Fairchild Semiconductor TMC22071A Datasheet
TMC22071A
Genlocking Video Digitizer
www.fairchildsemi.com
Features
• Fully integrated acquisition
• 3-channel video input multiplexer
• Two-stage video clamp
• Automatic gain adjustment
• Sync detection and separation
• Pixel and subpixel adjustment of HSYNC-to-Video
timing
• Genlock to NTSC or PAL inputs
• Clock generation
• 8-bit video A/D converter
• Microprocessor interface
• Line-locked pixel rates
- 12.27 MHz NTSC
- 13.5 MHz NTSC or PAL
• Direct interface to TMC22x9x encoders
• Built-in circuitry for crystal oscillator
• No tuning or external voltage reference required
• 68 Lead PLCC or 100 Lead MQFP package
Applications
• Frame grabber
• Digital VCR/VTR
• Desktop video
Description
The TMC22071A Genlocking Video Digitizer converts standard baseband composite NTSC or PAL video into 8-bit digital composite video data. It extracts horizontal and vertical
sync signals and generates a pixel clock for the on-board
8-bit A/D converter and a 2x clock for the transfer of data to
subsequent video processing decoding or encoding with the
TMC22x5y Video Decoder or TMC22x9x Digital Video
Encoder family. It also measures the color subcarrier phase
and frequency and provides this data to the Encoder (for genlocked color NTSC or PAL encoding), or a frame buffer (for
frame capture) over the digital composite video port.
The TMC22071A includes a three-channel video input multiplexer, analog clamp, variable gain amplifier, and digital
back porch clamp. The on-board oscillator circuitry generates the clock from a 20 MHz crystal or the clock source may
be an external oscillator. It is programmable over a microprocessor interface for NTSC or PAL operation. No external
component changes and no production tuning or service
adjustments are ever required.
The TMC22071A is fabricated in an advanced CMOS
process, and is packaged in a 68 Lead PLCC or 100 Lead
MQFP. Its performance is guaranteed from 0°C to 70°C.
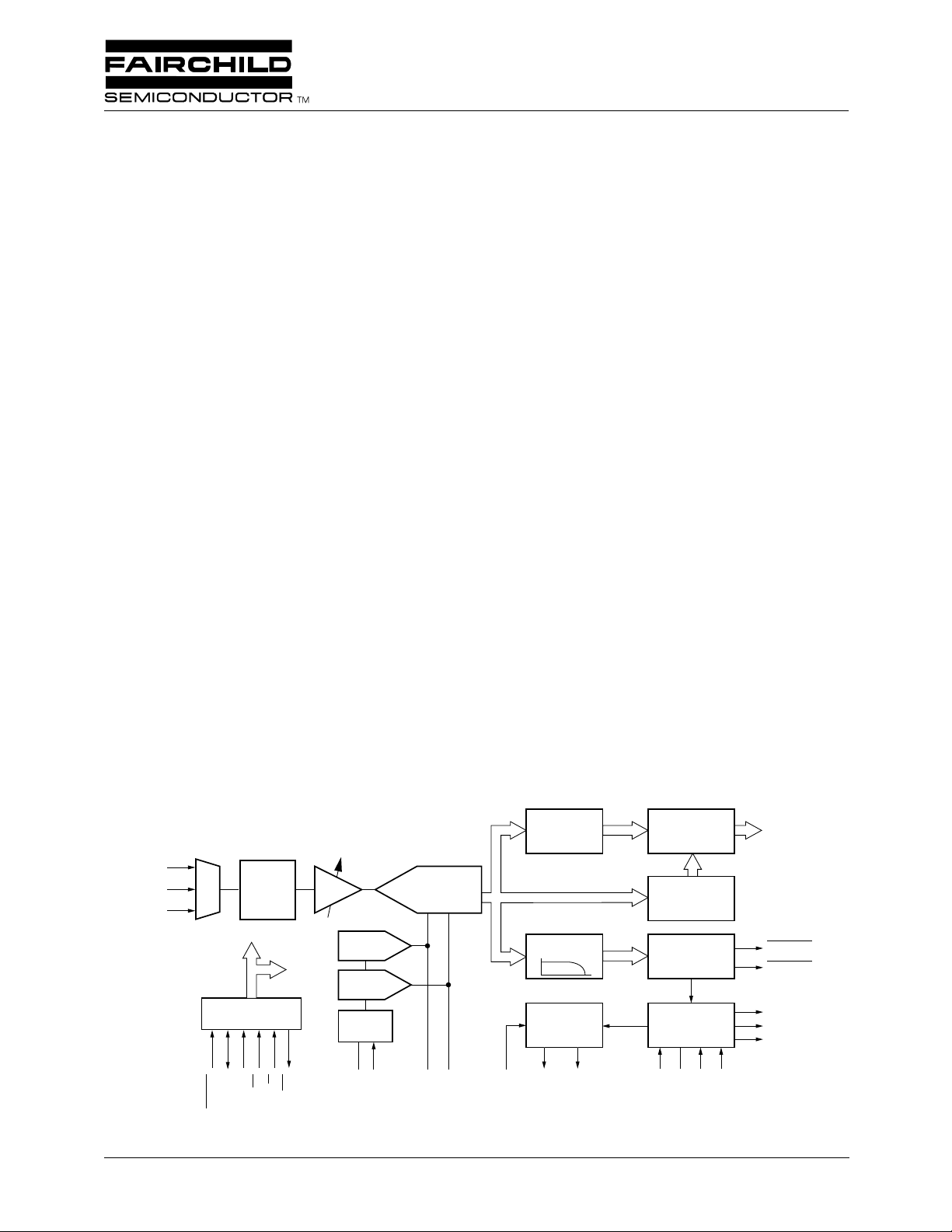
Block Diagram
V
IN1
V
IN2
V
IN3
MUX
CONTROL
0
D
RESET
MICROPROCESSOR
INTERFACE
ANALOG
CLAMP
0
A
CS
R/W
INT
BACK PORCH
CLAMP
GAIN
D/A
D/A
+1.2V
REF
V
COMP
ANALOG INTERFACE DDS/PIXEL CLOCK INTERFACE
A/D
R
LOWPASS
FILTER
DIRECT
DIGITAL
SYNTHESIZER
T
B
R
CLK IN
CLK
OUT
DDS
OUT
DATA
SELECTOR
SUBCARRIER
PHASE-LOCKED
LOOP
SYNC
SEPARATOR
HORIZONTAL
PHASE-LOCKED
LOOP
BYP
C
PFD IN
PXCK SEL
65-22071-01
EXT PXCK
CVBS
7-0
GVSYNC
GHSYNC
PXCK
LDV
VALID
Rev. 1.0.5

TMC22071A PRODUCT SPECIFICATION
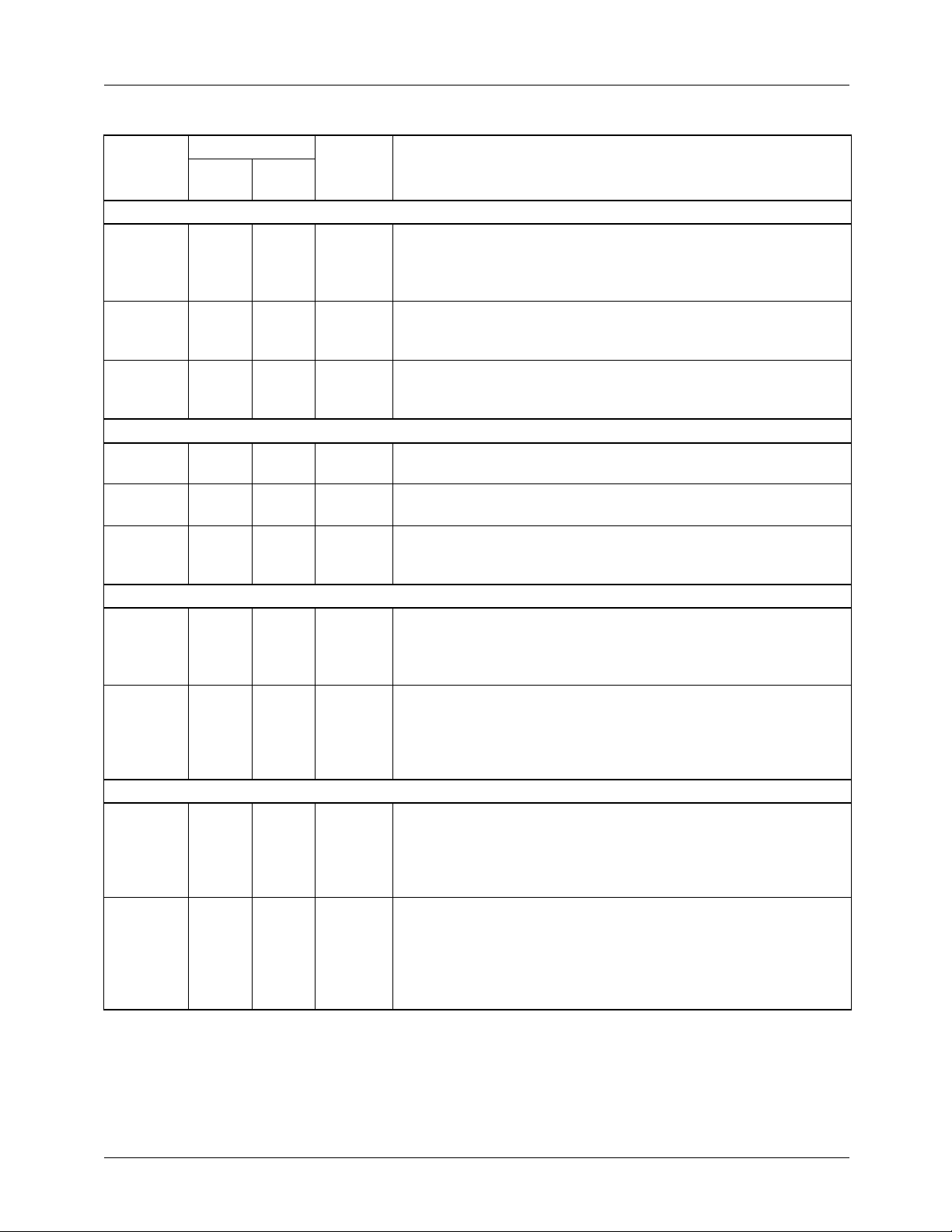
Functional Description
The TMC22071A is a fully-integrated genlocking video A/D
converter which digitizes NTSC or PAL baseband composite
video under program control. It accepts video on three
selectable input channels, adjusts gain, clamps to the back
porch, and digitizes the video at a multiple of the horizontal
line frequency. It extracts horizontal and vertical sync, measures the subcarrier frequency and phase (relative to the sampling clock), and provides the data along with digital
composite video data over an 8-bit digital video port. Two
sync outputs (GHSYNC
generates 1x (LDV) and 2x (PXCK) pixel clocks for data
transfer. PXCK also serves as a master clock for the companion TMC22x9x Encoders and TMC22x5y decoders.
Operating parameters are set up via a serial microprocessor
port. Internal or external voltage reference operation is available
Timing
The TMC22071A operates from an internally-synthesized
clock, PXCK, which runs at twice the pixel data rate. The
nominal pixel rates may be set to 12.27 Mpps for NTSC and
13.5 Mpps for NTSC and P AL. Customers requiring 14.75 or
15 Mpps PAL operation should consult factory.
Video Input
Three high-impedance video inputs are selected by an internal multiplexer under host processor control. The device
accepts industry-standard video levels of 1.23 Volts (sync tip
to peak color = 1 volt sync tip to reference white). Good
channel-to-channel isolation allows active video on all three
inputs simultaneously. Antialiasing filtering (if used) and
line termination resistors must be provided externally. The
input selection is controlled by two bits in the Control Register.
Analog Clamp
The front-end analog clamp ensures that the input video falls
within the active range of the A/D converter. The digitized
composite video output can be clamped to the back porch by
a secondary digital clamp.
Automatic Gain Adjustment
Since video signals may vary substantially from nominal levels, the TMC22071A performs an automatic level setting
routine to establish correct signal amplitudes for digitizing.
The TMC22071A relies upon the presence of the sync
tip-to-back porch voltage to determine the gain required for
the input video signal.
Sync tip compression or clipping is often affected by APL
(Average Picture Level) variation. Rather than tracking
minor variations in sync tip amplitude and constantly adjusting video gain, the TMC22071A establishes proper signal
and GVSYNC) are also provided. It
amplitudes during initial genlock acquisition, and then
(optionally) holds the gain constant. This results in a stable
picture under variable signal conditions.
Improperly terminated or weak video signals are handled in
the TMC22071A by a selectable gain of +1.0 or +1.5. The
higher gain can amplify a doubly-terminated signal which is
reduced in amplitude by 2/3.
If the input signal levels are well controlled, the automatic
gain adjustment can be disabled and the gain held at its nominal value (unity or 1.5X).
Analog-to-Digital Converter
The TMC22071A contains a high-performance 8-bit A/D
converter. Its gain and offset are automatically set as a part of
the automatic gain adjustment process during initial signal
acquisition, and require no user attention.
The reference voltages to the A/D converter are set up by
internal D/A converters under automatic control during genlock acquisition. These voltages determine the gain and offset of the A/D converter with respect to the video level
presented at its input.
Low-Pass Filter
The digitized composite video stream is digitally low-pass
filtered to remove chrominance components from the sync
separator. Filtering provides robust operation by optimizing
the signal-to-noise ratio of the synchronizing/blanking portion of the video, improving the accuracy of the back porch
blanking level detector.
A digital sync separator provides the output sync signals,
GHSYNC and GVSYNC, and times internal operations.
Horizontal Phase-Locked Loop
A phase-locked loop generates PXCK, at twice the pixel
rate. The reference signal for the horizontal phase-locked
loop is generated by the Direct Digital Synthesizer (DDS).
The DDS output is constructed with an internal D/A converter and is output from the TMC22071A via the DDS OUT
pin. This signal is passed through an external LC filter and
input to the horizontal phase-comparator.
The frequency of the DDS output is one ninth of that of
PXCK.
A 20 MHz clock is required to drive the DDS. Preferably,
this may be input to the TMC22071A via CMOS levels on
the CLK IN pin. Alternately, a 20 MHz crystal may be
directly connected between CLK IN and CLK OUT with
tuning capacitors to activate the internal crystal oscillator circuitry.
If incoming video is lost or disconnected after the
TMC22071A has acquired and locked, PXCK, GHSYNC,
2
PRODUCT SPECIFICATION TMC22071A
GVSYNC and GRS data will continue. The GRS data will
be the initial subcarrier frequency and phase values selected
by the Format select bits of the Control Register. The
TMC22071A will acquire and lock to incoming video within
two frames after video is restored.
Subcarrier Phase-Locked Loop
A fully-digital phase-locked loop is used to extract the phase
and frequency of the incoming color burst. These frequency
and phase values are output over the CVBS bus during the
horizontal sync period. Fairchild’s video decoder and genlockable encoder chips will accept these data directly.
Back Porch Digital Clamp
A digital back-porch clamp is employed to ensure a constant
blanking level. It digitally offsets the data from the A/D converter to set the back porch level to precisely 3Ch for NTSC
and 40h for PAL. When the digital clamp is enabled, the
CVBS video output data is determined from the A/D conversion result minus the back porch level + 3Ch (40h for PAL).
Digitized Video Output
The digitized 8-bit video output is provided over an 8-bit
wide CVBS data port, synchronous with PXCK and LDV.
Subcarrier frequency, subcarrier phase, and Field ID data
(GRS) are transmitted in 4-bit nibbles over CVBS
3-0
during
the horizontal sync tip period at the PXCK rate.
Microprocessor Interface
Since microprocessor buses are notoriously noisy from a
wide-band analog point of view, the microprocessor interface bus is only one bit wide, rather than the more customary
eight. The operation of this bus is similar to other buscontrolled devices except that the TMC22071A internal
Control Register is accessed one bit at a time.
A sequence of 47 bits is written to or read from the LSB of a
standard microprocessor port. Writing to or reading from the
secondary address results in the transfer of data to or from
the internal shift register.
The RESET
machines to their initialized conditions. Returning the
RESET pin HIGH starts the signal acquisition sequence
which lasts until locking with the gain-adjusted and clamped
video signal is achieved.
input, when LOW, sets all internal state
Pin Assignments
1
68
65-22071-02
Pin Name Pin Name
V
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
DD
CVBS
0
CVBS
1
CVBS
2
CVBS
3
CVBS
4
V
DD
D
GND
CVBS
5
CVBS
6
CVBS
7
GHSYNC
GVSYNC
VALID
D
GND
D
GND
LDV
V
18
DD
PXCK
19
D
20
GND
D
21
GND
V
22
DD
V
23
DDA
A
24
GND
V
25
DDA
V
26
DDA
A
27
GND
R
28
B
V
29
IN3
V
30
DDA
V
31
IN2
A
32
GND
V
33
DDA
V
34
IN1
Pin Name Pin Name
A
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
GND
R
T
A
GND
V
REF
A
GND
V
DDA
A
GND
C
BYP
PFD IN
A
GND
DDS OUT
PXCK SEL
V
DDA
COMP
A
GND
D
GND
CLK IN
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
V
DD
CLK OUT
EXT PXCK
D
GND
D
GND
D
GND
V
DD
V
DD
A
0
R/W
CS
V
DD
RESET
D
GND
D
0
INT
D
GND
3
TMC22071A PRODUCT SPECIFICATION
Pin Assignments (continued)
5180
81
100
130
Notes:
1. NC = Do Not Connect.
* These pins are not connected in the
TMC22071A. However, you should
connect these pins as shown for
compatibility with future genlock ICs.
Pin Name Pin Name
A
1
0
NC
2
50
31
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16*
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
NC
R/W
CS
V
DD
RESET
D
GND
D
0
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
D
GND
INT
V
DD
NC
NC
CVBS
CVBS
CVBS
CVBS
CVBS
Pin Name Pin Name
V
26
DD
D
27
GND
CVBS
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41*
42*
43
44
45
46
0
47
1
48
2
49
3
50
4
5
CVBS
6
CVBS
7
NC
GHSYNC
GVSYNC
VALID
NC
NC
NC
D
GND
D
GND
LDV
D
GND
V
DD
NC
V
DD
PXCK
D
GND
D
GND
V
DD
V
DDA
A
GND
V
51
DDA
V
52
DDA
NC
53
NC
54
A
55
GND
NC
56
R
57
B
V
58
IN3
NC
59
V
60
DDA
V
61
IN2
NC
62
A
63
GND
V
64
DDA
V
65
IN1
NC
66
A
67
GND
R
68
T
A
69
GND
V
70
REF
NC
71
A
72
GND
V
73
DDA
A
74
GND
C
75
BYP
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
NC
PFD IN
NC
NC
NC
A
GND
DDS OUT
NC
NC
NC
PXCK SEL
V
DDA
COMP
A
GND
D
GND
CLK IN
V
DD
CLK OUT
EXT PXCK
D
GND
D
GND
D
GND
V
DD
NC
V
DD
65-22071-02B
Pin Definitions
Pin Number
68 pin
Pin Name
PLCC
Video Input
V
IN1-3
34, 31, 2965, 61, 581.23Vp-p Composite Video Input. Video inputs,1.25 Volts peak-to-peak, sync
Clocks
CLK IN 51 91 CMOS 20 MHz DDS clock input. 20 MHz CMOS clock input to DDS. This
OUT 53 93 CMOS Inverted clock output. Inverted DDS clock output. This pin may also
CLK
PXCK 19 45 CMOS 2x Pixel clock output. 2x oversampled line-locked clock output.
LDV 17 40 CMOS Pixel clock output. Delayed pixel clock output. LDV runs at 1/2 the
EXT PXCK 54 94 CMOS External PXCK input. Input for external PXCK clock source.
PXCK SEL 46 86 CMOS PXCK source select. Select input for internal or external PXCK.
100 pin
MQFP
Pin Type Function
tip to peak color
pin may also be used along with CLK OUT for directly connecting
crystals.
be used along with CLK IN for directly connecting a crystal.
rate of PXCK and its rising edge is useful for transferring CVBS
digital video from the TMC22071A to the TMC22x9x Digital Video
Encoders.
When HIGH, the internally generated line-locked PXCK is selected.
When LOW, the external PXCK source is enabled.
4
TMC22071A PRODUCT SPECIFICATION
Pin Definitions (continued)
Pin Number
68 pin
Pin Name
PLCC
Digital Video
GHSYNC 12 32 CMOS Horizontal sync output. When the TMC22071A is locked to
GVSYNC
CVBS
11-9, 6-230-28,
7-0
mP l/O
D
0
A
0
CS 62 5 TTL Chip select. When CS is HIGH, D0 is in a high-impedance state and
RESET 64 7 TTL Master reset input. Bringing RESET LOW forces the internal state
R/W 61 4 TTL Bus read/write control. When R/W and A0 are LOW, the
INT 67 17 TTL Interrupt output. This output is LOW if the internal horizontal phase
VALID 14 34 TTL HSYNC locked flag. This output, when HIGH indicates that
100 pin
MQFP
Pin Type Function
incoming video, the GHSYNC pin provides a negative-going pulse
after the falling edge of the horizontal sync pulse. There is a fixed
number of PXCK clock cycles between adjacent falling edges of
GHSYNC, except following a VCR headswitch.
13 33 CMOS Vertical sync output. When the TMC22071A is locked to incoming
video, the GVSYNC pin provides a negative-going edge after the
start of the first vertical sync pulse of a vertical blanking interval.
CMOS Composite output bus. 8-bit composite video data is output on this
25-21
bus at 1/2 the PXCK rate. During horizontal sync, field ID, subcarrier
frequency, and subcarrier phase are available on this bus.
66 9 TTL Data l/O port. Microprocessor data port. All control parameters are
loaded into and read back from the Control Register over this 1-bit
bus.
60 1 TTL mP port control. Microprocessor address bus. A LOW on this input
loads the l/O Port Shift Register with data from D0 and CS. A HIGH
transfers the l/O Port Shift Register contents into the Control Register
on the last falling edge of CS.
ignored. When CS is LOW, the microprocessor can read or write D0
data into the Control Register.
machines to their starting states, loads the Control Register with
default values, and disables outputs. Bringing RESET HIGH restarts
the TMC22071A in its default mode.
microprocessor can write to the Control Register over D0. When R/W
is HIGH and A0 is LOW, the contents of the Status Register are read
over D0.
lock loop is unlocked with respect to incoming video for 128 or more
lines per field. After lock is established, INT goes HIGH.
incoming horizontal sync has been detected within the ±16 pixel
window in time established by previous sync pulses. When LOW, it
indicates that incoming horizontal sync has not been found within the
expected time frame. VALID will toggle if the time stability of
incoming video is such that sync positioning varies more than
±16 pixels or if occasional horizontal sync pulses are missing.
5
PRODUCT SPECIFICATION TMC22071A
Pin Definitions (continued)
Pin Number
68 pin
Pin Name
Analog Interface
V
REF
COMP 48 88 0.1 mF Compensation capacitor. Compensation for DDS D/A converter
RT,R
B
PLL Filter
DDS OUT 45 82 Internal DDS output. Analog output from the internal Direct Digital
PFD IN 43 77 Horizontal PLL input. Analog input to the Phase/Frequency
C
BYP
Power Supply
V
DDA
V
DD
Ground
A
GND
D
GND
PLCC
36, 28 68 0.1 mF A/D V
23, 25,
26, 30,
33, 40,
1, 7,18,
22, 52,
58,59,63
24, 27,
32, 35,
37, 39,
41, 44,
49,
8, 15,
16, 20,
21, 50,
55-57,
65, 68
100 pin
MQFP
38 70 +1.23 V V
42 75 1 mF Comparator bypass. Decoupling point for the internal comparator
49, 51,
52, 60,
64, 73,
47
87
6, 18,
26, 42,
44, 48,
92, 98,
100
50, 55,
63, 67,
69, 72,
74, 81,
89
8, 16,
27, 38,
39, 41,
46, 47,
90, 95-
97
Pin Type Function
input/output. +1.23 Volt reference. When the internal voltage
REF
reference is used, this pin should be decoupled to A
mF capacitor. An external +1.2 Volt reference may be connected
here, overriding the internal reference source.
circuitry. This pin should be decoupled to V
capacitor.
decoupling. Decoupling points for A/D converter voltage
REF
references. These pins should be decoupled to A
capacitor.
Synthesizer D/A converter, at 1/9 the PXCK frequency.
Detector of the horizontal phase-locked loop.
reference of the Phase/Frequency Detector. This pin should be
decoupled to A
+5 V Analog power supply. Positive power supply to analog section.
+5 V Digital power supply. Positive power supply to digital section.
0.0 V Analog ground. Ground for analog section.
0.0 V Digital ground. Ground for digital section.
with a 0.1 mF capacitor.
GND
with a 0.1 mF
DDA
GND
with a 0.1
GND
with a 0.1 mF
6
PRODUCT SPECIFICATION TMC22071A
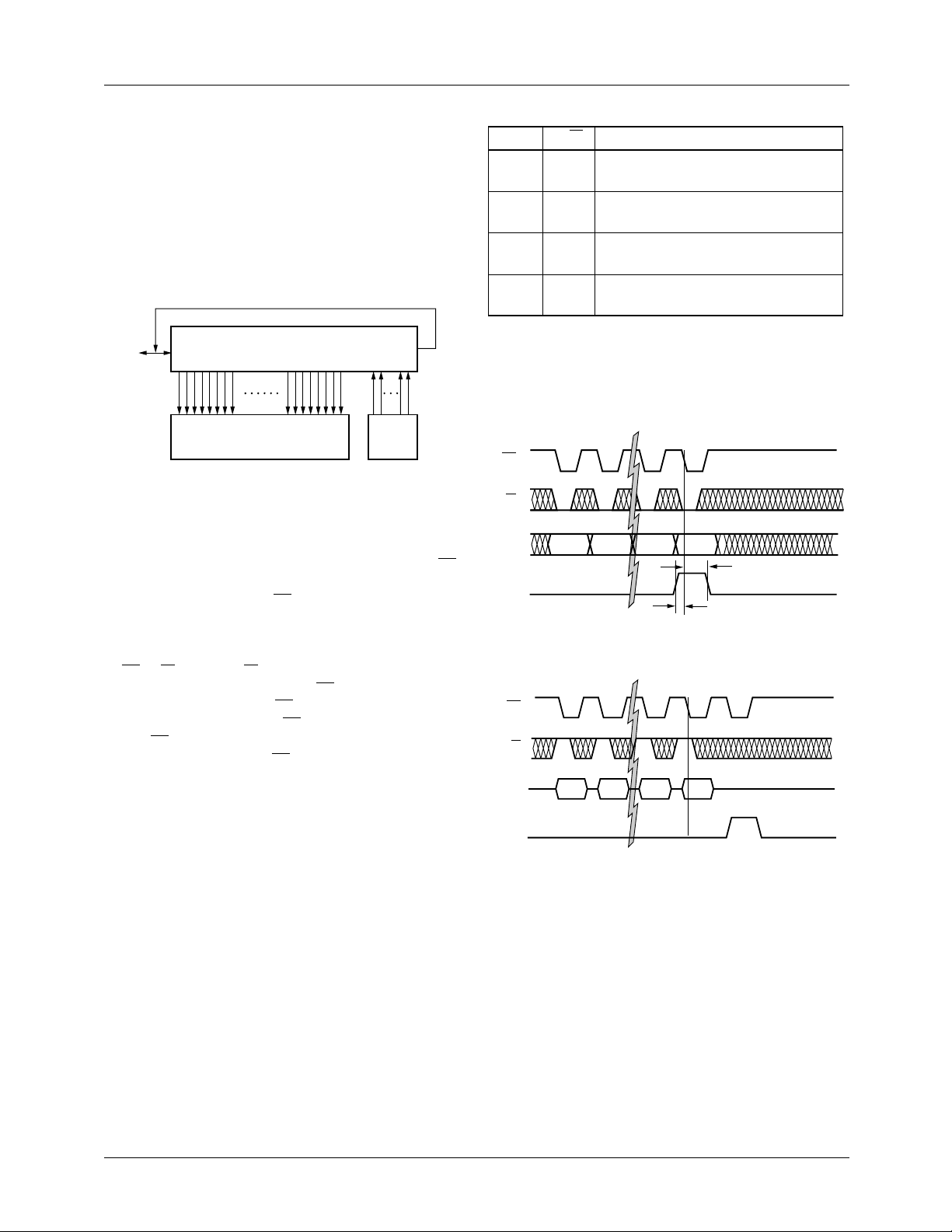
Control and Status Registers
The TMC22071A is controlled by a single 47-bit long Control Register. Access to the Control Register is via the I/O
Port Shift Register arranged as shown in Figure 1. The Control Register can be written, with the desired programming.
The 12-bit Status Register is read-only and accessed through
the same l/O Port Shift Register. Reading the Status Re gister
yields information about blanking level, subcarrier presence,
and whether or not PXCK is locked or unlocked with respect
to the line rate.
D
0
0464758
Figure 1. Control and Shift Register Structure
The host processor writes data into the TMC22071A using
only one bit of the microprocessor’s data and address b us. As
shown in Figure 2, the user should bring A0 high for the CS
falling edge preceding the introduction of bit 0 to the D0
port. The next rising edge of CS completes the preloading of
the control data, which transfer into the control register on
the next rising edge of the pixel clock. The I/O Port Shift
Register, Control Register and Status Register are governed
by CS, R/W, and A0. R/W and A0 are latched by the
TMC22071A on the falling edge of CS and data input D0 is
latched on the rising edge of CS. Data read from D0 is
enabled by the falling edge of CS and disabled by the rising
edge of CS
. When the Control Register is read more than
once consecutively, an extra CS pulse and accompanying A0
is needed to align the circulated shift register data.
I/O Port Shift Register
Control Register
Status
Register
65-22071-03
Table 1. Microprocessor Port Control
A
The full sequence of 47 bits of Control Register data must be
written each time a change in that data is desired. All or a
few of the Control and Status Register bits may be read,
but the sequence always begins with bit 58 of the Status
Register.
CS
R/W
D
A
CS
R/W
R/W Action
0
0 0 Write data from D0 into l/O Port Shift
Register
0 1 Read D0 data from last stage of l/O
Port Shift Register
1 0 Transfer l/O Port Shift Register
contents to Control Register
1 1 Enables continuous update of status
bits in l/O Port Shift Register
0
0
D
46 45 1 0
Figure 2. Data Write Sequence
0
58 57 1 0
t
H
t
S
65-22071-04
A
0
65-22071A-05
Figure 3. Data Read Sequence
7
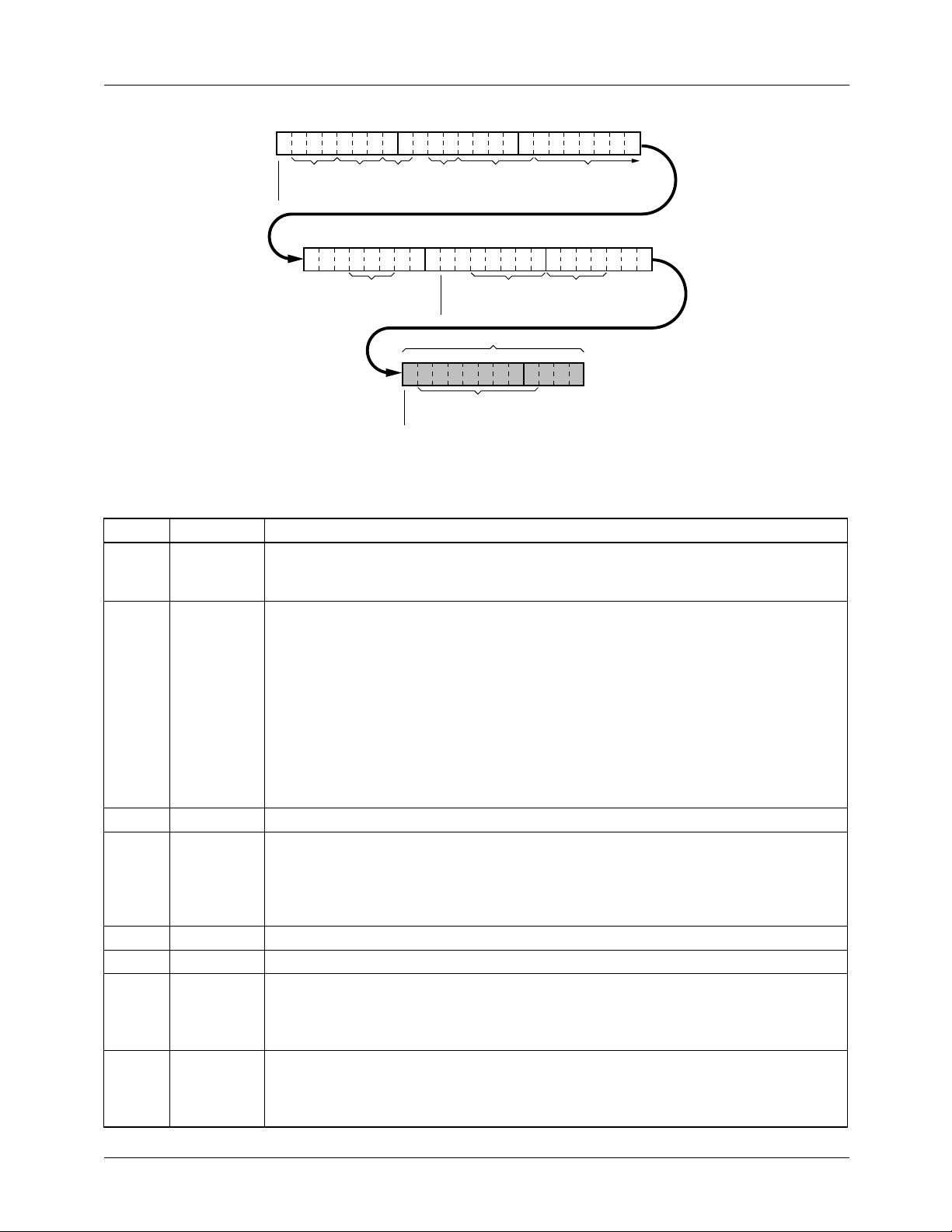
TMC22071A PRODUCT SPECIFICATION
0
SRESET
FORMAT
24 31 32 39 40 46
AGC
LEADLAG
7 8 15 16 23
00
000
VGAIN
TEST
000 00000 001
TEST
FREERUN
TEST
SOURCE
TEST
VCR/TV
BPFOUT
CVBSEN
STATUS REGISTER
47 54
(LSB)
COLOR
SUBPIX
DCLAMP
BLKAMP
TEST
55 58
(MSB)
(LSB)
LOCK
STVAL
TEST
TEST
LEADLAG
TEST
65-22071-06
TEST
GRSONLY
Figure 4. Control Register Map
Control Register Bit Functions
Bit Name Function
0 SRESET Software reset. When LOW, resets and holds internal state machines, resets Control
Register with previously written values, and disables output drivers. When HIGH,
SRESET starts and runs state machines, PXCK, and enables outputs.
1-3 FORMAT Input signal format select.
Bit 3 is the MSB.
000 NTSC at 12.27 Mpps.
001 NTSC at 13.5 Mpps.
010 Reserved.
011 Reserved.
100 PAL at 13.5 Mpps.
101 Reserved.
11x Reserved.
4-6 TEST Factory test control bits. These should be set LOW.
7,8 SOURCE Video source select. Bit 8 is the MSB.
00 V
IN1
01 V
IN2
1x V
IN3
9 VGAIN Video gain. When LOW, gain is set to unity. When HIGH, gain is set to 1.5X.
10-11 TEST Factory test control bits. These should be set LOW.
12-16 SUBPIX These control bits allows the HSYNC, VSYNC, and sample clock to be time-shifted by
-16/32 to +15/32 pixels. Bit 16 is the two’s complement MSB. When SUBPIX is 00h,
HSYNC and incoming video are subject to LEADLAG. A value of 18h delays HSYNC
1/4 pixel. A value of 08
17-24 LEADLAG This control word allows the HSYNC and VSYNC to be time-shifted -122 to +132 LDV
cycles. When LEADLAG is 7B
83h delays HSYNC eight LDV cycles. A value of 73h advances HSYNC eight LDV
cycles. Bit 24 is the MSB.
advances HSYNC 1/4 pixel.
h
, HSYNC and incoming video are in alignment. A value of
h
8
 Loading...
Loading...