source before
working on or near motor, its connected load or control
box and wiring. If the power disconnect is out of sight,
lock it in the open position and tag to prevent unexpected
application of power.
1. Proceed with electrical hook-up matching cable colors
and following the wiring diagrams (Figures 9, 10 &11)
or inside the lid of the control box.
WARNING: Connect motor leads momentarily for correct
rotation before installing pump in well.
FUSE SIZES
Figure 9 — Single Phase Control Box
Figure 10 —
Single Phase Control Box with Contactor
Figure 11 — Three Phase Magnetic Starter
1. For proper sizing of fuses for fuse disconnect box,
see Motor Data Charts. Improperly sized fuses will
result in fuses blown or circuit breakers tripped.
GROUNDING
Proper Grounding of Submersible Motors
1. The purpose of grounding any electrical apparatus is
to prevent an electrical shock hazard if exposed metal
becomes connected to an electrical circuit. This can
occur from a defect in construction of the electrical
equipment, physical damage, or a breakdown in the
insulation of the equipment. Grounding prevents
shock hazard by keeping exposed metal from
reaching a voltage level which could endanger
anyone coming in contact with the electrical
equipment. Fault current is “drained” by the ground
conductor, and if the fault is severe enough, the
circuit will be opened by the fuse or circuit breaker.
2. The U.S. National Electrical Code (NEC) requires that
motor-operated water pumps, including submersible
type regardless of voltage, shall be grounded. The
Canadian Electrical Code specifically discusses
grounding requirements for submersible pumps.
Interpretation of these and other codes may vary
in different states and localities, but all applicable
national, state, and local codes should always be
followed.
3. Any submersible motor which is to be run tested out
of the well should be grounded to prevent possible
shock hazard during the test.
NOTE: Always disconnect all power when making
ohmmeter check and while pulling or installing a pump.
4. The most logical way to “frame” ground a submersible
motor is normally as follows:
a. Run an extra wire with the motor power conductors.
This wire must be sized to meet Table 250-95 in the
U.S. National Electrical Code. If code information
is unavailable, using the same size wire as the
power conductors is normally adequate.
b. The ground wire may be insulated or bare. If
insulated, it must be green with or without yellow
stripe(s). The ground wire may be part of, or
separate from the supply cable. It may be
continuous or spliced above the pump along with
the supply cable.
c. Connect the green or bare ground wire to the
green ground wire of the submersible motor lead
assembly. If the lead wire assembly does not
include a separate ground wire, attach a lug to
the ground wire and place the lug over one of the
motor studs above the pump intake flange so the
pump will not be cocked. The ground lug will then
be secured with the nut which holds the pump on
the motor.
d. Connect the other end of the ground wire to the
power supply grounding terminal or to the control
panel ground bar if it is connected to the power
supply ground.
e. All connections should be tight and corrosion
resistant, including screws, lugs or clamps.
Grounding Control Boxes
1. It is recommended the control box grounding terminal
always be connected to circuits which include a
grounding conductor. In fact, this is a requirement
of the National Electrical Code. If the circuit has no
grounding conductor and no metal conduit from the
box to supply panel, use a wire at least as large as
line conductors and connect from supply panel to the
control box and to the motor lead ground wire.
WARNING: Failure to ground the box frame can result in a
fatal electrical shock hazard if a circuit fault occurs.
WARNING: Serious or fatal electrical shock may result
from failure to connect all metal plumbing, and the motor
if outside a drilled well, to the power supply grounding
terminal with wire no smaller than motor cable wires. Do
not use motor in swimming area.
Copyright © 2014. All rights reserved • 95 North Oak St. • Kendallville, IN 46755
8
Copyright © 2014. All rights reserved • 95 North Oak St. • Kendallville, IN 46755
9
Page 6

IL0104
Grounding Lightning Arrestors In Control Boxes
IL0103
Pump Body
Stainless Steel
Worm Gear Clamps
Intake Screen
Flow Inducer Screen
(Corrosion Resistant
Material)
Submersible Motor Centering Bolt
Corrosion Resistant
(3 Places)
All Water Flows
Past Motor
1. When the box has a lightning arrestor, it must be
grounded, metal to metal, all the way to the water
strata for the lightning arrestor to be effective.
Grounding the arrestor to a driven ground rod
provides little or no protection for the motor.
SUBMERSIBLE MOTOR COOLING
1. When the pump is set below any screen openings
or below the bottom of the casing a top feeding well
condition can exist which reduces the rate of cooling
water flow past the motor.
2. If the flow rate is less than specified a flow indicator
sleeve or an alternate method of increasing water
velocity past the motor must be used for proper
cooling.
Minimum Velocity Past the Motor
4” dia. motor – .25 ft./sec. (7.62 cm/sec)
6” dia. motor – .5 ft./sec/ (15.24 cm/sec)
3. A flow inducer sleeve is a tube over the motor, closed
off above the pump intake and extended to the bottom
of the motor or lower. The sleeve material is corrosion
resistant metal or heavy plastic (See Figure 12).
Figure 12
4. A flow inducer sleeve should always be used when
the pump is in an open body of water. Make sure
that such an installation is grounded.
Required Cooling Flow
Minimum GPM required for motor cooling in water
up to 86ºF (30ºC).
Inches
Casing or
Sleeve I.D.
4
5
6
7
8
10
12
14
16
4” High
Thrust Motor
.25 ft/sec
GPM
1.2
7
13
20
30
50
80
110
150
6” Motor
.5 ft/sec
GPM
—
—
9
25
45
90
140
200
280
8” Motor
.5 ft/sec
GPM
—
—
—
—
10
55
110
170
245
SERVING SUBMERSIBLE MOTOR AND CONTROLS
1. The following is included to assist in motor installation
and servicing. These procedures are limited to the
motor and control system: they do not include pump
requirements.
TIGHTENING LEAD CONNECTOR JAM NUT
1. It is recommended that possible damage from removal
may prevent resealing. Torque the jam nut from 15 to
20 lb. ft. on 4” motor and 60 to 70 lb. ft. on a 6” motor.
CABLE IDENTIFICATION WHEN COLOR CODE IS
LOST
(Single Phase Only)
If the colors on the individual drop cables cannot be
determined and the leads cannot be positively identified,
proceed as follows:
1. Disconnect all three drop cables from the control box.
For temporary identification, tie a numbered tag to
each cable (1, 2, 3).
2. Using an ohmmeter, check the resistance
between cables as follows:
Unknown Value Known Value
Cable 1 to Cable 2
Cable 1 to Cable 3
Cable 2 to Cable 3
Lowest - Black to Yellow
Intermed. - Red to Yellow
Highest - Black to Red
NOTE: The “yellow” cable is that giving lowest and
intermediate readings and the “red” cables gives highest
and intermediate readings.
Example:
• 1 to 2 gives 7 ohms (highest reading)
• 1 to 3 gives 5 ohms (intermediate reading)
• 2 to 3 gives 2 ohms (lowest reading)
• Cable 3 gave both intermediate and lowest reading
• Cable 3 is the yellow cable
• Cable 1 gave both highest and intermediate readings
• Cable 1 is the red cable
• Cable 2 is the black cable
The actual ohm values are not important. The method
works regardless of the actual ohm readings; what
matters is which reading is highest, which intermediate,
and which lowest.
THREE PHASE POWER UNBALANCE
1. A full three phase supply is recommended for all
three phase motors, consisting of three individual
transformers or one three phase transformer.
So-called “open” delta or wye connections using only
two transformers can be used, but are more likely to
cause problems from current unbalance.
2. Transformer ratings should be no smaller than listed
in the table for supply power to the motor alone.
Open Wye or Delta systems often suffer from line
unbalance, which can cause poor motor performance,
nuisance overload tripping, or premature motor
failure. For the best performance current unbalance
should not exceed 5 percent. If the unbalance cannot
be corrected by rolling leads, contact the power
company.
Transformer Capacity Required for
Submersible Motors
Smallest KVA Rating — Each
Open WYE or
2 Transformers
DE LTA
2
2
3
5
7.5
10
15
15
20
25
30
35
40
50
65
Transformer
Closed WYE or
DE LTA
3 Transformers
1.5
7.5
10
10
15
20
20
25
30
40
1
2
3
5
5
Motor
HP
1-1/2
2
3
5
7-1/2
10
15
20
25
30
40
50
60
75
100
Total
Effective
KVA
Required
3
4
5
7.5
10
15
20
25
30
40
50
60
75
90
120
INSULATION RESISTANCE
Unbalance Formula
Percent
Current = Max difference from average x 100
Unbalance average
Example:
Currents are 80, 79, 84 amps (Lines 1-2 & 3)
Avg. Currents = 80 + 79 + 84 = 81
3
Percent
Current
Unbalance
84 - 81 x 100 = 3.7%
81
Open Delta
Full Three Phase
Figure 13
Insulation resistance tests indicate the value of the motor,
cable, and splice insulation system by measuring
resistance in ohms between motor leads and ground.
Low readings indicate a breakdown somewhere in the
insulation system.
1. Set ohmmeter to RX100K or highest scale. (For best
results use a megohmmeter).
2. Short meter leads together and adjust indicator to
zero.
3. Be sure power is turned off!
4. Connect one meter lead to a motor lead and the other
meter lead to ground.
a. If motor is out of water, measure from lead to
motor frame.
b. If motor is installed in water, ground reference
should be metal well casing (if submerged), metal
drop pipe, or an extra wire extending into the
ground water.
5. Readings and Conditions, motor installed in well:
a. 2,000,000 ohms or more - insulation completely
acceptable.
b. 500,000 to 2,000,000 ohms - insulation in
reasonably good condition. Acceptable. Should
be considered marginal for new motor.
c. 20,000 to 500,000 ohms - insulation seriously
damaged, but motor may still operate.
d. Less than 20,000 ohms - severe insulation
damage. Motor probably not operable.
WINDING RESISTANCE
Winding resistance tests indicate whether or not windings
are internally correct, shorted, or open. Winding
resistance should be considered independently of
insulation resistance readings.
1. Set ohmmeter to RX1. Short meter leads together
and adjust indicator to zero.
2. Be sure power is turned off.
3. Connect ohmmeter between two motor leads.
MAINTENANCE
Copyright © 2014. All rights reserved • 95 North Oak St. • Kendallville, IN 46755
10
Copyright © 2014. All rights reserved • 95 North Oak St. • Kendallville, IN 46755
11
Page 7

a. Three wire single phase: Yellow-Black indicates
main winding resistance; Yellow-Red indicates
start winding resistance.
b. Three phase: Resistance values should be equal
on all three phases: Yellow-Black; Yellow-Red;
Black-Red.
4. Correct readings should be equal to the Line-to-Line
resistance values from the specifications section for a
given motor, plus the resistance of the drop cable from
the table below.
5. Conditions:
Resistance (Ohms) Per 100 Feet of Copper Cable
(Round Trip)
AWG 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0
Ohms .5 .3 .2 .12 .08 .05 .03 .02
a. If one ohm value is less than specified, that
winding is shorted.
b. If one ohm value is greater than specified, that
winding is open, or there is a poor connection in
that circuit.
c. On 3-wire single phase, if one ohm value is
greater than specified and one ohm value is less
than specified, the leads are mixed. See the
section entitled “Cable Identification When Color
Code Is Lost.”
ONE YEAR LIMITED WARRANTY
This product is warranted for one year from the date of purchase or two
years from the date of manufacture, whichever occurs first. Subject to the
conditions hereinafter set forth, the manufacturer will repair or replace to the
original consumer, any portion of the product which proves defective due to
defective materials or workmanship. To obtain warranty service, contact the
dealer from whom the product was purchased. The manufacturer retains
the sole right and option to determine whether to repair or replace defective
equipment, parts or components. Damage due to conditions beyond the
control of the manufacturer is not covered by this warranty.
THIS WARRANTY WILL NOT APPLY: (a) To defects or malfunctions
resulting from failure to properly install, operate or maintain the unit in
accordance with printed instructions provided; (b) to failures resulting
from abuse, accident or negligence or use of inappropriate chemicals or
additives in the water; (c) to normal maintenance services and the parts
used in connection with such service; (d) to units which are not installed in
accordance with normal applicable local codes, ordinances and good trade
practices; and (e) the unit is used for purposes other than for what it was
designed and manufactured.
RETURN OF WARRANTED COMPONENTS: Any item to be repaired
or replaced under this warranty must be returned to the manufacturer at
Kendallville, Indiana or such other place as the manufacturer may designate,
freight prepaid.
TESTING LOAD CURRENT AMPS
To test load current amps a clamp-on ammeter is
required. Since the ammeter measures current flow, the
motor must be running.
1. Pull the motor lead wire, being measured, (red, yellow
or black) away from all other wires.
2. Set ammeter to the highest scale. (If starting a motor
leave on the scale until current settles down).
3. Place tongs of meter around wire.
4. Change meter scale to one that gives the best
accuracy. This will be a reading between mid scale
and full scale.
5. Compare reading with current load amps on motors
data chart.
6. Test each motor lead.
THE WARRANTY PROVIDED HEREIN IS IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER
EXPRESS WARRANTIES, AND MAY NOT BE EXTENDED OR MODIFIED
BY ANYONE. ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES SHALL BE LIMITED TO
THE PERIOD OF THE LIMITED WARRANTY AND THEREAFTER ALL
SUCH IMPLIED WARRANTIES ARE DISCLAIMED AND EXCLUDED. THE
MANUFACTURER SHALL NOT, UNDER ANY CIRCUMSTANCES, BE
LIABLE FOR INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL OR SPECIAL DAMAGES,
SUCH AS, BUT NOT LIMITED TO DAMAGE TO, OR LOSS OF, OTHER
PROPERTY OR EQUIPMENT, LOSS OF PROFITS, INCONVENIENCE, OR
OTHER INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES OF ANY TYPE
OR NATURE. THE LIABILITY OF THE MANUFACTURER SHALL NOT
EXCEED THE PRICE OF THE PRODUCT UPON WHICH SUCH LIABILITY
IS BASED.
This warranty gives you specific legal rights, and you may have other rights
which vary from state to state. Some states do not allow limitations on
duration of implied warranties or exclusion of incidental or consequential
damages, so the above limitations may not apply to you.
WARRANTY VALID IN CANADA AND MEXICO.
Single Phase Control Box Checking and Repairing Procedures
CAUTION: Turn power off and discharge capacitors before using ohmmeter.
TEST PROCEDURE
General Procedures 1. Disconnect line
2. Inspect for damaged or burned parts, loose connections, etc.
3. Check for misconnections against diagram in control box
4. If problem has not been found, check motor per Motor Data Chart and
control box as indicated below
Use of Ohmmeter 1. Ohmmeter such as Simpson Model #372 or #260, Triplett Model #630 or
#666 may be used
2. Whenever scales are changed, short ohmmeter leads and “zero balance”
meter
Ground (Insulation Resistance) Test 1. Ohmmeter Setting: Highest scale (usually R x 100K or 4 x 10,000)
2. Terminal Connections: One ohmmeter lead to “Ground” terminal on control
box and touch other lead to each of the other terminals on terminal board
3. Ohmmeter Reading: Pointer should remain at (∞) and not deflect
Overload Protector 1. Ohmmeter Setting: R x 1
2. Terminal Connections: Connect one ohmmeter lead to Terminal Black and
other lead to:
a. Terminal L
b. Terminal L
3. Ohmmeter Reading: Should be 0 to 0.5 ohms maximum
Capacitor Tests 1. Ohmmeter Setting: R x 1,000
2. Terminal Connections: One ohmmeter lead to relay terminal #1 and other to
black terminal on terminal board
3. Ohmmeter Reading: Pointer should swing toward “zero” and “float” back
to (∞). Capacitor is shorted if pointer does not move back to (∞), open if it
does not move from (∞)
4. If reading is not as above, disconnect capacitor from overload and test each
component
Relay Coil Test
(potential relays only)
Relay Contact Test
(potential relays only)
Contactor Test 2. Ohmmeter setting R x 100.
1. Ohmmeter Setting: 4 x 1,000 (or R x 100)
2. Terminal Connections: #6 and #2 on Relay
3. Ohmmeter Reading:
Most of the cases of inoperative relay contacts can be detected as follows:
1. Ohmmeter Setting: 4 x 1.
2. Terminal Connections: Terminal #1 and Terminal #2 on Relay.
3. Ohmmeter Reading: Should be “zero”.
NOTE: This test verifies “making” of contacts. If it is desired to test
“Opening” and closing of contacts:
a. Connect control box components in control box as indicated on diagram in
control box cover.
b. Connect three leads from motor of correct rating to control box terminal
board.
c. Connect power source voltage to L
d. Current in Red lead should momentarily be a high value - then drop
(within one second) to values on Motor Data Chart
1. Disconnect one coil lead.
3. Check coil resistance: 180 to 1400 ohms.
4. Remove contact cover and inspect contacts.
in four-terminal boxes
¹
in five-terminal boxes.
²
G.E. 4.5 - 7.0 (4500-7000 ohms)
Cardinal 2.8 - 4.2 (2800-4200 ohms
and L².
¹
For 230 Volt Boxes
Copyright © 2014. All rights reserved • 95 North Oak St. • Kendallville, IN 46755
12
Copyright © 2014. All rights reserved • 95 North Oak St. • Kendallville, IN 46755
13
Page 8

Troubleshooting Chart
Symptom Possible Cause(s) Corrective Action
Fuses blow when motor starts 1. Incorrect voltage
2. Incorrect fuses
3. Defective pressure switch
4. Control box malfunction
5. Bound pump
6. Defective cable or motor winding
7. Shorted or open motor winding
Motor runs but fuses blow 1. Incorrect voltage
Motor does not start and fuses
do not blow
Pump runs, but delivers little or
no water
Pump keeps running 1. Pressure switch
Pump starts too often 1. Pressure switch
2. Overheated protectors
3. Improperly wired control box
4. Defective motor or cable
5. Defective pump
6. Defective installation
1. No power
2. Defective pressure switch
3. Defective wiring
1. Air locked pump
2. Low water level in well
3. Pump rotation wrong
4. Check valve stuck or installed improperly
5. Leak in drop pipe
6. Pump screen locked
7. Worn pump
8. Loose or broken motor shaft
2. Low level well
3. Leak in system
4. Worn pump
2. Leak in system
3. Check valve
4. Air supply (waterlogged tank - air under
pressure absorbed into the water)
1. Contact power company if voltage is incorrect after
first checking for correct wire size. See Wire Size
Chart
2. Replace with proper fuses
3. Replace pressure switch or clean contacts
4. Correct faulty wiring or tighten loose contacts
5. Sand bound pump can sometimes be corrected
by temporarily reversing black and red leads in
control box then returning to normal. If pump does
not rotate freely, it must be pulled and cleaned or
realigned and the well condition corrected
6. The pump must be pulled and the cable
disconnected and inspected. Damaged cable
should be correctly spliced or replaced. If cable is
good, the motor winding is grounded
7. The pump must be pulled and motor or drop cable
repaired or replaced
1. Contact power company in incorrect
2. Shade box, provide ventilation or move box away
from heat source
3. Rewire correctly
4. If ground, short or open circuit is indicated pump
must be pulled for repair
5. Pull pump, clean and repair
6. Pull pump, rechecking components and installation
1. Replace fuses or reset circuit breaker. Contact
power company if no power is reaching box
2. Clean contact points or replace switch
3. Correct faulty wiring or connections
1. Normal delivery may resume if pump is started and
stopped at one minute intervals
2. Throttle pump delivery through restricting valve.
Lower pump setting if depth of well is adequate
3. Check wiring connections
4. Replace or reinstall properly
5. Raise pipe, check for leak and replace damaged
section
6. Clean screen and reset at less depth. It may be
necessary to clean well
7. Pull pump and replace worn impellers, casing or
other close fitting parts
8. Check for damaged shafts if coupling is loose and
replace worn or defective units
1. Clean points or replace switch
2. Throttle pump output or reset pump to lower level.
Do not lower if sand may clog pump
3. Replace damaged section
4. Pull pump and replace
1. Reset limit or replace switch
2. Repair or replace tank or pipes
3. Remove and replace if defective
4. Clean or replace. Drain and recharge tank
Copyright © 2014. All rights reserved • 95 North Oak St. • Kendallville, IN 46755
14
 Loading...
Loading...