Page 1
EPSON
EPSON Stylus Color 600
SERVICE MANUAL
COLOR INK-JET PRINTER
SEIKO EPSON CORPORATION
4007367
Page 2
NOTICE
All rights reserved. Reproduction of any part of this manual in any form whatsoever
without SEIKO EPSON’s express written permission is forbidden.
The contents of this manual are subjects to change without notice.
All efforts have been made to ensure the accuracy of the contents of this manual.
However, should any errors be detected, SEIKO EPSON would greatly appreciate
being informed of them.
The above notwithstanding SEIKO EPSON can assume no responsibility f or any errors
in this manual or the consequences thereof.
EPSON is a registered trademark of SEIKO EPSON CORPORATION.
General Notice:
Other product names used herein are for identification purposes only and may be
trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies.
Copyright 1997 by SEIKO EPSON CORPORATION
Nagano, Japan
Page 3

PRECAUTIONS
Precautionary notations throughout the text are categorized relative to 1) personal injury and 2)
damage to equipment.
WARNING
CAUTION
The precautionary measures itemized below should always be observed when performing
repair/maintenance procedures.
Signals a precaution which, if ignored, could result in serious or fatal personal injury.
Great caution should be exercised in performing procedures preceded by
WARNING Headings.
Signals a precaution which, if ignored, could result in damage to equipment.
WARNING
1. ALWAYS DISCONNECT THE PRODUCT FROM BOTH THE POWER SOURCE AND
PERIPHERAL DEVICES PERFORMING ANY MAINTENANCE OR REPAIR PROCEDURES.
2. NO WORK SHOULD BE PERFORMED ON THE UNIT BY PERSONS UNFAMILIAR WITH
BASIC SAFETY MEASURES AS DICTATED FOR ALL ELECTRONICS TECHNICIANS IN
THEIR LINE OF WORK.
3. WHEN PERFORMING TESTING AS DICTATED WITHIN THIS MANUAL. DO NOT
CONNECT THE UNIT TO A POWER SOURCE UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO. WHEN THE
POWER SUPPLY CABLE MUST BE CO NNECTED, USE EXT REME CAUT ION IN W O RKING
ON POWER SUPPLY AND OTHER ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS.
CAUTION
1. REPAIRS ON EPSON PRODUCT SHOULD BE PERFORMED O NLY BY EPSON CERTIFIED
REPAIR TECHNICIAN.
2. MAKE CERTAIN THAT T HE SOURCE VOLT AGE IS THE SAME AS T HE RATED VOLT AGE,
LISTED ON THE SERIAL NUMBER/RATING PLATE. IF THE EPSON PRODUCT HAS A
PRIMARY AC RATING DIFFERENT FROM AVAILABLE POWER SOURCE, DO NOT
CONNECT IT TO THE POWER SOURCE.
3. ALWAYS VERIFY THAT T HE EPSON PRODUCT HAS BEEN DISCONNECT ED FROM THE
POWER SOURCE BEFORE REMOVING OR REPLACING PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARDS
AND/OR INDIVIDUAL CHIPS.
4. IN ORDER TO PROTECT SENSITIVE MICROPROCESSORS AND CIRCUITRY, USE
STATIC DISCHARGE EQUIPMENT, SUCH AS ANTI-STATIC WRIST STRAPS, WHEN
ACCESSING INTERNAL COMPONENTS.
5. REPLACE MALFUNCTIONING COMPONENTS ONLY WITH THOSE COMPONENTS BY
THE MANUFACTURE; INTRODUCTION OF SECOND-SOURCE ICs OR OTHER
NONAPPROVED COMPONENTS MAY DAMAGE THE PRODUCT AND VOID ANY
APPLICABLE EPSON WARRANTY.
Page 4

PREFACE
This manual descr ibes functions , theory of electrical and m echanical operations , maintenanc e, and
repair of EPSON Stylus Color 600.
The instructions and procedur es included herein are intended for the experience r epair technician,
and attention should be given to die precautions on the preceding page. The Chapters are
organized as follows:
CHAPTER 1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Provides a general product overview, lists specifications, and illustrates the main components of the
printer.
CHAPTER 2. OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Describes the theory of printer operation.
CHAPTER 3. DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
Includes a step-by-step guide for product disassembly and assembly.
CHAPTER 4. ADJUSTMENT
Includes a step-by-step guide for adjustment.
CHAPTER 5. TROUBLESHOOTING
Provides EPSON-approved techniques for troubleshooting.
CHAPTER 6. MAINTENANCE
Describes preventive maintenance techniques and lists lubricants and adhesives required to
service the equipment.
APPENDIX
Describes connector pin assignments, circuit diagrams, circuit board component layout and
exploded diagram.
The contents of this manual are subject to change without notice.
Page 5
REVISION SHEET
Revision Issued Data Contents
Rev. A February 20,1997 First issue
Page 6

TABLE OF CONTENTS
CHAPTER 1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
CHAPTER 2. OPERATING PRINCIPLES
CHAPTER 3. DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
CHAPTER 4. ADJUSTMENT
CHAPTER 5. TROUBLESHOOTING
CHAPTER 6. MAINTENANCE
APPENDIX
Page 7

Chapter 1
Product Descriptions
1.1 Features....................................................................................................................1
1.2 Specifications..........................................................................................................2
1.2.1 Printing Specification................................................................................................................ 2
1.2.2 Paper Specification ................................................................................................................... 5
1.2.2.1 Cut Sheet...................................................................................................................... 5
1.2.2.2 Transparency Film / Glossy Paper............................................................................... 5
1.2.2.3 Envelope....................................................................................................................... 5
1.2.2.4 Index Card.................................................................................................................... 5
1.2.3 Adjust Lever Settings (PG adjust lever).................................................................................. 6
1.2.4 Printable Area ............................................................................................................................ 7
1.2.4.1 Cut Sheet...................................................................................................................... 7
1.2.4.2 Envelope....................................................................................................................... 8
1.2.5 Environmental Condition.......................................................................................................... 9
1.2.6 Ink Cartridge Specifications................................................................................................... 10
1.2.6.1 Black Ink Cartridge.....................................................................................................10
1.2.6.2 Color Ink Cartridge.....................................................................................................11
1.2.7 Physical Specification............................................................................................................. 12
1.2.8 Electric Specification .............................................................................................................. 13
1.2.9 Reliability.................................................................................................................................. 13
1.2.10 Safety Approvals ................................................................................................................... 13
1.2.11 Acoustic Noise....................................................................................................................... 13
1.2.12 CE Marking............................................................................................................................. 13
1.2.13 Printer Language and Emulation......................................................................................... 14
1.3 Interface..................................................................................................................16
1.3.1 Parallel Interface (Forward Channel)..................................................................................... 16
1.3.2 Parallel Interface (Reverse Channel)..................................................................................... 17
1.3.2.1 Prevention Hosts from Data Transfer Time-out......................................................... 19
1.3.3 Serial Interface......................................................................................................................... 20
1.4 Control Panel .........................................................................................................21
1.4.1 Indicators.................................................................................................................................. 21
1.4.2 Panel Functions....................................................................................................................... 22
1.4.3 Printer Condition and Panel Status....................................................................................... 23
1.5 Error Status............................................................................................................24
1.5.1 Ink Out ...................................................................................................................................... 24
1.5.2 Paper Out.................................................................................................................................. 24
1.5.3 Paper Jam................................................................................................................................. 24
1.5.4 No Ink-Cartridge Error............................................................................................................. 25
1.5.5 Maintenance Request.............................................................................................................. 25
1.5.6 Fatal Errors............................................................................................................................... 25
1.6 Printer Initialization ...............................................................................................26
1.6.1 Initialization Settings............................................................................................................... 26
Page 8

1.7 Main Components.................................................................................................27
1.7.1 Printer Mechanism................................................................................................................... 27
1.7.2 C200 MAIN Board..................................................................................................................... 28
1.7.3 C206 PSB/PSE Board...............................................................................................................29
1.7.4 C206 PNL Board....................................................................................................................... 29
Page 9

Chapter 1 Product Description
1.1 Features
EPSON Stylus Color 600 is designed for low price for that high performance. The major printer features
are;
High color print quality
1440(H) x 720(V) dpi printing
Standard 4 color printing (CMY+Bk)
Traditional and New Microwave control to eliminate banding
Built-in auto sheet feeder
Holds 100 cut-sheets (64g/‡u)
Holds 10 envelopes
Holds 10 transparency films
Holds 65 special papers
High-speed print
200cps (at LQ/10CPI; No-Draft mode)
By driving the printhead at frequency; 14.4KHz, printing speed is twice faster than Stylus Color.
Compact size
Non-operating : 429mm(W) x 275mm(D) x 168mm(H)
Operating : 429mm(W) x 613mm(D) x 309mm(H)
Weight : 5.2Kg (without cartridge)
Acoustic noise
Approximately 47dB(A)
Two built-in standard I/F
Bi-directional Parallel I/F (IEEE-1284 level 1 device)
Serial I/F (Macintosh-compatible / up to 900Kbps)
The table below shows consumable for EPSON Stylus Color 600.
Table 1-1 Available Consumable
Item Code Remark
Black Ink Cartridge S020093 Color: Black
Color Ink Cartridge S020089 Color: Cyan/Magenta/Yellow
EPSON 360 dpi Ink Jet Paper S041025 Size: A4(200 sheets)
EPSON 360 dpi Ink Jet Paper S041059 Size: A4(100 sheets)
EPSON 360 dpi Ink Jet Paper S041060 Size: Letter(100 sheets)
Photo Quality Ink Jet Paper S041026 Size: A4(200 sheets)
Photo Quality Ink Jet Paper S041061 Size: A4(100 sheets)
Photo Quality Ink Jet Paper S041062 Size: Letter
Photo Quality Ink Jet Paper S041067 Size: Legal
Photo Quality Glossy Paper(New Release) S041126 Size: A4
Photo Quality Glossy Paper(New Release) S041124 Size: Letter
Photo Quality Glossy Film S041071 Size: A4
Photo Quality Glossy Film S041072 Size: Letter
Photo Quality Glossy Film S041107 Size: A6
Ink Jet Transparencies S041063 Size: A4
Ink Jet Transparencies S041064 Size: Letter
Photo Quality Ink Jet Card S041054 Size: A6
Photo Quality Ink Jet Card S041121 Size: 5 x 8 inches
Photo Quality Ink Jet Card S041122 Size: 10 x 8 inches
Photo Quality Self Adhesive Sheet S041106 Size: A4
Rev. A
1-1
Page 10
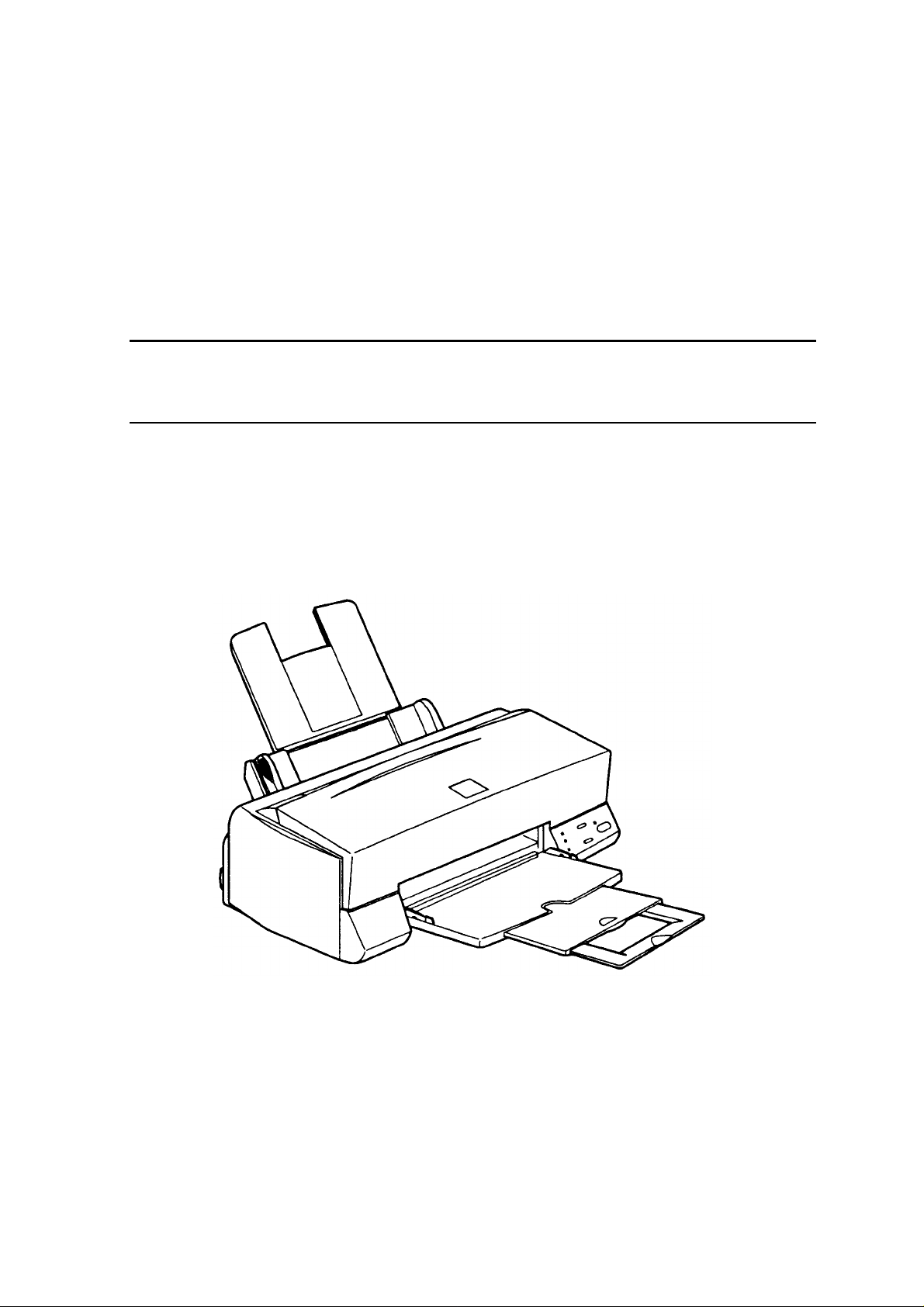
EPSON Stylus Color 600
2
1.2 Specifications
This section describes the product specifications for EPSON Stylus Color 600.
1.2.1 Printing Specification
Print method
On-demand color ink jet printing
Nozzle configuration
Black: 64 nozzles (32 nozzles x2 staggered / Nozzle pitch = 180dpi/vertical)
Color: 32 nozzles (per color (CMY) / Nozzle pitch = 90dpi/vertical)
Print Direction
Bi-directional printing with logical seeking for text and graphics
Print Buffer: 32KBytes
Print speed and Printable Columns
Table 1-2 Print Speed (Text Mode)
Character Pitch Printable
Column
Draft Speed
(CPS)
10 CPI (Pica) 80 400 200
12 CPI (Elite) 96 480 240
15 CPI 120 600 300
17 CPI (Pica Condensed) 137 684 342
20 CPI (Elite Condensed) 160 800 400
Table 1-3 Print Speed (Raster Graphics Mode)
Horizontal Resolution Printable
Available Dot CR Speed
Area
180 dpi 8.26 inch 1488 20
360 dpi 8.26 inch 2976 20
720 dpi 8.26 inch 5952 20
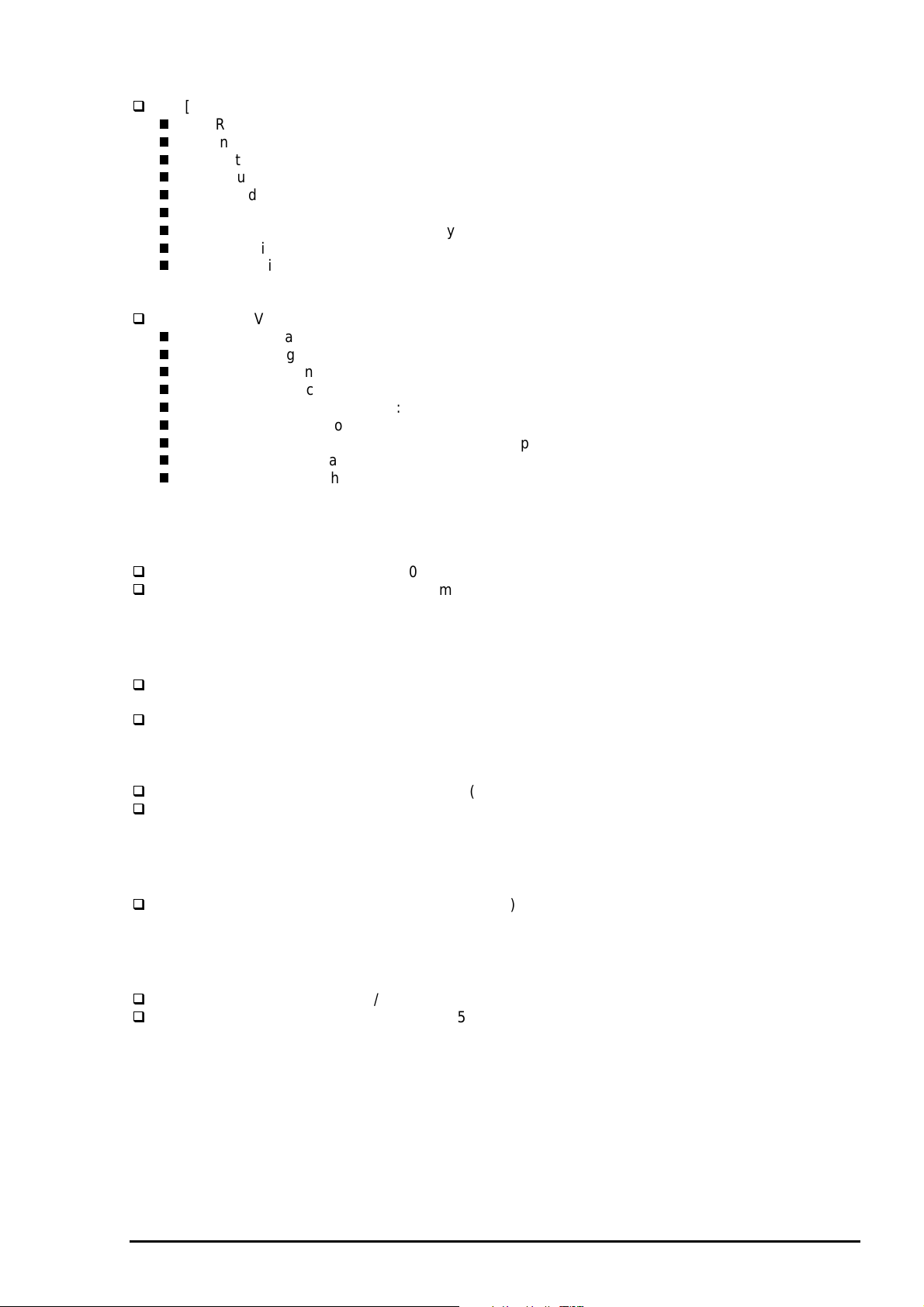
Nozzle arrangement: See figure below.
320/360" (22.5778mm)
144/360" (10.16mm)
32/360" (2.2578mm)
#64
#63
#32 #32 #32
32/360" (2.2578mm)
LQ Speed
(CPS)
(IPS)
Paper feed
direction
180dpi
Black Cyan Magenta Yellow
#3
#2
#1
*Viewed from the back of the head
#1 #1 #1
90dpi
Figure 1-1. Nozzle Layout
1-
Rev. A
Page 11

3
Paper Feeding Method
Friction feed with built in ASF (Auto Sheet Feeder)
Line Spacing
1/6 inch or programmable at 1/360 inch
Paper Path
Top entry (from ASF) only
Feeding Speed
66.6 ms (at 1/6 inch line-feed)
3.0 inch/sec (76.2 mm/sec / at continuous-feed)
ASF Capacity
Size :Index card to Legal
Thickness *1 :Less than 8mm
Paper capacity *2 :Normal cut sheets =100 sheets (64g/m
:Envelops =10
:Coated papers (360dpi) =65
:Coated papers (720dpi) =65
:Glossy papers *3 *4 =30
:Transparency films *4 =30
:Index cards *4 =30
Notes) *1: Total thickness of paper stack on the ASF.
*2: Those numbers above should be considered as reference. The actual paper accumulation
should be considered first.
*3: Only when the top margin is set for 30mm with A4/Letter size paper, otherwise only one sheet
can be set at a time.
*4: Specified paper must be set at the bottom of stack to ensure proper feeding operation:
Chapter 1 Product Description
2
)
Normal paper =Glossy paper, Transparency film
Card Board =Index card
(The one packed with the index card package)
Rev. A
1-
Page 12
EPSON Stylus Color 600
4
Control Code
ESC/P2 and expanded raster graphics code
EPSON Remote command
Character Tables
Legal and 14 international character sets
Standard version: 11 character tables (See Table 1-4 for details)
NLSP version: 19 character tables (See Table 1-4 for details)
Typeface *1
Bit map LQ font: EPSON Roman (10/12/15 CPI, Proportional)
EPSON Sans Serif (10/12/15 CPI, Proportional)
EPSON Courier (10/12/15 CPI)
EPSON Prestige (10/12/15 CPI)
EPSON Script (10/12/15 CPI)
Scaleable font: EPSON Roman (10.5 pt, 8 to 32 pt (every 2 pt))
EPSON Sans Serif (10.5 pt, 8 to 32 pt (every 2 pt))
EPSON Roman T (10.5 pt, 8 to 32 pt (every 2 pt))
EPSON Sans Serif H (10.5 pt, 8 to 32 pt))
Note) *1: Each typeface has four different font style; Normal, Bold, Italic and Bold-Italic.
Table 1-4 Character Table and Typeface
Version Character Table Bit-map Font Scaleable Font
Common EPSON - ;
Roman
Sans Serif
Courier
Prestige
Script
Standard Italic
PC437 (US / Standard Europe)
PC850 (Multilingual)
PC860 (Portuguese)
PC861 (Icelandic)
PC863 (Canadian-French)
PC865 (Nordic)
BRASCII
Abicomp
Roman 8
ISO Latin 1
NLSP Italic
PC437 (US / Standard Europe)
PC850 (Multilingual)
PC437 Greek
PC852 (East Europe)
PC853 (Turkish)
PC855 (Cyrillic)
PC857 (Turkish)
PC866 (Russian)
PC869 (Greek)
MAZOWIA (Poland)
Code MJK (CSFR)
ISO 8859-7 (Latin/Greek)
ISO Latin 1T (Turkish)
Bulgaria (Bulgaria)
PC774
Estonia
ISO 8859-2 (ISO Latin 2)
PC866 LAT
Supported Supported Supported
Supported Supported Supported
Supported Supported Not
EPSON - ;
Roman
Sans Serif
EPSON - ;
Roman T
Sans Serif H
Supported
1-
Rev. A
Page 13

5
1.2.2 Paper Specification
This section describes the types of paper that can be used in this printer.
1.2.2.1 Cut Sheet
[Size]
:A4 [Width 210mm (8.3”) x Length 297mm (11.7”)]
:Letter [Width 216mm (8.5”) x Length 279mm (11.0”)]
:B5 [Width 182mm (7.2”) x Length 257mm (10.1”)]
:Legal [Width 216mm (8.5”) x Length 356mm (14.0”)]
:Half Letter [Width 139.7mm (5.5”) x Length 215.9mm (8.5”)]
:Exclusive [Width 190.5mm (7.5”) x Length 254mm (10”)]
Chapter 1 Product Description
[Thickness]
[Weight]
[Quality]
:0.08mm (0.003”) - 0.11mm (0.004”)
:64g/m
:Exclusive paper, Bond paper, PPC
2
(17Ib.) - 90g/m2 (24Ib.)
1.2.2.2 Transparency Film / Glossy Paper
[Size]
[Thickness]
Note) Transparency printing is only available at normal temperature.
:A4 [Width 210mm (8.3”) x Length 297mm (11.7”)]
:Letter [Width 216mm (8.5”) x Length 279mm (11.0”)]
:A6 [Width 105mm (4.1”) x Length 148mm (5.8”)]
:0.13mm (0.005”) - 0.15mm (0.006”)
:0.17mm (0.007”) - 0.18mm (0.007”) for glossy paper
1.2.2.3 Envelope
[Size]
[Thickness]
[Weight]
[Quality]
Note) 1. Envelop printing is only available at normal temperature.
2. Keep the longer side of the envelope horizontally at setting.
: No.10 [Width 241mm (9 1/2”) x Length 104.8mm (4 1/8”)]
: DL [Width 220mm (8.7”) x Length 110mm (4.3”)]
: C6 [Width 162mm (6.4”) x Length 114mm (4.5”)]
: 0.16mm (0.006”) - 0.43mm (0.017”)
: 45g/m
: Bond paper, Plain paper, Air mail
2
(12Ib.) - 75g/m2 (20Ib.)
1.2.2.4 Index Card
[Size]
[Thickness]
[Weight]
Note) 1. No curled, wrinkled, scuffing or torn paper be used.
2. Set the lever to the proper position according to the paper type you print. (Refer to section
1.2.3 for details)
3. Printing should be performed at room temperature in spite of the paper types.
:A6 Index card [Width 105mm (4.1”) x Length 148mm (5.8”)]
:5x8” Index card [Width 127mm (5.0”) x Length 203mm (8.0”)]
:10x8” Index card [Width 127mm (5.0”) x Length 203mm (8.0”)]
:Less than 0.23mm(0.0091”)
:188g/m
2
Rev. A
1-
Page 14
EPSON Stylus Color 600
6
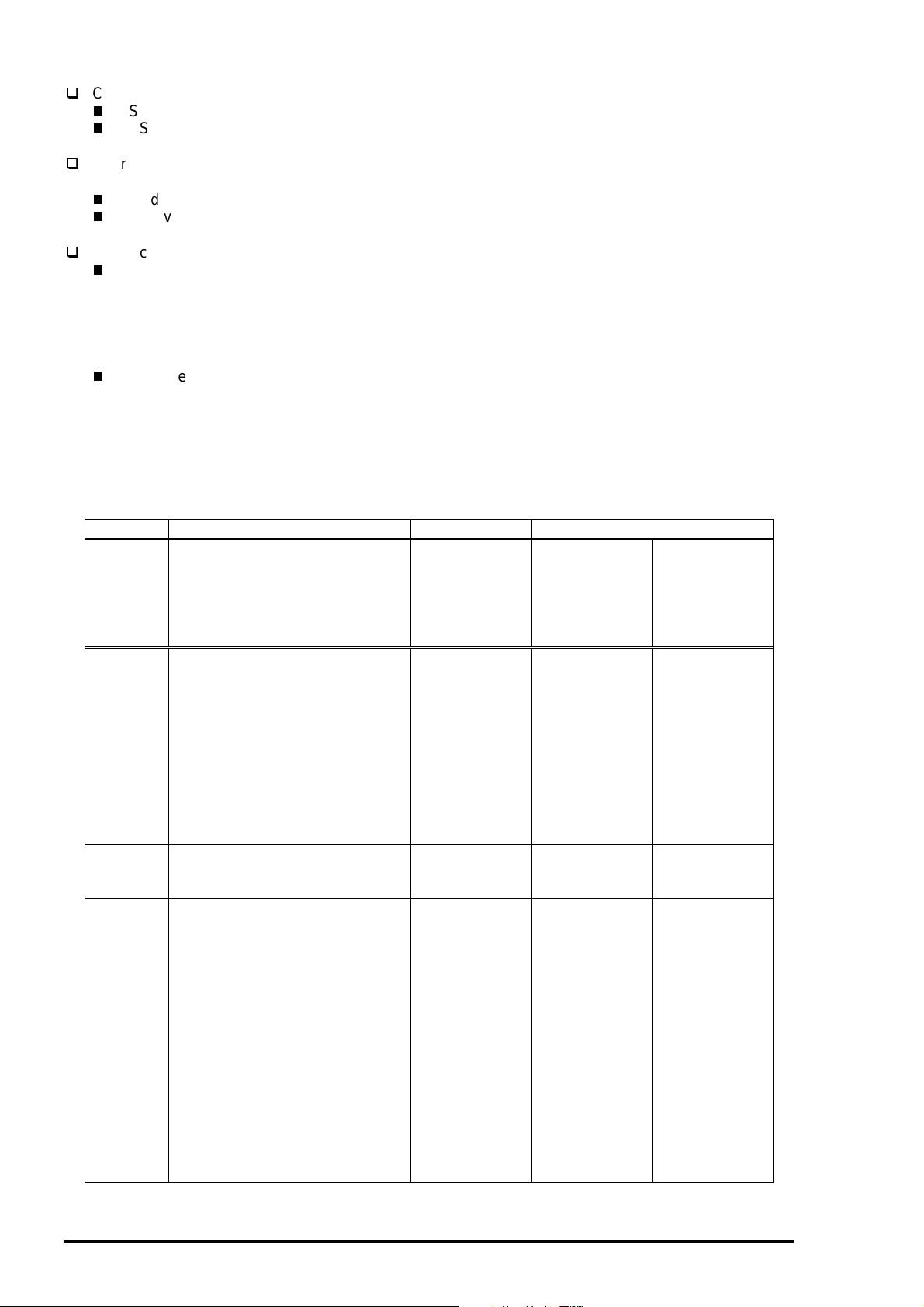
1.2.3 Adjust Lever Settings (PG adjust lever)
The adjust lever located on the right side (blue knob) under the printer cover needs to be set to the proper
position according to the paper you print (Refer to the table below). Also, if there is any dirt caused by
friction on the wavy or wrinkled paper, this can be prevented by changing the lever position to rear position
(marked with “+”) in spite of paper types.
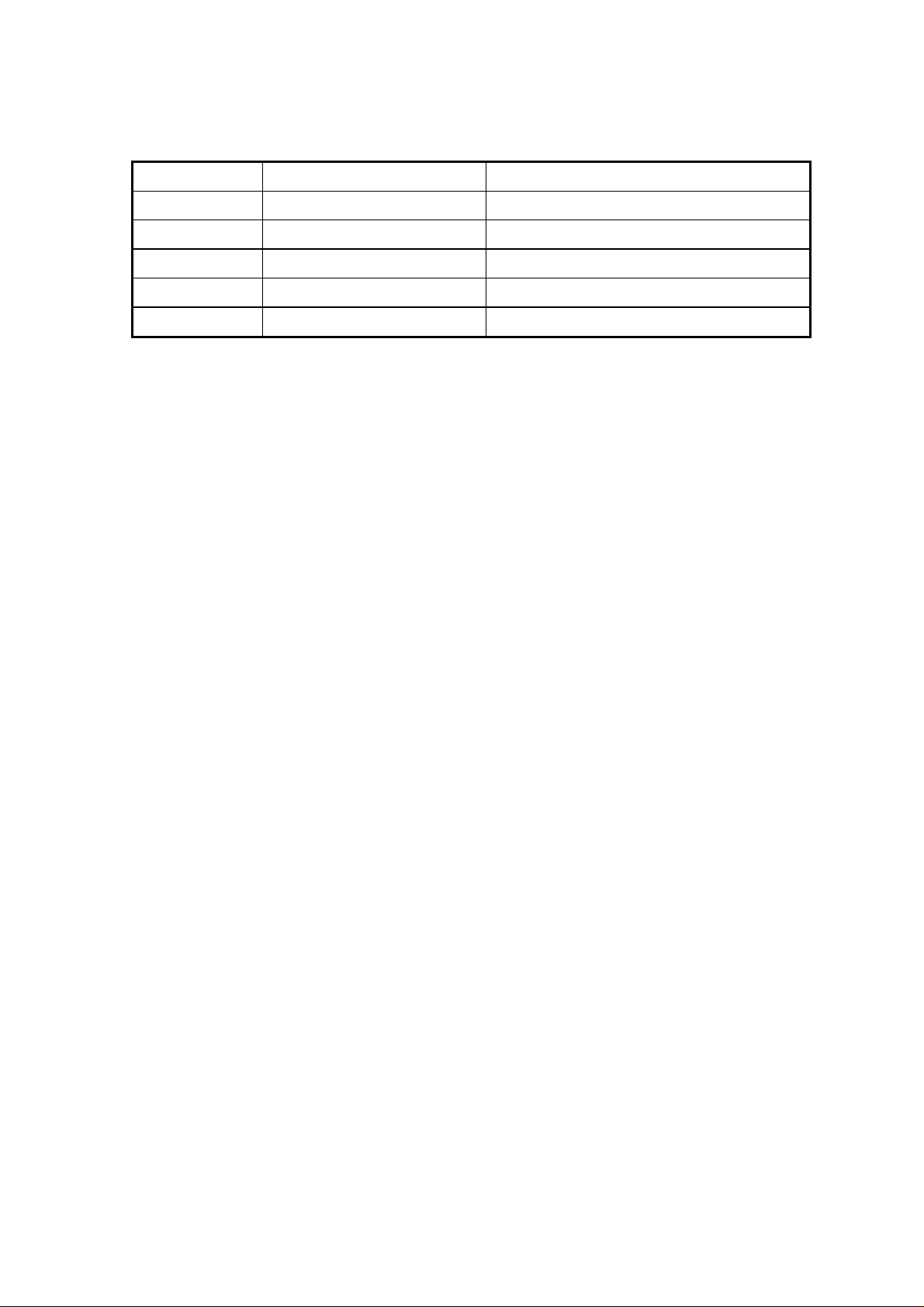
Table 1-5. Adjust Lever Settings
Paper Lever position PG adjustment value
Normal paper,
Coated paper
Transparency film
Label
Envelopes Rear 0.9 mm (2.0mm between head and platen)
Front (Mark "0")
Front 0 mm (1.1mm between head and platen)
+
Rear (Mark "
")
Level adjustment lever
CR Guide Shaft
Bush
Figure 1-2. Adjust Lever Settings
1-
Rev. A
Page 15
Chapter 1 Product Description
7
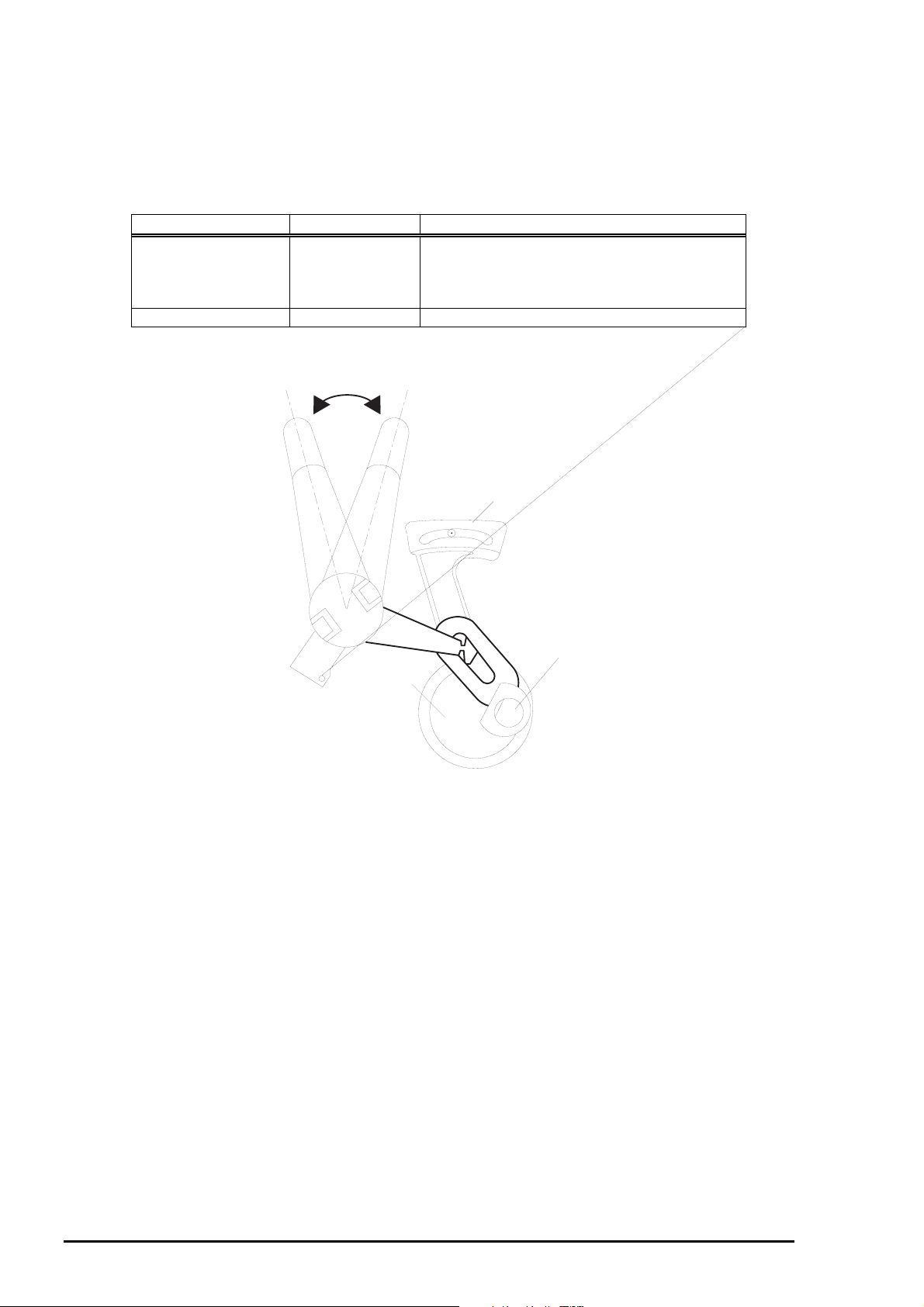
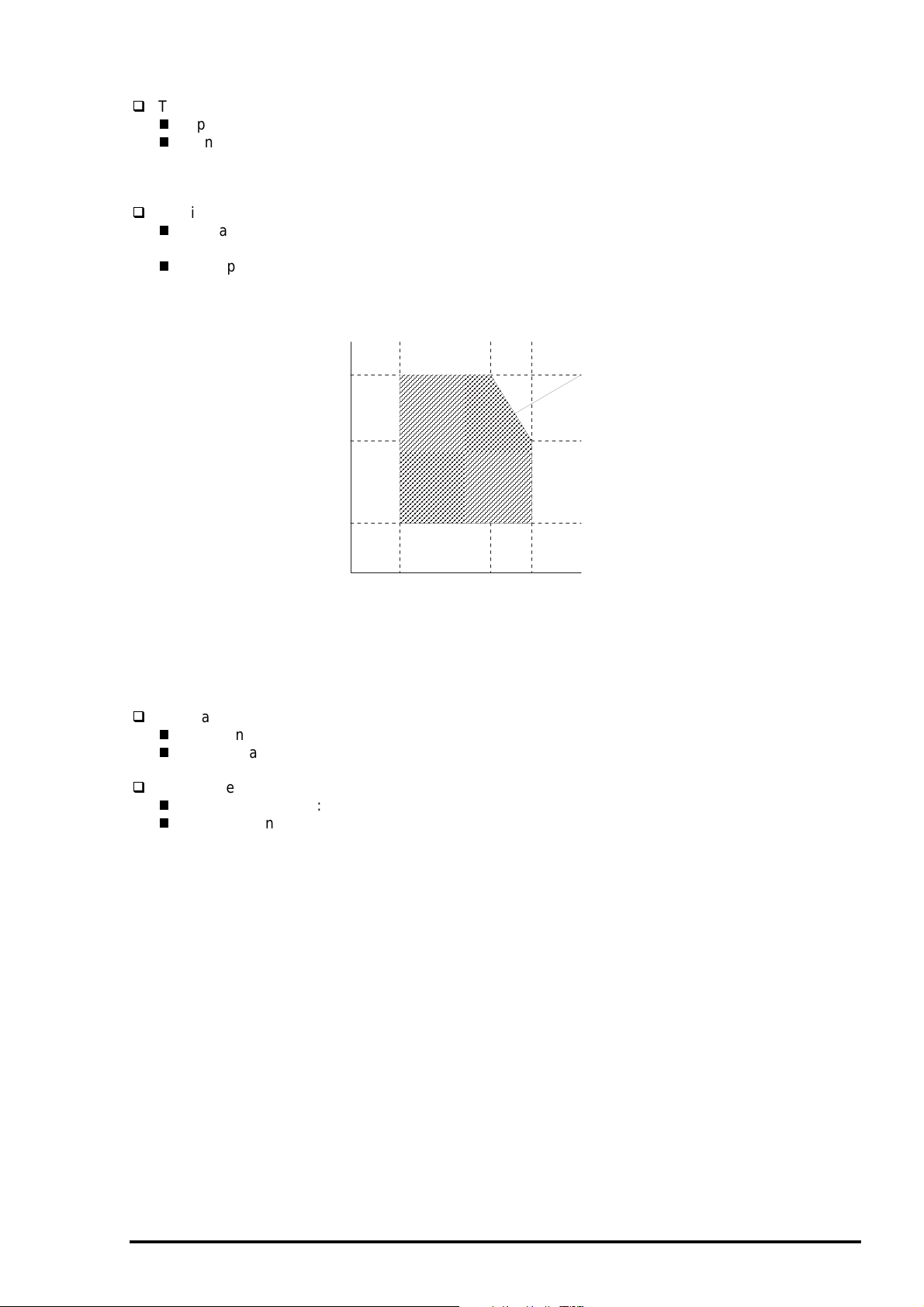
1.2.4 Printable Area
1.2.4.1 Cut Sheet
Following tables show printable areas at Character mode and Raster Graphics mode.
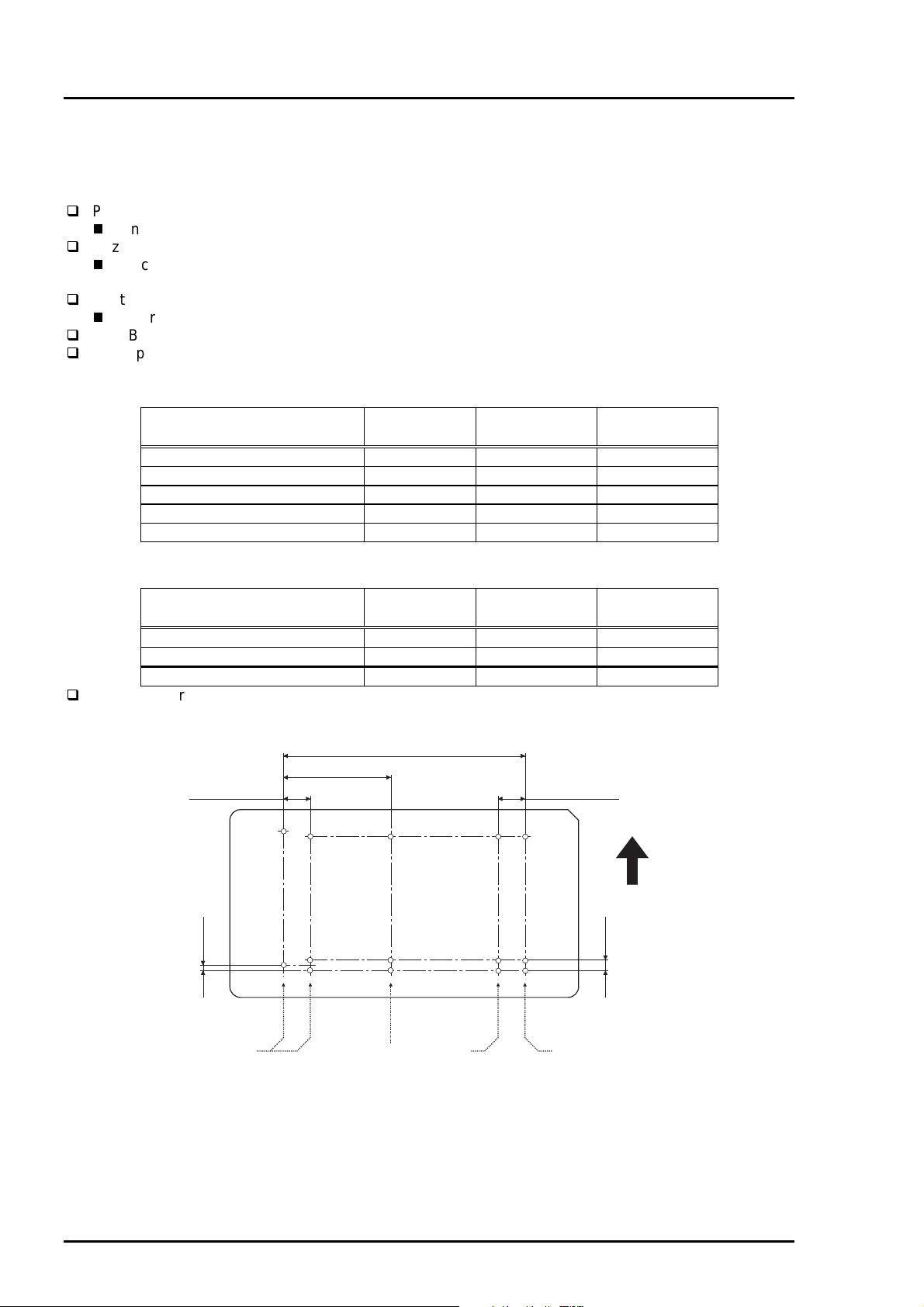
Table 1-6. Character Table
Paper size PW
(Paper width)
(typ.)
PL
(Paper
Length)
(typ.)
LM
(Left margin)
(min.)
RM
(Right
margin)
(min.)
TM
(Top margin)
(min.)
BM
(Bottom
margin)
(min.)
A4 210mm(8.3”) 297mm(11.7”) 3mm(0.12”) 3mm(0.12”) 3mm(0.12”) 14mm(0.54”)
Letter 216mm(8.5”) 279mm(11.0”) 3mm(0.12”) 9mm(0.35”) 3mm(0.12”) 14mm(0.54”)
B5 182mm(7.2”) 257mm(10.1”) 3mm(0.12”) 3mm(0.12”) 3mm(0.12”) 14mm(0.54”)
Legal 216mm(8.5”) 356mm(14.0”) 3mm(0.12”) 9mm(0.35”) 3mm(0.12”) 14mm(0.54”)
Statement 139.7mm(5.5”) 215.9mm(8.5”) 3mm(0.12”) 3mm(0.12”) 3mm(0.12”) 14mm(0.54”)
Executive 190.5mm(7.5”) 254mm(10”) 3mm(0.12”) 3mm(0.12”) 3mm(0.12”) 14mm(0.54”)
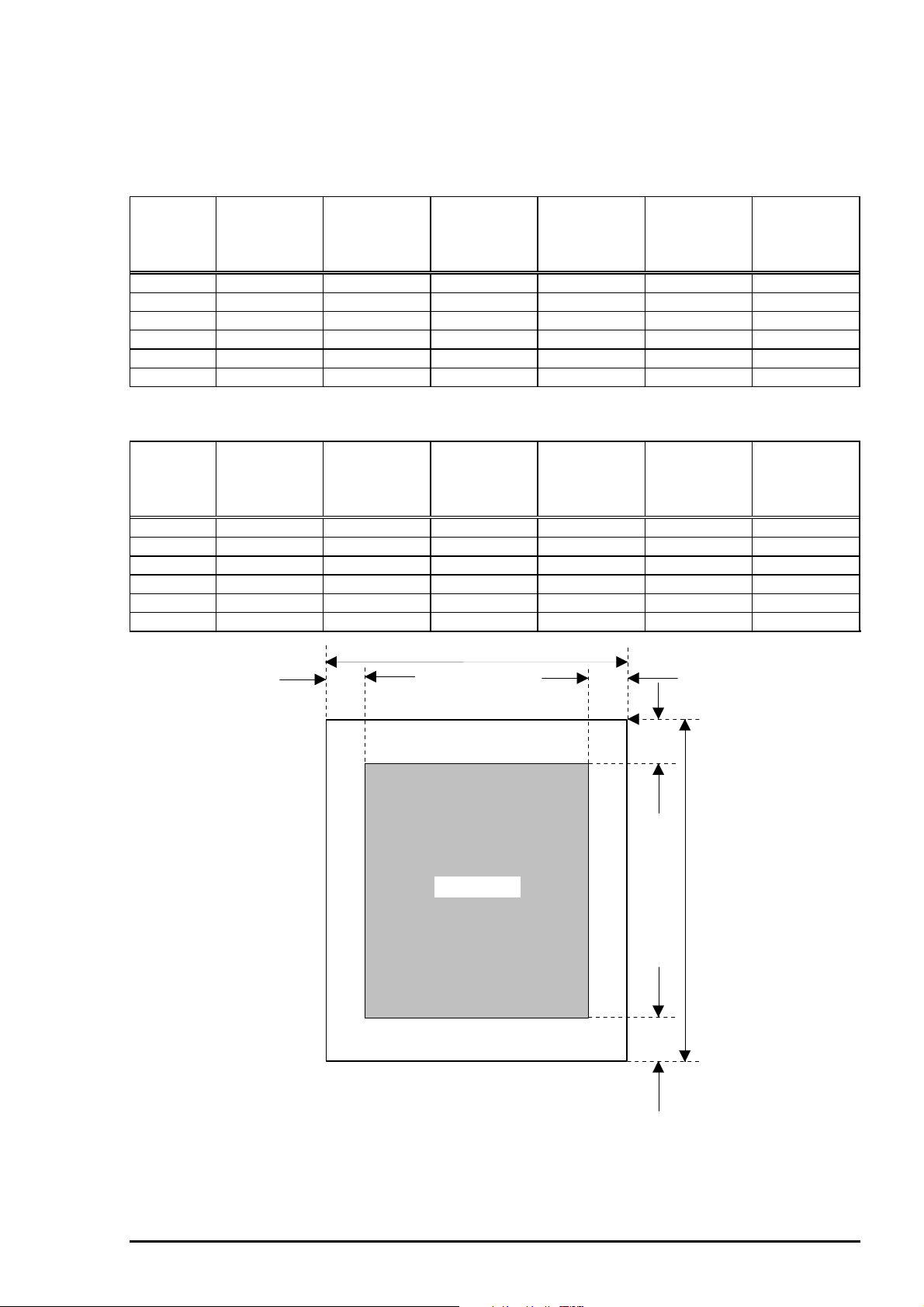
Table 1-7. Raster Graphics Mode
Paper size PW
(Paper width)
(typ.)
PL
(Paper
Length)
(typ.)
LM
Left margin)
(min.)
RM
(Right
margin)
(min.)
TM
(Top margin)
(min.)
BM
(Bottom
margin)
(min.)
A4 210mm(8.3”) 297mm(11.7”) 3mm(0.12”) 3mm(0.12”) 3mm(0.12”) 14mm(0.54”)
Letter 216mm(8.5”) 279mm(11.0”) 3mm(0.12”) 3mm(0.12”) 3mm(0.12”) 14mm(0.54”)
B5 182mm(7.2”) 257mm(10.1”) 3mm(0.12”) 3mm(0.12”) 3mm(0.12”) 14mm(0.54”)
Legal 216mm(8.5”) 356mm(14.0”) 3mm(0.12”) 3mm(0.12”) 3mm(0.12”) 14mm(0.54”)
Statement 139.7mm(5.5”) 215.9mm(8.5”) 3mm(0.12”) 3mm(0.12”) 3mm(0.12”) 14mm(0.54”)
Executive 190.5mm(7.5”) 254mm(10”) 3mm(0.12”) 3mm(0.12”) 3mm(0.12”) 14mm(0.54”)
PW
LM RM
Printable Area
Figure 1-3. Printing Area for Cut Sheet
TM
PL
BM
Rev. A
1-
Page 16
EPSON Stylus Color 600
8
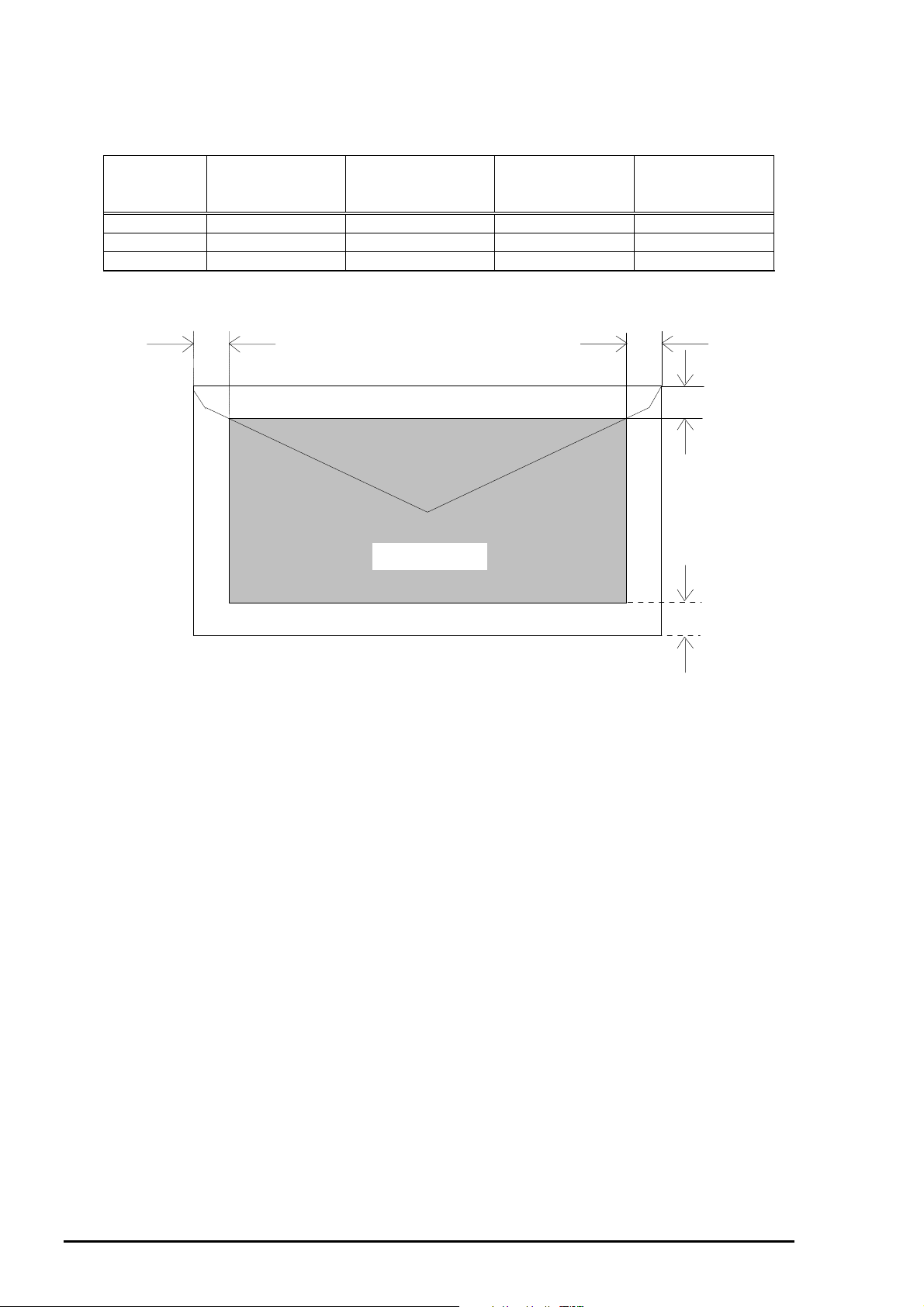
1.2.4.2 Envelope
The table and figure below show the printable area for envelopes.
Table 1-8. Envelope
Paper Size LM
(Left Margin)
(min.)
#10 3mm (0.12”) 28mm (1.10”) 3mm (0.12”) 14mm (0.55”)
DL 3mm (0.12”) 7mm (0.28”) 3mm (0.12”) 14mm (0.55”)
C6 3mm (0.12”) 3mm (0.12”) 3mm (0.12”) 14mm (0.55”)
LM
RM
(Right Margin)
(min.)
Printable area
TM
(Top Margin)
(min.)
BM
(Bottom Margin)
(min.)
RM
TM
Figure 1-4. Printing Area for Envelope
BM
1-
Rev. A
Page 17
Chapter 1 Product Description
9
1.2.5 Environmental Condition
Temperature
Operating :10 - 35°C (Refer to the figure below for condition)
Non-operating :-20 - 60°C (with shipment container)
Note) Storage should be within one month at 40°C and 120 hours at 60°C.
Humidity
Operating :20% - 80% RH
(without condensation. Refer to the figure below for condition)
Non-operating :5% - 85% RH
(without condensation and with shipment container)
Humidity
(% RH)
80%
55%
Guaranteed range
20%
10°C
(50°F)
27°C
(80°F)
35°C
(95°F)
°C
(°F)
Figure 1-5. Temperature/Humidity of Range
Resistance to shock
Operating :1G, within 1 ms (X,Y,Z directions)
Non-operating :2G, within 2 ms (X,Y,Z directions/with shipment container)
Resistance to vibration
Operating :0.15G, 10•`55Hz (X,Y,Z directions)
Non-operating :0.50G, 10•`55Hz (X,Y,Z directions/with shipment container)
Note) 1. During non-operating, make sure that the head is capped.
2. During the transport, make sure that the head is capped and ink cartridge is installed to the
printer.
3. If the head is not capped at the power-off state, turn the power on with the ink cartridge
installed and turn off the power after confirming that the head is correctly capped.
4. Ink will be frozen under -4°C environment, however it will be useable after placing it more than
3 hours at 25°C.
Rev. A
1-
Page 18
EPSON Stylus Color 600
0
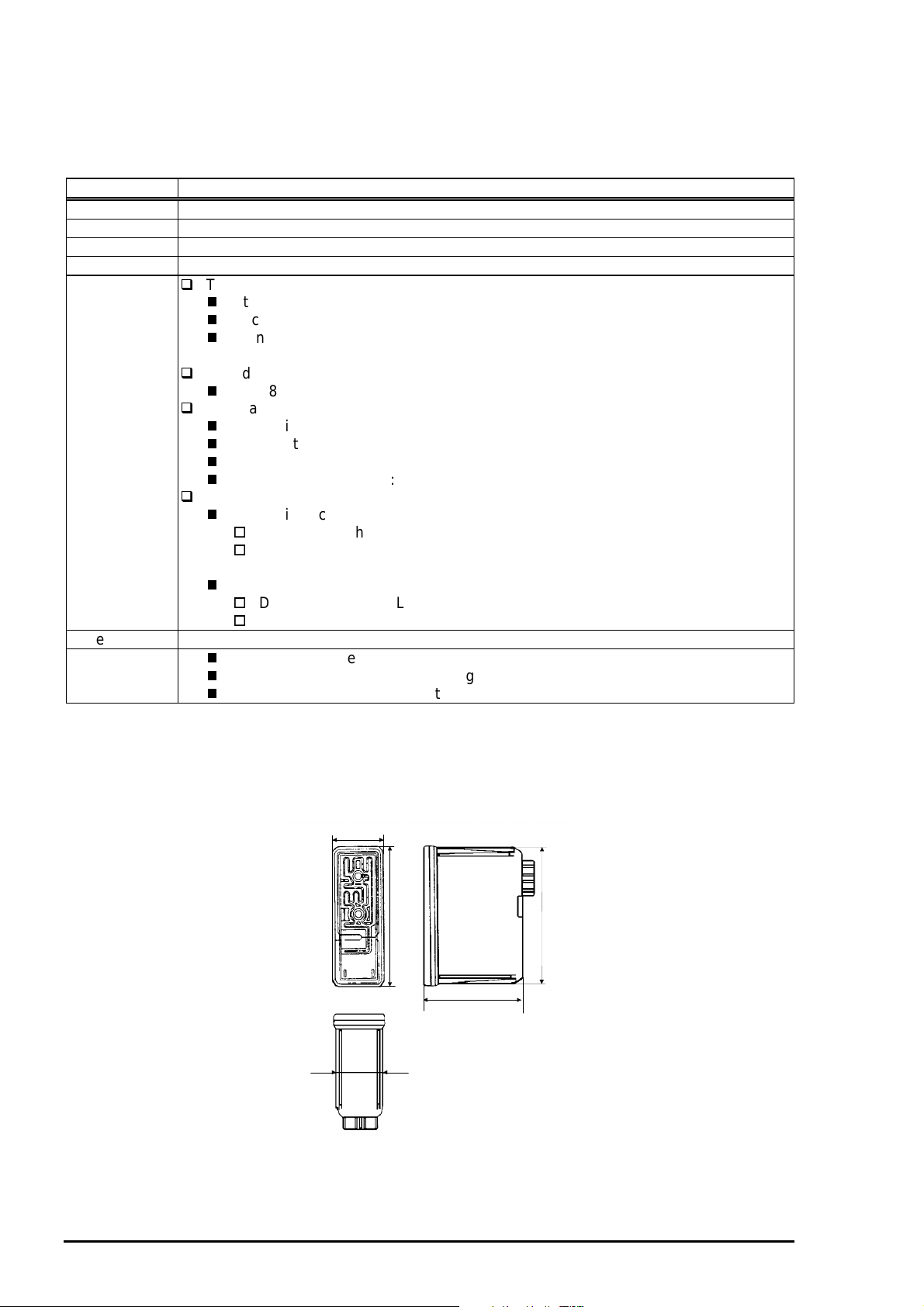
1.2.6 Ink Cartridge Specifications
1.2.6.1 Black Ink Cartridge
Table 1-9. Black Ink Cartridge Specifications
Item Specifications
Type Black Ink Cartridge(Code: S020093)
Color Black
Print capacity 540 pages / A4 (ISO/IE10561 Letter Pattern at 360 dpi)
Validity 2 years (sealed in package) / 6months(out of package)
Environmental
conditions
Dimension 19.8mm(W) x 52.7(D) x 38.5mm(H)
Weight
Temperature
Storage :-20 - 40°C (within a month at 40°C)
Packing storage :-30 - 40°C (within a month at 40°C)
Transit :-30 - 60°C (within 120 hours at 60°C and within a
month at 40••)
Humidity
5% - 85% (without condensation)
Resistance to vibration
Sealed in package :5 - 55Hz
Acceleration :Less than 29.4m/s (3G)
Direction :X, Y, Z direction
Time :1 hour
Drop
Sealed in package:
Dropping height :Less than 0.80m
Direction :Drop the package facing the bottom, sides and one
edge down.
Out of package:
Dropping height :Less than 1.50m
Frequency :Once
Total ink cartridge :54g
Total ink :16.4•}0.5g (Amount in the ink cartridge)
Consumable ink :More than 12.1g(Useable ink quantity until ink ends)
Note) 1. Ink cartridge can not re-fill, only ink cartridge is prepared for article of consumable.
2. Do not use the ink cartridge which is passed away the ink life.
3. Ink will be frozen under -4••environment, however it will be usual after placing it more than 3
hours at room temperature.
19.8
52.7
38.5
18.3
51.2
Figure 1-6. Ink Cartridge (Black)
1-1
Rev. A
Page 19
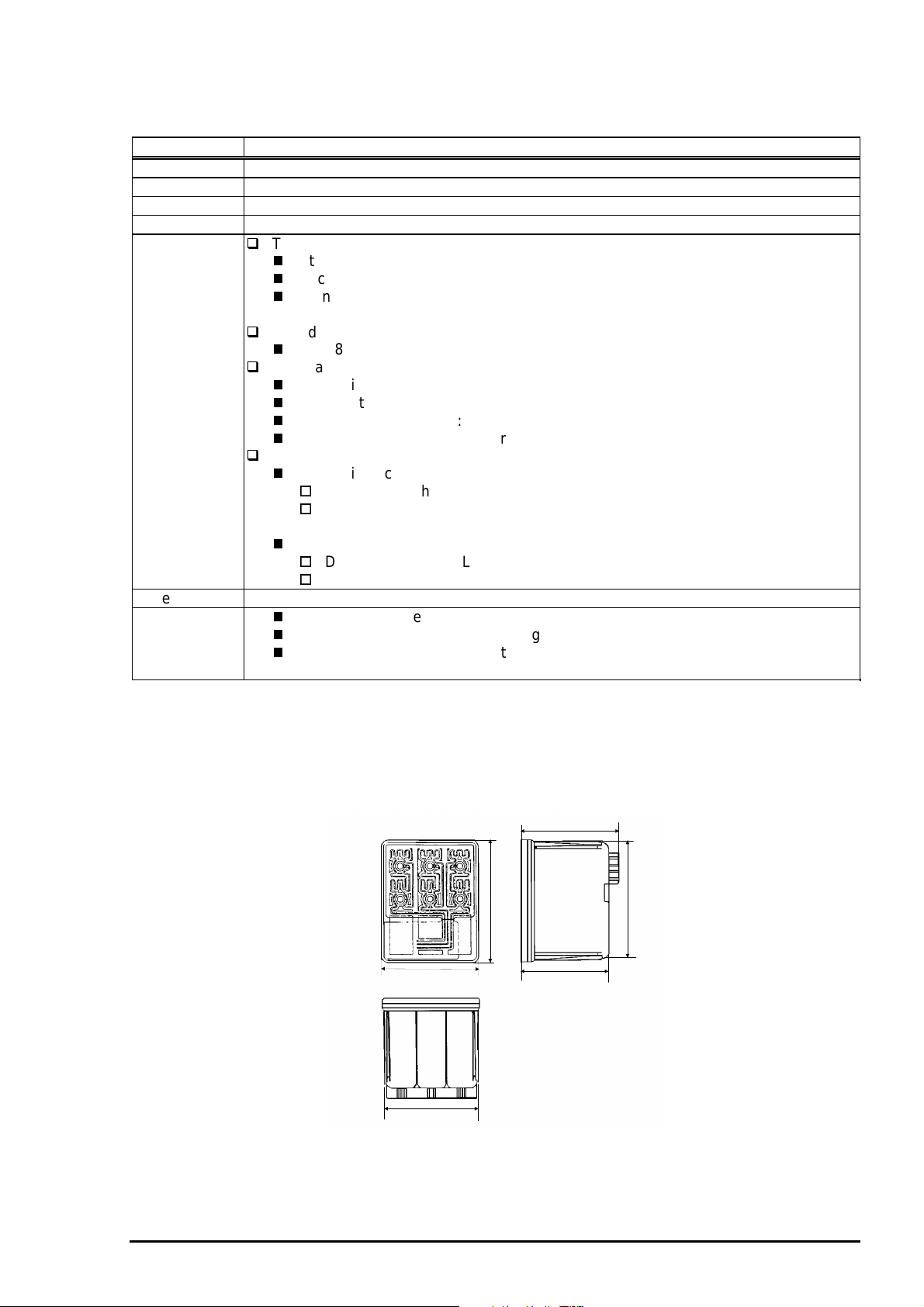
1.2.6.2 Color Ink Cartridge
Table 1-10. Color Ink Cartridge Specification
Item Specifications
Type Color Ink Cartridge(Code: S020089)
Color Magenta/Cyan/Yellow
Print capacity 300 pages / A4 (360 dpi, 5% duty each color)
Validity 2 years (sealed in package) / 6months(out of package)
Environmental
conditions
Dimension 42.9mm(W) x 52.7(D) x 38.5mm(H)
Weight
Temperature
Storage :-20•• - 40•• (within a month at 40••)
Packing storage :-30•• - 40•• (within a month at 40••)
Transit :-30•• - 60•• (within 120 hours at 60••and within a
month at 40••)
Humidity
5% - 85% (without condensation)
Resistance to vibration
Sealed in package :5 - 55Hz
Acceleration :Less than 29.4m/s (3G)
Direction :X, Y, Z direction
Time :1 hour
Drop
Sealed in package :
Dropping height :Less than 0.80m
Direction :Drop the package facing the bottom, sides and one
edge down.
Out of package:
Dropping height :Less than 1.50m
Frequency :Once
Total ink cartridge :68g
Total ink :13.3•}0.5g (Amount in the ink cartridge)
Consumable ink :More than 10.1g/each color (Useable ink quantity until
ink ends)
Chapter 1 Product Description
Note)
1. Ink cartridge can not re-fill, only ink cartridge is prepared for article of consumable.
2. Do not use the ink cartridge which is passed away the ink life.
3. Ink will be frozen under -4••environment, however it will be usual after placing it more than 3
hours at room temperature.
43.2
51.2
42.9
41.4
52.7
38.5
Figure 1-7. Ink Cartridge (Color)
Rev. A
1-11
Page 20
EPSON Stylus Color 600
2
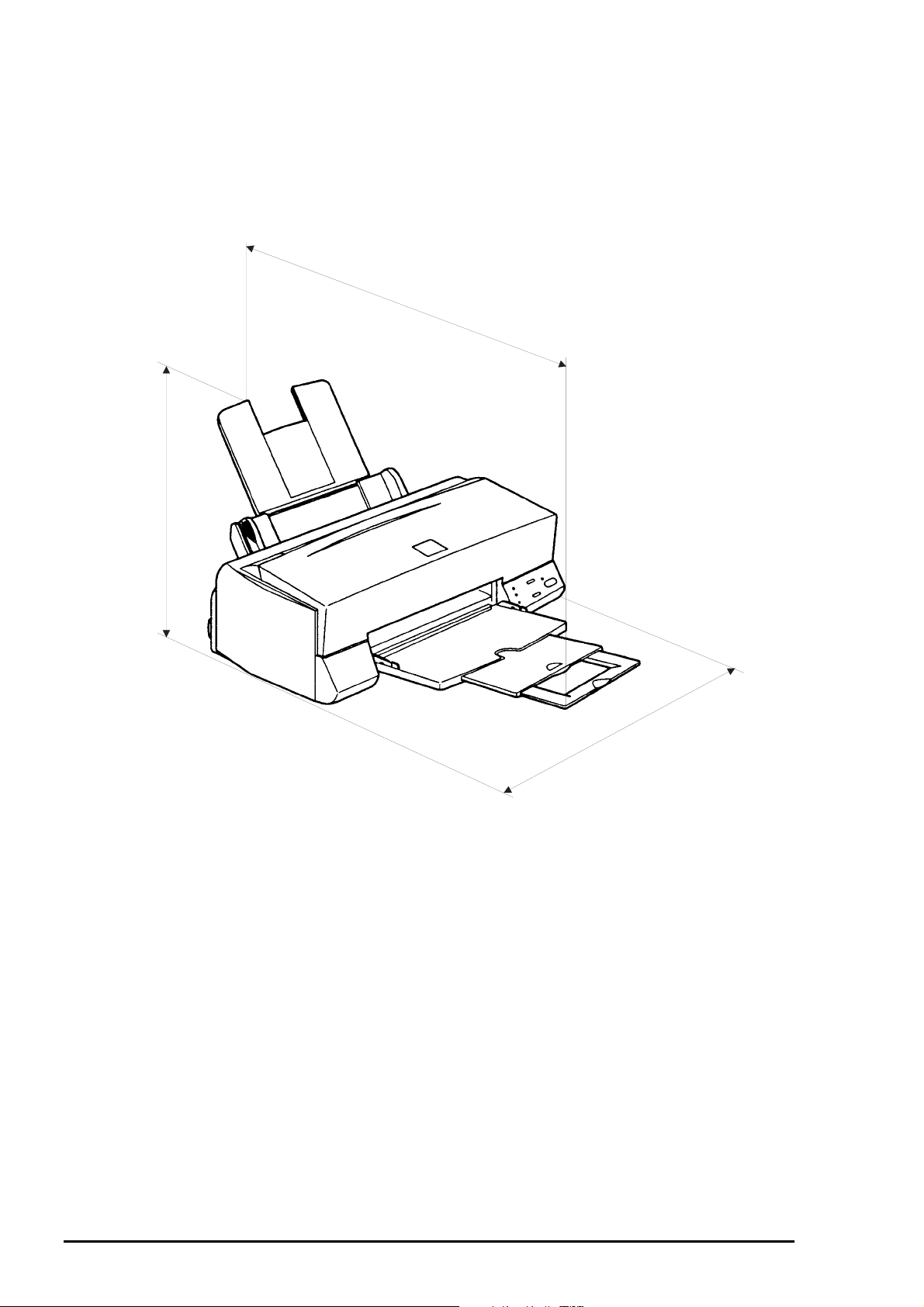
1.2.7 Physical Specification
[Dimension]
[Weight]
309mm
:429mm(W) x 234mm(D) x 162mm(H)
:429mm(W) x 695mm(D) x 309mm(H) with extended stacker and paper support.
:5.2Kg
695mm (Max)
Figure 1-8. Dimension
429mm
1-1
Rev. A
Page 21
3
1.2.8 Electric Specification
[120V] Version
[Rated voltage] :AC120V
[Input voltage range] :AC103.5 - 132V
[Rated frequency range] :50 - 60Hz
[Input frequency range] :49.5•`60.5Hz
[Rated current] :0.4A(Max. 0.5A)
[Power consumption] :Approx.15W(ISO/IEC 10561 Letter pattern)
[Insulation Resistance] :10M ohms min.(between AC line and chassis, DC500V)
[Dielectric strength] :AC1000 V rms. 1 minute or AC1200Vrms. 1 second
(Energy Star compliant)
(between AC line and chassis)
Chapter 1 Product Description
[220 - 240V] Version
[Rated voltage] :AC220V - 240V
[Input voltage range] :AC198 - 264V
[Rated frequency range] :50 - 60Hz
[Input frequency range] :49.5 - 60.5Hz
[Rated current] :0.2 A(Max. 0.3A)
[Power consumption] :Approx.15W(ISO/IEC 10561 Letter pattern)
[Insulation Resistance] :10M ohms min.(between AC line and chassis, DC500V)
[Dielectric strength] :AC1500 V rms. 1 minute (between AC line and chassis)
1.2.9 Reliability
Total print volume :10,000 pages(A4, letter)
Print head life :2000 million dots/nozzle
1.2.10 Safety Approvals
[120V version]
Safety standard :UL1950 with D3
EMC :FCC part 15 subpart B class B
(Energy Star compliant)
:CSA22.2 No.950 with D3
:CSA C108.8 class B
[220 - 240V]
Safety standard :EN 60950(VDE and NEMKO)
EMC :EN55022(CISPR Pub.22) class B
1.2.11 Acoustic Noise
Noise Level :Approx.45 dB(A) (According to ISO 7779)
1.2.12 CE Marking
[220 - 240V version]
Low voltage Directive 73/23/EEC :EN60950
EMC Directive 89/336/EEC :EN55022 Class B
:AS/NZS 3548 class B
:EN61000-3-2
:EN61000-3-3
:EN50082-1
:IEC801-2
:IEC801-3
:IEC801-4
Rev. A
1-1
Page 22
EPSON Stylus Color 600
4
1.2.13 Printer Language and Emulation
Printer Language :ESC/P2
:EPSON Remote
ESC/P control codes
General Operation:
Initialize Printer : ESC @
Unidirectional Printing : ESC U
CSF Mode Control : ESC EM
Paper feeding:
Form Feed : FF
Line Feed : LF
Line Spacing : ESC 0, ESC 2, ESC 3, ESC +
Carriage Return : CR
Page format:
Page Length :ESC (C, ESC C, ESC C0
Left / Right Margin :ESC Q, ESC1
Top / Bottom Margin :ESC (c, ESC N, ESC O
Printer position motion:
Horizontal Print Position :ESC $, ESC\
Vertical Print Position :ESC(V, ESC (v
Tab Horizontally :ESC D, HT
Tab Vertically :ESC B, VT
Advance paper :ESC J
Font Selection:
Typeface :ESC k, ESC x
Pitch and Point :ESC X
Pitch :ESC P, ESC M, ESC g, ESC p
Italic Font :ESC 4, ESC 5
Bold Font :ESC E, ESC F
Master Select :ESC!
Font enhancement:
Double-Width :ESC W, DC4, SO
Condensed :DC2, SI
Double-height :ESC w
Double-Strike :ESC G, ESC H
Super / Subscript :ESC T, ESC S
Underline :ESC-
Line / Score :ESC(-
Character Style :ESC q
Spacing:
Intercharacter Space :ESC Space
HMI :ESC c
Define Unit :ESC (U
Character handling:
Character Table :ESC t, ESC (t
International Character :ESC R
User-Defined Characters :ESC %, ESC &, ESC:
Upper Control Codes :ESC 6, ESC7
Print Data as Characters :ESC(^
1-1
Rev. A
Page 23

5
Bit image:
Bit Image :ESC*
Graphics:
Graphics Mode :ESC (G
Raster Graphics :ESC.
Microweave control :ESC (i
Dot size control :ESC (e
Horizontal Position :ESC (\
Printing Speed :ESC(s
Printing mode:
Printing mode :ESC (K
Color:
Printing Color :ESC r, ESC (r
EEPROM control
EEPROM control
ESC
:
Chapter 1 Product Description
Rev. A
1-1
Page 24
EPSON Stylus Color 600
6
1.3 Interface
This printer provides both parallel and serial interface as standard.
1.3.1 Parallel Interface (Forward Channel)
[Transmission mode]
[Synchronization]
[Handshaking]
[Signal level]
[Adaptable connector]
BUSY signal is set high before setting either/ERROR low or PE high and held high until all these signals
return to their inactive state.
BUSY signal is at high level in the following cases.
During data entry (see Data transmission timing)
When input data buffer is full
During -INIT signal is at low level or during hardware initialization
During printer error (See /ERROR signal)
When the parallel interface is not selected.
ERROR signal is at low level when the printer is in one of the following states.
Printer hardware error (fatal error)
Paper-out error
Paper-jam error
Ink-out error
:8 bit parallel, IEEE-1284 compatibility mode
:By /STROBE pulse
:BY BUSY and /ACKNLG signal
:TTL compatible level
:57-30360 (amphenol) or equivalent
PE signal is at high level during paper-out error.
Table 1-11 shows the signal and connector pin assignments for parallel interface(forward channel*1). In
case of these signals, twist pair line is used and returning side is connected to signal GND (*1). Forward
channel is the mode when the ordinary data such as print data is sent from the PC to the printer.
Table 1-11. Signal and Connector Pin Assignment for Parallel Interface
Pin No. Signal Name Return GND pin I/O Functional Description
1 /STROBE 19 In The strobe pulse. Read-in of data is performed at
the falling edge of this pulse.
2-9 DATA0-7 20-27 In The DATA0 through DATA7 signals represent
data bits 0 to 7, respectively. Each signal is at
high level when data is logical 1 and low level
when data is logical 0.
10 /ACKNLG 28 Out This signal is a negative pulse indicating that the
printer can again accept data.
11 BUSY 29 Out A high signal indicates that the printer cannot
receive data.
12 PE 28 Out A high signal indicates paper-out error.
13 SLCT 28 Out Always at high level when the printer is powered
on.
14 /AFXT 30 In Not used.
31 /INIT 30 In The falling edge of a negative pulse or a low
signal on this line causes the printer to initialize.
Minimum 50 us pulse is necessary.
32 /ERROR 29 Out A low signal indicates printer error condition.
36 /SLIN 30 In Not used.
18 Logic H - Out Pulled up to +5V via 3.9K ohm resistor.
35 +5V - Out Pulled up to +5V via 3.3K ohm resistor.
17 Chassis GND - - Chassis GND.
16,33,19-30 GND - - Signal GND.
15,34 NC - - Not connected.
Note) “I/O” refers to the direction of signal flow from the printer’s point of view.
1-1
Rev. A
Page 25
7
1.3.2 Parallel Interface (Reverse Channel)
[Transmission mode]
[Synchronization]
[Handshaking]
[Data transmission timing]
[Signal level]
[Adaptable connector]
[Extensibility request]
Note) The printer sends following device ID string when it is requested.
00H 3CH Contents
MFG EPSON Production Maker
CMD ESCPL2,BDC Command system
MDL Stylus[SP]Color[SP] 600 Model name
CLS PRINTER Class
:IEEE-1284 nibble mode
:Refer to the IEEE-1284 specification
:Refer to the IEEE-1284 specification
:Refer to the IEEE-1284 specification
:IEEE-1284 level 1 device
:TTL compatible level
:57-30360 (amphenol) or equivalent
:The printer responds affirmatively when the extensibility request values
are 00H or 04H, that mean;
00H :Request Nibble Mode Reverse Channel Transfer.
04H :Request device ID; Return Data using Nibble Mode Rev Channel
Transfer.
Table 1-12. Device ID Description
Chapter 1 Product Description
The table below shows pin assignment for reverse channel(*3). In these case of signals, twist pair line is
used and returning side is connected to Signal GND. (*3):Reverse channel is the mode that any data is
transferred from the printer to the PC.
Pin
No.
1 HostClk 19 In Host clock signal.
2-9 Data0-7 20-27 In The DATA0 through DATA7 signals represent data bits 0
10 PrtClk 28 Out Printer clock signal.
11 PtrBusy, Data Bit-3,7 29 Out Printer busy signal and reverse channel transfer data bit
12 AckDataReq, DataBit-2,6 28 Out Acknowledge data request signal and reverse channel
13 Xflag, DataBit-1,5 28 Out X-flag signal and reverse channel transfer data bit 1 or 5.
14 HostBusy 30 In Host busy signal.
31 /INIT 30 In Not used.
32 /DataAvail, DataBit-0,4 29 Out Data available signal and reverse channel transfer data
36 1284-Active 30 In 1284 active signal.
18 Logic-H - Out Pulled up to +5V via 3.9K ohm resister.
35 +5V - Out Pulled up to +5V via 3.3K ohm resister.
17 Chassis GND - - Chassis GND.
16,33
19-30
15, 34 NC - - Not connected.
[00H] denotes a hexadecimal value of zero. MDL value depends on the EEPROM setting.
MDL value depends on the EEPROM setting. Model name can be changed by
changing a certain address in the EEPROM.
Table 1-13. Pin Assignment for Reverse Channel
Signal Name Return
GND pin
GND - - Signal GND.
I/O Functional description
to7, respectively.
Each signal is at high level when data is logical 1 and low
level when data is logical 0. These signals are used to
transfer the 1284 extensibility request values to the
printer.
3 or 7.
transfer data bit 2 or 6.
bit 0 or 4.
Note) “I/O” refers to the direction of signal flow from the printer’s point of view.
Rev. A
1-1
Page 26
EPSON Stylus Color 600
8
Following lists “Notes” when using Parallel Interface.
“
Return GND pin” in the table means twist pair return and is used for all control signals except for
Logic H,+5V, Chassis, GND and NC. In this twist pair return, returning side is connected to
GND (16,33, 19-30 pin) for twist pair return. Also, these cables are shielded wires and it is
effective to connect to each chassis GND in the PC and printer for electrostatic noise.
Conditions for Interface are based on TTL level. Rise and fall time should be within 0.2µs.
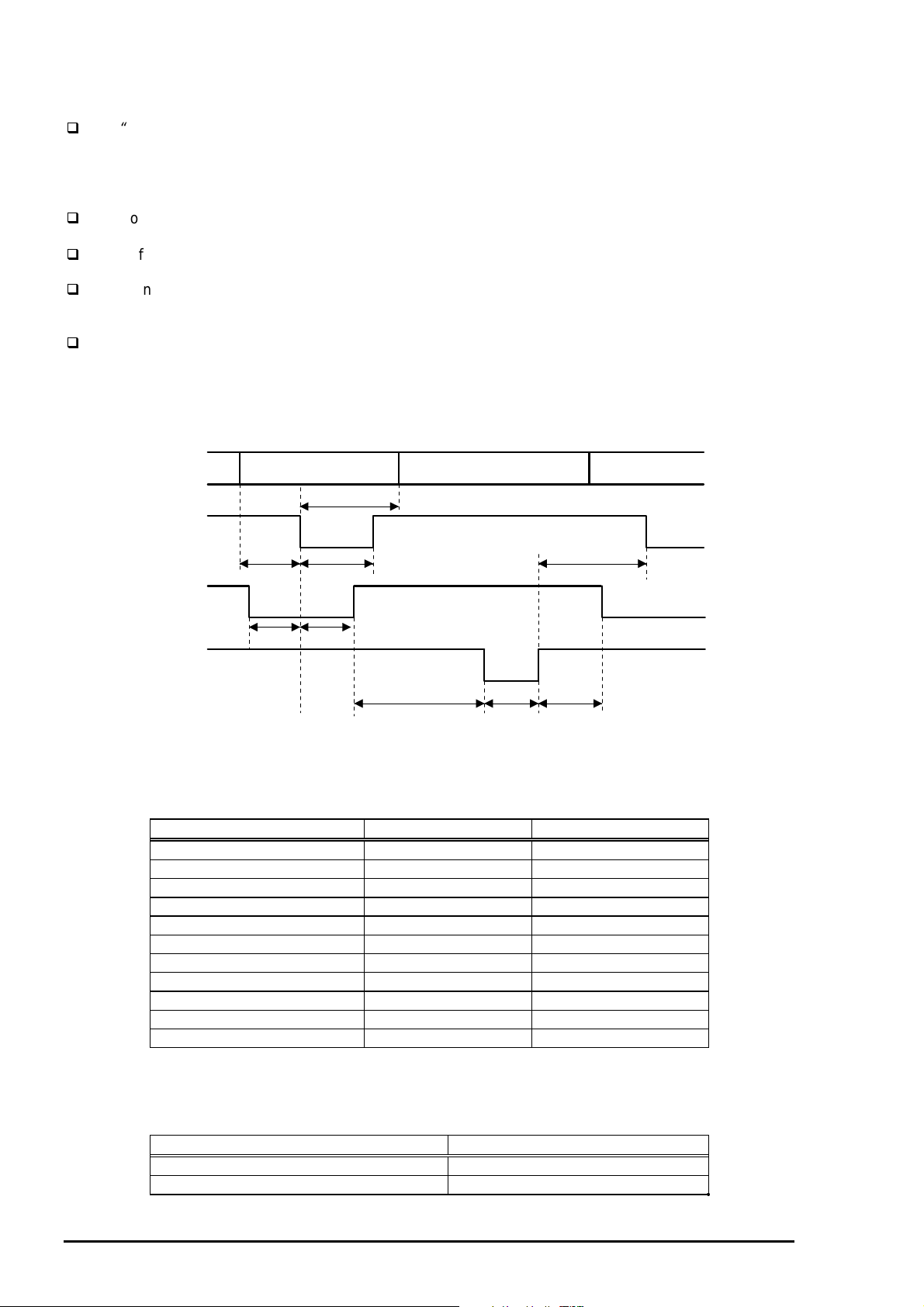
Refer to the figure 1-9 for transmission timing of each signals.
Do not perform data transmission ignoring /ACK or BUSY signal. (Perform the data transmission
after confirming that /ACK and BUSY signals are Low.)
It is possible to perform the printing test including interface circuit without using equipment from
outside when 8-bit data signal(20-27 pin) is set to appropriate word code and connect them
forcefully to /ACK and /STRB.
[Data Transmission Timing for Forward Channel]
Data
/STROBE
BUSY
Byte Data n Byte Data n+1
Thold
Tsetup
Tstrb
Tnext
/ACKNLG
Tready Tbusy
Treply
Tack Tnbusy
Figure 1-9. Parallel Interface Timing Chart(Forward Channel)
Table 1-14. Timing Parameters and Value
Parameter Minimum Maximum
tsetup 500ns ---
thold 500ns ---
tstb 500ns ---
tready 0 ---
tbusy --- 500ns
tt-out* --- 120ns
tt-in** --- 200ns
treply 0 ---
tack 500ns 10us
tnbusy 0 ---
tnext 0 ---
Note) *: Rise and fall time of every output signals.
**: Rise and fall time of every input signals.
Table 1-15. Typical Time of Tack
Parallel I/F mode Typical time of tack
High speed 2us
Normal speed 4us
1-1
Rev. A
Page 27
9
[Signal level: TTL compatible (IEEE-1284 level 1 device)]
Table 1-16. Signal Level
Parameter Minimum Maximum Condition
VOH* --- 5.5V
VOL* -0.5V ---
IOH* --- 0.32mA VOH = 2.4V
IOL* --- 12mA VOL = 0.4V
CO --- 50pF
VIH --- 2.0V
VIL 0.8V --IIH --- 0.32mA VIH = 2.0V
IIL --- 12mA VIL = 0.8V
CI --- 50pF
Note) *: A low logic level on the Logic H signal is 2.0V or less when the printer is
powered off and this signal is equal or exceeding 3.0V when the printer is
powered on. The receiver shall provide an impedance equivalent to
7.5K ohm to ground.
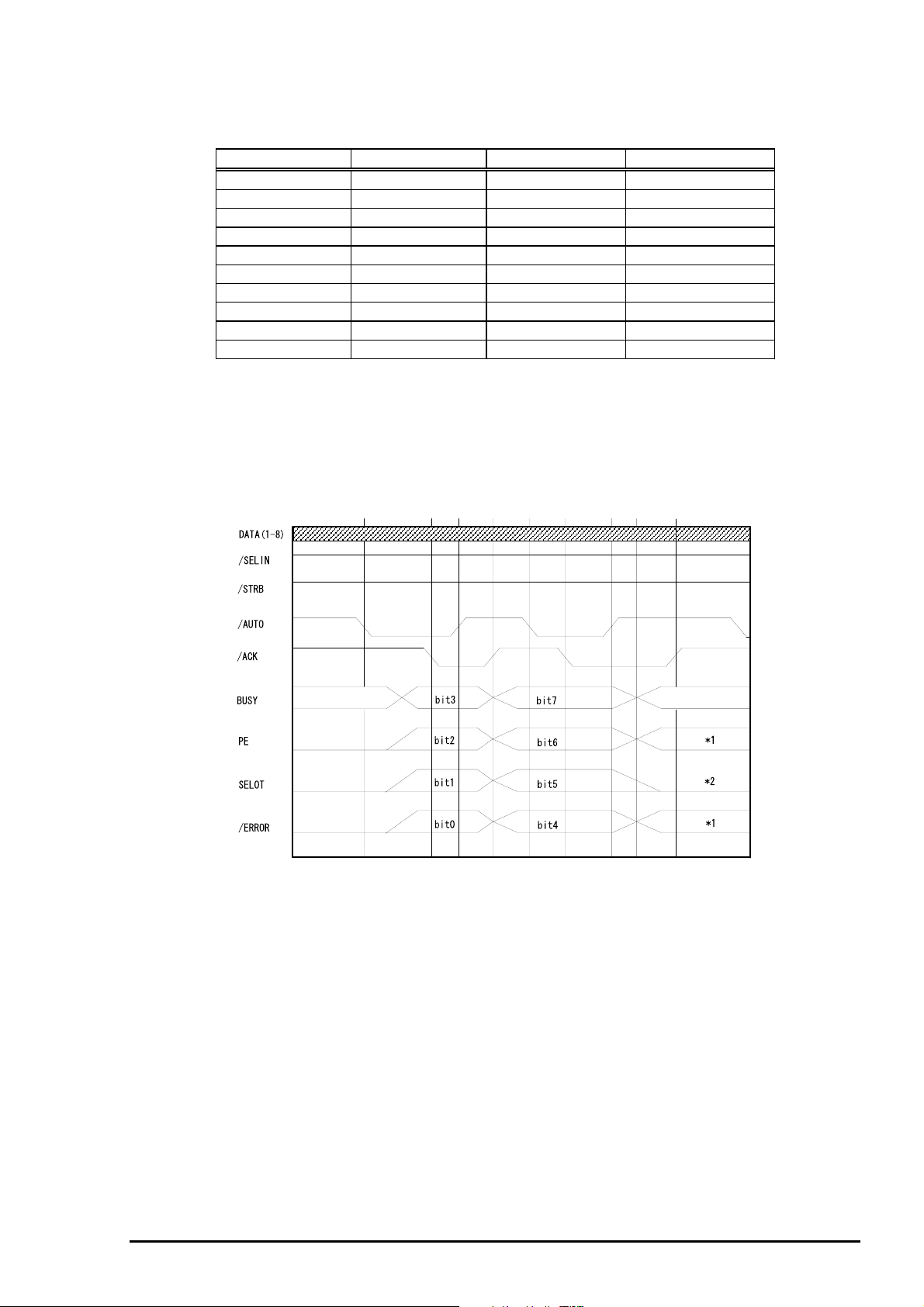
[Data Transmission Timing for Reverse Channel]
The figure below shows timing chart of Parallel Interface Reverse channel.
Chapter 1 Product Description
Virtual Busy Status
Virtual Busy Status
Figure 1-10. Parallel Interface Timing Chart(Reverse Channel)
1.3.2.1 Prevention Hosts from Data Transfer Time-out
Generally, hosts abandon data transfer to peripherals when a peripheral is in the busy state for dozens of
seconds continuously. To prevent hosts this kind of time-out, the printer receives data very slowly, several
bytes per minute, even if the printer is in busy state. This showdown is started when the rest of the input
buffer becomes several hundreds of bytes. Finally, the printer is in the busy state continuously when the
input buffer is full.
Rev. A
1-1
Page 28
EPSON Stylus Color 600
0
1.3.3 Serial Interface
[Standard] :Based on RS-423
[Synchronization] :Synchronous
[Bit Rate] :Approx. 900Kbps
[Handshaking] :X-ON/X-OFF, DTR Protocol
[Word Format] :Data Bit = 8 bits
:Parity Bit = None
:Start Bit = 1 bit
:Stop Bit = 1 bit
[Connector] :8-pin mini-circular connector
[Recommended Cable] :Apple System Peripheral-8 Cable
(Part #: M0197)
Table 1-17. Pin Assignment
Pin No. Signal Name I/O Description
1 SCLK O Synchronous clock signal
2 CTS I Clear To Send
3 TXD- O Transmit Data (-)
4 SG I (Signal Ground)
5 RXD- I Receive Data (-)
6 TXD+ O Balanced Transmit Data (+)
7 DTR O Data Terminal Ready
8 RXD+ I Balanced Receive Data (+)
Table 1-18. X-ON/X-OFF and DTR Status
State Buffer Space X-ON/X-OFF DTR
Busy Less than 3072 bytes Send X-OFF code OFF
Ready More than 5120 bytes Send X-ON code ON
1-2
Rev. A
Page 29
Chapter 1 Product Description
1.4 Control Panel
Since EPSON Stylus Color 600 does not require many buttons since printer driver can start various
settings and motions. Therefore, there are only 2 non-lock type push switches, 1 lock type push switch
and 4 LEDs.
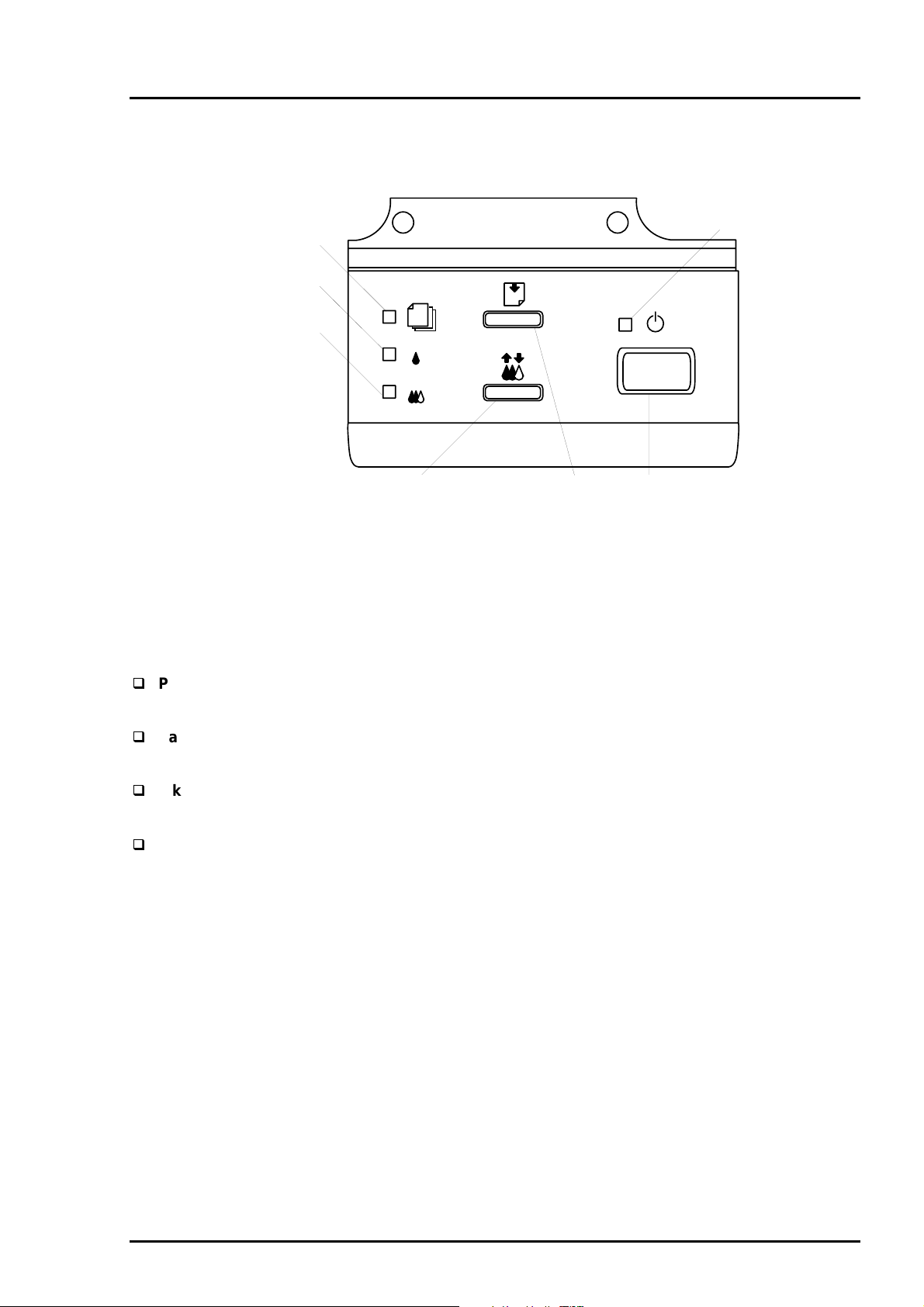
Following figure shows control panel of EPSON Stylus Color 600.
Paper out LED
Ink out(Black)LED
Ink out(CMY)LED
1.4.1 Indicators
Cleaning Switch
(Ink maintenance)
Figure 1-11. Control Panel
Load/Eject switch
Power
Power switch
LED
Power
Lights when the operate switch is “ON”, and AC power is supplied.
Paper out
Lights during the paper-out condition, and blinks during the paper-jam condition.
Ink Out (Black)
Lights during no Black ink condition, and blinks during the Black ink low condition.
Ink Out (Color)
Lights during no Color ink condition, and blinks during the Color ink low condition.
Rev. A
1-21
Page 30
EPSON Stylus Color 600
2
1.4.2 Panel Functions
Table 1-19. Panel Function
Switch Function
Load/Eject
(Pushing within 0.5 seconds*)
Load/Eject
(Pushing for 2 seconds*)
Cleaning
(Pushing for 2 seconds*)
Cleaning
(Pushing within 2 seconds*)
Note) *: 3 seconds is required at the User’s manual.
**: This function is not available in printing status.
***: The time to complete the sequence may vary depending on the printer’s status.
Panel Functions with Power ON
Switch Function
Load/Eject
Cleaning
Load/Eject
+
Cleaning
Note) **: status printings prints firmware version, ink counter, selected code page and nozzle check
patterns.
Loads or Eject the paper.
When the carriage is on the Ink Cartridge change position, return the
carriage from Ink Cartridge change position.
Starts the Ink Cartridge change sequence.**
Moves the carriage to cartridge change position.
Starts the Head Cleaning sequence. ***
In the condition of “Ink Low” or “Ink Out” or “No Ink Cartridge” starts
the Ink Cartridge change sequence.**
When carriage is on the Ink Cartridge change position, return carriage
from Ink Cartridge change position.
Table 1-20. Panel Function with Power ON
Starts status printings.**
Enter the Default Setting mode
Enters the particular settings mode. (Factory use only.)
To enter the particular settings mode, it is necessary to push
followings switch while Paper Out LED is blinking.(It blinks about 5
seconds)
Particular setting mode
Table 1-21. Particular Setting Mode
Switch Function
Load/Eject
Note) ***: Refer to EEPROM map.
Initialize EEPROM *** and reset Timer IC.
1-2
Rev. A
Page 31

Chapter 1 Product Description
3
By performing a particular setting mode, Maintenance error can be cleared and certain addresses of
EEPROM can also be reset.
Maintenance Error Clear
[Step 1] Turn the printer on while holding down Load/Eject and Cleaning switches at the same time.
(By operating this performance, the Paper Out LED starts blinking.)
[Step 2] Push the Load/Eject switch while the Paper Out LED is blinking (5 seconds).
Following shows the lists that will be cleared by this performance.
Clear the value of Ink Counter
Clear Time IC
Initialization of I/F selection (returns to AUTO)
WARNING
EPSON Stylus Color 600 does not have “EEPROM All Clear” function like other printers. If the
printer does not function well and falls into fatal error condition, replace the main board to see if
the problem is rectified. (Refer to Chapter 4 “Adjustment” when you replace the main board since
some adjustments will be necessary.)
Be sure to replace a waste ink pad in the printer enclosure with a new one after you perform
Maintenance error clear operation.
1.4.3 Printer Condi ti on and Panel Status
The table below shows printer condition and panel status. Since this table shows various error status and
also present printer status, you can judge appropriate repair ways from this table.
Table 1-22. Printer Condition and Panel Status
Printer status Indicators Priority
Power Ink Out
(Black)
Power on condition On --- --- --- 9
Ink sequence Blink --- --- --- 6
Ink Cartridge change mode Blink --- --- --- 5
Data processing Blink --- --- --- 8
Paper Out --- --- --- On 4
Paper jam condition --- Off Off Blink 3
No Ink cartridge or Ink end(black) --- On --- --- 7
Ink level low(black) --- Blink --- --- 7
No Ink cartridge or Ink end(color) --- --- On --- 7
Ink level low(color) --- --- Blink --- 7
Enter EEPROM and Timer IC reset --- On
(1 second
only)
Maintenance request Blink Blink Blink Blink 2
Fatal error Blink On On Blink 1
Ink Out
(Color)
On
(1 second
only)
Paper Out
On
(1 second
only)
--
Note) “—“ means no changes.
Rev. A
1-2
Page 32

EPSON Stylus Color 600
4
1.5 Error Status
When following status occur, the printer goes to the error status and stops taking data, setting the
/ERROR signal in the interface as “Low”, and Busy signal as “High”. At this time, the printer goes to non
printable status. Refer to section 1.4.2 for more details of LED Panel indicators during the various error
status.
1.5.1 Ink Out
When the printer runs out the most part of the ink of any one color, it warns ink-low and keeps printing.
When the printer runs out the whole ink of any one color, it stops printing and indicates ink-out error. User
is requested to install a new ink-cartridge in this state. An ink-cartridge once taken out should never be
used again. Re-installation of the cartridge not filled fully upsets the ink level detection and may cause a
serious problem in the print head as a result.
WARNING
Never use the ink cartridge once taken out from the printer.
Following explains the reason of the above warning.
After the cartridge is once taken out, airs come in from the ink supply hole located at the top of
cartridge and becomes bubbles, and they are absorbed into the head during printing performance.
Therefore, the head will be unable to discharge the ink properly. Also, inevitable entering of bubbles
when installing a new ink cartridge can be absorbed to ink itself since the ink itself in the cartridge is
deaerated during the production process. However, this absorbing ability can last only about one hour
after the cartridge is installed.
Even after the bubble absorbing ability described above stops, there is no worry about entering
bubbles as long as the ink cartridge is being installed to the printer. However, if the ink cartridge which
does not have absorbing ability any more is once removed from the printer, new coming bubbles into
the cartridge will never disappear naturally. These bubbles may cause not only printing malfunction but
also thickening ink. This thickened ink goes into the head and clogs ink path in the head or nozzle and
may cause serious head damage.
As standard specification for EPSON Stylus Color 600, ink consumption counter is reset when the ink
cartridge is removed. If an ink cartridge is removed and re-installed unnecessarily the value on the ink
consumption monitor which the user can check will be wrong and printer may keep printing even
though the ink cartridge is installed empty. This may cause head damage.
1.5.2 Paper Out
When printer fails to load a sheet after power on operation including timer-cleaning is done and Load/Eject
button on the FF command or operation panel is pressed, it goes paper out error.
1.5.3 Paper Jam
When printer fails to eject a sheet even after feeding motion is completed or Load/Eject button on the FF
command or operation panel is pressed, it goes paper jam error.
1-2
Rev. A
Page 33

5
1.5.4 No Ink-Cartridge Error
Following reasons can be the causes when printer goes this error mode.
Chapter 1 Product Description
according to the ink cartridge exchange operation.)
When the printer is turned on for the first time.
(This is a normal error state and it returns to the normal state after installing an ink cartridge
Ink cartridge exchange operation is done correctly. After the position of carriage is moved by
exchange operation, if the cleaning switch is pushed without installing ink cartridge or if the
carriage returns to the home-position automatically without doing any operation, it is considered as
handling mistake. However, it returns to normal state by performing ink exchange operation again
and installing cartridge correctly.
If “No ink-cartridge error” appears even after the ink cartridge is installed, the printer must be
something wrong and around the sensor area in the carriage need to be repaired.
If sometimes printer can print normally but also sometimes “No ink-cartridge error” appears, the
printer must be something wrong. (Same reason as above)
1.5.5 Maintenance Request
When the total quantity of ink wasted through the cleanings and flushing reaches to the limit, printer
indicates this error and stops. The absorber in the printer enclosure is needed to be replaced with new
one by a service person. The ink quantity that is absorbed by the absorber (waste ink pad) is monitored by
the software counter as “total ink counter”. This counter is added by point system and absorber’s
maximum ability is set at the following reference value.
29500 X 0.012 ml = Approximately 301ml
However, considering dispersion of ink absorbing quantity and the number of using nozzles, ink total value
is calculated by the following formula.
1-point = 0.0102 ml (the value which is multiplied evaporating rate and 1-dot ink weight 0.02
ml)
29500 = Maximum point number (Maintenance error threshold)
301 X 1.1/63% = 526ml (but up to 532ml can be retained)
WARNING
When you perform self- test after completing repairs, it is possible to check the present value of total
ink counter and ink discharge conditions from all nozzles by performing status printing in the built-in
function. Therefore, make sure that the printer has enough value of total ink counter (if the number is
close to 29500 or not). If there is not enough value, the service man is required to judge if it is
necessary to clear EEPROM after replacing the absorber (waste ink pad) or not. Refer to section 1.3.1
if you need to perform EEPROM Clear.
1.5.6 Fatal Errors
When printer detects fatal errors such as carriage control error or CG access error, it goes to this error
mode. Refer to followings for each error.
Carriage control Error: Parallel adjustment malfunction, Home-position malfunction, Timing belt
tension malfunction, shortage of lubricant on the carriage guide shaft, etc.
CG Access Error: Short circuit, etc.
Rev. A
1-2
Page 34

EPSON Stylus Color 600
6
1.6 Printer Initialization
EPSON Stylus Color 600 has three kinds of initialization methods. Following explains each initialization.
Power-on initialization
This printer is initialized when turning the printer power on, or printer recognized the
cold-reset command (remote RS command). When printer is initialized, following action is
performed.
Initializes printer mechanism.
Clears input data buffer.
Clears print buffer.
Sets default values.
Operator initialization
This printer is initialized when turning the printer power on again within 10 seconds from last
power off, or printer recognize the /INIT signal (negative pulse) of parallel interface. When
the printer is initialized, following action is performed.
Cap the printer head.
Eject a paper.
Clears input data buffer.
Clears print buffer.
Sets default values.
Software initialization
The ESC@ command also initialize the printer. When printer is initialized, following action is
performed.
Clears print buffer.
Sets default values.
1.6.1 Initialization Settings
EPSON Stylus Color 600 initializes following settings when the initialization is performed. Also, if the user
changes the settings in the Panel setting, Default setting or Remote command setting, values or settings
which are possible to be stored are initialized as initialization settings.
Page position :Page heading location as present paper location
Line spacing :1/6 inch
Right margin position :80 lines
Left margin position :first line
Character pitch :10CPI
Printing mode :Text mode (Not Raster graphics mode)
1-2
Rev. A
Page 35

Chapter 1 Product Description
7
1.7 Main Components
EPSON Stylus Color 600 has following major units. Also, it is one of the major characteristics that the
bottom of the Printer mechanism plays the role as lower case at the same time.
Upper case
Printer Mechanism
C200 MAIN Board (Main control circuit board)
C206 PSB/PSE Board (Power supply circuit board)
C206 PNL Board (Control panel circuit board)
1.7.1 Printer Mechanism
Unlike EPSON’s previous ink jet printer mechanisms, one of the major characteristics of EPSON Stylus
Color 600 is that the printer has no Engage/Disengage mechanism in order to change over pump
mechanism and paper feeding mechanism. Instead, however, this change-over control is done by the
distinction between turning direction of PF motor and position of present carriage unit. Also, another major
characteristic is that print head is changed to be one unit combined with black and CMY. Nozzle
configuration for black is 64 nozzles (the nozzle pitch of each column is 90dpi and between two
consecutive nozzles in number (e.g. #1 and #2) is 180dpi). On the other hand, CMY nozzle has 32 nozzles
(90dpi) for each color. Following figure shows exterior of mechanism.
CR Motor
Carriage
PF Motor
Control Panel
Hopper
(Exit paper tray)
*ASF is not shown in the above figure.
Figure 1-12. Exterior view of the Printer Mechanism
Rev. A
1-2
Page 36

EPSON Stylus Color 600
8
1.7.2 C200 MAIN Board
The C200 MAIN board controls whole mechanism operations and a data processing operation. Most of
the functions of the circuit are integrated into single ASIC; E05B43YA (IC2) and this makes the board
design very simple and reliable.
IC7
Printhead Driver
IC15
PF Motor Driver
IC14
CR Motor Driver
IC2
ASIC
(E05B43YA)
IC1
CPU
(TMP95C0618F)
IC5
DRAM(4MBit)
IC6
Mask ROM (CG)
Parallel I/F(CN1)
Serial I/F (CN2)
IC3
PROM(4MBit)
Lithium Battery
Figure 1-13. Exterior view of C200 Main Board
1-2
Rev. A
Page 37

Chapter 1 Product Description
9
1.7.3 C206 PSB/PSE Board
The C206 PSB/PSE board is a switching regulator type power supply unit and constantly supplies stable
logic and power voltages to the printer mechanism and the main control board. Also, since this C206
PSB/PSE board has the power switch in the secondly side of the circuit, it is possible to keep supplying
electricity to the C200 MAIN control board for 30 seconds even after the power switch is turned off. Using
this time difference, even when mis-operation is done by the user such as turning off the power during the
middle of printing work, it prevents unexpected trouble with the printhead from occurring, by transferring
the printhead to the cap position before complete shut down. The C206 PSB Board is for AC100 - 120V
input voltage and the C206 PSE Board is for AC220 - 240V input voltage.
FUSE (F1)
AC input (CN1)
Q1
FET (Switching)
Power line to
C200 MAIN/Mechanism
(CN2)
PC1
Photo-coupler
Figure 1-14. Exterior view of C206 PSB Power Supply Board
1.7.4 C206 PNL Board
The C206 PNL board is located in the panel case where is in the right bottom of the front of printer and
consists of 3 switches, 4 LEDs.
Figure 1-15. Exterior view of C206 PNL Board
Rev. A
1-2
Page 38

Chapter 2
Operating Principles
2.1 OVERVIEW...............................................................................................................1
2.1.1 Printer Mechanism .................................................................................................................... 1
2.1.1.1 Printing Mechanism......................................................................................................2
2.1.1.2 Carriage Mechanism .................................................................................................... 7
2.1.1.3 Paper Feed Mechanism and Pump Mechanism.........................................................11
2.1.1.4 Ink System.................................................................................................................. 14
2.2 Electrical Circuit Operating Principles................................................................18
2.2.1 C206 PSB/PSE Board.............................................................................................................. 19
2.2.2 C200 MAIN Board..................................................................................................................... 21
2.2.2.1 Reset Circuits............................................................................................................. 23
2.2.2.2 Sensor Circuits........................................................................................................... 24
2.2.2.3 EEPROM Control Circuits .......................................................................................... 25
2.2.2.4 Timer Circuit............................................................................................................... 26
2.2.2.5 DRAM Control ............................................................................................................26
2.2.2.6 Print Head Control Circuit........................................................................................... 27
2.2.2.7 PF(Pump) Motor Drive Circuit .................................................................................... 30
2.2.2.8 CR Motor Drive Circuit ............................................................................................... 31
2.1.1.1.1 Printing Process................................................................................................ 3
2.1.1.1.2 Printing Method................................................................................................. 4
2.1.1.2.1 Paper Gap Adjust Mechanism ........................................................................ 10
2.1.1.4.1 Pump Mechanism ........................................................................................... 15
2.1.1.4.2 Cap Mechanism.............................................................................................. 17
Page 39

Chapter2 Operating Principles
2.1 OVERVIEW
This section describes Printer Mechanism, electric circuit board (C206 PSB, C200 Main, C206PNL
board) of Stylus Color 600.
2.1.1 Printer Mechanism
Unlike previous EPSON Ink Jet printers, printer mechanism of Stylus Color 600 does not have exclusive
mechanism to change over paper feeding and Pumping operation. In stead, this control is done by the
turning direction of paper feed/pump motor and position of carriage at that time. Also, unlike previous print
heads, print head of this printer became one unit combined with black and CMY head. Black head has
64 nozzles, 180 dpi(vertical direction) and CMY head has 32 nozzles, 90 dpi (vertical direction). Also,
since these print head is driven by frequency 14.4KHz, this printer can print double resolution(1440
dpi/100-dpi) than Stylus Color. Following figure2-1 shows outline of printer mechanism.
Since the head drive frequency of Stylus Color was 7.2KHz, it could be only 720-dpi printing when it
driven by 100 cps carriage speed. It performs two-pass carriage operation when Stylus Color 600
performs the 1440 dpi printing towards the horizontal line.
Carriage Unit
(Prinr Head Unit)
Platen Drive Mechanism
Paper Pickup Mechanism
Pump Drive Mechanism
Timing Belt
Paper Pick Up
Trigger Lever
Pumping Position
Paper Feed Motor
Rev. A
Carriage Motor
Figure 2-1. Stylus Color 600 Printer Mechanism Block Diagram
2-1
Page 40

EPSON Stylus Color 600
2
As major printer mechanisms in the figure 2-1, there are four major mechanisms as they are listed below.
1) Printing mechanism 2) Carriage unit 3) Paper pick up mechanism4) Pump drive mechanism
2.1.1.1 Printing Mechanism
Basic principles of the print head which plays major role of printing mechanism is the same as previous
models; on demand type MACH head method, but there is some difference in the resolution. (Refer to
figure1-1) Also, unlike Stylus Color II, Stylus 820 and Stylus Color 200 automatic correction type, in order
to fix the dispersion of mufti layer piezo electric element which is used for driving each nozzles, it is
necessary to input the VH value written on the side of print head by using exclusive program when you
replace print head, control board, or the printer mechanism.(However, there are no resistor array for
decide the VH voltage on the main control board.) Following explains print head.
PZT
Cavity Set
Nozzle Plate
Filter
PZT is an abbreviation of Piezo Electric Element. Print signal from C200 board is sent through
the driver board on the print head unit and to the PZT . Then, the PZT pushes the top cavity
which has ink stored, and make the ink discharge from each nozzle located on the nozzle
plate.
Ink which is absorbed from ink cartridge go through the filter and will be stored temporarily in
this tank, which is called “cavity” until PZT is driven.
The board with nozzle holes on the printer head surface is called Nozzle Plate.
When the ink cartridge is installed, if any dirt or dust around the cartridge needles are
absorbed into the head inside, there is a great possibility of causing nozzle clog and
disturbance of ink flow and finally causing alignment failure and dot-missing. In order to
prevent this, filter is set at cartridge needle below and ink is once filtered here.
PZT
Nozzle Plate
Printhead driver board
Ink Cartridge Sensor
Actuator
Cartridge needle
(Ink Cartridge)
Filter
Ink Supply Tube
Cavity set
Figure 2-2. Print Head Sectional Drawing
2-
Rev. A
Page 41

Chapter2 Operating Principles
3
2.1.1.1.1 Printing Process
Following figures indicate the sectional drawing of normal state and ejecting state of print head.
(1) Normal State:
When the print signal is not output, PTZ also does not move in the waiting state(normal state).
PZT
Cavity
Ink Course
Nozzle
Figure 2-3. Print Head Normal State
(2) Ejecting State:
When the print signal is output from the C200 main board, IC(IR2C72C and IR2C73C:Nozzle
Selector) located on the print head unit latches the data once by 1-byte unit. Appropriate PZT latched
by nozzle selector is pushed in to the cavity by applying common voltage from the C200 main
board. By this operation, ink that is stored in the cavity pops out from nozzles.
Nozzle Plate
Rev. A
Figure 2-4. Print Head Ejecting State
2-
Page 42

EPSON Stylus Color 600
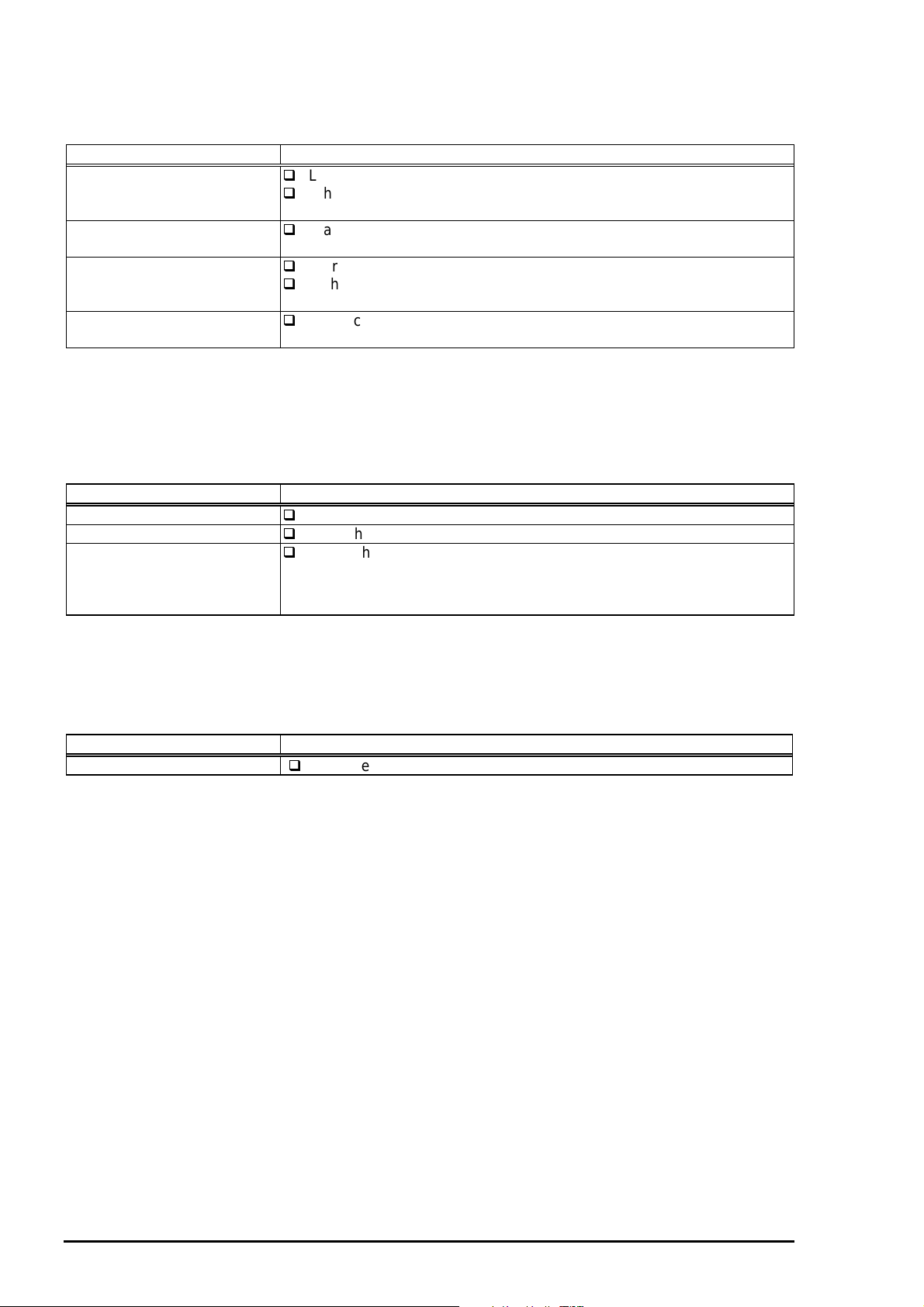
4
2.1.1.1.2 Printing Method
This section explains printing method of actual printing such as printing text at various resolution
select/printing mode and graphics printing. In order to prevent white or color banding which are peculiar
problem of ink-jet, new Micro-Weave functions are added to the previous Micro-Weave function. The
number of nozzles and printing mode according to the selected resolution are used separately by a user.
The table below shows relation between selected resolution and printing mode.
1) Full Overlap Micro-Weave
2) Part Line Overlap Micro-Weave
3) Micro-Weave: (same as previous control)
Table 2-1. Resolution and Printing mode
Vertical
direction
Note1:
Note2:
Note3:
Note4:
[dpi]
360 FOL M/W 15/360 #16•`#30 --- #1•`#15 #31•`#32
720 FOL M/W 15/720 #16•`#30 --- #1•`#15 #31•`#32
M/W means Micro-Weave.
FOL means Full Overlap Micro-Weave.
POL means Part line Overlap Micro- Weave
Forward Overlap-Nozzle and backward Overlap -Nozzle are described in the [1.Full Overlap
Mirco-Weave] and [2.Part line Overlap Micro-Weave] below.
Printing
mode
M/W 31/360 --- #1•`#31 --- #32
POL M/W 29/720 #30•`#32 #4•`#29 #1•`#3 ---
Paper feed
pitch
[inch]
Forward
Overlap-
Nozzle
Non
Overlap-
Nozzle
Backward
Overlap-
Nozzle
Not used
Nozzle
.
Following explains operation outlines of new Micro-Weave functions listed above.
[1. Full Overlap Micro-Weave]
In order to print one line at horizontal direction, this printing method is designed to complete a printing
pattern by two-pass carriage operation with two different types of dot. When this two different types of dot
pass one same line twice, it does not print the same dot twice.
Note1)
The nozzles whose configuration completely match to the black and CMY nozzle are used.
(Usually Micro-Weave type)
Therefore, all nozzles in case of CMY nozzle and #1•`#63 nozzles in the B2 line in case of
black head are its objects. (B1 line is not used at Micro-Weave. Refer to figure1-1 for detail of
nozzle configuration.)
Out of these 4 color nozzle objects, the number of all nozzles which are going to be used are
divided equally into 2 groups.
Paper feeding will be done as many as each number of nozzles which are divided into two
groups and the same number of dots.(for example, if there are two 10-nozzle groups during
360-dpi printing at longitudinal direction, paper feeding of 10/360-inch becomes available.)
At this time, two groups perform Micro-Weave individually and particular lines are passed by
two different nozzles.
These nozzles which are divided into two groups must be set and divided in order to
be a pair of odd and even number.
2-
Rev. A
Page 43

5
Note2)
Chapter2 Operating Principles
Two groups which are divided according to each elements will be divided either even dot or
odd dot when particular lines(level direction line) are formed and eventually, these lines will be
completed at selected resolution. Following is a conceptual figure when full overlap micro weave orms a particular line.
Nozzle No.#9
Condition: 360-dpi printing
Nozzle: Total 10 nozzle/each color
Nozzle No.#4
Particular line(Completed line)
Figure 2-5. Full Overlap Micro-Weave
Note 3) The way firmware decides which nozzle becomes even dot or odd dot is determined
as it is described below.
If the line which is about to be printed is even line:
First dot prints odd dot lines and 2nd dot prints even dot lines.
If the line which is about to be printed is odd line:
1st dot prints even dot lines and 2nd dot prints odd dot lines. Eventually, horizontal resolution
will be the same resolution as selected one.
[2.Part Line Overlap Micro-Weave]
This printing method is to perform Micro-Weave printing, overlapping a part of nozzles which are
used for printing. As a result, a part of raster which is overlapped consists of different browse with
different nozzles. The figure below shows 1-line Overlap at 5-dot sending as an example with
explanation on the next page.
360-dpi
Pass1
#1
#2
#3
#4
#5
#6
2
Note1: The paper feed pitch is 5/360-dpi in this figure.
Note2: Mark of and mean overlap nozzle.
3
4
5
6
Raster 1
Raster 10
7
8
9
10
11
Figure 2-6. Part line Overlap Micro-Weave
Rev. A
2-
Page 44

EPSON Stylus Color 600
6
1) Overlap Nozzle : Head drive frequency is driven half of the ordinal one like 2)
below.
2) Nozzle other than Overlap nozzle : Head drive frequency is twice as much as overlap nozzle.
Usually, the firmware changes over automatically these full overlap Micro-Weave, Part line Overlap
Micro-Weave, and ordinal Micro-weave according to the selection of resolution. Also, when these three
printing modes are performed by the Stylus Color 600, the printer performs top and bottom margin
process in order to control the overprinting volume as little as possible.
The difference between Full-Overlap Micro-Weave and Part line Overlap Micro-Weave are
following;
Full-Overlap Micro-Weave:
Printing is performed, judging if nozzles are even or odd dot by 2 different dots with all
different rasters.
Part line Overlap Micro-Weave:
After particular nozzles(only#1, and #6 in the figure2-7) are determined as overlap nozzles,
even or odd dot will be determined like Full-overlap Micro-Weave does.
(Forward Overlap Nozzle is determined as even and backward nozzle is odd.)
Also, nozzles other than particular nozzles can print at even and odd dot just by one
nozzle.
2-
Rev. A
Page 45

Chapter2 Operating Principles
7
2.1.1.2 Carriage Mechanism
Carriage mechanism is to drive the carriage with print head mounted from left to right or vice versa.
The carriage drive motor in this printer is a 4-phase, 200-pole, stepping motor and is driven by
1-2phase, 2-2phase and W1-2phase drive method. This stepping motor allows the carriage to
move freely to the particular positions which is necessary for various operation, such as paper feeding,
ink absorbing, flashing, ink exchange and cleaning operations. The tables below shows carriage motor
specifications and motor controls at each mode.
Table 2-2. Carriage Motor Specification
Item Description
Motor type 4-phase/200-pole Stepping motor
Drive voltage Range 42VDC ±5%
Internal coil resistance 7.8 ohms ±10%
(per phase under 25°C environment)
Driving speed(frequency) range[cps (pps)] 5(60) - 340(4080)
Control method Bi-pola Drive
Table 2-3. Motor Control at Each Mode
Mode Driving speed
[CSP]
High speed skip 340 4080 W1-2, 2-2,1-2phase drive*
Printing(Normal) 200 2400 W1-2phase drive
Printing(SLQ) 100 1200 W1-2phase drive
Capping 80 960 W1-2phase drive
Wiping 40 480 W1-2phase drive
Cap(valve release) 20 240 W1-2phase drive
Withdrawal of cap 5 60 W1-2phase drive
Drive frequency
[PPS]
Drive method
*Note 1):
• Acceleration 1 mode •¨ • Acceleration 2 mode •¨ • Deceleration 1 mode •¨ • Deceleration 2 mode
The reason why plural drive methods exist is that following some sequences described below
exist in the each mode and stable carriage operation and printing are performed individually
by different drive methods. This drive method is especially necessary for high speed skip.
A
/A
C200 MAIN Board
Rotor
Connecter CN6(CN7)
B
/B
Figure 2-7.CR(PF/Pump) Motor Internal Block Diagram
Rev. A
2-
Page 46

EPSON Stylus Color 600
8
The table below shows W1-2 phase drive sequence at each steps when the rotor of carriage motor
makes one rotation. In the Stylus Color 600, in addition to a function that printing is performed with W1-2
drive phase, high speed skip mode which is a function to skip over the blank from the end of the printing
data to the next data starting point with high seed can be also performed by 2-2 and 1-2 phase drive.
W1-2 phase requires 4 times as much steps as 2-2 phase drive, calculating 2-2 phase as standard.
By using this method, it becomes possible to supply constant stable torque to the motor. As a result, it
also became difficult to be influenced by vibration from the printer mechanism during printing.
Table 2-4. Motor Drive Sequence(W1-2 phase drive)
Sequence
Number
Phase a 10a l1a Current
0010+2/3010+2/3
1001+1/3000+1
2X110000+1
3101-1/3000+1
4110-2/3010+2/3
5100-1X01+1/3
6100-11110
7100-1101-1/3
8110-2/3110-2/3
9101-1/3100-1
10X110100-1
11001+1/3100-1
12010+2/3110-2/3
13000+1101-1/3
14000+1X110
15000+1001+2/3
Phase A Phase B
Phase b 10b l1b Current
Duty
Duty
This W1-2 phase drive (or 2W1-2 phase drive) is called Micro-step and is attached with so called
2/3•EVref or 1/3•EVref factor, compared with drive current value (Vref100%) which is supplied at 22phase drive. This Micro-Step allows the rotor to have delicate rotation. In the 2-2 phase drive m ethod, it
is usually
required to take 4-step sequence in order to rotate the rotor once. However, in case of W1-2 phase,
it is required to take 16-step sequence(in the table 2-4, sequence 0•`15) which is 4 times more than
2-2 phase method to do that. Also, in case of 2W1-2 phase drive which can be seen in the Stylus Color
etc., it takes 2-step to rotate the rotor once. The table below shows relation of rotation direction of rotor
and carriage proceeding direction.
Table 2-5. Relationship Between Rotor Direction and Carriage Operation
Carriage proceeding
direction
HP→80 column direction
80 column→HP direction
Rotation direction of
Rotor
Looking from rotor output
side, clockwise direction
Looking from rotor output
side, counterclockwise
direction
Drive method Proceeding order of
sequence
2-2, 1-2, W1-2 phase
2-2, 1-2, W1-2 phase
Sequence No.0→15
Sequence No.15→0
2-
Rev. A
Page 47

Chapter2 Operating Principles
9
The figure below shows carriage mechanism. The print head as a core of the printing mechanism is
stored in the carriage unit. This print head keeps the tilt of print head in flexible and adjustable structure by
moving the adjustment lever up and down by the tilt adjustment mechanism. (Refer to chapter 4 for more
details) Also, parallelism adjustment lever is mounted on the left and right side of carriage guide shaft and
it adjusts parallelism degree between platen and shaft when this shaft is installed to the printer
mechanism.
After this adjustment is completed and operate PG adjustment lever, it becomes possible to change the
space between platen surface and print head surface into 2 phases; either 1.1mm to 1.8mm. It is possible
to vary the space between platen surface and print head by rotating the axis of carriage guide shaft which
itself is decentralized, with the operation of PG lever. This is the mechanism that user can adjust the
appropriate PG value by himself according to the paper thickness or any other environmental conditions
such as paper curl.
Carriage lock mechanism is to prevent the carriage from being left at uncap position for a long time
because of vibration during the printer transport or mishandling by the users. If the carriage is left at uncap
position and uncap state of the print head for long time, an ink on the print head surface gradually
becomes viscosity. As a result, the nozzle will be unable to discharge an ink. To make matters worse, the
holes(crater) of nozzle may be completely clogged by the viscosity ink and it may not be able to return to
the normal condition just by cleaning operation. In order to prevent this, printer goes to carriage lock state
at the following conditions.
After Power OFF operation:
If the power is turned off on the way of printing or any other performance, carriage lock will be
performed in the end after completing initialize operation.
After power ON operation:
After power is turned on and automatic P-On Cleaning is performed, then carriage lock will be
performed. P-On Cleaning is an automatic head cleaning that is performed when the power is
turned on. The timer IC always calculates printer’s power OFF time by the power of lithium
battery mounted on the C200 main board. P-on cleaning function automatically selects the
cleaning level according to the time which the printer is not in used.
After Eject the paper:
After Load/Eject button is pressed and the paper is ejected, if the data is not input, the printer
performs carriage lock and goes to standby state. However, if the paper is loaded to the printer
inside by Load/Eject button, the printer does not perform the carriage lock operation.
Paper Feed Motor
Eject Roller
Paper guide(Front)
Carriage home position Sensor
PF Roller
Timing Belt
Carriage Unit
Figure 2-8. Carriage Mechanism(Top Viewing)
Front Side
Carriage
Guide Shaft
Carriage Motor
Rear Side
Parallelism
Adjust Lever
Fixing Bush
Rev. A
2-
Page 48

EPSON Stylus Color 600
0
2.1.1.2.1 Paper Gap Adjust Mechanism
This mechanism can be set by the users and can prevent various problems related to low image density
or print with any dirt by changing the positions of PG lever according to the paper types.
Table 2-6. Paper Gap Adjust Lever Setting
Paper Lever position PG adjustment value
Normal paper,
Coated paper
Envelops Rear 0.9mm
It is a major premise that parallel adjustment is done correctly for the space between head and platen
(PG adjustment value above) which can be changed by platen gap adjustment.
Parallel adjustment should be done when the serviceman mounts the carriage guide shaft on the printer
mechanism during the production process or repair service. In the adjustment, the space between
parallel adjustment lever and gauge should be 1.04 mm.
Front 0 mm
(1.1mm between head and platen)
(2.0mm between head and platen)
2-1
Rev. A
Page 49

Chapter2 Operating Principles
2.1.1.3 Paper Feed Mechanism and Pump Mechanism
Mechanisms that send the paper in the hopper to inside the printer and perform constant paper
feed in order to perform printing on the sent paper are called paper feed mechanism as generic name.
In the Stylus Color 600, 4-phase, 200-pole hybrid type pulse motor is used in the PF motor as a motive
power of the paper mechanism and driving is done at 2-2 and 1-2 phase drive method. This motor is
not only used as a power source for paper feed mechanism but also used as power source of pump
mechanism which is necessary for print head cleaning. By using this pulse motor, it becomes possible
to use high speed driver or intermittent drive for the various paper feeds and pump operations such as
paper feed, slight paper feed, high and low speed absorption of pump operations. Following tables(Table
2-7 and 2-8) show PF motor specifications and control method at each mode.
Table 2-7. PF Motor Specification
Item Description
Motor type 4-phase/200-pole Stepping motor
Drive voltage
Coil Resistance
Drive frequency [cps (pps)] 400 - 4320Hz
Control method Bi-pola Drive
Table 2-8. Motor Control Method at Each Mode
Mode Drive Method Drive Frequency
Paper feed A 2-2 phase 4320 231
Slight paper feed 1-2 phase 400 2500
Slight paper feed 1-2 phase 2400 417
High speed attraction of pump 2-2 phase 4100 243
Low speed attraction of pump 1-2 phase 1800 555
Low speed paper feed 1-2 phase 1200 833
Paper feed B 2-2 phase 3400 294
Paper feed C 1-2 phase 4000 250
Ordinal absorption of pump 1-2 phase 4100 243
42VDC ±5%
7.8 ohms ±10%
(per 1 phase under 25°C environment)
Pulse Space
[Hz]
(ƒÊs)
Following tables show 1-2phase drive method at PF motor drive and each drive sequence at 2-2phase
drive method.
Table 2-9. 1-2 Phase Drive Method
Step No. Clockwise Counter clockwise
Phase A Phase B Phase A Phase B
1 +2/3 +2/3 +2/3 +2/3
0+1+10
2 -2/3 +2/3 +2/3 -2/3
-1 0 0 -1
3 -2/3 -2/3 -2/3 -2/3
0-1-10
4 +2/3 -2/3 -2/3 +2/3
+1 0 0 +1
Table 2-10. Drive Sequence at 2-2 Phase Drive
Step No. Clockwise(CW) Counter clockwise(CCW)
AB A B
1 +2/3 +2/3 +2/3 +2/3
2 -2/3 +2/3 +2/3 -2/3
3 -2/3 -2/3 -2/3 -2/3
4 +2/3 -2/3 -2/3 +2/3
Rev. A
2-1 1
Page 50
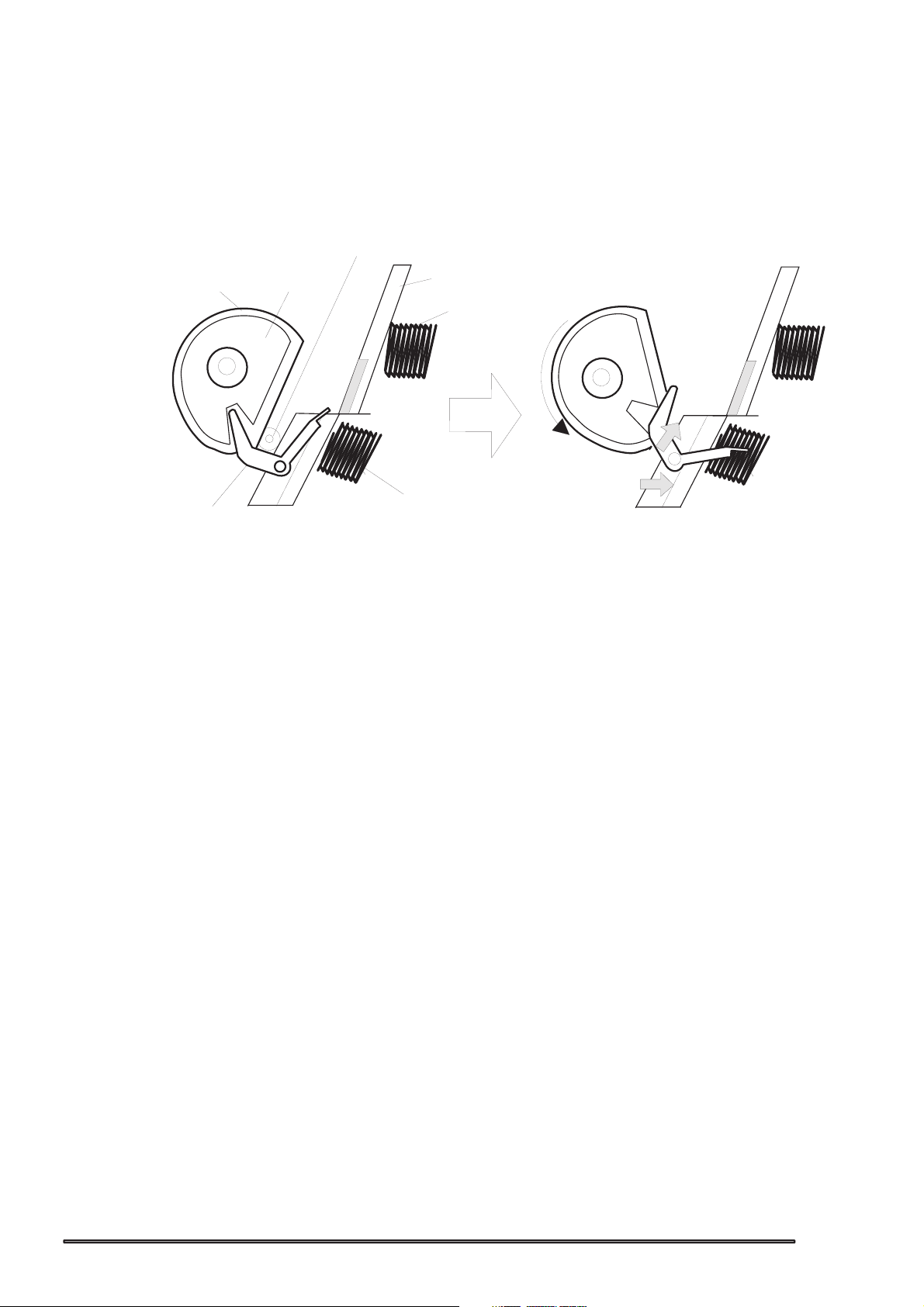
EPSON Stylus Color 600
2
Papers on the ASF (auto-sheet-feeder) supplied by the user are carried to the printer inside by paper
pick up sequence. Unlike the previous models, ASF of Stylus Color 600 has mufti feed prevention
mechanism. Following explains this function and figure below shows its mechanism.
[1. Multi feed prevention mechanism]
When the Load/Eject button is pressed, reversed rotation of PF motor is performed.
The return lever resets papers which are already in the out of stand by position in the stand by position
and make it possible to perform stable paper feeding by picking up the paper again.
Pintch Roller
D-Cut Roller
CAM
Hopper
Hopper spring
2)
1)
2)
Pad spring
Return Lever
[Standby state]
Figure 2-9. Multi Paper Feed Prevention Mechanism
Following explains process of multi feed prevention step by step. Refer to the figure above and confirm
its operation.
[Returning state]
[Step 1]
[Step 2]
[Step 3]
[Step 4]
When the load/Eject switch is pressed or printing order is input from the PC, PF motor rotates
counterclockwise and makes the CAM rotate towards direction of 1 in the figure above.
When the CAM covers the notch by the return lever, that position is considered as home
position, being monitored by ASF sensor.
When the CAM rotates toward 1 in the figure above, the return lever is pushed by the notch
of CAM and falls towards 2. At this time, the return lever moves to direction 3 by this
motion, and push down the pad which is waiting in the below part. At this time, friction of
pinch roller and pad will be canceled.
The papers which are out of stand by position by the previous paper feed motion are
returned to the paper stand by position by flip over strength of return lever. After this,
PF motor rotates clockwise and the printer goes to pick up sequence.
2-1
Rev. A
Page 51

Chapter2 Operating Principles
3
In the paper pick up mechanism of Stylus Color 600, same mechanism as Stlylus Color IIs/820
are applied. This mechanism changes adjoined lines of gear by colliding trigger lever with carriage
unit and convey the motive power on the platen to the ASF side(paper roller). The figure below
shows mechanism with explanation.
[2. Paper pick up mechanism]
When the Load/Eject switch is pressed or printing order is input, the carriage unit moves until
the left edge and collides with paper pick up trigger lever. When the carriage collides with this trigger
level, a planetary gear located on the same axis is also pushed at the same time and conveys
the motive power on the platen to the adjoined gear line side for ASF drive.
Paper Pick Up
ASF Roller Drive Gear
Planetary Gear
Trigger Lever
Eject Roller Drive Gear
Eject Roller
Transmission Gear
PF Motor Pinion Gear
ASF Roller Transmission Gear
Platen Roller Drive Gear
Platen Roller Transmission Gear
Figure 2-10. Paper Pick Up Mechanism
[3. Paper feed mechanism]
After papers in the ASF receive controls from pick up and multi feed prevention mechanism, they are
sent to the printer inside. The papers picked up by paper roller in the ASF goes to between platen
and roller support. Also, the eject roller pushes out the paper completely until the end and the roller
support drops the paper in the eject tray. The eject roller is driven with an eject paper notched roller as
pair where is located on the paper eject roller. Paper eject notched roller solves the deflection of paper
that is in the between platen eject notched roller and paper eject roller and always keep a certain space
between print head and paper surface. The figure below shows paper feed mechanism.
Paper
Eject Notched Roller
Support Roller
PF Roller
Eject Roller
Figure 2-11.Paper Feed Mechanism
Rev. A
2-1
Page 52

EPSON Stylus Color 600
4
2.1.1.4 Ink System
Ink system mechanism consists of 1)cap mechanism, 2)pump mechanism, 3)carriage lock
mechanism, 4)waste ink absorber and 5)ink sequence. Out of these mechanism, from 1) to 4)
are physical mechanism and parts which are mounted on the printer mechanism and 5) ink
sequence is performed automatically by firmware. Also, unlike previous models, since
Stylus Color 600 has no engage/disengage mechanism to change over pump mechanism and
paper feed mechanism, it is one of the major characteristics that pump and platen are always
at work whenever the PF motor is driven. The figure below shows head positions when the ink
system and various ink sequence are performed.
Platen Drive Gear
Eject Roller Drive Gear
Eject Roller
Trasmission Gear
Head Cleaner
Carriage Lock
PF(Pump) Motor Pinion
Figure 2-12. Ink System Mechanism
Printable Area
2975 dot
Pump Roller
Cap Unit
CRHP
ABCDEFGH
A: Dummy pumping position
B: Home position
C: Flashing position(right side)
D: I/C replacing position
E: Wipping complete/Rubing start position
F: ASF Standby position
G: Flashing position
H: ASF pick up position
Figure 2-13. Major Ink Sequence Position on the Carriage Mechanism
2-1
Rev. A
Page 53
Chapter2 Operating Principles
5
2.1.1.4.1 Pump Mechanism
In the Stylus Color 600, there is no switch or mechanism to change over the pump/paper feed
mechanism. Therefore, whenever the paper feed/pump motor rotate, pump drive roller in the pump unit
inside rotates. However, ink absorption/non ink absorption are separated by the roller rotational direction.
Also, even if the pump driver rotates toward ink absorption and the carriage position is in the false
absorption position, only driving in the pump mechanism is performed and actual ink attraction is not
done. The figure below shows process of conveying motive power to the pump drive roller.
Gear A
Axis of Paper Eject Roller
Gear B
Gear C
Actually, these parts
are one unit.
Compression
Spring
Pump Drive Roller
Figure 2-14. Pump Mechanism Power Transmission Process
The process of conveying the motive power to the paper eject roller by rotating the pinion of PF motor
is descried in figure 2-14. This motive power is conveyed to the Gear C through Gear B.
In the figure above, although the lever in order to drive Gear C, carriage lock, head cleaner mechanism
is shown separately, it is constructed as one unit. Since the engagem ent of these two parts depends on
the tension of the compression spring, if the lever is burdened, only Gear C and pump roller rotate and no
more motive power is conveyed to the lever part.
Rev. A
2-1
Page 54

EPSON Stylus Color 600
6
The table below shows PF/Pump motor rotational direction and pump system operation.
able 2-11. Relationship Between Pump Motor Rotation and Pump Operation
T
PF/Pump motor rotational direction Pump unit operation
Clockwise(CW)
forward rotation
Counterclockwise(CCW)
backward rotation
The figure below shows the pump operation at clockwise and counterclockwise rotation.
1)Release from the Pump pressure welding
2)Head cleaner reset
3)Carriage lock reset
1)Rotation towards pump pressure welding
2)Head cleaner set
3)Carriage lock set
CW Rotation
Tube pressured
Figure 2-15. Pump Roller Rotation and it’s Operation
In the ink absorptive operation such as cleaning, flushing initial ink charge except for printing operation,
ink in the ink cartridge drains to the waste ink absorber(pad) through the cap by the pump unit drive.
In case of printing and flashing drive, ink is popped out by the PZT in the print head, but in case of
absorptive operation such as cleaning and initial ink charge, ink absorption is performed
only by the pump drive without PZT drive after the head surface is adhered to the cap.
The next page explains cap mechanism and relation between printer operation and cap.
CCW Rotation
Tube released
2-1
Rev. A
Page 55

Chapter2 Operating Principles
7
2.1.1.4.2 Cap Mechanism
In the cap mechanism, in order to prevent ink from being thickened on the head surface, it is controlled
that the head surface stays adherent to the rubber frame of the cap surface when the power is off.
The absorber is spread in the cap and can hold a certain amount of ink which is absorbed from the
head without draining it to the waste ink pad. Also, in the bottom of abs orber, there are two valves in order
to control adhesion of head and cap surface, and one exit to drain ink to the waste ink pad.
A
Flag for Carriage
Ink Eject Valve
Negative pressure
release valve
Valve
Close state
B
Release state
Flag for frame
Head surface and
cap are adhered
each other.
Actual and false
absorptions.
During cleaning, initial ink
charge, and right flushing.etc.
Ink absorption in
the cap.
During left flushing and paper
feeding,etc.
Figure 2-16.Cap Mechanism Operation Principle
If the carriage is out of HP(in this case, in the printable area or paper feed position), the valves on the
cap mechanism stays in the position A in the figure above and are always closed. In this condition,
the carriage collides with flag, actual ink absorption and slight ink absorption are performed.
Also, by moving the carriage to further right side and colliding the flag for opening the valves with
the frame, negative pressure is released in the state that head surface and cap are adhered. This
makes it possible for ink on the nozzle plate surface to be ready for leaving from the cap in the stable
condition.
Rev. A
2-1
Page 56

EPSON Stylus Color 600
8
2.2 Electrical Circuit Operating Principles
Stylus Color 600 contains the following four electric circuit boards.
C206 PSB/PSE board
C200 Main board
Head Driver board
C206 PNL board
C206 PSB/PSE, C200 board are explained in this section. The head drive board is installed in the head
uniton the carriage. The figure below shows major connection of the 3 boards and their roles.
AC100V
RCC Switching Regulator
(C206 PSB/PSE Board)
CR Motor
PF MOTOR
(Pump Motor)
+5 V DC
+42 V DC
Main Control Board
(C200 Main Board)
PE Sensor
BCO/CCO Sensor
INK END Sensor
(Firm Wear)
+5 V DC
+42 V DC
ASF Lever
Position Sensor
2-1
Thermistor
Print Head
Head Drive Board
Figure 2-17. Electric Circuit of Stylus Color 600
Rev. A
Page 57

Chapter2 Operating Principles
9
2.2.1 C206 PSB/PSE Board
C206 PSB/PSE board is a power supply board with a RCC switching regulator, which generates +42VDC
for drive part and +5VDC for logic part to drive the printer. One of the major c haracteristic of this board is
that the same secondary switch is used as Stylus Color series printer. By using this switch, the following
difference can be seen as superficial phenomena compared with products applied with primary switch
method, such as Stylus Color IIs, II and Stylus 800/1000 series printer. The table 2-12 below shows
application of voltages generated by C206 PSB/PSE board.
1) Even if the switch is turned off during the middle of printer operation, since the driving
power is turned off after the carriage goes back to the carriage lock position,
the possibility of clogging ink nozzle will be decreased.
2) If the switch is turned off when the papers in the printer are still being carried except for
the papers in the hopper, the same operation mentioned above is performed and the
driving power is turned off after the paper is completely ejected.
Table 2-12. Application of DC V oltage
Voltages Application
+42VDC
+5VDC
CR Motor
PF/Pump Motor
Head driving power supply
Power supply for logic control
System control signal
Sensor circuit power supply voltage
LED panel drive power supply
Nozzle selector control signal power supply voltage
Figure 2-18 shows block diagram of C206 PSB/PSE board. The process from the input of AC100V to the
output of DC42V and 5V is explained below.
1) Regardless of the state of power switch(On or OFF), the voltage is always applied in the primary
side of the power supply board from the moment or at the state that AC-plug is plugged in.
At this time, F1 plays a role of preventing AC100V from coming into the F1.
L1 and R1-R2 also prevent high harmonic wave noise generated in the RC circuit filter which consist
of C1•`C4 and R1•`R2 from going out, and eliminate the noise from outside here.
2) The AC is full-wave rectified by diode bridge DB1, and converted to
electrolytic capacitor C11.
3) The pressured up direct current makes Q1 On through the starting resistor R31 and starts the primary
side of the circuit.
4) When the primary side is On state, the energy(current) led by the electromagnetic induction through
the trans (T1) does not flow to the secondary side since the diode(D51) on the secondary side
is installed in the opposite direction.
5) When the energy which is charged in the trans is reaching the saturated state, the voltage which
makes the Q1 On becomes weak gradually. At the point that this voltage drops at the
certain voltage, C13 absorbs the current in the opposite direction and Q1 is quickly shut off by
the resulting sharp drop.
6) When the primary side is turned off, the energy charged in the T1 is opened according to the
diode(D51) direction which is installed on the secondary side. Basically, 42 V DC is output
by these circuit operations and the number of T1 spiral coil .
x AC in voltage by smoothing
2
7) +5VDC is generated by pressured down this +42 V DC as power supply. IC51 pressures down the
+42 V DC and generates precise +5V DC by chopping off the output, forming the standard santooth
waveform by the outer RC integration circuit.
Rev. A
2-1
Page 58

EPSON Stylus Color 600
0
DB1 C11
Full Wave
Rectifier circuit
L1,R1-R2 C1-C4
Filter Circuit
F1
Prevention of
current flow
Smoothing
circuit
Q1
Main switching
circuit
Q2,Q3,
Feedback
circuit
Q31,PC1
T1
D51
C51
Smoothing
circuit
T
R
A
N
S
C84,Q84
Power OFF
Delay circuit
ZD81-86,
ZD51
+42V constant
voltage control
circuit
+42V overvoltage
protection circuit
ZD52,87
+5V generation
(IC51)
circuit
ZD53
+5V overvoltage
protection circuit
+42VDC
+5VDC
PC1
Photo coupler
PSO Signal
AC100V
Figure 2-18. C206 PSB/PSE Board Block Diagram
The C206 PSB/PSE board has various control circuits to stop output if malfunction on the power supply
board, on the main board or on the duty of printer mechanism happen. Following explains each control
and protection circuits.
1) +42V Line Constant Voltage Control Circuit:
The output level of the +42V line is monitored by a detection circuit consisting of seven Zener diodes.
This circuit prevents voltage from dropping for constant output voltage.
2)+5V Line Over voltage Protection Circuit:
This protection circuit is in the same line as +42V overvoltage protection circuit is located. The output
voltage level of the +5V line is monitored by a Zener diode. This circuit shuts down the circuit
operation forcefully when the voltage level exceeds +9V.
3) +42VDC Line Over voltage Circuit
This ciruit is in the same line as +5V line over voltage protection circuit is located. The output level is
monitored by two Zener diodes. If the voltage level exceeds +48VDC, this circuit stops circuit
operation forcefully.
4) +5V Line Constant Voltage/Constant Current Control Circuit:
The output current is monitored by a +5VDC generation switching control IC(IC51), which also
monitors the output voltage. This information is input to the internal comparator and stabilizes+5V
line. Also, operation of the secondary side switch is explained below.
1) When the power is turned on, Q1 repeats ON/OFF automatically along with the increase and
decrease of energy on the trans coil at the primary side. While the power is being on, PSC
signal is input to the power supply board from the C200 main board.
2) This signal turns Q84 on and it becomes possible to discharge energy between 8-9 of T1.
At this time, even if the power is turned off, the electrolytic capacitor keeps Q84 on for a while.
By this electrolytic capacitor, output is hold at least 30 seconds even after the power is turned off.
This time helps the printer to complete the P-Off operation.
2-2
Rev. A
Page 59

Chapter2 Operating Principles
2.2.2 C200 MAIN Board
Various DC voltage generated on the C206 PSB/PSE board is added various signals in order to drive the
printer function on the C200 MAIN board, and the drive of CR/PF(Pump) motor and printing head is
performed. This control board consists of system part and drive part. In the system part, there are
formation and controls of various signals in order to drive the CR/PF(pump) motor, sequence control
by input from the sensor circuit, and also output of signal to select appropriate nozzle for the printing
head. On the other hand, the drive part has constant current drive by the driver IC for the CR/PF(pump)
motor drive and trapezoidal waveform circuit for head drive.
C200 MAIN Board
PROM4M
(IC3:EPROM)
M5M411664
(IC4:D-RAM)
4-32M
(IC6:CG)
System
DRAM Control
Head Temperature
From A
From B
From B
TPM 95C061
(IC1:CPU)
SN75LBC775
(IC16 Transceiver)
H8D2813D
(IC7)
LB1845
(IC14)
LB1845
(IC15)
Timer (IC10)
E05B43
(IC2: Gate Array)
EEPROM (IC11)
Print Head
Carriage Motor
PF(Pump) Motor
CR/PF Motor Drive
Panel I/F
Head Common Drive
Power
to B
to A
Centornics I/F
Serial I/F
Sensor Circuit
Figure 2-19. C200 MAIN Control Board Block Diagram
[CPU]
The C200 MAIN board is controlled by a 16-bit CPU(TMP95C061AF) running at 25MHz. Gate array
manages most of controls and monitors. Likewise Stylus Color, the D-RAM is applied for RAM
which is used as work area for receiving data and developing the data and CPU manages its control
such as CE, RAS/CAS controls.
[Gate Array]
E05B43 controls following functions.
Motor control : Each motor performs data transmission(W1-2 phase) that motives
Micro-Step.
Head voltage control: In the ink jet printers, drive voltage wave form(trapezoidal wave form)
in order to drive PZT is formed in the various shapes according to the
types of the printers.
Therefore, it is necessary to form appropriate drive form for each head.
Head voltage control forms necessary waveform for each control
signals and outputs them.
EEPROM control: The correction value to eliminate the error of each printers at the
production process is installed in the fixed address of IC.
When the power is turned off, the contents set by users is written
instantly, and is red to the RAM when the power is turned on.
Sensor Data: The sensor detects information at the various conditions, which is
necessary for the printer operation. The gate array recognizes signals
and changes over to the next control.
Rev. A
2-21
Page 60

EPSON Stylus Color 600
2
Timer Data: The timer IC that uses lithium battery as power source monitors how
long the power is off. When the power is turned on, it is changed to
appropriate cleaning level according to the time that the power is off.
[Common Driver IC]
The trapezoidal wave form circuit for head drive is became to HIC from the previous discreate structure.
Because of this, it is not necessary to adjust the adjustable VR on the board during production process.
Various electric charge/discharge control signals are all processed in the HIC.
[CR/PF Motor Drive Circuit]
Constant current drive is performed by the HIC. Out of this, only CR Motor is controlled for Micro-Step
control and HIC becomes poss ible to flow the appropriate current value at each steps. ( PF Motor has
only 1-2, 2-2phase drive method). Also, bipolar drive is performed on the 4 cables individually. Following
pages explain each major control circuit.
Serial Data: The gate array receives serial data through the transceiver IC.
Parallel I/F control: With the use of IEEE1284 Nibble mode, it became possible not only to
receive the data from the host but also to return various information
which the printer possesses to the host.
2-2
Rev. A
Page 61

Chapter2 Operating Principles
3
2.2.2.1 Reset Circuits
The reset circuit prevents the CPU from running away, which is caused by the unstable voltage in the
logic line during the power ON/OFF. Also, this circuit monitors level of power voltage at the overloading
or malfunction on the circuit and manages the printer to operate normally, keeping the damage to the
printer minimum during the abnormal situations. On the C200 main board, 2 ICs are mounted ; IC for
monitoring the voltage level (logic line) and IC for monitoring the voltage level (power line) and both
are monitored by the gate array and CPU.
The figure below shows reset circuit block diagram with explanation on the next page.
+5V
+5V
+42V
R10
R6
PST592D
(IC8)
TMP95C061
(IC1)
15
P84
10
/NMI
M51955B
(IC9)
2
IN
4
GND
Vout
NRES
Vcc
GND
P85
/RESET
1
2
3
4
16
30
NC8
VCC
OUT
NC5
C47
8
7
6
5
+5V
176
R1
R138
E05B43
(IC2)
/RESET
Figure 2-20. Reset Circuit Block Diagram
[PST592(IC8)]
The actual operation of the circuit is to keep outputting Low signal until +5V line goes up to +4.2V
when the power is on, and to cancel the reset signal with output of High signal when the voltage goes up
more than 4.2V.
[M51955(IC9)]
This IC also performs as monitor on the power line same as the reset IC for logic described above.
High/Low is judged at the 33.2V.
[Relation between IC8 and IC9]
Reset signal which is low and output by IC9 is input to the CPU and gate array and system reset operation
is performed. Also, this signal is detected on the IC9(IC for reset monitor, power line) and outputs the
same Low signal towards CPU/NMI terminal by being input to NC5.
Rev. A
2-2
Page 62

EPSON Stylus Color 600
4
2.2.2.2 Sensor Circuits
The following sensor circuits are mounted in the Stylus Color 600 and selects appropriate operations
based on the returned information.
ASF Sensor: An ASF sensor detects the position of return lever when the power is
(Photo) turned on, and causes the paper to be picked up by the pick up roller
from the normal initial condition. (Refer to section 2.1.1.3 for detail.)
PE Sensor: A PE sensor determines if there is paper in the printer. Based on the
(Photo) signal form this sensor, a particular paper edge treatment such as
Micro-weave printing is performed.
HP Sensor: A HP sensor detects the carriage home position.
(Photo) It is used for managing printing position and cleaning, etc.
Thermistor Sensor: A thermistor sensor keeps stable printing quality, changing PZT drive
voltage(VH) slightly according to changes of environmental
temperature.
Cartridge Sensors: Cartridge sensors are built into the Bk, CMY cartridge on the carriage
unit respectively to determine if the cartridge is installed or not when it
is exchanged or the power is turned on. In case of Stylus Color 600,
the counter is reset at every time the cartridge is removed.
The figure below shows sensor circuit. Out of the data such as EPW with IEEE 1284 Nibble mode
to be returned to the host, the data to indicate ink consumption is calculated and managed by the
counter of the firmware. Therefore, it is omitted here.
TMP95C061
+5V
(IC1)
18
Vref
CCO
CN8
BCO
+5V
+5V
3
AGND
AN0
17
20
3
THM
CN8
E05B43
(IC2)
SW8
SW7
SW6
SW5
SW4
CCO(199)
BCO(201)
PE(203)
HP(205)
ASF(207)
Figure 2-21. Sensor Circuit Block Diagram
+5V
2
1
PEV
GND
PE
HPV
GND
HP
ASFV
GND
ASF
3
2
1
3
2
1
3
2
1
CN4
CN5
CN11
F
2-2
Rev. A
Page 63

Chapter2 Operating Principles
5
2.2.2.3 EEPROM Control Circuits
The EEPROM of Stylus Color 600 has following contents. Gate array E05B43(IC2) controls operations of
reading data when the power is on and writing data when the power is off.
Ink consumption(Bk, CMY)
CL counter(Various cleaning operations that are previously done are memorized)
Destination information
Information of various adjustment values(Bi-D, VH voltage, etc.)
CPSI pass word
Other various setting values by the user
EEPROM is connected to the Gate array by 4 lines and performs following functions.
The figure below shows EEPROM control circuit.
CS : Chip selection signal
CK : Data synchronism clock pulse
DI : Data writing line(serial data) at power off.
DO : Data reading line(serial data) at power on.
+5V
93C46(IC11)
8
VCC
6
ORG
5
GND
CS
CK
DI
DO
1
130
129
2
3
128
4
127
E05B43(IC2)
ECS
ECK
EDO
EDI
Figure 2-22. EEPROM Circuit Block Diagram
Rev. A
2-2
Page 64

EPSON Stylus Color 600
6
2.2.2.4 Timer Circuit
The lithium battery is mounted on the C200 MAIN board and calculates how long the printer is not in used.
The timer IC(IC10) starts counting with oscillation motivated by the CR3 using this battery as a power
source. The figure below shows connection of the Timer circuit.
+5V
D1
D4
BAT1
CR3
8
VDD
2
XOUT
3
XIN
4
VSS
S-3510ANFJ
(IC10)
CS
/SCK
SIO
+5V
Figure 2-23. Timer Circuit Block Diagram
The followings explain about operation of this circuit.
When the printer is on, power is supplied to the Timer IC by applying +5V quickly through
the D4.
This power is also used for the power to oscillate the outer CR3. The oscillation wave form is
input to XIN terminal.
Since the oscillation wave form of CR1 is analog waveform, it is processed into the
pulse form in the Timer IC.
When the printer is turned on, the Timer IC outputs power off time as serial data to the gate
array.
Once the printer is turned off, 3VDC of BAT1(lithium battery) is supplied as power source for
the Timer IC through D1.
Since +5V at the power on is higher than +3V of the lithium battery, the power is not being
consumed from the lithium battery.
1
6
7
125
122
123
126
TCE
TIO
TCLK
TDATA
E05B43(IC2)
2.2.2.5 DRAM Control
In the Dynamic RAM control, output and formation of CAS and RAS control signals become necessary
in addition to the output of CS signal. The CPU TMP95C061AF not only controls that but also perform
the output of CS signal of P-ROM. Refresh timing is performed in the CAS Before RAS.
2-2
Rev. A
Page 65

Chapter2 Operating Principles
7
2.2.2.6 Print Head Control Circuit
The print head control circuit of Stylus Color 600 has following characteristics.
Common waveform circuit became one HIC.
Micro-vibration mode is added.(when the CR motor is accelerating)
High speed drive 14.4KHz (trapezoidal wave form
Enhanced Nozzle configuration (resolution in the vertical direction)90dpi
(However, black nozzle is 2 lines structure)
Also, Stylus Color 600 has Micro-dot control as dot shooting control. There are total three dot shooting
controls on this printer.
• Normal Dot mode(Single Firing)
• Normal Dot mode(Dual Firing)
• Micro Dot mode
• Micro-Vibration(Not printed)
The control circuit is considered as two divided parts; 1) trapezoidal wave form generation circuit
(common drive circuit) to drive PZT in the head, and 2) Nozzle-selector drive circuit to determine
which nozzle should be used. The Nozzle-Selector is attached to the head unit just like the previous
models. The common drive circuit is became as HIC and mounted on the C200 main board.
[Common drive circuit]
+5V
+42V
F1
H8D2813D
(IC7)
E05B43
(IC2)
CHG
KC1
ND1
ND2
MD1
MD2
DATA
DATA
/STB
CLK
VM
VCC
CHG
KC1
ND1
ND2
MD1
MD2
DATA
DATA
/STB
CLK
CTC
DTB
GND1
GND2
23
22
21
CN8
20
19
18
Figure 2-24. Print Head Control Circuit Block Diagram
The shape of trapezoidal wave form will be different according to the printing operation, slight vibrations at
the non-printing nozzle and waiting condition. However, IC7(H8D2813) generates all wave forms as drive
wave forms by resistance(electric) welding control of common voltage drive control signal that is output
from the IC2(E05B43) in the figure above.
Table 2-13. Specifications of H8D2813 Operation
Item Contents
Power Voltage
42V ±5%
Starts supplying after 5V rises and be stabilized./ Stops
supplying before +5V drops.
Final drive element
Reset Operation
2SC3746(for charging), 2SA1469(for discharging)
Off on the both charging and discharging sides.
Supplies drive power source.
This common voltage trapezoidal wave form can be observed anytime after the +5V rises even if there is
printing data or not. (Q7:3-pin, or Q9:3-pin and GND on the C200 main board)
Rev. A
2-2
Page 66

EPSON Stylus Color 600
8
[Nozzle Selector Drive Circuit]
In order to motivate the print head to carry out printing, it is necessary to transmit the print data to the
appropriate nozzles, which becomes direct signals to drive PZT. This data transmission is performed
by the serial transport method, however the data output for each black and CMY head is transmitted by
the parallel method. The figure below shows data transmission circuit.
VH
COM
NCHG
Gate Array
E05B43(IC2)
U102
IR2C73C
SI
SCLK
LAT
XCHG
COM
VHV
VD1/2
For Cyan & Yellow
data latch
CLK
SI1
SI2
SI3
LAT
THM
Figure 2-25. Nozzle Selector Circuit Block Diagram
SI
SI1
SCLK
LAT
XCHG
COM
VHV
VD1/2
For Black & Magenta
data latch
CLK(Clock) pulse considered as source of serial communication is commonly used for both black and
CMY. The serial data transmits data as 64-Clock unit, synchronizing with this pulse. After the data
transmission of 64-Clock is completed, LAT(Latch) signal is activated and is hold temporarily in the
IR2C72C(U101) At this time, since the num ber of nozzle for Color head is fewer(21- nozzles) and differ ent
from the ones for black head, 0 is transmitted forcefully for the data for 43 nozzle (64-21=43).
2-2
Rev. A
Page 67

Chapter2 Operating Principles
9
After the data transmission by the nozzle selector(IR2C72C, IR2C73C) is completed and a certain time
passes, trapezoidal wave form generated by the common drive circuit once sends electric current to the
PZT for the proper nozzles which are determined in the nozzle selector circuit. This motivates PZT and
ejects the ink in the cavity. The figure below shows normal dot data transmission timing in order to from
1-dot.
Common Waveform
Com
64-dot
SCLK
LAT
NCHG
CHG
ND1
ND2
KC1
Figure 2-26. Common Drive Circuit Block Diagram
Rev. A
2-2
Page 68

EPSON Stylus Color 600
0
2.2.2.7 PF(Pump) Motor Drive Circuit
IC15(UDN2917) is used for driving PF(Pump) motor. In the IC, Bi-pola drive PWM current control type is
performed, making it possible to provide stable current to each phase of motor. Also, it makes possible to
change over the reference voltage as drive current settings by making 3 combinations(100%,66% and
33%), using 4 current setting ports(input). (Refer to 2.1.1.3 for motor and details about sequence)
However, firmware does not drive Micro-step in the Stylus Color 600. The figure below shows the block
diagram of Unlike using Uni-Pola drive, there is no cable for GND in the motor since Bi-Pola drive is
performed in the PF motor.(Refer to section 2.1.1.2 since carriage motor interior connection diagram has
the same connection as the PF motor’s phase connection. This helps to understand the reason why the
direction of current is controlled freely in each phase by the combinations of high/low control signals.
E05B43(IC2)
PFV0-PFV3
PFA0
PFA1
PFB0
PFB1
PFAPH
PFBPH
57
58
55
56
59
50
46-49
Current Selection
Resistor
UDN2917(IC15)
2
I10
1
I11
23
I20
24
I21
43
PH1
26
PH2
44
Vref1
25
Vref2
4
SENS1
5
E1
SENS2
E2
1
2
3
4
Figure 2-27. PF(Pump) Motor Circuit Block Diagram
The current control is perf ormed by output port(46•`49 pin) of E05B43(IC2), its outer res istance circuit
and driver IC15(UDN2917). First, firmware possesses 16 ways of current values as current table out of
combinations made by 5 resistance which are connected to the output por ts( 46 •`49 pin) in the gate ar ray.
On the other hand, signals which are output by combination of these res istanc e’s on/off are input in the 25
and 44 pins. HIC is driven at the same standard voltage for each A and B phase.
PFA
PF/A
PFB
PF/B
Actual on/off control to send electricity through the motor is performed by the process that SEN1 and
SEN2 terminals (2 and 13 pin) detect the input signal from the gate array which is monitored by the
interior comparator, confirm the current that actually flew the phase as current value again and
perform the feed back to the on/off. The figure below shows relation between input signal to the
driver IC and motor control.
+42V
R4
+5V
Ra
Rb
It varies load resistance
by the control signal and
changes the ratio of partial
pressure.
If feeds back the current
RS
that actually flew in the
coil to the comparator.
Note:
In case of PF motor,
same reference voltage
is input to UDN2917 for
both phase A and B, but
differet reference voltage
is set individually for
phase A and B, in case of
CR motor.
E05B43(IC2)
Gate Array
R1
R2 R3
UDN2917(IC14,IC15)
Figure 2-28. PF(Pump) Motor Driver Internal Block Diagram
2-3
Rev. A
Page 69

Chapter2 Operating Principles
2.2.2.8 CR Motor Drive Circuit
In the CR motor, the same UPD2917(IC14) as the PF motor has used. In the IC, Bi-pola drive PWM
current control type is performed, making it possible to provide stable current to each phase of motor.
Also, it makes possible to change over the reference voltage as drive current settings by making 3
combinations(100%, 66% and 33%), using 4 current setting ports(input). (Refer to 2.1.1.3 for motor and
details about sequence) In the carriage motor, firmware supports the micro-step driving in the Stylus Color
600. The figure below shows carriage motor drive circuit.
E05B43(IC2)
CRA0
CRA1
CRB0
CRB1
CRAPH
CRBPH
MTBV0-V4
MTAV0-V4
75
76
72
73
77
74
Current Selection
Resistor
UDN2917(IC14)
2
I10
1
I11
23
I20
24
I21
43
PH1
26
PH2
44
Vref1
25
Vref2
4
SENS1
5
E1
SENS2
E2
A
1
PFA
3
/A
B
21
/B
2
PF/A
3
PFB
4
PF/B
Figure 2-29. Carriage Motor Circuit Block Diagram
Unlike using Uni-Pola drive, there is no cable for GND in the motor since Bi-Pola drive is performed in the
CR motor.(Refer to section 2.1.1.2 since carriage motor interior connection diagram has the same
connection as the PF motor’s phase connection. This helps to understand the reason why the direction of
current is controlled freely in each phase by the combinations of high/low control signals.
The current control is performed by output port(60•`67 / 70•`71 pin) of E05B43(IC2), its outer resistance
circuit and driver IC14(UDN2917). First, 10 resistance which are connected to the output port of the gate
array divide each current values of phase A and B in the CR motor.
The firmware possesses 16 different ways of current values individually as current table out of
combinations made by 5 resistance which are connected to the output ports(46•`49 pin) in the gate array.
On the other hand, signals which are output by combination of these resistance’s on/off are input
independently in the 25 and 44 pins. HIC is driven at the different standard voltage for each phase A and
B.
Actual on/off control to send electricity through the motor is performed by the process that SEN1 and
SEN2 terminals (2 and 13 pin) detect the input signal from the gate array which is monitored by the
interior comparator, confirm the current that actually flew the phase as current value again and
perform the feed back to the on/off. (Refer to before page since it is same as the one of PF motor)
Rev. A
2-31
Page 70

Chapter 3
Disassembly and Assembly
3.1 OVERVIEW...............................................................................................................1
3.1.1 Precautions for Disassembling the Printer............................................................................. 1
3.1.2 Specification for Screws........................................................................................................... 2
3.1.3 Tools........................................................................................................................................... 2
3.1.4 Work Completion Check........................................................................................................... 3
3.2 DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY ............................................................................4
3.2.1 Housing Removal ...................................................................................................................... 5
3.2.2 Circuit Boards Removal............................................................................................................ 6
3.2.3 Control Panel Removal ............................................................................................................. 8
3.2.4 Waste Ink Pad Assembly Removal .......................................................................................... 9
3.2.5 Disassembling the Printer Mechanism.................................................................................. 10
3.2.5.1 Printhead Removal..................................................................................................... 10
3.2.5.2 Pump Assembly and Cap Assembly Removal........................................................... 12
3.2.5.3 CR Motor Assembly Removal .................................................................................... 14
3.2.5.4 PF Motor Assembly Removal..................................................................................... 16
3.2.5.5 ASF Assembly Removal............................................................................................. 18
3.2.5.6 Carriage Assembly Removal...................................................................................... 24
3.2.5.7 PF Roller Assembly Removal..................................................................................... 26
3.2.5.8 PE Sensor Assembly Removal .................................................................................. 28
3.2.5.9 HP Sensor Assembly Removal .................................................................................. 29
3.2.5.5.1 ASF Disassembly............................................................................................ 20
3.2.5.5.2 Pick-Up Roller Assembly Removal ................................................................. 22
Page 71

Chapter 3 Disassembly and Assembly
3.1 OVERVIEW
This section describes procedures for disassembling the main components of EPSON Stylus Color 600.
Unless otherwise specified, disassembly units or components can be reassembled by reversing the
disassembly procedure. Therefore, no assembly procedures are included in this section. Precautions for
any disassembly or assembly procedure are described under the heading “WORK POINT”. Any
adjustments required after disassembling the units are described under the heading “REQUIRED
ADJUSTMENT”.
3.1.1 Precautions for Disassembling the Printer
See the precautions below when disassembling or assembling EPSON Stylus Color 600.
WARNING
Disconnect the power cable before disassembling or assembling the printer.
Wear protective goggles to protect y our eyes from ink . If ink gets in your eye, flush the eye with
fresh water and see a doctor immediately.
If ink comes into contact with your skin, wash it off with soap and water. If irritation occurs,
contact a physician.
A lithium battery is installed on the main board of this printer. Be sure to observe the following
instructions when servicing the battery:
Keep the battery away from any metal or other batteries so that electrodes of the opposite
polarity do not come in contact with each other.
Do not heat the battery or put it near fire.
Do not solder on any part of the battery. (Doing so may result in leakage of electrolyte from the
battery, burning or explosion. The leakage may affect other devices close to the battery.)
Do not charge the battery. (An explosive may be generated inside the battery, and cause burning
or explosion.)
Do not dismantle the battery. (The gas inside the battery may hurt your throat. Leakage, burning
or explosion may also be resulted.)
Do not install the battery in the wrong direction. (This may cause burning or explosion.)
CAUTION
Danger of explosion if the battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace only with the same or equivalent
type recommended by the manufacture. Dispose the used batteries according to government’s law
and regulations.
Risque d’explosion si la pile est remplacée incorrectment. Ne remplacer que par une pile du même
type ou d’un type équivalent recommandé par le fabricant. Eliminer les piles déchargées s elon les lois
et les règles de sécurité en vigueur.
CAUTION
Never remove the ink cartridge from the carriage unless manual specify to do so.
When transporting the printer after installing the ink cartridge, be sure to pack the printer for
transportation without removing the ink cartridge.
Use only recommended tools for disassembling, assembling or adjusting the printer.
Apply lubricants and adhesives as specified. (See Chapter 6 for details.)
Make the specified adjustments when you disassemble the printer. (See Chapter 4 for details.)
Rev. A
3-1
Page 72

EPSON Stylus Color 600 Service Manual
2
3.1.2 Specification for Screws
Table 3-1 lists the abbreviation of screws and its use. Refer to the scr ew number in the following table to
identify the type of screw shown in the disassembly procedures.
Table 3-1. Screw Identification Table
No. Shape Name Standard
1 CBS
(Cross/Bind/S-tight screw)
2 M3x10
M3x6
3 CBP
(Cross/Bind/P-tight screw)
4 M3x10
5 M3x8
6 CP
(Cross/Pan-head screw)
7 CBS with Washer
(Cross/Bind/S-tight screw with
washer)
M3x6
M3x4
M3x6
3.1.3 Tools
Table 3-2 lists the tools required for dis assem bling and assem bling the printer. Use only specified tools to
avoid damaging the printer.
Table 3-2. Required Tools
Name Availability EPSON
Parts Code
Philips Screw Driver (No.1) Commercially available B743800200
Philips Screw Driver (No.2) ditto B743800400
Tweez ers ditto B741000100
Hexagonal Box Driver (5.5mm) ditto B741700100
3-
Rev. A
Page 73

Chapter 3 Disassembly and Assembly
3
3.1.4 Work Completion Check
If any service is made to the printer, use the check list shown below, to confirm that all works are
completed properly and the printer is ready to return to the user.
Category Item Check Point Status
Main Unit Self-Print Test Is the printing successful?
Online Print Test Is the printing successful?
Printhead Are any nozzles broken?
(Missing dot)
Carriage Mechanism Does it moves smoothly?
Is there any abnormal noise in its
motion?
Is there any dirt or scratch with the
CR guide shaft?
Is the CR Motor at the correct
temperature? (Not too hot)
Paper Feeding
Mechanism
Adjustment Specified
Adjustment
Lubrication Specified Point Does all the lubrication made at
System ROM Version Version (Latest):
Packing Ink Cartridge Have brand-new ink cartridges
Protective Materials Have all relevant protective
Other Attachment,
Accessories
Is paper advance smoothly?
*No paper jamming
*No paper skew
*No multiple feeding
*No abnormal noise
Is the PF Motor at the correct
temperature? (Not too hot)
Is the paper path clear of all
obstructions?
Does all the adjustment made
correctly?
specified points?
Is the amount of lubrication
correct?
installed correctly?
materials been attached to the
printer?
Have all relevant items been
included in the package?
Checked/Not necessary
Checked/Not necessary
Checked/Not necessary
Checked/Not necessary
Checked/Not necessary
Checked/Not necessary
Checked/Not necessary
Checked/Not necessary
Checked/Not necessary
Checked/Not necessary
Checked/Not necessary
Checked/Not necessary
Checked/Not necessary
Checked/Not necessary
Checked/Not necessary
Checked/Not necessary
Checked/Not necessary
Rev. A
3-
Page 74

EPSON Stylus Color 600 Service Manual
4
3.2 DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
This section describes the step-by-step disassembly procedures shown in the diagram below.
Housing
Removal
Section 3.2.1
Circuit Boards
Removal
Section 3.2.2
Control Panel
Removal
Section 3.2.3
Waste Ink Pad Assembly
Removal
Section 3.2.4
Printer Mechanism
Disassembly
Seciton 3.2.5
Printhead
Removal
Section 3.2.5.1
Pump/Cap Assembly
Removal
Section 3.2.5.2
CR Motor Assembly
Removal
Section 3.2.5.3
PF Motor Assembly
Removal
Section 3.2.5.4
ASF Assembly
Removal
Section 3.2.5.5
ASF
Disassembly
Section 3.2.5.5.1
3-
Carriage Assembly
Removal
Section 3.2.5.6
PF Roller Assembly
Removal
Section 3.2.5.7
PE Sensor Assembly
Removal
Section 3.2.5.8
HP Sensor Assembly
Removal
Section 3.2.5.9
Figure 3-1. Disassembly Flow
Pick-Up Roller Assembly
Removal
Section 3.2.5.5.2
Rev. A
Page 75

Chapter 3 Disassembly and Assembly
5
3.2.1 Housing Removal
Since the EPSON Stylus Color 600 has no lower housing as previous EPSON printers, the printer
mechanism can be taken out by only removing the upper housing.
1. Open the printer cover and set the PG adjust lever on the right-hand side to (+) position.
2. Remove 4 screws (No.2) and remove the upper housing.
WORK POINT
Pull the front end of the upper housing while lifting up the upper housing to remove it.
CAUTION
Be careful not to pinch the cables with the posts of the upper housing when reins talling it. (Espec ially
with the cables from the motors and doing so causes fatal damage to the mechanism and the electric
circuitry.)
Upper Housing
Figure 3-2. Housing Removal
Rev. A
3-
Page 76
EPSON Stylus Color 600 Service Manual
6
3.2.2 Circuit Boards Removal
The electric circuit boards of the printer (Main control circuit board: C200 MAIN / Power supply circuit
board: C206 PSB/PSE) are both installed on single metal chassis and attached to the printer mechanism.
Therefore, first detach the metal chassis from the printer mechanism to remove the electric circuit boards.
1. Remove the upper housing (Refer to section 3.2.1)
2. Remove 5 screws (No.1 / three at the back of the printer mechanism and one each at both sides
of the printer mechanism)
3. Slightly pull out “SHIELD PLATE, M/B” (metal chassis) from the printer mechanism and take out
the cable holders inserted to the edge of “SHIELD PLATE, M/B”.
4. Fully separate “SHIELD PLATE, M/B” from the printer mechanism and remove all cables
connected to the connectors on the main board; C200 MAIN.
5. If you need further to remove each electric circuit board from “SHIELD PLATE, M/B”, remove the
screws fixing each board and remove it.
C200 MAIN BOARD: 10 screws (No.1 = 7 screws, No.6 = 3 screws)
C206 PSB/PSE BOARD: 4 screws (No.1)
Also disconnect the cable from the connector; CN10 (locking type) on the C200 MAIN, when you
remove the C206 PSB/PSE BOARD.
WORK POINT
Unlock the connector CN6/7 on the C200 MAIN by pulling its loc k before disconnect the cables, and
be sure to lock it when reconnecting the cables.
[Cable Holders]
SHIELD PLATE, M/B
Figure 3-3. SHIELD PLATE M/B Removal
3-
Rev. A
Page 77

7
Power Supply Board
(C206 PSB/PSE)
Chapter 3 Disassembly and Assembly
MAIN Board
(C200 MAIN)
SHIELD PLATE, M/B
Figure 3-4. Circuit Boards Removal
REQUIRED ADJUSTMENT
Be sure to perform the following adjustments when the C200 MAIN board is replaced:
1) VH Voltage value writing (Refer to Chapter 4 / Section 4.2.2.3.)
2) Printhead Angle Adjustment (Refer to Chapter 4 / Section 4.2.2.4.)
3) Bi-D Alignment Adjustment (Refer to Chapter 4 / Section 4.2.2.5.)
Rev. A
3-
Page 78

EPSON Stylus Color 600 Service Manual
8
3.2.3 Control Panel Removal
1. Remove the upper housing (Refer to Section 3.2.1)
2. Remove 2 screws (No.1) and remove the control panel assem bly from the printer mechanism and
disconnect the flat cable from the connector of the panel assembly.
WORK POINT
By removing the control panel assembly, the stacker assembly is also detached from the printer
mechanism as it held by the control panel assembly.
SHIELD PLATE, PANEL
C206 PNL Board
HOUSING, PANEL, LEFT
PANEL, ASSEMBLY
STACKER, ASSEMBLY
Figure 3-5. Control Panel Removal
3-
Rev. A
Page 79

Chapter 3 Disassembly and Assembly
9
3.2.4 Waste Ink Pad Assembly Removal
1. Removing the upper housing (Refer to section 3.2.1)
2. Removing the control panel assembly (Refer to section 3.2.3)
3. Remove 1 screw (No.4) at the right-hand side of the printer mechanism, that fixing “Waste Ink Pad
Assembly”.
4. Remove “SPACER, TRAY” fixing “Waste Ink Pad Assembly” at the left-hand side of the printer
mechanism and remove “Waste Ink Pad Assembly” by pulling it downward.
CAUTION
When you replace “Was te Ink Pad Assembly” to new one, be sure to perform the ink counter reset
operation. (Refer to Chapter 1 / Section 1.4.2 for details)
WORK POINT
When re-installing “Waste Ink Pad Assembly ”, be sure that “Stopper, Stacker” that attached to the exit
roller shaft is correctly pushed in to back of the projections of “Waste Ink Pad Assembly”.
SPACER, TRAY
Section (A)
[Projections]
Paper Exit Roller Shaft
Front side
STOPPER, STACKER
Push it to the back of
projection
Figure 3-6. Waste Ink Pad Assembly Removal
Waste Ink Pad Assembly
Rev. A
3-
Page 80

EPSON Stylus Color 600 Service Manual
0
3.2.5 Disassembling the Printer Mechanism
This section describes the procedures for removing the main components consisting the printer
mechanism.
3.2.5.1 Printhead Removal
1. Removing the upper housing. (Refer to section 3.2.1)
2. Rotate “Gear, 67.2” (largest gear at the left-hand side of the printer mechanism) toward the front to
disengage the carriage lock mechanism, and move the carriage assembly to the middle of the
printer.
3. Remove both black and color ink cartridges.
4. Remove both carriage cover assemblies from the carriage.
5. Remove “Twist Spring, 49” at left-hand side of the carriage and remove 1 screw (No.3) fixing
“FASTNER, HEAD”. Then, remove “FASTNER, HEAD” from the carriage.
6. Unhook the flat cables from the carriage assembly and tae out the printhead unit from the
carriage.
7. Disconnect the cables from the connector of the printhead unit.
WORK POINT
Notice that the grounding plate is installed in correct pos ition. (there are two fixing pins in the
carriage)
Be sure that fixing pin of the carriage is correctly located into the cut out of the printhead unit.
CAUTION
Once the ink cartridge is removed, it is not re-usable and always install brand-new ink cartridge
before returning the printer to the user.
When returning the printer to the user, be sure that the ink cartridge is installed and the carriage
is at the capping position. (Turn the printer off while the carriage is at the capping position and
pack it)
This part should
be touching the
CR axis receiver.
Make sure that this
protrusion is in the
U ditch of the priht head
side.
Make sure that protrusion
of carriage is in the hole
of the earth board.
Carriage Assembly
Print Head
Figure 3-7.Printhead Installation
3-1
Rev. A
Page 81

Printhead Unit
TWIST SPRING, 49
Chapter 3 Disassembly and Assembly
Flat Cable
FASTNER, HEAD
Figure 3-8. Printhead Unit Removal
REQUIRED ADJUSTMENT
When you remove or replace the printhead unit, be sure to perform the following adjustments:
1) Ink Initial Charge Operation (Refer to Chapter 4 / Section 4.2.2.2.)
2) VH Voltage Writing Operation (Refer to Chapter 4 / Section 4.2.2.3.)
3) Head Angle adjustment (Refer to Chapter 4 / Section 4.2.2.4.)
Rev. A
3-1 1
Page 82

EPSON Stylus Color 600 Service Manual
2
3.2.5.2 Pump Assembly and Cap Assembly Removal
1. Removing the upper housing. (Refer to Section 3.2.1)
2. Removing the control panel assembly. (Refer to section 3.2.3)
3. Removing “Waste Ink Pad Assembly”. (Refer to section 3.2.4)
4. Loosen 2 screws (No.1) fixing the exit frame assembly and disengage the frame from the side
frames. Then, put the printer mechanism on its back as you see the bottom of the mechanism.
5. At the right-hand of the mechanism, unhook the cap assembly by releasing one hook and take out
the cap assembly by lifting up the right end of it. (Note that the cap assembly is still connected to
the pump assembly by the ink tube.)
6. Remove 2 screws (No.5) fixing the pump assembly to the frame.
7. Unhook the pump assembly by releasing one hook and slide the pump assembly to the right
direction to remove it.
CAUTION
Be careful not to damage rubber part of the cap assembly. (Damaging the rubber part causes
incomplete capping and the nozzle condition become unstable.)
Be careful with the followings when you handle “CLEANER, HEAD”:
Do not handle it with bare hands and avoid attaching any oil or dust.
Make sure that the rubber side of “CLEANER, HEAD” is facing to the right.
WORK POINT
Be careful not to popping the components from the pump assembly when you remove it from the
mechanism, as there is a spring inside the pump assembly.
Be sure that the ink tube from the cap assembly is routed to the correct position and not pinched
by the cap assembly ad the frame.
Verify that “CLEANER, HEAD” moves smoothly by rotating “GEAR, 67.2” after you re-assemble
the pump assembly. (Hold the cap assembly to the right while you rotating the gear for check)
Ink Tube Routing
OK
(Ink tube goes behind of
the cap assembly)
Viewed from front
NG
(The ink tube is on the part of
the cap assembly)
Figure 3-9. Ink Tube Routing
3-1
Rev. A
Page 83

3
Loosen screw and
lift up the exit frame
PUMP ASSEMBLY
Chapter 3 Disassembly and Assembly
Unhock the cap assembly
CAP ASSEMBLY
CLEANER, HEAD
Remove 2 screws and unhook the hooks
to remove the pump assembly
Figure 3-10.Cap Assembly Removal
Pump Components
Assembly Order
Figure 3-11.Pump Assembly Removal
Rev. A
3-1
Page 84

EPSON Stylus Color 600 Service Manual
4
3.2.5.3 CR Motor Assembly Removal
1. Removing the upper housing. (Refer to section 3.2.1)
2. Rotate “Gear, 67.2” (largest gear at the left-hand side of the printer mechanism) toward the front to
disengage the carriage lock mechanism, and move the carriage assembly to the middle of the
printer.
3. Push “HOLDER, PULLEY, DRIVEN” inward to loosen the timing belt and detach the timing belt
from the drive pulley of CR Motor assembly.
4. Remove 2 screws (No.1) and remove “MOTOR, ASSEMBLY, CR” from the mechanism.
WORK POINT
Be sure that the projections of the motor bracket is inserted to the holes of the frame properly.
REQUIRED ADJUSTMENT
When you replace “MOTOR, ASSEMBLY, CR”, be sure to perform the following adjustment:
1) Bi-D Alignment Adjustment (Refer to Chapter 4 / Section 4.2.2.5.)
COMPRESSION SPRING, 19.6 PULLEY, ASSEMLBLY, DRIVEN
Outside side frame
TIMING BELT
Inside side frame
HOLDER, PULLEY, DRIVEN
Figure 3-12. Driven Pulley Removal
3-1
Rev. A
Page 85

Chapter 3 Disassembly and Assembly
5
The projections of motor assembly must
locate inside the holes
Figure 3-13. CR Motor Removal
Rev. A
3-1
Page 86

EPSON Stylus Color 600 Service Manual
6
3.2.5.4 PF Motor Assembly Removal
1. Removing the upper housing. (Refer to section 3.2.1)
2. Removing “Waste Ink Pad Assembly”. (Refer to section 3.2.4)
3. By referring the figure below, remove the specified gears from the mechanism:
“GEAR, 67.2”
“COMBINATION GEAR, 8, 14.4”
“COMBINATION GEAR, 8.8, 21.6”
“GEAR, 36”
4. Remove 2 hexagonal lock nut and remove “MOTOR, ASSEMBLY, PF”.
WORK POINT
When removing the PF Motor, first, slightly pulling out the PF Motor from the frame and slide the
motor shaft to a larger cut out of the frame and remove it.
Be careful with the routing direction of the cable from the PF motor.
COMPRESSION SPRING, 0.9
GEAR, 67.2
MOTOR, ASSEMBLY, PF
Hexagonal Nut
COMBINATION GEAR, 8, 14.4
COMBINATION GEAR, 8.8, 21.6
GEAR, 36
Lock Ring
Figure 3-14. PF Motor Removal
3-1
Rev. A
Page 87

7
MOTOR, ASSEMBLY, PF
(behind the frame)
Cable Direction
Chapter 3 Disassembly and Assembly
Put the motor shaft once in a larger holde
then slide it to a smaller hole
Figure 3-15. PF Motor and Frame
Rev. A
3-1
Page 88

EPSON Stylus Color 600 Service Manual
8
3.2.5.5 ASF Assembly Removal
1. Removing the upper housing. (Refer to section 3.2.1)
2. Remove the locking pin from center of “GEAR, 34” and remove “GEAR, 34” from the shaft.
3. Unhook the cables from the cable hook of the ASF and the printer mechanism.
4. Remove 2 screws (Refer to the figures) fixing the ASF and remove the ASF from the mechanism
by detaching the projection of ASF (at left) from the hole of the mechanism.
WORK POINT
Make sure that the ASF is firmly attached to the mechanism.
Use proper type of screw at specified position (viewed from the back of the mechanism):
Right: “SHAFT, FIXING, CR”
Left: Screw - No.7 (CBS with washer)
CAUTION
When re-installing the ASF, be sur e that no cables (exc ept the flat cable to the printhead) are pinc hed
between the ASF and the frame.
Especially, if the cables from CR/PF Motor is pinched, there is a danger of short-circuit with the frame
and possibly causes hazardous problem like over-heating, burning of components.
3-1
Rev. A
Page 89

9
[CBS with washer]
Chapter 3 Disassembly and Assembly
SHAFT, FIXING, CR
GEAR, 34
The projections of ASF must be
in these holes
Figure 3-16. ASF Assembly Removal
Rev. A
3-1
Page 90

EPSON Stylus Color 600 Service Manual
0
3.2.5.5.1 ASF Disassembly
1. Removing the ASF. (Refer to section 3.2.5.5)
2. Remove “TWIST SPRING, 41.2” by unhooking one end from the ASF frame and remove “LEVER,
BRAKE”.
3. Remove “BUSH, FIXING, SHAFT” from the right end of “SHAFT, ROLLER, LD” and remove
“LEVER, HOPPER, RELEASE”.
4. Move the left paper pack-up assembly to the middle of the ASF and remove “BUSH” from the
shaft.
5. Push out “SHAFT, ROLLER, LD” to the left and remove “BUSH, FIXING, SHAFT, LEFT” from the
left-end of the shaft by unhook it.
6. Unhook the top of “HOPPER, ASSEMBLY” from the both sides of “FRAME, ASF”.
7. Push out “SHAFT, ROLLER, LD” to the right while pulling up “PICKUP, ROLLER ASSEMBLY,
RIGHT” slightly. Then, detach the left end of “SHAFT, ROLLER, LD” from “FRAME, ASF”.
8. Holds “HOPPER, ASSEMBLY” and remove the right cam part of “HOPPER, ASSEMBLY” through
the hole at the right side of “FRAME, ASF”.
To this point, the ASF assembly is disassembled and both lef t and right “PICKUP, RO LLER ASSEMBLY”
and “HOPPER, ASSEMBLY” are separated.
WORK POINT
When removing “HOPPER, ASSEMBLY”, be careful that the grease that applied to the cam part
of it, is not attaching to other part of the ASF. If so, wipe it off completely.
Make sure that bushes at the both ends of the shaft are firmly attached.
3-2
Rev. A
Page 91

LEVER, BRAKE
BUSH, FIXING, SHAFT, LEFT
Chapter 3 Disassembly and Assembly
HOPPER, ASSEMBLY
TWIST SPRING, 41.2
CAM part
FRAME, ASF
LEVER, HOPPER, RELEASE
BUSH
SHAFT, ROLLER, LD
BUSH, FIXING, SHAFT
Figure 3-17. ASF Disassembly
Rev. A
3-21
Page 92

EPSON Stylus Color 600 Service Manual
2
3.2.5.5.2 Pick-Up Roller Assembly Removal
1. Disassemble the ASF and separate “PICKUP, ROLLER ASSEMBLY” and “HOPPER,
ASSEMBLY”. (Refer to section 3.2.5.5.1)
2. Remove “COMPRESSION SPRING, 1.66” from the back of “HOPPER, ASSEMBLY”.
3. Pull out the right cam part of “HOPPER, ASSEMBLY” though the hole of right frame of “PICKUP,
ROLLER ASSEMBLY, RIGHT”.
<To this point, “HOPPER, ASSEMBLY” and “PICKUP, ROLLER ASSEMBLY” is separated>
4. Unhook “ROLLER ASSEMBLY, LD” from the assembly frame and remove “COVER, ROLLER, LD”
by unhooking it from the assembly frame. Then, remove “ROLLER ASSEMBLY, LD”.
WORK POINT
When you re-assemble, be sure that “ROLLER ASSEMBLY, LD” is hooked to assembly frame
firmly.
Before re-assemble the unit, make sure that “COMPRESSION SPRING, 1.66” is set on the
assembly frame and hooked to the hooks as shown in the figure. This helps you easier assembly.
After assemble the unit, do not forget to unhook the springs by rotating the spring from the holes
located at the back of the ASF assembly.
3-2
Rev. A
Page 93

3
COVER, ROLLER, LD (L/R)
+
HOLDER, SHEET, PF
ROLLER, ASSEMBLY, LD (L/R)
Chapter 3 Disassembly and Assembly
COMPRESSION SPRING, 1.66
ASSEMBLY FRAME
Set the spring and hook it
to the assembly frame as
illustrated, before re-assembly
Figure 3-18. Pick-Up Roller Removal
Rev. A
3-2
Page 94

EPSON Stylus Color 600 Service Manual
4
3.2.5.6 Carriage Assembly Removal
1. Removing the upper housing. (Refer to section 3.2.1)
2. Push “HOLDER, PULLEY, DRIVEN” inward to loosen the timing belt and detach the timing belt
from the drive pulley of CR Motor assembly.
3. Take out “COMPRESSION SPRING, 19.6” from “HOLDER, PULLEY, DRIVEN”.
4. Remove “PULLEY, ASSEMBLY, DRIVEN” and the timing belt together from “HOLDER, PULLEY,
DRIVEN” and remove “HOLDER, PULLEY, DRIVEN” from the mechanism.
5. Unhook “LEVER, PG” and remove it.
6. Unhook “LEVER, PG, SUB” and remove “LEVER, PG, SUB” and a spring washer from the end of
“SHAFT, CR, GUIDE”.
7. Remove 1 screw (No.7) and rotating “BUSH, PARALLEL ADJUST, RIGHT” to match it with the cut
out of the frame. Then, take out “BUSH, PARALLEL, ADJUST, RIGHT”.
8. Remove “CARRIAGE, ASSEMBLY” together with “SHAFT, CR, GUIDE”.
WORK POINT
It is good idea to marking the current position of “BUSH, PARALLEL ADJUST, RIGHT” before
removal. This enables you to omit the paper gap adjustment after the assembly .
Be careful with the direction of spring washer at the assembly. (A convex side must facing the
bush)
REQUIRED ADJUSTMENT
When you remove or replace the carriage assembly, be sure to perform the following adjustments:
1) Paper Gap Adjustment (Refer to Chapter 4 / Section 4.2.1.)
2) Head Angle Adjustment (Refer to Chapter 4 / Section 4.2.2.4.)
3) Bi-D Alignment Adjustment (Refer to Chapter 4 / Section 4.2.2.5.)
BUSH, PARALLEL ADJUST, RIGHT
BUSH, PARALLEL ADJUST, RIGHT
Side frame of
printer mechanism
Figure 3-19. BUSH PARA LLEL ADJUST Removal
3-2
Cut out of side frame
Rev. A
Page 95

5
BUSH, PARALLEL ADJUST, LEFT
Chapter 3 Disassembly and Assembly
Carriage Assembly
SHAFT, CR, GUIDE
Spring Washer
(Convex side must be facing the bush)
Figure 3-20. Carriage Assembly Removal
BUSH, PARALLEL ADJUST, RIGHT
LEVER, PG, SUB
Rev. A
3-2
Page 96

EPSON Stylus Color 600 Service Manual
6
3.2.5.7 PF Roller Assembly Removal
1. Removing the upper housing. (Refer to section 3.2.1)
2. Removing the carriage assembly (Refer to section 3.2.5.6)
3. Remove 2 screws (No.1) at the top of mechanism and remove “GUIDE PLATE, CABLE”.
4. From the back of the mechanism, unhook the springs from the frame and remove “PAPER
GUIDE, ASSEMBLY, UPPER” (total 6 pieces).
5. Unhook “PAPER GUIDE, FRONT;B” and remove it.
6. Unhook the both shaft holders of “ROLLER, ASSEMBLY, PAPER EXIT” and remove it.
7. Unhook the left shaft holder of “ROLLER, ASSEMBLY, PF” and rotate it as to match with the cut
out of the frame.
8. Slide “ROLLER, ASSEMBLY, PF” to the left and pulling it out.
WORK POINT
When reinstalling “PAPER GUIDE, ASSEMBLY, UPPER” at right-most position (viewed from the
front), be careful with the detection lever of the PE sensor.
Be careful not to damage the hook of “PAPER GUIDE, FRONT;B” during disassembly and
assembly.
Be careful not to damage the black coated part of “ROLLER, ASSEMBLY, PF” during
disassembly and assembly.
Be careful not to damage the gears.
PAPER GUIDE, LEFT
GUIDE PLATE, CABLE
PAPER GUIDE, ASSEMBLY, UPPER
SHAFT, PAPER GUIDE, UPPER
TWIST SPRING, 117.6
(6 pieces)
Figure 3-21. PAPER GUIDE ASSEMBLY Removal
3-2
Rev. A
Page 97

7
PAPER GUIDE, LEFT
GUIDE PLATE, CABLE
Chapter 3 Disassembly and Assembly
PAPER GUIDE, ASSEMBLY, UPPER
SHAFT, PAPER GUIDE, UPPER
TWIST SPRING, 117.6
(6 pieces)
Figure 3-22. ROLLER, ASSEMBLY, PAPER EXIT Removal
ROLLER, ASSEMBLY, PAPER EXIT
PAPER GUIDE, FRONT;B
Figure 3-23. ROLLER, ASSEMBLY, PF Removal
Rev. A
3-2
Page 98

EPSON Stylus Color 600 Service Manual
8
3.2.5.8 PE Sensor Assembly Removal
1. Removing the upper housing. (Refer to section 3.2.1)
2. From the front side of the mechanism, unhook two hooks fixing “SENSOR, ASSEMBLY, PE” to the
3. mechanism. Then, slide it to upward to remove it. After removal, disassemble the assembly if
necessary.
WORK POINT
When re-install the assembly, be sure that the sensor lever is corr ectly insert ed into a hole of “PAPER
GUIDE, ASSEMBLY”, UPPER”.
Release these hooks to
remove the PE Sensor Assembly
From the back side of
the mechanism
3-2
HOLDER, PE
To frame
BOARD ASSY., PE
Figure 3-24. PE Sensor Assembly Removal
LEVER, PE
Rev. A
Page 99

Chapter 3 Disassembly and Assembly
9
3.2.5.9 HP Sensor Assembly Removal
1. Removing the upper housing. (Refer to section 3.2.1)
2. Detach the cable from the sensor and remove it by unhook it from the frame.
SENSOR, HP
Rev. A
CR MOTOR
Figure 3-25. HP Sensor Removal
3-2
Page 100

Chapter 4
Adjustment
4.1 OVERVIEW...............................................................................................................1
4.1.1 Required Adjustments .............................................................................................................. 1
4.1.2 Tools Required for Adjustment................................................................................................ 1
4.2 Adjustments.............................................................................................................2
4.2.1 Paper Gap Adjustment.............................................................................................................. 2
4.2.2 Adjustment using Adjustment Program.................................................................................. 4
4.2.2.1 Overview of Adjustment Program ................................................................................ 4
4.2.2.2 Ink Charge Operation................................................................................................... 5
4.2.2.3 VH Setting .................................................................................................................... 7
4.2.2.4 ead Angular Adjustment............................................................................................... 9
4.2.2.5 Bi-D Alignment Adjustment .........................................................................................11
 Loading...
Loading...