Page 1

Capa
Page 2

MP-2100 TH User´s Manual
P/N: 5686 . Rev.1.1
November 2005
(First edition: July 2004)
Copyright© by Bematech S.A. Curitiba-PR, Brazil.
All rights reserved.
No part of this publication may be copied, reproduced, adapted or translated without the prior written permission
of Bematech S.A., except when allowed by patent rights.
Information in this publication is purely informative, subjected to change without notice and no liability is assumed
with respect to the use of this. However, as product improvements become available, Bematech S.A. will make every
effort to provide updated information for the products described in this publication. The latest version of this
manual can be obtained through Bematech website:
www.bematech.com
Notwithstanding the other exceptions contained in this Manual, the consequences and responsibility are assumed
by the Purchaser of this product or third parties as a result of: (a) intentional use for any improper, unintended or
unauthorized applications of this product, including any particular purpose; (b) unauthorized modifications,
repairs, or alterations to this product; (c) use of the product without complying with Bematech S.A. Corporation’s
operating and maintenance instructions; (d) use of the product as component in systems or other applications in
which the failure of this could create a situation where personal injury or material damages may occur. In the events
described above, Bematech S.A. and its officers, administrators, employees, subsidiaries, affiliates and dealers shall
not be held responsible or respond by any claim, costs, damages, losses, expenses and any other direct or indirect
injury, as well as claims which alleges that Bematech S.A. was negligent regarding the design or manufacture of the
product.
Bematech S.A. shall not be liable against any damages or problems arising from the use of any options or any
consumable products other than those designated as original Bematech products or approved products by
Bematech S.A.
Any product names or its logotypes mentioned in this publication may be trademarks of its respective owners and
shall be here recognized.
Product warranties are only the ones expressly mentioned in the User’s Manual. Bematech S.A. disclaims any and
all implied warranties for the product, including but not limited to implied warranties of merchantability or fitness
for a particular purpose. In addition, Bematech S.A. shall not be responsible or liable for any special, incidental or
consequential damages or lost profits or savings arising from the use of the product by the Purchaser, the User or
third parties.
Page 3
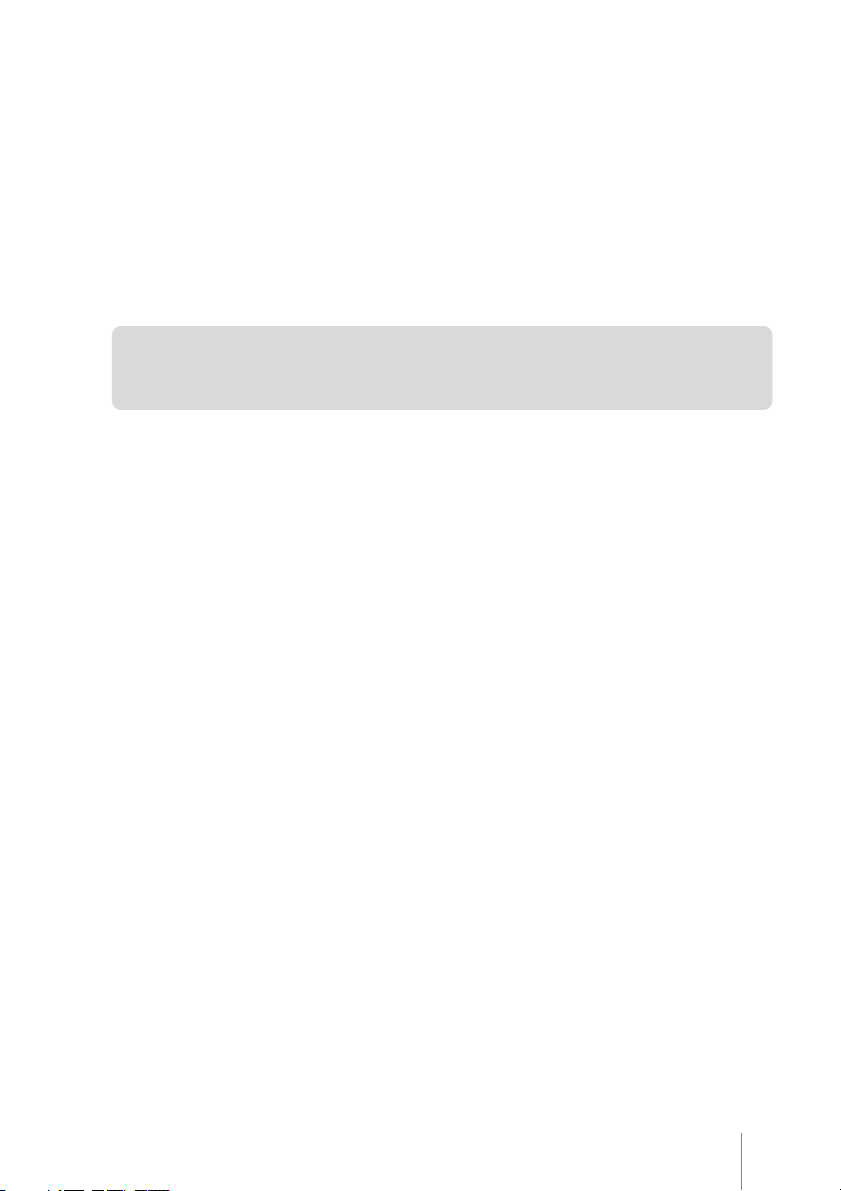
MP-2100 TH · Revision 1.1
EMC and Safety Standards Applied
Product Name: MP-2100 TH
Model Name: All
*EMC is tested using an EPSON PS180 power supply
Europe:
CE marking
Safety: EN60950
North America:
EMI: FCC Class A
Unauthorized changes or modifications on the equipment could void the certifications described in this page.
Please contact your dealer for further information.
WARNING
CE Marking
The printer conforms to the following Directives and Norms:
Directive 89/336/EEC
EN 55022 Class B (Conducted and Radiated emission)
EN 55024
IEC 61000-4-2 ESD
IEC 61000-4-3 Radiated immunity
IEC 61000-4-4 EFTB
IEC 61000-4-5 Surge
IEC 61000-4-6 Conducted immunity
IEC 61000-4-11 Voltage Dips
FCC CLASS A
DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital service,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against
harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment
generates, use and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with
the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to the radio communications. Operation of this
equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which case the user will be
required to correct the interference at his own expense.
3
Page 4

User’s Manual
Safety Precautions
This section presents important information intended to ensure safe and effective use of this product. Please read
this section carefully and store it in an accessible location.
English
WARNING:
Immediately unplug the equipment if it produces smoke, a strange odor, unusual noise or if foreign matter including
water or other liquid falls into the equipment. Continued use may damage it or lead to fire *. Please contact your
dealer or a BEMATECH service center for advice.
Never attempt to repair this product yourself. Improper repair work can be dangerous.
Never disassemble or modify this product. Tampering with this product may result in injury or fire *.
Be sure to use the specified power source. Connection to an improper power source may cause malfunction or fire *.
CAUTION:
Do not connect cables in ways other than those mentioned in this manual. Different connections may cause
equipment damage and burning *.
Be sure to set this equipment on a firm, stable surface. The product may break or cause injury if it falls.
Do not install this equipment in locations that do not comply with the environmental requirements specified in this
manual.
Do not place heavy objects on top of this product. Never stand or lean on this product. Equipment may fall or
collapse, causing breakage and possible injury.
To ensure safety, unplug this product before leaving it unused for an extended period. In this case, please be sure
to place a piece of paper between the platen and the paper roll, in the thermal mechanism, to avoid damage when
restarting the printer.
* Note that this equipment was developed complying with international safety standards and therefore contains
only limited flammability components.
4
Page 5

MP-2100 TH · Revision 1.1
SummarSummar
Summar
SummarSummar
yy
y
yy
Chapter 1 - Presentation .......................................................................... 6
Chapter 2 - Technical Specifications MP-2100 TH ................................ 10
Chapter 3 - Communication Interfaces .................................................... 11
Serial Interface ........................................................................................................................ 11
Parallel Interface ...................................................................................................................... 12
USB Interface .......................................................................................................................... 13
Chapter 4 - Character Tables ................................................................... 14
ASCII Table ............................................................................................................................ 14
Code Page 850 ...................................................................................................................... 14
Code Page 437 ...................................................................................................................... 15
Code Page 858 ...................................................................................................................... 15
Code Page 860 ...................................................................................................................... 16
Chapter 7 - MP-2100 TH Commands ...................................................... 17
Direct Command ..................................................................................................................... 17
Control Sequence .................................................................................................................... 17
Using The Command Summary ............................................................................................... 17
Chapter 8 - Command tables ................................................................... 18
Operation ............................................................................................................................... 18
Vertical Positioning .................................................................................................................. 18
Horizontal Positioning .............................................................................................................. 19
Character Types ...................................................................................................................... 19
Print Width, Character Width and Height ............................................................................... 20
Barcodes ................................................................................................................................ 20
Bit Images and Graphics ........................................................................................................ 22
Graphic Commands Examples .................................................................................................. 22
Data Control .......................................................................................................................... 23
Communication ........................................................................................................................ 23
Appendix I - Troubleshooting ................................................................... 25
Appendix II - Automatic Line Advance ..................................................... 26
Appendix III - Cutter (Optional) ............................................................... 27
Appendix IV - Special Care....................................................................... 28
Appendix V - Drawer Activation ............................................................... 30
Appendix VI - Error Signaling Table ......................................................... 31
5
Page 6
User’s Manual
Chapter 1
Presentation
Printer Description
Explanations about how each MP-2100 TH part operates are described in this manual.
Whenever some note refers to one of the parts, the corresponding number of such part will be in brackets,
next to the note.
Led PAPER
Led ON LINE
Led POWER
PAPER key
ON LINE key
Back Cover
Figure 3
Figure 1
Front Cover opening knob
Base
DC Power Supply Connector
Drawer
Parallel Interface or USB (optional)
Serial Interface
Front Cover
Figure 2
6
Page 7
MP-2100 TH · Revision 1.1
Unpacking
Take the printer out of its box and verify that the following items are included:
• Printer
• User´s Manual
Keep the box and packing materials for future use if necessary.
The appropriate thermal paper should be used. Refer to the Technical Specifications section in this
manual for paper details.
Powering
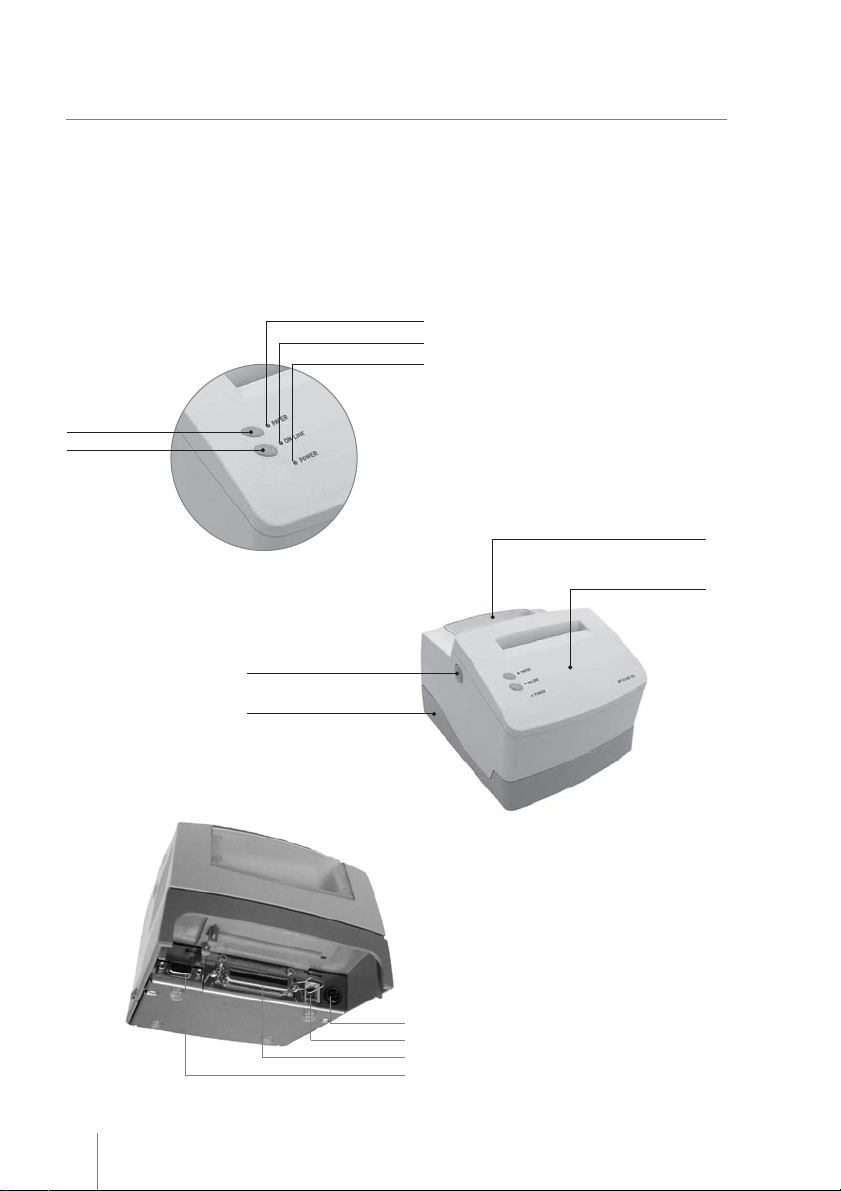
GROUND
Make sure that the printer is turned off.
Connect the power cord to the power supply‘s
AC connector and to an electrical outlet. This
outlet must have its ground pin connected as
shown on the right:
Figure 4
Connect the DC cable of the power supply in the printer as shown below – note that the arrow in the connector
must be facing down:
Figure 5
DC Connector
Turn on the printer using the on / off switch located on the printer. Check, also in the panel, if the Power LED is lit.
If no paper is present, the Paper LED will also be lit.
7
Page 8
User’s Manual
Inserting the Paper
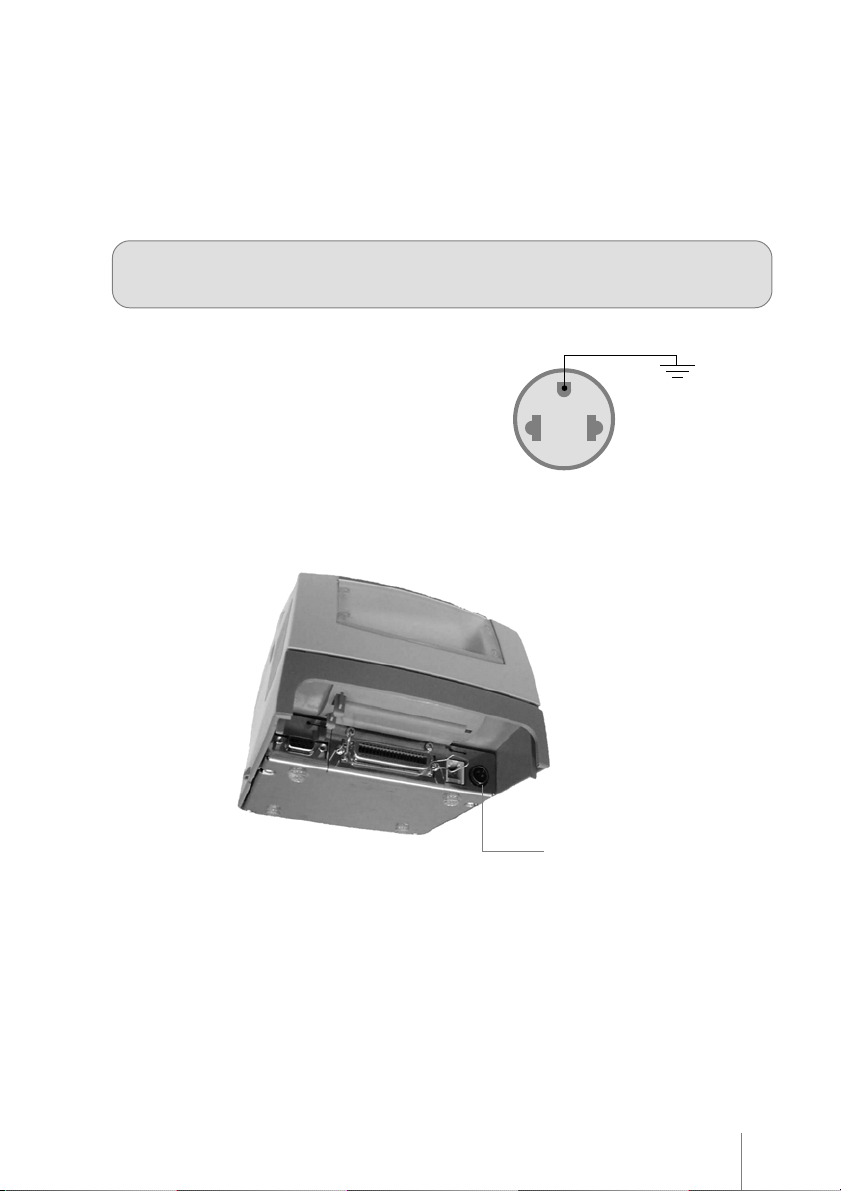
To insert the paper roll, open the back cover and the front cover according to Figures 6 and 7. Release the roll
from the rollers.
Figure 6 Figure 7
The MP-2100 TH offers easy automatic paper placement . Just position it in the gutter entrance
pushing it inwards (Figures 6 and 7). That makes the mini-printer to activate the automatic paper
advance mechanism, thus making the paper replacing easier.
To make the paper insertion
easier, cut the paper end
according to the illustration .
The paper will slip easier into
the mechanism.
Figure 8
8
Page 9

MP-2100 TH · Revision 1.1
Operation Modes
The printer can be operated in the following modes:
Normal (Remote mode)
In this state, the printer is being controlled by the host through the serial, parallel or USB interfaces.
Dump mode
In this mode advanced users and programmers can identify communication problems between the host and the
printer or check if a certain programmed data is correctly being sent to the printer, thus being a debugging tool. To
start the hexadecimal dumping, turn on the printer while pressing the paper feed switch. A message will be
printed on the paper asking you to press once more the paper feed switch if Dump mode is desired, as shown:
- Press PAPER switch once for DUMP MODE
Self-testing
To run a self-test press and hold the Paper Feed switch and turn it on. When the printer starts printing, the paper
feed button can be released. A message will be printed asking you waiting for the self-test. In the self-test you will
find the printer firmware version.
Printer head cleaning procedure
Please releve to Appendix IV “Special Care” (page 28).
9
Page 10
Chapter 2
Technical Specifications
User’s Manual
Characteristics
Printing
Features
Printing Paper
Entry Buffer
Communication Interfaces
Power Supply
Detection Functions
Environmental Conditions
Size
Life Expectation - MCBF
Power Activation
Mass
Cutter
Specifications
Method: lines of thermal dots
Dot Density: 8 dots per mm
Width: 72 mm
Speed: 80 mm/s
Paper forward unit: 0.125 mm
Characters supported: CODE PAGE850, CODE PAGE 858,
CODE PAGE 860 and CODE PAGE 437
Code of bars supported: UPC-A, UPC-E, EAN13, EAN8, CODE
39, ITF, CODABAR, CODE 93, CODE
128, ISBN, MSI, PLESSEY, PDF0417.
Paper max width: 78 mm to 80 mm
Thickness: 50 to 120 g/mm
2
Max. Coil diameter: 65 mm
Type: KPH756 thermo script, manufactured
by VCP or equivalent
Polling force: 2N minimum
8 Kbytes
Serial: RS-232C
•Transmission rate: 9600 bauds
•Protocol: RTS/ CTS
•Format: 8 bits without parity / 1 stop bit
Parallel (optional): Centronics
USB (optional): compatible 1.1 version
Voltage: 24 VDC
Consumption: Switched-off, 15 W
In operation: 35 W
Print head temperature (termistor), paper presence (phototransistor),
print head lifted (optical key).
Environmental storage conditions:
Temperature: 0ºC to 50ºC
Relative humidity: 10% to 95%.
Environmental storage conditions:
Temperature: -20°C to 70°C
Relative humidity: 10% to 95%
Height: 132 mm
Width: 152 mm
Depth: 196 mm
Head: Abrasion: 80 km exclusively for certified paper
(printing 20% of the line)
Cutter: 1.5 millions cuts (for certified paper of
56g/mm
2
)
Drawer
Mass: 1,2 kg
With Cutter: 1,3 kg
Cutting Options: Total or partial cut (option per way of activation ).
10
Page 11
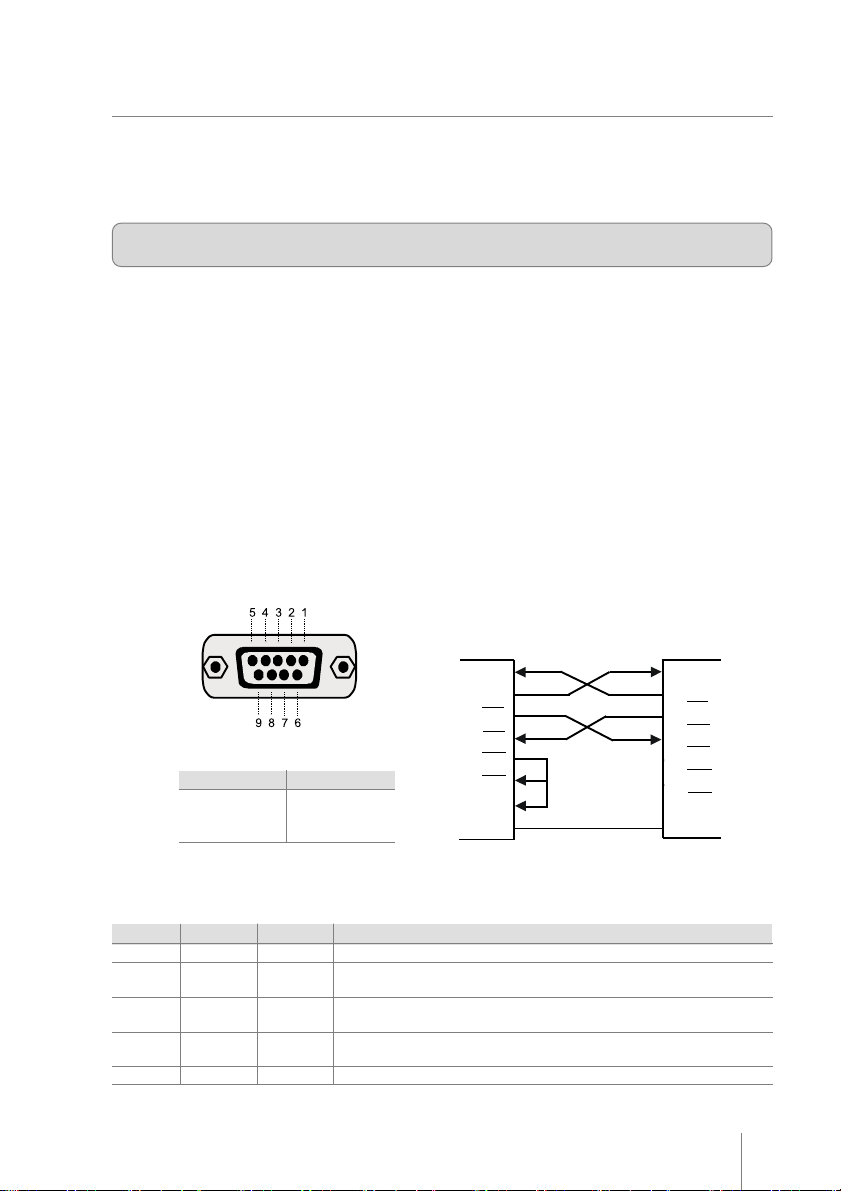
MP-2100 TH · Revision 1.1
Chapter 3
Communication InterfacesCommunication Interfaces
Communication Interfaces
Communication InterfacesCommunication Interfaces
Communication between a host and the printer can be performed in three communication interface: USB, Parallel
or Serial RS-232, according to the printer model.
Communication cables are not supplied with the printer
Serial Interface
The RS232 serial interface uses a female DB-9 connector. The serial port can operate using the RTS/CTS mode, with
8 data bits, without parity, one start bit and one stop bit. In the RS232 standard, the logic low level corresponds
to a +12V voltage level and a logic high level corresponds to a –12V voltage level.
RTS/CTS mode
In this mode, the printer’s RTS line controls the flow of data sent from the host’s TX line and received by the printer’s
RX pin. In this case, when the printer’s RTS signal is low (+12V) the printer requests the host to send data. When
the RTS signal is high (-12V) the printer tells the host to stop sending data.
DB-9 Serial connector
Figura 9
Logic Level Voltage
0
1
Pin Sign Direction Description
2
3
7
8
5
Rx
Tx
RTS
CTS
GND
+ 12 V
- 12 V
Through this pin the data are received by the printer.
IN
Through this pin the data are transmitted from the printer to the
OUT
device to her connected.
When in low level the printer requests the sending of data. When in
OUT
high level the printer is without document.
When in low level, the printer sends data (if there is). When in high
IN
level, the printer for of sending data, if she is sending.
Logic ground.
DB - 9 DB - 9
2 - RxD 2 - RxD
3 - TxD 3 - TxD
7 - RTS 7 - RTS
8 - CTS 8 - CTS
6 - DTR 6 - xNC
4
4 - DSR 4 - xNC
6
1 - DCD 1 - xNC
5 - GND 5 - GND
PC Printer
4
6
11
Page 12

Parallel Interface
The unidirectional parallel interface has the following specifications:
• Synchronization: Externally supplied Strobe signal
• Handshaking: Ack and Busy signal
• Signal levels: TTL compatible
• Data transmission: 8-bit parallel
Parallel Interface Pin Assignments
.................17.................16.................13.................12.................11.................10.................09.................08.................07.................06.................05.................04.................03.................02.................
.............35.............33.............32.............31.............30.............29.............28.............27.............26.............25.............24.............23.............22.............21.............20.............19.............
36
Figura 10
User’s Manual
01
Signal pin
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
12
Associated
return pin
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
Signal
/STROBE
Data 1
Data 2
Data 3
Data 4
Data 5
Data 6
Data 7
Data 8
Direction
IN
IN
Description
Strobe pulse for data reading. The pulse’s width
must be larger than 0.5 us.
Data in signals (LSB is Data 1). The signal high
level corresponds to bit 1 and the low level
corresponds to 0.
Page 13

MP-2100 TH · Revision 1.1
Signal pin
10
11
12
13
14,15,18,36
16
17
19-30
31
32
33
34
35
Associated
return pin
28
29
30
Signal
/ACK
BUSY
PE
OL OUT
NC
GND
Frame
GND
/INIT
/ERROR
GND
NC
PULLUP
Direction
OUT
OUT
OUT
OUT
IN
OUT
OUT
Description
This pulse is active low and indicates that data
sent to the printer has been received. The pulse
width must be larger that 10us.
When high, indicates that the printer cannot
receive data.
1 – Paper end.
On line Out. When high, indicates operation in
remote mode. When low, indicates operation in
local mode.
Not connected.
Circuit ground.
Frame ground.
Circuit ground.
When low initializes the printer. It may be larger
than 50us.
Paper absence.
Circuit ground.
Not connected.
“Pulled Up” to +5V
USB Interface
The USB interface is compatible with the Universal Serial Bus Specification 1.1. It is a 12 Mbps serial channel using
the Bulk mode with a “B” receptacle as show below. The USB cable must have in one side an “A” plug to connect
in the host, and in the other side an “B” plug to connect in the printer. The printer is self-powered and does not draw
power from the standard type B USB interface cable.
Type “B” Receptacle
2 1
3 4
Figure 11
Using the USB interface, the printer can be connected in the host even if both parts are powered. The first time
you connect the printer in the host, the operational system will ask for the printer driver. Please download the
printer driver from our website (www.bematech.com). For more details please contact your dealer.
Signal pin Signal
1NC
2DATA+
3DATA -
4 GND
13
Page 14

User’s Manual
Chapter 4
Character TCharacter T
Character T
Character TCharacter T
ASCII Table
The codes from 00h up to 7Fh are shown below:
Characters from 00h to 1Fh are “command characters” and therefore are not represented in the following tables
Code Page 850
ablesables
ables
ablesables
14
Page 15

MP-2100 TH · Revision 1.1
Code Page 437
Code Page 858
15
Page 16

Tabela de Caracteres Code Page 860
User’s Manual
16
Page 17

MP-2100 TH · Revision 1.1
Chapter 5
MPMP
-2100 TH Commands-2100 TH Commands
MP
-2100 TH Commands
MPMP
-2100 TH Commands-2100 TH Commands
This section contains general information regarding the MP-2100 TH commands.
The MP-2100 TH printer has a series of programming commands that may be used in the remote mode. Two types
of commands can be sent:
Direct Command
In this mode, a simple ASCII code is enough to command the printer. For example:
ASCII Code: LF
Decimal: 10
Hexadecimal: 0A
This command causes the printer to perform a line feed.
Control Sequence
In this mode, more than one code may be sent to command or program the printer. This “control sequence”
always starts with the ASCII code “ESC” or “GS”. For example:
ASCII Code: ESC W 1
Decimal: 27 87 01
Hexadecimal: 1B 57 01
This command switches the printing mode to “expanded”.
Following is a summary of commands accepted by the MP-2100 TH printer.
Using The Command Summary
The following section lists and describes all resident MP-2100 TH commands including command parameters. The
command syntax is as follows:
• ESC P is a command without parameters;
• ESC Q n is a command with one parameter only;
• ESC K n1 n2 is a command with two parameters;
• ESC D *! n1n2 b1...bn is a command with a variable number of parameters.
Some commands may be redundant. This is done to maintain compatibility with old command settings
or different types of customized command settings.
17
Page 18

Chapter 6
Command TCommand T
Command T
Command TCommand T
ablesables
ables
ablesables
Operation
ASCII Dec Hex Description
ESC @ 64 40 Initializes the printer
ESC b n 98 62 Enable (1): Status drawer sensor
ESC v n 118 76 Activate drawer (n miliseconds)
ESC w 119 77 Performs a paper cut
ESC x 120 78 Enable Dump Mode
ESC y n 121 79 Enable (1) or Disable (0). Keyboard default (1)
ESC z 1/0 122 7A Enable automatic line feed (n=1). Disable automatic line feeed (n=0)
ESC m 109 6D Performs a parcial paper cut
Disable (0): Status paper sensor
-50ms < n < 200ms
User’s Manual
Vertical Positioning
ASCII Dec Hex Description
ESC C n 67 43 Programs the page size in lines where n is the number of lines
ESC c n1 n2 99 63 Programs the page size in millimeters where Size=0,125mm*n1*n2.
ESC J n 74 4A Performs the feeding of n*0,125mm of paper.
FF 12 0C Feeds one page.
LF 10 0A Feeds one line.
ESC 2 50 32 Line feed of 1/6” – default line feed
ESC 3 n 51 33 Line feed of n/144 of an inch, where n goes from 18(d) up to 255(d).
ESC f 1 n 102 66 Vertical skipping of n characters.
ESC A n 65 41 Performs the feeding of n*0,375mm of paper.
18
(single height). The standard is 12 lines (of single height).
Page 19

MP-2100 TH · Revision 1.1
Horizontal Positioning
ASCII Dec Hex Description
ESC f 0 n 102 66 Horizontal skipping of n characters.
ESC Q n 81 51 Program right margin to column n
ESC I n 108 6c Program left margin to column n
ESC a n 97 61 Aligning the characters. Centering if n=1 or left end alignment if
n=0.
Character Types
ASCII Dec Hex Description
ESC - n 45 2D Underlined mode on (n=1) or off (n=0).
ESC 4 52 34 Italic mode on.
ESC 5 53 35 Italic mode off.
ESC E 69 45 Emphasized mode on.
ESC F 70 46 Emphasized mode off.
ESC t n 116 74 Selects code page:
ESC S n 83 53 n=0 (enable superscript characters)
ESC T 84 54 Disable superscript and subscript modes
ESC N n 78 4E n=0 (density very weak) n=1 (density weak)
ESC } n 125 7D n=1 (inverted mode enable)
n=2 (CODEPAGE 850 - Default)
n=3 (CODEPAGE 437)
n=4 (CODEPAGE 860)
n=5 (CODEPAGE 858)
n=1 (enable subscript characters)
n=2 (density normal) n=3 (density strong)
n=4 (density very strong)
n=0 (inverted mode disable)
19
Page 20

User’s Manual
Print Width, Character Width And Height
ASCII Dec Hex Description
DC2 18 12 Condensed mode (42 columns) off.
DC4 20 14 One-line expanded mode off.
ESC d n 100 64 Double height on (n=1) or off (n=0).
ESC H 72 48 48-column mode on (default).
ESC P 80 50 48-column mode on (default).
ESC SI 15 0F Condensed mode (64 columns) on.
ESC SO 14 0E One-line expanded mode on.
ESC V 86 56 One-line double height on.
ESC W n 87 57 Expanded mode on (n=1) or off (n=0).
SI 15 0F Condensed mode (64 columns) on.
SO 14 0E One-line expanded mode on.
Barcodes
Barcodes are obtained using the GS command sequences show below. Please note that all parameters and
numbers are in decimal format, unless noted.
11
6
Hexadecimal
Decimal
1D 68 n
29 104 n
1D 77 n
29 119 n
1D 48 n
29 72 n
1D 66 n
29 102 n
1D 6B 00 d1...d
29 107 0 d1...d
1D 6B 41 0B d1...d
29 107 55 11 d1...d
1D 6B 01 d1...d6 00
29 107 1 d1...d6 0
1D 6B 42 06 d1...d
29 107 66 6 d1...d
1D 6B 02 d1...d
29 107 2 d1...d
11
11
12
12
Description
Sets the height n of the barcode generated – each height unit corresponds
t a dot of 0.125 mm, so the final height is n x 0.125 mm where 1 - n
- 255. The default is n=162.
Determines the width of the barcode, where n=2 corresponds to normal width, n=3 is double width and n=4 is quadruple width. The
default is n=3.
Choose the position of the human readable information (HRI) of the
barcode.
n=0: No HRI
n=1: On top of the barcode (default)
n=2: On the bottom of the barcode
n=3: Both on top and on the bottom of the barcode.
Sets the font used to print the human readable information (HRI). The
default is n=0.
n=0 or n=48 – normal
n=1 or n=49 – condensed
00
0
Prints an UPC-A barcode where d1...d11 is a sequence of 11 bytes
containing the barcode information with 48 -d -57.
11
11
Prints an UPC-E barcode where d1...d6 is a sequence of 6 bytes containing
the barcode information with 48 -d -57.
6
6
00
Prints an EAN-13 barcode where d1...d
0
containing the barcode information with 48 -d -57.
is a sequence of 12 bytes
12
Comand
GS h n
GS w n
GS H n
GS f n
GS k 0 d1...d11 NUL
GS k 0 65 11d1...d
GS k 1 d1...d6 NUL
GS k 66 6 d1...d
GS k 2 d1...d
NUL
12
20
Page 21

MP-2100 TH · Revision 1.1
Comand
GS k 67 12 d1...d
12
GS k 3 d1...d7 NUL
GS k 68 7 d1...d
7
GS k 4 d1...dn NUL
GS k 69 n d1...d
n
GS k 5 d1...dn NUL
GS k 70 n d1...d
n
GS k 5 d1...dn NUL
GS k 71 n d1...d
GS k 72 n d1...d
GS k 73 n d1...d
GS k 128 n1 n2 n3 n4 n
n6 d1...d
n
n
n
n
GS k 21 d1...d9 NUL
GS k 129 9 d1...d
9
GS k 22 d1...dn NUL
GS k 130 n d1...d
n
GS k 23 d1...dn NUL
GS k 131 n d1...d
GS k 132 n1 n
n
2
Hexadecimal
Decimal
1D 6B 43 0C d1...d
29 107 67 12 d1...d
1D 6B 03 d1...d7 00
29 107 3 d1...d7 0
1D 6B 44 07 d1...d
29 107 68 7 d1...d
1D 6B 04 d1...dn 00
29 107 4 d1...dn 0
1D 6B 45 n d1...d
29 107 69 d1...d
1D 6B 05 d1...dn 00
29 107 5 d1...dn 0
1D 6B 46 n d1...d
29 107 70 d1...d
1D 6B 06 d1...dn 00
29 107 6 d1...dn 0
1D 6B 47 n d1...d
29 107 71 d1...d
1D 6B 48 n d1...d
29 107 72 d1...d
1D 6B 49 n d1...d
29 107 73 d1...d
1D 6B 80 n1 n2 n3 n4 n
n6 d1...d
5
n
29 107 128 n1 n2 n3 n
n5 n6 d1...d
1D 6B 15 d1...d9 00
29 107 21 d1...d9 0
1D 6B 81 9 d1...d
29 107 129 9 d1...d
1D 6B 16 d1...dn 00
29 107 22 d1...dn 0
1D 6B 82 n d1...d
29 107 130 n d1...d
1D 6B 17 d1...dn 00
29 107 23 d1...dn 0
1D 6B 83 n d1...d
29 107 131 n d1...d
1D 6B 84 n1 n
29 107 132 n1 n
Description
12
Prints an EAN-13 barcode where d1...d
12
containing the barcode information with 48 -d -57.
Prints an EAN-13 barcode where d1...d7 is a sequence of 7 bytes
containing the barcode information with 48 -d -57.
7
7
Prints a CODE 39 barcode where n indicates the number of bytes that
will be sent and d1...dn is the sequence of n bytes containing the barcode
information. The bytes that can be used in d are 32, 36, 37, 43, 45 to
57 and 65 to 90 (upper case letters) or 97 to 122 (lower case letters).
n
Lower case and upper case letters can’t be conbined in the same barcode.
n
Prints an ITF barcode where n indicates the number of bytes that will be
sent and d1...dn is the sequence of n containing the barcode information
with 48 < d < 57.
n
n
Prints a CODABAR barcode where n indicates the number of bytes that
will be sent and d1...dn is the sequence of n bytes containing the barcode
information. The bytes that can be used in d are 36, 43, 45 to 57 and
65 to 68 (upper case letters) or 97 to 100 (lower case letters). Lower
n
case and upper case letters can’t be conbined in the same barcode.
n
Prints a CODE 93 barcode where n indicates the number of bytes that
n
will be sent and d1...dn is the sequence of n bytes containing the barcode
n
information. This code can use all bytes from 0 to 127.
Prints a CODE 128 barcode where n indicates the number of bytes that
will be sent and d1...dn is the sequence of n bytes containing the barcode
n
information. This code can use all bytes from 0 to 127. The subset is
n
automatically chosen by the printer based on the data received.
Prints a PDF-417 barcode where:
n1 is the ECC level (from 0 to 8)
n2 is the pitch height (from 1 to 8) where height=n2 x 0.125 mm.
5
n3 is the pitch height (from 1 to 4) where height=n3 x 0.125 mm.
n4 is the number of codewords per row – if n4 is 0, the maximum number
of columns allowed for the pitch width informed will be used. If the
4
n
2
barcode can’t fit the print width the printer automatically adjusts it for
the maximum permitted width within the line field.
n5 and n6 indicate the number of bytes that will be coded, where
total=n5+n6 x 256.
d1...dn is the actual sequence of bytes that will be coded.
Prints an ISBN barcode where d1...d9 is the sequence of 9 bytes
containing the barcode information. The bytes that can be used in d are
45, 48 to 57 and 88 – note that the hyphens are not computed in the
9 bytes received.
n
n
Prints a MSI barcode where n indicates the number of bytes that will be
sent and d1...dn is the sequence of n bytes containing the barcode
information. The bytes that can be used in d are 48 to 57. The limitation
of size for this barcode is given by the print field as well as the configured
n
bar width.
n
Prints a PLESSEY barcode where n indicates the number of bytes that
will be sent and d1...dn is the sequence of n bytes containing the barcode
information. The bytes that can be used in d are 46 to 57 plus 65 to 70
(upper case letters) or 97 to 102 (lower case letters). Lower case and
upper case letters can’t be combined in the same barcode. The limitation
n
of size for this barcode is given by the print field as well as the configured
n
bar width.
Programs the position of the bardode’s left margin position given by
n1+n2 x 256.
2
is a sequence of 12 bytes
12
21
Page 22

Bit Images And Graphics
ASCII Dec Hex Description
User’s Manual
ESC $ n1 n2 36 24 Fill in blank bit columns, from the actual column until column number
(n1+n2*256), where n1+n2*256<=576.
ESC * ! n1 42 33 2A 21 24-bit graphics. Programs bit image for 24 bits, in double density
n2 b1...bn where n1+n2*256 is the number of bit-columns that will be sent
(see below) and b1...bn are the bytes that compose the bit image.
For each column one may need 3 bytes to complete. So, if you need
to send an image with an 8-column width you may send 24 bytes to
fill those columns. A full line has 576 bit columns so a full line will
need 576*3 = 1728 bytes.
ESC K n1 75 4B 8-bit graphics. Selects the “8 pin” bit image (compatible with
n2 b1...bn matrix printers) where you use n1+n2*256 columns, with 1 byte
per column thus using a lower resolution and up to 576 columns.
Graphic Commands Examples
24-bit graphics
1st byte
2nd byte
3rd byte
1st bitcolumn
8th bitcolumn
MSB (bit 7)
LSB (bit 0)
For this 24-bit graphic pattern we have eight bitcolumns, each with a height of 3 bytes (24 bits). The
printer must, after the command is stated, receive the
1st , 2nd and 3rd bytes of the first bit-column, than
the 1st , 2nd and 3rd bytes of the second bit-column
and so on, until the last bit-column is filled.
Figure 12
The command sequence to print this graphic pattern would be (numbers in decimal):
ESC * ! 8 0 1 1 1 2 2 2 4 4 4 8 8 8 16 16 16 32 32 32 64 64 64 128 128 128
Where you have 8 + 0 * 256 = 8 bit-columns to be filled, each with 3 bytes that will give us a total of 24 bytes
to be sent (excluding the command sequence).
8-bit graphics
1st bit-column
8th bit-column
For this 8-bit graphic pattern we have eight bit-columns,
each with a height of 1 byte (8 bits). The printer must,
after the command is stated, receive the byte for the
1 byte
MSB (bit 7)
first bit-column, than the byte for the second bit-column
and so on, until the last bit-column is filled. The
resolution is lower but needs less bytes to be sent to
the printer.
LSB (bit 0)
Figure 13
22
Page 23

MP-2100 TH · Revision 1.1
Data Control
ASCII Dec Hex Description
CAN 24 18 Cancel last line
DEL 127 7F Cancel last character
Communication
ASCII Dec Hex Description
ENQ 05 05 Serial communication status inquiry. After this command is issued,
ETX 03 03 Ends buffer – the printer will be BUSY while the printing is performed,
STX 02 02 Clears the buffer.
Parallel interface status byte
The table below shows the printer statuses obtained through the parallel interface, with the PC BIOS function “Get
status printer” (Int 17h – Printer I/O):
Parallel Interface Status Byte Description
/BUSY /ACK PE SEL ERROR X X X HEX
1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 90h On Line (Remote mode)
1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 A8h Paper end
1 0 x 1 1 0 0 0 98h/B8h Head Up
the printer returns a status, defined below.
changing status only when the buffer is empty. On serial interfaces
DTR (RTS) will be high while the printing is performed.
23
Page 24

User’s Manual
Serial interface status byte
The serial interface status byte is composed of 8 bits – 7 through 0 – the most significant bit is Bit 7 and the least
significant bit is Bit 0.
Status bit number Logic “0” Logic “1”
0 Printer Off Line Printer On Line
1 Printer has paper Printer without paper
2 (After ESC b 1) Drawer sensor level low Drawer sensor level high
3 Print head down Print head raised
4 – 7 Not used (will always be logic “0”)
USB interface status bytes
Byte
Bit
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1. Printer Status
0
0
Reserved
ON/OFF LINE
0
Status
buffer
1
2. OFF-LINE
Status
1
0
Reserved
Head-up
Reserved
No paper
Error
1
3. Error Status
0
0
Cutter Installed
Paper Cut Error
1
Non Recov Error
Recov Error
1
4. Continuous Paper
Sensor Status
1
0
Head Temp.
Reserved
1
Int. Paper Jam
Reserved
1
5. Firmware
Version
Minor Firmware
version digit
Major Firmware
version digit
0
24
Page 25

MP-2100 TH · Revision 1.1
Appendix I
TT
rr
oubleshootingoubleshooting
T
r
oubleshooting
TT
rr
oubleshootingoubleshooting
The following table described some of the problems that might occur while using the printer. For every problem
there is a possible cause described here and a suggested procedure to solve the problem.
Problem
The printer does not turn on.
The printer does not respond
to the commands sent.
Parallel communication is
faulty.
Serial communication is faulty.
The printer stops printing
Possible Cause
There is no power in the electric
outlet.
A problem with the power cord – it
may be broken or not well
connected to the printer and / or
outlet.
The parallel / serial / USB cable has
one or more lines with faulty
connections / broken wires.
Wrong programming sequences.
The parallel cable has one or more
lines with faulty connections /
broken wires.
The pin layout does not follow the
Centronics standard.
The serial cable has one or more
lines with faulty connections /
broken wires.
The pin layout does not follow the
correct protocol.
The baud rate is incorrectly set.
Overheating of the print head
Possible Cause
Check if there is a central switch for
the room / outlets. Connect some
other equipment to the outlet to
check its operation.
Turn off the printer, check the power
cord’s continuity and a perfect
connection between the printer and
the electric outlet.
Check for a good connection
between the printer and the host or
change the cable.
The programming sequences can be
checked in the dump mode. Put the
printer in dump mode and run your
application again. The printer will
show the hexadecimal and ASCII
codes of all bytes being received
from the host.
Check for a good connection
between the printer and the host or
change the parallel cable.
Check the correct pin layout in this
manual.
Check for a good connection
between the printer and the host or
change the serial cable.
Check if the pin layout used
complies with the protocol being
used for data transmission.
Remember that the printer uses the
RTS/CTS protocol.
If the baud rate set on the printer is
different from the baud rate of the
host, the printer will print random
characters or not print at all. Check
carefully the host’s serial baud rate
configuration.
Wait until the temperature of the
print head goes below 140°F. The
printer will continue to print from
where it stopped. Open the covers
to help the printer to cool down
faster.
25
Page 26

User’s Manual
Appendix II
Automatic Line Advance
When the automatic line forward (Automatic LF) is turned on, it makes the MP-2100 TH to automatically go
ahead one line, after receiving a CR command (Carriage Return).
When it starts, the MP-2100 TH's automatic line forward is turned off.
In order to turn it on, just use the ESC z 1 command, as described in Chapter 5.
26
Page 27

MP-2100 TH · Revision 1.1
Appendix III
Cutter (Optional)
The following considerations will be valid only if your printer contains a cutter.
Head Handle
Cutter Latch
Figure 17
About the Cutter
The cutter is a shearing blade that cuts the paper totally or partially, doing away with the use of a cutting edge
.
For a perfect operation of the equipment, do not insert any object that should obstruct this shearing blade
course. It will cause a permanent damage to the printer.
In order to assure the cutter operation, do not pull the paper before it has concluded the cutting.
27
Page 28

User’s Manual
Appendix IV
Special Care
MP-2100 TH Cleanup
In order to maintain your printer in good shape, you should clean it regularly according to the following
procedure:
1. Turn the MP-2100 TH off;
2. Open the front cover;
3. Unlock and open the cutter activating the green lock (in case your printer has a cutter);
4. If the paper is inserted, lift up the thermal head handle by activating the green handle;
5. Open the back cover and remove the paper coil;
6. Use a soft flannel or cloth and remove carefully the accumulated dust;
7. If the machine cabinet is dirty, clean it with a soft cloth wetted with water or natural detergent. Never use
a chemically treated tow or chemical materials of any kind. The use of such products may cause the
cabinet to change the color or become deformed.
Never introduce objects or tools into the printer.
Cleanup of the Thermal Printing Head
When your printer presents degradation of printing quality, probably a dirt accumulation in the thermal
printing head has occurred. It usually takes place after printing more than 100 paper coils. In order to clean
it up do as follows:
1. Be sure that the printer is turned off;
2. Open the two printer covers;
3. Open the cutter by activating the green lock (for models with cutter);
4. Lift up the thermal head by activating the green handle;
5. Remove the paper from the printer;
6. Use a swab wetted with alcohol and passes it softly over the black line of the thermal head in order to remove
the accumulated dirt. Be sure to avoid the alcohol from flowing to other parts of the printer and be sure not to
scratch or damage the thermal printer head.
7. Be sure that the thermal head is clean and dry;
8. Close the head and the cutter;
9. Turn the printer on;
10. Insert the paper, according to item "INSERTING THE PAPER".
Tests revealed that this procedure becomes necessary more often as the printer head gets used.
28
Page 29

MP-2100 TH · Revision 1.1
Use Location
The MP-2100 TH should operate placed on a plain surface where its air inlets are kept unobstructed.
Avoid placing the printer in humid places, subject to dust or to heat action, such as sun light and
heaters.
29
Page 30

User’s Manual
Appendix V
Drawer Activation
A connector is located in your MP-2100 TH's rear for the drawer activation. Its pinning is described below:
Figure 18
• Pin 1 = GND
• Pin 2 = Solenoid activation for drawer opening
• Pin 3 = Sensor of open/close drawer (the Printer comes back 1 for sensor open and 0 for sensor closed).
• Pin 4 = +24V
• Pin 5 = NC
• Pin 6 = GND
IMPORTANT
Watch the drawer's mark before connecting it to the MP-2100 TH, since inverting the drawer may
damage the printer.
30
Page 31

MP-2100 TH · Revision 1.1
Appendix VI
Errors Signaling Table
In case an error occurs, it may be indicated through the LED PAPER. The quantity of LED blinks will indicate
a possible error. After the corresponding quantity of blinks to the possible error, a pause will occur. The blinks
and the pause are cyclical, according to the following table:
Error Quantity of blinks Possible Cause
Mechanism 3 Thermal head damaged or connection problem
Cutter 4 Cutter not operating.
Power supply 5 Power supply voltage below 20 V
Temperature 6 Thermal head temperature above safe conditions
of the mechanism with the controlling board.
31
Page 32

Annotations
User’s Manual
32
Page 33

MP-2100 TH · Revision 1.1
Annotations
33
Page 34

Page 35

Page 36

 Loading...
Loading...