Page 1

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE TABLE OF CONTENTS
Setting the Receiver Audio Input Level
................................
............................
22
Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION......................................................................................................... 1
COMPUTER INTERFACING......................................................................................4
MFJ Starter Packs .................................................................................................. 4
Computer Interface with MFJ Starter Pack............................................................5
Computer Interface without MFJ Starter Pack.......................................................5
SERIAL PORT SIGNALS............................................................................................5
COMPUTER WITH SPECIFIC SERIAL INTERFACES............................................6
Apple Macintosh.................................................................................................... 6
Commodore C64, C128 and VIC-20...................................................................... 7
IBM PCjr................................................................................................................ 7
Radio Shack Color Computer ................................................................................ 8
Color Computers.................................................................................................... 8
IBM PC/XT/AT/386/486 and compatibles Computer ........................................... 8
Other Computers with Nonstandard Serial Ports....................................................9
TERMINAL SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS............................................................ 10
Apple Macintosh.................................................................................................... 10
Apple II, II+, IIe, IIc .............................................................................................. 10
Commodore C64, C128 and VIC-20...................................................................... 11
IBM PCjr................................................................................................................ 11
IBM and Compatible Computers ........................................................................... 11
Radio Shack Color Computer ................................................................................ 12
Radio Shack Model 100/102 and NEC 8201......................................................... 12
MFJ-1278B SERIAL PORT PIN FUNCTIONS........................................................... 12
COMPUTER BAUD RATE ......................................................................................... 13
Autobaud................................................................................................................13
Changing Terminal Baud Rate............................................................................... 14
VERIFYING SERIAL PORT OPERATION................................................................ 15
PARALLEL PRINTER PORT...................................................................................... 16
Printer Port Connection.......................................................................................... 16
Printer Consideration ............................................................................................. 17
Printer Port Test..................................................................................................... 17
RADIO INTERFACING............................................................................................... 18
MFJ-1278B Radio Ports ........................................................................................ 18
RADIO PORTS CONNECTION..................................................................................19
HANDHELD RADIO CONNECTION ........................................................................ 20
RADIO INTERFACING METHODS .......................................................................... 21
Method 1: Direct Connection to Microphone and Speaker....................................21
Transmit Audio Level Adjustment for Method I Interface ............................... 21
Page 2

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE TABLE OF CONTENTS
FSK CONNECTION.....................................................................................................29
GETTING STARTED .................................................................................................. 30
First Steps............................................................................................................... 30
Basic Commands .............................................................................................. 30
SERIAL PORT CONFIGURATION............................................................................ 31
Parity and Word Length......................................................................................... 32
Echos...................................................................................................................... 32
New Lines and Line Wrapping...............................................................................33
THE MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE MODEM................................................................33
OPERATIONAL MODES............................................................................................ 35
Verifying Operation Status..................................................................................... 35
Mode Switching With the MODE Command.........................................................35
Radio Port Switching ............................................................................................. 36
MEMORY BUFFERS................................................................................................... 36
Loading the Memory Buffers................................................................................. 37
Transmitting the Memory Buffers..........................................................................37
Buffer Serial Numbering........................................................................................37
Memory Repeat and Buffer Repeat Time...............................................................38
Chaining the Memory Buffers................................................................................38
TUNING INDICATOR.................................................................................................39
PACKET OPERATION................................................................................................ 40
VHF Packet............................................................................................................40
A Connecting and Disconnecting Exercise.......................................................40
Digipeating ....................................................................................................... 42
Unsuccessful Connections ................................................................................ 43
Monitoring Channel Activity............................................................................ 43
Your First Packet QSO..................................................................................... 45
Starting the QSO ......................................................................................... 45
Digipeating.................................................................................................. 46
Monitoring on the Air.................................................................................. 47
Special Input Characters................................................................................... 47
BASIC HF PACKET OPERATION.............................................................................49
HF Packet Operation Hints .................................................................................... 50
PACTOR.......................................................................................................................51
What is Pactor?...................................................................................................... 51
PACTOR Operation...............................................................................................51
FEC Unproto operation..........................................................................................52
PACTOR ARQ ...................................................................................................... 53
Changeover.......................................................................................................53
Monitoring........................................................................................................ 53
Monitoring AMTOR ARQ requests.......................................................................54
Page 3

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE TABLE OF CONTENTS
CONNECT............................................................................................................. 56
SPEEDup/SPEEDdown ......................................................................................... 56
AUTOMATIC ON-LINE COMPRESSION..........................................................56
FLOW CONTROL.................................................................................................56
AMTOR while in PACTOR mode......................................................................... 56
Amtor Detection in Pactor......................................................................................57
PACTOR STATUS INDICATORS..............................................................................57
PACTOR MAILBOX ................................................................................................... 58
Setting Up your Pactor Mailbox............................................................................. 58
General Overview .................................................................................................. 60
Detailed Pactor Mailbox Overview .................................................................. 63
Mailbox Messages.................................................................................................. 67
CW OPERATION......................................................................................................... 68
Receiving CW........................................................................................................ 69
Transmitting CW.................................................................................................... 70
Transmitting from Memory Buffers.................................................................. 71
CW Weighting.................................................................................................. 71
Tuning your Radio ................................................................................................. 72
Random Code Generator........................................................................................72
Setting Up the for Code Practice ...................................................................... 73
CW CONTEST MEMORY KEYER OPERATION..................................................... 74
Sending CW with External Key Paddle ................................................................. 74
MODULATED CW OPERATION............................................................................... 75
BAUDOT RTTY & ASCII OPERATION.................................................................... 76
Setting Up for ASCII and RTTY Operation .......................................................... 76
RTTY and ASCII Receiving.................................................................................. 77
RTTY and ASCII Transmitting.............................................................................. 77
BAUDOT RTTY OPERATION HINTS...............................................................78
Commercial RTTY Reception.......................................................................... 79
AUTOMATIC SIGNAL ANALYSIS...........................................................................80
ASA OPERATION................................................................................................ 80
MARS OPERATION....................................................................................................82
Configuring for MARS .......................................................................................... 82
Operating MARS with MultiCom for IBM............................................................ 83
The MARsmode Command..............................................................................83
MARSMODE 1- QSO Mode ...................................................................... 84
MARSMODE 3- Storage Mode.................................................................. 84
AMTOR OPERATION................................................................................................. 85
Mode A "ARQ"...................................................................................................... 85
Setting up for Mode A Operations....................................................................85
Operating Mode A............................................................................................ 86
Page 4

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE TABLE OF CONTENTS
Summary of AMTOR Contact Sequence...............................................................90
NAVTEX OPERATION............................................................................................... 91
Navtex Stations and Frequencies ........................................................................... 91
Navtex Operation................................................................................................... 91
FAX OPERATION....................................................................................................... 94
FAX Formats.......................................................................................................... 95
FAX Frequency......................................................................................................96
FAX Installation..................................................................................................... 96
Printer Connection ................................................................................................. 96
Receiving FAX....................................................................................................... 97
Receiving FAX to the Printer ........................................................................... 97
Display FAX Picture on Computer Screen & Save it to Disk........................... 99
Two Level FAX Picture Format.................................................................. 99
Multi-level FAX Picture Raw Data Format.................................................100
Transmitting FAX.................................................................................................. 101
Two Level FAX Transmitting........................................................................... 101
Multi-level FAX Transmitting.......................................................................... 102
Creating FAX Pictures for Transmitting................................................................104
SLOW SCAN TELEVISION OPERATION................................................................105
SSTV Formats........................................................................................................ 106
SSTV Installation...................................................................................................106
Printer Connection............................................................................................ 106
Receiving SSTV Pictures.......................................................................................107
SSTV Printing to the Printer.............................................................................107
Printing SSTV Pictures to the Screen............................................................... 110
Saving SSTV Pictures to Disk.......................................................................... 111
Terminating SSTV Printing.............................................................................. 111
Transmitting SSTV Pictures................................................................................... 111
Creating SSTV Pictures for Transmitting .............................................................. 112
ADVANCED PACKET OPERATION.........................................................................114
SPECIAL CHARACTERS ........................................................................................... 114
PACKET OPERATING MODES................................................................................. 115
Command Mode..................................................................................................... 115
Entering Data-Transfer Modes...............................................................................116
Converse Mode...................................................................................................... 117
Transparent Mode.................................................................................................. 118
FLOW CONTROL........................................................................................................ 119
XON/XOFF Flow Control ..................................................................................... 120
Hardware Flow Control.......................................................................................... 121
Type-in Flow Control............................................................................................. 121
DETAILED VHF PACKET OPERATION.................................................................. 121
Page 5

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE TABLE OF CONTENTS
Packet Timing...................................................................................................125
Radio Baud Rate...............................................................................................126
Special Protocol Timing...................................................................................127
Monitor Functions..................................................................................................127
Real-Time Clock and Time Stamping.................................................................... 128
Multi-Connect Guide..............................................................................................129
Setting the MFJ-1278B to Normal Operation...................................................129
How do I Invoke Multi-Connect?..................................................................... 129
Easy-Mail Mailbox................................................................................................. 130
Setting Up your Easy-Mail Mailbox................................................................. 131
Mailbox Operation............................................................................................ 136
Additional Mailbox Features ............................................................................ 140
Forwarding:................................................................................................. 140
Eliciting Reverse Forwards: ........................................................................ 141
Remote Heard Log: ..................................................................................... 141
Chat Mode:..................................................................................................141
Page SYSOP:...............................................................................................141
Remote SYSOP:.......................................................................................... 142
Mailbox CText:...........................................................................................142
Idle Timeout:............................................................................................... 142
Abort: .......................................................................................................... 142
Mailbox Messages............................................................................................142
Slotting and Acknowledgment Priority..................................................................144
Description........................................................................................................ 144
New Parameters................................................................................................ 146
Other Related Parameters ................................................................................. 148
Initial Parameter Settings Summary.................................................................. 149
What to Expect ................................................................................................. 149
Packet Picture Transfer.......................................................................................... 151
Printing Packet Pictures thru Built-in Printer Port............................................151
Using PKTPIX ............................................................................................ 151
Packet Picture transfer to the computer screen.................................................151
DETAILED HF PACKET OPERATION..................................................................... 152
Radio Setup for HF Packet Operation .............................................................. 152
Operating HF Packet......................................................................................... 155
MFJ-1278B KISS MODE, TNC-2 MODE, HOST MODE.......................................... 161
KISS INTERFACE FOR TCP/IP..................................................................................161
COMMAND PREFACE............................................................................................... 163
ENTERING COMMANDS .......................................................................................... 163
Command List........................................................................................................ 164
COMMAND NAME ........................................................................................ 164
Page 6

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE TABLE OF CONTENTS
Link Status Messages............................................................................................. 302
MFJ-1278B SPECIFICATIONS...................................................................................305
GENERAL DESCRIPTION ......................................................................................... 306
DETAILED CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION ....................................................................... 307
Oscillator................................................................................................................ 307
Dividers and Baud-rate Generator.......................................................................... 307
CPU Complex........................................................................................................308
Serial Interface....................................................................................................... 308
Watch-dog Timer................................................................................................... 309
Modem................................................................................................................... 309
Power Supply......................................................................................................... 309
RS-232C HANDSHAKING PROTOCOL.................................................................... 310
JUMPER FUNCTIONS................................................................................................ 312
PARALLEL PRINTER PORT PIN FUNCTION,J12................................................... 315
TTL INTERFACE PORT PIN FUNCTION,J5............................................................ 316
MULTI-LEVEL INTERFACE CONNECTOR,J13...................................................... 317
EXTERNAL MODEM INTERFACE CONNECTOR - J14......................................... 317
MODEM DISCONNECT HEADER, J4....................................................................... 318
HF TUNING INDICATOR .......................................................................................... 320
GENERAL TESTS ....................................................................................................... 321
Step 1: Power Supply............................................................................................ 322
Step 2: Obvious Problems.....................................................................................322
Step 3: Assembly Problems................................................................................... 322
Step 4: Cabling Problems......................................................................................323
SPECIFIC SYMPTOMS............................................................................................... 323
Symptom: TNC appears dead ............................................................................... 323
Oscillator and Reset Circuits ............................................................................ 323
Digital Logic Lines........................................................................................... 323
Symptom: Modem won't calibrate or key transmitter............................................ 324
Symptom: Uncopyable transmitted or received packets........................................ 325
TERMINAL INTERFACE TROUBLESHOOTING.................................................... 325
Symptom: MFJ-1278B won't sign on to the terminal............................................325
Symptom: The MFJ-1278B appears to be signing on but only gibberish is
printed on the terminal ........................................................................................... 326
Symptom: The MFJ-1278B signs on OK but won't accept commands ................. 326
Symptom: The MFJ-1278B appears to have "lock-up" i.e. not responding to any
commands .............................................................................................................. 326
EXPLANATION OF PROTOCOL............................................................................... 327
Physical Layer........................................................................................................327
Data Link Layer ..................................................................................................... 327
HDLC FRAMES........................................................................................................... 328
Page 7

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE TABLE OF CONTENTS
Comprehensive Alignment Procedure....................................................................340
Set Modulator Tones Using Built-in Calibration Software...............................340
Demodulator Center Frequency Alignment ...................................................... 341
Tuning Indicator Alignment...................................................................................342
CW MODEM TUNE-UP PROCEDURE ..................................................................... 346
Detailed CW Demodulator Alignment Procedure..................................................347
AUDIO OUTPUT CALIBRATION ............................................................................. 350
Audio Output Level Adjustment Procedure........................................................... 350
HF RADIO ALIGNMENT ........................................................................................... 352
FIRST METHOD: NOISE AVERAGE FREQUENCY ............................................... 352
SECOND METHOD: FILTER SKIRT AVERAGE FREQUENCY............................ 353
CONVERTING THE MFJ-1278B TO "LIKE-TNC 2"................................................354
MFJ-1278B 2400 BPS PACKET.................................................................................. 356
2400 BPS PACKET SETUP.........................................................................................356
2400 BPS Receive Audio Setting........................................................................... 357
2400 BPS Transmit Audio Setting......................................................................... 357
JUMPER FUNCTIONS AND LOCATIONS............................................................... 358
COMMAND SUMMARY............................................................................................ 362
MFJ-1278B/1278BT PARTS LIST .............................................................................. 373
Page 8

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page 9

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE INTRODUCTION
INTRODUCTION
Welcome to the exciting world of Amateur Digital Communications. By choosing the MFJ1278B, you have chosen the most versatile and powerful Multi-mode Data Controller
manufactured for the Amateur Radio Service.
The MFJ-1278B interfaces your radio with any personal computer that has an RS-232 or
TTL level Serial Port and a terminal program. While most communications programs will
work, MFJ recommends the use of MFJ Starter Pack for those who have IBM or compatible,
Macintosh, Amiga or Commodore C64/128 computers. With an IBM or compatible
computer, the MFJ Multicom terminal program gives you some added features that a standard
terminal program just can not offer. Features such as color SSTV, color FAX, 16 gray level
FAX, and color VGA packet picture transfer, just to mention a few. Multicom is menu
driven, making it easy to operate all modes offered by the MFJ-1278B. Dedicated functions
keys are programmed to operate most functions with a single key stroke.
Even though the MFJ Multicom programs offered for other computers may have features
different from the IBM version, they do offer features that will make operating the MFJ1278B very fun and very easy.
This compact versatile controller employs the genuine TAPR TNC 2 AX.25 protocol packet
firmware plus many added features to receive and transmit VHF packet, HF packet, AMTOR,
CW, ASCII, RTTY, color FAX, and color SSTV. The new 16 gray level fax board built in
the MFJ-1278B gives you the ability to receive and transmit color SSTV and multi-gray level
FAX pictures. In addition, MFJ-1278B lets you monitor the new and growing NAVTEX
broadcasting system. The MFJ-1278B also has a Contest Memory Keyer mode.
Also a feature which so many have asked about, Pactor has been added to the operating
modes. The new Pactor mode gives the user operating features such as Digital Memory
ARQ, full On-Line Data Compression, FEC Unproto operation, just to mention a few.
Also included with the PACTOR mode is a PACTOR Mailbox. With the Pactor mode also
comes the ability to monitor AMTOR ARQ connect requests.
The MFJ-1278B offers the most versatile mailbox available when compared to the mailbox in
other controllers. This mailbox allows a dedicated mailbox callsign so that the mailbox stays
on while you operate packet. Other features like auto forwarding or reverse forwarding of
mail to and from other BBS systems, remote sysop access, sysop paging, mailbox ctext, chat
mode and a "has mail" LED indicator. The MFJ-1278B has 32K mailbox memory which is
user expandable to 128K or 512K by simply replacing the mailbox memory IC -- a feature
that no other controller offers.
Page 10

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE INTRODUCTION
The new "packet collision prevention" features -- Prioritized Acknowledgments and Slottime
are installed. This new technology helps prevent many packet collisions inherent in the
current packet protocol.
The EPROM containing the MFJ-1278B firmware, previously 512K bits, has been expanded
to 1 Megabits giving the MFJ-1278B twice the room to grow in.
You also get a Key Paddle input jack so you can use your MFJ-1278B as an Iambic Keyer or
Memory Keyer. The ten user-programmable memory buffers are provided for use with the
contest memory keyer function. In addition you also get contest serial numbering and a
random code generator.
A speaker jack lets you plug in a speaker and monitor transmit and receive audio and CW
side tone as it is received and transmitted by your MFJ-1278B. The speaker output also
provides for the packet connect signal alarm.
A Centronics compatible parallel printer port (DB-25) lets you directly interface your printer
to the MFJ-1278B for printing received text, Packet, FAX and SSTV pictures.
The MFJ-1278B provides dual radio ports for HF and VHF operation. These dual radio
ports let you connect 2 radios at the same time in any combination. Independent transmit
audio output controls provide even further flexiiblity. This will enable the user to
individually adjust the audio output for each radio port. The radio ports are not dedicated to
either VHF or HF operation. They are totally independent of each other.
You also get a Threshold control for optimizing your demodulator filter for the different
modes of operation. This is a very useful tool when trying to receive signals during bad band
conditions.
A 20-pin header provided for the MFJ-1278B to operate packet at 2400 or 9600 baud packet
by simply plugging in an optional modem board. The MFJ-1278BT already has a 2400
modem installed. If your MFJ-1278B does not have the 2400 modem installed, it can be
purchased separately (MFJ-2400) and installed by you. With the 2400 modem installed, your
MFJ-1278B can operate 300, 1200 and 2400 packet. You may also purchased the MFJ-9600
modem board that allows the MFJ-1278B to operate at 9600 baud packet.
The list goes on.... This is just a few of the features available. In short the MFJ-1278B offers
you tons of features that the other multi-mode controllers just can't match. This in
conjunction with the new MFJ Multicom (TM) software will put you leagues ahead in the
ever changing field of Ham Radio Digital communications.
Page 11
MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE INTRODUCTION
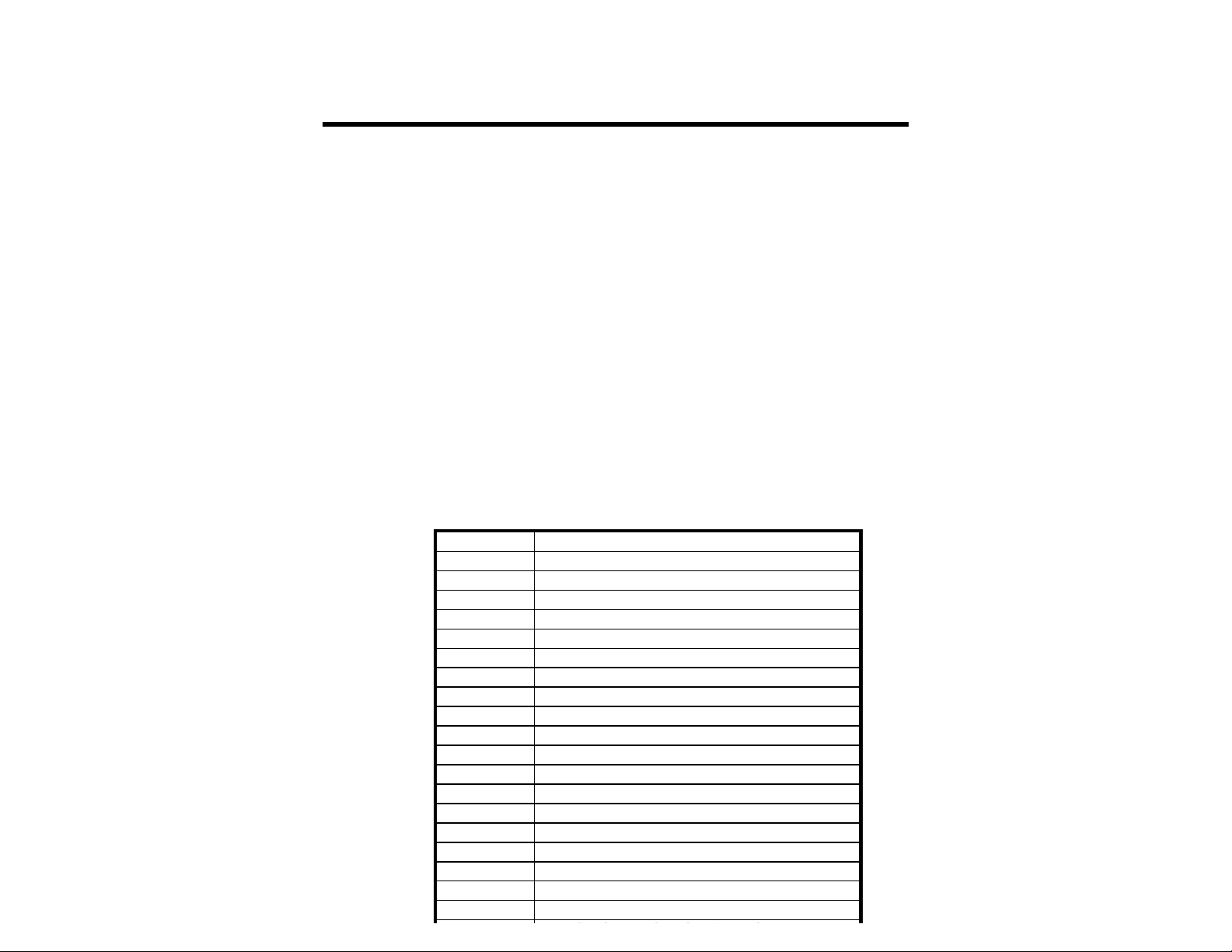
Items supplied with MFJ-1278B/MFJ-1278BT package
1. One MFJ-1278B or MFJ-1278BT Multi-Mode Data Controller
2. One AC adapter power supply for 110V AC. 240V AC adapter supplied for MFJ1278BX (export model for country which operate on 220-240V AC).
3. Two open end radio port cables with 5-pin DIN male connectors.
4. One 10-pin connector for the TTL port.
5. One MFJ-1278B Instruction Manual.
6. One MFJ-1278B Fast-Start Manual.
There are many additional items available for the MFJ-1278B. In the table below is a list of
these items:
Optional items available for the MFJ-1278B
Model No Description
MFJ-1289 Advanced Starter pack for IBM & compatibles
MFJ-1289M Same as MFJ-1289 but on 3.5" Disk
MFJ-1282B Starter pack for Commodore C64/128
MFJ-1287B Starter pack for Macintosh
MFJ-1290 Starter pack for Amiga
MFJ-1272B MFJ-1278B to Microphone switch box
MFJ-5024 Radio connecting cable for Icom/Yaesu/RS HTs
MFJ-5026 Radio connecting cable for Kenwood HTs
MFJ-5080 Radio connecting cable for Yaesu 8-pin radio
MFJ-5084 Radio connecting cable for ICOM 8-pin radio
MFJ-5086 Radio connecting cable for Kenwood 8-pin radio
MFJ-280 Monitor speaker for transmit/receiver audio
MFJ-1292 Video digitizer for IBM & compatibles
MFJ-48BE Packet encryption EPROM
MFJ-43 TNC Real time clock, keeps your 1278B on-time
MFJ-44 Internal Scope tuning board
MFJ-45B 128K RAM IC for additional mailbox memory
MFJ-45C 512K RAM IC for additional mailbox memory
MFJ-2400 2400 bps internal modem for packet
Page 12

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE COMPUTER INTERFACING
COMPUTER INTERFACING
You are now ready to connect your MFJ-1278B to your station's computer or terminal.
Throughout this manual we will use the term "computer" to refer to the computer or terminal
you use to communicate with your MFJ-1278B.
The MFJ-1278B communicates with your computer through a serial port, using signals
corresponding to a standard called RS-232C. Why an RS-232C interface? Nearly every
computer in production today either incorporates an RS-232C style serial port as a standard
feature, or has one available as an optional accessory, either from the computer manufacturer
or from a manufacturer of computer accessories. In addition to the RS-232C port, the MFJ1278B has a built-in TTL port to allow interfacing with computers which need TTL signals
such as the Commodore C-64, C-128 or the VIC-20.
In order to use the MFJ-1278B with your computer, the computer must have an RS-232C
serial port, or a TTL serial port. Also a program which supports the serial or TTL port must
be used. The program will typically be called a modem program, terminal emulator, or
communications program.
Since there are so many computers on the market today, it is impractical for this chapter to
provide detailed instructions for each computer. Detailed information is given for some of
the popular models available in the United States. Also provided is general computer
interfacing information.
MFJ Starter Packs
MFJ Enterprises, Inc. offers Starter Packs for some of the most popular computers. These
Starter Packs contain a terminal program and a cable for connecting the MFJ-1278B to your
computer. The Starter Packs available are as follows:
MFJ-1282B: Commodore VIC-20, C64, C128 in 5-1/4" diskette.
MFJ-1283: Commodore VIC-20, C64 on tape.
MFJ-1289: IBM PC & compatibles in 5-1/4" diskette.
(Supports color SSTV and 16 gray-level FAX)
MFJ-1289M: IBM PC & compatibles in 3-1/2" diskette.
(Supports color SSTV and 16 gray-level FAX)
MFJ-1287B: Macintosh, in 3-1/2" diskette.
(Supports color SSTV and 16 gray-level FAX)
MFJ-1290: Amiga in 3-1/2" diskette.
(Supports 8 levels SSTV and 8 levels FAX)
Page 13
MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE COMPUTER INTERFACING
Computer Interface with MFJ Starter Pack
If you are using one of the MFJ Starter Packs, you should use the cable provided to connect
the MFJ-1278B to your computer. Follow the instruction manual provided with the Starter
Pack to operate the terminal program and to connect the MFJ-1278B to your computer.
When finished with installation of the MFJ-1278B proceed to the "Computer Baud Rate", for
further information about TNC installation. The "Computer Baud Rate" section in this
chapter will continue to explain installation of the MFJ-1278B.
Computer Interface without MFJ Starter Pack
If you are not using an MFJ Starter Pack you should follow the instructions in this chapter for
computer interfacing.
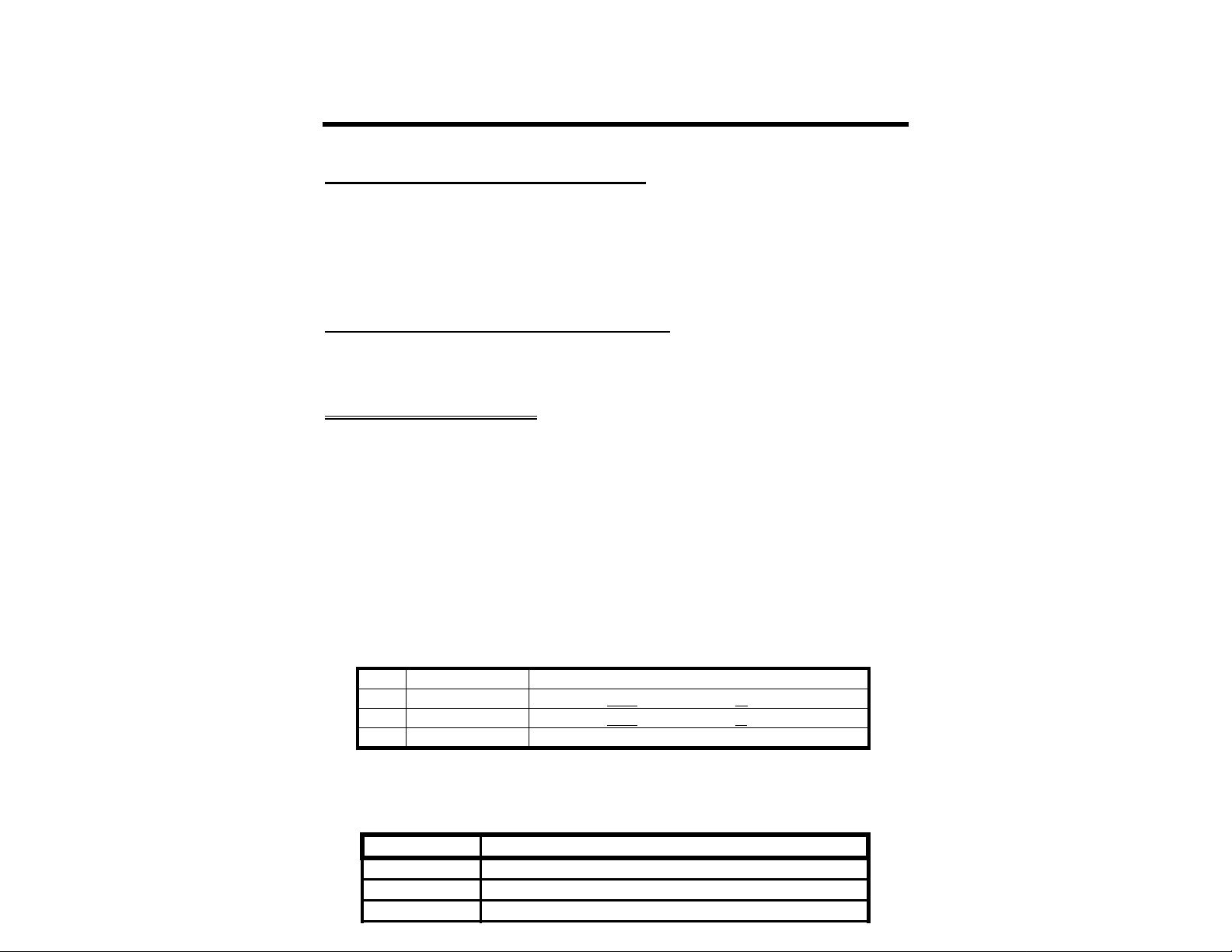
SERIAL PORT SIGNALS
The serial port connector is on the rear panel your MFJ-1278B. There are several signals
available at this connector labeled "RS-232 SERIAL". You will not need all of these serial
port signals for normal operation. For some special applications, such as binary file transfers
or some Bulletin Board operations, you may want to use more of them. In that case, see
MFJ-1278B Serial Port Pin Functions in this chapter.
In Table 2-1 the user will see a list of the serial port pins that must be used, between the MFJ1278B and the computer. The pins listed are required by the MFJ-1278B for normal
operation. Note that the MFJ-1278B connects to a computer exactly as if the MFJ-1278B
were a standard RS-232C modem. If you have successfully used your computer with a
telephone modem, then hook it up to the MFJ-1278B in the same way. Use whatever
program you ordinarily use to communicate with the modem.
Pin Signal Name Description
2 Transmit Data Serial data from your computer to the MFJ-1278B.
3 Receive Data Serial data fromtheMFJ-1278B to your computer.
7 Signal Ground The common ground for both data lines.
Table 2-1. Serial port signals required by MFJ-1278B.
If your computer is listed in Table 2-2, refer to the specific information in the following
sections to connect your MFJ-1278B to your computer.
Manufacturer Model
Apple Macintosh (tm)
Apple II,II+,IIe,II-gs(tm)
Commodore VIC-20 (tm),C-64 (tm),C-128 (tm)
Page 14
MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE COMPUTER INTERFACING
Many computers require a serial port adapter card. These cards incorporate the circuitry
necessary to add an RS-232C port to the computer. Some popular models in this category are
the Apple II series, the IBM Personal Computer, many Radio Shack computers, and the
Sanyo MBC-55X series. If you have one of these computers with an "add-in" serial port, or
if you have another computer we haven't mentioned, you should skip to one of the sections on
"other computers." If your computer has a 25-pin RS-232C serial port, refer to the section on
Other Computers with 25-pin RS-232C Ports. Otherwise refer to the section Other
Computers with Nonstandard Serial Ports.
Some computers have no serial port and no adapter is commercially available. Such
computers are not suitable for use with the MFJ-1278B.
COMPUTER WITH SPECIFIC SERIAL INTERFACES
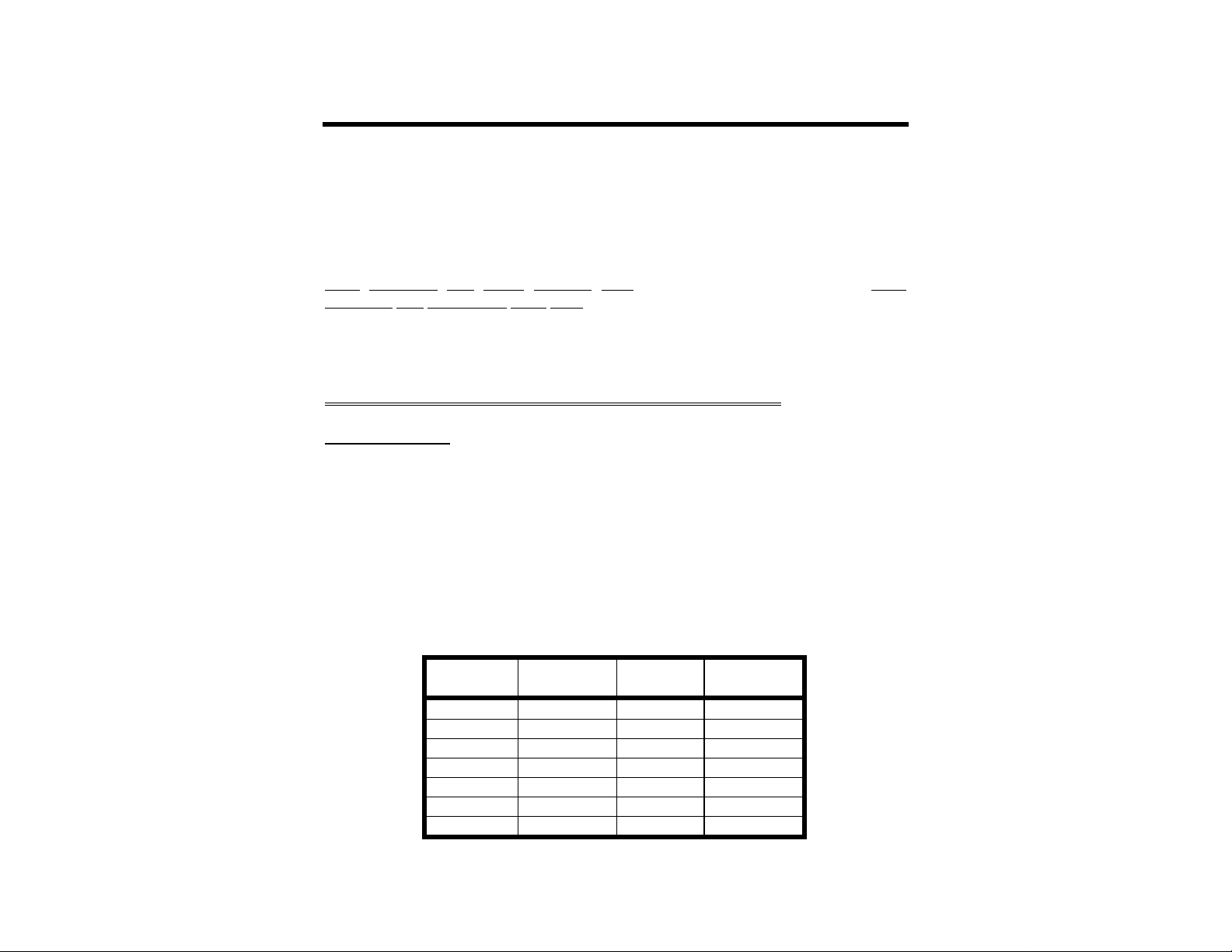
Apple Macintosh
The Macintosh serial port is an RS-422 compatible port, but it will work fine with the RS232C serial port on your MFJ-1278B.
MFJ Enterprises, Inc. offers an optional Starter Pack for the Macintosh. The Macintosh
Starter Pack is available from MFJ Enterprises, Inc. or any dealer of MFJ products. The
Starter Pack includes a cable for
connecting the MFJ-1278B to the Macintosh and a terminal program. The Starter Pack for
Macintosh is MFJ-1287B. If you wish to use your own cable, you will need a cable wired as
shown in Fig. 2-1.
Macintosh
8 Pin
1 (HSKO) 4 1 1
2 (HSKI) 6 5 2
3 (TXD-) 2 9 3
4 (GND) 7 3 7
5 (RXD-) 3 7 8
6 (TXD+) N/C 6 4
7 (GPi) N/C
MFJ-1278B
DB-25P
Macintosh
DB-9P
MFJ-1278B
DB-25P
Fig. 2-1. Serial port wiring for Apple Macintosh.
Note that pin 1 of the DP-9P connector is not connected inside the Macintosh or the MFJ1278B. We highly recommend the use of shielded cable, when making interconnections
Page 15
MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE COMPUTER INTERFACING
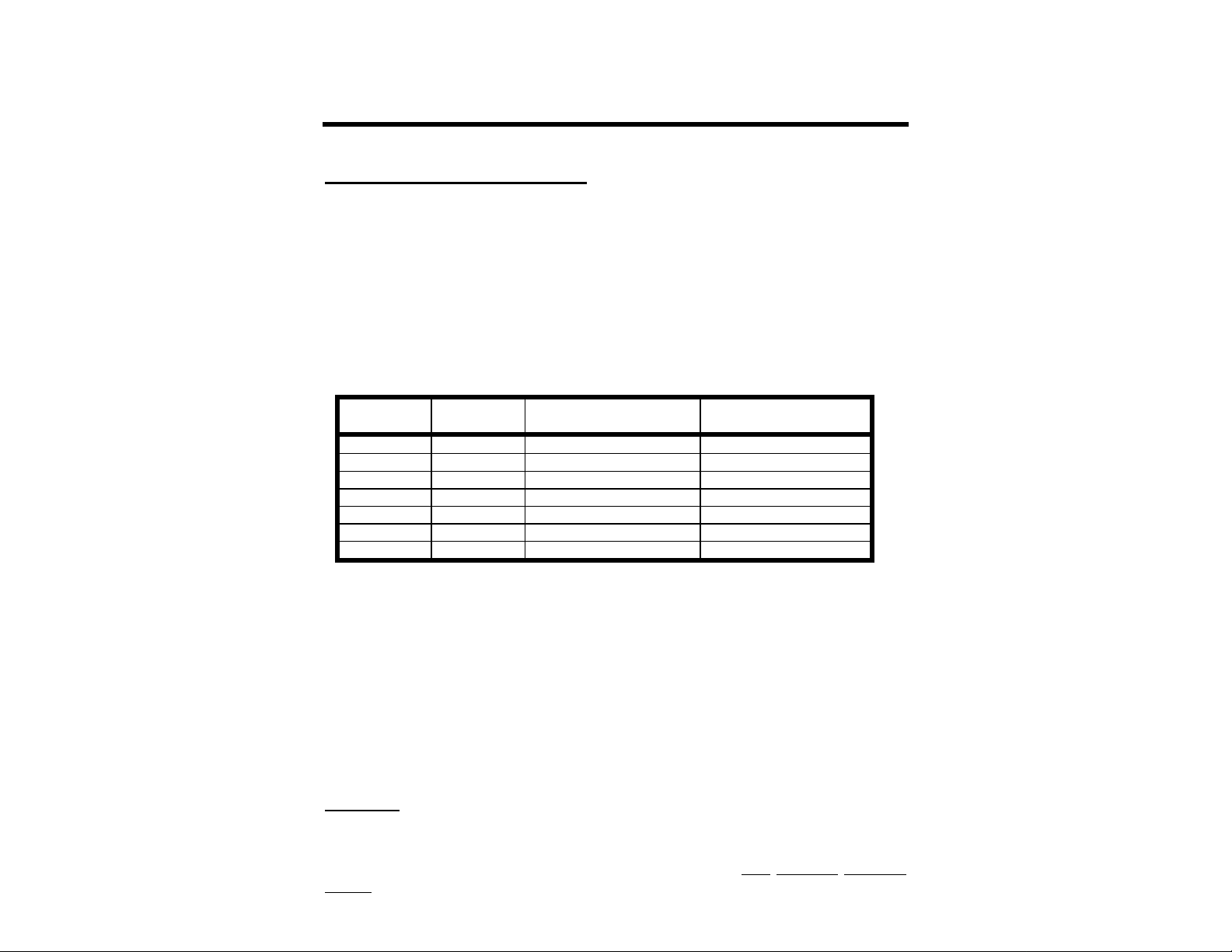
Commodore C64, C128 and VIC-20
The MFJ-1278B has a built-in TTL-level port for interfacing with the Commodore C64,
C128 or the VIC-20 computers. You do not need a RS-232C converter to interface with the
MFJ-1278B.
An optional Starter Pack for the C-64, C-128 or the VIC-20 is available from MFJ
Enterprises, Inc. or any dealer of MFJ products. The Starter Pack includes a cable from the
MFJ-1278B TTL port to the user I/O port on the Commodore computer. Included also is a
terminal program. To order, specify MFJ-1282B for software on disk or MFJ-1283 for
software on tape. If you wish to construct your own cable, the information below in Figure 22A will be helpful:
MFJ-1278B
J-5,Pin#
1 RXD Receive Data B,C
2 DCD Data Carrier Detected H
3 GND Ground (Frame and Signal) N
4 RTS Ready To Send E**
5 TXD Transmit Data M
6 DSR Data Set Ready L
7 CTS Clear to Send K
Mnemonic
Name
C-64/128*, VIC-20 Pin#
Fig. 2-2A TTL Port wiring for VIC-20, C64 and C128
*C-128 is used in the C-64 mode for these connections.
**Pin E is not needed when using terminal program referred to in this chapter for the
Commodore computers.
The TTL port (J5), is numbered from left to right as viewed from the back panel of the MFJ1278B. The user's terminal program may not use all of these connections. The MFJ-1278B
requires RXD, TXD and GND connected for proper operation. Programs that utilize file
transfer and printer routines will probably use RTS and CTS as well. Consult your software
documentation.
IBM PCjr
The PCjr uses standard serial voltage levels for it's RS-232C interface; however, the
connector used is non-standard and not readily available from electronic supply dealers. The
pin-out information for this connector is refered to in the IBM PCjr Technical Reference
Manual.
Page 16

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE COMPUTER INTERFACING
Radio Shack Color Computer
The Color Computer series (except for the Micro Color Computer) uses a 4-pin DIN-style
connector for its serial port. If you wish to construct your own cable, the information in
Figure 2-2 will be helpful. All necessary parts should be available from Radio Shack dealers.
Color Computer DB-25P
4 2
2 3
3 7
Fig. 2-2. Serial port wiring for Radio Shack
Color Computers
Radio Shack Model 100/102 and NEC 8201Radio Shack Model 100, serial port
interfacingThese computers have built-in standard RS-232C serial ports that are compatible
with the MFJ-1278B. You will need a standard male-to-male RS-232C cable to connect the
computer to the MFJ-1278B.
IBM PC/XT/AT/386/486 and compatibles Computer
"Include other computers with 25-pin RS-232 Ports"If your computer is an IBM or
compatible, you should have a serial port with standard DB-25 or DB-9 pin connector. You
may use a standard IBM serial modem cable with the correct gender on each end of the
cable.
MFJ Enterprises, Inc. offers optional Starter Pack (MFJ- 1289) for the IBM or compatible
computers. A computer connecting cable is included with the Starter Pack. The supplied
cable is of male to female gender, to connect your MFJ-1278B to the computer.
For other computers with a 25-pin RS-232C port, consult the manual for your computer or
accessory to see which pins it uses to send and receive data on, as well as the pin used for
signal ground. Follow the computer manufacturer's recommendations for connecting the
serial port to a modem. You may also find the technical information in this section useful.
Your MFJ-1278B is configured as Data Communications Equipment (DCE), the technical
term for an RS-232C modem. Most computers are configured as Data Terminal Equipment
(DTE). If this is the case for your computer, you may be able to wire pin 2 of the MFJ1278B connector to pin 2 of your computer's RS-232C port. Then wire pin 3 to pin 3 and pin
7 to pin 7 on the computer's RS-232C port. You can provide these connections with a
standard 3-wire male-to-female or male-to-male RS- 232C extension cable, depending on
whether your computer has a DB25S or DB25P connector.
Page 17

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE COMPUTER INTERFACING
If your computer is configured as DCE, you will have to wire pin 2 of your MFJ-1278B to
pin 3 of the computer RS-232C connector. Then wire pin 2 of the computer's RS-232C
connector to pin 3 of your MFJ-1278B. Please note that pin 7 of the computer's RS-232C
connector will still connect to pin 7 of your MFJ-1278B serial port. Some computers may
require that pin 5 of the computer serial port connector be connected. Others may require
connections for pin 8 and pin 20. You can use the computer's output signals on pins 4 and 6
as shown in Fig. 2-3.
MFJ-1278B RS-232C Computer RS-232C
2 2
3 3
7 7
| 4
| 5
| 6
| 8
| 20
Fig. 2-3. Serial port wiring with jumpers for
auxiliary signals.
Other Computers with Nonstandard Serial Ports
Computers with non-standard serial ports must meet the following conditions.First, the signal
levels should be RS-232C compatible. The MFJ-1278B requires that the voltage levels sent
from the computer be greater than about +3 volts in one state and less than about +1 volt in
the other state.
Second, the polarity of the signals must conform to the RS- 232C standard. This means that
the low voltage state must correspond to a logical "1" and the high voltage state to a logical
"0".
Third, the computer must be able to correctly receive a signal that meets the RS-232C
specification. The MFJ-1278B supplies signals that meet this specification.
Make or buy a cable that provides the following connections. The common pin on the
computer's RS-232C serial port must be connected to pin 7 on the MFJ-1278B serial port.
Connect the line that sends data from the computer to pin 2 on the MFJ-1278B RS-232C
port. Connect the line that your computer receives data on to pin 3 on the MFJ-1278B RS232C port.
Page 18
MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE COMPUTER INTERFACING
There are others that may be compatible with the MFJ
-
1278B, but have not been tested.
TERMINAL SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS
Any software package that enables your computer to act as an ASCII terminal with an
ordinary telephone modem should work with your MFJ-1278B. If you have a program that
you have used successfully with a telephone modem and that you are familiar with, use that
program to communicate with your MFJ-1278B.
If you are using a terminal program provided by the MFJ Starter Pack, proceed to the
"Computer Baud Rate" section in this chapter. Follow the instruction provided by the
program.
If you are not using a MFJ terminal program, then proceed with the instruction for your type
of computer.
Note: Some terminal programs require the initialization of DCD before they receive any
characters. This is also true for different types of serial port cards (such as the Apple
II+ Super Serial Card). If this is the case, place a jumper across pin 1 and 2 of JMP
1. The DCD LED on the front panel will function normally indicating received
packets.
Apple Macintosh
There is an MFJ Starter Pack available for Macintosh, the MFJ-1287B. Included in the MFJ1287B is a terminal program to allow compatibility between MFJ-1278B and the Macintosh.
Also included is a cable
to connect the MFJ-1278B to the Macintosh. In Table 2-3 you will find a list of parameters
should want to use a terminal program such as MacTerm.
Compatibility Terminal
1200 baud VT100
7 bits/character ANSI
even parity UNDERLINE
Handshake Xon/Xoff US
modem connection 80 Columns
"telephone" port ON LINE UTOREPEAT
Table 2-3. MacTerm Parameters for MFJ-1278B
Apple II, II+, IIe, IIc
For the Apple II family of computers with Apple or third- party RS-232C serial cards, you
may use ASCII Express Pro, Hayes Smartcom IIe and DataCapture 4.0 for the MFJ-1278B.
Page 19

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE COMPUTER INTERFACING
Commodore C64, C128 and VIC-20
The optional Starter Pack for the C-64, C-128 and VIC-20 is available from MFJ Enterprises,
Inc. or from any dealer of MFJ products. Included in the Starter Pack is a cable to connect
the MFJ-1278B TTL port to the user I/O port on the Commodore computer. Also included
with the Starter Pack is a terminal program. The terminal program allows compatibility
between the MFJ-1278B and the Commodore computer. To order, specify MFJ-1282B for
software on disk or MFJ-1283 for software on tape.
If you do not have the MFJ Starter Pack, then you may use the BASIC communications
program given in the Programmer's Reference Guide published by Commodore. Use the
program listing for "true ASCII," as these computers use a modified ASCII format internally.
You will probably want to run your MFJ-1278B at 300 baud on the serial port with these
computers.
NOTE: When using the BASIC communications program above, you must first use the
"COMMODORE" key to shift to lower case before using this program. Also line 200 should
read For J=0 to 64:T%(J)=J:NEXT.
The information given on page 5 of this chapter is used to make a cable for use with the
BASIC communications program mentioned above. However, do not use pin E connection
for this program.
IBM PCjr
The IBM PCjr has a built-in terminal program in the BASIC cartridge. Start this program by
typing TERM. Refer to your PCjr BASIC manual for details on this program. For best
results with PCjr, do not run the MFJ-1278B serial port faster than 1200 baud.
IBM and Compatible Computers
The optional Starter Pack, (MFJ-1289) for the IBM PC and compatible computers is
available from MFJ Enterprises, Inc. or from any dealer of MFJ products. Included in this
Starter Pack is a graphics terminal program. This program allows compatibility between the
MFJ-1278B and the computer. Also included is a cable used to connect the MFJ-1278B to
your computer. The MFJ-1289 program allows you to transmit and receive 16 gray level
FAX as well as color SSTV pictures. The MFJ-1289 also allows for display of these signals
on the computer screen. It will also store the pictures on disk for later viewing or
transmitting. This software also sets up compatibility between the MFJ-1278B and the
computer when operating the other mode, that the MFJ-1278B has to offer.
You may also use many commercial, "shareware" and public- domain terminal programs for
the IBM PC and compatible computers. Special programs written for packet radio and
Page 20
MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE COMPUTER INTERFACING
Radio Shack Color Computer
There are several terminal programs available for the Color Computer. You will probably
want to use a commercial program (rather than writing your own) since the Color Computer
has a "software UART" that is difficult to program in BASIC.
Some of the terminal programs available are COLORCOM 64, AUTOTERM and
RICKEYTERM (for Coco III). Others are WIZ and XTERM for OS-9.
Radio Shack Model 100/102 and NEC 8201
These computers have built-in terminal programs in ROM. Consult your computer's
documentation for instructions in their use.
MFJ-1278B SERIAL PORT PIN FUNCTIONS
This section describes the pins used on the MFJ-1278B RS-232C serial port connector. It is
intended for users with special applications requiring hardware handshaking. This
information should not be needed by most users.
Pin # Mnemonic Name
1 FG Frame Ground
2 TXD Transmit Data
3 RXD Receive Data
4 RTS Request To Send
5 CTS Clear To Send
6 DSR Data Set Ready
7 SG Signal Ground
8 DCD Data Carrier Detect
9 --- + 12V unregulated reference
10 --- - 12V unregulated reference
Table 2-4. RS-232C Pin Designations
Pin 1 Frame Ground
The Frame Ground pin is provided for attachment to the chassis of the MFJ-1278B
and the chassis of the attached device (computer or terminal). This pin is available
at a feed-through hole on the MFJ-1278B PC board near pin 1 of the serial
connector. It is not electrically connected anywhere else on the MFJ-1278B circuit
board.
Pin 2 Transmit Data
Page 21

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE COMPUTER INTERFACING
Pin 3 Receive Data
The Receive Data pin is an output line from the MFJ-1278B on which the attached
device receives data. The attached device is generally a computer or data terminal.
Pin 4 Request To Send
The Request To Send pin is an input line to the MFJ-1278B on which the attached
device requests clearance to transmit data to the MFJ-1278B.
Pin 5 Clear To Send
The Clear To Send pin is an output from the MFJ-1278B signaling the attached
device to send or refrain from sending data to the MFJ-1278B. This line is used for
systems that require hardware flow control.
Pin 6 Data Set Ready
The Data Set Ready pin is an output from the MFJ-1278B telling the attached device
that the MFJ-1278B is operational.
Pin 7 Signal Ground
The Signal Ground pin is the common or return path for all signals between the
MFJ-1278B and the attached device.
Pin 8 Data Carrier Detect
The Data Carrier Detect pin is an output from the MFJ-1278B. As normally
configured, DCD reflects the status of the CON LED: It is true when an AX.25
connection exists between your MFJ-1278B and another station; it is false when no
connection exists. This configuration is useful when the MFJ-1278B is used with a
telephone style Bulletin Board system. Since the AX.25 protocol connection,
analogous to a modem signal on the telephone, indicates the presence of a user.
Shorting pins 1 and 2 of JMP1 on the MFJ-1278B mother board will cause this
output to always be true.
COMPUTER BAUD RATE
Autobaud
The MFJ-1278B performs an AUTOBAUD routine upon each power on cycle of the MFJ1278B. The AUTOBAUD command is user selectable. The AUTOBAUD command is
Page 22

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE COMPUTER INTERFACING
time the MFJ-1278B signs on you will not need to press the return key to execute the
Autobaud routine. In setting AUTOBAUD to OFF, you should remember that if you change
the terminal program baud rate is changed, then MFJ-1278B will no longer be able to match
the new baud rate. You must change the baud rate of your terminal program to match the
baud rate you set for the MFJ-1278B or you may remove JMP 5 on the MFJ-1278B board to
reset the battery back-up RAM. Once reset, the MFJ-1278B will restore all parameters to the
default values, including the AUTOBAUD command. The default setting for the
AUTOBAUD command is ON. When the MFJ-1278B is powered on after resetting
memory, it will attempt to match the new baud rate and sign on after receiving the return key
presses sent by the user.
Changing Terminal Baud Rate
The MFJ-1278B RS-232 port will operate at the rate of 300*, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600 or
19,200* baud.
The MFJ-1278B employs an AUTOBAUD routine that automatically matches it's terminal
baud rate to that of the rate set on the terminal program. The AUTOBAUD routine is
executed by pressing the "Return" key several times upon each power on cycle of the MFJ1278B. This means if the terminal program baud is set at 9600 baud, the MFJ-1278B will set
it's terminal speed to 9600 baud to match the program.
We suggest that once you select a terminal baud rate that you wish to operate your MFJ1278B on, you should set AUTOBAUD command to OFF. Once AUTOBAUD is turned
OFF, the MFJ-1278B will automatically sign-on without you having to press the "Return"
key. This is important if power a outage occurs, the MFJ-1278B will sign-on when power is
on again. If AUTOBAUD is OFF, and the terminal program baud rate does not match the
MFJ-1278B, then once the MFJ-1278B is turned off, it will not sign on again. If you reset
the MFJ-1278B or the terminal program baud rate, then the MFJ-1278B will sign-on. Once
reset, the MFJ-1278B will default AUTOBAUD to ON and it will sign on upon power up
and with a few strikes of the return key. The MFJ-1278B can be reset by removing JMP 5 on
the main PC board of the MFJ-1278B.
*The MFJ-1278B terminal baud rates of 300 and 19,200 is selectable by a jumper on JMP 18
on the mother board. Please refer to Chart XX on page ?? to locate JMP 18. For 300 baud
set the shorting jumper to positions 2-3 and for 19,200 baud set the shorting jumper to
positions 1-2. The factory setting for JMP18 is positions 1-2.
Page 23

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE COMPUTER INTERFACING
1278B, type:
VERIFYING SERIAL PORT OPERATION
Now that you have a terminal program and the connecting cable for attaching the MFJ-1278B
to your computer, you are ready to verify that the MFJ-1278B will communicate with your
computer.
1. Turn on your computer. Load and run the terminal program.
2. Set the parameter of the terminal program as follow:
Word Length 8 bits
Duplex Full
Parity None
Stop Bits 1
Baud Rate 300, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, or 19,200
3. Turn on your MFJ-1278B, and note that the PWR, STA and CON LEDs are lit.
4. If the MFJ-1278B terminal parameters match your terminal program parameter, the
MFJ-1278B will sign on and the STA and CON LEDs will extinguish. If not, you will
see an asterisk (*) or other meaningless characters on the screen at this time. This is
because the MFJ-1278B has not been set to match the parameter of your terminal
program. You will need to execute the AUTOBAUD routine.
5. Execute the AUTOBAUD routine by pressing the RETURN key few times in
succession on your computer. The MFJ-1278B will execute the AUTOBAUD routine
and set itself to the terminal program parameter. Your computer screen will display the
sign-on message:
*:J
bbRAM:LOAD WITH DEFAULTS
|A
MFJ ENTERPRISES, INC.
MODEL MFJ-1278B
AX.25 LEVEL 2 VERSION 2.0
RELEASE XXXXX (date) - 32K RAM
CHECKSUM XXX
cmd:
After the sign-on message the STA and CON on the MFJ-1278B will extinguish. If the signon message fails to appear, you should check the connecting cable between and the computer
and the MFJ-1278B. When you can successfully read the sign-on message from the MFJ-
Page 24
MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE COMPUTER INTERFACING
The MFJ-1278B has a parallel printer port in which to attach a parallel printer. The parallel
printer port is located on the left-hand side of the MFJ-1278B. The printer port can be used
to make hard copies of either text or graphics.
Printer Port Connection
The printer port is configured as a Centronics compatible parallel port. A cable with male
DB-25 on one end and a 36 pin Centronics male connector for the printer end should be used.
You may use a standard IBM parallel printer cable instead of trying to wire your own. A
Printer cable for connection from the MFJ-1278B printer port to a Centronics compatible
printer is available from MFJ Enterprises, Inc. Model No. is MFJ-5412.
If you are using a terminal program that supports graphic printing from the computer to the
printer, then you should connect the printer to the computer printer port and not to the MFJ1278B printer port.
The MFJ-1278B printer port is available for printing graphics. This feature can be used
whether your terminal program supports graphics printing to the computer screen or not. It
can be used to print graphics such as Packet, SSTV or FAX pictures. If you want to print
graphics, then you should connect the printer to the MFJ-1278B printer port. In this case the
printer must be either EPSON or IBM graphic compatible in order to insure successful
graphic receiving to the printer.
The MFJ-1278B printer port configuration is shown in Table 2-5.
MFJ-1278B DB-25
Printer Port Pin #
1 Strobe
2 Data Bit 1
3 Data Bit 2
4 Date Bit 3
5 Data Bit 4
6 Data Bit 5
7 Data Bit 6
8 Data Bit 7
9 Data Bit 8
10 Acknowledge
11 Busy
12 thru 17 No connection
18 thru 25 Ground
Name
Page 25

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE COMPUTER INTERFACING
Printer Consideration
The MFJ-1278B printer port will work with any printer that is compatible with EPSON or
IBM graphics. Printers that are not EPSON or IBM graphics compatible can not be used to
print FAX or SSTV pictures.
In addition to being able to print such as weather FAX, FAX and SSTV pictures, the printer
connected to the MFJ-1278B printer port can also print incoming text in all modes as it is
received on the screen. This means that you can keep a log of all your QSOs. To print text
to the printer, you will need to connect an IBM compatible parallel printer to the MFJ1278B printer port. Printers without Epson compatible graphics will not be able to print
Weather FAX, FAX or SSTV.
Printer Port Test
After properly connecting your printer to the MFJ-1278B, you may verify its compatibility as
follows:
1. Turn on your computer. Load and run the terminal program.
2. Turn on the MFJ-1278B. The MFJ-1278B should sign-on with the cmd: prompt sign.
3. Type: PRINTTES <CR>
If the printer is connected correctly and is compatible, it will print a string of 223 characters.
Again this only shows that the printer connected can print text. It does not necessarily
indicate that your printer can print graphics unless it is Epson or IBM graphics compatible.
4. Printing will start with ASCII SPACE (value 32 decimal) and end with the value 255
decimal that is not an ASCII character but may be a graphics character.
5. Once the printer has completed the printing, the MFJ-1278B will return to cmd: prompt
sign.
This completes the printer test. If the printer test was satisfactory, proceed to connect your
radios to the MFJ-1278B.
The above test is only valid if your printer is connected to the MFJ-1278B parallel port. This
test can not be performed if the printer is connected to the parallel port of the computer.
Page 26
MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE RADIO INTERFACING
RADIO INTERFACING
Computer interfacing, covered in the previous chapter, is only half the interfacing task. The
other half is connecting your MFJ-1278B to your radios.
MFJ-1278B Radio Ports
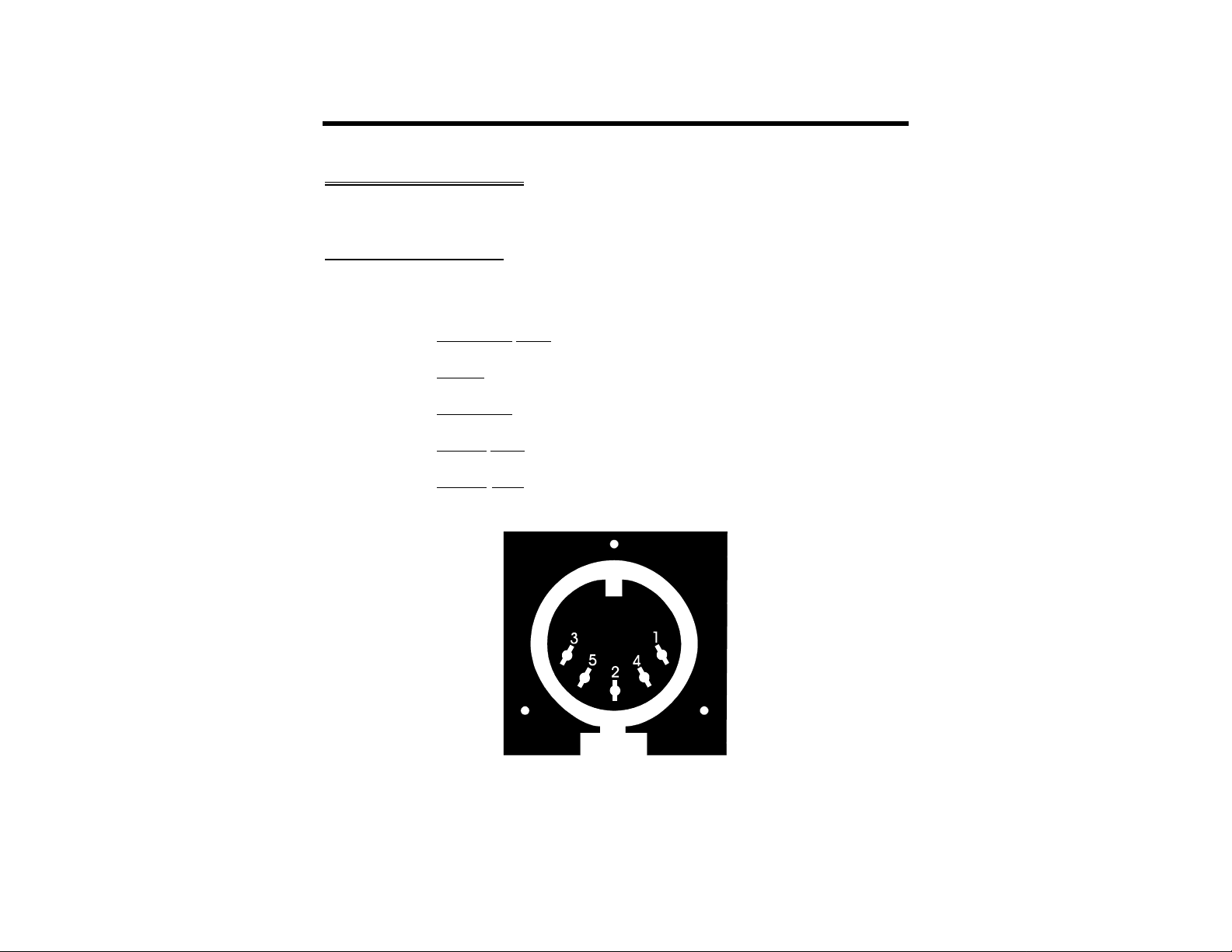
Interfacing the MFJ-1278B to your radios involves connecting the following signals at Radio
Port 1 and Radio Port 2. The pin outs of Radio Port 1 and Radio Port 2 are shown in Fig. 3-1.
Pin1 Microphone audio, from the MFJ-1278B to your transmitter.
Pin 2 Ground, audio and PTT common.
Pin3 Push-to-talk, to allow the MFJ-1278B to key your transmitter.
Pin 4 Receive audio, from your receiver to the MFJ-1278B.
Pin 5 Squelch input (optional) to allow the MFJ-1278B to detect activity on a
shared-mode channel.
Fig.3-1 Radio Port 1 and Radio Port 2 Connector
This chapter describes how to connect the MFJ-1278B to your radio and how to adjust the
receive and transmit audio levels appropriately. The interconnection needs to be well thought
out, to minimize pickup of stray audio and RF noise by the lines. If possible, you should set
up your station with a monitor speaker and be able to operate on voice without disconnecting
the MFJ-1278B.
Page 27
MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE RADIO INTERFACING
RADIO PORTS CONNECTION
The MFJ-1278B gives the user two (2) radio ports. This allows for both FM and HF
operation from either radio port. Since the radio ports are independent of each other, the user
is not restricted to FM or HF operations. The radio ports on the MFJ-1278B allow an FM
radio and an HF radio to be connected at all times. In fact you can have any combination of
HF radios or VHF radios connected to the radio ports at any time. The pin designations for
both radio ports are exactly the same. See Fig. 3-1 for the radio port pin designations. The
radio ports on the MFJ-1278B are switched by using the RADio command. We will discuss
radio port switching in the next chapter.
Once the user obtains the proper microphone connector (not provided), use Fig. 3-2 to wire
the 5 pin DIN cable (provided) to the microphone connector. If two radios are to be used
with the MFJ-1278B, you will need to wire two radio cables.
You may obtain the specific pin designations for your radio's microphone connector from
your radio's manual. Appendix A at the end of this Instruction Manual lists pin assignments
for some of the most popular radios. The accuracy of this information is not guaranteed.
You should verify this information with your radio manual.
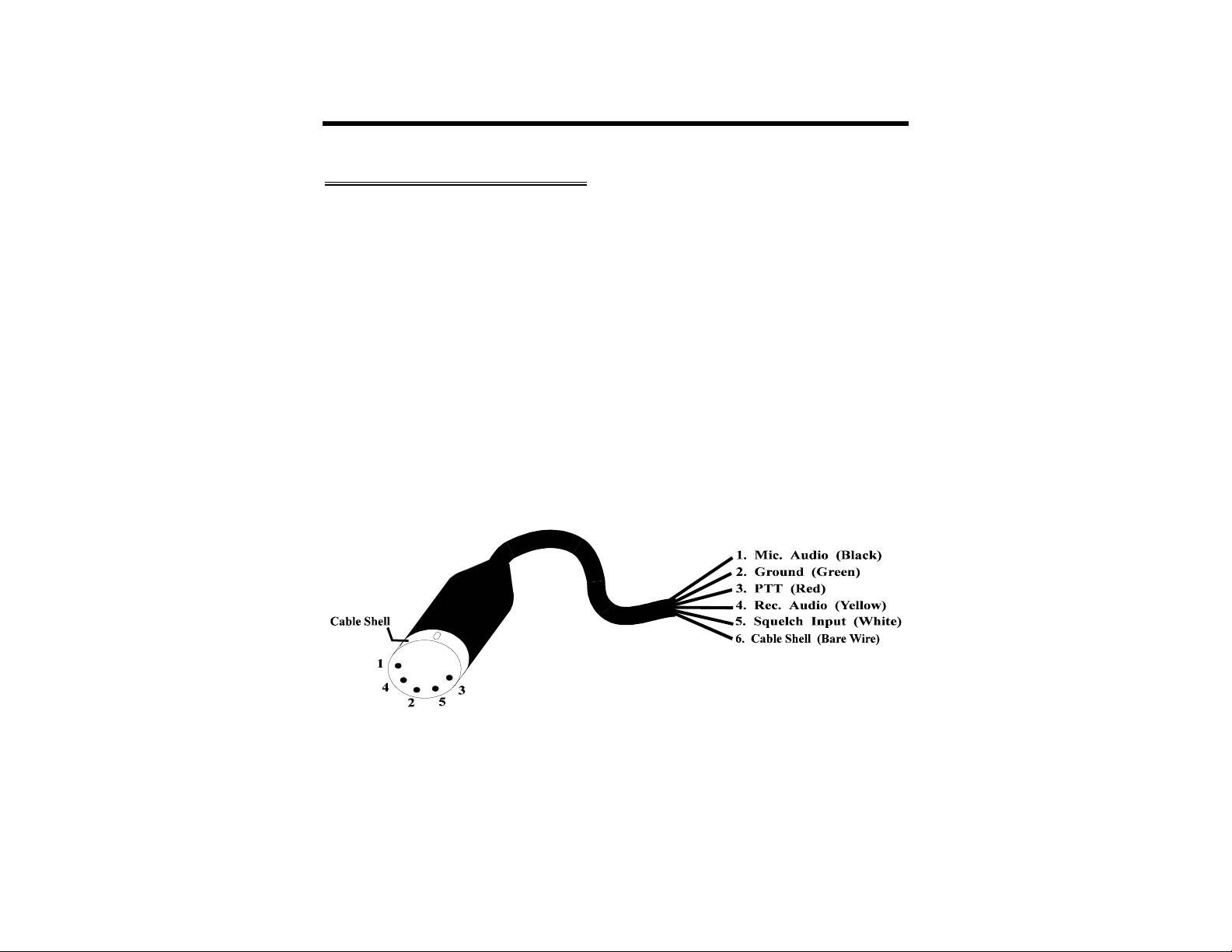
Fig. 3-2 Radio Connector Pin Diagram
Two 5-pin male DIN cables are provided with the MFJ-1278B. These cables have a 5-pin
DIN connector on one end, with the other end of each cable being unterminated. The
unterminated end of each cable is for wiring the appropriate microphone connector which
matches your radio.
CHECK THIS CABLE WITH AN OHM METER TO IDENTIFY EACH
WIRE BEFORE WIRING IT TO THE MIC CONNECTOR THAT FITS
YOUR RADIO.
Page 28
MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE RADIO INTERFACING
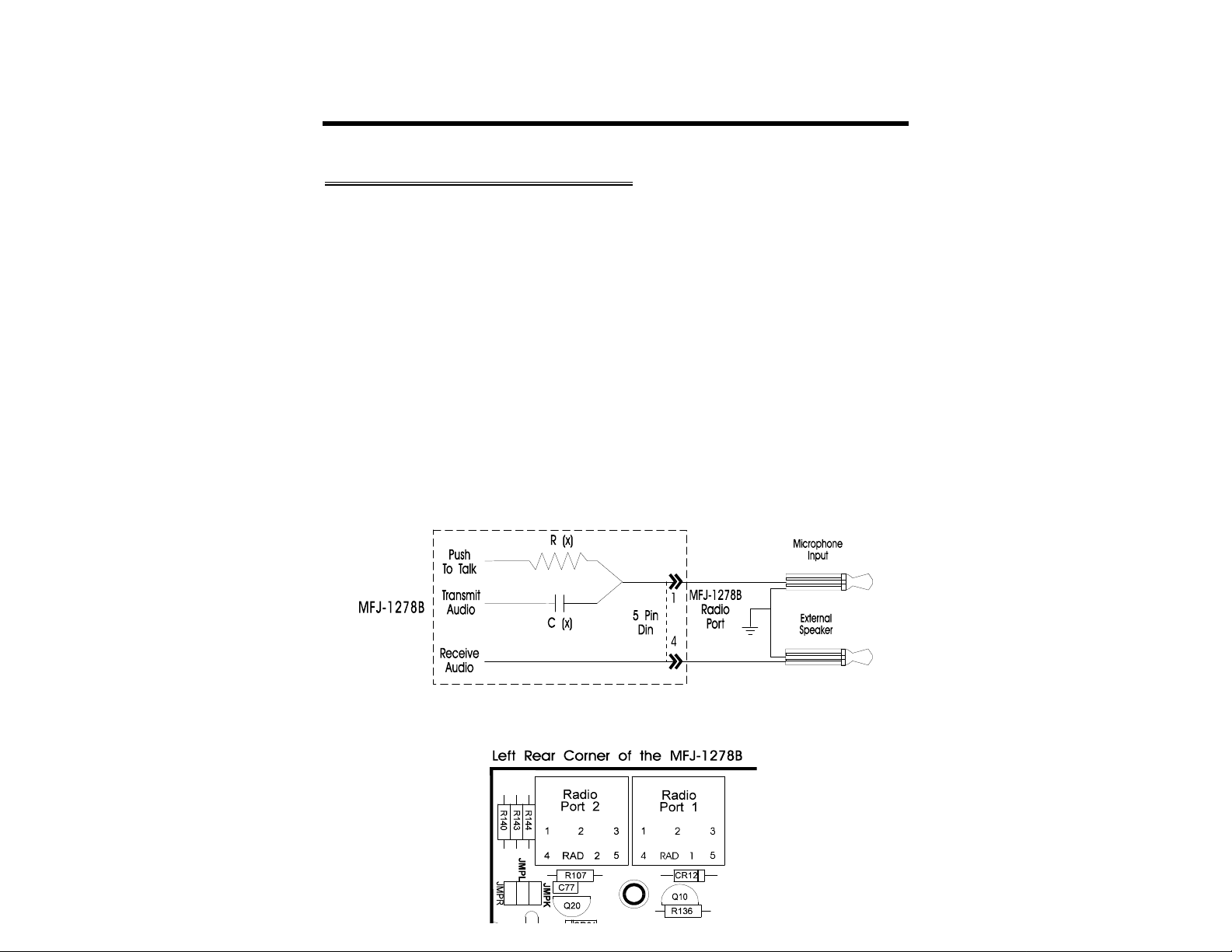
HANDHELD RADIO CONNECTION
Some HTs key the transmitter by drawing a small amount of current from the microphone
input pin (see Fig. 3-3 below). Radios with this type of special keying circuit are ICOM-2AT
(tm) and Yaesu FT-x09, FT-x3, FT-727 (tm) and others.
Appendix A at the end of this instruction manual provided pin designation for some of the
radios. Also consult the instruction manual of your radio.
If your HT has this type of microphone circuit, you can wire the microphone like the one
shown in Fig. 3-3 or you can remove the cover of the MFJ-1278B and install a shorting
jumper at JMP L for Radio Port 1 or JMP K for Radio Port 2. Installing JMP K or JMP L
will eliminating the need of soldering "Cx" and "Rx" to the microphone cable. "Cx" and
"Rx" are installed on the MFJ-1278B mother board. Fig. 3-4 shows the location of JMP L
and JMP K connectors. On the MFJ-1278B mother board, the "Rx" resistor for Radio Port 1
is R140 and the "Rx" resistor for Radio Port 2 is R107. If your radio still will not key
properly after installing JMP L or JMP K, you may need to change R140 or R107 to a
smaller value. Be sure to remove JMP K or JMP L when connecting the MFJ-1278B to
another type of radio.
FIG. 3-3 HT Special Keying Circuit
Page 29
MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE RADIO INTERFACING
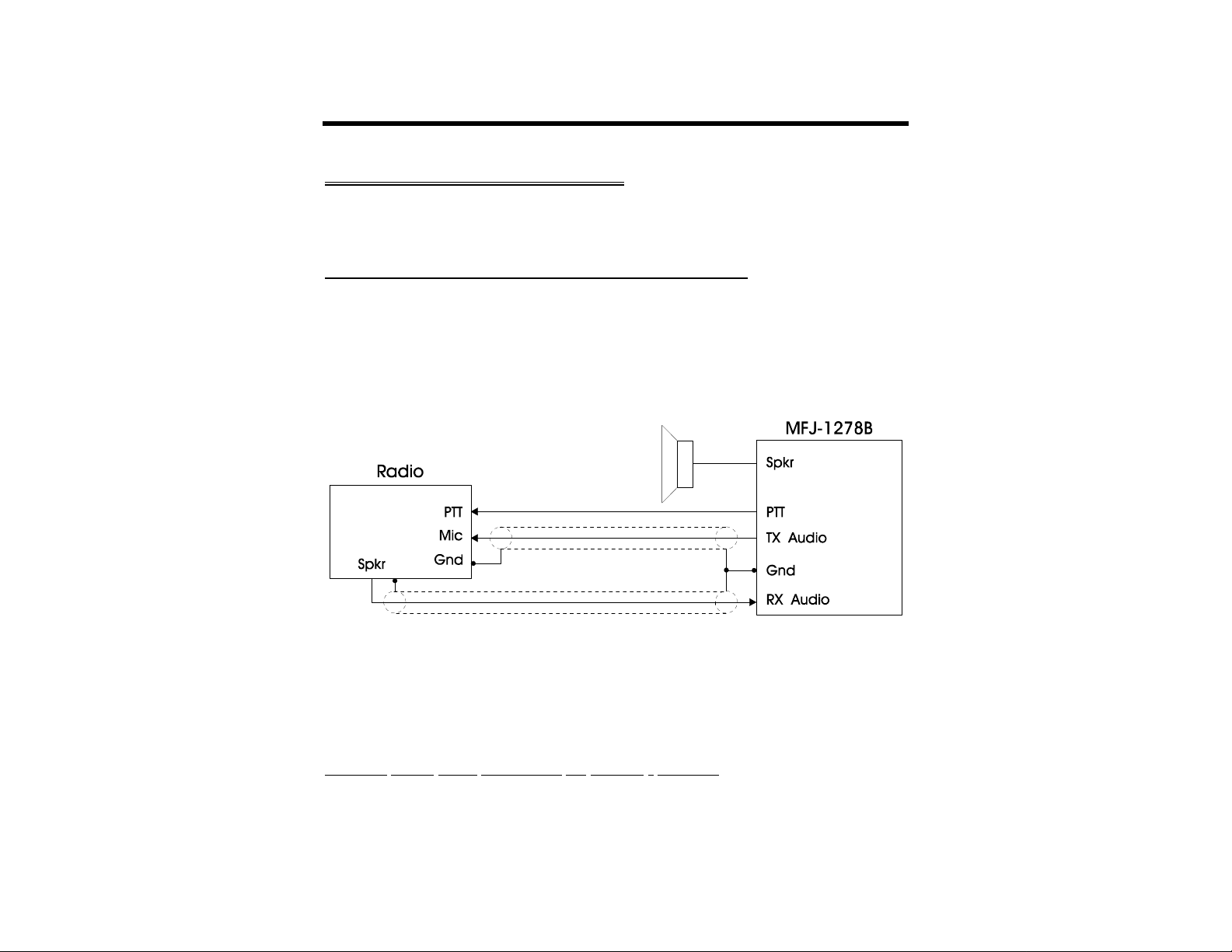
RADIO INTERFACING METHODS
The MFJ-1278B allows radio connection without any modifications to the radio or any signal
balancing devices in the cables. There are two types interfacing methods presented in this
chapter.
Method 1: Direct Connection to Microphone and Speaker
For Method 1, shown in Fig. 3-5, the MFJ-1278B's audio is fed directly into the microphone
connector or similarly connected auxiliary jack. The output of the MFJ-1278B will be
adjusted to give a proper modulation level. The receiver audio will be taken from an
earphone plug or speaker jack and fed directly to the MFJ-1278B. The user can connect a
monitor speaker to the SPEAKER jack of the MFJ-1278B. This allows you to monitor the
transmit and receive audio on the channel.
Fig. 3-5 Method One Interconnect.
The transmit audio levels for both radio ports are factory preset at 250 mV p-p to be
compatible with the mic input of most radios. However, if the transmit audio is too low or
distorted, then adjust the appropriate output level control as stated in the section. Use the
following procedure to calibrate:
Transmit Audio Level Adjustment for Method I Interface
1. Connect your MFJ-1278B and radio as shown in Fig. 3-5. Turn on the MFJ-1278B and
computer and start your terminal program. Connect the radio to a dummy load and
listen to the transmission with another nearby radio.
2. Enter the modem calibration procedure by typing
CALIBRA
Page 30

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE RADIO INTERFACING
3. With the MFJ-1278B keying the transmitter and transmitting the higher of the two
tones, adjust the transmit audio level as follows. With a small flat-tipped screwdriver,
adjust trimpot located on the left side of them MFJ-1278B (R157 for radio 1 or R158
for radio 2) while you listen to the monitoring receiver. Adjusting the trimpot CW
increases the output, while CCW decreases the output. Turn the adjustment on the
trimpot clockwise (CW) until no increase in output level is heard at the monitoring
receiver.
4. Rotate the adjustment on the trimpot counter-clockwise until the audio signal on the
monitoring receiver decreases by half of the maximum level. This can be estimated by
ear or accurately by measuring the output voltage at the transmit audio pin of the radio
port with an oscilloscope or AC voltmeter.
5. Press the K key to return to receive mode and type Q to exit the calibration routine. Be
sure to remove JMP4 if you placed it to defeat the watch-dog timer. You have now set
your transmitter deviation to approximately the correct level.
If you notice a significant hum level in the monitored audio in Step 3, take measures to
remove it. This may require shielded wire (recommended in any event) in your microphone
audio circuit. The use of shielded cable is always necessary, in projects such as this. If your
transmitter has an adjustable microphone gain control, try reducing the sensitivity of the
transmitter microphone circuit and increasing the signal level from the MFJ-1278B to
minimize hum or other noise problems.
Setting the Receiver Audio Input Level
The modem in your MFJ-1278B implements an advanced phase coherence type data carrier
detection (DCD). There is a threshold control and a sensitive tuning indicator. Together they
set the correct receive audio level for the modem, also to optimize the DCD characteristics
for the various methods of operation.
With your radio in the receive mode, open the squelch control so that a steady hiss is present
on a speaker. Set the volume control to the minimum volume position. The tuning indicator
on the MFJ-1278B should drift off to one side of the display and become stationary. It may
drift enough to disappear off the end of the display. Slowly advance the audio output level
with the volume control until the tuning indicator "springs to life" and dances around a point
near the middle of the display. This is the absolute minimum audio level for marginal copy.
Continue to advance the volume control until there is approximately twice as much audio
present at the receiver output. This can be estimated by ear or measured with an oscilloscope
or AC voltmeter. This will be near the correct amount of audio for NBFM operation. Levels
higher than this will not degrade the modem performance as long as the receiver audio
amplifier is capable of producing the chosen output level without distortion (clipping).
Page 31

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE RADIO INTERFACING
The bandwidth of the receiver audio will have an effect on modem sensitivity to false DCD.
Some receivers produce wideband audio that will NOT produce any false DCD activity
regardless of the threshold control setting. In this case, set the DCD threshold control to its
maximum clockwise rotation. This will not effect modem performance.
Method 2: Accessory Jack or Interface Box Connection
If your radio has an accessory jack with PTT, transmit audio, and receive audio signals, the
interconnection can be done through this jack (shown in Fig. 3-6).
Fig. 3-6 Accessory Jack Interface.
If your radio does not have an accessory jack and you don't wish to add a connector to your
radio, you may construct a separate external interface box. This box will permit simultaneous
connection of your MFJ-1278B and a microphone. Figure 3-7 shows a schematic of an
external interface box.
A microphone interface box similar to the one shown in Fig. 3-7 is available from MFJ
Enterprises, Inc. or from any dealer of MFJ products. The Model No. of the microphone
interface box is MFJ-1272B.
Regardless of whether you use an accessory jack or an external interface box, you should use
shielded wire for all signal carrying leads. The connectors and fittings on your radio will be
the deciding factor, as to what hardware you will need. The user may also want to refer to
Page 32

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE RADIO INTERFACING
Fig. 3-7 External Interface Box
If you built the external interface box as in Fig.3-7, then follow this procedure to adjust R(s).
1. Install JMP J on the MFJ-1278B PC board.
2. Temporarily solder a variable resistor in place of R(s) Fig. 3-7. The maximum value of
this resistor can be determined by experiment. However, a 500K resistor should be
adequate most cases. Connect your MFJ-1278B to the radio. Connect the microphone
to the radio, or to the interface box if one is being used. Connect the radio to a dummy
load and listen to the transmission with another nearby radio. Adjust R(s) for proper
modulation as the next sections describe.
Page 33

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE RADIO INTERFACING
Transmit Audio Level Adjustment for Interface Method II
1. Turn on the MFJ-1278B and computer and start your terminal program. Enter the
modem calibration procedure by typing
CALIBRA
Press the K key to key the transmitter, then tap the space bar until the higher of the two tones
is heard. Pressing the K key again will unkey the transmitter. After the transmitter has been
keyed for a few seconds, it will shut off automatically by the transmit watch-dog circuit. As
you perform the adjustments below, you will have to periodically unkey then re-key the
transmitter by typing the K key. If you wish to defeat the watch-dog timer, place a shorting
jumper at JMP4.
2. With the MFJ-1278B keying the transmitter and transmitting the higher of the two
tones, adjust the transmit audio level as follows.
3. Adjust R(s) the variable resistor installed for proper modulation level (typically between
3.0 and 4.5 kHz deviation for Amateur FM). If FM test equipment is not available,
adjust R(S) until the audio signal on the monitoring receiver is decreased by half of the
maximum level. This can be estimated by ear or accurately determined by measuring
the output voltage across the speaker with an oscilloscope or AC voltmeter. If there is
not adequate audio level from the MFJ-1278B to make adjustment of R(s), then you can
increase the output level of the MFJ-1278B by adjusting R157 for radio port 1 or R158
for radio port 2. The transmitting audio output of both radio ports is factory set at 250
mV p-p.
4. Press the K key to return to receive mode and type Q to exit the calibration routine.
You have now set your transmitter deviation to approximately the correct level.
Remove JMP4 if you placed it in Step 4.
5. Carefully remove the variable resistor and measure its value. This is the proper value of
R(S) for your particular radio.
6. Select the nearest standard value fixed resistor (1/4 watt is fine) and permanently install
this resistor as R(S) in the interface circuit.
7. If you have access to FM test equipment, check to see that the modulation level is still
within the limits of 3 to 4.5 kHz deviation. If the modulation level is not within 3 to
4.5kHz limits, then make a final adjustment with the MFJ-1278B transmit audio level
controls. These controls are R157 for Radio 1 and R158 for Radio 2.
Page 34

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE RADIO INTERFACING
Receiver Audio Setting
The modem in your MFJ-1278B is equipped with an advanced phase coherence type data
carrier detection (DCD). A threshold control and a sensitive tuning indicator is also
provided. Together these can be used to set the correct receive audio level for the modem.
These can also be used to optimize the DCD characteristics for the various methods of
operation.
With your radio in the receive mode, open the squelch control so that a steady hiss is heard
on a speaker. Set the volume control to the minimum volume position. The tuning indicator
on the MFJ-1278B should drift off to one side of the display and become stationary. It may
drift enough to disappear off the end of the display. Slowly advance the audio output level
with the volume control until the tuning indicator "springs to life" and dances around a point
near the middle of the display. This is the absolute minimum audio level for marginal copy.
Continue to advance the volume control until there is approximately twice as much audio
present at the receiver output. This can be estimated by ear or measured with an oscilloscope
or AC voltmeter. This will be near the correct amount of audio for NBFM operation. Levels
higher than this will not degrade the modem performance as long as the receiver audio
amplifier is capable of producing the chosen output level without distortion (clipping).
While still listening to unsquelched receiver noise, rotate the DCD threshold control on the
front panel of your MFJ-1278B clockwise until the DCD LED just flickers with false data
carrier indications. This control should be set to produce approximately a 10% duty cycle of
false DCD activity when receiving unsquelched NBFM receiver noise.
The modem sensitivity to false DCD will be affected by the bandwidth of the audio coming
out of the receiver. some receivers produce wideband audio which will NOT produce any
false DCD activity regardless of the threshold control setting. In this case, set the DCD
threshold control to its maximum clockwise rotation. Modem performance will not be
affected.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Harmonics Interference
If you experience harmonic interference from the crystal oscillator in the MFJ-1278B, adjust
trimmer capacitor, C47. Trimmer capacitor C47 is located near the crystal. Slowly adjust
C47 to move the frequency of the harmonic.
Page 35

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE RADIO INTERFACING
MONITOR SPEAKER CONNECTION
The MFJ-1278B has a built audio amplifier to provide audio for an external monitor speaker.
A Monitor speaker such as the MFJ-280, can be can be connected to the SPEAKER jack on
the MFJ-1278B. The MFJ-1278B requires only one speaker for RADIO 1 and RADIO 2.
The MFJ-1278B will automatically switch the monitor speaker to the radio port in use.
If wiring of a speaker plug is necessary, use a 3.5 mm (1/8") mono or stereo plug for this
connection. The tip of the plug is positive and the sleeve of the plug is negative. The tip of
the plug must be connected to the positive side of the speaker. The sleeve of the plug must
be connected to the negative side of the speaker. Note that only one speaker is needed for
both radio ports. The MFJ-1278B will automatically switch the speaker to the correct radio
port in use.
The speaker jack on the MFJ-1278B is for monitoring of received and transmitted audio
including CW side tone. The speaker is used to provide a signal to the operator when a
packet connection has been established. A small audio amplifier is built in the MFJ-1278B to
drive the external speaker. Volume of the monitor speaker is adjustable by using the
"Monitor" control on the left side of the MFJ-1278B. If the internal amplifier of the MFJ1278B does not provide adequate volume you may use an external audio amplifier.
You can disable received audio, transmitted audio or the packet connect tone from the
speaker monitor jack by cutting a trace between the pins of the following jumpers. See
Appendix G for the locations and functions of JMP jumpers:
JMP X Transmitting Audio
JMP Y Receiving Audio
JMP Z Packet Connect Tone
For example, if you like to have the packet connect tone, then leave JMP Z intact. If you do
not wish to hear the transmitted or received packet signal, then disconnect JMP X to disable
the transmitted audio and JMP Y for received audio.
Page 36

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE RADIO INTERFACING
CW INSTALLATION
The MFJ-1278B user can send and receive CW by using your computer keyboard. However,
the MFJ-1278B expands CW operating fun by allowing you to connect an iambic paddle to
the KEY input jack of the MFJ-1278B. This feature allows you to use the MFJ-1278B as a
CW memory keyer. So now the user can operate CW from either the computer or an iambic
paddle. Connect the MFJ-1278B for CW operation as follows:
Keying Connection
Connect a two-conductor shielded cable from the Keying Output jack of the MFJ-1278B to
the keying input of your radio. The keying output jacks of the MFJ-1278B accept a standard
RCA phono plug.
The keying output of the MFJ-1278B provides both the "Direct" or "Grid Block" type of
keying output for your radio. The default output setting for the MFJ-1278B is "Direct" type
keying. If your radio requires "Grid Block" type of keying, you may set the keying output to
"Grid Block" by moving the shorting jumper on JMP22 from positions 2 & 3 to positions to 1
& 2. See Appendix G at the end of this manual to locate JMP 22 on the MFJ-1278B mother
board. After properly connecting the keying cable, you must determine what kind of keying
circuit your radio has. If your radio is a solid state or cathode keyed type, then you should
use the DIRECT keying output. If your radio is tube type you should use the GRID
BLOCK keying output. If you are unsure of which output to use, try both outputs. The
keying outputs of the MFJ-1278B are diode protected. If the wrong output is used you will
notice a constant key down effect on the transmitter. The DIRECT output keys a positive
voltage to ground. The GRID BLOCK output keys a negative voltage to ground.
Key Paddle Connection
The KEY paddle input jack of the MFJ-1278B accepts a 3.5mm stereo plug. (Radio Shack
Part No. 274-284). DO NOT USE A MONO plug, IT WILL SHORT OUT THE KEY
INPUT. A two conductor fully shielded cable should be used. Wire the tip of the plug for
the dash contact and the ring of the plug for the dot contact (See Figure 3-8 below). Be sure
to use the shield of the cable for the paddle ground contact.
Page 37

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE RADIO INTERFACING
FSK CONNECTION
If your HF radio permits FSK operation, an FSK output is provided. The FSK output is at
pin 8 of the TTL port on the rear panel of the MFJ-1278B. Only two lines (Pin-8 FSK and
Pin- 3 ground) are needed in making the FSK connection to your radio. Use the 8-pin IDC
connector supplied with your MFJ-1278B to make the FSK cable. See Figure 3-9 below.
Figure 3-9 FSK Cable
Note: The factory setting of the FSK signal polarity is normal on the MFJ-1278B. If your
radio requires you to provide a reverse FSK signal you will need to relocate the shorting
jumper to position 2 & 3 of the JMP 14 header on the MFJ-1278B mother board.
Page 38

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
GETTING STARTED
This chapter will guide you through the basic operation on all the modes that the MFJ-1278B
is capable of performing. It contains the basic information required to operate PACKET,
PACTOR, RTTY, ASCII, CW, AMTOR, NAVTEX, FAX, SSTV and CW Memory Keyer.
Note: In this section you will see this symbolism, <ENTER>. This means to press the
Carriage Return or Enter key on your keyboard.
First Steps
1. Make sure that your computer is connected to the RS-232C port or the TTL port on the
MFJ-1278B according to Chapter 2.
2. Make sure that your radios are connected to the MFJ-1278B according to Chapter 3.
3. Turn on your computer. Load and run the terminal program.
4. Turn on the MFJ-1278B. The MFJ-1278B will sign on with "cmd:" prompt sign. If the
MFJ-1278B fails to sign-on, press the return key on your computer a few times in
succession, the MFJ-1278B will sign-on as as follow:
*:J
bbRAM:LOADED WITH DEFAULTS
|A
MFJ ENTERPRISES, INC.
MODEL MFJ-1278B
AX.25 Level 2 Version 2.0
Release XXXXX (date) - XX K RAM
Checksum XXX
cmd:
Note: The "|A" may display as a vertical-bar and any capital letter from "A" through "J".
The first five lines are the sign-on message, which you will normally see only when you
power up the MFJ-1278B. The Command Mode prompt, cmd: will appear when the MFJ1278B is in Command Mode. The cmd: prompt indicates that he MFJ-1278B is now ready
to accept your instructions. Upon sign-on the MFJ-1278B is in the VHF packet mode.
Before the MFJ-1278B can be fully operational, some of the basic parameters must be set.
Basic Commands
With the MFJ-1278B signed-on and in the VHF packet mode, you are ready to start setting
up the basic commands you will use. The commands in the MFJ-1278B are set to their
Page 39

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
followed by a carriage return. Now let's try entering your callsign using one of the basic
commands, MYCALL, by typing from the cmd command prompt:
MYCALL K5FLU
followed by a carriage return.
The MFJ-1278B will respond with:
MYCALL was NOCALL
cmd:
followed by the the system command mode prompt, cmd:. Of course, you should substitute
your own call sign for K5FLU. Do not forget the <ENTER> at the end of the line. Your
callsign will be used by the MFJ-1278B as its "address." The MFJ-1278B responds by
telling you the previous value of the MYCALL parameter, and gives you a new Command
Mode prompt.
Note that commands are entered by inserting a carriage return <ENTER> after each
command is typed. Note also that carriage return may also be marked as <ENTER> on some
computer keyboards.
Now try typing just the command by itself:
cmd: MYCALL
The MFJ-1278B will respond with:
MYCALL K5FLU
You can see the current value of most parameters by typing the command that sets the
parameter followed by just a <ENTER>. This verifies that the MFJ-1278B accepted your
callsign.
The next section describes the commands you will use to configure the MFJ-1278B for
proper text display for your particular computer. You may not use these commands again
unless you change computers or terminal programs.
SERIAL PORT CONFIGURATION
This section describes the commands you will use to set up the MFJ-1278B to work best with
your computer. These commands will determine how the computer or terminal and the MFJ1278B communicate back and forth. There are commands that determine how the MFJ1278B displays data on your computer or terminal screen. So let's start talking about Serial
Port Configuration.
Page 40

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
Parity and Word Length
If you are using one of the optional MFJ Starter Packs, then you should follow the
instructions given by the terminal program documentation with the starter pack. If you are
not using one of the MFJ starter packs, then you should use the following instructions to set
the parity and word length for the MFJ-1278B.
If messages from the MFJ-1278B appear garbled, with incorrectly displayed characters, you
may need to change the MFJ-1278B's serial port parity and word length. There could also be
a problem with the terminal baudrate. See Chapter 2 if the baud rate needs to be changed.
The MFJ-1278B's default value is 8 bits and no parity. If your computer receives 8 bits as
data, you may have to set space parity, since text may otherwise be interpreted as graphics or
other special characters. The Awlen and Parity commands set the word length and parity,
respectively. To set the wordlength to 8 bits, and parity to NONE, use the following
combination:
AWLEN 8 (8-bit words)
PARITY 0 (no parity bit)
For setting a wordlength of 7 bits, and even parity, set
AWLEN 7 (7-bit words)
PARITY 3 (even parity)
One of these combinations will satisfy most computers. You are more likely to require a
different setting if you have a terminal rather than a computer, or if you have configured your
terminal port for some special application.
If your computer requires odd parity, set PARITY 1. If your computer detects framing
errors, try setting
AWLEN 7 (7-bit words)
PARITY 0 (no parity bit)
for shorter characters. For longer characters, set:
AWLEN 8 (8-bit words)
PARITY 1 or PARITY 3
Echos
You may see two characters on your screen for every character you type, for example:
cmd: RREESSEETT
Your computer is echoing the characters you type, and the MFJ-1278B is also echoing them.
Page 41

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
New Lines and Line Wrapping
If everything displayed appears to be double-spaced, your computer is adding an extra
linefeed (<LF>) whenever it displays a carriage return (<ENTER>). Set AUTOLF OFF to
keep the MFJ-1278B from also adding an <LF>. If you change equipment you may have to
set AUTOLF ON to restore the MFJ-1278B's automatic linefeeds.
The screen-width parameter is set by default to 80, the width of many CRT displays. The
MFJ-1278B will send an extra <ENTER> (or <ENTER> <LF> if AUTOLF is ON) when 80
characters have been displayed on a line. If your computer does not automatically break long
lines, you will need to set the screen width to the width of your display. For example, for a
computer using a TV set for a display, you would set SCREENLN 40. If your computer
does automatically break long lines, you should set SCREENLN 0 to disable this feature on
the MFJ-1278B. Otherwise, you will get two <ENTER>s when the line wraps around.
A few computers will frequently lose the first characters of a line when several lines are typed
in rapid succession, for example, in the sign-on message. You can give the computer more
time between lines by setting NUCR ON (delay after <ENTER>), or NULF ON (delay after
<LF>). The delay is adjusted by NULLS parameter. The NULLS parameter sets a number
of character-times for the delay.
With the basic parameters set up which enable the MFJ-1278B to be able to communicate
with your computer, we can now discuss some basic functions and features of the MFJ1278B.
Page 42

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
THE MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE MODEM
The MFJ-1278B modem has five sets of pre-set modem components. These modem
components allow the MFJ-1278B to operate efficiently in its various modes of operation.
These modes of operation include VHF and HF Packet, PACTOR, AMTOR, VHF RTTY,
HF RTTY, VHF ASCII, HF ASCII, CW, Modulated CW, CW Memory Keyer, 16 gray level
FAX (including Weather FAX), color SSTV and monitoring of NAVTEX.
All modem components have been individually calibrated for each mode of operation. The
MFJ-1278B has been factory calibrated and does not require re-calibration when operating
any the operational modes.
The modes used with each modem are shown in Table 4-1. The tones and shifts produced by
each modem are shown in Table 4-2.
MODEM OPERATION MODES
P
H
V
C
M
VHF Packet, 2 level FAX
HF Packet, HF Baudot RTTY, HF ASCII, PACTOR,
AMTOR, NAVTEX
VHF RTTY, VHF ASCII
CW, Memory Keyer, Modulated CW
Multi-level FAX, Color SSTV
Table 4-1: MFJ-1278B Modem and Operation Modes
MODEM LOW TONE(Hz) HIGH TONE(Hz) SHIFT(Hz)
P
H
V
V*
C
M
* The MFJ-1278B will transmit and receive these tones when shorting jumpers for JMP E, F,
G, and H are removed on the mother board.
1100, 1200, 1300, 1500 and
1550 thru 2250 in 50-Hz steps
Table 4-2: Tones & Shifts Produced by the MFJ-1278B Modems.
1200 2200 1000
2125 2295 170
2125 2975 850
1275 1445 170
700 ---- ----
Page 43

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
OPERATIONAL MODES
Verifying Operation Status
Upon initial power up, the MFJ-1278B defaults to VHF Packet mode. The radio baud rate
defaults to 1200 baud. Radio port 1 is the default radio connection. You can verify the
operating status of the MFJ-1278B at any time by using the command MODE after the
display of the CMD: prompt. To check operation mode, type:
MODE <ENTER>
The MFJ-1278B will respond with modem status display lines followed with the cmd:
prompt.
Mode Switching With the MODE Command
Since the MFJ-1278B is a multi-mode controller, you will need to familiarize yourself with
the commands for changing operating modes from one to another.
The MFJ-1278B provides an easily used command to change the mode of operation. The
MODE command allows you to enter any operational mode. The MODE command also
enables the selection of any desired radio baud rate and modem. Table 4-3 lists the valid
codes that are used by the MODE command. The format for the MODE command is:
MODE xx,bbbb,m <ENTER>
Where xx is a 2 letter operational mode code as listed in Table 4-3, bbbb is the desired baud
rate or speed, and m is the desired modem as listed in Table 4-1. Leaving the m parameter
off of the MODE command, will cause the MFJ-1278B to select the default modem for the
selected mode using the modem as listed in Table 4-1. Most of the time, there is no need to
alter the baud rate settings, because the default settings are sufficient. So to specify HF
RTTY operation at the default baud rate of 45 baud and using the default narrow shift
modem, for example, you would type:
MODE HB <ENTER>
The user can alter any of the three parameters without having any effect on the other two.
We can change the operational mode to HF RTTY at 110 baud, just by adding the number
110 on the end of the MODE command entry. You would do this by entering the following
command:
MODE HB,110 <ENTER>
Similarly, to select the wide shift modem without changing either the operating mode or the
baud rate you would type:
MODE HB,110,V <ENTER>
Page 44

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
On the CW, MCW and Memory Keyer operation modes, instead of selecting a baud rate you
will select CW sending speed by entering a number from 5 thru 99. If you do not select a
speed, the MFJ-1278B will use the last speed selected. The default value is 20 WPM.
MODE
CODE
VP
HP
PT
VB
HB
VA
HA
AM
CW
MC
FX FAX(2-level)**
TV SSTV**
OPERATION
MODE
VHF Packet 1200
HF Packet 300 300
Pactor 100 100, 200
VHF Baudot RTTY 45 45, 50, 57, 75, 100, 110,150, 200, 300
HF Baudot RTTY 45 45, 50, 57, 75, 100, 110,150, 200, 300
VHF ASCII RTTY 110 45, 50, 57, 75, 100, 110,150, 200, 300
HF ASCII RTTY 110 45, 50, 57, 75, 100, 110,150, 200, 300
AMTOR/NAVTEX 100 100
CW/ Mem. Keyer 20 5 WPM thru 99 WPM
Modulated CW 20 5 WPM thru 99 WPM
FAX(16-level)***
Color SSTV***
DEFAULT
BAUD RATE
3(120L/M) 60, 90, 120, 180, 240, 360, 480 (LPM)
1 (8.5S) 8.5, 12, 17, 24, 36(s)
-------- Robot 72, Scotty 1, 2 Martin 1, 2
SELECTABLE
BAUDRATE/SPEED/FORMAT
300, 1200, 2400*, 9600*
Table 4-3: MODE Command Codes and Baud Rates.
* With optional internal modem
** Supported by the built-in printer port: 2-level FAX and 4-level B&W SSTV.
*** When using MFJ Multicom terminal program MFJ-1278B will support 16-level FAX
and Color SSTV.
Radio Port Switching
The MFJ-1278B provides the user with two independent radio ports, Radio 1 and Radio 2.
The MFJ-1278B selects Radio port 1 when first initialized. After receiving the cmd:
command prompt, you can select the desired radio port by typing "RAD 1" or "RAD 2"
followed by a "Return" key press.
MFJ-1278B will display a new operation status and end with cmd: prompt.
MEMORY BUFFERS
The MFJ-1278B gives you ten user programmable memory buffers. The Memory Buffers are
numbered 0 thru 9. These Memory Buffers are accessible by the BUF command. Each
memory buffer is capable of storing up to 120 characters, including puncuations. The user
Page 45

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
Loading the Memory Buffers
The ten memory buffers are empty when the MFJ-1278B is first initialized. To load the
memory buffers the user can invoke the BUF command.
To load the memory buffers, please note the example below for loading buffer 1. The MFJ1278B must be in COMMAND mode:
BUF1 The QTH here is Starkville, Mississippi. <ENTER>
Where 1 is the memory buffer number, that can range from 0 thru 9. "The QTH here is
Starkville, Mississippi," is the buffer message. Messages of up to 120 characters, including
puncuations are permitted.
Note: Notice that there is NO space between "BUF" and "1" but remember to put a space
between the buffer number and the buffer message.
Transmitting the Memory Buffers
The Memory Buffers can be transmitted by using the BUFKEY command. If BUFKEY is
left at the default value of "9," then the user can transmit any buffer (0-9) by pressing the
"TAB" key followed with a buffer number (0 thru 9). The MFJ-1278B will return to the
receive mode when finished transmitting the buffer. Users do not have to type "CTRL-R" to
go back to receive. The BUFKEY command is functional only in the CW/MCW modes.
The BUFKEY command is not valid in the RTTY or ASCII modes. In the RTTY and ASCII
modes you will press a "CTRL-T" and a buffer number to initiate a buffer transmit and you
will press a "CTRL-R" to revert the MFJ-1278B to the receive mode.
If you are using the MFJ-1278B with MFJCOM, IBM terminal program, you must change the
BUFKEY value of "TAB" (9) key to "\" ($5C) key.
Buffer Serial Numbering
If the memory buffer text includes a # sign, the MFJ-1278B will replace the # with a number.
This is performed each time the user sends the buffer. The number is the current value of the
serial number counter, SERIALNO. Once used, this serial number counter value is
incremented by one up to a maximum of 65535, where the counter rolls over to zero.
If for any reason the serial number must be changed, you may return to the CMD: command
prompt and enter the new serial number by typing:
SERIALNO ##### <ENTER>
Where ##### is the desired serial number from 0 to 65535.
Page 46

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
Memory Repeat and Buffer Repeat Time
Of the ten memory buffers provided by the MFJ-1278B, memory buffer 0 has a repeat
function. The user can enable the repeat function, moreover specify a time interval. The
BUFTIME specifies the time interval between repeats of memory buffer 0. Values from 0 to
65,535 are suitable for the BUFTIME command. The increments of the BUFTIME are in
seconds. A BUFTIME of 0 seconds represents no repeat after sending Buffer 0, thus
disabling the repeat of Buffer 0. The BUFTIME command is usable only in the CW, MCW
and Memory Keyer modes. The BUFTIME command is not effective for memory buffers 1
thru 9.
BUFTIME is the TOTAL time for one cycle of the Buffer 0 message. This means that if
your buffer message is 10 seconds long, then you must set the BUFTIME command longer
than ten seconds. So if you need to have a 5 second delay between repeats, then set
BUFTIME to 15 If you do not set the BUFTIME command longer than your message, then
the message will be repeated maybe before it is finished. This will result in incomplete copy
by the receiving station of the Buffer 0 message.
If your buffer 0 message is 10 seconds long, and you want Memory Buffer 0 to repeat every 5
seconds, under CMD: command prompt, type:
BUFTIME 15 <ENTER>
Memory buffer 0 will repeat every 5 seconds. To stop memory buffer 0 from repeating, set
BUFTIME TO 0.
If BUFTIME is a non-zero value, the MFJ-1278B will automatically release the PTT line
and revert to the receive mode between repeats. This allows you to monitor the frequency,
possibly for a reply message. If uninterrupted during the pre-set delay time, then the MFJ1278B will continuously repeat buffer 0, until BUFTIME is set to non-zero value.
Chaining the Memory Buffers
Chaining of the ten memory buffers in order is possible. This enables the transmitting of the
buffers in any order. For example, you may transmit memory buffers 0, 2, and 5 respectively
in one transmission. To achieve this, you should program the message in memory buffers as
follows from the cmd: prompt type:
CMD: BUF0 XXXXXXXXXXX....XXXXX CTRL-T 2 <ENTER>
CMD: BUF2 XXXXXXXXXXX....XXXXX CTRL-T 5 <ENTER>
CMD: BUF5 XXXXXXXXXXX....XXXXX <ENTER>
Where XXXX is the desired text you wish to program into the memory buffers.
Page 47

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
Note: If BUFTIME is a non-zero value, MFJ-1278B will automatically release the PTT line
and revert to the receive mode between repeats. This allows you to monitor the
frequency for any replies to your message. If the MFJ-1278B is not interrupted
during the pre-set delay time, it will continually repeat until buffer 0 is interrupted.
TUNING INDICATOR
Your MFJ-1278B comes equipped with a very accurate and sensitive tuning indicator. The
tuning indicator is extremely useful not only for tuning to signals for optimum reception, but
also for filter alignment and audio level indication.
The position of the tuning indicator LED is only meaningful for tuning a signal under the
following conditions:
1. The station is transmitting data (both tones NOT just a single carrier).
2. The DCD LED is lit indicating that the signal is within the capture range of the PLL
demodulator.
3. That there is sufficient audio output from the receiver for proper operation of the
demodulator.
If the conditions above are met, tuning in a station with the tuning indicator is quite simple.
Just set the receiver frequency so that the tuning indicator LED is centered in the display.
Actually there are 2 LEDs which represent the center of the display. Either or both may be
used. The use of the tuning indicator will be further discussed later in each mode of
operation.
Page 48

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
PACKET OPERATION
VHF Packet
If you are not familiar with packet operation, then you can learn quite a bit about it with the
MFJ-1278B without transmitting anything. For your first experiments, the MFJ-1278B will
be "talking to itself," allowing you to become familiar with it before you go on the air.
If you are already familiar with the packet operation, then you may not want to perform this
exercise. In this case go the other modes of operation in this chapter.
Disconnect your radio from the MFJ-1278B and turn off the MFJ-1278B. Install the digital
loopback jumper, JMP10. Do not install the analog loopback jumper JMP7 while JMP10 is
in place. Connect your computer to the MFJ-1278B with your serial cable. Turn on the
computer and start your terminal program.
A Connecting and Disconnecting Exercise
A connect sequence initiates all Packet radio QSOs. The connect sequence sets up the
"handshaking" between the two stations that ensures error-free communications. A
disconnect sequence terminates all Packet radio QSOs. The disconnect sequence leaves both
stations free to start new Packet QSOs. Packet QSOs can also make use of digipeaters, other
packet stations that can automatically relay packets from one station to the other over a
specified route.
To see how this works, you can have the MFJ-1278B connect to itself. Since you have set
the MFJ-1278B up for digital loop-back, it will receive all packets that it sends. Try the
following:
cmd: FULLDUP ON
cmd: CONNECT K5FLU
*** CONNECTED to K5FLU
replacing K5FLU with your own call sign. The MFJ-1278B generates packets initiating and
confirming the connection. The packets are not actually converted to audio signals and
transmitted over the radio, but they are otherwise just like packets you will be transmitting
later on.
The *** CONNECTED to message tells you that the connection was successful. You
should also notice that the CON LED has lit up and that you do not see a new cmd: prompt
on the next line. You are now in Converse Mode, ready to start talking. Try it.
Page 49

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
The <ENTER> causes your message to be put into a packet, or "packetized," and transmitted.
(We explain in the next chapter how you can use a different character to send packets.) The
underlined text is a message that the MFJ-1278B received in a packet and displayed.
Whenever you are in Converse Mode anything you type will be assembled into a packet
addressed to the station you are talking to and transmitted. If there is not a QSO (connection)
in progress, the packet will be sent to the address CQ.
In the example above, the MFJ-1278B entered Converse Mode automatically after the
connect took place. You can also command the MFJ-1278B to move back and forth between
Command Mode and Converse Mode.
To return to Command Mode, you must enter a special character, Control-C (abbreviated
<CTRL-C>), or else send a BREAK signal. "Control" characters are usually entered by
holding down a special control key and then typing another key without releasing the control
key. If your keyboard does not have a key marked CTRL or something similar, consult the
documentation for your computer or terminal program to see how to enter control characters.
A BREAK signal is a special transmission (not an ASCII character) which your computer
may be able to produce.
NOTE: If <CTRL-C> will cause your computer to do something to interfere with packet
operations, such as halting the terminal program, and you can't send BREAK
signals, you will have to change the character that returns you to Command Mode.
See the section on "Special Input Characters," below.
Now type a <CTRL-C>. The MFJ-1278B does not echo the <CTRL- C>, but you should
immediately see a Command Mode prompt. To return to Converse Mode, enter the
command CONVERS:
<CTRL-C>
cmd: CONVERS
Whatever I type in Converse Mode is transmitted.
Whatever I type in Converse Mode is transmitted.
<CTRL-C>
cmd:
To terminate the QSO, you must end the connect by giving the DISCONNE command. The
MFJ-1278B will transmit packets terminating the conversation and notify you when the
disconnect is complete:
cmd: DISCONNE
*** DISCONNECTED
An actual QSO might be terminated by the other station, of course. In that case, you would
Page 50

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
Be sure to remove the jumper from JMP10 after you complete this "Connecting and
Disconnecting Exercise".
Digipeating
You may wish to have a QSO with another packet station that is beyond your direct radio
range. If a third packet station is on the air and both you and the station you want to talk to
are in range of this third station, that station can relay your packets. You set up the packet
routing when you initiate the connection. The MFJ-1278B will then automatically include
the routing information in the packets it sends.
The diagram below shows Example 1 situation in which digipeating is useful.
AD7I
/ \
N2WX ________ / \_________ K5FLU
You are station K5FLU, and you want to have a packet QSO with N2WX. There is a
mountain in the way and you are not in simplex range of each other. However there is a
station located on the ridge, AD7I, which is in range of both you and N2WX.
You direct the MFJ-1278B to set up a connection to N2WX using AD7I as an intermediate
digipeater as follows:
cmd: CONNECT N2WX VIA AD7I
You can specify a routing list of up to eight intermediate stations. Consider Example 2
below, as a modification of Example 1 above:
____
/ \
N2WX ________/ \_________ K5FLU
. .
. .
KV7D. . . . . .NK6K
AD7I has turned off his station, but you can contact N2WX by going around the mountain
through NK6K and KV7D. This time you issue the connect command like this:
cmd: CONNECT N2WX VIA NK6K, KV7D
You specify the digipeaters in the order you would encounter them going from your station to
the station to which you wish to connect.
Page 51

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
Unsuccessful Connections
Sometimes you will initiate a connect sequence that can't be completed. The station may not
be on the air, or it may not be within range of your station. You may have even mis- typed
the other call sign. If the MFJ-1278B does not get a response to its first connect packet, it
will try again. You can control the number of attempts the MFJ-1278B will make with the
command RETRY. The default number of retry attempts is 10. If the MFJ-1278B does not
get an answer after this number of transmissions, it will give up and display the message:
*** retry count exceeded
*** DISCONNECTED
The retry count is also used once the QSO has started. Each transmission sent to the other
station is "acknowledged," or ACKed by the other station, and vice versa. The ACK means
that the packet was received and that the CRC checksum indicated that it was received
without errors. This is the means by which packet radio can ensure error-free
communications. Sometimes a packet will not be received correctly by the other station,
either because of accidental interference from another packet station (a collision), or because
of other channel noise.
If the MFJ-1278B does not get an ACK soon enough, it retransmits the packet and
increments the retry count. If the count set by RETRY is exceeded, the MFJ-1278B will
automatically disconnect and display the same message:
*** retry count exceeded
*** DISCONNECTED
The automatic disconnect feature keeps a MFJ-1278B from indefinitely retransmitting a
packet and tying up the channel under hopeless conditions. For example, an intermediate
digipeater might have been shut down, or the RF channel might have deteriorated to the point
of being unusable. The other operator might have even turned off his station without
disconnecting. If you are operating under special conditions, such as a marginal HF channel,
you can set RETRY 0 to disable all automatic disconnects (the retry limit is never reached).
Monitoring Channel Activity
The MFJ-1278B can monitor packet activity on the channel while connected to another
station. You can "read the mail," displaying packets between other stations. The MFJ1278B will also keep track of stations heard during a session. This section will describe
some of the monitor functions.
Monitoring is enabled or disabled by the MONITOR command. You can try this out in
digital loop-back mode while disconnected. Type:
cmd: MONITOR ON
cmd: CONVERS
Page 52

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
Since you are not connected to another station your packets are sent to the address "CQ," i.e.,
anyone. The packet you sent was "heard" by the MFJ-1278B and displayed, along with the
sending station and the destination.
If you also want to see any intermediate digipeater stations being used, you can set MRPT
ON. This feature would be useful if you later want to connect to one of the stations you are
monitoring and will need a digipeater route in order to reach it. For example, you might see
the following display:
WB6YMH>WD0ETZ,KV7B:Hello, Bill!
This packet was sent from WB6YMH via KV7B to WD0ETZ.
If there are several digipeaters, or if the message lines are long, the display may be difficult to
read. The HEADERLN command can make reading the displayed information much easier.
You can put the address header on a separate line from the text by setting HEADERLN ON:
WB6YMH>WD0ETZ,KV7B:
Hello, Bill!
Ordinarily, the MFJ-1278B will stop displaying monitored packets if you connect to another
station, permitting you to converse without interruption. The reason for this is that the setting
of the MCON command. The MCON command is defaulted to the OFF state. If you want to
monitor activity while connected to a packet station, set MCON ON.
While the MFJ-1278B is monitoring the packet frequency, it is keeping a record of all the
stations heard. These stations are recorded into the MHEARD log or list. To display the list
of stations heard since the last time your MFJ-1278B was powered up, type the following
from the cmd: prompt:
MHEARD <ENTER>
the MFJ-1278B will respond with a l,ist of stations much like the example below:
AD7I
WA7GXD
N2WX
NK6K
KV7B*
followed by the cmd: prompt. The last several stations whose packets were heard by your
MFJ-1278B are displayed. The entry "KV7B*" means that KV7B was heard digipeating a
packet rather than sending one of his own. You can clear the "heard log" with the
MHCLEAR command.
Page 53

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
Your First Packet QSO
Although there are still a number of features you should be familiar with, you are probably
eager to get on-the-air and try out your new MFJ-1278B. Arrange to have another packet
operator get on the air to help you get started. Make sure that your friend will be close
enough to ensure solid copy, with no FM "popcorn" noise.
It's best if you can get an experienced packet operator to help you get started. If you are both
beginners, try to have both stations in the same room and operate on low power or into
dummy loads.
The first step in starting packet radio operating is to remove the shorting jumper from Digital
Loopback header, JMP10. Connect your radio to the MFJ-1278B. Turn on your computer,
the MFJ-1278B, and your radio. Be sure you have adjusted the MFJ-1278B and radio
according to one of the methods described in Chapter 3. When the other station transmits,
the DCD LED on the MFJ-1278B should glow steadily for the duration of the transmission.
You can work through the remainder of the examples in this chapter while you try out the
MFJ-1278B on the air.
Starting the QSO
Once you have the MFJ-1278B connected to your radio, you are ready to initiate a connect.
For the sake of example, we will continue to use K5FLU in place of your call sign, and we
will use WB0QRP for your friend's call. Make sure you are in Command Mode, and type:
cmd: CONNECT WB0QRP
After a moment you should see the message:
*** CONNECTED to WB0QRP
and you will be in Converse Mode. Your friend will see the message:
*** CONNECTED to K5FLU
and he will also be in Converse Mode. You have just begun your first packet QSO.
If you have trouble connecting, make sure your microphone drive level is set properly, as
described in Chapter 3. It may be helpful to have an experienced packet operator monitor
your transmissions with his TNC. You can also try the following procedure:
a. Both you and your friend should set MONITOR ON.
b. Enter Converse Mode and send some packets.
c. Each station should display packets sent by the other. If only one station is
"hearing" properly, you can concentrate on the modulator and transmitter of
that station and the demodulator and receiver of the other station. You can try
experimenting with the TXDELAY timing command for the sending TNC.
Page 54

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
Exchange several messages to get a feel for this new mode. If you monitor the radio transmit
indicators and listen to the speaker audio from the two rigs, you will have a better idea of
what is happening. Your radio will be inactive most of the time, even while you are actually
typing. When you come to the end of a line while typing, press the <ENTER> to send the
data to the MFJ-1278B. The MFJ-1278B will key the radio briefly, after it receives the data
you typed. When the MFJ-1278B keys the radio, data will be sent to the radio, and your
friend will hear a "brrraaappp" sound on his speaker. As your friends TNC displays your
message on his screen, his radio will key for even a shorter time. When your friends TNC
sends data back to your station, you will hear a short "brrapp" sound on your speaker. The
short "brrapp" sound on your speaker is an ACK, or packet acknowledgment. The MFJ1278B takes note that the packet was received correctly, but nothing is displayed on your
screen.
Digipeating
Now that you are on the air, you and your friend can try out the MFJ-1278B's digipeating
capabilities. This is actually more interesting if you have at least three stations participating,
but you can get the feel for it with two stations.
Return to the Command Mode and disconnect from the other station:
<CTRL-C>
cmd: DISCONNE
*** DISCONNECTED
Now issue the following command.
cmd: CONNECT K5FLU VIA WB0QRP
As before, substitute your call for K5FLU and your friend's call for WB0QRP. You are
requesting a connect to yourself, as you did before in digital loop-back mode, but this time
you are using a sort of RF loop-back. You transmit packets to your friend's TNC, which
relays them back to you. When the connection is established you will see
*** CONNECTED to K5FLU VIA WB0QRP
and you will be in Converse Mode. Your friend will not see anything displayed on his
computer and his TNC's state will not be affected at all by your QSO. In fact, your friend
could issue this connect request,
cmd: CONNECT WB0QRP VIA K5FLU
and you can carry on two separate conversations completely independently. Monitor the
radio transmit indicators and listen to the speaker audio. See if you can follow the packets
and the acknowledgments back and forth.
Page 55

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
Monitoring on the Air
This is a good time to try out the MFJ-1278B's monitor functions. While you and your friend
are separately connected, type
<CTRL-C>
cmd: MONITOR ON
cmd: MCON ON
cmd: CONVERS
You will be able to see both your "conversation" and your friend's conversation. Also try
HEADERLN ON and MHEARD.
Special Input Characters
The MFJ-1278B has a number of special characters that can be used to control its actions.
Many of these special characters can be used to "edit" commands and packet text as they are
entered. These features can all be customized to suit you and your computer. Most of the
special input characters we will describe are active in both Command Mode and Converse
Mode; the exceptions will be noted.
The character used to return to Command Mode from Converse Mode is by default a
<CTRL-C>. (Sending a BREAK signal also works.) This character does nothing in
Command Mode, so if you accidentally enter it twice you will not mess up the next command
line. You can change the Command Mode entry character with the command COMMAND.
This is one of several commands that set special character functions. You can choose any
character for this function, by entering the ASCII character code for the key. For example,
you can use a <CTRL-E> to enter Command Mode by setting
cmd: COMMAND 5
was $03
The MFJ-1278B displays the previous value in hex, and you can also enter character codes in
hex if you prefer. All of the special characters described below can be changed in the same
way as COMMAND.
We have already mentioned that you can erase mis-typed characters by typing the
<BACKSPACE> character. You can change this character with the command DELETE. If
you set DELETE ON, you can erase characters by typing the <DELETE> character; setting
DELETE OFF returns to using <BACKSPACE>. You will probably want to use the same
key that your computer normally uses to rub out characters. <BACKSPACE> is more
commonly used than <DELETE> by personal computers.
If you are not sure whether your rubout key produces <DELETE> or <BACKSPACE>
Page 56

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
If you make several mistakes in a line, or if you change your mind, you may want to cancel
the whole line rather than rubbing out the characters one at a time. You can cancel the line
by typing <CTRL-X>. The MFJ-1278B will display a <BACKSLASH> followed by a
<ENTER>. If you are in Command Mode, you will see a new prompt:
cmd: Hi, John, how are you?<CTRL-X>\
[You started typing text while in Command Mode.]
cmd: CONVERSE
Hi, John, how are you?
The cancel-line character can be changed to any ASCII character by the command
CANLINE.
If you have changed your input by rubbing out and retyping characters, you may want to see a
"fresh" copy of your input, especially if you have set BKONDEL OFF. The MFJ-1278B
will retype the line you are entering when you type <CTRL-R>:
cmd:CONNECT KB7\\\WA7<CTRL-R>\
[You mis-typed the call sign.]
cmd:CONNECT WA7GXD
Here the user mis-typed the first three characters of the call sign and rubbed them out. The
MFJ-1278B displayed "\" for each character rubbed out. The user then retyped the characters
correctly and redisplayed the line. He finished typing the call sign on the new line. The
redisplay-line character can be changed to any ASCII character by the command
REDISPLA.
If the MFJ-1278B displays information faster than you can read it before it scrolls off the
screen, you can halt the display by typing <CTRL-S>. To resume output from the MFJ1278B to your computer, enter <CTRL-Q>. These characters can be changed to any ASCII
character by the commands STOP and START, respectively.
You may occasionally want to include one of the special input characters in a packet. For
example, to send several lines at once in the same packet, you would have to include
<ENTER> in the packet at the end of each line, bypassing its "send-packet" function except
at the actual end of the packet. You can include any character in a packet including all
special characters by prefixing it with the pass character, <CTRL-V>. For example,
I wasn't at the meeting.<CTRL-V><ENTER>
What happened?
Ordinarily, this message would be sent as two packets. By prefixing the first <ENTER> with
<CTRL-V>, the operator sends it all at once, but maintains the <ENTER> in the text. The
Page 57

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
BASIC HF PACKET OPERATION
The requirements for optimum performance with a typical HF or OSCAR 10 path are very
different compared to local VHF FM environment. Lower signal to noise ratios require lower
baud rates, noise spikes and fades require shorter packet lengths, and a higher rate of false
carrier detects lowers the total usable dynamic range in the audio input. The MFJ-1278B
hardware and software improves throughput in the noisy and fading HF environment. The
setting of the MAXFRAME and PACLEN commands in the MFJ-1278B, provide the
possibility of several continuous frames of long data length. For HF operation at 300 baud,
we recommend setting MAXFRAME to 1. Depending on HF band conditions a setting of
128 or less for the PACLEN command.
The MFJ-1278B detects a busy channel by monitoring the lock- detect signal from the
demodulator. The presence of a lock-detect signal is indicated by the Data Carrier Detect
(DCD) LED. Each time DCD goes off the MFJ-1278B will start a DWAIT interval which
must elapse before the channel is considered to be available. On a noisy channel spurious
lock-detect signals may be generated. For HF and OSCAR operation you should set DWAIT
to 0. The random wait before retry transmissions can be disabled by setting TXDELAY 0
and using AXDELAY to set the required keyup delay. Of course, AXHANG should be 0 for
this application.
If you are operating a full-duplex radio station (simultaneous transmit and receive) such as an
OSCAR 10 station, you should set FULLDUP ON. The MFJ-1278B is always electrically
capable of full duplex operation, but this parameter causes the protocol to behave differently
in acknowledging packets. In addition, the MFJ-1278B will ignore the state of the DCD line.
Although intuition tells you that lower baud rates will reduce the number of packet retries,
there is usually a small range between "too fast" and "too slow." A slower packet takes
longer to transmit and is therefore a larger target for fades and static crashes. The entire
packet must be received correctly in order to be accepted. Data rates of 1200 baud have been
used on both HF and through OSCAR 10.
HF activity may generally be found on 7.090 to 7.106 or 14.090 to 14.107 MHz. Use LSB or
USB - it really does not matter (although most stations use LSB when referring to the
suppressed carrier frequency).
Tune through a few packet signals. Tune slowly! You will find a point at which the display
becomes bright. As you continue tuning, you will see the moving bar display slide across
your tuning indicator. When one of the center LEDs is illuminated, you are tuned in and you
should be able to copy the packets.
Page 58

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
If you cannot contact anyone using another frequency, call CQ on one of the above
mentioned frequencies. If you do make a contact with someone, then QSY immediately
after establishing contact! Be careful on 20 meters especially that you don't operate +/2KHz around 14.100 MHz (you will cause interference to propagation beacons and give
packet a bad name...).
HF Packet Operation Hints
There are a few operating hints which apply to HF Packet. These few hints are listed below:
1. Try to keep all packets below 80 characters in length.
2. Set MAXFRAME to 1. This will minimize transmission time.
3. Avoid multiple connections and digipeated packet operation.
4. Qsy away from the standard calling frequencies as soon as possible.
5. Set FRACK to a sensible long value.
For more details on HF packet operation please refer to the next chapter in this instruction
manual.
Page 59

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
PACTOR
In this section of this manual we will talk about PACTOR operation. We will cover basic
operation along with an explanation of the commands related to PACTOR, including the
new Pactor Mailbox. Before we talk about Basic Operation, let's explain a little about
PACTOR.
NOTE: Pactor operations apply to the Model MFJ-1278B or MFJ-1278 TNC2 only. The
MFJ-1278 must have the MFJ-56A, B, or C installed to take advantage of the Pactor option.
What is Pactor?
PACTOR is a new form of digital communications. PACTOR was brought about to
compensate for the shortcomings in both Packet and Amtor, for HF operation.
PACTOR combines some of the features of both the AMTOR and the HF Packet modes.
Pactor retains the short frame sizes and synchronous transmission format of AMTOR. It also
allows the data flexibility of which Packet users have grown accustomed to.
The radio used for PACTOR HF operations must be capable of switching between transmit
and receive modes in 130 milliseconds. A radio capable of operating in the AMTOR mode
will operate well in the PACTOR mode as well.
Now that we have explained a little about PACTOR, let's get into the Basic Operation.
PACTOR Operation
The PACTOR operation section will deal mainly with PACTOR operations. We will briefly
explain about the different operating modes and what they will do. We will explain about the
new PACTOR mailbox feature and how it works. There are also several operational
commands that are related to Pactor operation. These operational commands are explained in
Chapter 6 in detail. So without any further delay here we go into PACTOR Operation.
First we need to get the MFJ-1278B to sign-on. To sign-on the MFJ-1278B please perform the
following:
1. Verify the power switches to both the computer and the MFJ-1278B are OFF.
2. Connect the MFJ-1278B to both the radio and the computer.
3. Connect the radio to a dummy load.
4. Set the POWER switch on the computer to the ON position, then load the terminal
program.
Page 60

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
Now that we have the MFJ-1278B signed-on to the computer, let's put it into the PACTOR
mode.
To put the MFJ-1278B into PACTOR mode, please type the following:
MODE PT <ENTER>
The MFJ-1278B will respond with:
[MFJ PACTOR $2c-1022 free]
p_cmd:
At the above prompt, you are in the PACTOR mode. Any commands entered such as
TXDELAY or ECHO, will only affect the PACTOR mode. Many of the commands of
PACTOR have the same name as the general commands but DO NOT share the same
parameters. At the p_cmd: prompt, you can monitor AMTOR ARQ requests to your
SELCALL, PACTOR ARQ requests, and PACTOR FEC.
Enter your call in the MYCALL parameter (up to 8 characters). The format of the MYCALL
command is as follows:
MYCALL n <ENTER>
where n is your amateur callsign up to 8 characters.
FEC Unproto operation
There are two FEC modes, 100 baud and 200 baud. Properly tune the radio before entering
either of the FEC modes. The reason for this is as soon as you initiate an FEC unproto mode
the radio will start transmitting immediately. To initiate 100 baud FEC, please type the
following from the p_cmd: prompt:
U1 <ENTER>
The cursor will go to the next line. At this point start typing whatever you want. You
normally issue your CQ's in FEC mode. Someone will see your FEC mode CQ's and
probably try to "connect" with you.
To terminate an unproto session type a CTRL-C followed by the letter D and the <ENTER>
key. This is done after sending CQ or when terminating a Pactor contact. If the standard D
command does not work, then use the DD command to terminate the unproto session.
The situations in which the two FEC modes are different. Generally, the U1 or 100 Baud
FEC mode is for use in normal HF band conditions, while the U2 or 200 Baud FEC mode is
for use in clear HF band conditions. Your transmitter must be capable of transmitting 100%
duty cycle. Because when transmitting PACTOR FEC, you are ALWAYS transmitting a
signal- just like RTTY.
Page 61

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
PACTOR ARQ
For ARQ operation you will need to know the other person's callsign. Normally you can get
the other person's call by monitoring the channel for connect requests or other ARQ contacts.
To establish contact with another station, you must be at the p_cmd: prompt. To initiate a
connect sequence, please type the following:
C n <ENTER>
where n is the CALLSIGN of the station you want to connect with. The callsign is not to be
over eight characters in length. Again, properly tune the radio, because you will immediately
start transmitting packets.
When a station is over 40,000 Km away, the LC command should be used. The LC is the
abbreviation for Longpath Connect. To initiate a Longpath Connect sequence, please type
the following:
LC n <ENTER>
where n is the CALLSIGN of the station you want to connect with. Callsigns are not to be
over 8 characters in length. Again properly tune the radio, because you will immediately start
transmitting packets. If the C command does not work, the LC command might. Generally,
if one command works the other will not.
Changeover
In AMTOR the changeover (from TX to RX) command is +?. In PACTOR the changeover
command is CTRL-Y, i.e, hold down the CTRL key then press the Y key. The changeover
character can be re-defined with the CHOCHAR command. How the CHOCHAR character
is re-defined will discussed later. When in Pactor Mailbox operations, the changeover is
semi-automatic. The remote user must issue a manual changeover, CTRL-Y, when talking
to the Pactor Mailbox. The Pactor Mailbox always issues an automatic changeover, when it
is finished sending its information back to the remote user.
To terminate an ARQ contact, type CTRL-C, then D, then <ENTER>. This will cause a
graceful disconnect at the other end. If you do a "dirty disconnect" or DD, the other Station
will still be trying to acknowledge your packets. The use of DD automatically tears down the
contact and does not wait for acknowledgments from the other station. The use of the DD
command is considered bad manners. Always do a D disconnect, if possible.
Monitoring
While in the PACTOR mode, you are always in Listen mode. There is no listen command in
the Pactor protocol. Therefore you do not need to issue listen command just to listen on a
Page 62

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
controller switches to 200 baud you may have more retries on a noisy channel. It's better to
information how the CON and STA leds react to incoming signals please refer to the chart on
Page 30 of this chapter..
Monitoring AMTOR ARQ requests
AMTOR ARQ requests monitored while the MFJ-1278B in PACTOR mode. If the
controller detects your selcall in an AMTOR ARQ request packet, the controller will switch
to AMTOR and try to establish the link. This feature allows someone who doesn't have
PACTOR capability to connect to you in AMTOR mode. Upon termination of the link, the
MFJ-1278B will switch back to the PACTOR. The a_cmd: is active when the MFJ-1278B
switches to the AMTOR operation. When the MFJ-1278B switches back to the PACTOR,
you will see the p_cmd: prompt again.
Exiting PACTOR Mode
To exit the PACTOR mode, please type CTRL-C and the p_cmd: prompt will appear. Once
the p_cmd: prompt is on the computer screen, type the following:
EXIT <ENTER>
the MFJ-1278B will respond with the standard cmd: prompt. Once back at the cmd: prompt
you can go to any other mode by use of the MODE command as discussed earlier in this
instruction.
Operating Hints
Threshold Control Setting
Adjustment of the Threshold control on the MFJ-1278B is critical during PACTOR operations.
Adjust the Threshold control until the DCD lights with each received packet and goes out when
not receiving. If the threshold control is improperly adjust, communications will not be good.
This could result in the inability to make a contact or monitor a PACTOR conversation.
TXDELAY (TXD)
Timing in PACTOR is more critical than any other mode. This is where the TXDELAY or
TXD command comes into play. The TXDELAY command is one of the more critical
parameters. If you are having problems connecting, try adjusting TXD a little higher than the
default value of 2. This is especially good practice on the lower frequency bands such as 80
meters. A typical setting for 80 meters may be 4 or 6. The setting of TXDELAY is also
dependent on the time required for the radio to switch between transmit and receive.
NO200
If you turn the parameter NO200 to ON, the MFJ-1278B will stay in 100 baud. For noisy band
conditions setting NO200 to ON may get your data through quicker. This is because if the
Page 63

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
As indicated in the preceding paragraph, the usual terminal/radio/modem parms are available.
As in Packet, Pactor also contains COMMAND and CONVERSE modes. Please note that
switching between them is modeled on the "NEWMODE ON" procedures in packet. The MFJ1278B is in COMMAND mode, if the p_cmd: prompt is on the computer screen. To switch
to CONVERSE mode from COMMAND mode the K key followed by an <ENTER> is issued
by the user. The CMDCHR character switches the MFJ-1278B from CONVERSE mode
back to COMMAND mode. The CMDCHR character is defined as CTRL-C. Once
connected, the link acts much like AMTOR.
The station originating the connection is the master and he remains in transmit mode until he or
the slave initiates a changeover. Either station may reverse the direction of the link by issuing
a control-Y changeover (^Y) in converse mode.
PACTOR FEATURE DEFINITIONS
DIGITAL MEMORY ARQ
The MFJ-1278B's Pactor incorporates a Digital Memory ARQ mode. Digital Memory
ARQ enables reconstruction of a good packet from a bad packet. A bad packet is one
repeatedly received with on or more bit errors. Digital Memory ARQ accumulates the bit
value, 1 or 0 derived from the RF port during successive reception of the same error-laden
packet. These bit accumulations are sent to the receiver shift register. Thus a good packet is
reconstructed from 2 or more "bad" packets.
The MAXSUM parameter controls the number of accumulations performed for each bit.
Larger MAXSUM values increase the effectiveness of the Digital Memory ARQ scheme, but
only to a certain point. The reception of an almost perfect packet will be inadequate to
overcome the accumulated noise, if MAXSUM is too large. Also the presence of excessive
QRM, QRN, or QSB effects the reception of good packets. On the other hand, if MAXSUM is
too small the accumulation of samples will be too few to correct for moderate error rates. The
factory setting for MAXSUM represents a good compromise--feel free to play with it.
FEC UNPROTO
Unproto: "FEC/UNPROTO" packets are transmitted UREPEATS+1 times. Selecting larger
values of UREPEATS reduces throughput, but enhances reliability. To transmit in UNPROTO
mode, issue the appropriate unproto command and type away. When done, break out to
"p_cmd:" mode and type 'D' or 'DD' to terminate transmission.
MONITORING
Monitoring unproto: If MONITOR is ON the MFJ-1278B is always in listen mode,
Page 64

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
while entering commands at the "p_cmd:" prompt.
To prevent Uncontrolled Disconnects, we are unable to listen to all kinds of third party Pactor
transmissions for (WAIT x Cycle_Time) seconds after receiving the other side's last
disconnect. This includes all unproto and connected packets, along with connect requests. The
actual cycle time is 1.25 or 1.4 seconds.
CONNECT
[Connect] message: The MFJ-1278B monitors connect attempts received from other
station's with a message containing the called station's callsign when idle. To successfully
monitor a connect attempt to someone else, the called callsign must be at least 4 characters
in length, and the signal be of sufficient quality that the 200 baud area be error-free when
received. Unfortunately, the callsign in the connect-attempt packet (unlike all other
monitored data) is subject to corruption; the Pactor protocol did not provide for error- free
connect packets. Therefore, you may at times see a garbled callsign in a [Connect] message,
but it should be rare. Remember, this "garbling" affects only monitored connect-attempt
packets. It does NOT affect ARQ or FEC data packets because they are error-protected by a
sophisticated CRC checking scheme.
SPEEDup/SPEEDdown
Speedup and speeddown: When the MFJ-1278B is the receiving station or IRS, and after
four consecutive failures to receive a 200 baud packet the TNC requests a SPEEDDOWN to
100 baud. A SPEEDUP occurs when the MFJ-1278B receives 10 error free 100 baud
packets. If NO200 is set to ON all SPEEDUP requests are inhibited
Bad band conditions: During poor band conditions links will be quicker by avoiding use of
the 200 baud mode. Setting NO200 to ON instructs the MFJ-1278B to avoid 200 baud
operation in a compatible way.
AUTOMATIC ON-LINE COMPRESSION
Huffman coding: Huffman coding offers somewhere between 2:1 and 4:1 compression on
lower case German and English plain text. In receiving modes, conversion to 8 bit data is
automatic.
On transmit, the MFJ-1278B packetizes outgoing data and transparently selects the mode.
Huffman coding will be used if a) all data are 7 bit ASCII characters, and b) Huffman
coding is at least as efficient as straight 8-bit coding.
FLOW CONTROL
Flow control: Hardware flow control is always on. Software flow control defaults to on
using the XON and XOFF parameters. Unlike TNC operations, the same characters are used
for receive flow control as for transmit flow control. Type-in flow control is only effective
Page 65

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
AMTOR selective callsign in the "a_cmd:" MYSELCAL parameter. Furthermore, you must
have the appropriate sideband, usually, LSB selected because unlike PACTOR, AMTOR is
polarity dependent.
Amtor Detection in Pactor
The MFJ-1278B's Pactor continuously monitors the channel for Pactor packets, and for
AMTOR call packets that match your AMTOR SELCALL. When PACTOR hears your
AMTOR SELCALL, the TNC enters the "a_cmd:" AMTOR mode in an attempt to complete
the link. After entry into the AMTOR mode the MFJ-1278B will automatically return to
Pactor mode if the link is not established within 30 seconds. If the link is established, the
MFJ-1278B remains in AMTOR mode for the duration of the contact, and for an additional
30 seconds after the link terminates.
PACTOR STATUS INDICATORS.
While in the PACTOR mode of operation, you have PACTOR mode Status Indicators
avialable to you. These Status Indicators are comprised of the CON and STA leds. These leds
react in different ways according to what is happening. Below is a table as to how the leds will
act:
Status Indicator
STA CON Pactor Status
0 0 RX N/A
TX N/A
MON The TNC is idling and has not monitored
any information packets in the past
second.
0 1 RX Sending ack control signal
TX Last packet acknowledged
MON Received new packet
1 0 RX Dupe rcvd; sending Request control signal
TX Received request control
MON Received dupe packet
1 1 RX Info packet missing; sending request
TX Control sign missing; retransmitting
MON N/A
Page 66

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
Whenever we
refer to <ENTER> in this instruction this means to press the RETURN
PACTOR MAILBOX
The MFJ-1278B now includes a new feature called a PACTOR MAILBOX. In this section
we will cover basic operation of the new Pactor Mailbox, and the operative commands. The
Pactor Mailbox includes the basic commands of the Packet mailbox. The Pactor Mailbox is
very simple and easy to use. Any amateur radio operator who has Pactor capability can
access your Pactor Mailbox, after establishing the initial connection to your station. You
MFJ-1278B must be in the PACTOR operating mode. You must also have the MAILBOX
command ON in the Pactor command set. The Pactor MAILBOX command is separate
from the Packet mailbox command. The Packet MAILBOX command needs to be ON too.
The Packet MAILBOX command defaults to ON. Once the remote user connects to your
Pactor Mailbox the user can obtain a list of the messages in your mailbox, read or kill any
message addressed to him. A few functions such as the SYSop command, forwarding, and
reverse forwarding are performed from the Packet mailbox.
The Pactor Mailbox in the MFJ-1278B provides the sysop with about 32K of RAM for
message storage. The Pactor and Packet Mailboxes share the same 32K RAM. The mailbox
RAM is in addition to the system RAM. However, you can increase the RAM size to 128K
or even an enormous 512K. You can increase the RAM size by simply replacing the mailbox
RAM chip on the MFJ-1278B motherboard. The mailbox RAM is battery backed up, just
like the system RAM. Additional RAM chips are available from MFJ Enterprises, Inc. and
easily installed by the user. The user can order the 128K RAM chip as the MFJ-45B, or the
512K RAM chip as the MFJ-45C. The number of slots and space available for each memory
size are as follows:
Memory Size # of Slots Bytes Avail.
32K 99 32,000
128K 99 per bank 128,000
512K 99 per bank 512,000
Setting Up your Pactor Mailbox
The new Pactor Mailbox is operative only while the MFJ-1278B is in the Pactor mode of
operation. The Pactor mailbox uses the callsign used during standard Pactor operations. The
user must set a few of the Pactor commands before operating the Pactor mailbox. As we
mentioned earlier there are a few functions that are performed only in the Packet mailbox.
The functions that are performed only in the Packet are the SYSop command, forwarding,
and reverse forwarding. We will go over the different commands while we talk about the
Pactor setup.
NOTE:
Page 67

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
1. From the cmd: prompt please type the following:
MODE PT <ENTER>
the MFJ-1278B will respond with:
[MFJ PACTOR $2c-1022 free]
followed by the p_cmd: prompt on the next line. The $2c is the checksum of MFJ's Pactor
release. You will probably notice a slight delay in obtaining the p_cmd: prompt. This is
because the MFJ-1278B is figuring up the Pactor checksum, this is perfectly normal.
2. Under the p_cmd: prompt, type:
MYCALL n <ENTER>; where n is your standard amateur callsign.
The MFJ-1278B will respond with:
MYCALL n
where n is the callsign you entered in the MYCALL parameter. The MFJ-1278B will give
the p_cmd: prompt on the next line.
3. If you want your messages time and date stamped, then set DAYTIME with the current
information.
The DAYTIME command is in the standard Packet command set, not in the Pactor
commands.
NOTE: An optional TNC real-time clock, the MFJ-43 for the MFJ-1278B is available from
MFJ Enterprises. With this real-time clock module installed in your MFJ-1278B, the
clock will continue to keep time even with the MFJ-1278B turned off. You will not
have to set your MFJ-1278B's "DAYTIME" every time your MFJ-1278B is powered
up.
4. From the p_cmd: prompt, type:
MAILBOX ON <ENTER>
As we mentioned earlier, there are two MAILBOX commands. One of the MAILBOX
commands is in the Packet command set, the other being in the Pactor command set. Both of
the MAILBOX commands must be ON. If either of the MAILBOX commands is OFF, then
the Pactor mailbox will not function.
Your MFJ-1278B is ready for Pactor Mailbox operations. As we mentioned earlier, the
SYSop command must be issued from the Packet mailbox. You can access the SYSOP in
Page 68

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
These are the basic commands, however there are derivatives of the basic commands.
The MFJ-1278B will respond with the standard cmd: prompt. From the cmd: prompt type:
SYSOP <ENTER>
Your MFJ-1278B will respond with:
|K[MFJ-2.1-IH$]
Mailbox ready
n free Mailbox (B, E, H(elp), J, K, L,M, R, S, T)>
You are now in the Packet mailbox, as the SYSOP. All of the above command are available
to you as the SYSop. Please refer to the Easy-Mail™ mailbox section in Chapter 5 of this
manual, for further information on the above command.
From this prompt you as the SYSop can Kill, List, Read, Send messages in the mailbox. You
can also send private messages, edit the messages headers, bank switch the mailbox RAM.
General Overview
This section will deal with the Pactor Mailbox in general. We will take a look at the Pactor
mailbox from mainly a remote user's stand point. However, lets take first things first. You
very well cannot operate the Mailbox without knowing the functions of the commands.
When a remote user connects to the Pactor mailbox, and issues the changeover, your mailbox
will present the following prompt:
Mailbox Ready
n free de callsign (H(elp), K, L, R, S)>
The Pactor mailbox will automatically issue a changeover, after it sends the proper response
to the user's commands. The n free is the amount of RAM space available for messages.
The de callsign is the callsign of your Pactor mailbox, that the mailbox sends back to the
remote user. So, lets take a brief look at the command functions of the Pactor Mailbox
commands. The command functions are as follows:
H(elp)
The Help command displays the Pactor Mailbox help list to the remote user. A brief
description of the commands available to the remote user is given. Below is an example
of the Help list, as seen by the remote user:
H This message
K Kill msgs
L List msgs
R Read msgs
S Send msg
Page 69

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
Kill
Allows the remote user to kill messages that are addressed specifically to the user. If
the message is not addressed to the user, then the mailbox will respond with "not
yours", and present the user with the mailbox prompt.
Kill ##
Allows the remote user kill a message in a particular slot, nn. Slot nn is a particular
slot number from 1 to 99. Remote users may only kill messages that are addressed only
to them or originated by them. The local and remote SYSOP can kill any messages,
depending on the setting of the command REMsysop. Please refer to the REMsysop for
more detailed information.
There are three (3) different methods to kill messages in the mailbox, when the remote user is
connected. We will give you a brief overview of these methods below:
1. The remote user can kill a message in a particular slot, when connected to the mailbox.
To kill a message in a certain slot, type:
K## <ENTER>, followed by a changeover character, CTRL-Y.
Where the ## is the slot number of the message the remote user wants to kill.
The Mailbox will respond with:
Mailbox Ready
n free de callsign (H(elp), K, L, R, S)>
The n free is the amount of RAM space available for messages. The n will be no higher than
65K, if a 512K or a 128K Mailbox is in operation. If the Mailbox is 32K then nn will be
32K.The de callsign is the callsign of your Pactor mailbox, that the mailbox sends back to
the remote user.
2. The remote may also kill any message that is addressed to specifically to the user. To
kill a message that is addressed only to the user, type:
K <ENTER>, followed by a changeover character, CTRL-Y.
This is whether or not the message flag is set to an N or a Y. Note that the remote users may
only kill messages which are addressed them. The originator can kill any message that he/she
originated. The local SYSOP can kill any or all messages in the Mailbox.
3. The remote user can perform a Global Kill on a group of messages that are under the
same callsign. To perform a Global Kill on a group of messages, the following
conditions apply:
Page 70

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
After the automatic changeover is sent, the mailbox will send a CTRL
-
G character back to
If the above conditions are met then all the remote user must type:
K <ENTER>, followed by a changeover characters, CTRL-Y.
This will go out to Mailbox, then the messages with the message flags set to Y with all of the
proper callsigns will be killed. The Mailbox will respond back to the remote user with all
message numbers killed during the Global Kill process. Also the Mailbox prompt will be
given again. The Mailbox will update the "bytes free" indicator when the messages are
killed. The local SYSOP cannot perform a Global Kill. The SYSOP must individually kill
any messages.
List
This command allows the remote user, local or remote SYSOP to list all messages in the
mailbox. All of slots that are currently in use will be listed. They all will have the slot
number, flag field, the destination callsign, originator callsign, subject field. Also the
Mailbox command line will be on the next line.
To List the messages in the Mailbox, first the Mailbox prompt must be obtained by either a
connection to the Mailbox or through the local SYSOP command. The local SYSOP
command in accessible through the Packet Mailbox. Please type the following to List
messages from the Mailbox:
L <ENTER>, followed by a changeover character, CTRL-Y.
The Mailbox will respond with a listing of currently used slots in the following format:
Slot:## t m To: From: Subject:
Where Slot## column is the number of the slot that the message is in. The number of
message slots present in the standard 32K Mailbox is 99. The lower case t is the Type Flag
block. The lower case m is the Message Flag block. The To: column will contain the
callsign of the person who the message is addressed to. The From: column will contain the
callsign of the person who left the message. The Subject: column will contain a brief
message title.
After the Mailbox lists all messages it will issue the Mailbox prompt:
nn free de callsign(H(elp), K, L, R, S)>
The n free is the amount of RAM space available for messages. The n will be no higher than
65K, if a 512K or a 128K Mailbox is in operation. If the Mailbox is 32K then nn will be
32K.The de callsign is the callsign of your Pactor mailbox, that the mailbox sends back to
the remote user.
The Pactor Mailbox will send an automatic changeover after it lists all mailbox messages.
Page 71

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
Read
This command lets you read messages addressed to you. When you list the messages in
the mailbox you notice an N flag next to the messages which you have not read. Once
you read those messages the N flag will change to a Y flag. This is an indicator to both
you and the SYSOP that the messages have been read. From there you can perform a
global kill on all of your messages or the SYSOP can kill them individually.
NOTE: The only way an N flag can get changed to Y flag during a read is that the person
who the message is addressed to needs to read it. The flag will not change for any
other person who reads the message.
Read ##
Allows you to read the message in slot ##. Where ## is a particular slot number. This
command works the same as the R command, except its for reading the individual slots.
Send call
This allows the remote user, local or remote SYSOP to send a message to the
designated callsign. "CALL" must be a callsign valid under the same format as the
MYCALL, CONNECT or other callsign commands. You can also send messages in
NTS (National Traffic System) format. You will need to refer to the ARRL NET
DIRECTORY for more detailed information on the NTS system.
SP call
This allows the remote user, local or remote SYSOP to send a personal message to the
designated callsign. This is a private message and only the person to whom the message
is addressed can read or kill it. The SYSOP can also read the private messages. When a
private message is listed a P flag is shown in the "Message Type" flag block. The P flag
can also be inserted by the originator or the SYSOP through the Edit command.
Detailed Pactor Mailbox Overview
In the previous section, Brief Overview of Pactor Mailbox,we briefly discussed the Pactor
Mailbox in general. In this section, we will go into more detail about the commands that are
presented by the mailbox prompt shown below:
Mailbox Ready
n free de callsign (H(elp), K, L, R, S)>
The n free is the amount of RAM space available for messages. The n will be no higher than
65K, if a 512K or a 128K Mailbox is in operation. If the Mailbox is 32K then nn will be
32K. The de callsign is the callsign of your Pactor mailbox, that the mailbox sends back to
the remote user.
Page 72

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
files into the Mailbox. The 32K version has the same capability but with 32K RAM capacity.
1. First a remote must establish a connection to your Mailbox, via your Pactor callsign.
2. If your Pactor Mailbox is ON, then it will answer back with the Pactor Mailbox prompt:
Mailbox Ready
n free de callsign (H(elp), K, L, R, S)>
The n free is the amount of RAM space available for messages. The n will be no higher than
65K, if a 512K or a 128K Mailbox is in operation. If the Mailbox is 32K then nn will be
32K. The de callsign is the callsign of your Pactor mailbox, that the mailbox sends back to
the remote user.
Once the remote user receives the the Pactor Mailbox prompt, the user must issue a
changeover, CTRL-Y, to enter the Pactor Mailbox. Now at this point all of the Mailbox are
available to you. You may then type K to kill a message, L to list all messages, R to read the
messages, S to send a message, or H for the HELP menu.
3. To send a message the S or the SP commands must be used. The S or SP commands are
used in conjunction with a callsign as in the examples below:
S AA5XO <ENTER>, this will send an ordinary message to the callsign AA5XO.
or
SP AA5XO <ENTER>, this will send a private message to the callsign AA5XO.
The Mailbox will respond with:
Enter Subject: (Max. 40 Characters)
_
The remote user will enter the message subject or title at cursor prompt, then press the
<ENTER> key.
The Mailbox will respond with:
Send msg; Control-Z or /EX on it own line ends:
__
The remote user will then enter the message at the cursor prompt. The remote user needs to
press the <ENTER> key after entering the message. The remote user needs to enter /EX or
CTRL-Z, followed by a changeover, after the <ENTER> key press. This will tell your
Pactor mailbox to store the message, and to send the Pactor mailbox prompt back to the
remote user. Your Pactor mailbox will send an automatically changeover back to the remote
user. If you are using a 128K or even a 512K Mailbox, then you can actually upload disk
Page 73

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
4. There are two (2) different ways the remote user can kill messages. The first is give in
the example below:
a. To kill a message in a particular slot, the remote user would type:
K## <ENTER>
Where the ## is the message number the remote user wants to kill.
The Pactor Mailbox will respond with:
Message ## deleted;
nn free {n} Mailbox (H(elp),K, L, R, S)>
This is whether or not the message flag is set to an N or a Y. Note that the remote users may
only kill messages which are addressed them. The originator can kill any message that he/she
originated. The local SYSOP can kill any or all messages in the Mailbox.
b. You can perform a Global Kill on a group of messages that are under the same
callsign. To perform a Global Kill on a group of messages, the following conditions
apply:
I. All messages must have been read and the message flag must be a Y.
II. The callsign contained in the MYcall must be the same as the callsign in the
MYcall command.
If the above conditions are met then all the user must type:
K <ENTER>
This will go out to Mailbox, then the messages with the message flags set to Y and all of the
proper callsigns will be killed. The Mailbox will respond back to the remote user with all
message numbers killed during the Global Kill process. Also the Mailbox prompt will be
given again. The Mailbox will update the "bytes free" indicator when the messages are
killed. The local SYSOP cannot perform a Global Kill. The SYSOP must individually kill
any messages.
5. The remote user or local SYSOP can List messages from the Mailbox. In order to do
this first the Mailbox prompt must be obtained by either a connection to the Mailbox or
through the local SYSOP command. Please type the following to List messages from
the Mailbox:
L <ENTER>
Page 74

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
The Mailbox will respond with a list of currently used slots in the following format:
Slot:## t m To: From: Subject:
Where Slot## column is the number of the slot that the messages are in. The number of
message slots present in the standard 32K Mailbox is 99. The lower case t is the Type Flag
block. The lower case m is the Message Flag block. The To: column will contain the
callsign of the person who the message is addressed to. The From: column will contain the
callsign of the person who left the message. The Subject: column will contain a brief
message title.
After the Mailbox lists all messages it will issue the Mailbox prompt:
nn free {n} Mailbox (H(elp), K, L, R, S)>
The Pactor Mailbox will send an automatic changeover after it lists all mailbox messages.
After the automatic changeover is sent, the mailbox will send a CTRL-G character back to
the remote user. The CTRL-G character will sound the computer bell in the user's computer.
6. Anyone who accesses the Mailbox can read messages that are addressed to him/or her.
Also a message which is a addressed to ALL, such as bulletins are readable by anyone.
Messages are read by two (2) different methods. Below are the two methods:
a. This method will allow the remote user, local or remote SYSOP to read a group
of messages. This is only good for a group of messages with the same callsign as
MYcall. The set conditions of the Type or message flags have an effect on a
read process. They can be set to an N, Y or an F. To perform this type:
R <ENTER>
b. Messages can also be read individually by the slot number. This is good for
reading other messages like bulletins or messages addressed to ALL. In order do
an individual read type:
R## <ENTER>
Where ## is the slot number of the message that you wish to read.
c. The Mailbox will respond with the message from the slot specified.
All messages read will be in the following format.
Slot## tm To: From: Subject:
This is an example of a message from the Mailbox
Where Slot## column is the number of the slot which the messages are in. The lower case t
is the Type Flag block. The lower case m is the Message Flag block. The To: column will
Page 75

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
is proper Pactor etiquette. If you access your Mailbox via the SYsop command, then
you must issue a CTRL-C to exit the Mailbox and return to command mode. The
SYSOP mode is accessed through the Packet mailbox, as mentioned earlier in this
section. The command prompt will indicate the stream you are on. The command
prompt may look like this:
|Acmd: where |A indicates that you are on packet stream A.
To re-enter the Pactor mailbox you would type the following from the cmd: prompt:
PACTOR <ENTER>
This is the only way the remote users can access your Mailbox.
Mailbox Messages
You have new mail!
Upon accessing the mailbox this message will appear if there are any new messages are
addressed following the last time you logged into the mailbox.
You have mail!
Upon access to a mailbox, this message will appear if there are messages addressed to you.
?EH
This message occurs when a command issued is not understood by the mailbox. This could
be out of range slot number, missing slot number where one is required, or bad command.
Cannot, not yours
This message occurs when a remote user attempts to kill a message which is not his, or he
tries to read personal message by or for someone else.
?Mailbox full
This message occurs when either all of the available slots are full, or the actual message
space is full. Messages must be killed to recover from this error.
Not found
This message occurs when one attempts to read or kill a non-existent message from an empty
slot.
None found
A parameterless Kill or Read command did not find any messages addressed to the user.
No mail
Page 76

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
CW OPERATION
The MFJ-1278B provides many unique features in the CW mode that are not found in other
multi-mode controllers.
The MFJ-1278B can key your CW transceiver in the CW mode of operation. The MFJ1278B can accommodate either positive (direct) or negative (grid block) keying voltages.
The MFJ-1278B also has a code practice mode built-in, that can be used with VHF FM
radios in the Modulated CW (MCW) mode. This mode holds the radio PTT line down and
feeds keyed audio into the microphone input.
The CW mode in the MFJ-1278B is very easy and versatile. Take for instance, the user can
send code either from the computer keyboard or a key paddle. The key paddle must be
connected to the CW KEY-IN jack on the back panel of the MFJ-1278B. When working
CW on the MFJ-1278B with a key paddle you have a full fledged Memory Keyer at your
disposal. The MFJ-1278B provides the user with ten programmable memory buffers. These
memory buffers are able to be programmed with message of up to 120 characters. Besides
the buffer memory, MFJ-1278B provides automatic serial numbering. The WEIGHT
command determines the DOT/SPACE ratio. This is to allow compensation for leading or
trailing edge delays in many transceiver keying circuits. The built in random code generator
allows CW code practice. A TUNE command is also built in for radio tuning.
The MFJ-1278B supports all Alpha and Numeric characters. It also will transmit and receive
punctuations and major prosigns as listed in Table 4-4 below:
PROSIGNS ASCII CHARACTER Keyboard Symbol PROCEDURE
SK *
AS &
AR +
BT =
SN !
KA %
K K
DN /
KN (
PUNCTUATIONS
, COMMA : COLON
. PERIOD ; SEMI-COLON
? QUESTION MARK ' APOSTROPHE
$ DOLLAR SIGN - HYPHEN
( LEFT PARENTHESIS " QUOTATION
) RIGHT PARENTHESIS
End of Work
Wait
End of Message
Break
Understood
Signal Starting
Invitation to Transmit
Response from Contacted Call Only
Page 77

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
tuning of the signal has been established. The automatic LOCK and speed TRACKING
Receiving CW
The MFJ-1278B receives international Morse Code from 1 to 99 WPM. Reception of
alphabetic and numeric characters, including the puncuations and prosigns listed in Table 4-
4.
From command mode, put the MFJ-1278B in the CW Mode by typing:
MODE CW,xx <ENTER>, where "xx" is the CW transmit speed.
The MFJ-1278B will respond with the mode status lines, and end with the command prompt.
Note that if the user does not select a transmit speed, the MFJ-1278B selects the default
speed of 20 WPM.
The MFJ-1278B is now in the CW mode of operation. To receive CW you go into
CONVERSE mode. Enter CONVERSE mode by typing:
K <ENTER>
The MFJ-1278B is now ready to receive Morse code.
The Tuning Indicator and the DCD led on the front panel, assist the user in tuning in CW
signals Tune your receiver to approximately center the tuning indicator when there is a CW
audio tone actually present. Note that between code elements (dots and dashes), the tuning
indicator will indicate randomly. Once the CW signal has been coarsely tuned in by using the
tuning indicator, further CAREFUL tuning should reveal a spot where the DCD LED flashes
in synchronism with the incoming code. If the DCD LED does not light, then you must
rotate the THRESHOLD control on the MFJ-1278B clockwise until the DCD LED flashes
with the CW signal. If the DCD LED is lit, but does not flash with the CW signal, then rotate
the THESHOLD control counter-clockwise until the DCD LED does flash with the CW
signal.
The demodulator is an extremely narrow filter. It is much narrower than the 500 Hz CW
filter in your radio (if you have such a filter in the radio). This means that very careful tuning
will be required for proper CW demodulation. You should attempt to tune for the center of
the range where the DCD flashes with the incoming CW tone. Once tuned to that spot, the
THRESHOLD control setting should be reduced (counter-clockwise) to a point just above
where the DCD LED stops flashing with the incoming CW tone. The adjustment of the
THRESHOLD control is critical and must be based upon your judgment of best copy. Once
the optimum setting is found it can be pre-set and all remaining tuning done with the receiver
frequency control.
The MFJ-1278B will automatically LOCK and TRACK the speed of the signal, once proper
Page 78

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
If the AUTOTRAC command is OFF, then before the MFJ-1278B can copy the tuned-in
CW signal, it must be manually locked to the speed of the received signal. To manually
lock the MFJ-1278B to the incoming signal, type a CTRL-U. The MFJ-1278B will respond
with "locking...". The MFJ-1278B will analyze the incoming CW signal. When the analysis
of the incoming CW signal is complete, the MFJ-1278B will respond with
"Locking...xxwpm." The "xx" is the speed of the received CW speed from 1 thru 99. When
the MFJ-1278B issues the response "Lockingxxwpm," there will be CW copy on your
computer screen. You shouldn't have to re-lock unless the station you're listening to changes
its CW sending speed.
Transmitting CW
The MFJ-1278B will transmit International Morse code from 5 to 99 WPM.
The CW transmitting speed defaults to 20 WPM. The MSPeed command specifies the CW
transmit speed. If the FARnswor command is ON, and MSPeed signifies 15 WPM, then the
MFJ-1278B uses 15 WPM characters, but spaces the characters so the transmitted text is at a
slower speed. To set the MFJ-1278B to 15 WPM, type:
MSPeed 15 <ENTER>
or
MODE CW,15 <ENTER>
Be sure the MFJ-1278B is in command mode when issuing the MSPeed or MODE
command.
The MFJ-1278B provides yet another way to set the CW transmit speed, and that is the
CWSPEEDM command. If the CWSPEEDM command is ON, then the MFJ-1278B will
match your transmit speed with the transmit of the person you are in QSO with. The CW
speed matching feature causes your MFJ-1278B to adopt the speed of the received CW signal
as it's transmit CW speed. This is the same CW speed that the MFJ-1278B analyzed last,
either through the AUTOTrac or by use of the ALOCKCHAR character, CONTROL-U.
To give the user with more flexibility in controlling how the MFJ-1278B will transmit
CW/MCW, the CWSEndch command is provided. This command applies whether the
keyboard or key paddle is the transmit medium. CWSEndch is only effective for CW and
MCW modes.
The CWSEndch command determines which keyboard character transmits the CW/MCW
characters. This gives the user more control how pending characters are transmitted. For
example, setting the CWSEndch to $02 will tell the MFJ-1278B to buffer all CW characters,
until the user enters a CTRL-B from the computer keyboard. Entering the CTRL-R
Page 79

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
If CWSEndch is left at the default setting of 255 or $FF, the MFJ-1278B will transmit all
characters immediately when typed. The requirement for pressing the <ENTER> is
eliminated.
Note: If you are using a terminal program such as "PROCOMM" for IBM PC and
compatibles that buffers the transmit data, then a CARRIAGE-RETURN will be
needed to transmit.
The MFJ-1278B employs full CW break-in for transmitting in the CW/MCW modes. The
CWSEndch command enables the full CW break-in feature. Setting the CWSEndch to
something other than the default, will disable the break-in feature. Users do not have to press
Ctrl-R to force the MFJ-1278B to receive or to press Ctrl-T to force the MFJ-1278B to
transmit. MFJ-1278B will always go back to receiving mode at the end of each transmission.
CW break-in is effective for both CW and MCW mode.
Transmitting from Memory Buffers
The user can use the BUFKEY (nnn) command to define a particular key to transmit the
memory buffers. The MFJ-1278B uses the TAB key, ($09) as the default for the BUFKEY
command. The user can transmit any memory buffer, 0 through 9 by using the TAB and the
appropriate buffer number. For example, to transmit memory buffer 3, the user would press
the TAB key followed by the number 3 key. When pressing the TAB key, DO NOT hold the
TAB key down, just press it, then let up. Once the MFJ-1278B transmits the memory buffer,
the MFJ-1278B will revert to receive mode. There is no need to issue a CTRL-R to make the
MFJ-1278B go back to receive mode.
Note: If you are using MFJCOM terminal program, you will not be able to use the "TAB"
key as the BUFKEY. Change BUFKEY to another key on the keyboard. See
BUFKEY command in Chapter 6 for more detail.
CW Weighting
The MFJ-1278B allows you to increase or decrease the weight of the code elements
generated by the keyboard or key paddle. The user can set the WEIGHT by using the
WEIGHT command. The weight factor defaults to dot-to space ratio of 1:1. A number from
0 thru 255 represents the weight value used. The default setting of the WEIGHT command,
0 sets a weight factor of 1:1. Select a number from 1 to 127 to INCREASE the dot/space
ratio. Select a number from 128 to 255 to DECREASE the dot/space ratio (weight). You can
easily change the weight the MFJ-1278B uses by typing:
WEIGHT ### <ENTER>
Where ### is a number from 1 to 127 to increase weight, or from 128 to 255 to decrease
Page 80

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
Tuning your Radio
The MFJ-1278B lets you tune your radio with the TUNE command. The TUNE command is
issued from the command mode. The user can use the TUNE command in any of the MFJ1278B operating modes.
The TUNE command activates the PTT line for 30 seconds. After 30 seconds MFJ-1278B
will automatically return to command mode. To abort tuning before 30 seconds, press any
key on the keyboard.
Random Code Generator
If you want to improve your CW copying proficiency, you will find the CW Random Code
Generator helpful.
The RANDOMCW command invokes the Random Code Generator. Setting the
RANDOMCW command to ON, activates the Random Code Generator. The Random Code
Generator can generate Pseudo Ransom Code in two formats. The two formats of Pseudo
Random Code are NORMAL CW and FARNSWORTH CW. The MFJ-1278B uses the
setting of the FARnswor command to determine which format to send when RANDOMCW
is ON. To end CW random code generation, type:
CONTROL-C
to return to command mode and then type:
RANDOMCW OFF <ENTER>
CW random code speed is set by using the MSPEED command described above.
Many find training for CW tests with a FARNSWORTH method of code generation more
valuable. It teaches letter recognition at a speed fast enough to avoid the common learning
"plateau." The learning "plateau" proves to be difficult for some people to get over. This is
because as their code speed increases, they must re-learn the sound of the characters.
To select the Farnsworth method of random code generation, set the FARNSWOR command
to ON before entering the RANDOMCW mode.
When the FARNSWOR command is ON, the MFJ-1278B generates random code using
standard 15 word-per-minute timing for all code elements. When using the Farnsworth
generation method, the inter-character spacing is increased to send the text at the slower
selected speed. So with the FARNSWOR command ON, the code generator sends the CW
characters faster, but slows the text down to a slower speed. The FARNSWOR command
controls the transmission of CW characters, whether the computer keyboard or key paddles
Page 81

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
Setting Up the for Code Practice
You can monitor the random code sent by the MFJ-1278B without a radio connected. In
order to monitor the random code, attach a small speaker to the "SPEAKER" jack, located on
the back panel of the MFJ-1278B
Note: If a radio is connected and you do not wish to transmit the random code, the radio
should be turned OFF. The MFJ-1278B will key PTT line and the keying output is
active while RANDOMCW is ON.
Under the cmd: command prompt, type:
MODE MC,## <ENTER> (## is the desired code speed)
The MFJ-1278B will respond with the "Modem Status" display, verifying the operation
mode, and cmd: prompt will appear. Next type:
RANDOMCW ON <ENTER>,
Next type:
K <ENTER>
followed by a Ctrl-T. The MFJ-1278B will generate 5 letter groups and display them on the
computer screen. If you do not wish to see the characters as are sent, you can turn off your
computer screen. You can then turn on the computer screen once you finish copying the code
and compare the result.
To stop the random code sending, type:
Ctrl-R
To start the random code again, type:
Ctrl-T
To exit random code practice, type:
Ctrl-C
The MFJ-1278B will return to cmd: command prompt.
To stop random code generation, type:
RANDOMCW OFF <ENTER>
Page 82

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
CW CONTEST MEMORY KEYER OPERATION
For CW enthusiasts who like to use a key paddle to send CW, the MFJ-1278B provides an
input for an iambic key paddle. See CW KEY PADDLE INSTALLATION in chapter 3 in
this MFJ-1278B manual for installation of your iambic key paddle.
Sending CW with External Key Paddle
The MFJ-1278B sends key paddle generated CW at 5 to 99 WPM.
The transmission speed for key paddle CW defaults to the same speed as keyboard CW, 20
WPM. The user can change the transmit speed by changing the MSPEED command. To set
the MFJ-1278B to 15 WPM, you would type:
MSPEED 15 <ENTER>
Be sure you are in command mode when issuing the MSPEED command.
It is always a good idea to match your CW transmit speed with the person to whom you are in
QSO with. The MFJ-1278B makes it easier for you to match your transmit speed to someone
else's through the CWSPEEDM command. The CW speed matching feature causes your
MFJ-1278B to adopt the speed of the received CW as it's transmit speed. When the
CWSPEEDM command is ON, then the MFJ-1278B will match it's CW transmit speed with
the whatever speed was last locked to through the AUTOTRAC routine. The MFJ-1278B
will also adopt whatever transmit speed is locked-in by the ALOCKCHAR character,
CTRL-U will also be
The CWSEndch (nnn) command provides the user more flexibility in controlling how
CW/MCW characters are transmitted from the key paddle. The CWSEndch command is
only effective for CW and MCW modes.
The user needs to leave the CWSEndch command at the default value of 255 or $FF, when
sending CW using a key paddle. The MFJ-1278B will transmit all CW characters
immediately if the CWSEndch command is at the default setting of 255 or $FF. Once the
MFJ-1278B completes the CW transmission, the MFJ-1278B will revert to the receive mode.
Buffer transmission in the Memory Keyer Mode is the same as in the CW mode. Weighting
of key paddle CW is achieved by using the WEIGHT command. Please refer to the CW
mode section as to setting of the WEIGHT command.
Page 83

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
MODULATED CW OPERATION
The MFJ-1278B allows the transmission of CW code practice over a VHF FM radio. To
send code practice over a VHF FM radio, the user would use the Modulated CW mode, or
MCW. When using the Modulated CW, the MFJ-1278B will key the PTT line of the Radio
port and send a keyed audio tone to the microphone input of your radio. Modulated CW can
be used on either radio port1 or radio port 2.
You do not have to re-wire the Radio cable when operating Modulated CW. You can use the
same cable that you use for the other modes of operation.
To enter MCW mode type:
MODE MC <ENTER>
The MFJ-1278B will respond with the mode status as shown below, followed the cmd:
command prompt.
Radio: 1 Terminal: 9600
Mode: Modulated CW, 20
cmd:
Operation of MCW is the same as in standard CW. Please refer to "CW OPERATION" for
further details.
Page 84

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
BAUDOT RTTY & ASCII OPERATION
The user can configure the MFJ-1278B RTTY/ASCII modems to copy several shifts,
including 170, 425, and 850 Hz shifts. The user can use the MODE command to configure
the RTTY/ASCII modems for the different shifts. The MFJ-1278B will transmit and receive
RTTY and ASCII at speeds of 45, 50, 57, 75, 100, 110, 150, 200, and 300 baud.
The MFJ-1278B transmit and receive WIDE and NARROW shift RTTY or ASCII. Wide
shift RTTY/ASCII operates on standard tone pairs of 2125 Hz for MARK and 2975 Hz for
SPACE. The frequency shift for WIDE shift RTTY/ASCII is 850 Hz. Narrow shift
RTTY/ASCII operates on standard tone pairs of 2125 Hz for MARK and 2295 Hz for
SPACE. The frequency shift for NARROW shift RTTY/ASCII is 170 Hz.
In the RTTY mode, the MFJ-1278B will receive and transmit both the American Western
Union and the internationally recognized CCITT character set. In ASCII mode MFJ-1278B
will transmit and receive 7 bit ASCII code.
Note that the MFJ-1278B provides you with the option to select Low Tone RTTY/ASCII.
Low Tone RTTY/ASCII uses standard tones of 1275 Hz for MARK and 1445 Hz for
SPACE. The frequency shift for Low Tone RTTY/ASCII is 170 Hz. You can select Low
Tone RTTY/ASCII through the "V" modem. The Low Tone pairs are the standard used in
Europe for RTTY and ASCII operations. Please refer to APPENDIX H on how to select the
Low Tone pairs.
The MFJ-1278B can transmit or receive RTTY or ASCII by using inverted tone pairs. The
RXINVERT and TXINVERT commands allow inverting of the tone pairs, in the RTTY or
ASCII modes. When operating in the inverted mode, the tone pairs are MARK for the high
tone, and SPACE for the low tone.
The MFJ-1278B also allows you to transmit from any one of the ten memory buffers when in
one of the asynchronous modes. Memory buffer programming and use are the same as for
CW operation.
Setting Up for ASCII and RTTY Operation
From command mode, you can set the MFJ-1278B into the desired RTTY or ASCII mode by
using the MODE command. Type:
MODE ## <ENTER>
Where ## is the two letter code for the desired RTTY or ASCII mode.
Code designations for RTTY and ASCII modes are as follows:
VHF RTTY VB
Page 85

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
If you do not specify a baud rate for the RTTY or ASCII modes, the MFJ-1278B selects the
default baud rates. The default baud rates for the RTTY and ASCII modes are 45 and 110
baud respectively. You can select a desired speed by typing the baud rate after the two
character code. For example, to enter 110 baud VHF Baudot RTTY, you would type:
MODE VB,110 <ENTER>
Note: The only baud rates that you can select are those the MFJ-1278B is capable of
receiving and transmitting. Selecting an illegal baud rate will cause the MFJ-1278B
to respond with an error message, such as:
bad?
In this case the MFJ-1278B will change to default settings and return to the command mode.
RTTY and ASCII Receiving
After properly setting the MFJ-1278B to the desired RTTY or ASCII mode, type "K" on the
computer keyboard to enter CONVerse mode. The STA LED on the MFJ-1278B will light.
MFJ-1278B is ready to receive RTTY or ASCII signals tuned in by your radio.
Set the volume of your radio for normal listening level. Tune your radio until you hear a
signal that you want to decode. Fine tune your receiver until the 10th or 11th segments are lit
on the tuning indicator. When you have the signal tuned in properly, the DCD LED will light
and the MFJ-1278B will start to decode the signal.
If the displayed text appears garbled, then the specified speed in the MODE command might
be incorrect. Garbled displayed text may mean that the signal you are trying to copy is
encrypted. If you suspect an encrypted signal, you can use the RBITMASK command to
match the inversion pattern of the signal. If you suspect that the speed is incorrect, then you
can specify a new speed setting. The speed is set by using the MODE command.
RTTY and ASCII Transmitting
While the MFJ-1278B is in RTTY or the ASCII mode and it is in command mode, you can
initiate RTTY or ASCII transmission by typing:
K <ENTER>
followed by a CONTROL-T.
The MFJ-1278B is now ready to transmit. Type your message on the keyboard. The MFJ1278B will transmit your message as it is received from your computer.
Messages stored in memory buffers 0 thru 9 can be transmitted when in RTTY or ASCII
modes. To transmit a memory buffer, when already in transmit mode, type:
Page 86

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
Note: If the MFJ-1278B is not in transmit mode (i.e. in receive mode), then in order to
initiate transmission from a buffer, you must type CONTROL-T twice then enter a
number for the buffer. You can tell if the MFJ-1278B is in transmit mode, by
observing the PTT LED on the front panel. If PTT LED is lit, MFJ-1278B is in
transmit mode.
Once the MFJ-1278B completes the transmission, press a CONTROL-R. When the MFJ1278B receives the CONTROL-R from the computer, it will return to receive mode. When
the MFJ-1278B is in receive mode, note that the PTT and STA leds are not lit.
Some terminal programs do not support the CONTROL-T or CONTROL-R characters.
The MFJ-1278B require the CONTROL-T and CONTROL-R characters to swtich between
transmit and receive modes.
If the terminal program does not support the CONTROL-T and CONTROL-R characters,
you can re-assign the ASENDCHAR and ARCVCHAR commands in the MFJ-1278B to
other keys. See Chapter 6 of this manual for detail on the ASENDCHAR and ARCVCHAR
commands.
Note: When operating RTTY or ASCII it is recommended that you operate at about 50% of
full power. This is to prevent damage to the finals of your radio. Some modern
radios allow operation of RTTY and ASCII at full power. You should consult the
owner's manual of your radio to see what is the acceptable power level at which your
radio should operate.
BAUDOT RTTY OPERATION HINTS
In this section we will cover a few of operative hints for the RTTY and ASCII modes.
To set the MFJ-1278B to RTTY mode type:
MODE HB <ENTER>
for HF operation. This sets the MFJ-1278B to the standard RTTY mode that most amateurs
use. On HF this is 45 baud or 60 wpm. As mentioned earlier, if you do not designate a speed
after the two letter, the MFJ-1278B selects the default of 45 baud.
Some RTTY bulletin boards use 75 baud or 100 wpm, in which case you should type:
MODE HB,75
The number after the "HB" sets the character transmission and receive speeds in baud. Some
operators will refer to the speed as words-per-minute. However, the normal terminology is to
refer to the speed in BAUD RATE. Although speeds up to 300 baud are available, only 45
Page 87

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
To enter the converse mode type:
K
This will take the MFJ-1278B out of the command mode and into converse mode. When the
MFJ-1278B enters converse mode, the STA will illuminate. Also after entry into converse
mode the MFJ-1278B is in receive mode. You can enter transmit mode by typing
CONTROL-T. To re-enter receive mode type a CONTROL-R The command CONTROL-
C will return you to the command mode, where you will get the cmd: prompt on your screen.
Use lower side band, LSB unless you have an RTTY position on your rig. Tune your radio
until the 10th or 11th segments on the tuning indicator light during receive. Ensure that the
yellow DCD led is illuminated also during receive. It is possible to tune to the center of the
bar graph, and not have the DCD led lit. If the DCD led does not light, then check the setting
of the Threshold control on the front panel. The DCD led needs to be lit for reception. Some
bouncing of the LED is normal, since any audio other than the signal (QRM/QRN) will also
affect how it responds. From the converse mode you should now see text being printed on
the screen as it is heard. Contacts usually take place on a one-way at a time basis. So one
side will transmit and the other will receive, and then the sides are reversed.
To allow the MFJ-1278B to transmit RTTY or ASCII, type:
CTRL-T
while in converse mode to key the PTT on the radio. The green PTT light should light and
you should see power on your wattmeter. All keystrokes are now sent out over the air.
Alpha-numeric (numbers and upper/lowercase letters) characters are the only kind of
keystrokes accepted. Some punctuation is allowed. When the transmission standards were
set up, only mechanical typewriters (tele- type) were used and these were the only keys in
use. Most other characters such as Greek and graphics are usually translated wrong, and
you'll see the other guy's 'mistakes' when he types one of the characters. To go back to the
receive mode, type CTRL-R in converse mode to unkey the radio, and you will return to the
receive mode. This will start the transmit/receive cycle over.
Commercial RTTY Reception
Commercial RTTY presents a special problem for amateurs and short wave listeners. Several
conditions must be met before you can get a decent printout. You have to locate the
frequency of a particular station, get the schedule right, pick the sideband, set the baud rate,
set the frequency shift, and finally, unencrypt the text.
You can receive many of these stations using the 425 shift, 50 baud, and lower sideband
during the daylight hours. For this setup use MODE VB,50. Some military frequencies are
unencoded, as well as some of the UPI broadcasts. A good source of frequencies is Popular
Communications and Monitoring Times magazines.
Page 88

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
AUTOMATIC SIGNAL ANALYSIS
The Automatic Signal Analysis or ASA, feature installed in the MFJ-1278B firmware can
analyze received signals such as RTTY, ASCII, AMTOR mode b and HF Packet. ASA will
tell you the speed, data bits, and if the signal is inverted. ASA automatically switches the
MFJ-1278B to the correct mode once you accept the results of the signal analysis by typing
OK and <ENTER>. As you see ASA is extremely helpful when tuning across the amateur or
the shortwave bands. Let ASA help you determine what kind of signals you are listening to.
ASA OPERATION
ASA is effective in analyzing RTTY, ASCII, AMTOR FEC mode b and HF Packet. Once
invoked, ASA only takes a few seconds to analyze the tuned-in signal. Once the result is
displayed, the user can decide whether to accept by issuing the OK command. If the user
questions the results, ASA will continue to analyze the signal and will display the results after
each cycle.
When the ASA routine is entered, the MFJ-1278B will enter the "converse" mode
automatically and display:
Wtg:CD,
All the you have to do now is to tune in the signal you wish to decode. This is done in
accordance with the MFJ-1278B operations manual.
Once invoked, ASA will first display the speed and the confidence factor followed by a
pause. After a 5 to 10 second pause it will display the speed of modem used to analyze the
signal, data bits of the signal which will be either 5, 6, 7 or 8. Any data bit analysis of 6
should not be used and the signal should be re-analyzed. Last it will display the setting of
what it will change the RXInvert command to (On or Off). This is what ASA will switch the
MFJ-1278B to, if the user accepts its result.
The display is in the following format:
<Speed><Confidence Factor>.<Speed><Data Bits><RXInvert On/Off>
A typical result will look like this:
80 baud, 90% Confidence. 75 baud used 7 bits, RXInvert Off
Once the result is displayed, the user can exit ASA signal mode by pressing any key. MFJ1278B will return cmd: command prompt without changing the operation mode.
If the analyzed result is acceptable, the user will simply type:
OK <ENTER>
Page 89

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
In the case of analyzing a 300 baud signal, the MFJ-1278B will prompt the user that the
signal could be PACKET. If this occurs then the user can enter the following command from
the cmd: prompt:
OK Packet <ENTER>
The MFJ-1278B will switch to the 300 baud HF packet mode.
If the user just issues the OK command, then the MFJ-1278B will switch to the 300 RTTY or
ASCII mode. The number of data bits ASA analyzed, determines if the MFJ-1278B switches
into RTTY or ASCII modes. If data bits was 5, then ASA will switch the MFJ-1278B into
RTTY mode. If the data bits were 7 ASA will switch the MFJ-1278B into ASCII mode.
If the ASA result is a 100 baud signal, the MFJ-1278B will prompt the user that the signal
could be AMTOR. If this occurs then the user can enter the following from the cmd:
command prompt:
OK AMTOR <ENTER>
When the "OK AMTOR" command is given the MFJ-1278B will switch to AMTOR mode B.
Follow the AMTOR operating procedure to go to any of the other AMTOR modes.
If the user does not issue the "OK AMTOR" command the MFJ-1278B will switch to 100
baud RTTY.
Note that if RTTY or ASCII signals are analyzed, and the user accepted the result (by typing
OK) and the MFJ-1278B still does not copying the signal correctly. This may due to the
signal being encrypted with bit inversion. Most of the time, two or three bits of the RTTY
character may be inverted and it is possible for all 7 bits to be inverted.
If the baud rate and the type of signal has been determined by ASA and the MFJ-1278B still
does not copy correctly, the signal may be encrypted with bit inversion. In this case, you may
want to try to use the RBitmask command to set various inversion patterns to match the
receive signal, but manual setting of the RBitmask command is not necessary. The RBitmask
command can be invoked when the MFJ-1278B is in the RTTY or ASCII receive mode by
simply issuing the "CTRL-U" while the MFJ-1278B is in converse mode.
Once "CTRL-U" is pressed, MFJ-1278B will automatically cycle through each of the bit
combinations, and then display a sample text of each one of the combination on the screen.
Examine the list of the displayed text on the screen and if one of the 32 sample text looks
normal then make note of the combination number next to the text. Do the following to select
this combination:
Page 90

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
MODE HB,75 <ENTER>
MFJ-1278B will enter converse mode and begin to display text normally.
If another RTTY or ASCII signal from another station is received, RBIT must be reset to
copy that signal by following the same procedure as described above. RBIT can be set to
normal (no inversion) by setting it to "RBIT 0".
Note that when using ASA, noise will have major effect on the degree of its effectiveness. If
no signal is present while the MFJ-1278B is in ASA mode, the display will display:
Wtg:CD,
User will simply press the "Return" key to return to CMD: command prompt. There is no
need to type ASA to go back into the ASA mode, because once invoked ASA is always
active.
MARS OPERATION
The MFJ-1278B sets a few commands to simplify MARS operation. These commands are
PROfmars and MARsmode.
With PROfmars and MARsmode, the MFJ-1278B is more compatible with MARS than
ever. We have made operating MARS with the MFJ-1278B more fun and enjoyable. The
following section should be very useful to the MARS operator.
Configuring for MARS
When PROfmars is invoked, profiles the MFJ-1278B for MARS operations. When this
command is invoked it sets the following parameters as specified.
Command MARS Setting
AUTOLF OFF
CCITT OFF
DIDDLE OFF
LFADDALT OFF
LFIGNORE OFF
MARSMODE $01
UNSHIFT OFF
RXLFNOCR ON
Once the MFJ-1278B is profiled for MARS operations, the user must set the MFJ-1278B
into HF RTTY mode by typing:
Page 91

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
Once you have set your operating mode, the user must press the K key and a <ENTER> in
order to enter RECEIVE mode. The MARS operator is now ready to receive MARS traffic.
The operator must then tune the VFO on the radio so the tuning indicator on the MFJ-1278 is
centered on the bar graph display. The received traffic should be coming to the screen, in the
proper MARS format.
Operating MARS with MultiCom for IBM
Operating MARS using the MFJ-1278B and the MultiCom™ software, makes operating
much easier. Let's say that you have 20 pieces of traffic, but you only need to send 10 of
them, this is where MultiCom™ comes in handy. The MultiCom™ software has a very good
text editor, Multi Word™. You can use the Multi Word™ editor to send MARS messages.
All received data is stored in a 32K COMM buffer that MultiCom™ opens when loaded. So,
at anytime the operator can see all traffic that has been received. The operator can go into the
Multi Word™ editor by pressing the F10 key, followed an ALT-B. The ALT-B key
sequence fills the Multi Word™ editor with the contents of the COMM buffer.
Insert a CTRL-T at the beginning of each piece of traffic and a CTRL-R at the end of each
piece of traffic. Use the Multi Word™ commands, F1 and F2 respectively, to block off the
pieces of traffic you want to send. After blocking off the traffic, use the F9 key to send the
traffic to the MFJ-1278B to be transmitted.
The operator will need to perform this operation for each piece of traffic to be sent. If all
pieces of traffic are all together, one right after the other then the procedure will only need to
be done once.
The MARsmode Command
The MARsmode command provides two levels of MARS compatibility. The "QSO" mode
provides minimal translation. In the QSO mode, the MFJ-1278B assumes the user is
manually sending and receiving. Maximum translation is provided for sending and storing
files of MARS messages, while preserving all of the formatting information, using the special
MARS ASCII equivalent characters, and differs from QSO mode only because of its extra
ASCII output translations.
Page 92

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
MARSMODE 1- QSO Mode
In the MARS QSO mode the Transmit translations are as follows:
1. All carriage returns are converted to CR/CR/LF, or to LF only if preceding character
was also CR.
2. "NNNN" is sent as "NNNN" followed by 12 LTRS
3. Characters are translated as follows:
Key Press Trans. Characters
* CR
= LF
+ 12 LTRS
@ BELL
\ NULL
> FIGS
< LTRS
MARSMODE 3- Storage Mode
The MARS Storage Mode has all of the same transmit translations as the QSO mode, plus
these Receive translations:
Received Char Printed Char
CR *
LF =
BELL @
NULL \
Page 93

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
AMTOR OPERATION
AMTOR, AMateur Teletype Over Radio), an error correcting protocol suite, is fully
supported by the MFJ-1278B. Two modes are available with AMTOR. These are mode A
and mode B.
From command mode, AMTOR modeB is entered by typing:
MODE AM <ENTER>
Note that the MFJ-1278B displays an "a_cmd:" once the AMTOR mode has been entered.
This "a_cmd:" command prompt lets you know that you are in AMTOR mode and only
AMTOR commands are recognized by the MFJ-1278B. To issue other non AMTOR
commands you will have to return to the normal command mode ("cmd:" command prompt)
by typing "CTRL-C".
Operation of the Tuning Indicator in the AMTOR mode is the same as all other modes.
Simply tune the signal so that the center LED segment of the Tuning Indicator is lit with each
burst of AMTOR signal received.
Mode A "ARQ"
Automatic request for re-transmission mode, known as "Mode A", is similar to packet radio
in a number of ways.
The calling station must know the ID of the station being called, in order for communications
to occur.
The "ARQ"command initiates a link attempt with the station being called. A link attempt in
AMTOR, is similar to a CONNECT attempt in Packet.
Mode A is a one-on-one protocol, meaning that it is used for QSOs, and not for calling CQ or
broadcasting. (see FEC and SELCALL for more on broadcasting.)
ARQ Mode A introduces a few new terms, "Information Sending Station," (ISS) and
"Information Receiving Station," (IRS). In ARQ, a station must be either the ISS or the
IRS, and the station that is transmitting data is called the ISS.
One becomes an ISS either by issuing a successful AMTOR call, with the ARQ command, or
when the ISS relinquishes control of the link through the changeover, +?. Finally, if an IRS
link CHANGE is requested.
Setting up for Mode A Operations
Page 94

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
Examples are:
Amateur callsign is N2WX; Amtor MYSELCAL is NNWX
Amateur callsign is WB2SPE; Amtor MYSELCAL is WSPE
AMTOR depends on everyone having a unique selective call. If you find there is already a
station using the same call that you would use then you may need to base your ID upon the
call district that you're in. Select a letter based upon the table below:
1=Q 2=W 3=E 4=R 5=T 6=Y 7=U 8=I 9=O 0=P
Example:
N2WX becomes NWWX (using zone 2)
When MYSELCALL is set the MFJ-1278B is ready to receive and respond to AMTOR
calls.
Operating Mode A
To start the ARQ call, type "ARQ <selcall>" and <ENTER>. The <selcall> must be four
characters long. Both the CON and STA leds on the MFJ-1278B will light, and your
transmitter will start keying on and off repetitively. If the other station responds, you can
start sending data or you can abort the call by typing QRT or R.
When the CON lights a link is established. You may now type CONVERSE or K to enter
the data mode and start transmitting data. The CON and STA will be turning on and off at
various times depending on how much data you transmit and how good the link is.
When you are through transmitting, always use the AMTOR ending signal "+?". NEVER
use a "K" since this will not relinquish the ISS function and the station you're working will be
unable to transmit until the information sender sends a "+?".
If you wish to end the contact, go back to AMTOR command mode with a CTRL-C and type
"QRT".
While you are the current receiving station, you can't send any new data to the other station.
Should you wish to break in for some reason before the other station sends "+?", and you
want to become the transmitter, go to AMTOR command mode with CTRL-C and type
CHANGE. This forces the remote ISS to revert to the IRS. Then you can start transmitting
data.
If the CPU oscillator of the MFJ-1278B is improperly set, then you may experience a phasing
problem or a loss of sync, during ARQ operations. The CPU oscillator is factory set at
Page 95

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
Monitoring Mode A, "ARQ"
The LISTEN command is useful for monitoring other people's ARQ contacts. To use, tune
in a Mode A signal and type LISTEN. Both the CON and STA leds will light until the
station is synchronized, at which time the MFJ-1278B will start to receive.
Since the monitoring of MODE A signals is not error protected, you may see occasional
errors. How well the MFJ-1278B receives Mode A signals depends on the quality of the
signal. The quality of Mode A signals depends on how well the MFJ-1278B hears both sides
of the QSO. Band conditions also have an effect on Mode A signal quality. The LISTEN
mode is most useful for allowing amateurs to continue to self police their bands.
Mode B "FEC"
Mode B FEC is a "One transmitter, many receivers" mode. Unlike packet or ARQ, FEC
does not establish a one-on-one link setup, nor does it have a re-transmission feature. Mode
B, FEC is mainly used for calling CQ. The amtor operator would first call CQ in Mode B,
then wait for a call from another operator in Mode A.
Setting up for Mode B "FEC"
Setup for Mode B FEC is the same as ARQ, although a selective call is not required.
Mode B "FEC" Operations
To receive Mode B FEC, tune the FEC signal in so the center segments on the MFJ-1278B
tuning indicator light. When the MFJ-1278B detects the synchronization pattern, either the
CON or STA led will light. The exact point in the transmission to which you tuned to,
determines if the CON or STA led lights. When either the CON or STA led lights the
received data will begin to display on the terminal screen.
Use Mode B FEC, for calling CQ, operating in round tables, and for transmitting bulletins to
more than one station at a time. To transmit MODE B FEC, type FEC followed by a
carriage return, at which time your transmitter will key up. Now type CONVERSE or K to
enter the data mode and you're on the air with FEC. Anything entered from the keyboard
once in the data mode is transmitted.
When you're done transmitting, return to the AMTOR command mode, a_cmd: with CTRLC. In order to release the transmitter type R or QRT followed by a carriage return. At this
point again the MFJ-1278B will automatically attempt to synchronize to any mode B signal it
hears.
Mode S "SELCALL"
Mode S is exactly like Mode B, EXCEPT that the broadcasting station can select one or a
Page 96

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
AMTOR Status LED Indicators
The CON and STA LEDs have special meanings in the AMTOR modes.
STA OFF CON OFF
This led combination indicates that Mode B is unlocked, and in STANDBY mode. Standby
mode is where the MFJ-1278B is ready to respond to Mode A or B "FEC" Amtor signals.
The MFJ-1278B will also print Mode S "SELCAL" signals, depending on the setting of the
SRXALL and MYSELCAL commands.
STA OFF CON ON
Indicates Mode B is locked in and is in the Idle mode. Broadcast text will be printed if in
receive mode. Also if in receive mode, the MFJ-1278B is receiving an AMTOR "idle"
signal. The other station is still being received ok, though he is not transmitting any text.
In Mode A, this signal could also mean that a send-receive CHANGE is pending or that the
sender is repeating a block.
STA ON CON OFF
This led combination indicates Traffic mode. The MFJ-1278B is currently sending or
receiving text.
STA ON CON ON
This is the phasing error mode. If in a Mode A contact, this means that the MFJ-1278B is
either trying to re-establish a link or is sending indication of a receive error.
If in Mode L or "Listen", the MFJ-1278B is hunting for a synchronization signal.
AMTOR OPERATION HINTS
To receive AMTOR, from the cmd: command line, type:
MODE AM <ENTER>
Now you should see the a_cmd: prompt. This mode is used for FEC type reception. To
enter Listen mode type:
LISTEN <ENTER>
To enter the ARQ listen mode to monitor ARQ signals type:
AMTOR <ENTER>
Page 97

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
in idle mode. If you can hear both sides, you can hear the alternate chirps as they are in sync
with each other.
If you operate Mode B or Mode S, then you should have no problems with AMTOR. These
are the broadcast modes and are almost identical to teletype in the way you make contacts.
The whole purpose behind Mode B (FEC) is, making the initial contact. After you make a
contact, you should arrange with your contact to move off the calling frequency to a working
frequency. Moving off the calling frequency is proper etiquette so that way others can then
use the calling frequency for the same purpose. Mode B allows you to make a blanket
broadcast to all stations within range. Think about teletype and you've got the right idea.
One side talks and the other listens, and then the stations change sides. To the ear, mode B
sounds almost identical to teletype. Type FEC to enter Mode B transmit and K to enter
converse mode. It works like teletype, because you transmit 100% of the time while keyed
up.
Mode S is almost identical to mode B, with the exception that it allows several stations to
link in a round-robin type of network between stations. Mode B and Mode S are not
necessarily error free, since there is no acknowledgement from the receiving station.
Mode A, ARQ mode is the mode used by most amateurs, and is sent with no errors once a
link is made between stations. Enter your own AMTOR 4-letter call at the AMTOR prompt
with:
MYSELCAL xxxx <ENTER>
Once you have a frequency selected, at the command line type:
ARQ xxxx <ENTER>
where the xxxx is the selected SELcall of the other station. The status light should remain lit
once a link is established.
Type K followed by the <ENTER> key to enter converse mode.
The MFJ-1278B will transmit all data typed just like you type it on the keyboard. You can
type as long as you like or as long as the other station does not get tired of listening, or the
band fades out. Type +? to transfer control of the link to the other station. Only one station
has control of the link at a time, so try to be considerate. If you want to take control of the
link to send a quick reply you would go back to the a_cmd: prompt and type CHANGE, then
type K to return to converse mode. Type CTRL-C once to take you back to the AMTOR
command line -- a_cmd:. If you make a mistake and type the Ctrl-C twice or more, it will
take you back to the main cmd: line. Type R or QRT at the a_cmd: to terminate the link.
It's usually a good idea to let the other station know before you do though. Think about how
Page 98

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
You can obtain hardcopy printouts from the bulit-in printer port of the MFJ-1278B.
Hardcopy printouts are done with the same printer that you used in the other modes of
operation. To make hardcopy printouts type the following at the a_cmd: command prompt:
PRINT ON <ENTER>
to activate the built-in printer port. Ensure that the printer is turned on and is ON-LINE.
Now all AMTOR received will go to the printer port, until a PRINT OFF command is
issued, or you exit back to the main cmd: line.
Summary of AMTOR Contact Sequence
1. At the cmd: command prompt, type MODE AM, this will take you to AMTOR mode B
(FEC) mode. Indicated by the a_cmd: command prompt.
2. LISTEN or LI allows you to monitor mode A (ARQ), and switches from mode B.
3. Issuing an R will switch from mode A to mode B from the a_cmd: prompt.
4. ARQ xxxx connects you with a station heard calling cq.
5. R or QRT in ARQ mode removes the link between stations.
6. FEC keys the transmitter and broadcasts a mode B message.
7. CRTL-C from the converse mode will return you to the a_cmd: prompt, and twice will
exit back to the main cmd: prompt.
Page 99

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
NAVTEX OPERATION
Navtex is a new direct printing service operating on 518 KHz.
NAVTEX stands for Navigational Telex. Navtex broadcasts urgent weather, navigational
and other information that is intended for ships.
Navtex Stations and Frequencies
Navtex Stations currently cover most coastal areas of Europe and the Eastern United States.
West Coast Stations for the United States are in various phases of planning or construction,
and will begin transmitting within a few years.
Currently operational Navtex stations in the United States include locations in Portsmouth,
Virginia, Boston, Miami, and New Orleans. A station in Sydney, Nova Scotia can also be
received in many parts of the United States.
Several Navtex stations are planned or already under construction on the West coast,
including locations in San Francisco, Astoria, Oregon, Adak and Kodiak, Alaska, Long
Beach, California and Honolulu.
The system is fully installed in Europe, and is well on its way to becoming an international
standard for navigational information.
A partial list of stations and their broadcasting time is listed in Table 4-5 below:
Station QTH Station ID Broadcast Time (UTC)
Miami O 0000,0600, 1200, 1800
Portsmouth M 0130, 0730, 1330, 1930
New Orleans G 0300, 0900, 1500, 2100
San Juan R 0415, 1015, 1615, 2215
Bermuda* B 0100, 0700, 1300, 1900
Table 4-5 Navtex Station & Frequencies
*Bermuda station is not yet on line.
Navtex Operation
Navtex is part of the Mode B (FEC) AMTOR mode. Each Navtex transmission is prefaced
by the characters ZCZC followed by a four character code of two letters that identify the
station and type of message followed by a number code from 00 to 99 that identifies the
Page 100

MFJ-1278B MULTI-MODE BASIC OPERATION
letter identifies the type of message. Refer to the following explanation of the NAVMSG
command for the different types of messages that are identified by this second letter.
The NAVMSG and NAVSTN commands allow you to choose both the types of messages
you receive and the stations you receive. The other command that applies is the NAVTEX
command.
To enter NAVTEX mode, you must first enter AMTOR mode by typing:
MODE AM <ENTER>
The MFJ-1278B will respond with the a_cmd: prompt. From the a_cmd: prompt type:
NAVTEX ON <ENTER>
The MFJ-1278B will display the Navtex command prompt, n_cmd:, indicating that it is
ready to monitor any Navtex messages. Once in the Navtex mode, tune your radio to the
Navtex frequency of 518 KHz.
To receive NAVTEX, the MFJ-1278B must first receive the ZCZC start message, followed
by the four character preamble described above. If this is not received intact, the message
will not be received. At the end of the message, NNNN will be received and the MFJ-1278B
will stop receiving the Navtex message.
The MFJ-1278B will remember the last 200 four character preambles received with less than
1/8 of its characters received in error. The MFJ-1278B will not reprint any of these messages
when they are re-transmitted from that Navtex station. If you exit the "a_cmd:" command
prompt, the preamble memory is erased.
Emergency messages are numbered 00 and will always be printed regardless of whether they
have already been received.
To prevent your MFJ-1278B from receiving certain Navtex stations, just type NAVSTN
XXXXXXXXXXXXX where each X is the identifying letter of the station you want to
receive. Your list of stations to receive may contain up to 26 letters, each representing a
station.
For example, if you want to receive only stations A, C and P, then you type NAVSTN ACP.
Only signals from these three stations will be received by your MFJ-1278B.
If you want to prevent certain stations from being received, leave then off the list. Then,
those stations will not be received while others within the receiving area will.
 Loading...
Loading...