Page 1

Administrator’s Manual
0450-0194
Rev. C
Page 2

About ESI
ESI (Estech Systems, Inc.) is a privately held corporation based in Plano, Texas, in the internationally known
“Telecom Corridor.” Founded in 1987, ESI designs and builds innovative telecommunications products for
businesses like yours. Because of their powerful combination of value and features, ESI products are consistently recognized by industry publications and leaders. In fact, ESI also creates telecommunications products
for major companies to market under their well-known brand names.
Copyright © 2002 ESI (Estech Systems, Inc.).
Visit ESI on the Web at http://www.esi-estech.com.
IVX is a registered trademark of Estech Systems, Inc. Ethernet is a registered trademark of Xerox Corporation. Motorola and ColdFire are
registered trademarks of Motorola, Inc. Act! is a registered trademark of Symantec Corporation. Goldmine is a trademark of Goldmine
Software Corporation. Microsoft, Windows, NT and Outlook are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Panasonic and DBS are
registered trademarks of Matsushita Electric Corporation of America. Novell and Netware are registered trademarks of Novell, Inc.
IP Series products are protected by U.S. Patent No. 6,067,349 and 6,252,944, and others pending.
ESI is an ISO 9001-certified company.
Page 3

Table of contents
General description.............................................................................................................A.1
System programming: an introduction.................................................................................. B.1
Function 1: System parameters ............................................................................................ C.1
Function 13: Administrator password .................................................................................................................................C.1
Function 14: Set time/date...................................................................................................................................................C.1
Function 17: System speed-dial ...........................................................................................................................................C.1
Function 3: Extension programming...................................................................................... D.1
Function 32: Extension feature authorization.......................................................................................................................D.1
Function 5: Voice mail programming ......................................................................................E.1
Function 53: Guest/info mailboxes...................................................................................................................................... E.1
Function 54: Group mailboxes and the broadcast mailbox.................................................................................................. E.2
Function 55: Message notification........................................................................................................................................ E.3
Function 56: Cascade paging mailboxes.............................................................................................................................. E.4
Function 57: Q & A mailboxes...............................................................................................................................................E.5
Function 6: Recording...........................................................................................................F.1
Function 61: Re-record system prompts................................................................................................................................ F.1
Function 62: Record directory names....................................................................................................................................F.2
Function 63: Message-on-hold (MOH) programming............................................................................................................F.3
Index
Appendix I: User’s guide
Appendix II: Worksheets
Page 4

(This page included for pagination purposes only.)
Page 5

IP Series Administrator’s Manual General description
General description
ESI’s IP Series (IP 200 and IP 40) IP telephony products are advanced business telecommunications
systems, each of which includes not only phone service but voicemail, an automated attendant,
automatic call distribution, and computer integration. These features are all provided over standard
Ethernet cabling, using the Internet Protocol and certain other protocols from the TCP/IP suite.
In IP telephony, voice is digitized at the telephone and then converted to IP data packets at the
telephone. Those packets are sent across an IP data network and then converted back to a voice
signal at the other party’s IP telephone or at the IP PBX for connections to outside lines.
The IP Series consists of an IP Feature Phone and two models of the IP PBX.
The IP Feature Phone provides all the features and functionality expected of business phones. It
looks and feels exactly like ESI’s popular IVX
the same Ethernet
®
cables used by PCs and data servers. Voice is carried over the network at an
uncompressed 64Kbps – the highest quality available.
The two IP PBXs differ only in the number of supported CO lines and stations. The IP 200 can be
configured to handle up to 66 CO lines and 96 stations, while the IP 40 can handle 30 lines and 28
stations. The IP PBXs reside on the Ethernet network and are both rack-mountable and wall-mountable
Telephone system features
®
digital telephone, but it connects to the system over
.
Your Installer can expand the IP Series cabinets from their basic configuration to handle as many as
66 CO lines (the IP 200) or 30 lines (the IP 40). Both cabinets support T1 and PRI modules.
• Impressive expansion capability – Can handle up to 66 CO lines and 96 stations.
• T1 and ISDN PRI support – Can connect to higher-bandwidth lines.
• IP Feature Phone – Compact and rugged design includes a high-quality speakerphone, large and
informative multi-functional display, and a specially designed key layout with several dedicated
keys to minimize or eliminate the need to memorize codes. The IP phone is TAPI compliant; you
can obtain a TAPI driver from your ESI Reseller.
• Extensive help – Verbal User Guide
™
uses spoken and displayed help prompts to help everyone
from the installer through the administrator down to the least experienced end user. Easily accessible with one press of the PROG/HELP key.
• Enhanced caller ID – Allows one-touch automatic message return.
• Live call recording — Can record any conversation or personal memo, with moving or copying of
any recording to another user’s voice mailbox (see “Voice mail features,” below).
• Call waiting — Includes helpful display, showing both calls’ caller ID information, and easy one-
key toggling between calls.
• Conference calling — Includes 24 conference bridges, and a conference may contain up to four
parties, so the IP Series can support six conferences of four parties each or eight conferences of
three parties each.
• Esi-Dex™ speed-dialing — Calls any number from any of the three separate lists (personal, sta-
tion, and system); uses Caller ID information or direct keypad entries.
A.1
Page 6

General description
Dedicated overhead paging interface
•
IP Series Administrator’s Manual
— Allows overhead paging through the user’s own over-
head paging system.
• 911 alert — Provides immediate line access if any station (except the Remote IP Feature Phone)
with line access dials 9 1 1 to report an emergency; sends a message via the serial port indicating
the start date, time, station number and end-time of the 911; also sounds a warning tone at the
operator station and displays (for example):
911 CALL FROM
X102 JOHN JAMES
Remote network features (VoIP)
In addition to a robust set of telephony features, the IP Series PBXs have the capability for extending PBX operation to any location that has access to a suitable high-speed data connection. This
capability is provided with the Remote IP Feature Phone and Esi-Link.
• Remote IP Feature Phone — Ideal for the remote site requiring one, or no more than a few,
extensions. Once this is installed, the remote user is provided a nearly identical capability and
connectivity of the phone user in the main office. Numerous remote sites can be supported from
a single IP PBX. Refer to the Remote IP Feature Phone Product Overview and the Remote IP
Feature Phone User’s Guide for more information.
• Esi-Link — Provides the capability of connecting up to 100 IP PBXs at different locations into a
single private phone system. The ESI IP PBX features that so far have been available to a single
location can now be extended across several locations, greatly enhancing the integration opportunities of a business with multiple locations. Refer to the Esi-Link Product Overview for a full
explanation of Esi-Link capabilities.
Voice mail features
• 16 built-in voice mail ports — These are in addition to the up-to-192 possible call-processing
ports; thus, you may build the system to its maximum for call-handling without having to balance voice mail needs versus call-handling needs.
• Highest-grade voice quality (64Kbps sampling) for voice mail and other storage of voice messages.
• Eight message-on-hold recordings — Among these are three prerecorded tracks; also supports
live input.
• Off-premises message delivery.
• Urgent messages — Can deliver higher-priority messages first.
• Several different mailbox types, including group, broadcast, informational, cascade paging
and Q & A.
• Message Recycle Bin (undelete) — Remembers, and can restore, each mailbox’s 10 most re-
cently deleted messages.
™
• Quick Groups
• Quick Move
• Virtual Mailbox Key
• New-message skip — Skip a new message and have it appear as “new” the next time.
• Message monitor key — Toggle the live-call screening with a single programmable key.
• Message move and delete — Move-and-save, or move-and-delete, messages.
• AutoPage
— Makes it easy to leave voice mail messages for several users.
™
— Automatically moves a message to a designated mailbox.
™
— Allows easy monitoring of a second mailbox.
™
— Allows a caller, when forwarded to voice mail, to page a station user.
A.2
Page 7

IP Series Administrator’s Manual General description
Call-handling features
• Off-Premises “reach me” — Lets callers reach their party while he or she is off premises.
™
• Virtual Answer Key
— Users can play pre-programmed prompts to inbound callers.
• Caller ID missed-call key — Stores caller ID for ten most recent missed calls.
• Auto-attendant trunk-to-trunk transfer — Create an auto-attendant outdial branch without the
need for Centrex lines.
• Separate hold/park recall timers — Separate recall timers for calls on park and hold.
• System-wide hold — Puts the CO line on hold, after which any user can pick up the call by press-
ing the line key.
• System-connect tone control — Allows the installer or administrator to disable the connect tone.
• CO line labeling — Labels the CO lines and has them appear in the display when they ring.
Auto attendant features
• Six levels, 100 branches — Allow you and your customer to set up a more caller-friendly
answering environment, including a company directory.
• Virtually unlimited call routing — Includes off-premises transfer, pager notification, more.
ACD features
• Routes calls within designated departments for quickest possible call answering.
• Uses IP Feature Phone display to provide up-to-the-second information on queues and
wait times.
A.3
Page 8

General description
(This page included for pagination purposes only.)
IP Series Administrator’s Manual
A.4
Page 9
IP Series Administrator’s Manual System programming: an introduction
System programming: an introduction
You can program the IP Series either from an IP Feature Phone or through the Windows® 95/98-based
Esi-Access package. Both methods follow the same programming steps. This manual focuses on
programming from an IP Feature Phone; the respective documentation for Esi-Access details the
differences in programming from that environment.
Read the User’s Guide first. Programming features require a clear understanding of the user inter-
face and application.
You can program the IP Series system from any IP Feature Phone while the system is operating.
Once you’ve accessed programming mode, the system will prompt for — and confirm — each keystroke action via voice commands and the LCD display. You program both configuration data and
recordings in the same manner.
Programming keys
During programming, the top line of the LCD will display the current item being programmed and
the bottom line will be the entry line. You can enter values as directed by the combination of the
voice prompts and LCD display. To enter multiple values, such as a list of extension numbers, separate each value by # (to exit the list, enter # #).
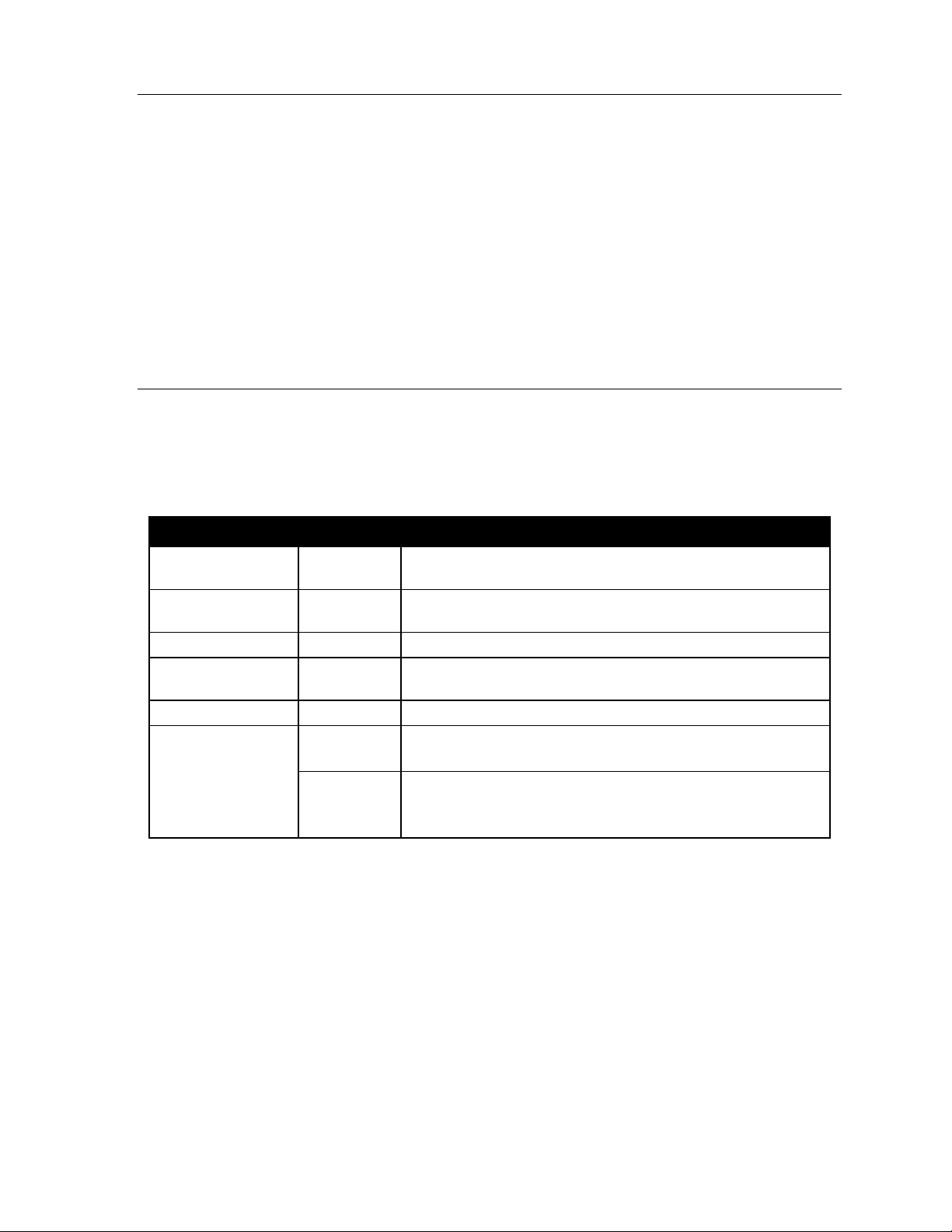
To .. . Press ... What this does
Enter #
Back up (i.e., re-
verse direction)
Delete HOLD
Exit
Help HELP
Select
/ Scroll
* Backs up to previous prompt without changing its value.
RELEASE (or
just hang up)
▼ (left-side
scroll key)
▲ (right-side
scroll key)
Confirms new or existing entry and advances to next programming step.
Deletes data or recording.
Exits programming mode and removes extension from DND.
Provides more detailed instructions during programming.
• During entry of a value, backs up
• If a list is present (> is displayed), scrolls to left
• Selects from options presented
• If a list is present (> is displayed), scrolls to right
• Inserts a space during entry of a name.
Note: Either < or > in the display indicates that additional choices or values are available by press-
ing a corresponding scroll (▼ or ▲) key.
B.1
Page 10

System programming: an introduction IP Series Administrator’s Manual
Entering alphanumeric characters
You enter names for extensions, departments, and branch IDs by pressing the dial pad key that
corresponds to the character to be entered. The key’s possible entries will change each time the key
is pressed, and the LCD will show this. When the LCD displays the desired character, press # to
confirm; the cursor will move to the next character position. You may move the cursor left (to correct
an entry) by pressing the left scroll key (▼) or move right (to add a space) by pressing the right
scroll key (▲).
Key entry Options
0 0, - (hyphen), _ (underline)
1 Q, Z, 1, “_” (space)
2 A, B, C, 2
3 D, E, F, 3
4 G, H, I, 4
5 J, K, L, 5
6 M, N, O, 6
7 P, R , S , 7
8 T, U, V, 8
9 W, X,Y, 9
▼ (left
scroll key)
▲ (right
scroll key)
# [Enter]
# # Ends the name
Example: To enter a B, press 2 twice (the possible options to scroll through are A, B, C and 2).
When B is displayed, press # to confirm; the cursor will move to the next character to
be entered. To complete the name, press # #.
Backs up and erases
Adds a space
Accessing user station programming
Should a user forget his password or if an employee leaves the organization, this feature allows the
Administrator to enter a user's station programming and operate within it as if he were the user. From
the user’s station, input the Administrator password when the system prompts for the user password.
Example: From station 105, entering 4 5 6 # instead of the user password (1 0 5 #) will enter the
station’s user programming. (Default passwords shown for this example).
B.2
Page 11

IP Series Administrator’s Manual System programming: an introduction
System fixed numbering plan
Number Function
IP 200 IP 40
0 Same Operator
1–66 1–30 CO lines
100–195 100–127 IP Feature Phone stations
199 Same Overhead paging port
200–229 200–205 Analog stations
290–299 Same Department pilots
300–489 Same Guest/info mailboxes
490–499 Same Q & A mailboxes
500 Same Broadcast mailbox
501–516 Same Group mailboxes
520–529 Same Cascade paging mailboxes
530–550 Same Recordable system prompts
560–589 Same Feature codes
590–598 Same MOH recordings
600–699 Same System speed dial
700–799 Same Remote IP PBX numbers (Esi-Link only)
B.3
Page 12

System programming: an introduction IP Series Administrator’s Manual
Remote setting of day, night, holiday and auto modes
Normally, the system’s day/night mode operation will be manually controlled at an IP Feature
Phone and/or set to follow the day/night mode tables (programmed by the Installer) automatically.
In addition, the Administrator can remotely change the mode and/or re-record the holiday greeting
to handle unexpected closings such as for inclement weather.
Remotely logging into the system with the Administrator password will allow the caller to re-record
the holiday greeting and manually change the mode for day/night/holiday.
To change the answer mode and main greetings remotely:
1. Dial the main number that the auto attendant answers.
2. At the main greeting, enter * * 4 5 6 # — or the new password — to enter remote programming
mode. You’ll hear prompts (see “Prompts for remote settings: An outline,” below) that will allow you to change the answer mode (day, night, holiday, day2, night2 or auto) and re-record the
day, night and holiday greetings. When you select any of the “record ... greeting” prompts, you’ll
hear the current greeting and then be prompted to press 1 to record a new greeting.
3. To exit or go back to the previous section, press * (you may also exit by hanging up).
For more information on day, night and holiday modes, refer to:
• “Function 61: Re-record system prompts,” page F.1.
• “Live Outside Calls • Operator Station,” in the IP Series User’s Guide (#0450-0189).
Prompts for remote settings: an outline
1 Set answer mode
1 Day mode
2 Night mode
3 Holiday mode
4 Use day/night table*
5 Day2 mode
6 Night2 mode
2 Record holiday main greeting
3 Record daytime main greeting
4 Record nighttime main greeting
5 Record day2 main greeting
6 Record night2 main greeting
*
This is used if the installer has programmed an automatic calendar.
B.4
Page 13

IP Series Administrator’s Manual System programming: an introduction
System programming overview
1 System parameters
13 Administrator password
14 Set time/date
17 System speed dial
3 Extension programming
32 Extension feature authorization
5 Voice mail programming
53 Guest/info mailboxes
54 Group mailboxes
55 Message notification options
551 Station delivery options
552 Delivery/paging parameters
56 Cascade paging mailboxes
561 Cascade mailbox options
562 Cascade paging parameters
57 Q & A mailboxes
6 Recording
61 Record system prompts
62 Record directory names
63 MOH programming
631 MOH source
632 Record MOH
633 MOH volume
Entering programming mode
You may program from any Feature Phone in the system. To enter programming mode:
1. Press PROG/HELP. The normal station programming menu prompt will begin to play.
2. Press PARK to stop the prompt.
3. Enter the Administrator password, followed by #.
4. Follow the system programming menu.
5. When finished, hang up.
Note: While in programming mode, the extension will be automatically placed in DND.
Note: The system will automatically exit programming mode after 10 minutes of inactivity.
Example: To enter programming mode, press PROG/HELP, PARK, 4 5 6 [or new Administrator
password], #. To exit programming mode, hang up.
B.5
Page 14

System programming: an introduction IP Series Administrator’s Manual
(This page included for pagination purposes only.)
B.6
Page 15

IP Series Administrator’s Manual Function 1: System parameters
Function 1: System parameters
Function 13: Administrator password
This will display the existing password and prompt for input of a new password. The password can
be 2–8 digits long, followed by #. Only those functions listed in this manual can be programmed
via this password; other functions require the Installer. The default password is 456.
Note: Be sure to write down the new password and store it in a safe place.
Note: You can use the Administrator password to access a user’s station programming. At the
station, when prompted for the user’s password, enter the Administrator password, then follow normal user programming procedures.
Function 14: Set time/date
1. Enter a new time in a twelve-hour format.
Example: Enter 1 2 3 3 for 12:33, or 3 1 5 for 3:15 (note that you need no leading zero for
the time).
2. Select AM or
3. Enter a new date in an eight-digit format, including leading zeroes.
Example: Enter 0 7 0 4 2 0 0 1 for July 4, 2001 (note that leading zeroes are required here,
4. Press # to finish the entry.
Note: A built-in battery maintains the correct time and date, even in the event of a power loss.
by pressing a scroll key (either ▼ or ▲).
PM
unlike in step 1).
Function 17: System speed-dial
Up to 100 system speed dial names and associated numbers can be stored, in location numbers
600–699, for access by any station. A user can initiate a system speed dial by dialing the speed
dial location number or by accessing the name through the Esi-Dex feature. In Function 32, access
to system speed-dial can be denied to individual stations (see page D.1).
1. Enter the 3-digit location number to program.
2. Enter a ten-character name (see “Entering alphanumeric characters,” page B.2).
3. Enter the number to be dialed (including the line group — 9, 8 or 71–76). Press the left scroll
key (▼) to delete any character or digit entered in error. Here’s an example:
1. 2. 3.
Location no. Name Number
601 AUTO RENTL 915552221212
C.1
Page 16

Function 1: System parameters IP Series Administrator’s Manual
The number dialed in step 3 can be up to 30 digits long including the following special codes:
Code What it produces
# # DTMF tone
*
F Flash hook
P 2-second pause
To insert a special code, press the right scroll key to select the desired special code: # , * , F or P.
Press # to confirm the inserted character and continue. Press # # to complete the entry.
Example: To create a System Speed Dial number that dials 9, then 972-555-5644,
then pauses for 4 seconds and finally dials #104, enter:
9 9 7 2 5 5 5 5 6 4 4 (scroll to) P # (scroll to) P # (scroll to) “#” # 1 0 4 #
* DTMF tone
Deleting a speed dial number
To delete an entire speed dial number and name, delete the location number (6 X X) by pressing
HOLD or the left scroll key (▼) during step 1 in the speed-dialing procedure described above.
C.2
Page 17

IP Series Administrator’s Manual Function 3: Extension programming
Function 3: Extension programming
Important: Where any gray shading (■) appears in an example, it represents values either
unavailable to the function or unused in the particular example.
Function 32: Extension feature authorization
The Administrator can allow or deny many extension features on an extension-by-extension basis.
A User, however, can only program and use allowed features (by using a combination of voice and
LCD prompts) from his/her phone.
Below is an example of a completed Programming Worksheet.
1.
Ext.
XXX Default Y Y N Y N Y Y N N N N
100 Jane Y Y N Y N Y Y Y N N N
101 Roger Y Y N Y N Y Y N N N N
102 Sally Y Y N N N Y Y Y N N N
200* Bill Y N Y Y N N N N
2.
Name
3.
Call
wait
4.
DND
5.
AA
block
6.
Rec.
7.
Svc.
obs.
8.
Toll
allow
9.
Sys.
spd.
dial
10.
Auto
page
11.
Ext.
fwdg.
12.
Fwdg. to
toll nos.
13.
Trunk-
to-trunk
xfer
Here is the sequence of programming. The programming steps are:
1. Extension number — Enter the extension number to program.
2. Extension name — Name the extension (if not previously named by the Installer).
For each of the following features, press a scroll key (▼ or ▲) to select YES or NO.
3. Call waiting — Allows the user to turn call waiting on or off for his station.
4. Do not disturb — Allows the user to activate DND from his station.
5. Auto attendant block — Blocks calls from being transferred to the station from the auto attendant;
follows the extension’s call forward day/night setting (programmed by the Installer).
6. Live recording feature — If enabled, will allow the user to record conversations.
7. Service observing — Allows the user to monitor the conversations of those stations listed
in the service observing list for his/her station. If this is enabled, you must enter a list of
allowed extensions.
Note: A Department number can be entered as an extension in the Service Observing list and
will then automatically include all members of the Department even if the members of
the Department are later changed.
8. Toll restriction — “YES” allows the user to place toll calls. If “NO,” the user can make only either
non-toll calls or calls to numbers listed in the allow exception table.
9. System speed dial — “YES” allows the user to access and place system speed dial calls.
*
An example of an analog phone.
D.1
Page 18

Function 3: Extension programming IP Series Administrator’s Manual
10. Auto-page
— Lets the user turn auto-page (defined below) on or off at his/her station.
Note: This feature is used in conjunction with the directory names recorded in Function 62 and
is not active until a directory name is recorded for the extension.
If the station user has his/her mailbox set to answer with personal greeting 3 and a caller
presses 3 to page that user, this feature automatically pages the station user in the page zones
entered in Function 31. If no page zone is entered, all Feature Phones on the system are paged.
Default: Disabled.
Note: When auto-page is enabled, the system will use the last installed idle digital port to per-
form the page. Therefore, if a phone is on the last installed port (e.g., X111 on a system
with a single 600 Card), the phone’s user may experience a brief delay in telephone operation if he/she picks up the handset (or presses SPEAKER) during the auto-page.
11. External forwarding — Allows the station user to enable the off-premises-“reach-me” feature
(the user can give, to callers who are forwarded to his/her voice mailbox, the option of trying to
reach him/her at another number). This requires a trunk-to-trunk transfer and will use two CO
lines for the length of the conversation. The user must set his/her mailbox to answer with personal greeting 2 and inform the caller to press 4 for this option. After the system dials the last
digit of the external forwarding number, it will begin to play a prompt saying, “You are receiving
a forwarded call. Press any key to accept.” This prompt will play continuously for 30 seconds.
When DTMF is detected at the remote end, both trunks are connected. If no DTMF is detected,
the caller is forwarded to the user’s voice mail.
Default: Disabled.
*
12. Forwarding to toll numbers — This feature is used in conjunction with external forwarding (see
previous item). When enabled, this feature lets the user program a long-distance number for
external forwarding.
Default: Disabled.
13. Trunk-to-trunk transfer — When enabled, this lets the station user initiate a trunk-to-trunk
transfer. The user, while connected to a CO line, can press TRANSFER, followed by his/her line
access code(s), dial an off-site number and then complete the trunk-to-trunk transfer by simply
hanging up. Both parties are then connected.
Default: Disabled.
Important:
USE OF FEATURES, SUCH AS TRUNK-TO-TRUNK TRANSFER, THAT REQUIRE TRUNK-TO-TRUNK
CONNECTIONS WILL INCREASE THE RISK OF TOLL FRAUD. IN NO EVENT SHALL ESI (ESTECH
SYSTEMS, INC.) BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL
DAMAGES WHATSOEVER INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, FRAUDULENT TOLL CHARGES,
LOSS OF BUSINESS PROFITS, BUSINESS INTERRUPTIONS OR ANY OTHER COSTS OR DAMAGES RELATED THERETO ARISING FROM THE USE OF THESE FEATURES.
*
While the two trunks are connected, the system constantly monitors the lines for open loops. If it detects an open loop
on either line, it terminates both CO connections. Additionally, the system periodically will monitor for voice on the connected COs. If it detects no voice traffic, it terminates both CO connections. Finally, if both COs are connected for a
programmable period (default is 60 minutes), the system will terminate the connection, regardless of the presence or
absence of activity.
D.2
Page 19

IP Series Administrator’s Manual Function 3: Extension programming
Example: Here is a portion of a completed Programming Worksheet (Appendix II)
for extension feature authorization. Note that:
• Extension 100 cannot record calls but can make toll calls (except those listed
in the deny table) and can access the system speed dial numbers.
• In comparison, Extension 102 cannot make general toll calls but also can call
any system speed dial number, even if it’s a toll call.
• (Extension 200 doesn’t have DND, AA block, record or service observing
capability because it’s an analog port.)
1.
Ext.
100 Jane Y Y N N N Y Y N N N N
102 Sally Y Y N Y N N Y Y N N N
200* Bill Y N Y Y N N N N
2.
Name
3.
Call
wait
4.
DND
5.
AA
block
6.
Rec.
7.
Svc.
obs.
8.
Tol l
allow
9.
Sys.
spd.
dial
10.
Auto
page
11.
Ext.
fwdg.
12.
Fwdg.
to toll
nos.
Trun k-
to-trunk
13.
xfer
*
An example of an analog phone.
D.3
Page 20

Function 3: Extension programming IP Series Administrator’s Manual
(This page included for pagination purposes only.)
D.4
Page 21

IP Series Administrator’s Manual Function 5: Voice mail programming
Function 5: Voice mail programming
To simplify initial installation, all programmed extensions will automatically have the generic personal greeting, “You have reached the mailbox for extension [xxx].” The mailbox user should
replace this with a personalized greeting.
Function 53: Guest/info mailboxes
Mailboxes numbered 300–489 can be programmed as either a guest or info mailbox. Enter the
mailbox number and select Guest or Info by pressing a scroll (▼ or ▲) key.
Guest mailboxes
Guest mailboxes are designed to be used by personnel, such as in outside sales or manufacturing,
who do not have an extension assigned to them. A guest mailbox requires no programming other
than the assigning of a name.
Note: A guest mailbox can be handled like a regular extension (i.e., listed in the directory, assigned
a station key, etc.).
If a programmable feature key is programmed as a virtual mailbox key with a guest mailbox number, the key’s LED will blink, to indicate that new messages exist.
station, press VOICEMAIL, * and then either the DSS key or dialing the mailbox number.
To record a greeting, press PROG/HELP, * and then the mailbox number, and follow the prompts.
The default password is the mailbox number.
To retrieve messages from the outside, press * and the mailbox number during the Main Greeting.
Default: 300–489 as Guest.
1
To retrieve messages from a
Info mailboxes
Info mailboxes can be used to give callers information on a variety of different subjects by
“publishing” these mailbox numbers. Info Mailboxes are identical to Guest Mailboxes except that
the caller will not be given a record tone after the personal greeting (the information to be played).
Instead, the caller will be forwarded as programmed in this function (default is the caller will be
disconnected after the information is played). The maximum length of the record time is 14 minutes.
Guest/info mailboxes are created or deleted here, but are turned “on” only when a personal greeting (the information to be played) has been recorded. Deleting the personal greetings will turn “off”
the mailbox.
To record a greeting, press PROG/HELP, * and then the mailbox number, and follow the prompts.
The default password is the mailbox number.
Below is an example of a completed Programming Worksheet, showing the sequence of programming:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
MB Name Type CF day CF night
300 Dana Guest
302 Literature Info X/MB/ID X/MB/ID
1
Otherwise, the key is a DSS key that allows for single-key transfer of a call with no message indication.
E.1
Page 22

Function 5: Voice mail programming IP Series Administrator’s Manual
Each programming step is defined as follows:
1. Mailbox number — Input a mailbox number, 300–489.
2. Name — The mailbox name is used for the LCD display, reports, and as a programming aid. The
name length can be no longer than 10 characters (see “Entering alphanumeric characters,”
page B.2).
Default: The Mailbox number.
3. Type — Select a mailbox type: Guest or Info.
Default: Guest.
4. & 5.
Call forward (info mailbox only) — An info mailbox can be set to call forward after the per-
sonal greeting has played to an extension, department, a mailbox or a branch ID for day mode
and differently for night mode.
Default: ID9999 (automatic disconnect)
Function 54: Group mailboxes and the broadcast mailbox
Broadcast mailbox
Mailbox 500, the broadcast mailbox, is a special group mailbox which can be used to leave mes-
sages for all of the system’s station users who have recorded a personal greeting. The broadcast
mailbox’s user list cannot be edited. Guest mailboxes are not included in the broadcast group.
Group mailboxes
You can assign up to 16 group mailboxes (501–516) to the IP Series system; each group mailbox
can have up to 45 members. Anyone who knows the password can leave messages for all users
listed as members of that group and who have recorded a personal greeting. The Installer, Administrator or group mailbox “owner(s)” may set or change the list of Group Mailbox members. To record
a greeting, press PROG/HELP, * and then the mailbox number, and follow the prompts. The default
password is the mailbox number.
Important: A group mailbox is turned “on” (able to record and playback messages) only when
its “owner” has recorded a greeting for it, such as “This is the group mailbox for East
Coast Regional Sales.” Similarly, deleting the group mailbox greeting will turn “off”
the group mailbox; any outstanding messages will remain in its members’ mailboxes
until erased by each member.
Note: If 0 (zero) is programmed as the password, anyone can leave group messages or program
the Group Mailbox.
Note: If a user saves a group message, it will be saved as a new message.
1. 2.
MB Group member mailboxes’ numbers
501 102 104 106 107 122 303 314
The sequence of programming is as follows:
1. Enter the group mailbox number — Range: 501–516.
2. Enter group member mailboxes’ numbers — Separate each by #; enter # # to end the list.
Range: User mailboxes (100–183) and guest mailboxes (300–489).
E.2
Page 23

IP Series Administrator’s Manual Function 5: Voice mail programming
Function 55: Message notification
On a mailbox-by-mailbox basis for user or guest mailboxes, the system can be programmed to call
an off-premises number or another extension to deliver messages and/or dial to an external commercial paging network to activate a user's pager. The IP Series system will call and/or page when
the first new message has been left in a mailbox and will repeat (at the interval of minutes programmed in this function) until the new message(s) have been deleted, saved or moved.
The user can program the numbers and delay and can also select to have only messages marked as
urgent delivered.
The Installer and Administrator can set, on an individual-station basis:
• The number to be called
• A delay period
• The number of attempts (maximum of 99)
• The interval between attempts
• A “quiet period" to suspend phone delivery — e.g., late at night (the quiet period is an on-and-
off time that applies to all days of the week)
Function 551: Station delivery options
Programming of the station options, as shown below, can be performed by the Installer or Administrator. In addition, the user can change his phone number and delay time or pager number (but not
pager delay time). The phone number’s maximum length is 24 digits.
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Number Delay Attempts Interval Quiet on Quiet off
1. Phone 2145556789 30 6 60 10:30PM 7:15AM
2. Pager 2145551234 10 30
To program, enter the extension number to program and select phone or pager to program. Then, enter:
1. Phone/pager number — The number to be dialed (without the CO Line Group [9, 8 or 71–76]).
2. Delay — How many minutes the system is to wait before dialing the phone number.
This allows the user to pick up a message if he is in the office.
Range: 0–500.
Default: 0.
3. Attempts — How many times that the system will call/page.
Range: 0–99. (0 turns off delivery.)
Default: 3.
4. Interval — How many minutes should elapse between attempts.
Range: 10–1440.
Default: 30.
5. Quiet period on — When the quiet period should begin.
Default: (None.)
6. Quiet period off — When the quiet period should end.
Default: (None.)
E.3
Page 24

Function 5: Voice mail programming IP Series Administrator’s Manual
Function 552: Delivery/paging parameters
The sequence of programming is as follows:
1. CO line access — Enter the CO Line Group (9, 8, or 71–76) that is to be accessed for delivery.
Default: 9.
2. Maximum lines — Enter the maximum number of lines (in the selected CO line group) that the
system can access simultaneously. Make enough lines available to accommodate high notification traffic (but be careful: if you make available all lines in the selected line group and high
notification traffic occurs, the system could tie up all lines).
Default: 1.
3. Pager dialing pause — When paging, the IP Series system will send the mailbox number to be
shown in the pager’s display. To allow time for the paging service to answer, enter the pause, in
seconds, that is to occur between when the IP Series system dials the pager number and when
it then dials the mailbox number.
Range: 0–20.
Default: 6.
Function 56: Cascade paging mailboxes
In addition to individual mailbox paging, the system can support up to 10 cascade paging mailboxes
(520–529). These can be assigned to anyone who requires escalating levels of paging beyond the
single level available in all user mailboxes. In this function, you program the paging numbers and
number of times each is to be paged before the next paging number is added; additionally, the
mailbox owner can program these settings. To record a greeting, press PROG/HELP, * and then the
mailbox number, and follow the prompts. The default password is the mailbox number.
Function 561: Cascade mailbox options
The user can program up to three paging numbers, of up to 24 digits each, to be paged whenever
the mailbox takes a new or urgent message. The system will page the first paging number (for the
number of times listed), then add the second paging number (for the number of times listed),
then add the third paging number and will continue to page all three pagers until the message
has been retrieved.
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
MB 1st Number Attempts 2nd Number Attempts 3rd Number
520 2145553232 2 2145554254 3 2145555452
To program this, enter:
1. The mailbox number — Range: 520–529.
2. First pager number — The number to be dialed (without the CO Line Group [9, 8 or 71–76]).
3. Attempts — How many times the system will page (up to 20) before adding the second
pager number. Range: 0–99. (0 turns off delivery.)
4. Second pager number — The number to be dialed (without the CO Line Group [9, 8 or 71–76]).
5. Attempts — How many times the system will page (up to 20) before adding the third
pager number. Range: 0–99. (0 turns off delivery.)
6. Pager number — The number to be dialed (without the CO Line Group [9, 8 or 71–76]).
E.4
Page 25

IP Series Administrator’s Manual Function 5: Voice mail programming
Function 562: Cascade paging parameters
The cascade paging mailboxes will use the same CO line group and pager dialing pause as programmed in Function 552 (see page E.4).
Paging interval
Enter the number of minutes for the interval between attempts.
Range: 10–1440.
Default: 30.
Function 57: Q & A mailboxes
You can create up to 10 question and answer (Q & A) mailboxes (490–499). Each Q & A mailbox
owner can record up to 10 questions. The questions are recorded in the same manner as recording
users’ multiple personal greetings (see Power user’s guide).
The individual answer segments recorded by the caller are stored as a single message, with the
answer segments separated by short beep tones. Each answer segment's maximum length will be
programmed by the Installer. Normal message handling capability — delete, save, etc. — applies to
the entire message (all segments).
The caller, when recording each answer, can be instructed to conclude by pressing 1 or to pause for
the next question (the system advances when it detects either a three-second period of silence or
the pressing of 1) — e.g., "Record your name at the tone and press 1 when finished”… “Record your
address at the tone and press 1 when finished.”
If the caller fails to respond to two questions in a row, the system disconnects the call.
Important: This programming creates or deletes Q & A mailboxes, but these mailboxes are
“turned on” only when the mailbox owner has recorded questions. Similarly,
deleting all questions “turns off” the mailbox.
To record questions, press PROG/HELP, * and then the mailbox number, and follow the prompts.
The default password is the mailbox number.
Below is an example of a completed Programming Worksheet.
1. 2. 3. 4.
MB Name CF day CF night
490 Employment X/MB/ID X/MB/ID
491 Survey X/MB/ID X/MB/ID
Each programming step is defined as follows:
1. Mailbox number — Input a mailbox number 490 to 499.
2. Name — The mailbox name is used for the LCD display, reports, and as a programming aid. The
name length can be no longer than 10 characters (see “Entering alphanumeric characters,”
page B.2).
Default: The mailbox number.
Call forward
& 4.
answered, to an extension, department, a mailbox or a branch ID for day mode and differently for
night mode.
Default: ID9999 (automatic disconnect).
— A Q & A mailbox can be set to call forward, after the last question has been
E.5
Page 26

Function 5: Voice mail programming IP Series Administrator’s Manual
(This page included for pagination purposes only.)
E.6
Page 27

IP Series Administrator’s Manual Function 6: Recording
Function 6: Recording
Function 61: Re-record system prompts
The IP Series system plays the system prompts to an outside caller at different points in the call
routing or mailbox functions. These system prompts have been pre-recorded at the factory but you
may re-record them, if preferred — e.g., in a different voice or with different instructions.
The auto attendant branch prompts (such as the main greeting or sub-menus) are also recorded
e.g.,
here — enter the branch ID number as the prompt number (
press #).
Note: Auto attendant branch IDs 1–8 include prompts for two daytime and two nighttime greet-
ings. For information on how these prompts are used, refer to:
• “Remote setting of day, night, holiday and auto modes,” page B.4.
• “Live Outside Calls • Operator Station,” in the IP Series User’s Guide (#0450-0189).
Recording a prompt
1.
Enter the branch ID number or system prompt and press #.
2. Practice recording and re-recording the prompt (start and stop by pressing 1).
3. When you have finished recording, press # to confirm.
Note: Deleting a system prompt by pressing HOLD (instead of #) restores to the
default recording.
for branch ID 1, enter 1 and
System prompts
Busy Prompt: 530
•
Default: "That extension is busy.”
• No Answer Prompt: 531 — Plays to the caller if an extension does not answer.
Default: "That extension does not answer.”
• Hold Prompt: 532 — Plays to the caller who makes a menu selection or enters an extension
number.
Default: "One moment, please.”
• Q/Z Prompt: 534 — Plays to a caller who has selected an alphabetic directory; instructs the caller
to press 1 for the letters Q or Z since these two letters do not appear on the phone keypad; plays
at the end of the first directory prompt (but only if a name in the directory starts with a Q or Z).
Default: "For the letters Q or Z, use key number 1.”
• No Names Matched Prompt: 535 — Played to the caller if, in a directory branch, the first letter
he/she selected does not have any names associated with it, or if he/she has listened to all of the
names played and has not made a selection. After playing the prompt, the IP Series system forwards the call to the extension, branch or mailbox as programmed in call forward no response.
Default: "No names matched; one moment please.”
• End of Message Prompt: 537 — Plays after a caller leaving a message presses 1 to stop re-
cording (or when he/she reaches the maximum message length); the prompt then tells the caller
his/her options.
Default: “To continue this recording, press 1; to return to the main menu, press 8; or, if finished,
press * and hang up.”
— Plays to the outside caller if an extension is busy.
F.1
Page 28

Function 6: Recording IP Series Administrator’s Manual
ACD Queue Prompt: 538
•
ACD department.
Default: “All agents are currently assisting other customers. Please hold; your call will be answered
in the order received.”
• ACD Hold Prompt: 539 — Is periodically played to callers on hold in an ACD department when all
extensions are busy.
Default: “All agents are still busy assisting other customers. Please hold; your call will be an-
swered in the order received.”
• Holiday Main Greeting Prompt: 540 — Plays to callers when the system has been manually
placed in holiday mode.
Default: "Thank you for calling. Our office is closed in observance of the holiday. You may dial
your party’s extension, at any time, or please call back during regular business hours.”
Note: While in holiday mode, the IP Series system follows night mode programming for call rout-
ing. The day/night mode setting and holiday greeting can be activated remotely (see
“Remote setting of day, night and holiday modes," page B.4).
— The first prompt played to a caller when all extensions are busy in an
Function 62: Record directory names
This function is accessible only if a Directory Branch has been created as part of Auto Attendant
programming. Enter the extension number and record the name (and, if this is a by-alpha branch,
input the name key.)
Important: Make photocopies of the blank worksheet for preparing directories and making fu-
ture changes. As names change, the Administrator can enter this function and
change any field via the Administrator password.
1. 2. 3.
Ext. Recorded name Key
102 George Straite 4
113 Janet Smith 5
Each programming step is defined as follows:
1. Extension number — Enter the extension number for the directory name.
2. Record name — Press 1 to begin recording and press 1 again when finished.
3. Name key — (Necessary if the directory type is indexed by-alpha; consult your Installer for
additional details.)
Enter the numeric equivalent to the letters appearing on a phone keypad (for Q or Z, use 1).
Note: To re-record the prompt that says, “Enter the first letter of the person’s last name,” you must
enter Function 61 and then enter the ID number of the directory branch.
F.2
Page 29

IP Series Administrator’s Manual Function 6: Recording
Function 63: Message-on-hold (MOH) programming
MOH can be:
• A live feed from an external music source connected to the MOH connector located on the side
of the cabinet.
• One of three default, generic MOHs pre-recorded by the factory.
• One of up to five custom MOHs loaded into the system by using a cassette recorder connected to
the MOH connector.
Note: If ACD is used, we recommend that you use Prompt 590, Prompt 591 or a custom prompt
without periodic “voice-overs,” since the ACD Hold Prompt also will be played while a caller
is on hold.
Function 631: MOH source
This selects the source that will be played to callers on hold.
Code Source
590
591
592
593 Pre-recorded with “dial 0 or extension from hold”
594-598
Default: 592 (generic message-on-hold).
Live external source
Pre-recorded music
Pre-recorded with “please continue to hold”
Customer-recorded message on hold
Function 632: MOH recording
1.
Connect the message/music source to the MOH port on the side of the cabinet.
Note: The connector is monophonic-only — if you use a stereo source, you must
either set it to output mono, if possible, or use a stereo-to-mono conversion
cable (or adapter).
2. Enter the prompt number to be recorded.
3. Press 1 to begin recording. To aid you in queuing, the source will be played through the
phone’s speaker.
Note: The recorded material should not have a “beginning” or “end” — so that playback can
loop continuously.
4. Press 1 when finished. The recording will play back so you can review it.
5. Press # to accept the recording.
Function 633: MOH volume
If a custom MOH is recorded, the output volume can be adjusted in this function.
Range: 1 (faint)–12 (loudest).
Default: 6.
Note: If an external audio source such as a radio is used for MOH, adjust the volume at
the source.
Note: To turn live MOH volume completely off, turn off volume at the source.
To turn recorded MOH volume completely off, select (in Function 631, above) one of the
prompts in the range of 594–598, but make sure it’s blank. These prompts are blank by
default; if you have recorded some audio on all of them, just select one and record a few
seconds of silence.
F.3
Page 30

Function 6: Recording IP Series Administrator’s Manual
(This page included for pagination purposes only.)
F.4
Page 31

Index
Alphanumeric characters, entering, B.2
Auto attendant block, D.1
Call waiting, D.1
Day/night mode, B.4
Remote setting, B.4
Do not disturb (DND), D.1
Esi-Access software, B.1
Esi-Dex, C.1
System speed dial, D.1
Features overview, A.1–A.2
ACD, A.3
Auto attendant, A.3
Phone, A.1
Voice mail, A.2
Functions
Function 6 — recording, F.1–F.3
Mailboxes
Cascade paging, E.4–E.5
Group, E.2
Guest/info, E.1–E.2
Q & A, E.5
MOH, F.2–F.3
Password, Administrator, C.1
Programming
Accessing user station programming, B.2
Keys, B.1
System, B.5
System fixed numbering plan, B.3
Prompts, re-recording, F.1–F.2
Re cordin g, D .1, F.1–F.3
MOH pr ogramming, F.2–F.3
Recording directory names, F.2
Re-recording system prompts, F.1–F.2
Service observing, D.1
Speed-dialing. See Esi-Dex
System prompts, re-recording, F.1–F.2
Time/date, setting, C.1
Toll restriction, D.1
Voice mail programming
Cascade paging mailboxes, E.4–E.5
Group mailboxes, E.2
Guest/info mailboxes, E.1–E.2
Message notification, E.3–E.4
Q & A mailboxes, E.5
 Loading...
Loading...