Febco 880V, 860 Maintenance Manual

INSTALLATION, OPERATION, MAINTENANCE
Maintenance Manual
Reduced Pressure Assembly
IOM-F-860_880V
Models 860 & 880V 2
860
880V
Standard Configuration
1
/2" – 10"
880V
Vertical Configuration
INDEX
Vandalism. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Features and Operating Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Troubleshooting Procedures and Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
General Service Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Service Procedures for Models 860 and 880V (2
Testing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Freeze Protection Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Cut-a-Way View of Model 860 (21/2" - 10") (figure #6) . . . . . . . . . . 10
Cut-a-Way View of Relief Valve (2
Exploded View of 10" Disc (figure #9) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Cut-a-Way View of Model 880V (standard configuration) (figure #8) . . 11
Cut-a-Way View of 10" Disc (figure #10). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Parts List for Models 860 and 880V (2
How To Order Parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Kit Numbers for Models 860 and 880V (2
Warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Back Cover
1
/2" - 10") (figure #7). . . . . . . . . . 10
1
/2" - 10") . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
1
/2" - 10"). . . . . . . . 6
1
/2" - 10") . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Read and understand this manual prior to installing,
operating or servicing this equipment.

MAINTENANCE MANUAL MODELS 860 & 880V 21/2" – 10"
Vandalism
If the unit is installed where vandalism may be a problem, the assembly should be protected and secured. A chain can be looped through both
shutoff valve handwheels and locked in position to prevent tampering. Test cock valve handles can also be removed. On backflow prevention
assemblies installed in conjunction with fire sprinkler systems, a tamper switch can be placed on the OS&Y shutoff valves that will trigger an
alarm if an unauthorized closure should occur.
A protective enclosure can be installed over the unit to discourage vandals. If an enclosure is used, it should be installed so that adequate clearance is available for maintenance and testing.
Consult local codes before installing any type of protective enclosure.
2
MAINTENANCE MANUAL MODELS 860 & 880V 21/2" – 10"
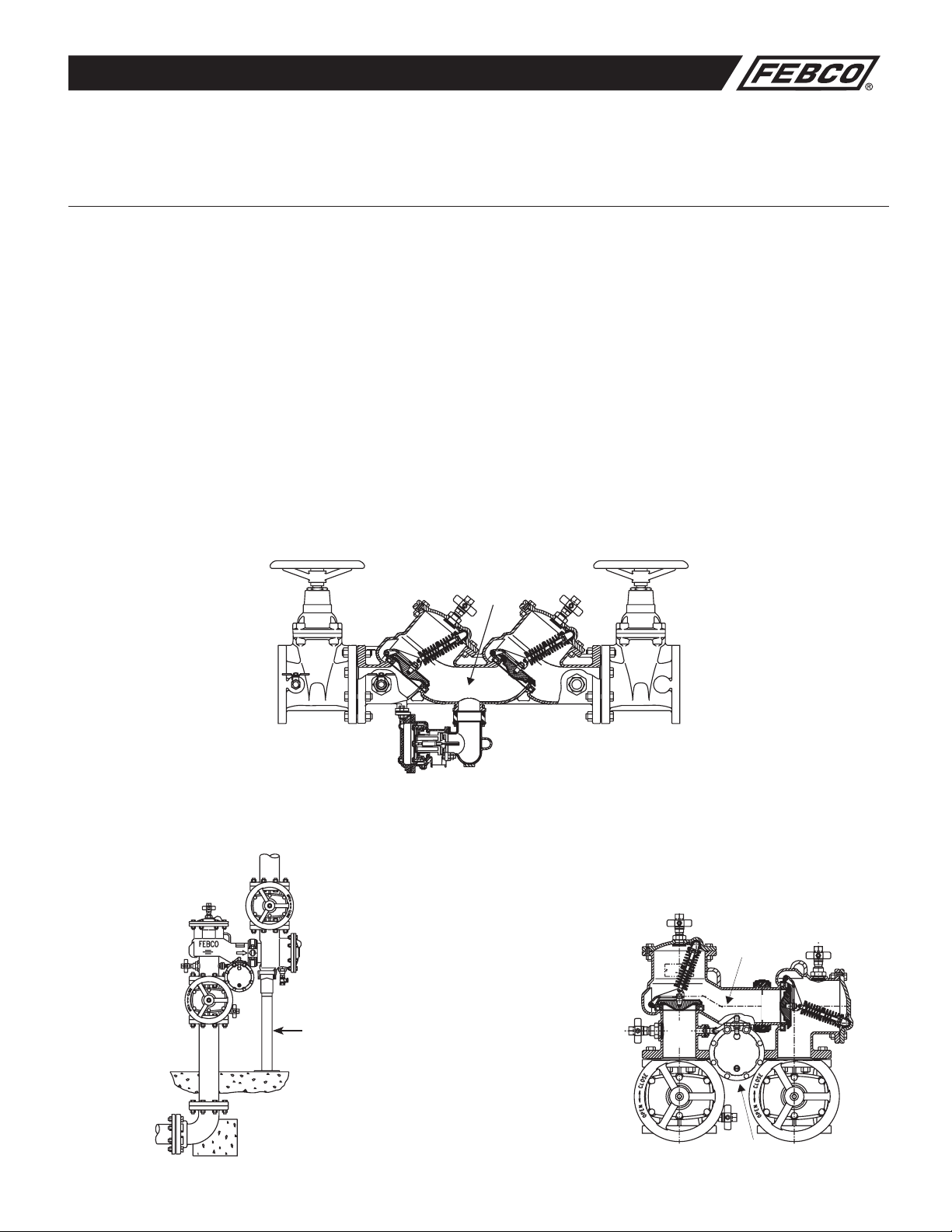
Features and Operating Procedures
Reduced Pressure Backflow Preventer
The FEBCO Reduced Pressure Backflow Preventer Assembly consists of two independently operating, spring loaded check valves with a pressure differential relief valve located between the two checks. The pressure drop across the first check valve is approximately 7.0psid with no
flow. The relief valve consists of a hydraulically balanced diaphragm with the high pressure side hydraulically connected to the upstream side of
the first check. The low pressure side is hydraulically connected to the reduced pressure zone, thus the relief valve remains closed during normal operation. The low pressure side of the diaphragm is spring loaded to force the relief valve open when the pressure drop across the first
check (and across the diaphragm) reduces to approximately 3.0psid. A complete assembly includes two shutoff valves and four test cocks.
Example sectional views below show typical components and flow passages with corresponding pressure readings (no flow conditions) at the
various locations within the assembly with 100psi line pressure.
NOTE: The 880V, when installed in the vertical orientation, must include vertical support under the second check body section. (See Figure #2.)
Model 860 (21/2"-10")
Figure #1
Inlet Shutoff
First Check
Reduced
Pressure
Zone
Second
Check
Outlet Shutoff
Model 880V (21/2"-10")
Figure #2
Vertical support for
second check
Installed in
vertical position
100
PSI
93
PSI
92
PSI
Relief Valve
Model 880V (21/2"-10")
Standard Confi guration
Figure #3
First Check
Reduced
Pressure
Zone
93
100
PSI
Inlet Shutoff
PSI
Relief
Valve
Second
Check
92
PSI
Outlet Shutoff
3
MAINTENANCE MANUAL MODELS 860 & 880V 21/2" – 10"
Troubleshooting Guide
With Differential Pressure Gauge
Symptom #1 Reading: Problem:
Check Differential Across 2 to 3 psid Leak in #1 or #2 check valve
#1 Check Valve 6 to 8 psid and steady Malfunctioning pressure relief valve
2 to 7 psid and fl uctuating Inlet pressure fl uctuating
Symptom #2 Reading: Problem:
Check Differential Across 2 to 3 psid #1 check valve held open
#1 Check Valve 6 to 8 psid and steady Malfunctioning pressure relief valve
Without Differential Pressure Gauge
Symptom #1 and #2 Result: Problem:
A) Close Gate Valve #2 If discharge stops Leak in #2 check valve
If discharge does not stop Go to “B”
B) Open #4 test cock to produce a fl ow If discharge stops Leak in #1 check valve
greater than differential relief valve If discharge does not stop Malfunctioning pressure relief valve
discharge
Symptom #1 Cause: Solution:
Continuous discharge from relief valve
during NO FLOW conditions (Discharge
stops with water fl ow)
With this symptom, the pressure drop
across the #1 check valve would be
2 to 3 psid. If a fl ow of water (more
than discharge) is created through
the valve, the pressure drop should
increase to approximately 7 PSI
A. Debris fouling #1 check valve
B. Outlet pressure higher than
inlet pressure and debris
fouling #2 check valve
C. Spring stem not moving freely
D. Damaged seat or seat disc
E. Leakage at seal under the seat ring
F. Large diaphragm damaged and leaking.
Inspect and clean
Inspect and clean
Inspect for dirt or other foreign material
Inspect and replace
Inspect and replace seal
Inspect and replace if required
Symptom #2 Cause: Solution:
Intermittent discharge from relief
valve during NO FLOW conditions.
With the symptom, the pressure drop
across the #1 check valve would be
varying from about 2 to 7 psid
A. Inlet line pressure variations
causing relief valve to discharge
B. Pressure surges (water hammer) causing
relief valve to discharge as pressure wave
passes through the zone
Eliminate or reduce pressure variations
by installing a soft seated, spring loaded
check on upstream side of device
Eliminate or reduce pressure surges
Symptom #3 Cause: Solution:
Continuous discharge from relief valve
during FLOW and NO FLOW conditions
With this symptom, the pressure drop
across the #1 check valve would be
7 psid or more at all times
4
A. Seat disc dislodged from cavity in
the main stem (this can be caused by
pressure surges during initial fi lling of
system lines)
B. Debris fouling the relief valve seat
C. Debris blocking the relief valve
sensing passage
D. Dirt or scale jamming main stem
E. Leakage at main stem, small
diaphragm damaged and leaking.
Reposition disc in main stem cavity.
Repressurize system slowly
Inspect and clean
Inspect and clean
Inspect and clean, or replace
Inspect and clean, or replace
MAINTENANCE MANUAL MODELS 860 & 880V 21/2" – 10"
Troubleshooting Guide Continued
Symptom #4 Cause: Solution:
Relief valve does not open above
2.0 psid during fi eld testing
A. Outlet gate valve not closed completely
B. Plugged low pressure hydraulic passage
(from "ZONE" to inner diaphragm)
C. Improper alignment of internal parts
during reassembly (causing high
resistance to movement)
D. Jammed main stem due to debris
Check for debris blocking gate valve
Inspect and clean
Reassemble
Clean
Symptom #5 Cause: Solution:
First check pressure drop is low
(less than 5 psid) during fi eld testing
A. Debris fouling fi rst check seat
B. Debris fouling second seat with
backpressure
C. Inlet pressure variations causing
inaccurate gauge reading
D. Disc does not move freely in arm.
(Therefore, disc not parallel to
seat ring)
E. Damaged seat or seat disk
F. Worn guide, bushing or stem
G. Bearing not properly seated in cover
Inspect and clean
Inspect and clean
Eliminate pressure variations.
(see symptom 2A)
Inspect and clean if required
Inspect and replace as required
Inspect and replace as required
Inspect and reassemble
Symptom #6 Cause: Solution:
Second check fails to hold back
pressure during fi eld testing
A. Outlet gate valve not closed completely
B. Debris fouling second check seat
C. Disc not moving freely in assembly
D. Damaged seat or seat disk
E. Worn guide, bushings or stem
F. Bearing not properly seated in cover
Check for debris blocking gate valve
Inspect for dirt or other foreign debris
Inspect and clean
Inspect and replace if required
Inspect and replace if required
Inspect and replace if required
Inspect and reassemble
Note: If check valve seat disc has been severely cut at the seat ring diameter, the assembly is being subjected
to extremely high and repeated back pressure. Either thermal water expansion or water hammer are the
most likely causes.
5
 Loading...
Loading...