Page 1

Instruction Manual
D100255X012
January 2020
Type 92C Steam Regulator
WARNING
!
Fisher™ regulators must be installed,
operated and maintained in accordance
with federal, state and local codes, rules
and regulations and Emerson Process
Management Regulator Technologies,
Inc. instructions.
Installation, operation and maintenance
procedures performed by unqualied
personnel may result in improper
adjustment and unsafe operation. Either
condition may result in equipment damage
or personal injury. Use qualied personnel
when installing, operating and maintaining
the Type 92C regulator.
Introduction
Scope of the Manual
This instruction manual provides installation,
maintenance and parts ordering information for the
Type 92C steam self-powered control valve and
the Type 6392 pilot. Both the pilot-operated and the
pressure-loaded constructions are covered. The
Type 92C is also available with a Type 6492HM or
6492HTM safety override pilot. The pressure-loading
device and accessories used with this valve are
covered in other manuals.
regulator or 670 Series panel-mounted regulator may
be used as the loading regulator.
A Type 6492HM (or 6492HTM) safety override pilot is
also available for the Type 92C. The Type 6392 pilot is
used in a series installation with the Type 6492HM (or
6492HTM) safety override pilot installed on the upstream
valve. The Type 6492HM (or 6492HTM) safety override
pilot senses pressure downstream of the second valve,
and prevents pressure from rising above safe operating
pressure in the event the downstream valve fails. This
system is approved by ASME B31.1-1989, 122.14.2.A,
and can replace an ASME safety valve when vent
piping is not practical and upstream pressure does not
exceed 400 psig / 27.6 bar. Local codes and standards
may require approval by an appropriate authority prior
to installation.
Type 92C
W3111_2
Figure 1. Type 92C Pilot-Operated Regulator
WARNING
!
Description
The Type 92C steam regulator is a gray cast iron,
steel or stainless steel pressure-reducing regulator for
steam or hot air service. This regulator is available with
a Type 6392 pilot for use as a pilot-operated regulator
(Figure 1) or without a pilot for use as a pressureloaded regulator. The pilot-operated version uses
inlet pressure as the operating medium; no separate
air supply is required. The pressure-loaded version
is used where remote adjustment of the regulator
pressure setting is required; a 67 or 1301 Series
The Type 92C safety override system
does not provide positive shuto in
dead end service. It is intended for
large distribution systems where steam
leakage will condense before steam
pressure builds up. Downstream piping
and components must be rated for
maximum upstream steam pressure for
dead end service. Failure to do so could
cause personal injury or death.
Page 2
Type 92C
Specications
This section lists the specications for Type 92C regulator. Additional specications for an individual regulator are
found on the regulator body and pilot nameplates.
Body Sizes and End Connection Styles
SIZE
NPS 1/2, 3/4 or 1 /
DN 15, 20 or 25
Gray Cast Iron Steel or CF8M Stainless Steel
NPT
BODY MATERIAL
NPT, CL150 RF, CL300 RF
or PN 16/25/40
Orice Sizes
NPS 1/2 / DN 15 Main Valve:
9/16 in. / 14 mm
NPS 3/4 and 1 / DN 20 and 25 Main Valves:
3/4 in. / 19 mm is standard; 9/16 in. / 14 mm
is optional
Maximum Allowable Inlet and Pilot
Supply Pressures
(1)
Gray Cast Iron Construction: 250 psig / 17.2 bar
Steel and Stainless Steel Construction:
300 psig / 20.7 bar
Regulator Pressure Drops
(1)
Minimum: 15 psi / 1.0 bar
Maximum Operating: 150 psi / 10.3 bar for
outlet pressure settings equal to or below
50 psig / 3.4 bar; 200 psi / 13.8 bar for outlet
pressure settings above 50 psig / 3.5 bar
Maximum Emergency
Gray Cast Iron construction: 250 psi / 17.2 bar
Steel and Stainless Steel construction:
Maximum Material Temperature Capabilities
Gray Cast Iron Construction: 406°F / 208°C
Steel and Stainless Steel Construction:
500°F / 260°C
Optional High-Temperature Steel or
Stainless Steel Body: 650°F / 343°C
Pressure Registration
With Pilot: External
Without Pilot: Internal
Downstream Control Line Connection
1/4 NPT (internal) in pilot body (downstream
control line not required for pressureloaded regulator)
300 psi / 20.7 bar
Loading Pressure Connection
Outlet Control Ranges
See Table 1
Maximum Outlet Pressures
(1)
Maximum Operating Outlet Pressure:
150 psig / 10.3 bar
Maximum Emergency Outlet (Casing) Pressure
Gray Cast Iron construction: 250 psig / 17.2 bar
Steel and Stainless Steel construction:
300 psig / 20.7 bar
Loading Pressure for Pressure-Loaded Regulator
(1)
1/4 NPT (internal) in main valve diaphragm ange
(this connection is factory-piped to the pilot on
pilot-operated regulator)
Pilot Spring Case Vent
3/32 in. / 2.4 mm drilled hole
Approximate Weights
Gray Cast Iron, Steel or Stainless Steel Body
with Pilot: 20 lbs / 9.1 kg
Gray Cast Iron, Steel or Stainless Steel Body
without Pilot: 16 lbs / 7.3 kg
See Figure 2 to determine loading pressure.
Maximum allowable loading pressure is 250 psig /
17.2 bar for gray cast iron construction and
300 psig / 20.7 bar for steel or stainless steel
construction; the maximum allowable diaphragm
dierential pressure of 150 psi / 10.3 bar
for gray cast iron, steel and stainless steel
constructions must not be exceeded.
1. Pressure/temperature limits in this Instruction Manual and any applicable code limitations must not be exceeded.
(1)
2
Page 3

TYPE 92C REGULATOR
PILOT LOADING LINE
Type 92C
26A3808-A
A2508-1
PRESSURE DROP ACROSS VALVE (bar)
2 4 6 8 10 12
20
15
10
5
0
DIAPHRAGM DIFFERENTIAL (psi)
PRESSURE DROP ACROSS VALVE (psi)
3/4 in. / 19 mm
orice size
9/16 in. / 14 mm
orice size
50 100 150 200
Figure 2. Diaphragm Dierential Pressure
for Pressure-Loaded Regulator
TYPE
6492HM
6492HTM
SPRING RANGE
psig bar
10 to 30 0.69 to 2.1 Yellow 5 psig / 0.34 bar over normal distribution pressure
25 to 75 1.7 to 5.2 Green
70 to 150 4.8 to 10.3 Red
80 to 250
15 to 100 1.0 to 6.9
PILOT SUPPLY
TYPE 6392 PILOT
1
0.5
DIAPHRAGM DIFFERENTIAL (bar)
TOP VIEW OF REGULATOR AND
PILOT CONNECTIONS
STRAINER
16A1548-B
A2522-1
Figure 3. Typical Pilot-Operated Type 92C
Regulator Installation
Table 1. Safety Pilot Outlet (Control) Pressure Ranges
MINIMUM PRESSURE AT WHICH MONITORING
10 psig / 0.69 bar over normal distribution pressure
5.4 to 17.2
SPRING COLOR
Unpainted
DOWNSTREAM
CONTROL LINE
BYPASS LINE
PILOT CAN BE SET
TYPE 6392 PILOT
DOWNSTREAM
CONTROL LINE
TYPE 92C REGULATOR
Table 2. Outlet Pressure Ranges
SPRING USAGE
Standard use up to
500°F / 260°C
High-pressure and/or High
temperature over 500°F / 250°C
OUTLET PRESSURE RANGE
psig bar In. mm In. mm
5 to 70 0.34 to 4.8 1E392627012, Green 0.170 4.32 2.00 50.8
20 to 150 1.4 to 10.3 1E392727142, Red 0.207 5.26 1.94 49.0
15 to 100 1.0 to 6.9 14B9941X012, Unpainted 0.192 4.88
80 to 200 5.5 to 17.2 14B9940X012, Unpainted 0.282 7.16
SPRING PART NUMBER
AND COLOR
Table 3. Flow Coecients
ORIFICE SIZE WIDE-OPEN FOR RELIEF SIZING
In. mm C
g
9/16 14 170 8.5 5
3/4 19 240 12 7.1
1. Cv = Cs x 20 ÷ C
1
C
s
C
SPRING WIRE DIAMETER SPRING FREE LENGTH
(1)
C
1
v
34 0.67
Table 4. IEC Sizing Coecients
BODY SIZE
NPS DN X
1/2 15
3/4 or 1 20 or 25 0.44 0.73 0.38 0.82
0.73
9/16 in. / 14 mm 3/4 in. / 19 mm
T
F
D
0.38
ORIFICE SIZE
F
L
0.82
X
T
F
D
- - - - - - - - - - - -
1.96 49.8
K
m
F
L
3
Page 4
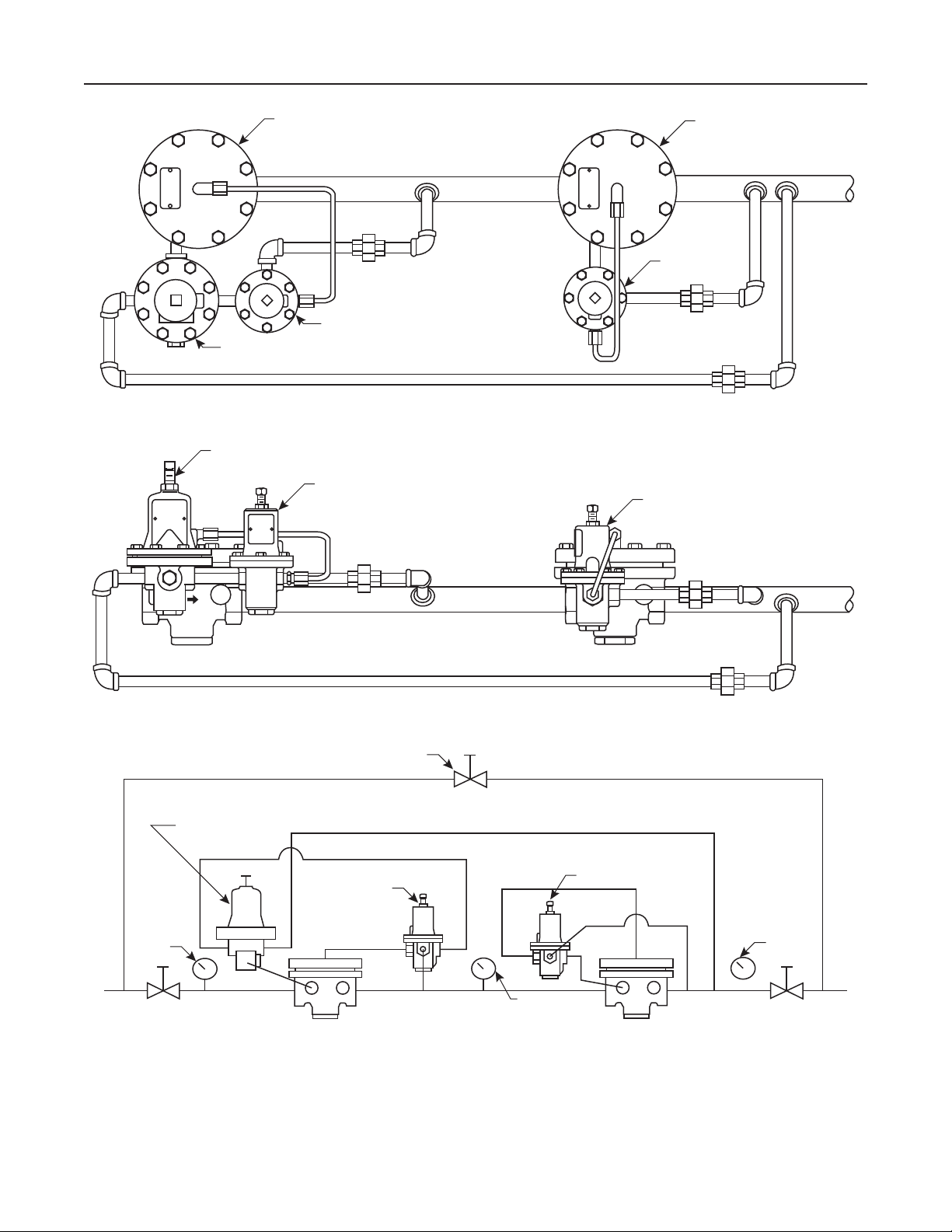
Type 92C
TYPE 92C MAIN VALVE
TYPE 6492HM SAFETY
OVERRIDE PILOT
TYPE 6492HM SAFETY
OVERRIDE PILOT
TYPE 92C MAIN VALVE
TYPE 6392 PILOT
TYPE 6392 PILOT
TOP VIEW
TYPE 6392 PILOT
TYPE 6392 PILOT
TYPE 92C MAIN VALVE TYPE 92C MAIN VALVE
E0656
E0657
TYPE 6492HM SAFETY
GAUGE
BLOCK VALVE
BLOCK VALVE
OVERRIDE PILOT
TYPE 6392 PILOT
TYPE 92C MAIN VALVE TYPE 92C MAIN VALVE
SIDE VIEW
GAUGE
TYPICAL TYPE 92C WITH TYPE 6492HM OR 6492HTM SAFETY OVERRIDE PILOT INSTALLATION
TYPE 6392 PILOT
GAUGE
BLOCK VALVE
Figure 3. Typical Pilot-Operated Type 92C Regulator Installations (continued)
4
Page 5

Type 92C
Note
To determine required loading pressure,
add the diaphragm dierential pressure
to the desired outlet pressure setting.
Principle of Operation
Pilot-Operated Regulator
Refer to Figure 5. Pilot supply pressure is piped from the
inlet side of the main valve to the pilot inlet connection.
Downstream pressure registers under the main valve
diaphragm through the pitot tube and under the pilot
diaphragm through the downstream control line.
When downstream pressure decreases to a value
below the setting of the pilot regulator spring, the pilot
spring forces the pilot valve plug open, increasing
the loading pressure on the top of the main valve
diaphragm. The increased loading pressure on top of
the main valve diaphragm and decreased downstream
pressure under the main valve diaphragm force the
main valve diaphragm and stem downward. This
opens the main valve plug, and increases ow to
the downstream system, thus restoring downstream
pressure to the setting of the pilot regulator spring.
When downstream pressure increases it registers
under the pilot diaphragm and overcomes the force
of the pilot spring. This allows the pilot valve spring to
close the pilot valve plug and causes excess loading
pressure to bleed to the downstream system through
the pilot bleed hole. At the same time, increased
downstream pressure registers under the main valve
diaphragm. The decreased loading pressure on top of
the main valve diaphragm and increased downstream
pressure under the main valve diaphragm force
the main valve diaphragm upward. This allows the
main valve plug spring to close the main valve plug,
reducing ow to the downstream system.
Pressure-Loaded Regulator
Refer to Figure 7. With a pressure-loaded regulator, a
remote, adjustable loading regulator provides loading
pressure to the top of the main valve diaphragm.
Downstream pressure registers under the main valve
diaphragm through the pitot tube.
When downstream pressure decreases, it registers
under the diaphragm and allows the stem and plug
to move downward, thereby opening the valve to
increase downstream pressure.
When downstream pressure increases, it registers
under the diaphragm and forces the stem and plug
to move upward. The upward force of the spring
causes the valve to close, which decreases ow to
the downstream system thus decreasing downstream
pressure. In hot air service, supply air above the
diaphragm becomes compressed and is vented to the
atmosphere. If a steam supply is used, the steam is
vented downstream.
Safety Override Pilot Principle
of Operation
Refer to Figure 6. Once placed in operation, the
upstream Type 6392 pilot senses the intermediate
pressure between both valves, and the Type 6492HM
(or 6492HTM) pilot senses downstream pressure
of the second valve. As demand for ow increases,
intermediate pressure will fall causing the Type 6392
pilot to open. As the Type 6392 pilot valve opens,
loading pressure to the main valve increases, opening
the main valve.
The Type 6492HM (or 6492HTM) safety override
pilot remains open because its setpoint is above the
setpoint of the downstream valve. In the unlikely event
that the downstream valve fails open, downstream
pressure will rise above the downstream valve’s
setpoint. This pressure is sensed by the Type 6492HM
(or 6492HTM) safety override pilot. As downstream
pressure increases the safety override pilot closes,
reducing loading pressure to the main valve, which
positions the main valve to maintain downstream
pressure as specied per ASME Boiler and Pressure
Vessel Code, section VIII.
In the event that the upstream valve fails, the
downstream regulator will prevent downstream
pressure from rising above safe operating levels.
It is recommended to install some type of warning
system, such as a sentinel relief valve, to warn the
operator that a valve has failed in the system. This
will prevent prolonged operation with one valve, which
could cause valve trim wear and noise associated with
operation at high dierential pressures.
When operating in most steam systems, valve
setpoints should be in strict accordance to
ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, section VIII.
The Type 6492HM (or 6492HTM) safety override
pilot should be set at 10 psig / 0.69 bar or 10% above
maximum downstream operating pressure of the
second valve, whichever pressure is greater. For
example, most HVAC systems operate at 15 psig /
1.0 bar, so the safety override pilot should be set no
higher than 25 psig / 1.7 bar.
5
Page 6

Type 92C
LOADING REGULATOR
STRAINER
16A1547-A
A2523-1
Figure 4. Typical Pressure-Loaded Type 92C Regulator Installation
Installation
WARNING
!
Personal injury, equipment damage
or leakage due to escaping steam
or bursting of pressure-containing
parts may result if this regulator is
overpressured or is installed where
service conditions could exceed the
limits given in Specications section on
page 2 and on the appropriate nameplate,
or where conditions exceed any ratings
of the downstream piping or piping
connections. To avoid such injury or
damage, provide pressure-relieving or
pressure-limiting devices to prevent
service conditions from exceeding
those limits. Type 92C regulators and
their installations should be checked
for compliance with all applicable codes
such as the ANSI B31.1-1977 Power
Piping standard and the ASME Boiler and
Pressure Vessel code.
Use a qualied personnel when installing, operating,
and maintaining a Type 92C regulator. Make sure
that there is no damage to or foreign material in the
regulator and that all tubing and piping are clean and
unobstructed. Install the regulator so that ow direction
matches the arrow marked on the regulator body.
Some typical Type 92C regulator installations are
shown in Figures 3 and 4.
The Type 92C regulator may be installed in any
orientation. However, the regulator should not be
BLEED RESTRICTION
OPTIONAL PIPING FOR
STEAM LOADING
TYPE 92C REGULATOR
BYPASS LINE
installed in a tall vertical pipeline where condensate
could collect and create a pressure head aecting
regulator performance.
Apply steam-compatible pipe compound to the
external pipeline threads. Then, using acceptable
piping procedures, install the regulator into
the pipeline.
If continuous operation of the system is required
during inspection and maintenance, install a three-
valve bypass around the regulator. If the owing
medium contains solids, install a proper size strainer
upstream of the regulator.
Pilot-Operated Regulator
The Type 6392 pilot has three 1/4 NPT connections
located in the pilot body. For proper operation of
a pilot-operated regulator, the pilot supply and the
regulator loading connections should be installed
parallel to the ow direction arrow marked on the pilot
body as shown in Figure 10, and the downstream
control line should be installed in the pilot body
connection as shown in Figures 3 and 10. If a pilotoperated regulator is ordered, the pilot supply and
the regulator loading connections will be made at
the factory.
Note
Pilot is shown here above the main valve
body for illustration purposes only. See
Figures 1 and 10 for actual pilot position
and appearance of pilot-supply line and
loading-pressure tubing.
6
Page 7

PILOT REGULATING SPRING
Type 92C Safety Override System
July 2008
Type 92C
Type 92C Safety Override System
July 2008
Type 92C
INLET PRESSURE
OUTLET PRESSURE
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
LOADING PRESSURE
Type 92C Safety Override System
July 2008
Type 92C
INLET PRESSURE
OUTLET PRESSURE
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
INTERMEDIATE PRESSURE
LOADING PRESSURE
PILOT DIAPHRAGM
DOWNSTREAM BLEED HOLE
Type 92C
36A1546-B
A2520-1
INLET PRESSURE
OUTLET PRESSURE
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
LOADING PRESSURE
PILOT
SUPPLY
PILOT
VALV E
PLUG PILOT
MAIN VALVE SPRING
VALV E
SPRING
MAIN VALVE PLUG
DOWNSTREAM
CONTROL LINE
MAIN VALVE
DIAPHRAGM
PITOT
TUBE
Figure 5. Operational Schematic of Pilot-Operated Type 92C Regulator
TYPE 6492HM SAFETY
OVERRIDE PILOT
TYPE 6392 PILOT
TYPE 92C MAIN VALVE
E0658
INLET PRESSURE
OUTLET PRESSURE
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
LOADING PRESSURE
INTERMEDIATE PRESSURE
Figure 6. Type 92C with Type 6492HM Safety Override Pilot Operational Schematic
TYPE 6392 PILOT
TYPE 92C MAIN VALVE
7
Page 8

Type 92C
Note
Since a clogged vent may cause
improper regulator functioning, install
and maintain the Type 92C regulator so
that the Type 6392 pilot spring case vent
remains clear and unobstructed.
To install a pilot-operated regulator:
1. Connect a downstream control line of at least
1/4 in. / 6.4 mm diameter pipe bushed down to the
1/4 NPT control line connection in the pilot body.
2. For both body-sized and swaged pipelines, locate
the pipeline control line connection in a section of
straight pipe at least 10 pipe diameters away from
the regulator or swage.
3. Do not locate the pipeline control line connection in
an elbow, swage or other area where turbulence or
abnormal velocities may occur.
4. If the pilot is mounted with the control line in a
position other than horizontal, make sure the
control line is sloped away from the pilot so that
condensate can drain into the pipeline.
5. Install a shuto valve (not a needle valve) in
the control line to completely isolate the pilot
during maintenance.
6. Install a pressure gauge in the control line or near
the regulator to aid in setting the outlet pressure.
Each pilot-operated regulator is factory-set for the
pressure setting specied on the order. If no setting
is specied, the unit is factory-set at 30 psig / 2.1
bar. In all cases, check the spring setting to make
sure it is correct for the application.
Pressure-Loaded Regulators
device. In all cases, check the pressure setting to
make sure it is correct for the application.
Startup
The maximum inlet pressure for a specic construction
is stamped on the main valve nameplate. Use
pressure gauges to monitor upstream and downstream
pressures during startup.
To put the regulator into operation:
1. Open the control line shuto valve.
2. For a pilot-operated regulator, open the
downstream block valve.
For a pressure-loaded regulator, open the shuto
valve in the pressure-loading piping or tubing.
3. Slowly open the upstream block valve.
4. If a bypass line is used, slowly close the bypass
line block valve.
5. To adjust the downstream pressure, follow the
appropriate procedure:
a. For a pilot-operated regulator, loosen the
jam nut (key 15, Figure 9). Turn the adjusting
screw (key 16, Figure 9) into the spring case
to increase the downstream pressure. Turn
the adjusting screw out of the spring case to
decrease the downstream pressure. When the
required downstream pressure is maintained for
several minutes, tighten the jam nut to lock the
adjusting screw in position.
b. For a pressure-loaded regulator, refer
to the Instruction Manual of the pressureloading device for downstream pressure
adjustment procedures.
To install a pressure-loaded regulator:
1. Install a shuto valve in the pressure-loading
piping or tubing.
2. Connect the piping or tubing to the 1/4 NPT
connection in the diaphragm ange (key 2, Figure 8).
If the loading regulator used with the pressureloaded regulator does not provide internal relief, an
atmospheric bleed (e.g., no. 60 drill size) is required if
the loading supply is air, or a downstream bleed line is
required if the loading supply is steam. This installation
is shown in Figure 4.
The pressure setting of a pressure-loaded regulator
is adjusted and determined by the pressure-loading
8
Safety Override Pilot Startup
and Adjustment
1. Loosen adjusting screws of the Type 6492HM (or
6492HTM) safety override pilot and Type 6392
intermediate pilot on the upstream valve until there
is no spring load. The screws should turn freely
by hand.
2. Loosen the adjusting screw of the Type 6392
pilot on the downstream valve until there is no
spring load.
3. Tighten the Type 6492HM (or 6492HTM) safety
override pilot of the upstream valve all the way in
to its highest spring setting.
Page 9

Type 92C
LOADING REGULATOR
MAIN VALVE PLUG
36A1546-B
A2947
INLET PRESSURE
LOADING PRESSURE
DOWNSTREAM PRESSURE
Figure 7. Operational Schematic of Pressure-Loaded
Type 92C Regulator
BLEED RESTRICTION
OPTIONAL
PIPING
FOR STEAM
LOADING
MAIN VALVE
DIAPHRAGM
PITOT TUBE
MAIN VALVE SPRING
4. Tighten the Type 6392 pilot of the upstream valve
all the way in to its highest spring setting.
5. Tighten the Type 6392 pilot of the downstream
valve to the desired downstream pressure.
6*. Loosen the Type 6392 intermediate pilot on
the upstream valve to the desired intermediate
pressure (normally 50% of inlet pressure).
7. Loosen the Type 6492HM (or 6492HTM) safety
override pilot of the upstream valve until there is no
spring load.
8. Tighten the Type 6392 pilot of the downstream
valve all the way in to its highest spring setting.
9. Tighten the Type 6492HM (or 6492HTM) safety
override pilot of the upstream valve to desired
pressure as specied per ASME Boiler and
Pressure Vessel Code, section VIII.
10.* Loosen the Type 6392 pilot of the
downstream valve to the desired downstream
pressure setpoint.
*Fisher™ recommends establishing setpoint by tightening the adjusting screw.
Shutdown
To take the regulator out of operation:
1. If a bypass line is used, slowly open the
bypass line block valve while monitoring the
downstream pressure.
2. Close the upstream block valve.
3. For a pilot-operated regulator, close the
downstream block valve.
For a pressure-loaded regulator, close the
shuto valve in the pressure-loading piping
or tubing.
4. Close the control line shuto valve.
5. Vent the regulator, the control line and the pilot
supply line to release any trapped pressure.
Maintenance
Regulator parts are subject to normal wear and must be
inspected periodically and replaced as necessary. The
frequency of inspection and replacement depends upon
the severity of service conditions and upon applicable
Federal, state and local codes and regulations.
WARNING
!
Avoid personal injury or property damage
from sudden release of pressure or
uncontrolled steam or other process
uid. Before starting disassembly:
• Isolate the regulator from the process,
• Release process pressure, and
• Vent the pilot supply and main valve
loading pressures.
This section contains separate procedures for regulator
and pilot maintenance.
Type 92C Regulator
Perform these procedures when replacing diaphragm,
the stem assembly, the valve plug or the orifice. Refer
to the correct section for the required instructions. Key
numbers refer to Figure 8 unless otherwise indicated.
The regulator may remain in the pipeline during
maintenance procedures unless the valve body is to
be replaced or removed for repairs. For pilot-operated
regulators, the pilot may remain on the pipe nipple
(key 23, Figure 10) unless the pilot body (key 1,
Figure 9) is to be removed or the entire pilot replaced
as a unit.
9
Page 10

Type 92C
Replacing Diaphragm and Stem Assembly
1. For the pilot-operated regulator, unscrew the
elbow and connector (keys 25 and 24, Figure 10)
so that the loading tubing (key 22, Figure 10) can
be removed.
For the pressure-loaded regulator, unscrew
the loading tubing (customer supplied) from the
1/4 NPT connection in the regulator diaphragm
ange (key 2).
2. Remove the cap screws (key 12) and the diaphragm
ange (key 2).
Lift out the upper diaphragm gasket (key 9), the
diaphragms (key 8), the lower diaphragm gasket
and for Steel/Stainless Steel constructions, the
diaphragm ring (key 15) and another diaphragm
gasket (key 9).
3. Lift out the stem assembly (key 11) consisting of
the pusher plate and the stem. Check that the pitot
tube (key 10) is clear and free of obstructions.
Clean the parts. Check for wear, scratches, nicks
and other damage, and replace parts as necessary.
4. Install the stem assembly (key 11) in the stem
guide bushing (key 6). Place one diaphragm
gasket (key 9) in the regulator body (key 1).
For Steel/Stainless Steel constructions, place the
diaphragm ring (key 15) and another diaphragm
gasket (key 9) on top of the rst gasket.
For all constructions, place the two molded
diaphragms (key 8) with the raised circle up,
another diaphragm gasket and the diaphragm
ange (key 2) on the body. Insert and tighten the
cap screws (key 12).
5. For the pilot-operated regulator, reconnect
the elbow, the loading tubing and the connector
(keys 25, 22 and 24, Figure 10).
For the pressure-loaded regulator, reconnect
the pressure-loading tubing.
6. When maintenance is completed, refer to the
Startup section to put the regulator back in
operation and to adjust the pressure setting.
Replacing Valve Plug and Orice
1. Remove the valve plug guide (key 5).
2. Remove the valve plug (key 4) and the valve
plug spring (key 7). Inspect the valve plug
seating surface for nicks or scratches. Replace
as necessary.
3. Unscrew the orice (key 3), and inspect the
seating surface for nicks and scratches. Replace
if necessary.
4. Clean the valve plug guide, the valve plug, the
valve plug spring and the orice (keys 5, 4, 7
and 3, respectively).
5. Coat the orice threads with Never-Seez
®
or
equivalent lubricant. Then, being careful not to
damage the seating surface, thread the orice
(key 3) into the regulator body (key 1).
6. Place the valve plug spring (key 7) into the
valve plug guide (key 5). Then slide the valve
plug (key 4) over the spring and into the valve
plug guide.
7. Apply Lok-Cease® 20/20 sealant or equivalent
to the valve plug guide threads, and screw the
valve plug guide (key 5) with attached parts
into the regulator body (key 1), applying 130 to
160 ft-lbs / 176 to 217 N•m of torque.
8. When maintenance is completed, refer to the
Startup section to put the regulator back in
operation and to adjust the pressure setting.
Type 6392 Pilot
Perform this procedure if inspecting, cleaning or
replacing any pilot parts. Key numbers refer to Figure 9
unless otherwise specied.
All pilot maintenance may be performed with the pilot
body (key 1) attached to the pipe nipple and connector
(keys 23 and 24, Figure 10) unless the pilot body must
be removed or the pilot is to be replaced as a unit.
1. Loosen the jam nut (key 15), and turn the
adjusting screw (key 16) counterclockwise until all
compression is removed from the control spring
(key 13). Remove the loading tubing from the
pilot outlet connection. Remove the cap screws
(key 17), spring case (key 2), control spring
(key 13) and upper spring seat (key 14) from
the body.
2. Remove the lower spring seat (key 9), the diaphragm
(key 7) and the diaphragm gasket (key 8) from the
body. Lift out the stem assembly (key 6) consisting
of the stem and the pusher plate. Clean the
1/16 in. / 1.6 mm diameter pilot bleed hole. Clean
and replace parts as necessary, and assemble the
stem assembly, the gasket, the diaphragm and the
spring seat in the order shown in Figure 9.
Never-Seez® is a mark owned by Never-Seez Corp.
Lok-Cease® is mark owned by Certied Laboratories.
10
Page 11

Type 92C
3. Install the control spring (key 13), the lubricated
upper spring seat (key 14) and the spring case
(key 2). Insert and tighten the cap screws (key 17).
Lubricate the adjusting screw (key 16) with
Never-Seez® or equivalent lubricant, and thread it
into the spring case.
4. Unscrew the valve plug guide (key 5). Remove
the strainer screen (key 12), the valve plug
(key 4), the valve plug cap (key 26) and the valve
plug spring (key 11). Unscrew the orice (key 3).
Clean and replace parts as necessary. Apply
Never-Seez® or equivalent lubricant to the orice
threads, and screw the orice into place.
5. Place the valve plug spring (key 11) into the valve
plug guide (key 5). Insert the valve plug cap (key 26)
into the valve plug (key 4), and then slide both
parts over the spring and into the valve plug guide.
Place the strainer screen (key 12) onto the valve
plug guide. Apply Lok-Cease® 20/20 sealant or
equivalent (key 21) to the valve plug guide threads,
and screw the valve plug guide with the attached
parts into the pilot body (key 1).
6. When maintenance is completed, refer to the
Startup section to put the regulator back into
operation, and adjust the pressure setting.
Types 6492HM and 6492HTM
Safety Override Pilots
These procedures are to be performed if inspecting,
cleaning or replacing any pilot parts or of cycling,
erratic control or too high or too low an outlet (control)
pressure is noted. Perform only those procedures
in this section required to correct the problem. Key
numbers refer to Figure 11.
Note
Before performing any maintenance,
loosen the hex nut (key 16), if used,
and turn the adjusting screw (key 15) or
handwheel (key 31) counterclockwise
until all compression is removed from
the control spring (key 12). Remove the
pilot spring from the pipe nipple and
connectors (keys 82 and 83, Figure 12).
2. Clean and replace parts as necessary. Apply
sealant to the orice threads. Thread the orice
into place and tighten using 19 to 25 ft-lbs / 26 to
34 N•m of torque.
3. Handle parts carefully, and place the plug spring
(key 3) in the plug guide (key 2). Slide the inner
valve (key 4) over the spring and into the plug
guide. Place the screen (key 77) onto the plug
guide. Place the stem (key 7) in the center hole
of the plug guide. Apply sealant to the plug guide
threads, and screw the guide plus attached parts
into the body (key 1).
4. Remove the pipe plug (key 74). Then remove the
pipe plug (key 94). Clean and replace the pipe
plugs as necessary.
5. Apply sealant to the threads of the pipe plug
(key 94) and install.
6. Apply sealant to the threads of the pipe plug
(key 74). Thread the pipe plug into place and
tighten using 5 to 15 ft-lbs / 6.8 to 20 N•m
of torque.
7. Remove the cap screws (key 17), spring case
(key 14), control spring (key 12) and upper spring
seat (key 13) from the body (key 1).
8. Remove the lower spring seat (key 11),
diaphragms (key 10) and diaphragm gasket
(key 18) from the body. Inspect and clean the
diaphragm gasket, and replace if necessary.
9. Unscrew the bellows retainer (key 8) and remove
the bellows (key 9). Replace worn parts as
necessary, and install the bellows and bellows
retainer. Tighten the bellows retainer using 19 to
25 ft-lbs / 26 to 34 N•m of torque.
10. Install the diaphragm gasket. Install both
diaphragms with their raised performed centers
facing toward the spring case.
11. Lubricate the upper spring seat and the exposed
threads of the adjusting screw. Install the lower
spring seat (key 11), control spring (key 12), upper
spring seat (key 13) and spring case (key 14).
Insert and tighten the cap screws (key 17) in a
crisscross bolting pattern using 12 to 18 ft-lbs /
16 to 24 N•m of torque.
1. Unscrew the plug guide (key 2). Remove the
screen (key 77), inner valve (key 4), plug spring
(key 3) and stem (key 7). Unscrew the orice
(key 5). Examine the orice and plug seating
surfaces for damage.
Never-Seez® is a mark owned by Never-Seez Corp.
Lok-Cease® is mark owned by Certied Laboratories.
Parts Ordering
When corresponding with your local Sales Oce about
this equipment, always specify the equipment serial
number as found on the regulator nameplate.
When ordering replacement parts, specify the
complete 11-character part number of each needed
part as found in the following parts list.
11
Page 12

Type 92C
Parts List
Regulator
Key Description Part Number
Parts Kit (included are keys 3, 4, 7, 8 and 9)
For 1/2 and 3/4 NPT body
9/16 in. / 14 mm orice R92CX000042
For 1 NPT body
3/4 in. / 19 mm orice R92CX000032
1 Regulator Body Assembly with Bushing
(See key 6 for bushing)
Gray Cast Iron
NPS 1/2 / DN 15 36A1539X012
NPS 3/4 / DN 20 36A1540X012
NPS 1 / DN 25 36A1541X012
Steel
1/2 NPT 36A1542X012
3/4 NPT 36A1543X012
1 NPT 36A1544X012
CL150 RF
NPS 1/2 / DN 15 14B3428X012
NPS 3/4 / DN 20 14B3428X022
NPS 1 / DN 25 19A5459X012
CL300 RF
NPS 1/2 / DN 15 14B3428X032
NPS 3/4 / DN 20 14B3428X042
NPS 1 / DN 25 14B0037X012
PN 16/25/40 RF
NPS 1/2 / DN 15 14B3428X052
NPS 3/4 / DN 20 14B3428X062
NPS 1 / DN 25 14B3428X072
Stainless Steel
1/2 NPT 36A1542X022
3/4 NPT 36A1543X032
1 NPT 36A1544X022
CL150 RF
NPS 1/2 / DN 15 14B3428X082
NPS 3/4 / DN 20 14B3428X092
NPS 1 / DN 25 19A5459X022
CL300 RF
NPS 1/2 / DN 15 14B3428X102
NPS 3/4 / DN 20 14B3428X112
NPS 1 / DN 25 14B0037X022
PN 16/25/40 RF
NPS 1/2 / DN 15 14B3428X122
NPS 3/4 / DN 20 14B3428X132
NPS 1 / DN 25 14B3428X142
2 Diaphragm Flange
Gray Cast Iron 26A1533X012
Steel 26A1534X012
Stainless Steel 26A1534X022
3 Orice
For 1/2 and 3/4 NPT body,
9/16 in. / 14 mm, 416 Stainless Steel 16A1529X012
For 1 NPT body
3/4 NPT / 19 mm, 416 Stainless Steel 16A1528X012
For 3/4 and 1 NPT body,
9/16 in. / 14 mm, Ethylenepropylene (EPDM),
410/416 Stainless Steel 1E399535132
4 Valve Plug, heat-treated, 416 Stainless Steel 1E398146172
5 Valve Plug Guide
Brass (for Gray Cast Iron body) 1E398214012
416 Stainless Steel (for Steel/Stainless Steel body) 1E398235132
6 Stem Guide Bushing, heat-treated
416 Stainless Steel (included in key 1)
For Gray Cast Iron body 1E398535132
For Steel/Stainless Steel body 16A1530X012
7 Valve Plug Spring, Stainless Steel 1E398837022
8* Diaphragm, Stainless Steel (2 required) 1E399236012
Regulator (continued)
Key Description Part Number
9* Diaphragm Gasket
(2 required for Gray Cast Iron body;
3 required for Steel/Stainless Steel body with
Ethylenepropylene (EPDM) seat) 16A1526X012
Steel/Stainless Steel body with metal seat,
3 required 1E3993X0012
Steel/Stainless Steel body with metal seat
(High temperature), 3 required 16A1526X022
10 Pitot Tube
For Gray Cast Iron body, Copper
NPT 16A1525X012
For Steel body, Copper
NPT 1E399417012
CL150 RF 16A1525X012
CL300 RF and PN 16/25/40 1E399417012
For Stainless Steel body, 304 Stainless Steel
NPT 1E399438072
CL150 RF 16A1525X022
CL300 RF and PN 16/25/40 1E399438072
11 Stem Assembly, 416 Stainless Steel 16A1524X012
12 Cap Screw, Zinc-plated steel (8 required)
For Gray Cast Iron body 1A914524052
For Steel/Stainless Steel body 1A782024052
14 Drive Screw, Stainless Steel (2 required) 1A368228982
15 Diaphragm Ring
For Steel body, Steel 16A1531X012
For Stainless Steel body, Stainless Steel 16A1531X022
Type 6392 Pilot (See Figure 10)
Key Description Part Number
Parts Kit (included are keys 3, 4, 8, 7, 11, 12 and 26)
Standard Trim R6392X00012
1 Pilot Body
Gray Cast Iron 26A1518X012
Steel 26A1517X012
Stainless Steel 26A1517X022
2 Spring Case
Gray Cast Iron 2E391219012
Steel 2J127522012
Stainless Steel 2J1275X0012
3 Orice, heat-treated
416 Stainless Steel 16A1511X012
4 Valve Plug, heat-treated
416 Stainless Steel 16A1516X012
5 Valve Plug Guide
Brass (for Gray Cast Iron pilot) 1E391814012
Heat-treated, 416 Stainless Steel
(For Steel pilot) 1E391835132
For Gray Cast Iron and Steel pilot,
Heat-treated, 416 Stainless Steel 1E391835132
For Stainless Steel pilot 1E391835072
6 Stem Assembly, 416 Stainless Steel
For Stainless Steel seat 16A1515X012
For Ethylenepropylene (EPDM) seat 16A1515X022
7 Diaphragm, Stainless Steel (2 required) 1E392836012
8* Diaphragm Gasket
Elastomer seat 1E393104022
Stainless Steel seat, Graphite 1E3931X0012
9 Lower Spring Seat, Aluminum 1E392309012
10 Stem Guide Bushing, 416 Stainless Steel 1E392235132
11 Valve Plug Spring, Stainless Steel 1E392437022
12 Strainer Screen, Stainless Steel 16A1512X012
*Recommended spare part
12
Page 13

Type 92C
Type 6392 Pilot (See Figure 10) (continued)
Key Description Part Number
13 Control Spring,
Standard springs, 416 Stainless Steel
5 to 70 psig / 0.34 to 4.8 bar, Green 1E392627012
20 to 150 psig / 1.4 to 10.3 bar, Red 1E392727142
Spring for use over 500°F / 260°C,
17-7 PH Stainless Steel
15 to 100 psig / 1.0 to 6.9 bar 14B9941X012
20 to 25 psig / 1.4 to 1.7 bar 14B9940X012
14 Upper Spring Seat, Zinc-plated steel 1B798525062
15 Jam Nut, Plate steel 1A352224122
16 Adjusting Screw, Plated steel 1E639928992
17 Cap Screw, Zinc-plated steel (6 required)
For Gray Cast Iron body 1A407824052
For Steel/Stainless Steel body 1A391724052
26 Valve Plug Cap, heat-treated
416 Stainless Steel 16A1549X012
Type 6392 Pilot Mounting Parts
Key Description Part Number
22 Loading Tubing
Copper 16A1527X012
Stainless Steel 16A1527X022
23 Pipe Nipple, Steel 1N584226232
24 Connector
Brass 15A6002X212
Stainless Steel 15A6002X642
25 Elbow
Brass 15A6002X172
Stainless Steel 15A6002X632
Types 6492HM and 6492HTM
Safety Override Pilots (See Figure 12)
Key Description Part Number
1 Pilot Valve Body
WCC Steel 22A0403X052
CF8M Stainless Steel 22A0403X072
2 Valve Guide, Stainless Steel
Steel body, 416 Stainless Steel 1E391835132
Stainless Steel body, 316 Stainless Steel 1E391835072
3 Valve Spring, 302 Stainless Steel 1E392437022
4 Inner Valve
Steel body, 416 Stainless Steel 1F967446172
Stainless Steel body, 316 Stainless Steel 1F9674X0012
5 Orice
Steel body, 416 Stainless Steel 1H564446172
Stainless steel body, 316 Stainless Steel 1H5644X0012
7 Valve Stem
Steel body, 410/416 Stainless Steel 1F967835132
Stainless Steel body, 316 Stainless Steel 1F9678X0012
8 Bellows Retainer
Steel body, Brass 1F971214012
Stainless Steel body, 316 Stainless Steel 1F9712X0012
9 Bellows
Steel body, Brass 1F971318992
Stainless Steel body, 321 Stainless Steel 1F9713X0012
10 Diaphragm, 302 Stainless Steel (2 required) 1E395836012
11 Lower Spring seat
Type 6492HM, Aluminum 1E395408012
Type 6492HTM
Steel 1E3954X0052
Stainless Steel 14B9948X012
Types 6492HM and 6492HTM
Safety Override Pilots
(See Figure 12) (continued)
Key Description Part Number
12 Spring
Type 6492HM, Steel
10 to 30 psig / 0.69 to 2.2 bar 1E395627022
25 to 75 psig / 1.7 to 5.2 bar 1D7455T0012
70 to 150 psig / 4.8 to 10.3 bar 1E395727192
Type 6492HTM, Stainless Steel
15 to 100 psig / 1.0 to 6.9 bar 14B9943X012
80 to 250 psig / 5.5 to 17.2 bar 14B9942X012
13 Upper Spring seat, Steel
Type 6492HM 1D667125072
Type 6492HTM 14B9951X012
14 Spring Case
Steel
With standard adjusting screw 2L416322012
With sealed adjusting screw 2L442022012
Stainless Steel
With standard adjusting screw 2L416333092
With sealed adjusting screw 2L4420X0012
15 Adjusting Screw, Steel
Standard 1D995448702
Handwheel 1J496428982
16 Hex Nut, Zinc-plated steel 1A353724122
17 Cap Screw (8 required)
Type 6492HM
Steel 1A381624052
Stainless Steel 1A3816X0152
Type 6492HTM
Steel 1A3816X0132
Stainless Steel 1A3816X0152
18 Diaphragm Gasket
Type 6492HM, Composition 1E396104022
Type 6492HTM, Graphite 1E3961X0012
34 Machine Screw for use with handwheel, Steel 16A5763X012
38 Handwheel, Zinc 1J496144012
39 Lock Washer for use with handwheel, Steel 1A352332992
74 Pipe Plug
Steel 0Z020128992
Stainless Steel 0Z020135072
77 Screen, 304 Stainless Steel 16A1512X012
78 Reducing Bushing
Steel 1C379026232
Stainless Steel 1C3790X0012
87 Sealed Adjusting Screw Sealing Washer 1V205699012
94 Pipe Plug, Stainless Steel 1E823135042
95 Warning Label 19B0429X0A2
Type 6492HM Pilot Mounting Parts
Key Description Part Number
81 Tubing 0500103809W
82 Pipe Nipple (2 required)
Steel 1C559926232
Stainless Steel 1C5599X0012
83 Connector
Steel 15A6002XY72
Stainless Steel 15A6002X642
84 Elbow
Steel 15A6002XY52
Stainless Steel 15A6002X632
*Recommended spare part
13
Page 14

Type 92C
26A1536-A
APPLY SEALANT:
S = ANTI-SEIZE COMPOUND
9
15
STEEL/STAINLESS STEEL CONSTRUCTION
14
13
9
2
9
6
11
S
3
GREY CAST IRON CONSTRUCTION
Figure 8. Type 92C Steam Regulator Assembly
8
2
9
12
8
1
10
4
S
7
5
16
2
14
13
17
7
1
10
6
3
15
L
18
19
9
8
L
26
4
S
11
5
16A1520-B
APPLY LUBRICANT/SEALANT:
L = ANTI-SEIZE LUBRICANT
S = ANTI-SEIZE COMPOUND
14
12
Figure 9. Type 6392 Pilot Assembly
Page 15

Type 92C
36A1545-A
A2521-1
25
23
1/4 NPT PILOT
SUPPLY CONNECTION
22
24
1/4 NPT REGULATOR
SUPPLY CONNECTION
1/4 NPT DOWNSTREAM
CONTROL LINE CONNECTION
Figure 10. Type 6392 Pilot Mounting Parts
15
11
10
18
5
77
3
E0660
16
13
12
9
8
7
4
2
14
20
19
17
94
74
Figure 11. Type 6492HM or 6492HTM Safety Override Pilot Assembly
95
1
78
15
Page 16

Type 92C
TYPE 6492HM
E0659
TYPE 6392
84
82
83
81
Figure 12. Type 92C with Safety Override Pilot Assembly
91 82
Webadmin.Regulators@emerson.com
Fisher.com
Emerson Automation Solutions
Americas
McKinney, Texas 75070 USA
T +1 800 558 5853
+1 972 548 3574
Europe
Bologna 40013, Italy
T +39 051 419 0611
Facebook.com/EmersonAutomationSolutions
LinkedIn.com/company/emerson-automation-solutions
Twitter.com/emr_automation
Asia Pacic
Singapore 128461, Singapore
T +65 6777 8211
Middle East and Africa
Dubai, United Arab Emirates
T +971 4 811 8100
D100255X012 © 1979, 2020 Emerson Process Management Regulator
Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved. 01/20.
The Emerson logo is a trademark and service mark of Emerson
Electric Co. All other marks are the property of their prospective owners.
Fisher™ is a mark owned by Fisher Controls International LLC, a
business of Emerson Automation Solutions.
The contents of this publication are presented for informational purposes
only, and while every eort has been made to ensure their accuracy, they
are not to be construed as warranties or guarantees, express or implied,
regarding the products or services described herein or their use or
applicability. All sales are governed by our terms and conditions, which
are available upon request. We reserve the right to modify or improve the
designs or specications of such products at any time without notice.
Emerson Process Management Regulator Technologies, Inc. does not
assume responsibility for the selection, use or maintenance of any
product. Responsibility for proper selection, use and maintenance of any
Emerson Process Management Regulator Technologies, Inc. product
remains solely with the purchaser.
 Loading...
Loading...