Page 1

SX386MC
OPERATIONS
GUIDE
Page 2

SX386MC
OPERATIONS
GUIDE
Page 3

GERMAN RFI DECLARATION FOR CLASS B SELF
CERTIFICATION
Hiermit wird bescheinigt, dass der TriGem SX386MC in
Übereinstimmung mit den Bestimmungen der Vfg 1046/1984
funk-entstort ist.
Der Deutschen Bundespost wurde das Inverkehrbringen dieses
Gerätes angezeigt und die Berechtigung zur Überprüfung der
Serie auf Einhaltung der Bestimmungen eingeräumt.
TriGem Inc.
4 NaengChun-Dong, Seodaemun-Ku
Seoul, Korea
English translation:
We hereby certify that the TriGem SX386MC complies
with the RFI suppression requirements of Vfg 1046/1984. The
German Postal Service was thenotified that equipment is being
marketed; The German Postal Service has the right to re-test
the equipment and verify compliance.
Note: Replace 1046 with 1045 for household appliances tested
per VDE 0875.
ii
Page 4

IMPORTANT NOTICE
DISCLAIMER OF WARRANTY
TriGem Computer, Inc. makes no representations or warranties with
respect to this manual, and shall not be held liable for technical or
editorial omissions made herein; nor incidental or consequential
damages resulting from the furnishing, performance, or use of this
manual. Further, TriGem Computer, Inc. reserves the right to make
changes in the specifications of the product described within this
manual at any time without notice and without obligation of
TriGem Computer, Inc. to notify any person of such revision or
changes.
COPYRIGHT NOTICE
Copyright (C) 1990 by TriGem Computer, Inc. All rights are
reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, transmitted,
transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any
language or computer language, in any form or by any means,
electronic, mechanical, magnetic, optical, chemical, manual, or
otherwise, without the prior written permission of TriGem
Computer, Inc.
iii
Page 5

TRADEMARKS
TriGem is a registered trademark of TriGem Computer, Inc.
AMI BIOS is a trademark of American Megatrends Inc.
IBM, PC, PC/XT, PC/AT, MDA, Monochrome Display Adaptor,
EGA, Enhanced Graphics Adaptor, VGA, and Video Graphics
Array are trademarks of International Business Machines
Corporation.
Intel is a registered trademark of Intel Corp.
Intel 386sx is a trademark of Intel Corp.
Intel 387sx is a trademark of Intel Corp.
AMD is a registered trademark of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
EGA Wonder is a trademark of ATI Technologies, Inc.
HP LaserJet Series II is a product of HewlettPackard, Inc.
MS-DOS and GW-Basic are trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
Windows is a trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
Seagate is a registered trademark of Seagate Technologies, Inc.
Hercules is a registered trademark of Hercules Computer
Technology, Inc.
Norton SI is a trademark of Peter Norton Computing, Inc.
Apple is a registered trademark of Apple Computer, Inc.
CP/M and CP/M-86 are trademarks of Digital Research, Inc.
Western Digital is a registered trademark of Western Digital Inc.
MultiSync is a trademark of NEC information Systems, Inc.
MultiScan is a trademark of Sony Corporation.
iv
Page 6

FCC COMPLIANCE STATEMENT
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits
for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against
harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment
generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and if not
installed and used in accordance with the instructions may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no
guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation.
If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the
equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
l
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
l
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
l
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from
that to which the receiver is connected.
l
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for
help.
If you experience problems with radio and/or television reception
through the use of this product, the following booklet, published by
the FCC, may prove helpful:
How to identify and Resolve Radio-TV Interference Problems
(Stock No. 004-000-00398-5)
This booklet is available from the U.S. Government Printing Office,
Washington, D.C. 20402.
V
Page 7

SAFETY
The following instructions pertain to the risk of fire, electric shock
or bodily injury. Please read all of these instructions carefully.
Follow all of the instructions and warnings marked on this
product or included in this manual.
Do not use this computer on an unstable cart, stand or table.
Slots and openings in the cabinet and the back have been
provided for ventilation. To ensure the reliable operation of your
computer, and to protect it from overheating, these openings
must not be blocked or covered. Don’t use this product on a
bed, sofa, rug, or other similar surface.
Never push objects of any kind into the computer through the
cabinet openings, as they may touch dangerous voltage points or
short out parts that could result in a fire or electrical shock.
This computer should only be connected to the AC power
source indicated on your computer system’s information label. If
you are not sure of the type of AC power available, consult your
dealer or local power company. Only connect this computer to a
power outlet that matches the power requirements of this
computer.
Do not allow anything to rest on the power cord. Do not locate
this product where people will walk on the cord.
If you have to use an extension cord with this computer, make
sure that the total amperage rating of all equipment plugged into
it does not exceed the amperage rating of the extension cord.
Also, make sure that the total of all products plugged into the
main AC power outlet does not exceed 15 amps.
Unplug your computer from the main electrical power outlet
before cleaning.
Do not use this computer near water.
vi
Page 8
MAINTENANCE
Except as explained in Chapter 7, “Expanding Your System,” do
not attempt to modify or service this product yourself. Opening or
removing those covers that are marked “DO NOT REMOVE” may
expose you to dangerous voltage points or other risks. Refer all
servicing problems to qualified service personnel.
If the product does not operate normally, adjust only those controls
that are covered by the operating instructions. Improper adjustment
of other controls may result in damage and may require extensive
repair work to restore the product to normal operation.
Unplug this product from the main power outlet and call for service
under any of the following conditions:
If the power cord or plug is damaged or frayed
If liquid has been spilled into the product
If the product has been exposed to rain or water
If the product has been dropped or the cabinet has been
damaged
If the product exhibits a distinct change in performance,
indicating a need for service
vii
Page 9

Stop!
If you ever have to remove the main system unit cover, observe the
following precautions:
The power supply cord must be unplugged before the main
system unit cover is removed. (Separe le cordon d’alimentation
et puis enleve le couvercle.)
Once removed, the cover must be replaced and screwed in
position before the power supply cord is plugged back in. (Apres-
le couvercle a enleve, visse le couvercle en place et remettre le
cordon d’alimentation.)
RELATED READING
For more information about MS-DOS commands and GW-Basic
programming, please refer to the user’s manuals provided with this
computer.
Page 10

Wichtige Sicherheitsvorschriften
Unbedingt beachten!
Allgemeine Sicherheit
Die nachfolgenden Anweisungen betreffen die Gefahr von
Verletzungen durch elektrische Spannung, Feuer und mechanische
Einwirkung. Bitte lesen Sie diese Anweisungen sorgfältig.
Beachten Sie alle Hinweise, die am Gerät selbst angebracht oder
in den zugehörigen Handbüchem vermerkt sind.
Stellen Sie das Gerät an einem sicheren, stabilen Arbeitsplatz
auf.
Am Gerät angebrachte Öffnungen (Schlitze und sonstige
Offnungen) dienen der Belüftung des Gerätes. Um ein
zuverlässiges Arbeiten des Geräts zu gewährleisten und um
Überhitzung zu vermeiden, müßen diese Öffnungen unbedingt
freigehalten werden. Betreiben Sie das Gerät nie auf Betten,
Sofas oder anderen, wiechen Unterlagen.
Stecken keine Gegegenstände (Schraubenzieher, Büroklammem
etc.) in die Öffnungen. Sie würden damit Kurzschlüsse
herbeiführen die zur Zerstörung des Geräts führen, sich der
Gefahr eines Stromschlages aussetzen oder das Gerät in Brand
setzen.
Das Gerät darf nur an vorschriftmäßige Steckdosen mit der auf
dem Gerät angegebenen Netzspannung angeschlossen werden.
Wenn Sie nicht sicher sind, welche Netzspannung richtig ist,
wenden Sie sich an den Lieferanten des Gerätes oder an das
zuständige Elektriziträtswerk. Bitte nur an genügend stark
abgesicherte Steckdosen anschließen, die der Leistungsaufnahme
des Gerätes entsprechen.
ix
Page 11

Auf das Netzanschlußkabel dürfen keine Gegenstände gestellt
werden. Legen sie das Netzkabel so, daß niemand darauftreten
oder darüber stolpem kann.
Wenn Sie Verlängerungskabel benutzen, müßen Sie sicher sein,
daß die gesamte Leistungsaufnahme nicht größer ist als das
Verlängerungskabel zuläßt. Der gesamte Stromverbrauch aller
angeschlossenen Geräte darf nicht mehr als 15 A betragen.
Wenn Sie das Gerät reinigen, muß das Netzkabel aus der
Steckdose gezogen werden.
Das Gerät dürfen Sie nicht in der Nähe von Wasserleitungen
benutzen.
Wartung des Computers
Wenn der Computer nicht ordnungsgemäß arbeitet, durfen Sie nur
die Finstellungen vomehmen, die im Handbuch genannt werden.
Andere Einstellungen oder Veränderungen können den Computer
beschädigen oder zerstören. Umfangreiche und kostspielige
Reparaturen würden notwendig werden, um das Gerät wieder
betriebsfähig zu machen.
Ziehen Sie den Netzstecker aus der Steckdose und verständigen Sie
den zuständigen Kundendienst bei folgenden Störungen:
netzkabel ist defekt oder strak abgenutzt.
Flüssigkeit ist in dassGerät geschüttet worden.
Das Gerät war Regen oder Leitungswasser aus-gesetzt.
Das Gerät ist heruntergefallen oder das Gehäuse ist beschädigt.
Das Gerät arbeit nicht mehr richtig.
X
Page 12

ACHTUNG:
Wenn Sie das Gerät öffnen mößen (Abnahme der verschraubten
Haube), ist unbedingt folgendes zu beachten:
Das Netzkabel muß aus der Steckdose gezogen werden und zwar
bevor Sie das Gerät öffnen.
Die Haube muss wieder monitert und verschraubt werden. Erst
dann darf das Netzkabel wieder eingesteckt werden.
xi
Page 13

Contents
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
How to Use This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Chapter 1
1. Unpacking
2. Choosing a Location
3. Connecting a Monitor
4. Connecting a Printer, Mouse, or Modem
Using the Parallel Interface
Using the Serial Interface
5. Connecting the Power Cord
6. Connecting the Keyboard
Adjusting the Keyboard Angle
7. Turning On the Computer
The Command Prompt
8. Copying System Diskettes
9. Resetting Your Computer
Chapter 2
Introduction
When to Run Setup
Using Setup
Entering Setup
Parameters
Leaving the Setup Program
Setting Up Your System
......................................
..............................
.............................
.......................
.........................
.........................
............................
.....................
..........................
..........................
..........................
...........................
The CMOS Setup Program
......................................
................................
..................................
....................................
...................................
...........................
...............
1-1
1-2
1-4
1-6
1-6
1-7
1-8
1-10
1-11
1-12
1-15
1-15
1-18
2-1
2-1
2-2
2-3
2-5
2-10
Contents xiii
Page 14

Chapter 3
Using Your Computer
Changing the Operating Speed
Special Keys on Your Keyboard
Stopping a Command or Program
Using Disks and Disk Drives
How Disks Store Data
Types of Diskette Drives
Caring for Diskettes and Diskette Drives
Inserting and Removing Diskettes
Write-protecting Diskettes
Making Backup Copies
Using a Single Diskette Drive
Using a Hard Disk Drive
Chapter 4
Inserting Diskettes
Disk Drive Letters
Starting MS-DOS
System Prompt
Cursor
MS-DOS Commands
Case Sensitivity
Function Keys and MS-DOS
BACKSPACE Key
Default Drive
Copying Your MS-DOS Diskettes
Copying on Single Drive Systems
Copying on Dual Drive Systems
...........................................
Files
FileTypes
Filenames and Extensions
Disk Directories
The DIR Command
File Searches
Using MS-DOS With Your Computer
.................................
..................................
..................................
................................
........................................
...............................
...............................
..............................4-8
.....................................
................................
...................................
.................................
...........................
........................
......................
..........................
..........................
.........................
........................
.........................
...................
........................
.........................
.....................
..........................
...........................
.............
.................
.................
...................
3-1
3-2
3-5
3-5
3-6
3-8
3-10
3-12
3-14
3-15
3-16
3-17
4-2
4-2
4-4
4-5
4-6
4-6
4-7
4-7
4-10
4-11
4-12
4-16
4-19
4-20
4-20
4-23
4-23
4-24
xiv Contents
Page 15

Multiple Disk Drive Systems
Wildcards
Application Software
....................................
...............................
.....................
4-25
4-26
4-27
Chapter 5
Description
HOW
Formatting Diskettes
The FORMAT Command
Option Switches
Copying Files
WiIdcards
Chapter 6
What is a Hard Disk Drive?
Care of Hard Disk Drives
Preparing Your Hard Disk
Changing Your SETUP
Partitioning Your Hard Disk
Formatting Your Hard Disk
Organizing Your Hard Disk
Backing Up Your Hard Disk
The BACKUP Command
How Many Diskettes?
The RESTORE Command
Using Floppy Disks
.......................................
Floppy Disks Work
................................
...........................
.....................................
....................................
Using Your Hard Disk
............................
............................
..................
.......................
..........................
.........................
.....................
......................
..........................
..........................
.......................
...........................
......................
5-l
5-2
5-3
5-4
5-6
5-10
5-12
6-l
6-2
6-3
6-4
6-7
6-9
6-11
6-16
6-16
6-17
6-19
Contents xv
Page 16

Chapter 7
Expanding Your System
Connecting Peripherals
Serial Ports
Parallel Ports
Connecting Printers
Connecting Modems
Connecting External Disk Drives
System Expansion & Upgrades
Tools Required
General Precautions
Opening and Closing the Cabinet
Installing Circuit Boards
Disk Drive Compartments
Internal Hard Disk Drive
Appendix A
Computer System
System MotherBoard
CPU Logic
System Memory
System I/O
SystemTiming
I/O Address Map
...................................
Specifications
......................................
....................................
......................................
...................................
.............................
.................................
............................
............................
................................
.............
.........................
...................................
................................
...................................
..................
........................
..............
.................
.......................
........................
7-1
7-3
7-4
7-4
7-4
7-5
7-4
7-4
7-6
7-8
7-10
7-13
7-15
A-1
A-1
A-2
A-3
A-4
A-4
A-4
Appendix B
Hardware Settings
Removing the MotherBoard
Headers
Connectors
xvi
Contents
System MotherBoard
...................................
.........................................
........................................
...........................
B-1
B-3
B-3
B-4
Page 17

Appendix C
Video Monitor Systems
Monitor System Resolution
Video Controller Boards
Monitor Types
Appendix D
I/O Ports
.....................................
Connector Pinouts
........................................
Expansion Slot Connectors
Appendix E
Introduction
Advanced ROM Diagnostics
.......................................
...........................
..............................
...........................
When to Run Advanced Diagnostics
Starting Advanced ROM Diagnostics
Advanced ROM Diagnostics Tests
Hard Disk Diagnostics
Floppy Diagnostics
Keyboard Diagnostics
Video Diagnostics
Miscellaneous Diagnostics
..............................
.................................
................................
...................................
............................
......................
....................
..................
C-1
C-1
C-4
D-1
D-5
E-1
E-1
E-2
E-4
E-5
E-32
E-48
E-49
E-5I
Contents
xvii
Page 18

Introduction
Your TriGem computer is powerful, versatile, and easy to use.
After setting up your system with the simple instructions in this
manual, you’ll soon be using your favorite software programs.
This computer is available in these configurations:
The System provides one 1.2MB (megabyte) diskette drive
and an optional 40MB (or 80MB) hard disk drive.
You can operate a lot of application programs very fastly
and efficiently with this system because it provides 32KB
cache memory.
This model comes with 2MB of internal memory, a total of five
internal option slots, a System Motherboard an on board IDE
type HDC and built-in serial and parallel interfaces.
Your computer comes with MS-DOS —
by Microsoft. In addition to the introduction to MS-DOS
provided in this manual, you’ll find a complete reference
manual for the operating system packed in the box with the
computer.
the operating system
As your needs grow, so can your computer; you can expand
your system by adding a wide variety of options. You can install
most option cards compatible with the IBM Personal
Computer. If you use software that executes lengthy
mathematical calculations, you may want to install an 387sx™
math coprocessor to speed up processing.
Introduction 1
Page 19

How to Use This Manual
This manual explains how to set up and care for your
computer.
It also describes how to use your computer.
The instructions in this manual apply to your system, except
where otherwise indicated.
You probably don’t need to read everything in this book; see
the following chapter summaries.
Chapter 1 provides simple step-by-step instructions for setting
up your computer.
Chapter 2 describes how to run the Setup program to setup
your computer’s configuration.
Chapter 3 covers some general operating procedures, including
how to use and care for your disks and disk drives.
Chapter 4 provides basic instructions for using MS-DOS with
your computer.
Chapter 5 takes you into the more advanced techniques of
floppy disk file manipulation, such as formatting and copying.
Chapter 6 shows you how to set up and use the vast storage
capabilites of this system device.
Chapter 7 contains “how-to” information on adding
components (such as additional disk drives or expansion
boards), to your computer.
At the end of this guide is a set of Appendices which contain
technical information for the advanced user or field technician.
2 Contents
Page 20

Chapter 1
Setting Up Your System
Setting up your personal computer is easy. Just follow the nine
steps in this chapter.
When you finish setting up your computer, go on to Chapter 2
and follow the instructions there to run the Setup program.
The Setup program updates the list of equipment installed in
the computer and any time options are added or changed.
Unpacking
1
As you unpack the different parts of your computer system, be
sure to inspect each piece. If anything is missing or looks
damaged, contact the place where it was purchased for missing
items or replacements. If you cannot obtain the necessary part
of parts, call your TriGem Computer dealer for assistance.
Please have the computer’s serial number ready when you call.
Figure 1-1. Unpacking Your System
Setting
Up Your System
1-1
Page 21

Besides this manual, you should have the following:
The computer and power cord
The Keyboard with attached cable
MS-DOS diskettes
GW-BASIC diskette
MS-DOS User’s Guide
GW-BASIC User’s Guide
In addition to these items, you need a compatible monitor to
use with the computer.
Be sure to keep your packing materials. They provide the best
protection for your computer if you need to transport it later.
Choosing a location
2
Before you set up your computer, it is important to choose the
right location. Select a spot that provides the following:
1-2
Setting Up Your
A large, sturdy desk or table that can easily support the
weight of your system, including all of its components:
Make sure the surface is hard and flat. Soft surfaces like
beds and carpeted floors can generate static electricity,
which may erase data on your disks and damage the
computer’s circuitry. Soft surfaces also prevent proper
ventilation.
Good air circulation: Air must be able to move freely
under the system as well as behind it. Leave several inches
of space around the computer to allow ventilation.
Moderate environmental conditions: Protect your computer
from extremes in temperature, direct sunlight, or any other
System
Page 22

source of heat. High humidity also hinders operation, so
select a cool, dry area. Avoid dust and smoke, which can
damage disks and disk drives and cause you to lose valuable
data.
Appropriate power sources: To prevent static charges,
connect all your equipment to three-prong, grounded
outlets. You need one outlet for the computer, one for the
monitor, and additional outlets for a printer and any other
peripherals.
If it has the appropriate power cord, you can plug the
monitor into the auxiliary power outlet on the back panel
of the computer,. reducing the number of wall outlets you
need. (The current required by the peripheral must not
exceed 1 amp.) If you need more outlets, you may want to
buy a power strip-available at any electronics store-to
provide extra outlets. A power strip with surge suppression
is recommended.
No electromagnetic interference: Locate your system away
from any electrical device, such as a telephone, that
generates an electromagnetic field.
Setting Up Your System
1-3
Page 23

Connecting a Monitor
3
The video display monitor is the device used by-the computer
to communicate with you. Your software will use the screen to
display information, such as prompts, text, graphics (charts and
pictures), etc.
Several types of monitor are available as options. A typical
video display system provides a high resolution monochrome
(green or amber screen) screen display. Your computer can be
with either monochrome, color video monitors, EGA or VGA
monitor.
In addition to the display monitor itself, the video system
includes a video controller board. This board generates the
letters, numbers, and graphics symbols displayed on the
monitor screen.
Connectors are provided for the display type that is supported
by the board (monochrome, RGB color, high resolution EGA,
VGA etc.). Certain boards support more than one type of
display, and may provide a switch to select either color or
monochrome modes.
The procedure you use to connect your monitor to the
computer depends on the type of monitor you have. See your
monitor manual for detailed instructions, or follow these
general guidelines:
1.
Place your monitor on top of or near the computer. It is
easiest to connect the monitor cable if you are facing the
back panels of both the monitor and the computer.
Setting Up Your System
1-4
Page 24
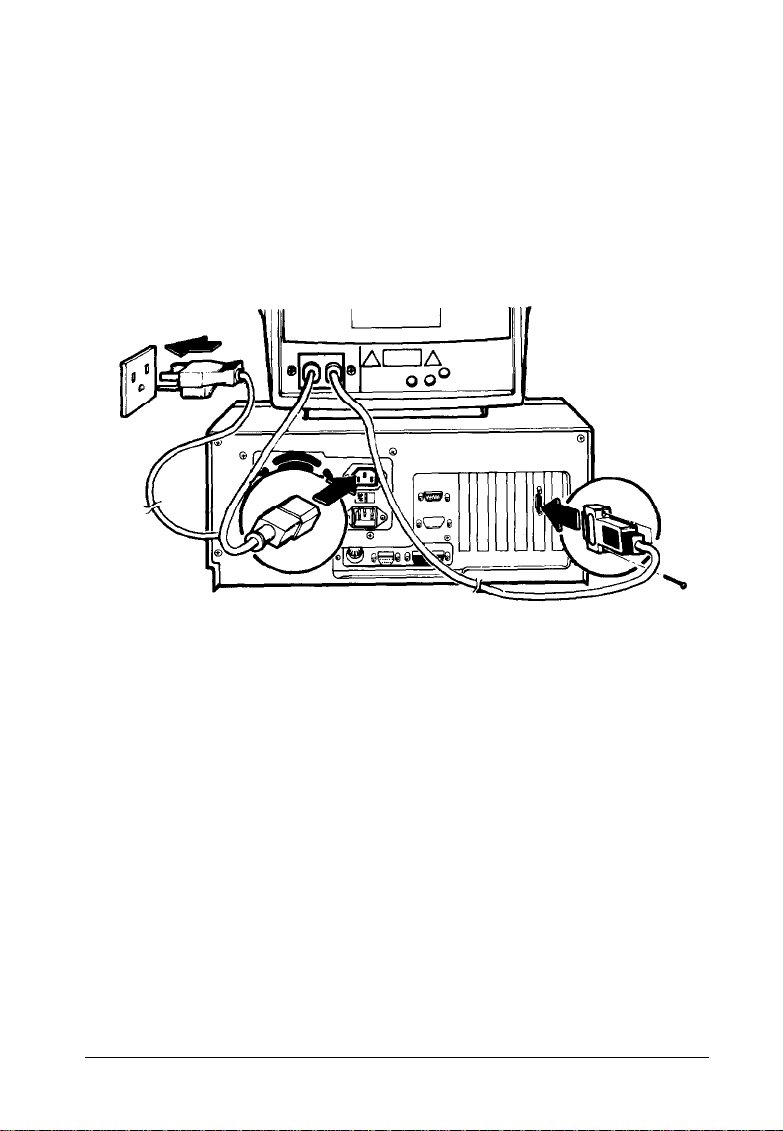
2.
If necessary, connect the monitor cable to the monitor.
(Some monitors come with permanently attatched cables.)
3.
Connect the monitor cable to the video connector on the
back of the computer, as shown below. If the plug has
retaining screws, tighten them securely.
Figure 1-2. Connecting the Monitor
4. Plug the other end of monitor’s power cord into an
electrical outlet.
Setting Up Your
System
1-5
Page 25

Connecting a Printer, Mouse, or Modem
4
The computer has a parallel interface and two serial interfaces
on the back panel, so you can easily connect a printer or other
type of device with either type of interface.
For example, you can use the parallel port to connect a parallel
printer (most printers have a parallel interface). You can use ,
the serial port to connect a serial printer, a serial mouse, or an
external modem.
Follow the steps in this section to connect a printer or other
peripheral device to either the parallel or serial interface.
Using the Parallel Interface
The parallel interface on your computer is Centronics
compatible and uses a 25-pin connector. To connect a parallel
printer to your computer, you need an IBM-compatible printer
cable. If you are not sure which one you need, or whether you
have the right one, check with the store where you purchased
the printer.
Once you have the correct printer cable, follow these steps to
connect the printer to the parallel interface on the computer.
1.
Place the printer next to your computer.
2.
One end of the printer cable has a 25-pin, male connector.
Connect this end to the parallel port on the back panel of
the computer, as shown below.
If the plug has retaining screws, tighten them securely.
1-6 Setting Up
Your
System
Page 26
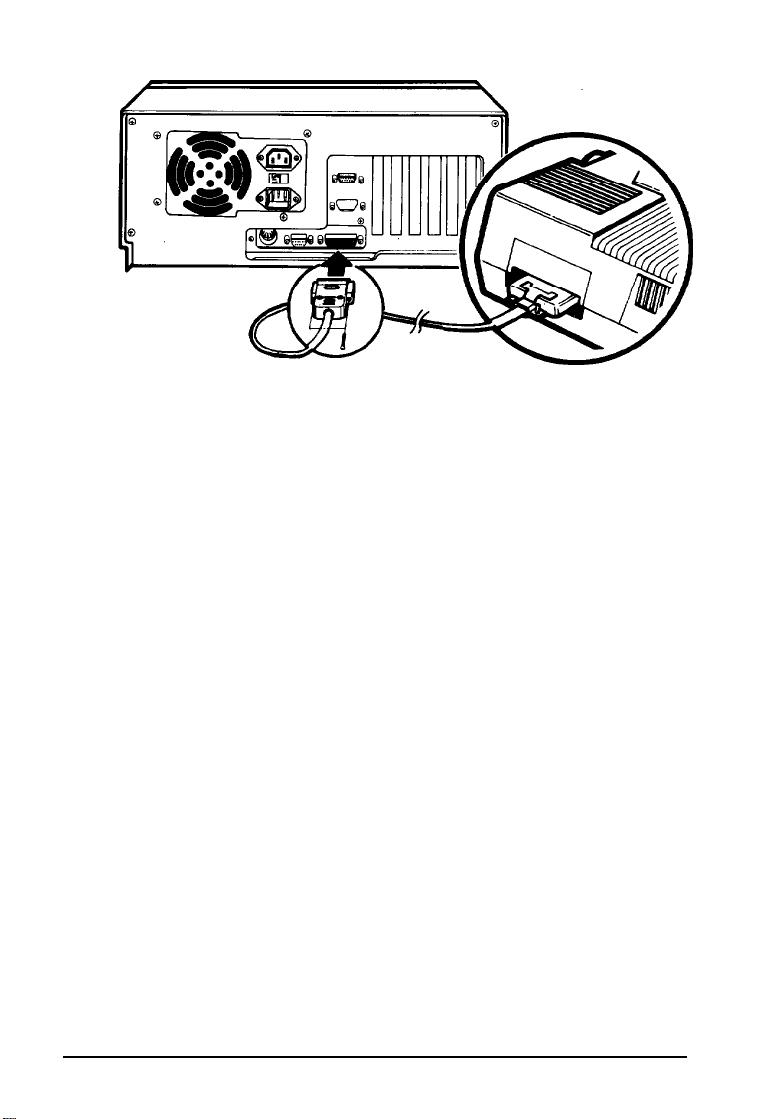
Figure 1-3. Connecting the Printer
3.
Connect the other end of the cable to the printer, as
shown below. If the printer has retaining clips on each side
of the printer port, squeeze the clips together to secure the
cable.
4. Plug the printer’s power cord into an electrical outlet.
Using the serial Interface
If you have a serial printer, modem, mouse, or any other
peripheral with a serial interface, you can connect it to one of
two serial (RS232C) ports on the back of the computer. Your
computer uses IBM-compatible, 9-pin, male connector, so be
sure you have the proper cable. If you are not sure which one
you need, or whether you have the right one, check with the
store where you bought the cable.
To connect a serial device, follow the same steps outlined
above for a parallel device, but connect the cable to the serial
port, shown below.
Setting Up
Your
System
1-7
Page 27
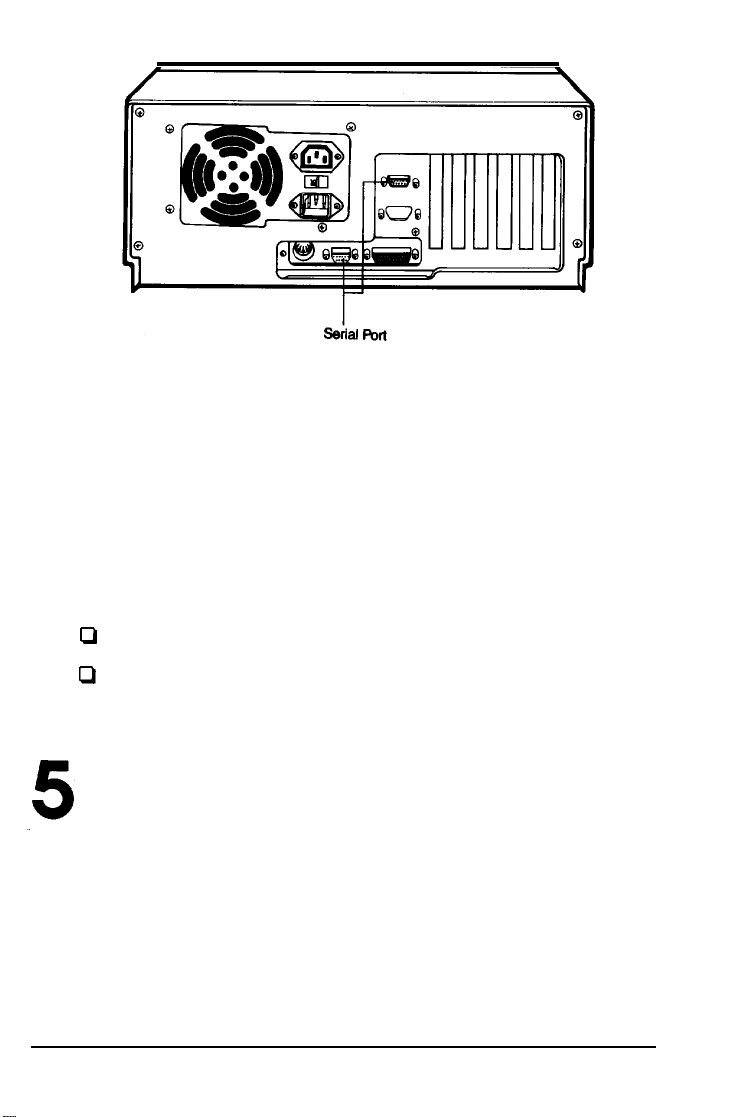
Figure 1-4. Serial Port
Setting up-the serial port for a printer
If you are using a serial printer but your software does not
support a serial printer, you must do two things before you can
print:
o
Set up the data transmission parameters for the serial port.
0
Tell the computer to redirect printer data from the parallel
port to the serial port.
Connecting the Power Cord
Follow these steps to connect the power cord:
1.
Insert the power cord into the AC inlet on the computer’s
back panel, as shown below. To avoid an electric shock, be
sure to plug the cord into the computer before plugging it
into the wall socket.
Setting Up Your System
1-8
Page 28
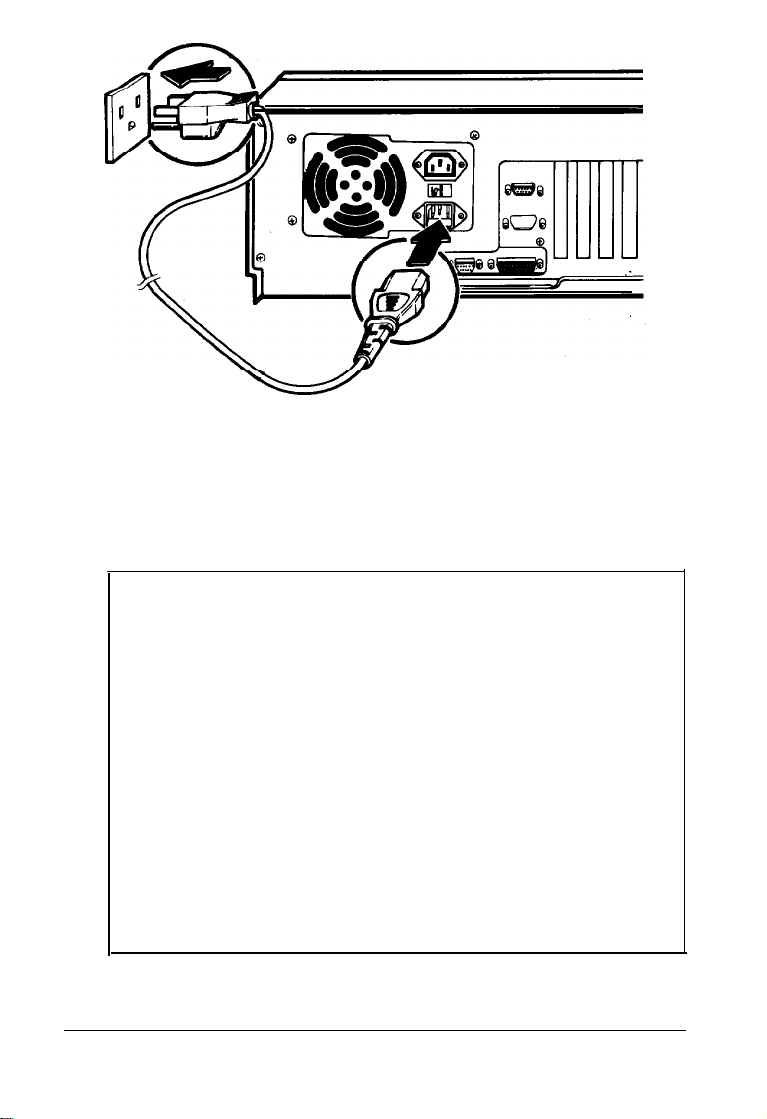
Figure 1-5. AC Power Connections
Plug the other end of the power cord into a three-prong,
2.
grounded electrical outlet.
Note
The socket-c&let should be installed near the equipment
and should be easily accessible.
Die Verbindung zwischen Steckdose solite mölichst Kurz
sein. Die steckdose sollte frei zugäglich sein.
For units to be installed in European countries, a power
supply cord of type HAR, with H05W-F should be
used.
Für Geräte, die in europäschen Ländern eingesetzt werden,
sollte ein Netzkabel Typ HAR mit der Mummer H05 W-F
benutzt werden.
Setting Up Your
System
1-9
Page 29
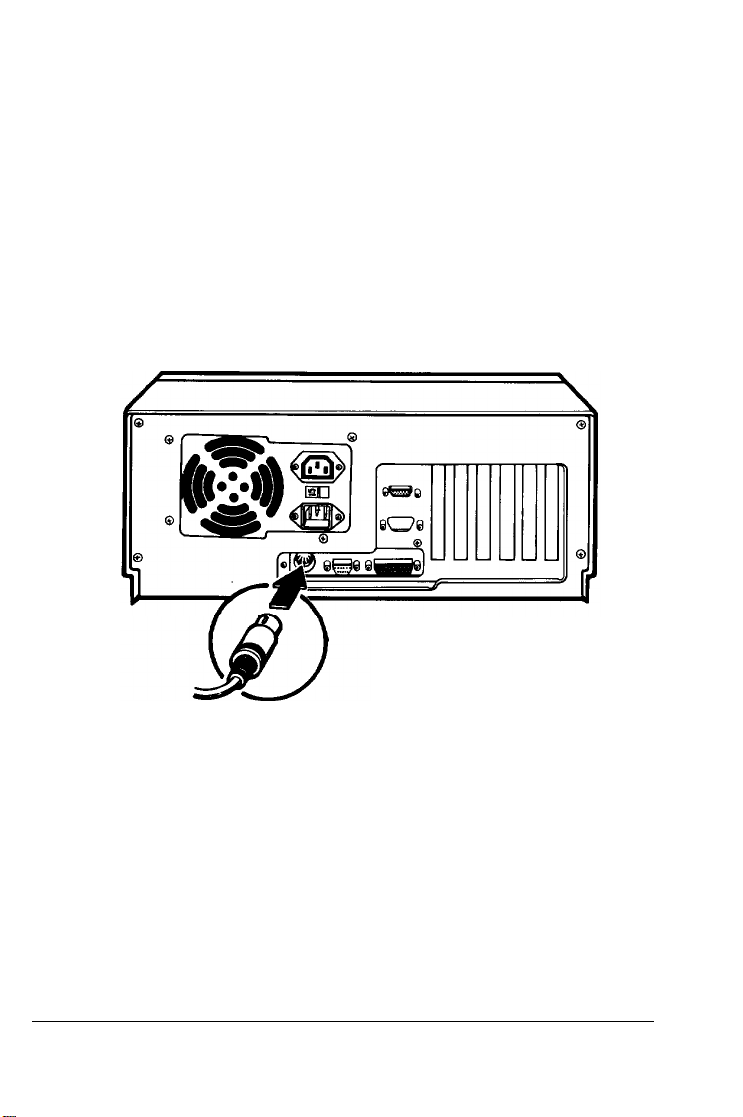
6
Connecting the Keyboard
Your keyboard has only one cable to connect.
This simply plugs into the keyboard connector located at the
bottom of the main system unit’s rear panel. This connector is
designed to prevent insertion if the pins don’t line up, so it
may be necessary to rotate the cable connector until it plugs in
easily.
l-l0
Setting
Figure l-6. Connecting the Keyboard
Up
Your System
Page 30
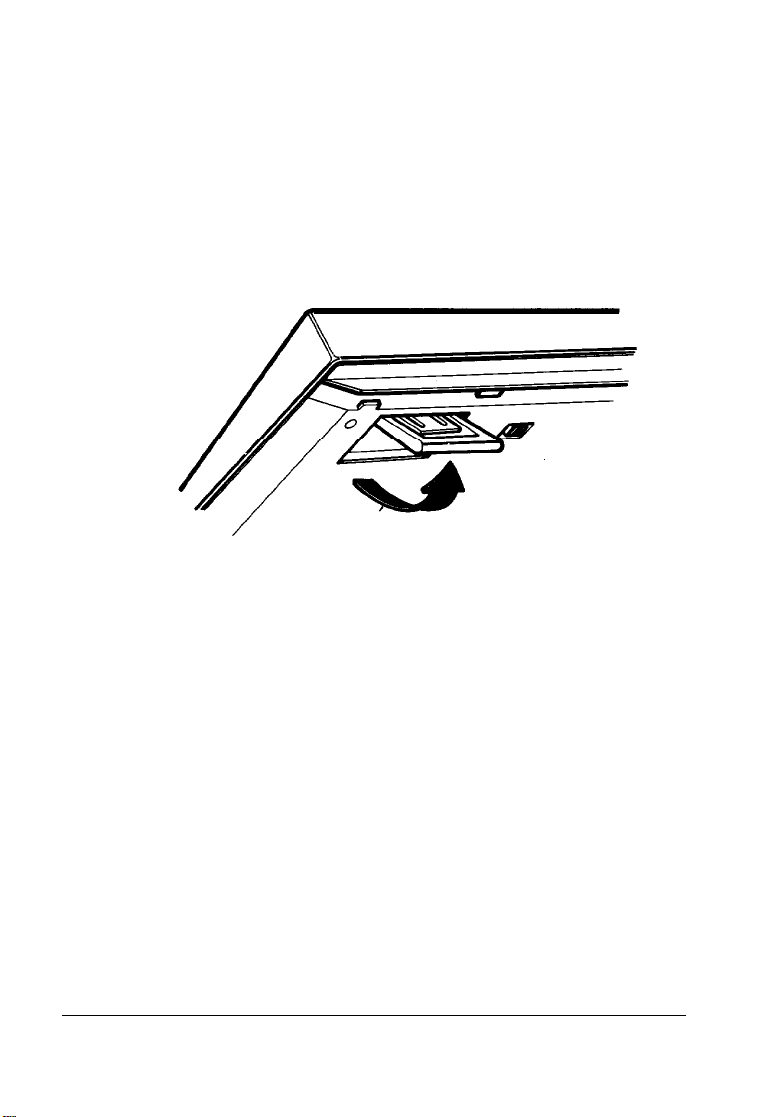
Adjusting the Keyboard Angle
You can change the angle of the keyboard by adjusting the legs
on the bottom. Turn the keyboard over and lift each leg
upward until it locks into place, as shown below. You lock the
legs into a low or high position, or leave them flat.
Figure 1-7. Adjusting the Keyboard Angle
Setting Up Your
System
1-11
Page 31

Turning On the Computer
7
Before you turn on your computer, read the following safety
rules to avoide accidentally damaging the computer or injuring
yourself:
Do not unplug cables from the computer when the power
switch is on.
Never turn off or reset your computer while a disk drive
light is on. This can destroy data stored on disk or make an
entire disk unusable. Similary, never remove a diskette
from a diskette drive while the drive light is on.
Always wait at least five seconds after you switch off the
power before you switch it on again. Turning the power off
and on rapidly can damage the computer’s circuitry.
Do not leave a beverage on top of or next to your system
or any of its components. Spilled liquid can damage the
circuitry of your equipment.
Do not attempt to dismantle any part of the computer.
Only remove the cover to install and remove optional
devices.
1-12 Setting Up Your System
Page 32

Follow these steps to turn on your system:
1.
Turn on the monitor, printer, and any other peripheral
devices connected to the computer.
2. To turn on the computer, press the power switch.
Figure
1-8. Power Switch
The power indicator on the front panel lights up. After a few
seconds, the computer starts to perform an internal self test.
This is a series of checks the computer completes each time
you turn it on to make sure everything is working correctly.
If anything is wrong, an error message appears on the screen.
After the self test is complete, you see a message on the screen
smiliar to this:
Setting Up Your System 1-13
Page 33

388-BIOS (C) 1989 American Megatrends Inc.
(C) 1989 TriGem Computer Inc.
XXXX KB OK
Press <ESC> to bypass MEMORY test
SIZING CACHE MEMORY, 32KB FOUND
TESTING CACHE MEMORY, 32KB OK
CACHE TEST COMPLETED
(C) American Megatrends Inc,.
DVSX-6080-060290-KB
The computer continually updates this display as it tests its
memory. This test takes about 1.5 seconds to complete.
You may see a message similar to this:
This means that the computer is not yet set up for the
equipment you have installed and you must run the Setup
program, described in Chapter 2. For now, press the Fl key on
the upper left comer of the keyboard to acknowledge the
message and continue.
If you cannot see the screen display clearly, use the controls on
you monitor to adjust the brightness and contrast until
characters on the screen are clear and bright.
The computer then loads MS-DOS, the operating system, from
the hard disk into memory. MS-DOS must be in the
computer’s memory before you can run any program, such as a
word processing program or a spreadsheet program.
1-14
Setting Up Your System
Page 34

The Command Prompt
After the computer has loaded MS-DOS from the hard disk,
you see the MS-DOS command prompt on the screen:
The command prompt tells you that your computer is ready to
receive instructions. It also identifies the current operating
drive: A or C, for example. The command prompt appears on
the screen whenever you load MS-DOS, complete an MS-DOS
command, or exit an application.
In your computer, the diskette drive is A and the hard disk is
drive C. If you have an optional second diskette drive, MS-DOS
identifies it as B.
Copying System Diskettes
8
Now that you have started your system and loaded MS-DOS, it
is important that you make copies of your MS-DOS diskettes
right away. Use the copies (called working copies) as they are
needed and store the originals in a safe place.
Each of the system diskettes is formatted for 1.2MB.
(Formatting prepares a diskette to store data and is described in
Chapter 3 and Chapter 5.)
To copy them, you need eleven 1.2MB highdensity,
diskettes.
Note
If you do not have any 1.2MB diskettes, you can use
unformatted 360KB diskettes. When copying from 1.2MB
diskettes, the DISKCOPY program formats the 360KB
diskettes for 1.2MB.
Setting Up
Your System
51/4inch
l-15
Page 35

Follow these steps:
The C > prompt should be on the screen. If not, type C:
1.
and press Enter.
Type the following and press Enter:
2.
The screen displays this message:
Insert the MS-DOS diskette in drive A, as shown below.
3.
Hold the diskette with the label facing up and the
read/write slot into the drive.
1-16
Figure 1-9. Inserting a Floppy Disk
Setting Up Your System
Page 36

4. Press any key. The DISKCOPY program copies the
contents of the MS-DOS diskette to the computer’s
memory, and then you see the following:
If the diskette is not formatted, the DISKCOPY program
formats it. Then the program begins copying the data from
the computer’s memory to the formatted diskette. When
the copy is complete, you see this prompt:
5.
Remove the MS-DOS diskette and insert a blank diskette
(which is to be the target diskette) in drive A. Then press
any key.
6. Press Y so you can make a copy of another MS-DOS diskette.
Again, you see the prompt to insert the source diskette.
7.
Remove the copy of the MS-DOS diskette which you just
made
and insert the another MS-DOS diskette into drive A.
Then press any key. Follow the prompts on the screen to
make a copy of this diskette as you did for the first MS-DOS
diskette.
8. When you finish copying the last diskette and the
prompt appears, press N to return to the MS-DOS
command prompt C > .
After you have copied the MS-DOS diskettes, be sure to label
them carefully so you know which one is which. Write on the
Setting Up Your System
1-17
Page 37

labels before you attach them to the diskettes in order to
prevent damaging the diskettes. Store the originals in a safe
place and use the copies as they needed.
Resetting Your Computer
9
If your computer system should “lockup”, it may be necessary
to reset the computer. Resetting the computer causes the CPU
to clear its instruction set and the system memory. This ensures
there is no “garbage” left in memory to interfere with new
program information.
There are two basic ways to reset your computer. They are:
CONTROL-ALT-DEL (Keyboard Reset)
Press the CONTROL key and the ALT key at the same
time. While holding these keys down, press the DELETE
key, then release all three keys. This will reset your
computer without running the full self-test diagnostics.
The POWER Switch
Turn the main system POWER switch off, wait ten
seconds, then turn it back on. The computer will then run
the complete self-test diagonistic routine.
Caution!
Any time you RESET your computer, the memory will be
cleared. This will erase any software programs loaded into
the system RAM. You may lose important data or have
problems using your software after the system re-boots.
Only RESET your system if you are sure that all of your
data has been: saved to disk, or is is no other way
escape a “lockup condition,
You should now be able to reset your computer if you run into
trouble. At this point, you can complete the installation of
your system by running the SETUP program. For detailed
information on the SETUP program, see the following chapter.
1-18 Setting Up Your System
Page 38

Chapter 2
The CMOS Setup Program
Introduction
The Setup program keeps a record of the host computer’s
system parameters (such as memory amounts, disk drives, video
displays, and numeric coprocessors). Setup resides in the Read
Only Memory Basic Input/Output System (ROM BIOS) so that
it is available each time the host is turned on. Setup stores the
information in the complementary metal oxide semiconductor
(CMOS) memory. When the host is turned off, a back-up
battery retains system parameters in the CMOS memory.
As soon as the host is turned on, the power-on diagnostics
routines check memory, attempt to prepare peripheral devices
for action, and offer you the option of pressing <DEL> to
run Setup.
When
to Run Setup
During normal daily operation, you do not have to run Setup
when you start the host computer.
Under the abnornal conditions, an appropriate message
displays, advising you to run the Setup program. These
conditions indicate that an error has occurred during the
power-on self-tests (POSTS).
The CMOS Setup Program
2-1
Page 39

Note
Note that you can bypass the memory test by pressing the
< ESC > key. This option would be useful when the
memory on the system is quite large. You should hit the
<ESC> key when the following message appears on the
screen.
Press <ESC> to bypass MEMORY test
Using Setup
Immediately after the memory test, you will get the following
prompt on the screen depending upon the type of BIOS you
have:
Press <DEL> if you want to run SETUP or DIAGS
Hit <DEL > key to get into the Setup Mode
Note
<DEL > key will get you into the setup mode, only when the
above message is displayed on the screen.
If you hit < DEL > key, a menu appears on the screen giving
you the option of
2-2
The CMOS Setup Program
Page 40

Use <Up “ > and <Down ” > keys to set the reverse video
cursor on the option you want to select and use < Enter > to
get into the option.
This means that the SETUP program options have been set at
the factory. Since there were no errors detected, the computer
tried to load MS-DOS from the floppy disk drive, before you
have inserted the MS-DOS main system diskette. For now
ignore this message.
If you want to run the “DIAGNOSTICS” program, see
Appendix E for the detailed description of it.
Entering SETUP
To enter the setup program, hit < DEL > key at the time the
following prompt is displayed on the screen immediately after
the memory test.
The CMOS Setup Program
2-3
Page 41

If you hit <DEL> key, you will see a menu like as following.
Set the reverse video cursor on the “RUN CMOS SETUP”
using <Up “ > and < Down ” > and press <ENTER>. Then
the screen will be replaced by the following.
This screen is the SETUP MENU. ‘This lists the parameters
you can change with the SETUP program. A solid cursor bar
highlights the parameter currently available to be changed. You
can use the following key conventions.
2-4
‘The CMOS Setup Program
Page 42

< Enter >
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
moves the selection bar
<
‘
< PgUp > < PgDn >
<ESC>
< Ctrl > < Alt > < Del >
Parameters
0
Date and Time Setup
The first entry in the Setup screen is current date. A
calendar has been provided for the user to facilitate him in
this procedure. Again, simply press the < PgUp > or
< PgDn > keys to select the appropriate value for the
month, date and year.
The procedure for setting the time is similar to that of
setting the date. The time here is 24-hour time so don’t be
alarmed when hour 13 shows up on the screen. Simply
highlight either the hours, minutes, or the seconds and
press the <PgUp >/ < PgDn > keys to step through the
numbers.
Cl
Floppy Disk Drive Setup
> <
’
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
>
. . . . . . ...
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . .
moves the selection bar
scrolls allowable settings
exit and save CMOS register
exit without save
Drives a: and/or b: may be one of the following types:
Allowable Drive Types
36OKB
1.2MB
720KB
1.44KB
not installed
51/4"
51/4"
31/2"
31/2"
The CMOS Setup Program
2-5
Page 43

Hard Disk Drive Setup
Drives c: and d: are the hard disk drives in the system. 46
drive types have been defined by AMI. If for some reason
or other your particular drive is not one of the 46 pre-defined
types, simply scroll down to type 47 and enter the
following drive specifications: cylinders, heads, WPcom,
LZone, and sectors. Please consult the documentation
received with the drive for the specific values that will give
you optimum performance.
Display Type Setup
The next option is primary display selection. The options
are as follows:
Type of Display Allowed
Monochrome
Color 40 x 25
Color 80 x 25
VGA or EGA
Not Installed
Keyboard Setup
The keyboard Setup is the next option for the user. You
may either choose to enable or disable the Keyboard test
during Power On Self Test by setting keyboard as
“Installed” or “Not Installed”.
Scratch RAM Option.
The next option is the setting of the scratch RAM. The
purpose of this element is to
(1) Save the user definable drive type 47
(2) Translate 80386 Loadall function for programs like
OS/2, RAMDRIVE etc.
2-6
The CMOS Setup Program
Page 44

If Shadow RAM is not enabled, the parameters of the drive
must be stored in normal RAM, but the integrity of the
data must be maintained. The options you have are the
following:
1.
The BIOS to use 100 bytes at 30h:0
2. The BIOS to reduce the size of the base memory by 1KB.
The default is 1. If you are not using Drive type 47 or not
running programs like OS/2, RAMDRIVE this RAM will
never be used by so you may leave the value as 1.
P
start-up speed
This parameter is used to select the system’s default speed.
The options are:
l
High speed
Under this option, your system is initially booting with
20MHz
l
CPU speed when you turn the power on.
Low speed
Select this option is to boot your system with 6MHz
CPU speed as turning the power on.
00 Special Memory
This parameter is used to boost your system’s performance
by loading the BIOS and/or VIDEO controller code into
the RAM space between 640K and lM-byte. The options
are:
l
None
Select this option is you are not going to use shadow
RAM.
l
BIOS
Use this parameter to copy the system BIOS into shadow
RAM during the start-up routine.
The CMOS Setup
Program
2-7
Page 45

l
Video
This parameter loads the program code from your video
card into shadow RAM during system start up.
l BIOS + Video
This option loads the BIOS and video code into shadow
RAM.
l
Ext. Memory
If you use the extended memory on your system, select
this option. The Ext. Memory size is determined
according to the EMS Size and displays on the upper
right comer of the Setup message.
l
EMS Memory
You can use the EMS memory using this option.
0
EMS Size
The options available are used to describe how your system
will use the EMS memory above lM-byte, as follows:
l
The EMS memory size is preset according to the on
board memory size. If you want to use EMS memory, you
should select the EMS memory size you are using in this
option.
The CMOS Setup Program
2-8
Page 46

0
Peripheral Setup
When you scroll down to this parameter, the following
message will be displayed on the right side of the Setup
message.
Peripheral Setup
Serial 1: Enabled
Serial 2: Enabled
Parallel: Enabled
FDC: Enabled
HDC: Enabled
l
Serial 1
If you’d like to the on board serial port 1 for COM 1, set
this option “Enable”.
But, when you install the external
card to use another serial port for COM 1, you should
select “Disable” on this option to disable the on board
serial port.
l
Serial 2
Set this option “Enable” if you want to use the on board
serial port 2 for COM2. Like as serial 1, you should also
disable this option when you install the external card to
use another serial port for COM2.
Note
Although you need only the on board serial 2 port for
COM2, do not disable the serial 1. If you disable serial 1
and enable aerial 2 when you don’t have any external I/0
adapter, the serial 2 automatically set to CDM1.
l
Parallel
If you use on board parallel port, enable this option.
However if you want to use another parallel port using
external I/O card, you should disable this option.
The CMOS Setup Program 2-9
Page 47

l
FDC
Your system provide on board FDC and it supports two
floppy disk drive to your system. If you use another FDC
in your system using external Card, you should disable
this option.
l
HDC
The system has on bord IDE type HDC. If you’d like to
another type of HDC (for example, SCSI, or ESDI etc.),
disable this option and install your HDC Card to the
expansion slot on the backplane board.
Leaving
When you have completed the changes, press the < ESC >
key. The SETUP
Write data into CMOS and exit (Y/N)?
If you have made any mistakes, press N for No, then move the
cursor back up to the beginning and verify each parameter,
making any corrections necessary. When you are satisfied with
the option settings, press the <ESC> key, then press Y to
write the new settings into the configuration RAM. Your
computer will run through the self test diagnostics again and
try to read a diskette in the first floppy disk drive.
As mentioned above, you may see an error message if you don’t
have a system diskette inserted into the floppy disk drive.
the
Setup Program
program will display the message:
2-10 The CMOS
Setup Program
Page 48

Chapter 3
Using Your Computer
This chapter covers the following basic procedure for using
your computer:
00 Changing the operating speed
00
Using special keys on the keyboard
Cl
Stopping a command or program
00 Using disks and disk drives.
Changing the Operating Speed
Your computer can operate two speeds; 8MHz or 20MHz.
At 20MHz, the computer performs all tasks faster, and almost
all programs may be run at 20MHz. However, some option
cards and application programs require the lower speed. See
your option card or application program manual to make sure
that you can use the higher speed before selecting it.
Keyboard Method
The following keystroke sequences can be used to set the
processor clock speed.
l Ctrl-Alt- < - >
Hold down the < Ctrl > and < Alt >
keys and press < - > on the numeric
keypad to place the system in low speed
mode.
Using Your Computer 3-1
Page 49

l
Ctrl-Alt- < + >
Hold down the < Ctrl > and < Alt >
keys and press < + > on the numeric
keypad to place the system in high
speed.
Changing the operating speed may be performed with the
TriGem Utility TGSS.COM. This program is located on the
MS-DOS diskette supplied with the system. You can find the
detailed description of TGSS.COM in your MS-DOS User’s
Guide.
Special Keys on your Keyboard
Certain keys on your keyboard serve special functions when
your computer is running programs. The illustration below
shows the TriGem keyboard, and the table that follows
describes the special keys.
3-2
Figure 3-1. Keyboard (101 key)
Using Your Computer
Page 50

Key
Purpose
F1-F12
Tab
Ctrl
Shift Produces uppercase characters or the top symbols
Alt
Backspace
(-)
Enter
Caps Lock
Perform special functions within application program
(Some keys also function with MS-DOS. See your
MS-DOS Reference Manual for more information.)
Moves the cursor one table to the right in normal
mode (and one tab the left in shift mode when using
some application programs.)
Works with other key to perform special (control)
function, such as editing operations.
on the keys when used with the main character keys.
Produces lowercase characters when Caps Lock is
on.
Works with other keys to enter alternate character
codes or functions.
Moves the cursor back one space, deleting the
character to the left of the cursor
Ends a line of keyboard input or executes a
command (may be called the Return key in some
application program manuals).
Changes the letter keys from lower-to uppercase;
changes back to lowercase when pressed again.
The numeric/symbol keys on the top row of the
keyboard are not affected.
Esc
Num Lock
Scroll Lock
Break
Cancels the current command line or operation in
MS-DOS. Esc can also have special uses in
application programs.
Changes the function of the keys on the
numeric/cursor keypad from numeric entry to cursor
positioning; changes back when pressed again.
Controls scrolling in some application programs.
When pressed with the Ctrl key (hold down Ctrl and
press Break), sends a break signal to the computer
to terminate the current operation.
Using Your Computer 3-3
Page 51

Key
Purpose
SYS Req
PrtSc
Home, End,
PgUp, PgDn
et-1
Ins
Del
Produces the system request function in certain
applications.
Prints the screen display on a dot-matrix printer
Control cursor location in some applications, such as
word processors, game programs, and
spreadsheets.
Turns the insert function on and off in some
application programs.
Deletes the character at the cursor position.
The Num Lock, Scroll Lock, and Caps Lock keys work as
toggles; press the key once to turn on a function and again to
turn it off. When the function is enabled, the corresponding
light on the top right comer of the keyboard is on. When the
function is disabled, the light is off.
3-4
Figure 3-2. Keyboard LED
Using Your Computer
Page 52

Stopping a Command or Program
You may sometimes need to stop a command or program while
it is running. Many application programs provide a command
you can use to stop or even cancel (undo) an operation. If you
have entered an MS-DOS command that you want to stop, try
one of the following commands:
Hold down the Ctrl key and press C
0
Hold down the Ctrl key and press Break
0
These methods may also work in your application program.
If you cannot stop a particular operation, however, you may
need to reset the computer, as described in the following
section.
caution!
It is best not to run off the computer to stop a program or
command. If you have created new data that you have not
yet stored, it will be erased if you turn off the computer.
Your computer stores data in its memory until you save it;
but the memory area is erased each time you turn off or.
reset the computer.
Using Disks and Disk Drives
The disk drives in your computer allow you to store data on
disk and retrieve it when you want it.
This section explains how disks work and tells you how to do
the following:
0
Choose diskettes
Using Your Computer
3-5
Page 53

o
Care for your diskettes and diskette drives
0
Insert and remove diskettes
0
Write-protect diskettes
0
Make backup copies of your diskettes
0
Use a single diskette drive
0
Use a hard disk drive
How Disks Store Data
The diskette you insert in your computer’s diskette drive is
made of flexible plastic, coated with magnetic material. It is
enclosed in a square jacket. Your computer stores data on the
diskette by recording on the magnetic surface.
Unlike a diskette, a hard disk is rigid and fixed in place. It is
sealed in a protective case to keep it free from dust and dirt. A
hard disk stores data the same way that a diskette does, but it
works faster and has much larger storage capacity.
All disks are divided into data storage compartments by sides,
tracks, and sectors. Double-sided diskettes - like the ones you
use in your computer - store data on both sides. On your disk
there are concentric rings, called tracks, in which a disk can
store data. Double-density diskettes (such as 360KB diskettes)
have 40 tracks, and high-density diskettes (such as 1.2MB or
1.44MB diskettes) have 80 tracks. But 720KB double density
diskette has 80 tracks.
A hard disk consists of two or more magnetically-coated
platters stacked on top of one another, so it has four or more
sides with many more tracks than a diskette.
3-6
Using
Your Computer
Page 54

A disk is further divided b
y sectors. To understand what a
sector is, picture the spokes on a bicycle wheel radiating from
the center of the wheel to the tire. The space between one
spoke and the next is like a sector on a diskette. (See the figure
below.) Each track on a 1.2MB diskette has 15 sectors, and
each sector holds 512 bytes.
Figure 3-3. Sectors and Tracks
Your computer uses the read/write heads in a disk drive to store
and retrieve data on a disk. There is one head above the
diskette and one below, so the drive can write to both sides of
the diskette. To write to a disk, the computer spins it in the
drive to a position where one of the read/write heads can access
the diskette through the read/write slot. The read/write slot on
a diskette exposes the diskette’s magnetic surface so the
read/write head can write on the appropriate area.
Because data is stored magnetically, you can retrieve it, record
over it, and erase it - just as you play, record, and erase music
on a cassette tape.
Using Your Computer 3-7
Page 55

Types of Diskette Drives
You computer has at least one 1.2MB diskette drive. With this
drive, use 51/4+inch, double-sided, high-density, 96 TPI, 1.2MB
diskettes. These diskettes contain 80 tracks per side, 15 sectors
per track, and hold up to 1.2MB of information, which is
approximately 500 pages of text. You can also format these
diskettes for 360KB - see your MS-DOS Reference Manual for
more information.
In addition, you may have a diskette drive of a different type.
The following list describes the types of optional diskette drives
you can use in your computer and which diskettes you should
use with them:
0
360KB drive - With this drive, use 51/4-inch, doublesided, doubledensity, 48 TPI (tracks per inch), 360KB
diskettes. (You can also use single-sided, 160KB or 180KB
diskettes). These diskettes contain 40 tracks per side, 8 or 9
sectors per track, and hold up to 360KB of information,
which is approximately 150 pages of text. (With 8 sectors
per track, a diskette holds up to 320KB.)
cl
720KB drive - With this drive, use 3l/2-inch, doublesided, double-density, 135 TPI, 720KB diskettes. These
diskettes contain 80 tracks per side, 9 sectors per track, and
hold up to 720KB of information - approximately 300
pages of text.
1.44MB drive - With this drive, use 3l/2-inch, double-
0
sided, highdensity, 135 TPI, 1.44MB diskettes. These
diskettes contain 80 tracks per side, 18 sectors per track,
and hold up to 1.44MB of information, which is
approximately 600 pages of text.
If your computer has more than one type of these drives or if
you use diskettes from other computers, you need to be aware
of certain incompatibilities between the drives and the
diskettes they use.
3-8
Using
Your Computer
Page 56

Note
You must format new diskettes before you can use them
with an operating system. Formatting erases all the data on
a diskette and prepares it to receive new data, so be sure to
format only new blank diskettes or diskettes that contain
data you want to erase. See Chapter 5 for instructions on
formatting diskettes.
Drive
and diskette incompatibilities
Because of the size difference, you cannot use 31/2-inch
diskettes in a 51/4-inch drive or vice versa. There are also
certain limitations on using diskettes that are the same size as
the drive but have different capacities. The following tables
summarize the possiblities and limitations.
5l/4-inch drive/diskette compatibility
Drive type
360KB
1.2MB
Diskette types it can read from and write to
180KB, or 360KB
180KB, 360KB, or 1.2MB
31/2-inch drive/diskette compatibility
Drive type
720KB
1.44MB
Diskette types it can read from and write to
720KB
720KB, or 1.44MB
Using
Your Computer
3-9
Page 57

Because of these incompatibilities, you should indicate the
density and diskette type when you label your diskettes.
(Usually this information appears on the manufacturer’s label.)
If you have any combination of the above drives (360KB,
1.2MB, 720KB, or l.44MB), y
to another - using the COPY or XCOPY command - as long
as the correct diskette type is in each drive. You can use these
commands to copy files between the hard disk and any type of
diskette. You cannot use the DISKCOPY to copy from one
drive to another if the two drives are not the same type.
ou
can copy files from one drive
Caring for Diskettes and Diskette Drives
Follow these basic precautions to protect your diskette and
avoid losing data:
Cl
Do not remove a diskette from the diskette drive or turn
off the computer while the drive light is on. This light
indicates that the computer is copying data to or from a
diskette. If you interrupt this process, you can destroy data.
0
Remove all diskettes before you turn off the computer.
0
Keep diskettes away from dust and dirt. Small particles of
dust or dirt can scratch the magnetic surface and destroy
data. Dust can also ruin the read/write heads in a diskette
drive.
D Never wipe, brush, or try to clean diskettes in any way.
0
Keep diskettes in a moderate environment. They work best
at normal room temperature and in normal humidity. Do
not leave your diskettes sitting in the sun, or in extreme
cold or heat.
3-10
Using Your Computer
Page 58

Keep diskettes away from magnetic fields. (Remember that
diskettes store information magnetically.) There are many
sources of magnetism in your home or office, such as
electrical appliances, telephones, and loudspeakers.
Do not place diskettes on top of your monitor or near an
external disk drive.
Never touch a diskette’s magnetic surface. The oils on your
fingertips can damage it. Always hold a diskette by its
protective jacket. If you are using a 31/2-inch diskette, do
not slide the metal shutter; this exposes the diskette’s
surface.
Do not place anything on top of your diskettes and be sure
they do not get bent. A diskette does not rotate properly in
the drive if it has been damaged.
Carefully label your diskettes. Attach labels firmly but
gently, and only along the top of a diskette (next to the
manufacturer’s label). Do not stick several labels on top of
one another-too many labels can make it difficult to insert
the diskette into the drive.
It is best to write on the label before you attach it to the
diskette. If you need to write on a label that is already on a
diskette, use only a soft-tip pen, not a ballpoint pen or a
pencil. Always indicate the storage capacity and density
type on the label.
Store diskettes in a proper location, such as a diskette
container. Do not store diskettes flat or stack them on top
of each other. When you are not using them, keep your
diskettes in their protective envelopes.
Follow these additional precautions to protect your hard disk
drive and its data:
Using Your Computer
3-13
Page 59

0
Never turn off the computer when the hard disk drive light
is on. This light indicates that the computer is copying
data to or from the hard disk. If you interrupt this process,
you can lose data.
Cl
Never attempt to open the hard disk drive. The disk itself
is enclosed in a sealed container to protect it from dust.
Inserting and Removing Diskettes
To insert a diskette into the drive, hold it with the label facing
up and the read/write slot leading into the drive, as shown
below.
Figure 3-4. Inserting a Diskette (5 1/4”)
Slide the diskette into the slot until it is in all the way. Then
turn the drive latch down to lock it in a vertical position. This
keeps the diskette in place and enables the read/write heads in
the diskette drive to access the diskette.
3-12
Using
Your
Computer
Page 60

If a diskette is in the drive but the latch is up (horizontal) and
you enter a command for that drive, the computer cannot
tell
there is a diskette in the drive and displays an error message
such as:
Close the latch and press R.
To remove the diskette, turn the drive latch up until it is
horizontal and the edge of the diskette pops out. Carefully pull
out the diskette, place it in its protective envelope, and store it
in a proper location, such as a diskette container.
If you have an optional 31/2-inch diskette drive, insert the
diskette with the label facing up and the metal shutter leading
into the drive, as shown below. Slide the diskette into the
drive until it clicks into place.
Figure
3-5.
Inserting a Diskette
Using Your Computer
(31/2”)
3-13
Page 61

To remove a 3’/2-inch diskette, press the release button to
release it. When the edge pops out of the drive, pull out the
diskette and store it properly.
warning
Never remove a diskette or turn off the computer while the
drive indicator light is on. You could lose data, Also be
sure to remove all diskettes before you turn off the
computer.
Write-protecting Diskettes
You can write-protect a diskette to prevent its data from being
altered. When a diskette is write-protected, you can read it and
copy data from it, but you cannot store new data on the
diskette or delete any files it contains. If you try to change data
stored on a write-protected diskette, MS-DOS displays an error
message.
To write-protect a 51/4-inch diskette, cover the small,
rectangular notch (shown below) with an adhesive write-protect
tab. Write-protect tabs usually come with new 51/2inch
diskettes when you buy them.
3-14
Figure 3-6. 5’/4” Diskettes & Write-Protect Tab
Using Your Computer
Page 62

Some program diskettes, such as your MS-DOS diskettes,
have no notch so they
any permanently write-protected.
This protects them from being accidentally erased or
altered.
On a 31/2inch diskette, the write-protect device is a small
switch on the lower-right comer on the back, shown below. To
write-protect a 3l/2-inch diskette, slide the switch toward the
edge of the diskette until it clicks into position, exposing a hole
in the comer.
Figure 3-7. 3’/2” Diskette & Write-Protect SW
To remove the write protection, slide the switch toward the
center of the diskette so the hole is covered.
Making Backup Copies
It is important to make copies of all your data and system
diskettes. Copy all diskettes that contain programs, such as the
original MS-DOS diskettes that come with your computer, and
use
only the copies. Store your original MS-DOS diskettes in a
Using Your Computer 3-15
Page 63

safe place away from your working copies. Backup your data
diskettes regularly, whenever you revise them, to keep them
up-todate, and store them away from your originals.
Chapter 1 describes how to use DISKCOPY to copy your
MS-DOS diskette. For more detailed information to make
backups of other diskettes, refer to Chapter 4 “Using MS-DOS
with your computer”.
It is best to put most of the programs and data files you use
regularly on the hard disk. Keep backup copies of all your
program files on diskettes, however, and regularly copy
important data files to diskettes as well.
Using a Single Diskette Drive
The operating system expects the computer to have at least
two diskette drives, and it displays prompts and messages
accordingly. If the computer has only one diskette drive, MS-DOS
treats the one drive like two logical drives. This helps you
perform operations that normally require two diskette drives.
Usually, MS-DOS recognizes the first diskette drive (the top
drive) as drive A and the second diskette drive as drive B.
If you have only one diskette drive, MS-DOS recognizes it as
both A and B.
For example, if you give a command to copy from A to B,
MS-DOS copies data from the diskette you place in the single
drive (A) to the computer’s memory. Then MS-DOS
automatically prompts you to insert another diskette in the
same drive, which it now identifies as drive B. It copies the
data from memory to the new diskette. When the copying is
complete, MS-DOS identifies the drive as drive A again, and
you see a prompt to insert the original diskette into drive A.
3-16
Using Your Computer
Page 64

You can load the opeating system and application programs
from the hard disk, create and store your data there, and use
the diskette drive just for copying data to and from diskettes.
Note
If you only have one diskette drive and no hard disk, you
need to use that drive to load the operating system as well
as the application programs you are using. First load the
operating system; this copies it into the computer’s memory
(RAM) so you do not need to leave the diskette in the drive.
Then you can remove that diskette and insert the program
diskette you want to use, and load that into memory too.
See your application program manual for detailed
instructions.
Using the Hard Disk Drive
You can create and revise files on a hard disk
on a diskette. The hard disk, however, provides several
advantages:
Cl
The 20MB hard disk can store more data than 16x 1.2MB
diskettes and the 40MB hard disk can store twice as much.
Your computer can perform all disk-related operations faster.
0
0
You can store all your frequency used programs and data
files on the hard disk, eliminating the inconvenience of
inserting and removing diskettes to access different files.
The added storage capacity makes it easy to move back and
forth between different programs and data files. However,
because it is so easy to add programs and files to your hard disk,
you may find yourself trying to organize hundreds of files.
MS-DOS lets you keep related files together in directories and
subdirectories so they are easier to find and use.
Using Your Computer 3-17
just
as you can
Page 65

Backing up hard disk Ales
While the hard disk is very reliable, it is essential to back up
your hard disk files to diskettes in case you lose some data
accidentally. Make copies of all your system and application
program diskettes before copying the programs to the hard disk.
After you create data files on the hard disk, be sure to copy
them to diskettes whenever you revise them to keep your
backup diskettes up-todate.
You can see the more detailed information of backing up hard
disk files on the Chapter 6.
Preparing the hard disk for moving
Before you move the computer, you need to secure the
read/write heads inside the hard disk drive. Securing the
read/write heads moves them to a region of the disk surface
that does not contain data, and locks them in position. This
prevents the disk from being damaged if it is bumped
accidentally.
To secure the read/write heads for moving, run the TGSHIP
program. Follow these steps to run TGSHIP:
1.
Exit any program you are using so the MS-DOS command
prompt is on the screen.
2.
Insert the MS-DOS diskette in drive A.
3. Type the following and press Enter:
3-18
Using Your Computer
Page 66

You see a message on the screen that tells you the disk drive’s
read/write heads will remain locked until you reset the
computer or turn the power off and on again. The computer
locks the heads and disables the keyboard. You can now turn
off the computer and prepare to move it to the new location.
The TGSHIP command should be run whenever you are going
to move the main system unit. This command moves the
read/write heads inside the hard disk drive to a “safety zone,”
where they won’t accidentally scratch the surface of the drive
platters. TGSHIP.COM
is a special DOS command file
included with your system. You should copy this file into the
root directory of your hard disk drive.
See MS-DOS reference manual for more information of
TGSHIP command.
Using
Your
Computer
3-19
Page 67

Chapter 4
Using MS-DOS With Your Computer
Once you have your computer system “up-and-running,” you
may begin to work with MS-DOS.
Virtually all application software available for IBM PCiXT and
PC/AT-compatible computer systems runs “under” MS-DOS.
Therefore, in order to use these programs, you need to learn
how to use MS-DOS. This chapter will give you a basic
understanding of MS-DOS and provide you with the basic
tools you need run application software on your computer
system. For more detailed explanation of the MS-DOS
operating system, see your MS-DOS USER’S GUIDE.
MS-DOS is an acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System.
The disk operating system is a collection of programs that allow
you to control all the elements of your computer. When booting
up, the MS-DOS command file is copied from the MS-DOS
main disk into your computer’s memory. From there, it
controls the rest of the system.
During a normal operating session, you will want your
computer system to boot up in MS-DOS. Before that can
happen, however, you may need to install MS-DOS on your
system.
If your system does not have a hard disk system, you must
perform the installation routine to configure MS-DOS for
floppy disk-based operation.
If you do have a hard disk drive, but MS-DOS has not been
installed you must perform the installation routine to configure
MS-DOS for use on the hard disk system.
For complete instructions on installing MS-DOS, see your
MS-DOS User’s manual.
Using
MS-DOS With Your Computer
4-1
Page 68

Inserting Diskettes
Your MS-DOS software package contains of the following items:
a
One MS-DOS Install Diskettes
0
One MS-DOS Select Diskette
0
Three MS-DOS Operating Diskettes
Q
One MS-DOS Shell Diskette
0
The MS-DOS User’s Guide & User’s Reference
0
The MS-DOS Shell User’s Guide
Begin the installation procedure by placing the MS-DOS
Install diskette in the A drive and turning your computer on.
Disk Drive Letters
The various disk drives on your computer are assigned letters.
As you work with MS-DOS, you will see that these letters are
used to identify which drive is to be used at any given time.
The microcomputer industry has standardized the use of letter
identification for MS-DOS-type machines as follows:
0
The first floppy disk drive is referred to as the “A:” drive.
Cl
The second floppy disk drive is referred to as the “B:”
drive.
0
The first hard disk drive is referred to as the “C:” drive.
4-2 Using MS-DOS With
Your Computer
Page 69

To insert a diskette into the drive:
0
Open the drive door
0
If you haven’t already done so, remove the protective
cardboard insert from the drive.
0
Gently insert the diskette into the drive entry slot with its
label facing up, and the write protect notch to the left.
Cl
When the diskette is all the way in, close the drive door by
turning the door latch handle down.
Caution!
If any resistance is felt when closing the drive door, stop
and reinsert the diskette.
To remove a diskette from a floppy disk drive:
0
Be sure the drive indicator light is off
Caution !
It is very important that you never remove a diskette from
an active drive. Doing so can destroy the information on
the diskette. If the computer. system is “locked-up” with
the drive indicator light on, RESET the computer before
removing the diskette.
Turn the door latch to open the drive.
0
Remove the diskette and insert it into its protective
0
envelope.
Using
MS-DOS With Your Computer
4-3
Page 70

Starting MS-DOS
To start MS-DOS 4.01 on a floppy disk-based system (that is,
one without a hard disk drive), follow these steps given below.
For a detailed description of how to start MS-DOS 4.01,
consult the Getting Started section in your MS-DOS 4.01
User’s Guide.
Cl
Remove the MS-DOS Install diskette from its protective
envelope and insert it into the A drive.
Cl
Close the disk door and turn your computer on.
0
Remove the Install disk and insert the Select disk.
Cl
Press ENTER.
CI
Remove the Select disk and insert the Install disk.
D
Press ENTER.
The Welcome screen appears. This screen contains information
about the number of disks required to install the operating
system.
0
Press ENTER
The Introduction screen appears. This screen contains
information about the function keys used to run the Select
program.
Cl
Press ENTER
The first screen of the Select program appears. For more
information about the Select program, consult the Getting
Started section in your MS-DOS 4.01 User’s Guide.
If your computer has a hard disk drive, and MS-DOS has been
installed, simply turn your system on. Your computer will
perform its self-test diagnostics and display the DOS Shell
menu screen.
4-4 Using MS-DOS With Your Computer
Page 71

Notice that the words “Command Prompt” are highlighted by
a solid bar. This is a DOS Shell option that allows you to work
directly with MS-DOS.
Your computer system is now “running under DOS.”
For now, press ENTER to run the Command Prompt option.
System Prompt
After you press the ENTER key to either accept the time
shown or enter a new one, MS-DOS will show a new prompt
on the monitor:
Using MS-DOS With Your Computer
4-5
Page 72

This is the system prompt. When it is displayed, it means
that MS-DOS is waiting for you to tell it what to do. This is
done by typing a DOS command, then pressing the ENTER
key.
Cursor
Following the system prompt, you will see a blinking underline
( _ ) character.
This is the “cursor”. The cursor shows you where the next
character you type will appear on the screen. As you can see
here, any command you type will appear immediately to the
right of the system prompt and on the same line. Application
software often uses the cursor as well, allowing you to use the
cursor control keys to move the cursor around on the screen.
MS-DOS Commands
DOS commands instruct your computer to perform tasks such
as display a disk directory, copy a file, delete a program, etc.
These are called internal commands and can be used anytime
after the system has loaded MS-DOS into memory. They do
not require the MS-DOS main system diskette to function.
More complex DOS commands are actually separate programs
that provide powerful features for your computer. These are
called external commands, and perform such tasks as
formatting a diskette, comparing files on different disks,
backing up a hard disk, etc. These commands require one or
more of the MS-DOS diskettes.
Hard disk system user’s can run any DOS command without
diskettes because the programs are stored on the hard disk
drive.
4-6 Using MS-DOS With Your Computer
Page 73

Case Sensitivity
MS-DOS does not differentiate between upper and lower case
letters in commands and filenames. This manual will show
commands in upper case for clarity, but you may enter them
either way. For example, both of these commands will generate
a directory listing of a diskette:
and
Function Keys
As mentioned earlier, MS-DOS uses several of your keyboard’s
function keys to provide you with shortcuts. When you press
the ENTER key after typing a command, MS-DOS copies the
command into a “buffer” memory. By using the function keys,
you can edit and reuse the command without having to retype
the entire line.
- Fl key
Copies one character at a time from the buffer to the command
line
- F2 key
Copies the entire buffer up to the next character you type
- F3 key
Copies the entire buffer to the command line
and
Using
MS-DOS
MS-DOS With
Your
Computer
4-7
Page 74

- F4 key
The opposite of F2, deletes all characters from the buffer up to,
but not including, the next character you type
- F5 key
Moves the current line you are typing into the buffer without
ENTERing it
- F6 key
Places an “end-of-file” marker when you copy from the
monitor to a disk file
- ESC key
Cancels the current command line without changing the buffer
- INS key
Inserts characters into the command line as you copy
characters from the buffer
- DEL key
Deletes characters from the buffer
BACKSPACE Key
From time to time, you may make a typing error. This is not
usually a problem if you correct the error before you ENTER
the command. You can use the BACKSPACE key for this
purpose.
Note
Occasionally, you might happen to enter the wrong
command by mistake. If this incorrect command will result
in the loss of data, MS-DOS will Usually warn you, and
give you a change to change your mind.
4-8 Using MS-DOS With Your Computer
Page 75

The BACKSPACE key on your keyboard works just like a
backspace key on a regular typewriter: it moves the cursor back
one position. In addition, however, it erases the last character
typed. Press the BACKSPACE key as many times as necessary
to erase the typing mistake, then type out the command
correctly. For instance, type the following (but do not press
ENTER):
Press the BACKSPACE key twice to erase the I and the R.
Retype:
Then press the ENTER key. Your computer will respond by
producing the directory of the disk in the A drive. Now type
this:
Then press the ENTER key. Your computer will respond:
Using
MS-DOS With Your Computer
4-9
Page 76

Default Drive
MS-DOS will only look at one disk drive at a time. Normally,
this is the “default” drive. You can tell which disk drive is the
current default drive by looking at the system prompt.
For example:
indicates that the “A” drive is currently the default drive.
Unless you specify otherwise, MS-DOS will direct any disk
activity to the “A” floppy disk drive.
You can easily change the default drive with an internal DOS
command. For instance, to change from the “A” drive (floppy
disk), to the C d
The computer will respond:
(hard disk), enter:
rive
As you can see, the system prompt has changed to show the
new default drive letter.
Note
If the computer responds:
Invalid Drive Specification
it may mean that either there is no hard disk system
installed, or your hard disk drive has not been configured
yet. See Chapter 6, “Using Your Hard Disk,” for
instructions.
4-10
Using
MS-DOS With Your Computer
Page 77

From the A. prompt command, try the command:
The computer will respond:
Press ENTER after you insert the diskette into the drive, then
the system prompt will be:
If you have a dual floppy disk drive system, the second, or “B”
drive is now the system default drive, as indicated by the new
system prompt. If performed on a single drive computer system,
this command will still change the system prompt to B > , even
though there is only one physical drive present.
The BIOS “pretends” there are two disk drives present. It
routes all commands intended for the B drive back to the A
drive.
This feature is intended to allow owners of single drive systems
to use application software designed for dual drive systems.
Copying Your MS-DOS Diskettes
The first important task you must complete with your new
system is to make a “backup” copy of your MS-DOS diskettes.
To do this, you will need seven blank diskettes. It is a good
idea to prepare seven diskette labels at this time. Write the
following on those diskette labels, using a felt tipped pen:
Using
MS-DOS With Your Computer 4-11
Page 78

Write down the MS-DOS version number on each diskette
labels. This will avoid confusion later if you upgrade your
operating system to a new version. As you finish copying and
checking each MS-DOS master diskette, peel the correct label
off of the backing paper and place it on the upper left-hand
side of the front face of the new diskette.
The following procedures will show you how to make backup
copies of your MS-DOS master diskettes on both single and
dualdrive systems.
Copying on Single Drive systems
MS-DOS uses the external command DISKCOPY to copy
entire diskettes. DISKCOMP is used to compare the original
and backup diskettes to ensure that the copy is accurate.
To copy your master diskettes, first turn your computer on and
boot up MS-DOS. Choose the Command Prompt option from
the DOS shell menu. The system prompt will appear.
Enter the following command:
The following message will be displayed:
4-12 Using MS-DOS With
Your
Computer
Page 79

The “SOURCE” diskette is the disk that you will be copying
from. Insert the MS-DOS master diskette into the A drive.
Press any key, such as the % SPACEBAR. The floppy disk drive
will be activated, and your computer will display:
The contents of the disk are being read into your computer’s
memory. After a few moments, the following message will
appear:
When the drive indicator light goes out, remove the MS-DOS
master diskette from the floppy disk drive. Insert a new, blank
diskette into the drive. This is the “TARGET” diskette.
Press the SPACEBAR key. The drive will turn
on,
indicating
that the computer formatting the new diskette, then writing
the copied information onto it. After a few moments, the drive
will turn off, and the system will display:
Using MS-DOS With Your
Computer 4-13
Page 80

For now, type N. The system prompt will reappear. To
compare the backup diskette with the original, you will use the
DISKCOMP command. Enter the command at the system
prompt:
The computer will respond:
Remove the backup diskette from the drive, and put it in its
protective jacket. Set it aside for a moment, making sure that
you don’t mix it up with the second blank diskette. Put the
original “master” MS-DOS main system diskette back into the
floppy disk drive, then press the SPACEBAR key. As with the
DISKCOPY command, your computer will read the entire
contents of the diskette into system memory, and will display:
When the computer is finished reading, the drive will turn off,
and the following message will appear:
Using
4-14
MS-DOS With Your Computer
Page 81

Remove the master MS-DOS diskette from the floppy disk
drive, and put it in its protective envelope. Take out the
backup copy diskette, insert it into the disk drive, and press the
SPACEBAR key.
The computer will read the contents of the backup diskette,
and compare them with the copy of the master diskette that it
has stored in memory. If the information on the two diskettes
is identical, the computer will respond:
Type N to return to the system prompt.
If there is a problem with the backup diskette, or if you put the
wrong diskette into the drive by mistake, the computer will
respond:
Compare error on
side x, track x
If the computer shows compare errors, start the copying
procedure over again at the beginning. The backup copy of the
MS-DOS diskette must be identical to the original. After you
have confirmed that the backup diskette is a good copy of the
master MS-DOS diskette, you may put your master diskette
away in a safe place. From now on, only use the master MS-DOS
diskette to make copies. For all other purposes, use the backup
copy of the MS-DOS diskette. By using the backup copy, you
ensure that any accidental erasures can be replaced.
Using MS-DOS With Your Computer
4-15
Page 82

Copying on Dual Drive Systems
To make backup copies of your MS-DOS diskettes on a dualdrive
system, follow the instructions below:
First, turn your computer on and boot up MS-DOS. Choose
the Command Prompt option from the DOS shell menu.
The system prompt will appear. Enter the following command:
This command indicates to MS-DOS that you want to copy
the contents of a diskette in the A drive to a new diskette
located in the B drive.
The following message will be displayed:
The “SOURCE” diskette is the disk that you will be copying
from. The “TARGET” diskette is the one you will be copying to.
Put your master MS-DOS diskette in the A drive, and a new,
blank diskette in the B drive.
Warning!
If you have any doubts about which diskette goes in which
drive, check them carefully. Make sure that the write
protect notch on the master MS-DOS diskette is covered
with a
4-16
write protect
Using
MS-DOS With
tab.
Your
Computer
Page 83

Close bath drive doors. Press any key, such as the
SPACEBAR. The A drive will be activated, and your
computer will display:
The contents of the disk are being read into your computer’s
memory.
After a few moments, the following message will
appear:
For now, type N. The system prompt will reappear. To
compare the backup diskette with the original, you will use the
DISKCOMP command. Enter the command at the system
prompt:
The computer will respond:
Since both diskettes are already in their correct locations, press
the SPACEBAR key. While the comparisons are being made,
the computer will display:
Using
MS-DOS with
Your Computer
4-17
Page 84

When the computer is finished comparing the diskettes, the
drives will turn off, and the following message will appear:
Type N to return to the system prompt.
If there is a problem with the backup diskette or if you put the
wrong diskette into the drive by mistake, the computer will
respond:
After you have confirmed that the backup diskette is a good
copy of the master MS-DOS diskette, you may put your master
diskette away in a safe place and put the label on the backup
diskette. From now on, only use the master MS-DOS diskette
to make copies. For all other purposes, use the backup copy of
the MS-DOS diskette. By using the backup copy for everyday
computing, and saving the master diskette, you ensure that any
accidental erasures can be replaced.
From now on, when this manual refers to the “main system
diskette,” use the backup MS-DOS diskette.
4- 18
Using MS-DOS With
Your Computer
Page 85

FILES
In the same way that you can keep information grouped
together in manila folders, MS-DOS organizes data into files.
While you may store these folders in a cabinet, your computer
stores these files on disks. Separating information into files
allows you to work with that information more efficiently.
File Types
There are two basic file types:
B
Program files
0
Data files
Program files are files that perform a task. They manipulate the
computer and data files in order to achieve a result. MS-DOS is
a collection of program files, as are the control programs found
in application software.
Data files are files that contain the information (data) used by
program files. A file containing a list of names and addresses
would be a data file.
The two types of files are closely related. Program files usually
create data files. These may be the documents created by a
word processor, the numerical array created by a spreadsheet, or
some other collection of information.
A data file containing a written report can’t do anything by
itself. On the other hand, a word processor is useless without
documents to work on.
Using MS-DOS With Your Computer
4- 19
Page 86

Filenames and Extensions
Needless to say, each file on a disk must be uniquely
identifiable. To achieve this, MS-DOS requires that you name
every file you create, as you create it.
In order to be able to manipulate files easily, MS-DOS has
certain rules that you must follow when naming files. As you
will see, these rules leave you a great deal of freedom in your
selection of filenames.
Each filename can be up to eight characters long. To this eight
character name can be added an “extension ‘.’ Extensions
always begin with a period ( . ) which is followed by up to three
characters.
The format for a valid MS-DOS filename is:
ABCDEFGH.JKL
Most of the characters and symbols on your keyboard are
available for use in filenames. These are:
Cl
The letters A through Z
4-20
0
The numbers 0 through 9
0
The following symbols:
!
@
#
$
O/O
&
Using MS-DOS With Your Computer
(exclamation point)
(“at” sign)
(number sign)
(dollar sign)
(percent sign)
(ampersand)
Page 87

(and) (parenthesis)
-
(minus sign or hyphen)
{ and } (brackets)
-
(underline character)
The following are examples of allowable filenames:
JANUARY
CHAPTER.001
MEMO.APR
MAYSALES.$
$$,SALES.OCT
These filenames are valid because none of them are too long,
and only legal characters have been used. The following are
examples of illegal filenames, along with an explanation:
3RDQUARTER.SALES
This is too long. MS-DOS will accept this filename, but it
will be shortened to fit the size limits. The altered filename
would read 3RDQUART.SAL. As you can see, both the
filename and its extension have been shortened to the legal
length.
CHAPTER/4
The slash ( I ) is an illegal filename character. MS-DOS
will reject the filename and ask for another.
NEW EMPL.LTR
This would be rejected by MS-DOS because of the space in
the filename.
Using
MS-DOS With Your Computer
4-21
Page 88

Certain filename extensions have been set aside so that MS-DOS
can recognize program files. These are:
Cl
COM
Cl
EXE
0
BAT
(for COMMAND file)
(for EXECUTABLE file)
(for BATCH file)
Program files should always have one of these three filename
extensions. Data files should never use these reserved
extensions. They can, however, use any other extension.
Filename extensions are optional with data files, so you can
leave them off entirely, if you want. Using filename extensions
with data files allows you to have many different variations for
a set of filenames. For instance, different chapters of a book
might be named:
CHAPTER.001
CHAPTER.002
CHAPTER.003
and so on.
Like MS-DOS commands, filenames and extensions can be
entered in either upper or lower case, but are always displayed
on the screen in upper case. However, since MS-DOS converts
lower case filenames into upper case, it is possible to
inadvertently erase an existing file by saving a new file with a
lower case name. To be safe, always make sure that you have
given a unique name to each file on a disk.
4-22
Using MS-DOS With
Your Computer
Page 89

Disk Directories
MS-DOS keeps track of the files stored on your disks by
maintaining a “directory” on each disk. These directories are
listings of the filenames and extensions, along with certain
information about the files themselves, such as when the file
was created or updated last.
The DIR Command
MS-DOS provides a simple command that allows you to look
at the directory of any particular disk. This is the DIR
command. Enter the command as follows:
The computer will display a listing similar to the following:
Some of the names and symbols may be different, but the
screen should show these five columns, and a similar last line.
Using MS-DOS With Your Computer
4-23
Page 90

The information presented by the DIR command is as follows:
D
The filename & extension
Cl
The file size (in bytes)
Q
The date the file was created or last updated
Q
The time the file was created or last updated
0
The number of files listed in the directory
0
The number of unused bytes of space remaining on the disk
File Searches
You can also use the DIR command to search for specific files
on a disk. To do this, enter the DIR command in the following
format:
For instance, if you want to find the directory entry for a file
named “MAYSALES.RFT” on the diskette in drive A, enter
the command:
The computer will search the entire directory of the diskette
for a file named MAYSALESRPT. If a file is found, it will
appear as the only entry in the diskette’s directory. If there is
no MAYSALES.RPT file on the diskette, the computer will
display:
4-24 Using MS-DOS With Your Computer
Page 91

Multiple Disk Drive Systems
The DIR command can be used to read the directories of other
drives
the directory of the B drive, when you are logged onto drive A,
enter the command:
in
your system, if any are installed. For instance, to read
The computer will display the directory of the diskette inserted
in the B drive. A similar command:
will cause the computer to display the directory of your hard
disk.
Note that in both examples, the A drive remains the default
drive. To change the default drive from A to B, and then
display a directory listing, enter the command series:
The computer will display the B drive diskette’s directory, then
remain logged to the B drive.
Using
MS-DOS With Your Computer
4-25
Page 92

Wildcards
Quite often, when dealing with disk files, you may find yourself
looking through directories for a particular file or group of files.
MS-DOS has a way to help you sort out those files you want
without having to read through the entire directory listing.
This is through the use of “wildcard” characters. Wildcard
characters are used to make a single command cover a number
of similarly named files.
While MS-DOS provides several wildcard characters, the most
one you will be using most often is the asterisk ( * ). The
asterisk matches any number of sequential characters in a
filename or extension.
For instance, to look at a listing of all the .EXE program files
on your main system diskette, enter the command:
This will produce a directory that looks like this:
4-26
Using
MS-DOS With Your Computer
Page 93

Application Software
Now
that you know how to make backup copies of your
diskettes and how to work with MS-DOS, you can proceed to
use application software. Most software packages come with
detailed instructions for their set-up and use. These instructions
will often ask you to use the information in this chapter to find
specific files in the disk directories, or back up the master
diskettes provided with each package. Most software packages
can be backed up simply by using the MS-DOS DISKCOPY
command, as described above.
Using
MS-DOS With Your Computer
4-27
Page 94

Chapter 5
Using Floppy Disks
Description
Your computer works with a large electronic memory array
called RAM. This stands for Random Access Memory. Your
system’s RAM is actually an array of electronic circuits. As
long as the computer is powered up, this circuit array will
“remember” whatever is placed in it. When you turn the
power off, however, these circuits will “forget.” Therefore, you
need some way of retaining your programs and data after you
turn the system off. The most usual way of storing data, at least
on DOS-based computer systems, is on floppy disks.
Virtually all commercially available programs are distributed on
floppy diskettes. Before you buy an application software
package for your computer, you should make sure that it will
run under MS-DOS. Products labeled “for IBM PC,” “for IBM
PC/AT,” “
run properly. Products intended for other types of computer
operating systems, such as CP/M or Apple, will not run on
your system.
PC-compatible,” or “MS-DOS-compatible” should
Note
If you should accidentally try to run CP/M or Apple
software, your computer will inform you that you are using
non-DOS diskettes. This will not damage your computer.
The most frequent use that you will have for diskettes is to save
the data, text, files, etc. that you create. You will use diskettes
to store your data between sessions on the computer, as well as
to back up your valuable software.
Using Floppy Disks
5-1
Page 95

How Floppy Disks Work
Floppy disks, or diskettes, are made from a flexible plastic that
is coated with a magnetic oxide. The floppy disk drive encodes
this oxide with the data generated by the computer. After you
turn your system off, unlike electronic RAM, the encoded
oxide retains this data. Your data can then be read by the
floppy disk drive at a later time.
The magnetic oxide coating on the floppy disk will hold its
encoded data almost indefinitely unless you deliberately erase
it. This is done intentionally when you want to update the
information stored on the diskette.
The plastic disk is safely protected by a thin cardboard jacket.
The diskette spins inside this jacket, allowing the entire surface
of the diskette to be scanned by the drive’s circuitry. Data is
read from or written onto the diskette through the oval-shaped
slots in the jacket.
Normally, the computer will write new information onto the
unused space on the diskette. If there is no unused space, your
computer will inform you that the disk is full. You can instruct
the computer to write over the information that is already on
the diskette. You might do this to update an inventory file, or
change an address and phone number in a database.
5-2
Using
Floppy Disks
Page 96

Formatting Diskettes
When you get a new carton of diskettes, they are not yet ready
to be used. First, they must be prepared to accept data. This is
called “formatting” the diskette.
MS-DOS uses the same formatting method regardless of the
computer used. This is one of the keys to intermachine
compatibility. Since all PC-compatible computers use MS-DOS,
they can read all disks created by any other PC-compatible
machine.
To see what happens when you attempt to use an unformatted
disk, insert a new blank diskette into the A drive and close the
drive door. Then enter the following command:
Since the new disk hasn’t been formatted yet, your computer
cannot read it. After failing three times, your computer will
respond:
If you type R (for Retry), or A (for Abort), the computer will
attempt to read the diskette again, and will finally display the
same message.
Using Floppy Disks
5-3
Page 97

I
When you type F (for Failure), the
computer
will automatically
cancel the attempt and will display the following message.
Remove the unformatted disk from the drive.
The FORMAT Command
MS-DOS provides an external command program called
FORMAT.COM, that will format your blank diskettes. When
running this program, there are options available that allow
you to format several different types of diskette.
The following routines will show you how to use the
FORMAT command. These procedures assume that you are
formatting double-sided, high-density, 1.2M-byte diskettes
(AT-compatible). Information on formatting 180K-byte and
360K-byte diskette will be discussed under the /l and /4
switch options below.
First, if you have a hard disk installed MS-DOS on your system,
then enter:
The computer will load the FORMAT command file into
system memory, then will respond:
5-4
Using Floppy Disks
Page 98

Insert the new diskette to be formatted and press the ENTER
key.
The computer will display:
The formatting process takes a minute or two. The computer
will wait until the formatting process is complete, then display:
Press ENTER if you don’t want to have a label of your disk.
Then the screen will display the following message.
XXXXXXX bytes total disk space
XXXXXXX bytes available on disk
XXX bytes in each allocation unit
XXXXX allocation units available on disk
Volume Serial Number is XXXX-XXXX
Format another (Y/N)?
Don’t be concerned if the message displayed is slightly different
from the example. Enter N to return to the system prompt.
The new disk is now formatted and is ready for use. Remove it
from the disk
drive
and replace it in its protective envelope.
Using Floppy Disks
5-5
Page 99

Option Switches
To format 180K-byte sigle-sided, sigle-density diskettes in the
computer’s high capacity disk drive, enter the FORMAT
command using the 11 option switch:
The computer will proceed to format the diskette. Upon
completion, you will see this message:
And the following screen will appear if you press ENTER.
(If you want to have a volume label, type the characters and
enter.)
5-6
XXXXXXX bytes total disk space
XXXXXXX bytes available on disk
XXX bytes in each allocation unit
XXXXX allocation units available on disk
Volume Serial Number is XXXX-XXXX
Format another (Y/N)?
Using Floppy Disks
Page 100

The /4 option switch
is used to format 360K-byte double-sided,
double-density diskettes in the computer’s high capacity disk
drive. To do this enter the command:
The computer will proceed to format the diskette. Upon
completion, you will see this message:
Press ENTER not to have a label of your disk. Then the screen
will display;
XXXXXXX bytes total disk space
XXXXXXX bytes available on disk
XXX bytes In each allocation unit
XXXXX allocation unite available on disk
Volume Serial Number is XXXX-XXXX
Format another (Y/N)?
Enter N to return to the system prompt. Remove the diskette
from the
drive
and place it in its protective envelope.
Using Floppy Disks
5-7
 Loading...
Loading...