Page 1

SSP 200
Surround Sound Processor
User Guide
Audio Products
68-3281-01 Rev. A
02 21
Page 2

Safety Instructions
Page 3

Copyright
© 2021 Extron. All rights reserved.
Trademarks
All trademarks mentioned in this guide are the properties of their respective owners.
The following registered trademarks(
®
), registered service marks(
current list of trademarks on the Terms of Use page at www.extron.com):
Extron, Cable Cubby, ControlScript, CrossPoint, DTP, eBUS, EDID Manager, EDID Minder, Flat Field, FlexOS, Glitch Free, Global Configurator,
GlobalScripter, GlobalViewer, Hideaway, HyperLane, IPIntercom, IPLink, KeyMinder, LinkLicense, LockIt, MediaLink, MediaPort, NAV,
NetPA, PlenumVault, PoleVault, PowerCage, PURE3, Quantum, Show Me, SoundField, SpeedMount, SpeedSwitch, StudioStation,
SystemINTEGRATOR, TeamWork, TouchLink, V‑Lock, VideoLounge, VN‑Matrix, VoiceLift, WallVault, WindoWall, XPA, XTP, XTPSystems, and
ZipClip
Registered Service Mark
(SM)
: S3 Service Support Solutions
AAP, AFL (Accu‑RATEFrameLock), ADSP(Advanced Digital Sync Processing), CableCover, CDRS(ClassD Ripple Suppression),
Codec Connect, DDSP(Digital Display Sync Processing), DMI (DynamicMotionInterpolation), DriverConfigurator, DSPConfigurator,
DSVP(Digital Sync Validation Processing), eLink, EQIP, Everlast, FastBite, Flex55, FOX, FOXBOX, IP Intercom HelpDesk, MAAP, MicroDigital,
Opti‑Torque, PendantConnect, ProDSP, QS‑FPC(QuickSwitch Front Panel Controller), RoomAgent, Scope‑Trigger, ShareLink, SIS,
SimpleInstructionSet, Skew‑Free, SpeedNav, Triple‑Action Switching, True4K, Vector™ 4K , WebShare, XTRA, and ZipCaddy
SM
), and trademarks(TM) are the property of RGBSystems, Inc. or Extron (see the
Registered Trademarks (
Trademarks (™
)
®
)
Page 4
FCC Class A Notice
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital
device, pursuant to part15 of the FCC rules. The ClassA limits provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial
environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and,
if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is
likely to cause interference. This interference must be corrected at the expense of the user.
ATTENTION:
NOTES:
• The Twisted Pair Extension technology works with unshielded twisted pair (UTP)
or shielded twisted pair (STP) cables; but to ensure FCC Class A and CE
compliance, STP cables and STP Connectors are required.
• La technologie extension paires torsadées fonctionne avec les câbles paires
torsadées blindées(UTP) ou non blindées(STP). Afin de s’assurer de la
compatibilité entre FCC ClasseA et CE, les câbles STP et les connecteurs STP
sont nécessaires.
• This unit was tested with shielded I/O cables on the peripheral devices. Shielded
cables must be used to ensure compliance with FCC emissions limits.
• For more information on safety guidelines, regulatory compliances, EMI/EMF
compatibility, accessibility, and related topics, see the Extron Safety and
Regulatory Compliance Guide on the Extron website.
Battery Notice
This product contains a battery. Do not open the unit to replace the battery. If the
battery needs replacing, return the entire unit to Extron (for the correct address, see the
Extron Warranty section on the last page of this guide).
CAUTION: Risk of explosion. Do not replace the battery with an incorrect type. Dispose
of used batteries according to the instructions.
ATTENTION : Risque d’explosion. Ne pas remplacer la pile par le mauvais type de pile.
Débarrassez-vous des piles usagées selon le mode d’emploi.
Page 5
Conventions Used in this Guide
Notifications
The following notifications are used in this guide:
WARNING: Potential risk of severe injury or death.
AVERTISSEMENT : Risque potentiel de blessure grave ou de mort.
CAUTION: Risk of minor personal injury.
ATTENTION : Risque de blessuremineure.
ATTENTION:
• Risk of property damage.
• Risque de dommages matériels.
NOTE: A note draws attention to important information.
TIP: A tip provides a suggestion to make working with the application easier.
Software Commands
Commands are written in the fonts shown here:
^AR Merge Scene,,Op1 scene 1,1 ^B 51 ^W^C
[01] R 0004 00300 00400 00800 00600 [02] 35 [17] [03]
E X! *X1&* X2)* X2#* X2! CE}
Computer responses and directory paths that do not have variables are written in the font
shown here:
Variables are written in slanted form as shown here:
Selectable items, such as menu names, menu options, buttons, tabs, and field names are
written in the font shown here:
Specifications Availability
Product specifications are available on the Extron website, www.extron.com.
Extron Glossary of Terms
A glossary of terms is available at http://www.extron.com/technology/glossary.aspx.
NOTE: For commands and examples of computer or device responses mentioned
in this guide, the character “0” is used for the number zero and “O” is the capital
letter “o.”
Reply from 208.132.180.48: bytes=32 times=2ms TTL=32
C:\Program Files\Extron
ping xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx —t
SOH R Data STX Command ETB ETX
From the File menu, select New.
Click the OK button.
Page 6

Page 7
Contents
Introduction ...............................................1
About the SSP 200.............................................. 1
SSP 200 Features ............................................... 2
Application Diagrams ........................................... 3
Mounting ............................................................. 5
Tabletop Placement ......................................... 5
Rack Mounting ................................................ 5
Under-desk Mounting ...................................... 5
Panel Features ...........................................6
Rear Panel Features ............................................ 6
Securing an HDMI Connector ............................ 10
Front Panel Features .......................................... 11
Source Format ............................................... 11
Input Selection ............................................... 12
Volume Adjustment ........................................ 13
Analog Input Gain Level ................................. 13
System Reset ................................................ 14
Front Panel Security Lockout
(Executive Mode) .......................................... 15
Connecting to the USB Port .............................. 16
Speaker Setup ......................................... 18
Speaker Placement ........................................... 18
Back Speakers .................................................. 21
Bass Management ............................................ 21
Speaker Settings ........................................... 21
Speaker Delay Settings...................................... 22
Test Signals ....................................................... 22
Output Channel Trim Settings ............................ 23
Listening Mode Settings .................................... 23
Equalization ....................................................... 23
Reference ................................................24
Source Formats ................................................. 24
Dolby Digital Source Formats ......................... 25
DTS Source Formats (DTS) ............................ 25
PCM Digital Source Format (PCM) ................. 26
2-Channel Source Format (2CH) .................... 26
Sampling Frequency ...................................... 27
Listening Mode Options and Usage ................... 27
Listening Mode Options ................................. 27
Product Configuration Software ..............29
Downloading PCS from the Extron Website ....... 29
Using PCS Software .......................................... 30
Connecting to the SSP 200 ........................... 30
Main Menu .................................................... 31
I/O Panel ....................................................... 32
Input/Output Config ....................................... 32
EDID Minder .................................................. 35
Audio Config .................................................. 41
General Settings ............................................ 50
Device Menu.................................................. 57
Reset Device ................................................. 57
PCS Help File ................................................ 58
Updating Firmware Using PCS .......................... 58
Downloading the SSP 200 Firmware.............. 58
Loading the Firmware to the SSP200 ........... 59
viiSSP 200 • Contents
Page 8

SIS Configuration and Control .................62
Connection Options ........................................... 62
RS-232 Port .................................................. 62
Front Panel Configuration Port ....................... 62
Ethernet (LAN) Port ........................................ 63
Verbose Mode ............................................... 64
Host-to-device Communications ....................... 64
Password Information .................................... 64
Error Responses ............................................ 65
Using the Command and Response Tables ....... 65
Symbol Definitions ............................................. 65
Command and Response Tables ....................... 69
Internal Web Page ...................................80
Overview of the Internal Web Page .................... 80
Accessing the Internal Web Page ...................... 80
Web Page Components .................................... 81
Device Info ..................................................... 81
Device Status ................................................ 82
Network Settings ........................................... 83
Inputs ............................................................ 84
Outputs ......................................................... 84
RS-232 .......................................................... 85
Roles and Permissions .................................. 85
Firmware ....................................................... 86
SSP 200 • Contents viii
Page 9

Introduction
This manual explains how to mount, install, and configure the Extron SSP200 Surround
Sound Processor.
Unless otherwise specified, references in this manual to the SSP200, “SSP”, “surround
sound processor”, or “processor” all refer to the SSP200 device.
About the SSP 200
The SSP 200 is a high-performance digital audio surround sound processor in a half-rack,
1U form-factor. The SSP 200 automatically decodes Dolby® and DTS® formats from digital
sources to discrete audio outputs.
The SSP 200 is compatible with all Extron (and non-Extron) products that accommodate
analog balanced or unbalanced line level inputs. EXP expansion input connectivity allows
the SSP 200 to integrate directly with EXP-enabled Extron products, such as the DMP Plus
series and AXI 016 interface.
The SSP200 can decode and process licensed, branded digital source formats from
DolbyDigital and DTS, in their originally encoded formats. These include:
• Dolby Digital 2/0 • DTS Digital Surround
• Dolby Digital 2/0 Surround • DTS 96/24
• Dolby Digital 5.1 • DTS-ES® Matrix 6.1
• Dolby Digital Surround EX
• Dolby Digital Plus • DTS-ES Discrete 6.1
• Dolby Digital TrueHD • DTS-HD High Resolution Audio
• Dolby Atmos • DTS-HD Master Audio
• DTS 2-channel
™
™
™
™
• DTS 96/24 ES Matrix 6.1
™
™
™
NOTES:
• Dolby, Dolby Atmos, and the double-D symbol are trademarks of Dolby
Laboratories. Manufacturied under license from Dolby Laboratories.
• For DTS patents, see http://patents.dts.com. Manufactured under license from
DTS, Inc. DTS, the Symbol, DTS and the Symbol together, DTS:X, and the DTS:X
logo are registered trademarks or trademarks of DTS, Inc. in the United States
and/or other countries. © DTS, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
SSP 200 • Introduction 1
Page 10

SSP 200 Features
• Supports the latest immersive 3D audio formats as well as legacy surround
formats:
• Dolby Atmos • DTS:X
• Dolby TrueHD • DTS-HD Master Audio
• Dolby Digital Plus • DTS-HD High Resolution Audio
• Dolby Surround • DTS Neural:X
• Dolby Digital EX • DTS-ES
• Dolby Digital • DTS 96/24
• Dolby Pro Logic IIx • DTS NEO:6
• Dolby Pro Logic II
• Automatic surround sound format detection and decoding — Automatically
detects the format of the incoming audio signal, applies the necessary decoding, and
then sends signals to the appropriate outputs.
• Supports video resolutions up to 4K/60 @ 4:4:4 — Supports video signal passed
through unaltered.
• Upmix listening mode converts source program into immersive or standard
surround playback — Converts from any input format to any selected higher output
channel count format.
• Integrated test signals for calibration and connectivity validation during set up.
• Pink noise generator to calibrate a speaker interaction within the environment.
• Dolby Noise: bandpass noise generator to balance speaker levels.
• External option: Can use test disc, or other calibration sources for specific decoding
outputs.
• EXP expansion output port — Provides easy I/O connection to an Extron
DMPPlusSeries audio DSP processor. This allows for a higher output count and
seamless integration with all DMP capabilities including Dante transport.
• Lip Sync Offset — 0 ms to 300 ms per input.
• Supports commonly used speaker output configurations:
• 5.1, 7.1, and 5.1.2 with stereo downmix on outputs 9 and 10.
• 5.1.4, 7.1.2, and 7.1.4 with stereo downmix on the EXP expansion bus.
• EXP expansion bus connection to a DMP Plus Series processor is required for
7.1.4.
• Supported HDMI 2.0b specification features include data rates up to 18 Gbps,
HDR, Deep Color up to 12-bit, 3D, and HD lossless audio formats.
• HDMI Loop Output supports Downmix:
• Local monitor output audio modes.
• Original Audio – Multichannel or two channel.
• Stereo Downmix – Independent of speaker output configuration.
• No Audio.
SSP 200 • Introduction 2
Page 11
• PCM input formats:
• Uncompressed stereo digital audio signals can be processed from the HDMI,
• Uncompressed 7.1 digital audio signals can be processed from the HDMI inputs.
• Front panel input selection with LED indication.
• Supports 802.1X Authentication — Provides support for IEEE 802.1X authentication
standard for port-based Network Access Control.
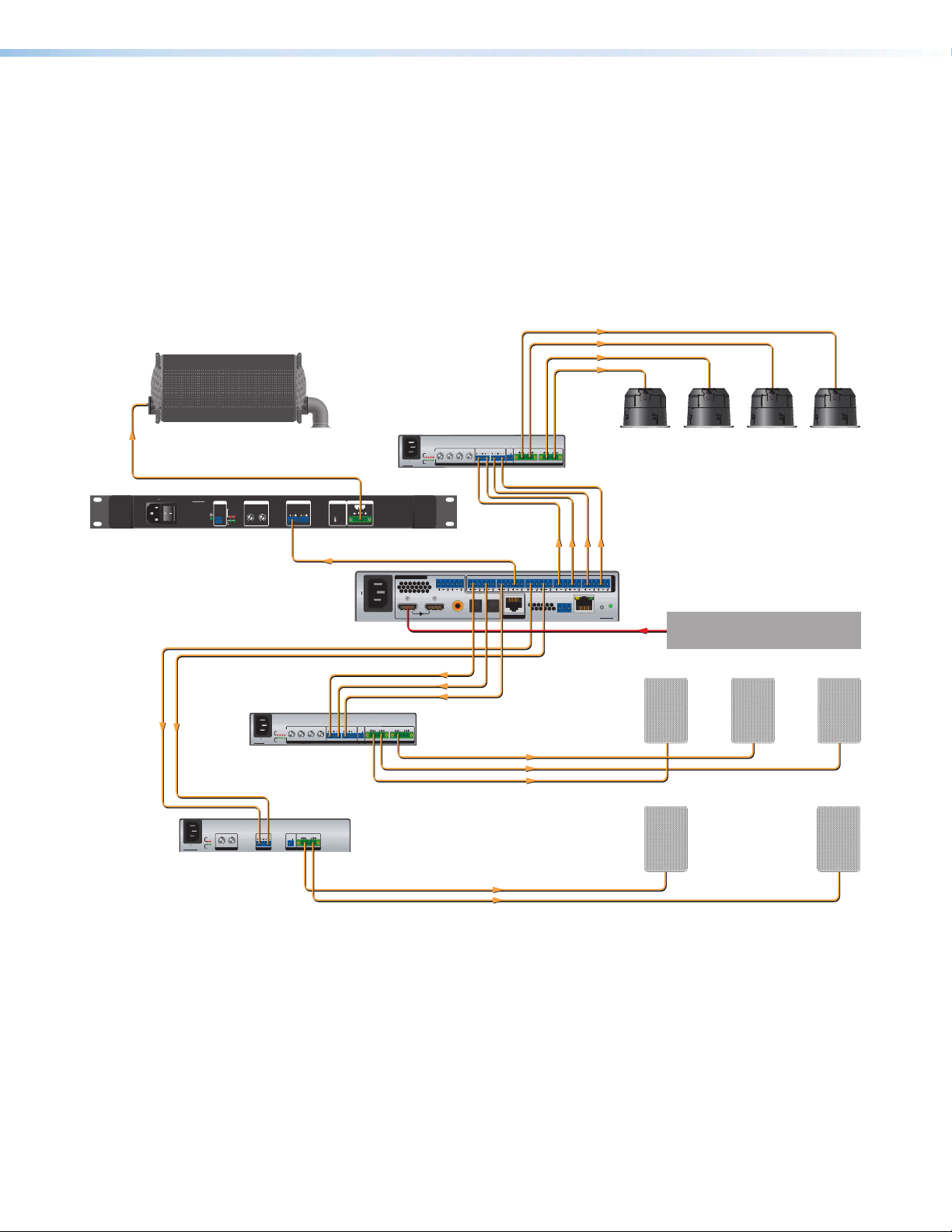
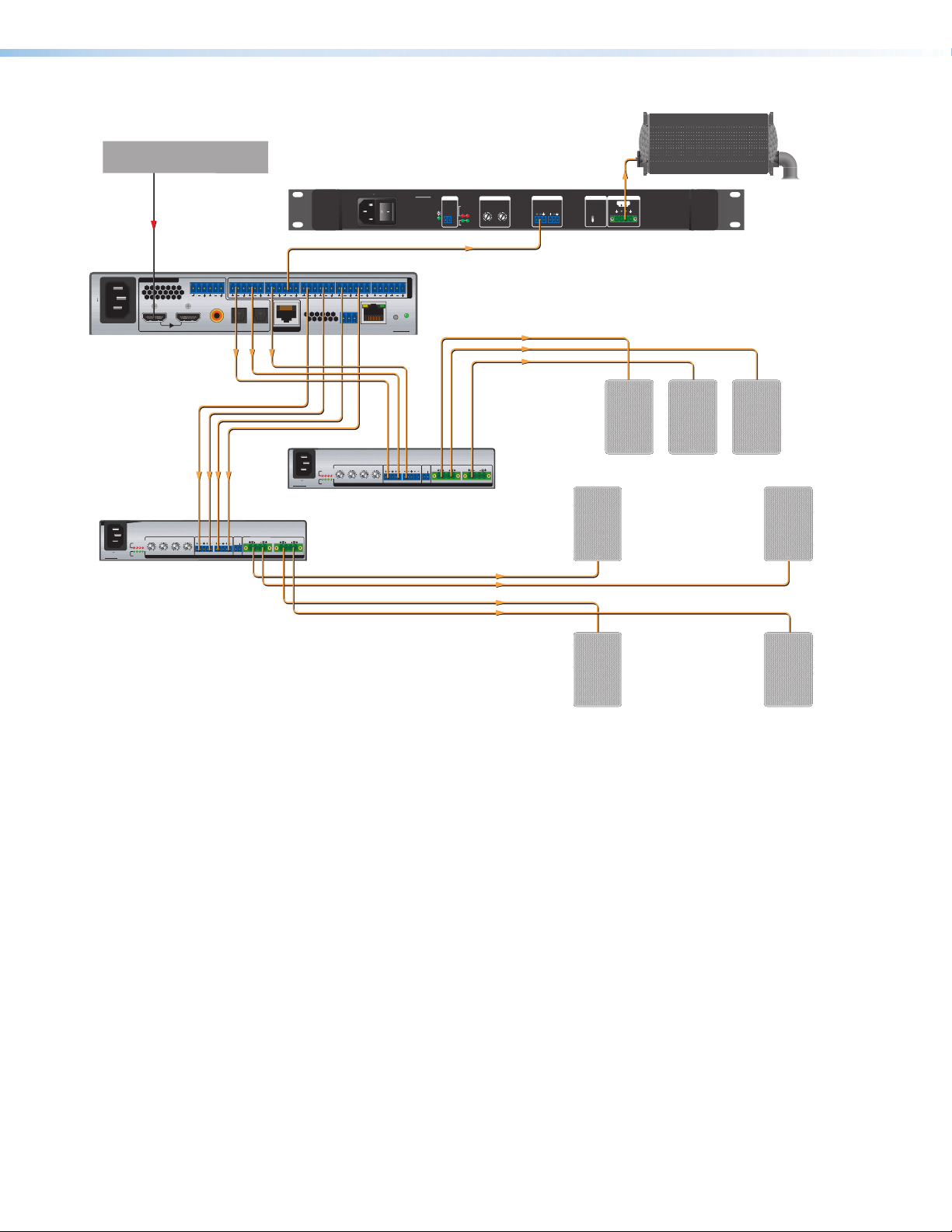
Application Diagrams
Ch. 1 & 2
Bridged
Extron
XPA 4 002
Power Amplier
Extron
SF 10C SUB
Subwoofer
100-240V 1.5A, 50-60 Hz
XPA 4002
GREEN - ACTIVE
AMBER - STANDBY
ATTENUATION
REMOTE
LIMITER/
PROTECT
1G2
14
STANDBY
18
26
SIGNAL
1
2 1 2
(BRIDGE)
10
10
12
12
8
8
6
6
14
18
4
4
2
2
26
0
0
∞
∞
Extron
SSP 20 0
Surround Sound
Processor
INPUTS
TOSLINK, or Coaxial inputs.
Extron
XPA U 1004
Power Amplier
10
10
10
10
12
12
12
12
8
8
8
8
6
6
14
14
18
4
1
1
2
26
0
0
∞
∞
1
2
ATTENUATION 8Ω/4Ω OUTPUTSREMOTEINPUTS
LR1 (LF)
5
123
6
6
14
14
4
4
4
1
1
2
2
2
0
0
∞
∞
3
4
BRIDGE MODE 8Ω / 4Ω OUTPUTS
Audio
LIMITER/
PROTECT
100-240V 1.0A, 50-60Hz
1 2 3 4
SIGNAL
XPA U 1004
BRIDGE
BRIDGE
8Ω ONLY
1 2
ON
OFF
CLASS 2 WIRING
INPUTS
100-240V --A MAX
50-60Hz
THRU
1 2 3 4
LHF RHF LHB RHB
CLASS 2 WIRING
123
STANDBY
4
G
4
Extron
SF 26CT
Two-Way Ceiling Speakers
Audio
3 (C)
5 (LS)
2 (RF)
4 (SUB)
DMP EXP
6 (RS)78910(MIX)
RS-232
Tx
Rx G
OUTS
RESET
LAN
SSP 200
HDMI
HDMI Source
LF
C RF
Audio
Audio
10
10
12
12
8
LIMITER/
6
14
14
PROTECT
18
4
1
1
2
26
0
∞
∞
100-240V 0.6A, 50-60Hz
1
2
1 2
SIGNAL
XPA U 1002
ATTENUATION
Extron
XPA U 1002
Power Amplier
8
6
4
2
0
10
10
12
12
8
8
LIMITER/
6
14
14
PROTECT
18
4
1
1
2
26
0
0
∞
∞
100-240V 1.0A, 50-60Hz
1
2
1 2 3 4
SIGNAL
XPA U 1004
Extron
XPA U 1004
Power Amplier
ATTENUATION 8Ω/4Ω OUTPUTSREMOTEINPUTS
CLASS 2 WIRING
STANDBY
1
1
2
G
REMOTEINPUTS 8Ω/4Ω OUTPUTS
10
10
12
12
8
8
123
6
6
6
14
14
4
4
4
1
1
2
2
2
0
0
∞
∞
3
4
2
CLASS 2 WIRING
123
STANDBY
4
G
4
Extron
SM 28
Speake rs
Extron
SM 26
Speake rs
Extron Extron Extron
LS
Extron Extron
RS
Figure 1. Typical Application with 5.1.4 Speaker Setup
SSP 200 • Introduction 3
Page 12
100-240V --A MAX
50-60Hz
Extron
SSP 20 0
Surround Sound
Processor
HDMI Source
HDMI
L
INPUTS
THRU
1 2 3 4
Audio
R
5
Audio
1 (LF)
Extron
SF 10C SUB
Subwoofer
100-240V 1.5A, 50-60 Hz
XPA 4002
GREEN - ACTIVE
AMBER - STANDBY
Ch. 1 & 2 Bridge d
ATTENUATION
REMOTE
LIMITER/
2 1 2
1
PROTECT
10
12
1G2
14
STANDBY
18
26
∞
SIGNAL
(BRIDGE)
10
12
8
8
6
6
14
18
4
4
2
2
26
0
0
∞
BRIDGE MODE 8Ω / 4Ω OUTPUTS
INPUTS
BRIDGE
BRIDGE
8Ω ONLY
1 2
ON
OFF
CLASS 2 WIRING
Extron
XPA 4 002
Power Amplier
Audio
3 (C)
DMP EXP
4 (SUB)
100-240V 1.0A, 50-60Hz
XPA U 1004
5 (LS)
6 (RS)78
LIMITER/
PROTECT
1 2 3 4
SIGNAL
2 (RF)
RS-232
Tx
Rx G
10
10
12
12
12
8
8
6
6
14
14
14
18
4
4
1
1
2
2
26
0
0
∞
∞
∞
1
2
ATTENUATION 8Ω/4Ω OUTPUTSREMOTEINPUTS
9
10(MIX)
OUTS
RESET
LAN
SSP 200
LF
10
10
12
8
8
123
6
6
14
4
4
1
1
2
2
0
0
∞
3
4
4
STANDBY
G
CLASS 2 WIRING
123
Extron
4
XPA U 1004
Power Amplier
LS
C RF
Extron ExtronExtron
Extron
SM 28
Speaker s
RS
100-240V 1.0A, 50-60Hz
XPA U 1004
10
12
LIMITER/
14
PROTECT
18
1
26
∞
1
1 2 3 4
SIGNAL
10
10
10
12
12
12
8
8
8
8
6
6
6
14
14
14
4
4
4
1
1
1
2
2
2
0
0
0
0
∞
∞
∞
2
3
4
ATTENUATION 8Ω/4Ω OUTPUTSREMOTEINPUTS
6
4
2
123
4
STANDBY
G
CLASS 2 WIRING
123
Extron
4
XPA U 1004
Power Amplier
Extron
Extron
SM 26
Extron
Speaker s
LB RB
Extron
SM 26
ExtronExtron
Speaker s
Figure 2. Typical Application with 7.1 Speaker Setup
SSP 200 • Introduction 4
Page 13

Mounting
The SSP 200 can be set on a table, mounted on a rack shelf, or mounted under a desk,
podium, or table.
ATTENTION:
• Installation and service must be performed by authorized personnel only.
• L’installation et l’entretien doivent être effectués uniquement par un technicien
qualifié.
Tabletop Placement
Attach the four provided rubber feet to the bottom of the unit and place it in any convenient
location.
Rack Mounting
See the Extron website for a list of optional rack mounting kits that are suitable for the
SSP200. Follow the instructions provided with the kit.
UL Guidelines for Rack Mounting
The following Underwriters Laboratories (UL) guidelines are relevant to the safe installation of
these products in a rack:
1. Elevated operating ambient temperature — If the unit is installed in a closed or
multi-unit rack assembly, the operating ambient temperature of the rack environment
may be greater than room ambient temperature. Therefore, install the equipment in
an environment compatible with the maximum ambient temperature (Tma: +122° F,
+50°C) specified by Extron.
2. Reduced air flow — Install the equipment in the rack so that the equipment gets
adequate air flow for safe operation.
3. Mechanical loading — Mount the equipment in the rack so that uneven mechanical
loading does not create a hazardous condition.
4. Circuit overloading — Connect the equipment to the supply circuit and consider the
effect that circuit overloading might have on overcurrent protection and supply wiring.
Appropriate consideration of the equipment nameplate ratings should be used when
addressing this concern.
5. Reliable earthing (grounding) — Maintain reliable grounding of rack-mounted
equipment. Pay particular attention to supply connections other than direct connections
to the branch circuit (such as the use of power strips).
Under-desk Mounting
See the Extron website to find the optional under-desk mounting kit that is suitable for the
SSP200. Follow the instructions provided with the kit.
SSP 200 • Introduction 5
Page 14

Panel Features
e
SSP 200
CONFIG
PCM
2-CH
ATMOS
HDCP
EXP
SURROUND SOUND PROCESSOR
SOURCE INPUT VOLUME
1 2 3 4 5
AAA
BBB CCC
DDD EEE
DTS
D
PCM
2-CH
DTS: X
ATMOS
HDCP
EXP
SOURCE
INPUT
1 2 3 4 5
VOLUME
34
This section describes:
• Rear Panel Features
• Front Panel Features
Rear Panel Features
HHH
INPUTS
--A MAX
100-240V
50-60 Hz
1 THRU
AAA CCC
LR
5
BBB
1(LF) 2(RF) 3(C) 4(SUB) 5(LS) 6(RS)789 10(MIX)
RS-232
2
34
DMP EXP
Tx Rx G
DDD EEE FFFGGG
LAN
Figure 3. SSP200 Rear Panel Features
AC power input
A
Audio inputs
B
DMP expansion port
C
RS-232 port
D
AC power input — Use an IEC power cable to connect the processor to a
A
LAN port
E
Reset button
F
Status LED
G
Analog outputs
H
100‑240VAC, 50 ‑ 60 Hz, power source.
Audio inputs — The SSP200 accepts four digital inputs and one analog input (see
B
figure4).
INPUTS
LR
5
1 THRU
2
OUTS
RESET
SSP 200
Figure 4. SSP200 Audio Inputs
• Input 1 accepts digital signals through an HDMI cable (see Securing an HDMI
Connector on page10). The THRU connection passes the original HDMI video
signal out, unaltered, to another device. Audio passed to the THRU connection is
configurable (see Input/Output Config on page32).
• Input 2 accepts digital signals through a S/PDIF coaxial cable.
• Inputs 3 and 4 accept digital signals through S/PDIF optical (TOSLINK) cables.
SSP 200 • Panel Features 6
Page 15
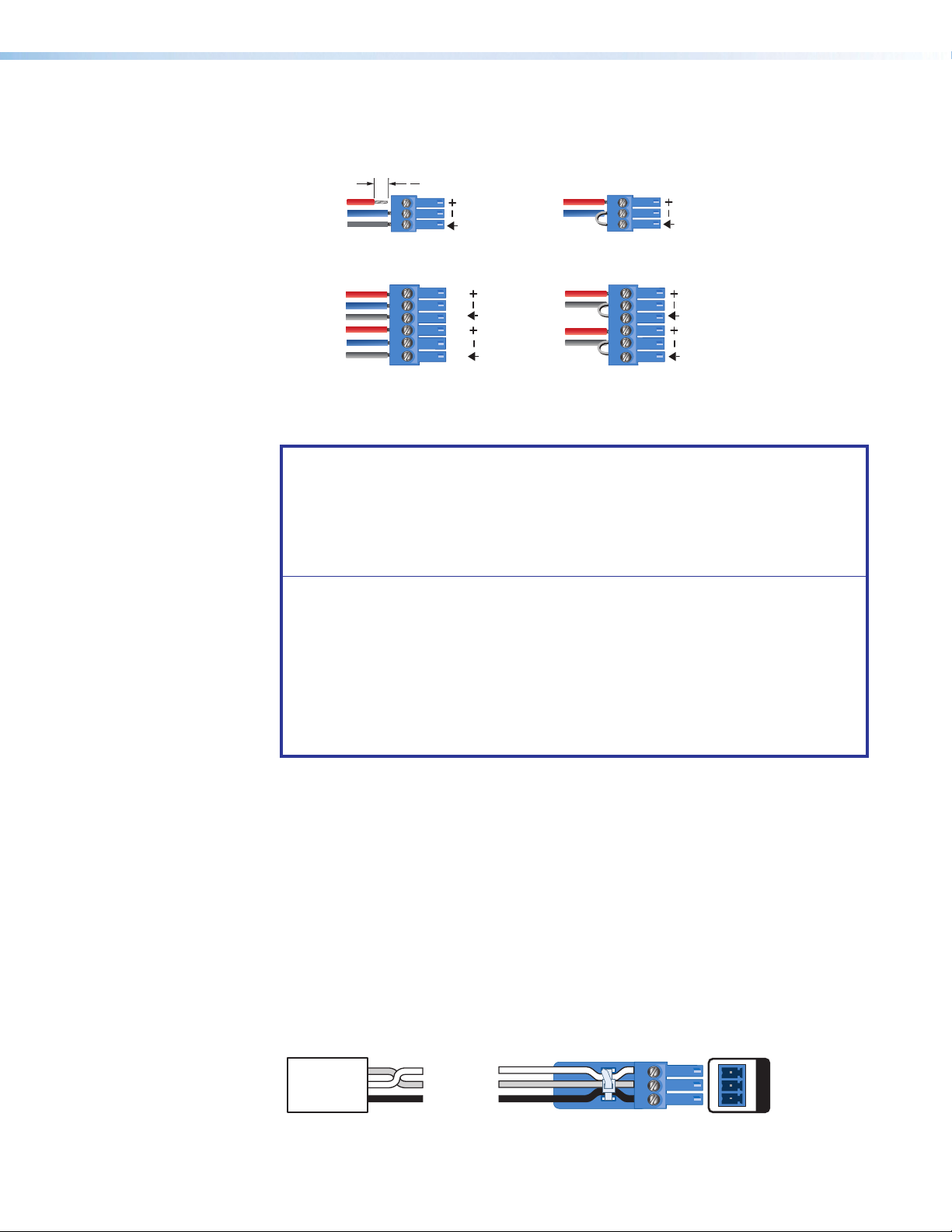
• Input 5 accepts a balanced or unbalanced, stereo or mono, analog input through
Sleev
Slee
Slee
Tip
REMOTE RS-232
RS-232 Device Bidirectional
a 6‑pole captive screw connector. Figure 5 shows the correct wiring for different
analog input signals using either 3‑pole or 6‑pole connectors.
3
"
(5 mm) MAX. (typ)
Tip
Ring
e
Balanced Input
16
Tip
Sleeve
Jumper
Unbalanced Input
3-pole Audio Input Wiring
Tip
Ring
ve
Tip
Ring
ve
Balanced Input Unbalanced Input
Sleeve
Jumper
Tip
Sleeve
Jumper
6-pole Audio Input Wiring
Figure 5. Analog Input (Input 5) Wiring
ATTENTION:
• Do not tin the wire leads before installing into the connector. Tinned wires are
not as secure in the connector and could be pulled out.
• Ne pas étamer les conducteurs avant de les insérer dans le connecteur. Les
câbles étamés ne sont pas aussi bien fixés dans le connecteur et pourraient
être tirés.
• The length of the exposed wires in the stripping process is important. The
ideal length is 3/16 inches (5 mm). Any longer and the exposed wires may
touch, causing a short circuit between them. Any shorter and the wires can be
easily pulled out even if tightly fastened by the captive screws.
• La longueur des câbles exposés est importante lorsque l’on entreprend de
les dénuder. La longueur idéale est de 5mm (3/16inches). S’ils sont
trop longs, les câbles exposés pourraient se toucher et provoquer un court‑
circuit. S’ils sont trop courts, ils peuvent être tirés facilement, même s’ils sont
correctement serrés par les borniers à vis.
DMP Expansion port — This proprietary Extron DMP Expansion port provides 14
C
output channels and 2 input channels (for use as a stereo input) for exclusive use with
EXP‑compatible Extron devices. The first 10 EXP output channels are duplicates of
the 10 analog outputs (except for Downmix Left and Right, which always appear on
EXP outputs 15 and 16). Two additional EXP Outputs are available for 7.1.4 speaker
configurations.
The EXP port is limited to a sample rate of 48 kHz at 24‑bit depth per channel. High
sample rate codecs (such as DTS 96/24 at 96 kHz and Dolby TrueHD at a maximum
192 kHz are first resampled to 48 KHz before transport via the EXP bus.
RS-232 port — The SSP200 can be configured with Extron Product Configuration
D
Software (PCS) or Simple Instruction Set (SIS) commands using this 3‑pole captive
screw connector (see Product Configuration Software starting on page29 and
SIS Configuration and Control starting on page62)
Tx Rx
RS-232
G
Transmit (Tx)
Receive (Rx)
Ground(Gnd)
Transmit (Tx)
Receive (Rx)
Ground(Gnd)
Figure 6. RS-232 Wiring Example
SSP 200 • Panel Features 7
REMOTE
Page 16

LAN port — RJ‑45 connector allows the SSP 200 to be connected to a Local Area
12345678
RJ-45
Connector
Insert Twisted
Pair Wires
Pins:
A cable that is wired as TIA/EIA T568A at one
end and T568B at the other (Tx and Rx pairs
reversed) is a "crossover" cable.
A cable wired the same at both ends is called
a "straight-through" cable because no pin/pair
assignments are swapped.
T568B T568A T568B T568B
Straight-through Cable
(for connection to a switch, hub, or router)
End 1 End 2
Pin Wire Color Pin Wire Color
1 white-orange 1 white-orange
2 orange 2 orange
3 white-green 3 white-green
4 blue 4 blue
5 white-blue 5 white-blue
6 green 6 green
7 white-brown 7 white-brown
8 brown 8 brown
Crossover Cable
(for direct connection to a PC)
End 1 End 2
Pin Wire Color Pin Wire Color
1 white-orange 1 white-green
2 orange 2 green
3 white-green 3 white-orange
4 blue 4 blue
5 white-blue 5 white-blue
6 green 6 orange
7 white-brown 7 white-brown
8 brown 8 brown
DTS
D
PCM
2-CH
DTS: X
ATMOS
HDCP
EXP
SOURCE
INPUT
1 2 3 4 5
VOLUME
91
1 THRU
INPUTS
2
5
LR
34
E
Network (LAN) connection for control and configuration. As with the RS‑232 and
USB connections, the device can be controlled using SIS commands through an
external control system or via PCS in order to configure the device and receive status
information as required.
The Ethernet cable can be terminated as a straight‑through cable or a crossover cable
and must be properly terminated for your application (see figure7 for wiring information).
• Crossover cable — Direct connection between the computer and the SSP 200.
• Patch (straight) cable — Connection of the SSP 200 to an Ethernet LAN.
Figure 7. RJ-45 Ethernet Connector Pin Assignment
Reset button — The Reset button initiates various levels of soft resets, which restore
F
various tiers of SSP 200 settings to their defaults (see System Reset on page14).
Use a pointed stylus or small screwdriver (such as an Extron Tweeker) to press the internal
button.
Status LED — The Status LED is used in conjunction with the Reset button (see
G
System Reset on page14).
Analog outputs (see figure8) — Outputs are balanced or unbalanced line level analog
H
signals that feed into multichannel amplifiers for configurations up to 7.1.2 or 5.1.4
surround sound. For more information, see Speaker Placement on page18.
1(LF) 2(RF) 3(C) 4(SUB) 5(LS) 6(RS) 78
Figure 8. Analog Audio Outputs
0(MIX)
OUTS
SSP 200 • Panel Features 8
Page 17
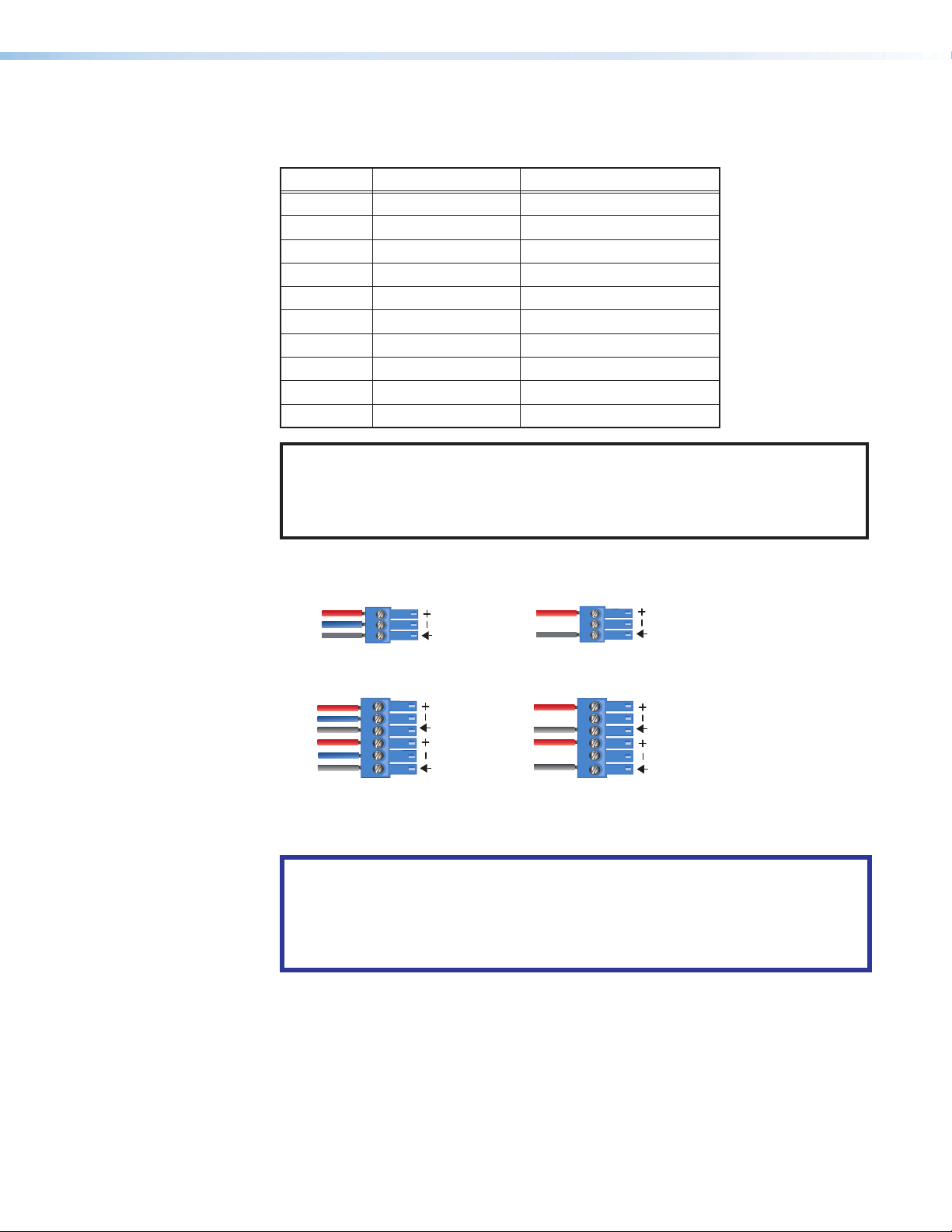
Individual output settings are configured through PCS (see Speaker Placement) or
Sleev
Slee
Slee
6-pole Audio Output Wiring
t
SIS commands (Layouts and Speakers on page78). Refer to the following table for
output designations.
Numbers Abbreviations Channel Description
1 LF Left Front
2 RF Right Front
3 C Center
4 SUB Subwoofer (Mono)
5 LS Left Surround
6 RS Right Surround
7 see note below
8 see note below
9 see note below
10 see note below
NOTES:
• Numbers 7 through 10 are configurable as Back, Height, or Downmix using PCS.
• The default configuration is 7.1 with Downmix on numbers 9 and 10
enabled.
For information about speaker configuration and output formats, see Listening Mode
Options and Usage on page27. See figure9 for audio output connector wiring.
Tip
Ring
e
Balanced Output
3-pole Audio Output Wiring
Tip
NO Ground Here
Sleeve
Unbalanced Output
Tip
Ring
ve
Tip
Ring
ve
Balanced Output Unbalanced Outpu
Tip
NO Ground Here
Sleeve
Tip
NO Ground Here
Sleeve
Figure 9. Audio Output Wiring
ATTENTION:
• For unbalanced audio, connect the sleeves to the ground contact. DO NOT
connect the sleeves to the negative (–) contacts.
• Pour l’audio asymétrique, connectez les manchons au contact au sol. Ne PAS
connecter les manchons aux contacts négatifs (–).
SSP 200 • Panel Features 9
Page 18
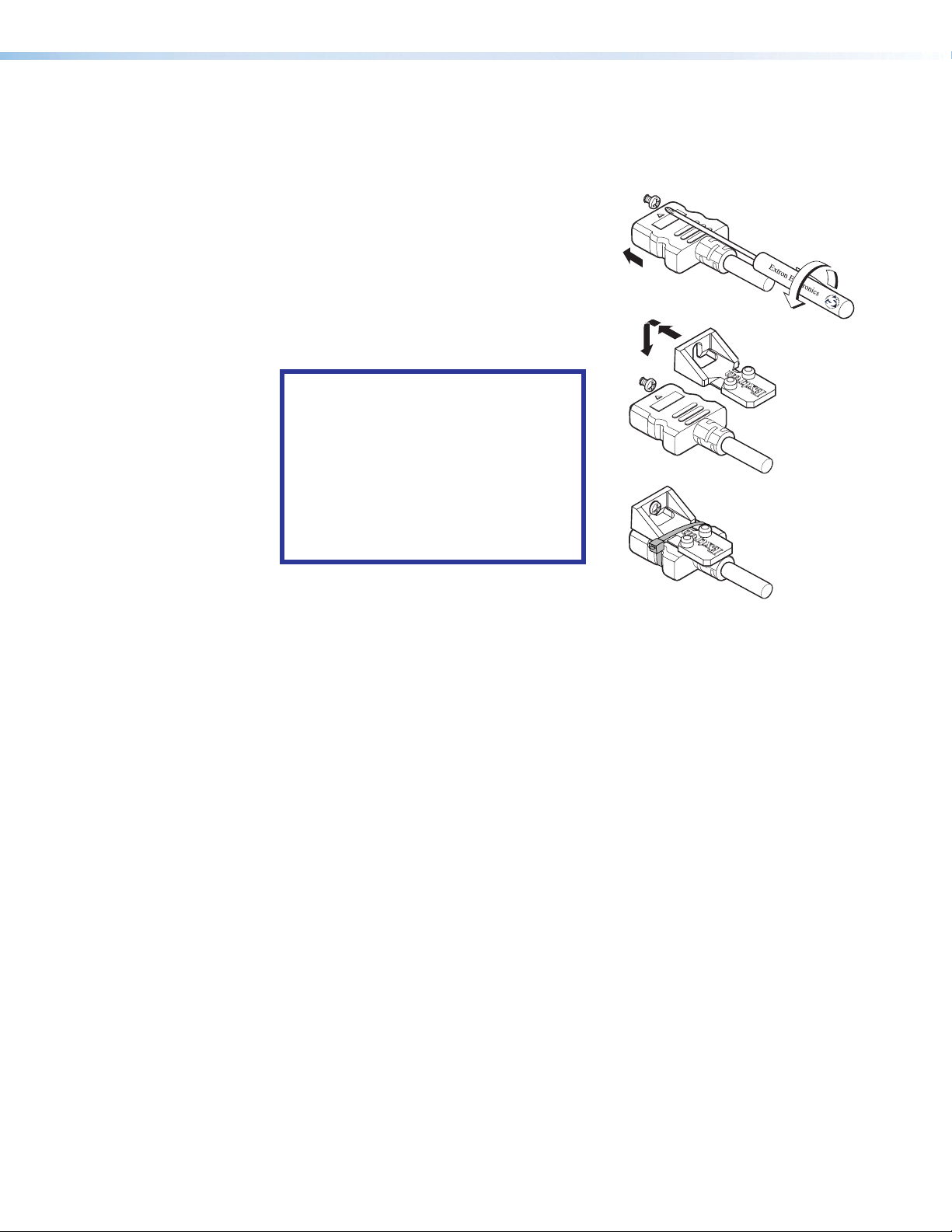
Securing an HDMI Connector
2
3
4
5
Follow these instructions to secure the HMDI connectors to the processor with the LockIt
HDMI lacing bracket provided:
Plug the HDMI cable into the processor rear
1
panel connection.
Loosen the HDMI connection mounting screw
2
from the panel enough to allow the LockIt lacing
bracket to be placed over it. The screw does
not have to be removed.
Place the LockIt lacing bracket on the screw
3
and against the HDMI connector, then tighten
the screw to secure the bracket.
ATTENTION:
• Do not overtighten the HDMI
connector mounting screw. The
shield it fastens to is very thin and
can easily be stripped.
• Ne serrez pas trop la vis de montage
du connecteur HDMI. Le blindage
auquel elle est attachée est très fin
et peut facilement être dénudé.
111
3
3
4
4
2
2
3
5
Loosely place the included tie wrap around the
4
HDMI connector and the LockIt lacing bracket
as shown.
While holding the connector securely against the lacing bracket, tighten the tie wrap,
5
then remove any excess length.
5
SSP 200 • Panel Features 10
Page 19
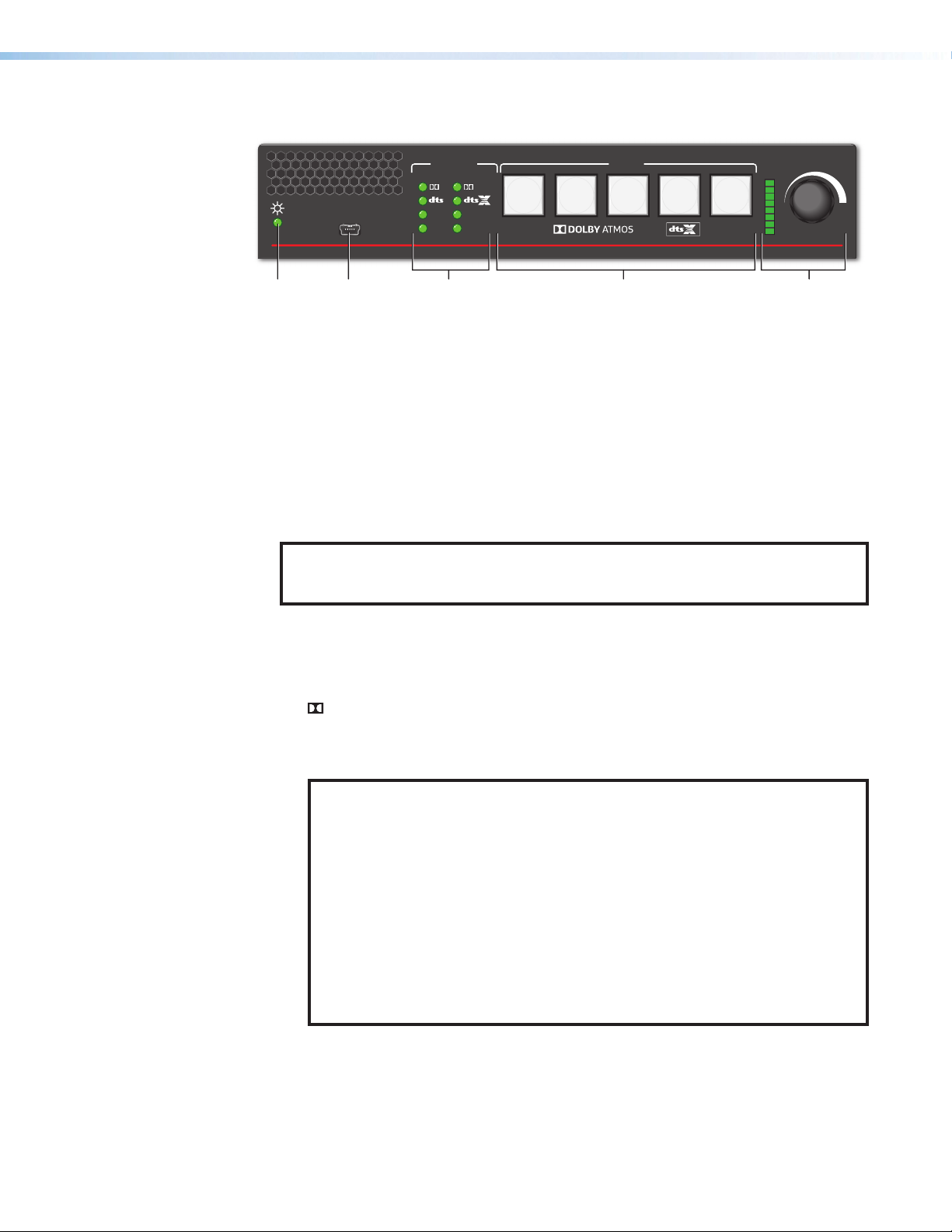
Front Panel Features
AAA
BBB CCC
DDD EEE
e
Figure 10. SSP200 Front Panel Features
CONFIG
SOURCE INPUT VOLUME
ATMOS
1 2 3 4 5
PCM
HDCP
2-CH
EXP
SURROUND SOUND PROCESSOR
SSP 200
Status LED
A
Configuration port
B
Input Source format indicators
C
Status LED — This LED indicates the current power and boot status of the SSP 200.
A
Configuration port — The SSP200 can be configured via PCS or by using Extron
B
Simple Instruction Set (SIS) commands via this USB mini‑B port or via the LAN and
RS‑232 ports on the rear panel (see SIS Configuration and Control starting on
page62). In addition, this configuration port is used for firmware updates from a PC.
NOTE: The front panel configuration port, the rear panel RS‑232 port, and the rear
panel LAN port can all be used at the same time. No connection has precedence.
The SSP200 responds to commands in the order received.
Input Selections
D
Volume Adjustment
E
Source Format
Input Source format indicators — The bank of eight LEDs identify the format of the
C
audio input (see Source Formats starting on page24).
• : Dolby source material
• DTS: DTS source material
• PCM: 2‑channel uncompressed digital source format up to 7.1 multi‑channel
NOTES:
• A digital signal that does not have a supported sampling rate or is
compressed PCM is considered an unrecognized signal and is muted.
• When a media player is paused during playback, the SSP200 may or
may not continue to receive source format information from the player.
Some players continue to send the same source format information in a
loop, allowing the SSP200 to retain the previous settings. Other players
completely disconnect the signal from the SSP200 (unlocked state) so that
the active input appears as if there is no connection present. The remainder
of players change the source output to PCM without an actual signal being
sent (digital silence). During digital silence, the PCM LED lights but the
2‑CH source LED does not.
SSP 200 • Panel Features 11
Page 20
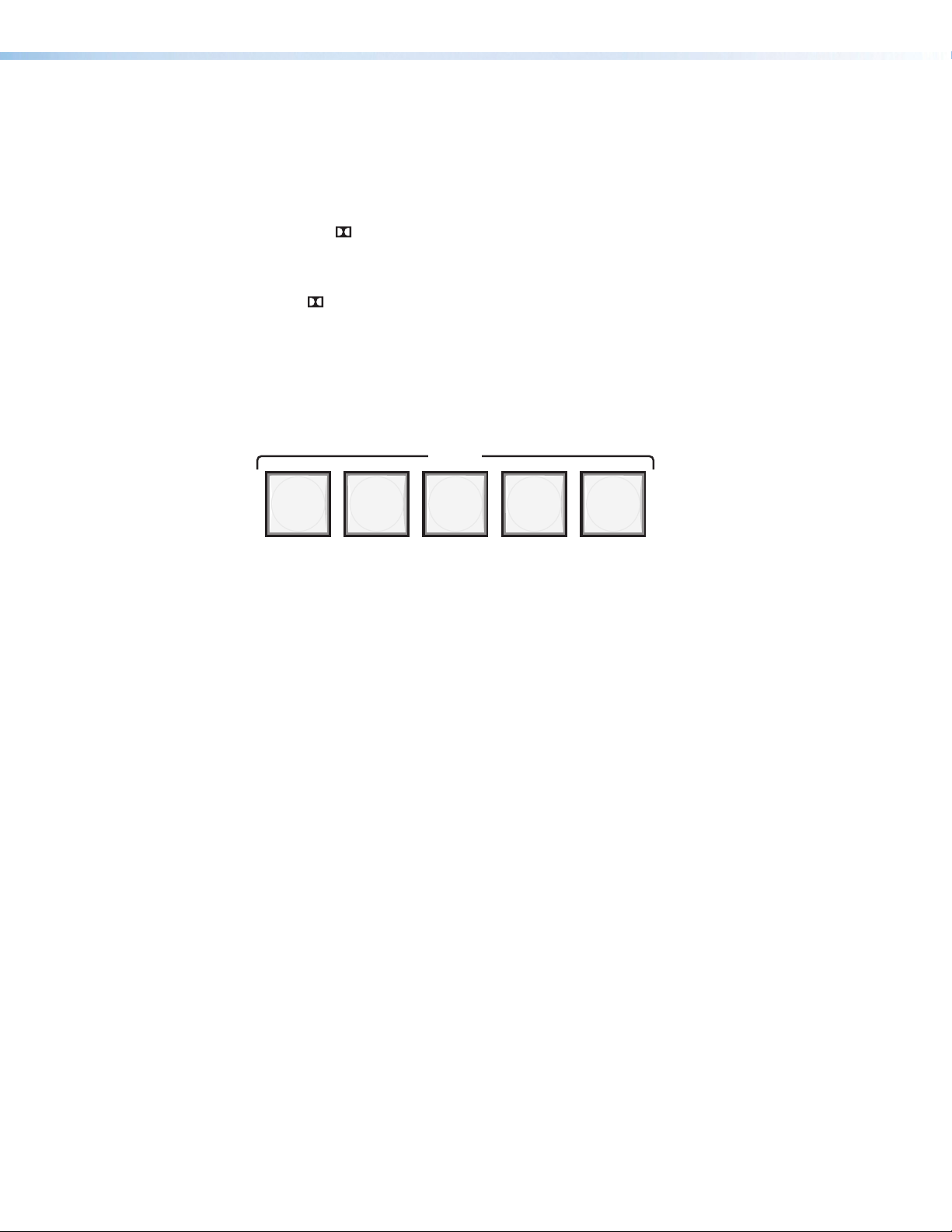
Input Selection
DTS
D
PCM
2-CH
DTS: X
ATMOS
HDCP
EXP
SOURCE
Figure 11. SSP200 Input Selection Switches
• 2-Channel (2-CH):
• Any source coming through analog input 5.
• If a 2‑Channel PCM digital signal is present on any of the digital inputs, both the
PCM and the 2‑CH LEDs light.
• If a Dolby Digital 2/0 or Dolby Digital 2/0 Surround source is present, both the
and the 2‑CH LEDs light.
• If a DTS 2‑Channel source format is present, both the DTS and 2‑CH LEDs
light.
• ATMOS: Dolby Atmos source material
• DTS:X: DTS:X source material (HDMI only)
• HDCP: HDMI source material (HDMI only)
• EXP: Valid EXP connection. Blinks when the assigned EXP input is selected.
INPUT
1 2 3 4 5
Input selection buttons — Push one of the buttons to select between the five audio
D
inputs. When a button is selected, the button lights green indicating it is the active input.
For digital inputs 1 through 4, the button turns amber when it is selected and the digital
clock signal has not been detected.
The Input 5 button turns red when the analog input is clipping. The Analog Input Gain
Level can be adjusted with the volume adjustment knob (see page 13).
The SSP accepts four digital inputs and one analog input (see Rear Panel Features
on page6):
• Input 1 accepts digital signals through an HDMI cable.
• Input 2 accepts digital signals through a S/PDIF coaxial cable.
• Inputs 3 and 4 accepts digital signals through S/PDIF optical cables. The SSP 200
supports TOSLINK or TOSLINK‑compatible optical connectors that conform to
IEC‑958, S/PDIF standards.
All four digital inputs accept 16‑ to 24‑bit PCM audio at 32kHz, 44.1kHz, 48kHz,
88.2kHz, 96kHz, and 192kHz sample rates. They support Dolby Digital and DTS
source formats.
• Input 5 accepts a balanced or unbalanced analog input through a 6‑pin captive
screw connector. The unit can be configured to accept:
• A stereo signal
• A mono signal (see Listening Mode Options on page27)
The input can also be selected using PCS (see Product Configuration Software on
page29) and SIS commands (see SIS Configuration and Control on page62).
SSP 200 • Panel Features 12
Page 21

Volume Adjustment
Volume control and LED bar — Use the rotary encoder to adjust the output volume
E
from 0%to100%. The default setting is 80%.
As the volume increases or decreases, the LED bar lights to indicate the current volume
setting (see the table below). As the volume is increased or decreased, the top LED
flashes.
If the audio is muted using PCS or SIS, the entire LED bar blinks to indicate a muted
state. The LEDs return to their previous state when the audio is unmuted.
VOLUME
Figure 12. Volume Control and LED Bar
Volume steps for each LED LEDs lit
96% to 100% All 8 LEDs on
91% to 95% Bottom 7 LEDs on
86% to 90% Bottom 6 LEDs on
81% to 85% Bottom 5 LEDs on
71% to 80% Bottom 4 LEDs on
51% to 70% Bottom 3 LEDs on
31% to 50% Bottom 2 LEDs on
1% to 30% Bottom LED on
0% All LEDs flashing
The volume can also be controlled using SIS (see Volume on page77).
Analog Input Gain Level
Alternatively, the rotary encoder controls the gain level of the analog signal on Input 5.
Analog input gain is adjustable from ‑18 dB to +24 dB.
To adjust input gain, press and hold the Input 5 button, then turn the rotary encoder to
increase or decrease the gain level of the input signal (see figure13 on the next page).
When the Input 5 button is released, the input gain level control is deactivated. All active
(input level) LEDs in the LED array bar deactivate momentarily, and then re‑activate to
display the current volume setting.
SSP 200 • Panel Features 13
Page 22
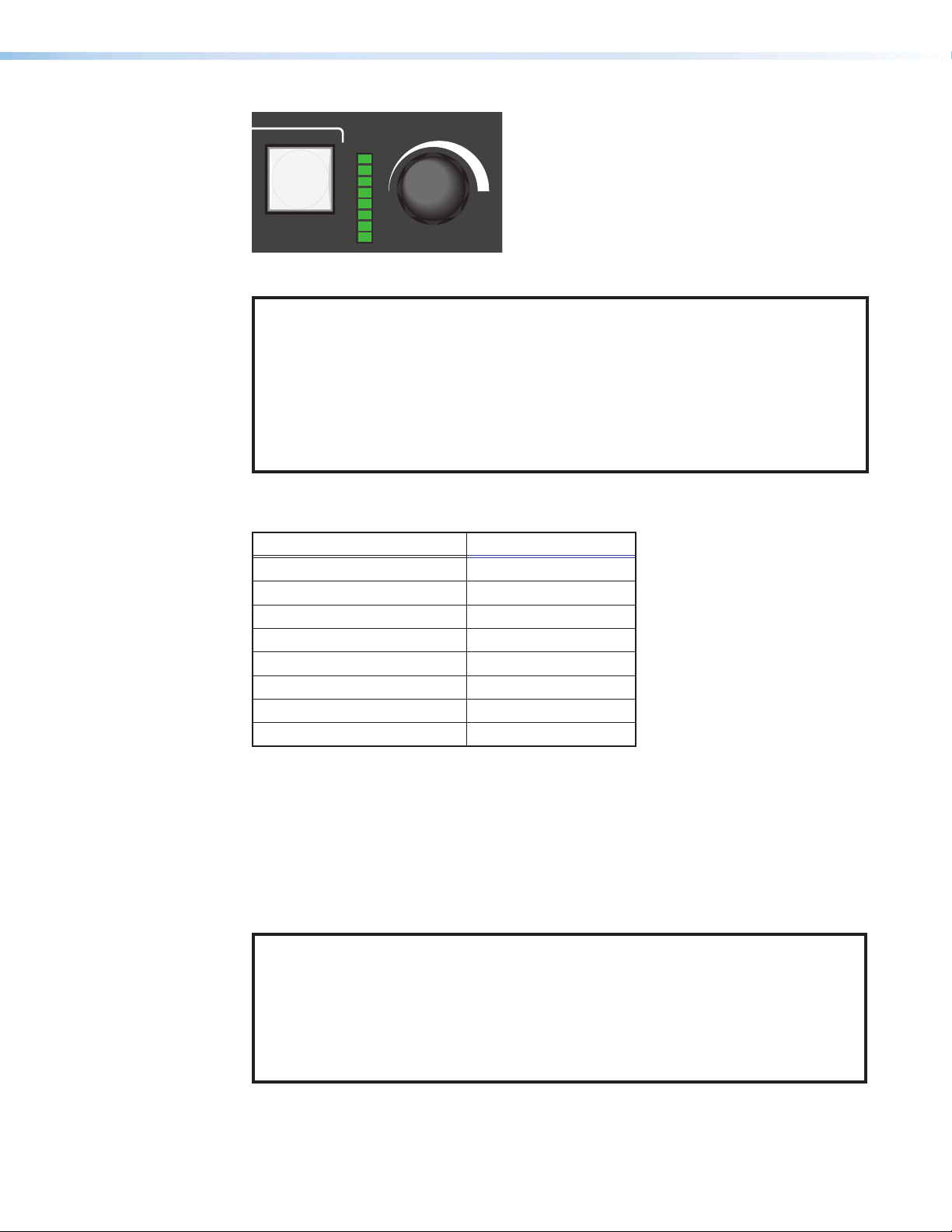
VOLUME
5
Figure 13. Analog Gain Control
NOTES:
• If the gain level is too high, clipping may occur. When clipping occurs, the Input 5
button lights red.
• When using Mono or Mono to All listening mode, the left and right signals are
summed (in the digital domain), which can cause a boost in level up to 6 dB. This
type of clipping does not cause the clip indicator LED to light but is audible. If
using a mono mode, it is recommended that the input gain be reduced by 9 dB to
prevent clipping from occurring.
While the Input 5 button is held down, the LED bar lights from the bottom up to indicate the
current gain level (see tablebelow).
Gain steps for each LED LEDs lit
19 dB to 24 dB All 8 LEDs on
13 dB to 18 dB Bottom 7 LEDs on
7 dB to 12 dB Bottom 6 LEDs on
1 dB to 6 dB Bottom 5 LEDs on
‑5 dB to 0 dB Bottom 4 LEDs on
‑11 dB to ‑6 dB Bottom 3 LEDs on
‑17 dB to ‑12 dB Bottom 2 LEDs on
‑18 dB Bottom LED on
System Reset
The rear panel has a recessed Reset button that initiates various levels of soft resets
restoring various tiers of SSP 200 settings to their defaults. For different reset levels, press
and hold the button while the SSP 200 is running.
(such as an Extron Tweeker) to press the button.
The following Reset Modes Summary table provides a list of the available reset modes,
how to activate them, and the result of that activation.
Use a pointed stylus or small screwdriver
NOTES:
• The reset modes listed on the next page close all open IP and Telnet connections,
as well as close all sockets.
• The factory configured passwords for all accounts on this device have been set to
the device serial number. Passwords are case sensitive. If the SSP 200 is reset, the
passwords revert to the default, which is extron. A new password would need to
be configured to secure the device.
SSP 200 • Panel Features 14
Page 23
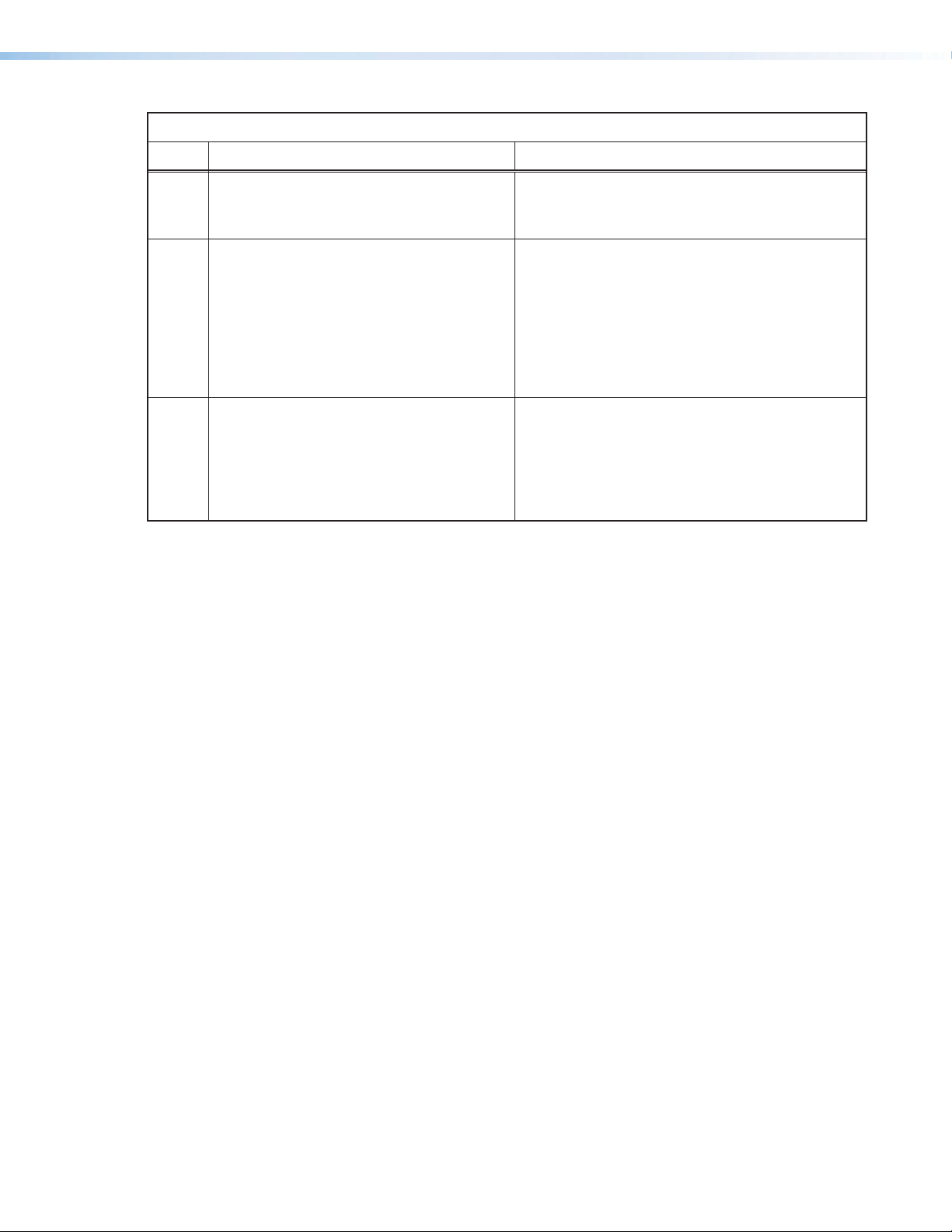
Reset Modes Summary
Mode Activation Result
1
Hold in the recessed Reset button while
applying power to the device.
4
Hold in the Reset button until the Reset
LED blinks twice (once after approximately
3 seconds and again after 6 seconds).
Then, within 1 second press Reset
momentarily (for less than 1 second).
5
Hold in the Reset button until the Reset
LED blinks three times (once after
approximately 3 seconds, again after
6 seconds, and then again after 9 seconds);
then within 1 second press Reset
momentarily (for less than 1 second).
Full system resets can also be performed using SIS commands (see Resets on page78).
• Restores the factory‑installed firmware.
• Maintains all user settings (audio adjustments,
IP settings, and so on).
• Sets the IP address, subnet address, and
gateway address to the factory defaults.
• Sets port mapping to the factory default.
• Turns DHCP off.
• Turn event scripts off.
The Reset LED blinks four times in quick
succession during the reset.
Performs a complete reset to factory defaults. The
password reverts to extron.
The Reset LED blinks four times in quick
succession during the reset.
Front Panel Security Lockout (Executive Mode)
When the front panel is locked, the user cannot make any input changes from the front
panel. If the user attempts to make changes with the front panel locked out, all the input
button LEDs flash simultaneously. The lockout does not block changes made using SIS
commands or PCS. There are three lockout modes available:
• Mode 1 — All front panel controls are locked. No adjustments can be made.
• Mode 2 — All front panel controls are locked except for volume control. This allows the
volume to be adjusted, without the ability to change inputs.
• Mode 3 — All front controls are locked, except for input selection buttons.
This feature can only be set using SIS commands (see SIS Configuration and Control on
page62) or PCS (see Front Panel Lockout (Executive Mode) on page52).
SSP 200 • Panel Features 15
Page 24

Connecting to the USB Port
1
2
3
4
Use the USB mini‑B port on the front panel to connect the processor to a host computer to
configure the unit with PCS or SIS commands.
1. Connect a USB A to mini‑B cable between the front panel USB CONFIG port and a
USB port on the PC (see figure14).
WiFi
1234
e
SSP 200
CONFIG
Mini Type B
USB
USB Cable
SOURCE INPUT VOLUME
D
ATMOS
DTS
DTS: X
PCM
2-CH
1 2 3 4 5
HDCP
EXP
Type A
USB
SURROUND SOUND PROCESSOR
USB
Ports
SSP 200
PC
Figure 14. Connecting a PC to the SSP 200 Front Panel USB Port
If this is the first time the SSP200 has been connected to the PC, the Found New
Hardware Wizard opens (see figure15).
The first screen offers to connect to Windows Update to search the web for the
appropriate driver needed for the USB port to communicate with the SSP 200. This is
not necessary if the USB driver is already on your PC.
Figure 15. Found New Hardware Wizard Opening Screen
2. Click on the appropriate radio button (see figure15).
• Select the Yes, this time only radio button (1) if you want your computer to
connect to Windows Update only this one time.
SSP 200 • Panel Features 16
Page 25
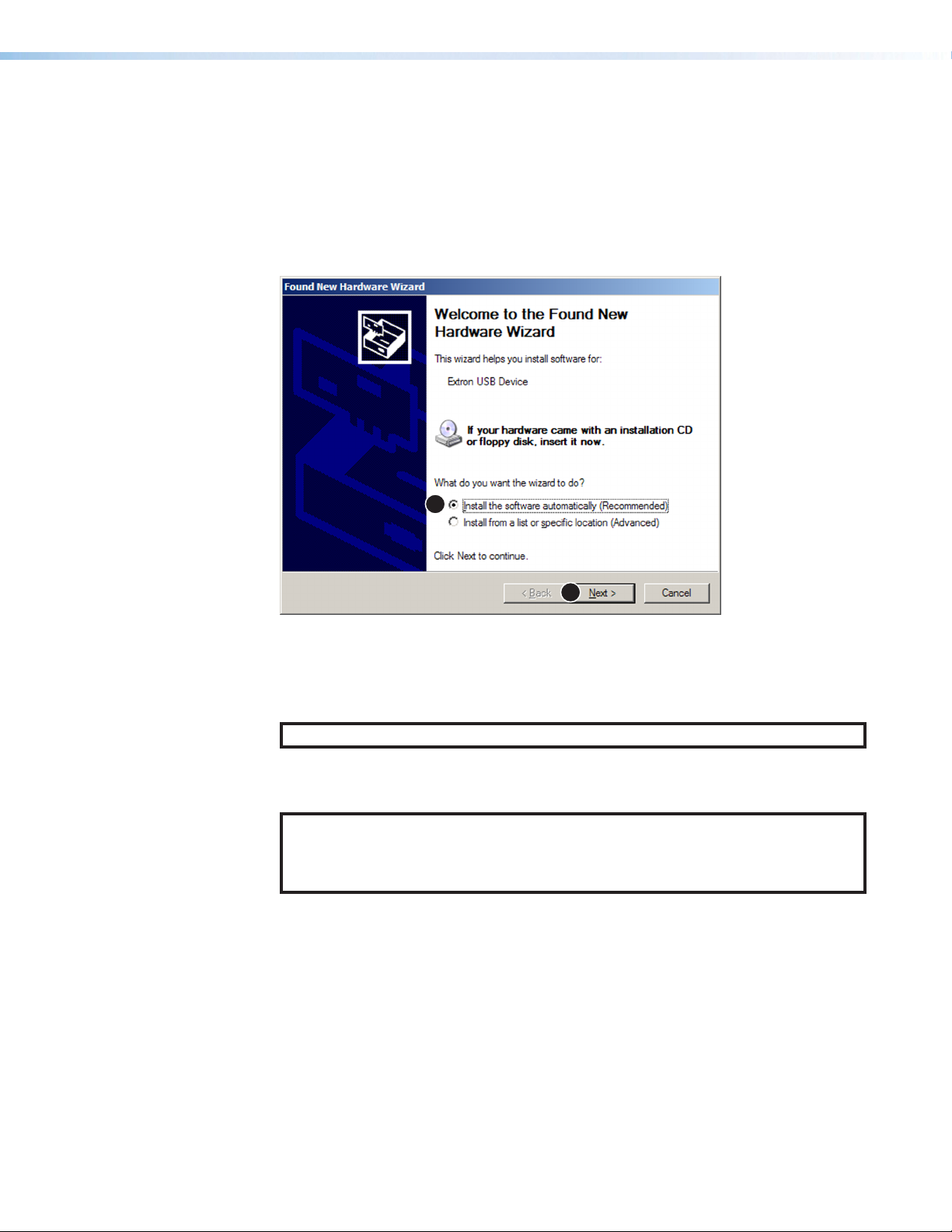
• Select Yes, now and every time I connect a device (see figure15, 2, on
the previous page) if you want the computer to automatically connect to Windows
Update to search the web every time the processor is connected to this USB port.
• Select No, not this time (3) if you do not want the computer to connect to
Windows Update to search the web at this time (for example, if the driver is already
on your computer).
3. Click Next (4).
The next screen of the Wizard opens:
1
2
Figure 16. Installing the Software Automatically
4. Select the Install the software automatically (Recommended) radio button
(see figure16, 1).
5. Click Next (2).
NOTE: You do not need to insert a disc.
The PC locates the driver needed and installs it in the correct location on the hard drive.
6. When the Completed screen appears, click Finish to close the wizard.
NOTE: The wizard opens only on the first occasion you connect the SSP 200 to
that USB port. The wizard reappears if you connect the unit to a different USB
port or if you connect a different piece of equipment, requiring a different driver, to
the same USB port.
7. Configure the processor as desired using SIS commands (see SIS Configuration
and Control starting on page62) or PCS (see Using PCS Software starting on
page30).
SSP 200 • Panel Features 17
Page 26
Speaker Setup
C
This section provides background information about arranging speakers in a room and
the settings that can be adjusted by the Product Configuration Software (PCS). Extron
recommends that the PCS is used to make configuration changes to the SSP200 (see
Product Configuration Software starting on page29). Topics in this section include:
• Speaker Placement
• Back Speakers
• Bass Management
• Speaker Delay Settings
• Test Signals
• Output Channel Trim Settings
• Listening Mode Settings
• Equalization
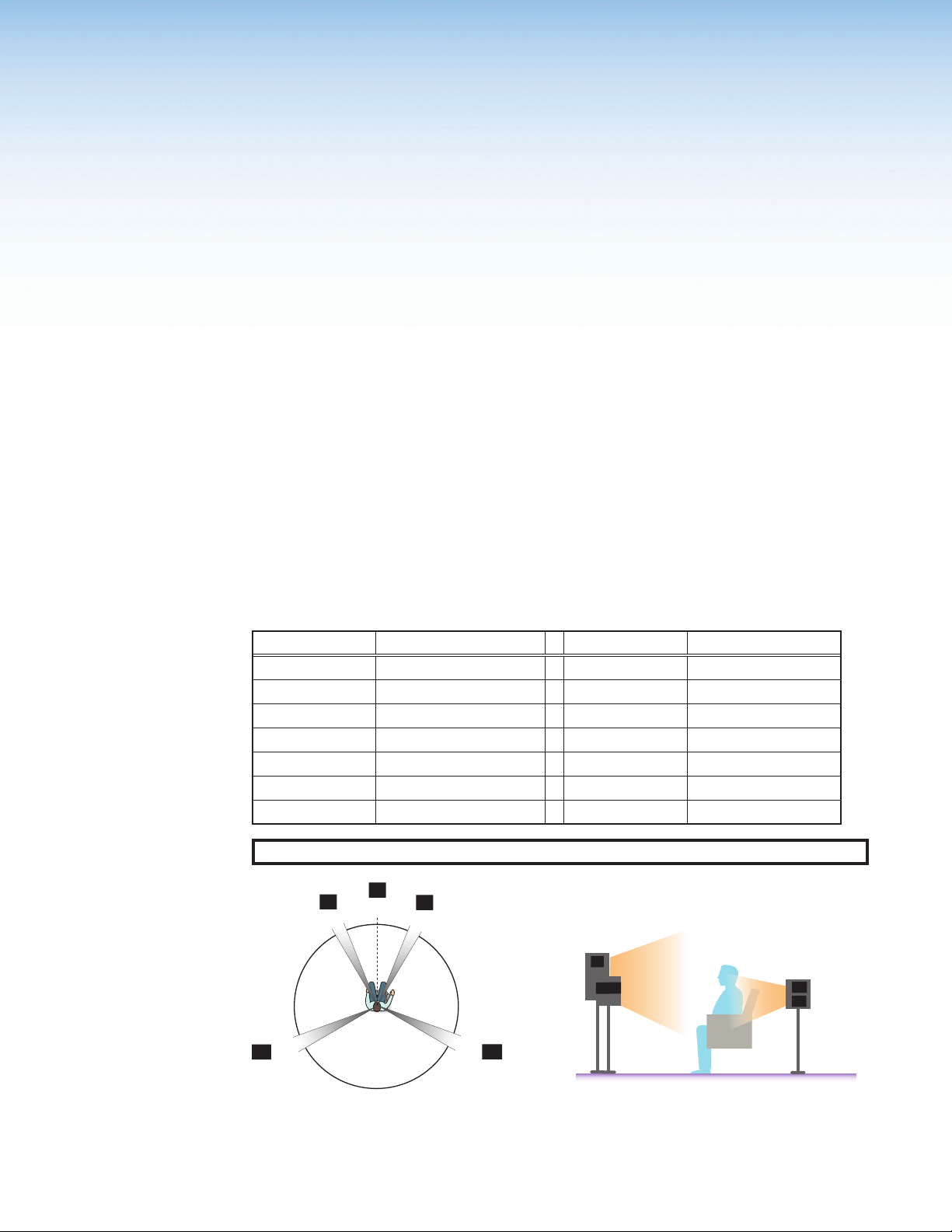
Speaker Placement
The following figures show the recommended speaker placement, relative to the listener, for
some of the most common speaker configurations.
Speaker Abbreviations
Abbreviations Channel Descripton Abbreviations Channel Descripton
LF Left Front RB Right Back
RF Right Front LH Left Height
C Center RH Right Height
SUB Subwoofer (Mono) LHF Left Height Front
LS Left Surround RHF Right Height Front
RS Right Surround LHB Left Height Back
LB Left Back RHB Right Height Back
NOTE: All speakers should be angled inwards so that they face towards the listener.
L
30°
LB
110°
120°
22°
0°
22°
R
30°
110°
120°
RB
C
R
L
RB
LB
Figure 17. Speaker 5.1 Setup
SSP 200 • Speaker Setup 18
Page 27
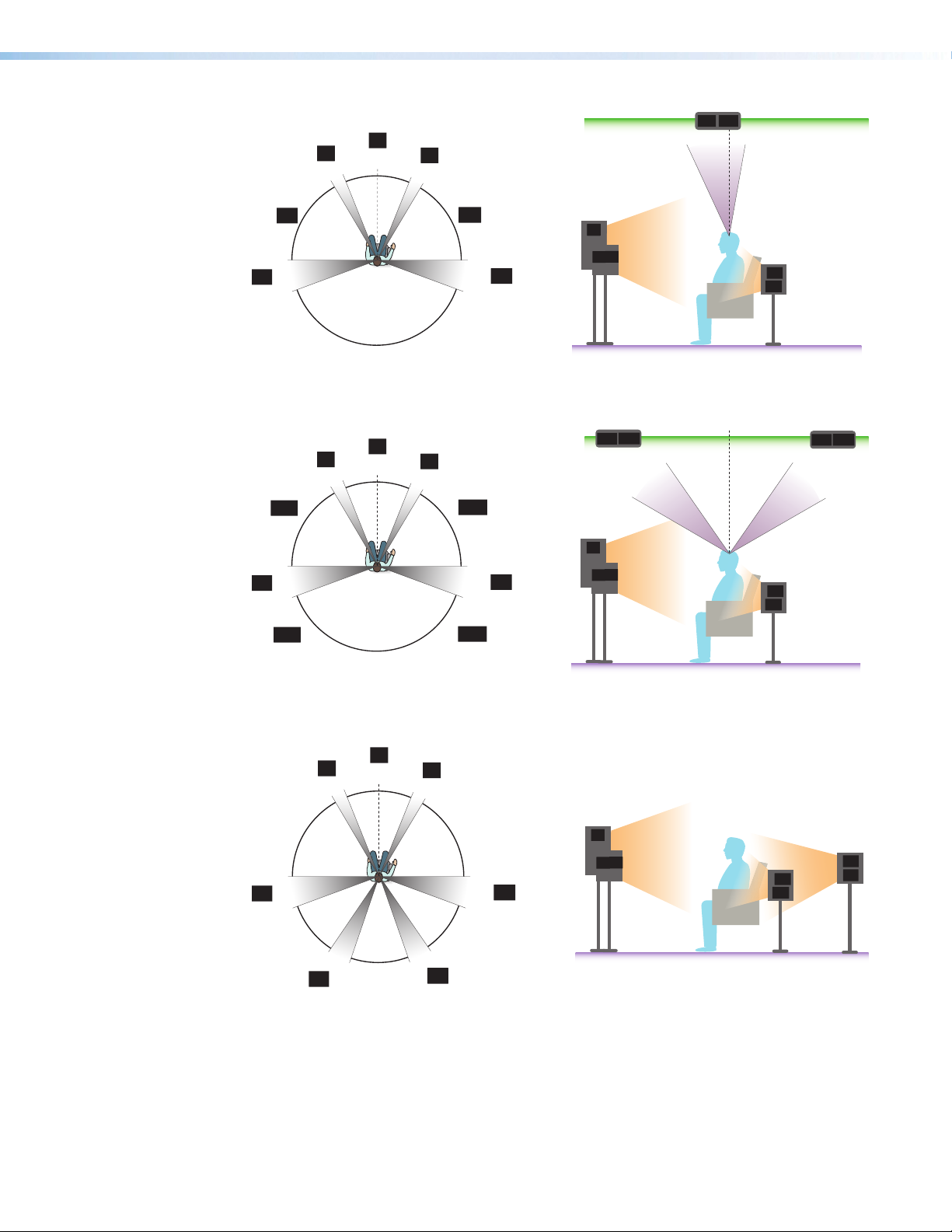
30°
C
RH
LH
L
22°
0°
22°
R
30°
C
65°
100°
LH
90°
RH
90°
LS
110°
110°
Figure 18. Speaker 5.1.2 Setup
22°
C
22°
R
30°
0°
RHF
90°
110°
RHB
L
30°
LHF
90°
LS
110°
LHB
RS
RS
C
C
R
L
RS
LS
RHF
LHF
55°
30°
C
R
L
125°
RS
LS
LHB
RHB
150°
Figure 19. Speaker 5.1.4 Setup
L
30°
90°
22°
0°
LS
110°
135°
150°
LB
22°
150°
R
30°
135°
RB
90°
110°
RS
C
R
L
RS
LS
RB
LB
Figure 20. Speaker 7.1 Setup
SSP 200 • Speaker Setup 19
Page 28
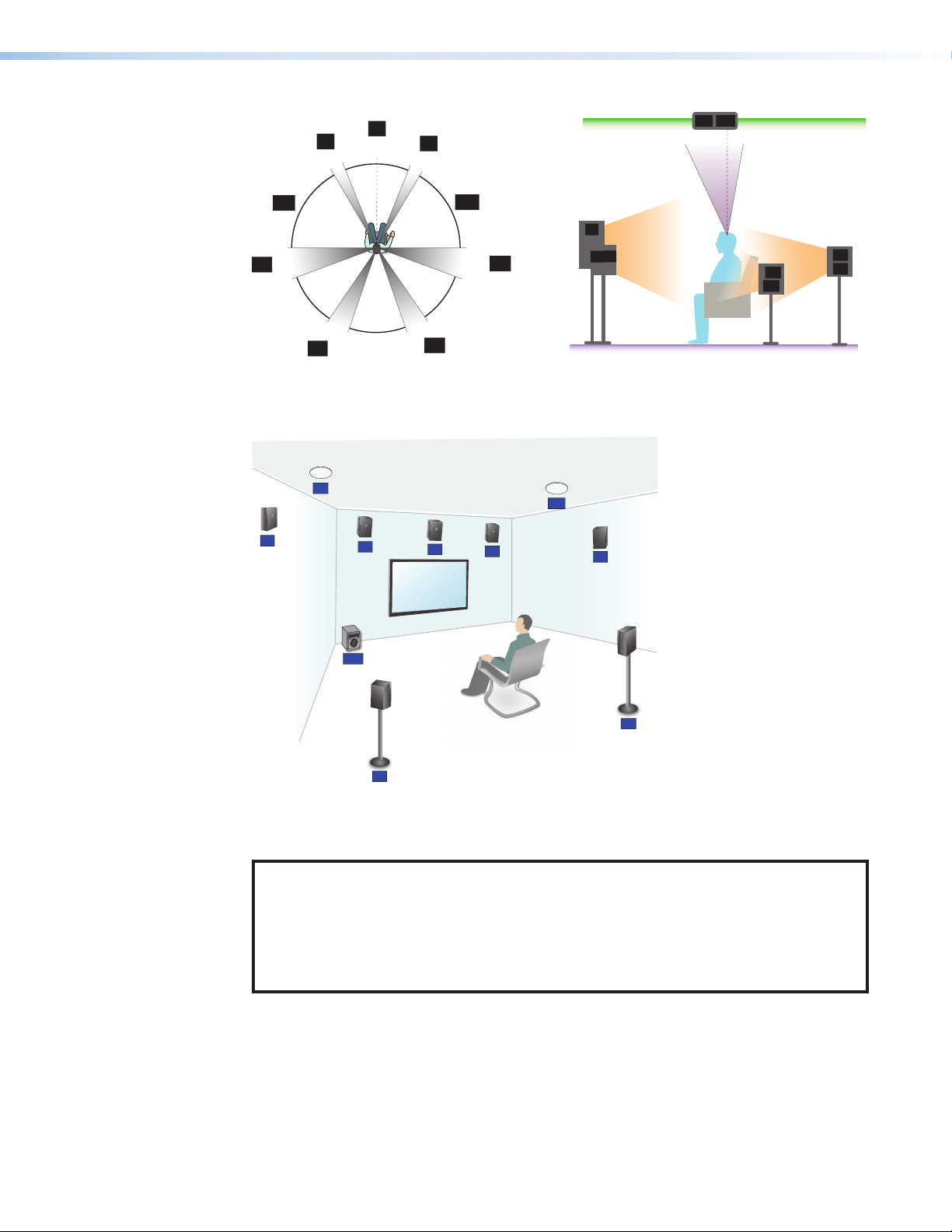
30°
RH
L
22°
0°
22°
R
30°
C
65°
LH
100°
LH
90°
RH
90°
LS
110°
135°
LB
150°
150°
110°
135°
RB
Figure 21. Speaker 7.1.2 Setup
LH
LS
L
C
RS
R
RH
C
L
RS
R
RS
LS
RB
LB
SUB
RB
LB
Figure 22. Subwoofer Placement
NOTES:
• To produce a good bass response, the subwoofer should be located at the front of
the room, somewhere between either corner and a point about one third of the way
along the front wall.
• The output channel used for the Left Back speaker in 7.1 configurations is also
used for the Center Back speaker in 6.1 configurations.
SSP 200 • Speaker Setup 20
Page 29

Back Speakers
Back speakers can only be enabled if the Surround L/R speakers are enabled. Speaker
enablement can be configured within the Speaker Configuration tab of PCS (see
figure37 on page41.
The drop-down list of the Speaker Configuration tab determines whether the audio
output channels for the back speakers are passed to the left back and right back (in 7.1
setups) or to a center back (in 6.1 setups).
To enable a configuration utilizing a center back speaker, the Center and Surround L/R
channels must be enabled, and the Height/Downmix channel must be disabled.
If the two speaker option is selected, then source formats with discrete or matrix mixed 6.1
encoded channels outputs the back channel signal to both the left and right back channels
equally.
By default, the back speaker option is set to 2 Speakers.
Bass Management
Low frequency sound is usually better handled by the subwoofer. Bass management
creates the subwoofer channel by separating the low frequency information from the satellite
speakers at a user-defined crossover point. This is summed with the Low Frequency Effects
(LFE) information encoded in the source format. When no subwoofer is present, subwoofer
content is sent to speakers set to Full Range (excluding the center speaker).
Speaker Settings
This feature sets bass management on or off for a particular speaker, defining the frequency
range output by that speaker (see figure37 on page41). These settings also enable or
disable the subwoofer and set the crossover frequency.
• Left and right front speakers and left and right surround speakers are set in pairs.
• The center speaker is set as an individual speaker.
• Back speakers can be set as a single speaker or as a pair of speakers, depending on
the system configuration.
Bass Management
Small speakers are those which are set to Bass Management. The output to each speaker
(other than the subwoofer) is limited to frequencies above the crossover frequency. By
default, center, surround, and back speakers are set to Bass Management.
Full Range
Large speakers are those which are set to Full Range. The full range of audio frequencies
from the audio source is fed through the output of each individual channel. By default, front
speakers are set to Large.
Subwoofer
This option allows the subwoofer to be enabled or disabled. When the subwoofer is
enabled, the signal contains filtered low frequency signals from speakers set to Bass
Mangement in addition to the LFE signal from the input source. If the subwoofer is disabled,
the LFE signal is mixed with the bass information of all speakers in the system that are set to
Large, except the center speaker.
SSP 200 • Speaker Setup 21
Page 30

Crossover Frequency
The crossover frequency sets the boundary where the low frequency signals from
designated output channels are incorporated into bass management. Low frequency signals
are only taken from speakers that have been set to Bass Management (see Speaker
Settings on the previous page). The bass management signal is passed to the subwoofer
(if present) or speakers that have been set to Large (except for the center speaker) if a
subwoofer is not present.
The crossover frequency can be adjusted within the range of 40Hz to 250Hz, with a default
setting of 100 Hz. Speakers set to Bass Management (see Speaker Settings) output only
signals above the set frequency.
Speaker Delay Settings
There are two different signal delays that compensate for different needs (see figure38 on
page42).
Speaker distance delay — In a room where speakers are not equidistant from the listener,
sound from the closest speaker reaches the listener before sound from the farthest speaker.
This feature allows the user to enter the speaker distance value for each speaker output
channel. The application calculates the delay values for the closest speakers, up to 700ms,
so that all audio arrives at a central location (the “sweet spot”) at the same time.
Lip sync offset — Video delays occur due to changes in programming from a source (TV,
cable, satellite, or Blu-ray player) and also if the video signal has to be processed through
another device between the source and the display. The lip sync offset feature allows the
user to delay the audio sent to all output channels so that video and audio output are
synchronized.
Since each source may need a different level of compensation, the lip sync offset for each
input is independently adjustable from 0.0 to 300.0 ms. Apply lip sync offset to the audio
until what is heard matches what is seen on the display.
Configure these settings using PCS (see Layouts and Speakers on page78).
Test Signals
Test signals are used during setup to calibrate the level for each channel and to ensure
proper connection between the individual output channels of the SSP200 and the line level
input channels of an audio signal processor, a receiver with built in amplifier, or a standalone
amplifier that powers the loudspeakers.
The three options for test signal source are Pink Noise, Dolby Noise, and Active Input.
By default, the test signal is switched Off (see figure39 on page44).
Pink Noise — Pink noise is a signal generated by the SSP200 that provides equal energy
per octave to provide a flat response over all frequencies. The main purpose of pink noise is
to calibrate the interaction of a speaker with its environment.
Dolby Noise — Dolby noise provides a bandpass-filtered noise, centered at 750 Hz with
a 12 dB/octave roll off. This signal is also generated by the SSP200 and is used to set
speakers to the same level when calibrating the room.
Active Input — This option requires an external signal source, such as a signal generator,
played through the selected input source. Generally, this is a device with an analog signal
output, with the SSP200 analog input used as the active input.
Signal generators are usually used to test specific decoding mode outputs. When the
Active Input option is chosen, the speakers that receive the test signal can be specified.
SSP 200 • Speaker Setup 22
Page 31

Output Channel Trim Settings
This control adjusts the output channel trim level for each output channel to match the levels
to the unique needs of any listening environment. The level can be adjusted within the range
from -24 dB to 0 dB. The default setting for each speaker is 0 dB (see Test and Output
Trim on page44 for more information).
Listening Mode Settings
The SSP 200 provides multiple output mode options for each supported input audio format.
By default, the device selects the most appropriate output mode based upon the channel
content of the input format and available output channels. This is referred to as Auto Mode.
The user may override this mode through Product Configuration Software (PCS). For
additional mode information, see Listening Mode Options and Usage on page27.
Equalization
Each analog output channel features a nine band parametric equalizer (or EQ) that allows
the control of amplitude of each band, center frequency (which can be shifted, widened, or
narrowed) and bandwidth (which is labeled “Q” for quality). Parametric equalization is used
to improve the audio output in a specific acoustic environment:
Resonance reduction — Reduces the level at specific frequencies that are too loud.
Speaker compensation — Compensates for peaks and dips in individual speaker output
response.
Tonal enhancement — Increases the level of frequencies within a broad or narrow range
that sound too quiet.
SSP 200 • Speaker Setup 23
Page 32

Reference
This section provides information about the following topics:
• Source Formats
• Listening Mode Options and Usage
Source Formats
Source Formats refer to how audio material is embedded on the digital program.
Blu‑ray and streaming content from such providers as Netflix, Hulu, and others, provide
multi‑channel audio tracks. While digital audio components and analog are converted to
2‑channel PCM audio. The following formats from the two leading theater‑surround formats
come from Dolby Laboratories and DTS. Here is a list of different formats and what you can
expect from them.
Audio Format Maximum Number
Dolby Digital 6 5.1 HDMI, Coax, Optical
Dolby Digital Plus 8 7.1 HDMI, Coax, Optical
Dolby Digital Plus
(Atmos)
Dolby TrueHD 8 7.1 HDMI only
Dolby TrueHD
(Atmos)
DTS (96/24) 6 5.1 HDMI, Coax, Optical
DTS‑ES 7 6.1 HDMI, Coax, Optical
DTS‑HD High
Resolution Audio
DTS‑HD
Master Audio
DTS Express 6 5.1 HDMI, Coax, Optical
DTS:X 8 7.1.4 HDMI only
NOTE: The SSP 200 down mixes any format to match the configuration if the speaker
configuration has fewer channels than discrete audio channels.
Maximum
of Discrete
Channels
8 7.1.4 HDMI, Coax, Optical
8 7.1.4 HDMI only
8 7.1 HDMI, Coax, Optical
8 7.1 HDMI only
Speaker
Configuration
Connection with
SSP 200
SSP 200 • Reference 24
Page 33

Dolby Digital Source Formats
These include inputs 1 to 4 only.
Dolby Digital (2/0, 2/0 Surround, 5.1, Surround EX)
Dolby Digital is a flexible, discrete, digital technology for carrying multi‑channel audio. Dolby
Digital supports up to six discrete audio channels; five full range front and surround channels
and a band‑limited LFE (Low frequency effects) subwoofer channel. Most legacy Dolby
Digital formats are supported by the SSP 200 including ProLogic (I & II), EX, and 2.0. Dolby
Digital formats are 16‑bit with up to 48 kHz sampling.
When the SSP 200 detects this source format the Dolby LED is lit. For stereo only
formats, the 2-CH LED is lit.
Dolby Digital Plus/Dolby Digital Plus Atmos
Dolby Digital Plus and Dolby Digital Plus Atmos are extensions of Dolby Digital with a higher
bit rate and channel count. Dolby Digital Plus supports up to eight discrete audio channels
plus encoded channels including Dolby Atmos immersive Height (ceiling) channels. The
SSP200 supports up to 12 total output channels. This is the preferred format for most
streaming services.
When this source format is present, the Dolby LED is lit. If Dolby Atmos content is
detected within the Dolby Digital Plus bitstream, the ATMOS LED is also lit.
Dolby TrueHD/Dolby TrueHD Atmos
Dolby TrueHD is a variable bitrate lossless codec, capable of supporting up to eight
full‑range channels (7.1) of 24‑bit audio at 96 kHz. Just like Dolby Digital Plus, TrueHD
Atmos content is encoded in the discrete channels. TrueHD formats offer the highest
qualityaudio experience.
When this source format is present, the Dolby LED is lit. If Atmos content is detected
within the TrueHD bitstream, the ATMOS LED is also lit.
DTS Source Formats (DTS)
These include inputs 1 to 4 only, unless otherwise noted.
DTS/DTS 96/24
Like Dolby Digital, DTS is a flexible, discrete, digital technology for carrying multi‑channel
audio. DTS supports up to six discrete audio channels; five full range front and surround
channels and a band limited LFE (Low frequency effects) subwoofer channel. All DTS
formats have 24‑bit depth, which allows more audio information to be stored compared
with the normal 16‑bit depth. DTS 96/24 formats improve audio further by using the 96 kHz
sampling frequency instead of the standard 48 kHz.
When this source format is present, the DTS LED is lit.
DTS ES (96/24, Matrix, Discrete)
Similar to standard 5.1 DTS formats, DTS ES (DTS Extended Surround) includes an
additional Back channel. This sixth channel allows the user to configure mono back
speakers or split it for a 7.1 configuration.
When this source format is present, the DTS LED is lit.
SSP 200 • Reference 25
Page 34

DTS-HD High Resolution Audio
DTS‑HD High Resolution Audio delivers up to 7.1 channels of audio at 96 kHz sampling
frequency and 24‑bit resolution. DTS‑HD High Resolution is implemented as a “base” DTS
stream plus an extension containing two additional channels; in this way, it is compatible
with legacy DTS‑only encoding.
When this source format is present, the DTS LED is lit.
DTS Express
DTS Express delivers up to 5.1 channels of audio at 48 kHz sampling frequency and 24‑bit
resolution.
When this source format is present, the DTS LED is lit.
DTS-HD Master Audio & DTS:X
DTS‑HD Master Audio adds support for lossless audio streams up to a maximum sample
rate of 192 kHz at 24‑bit resolution. It is also the carrier for DTS:X object‑based surround
sound with encoded channels providing content to Height (ceiling) speakers.
When this source format is present, the DTS LED is lit.
If DTS:X content is detected within the bitstream, the DTS:X LED is also lit.
PCM Digital Source Format (PCM)
These include inputs 1 to 4 only.
PCM source formats represent 2‑channel as well as multichannel (up to 7.1) uncompressed,
digital input signals. Multichannel PCM can be processed using only the HDMI input.
When the SSP200 detects a 2‑channel PCM source format, both the PCM and 2‑CH LEDs
light. When a multichannel PCM format is present, only the PCM LED lights.
2-Channel Source Format (2CH)
Analog
This includes input 5 only.
Any balanced or unbalanced stereo signal (or two balanced or unbalanced mono sources) is
accepted. When this input is selected, the front panel 2-CH LED is active.
Digital
These include inputs 1 to 4 only.
When the SSP 200 detects any two channel digital signal (including PCM 2‑channel, Dolby
Digital 2/0, DolbyDigital2/0Surround, or DTS 2‑channel) the 2-CH LED lights.
SSP 200 • Reference 26
Page 35

Sampling Frequency
The following table shows the most common sampling frequencies of digital inputs and the
uses with which they are most often associated.
Sampling
Frequency
(kHz)
32 Used for some cassette recordings, speech, and all other audio where
44.1 Audio CD, also commonly used with MPEG‑1 audio (VCD, SVCD, MP3).
48 Digital sound used for mini DV, digital TV, DVD, DAT, films, and professional
88.2 Sampling rates used by professional recording equipment when the
96 DVD‑Audio, some LPCM DVD tracks, DTS 96/24, and DTS 96/24
192
Use
smaller files are desired, with only slight compromise on sound quality. In
the past, used with products such as NICAMs.
Adopted from the PCM adaptor using PAL video tapes (294 lines by 3
samples by 50 frames per second).
audio.
destination is CD (multiple of 44.1 kHz).
ESMatrix6.1 source formats always output this sampling frequency.
Blu‑ray and HD‑DVD, Dolby TrueHD and DTS‑HD Master Audio output
this sampling frequency when there are six discrete channels.
Listening Mode Options and Usage
Listening Mode Options
The SSP 200 listening modes allow users to upmix or downmix audio content to match
their speaker configuration. By default, all listening modes are set to Auto. The auto setting
maximizes source formats to the required speaker configuration based on what is available
in the room. For example, Dolby Atmos or DTS:X downmixes to 5.1 if there are only 5 full
range speakers and a sub‑woofer in the speaker configuration.
Source formats that natively use fewer speakers such as an analog source or the original
5.1 release of older DVDs can be upmixed so all of the speaker channels are utilized.
Auto
The SSP 200 selects an appropriate output mode based on input format and available
ouput channels. The encoded channels pass through to the outputs if the required output
channels have been enabled in the speaker configuration. Otherwise, the encoded channels
are downmixed accordingly.
Stereo
This mode plays a stereo source in its pure, unprocessed form. Multichannel formats are
downmixed to a stereo output signal.
Mono
This mode plays mono source material or stereo source material that has been mixed to
a mono form. It can be used to downmix a multichannel source format into a single mono
output signal.
Additionally, the user can select whether the mono signals are output to the center channel
(Center Only) or a dual mono signal is sent to the right and left front channels (Front L+R
Only). The default option is Front L+R Only.
SSP 200 • Reference 27
Page 36

Stereo to All
This mode plays stereo or downmixed stereo sources through all output pairs in the system.
Mono to All
This mode plays mono or downmixed mono sources to all outputs in the system.
Dolby Surround
The Dolby Surround upmixing engine is utilized to upmix input audio to some or all available
output channels.
DTS Neural:X
The DTS Neural:X upmixing engine is utilized to upmix input audio to some or all available
output channels.
SSP 200 • Reference 28
Page 37

Product Configuration Software
The SSP 200 surround sound processor can be configured using Extron Product
Configuration Software (PCS). This section describes:
• Downloading PCS from the Extron Website
• Using PCS Software
• Updating Firmware Using PCS
Downloading PCS from the Extron Website
Visit www.extron.com to download and install the PCS software. An Extron Insider
Account is required and then the PCS program can be downloaded free of charge.
NOTE: Also you can download the latest version of firmware for your product (see
Updating Firmware Using PCS starting on page58).
1. Mouse over the Download tab at the top of the homepage (see figure23, 1).
Figure 23. PCS Software Link on Download Tab
2. Click the Software link (
Product Configuration Software link (
The PCS window opens with the current available version (see figure24).
) or, if the software is listed, click directly on the PCS
2
).
3
Figure 24. PCS Software Download Link
3. Click Download (1) and follow the on‑screen instructions.
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 29
Page 38

Using PCS Software
Connecting to the SSP 200
1. Ensure that PCS is installed on the control PC (see Downloading PCS from the
Extron Website on page29).
2. Connect the PC to the SSP 200 processor. PCS communicates with the SSP 200 via
the front panel configuration port with a standard USBmini‑B port (see Connecting
to the USB Port on page16), the rear LAN connector, or the rear panel RS‑232
connector.
3. Open PCS on the PC from the PCS icon loaded on the desktop (optional,
see image on the right) or from the Start menu, click Start > Programs > Extron
Electronics > Extron Product Configuration Software.
The Product Configuration Software opens to the Device Discovery screen (see
figure25). Devices that are either networked or connected to the PC via USB are listed.
Figure 25. PCS Device Discovery Screen
4. Select the SSP 200 device by clicking on it to highlight it in the list (1).
5. Click Connect (2).
The Product Configuration Software opens to the device main menu (see
figure26 on the next page).
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 30
Page 39

Main Menu
NOTE: The SSP 200 tab (top left) has a green indicator, indicating that the deivce
connection is live.
Figure 26. SSP200 PCS Main Menu
The configuration pages have a global navigation bar from which each of the individual
configuration pages can be accessed.
These tabs are:
Input/Output Config
1
EDID Minder
2
The I/O Panel (5) is always available and can be collapsed by clicking the arrow button on
the top right of the panel.
Audio Config
3
General Settings
4
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 31
Page 40

I/O Panel
The I/O Panel on the left side of the main window allows you to select an input and see its
current status. The fader on the bottom portion is the Main Volume. This sets the volume
level for all active speaker outputs of the SSP 200. Below the Main Volume fader is a Mute
button that mutes all active speakers (see figure27).
The master volume can be adjusted between 0% and
100%. The current volume setting is displayed in the text
box. The volume can be changed in any of the following
ways:
• Grab and drag the slider bar to adjust volume in 1%
steps.
• Click the slider bar to make it active and use the up
and down arrows beside the text box to adjust the
volume in 1% steps.
• Click in the text box and type a desired volume
percentage in 1% steps. Do not type the “%”
character.
• Click the slider bar to make it active and use the <up
arrow> and <down arrow> keys on the keyboard to
adjust the volume in 1% steps.
• Click the slider bar to make it active and use the
<Page Up> and <Page Down> keys on the keyboard
to adjust the volume in 5% steps.
The Mute button toggles between muting or unmuting all
channel outputs.
NOTES:
• Switching inputs disables the mute function and
restores the volume setting.
• The round indicator at Input Select buttons
1 through 4 turn green when the input selected
has an active input.
• Input Select buttons 2 through 4 show EXP
if the user configures an input to be replaced.
Figure 27. I/O Panel
• The round indicator at the Input 5 button
turns red when the analog input signal is
clipping.
Input/Output Config
The Input/Output Configuration panel allows the user to configure the active input and
output signals (see figure28 on the next page).
Input Configuration
The Input Configuration panel allows you to view the Resolution and HDCP Status of
the HDMI input and set the input to HDCP Authorized.
In addition, the panel allows you to enable and set the DMP EXP Input and adjust the gain
for Analog Input 5.
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 32
Page 41

Figure 28. Input/Output Configuration Panel
HDMI Input 1
Resolution — Displays the resolution of the HDMI input.
1
HDCP Status — Indicates the HDCP status of the input source. The HDMI input
2
negotiates and authenticates HDCP with the source device if the source requires HDCP
encryption.
Symbol Definition
The signal is HDCP encrypted.
The signal is not encrypted.
HDCP Authorized — Select this checkbox to turn HDCP Authorized on (default)
3
or off. When disabled (Off), the source is blocked from encrypting its output. This may
result in some content not being passed to the output.
DMP EXP Input
Replace Input channel — Enables the EXP Input by replacing one of the selectable
4
input channels Input 2 (Coaxial), Input 3 (Optical), or Input 4 (Optical).
Set EXP Input channel pair — Sets the EXP Input channel pair to two of the 16
5
possible audio channels.
Analog Input 5
Analog Input Gain — Adjusts the gain of the signal on Input 5. When Input 5
6
(Analog) is selected, the Analog Input Gain controls are available to adjust the gain
either by adjusting the fader manually or by entering a gain value in dB.
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 33
Page 42

Output Configuration
HDMI Loop Out
Audio — Establishes which audio stream is routed to the HDMI Loop Out. The three
7
options are No Audio, Follow Input audio, or the Downmix audio.
HDCP Status — Indicates the HDCP status of the output device. The HDMI input
8
negotiates and authenticates HDCP with the sink device, if the sink requires HDCP
encryption.
HDCP Mode — Allows the user to either Always Encrypt Output or to Follow
9
Input. When Always Encrypt Output is selected, the digital input reports as an
HDCP authorized sink to a source. For source devices that require encryption, enable
the HDCP Authorized checkbox (see figure28, 3, on the previous page).
Listening Mode Setup
This panel allows you to adjust the listening mode depending on the input and source
format (see figure29).
Figure 29. Listening Mode Setup
Listening Mode Setup — This drop‑down list allows you to select which input you
1
want to set the listening modes.
Input Source Format/Listening Mode — These drop‑down lists allow you to select
2
which listening mode you want to assign for each input source format within the
selected input.
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 34
Page 43

EDID Minder
EDID Minder manages the EDID information of the HDMI input. Click the EDID Minder tab
on the global navigation bar to open the EDID Minder page.
This section includes the following:
• EDID Minder Panels
• EDID Filters
• Adding EDID to the Favorites Panel
• Importing EDID to the EDID Library
• EDID Assignment
• Searching for EDID by Name
• EDID Report
The EDID properties currently assigned to the HDMI input are displayed in the list of inputs.
The audio input format listed in an EDID is determined by the audio input format selected on
the Audio Configuration page (unless a custom EDID is used).
NOTE: If an analog custom EDID file is assigned to a digital input or a digital custom
EDID file is assigned to an analog input, the display may not appear correctly.
Figure 30. EDID Minder
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 35
Page 44

EDID Minder Panels
• Filter — Displays various filters that can be enabled to easily locate specific EDID (see
figure31).
Figure 31. Filter Panel
• Favorites — Displays commonly used EDID which can be added to the panel for quick
access (see figure32).
Figure 32. EDID Favorites Panel
• Connected Outputs — Displays the EDID (color‑coded green) of the output connected
to the SSP 200 HDMI Thru port (see figure33).
Figure 33. Connected Outputs Panel
• Available EDID — Displays the available EDID located on the connected unit or the
local PC (see figure34).
• Blue ‑ Extron factory‑default EDID
• Yellow ‑ Custom user‑saved EDID
Figure 34. Available EDID Panel
• INPUTS — Displays the current EDID of the connected input (see figure35).
Figure 35. Inputs Panel
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 36
Page 45

EDID Filters
The filters can be used to easily locate specific EDID.
Applying a Filter
1. Navigate to the Filters panel on the EDID Minder screen.
2. Select an EDID setting from the drop‑down list of the associated filter.
The available EDID that match the filter selection are displayed in the library.
3. Repeat step 2 to apply more filters.
Clearing Applied Filters
To reset all the filters, click the Clear button.
Adding EDID to the Favorites Panel
Commonly used EDID can be added to the Favorites panel for quick access.
1. Navigate to the Favorites panel on the EDID Minder screen.
2. Click and drag the desired EDID to the Favorites panel.
The EDID is copied to the Favorites panel.
EDID can also be added to the Favorites panel by right‑clicking the desired EDID and
selecting Copy, then pasting the selected EDID into the Favorites panel.
Importing EDID to the EDID Library
Non‑factory‑default Extron EDID files can be imported into the local EDID library that is
locally stored on the connected PC.
Accessing the EDID library
1. On the EDID Minder screen, navigate to the top right of the Available EDID panel.
2. Click the blue link (highlighted in red box).
The EDID library on the local PC opens.
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 37
Page 46

Accessing a non-factory default EDID into the EDID library
1. On the EDID Minder screen, navigate to the Add EDID to Library button to the
right of the Available EDID search box.
2. Click Add EDID to Library. The Browse Add EDID to the Library pop‑up
window opens.
3. Locate the previously saved EDID file (EDID files have .BIN extensions) to be added to
the EDID library and click Open.
4. The following pop‑up window displays, indicating that the EDID file was added to your
EDID library. Click Close to continue using the software.
EDID Assignment
The following can be assigned to the inputs of the connected SSP 200:
• Extron factory‑default EDID
• EDID from the display connected to the SSP 200 output port
• Non‑factory default EDID that have been imported or saved to the PCS EDID library
Assigning a Factory-Default Extron EDID
1. Navigate to the Available EDID panel on the EDID Minder screen.
2. Select the desired EDID (represented by a blue display icon).
3. Select the check box for Input 1 on the INPUTS panel.
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 38
Page 47

4. Click Assign. The EDID is assigned to the input and is displayed in the INPUTS panel
Alternately, click Assign to All on the INPUTS panel if you would like to assign the
same EDID to all inputs.
EDID can also be assigned by dragging and dropping the desired EDID directly onto the
Inputs panel.
Assigning a Non-Factory-Default EDID
1. Navigate to the Available EDID panel on the EDID Minder screen.
2. Select the desired EDID (represented by a orange display icon).
3. Select the check box for Input 1 on the INPUTS panel.
4. Click Assign. The EDID is assigned to the input and is displayed in the INPUTS panel
Alternately, click Assign to All on the INPUTS panel if you would like to assign the
same EDID to all inputs.
EDID can also be assigned by dragging and dropping the desired EDID directly onto the
INPUTS panel.
Assigning EDID from a connected output
1. Navigate to the Connected Outputs panel on the EDID Minder screen.
2. Click the EDID displayed (represented by a green display icon).
3. Select the check box for Input 1 on the INPUTS panel.
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 39
Page 48

4. Click Assign. The EDID is assigned to the input and is displayed in the INPUTS panel
Alternately, click Assign to All on the INPUTS panel if you would like to assign the
same EDID to all inputs.
EDID can also be assigned by dragging and dropping the desired EDID directly onto the
INPUTS panel.
Searching for EDID by Name
1. On the EDID Minder screen, navigate to the search box located at the top of the
Available EDID panel (highlighted in red box).
2. Start typing the name of the desired EDID. Only EDID that contain the entered text are
left in the Available EDID panel.
EDID Report
Click the EDID Report tab to view the translated data contained within the selected EDID
file (see figure36).
Figure 36. EDID Report Tab
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 40
Page 49

Audio Config
The Audio Configuration page has four tabs.
NOTE: The Audio Configuration tabs should be adjusted in the order they appear.
• Speaker Configuration
• Speaker Delay
• Test and Output Trim
• Speaker Equalization/Output EQ
Speaker Configuration
Click the Audio Config button (see figure26, 3, on page31). The Audio
Configuration window opens to the Speaker Configuration panel (see figure37).
Figure 37. Speaker Configuration
The various controls can be adjusted to configure the speakers as needed.
Speaker Enablement — This feature determines which output speaker channels
1
are enabled and pass audio. There are additonal drop‑down lists for Back and Height
speakers in those positions or if a stereo downmix on the analog output is required.
Bass Management/Full Range — This selection is only enabled when its
2
corresponding speaker channel is enabled. When Bass Management is selected, only
frequencies above the crossover frequency threshold is sent to the corresponding
speaker channels. When Full Range is selected, all frequencies are sent to the
corresponding speaker channels.
Crossover Frequency — When Bass Management is selected for a particular
3
channel, the frequencies below this threshold are sent to the subwoofer channel (or
Full Range speaker channels when the subwoofer channel is disabled) and the
frequencies above this threshold are sent to the speaker channel.
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 41
Page 50

Configuration Display — This graphics box shows which speaker channels are
4
active (see figure37 on the previous page). Only the speakers enabled are displayed.
If Full Range is selected for a particular channel then the speaker is represented by a
large icon. If Bass Management is selected for a particular channel then the speaker is
represented by a small icon.
Speaker Delay
These controls introduce a signal delay for each enabled speaker (see figure38). The two
main reasons to adjust the signal delay are:
• To compensate for unequal distances between the speakers and the listener, which
causes sound from different speakers to reach the listener at different times.
• To compensate for a lack of coordination between the audio and the accompanying
video signal.
Figure 38. Speaker Delay
Speaker Distance
When speakers are arranged in a room, there is a central location or “sweet spot” that
offers the best listening point. However, even in that central location, the speakers are not
necessarily all equidistant from the listener, and the sound from the closest speaker reaches
the listener before the sound from speakers that are further away.
Speaker distance settings delay the signals going to each individual speaker (from 0 to
700 ms) so that the signals from all the speakers are synchronized and reach the listener
simultaneously. The default setting for each speaker is 0 ms.
Speakers that are not available in the current configuration are not displayed. When the
back surround is set to one speaker, the right back speaker is unavailable and the left back
speaker is renamed as the center back.
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 42
Page 51

Use PCS to set speaker delays, using either of the following methods.
Two Person Setup
NOTE: Setting up speaker delays is easier with two people. If only one person is
available, the position of the ears of the listener must be marked precisely. A pile of
boxes could be used to ensure that the distances are consistently measured to the
correct height. Do not try to guess ear positions, as this introduces measurement
errors.
1. Pick an ideal central location where all speaker output signals converge.
2. Use a tape measure to measure the distance from each speaker to the convergence
location. Be sure to measure to the same spot from each speaker.
NOTE: Measurements from the speaker must be to the midrange driver in a three‑way
speaker or from halfway between the tweeter and the woofer in a two‑way speaker.
Measurements to the convergence location must be at ear height.
3. In the Unit of Measure box, click the Feet (ft) or Meters (m) radio button to
select the units and enter the Speaker Distance values for each speaker in the boxes.
The up and down arrows increase the distance in increments corresponding to steps of
0.1 ms (0.12 feet or 0.03 meters). The software automatically determines the farthest
speaker and calculates the delay time (in milliseconds) for each speaker.
These values are shown in the Calculated Delay box. The current values are shown
in blue, changes (yet to be saved) are shown in orange.
4. After all of the speakers have their measurement entered, the Apply button appears.
Click the button to save the changes. The new values (previously in orange) are shown
in blue as the current values and there are no values displayed in orange.
To retain the original values, click Cancel instead of Apply.
Setup with a Real Time Analyzer (RTA) calibration tool
1. Choose an ideal central location on which all speaker output signals converge.
2. Place the microphone from the RTA at ear level in the convergence location.
3. Select Active Input on the Test & Output Trim tab (see figure39 on the next
page).
4. Play the audio source. This can be an analog source, provided by the RTA.
5. Use the Test Signal Output buttons in the Test & Output Trim tab to select
which speakers are tested and the order in which the speakers are tested.
6. Use the RTA to measure the speaker distance (in ms) for each channel.
7. In the Unit of Measure box on the Speaker Delay tab, select the Milliseconds
(ms) radio button and enter the values for each speaker (in ms) into the boxes. The up
and down arrows increase the distance in increments of 0.1 ms.
These values are shown in the Calculated Delay box. The current values are shown
in blue, changes (yet to be saved) are shown in orange.
8. Repeat steps 5 through 7 until the speaker distance has been entered for all available
speakers.
NOTE: The maximum allowable distance for the furthest speaker is 700 ms
9. Click Apply. New values are shown as the current values, in blue. No values are
displayed in orange.
To retain the original values, click Cancel instead of Apply.
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 43
Page 52

Lip Sync Offset
Lip sync offset compensates for a lack of coordination between the audio and the
accompanying video signal. This frequently occurs if the video signal has undergone
complex manipulation that can delay it several milliseconds relative to the audio signal.
Since some sources may require more manipulation than others, the Lip Sync Offset
is set for each source individually to synchronize the audio for that source with the
corresponding video signal.
Enter the appropriate value for each input in the corresponding Lip Sync Offset box.
This delay is added to every available speaker to resynchronize the video and audio signals.
Test and Output Trim
Click the Test & Output Trim tab to access the various output controls (see figure39).
Figure 39. Test and Output Trim
Several factors can affect the sound level reaching the listener from different speakers.
These factors include the distance from the speaker to the listener, slight variations between
the output channels of a single amplifier, and variations between the individual speakers.
Use the output trim to set the output level of each individual channel to compensate for all
these variations and ensure that the sound level reaching the listener is the same from all
speakers.
This page also provides a test signal utility.
Test Signal Output
Test signals are used during setup to calibrate the level of each channel and to ensure
proper connection between the individual output channels of the SSP 200 and the line level
input channels of an audio signal processor, a receiver with a built in amplifier, or a stand
alone amplifier that powers the loudspeakers.
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 44
Page 53

Selecting test signal source
There are three test signal options: Dolby Noise, Pink Noise, or Active Input. They
are selected from the mutually exclusive Signal Type buttons. The Dolby Noise and
Pink Noise test signals are generated by the SSP 200.
NOTE: If the active input is selected as the test signal, then its listening mode is set to
Mono to All when the test sequence is active. Its listening mode is automatically
restored once the test sequence is set to Off.
Selecting speakers to be tested
The speakers enabled in the speaker configuration are displayed in the Send Test Signal
panel. Speakers that are not enabled are not displayed. Clicking on a speaker within the
graphics box selects or deselects it from the list of speakers to be tested. For an example,
the Right Back (RB) speaker in the illustration below has been deselected.
Speaker test sequence
To run an automatic test sequence:
1. Select the Automatic button.
2. Select the On button to start the test sequence. This sends the selected test signal to
each speaker channel individually. Each speaker channel receives the test signal for
two seconds before the test signal is routed to the next channel in the sequence. In
the example below, the Left Surround (LS) speaker is shown currently receiving the test
signal.
3. Select the Off button to switch off the test signal and end the test sequence.
To test the speakers manually:
1. Select the Manual Selection button.
2. Select the On button to start the test sequence.
3. Select a speaker in the graphics box to route the test signal to that speaker channel.
4. Select the Off button to switch off the test signal and end the test sequence.
NOTE: Enabling the global Mute in the I/O Panel disables an active test sequence.
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 45
Page 54

Output Trim
The Output Trim sliders control the audio signal level for each individual channel output.
Only channels that are enabled in the current speaker configuration are available. Output
trim is adjustable from -24 dB to +0 dB. The current value for each output channel is shown
in the text box.
Extron recommends using a Sound Pressure Level (SPL) meter to set the output trim for
each speaker:
1. Set up the SPL meter at the sweet spot in the room.
2. Send a test signal, generated as described in Test Signals on page22, to each
individual speaker in turn. Extron recommends using the Dolby Noise signal and
sending the signals to the speakers manually.
NOTE: The test signal should have a sound level at least 20 to 30 dB above
ambient levels.
3. Measure and write down the sound pressure for each speaker.
4. To avoid decreasing the maximum output volume (see the note above), Extron
recommends that you use the speaker with the lowest SPL reading as the zero
reference point. Then attenuate all the other speakers by the required amount to
balance all speakers.
In the following table, the SPL readings for five channels are given in second column.
Channel 4 has the lowest reading and is used as the zero reference point. The
difference between each speaker and the zero reference is calculated in column 3. This
is the adjustment that must be made to the output trim for that channel.
Channel SPL Reading Output Trim Adjustment (dB)
1 75 -1
2 76 -2
3 79 -5
4 74 0
(zero reference channel)
5 77 -3
5. Use any of these methods to adjust the output trim for each speaker.
• Grab and drag the slider bar to adjust output trim in 1 dB increments.
• Click the up and down arrows besides the text box to adjust it in 1 dB increments.
• Click one of the output trim slider controls to activate it and use the <up arrow>
and <down arrow> keys on the keyboard to adjust it in 1 dB increments.
• Click one of the output trim slider controls to activate it and use the <Page Up> and
<Page Down> keys on the keyboard to adjust it in 5 dB increments.
• Highlight the value in the text box, type a number (omit the dB), and press <Enter>
on the keyboard.
The Reset button returns the output trim values for all speakers to the default value (0 dB).
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 46
Page 55

Speaker Equalization/Output EQ
The Output EQ tab brings up the Speaker Equalization that provides nine parametric
EQs for each output channel (see figure40).
Figure 40. Speaker Equalization/Output EQ
The default frequency values correspond to a nine‑band graphic equalizer, which provides a
starting point for refining the output signal from each speaker channel.
All the properties of the SSP 200 parametric filters can be adjusted by the user.
The numbers are used to select the filters for utilizing the copy/paste function or to change
the focus on the graph to the left. Filters are automatically selected when a parameter is
adjusted.
The Active column has toggle buttons for activating (or unbypassing) a filter. A filter only
affects the signal if it is active (blue).
Speaker Selection
To begin the adjustment, first select the speaker to be configured from the Speaker
Equalization For drop‑down list.
Figure 41. Speaker Selection
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 47
Page 56

Filter Parameters
These four fields (on the right side of the page) control the parameters that can also be
adjusted in the graph.
• Filter number — Selects a filter to display on the graph or copy and paste functionality.
• Frequency — Adjusts the center frequency of the filter.
• Boost/Cut — Adjusts the amount of amplification or attenuation applied to that specific
filter.
• Q — Adjusts the bandwidth to where the boost or cut is applied. As the Q value
increases, the bandwidth becomes narrower.
NOTE: When values are altered in the filter parameter fields, the graphic display is
updated to reflect the changes.
Modifying Filter Parameters
The graph in the Filter dialog box displays a graphical representation of the selected and
composite filters.
• An orange line indicates the composite curve of all active filters.
• A blue line indicates the selected filter.
• Inactive filters do not contribute to the orange composite curve. However, when
selected, an inactive filter appears as a dotted line independent of the composite curve.
To modify Frequency
1. In the Filter dialog box, select the filter to be modified. To do so, either click the filter
number at the left of the Filter menu (figure42) or click the appropriate Frequency
handle below the graph (figure43).
Figure 42. Filter Menu
Figure 43. Frequency Handles
2. Click and drag the Frequency handle left or right to desired position or value.
Alternatively, enter the value in the Frequency field for the selected filter, or click the up
or down arrows next to the field until the desired value is displayed.
To modify Boost/Cut (Parametric):
1. In the Filter dialog box, select the filter to be modified. To do so, either click the filter
number to the left of Filter menu or click the appropriate Frequency handle below
the graph.
2. Click and drag the Boost/Cut handle, located at the center frequency in the graph (see
figure44 on the next page), up or down to the desired position or value. Alternatively,
enter the value in the Boost/Cut field for the selected filter, or click the up or down
arrows next to the field until the desired value is displayed.
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 48
Page 57

Figure 44. Center and Outer Handles
To modify Q (Parametric filters):
1. In the Filter dialog box, select the filter to be modified. To do so, either click the filter
number to the left of Filter menu or click the appropriate Frequency handle below the
graph.
2. Click and drag one of the Q handles within the graph, located at the lower or upper
frequency on the filter curve, left or right to the desired position or value.
Alternatively, enter the value in the Q field for the selected filter, or click the up or down
arrows next to the field until the desired value is displayed.
EQ Filter Copy and Paste
Copy and Paste buttons are available to streamline your repeat filter settings. The buttons
are located at the bottom right of the page.
Figure 45. EQ Filter Copy and Paste Buttons
To copy and paste a setting:
1. Click a number to select filter settings to copy.
2. Click the Copy ( ) button.
3. Click a different filter number to paste.
4. Click the Paste ( ) button.
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 49
Page 58

General Settings
General Settings
Click the General Settings button (see figure26, 3, on page31).
The General Settings panel (see figure46) allows you to adjust:
• Dolby Settings
• DTS Settings
• Dynamic Range Compression
• Mono Settings
• Front Panel Lockout (Executive Mode)
The General Settings panel also allows you to access:
• Hardware Settings
• Communication Settings (after opening the Hardware Settings panel)
Figure 46. General Settings
Dolby Settings
Depending on the listening environment, listener preference, or both, reducing the dynamic
range of an audio program may be desirable. To limit the dynamic range, Dolby TrueHD
DRC Mode applies dynamic range compression to the Dolby TrueHD audio content. When
dynamic range compression is applied, the high audio levels of content are cut (attenuated)
and the low levels are boosted (amplified).
Using the Virtualizer Mode on a Dolby signal gives you the effect of a virtual height
and surround effect from traditional speaker layouts without the use of height speakers in
systems with more than 2 channels.
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 50
Page 59

DTS Settings
The DTS Dialog Control setting determines the amount of gain increase (in dB) for the dialog
audio tracks in a DTS:X stream. This is useful for movies where the dialog is perceived as
too quiet when compared to the music or score.
Dynamic Range Compression
This setting determines the amount of compression applied. This setting does not apply to
Dolby TrueHD streams.
Mono Settings
This setting determines how the SSP 200 outputs its mono channels when a mono listening
mode is selected, either the center channel or both the front left and right only.
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 51
Page 60

Front Panel Lockout (Executive Mode)
This setting determines what functionality is available on the front of the device.
• Unlock Front Panel — Allows all of the buttons to operate normally.
• Mode 1 — Removes the functionality of every button on the front of the device.
• Mode 2 — Limits front panel functionality to just volume control.
• Mode 3 — Limits front panel functionality to just input selection.
Hardware Settings
Click the Hardware Settings button (see figure46 on page50) to access the Unit
Information, Device Name, Date and Time, and Password panels.
Unit Information
The Unit Information panel gives a non‑configurable view of information about the
connected device (see figure47 on the next page).
The following device information is displayed:
• Part number
• Model name
• Model description
• Firmware version
• Temperature (inside device)
• Device name
• DHCP status
• IP address
• Subnet mask
• Default gateway address
• DNS server
• MAC address
Click Edit Communication Settings (1) to go to the Communication Settings
panel. Click Cancel (2) to return to the General Settings panel.
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 52
Page 61

Figure 47. Hardware Settings: Unit Information
Device Name
The Device Name panel allows you to assign or change the name or hostname of the
connected device (see figure48).
Figure 48. Hardware Settings: Device Name
NOTE: The device name is used as the hostname of the SSP 200.
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 53
Page 62

To assign or change the hostname:
1. Enter a name for the device in the name field (see figure48, 1, on the previous page).
This name can be up to 63 characters in length with no spaces between characters.
Only alphanumeric characters and the hyphen are valid. The first character must be
alphabetical, and the last one cannot be a hyphen (–). If an invalid name is entered, a
red symbol appears to the right of the name field.
2. Click the Apply button (2) to change the name or click the Cancel button (3) to keep
the previous name.
To reset the device name to the default: Click the Reset to Default button (4).
The default device name consists of the model name, followed by the last three
hexadecimal character pairs of the product MAC (hardware) address. All parts of the
name are separated by hyphens (for example: SSP-200-FF-FF-FF).
Date and Time
1. Click the Date and Time button to access a menu to change the date, time, and
time zone of the device (see figure49). You can also click the Sync to PC button to
synchronize the device with a connected computer to align the current date and time.
2. Click the Apply button when done. Or click Cancel to return to the previous menu with
no changes.
Figure 49. Hardware Settings: Date and Time
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 54
Page 63

Password
The Password panel (see figure50) allows the user to set an administrator and user
password on the device. Administrators and users can view all settings on the device.
Administrators have the ability to make adjustments to any setting. Users can make
changes to a limited subset of settings.
Figure 50. Hardware Settings: Password
NOTES:
• A username is required to access the internal web pages or the device through the
PCS program. When prompted, enter admin as the username for administrator
passwords or user as the username for user passwords.
• A password can be up to 128 characters in length. All man‑readable characters
are permitted except “|”. Password cannot be a single space. Passwords are
case‑sensitive.
• The factory configured passwords for all accounts on this device have been set to
the device serial number. Passwords are case sensitive. If the SSP 200 is reset, the
passwords revert to the default, which is extron.
To create or change an administrator password:
1. In the Administrator Password field (1), enter the desired administrator password.
2. In the Confirm Password field (2), reenter the administrator password.
3. Click the Apply button (3).
To create a user password:
NOTE: A user password cannot be set until an administrator password has been set.
1. In the User Password field (4), enter the desired user password.
2. In the Confirm Password field (5), reenter the user password.
3. Click the Apply button (3).
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 55
Page 64

Communication Settings
Click the Edit Communication Settings button (see figure47, 6, on page53) on
the Hardware Settings panel to open the Communication Settings dialog box.
The Communication Settings dialog box (see figure51) allows you to view and adjust
device settings for RS‑232 and Ethernet connections.
Figure 51. Communication Settings
If you do not want to implement any changes, click Cancel (9) to return to the General
Settings panel or click the Go To Hardware Settings button (6) to return to the
Hardware Settings panel.
The Use DHCP check box (1) directs the SSP 200 to ignore any entered IP addresses
and obtain an IP address from a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server (if the
network is DHCP capable). Contact the local system administrator to determine if this is the
appropriate selection. Click the Apply button (8) to make changes take affect.
The device MAC address (6) is also displayed on this panel though it cannot be changed.
To configure the Ethernet settings for use with DHCP:
1. Select the Use DHCP checkbox (1).
2. Click the Apply button (8).
To configure the Ethernet settings with a static IP address:
1. Ensure the Use DHCP checkbox (1) is not selected.
2. In the IP Address field (2), enter an IP address.
3. In the Subnet Mask field (3), enter the subnet mask if required.
4. In the Default Gateway field (4), enter the default gateway if required.
5. In the DNS Server field (5), enter a DNS server name if required.
6. Click the Apply button (8).
To cancel changes, at any time, click the Cancel button (9) to keep the last saved
settings.
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 56
Page 65

Device Menu
Reset Device
The Device menu (see the imageon the right) allows the user to:
Disconnect the device from PCS.
1
Open the Hardware Settings or
2
Communication Settings.
Reset Device to factory default.
3
Update Firmware.
4
View the SSP-200 Help file.
5
View information About this Module.
6
This function resets all device settings to factory defaults with or without retaining the TCP/
IP settings.
To reset the device:
1. From the drop‑down Device list, select Reset Device....A dialog box opens (see
figure52).
2. Select from the three reset options shown in the figure.
3. Click Reset to perform the reset or Close to cancel the operation.
Figure 52. Reset Device
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 57
Page 66

PCS Help File
For assistance, Extron PCS Help contains
information about using the program to configure
the SSP200.
To access Extron PCS Help, click the button in
the right corner of the PCS program screen (see
the image on the right, 1) and click
Extron PCS Help (2).
Updating Firmware Using PCS
Firmware for the SSP 200 can be updated using PCS. Updates to the SSP200 firmware
are made available periodically via the Extron website. You can find out what version
of firmware is currently loaded on your SSP200 by entering the SISQcommand via the
RS‑232, USB, or LAN interface (see Firmware Version/Part Number/Information
Queries on page69) or listed in Hardware Settings in PCS (see Hardware Settings
on page52).
Downloading the SSP 200 Firmware
To download the latest version of firmware for the SSP200:
1. Go to www.extron.com, and mouse over the DOWNLOAD tab (see figure53,1).
Figure 53. Download Tab
2. Click the Firmware link (2) from the drop‑down list. The Firmware page opens (see
figure54).
Figure 54. Firmware Page with the Alphabetic Navigation Bar
3. Click the letter S on the alphabetic navigation bar (1).
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 58
Page 67

4. Scroll down the page until you locate the firmware for the SSP 200.
2
5. Click Download. The product download screen opens.
6. Enter the required user login information. An executable (.exe) file downloads to the PC.
Run this program to place the firmware on the PC. Make a note of the folder where the
firmware file was saved.
ATTENTION:
• The extension of the firmware file must be .eff. Opening a file with an incorrect
extension may cause the device to stop functioning.
• L’extension du fichier firmware doit être .eff. Si un fichier est ouvert avec une
mauvaise extension, l’appareil peut arrêter de fonctionner.
Loading the Firmware to the SSP200
To load a new version of firmware to the SSP200 using PCS:
1. Connect your computer to the SSP200 via either the device rear RS‑232 or LAN port
(see Rear Panel Features starting on page6) or the front panel USB Config port
(see Front Panel Features starting on page11).
2. If needed, download and install PCS to your computer (see Downloading PCS from
the Extron Website on page29).
3. If needed, download the latest version of SSP200 firmware to your computer (see
Downloading the SSP 200 Firmware on page58).
4. Open PCS by clicking the desktop icon, if available or using your desktop Start menu
to make the following selections: Start > All Programs > Extron Electronics >
Extron Product Configuration Software.
The Product Configuration Software window opens to the Device Discovery
screen (see figure55).
SSP 200 192.168.254.254 SSP 200
111
2
2
Figure 55. PCS Device Discovery Screen
5. On the Device Discovery screen, select the SSP 200 (1).
6. Click Connect (2).
7. The Product Configuration Software opens to the main page (see figure56). Click
the device menu arrow next to the name of the device (1).
Figure 56. Accessing the Device PCS Menu
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 59
Page 68

8. The Device menu drops down (see figure57). Click Update Firmware (1) and then
Update Firmware to this Device... (2).
Figure 57. Update Firmware to this Device
9. The Update Firmware window opens. Click Continue (see figure58, 1).
111
Figure 58. Update Firmware Window
10. The Update Firmware to this Device window opens. Click Open Firmware
File... to locate and select the file.
Figure 59. Update Firmware Window
11. An Explorer window opens. Navigate to the firmware file that has been downloaded to
the connected PC.
Figure 60. Select Firmware File
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 60
Page 69

ATTENTION:
• Valid firmware files must have the file extension .eff. A file with any other
extension is not a firmware upgrade for this product and could cause the
SSP200 to stop functioning.
• Les fichiers firmware valides doivent contenir l’extension fichier .eff. Un fichier
avec n’importe quelle autre extension n’est pas une mise à jour de firmware
pour cet appareil et l’appareil pourrait arrêter de fonctionner.
12. Click Open or double‑click the firmware file.
13. Click Update on the Update Firmware dialog box (see figure61). This uploads and
verifies the new firmware onto the connected device. The Installing Firmware
progress field shows the progress of the upload.
Figure 61. Update Firmware
14. After the upload is complete, a dialog box opens confirming that the update has been
successful. Click Close. The software returns to the Device Discovery window (see
figure55 on page59).
15. Select the SSP 200 from the Device Discovery menu. A connection must be
re‑established with the device before continuing to use the software.
16. Click Connect, or double‑click the device. The device reconnects to the software.
NOTE: The original factory‑installed firmware is permanently available on the
SSP200. If the attempted firmware upload fails for any reason, the device reverts
to the factory version.
SSP200 • Product Configuration Software 61
Page 70

SIS Configuration and Control
This section describes Simple Instruction Set (SIS) command programming and control of
the SSP 200, including:
• Connection Options
• Host-to-device Communications
• Using the Command and Response Tables
• Command and Response Tables
Connection Options
The SSP 200 can be configured and controlled using SIS commands or internal web pages.
Configure and control the SSP 200 remotely via a host computer or other device (such as
a control system) by connecting to the rear panel RS‑232 port, LAN port, or the front panel
USB Config port of the SSP device.
RS-232 Port
The SSP 200 has a rear panel serial port (see figure3 on page6) that can be
connected to a host device such as a computer running the Extron DataViewer utility. The
port makes serial control of the SSP possible. Use the protocol information listed below to
make the connection (see Host-to-device Communications on page64).
RS-232 protocol defaults:
• 9600 baud • no parity • 1 stop bit
• 8 data bits • no flow control
Front Panel Configuration Port
The USB mini‑B port is located on the front panel (see figure10 on page11). Connect to
a host computer for configuration using SIScommands with DataViewer, available at
www.extron.com. To connect the SSP 200 to a host computer, download the USB driver,
follow the on‑screen instructions, and configure the SSP as required.
SSP 200 • SIS Configuration and Control 62
Page 71

Ethernet (LAN) Port
The rear panel LAN connector (see figure3 on page6) on the device can be
connected to an Ethernet LAN or WAN. Communications between the SSP 200 and
the controlling device is via an SSH client using port 22023. The SIS commands and the
actions of the SSP 200 are identical to the commands and actions the processor has when
communicating with it via RS‑232.
By default, Telnet communication on TCP port 23 is disabled on the SSP 200. You can use
Telnet by setting the port using Dataviewer (see Connection Options on page62) with
SIS commands (see Set Telnet port map on page71).
LAN port defaults:
DHCP:
SSP 200 IP address:
Subnet mask:
Gateway IP address:
Ethernet Connection
The Ethernet cable can be terminated as a straight‑through cable or a crossover cable
and must be properly terminated for your application (see figure7 on page8 for the
Ethernet connector pin assignment).
• Crossover cable — Direct connection between the computer and the SSP.
• Patch (straight) cable — Connection of the SSP to an Ethernet LAN.
off
192.168.254.254
255.255.0.0
0.0.0.0
Establish a network connection to a SSP 200 processor via an SSH client:
1. Download the SSH client software.
2. Open the SSH software.
3. Enter the IP address of the SSP 200 in the Host Name or IP address field.
NOTE: If the local system administrators have not changed the value, the default IP
address is 192.168.254.254.
4. Enter 22023 in the Port field.
5. The SSP 200 is password protected, so the appropriate administrator or user name and
password must be entered.
a. Enter admin or user.
b. Enter the password next to the Password prompt).
• If the login and password are correct, the device responds with a copyright
message including the copyright year, the name of the product, firmware
version, part number, and the current date and time.
• If the login and password are incorrect, the login prompt returns. Enter the
administrator or user name and password again.
NOTES:
• The SSP 200 is shipped password‑protected. The factory configured
passwords for all accounts on this device have been set to the device serial
number
• In the event of a complete system reset, the passwords convert to the default,
which is extron. New passwords must be configured to secure the device.
SSP 200 • SIS Configuration and Control 63
Page 72

Connection Timeouts
The Ethernet link times out after a designated period of time with no communication. By
default, this timeout value is 5 minutes, but the value can be changed.
NOTE: Extron recommends leaving the default timeout at 5 minutes and periodically
Verbose Mode
SSH and Telnet connections can be used to monitor for changes that occur,
such as SIS commands from other SSH or Telnet sockets or serial port changes.
For a session to receive change notices, the session must be in verbose mode
1 or 3 (see Verbose Mode on page74). In verbose mode 1 or 3, the socket reports
changes in messages that resemble SIS command responses. Front panel changes are also
sent to users who are in verbose mode.
Tagged and Untagged Responses
When a query command is sent in verbose mode 0 or 1, only the “untagged” value is
returned. When a query command is sent in other verbose modes, the response is “tagged”
and resembles the response to a set command.
Example: The “View Specific Output Channel Trim” command EV8SSP} is sent. The
following responses appear depending on the verbose mode:
• Untagged (verbose 0 or 1): -10], just the dB value with no other information.
• Tagged (verbose 2 or 3): SspV8*-10], the type of query sent, the analog channel
issuing the Query (Q) command to keep the connection active. If there are long idle
periods, disconnect the socket and reopen the connection when another command
must be sent.
queried, and the dB value.
Host-to-device Communications
Password Information
SIS commands consist of one or more characters per command field. They do not require
special characters to begin or end the command sequence. Each response to an SIS
command ends with a carriage return and a line feed (CR/LF = ]), which signals the end of
the response character string. A string is one or more characters.
NOTE: Secure Shell (SSH) client connections may add an extra line feed in the final
terminator in SIS responses, for example, standard is
NOTE: The factory configured passwords for all accounts on this device have been set
to the device serial number. In the event of a complete system reset, the passwords
convert to the default, which is extron.
The ]Password: prompt requires a password (administrator level or user level) followed by
a carriage return. The prompt is repeated if the correct password is not entered.
If the correct password is entered, the unit responds with
]
Login User ], depending on the password entered. If passwords are the same for both
administrator and user, the unit defaults to administrator privileges.
X1!]
and SSH is
]
Login Administrator
X1!}]
.
]
or
SSP 200 • SIS Configuration and Control 64
Page 73

Error Responses
ASCII to HEX Conversion Ta ble
Space
.
When the SSP is unable to execute the command, it returns an error response to the host.
The error response codes and their descriptions are as follows:
Unrecognized command
–
E10
Invalid port number
–
E12
Invalid parameter (number is out of range)
–
E13
Not valid for this configuration
–
E14
Invalid command for signal type
–
E17
Using the Command and Response Tables
The Command and Response Tables begins on page69. Symbols used in the table
represent variables in the command and response fields. Command and response examples
are shown throughout the table. The SIS commands are not case sensitive. The ASCII to Hex
conversion table below is for use with the command and response table.
E18
E22
E24
E26
E28
System timed out
–
Busy
–
Privilege violation
–
Maximum connections exceeded
–
Bad file name or file not found
–
Symbol Definitions
Figure 62. ASCII to Hex Conversion
NOTE: For commands and examples of computer or device responses used in this
guide, the character “0” is the number zero and “O” is the capital letter “o”.
]
= CR/LF (carriage return with line feed) (hex 0D 0A)
}
or | = Soft carriage return (no line feed)
• = Space
E
or W = Escape
X!
= Firmware query
0 = Detailed version information (includes all 2Q, 3Q, and 4Q)
1 = Firmware version
2 = Final stage bootloader
3 = Factory base code version
4 = Updated firmware version
X$
= IP Timeout: The number of seconds before timeout on IP connections (min=1, max =65000
and default = 30 (300 seconds). If no data is received during the timeout period, the
Ethernet connection is closed. Each step = 10 seconds.
X1!
X1@
X1#
Baud rate: 300, 600, 1200, 1800, 2400, 3600, 4800, 7200, 9600, 14400,
=
= Parity: Odd, Even, None, Mark, Space [only use the first letter] (default=N=None)
= Data bits: 7, 8 (default=8)
19200, 28800, 38400, 57600, 115200 (default=9600)
SSP 200 • SIS Configuration and Control 65
Page 74

X1$
= Stop bits: 1, 2 (default=1)
X1%
= Port type: 0=RS232, 1=RS422, 2=RS485 (default=0=RS232)
X1^
= Flow Control: Hardware, Software, None [only use the first letter] (default=N=None).
X1&
= Data Pacing [specified in milliseconds between bytes]: 0000 to 1000 (default=0 ms). For
host port(s), this value is ignored – always returns 0.
X1(
= GMT offset value: This represent hours and minutes (hh:mm) offset from Greenwich Mean
Time.
X2)
= DHCP status
0 = Off (default)
1 = On
X2!
= Unit name: A text string up to 63 characters drawn from the alphabet (A to Z),digits (0 to 9),
and minus sign/hyphen (–).
X2@
= Local date and time format: MM/DD/YY-HH:MM:SS
X2#
= IP Address: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx . Leading zeros in each of the 4 fields are optional in setting
values and are suppressed in responses.
X2$
= Hardware MAC address: 00-05-A6-xx-xx-xx
X2%
= Subnet mask: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx . Leading zeros in each of the 4 fields are optional in
setting values and are suppressed in responses.
X2^
= NIC number: Network Interface Card number 1 or 2.
X2&
= Prefix (subnet mask bits): Subnet 255.255.0.0 is represented as a prefix value of /16.
X2*
= Date/Time returned in 7 Hex bytes month, day, year, hour minutes, seconds, day of the
week (1 begins on Sunday).
X2(
= NTP service mode
0 = Disable
1 = Enable
X3)
= Default name: Combination of model‑name and last 3 pairs of MAC address (for example:
SSP-200-00-02-3D).
X3!
= Password: Password: Up to 128 characters. All man‑readable characters are permitted
except “|”. Password cannot be a single space. Passwords are case‑sensitive.
X3@
= Responds with 4 asterisks (****) if password exists and empty if not, instead of actual
password.
X3#
= Connection security level
11 = User
X3&
= Device temperature (degrees Celsius)
X3*
= Verbose/response mode
X4)
= Serial Host‑control port mode:
X4!
= Connection status
X4@
= Input number: 1 to 5.
X4#
= EXP assignment (HDMI and analog inputs are unavailable for EXP assignment):
12 = Administrator
0 = Clear/none (IP default)
1 = Verbose mode (USB default)
2 = Tagged responses for queries
3 = Verbose mode and tagged responses for queries
0 = Device Control (no SIS)
1 = Standard Host control (SIS ‑ default)
2 = Disable Port
1 = Connected
2 = Not Connected
0 = EXP off (default)
2 = Input 2
3 = Input 3
4 = Input 4
SSP 200 • SIS Configuration and Control 66
Page 75

X4$
= EXP input channel pair:
1 = EXP Input 1 & 2 5 = EXP Input 9 & 10
2 = EXP Input 3 & 4 6 = EXP Input 11 & 12
3 = EXP Input 5 & 6 7 = EXP Input 13 & 14
4 = EXP Input 7 & 8 8 = EXP Input 15 & 16
X4%
= Source format:
0 = Not present 7 = Dolby TrueHD ATMOS
1 = Analog 8 = DTS or DTS 96/24
2 = PCM 9 = DTS‑ES (96/24, Matrix, or Discrete)
3 = Dolby Digital/EX 10 = DTS‑HD High Resolution Audio
4 = Dolby Digital Plus 11 = DTS‑HD Master Audio
5 = Dolby Digital Plus ATMOS 12 = DTS Express
6 = Dolby TrueHD 13 = DTS:X
X4^
= Decoded Sampling Rate
0 = None 4 = 88.2 kHz
1 = 32 kHz 5 = 96 kHz
2 = 44.1 kHz 6 = 176.4 kHz
3 = 48 kHz 7 = 192 kHz
X4&
= Source Encoded Channels (Front, Center, Surround, Back, Subwoofer, Height)
0 = None 8 = 4.1
1 = 1.0 9 = 5.0
2 = 1.1 10 = 5.1
3 = 2.0 11 = 6.0
4 = 2.1 12 = 6.1
5 = 3.0 13 = 7.0
6 = 3.1 14 = 7.1
7 = 4.0
X4*
= Signal Status:
0 = Signal not detected
1 = Signal detected
X4(
= Input HDCP status:
0 = No source is detected
1 = Source is detected with HDCP
2 = Source detected without HDCP
X5)
= Enable or Disable:
0 = Disable
1 = Enable (default)
X5#
= HDMI Loop Out mode:
0 = No audio
1 = Follow input
2 = Downmix (Default)
X5$
= Output HDCP status:
0 = No sink detected
1 = Sink detected with HDCP
2 = Sink detected without HDCP
X5%
= Output HDCP mode:
1 = Auto: Encrypt as required by input. Continuous trials for HDMI sinks (Default)
2 = Always Encrypt Output. Continuous trials for HDMI sinks
X5&
= Output channel (channels 7 to 10 change depending on layout and downmix settings):
1 to 10 or 15 to 16.
SSP 200 • SIS Configuration and Control 67
Page 76

Output Channels Table
1 Height Pair
(no Downmix)
1 Left front Left front Left front Left front
2 Right Front Right Front Right Front Right Front
3 Center Center Center Center
4 Subwoofer Subwoofer Subwoofer Subwoofer
5 Left Surround Left Surround Left Surround Left Surround
6 Right Surround Right Surround Right Surround Right Surround
7 Left Back Left Height Front Left Back Left Height Front
8 Right Back Right Height Front Right Back Right Height Front
9 Left Height Front Left Height Back Downmix L Downmix L
10 Right Height Front Right Height Back Downmix R Downmix R
X5*
= dB value: –24 to 0 (default 0)
X6)
= Audio Mute: 0 = Mute off (default) 1 = Mute on
X6@
= %: 0 to 100 (default 80)
X6%
= dB value: –18 to +24 (default 0)
X6&
= Executive mode number
0 = Unlock front panel (default)
1 = Lock front panel
2 = Limit front panel to volume control
3 = Limit front panel to input selection
X7&
X7*
X7(
X8!
X8(
X9)
X9#
X9*
X10(
X11!
X11@
X12)
X12!
X12@
Slot number: 1 = HDMI input 2 = Loop Thru
=
= 128 or 256 byte EDID raw HEX (text form) from currently assigned EDID.
= Native resolution and refresh rate from currently assigned EDID, for example: 1920x1080
@60 Hz.
= Connection status:
0 = Not connected
1 = Connected
= Offset: 0-3000, 10x time value, from 0.0 to 300.0 milliseconds
= Mono output mode:
1 = Center channel only (default)
2 = Front left and right only
= Subwoofer mode:
0 = All off
1 = LFE (SUB) (default)
= Listening mode:
1 = Auto (follow source) 5 = Mono to all
2 = Stereo 6 = Dolby Surround (Upmixer)
3 = Mono 7 = DTS Neural: X (Upmixer)
4 = Stereo to all
= Volume level: 0 to 100 (‑100 dB to 0 dB)
= Analog input gain: -18 to +24 dB
= Clip status:
0 = Off (no clipping)
1 = On (clipping)
= Text – up to 64 characters
= SNMP Trap target number (1 to 3)
= SNMP Trap version for target (2 or 3)
2 Height Pairs
(no Downmix)
0 Height +
Downmix
1 Height Pair +
Downmix
NOTE: Unless otherwise indicated, commands are not case‑sensitive.
SSP 200 • SIS Configuration and Control 68
Page 77

Command and Response Tables
Command SIS Command
(Host to Device)
Response
(Device to Host)
Firmware Version/Part Number/Information Queries
Query model name
Query model description
Query firmware version
Query firmware version
(advanced)
Query firmware version
(w/build)
Query Kernel/Library
version
Query system
messaging version
Query part number
KEY:
X!
= Firmware query 0 = Detailed version information (includes all 2Q, 3Q, and 4Q) 1 = Firmware version
2 = Final Stage bootloader version 3 = Factory Base Code version 4 = Updated Firmware version
1I
Verbose modes 2/3
2I
Verbose modes 2/3
Q
Verbose modes 2/3
X@
Q
Verbose modes 2/3
*Q
Verbose modes 2/3
**Q
Verbose modes 2/3
***Q
Verbose modes 2/3
N
Verbose modes 2/3
SSP•200]
Inf01*SSP•200]
Surround•sound•processor]
Inf02*Surround•sound•processor]
{version x.xx}]
Ver01*{version x.xx}]
{Specic version info}]
X!
Ver
*{Specic version info}]
{version x.xx.xxxx}]
Bld{version x.xx.xxxx}]
{version x.xx.xxxxLX}]
Lib{version x.xx.xxxxLX}]
{version}]
Idv{version x.xx}]
zz-zzzz-zz]
Pnozz-zzzz-zz]
Additional Description
Ethernet Data Port
Set current connector
port timeout
View current connector
port timeout
Set global IP port timeout
View global IP port
timeout
KEY:
X$
= IP Timeout: The number of seconds before timeout on IP connections (min=1, max =65000 and default = 30 (300
seconds). If no data is received during the timeout period, the Ethernet connection is closed. Each step = 10 seconds.
E0*X$TC} Pti0*X$]
E0TC} X$]
E1*X$TC} Pti1*X$]
E1TC} X$]
Serial Data Port (including Device control and Host control ports)
Configure parameters
View parameters
Configure mode
View mode
Configure flow control
View flow control
KEY:
X1!
= Baud rate: 300, 600, 1200, 1800, 2400, 3600, 4800, 7200, 9600, 14400, 19200, 28800,
38400, 57600, 115200 (default=9600)
X1@
For host port(s), this value is ignored – always returns 0.
= Parity:
X1#
= Data bits: 7, 8 (default=8)
X1$
= Stop bits: 1, 2 (default=1)
X1%
= Port type: 0=RS232 1=RS422 2=RS485 (default=0=RS232)
X1^
= Flow Control: Hardware, Software, None [only use the first letter] (default=N=None)
X1&
= Data Pacing [specified in milliseconds between bytes]: 0000 – 1000 (default=0 ms).
Odd, Even, None, Mark, Space
E1*X1!X1@X1#X1$CP} Cpn1•CcpX1!X1@X1#X1$]
E1CP} X1!X1@X1#X1$]
E1*X1%CY} Cpn1•CtyX1%]
E1CY} X1%]
E1*X1^X1&CF} Cpn1•CX1^X1&]
E1CF} X1^X1&]
[only use the first letter] (default=N=None)
SSP 200 • SIS Configuration and Control 69
Page 78

Command SIS Command
(Host to Device)
IP Setup Commands
Set Unit name
Set Unit name to factory
default
View Unit name
Set date/time
View date/time
Viiew date/time in Hex
View GMT offset
Set DHCP on
Set DHCP off
View DHCP mode
Set IP address
View IP address
View hardware address
(MAC)
Set subnet mask
View subnet mask
Set gateway IP address
View gateway IP address
Set IP
Set IP/Subnet
Set IP/Subnet/Gateway
View IP/Subnet/Gateway
(all)
Set DNS Server IP
address
View DNS Server IP
address
View connection listing
View device info
EX2!CN} Ipn•X2!]
E•CN} Ipn•X3)]
ECN} X2!]
EX2@CT} Ipt•X2@]
ECT} X2@]
E*CT} X2*]
ECZ}
Verbose modes 2/3
E1DH} Idh1]
E0DH} Idh0]
EDH} X2)]
EX2#CI} Ipi•X2#]
ECI} X2#]
ECH}
Verbose modes 2/3
EX2%CS} Ips•X2%]
ECS} X2%]
EX2#CG} Ipg•X2#]
ECG} X2#]
E1*X2#CISG} Cisg•1*X2#/X2&*X2#]
E1*X2#*X2%CISG} Cisg•1*X2#/X2&*X2#]
E1*X2#*X2%*X2#CISG} Cisg•1*X2#/X2&*X2#]
E1CISG}
Verbose modes 2/3
EX2#DI} Ipd•X2#]
EDI}
Verbose modes 2/3
ECC}
Verbose modes 2/3
EBC}
Response
Additional Description
(Device to Host)
X1(]
IpzX1(]
X2$]
Iph•X2$]
X2#/X2&*X2#]
X2#]
{Number of connections}]
Icc{Number of connections}]
<part number>null<rmware ver>null<box name>null
<6-byte MAC address in binary>
KEY:
X1(
= GMT offset value: This represent hours and minutes (hh:mm) offset from Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
X2)
= DHCP status: 0 = Off (default) 1 = On
X2!
= Unit name: A text string up to 63 characters drawn from the alphabet (A‑Z), digits (0‑9), and minus sign/hyphen (‑).
X2@
= Local date and time format: MM/DD/YY-HH:MM:SS
X2#
= IP Address: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx . Leading zeros in each of the 4 fields are optional in setting values and are suppressed
X2$
= Hardware MAC address: 00-05-A6-xx-xx-xx
X2%
= Subnet mask: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx. Leading zeros in each of the 4 fields are optional in setting values and are
X2&
= Prefix (subnet mask bits): Subnet 255.255.0.0 is represented as a prefix value of /16.
X2*
= Date/Time returned in 7 Hex bytes month, day, year, hour minutes, seconds, day of the week (1 begins on Sunday).
X3)
= Default name: Combination of model‑name and last 3 pairs of MAC address (for example: SSP-200-01-23-4D).
in responses.
suppressed in responses.
SSP 200 • SIS Configuration and Control 70
Page 79

Command SIS Command
(Host to Device)
Network Time Protocol (NTP)
Enable NTP to set the
time
Disable NTP
Sync NTP now
View NTP status
Set NTP IP address
Set NTP IP address to
default
View NTP IP address
Set NTP port map
Reset NTP port map
Disable NTP port
View NTP port map
E1NTEN} Nten1]
E0NTEN} Nten0]
E2NTEN} Nten2]
ENTEN} X2(]
EX2#NTIP} NtipX2#]
E•NTIP} Ntip]
ENTIP} X2#]
EN{port#}PMAP} PmapN{port#}]
EN123PMAP} PmapN00123]
EN0PMAP} PmapN00000]
ENPMAP} {port#}]
Response
(Device to Host)
Additional Description
KEY:
Port Assignment
X2#
X2(
Set Telnet port map
Reset Telnet port map
Disable Telnet port
View Telnet port map
Set Web port map
Reset Web port map
Disable Web port
View Web port map
Set SNMP port map
Reset SNMP port map
Disable SNMP port
View SNMP port map
Set SSH port map
Reset SSH port map
Disable SSH port
View SSH port map
Set SSL port map
Reset SSL port map
Disable SSL port
View SSL port map
Set FTP port map
Reset FTP port map
=
IP Address: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx . Leading zeros in each of the 4 fields are optional in setting values and are
suppressed in responses.
=
NTP service mode: 0 = Disable 1 = Enable
E{port#}MT} Pmt{port#}]
E23MT} Pmt00023]
E0MT} Pmt00000]
EMT} {port#}]
E{port#}MH} Pmh{port#}]
E80MH} Pmh00080]
E0MH} Pmh00000]
EMH} {port#}]
EA{port#}PMAP} PmapA{port#}]
EA161PMAP} PmapA00161]
EA0PMAP} PmapA00000]
EAPMAP} {port#}]
EB{port#}PMAP} PmapB{port#}]
EB22023PMAP} PmapB22023]
EB0PMAP} PmapB00000]
EBPMAP} {port#}]
ES{port#}PMAP} PmapS{port#}]
ES443PMAP} PmapS00443]
ES0PMAP} PmapS00000]
ESPMAP} {port#}]
EF{port#}PMAP} PmapF{port#}]
EF21PMAP} PmapF00021]
SSP 200 • SIS Configuration and Control 71
Page 80

Command SIS Command
(Host to Device)
Port Assignment (continued)
Disable FTP port
View FTP port map
Set TFTP port map
Reset TFTP port map
Disable TFTP port
View TFTP port map
EF0PMAP} PmapF00000]
EFPMAP} {port#}]
ET{port#}PMAP} PmapT{port#}]
ET69PMAP} PmapT00069]
ET0PMAP} PmapT00000]
ETPMAP} {port#}]
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
Set unit contact
Set unit contact to
default
View unit contact
Set unit location
Set unit location to
default
View unit location
Set community public
(read‑only)
Set community public to
default
View community public
Set community private
(read/write)
Set community private to
default
View community private
Enable SNMP access
and traps
Disable SNMP access
and traps
View SNMP access
setting
Set trap target
Remove trap target
View trap target
ECX12)SNMP} SnmpC*X12)]
EC•SNMP} SnmpC*Not•Specied]
ECSNMP} X12)]
ELX12)SNMP} SnmpL*X12)]
EL•SNMP} SnmpL*Not•Specied]
ELSNMP} X12)]
EPX12)SNMP} SnmpP*X12)]
EP•SNMP} SnmpP*public]
EPSNMP} X12)]
EXX12)SNMP} SnmpX*X12)]
ESnmpX*X12)} SnmpX*private]
EXSNMP} X12)]
EE1SNMP} SnmpE*1]
EE0SNMP } SnmpE*0]
EESNMP} X2(]
ETX12),X12!*X2#*X12@
SNMP}
ETX12!*0SNMP} SnmpT*,X12!*0.0.0.0*0]
ETX12!SNMP} X12),X2#*X12@]
Response
(Device to Host)
SnmpT*X12),X12!*X2#* X12@]
Additional Description
KEY:
X2#
=
IP Address: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx . Leading zeros in each of the 4 fields are optional in setting values and are
suppressed in responses.
X2(
=
NTP service mode: 0 = Disable 1 = Enable
X12)
=
Text – up to 64 characters
X12!
=
SNMP Trap target number (1 to 3)
X12@
=
SNMP Trap version for target (2 or 3)
SSP 200 • SIS Configuration and Control 72
Page 81

Command SIS Command
(Host to Device)
Password and Security Settings
Set admin password
Clear admin password
View admin password
EX3!CA} Ipa•X3@]
E•CA} Ipa•]
ECA} X3@]
Response
(Device to Host)
Additional Description
Set user password
Clear user password
View user password
Query session security
level
KEY:
X3!
X3@
X3#
=
Password: Up to 128 characters. All man‑readable characters are permitted except “|”. Password cannot
be a single space. Passwords are case‑sensitive. The factory configured password for this device is set to the
device serial number. When performing a factory reset, the password is set to the default password, which is extron.
=
Responds with 4 asterisks (****) if password exists and empty if not, instead of actual password.
=
Connection security level:
EX3!CU} Ipu•X3@]
E•CU} Ipu•]
ECU} X3@]
ECK}
Verbose modes 2/3
Directories
Change/create directory
Back to root directory
Up one directory
View current directory
Epath/directory/CJ} Dir•path/directory/]
E/CJ} Dir•/]
E..CJ} Dir•path/directory/]
ECJ} path/directory/]
File Commands
Erase user‑supplied web
page/file
Erase current directory
and contained files
Erase current directory
and subdirectories
List files from current
directory
Load file to user flash
memory
Retrieve file from user
flash memory
ElenameEF} Del1lename]
E/EF} Ddl]
E//EF} Ddl]
EDF} lename•date/time•length]
E+UFlesize,lename} Upl]
ElenameSF}
Backup/Restore Box Configuration
Save box configuration
(to filesystem)
Restore box
configuration
E1*{cong type}XF} Cfg1*{cong type}]
E0*{cong type}XF} Cfg0*{cong type}]
X3#]
PvlX3#]
11 = User 12 = Administrator
{responds with 4-bytes of le-size
+ raw unprocessed data in le}
SSP 200 • SIS Configuration and Control 73
Page 82

Command SIS Command
(Host to Device)
Miscellaneous
Reboot system
Reboot network
View temperature
E1BOOT} Boot1]
E2BOOT} Boot2]
E20STAT} X3&]
Response
(Device to Host)
Additional Description
KEY:
X3&
=
Device temperature (degrees Celsius).
Verbose Mode
Set verbose mode
View verbose mode
NOTE: Verbose mode reverts back to default in the event of a power cycle, disconnect from SSH client, or disconnect from the Ethernet.
KEY:
X3*
= Verbose/response mode: 0 = Clear/none (IP default) 1 = Verbose mode (USB default)
2 = Tagged responses for queries
EX3*CV} VrbX3*]
ECV} X3*]
3 = Verbose mode and tagged responses for queries
SIS over SSH (port 22023)
Enable Echo
Disable Echo
View Echo status
NOTE: Secure Shell (SSH) client connections may add an extra line feed in the final terminator in SIS responses, for example, standard is
and SSH is
KEY:
X1!}]
X5)
=
Enable or disable: 0 = Disable 1 = Enable (default)
E1ECHO} Echo1]
E0ECHO} Echo0]
EECHO} X5)]
Returns command entered
with response.
Returns response only.
Serial Host Control Port Mode
Standard Host control
(SIS)
Device control (no SIS)
Disable port
Query port mode
E1*1HSTM} HstmX4)*1]
E1*2HSTM} HstmX4)*2]
E1*0HSTM} HstmX4)*0]
E1HSTM} X4)]
X1!]
KEY:
X4)
=
Serial Host‑control port mode: 0 = Device Control (no SIS) 1 = Standard Host control (SIS ‑ default)
SSP 200 • SIS Configuration and Control 74
2 = Disable Port
Page 83

Command SIS Command
(Host to Device)
Input Selection
Select audio input
View audio input
Set EXP input
assignment
View EXP input
assignment
Set EXP input channel
pair
View EXP input channel
pair
View audio input source
View audio signal
presence (selected input)
View input HDCP status
Set HDCP authorization
View HDCP
authorization status
View incoming line count
X4@$ AudX4@]
$
Verbose modes 2/3
EEX4#SSP} SspEX4#]
EESSP}
Verbose modes 2/3
EPX4$SSP} SspPX4$]
EPSSP}
Verbose modes 2/3
33I
Verbose modes 2/3
E0LS}
Verbose modes 2/3
EIHDCP}
Verbose modes 2/3
EEX5)HDCP} HdcpEX5)]
EEHDCP}
Verbose modes 2/3
34I
Verbose modes 2/3
Example:
Response
Additional Description
(Device to Host)
X4@]
AudX4@]
X4#]
SspEX4#]
X4$]
SspPX4$]
SrcFormat•X4%•Sampling•X4^•EnChan•X4&]
Inf33SrcFormat•X4%•Sampling•X4^•EnChan•X4&]
X4*]
In00•X4*]
X4(]
HdcplX4(]
X5)]
HdcpEX5)]
<Total Lines>*<Vfreq>*<Hfreq>*<Hcount>]
Inf34*<Total Lines>*<Vfreq>*<Hfreq>*<Hcount>]
Inf34*1080*60.016788*67.498636*1920]
KEY:
X4@
=
Input number: 1 to 5
X4#
0 = Not present 1 = Analog 2 = PCM 3 = Dolby Digital/EX 4 = Dolby Digital Plus
5 = Dolby Digital Plus ATMOS 6 = Dolby TrueHD 7 = Dolby TrueHD ATMOS 8 = DTS or DTS 96/24
9 = DTS‑ES (96/24, Matrix, or Discrete) 10 = DTS‑HD High Resolution Audio 11 = DTS‑HD Master Audio
12 = DTS Express 13 = DTS:X
=
EXP assignment (HDMI and analog inputs are unavailable for EXP assignment):
0 = EXP off (default)
X4$
=
EXP input channel pair:
1 = EXP Input 1 & 2 2 = EXP Input 3 & 4 3 = EXP Input 5 & 6 4 = EXP Input 7 & 8
X4%
X4^
X4&
X4*
X4(
X5)
5 = EXP Input 9 & 10 6 = EXP Input 11 & 12 7 = EXP Input 13 & 14 8 = EXP Input 15 & 16
Source format:
=
=
Decoded Sampling Rate:
0 = None 1 = 32 kHz 2 = 44.1 kHz 3 = 48 kHz 4 = 88.2 kHz 5 = 96 kHz
6 = 176.4 kHz 7 = 192 kHz
= Source Encoded Channels (Front, Center, Surround, Back, Subwoofer, Height):
0 = None 1 = 1.0 2 = 1.1
6 = 3.1 7 = 4.0 8 = 4.1 9 = 5.0 10 = 5.1 11 = 6.0
12 = 6.1
=
Signal Status: 0 = Signal not detected 1 = Signal detected
=
Input HDCP status: 0 = No source is detected 1 = Source is detected with HDCP 2 = Source detected without HDCP
= Enable or Disable: 0 = Disable 1 = Enable (default)
2 = Input 2 3 = Input 3 4 = Input 4
13 = 7.0 14 = 7.1
3 = 2.0 4 = 2.1 5 = 3.0
SSP 200 • SIS Configuration and Control 75
Page 84

Command SIS Command
(Host to Device)
Outputs
Set HDMI Loop Thru
View HDMI Loop Thru
View Output HDCP
Status
Set Output HDCP Mode
View Output HDCP
Mode
EX5#LOUT} LoutX5#]
ELOUT}
Verbose modes 2/3
EOHDCP}
Verbose modes 2/3
ESX5%HDCP} HdcpSX5%]
ESHDCP}
Verbose modes 2/3
Response
(Device to Host)
X5#]
LoutX5#]
X5$]
HdcpOX5$]
X5%]
HdcpSX5%]
Additional Description
KEY:
X5#
=
HDMI Loop Out mode: 0 = No audio 1 = Follow input 2 = Downmix (Default)
X5$
=
Output HDCP status: 0 = No sink detected 1 = Sink detected with HDCP 2 = Sink detected without HDCP
X5%
= Output HDCP mode: 1 = Auto: encrypt as required by input. Continuous trials for HDMI sinks. (Default)
2 = Always Encrypt Output: Continuous trials for HDMI sinks
Level Control
Output Channel Trim Settings
Set specific output
channel trim
View specific output
channel trim
KEY:
X5&
(see Output Channels Table on page68 for details).
= Analog output channel (channels 7–10 change depending on layout and downmix settings):
X5*
=
dB value: –24 to 0 (default 0)
EVX5&*X5*SSP} SspVX5&*X5*]
EVX5&SSP}
Verbose modes 2/3
Audio Mute
Mute all output channels
(global mute)
Unmute all output
channels (global unmute)
View global mute status
Mute specific channel
Unmute specific channel
View mute of specific
channel
1Z
0Z
Z
X5&*1Z AmtX5&*X6)]
X5&*0Z AmtX5&*X6)]
X5&*Z X6)]
X5*]
SspVX5&*X5*]
AmtX6)]
AmtX6)]
X6)]
1 to 10 or 15 to 16
Sets mute to on for all
channels.
Sets mute to off for all
channels.
Returns 1 when all outputs
are muted. Returns 0 if any
outputs are unmuted.
Sets mute to on for selected
channel.
Sets mute to off for selected
channel.
Shows the mute status of
the selected channel.
KEY:
X5&
= Analog output channel (channels 7–10 change depending on layout and downmix settings):
(see Output Channels Table on page68 for details).
X6)
=
Audio Mute: 0 = Mute off (default) 1 = Mute on
1 to 12 or 15 to 16
SSP 200 • SIS Configuration and Control 76
Page 85

Command SIS Command
(Host to Device)
Volume
Specify volume
Increment volume (+)
Decrement volume (–)
View volume setting
X6@V VolX6@]
+V
–V
V
Verbose modes 2/3
Response
(Device to Host)
VolX6@]
VolX6@]
X6@]
VolX6@]
Additional Description
KEY:
X6@
=
Analog Input Level
Set analog input gain
level (input 5 only)
View analog input gain
level (input 5 only)
View clip status
KEY:
X6%
=
X11@
=
Executive Modes
Set Executive Mode
View Executive Mode
KEY:
X6&
=
EDID Minder
Import EDID (.bin) to
input (store) slot
Export EDID (.bin) to PC
View EDID in HEX format
View EDID native
resolution
%: 0 to 100 (default 80)
EAX6%SSP} SspAX6%]
EASSP}
Verbose modes 2/3
3S
Verbose modes 2/3
dB value: –18 to +24 (default 0)
Clip status:
0 = Off (no clipping)
X6&X ExeX6&]
X
Verbose modes 2/3
Executive mode number
2 = Limit front panel to volume control
0 = Unlock front panel (default)
EIX7&,<lename>EDID} EdidIX7*]
EEX7&,<lename>EDID} EdidEX7*]
EREDID}
Verbose modes 2/3
ENEDID}
Verbose modes 2/3
X6%]
SspAX6%]
X11@]
Sts3*X11@]
1 = On (clipping)
X6&]
ExeX6&]
3 = Limit front panel to input selection.
X7*]
EdidRX7*]
X7(]
EdidNX7(]
1 = Lock front panel
Import EDID from
<lename> to input slot x77
Export EDID from EDID table
slot x77 to <lename>
EDID record: 128 or 256
Bytes (delivered as Hex)
View native resolution &
refresh rate of EDID from
EDID table slot 1. Example:
1920x1080 @60.00Hz
KEY:
X7&
= Slot number: 1 = HDMI input 2 = Loop Thru
X7*
X7(
=
=
EXP Port
Get current device
connection status
KEY:
X8!
=
128 or 256 byte EDID raw HEX (text form) from currently assigned EDID
Native resolution and refresh rate from currently assigned EDID, for example: 1920x1080 @60 Hz.
EREXPP}
Verbose modes 2/3
Connection status:
0 = Not connected
1 = Connected
X8!]
ExppRX8!]
SSP 200 • SIS Configuration and Control 77
Page 86

Command SIS Command
(Host to Device)
Layouts and Speakers
Set lip‑sync offset
View lip‑sync offset
Set mono output mode
View mono output mode
EYX4@*X8(SSP} SspYX4@*X8(]
EYX4@SSP}
Verbose modes 2/3
EMX9)SSP} SspMX9)]
EMSSP}
Verbose modes 2/3
Response
(Device to Host)
X8(]
SspYX4@*X8(]
X9)]
SspMX9)]
Additional Description
KEY:
X4@
=
Input number: 1 to 5
X8(
=
Offset: 0 to 3000, 10x time value, from 0.0 to 300.0 milliseconds
X9)
= Mono output mode: 1 = Center channel only (default) 2 = Front left and right only
Subwoofer
Set subwoofer mode
View subwoofer mode
KEY:
X9#
=
Subwoofer mode: 0 = Off 1 = LFE (SUB) (default).
EJX9#SSP} SspJX9#]
EJSSP}
Verbose modes 2/3
X9#]
SspJX9#]
Surround
View listening mode
KEY:
X4@
=
Input number: 1 to 5
X4%
5 = Dolby Digital Plus ATMOS 6 = Dolby TrueHD 7 = Dolby TrueHD ATMOS 8 = DTS or DTS 96/24
9 = DTS‑ES (96/24, Matrix, or Discrete) 10 = DTS‑HD High Resolution Audio 11 = DTS‑HD Master Audio
12 = DTS Express 13 = DTS:X
6 = Dolby Surround (Upmixer) 7 = DTS Neural: X (Upmixer)
Source format: 0 = Not present 1 = Analog 2 = PCM 3 = Dolby Digital 4 = Dolby Digital Plus
=
X9*
= Listening mode: 1 = Auto (follow source) 2 = Stereo 3 = Mono 4 = Stereo to all 5 = Mono to all
ELX4@*X4%SSP}
Verbose modes 2/3
X9*]
SspLX4@*X4%*X9*]
Resets
System reset (factory
default)
Absolute reset including
IP settings
EZXXX} Zpx]
EZQQQ} Zpq]
SSP 200 • SIS Configuration and Control 78
Page 87

Description Response
(Device to Host)
Unsolicited Responses
Audio Input
Audio input source change
Volume level
Input listening mode
Analog level adjustment
Analog input clip status
Current device EXP connection status
EXP input assignment
AudX4@]
Inf33SrcFormat•X4%•Sampling•X4^•EnChan•X4&]
VolX10(]
SspLX4@*X9*]
SspAX11!]
Sts3*X11@]
ExppRX4!]
SspEX4#]
KEY:
X4!
=
Connection Status: 1 = Connected 2 = Not Connected.
X4@
0 = Not present 1 = Analog 2 = PCM 3 = Dolby Digital 4 = Dolby Digital Plus
5 = Dolby Digital Plus ATMOS 6 = Dolby TrueHD 7 = Dolby TrueHD ATMOS 8 = DTS or DTS 96/24
9 = DTS‑ES (96/24, Matrix, or Discrete) 10 = DTS‑HD High Resolution Audio 11 = DTS‑HD Master Audio
12 = DTS Express 13 = DTS:X
6 = Dolby Surround (Upmixer) 7 = DTS Neural: X (Upmixer)
=
Input number: 1 to 5.
X4#
=
EXP assignment (HDMI and analog inputs are unavailable for EXP assignment):
0 = EXP off (default)
X4%
Source format:
=
X4^
=
Decoded Sampling Rate:
2 = Input 2 3 = Input 3 4 = Input 4.
0 = None 1 = 32 kHz 2 = 44.1 kHz 3 = 48 kHz 4 = 88.2 kHz
X4&
5 = 96 kHz 6 = 176.4 kHz 7 = 192 kHz
= Source Encoded Channels (Front, Center, Surround, Back, Subwoofer, Height):
0 = None 1 = 1.0 2 = 1.1 3 = 2.0 4 = 2.1 5 = 3.0 6 = 3.1 7 = 4.0
8 = 4.1 9 = 5.0 10 = 5.1 11 = 6.0 12 = 6.1 13 = 7.0 14 = 7.1
X9*
= Listening mode: 1 = Auto (follow source) 2 = Stereo 3 = Mono 4 = Stereo to all 5 = Mono to all
X10(
=
X11!
=
X11@
= Clip status:
Volume level: 0 to 100 (0% to 100%)
Analog input gain: -18 to +24 dB
0 = Off (no clipping)
1 = On (clipping)
SSP 200 • SIS Configuration and Control 79
Page 88

Internal Web Page
This section gives an overview of the SSP 200 internal web page. Topics include:
• Overview of the Internal Web Page
• Accessing the Internal Web Page
• Web Page Components
Overview of the Internal Web Page
The SSP 200 internal web pages provide the software user interface for operating and
configuring the SSP 200 via a PC on the same network. This allows you to:
• View and edit the device name
• Set the date and time either manually or to sync with a connected PC
• View input and output details
• View and edit the network settings
• Update the firmware version
Connection is made via a LAN or WAN connection through the rear panel LAN (RJ-45) port,
using a web browser such as Microsoft® Edge®, Mozilla® Firefox®, Google Chrome™, or
Apple® Safari®.
Accessing the Internal Web Page
To access the internal web pages:
1. Using an RJ-45 cable, connect the device to a LAN via the rear panel LAN port (see
Rear Panel Features on page6).
2. Launch the web browser on your computer.
3. Enter the device IP address into a web browser address bar. If the IP address has not
been changed, the default address is 192.168.254.254.
4. Press the keyboard <Enter> key. The SSP200 web page requires user authentication
to continue. Click in the Password field and enter the appropriate administrator or user
password. Click OK.
NOTE: The factory configured passwords for all accounts on this device have been
set to the device serial number. Passwords are case sensitive. If the SSP 200 is
reset, the passwords revert to the default, which is extron.
SSP 200 • Internal Web Page 80
Page 89

Web Page Components
The SSP 200 web page (see figure63) has eight panels:
Device Info
1
Device Status
2
Network Settings
3
Inputs
4
Outputs
5
RS-232
6
Roles and Permissions
7
Firmware
8
Device Info
Figure 63. Web Page
The Device Info panel shows the current device name, description, part number, and
manufacturer. You can change the device name by first clicking EDIT (1) on the bottom of
the Device Info panel.
This opens the Device Info Settings dialog box (see figure64).
Figure 64. Device Info Settings Dialog Box
SSP 200 • Internal Web Page 81
Page 90

To change the device name:
1. Click into the Device Name field (see figure64, 1, on the previous page).
2. Enter a desired name.
3. Click SAVE (2). The new name is applied, the dialog box closes, and the device name
Device Status
The Device Status panel (see figure64, 2, on the previous page) displays the date,
time, and time zone for the connected SSP200, and allows the user to either synchronize
the date and time to a connected PC or set the date and time manually.
To synchronize to the connected PC:
1. On the Device Status panel, click SYNC TO PC.
2. If successful, you see a confirmation message and the current Date, Time, and
NOTE: The name can have alphanumeric characters and hyphens only. A hyphen
cannot be the first or last character. An incorrect name is ignored and the current
name is not changed.
in the Network Settings panel is also updated with the new name.
Click CANCEL (3) to exit the process without making any changes.
NOTE: The default name is a combination of the model name and last three pairs of
the MAC address (for example, SSP-200-18-FF-FF).
Timezone on the Device Status panel.
To set the information manually:
1. Click EDIT on the Device Status panel.
The Device Status Settings dialog box appears (see figure65).
2. Change Date and Time (1) and the Timezone (2) as appropriate.
3. Click SAVE (3) when done. You see the changes on the Device Status panel if the
update has been successful.
Click CANCEL (4) to exit the process without making any changes.
Figure 65. Device Status Settings
SSP 200 • Internal Web Page 82
Page 91

Network Settings
The Network Settings panel shows the current network settings for the SSP 200 (see
figure63 on page81). To change the settings, click EDIT to access the Network
Settings dialog box (see figure66).
Figure 66. Network Settings Dialog Box
To configure the settings for use with DHCP:
1. Set the DHCP slider (1) to On.
2. Click SAVE (5). An IP address is automatically assigned to the device. Contact your
ITadministrator for more information.
Click CANCEL (6) to exit the process without making any changes.
To configure the settings with a static IP address:
1. Ensure the DHCP slider (1) is set to Off.
1. In the IP Address field (2), enter an IP address for the device.
2. In the Subnet field (3), enter the subnet mask for the device.
3. In the Gateway field (4), enter the default gateway to be used.
4. Click SAVE (5) to apply the changes, or click CANCEL (6) to exit the process without
making any changes.
NOTE: The default TCP/IP settings are:
• IP address = 192.168.254.254
• Subnet Mask = 255.255.0.0
• Default Gateway = 0.0.0.0
SSP 200 • Internal Web Page 83
Page 92

Inputs
The Inputs panel displays the name and signal type of the active input as well as its HDCP
status (see figure63, 4, on page81).
The following HDCP status indicators may be displayed for a connected input:
Symbol Definition
The signal is HDCP encrypted.
The signal is not encrypted.
No Signal There is no signal detected.
Click 4 MORE to see the full Inputs panel showing the remaining inputs (see figure67).
This panel is not user-configurable. Click the X on the top right of the panel to return to the
main web page.
Outputs
Figure 67. Inputs Panel
NOTE: Input audio format details are only available when an input is selected.
This panel displays the status of the connected output (see figure63, 5). This panel is not
user-configurable.
The following status symbols may be displayed for the connected output:
Symbol Definition
The signal is HDCP compliant.
The signal is not compliant.
No Signal No display is connected.
SSP 200 • Internal Web Page 84
Page 93

RS-232
This panel displays RS-232 information (see figure63, 6, on page81). This panel is not
user-configurable.
Roles and Permissions
The Roles and Permissions panel on the main web page gives the user access to set
the admin and user passwords for the SSP200 (see figure63, 7).
To change them, click EDIT in this panel. The Roles and Permission Settings dialog
box opens (see figure68).
Figure 68. Role and Permission Settings
Change each password field as applicable. Click SAVE (1) to apply the changes or CANCEL
(2) to exit the process without making any changes.
NOTE: The factory configured passwords for all accounts on this device have been
set to the device serial number. Passwords are case sensitive. if the SSP200 is
reset, the passwords revert to the default, which is extron.
The maximum length of a password is 128 characters. All human-readable characters are
permitted except “|”. Passwords are case-sensitive and cannot be a single space.
NOTES:
• Only an administrator can set the admin password.
• The default admin name is admin and the default user name is user.
• An indicator of the current login status is shown on the top right corner of the
main screen.
SSP 200 • Internal Web Page 85
Page 94

Firmware
The Firmware panel (see figure63, 8, on page81) displays the current firmware
version and when it was last updated to the device (see figure69, 1).
Figure 69. Firmware Panel
NOTE: The latest firmware can be downloaded from the Extron website (see
Downloading the SSP 200 Firmware on page58).
To update the SSP200 firmware version:
1. Before starting, download the latest version of the firmware to your PC (see the note
above).
2. An executable (.exe) file is downloaded to the PC. Run this program to place the
firmware on the PC for future use. Make a note of the folder where the firmware file was
saved.
ATTENTION:
• The extension of the firmware file must be .eff. Opening a file with an incorrect
extension may cause the device to stop functioning.
• L’extension du fichier firmware doit être .eff. Si un fichier est ouvert avec une
mauvaise extension, l’appareil peut arrêter de fonctionner.
3. On the Firmware panel, click Select File (see figure69, 2). This opens an Explorer
window on your PC.
4. Browse to the location of the firmware and select the file (see figure70).
Figure 70. Selecting the Firmware File
SSP 200 • Internal Web Page 86
Page 95

5. Click Open. The window closes and the Firmware panel opens showing the firmware
file in the file name field (see figure71, 1).
Figure 71. Firmware Panel - Update
6. Click UPDATE (2). The firmware is uploaded to the connected device.
NOTE: The original factory-installed firmware is permanently available on the
SSP200. If the attempted firmware upload fails for any reason, the processor
reverts to the factory version.
SSP 200 • Internal Web Page 87
Page 96

Extron Warranty
Extron warrants this product against defects in materials and workmanship for a period of three years from the date
of purchase. In the event of malfunction during the warranty period attributable directly to faulty workmanship and/
or materials, Extron will, at its option, repair or replace said products or components, to whatever extent it shall
deem necessary to restore said product to proper operating condition, provided that it is returned within the warranty
period, with proof of purchase and description of malfunction to:
USA, Canada, South America,
and Central America:
Extron
1230 South Lewis Street
Anaheim, CA 92805
U.S.A.
Europe:
Extron Europe
Hanzeboulevard 10
3825 PH Amersfoort
The Netherlands
Africa:
Extron South Africa
3rd Floor, South Tower
160 Jan Smuts Avenue
Rosebank 2196, South Africa
This Limited Warranty does not apply if the fault has been caused by misuse, improper handling care, electrical
or mechanical abuse, abnormal operating conditions, or if modifications were made to the product that were not
authorized by Extron.
NOTE: If a product is defective, please call Extron and ask for an Application Engineer to receive an RA (Return
Authorization) number. This will begin the repair process.
USA: 714.491.1500 or 800.633.9876 Asia: 65.6383.4400
Europe: 31.33.453.4040 or 800.3987.6673 Japan: 81.3.3511.7655
Africa: 27.11.447.6162 Middle East: 971.4.299.1800
Asia:
Extron Asia Pte Ltd
135 Joo Seng Road, #04-01
PM Industrial Bldg.
Singapore 368363
Singapore
China:
Extron China
686 Ronghua Road
Songjiang District
Shanghai 201611
China
Japan:
Extron Japan
Kyodo Building, 16 Ichibancho
Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 102-0082
Japan
Middle East:
Extron Middle East
Dubai Airport Free Zone
F13, PO Box 293666
United Arab Emirates, Dubai
Units must be returned insured, with shipping charges prepaid. If not insured, you assume the risk of loss or damage
during shipment. Returned units must include the serial number and a description of the problem, as well as the
name of the person to contact in case there are any questions.
Extron makes no further warranties either expressed or implied with respect to the product and its quality,
performance, merchantability, or fitness for any particular use. In no event will Extron be liable for direct, indirect, or
consequential damages resulting from any defect in this product even if Extron has been advised of such damage.
Please note that laws vary from state to state and country to country, and that some provisions of this warranty may
not apply to you.
Contact Information
Worldwide Headquarters: Extron USA West, 1025 E. Ball Road, Anaheim, CA 92805, 800.633.9876
 Loading...
Loading...