Fairchild FAN5236 service manual

November 2010
FAN5236
Dual Mobile-Friendly DDR / Dual-Output PWM Controller
FAN5236 — Dual Mobile-Friendly DDR / Dual-Output PWM Controller
Features
Highly Flexible, Dual Synchronous Switching PWM
Controller that Includes Modes for:
- DDR Mode with In-phase Operation for
Reduced Channel Interference
- 90° Phase-shifted, Two-stage DDR Mode for
Reduced Input Ripple
- Dual Independent Regulators, 180° Phase
Shifted
Complete DDR Memory Power Solution
- V
- V
Tracks V
TT
Buffered Reference Output
DDQ/2
DDQ/2
Lossless Current Sensing on Low-side MOSFET or
Precision Over-Current Using Sense Resistor
V
Under-Voltage Lockout
CC
Converters can Operate from +5V or 3.3V or
Battery Power Input (5V to 24V)
Excellent Dynamic Response with Voltage
Feedforward and Average-Current-Mode Control
Power-Good Signal
Supports DDR-II and HSTL
Light-Load Hysteretic Mode Maximizes Efficiency
TSSOP28 Package
Applications
DDR V
and VTT Voltage Generation
DDQ
Mobile PC Dual Regulator
Server DDR Power
Hand-held PC Power
Description
The FAN5236 PWM controller provides high efficiency
and regulation for two output voltages adjustable in the
range of 0.9V to 5.5V required to power I/O, chip-sets,
and memory banks in high-performance notebook
computers, PDAs, and Internet appliances.
Synchronous rectification and hysteretic operation at
light loads contribute to high efficiency over a wide
range of loads. The Hysteretic Mode can be disabled
separately on each PWM converter if PWM Mode is
desired for all load levels. Efficiency is enhanced by
using MOSFET R
Feedforward ramp modulation, average-current-mode
control scheme, and internal feedback compensation
provide fast response to load transients. Out-of-phase
operation with 180-degree phase shift reduces input
current ripple. The controller can be transformed into a
complete DDR memory power supply solution by
activating a designated pin. In DDR mode, one of the
channels tracks the output voltage of another channel
and provides output current sink and source capability
— essential for proper powering of DDR chips. The
buffered reference voltage required by this type of
memory is also provided. The FAN5236 monitors these
outputs and generates separate PGx (power good)
signals when the soft-start is completed and the output
is within ±10% of the set point. Built-in over-voltage
protection prevents the output voltage from going above
120% of the set point. Normal operation is automatically
restored when the over-voltage conditions cease.
Under-voltage protection latches the chip off when
output drops below 75% of the set value after the softstart sequence for this output is completed. An
adjustable over-current function monitors the output
current by sensing the voltage drop across the lower
MOSFET. If precision current-sensing is required, an
external current-sense resistor may be used.
as a current-sense component.
DS(ON)
Related Resources
Application Note — AN-6002 Component
Calculations and Simulation Tools for FAN5234 or
FAN5236
Application Note — AN-1029 Maximum Power
Enhancement Techniques for SO-8 Power
MOSFET
© 2002 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation www.fairchildsemi.com
FAN5236 • Rev. 1.3.2
Ordering Information
Operating
Part Number
Temperature
Package Packing Method
Range
FAN5236MTCX -10 to +85°C 28-Lead Thin-Shrink Small-Outline Package (TSSOP) Tape and Reel
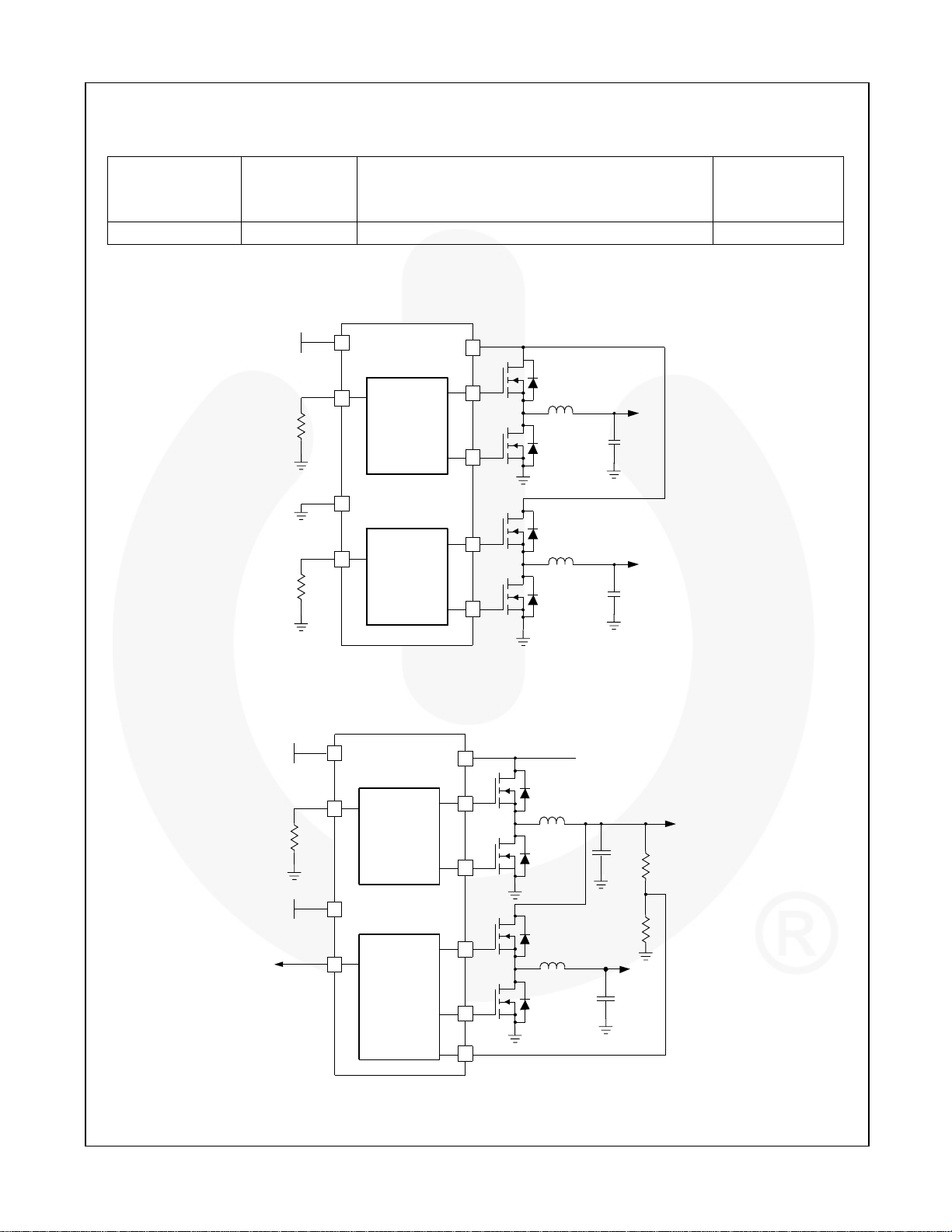
Block Diagrams
VCC
+5
ILIM1
FAN5236
PWM 1
DDR
ILIM2/
REF2
PWM 2
VIN(BATTERY)
= 5 to 24V
Q1
V
L
OUT1
Q2
Q3
V
L
OUT2
Q4
OUT1
=2.5V
OUT 2
=1.8V
C
OUT1
C
OUT2
FAN5236 — Dual Mobile-Friendly DDR / Dual-Output PWM Controller
Figure 1. Dual-Output Regulator
(BATTERY)
V
VCC
+5
ILIM1
FAN5236
PWM 1
DDR
+5
PG2/REF
1.25V
PWM 2
IL IM2/REF2
Figure 2. Complete DDR Memory Power Supply
IN
= 5 to 24V
Q1
L
OUT1
Q2
Q3
L
OUT2
Q4
VTT=
V
DDQ /2
V
=2.5V
C
OUT1
C
OUT2
DDQ
R
R
© 2002 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation www.fairchildsemi.com
FAN5236 • Rev. 1.3.2 2

A
/
Pin Configuration
FAN5236 — Dual Mobile-Friendly DDR / Dual-Output PWM Controller
GND
LDRV1
PGND1
SW1
HDRV1
BO
OT1
ISNS1
EN1
FPWM1
VSEN1
IL
IM1
SS1
DDR
VIN
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
FAN5236
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
VCC
LDRV2
PGND2
SW2
HDRV2
BOOT2
ISNS2
EN2
FPWM2
VSEN2
REF2
ILIM2
SS2
PG2/REF2OUT
PG1
Figure 3. Pin Configuration
Pin Definitions
Pin # Name Description
1 AGND
2 LDRV1
27 LDRV2
3 PGND1
26 PGND2
4 SW1
25 SW2
5 HDRV1
24 HDRV2
6 BOOT1
23 BOOT2
7 ISNS1
22 ISNS2
8 EN1
21 EN2
9 FPWM1
20 FPWM2
10 VSEN1
19 VSEN2
11 ILIM1
12 SS1
17 SS2
Analog Ground. This is the signal ground reference for the IC. All voltage levels are
measured with respect to this pin.
Low-Side Drive. The low-side (lower) MOSFET driver output. Connect to gate of low-side
MOSFET.
Power Ground. The return for the low-side MOSFET driver. Connect to source of low-side
MOSFET.
Switching Node. Return for the high-side MOSFET driver and a current sense input.
Connect to source of high-side MOSFET and low-side MOSFET drain.
High-Side Drive. High-side (upper) MOSFET driver output. Connect to gate of high-side
MOSFET.
BOOT. Positive supply for the upper MOSFET driver. Connect as shown in Figure 4.
Current-Sense Input. Monitors the voltage drop across the lower MOSFET or external
sense resistor for current feedback.
Enable. Enables operation when pulled to logic HIGH. Toggling EN resets the regulator
after a latched fault condition. These are CMOS inputs whose state is indeterminate if left
open.
Forced PWM Mode. When logic LOW, inhibits the regulator from entering Hysteretic Mode;
otherwise tie to V
Hysteretic Mode to PWM Mode. When V
. The regulator uses V
OUT
on this pin to ensure a smooth transition from
OUT
is expected to exceed VCC, tie to VCC.
OUT
Output Voltage Sense. The feedback from the outputs. Used for regulation as well as PG,
under-voltage, and over-voltage protection and monitoring.
Current Limit 1. A resistor from this pin to GND sets the current limit.
Soft Start. A capacitor from this pin to GND programs the slew rate of the converter during
initialization. During initialization, this pin is charged with a 5mA current source.
© 2002 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation www.fairchildsemi.com
FAN5236 • Rev. 1.3.2 3
Pin Descriptions (Continued)
Pin # Name Description
13 DDR
14 VIN
15 PG1
16
PG2 /
REF2OUT
18 ILIM2 / REF2
28 VCC
DDR Mode Control. HIGH = DDR Mode. LOW = two separate regulators operating 180° out
of phase.
Input Voltage. Normally connected to battery, providing voltage feedforward to set the
amplitude of the internal oscillator ramp. When using the IC for two-step conversion from 5V
input, connect through 100KΩ resistor to ground, which sets the appropriate ramp gain and
synchronizes the channels 90° out of phase.
Power Good Flag. An open-drain output that pulls LOW when V
range of the 0.9V reference.
Power Good 2. When not in DDR Mode, open-drain output that pulls LOW when the V
out of regulation or in a fault condition.
Reference Out 2. When in DDR Mode, provides a buffered output of REF2. Typically used
as the V
reference.
DDQ/2
Current Limit 2. When not in DDR Mode, a resistor from this pin to GND sets the current
limit.
Reference for reg #2 when in DDR Mode. Typically set to V
VCC. This pin powers the chip as well as the LDRV buffers. The IC starts to operate when
voltage on this pin exceeds 4.6V (UVLO rising) and shuts down when it drops below 4.3V
(UVLO falling).
OUT1 / 2
is outside a ±10%
SEN
.
OUT
FAN5236 — Dual Mobile-Friendly DDR / Dual-Output PWM Controller
is
© 2002 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation www.fairchildsemi.com
FAN5236 • Rev. 1.3.2 4
FAN5236 — Dual Mobile-Friendly DDR / Dual-Output PWM Controller
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Stresses exceeding the absolute maximum ratings may damage the device. The device may not function or be
operable above the recommended operating conditions and stressing the parts to these levels is not recommended.
In addition, extended exposure to stresses above the recommended operating conditions may affect device
reliability. The absolute maximum ratings are stress ratings only.
Symbol Parameter Min. Max. Unit
VCC VCC Supply Voltage 6.5 V
VIN V
BOOT, SW, ISNS, HDRV 33 V
BOOTx to SWx 6.5 V
All Other Pins -0.3 VCC+0.3 V
TJ Junction Temperature -40 +150 ºC
T
Storage Temperature -65 +150 ºC
STG
TL Lead Temperature (Soldering,10 Seconds) +300 ºC
Supply Voltage 27 V
IN
Recommended Operating Conditions
The Recommended Operating Conditions table defines the conditions for actual device operation. Recommended
operating conditions are specified to ensure optimal performance to the datasheet specifications. Fairchild does not
recommend exceeding them or designing to Absolute Maximum Ratings.
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
VCC VCC Supply Voltage 4.75 5.00 5.25 V
VIN V
TA Ambient Temperature -10 +85 °C
ΘJA Thermal Resistance, Junction to Ambient 90 °C/W
Supply Voltage 24 V
IN
© 2002 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation www.fairchildsemi.com
FAN5236 • Rev. 1.3.2 5
Electrical Characteristics
Recommended operating conditions, unless otherwise noted.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Units
Power Supplies
LDRV, HDRV Open, V
I
V
VCC
Current
CC
Regulation Point
Shutdown (EN-0) 30 µA
I
SINK
I
SOURCE
V
Current, Sinking VIN = 24V 10 30 µA
IN
VIN Current, Sourcing VIN = 0V -15 -30 µA
ISD VIN Current, Shutdown 1 µA
V
UVLO Threshold
UVLO
V
UVLO Hysteresis 300 mV
UVLOH
Rising V
Falling 4.10 4.25 4.45 V
4.30 4.55 4.75 V
CC
Oscillator
f
Frequency 255 300 345 KHz
osc
= 16V 2 V
V
VPP Ramp Amplitude
V
Ramp Offset 0.5 V
RAMP
G Ramp / VIN Gain
IN
VIN = 5V 1.25 V
≤ 3V
V
IN
1V < VIN < 3V 250 mV/V
Reference and Soft Start
V
Internal Reference Voltage 0.891 0.900 0.909 V
REF
ISS Soft-Start Current At Startup 5 µA
VSS
Soft-Start Complete
Threshold
1.5 V
PWM Converters
Load Regulators I
I
V
SEN
Bias Current 50 80 120 nA
SEN
from 0 to 5A, VIN from 5 to 24V -2 +2 %
OUTX
VOUT Pin Input Impedance 45 55 65
UVLO
Under-Voltage Shutdown % of Set Point, 2µs Noise Filter 70 75 80 %
TSD
UVLO Over-Voltage Threshold % of Set Point, 2µs Noise Filter 115 120 125 %
I
Over-Current Threshold
SNS
R
= 68.5KΩ, Figure 12
ILIM
Output Drivers
HDRV Output Resistance
LDRV Output Resistance
Sourcing 12.0 15.0
Sinking 2.4 4.0
Sourcing 12.0 15.0
Sinking 1.2 2.0
Forced Above
SEN
2.2 3.0 µA
125 mV/V
KΩ
112 140 168 µA
Ω
Ω
Continued on following page…
FAN5236 — Dual Mobile-Friendly DDR / Dual-Output PWM Controller
© 2002 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation www.fairchildsemi.com
FAN5236 • Rev. 1.3.2 6
 Loading...
Loading...