Enttec LED Mapper ELM Standard pixel mapping software, 16 universes (download), LED Mapper ELM Professional pixel mapping software (96 universes) (download), LED Mapper ELM Ultimate pixel mapping software (512 universes) (download), LED Mapper ELM Elite pixel mapping software (2048 universes) (download), LED Mapper ELM Super pixel mapping software (256 universes) (download) Enttec LED Mapper ELM handleiding
...
Effortless LED Mapping

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
2
Contents
Key Features ...................................................................................................................................................................... 3
Computer Requirements .............................................................................................................................................. 3
Licenses ............................................................................................................................................................................... 5
Software Updates ............................................................................................................................................................ 5
Definitions .......................................................................................................................................................................... 6
Getting Started With LED Strips ................................................................................................................................ 7
Quick Overview ................................................................................................................................................................ 8
ELM Tour ............................................................................................................................................................................ 9
Home Screen ................................................................................................................................................................ 9
New Stage Dialog .................................................................................................................................................... 10
Stages ........................................................................................................................................................................... 11
Status Indicator .................................................................................................................................................... 12
Stage Syncing ....................................................................................................................................................... 12
Stage Merging and Layering .......................................................................................................................... 13
Edit Zone ................................................................................................................................................................ 14
Strips Tab ............................................................................................................................................................... 16
Stage Tab ............................................................................................................................................................... 25
Testing Tab ............................................................................................................................................................ 27
Stages Manager ....................................................................................................................................................... 29
Media Library ............................................................................................................................................................ 30
Schedules .................................................................................................................................................................... 33
Live Mode ................................................................................................................................................................... 35
Settings ........................................................................................................................................................................ 37
Project ..................................................................................................................................................................... 37
Art-Net .................................................................................................................................................................... 38
sACN ........................................................................................................................................................................ 38
KiNet ........................................................................................................................................................................ 39
Audio ....................................................................................................................................................................... 39
Time ......................................................................................................................................................................... 40
Colors ...................................................................................................................................................................... 40
License..................................................................................................................................................................... 40
Remote Control ................................................................................................................................................... 41
Troubleshooting ........................................................................................................................................................... 48
EULA .................................................................................................................................................................................. 51

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
3
Key Features
ELM is all about displaying your video content on LED fixtures of any shapes, in the most
convenient way.
Vector-based editor
2048 DMX universes
Art-Net, sACN, KiNet
Scheduled playlists
Remote control via
DMX, OSC and HTTP
CITP/MSEX for
consoles and
visualizers
Computer Requirements
HD video + audio
playback
Spout + NDI
integrations for live
video inputs
Stream LED previews
to visualizers via NDI
DVI outputs for
projectors, TVs and
Martin P3 system
Over 100 high quality
animations included
Audio-reactive effects
RGB, RGBW, RGBA,
RGBAW
Multiple whites
support and WWA
16-bit color support
Extreme robustness for
permanent installations
ELM is compatible with Windows 7 and up, including Windows 8 and 10. 32-bit and 64-bit
versions are provided to suit your OS.
The .Net 4.7 framework is required and you’ll be prompted to install it if needed.
Minimum
- Windows 7+, dual core 2 GHz CPU, 2 GB RAM
- NVIDIA GeForce 600 series or Intel HD Graphics 5500, released after 2013 with OpenGL
3.3 support
Recommended
- Windows 8 or 10, quad core 3.5 GHz CPU, 8 GB RAM
- NVIDIA GeForce 900 series or NVIDIA 10 series or better
- SSD hard drive

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
4
CPU Speed x Cores
Full HD Videos
HD Videos
640x360 Videos
2 GHz x 2 2 4
10
3 GHz x 2 3 6
15
4 GHz x 2 4 9
20
2 GHz x 4 4 9
20
3 GHz x 4 6 13
30
4 GHz x 4 8 18
> 40
3 GHz x 8
10
22
> 40
The computer requirements depend on your media type. For example, playing multiple HD
videos requires a good computer. A rule of thumb is you can play one full HD video @ 30fps for
each 2 GHz CPU core. So if you have an Intel i7 4 GHz (4 cores), you should be able to play 8 full
HD videos. Increasing the playback speed to 2x means the fps also increases two times and the
number of videos you can play simultaneously is roughly divided by two.
The next table shows the approximate number of videos you can play simultaneously at 30 fps
depending on your CPU.
For live video performances, when you want to change the playback speed and go up to 10x,
the recommended video resolution is 640x360.
To use the built-in effects, particularly the eye candy effects, the video card will be doing the
hard work. If you’re using a laptop, make sure it can sustain a continuous use of the effects
without overheating. Usually, an integrated video card can render two eye candy effects. For
more effects, you need to have a discrete video card.
About the DMX output, a 1 Gigabit network should be able to handle 2048 universes @ 44fps.
For more universes, a supplementary network card and a second Ethernet network are
recommended.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
5
Licenses
The ELM’s licensing system has been built with reliability and simplicity in mind. Basically, once a
computer has been activated, it will be able to run ELM until it dies. No internet connection
required, so you can be completely off the grid without worrying about the license.
Each license is registered to one individual or company and covers the activation of the software
on a certain number of computers, so long as ELM is running on one computer at a time. For
example, you can activate a show and a backup computers but only one computer can run ELM
at a time.
The license is a simple file that you import once. No hardware dongles are needed, eliminating a
whole range of tricky problems: broken dongle, lost dongle, dongle suddenly not detected in
the middle of the show, etc.
The license is linked to your computer’s CPU and motherboard. You can upgrade any other
components and reinstall the OS without invalidating your license.
A license isn’t transferrable, meaning once your computer stops working, you can only activate
ELM on another computer if you still have activations left. Use this online form to activate a
computer: https://www.enttec.com/my-account/license-registration/.
To get more DMX universes, you can activate multiple licenses on the same computer. The DMX
universes of all licenses will be added.
Software Updates
You always have access to the latest and greatest version, free of charge.
To get the updates, go in the Settings/About menu and press the check for updates button.
Alternatively, you can go on the Enttec’s website and download the latest version.
https://www.enttec.com/products/controls/pixel-control-controls/software-pixel-mapping/

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
6
Definitions
Art-Net: Protocol to transmit DMX over a standard Ethernet network. Designed by and
Copyright Artistic Licence Holdings Ltd.
CITP/MSEX: Controller Interface Transport Protocol/Media Server Extension.
DMX: The most common protocol to control lighting fixtures. The full name is DMX512, which
stands for Digital Multiplex.
DMX universe: Represents 512 DMX channels. Enough for 170 RGB LEDs (1 LED takes 3
channels, one for red, one for green and one for blue).
FPS: Frames per second. It refers to an output rate for video or DMX.
KiNet: Protocol to transmit DMX over a standard Ethernet network. Designed by Color Kinetics.
LED strip/string: Lighting fixture that may contain many LED elements and have a certain
physical length. Some LED strips are flexible and can be bent to create curves and all kind of
shapes. ELM handles all lighting fixtures as if they were strips, giving you a lot of positioning
flexibility.
Mapping: Mechanism used to associate a pixel from a media source to a specific lighting fixture
element.
Media: Any type of visual content, including videos and pictures.
Network Device Interface (NDI): Protocol to stream live videos over the network. Developed
by NewTek - http://NDI.NewTek.com.
Open Sound Control (OSC): Network protocol allowing multimedia apps to communicate. ELM
can be remotely controlled via OSC.
RGB, RGBW, RGBA, RGBWA: Various color components: red, green, blue, white and amber.
sACN: Protocol to transmit DMX over a standard Ethernet network - like Art-Net. More
specifically, the E1.31 subset is used for DMX control. Developed by ESTA.
Spout: Real-time video sharing framework for Windows. Similar to Syphon on Mac.
http://spout.zeal.co/
Stage: A mapping surface defining the position of the media placeholder and the position of
lighting fixtures.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
7
Getting Started With LED Strips
ELM can control any DMX-enabled lighting fixtures – not only LED strips. This is made possible
because ELM outputs industry standard protocols like Art-Net, sACN and KiNet. This means that
ELM can control traditional DMX dimmers and any RGB, RGBW, RGBA and RGBAW lighting
fixtures. It’s also possible to control complex fixtures like moving heads.
Controlling LED strips is a little bit different than traditional DMX fixtures. The main difference is
that you need to use LED controllers to drive your strips. They replace the Art-Net nodes you
use for traditional DMX fixtures. The LED controller receives DMX via Art-Net/sACN and converts
to the special protocol the LEDs understand. Enttec offers the Pixelator which takes 48 DMX
universes and controls up to 8160 RGB LEDs.
The next step is to get LED strips and DMX fixtures. Since there are many LED protocols out
there, you need to make sure your LED controller fits with your LEDs. Common protocols for
RGB LEDs are WS2811 and WS2812/B. For more information about getting compatible LEDs,
contact your Enttec representative. Here’s the Enttec Pixelator that can be used to control the
Phero and Enttec LED tapes:

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
8
Quick Overview
ELM allows dividing your installation into multiple zones and layers called stages. You control
the media content independently for each stage. Stages can overlap and they are merged
(blended) to generate the final result. A common scenario is to create a stage spanning the
whole installation to map media across the board. To enable precise control over specific zones,
you create smaller stages inside the big stage. Then you activate these zones whenever you
want. For example, in the installation below, we can play a video on the overall stage - which
acts as the background layer - and when there’s a special event, we activate the logo zone and
make it flash.
To represent your LED strips and DMX fixtures inside a stage, ELM has a powerful vector-based
editor. This way, you can easily draw many types of shapes, including matrices, loops and curves.
ELM computes the position of each LED based on your drawing.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
9
New stage (alt-N)
Creates your first stage and start the mapping process.
Load project (ctrl-O)
Loads an existing project.
Recent projects (down arrow)
Loads a recent project. Click on the down arrow in the load
project button to show the list.
Media (alt-M)
Goes to the media library.
Schedules (alt-H)
Goes to the schedules.
Live (alt-L)
Goes to the live panel.
Settings (alt-I)
Goes to the settings panel.
ELM Tour
Let’s go over the main screens and controls of ELM.
Home Screen
Welcome! Start a new project or load an existing one. To see the keyboard shortcut keys, press
the alt key.
Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
10
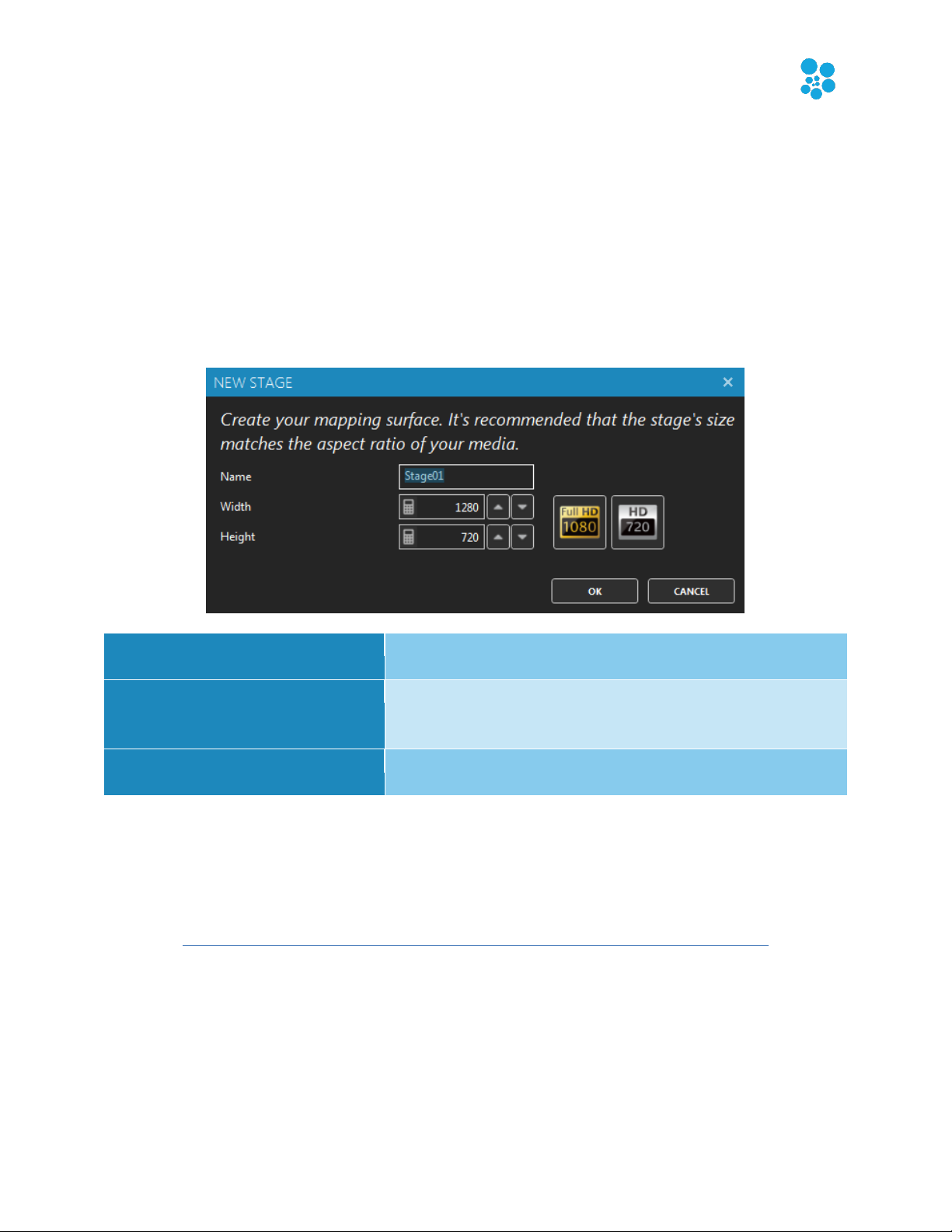
Name
The name of your new stage. Usually refers to its physical
location.
Width, Height
The desired size in pixels for the mapping surface used to
display media. This can be changed later without affecting
the mapping.
Full HD, HD buttons
Presets for common media sizes. Full HD is 1920x1080 and
HD is 1280x720.
New Stage Dialog
A rule of thumb is to create a stage with dimensions respecting the aspect ratio of your media.
Then you’ll position your LED strips on it to create the mapping. For example, you can create a
full HD stage - which has a rectangular aspect ratio - to fit your media sources, and then map a
20x20 square LED array on it.
You can easily change the dimensions later, so don’t worry. The minimum recommended size is
320x180. Smaller than this size, you’ll need to constantly work at a very high zoom level, which
isn’t very convenient. So it’s better to use a higher size and let ELM scale your media.
To help you position the strips like they are in the real world, use a
picture of your installation as the stage’s background (see Stage Tab).
No pictures handy? Use your phone’s camera to get one!

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
11
Stages
Shortcut key: alt-S
You can create as many stages as you want. Generally, you’ll want an overall stage
corresponding to the whole installation and multiple individual stages to target specific zones.
The overall stage allows you to map content across the board. Then the other stages allow you
to override specific parts of your installation whenever you want. You can select the current
stage by clicking its name at the top.
Different effects may demand different mapping layouts. One goal of
the mapping is to ease the content creation. So don’t hesitate creating
multiple stages with the same LED strips but positioned in different
ways.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
12
∙ Stage
Manual control mode, stage deactivated.
Stage
Manual control mode, stage activated.
R Stage
Remote control mode, stage deactivated.
R Stage
Remote control mode, stage activated.
S Stage
Schedule control mode, stage deactivated.
S Stage
Schedule control mode, stage activated.
A Stage
The audio reactive mix mode is active.
T Stage
The testing mode is active.
Status Indicator
At the left of the stage’s name, a small indicator tells you the current control mode and its
status. The activated status means a media is selected and the stage’s intensity (see Live Mode)
is greater than 0%.
Stage Syncing
All stages using the same media slot are considered to be synced. You can still change the
individual stage output parameters like the intensity and the color filter, but the media content
is the same on all synced stages. When applicable to the media type, the media playback speed
is determined by the maximum speed of all stages using this media.
To play the same video file on multiple stages but at different speeds,
load the video file in multiple media slots. Then use a different media
slot for each stage.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
13
Overwrite
Completely replaces the left stages. The right stage is fully opaque.
Multiply
Multiplies each pixel of the right stage with the corresponding pixel for
the left stage. The right stage becomes a video mask.
Screen
The values of the pixels in the two stages are inverted, multiplied, and
then inverted again. This yields the opposite effect to Multiply. The result
is a brighter picture.
Overlay
Combines Multiply and Screen modes. The parts of the right stage where
left stage is light become lighter, the parts where the left stage is dark
become darker.
Darken
Takes the smallest color component for each pixel.
Lighten
Takes the largest color component for each pixel.
Difference
Subtracts the left stage from the right stage or the other way round, to
always get a positive value.
Add
Adds pixel values of one stage with the other.
Subtract
Subtracts pixel values of the right stage to the left stage.
Black key
Shows the pixels of the left stage only where the pixels of the right stage
are black. In other words, black pixels are transparent.
IntensityCrossFade
The stage’s intensity determines its opacity level.
IntensityWhiteFade
The stage’s intensity determines its opacity level in a white fade fashion,
meaning that when the intensity is at 50%, both the current stage and
the ones under are merged at full opacity.
Stage Merging and Layering
When multiple stages contain the same LED strips, a merge occurs following the order as shown
in the Stages Manager. This allows creating complex visuals by layering multiple stages on top
of each other. You can target specific zones by creating stages with only a subset of all strips or
with parts of the strips outside the stage. A stage must be activated (a media is selected and the
stage’s intensity is greater than 0) otherwise it is considered to be transparent and will not be
part of the merge.
The merge modes are:
To easily target specific zones of an installation, first create the overall
mapping then select the strips corresponding to the individual zones and
right-click in the strip list to access the “new stages from strips” menu.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
14
Select strips/Deselect all (ctrl-d)
Click a strip to select. Hold the ctrl key to add to the
selection. Hold shift to use a selection window and select
all strips inside the rectangle. Press ctrl-a to select all strips
and ctrl-d to deselect.
Move a control point
Click on a control point and drag it. Hold shift while
dragging to align with the previous point.
Move selected strips
Right-click on a strip and drag it or use the move handle at
the top-left corner of the selection. You can also use the
ctrl-keyboard arrows.
Add a control point
Right-click on the stage (only one strip needs to be
selected) or on a control point to use the context menu.
Edit Zone
You can position your strips as they are in the real world or based on the effect you want to
create with your media.
A strip has start (green) and end (red) control points indicating the direction of the patch.
Multiple intermediate control points can be used to create various shapes. You can bundle
multiple strips together to simplify the handling of complex shapes.
You can position parts of your strips outside the stage. In this case, the LEDs outside the stage
will not be mapped. This is a common scenario when using the same strips in multiple stages
and you want to target specific parts in each stage.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
15
Delete a control point
Right-click on a control point and select the delete option.
Bundle/Unbundle strips (ctrl-b,
ctrl-shift-b)
Select multiple strips and right-click on one of them in the
Strip List. Then select the bundle menu item to create one
element with all selected strips. You can unbundle the
strips to edit or see the details.
Move around the stage
Click on the stage background and drag.
Zoom in/out (ctrl-plus, ctrlminus, ctrl-0, ctrl+mousewheel)
Use the zoom control at the top. Zoom out when you want
to offset the selected strips quickly. Ctrl-0 resets the zoom.
Show individual LED positions
When zoomed enough, the LEDs of the selected strips
should be visible. They are the blue dots. Put your mouse
over to see the LED number and its DMX address.
Copy/paste strips (ctrl-c ,ctrl-v)
Copy and paste the selected strips. You can paste the
strips in a different stage.
Delete selected strips (ctrldelete)
To delete the selected strips, use the ctrl-delete shortcut or
right-click in the strip list and select the delete menu item.
Undo (ctrl-z), Redo (ctrl-y)
You can always use Undo and Redo while editing.
As a group
This checkbox under the rotate section determines
whether strips are rotated, moved and scaled all together,
maintaining the overall shape or if the action is done to
each strip individually. This doesn’t apply when using the
move, rotate and resize handles. For example, if you
uncheck this option and enter 0 in the X position box, all
strips will move to the position 0.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
16
Strips Tab
Shortcut key: alt-P
Strip List
The strips for the current stage are shown in this list. Select one or multiple strips in the list to
also select them in the edit zone. Right-click in the list for more options. You can click the
column headers to sort. Type text in the filter box to filter based on the group names.
Use the group and sub-group fields wisely in order to use the filter box
and quickly select the strips you want.
Add Strips Dialog (Patching)
Shortcut key: alt-A
Quickly patch your strips and lighting fixtures to create arrays and any shapes you can imagine.
Multiple LED types (or color types) are supported, including RGB, RGBW, RGBA, RGBAW/RGBWA
and white (dimmers) in multiple configurable color temperatures like WWA. Most color
component orders (GRB, BGR, etc.) are supported. For lighting fixtures supporting high precision
colors, 16 bit color depth can be used via the RGB16, GRB16, RGBA16, RGBW16 and White16
types. RGBWmax activates all channels (RGB+white) when white is needed for maximum
brightness.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
17
Number of strips
The number of LED strips/fixtures you want to patch.
LEDs per strip
The number of LEDs per strip. Enter 1 to create a unique
fixture.
Type
Also named pixel type. Corresponds to the color
component order (RGB, BGR, GRB, etc.) and the capability
(white only, RGBW, etc.). Many LED strips have the color
components in a different order than red, green and blue.
Usually, LED controllers have the option to reorder the
color components but ELM can handle this for you.
Shapes
Select a predefined shape (lines, arches, circles, triangles,
hexagons, etc.) to position your strips on the stage. For
arrays, use lines. Remember that you can create any kind
of shapes by adding control points later.
Patching direction
For LED arrays, specify the way your strips are wired to let
ELM automatically assigns the proper DMX addresses.
Group and sub-group
Use these two groups to tag your strips and quickly find
them later. You can search for these keywords in the strip
list’s filter box.
DMX protocol
Select the output method for DMX: Art-Net, sACN or
KiNet. Select none to leave the strips un-patched at the
moment and not output any DMX.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
18
Start universe
The universe of the first strip to be patched.
Start address
The DMX address of the first strip to be patched.
LED address offset
ADVANCED The number of DMX channels between the
start of two consecutive LEDs. Increase it to leave holes
between your LEDs/fixtures, allowing merging ELM’s
output with another console. For example, you can control
moving heads by letting ELM handles the colors and a
console handles the movement.
Break universe after
ADVANCED Automatically start patching in the next
universe when reaching this limit (number of strips of
LEDs). Set to 0 to break only when the universe is full.
You’ve got the patching direction wrong? No problem. You can easily
flip your strips horizontally and vertically later. For snake mode, rightclick in the strip list and use the select odd/even option.
Want to control more complex DMX fixtures like moving heads? Let say
your moving head has 20 channels and the RGB channels start at 3. In
ELM, patch it with a start address of 3 and a LED address offset of 20.
ELM will send 0 for the unused channels, which allows merging the DMX
data from ELM with the DMX data from a console. The console should
provide the values for the pan and tilt and the all other channels except
the RGB.
Whites! You can get a more accurate preview by using the right type of
white LED type. Use the WhiteCool, WhiteNeutral, WhiteWarm and
WWA (cool, neutral and warm whites) LED types. Unlike the White LED
type which takes the perceived brightness of the media as its value, you
get finer control with the other whites.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
19
LED Type
Detail
Remark
RGB, RBG, BGR, BRG,
GBR, GRB
Red, green and blue.
RGBW, GRBW
Red, green, blue and white.
The white is automatically activated
based on the saturation of the media
color. The less saturated the color is,
the more the white LED is activated.
As the white is activated, the RGB
LED levels are reduced proportionally
until only the white LED is active for
a pure white color.
RGBWmax
Red, green, blue and white.
The white activation is calculated like
for RGBW but the RGB LEDs aren’t
reduced proportionally. The result is
that when a pure white color is
needed, all RGBW LEDs are activated.
While it gives a maximum brightness,
it also takes more power.
RGBA
Red, green, blue and amber.
The amber LED is automatically
activated the closer the media color
is to amber. As the amber is
activated, the RGB LED levels are
reduced proportionally until only the
amber LED is active for a pure amber
color.
RGBAW, RGBWA
Red, green, blue, amber and
white.
The white and amber LEDs are
activated following the same recipe
as for RGBW and RGBA.
White
White or one color component
only.
The activation level is based on the
perceived brightness of the media
color (using the luma calculation).
WhiteCool
White cool.
Special type of cool white LED that
you can use to get a more accurate
preview in the stage monitor. The
activation is based on the blue level
of the media color.
WhiteNeutral
White neutral.
Special type of neutral white LED
that you can use to get a more
accurate preview in the stage
Pixel Types

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
20
monitor. The activation is based on
the green level of the media color.
WhiteWarm
White warm or amber.
Special type of warm white LED that
you can use to get a more accurate
preview in the stage monitor. The
activation is based on the red level of
the media color.
WWA
White cool, white neutral and
white warm/amber.
There are 3 types of whites and you’ll
get an accurate preview in the stage
monitor. The white cool activation is
based on the blue level of the media
color, the neutral on the green and
the warm on the red.
WAW
White cool, white warm/amber
and neutral white.
See WWA.
AWW
White warm/amber, neutral
white and white cool.
See WWA.
…16
High resolution 16-bit per
color component.
All types ending with 16 are the 16bit version of the LED type. For
example, RGB16 takes 6 DMX
channels, 2 for red, 2 for green and 2
for blue. While it takes more
channels, it gives smoother color
transitions and more headroom for
color corrections.
For the color temperature settings to get a more accurate stage monitor preview, see Colors.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
21
Number of duplicates
The number of times you want to copy the selected strips.
Group and sub-group
Use these two groups to help you quickly find your strips
later. When creating multiple duplicates, the primary
group will automatically be appended with a counter.
Universe offset
The offset used to calculate the first DMX universe of the
newly created strips.
Address offset
The offset used to calculate the first DMX address of the
newly created strips.
X offset
The horizontal position offset applied to the newly created
strips.
Y offset
The vertical position offset applied to the newly created
strips.
Duplicate Strips Dialog
Shortcut key: alt-D
Copy the selected strips and create new strips by applying certain transformations.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
22
Rotate offset
The rotation in degrees applied to the newly created strips.
Rotate center, offset X, offset Y
The position where the rotation will occur and how to
offset the rotation center (for example, to leave a hole in
the middle of the rotated strips).
When you’re in the design phase of the lighting installation, keep in
mind the duplicate options. They allow creating complex shapes by
copying simple elements. This is a real time saver.
To make sure certain strips always stay together, use the bundle feature.
You can create complex shapes by combining multiple simple elements.
See the bundle/unbundle options in the Edit Zone.
To copy strips to another stage, select your strips and use the copy (ctrlc) and paste (ctrl-v) keyboard shortcuts. You can also right-click in the
Strip List to see all options.
Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
23
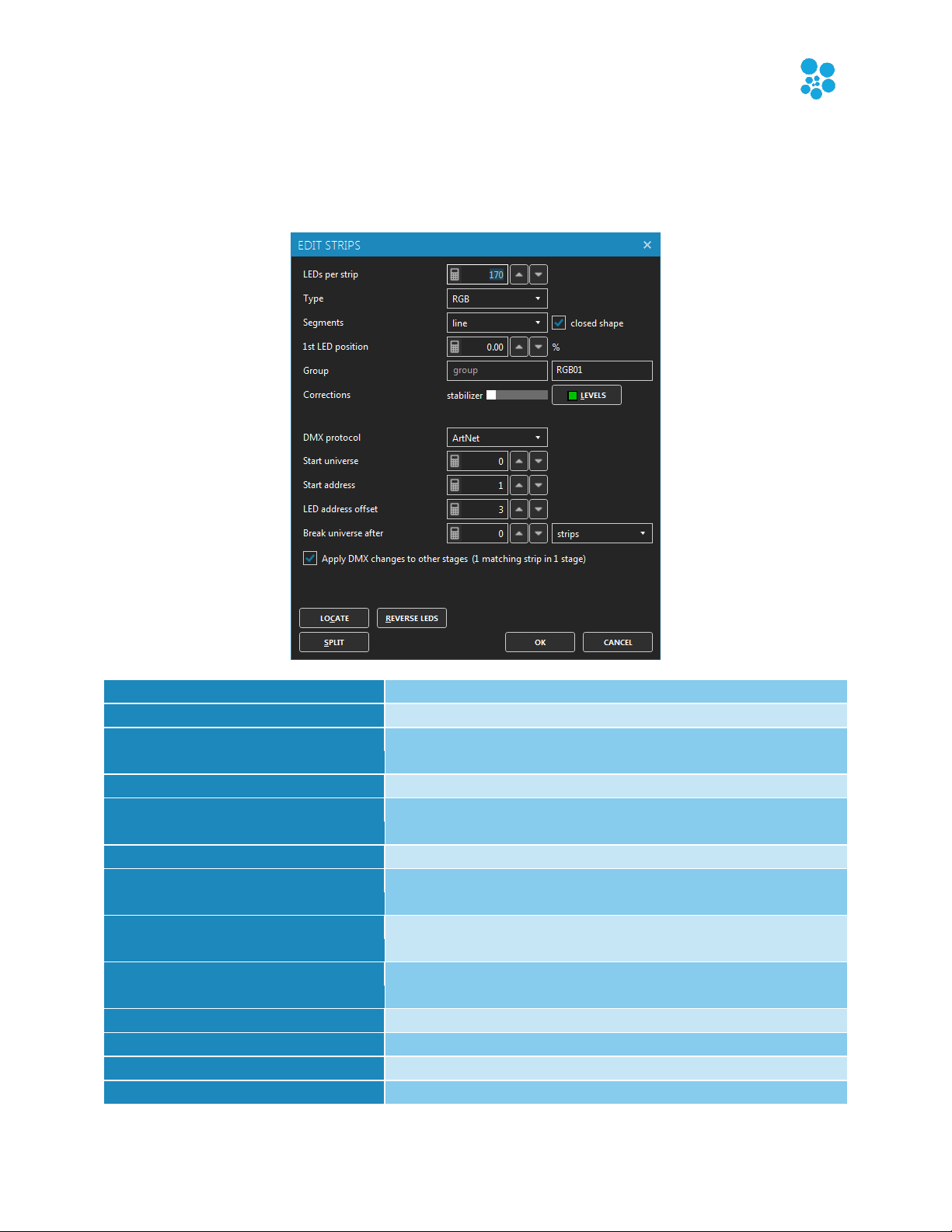
LEDs per strip
The number of LEDs per strip.
Type
The pixel type. See Add Strips Dialog (Patching).
Segments
Determines whether it’s straight lines or curves between
the points. Curves are perfect to represent flexible strips.
Closed shape
Determines whether you want a closed shape like a square.
1st LED position
For closed shape, you can move the first LED around the
shape to be exactly where the first LED is in reality.
Group – primary, secondary
Use these two groups to help you quickly find your strips.
Stabilizer
Takes the average of the media pixels around the LEDs to
reduce large jumps. May be used like an Ambilight feature.
Levels (alt-L)
Adjusts the intensity, temperature and tint to compensate
for manufacturing and age differences.
DMX protocol
Select the output method for DMX. For example, Art-Net
or sACN E1.31.
Start universe
The universe of the first strip to be patched.
Start address
The address of the first strip to be patched.
LED address offset
See Add Strips Dialog (Patching).
Break universe after
See Add Strips Dialog (Patching).
Edit Strips Dialog
Shortcut key: alt-E
Edit the selected strips and allow changing the patch.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
24
Apply DMX changes to other
stages
Executes your DMX changes on the matching strips in
other stages. It is handy when you have copied the same
strips in multiple stages in order to keep them in sync.
Locate (alt-C)
Locates each LED in the real world by going through a list.
Re-Patch (alt-P)
Forces redoing the patch to make sure all selected strips
are patched one after another.
Reverse LEDs (alt-R)
Reverses LEDs without changing the shape. This is handy
when the strip has been physically installed in the wrong
direction.
Split (alt-S)
Splits the strip in two and allows each part to be
configured independently.
Join (alt-J)
Joins all selected strips one after another to form only one
strip.
X
The position of the left boundary of the rectangle. A value
of 0 means the far left of the stage.
Y
The position of the top boundary of the rectangle. A value
of 0 means the top of the stage.
Width
The horizontal length.
Height
The vertical length.
Linked option
When checked, the initial aspect ratio is preserved when
changing the width or height.
Offset/Resize Strips Dialog
Shortcut key: alt-O
Precisely change the position and size of the selected strips.
Right-click in a numeric box and move the mouse left/right to quickly
change the value.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
25
Size
The mapping size of the stage.
Change it with the resize
button.
Preview opacity
Determines the visibility of the
preview. You can disable the
preview to save CPU by setting
the opacity to 0.
Schedules/Live
Controls how this stage appears
in the schedules and live views.
You can hide it or make it readonly.
Background image
To help you position the LED
strips like in the real world, you
can display an image on the
background of the stage.
Offset, scale and
rotate
Allows positioning the
background image where you
want.
Opacity
Determines the visibility level of
the background image.
Sticky notes
Puts notes anywhere on the
stage to remember key points
of the mapping and TODOs.
Snap strip points
(ctrl-P)
Snaps control points to help
positioning.
Grid (ctrl-G)
Configure the snap to grid
feature by specifying size of a
cell in pixels. Use the offset X-Y
to align the top-left cell with
your design.
Monitor (alt-O)
Opens a monitor window to
help you see the final result of
the mapping.
LED snapshot
Exports a PNG image showing
the exact position of every LED.
This is useful for motion
designers as they can use the
snapshot as a content guide.
Stage Tab
Shortcut key: alt-g

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
26
When you are editing and zoomed in very closely, if a media is playing
in the preview, your computer may have a hard time. To help it, disable
the preview by setting the preview opacity to 0%.
Here’s the monitor window. You can see the result of the stage only or after all stages have been
merged. When you don’t have access to the real fixtures, this is an indispensable tool while
creating effects. Alternatively, you can use any 3rd party visualizer able to receive the LED
rendering via NDI (see NDI output in the Stages Manager) or supporting Art-Net or sACN.
Try reducing the stage’s size and see if the output is still good. Also
reduce your videos and other media size accordingly to potentially save
a lot of CPU. High resolution media is not always a good thing!

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
27
Test patterns On/Off switch
Activates the generation of test patterns.
Color
Changes the color of the testing rectangle. It is handy to
test the color component order of your strips.
Width, Height
Changes the size of the testing rectangle.
Test selected strips only
If checked, only the selected strips in the
Strips Tab will be under test. The other strips will all be off.
Test 1st LEDs only
Only test the 1st LEDs of each strip to better see where
each strip starts.
Locate LEDs
Locates each LED in the real world by going through a list.
Alternatively, you can put the mouse over a LED in the
editor. The LED number and its DMX address are displayed
which is handy to count the LEDs and troubleshoot
addresses.
Conflicts
Analyzes all patched LEDs of the current stage and looks
for overlapping DMX addresses. In some situations you
may want to have duplicated LEDs on the stage but if this
isn’t the case, you should adjust the DMX addresses.
Testing Tab
Shortcut key: alt-T
Quickly test the mapping by generating a rectangle that you can move over the strips.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
28
Reduce the width and height of the testing rectangle and drag the
rectangle around the stage. This way, you can see if the patch order is
right. For example, if dragging the rectangle from left to right makes
the LEDs go on from right to left, then you know you need to flip them
horizontally. To do so, go in the Strips Tab and click the Flip X button.
Quickly test the red, green and blue component order of your LEDs by
generating a pure red, pure green and pure blue test. For each test, note
the color of your LEDs. If you’re not getting a RGB order, edit your LED
strips and select the LED type corresponding to the order you’ve
observed (BGR, GRB, GBR…).
While the testing mode is active, the DMX is constantly being outputted
at the full output rate, even when there’s no change. This is handy while
you’re configuring your LED controllers and want to see if it’s working.
This is also a good way to test whether your network supports the load.
Use the “test selected strips only” option, go in the Strips Tab and
change the selection in the strip list. This is similar to traditional
lighting consoles locate function.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
29
Name
The name of the stage. Select a stage to edit its name.
Size
The size in pixels of a stage.
Merge mode
Specifies how the values are merged when multiple stages
target the same LEDs. The merge starts with the stage at
the top of the list. You can reorder the stages with drag
and drop. See Stage Merging and Layering for more
details.
Testing
Activates the testing mode.
NDI output
Stream the LED rendering via NDI to be used by 3D
visualizers like WYSIWYG, Capture or Realizzer. This way
you don’t need to patch your LEDs in the visualizer and
you get a very high quality and live LED rendering.
Monitor
Opens a monitor window to help you see the final result of
the mapping for this stage.
Duplicate
Copies the stage to get a new media layer.
New
Creates a new stage.
Resize
Resizes all selected stages.
Delete
Deletes all selected stages.
Stages Manager
Shortcut key: alt-N
Select multiple stages in the list to modify them all at once. The first stage of the list is the
bottom media layer and the following stages can override any preceding stages. Drag and drop
stages to reorder.
Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
30
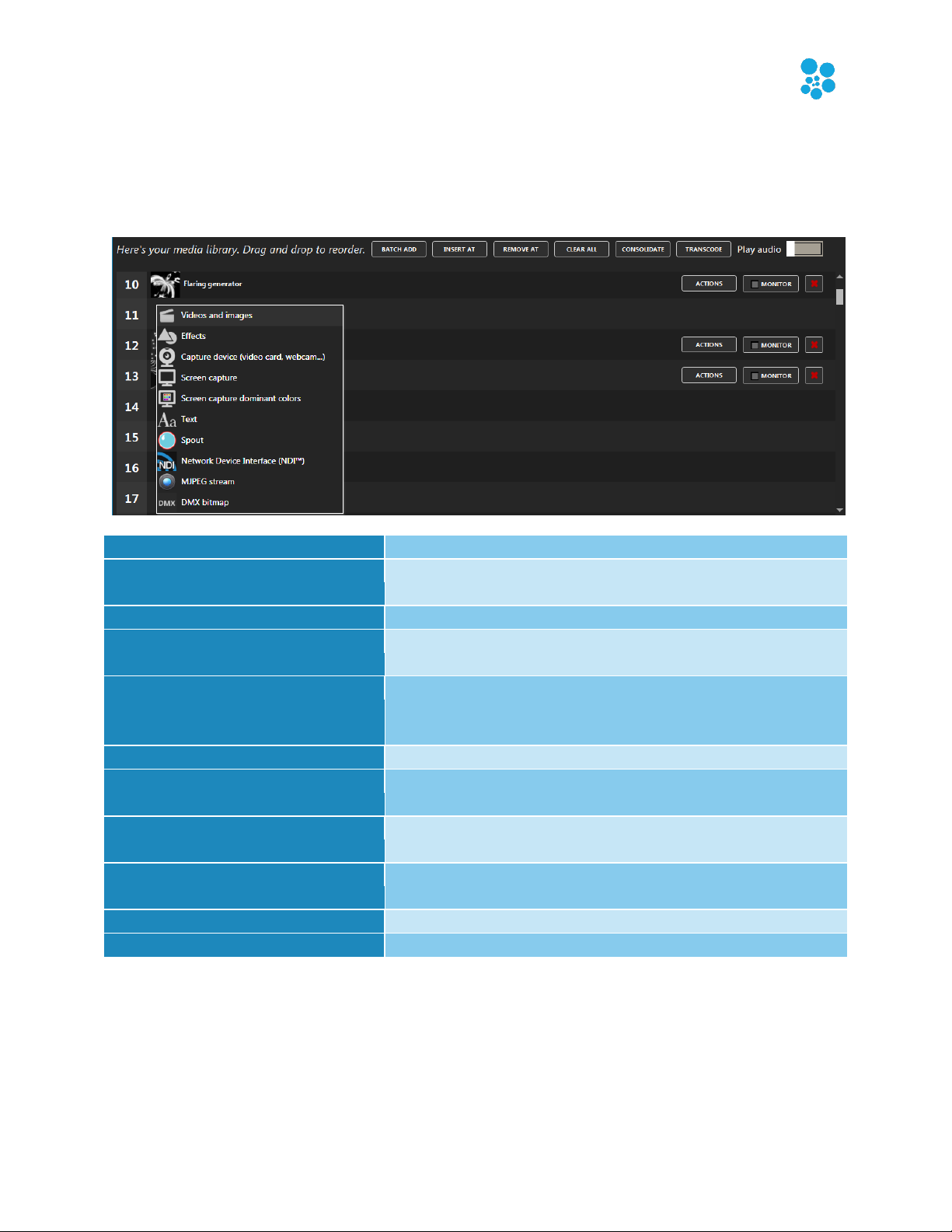
Batch add (alt-A)
Loads multiple video and picture files at once.
Insert At, Remove At
Inserts or removes a slot and offsets other media
accordingly.
Clear all
Resets the library.
Consolidate
Copies all files in the same directory to make it easy to
move your project file to another computer.
Transcode
Transcodes multiple videos at once. Converts to a MPEG4
format that should play on all computers. Also adjust
contrast and brightness.
Play audio
For videos, plays the audio track if available.
Playback position indicator
For videos, shows the position and allows seeking, which is
handy for long videos to test specific parts.
Actions
Depending on the media, you can rename a file, replace
the media and duplicate it.
Monitor
Opens a window showing the images coming from a
media source. Can also set a custom media thumbnail.
Delete button
Clears a media slot and allows selecting another media.
Swap items and reorder
You can swap items by using drag and drop.
Media Library
Shortcut key: alt-M
You can manage your media and see what’s active. Up to 255 media items can be loaded.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
31
Video Files (with or without audio)
Most video formats are supported when the appropriate DirectShow video codecs are installed.
By default, ELM can play these files: .mov, .avi, .wmv, .mpeg, .mp4, .mp2, .mkv, .webm, .ogv and
.ogg. There’s no video size and resolution limits. The audio track is played back on the default
sound device. If not needed, you can remove the audio by using the transcode button.
The recommended video format is MPEG4 in an avi file. For smaller files at the expense of a
higher CPU usage, you can use H264 in an avi file.
Picture Files
Use images like bmp, jpeg, gif (animated or not) and png.
Effects
The built-in effects give you pixel-perfect and configurable visuals. There are 100+ effects
available, each one configurable in multiple ways. Many effect parameters are controllable via
the DMX remote.
Capture Devices
Use live videos captured with a video card input or a connected camera like a webcam. Any
DirectX/DirectShow compatible hardware and software are supported.
Screen Capture
Capture any part of your screen and use it as a media in ELM. For example, play a video on
Youtube and map it to your LEDs. Another utility is to capture your video editor (like Adobe
After Effects) preview zone and let ELM generate a LED preview in real-time to assist your
content creation. This avoids having to render your video before trying it in ELM.
Screen Capture Dominant Colors
Capture any part of your screen and extract the dominant colors. This is useful to do color
matching between any kind of content and your LEDs.
Texts
Generate scrolling text with various fonts.
Spout (v. 2.006)
Use live videos generated by the most common video frameworks and VJ software.
This includes Resolume, Ableton Live, Processing, Max/Msp, TouchDesigner, Cinder,
OpenFramework, VVVV, Isadora, After Effects, Mapio, Unity3D and more. The Spout
integration gives you total control over the content and is the way to go when you
want interactive visuals.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
32
Network Device Interface (NDI v. 4.1)
Receive live video streams via the network, as commonly used in professional live
show productions. Easily connect ELM to a multitude of NDI compatible hardware
and software, including capture cards, IP cameras and video over the cloud. NDI has
been developed by NewTek - http://NDI.NewTek.com.
MJPEG Streams
It’s the most basic way to receive video streams via the network. If your IP camera doesn’t
support the more complete NDI protocol, it should at least support MJPEG streaming.
DMX Bitmap
This special media allows receiving DMX from a lighting console and convert it to a video. You
can then use this video like any other media and map it on your LEDs. A common usage
scenario is to control groups of LEDs with one RGB or intensity value.
To quickly test your installation without having the final videos, just use
the built-in effects. You can create your schedules and test everything
right away. Then when you’ll get your videos, replace the built-in
effects.
Media file paths are saved relatively to your project file. Use the
consolidate feature to copy all files in a directory next to your project.
Then copy everything to your other computer.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
33
Add playlist (alt-P)
Creates a playlist for the current stage.
Rename playlist
Right-click on a playlist to see the menu or double-click on
its name.
Copy/Paste playlist
Right-click on a playlist to see the menu.
Stop during daylight
Stops this stage’s schedule during daylight hours. Based on
the sunset and sunrise times.
Scheduler On/Off
Temporarily stops all schedules. It is handy to take over
and manually select what’s playing on each stage in the
live mode. This option isn’t saved to the project file.
Sunrise, Sunset times
Computed based on your location. See Time.
Add media (alt-A)
Adds one or multiple media to the playlist.
Delete
Removes the selected items from the playlist.
Start time
The time of the day to start the playlist.
Relative to
Determines how to interpret the start time.
Schedules
Shortcut key: alt-H
Each stage has its own schedule. A schedule can contain as many playlists as you need and you
trigger them with an activation time, date range and day of week.
Select a playlist to see its settings. Double click to play. The playlist settings are:

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
34
Duration
The duration of the playlist (end time).
Loop
Repeats the playlist indefinitely (loop).
Start and end dates
The date range (inclusive) when the playlist is active.
Active days
The days of the week when the playlist is active.
Transitions
The type and duration of transition effects, from the classic
crossfade to complex effects rotating and scaling the
media. If color filters are used, a nice transition will also
occur between the colors.
Intensity level
The luminosity level (dimmer). Set to 0 to deactivate the
stage.
Speed
The playback speed. Does nothing for live video streams.
Status
The playing status, indicating the playing time and number
of repetitions done.
Media
The associated media. Click to change it.
Duration
For some types of media like video, displays the total play
time.
Max play count
The maximum number of times to play this media before
playing the next one.
Max play time
The maximum number of seconds to play this media
before playing the next one.
Color filter
The RGB color filter to apply to the media. White means no
filter.
Drag and drop media items in the list to reorder. Select one or multiple items and right-click to
see the menu, allowing copying and pasting items across playlists. The settings for each media
item are:
If “infinite time” is displayed for the status of an item that means this item will play indefinitely
or until the playlist ends (if the playlist duration is specified). Specify a max play time if this isn’t
what you want.
Turn off the scheduler to temporarily take control of what’s playing on
your stage using the live mode.
Select multiple media items to change them all at once when modifying
the play count, play time and color filter.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
35
A and B media banks
Shows the loaded media. Click a media to select it.
A and B configuration panels
At the bottom of the right and left sides, the selected
media are displayed and you can expand the sections to
see the parameters of the media.
A-B Fader
Mix the media from the A and B sides, using the selected
transition/mix effect.
Execute
Automatically creates a transition from A to B or B to A
depending on the most active side.
Transition effect and duration
Selects one of the 40+ transition/mix effects and its
duration in seconds.
Intensity
The luminosity level (dimmer). Set to 0 to deactivate the
stage.
Color wheel
Filters the color output. It works like a color gel, where if
you select the red color, only red pixels will be visible at
the output.
Speed
The playback speed. Used for certain media types only,
including video files, built-in effects and texts. Does
Live Mode
Shortcut key: alt-L
The main goal of the live mode is to see what’s playing on each stage and configure the effects.
For example, if a playlist is running, you’ll see what’s happening in real-time, including the
transitions. If nothing is controlling the stage, you’ll be able to manually select what’s playing.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
36
nothing for live video streams.
Thumb size
Determines the size of the media thumbnails in the A and
B media banks.
Audio reactive mix
Automatically mixes your media in sync with the music. It’s
a kind of auto-pilot, which is handy to create a show very
quickly. Click the “…” button to select the audio input.
DVI
Opens a window to output the video to a projector or TV.
The position of the window is saved in the project file. You
can output the media or the LED map. The LED map is
exactly the size of the stage and one LED is exactly one
pixel. This is required for systems taking a video input like
Martin P3.
You can use ELM to output video to a projector or TV without controlling
LEDs. Simply create a stage and don’t put any LEDs on it. Then in the
live mode, click the DVI button.
Using black and white media allows you to use the color filter and get
exactly the RGB color you want as output.
Use the live mode as a monitor to help you see what’s going on while
remotely controlling ELM with another lighting console. You can also
open multiple DVI outputs (one per stage) and use them as monitors.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
37
New project
Closes the current project and start a new one.
Load (ctrl-o)
Opens an existing project.
Save as
Saves the project under a new name.
Save (ctrl-s)
Saves the project.
Import
Imports items from another project, including stages,
media and DMX settings.
Export patch
Creates an html file containing all strips/fixtures to be
opened in a web browser or Excel.
Firewall
Does the necessary firewall configuration for all network
protocols. ELM must be running as administrator.
DMX universes
The number of DMX universes used by your project. This is
the number used to calculate your license limit (if any).
Stages
The number of stages in your project.
Strips
The number of strips in all stages.
Mapped LEDs
The number of LEDs inside the mapping zones in all stages
(including duplicated LEDs).
Output rate (fps)
The number of times per second DMX packets are sent.
Default is 30, max 120. WARNING! Don’t set it higher than
what your LED controllers/fixtures support. This may result
in DMX packets being discarded and visual artefacts.
DMX output
Activates or temporarily disables the DMX output. This is
handy during testing.
Lock stages
Prevents accidentally editing the stages by requesting a
password to unlock (last 4 characters of the hardware ID).
Run at startup
Automatically runs ELM when Windows starts and loads
the last opened project file.
Settings
Shortcut key: alt-I
Project
This is the overall panel, displaying the most important info about your project status.
A project backup file is created every 5 minutes. To avoid slowdown during a live show, you
need to manually save the project to trigger the backup creation. To open a backup, select the
Backup file type in the file browser when opening a project. To set the backup to be the current
project, simply save the project.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
38
Adapter
Selects a network adapter for the output.
Universe display
By default, universes are in the hexadecimal format, where
the first digit is the Net (0 or 1) followed by the Sub-Net
(0-F) and then the universe (0-F). In decimal mode, the
universes are displayed from 0 to 511.
Scan nodes
Opens a window and shows the detected Art-Net nodes.
Click the configure unicast button to activate Art-Net
unicast and send the universes to the subscribed nodes.
Locate uni.
Locates universes by sending all channels at full. No LEDs
need to be patched.
Monitor
Shows the exact DMX values being sent.
Optimize frames
When activated, universes are sent only when there’s a
change and only the channels that have changed are sent,
which may considerably reduce the network load. Older or
low-powered nodes may not support it.
ArtSync
When activated, sends a ArtSync packet after all universes
have been sent. This makes sure all outputs to the lights
are in sync and prevents tearing problems.
Universe IP addresses
For each universe, enter an IP address to enable unicast
and send the DMX packet to a specific node. Type
broadcast to send the universe to all connected nodes in
the network. Unicast is preferred when using more than 64
Art-Net universes or a WiFi network.
Adapter
Selects a network adapter for the output and the input if
using remote control with sACN.
First universe
Since sACN supports thousands of universes, set the first
universe to use.
Priority
Selects the priority level used for merging multiple sACN
data sources. This is useful when using two ELM computers
and you want to use one as a backup by setting its priority
to a lower level than the main computer.
Locate uni.
Locates universes by sending all channels at full. No LEDs
need to be patched.
Monitor
Shows the exact DMX values being sent.
Optimize frames
When activated, universes are sent only when there’s a
Art-Net
Settings for the Art-Net universes.
sACN
Settings for the sACN universes.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
39
change, which may considerably reduce the network load.
sACN Sync
When activated, sends a sync packet after all universes
have been sent. This makes sure all outputs to the lights
are in sync and prevents tearing problems. The sACN
controllers need to support sACN sync.
Universe IP addresses
For each universe, enter an IP address to enable unicast
and send the DMX packet to a specific node. Type
multicast to send the universe to all subscribed nodes in
the network. Unicast is preferred when using more than 64
sACN universes with a network switch not IGMP v2 ready
or a WiFi network.
Adapter
Selects a network adapter for the output.
Locate uni.
Locates universes by sending all channels at full. No LEDs
need to be patched.
Monitor
Shows the exact DMX values being sent.
Device IP addresses
Enter the IP address of your device.
Port
Enter the destination port for each device (1-16).
Activation switch
Determines whether this audio input is activated.
Deactivate unused inputs to save resources.
Volume
Adjusts the input volume.
Falloff speed
Adjusts how fast the frequency bands go down.
Lower/higher frequencies (Hz)
Adjusts the frequency range to be used for the audio
analysis.
Up/down arrows
Moves the audio input to another slot. This way if the
position of an audio source changes, you’ll not need to
update all your audio reactive effects.
WaveIn/ASIO
Switch between the standard Windows Audio and the low
latency ASIO modes.
KiNet
Settings for the Philips Color Kinetics devices (power supplies). The protocol version is KiNet v2
(PORTOUT). You map each KiNet device’s port to a universe in ELM. You can map up to 2048
ports. Use Philips QuickPlay Pro to configure and get the IP addresses of your KiNet devices.
Audio
Activate and configure up to 8 audio inputs. The audio inputs are used by the audio reactive
effects and the audio reactive mix. Activate the loopback input to listen to what’s playing on this
computer.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
40
Your position
Your latitude and longitude position on Earth. You can also
select a preset in the list.
Offsets (minutes)
Offsets the sunrise and sunset times. For example, if you
want to start the installation 2 hours before sunset, you
enter (-120) in the sunset box.
Test helpers
Temporarily modifies the current time and date to help
you test your schedule. These values aren’t saved in the
project file.
Backup
Saves your license file in case you need to reinstall your
OS.
Import
Imports a license file.
Hardware ID
Your unique computer’s ID, used to generate the licenses.
Time
Settings for accurate sunrise and sunset times, automatically updated throughout the year
based on your location.
Colors
Adjust the color temperature and intensity of the various LED types in order to get a more
accurate preview in the stage monitor. This is particularly important when you’re using LEDs with
multiple types of whites. For example, the WWA LED type is composed of the cool white, neutral
white and warm white (or amber). Adjusting any of these whites will change the appearance of
the WWA LEDs in the stage monitor.
License
Manage your licenses. You can import multiple licenses to get more DMX universes.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
41
Input mode
Selects how you want to remote control ELM. The current
options are Art-Net, sACN and a Enttec USB Pro interface.
Network adapter
For Art-Net only, you can select a different network
adapter for output and input.
Universe
Selects the DMX input universe.
Monitor
Shows the exact DMX values being received.
Address
Selects the DMX address for the first stage.
Fixture mode
Selects the level of control you want (Basic or Extended).
DMX value mode
Percent: makes it easy for consoles working in percent.
Raw: makes it easy for consoles working in the 0-255 DMX
range.
Media remote
Maps DMX channels to be used to remotely control the
media parameters.
Remote Control
ELM can be remotely controlled in many ways. Multiple inputs can be active at the same time to
give you even more flexibility. The DMX input always takes priority.
DMX – Art-Net, sAcn and Enttec USB Pro
Settings for remotely controlling ELM with a lighting console.
The DMX sheet showing what can be controlled and by which channel is integrated in ELM. It is
dynamically generated based on the current remote settings and your stages. This way, you
can’t lose it!
When no DMX data is received for more than 5 seconds, the remote control mode will
automatically be deactivated. This is a failsafe feature in case the remote console has a problem.
When this happens, the schedule resumes right away. If there are no schedules, then the current
media will continue to play.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
42
Channel
Name
Values
Note
1
Remote control
mode
0: Remote control
deactivated
1-254: Reserved,
don’t use
255: Remote control
activated
Remote control activated only when
receiving 255. 0 disables the remote control
mode and the stage goes back to being
controlled via the schedule (if any) or
manually.
2
Media index
0: No function
1-99: Media index
The media to play. If needed, a transition
(crossfade) is automatically executed
between the current media and the new
one. This effectively controls the A and B
sides in the live panel for you.
3
Intensity level
0: Stage deactivated
1-255: Level
The output level (dimmer). When at 0%, the
stage is considered to be deactivated and
doesn’t override stages with a lower
precedence anymore - it becomes
transparent. To keep the stage activated
and force a black output, use the color
filters at 0%.
4
Red filter
0-255
Filters the color output.
5
Green filter
0-255
Filters the color output.
6
Blue filter
0-255
Filters the color output.
7
Playback speed
0: Paused
1-255: Speed up to
10x. 25 = 1x
For some type of media like videos, effects
and texts, the speed controls how fast the
playback goes. For live streams, the speed
has no effect.
8
Transition
duration
0: No transition
1-255: Duration up
to 20 seconds. 12 =
1s.
When transitioning between media, this
controls the duration of the crossfade.
Basic Fixture Mode (8 channels per stage)

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
43
Channel
Name
Values
Note
1
Remote control
mode
0: Remote control
deactivated
1-254: Reserved,
don’t use
255: Remote control
activated
Remote control activated only when
receiving 255. 0 disables the remote control
mode and the stage goes back to being
controlled via the schedule (if any) or
manually.
2
Intensity level
(MSB/coarse)
0: Stage deactivated
1-65535: Level
The output level (dimmer). When at 0%, the
stage is considered to be deactivated and
doesn’t override stages with a lower
precedence anymore - it becomes
transparent. To keep the stage activated
and force a black output, use the color
filters at 0%.
3
Intensity level
(LSB/fine)
4
Red filter
0-255
Filters the color output.
5
Green filter
0-255
Filters the color output.
6
Blue filter
0-255
Filters the color output.
7
Media A speed
0: Paused
1-255: Speed up to
10x. 25 = 1x
For some type of media like videos, effects
and texts, the speed controls how fast the
playback goes. For live streams, the speed
has no effect.
8
Media B speed
0: Paused
1-255: Speed up to
10x. 25 = 1x
For some type of media like videos, effects
and texts, the speed controls how fast the
playback goes. For live streams, the speed
has no effect.
9
Media A index
0: Empty
1-99: Media index
The media to play on side A.
10
Media B index
0: Empty
1-99: Media index
The media to play on side B.
11
Media mixing
position
(MSB/coarse)
0-65535
0: media A fully
active
65535: media B fully
active
Controls the position of the mixing effect,
from A to B.
12
Media mixing
position
(LSB/fine)
Extended Fixture Mode (15 channels per stage)

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
44
13
Mixing position
modifier
0: No function
1-255: Various
mapping functions
Spices up the mixing position by applying a
function like bounce, sigmoid and
exponential. See the list of functions in ELM.
14
Mixing effect
0: no effect
1: crossfade
2: black fade
3: white fade
4-255: Various
effects
Determines the effect to be applied when
mixing the A and B sides. From simple
crossfade to complex effects including
rotations, scaling and translations. See the
list of effects in ELM. When not needed,
select the ‘no effect’ to avoid wasting CPU.
15
Reserved
(unused)
CITP/MSEX
Activate this option to enable ELM to communicate with other CITP/MSEX compatible consoles
and software. CITP/MSEX version 1.0, 1.1 and 1.2 are available. The things ELM can do are:
- Send the media thumbnails to your console
- Stream the LED preview of every stage to your console or visualizer
- Send the stage statuses, including the current playing media

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
45
/elm/stages/{stage name}/
live/
intensity 0..1
rgb 0..1, 0..1, 0..1
media 0..99
speed 0..10
transitonFx 0..43
transitionDuration 0..9999 seconds
audioMixControlled {0: no, 1: yes}
remotelyControlled {0: no, 1: yes}
mix/
position 0..1
A/
media 0..99
speed 0..10
B/
media 0..99
speed 0..10
scheduler/
running {0: no, 1: yes}
playlists/{playlist name}
running {0: no, 1: yes}
Addresses and names are caseinsensitive.
Media index 0 is an empty slot.
RGB can be sent in 3 parts at the /r /g
and /b addresses.
audioMixControlled: controls the
audio mix activation.
remotelyControlled: determines
whether OSC overrides the scheduler.
Use * (wildcard character) in the stage
name to target multiple stages at
once. For example, /elm/stages/*/XYZ
targets all stages.
/elm/stages/background*/XYZ
targets all stages with a name
starting with background.
OSC
Settings for remotely controlling ELM via OSC (Open Sound Control) over the network. ELM
listens for incoming OSC on all network adapters.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
46
Request
Parameters
Output
GET /elm/status
statuses of all sub-systems like
under the settings/project menu
GET /elm/heartbeat
200 OK if the server is running
GET /elm/stages
includeState 0 (only names) 1 (ids,
names and other info)
list of stages
GET /elm/stages/{stage name or id}
Stage id, name and other info
GET /elm/stages/transitionFxNames
list of all transitionFx names
GET /elm/stages/{stage name or id}/live
state of the requested stage
POST /elm/stages/{stage name or id}/live
intensity 0..1
media 0..99
speed 0..10
transitionFx {name},
transitionDuration 0..9999
red 0..255
green 0..255
blue 0..255
audioMixControlled 0 or 1
remotelyControlled 0 or 1
activate the audio mix mode
if 0, let the scheduler or another
remote takes over.
GET /elm/stages/{stage name or id}/patch
list of all patched strips
GET /elm/stages/{stage name or id }/monitor
width. height, fps
MJPEG stream of the LED preview
GET /elm/stages/{stage name or id }/scheduler
state of a scheduler
POST /elm/stages/{stage name or id }/scheduler
running 0 (no) or 1 (yes)
RGBRemotelyControlled 0 or 1
intensityRemotelyControlled 0 or 1
starts/stops the scheduler
overrides the scheduler’s RGB
overrides the scheduler’s intensity
GET /elm/stages/{stage name or
id}/scheduler/playlists
includeState 1 (return playlist states)
list of playlist names
GET /elm/stages/{stage name or
id}/scheduler/playlists/{playlist name}
state of a playlist
POST /elm/stages/{stage name or
id}/scheduler/playlists/{playlist name}
running 0 (no) or 1 (yes)
starts/stops the playlist
GET /elm/media/slots
includeState 1 (return slot states)
list of filled media slot ids
GET /elm/media/slots/{id}
state of a media slot
GET /elm/media/slots/{id}/thumbnail
width, height
PNG image
GET /elm/media/slots/{id}/monitor
width. height, fps
MJPEG stream of the media
POST /elm/media/slots/{id}
path (load an existing local file)
form file (upload a new file)
state of the updated media slot
HTTP
Settings for remotely controlling ELM via HTTP, which is a protocol based on TCP/IP. This is the
most reliable way to integrate ELM with control systems like Crestron and Pharos or to create
custom web interfaces. ELM listens for incoming HTTP requests on all network adapters.
For example, to start the playlist “playlist01” of the stage “stage01”, the request is:
POST /elm/stages/stage01/scheduler/playlists/playlist01?running=1 HTTP/1.0\x0D\x0A
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded\x0D\x0A
Content-Length: 0\x0D\x0A
\x0D\x0A
\x0D\x0A

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
47
To get the info about this playlist, the request is:
GET /elm/stages/stage01/scheduler/playlists/playlist01 HTTP/1.0\x0D\x0A
\x0D\x0A
\x0D\x0A
Notes:
- Each line ends with \r\n characters which are in hexadecimal \x0D\x0A.
- There are two empty lines at the end of a request.
- Use * (wildcard character) in the stage name to target multiple stages at once for POST.
- All data is returned in JSON.
- Use the returned HTTP status code to do proper error handling.
- Addresses and names are case-insensitive.
- Parameters can be provided in the query string or form data.
- Media id 0 is an empty slot.
The base URL to access the API is: http://YOUR-COMPUTER-NAME:port/elm. If you prefer,
you can replace the computer name by its IP address or localhost if the server is running on the
same computer. The port can be omitted if it’s 80, which is the default for HTTP.
You can restrict the access to the API by activating the Basic Auth feature. For more details see
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Basic_access_authentication.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
48
Problem
Possible causes
Solutions
No Art-Net
nodes detected
in the scan
nodes dialog.
The node IP address may be
incorrectly configured. For example,
the computer’s IP is 192.168.1.X
and the node’s IP is 192.168.0.Y.
The wrong network adapter may be
selected in ELM.
The firewall is blocking ELM.
Change the IP address of your
computer or your node to be on the
same network, that is most of the
time, the 3 first numbers need to be
the same. The subnet masks (netmask)
also need to be the same. Usually, you
want to use 255.255.255.0 as the
subnet mask.
Go under the settings menu and make
sure the proper network adapter is
selected for each DMX protocol.
Use the firewall button in ELM.
Output
lag/shuttering
(working but
with intermittent
delays).
The network is overloaded, most of
the time due to the use of
broadcasting. By default with ArtNet, all universes are broadcasted
(sent to all connected devices on
the network). Some routers and
switches may have problems under
heavy load. With sACN, multicast is
used and may not be well
supported by your routers and
switches, resulting in broadcasts.
Enter your node IP addresses in the
universe boxes to enable unicast
sending. For Art-Net, click the scan
nodes button and then the configure
unicast button (see
Art-Net). This greatly reduces the
work your router/switch has to do.
Alternatively, you can lower the ELM’s
output rate (see Project).
Another way to reduce the network
load is to enable the optimize frames
option.
Some lights
wrongly stay on
for half a second
or so.
The most common cause is an
unreliable network like a WIFI
causing data packets to be
discarded.
Missed DMX packets due to a too
high output rate and the optimize
frames option being ON.
Disable the optimize frames option for
Art-Net or sACN. ELM will
continuously send data even when
there’s no change. You may need to
reduce the output rate to avoid
network overload.
When the optimize frames is ON, ELM
doesn’t send DMX unless there’s a
change. So if your LED controller or
Troubleshooting
Output - Art-Net/sACN/KiNet

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
49
fixture discards a packet because it’s
overloaded, visual artifacts will be
visible. Try deactivating the optimize
frames option or reducing the ELM’s
output rate.
The lights do
nothing.
The nodes may not be properly
configured or not plugged.
The strips may be configured to
use the wrong universes and/or
addresses.
The firewall may be blocking ELM.
Test the nodes with the configuration
utility from the manufacturer. Check
the IP address configuration as
described above.
Check the universes and addresses of
your strips. You can use an Art-Net
sniffer like the Artnetominator or
Wireshark to see what ELM is sending.
Disable your firewall. Use the locate
universe feature in ELM to force
sending all channels at full.
The lights
flicker.
The most common cause of flickers
when using LED strips is that the
wrong LED type or protocol has
been configured in the LED
controller. For example, selecting
TM1803 instead of WS2811.
Maybe some LEDs don’t have
enough power. It can cause flickers
at the end of the strips.
This may also be caused by using
video content with little noise in it
due to compression (may not be
problematic when displayed on a
screen but it becomes apparent on
LEDs).
Some older LED fixtures may not
work well when using the Art-Net
optimize frames option.
Start your LED controller configuration
utility and check the configured LED
type. Try different types if you’re
unsure.
Enable the testing mode (see
Testing Tab) and select a low
brightness color. This will cause the
LEDs to use less power. If the flickers
go away, then the problem is due to
not having enough power going to
the LEDs. You’ll need to inject more
power.
The testing mode generates a pure
color, so if this isn’t a power problem
and a full white test color doesn’t
cause flickers, that means the video
content is probably the problem.
Disable the optimize frames option
(see
Art-Net).

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
50
Problem
Possible causes
Solutions
ELM isn’t
starting and
saying a dll is
missing.
Probably the Visual Studio 2015
run-time component is missing.
Download and install the Visual C++
Redistributable for Visual Studio 2015
https://www.microsoft.com/enca/download/details.aspx?id=48145
Very high CPU
usage.
The computer can’t handle your
videos.
You are looking at a stage and the
computer is having a hard time
drawing pretty graphics.
The output rate is too high.
Reduce the resolution of your videos
by using the transcode button (see
Video Files). Transcoding can convert
to an easier to decode format which
may also save CPU.
If you’re using live video capture, try
reducing the capture resolution.
If the computer is already overloaded,
try not to unnecessarily leave ELM on
a graphic heavy screen. Minimize the
ELM window or go in the
setting/project tab. Also make sure to
close all monitor windows.
Alternatively, you can lower the ELM’s
output rate (see Project).
When moving
my project to
another
computer, the
media are
missing.
The ELM project file doesn’t contain
the media and the stage’s
background images.
You need to move the media to the
other computer and put them at the
same place relatively to the project
file. A good practice is to create a
media folder next to your project file.
Alternatively, use the consolidate
feature of the media library (see
Media Library).
I see a blank
screen when
using a remote
desktop app like
LogMeIn or VNC.
The ELM user interface uses
hardware acceleration (DirectX and
OpenGL). Some remote desktop
app doesn’t support it or need
special configuration.
You may need to configure your
remote desktop app to support
hardware acceleration. Alternatively,
TeamViewer works well with ELM.
The eye candy
effects aren’t
working on Mac
under Parallels.
ELM needs OpenGL 3.3 and
Parallels only supports OpenGL 3.2.
Use Bootcamp instead of Parallels.
General

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
51
EULA
This End-User License Agreement (EULA) is a legal agreement between you (either an individual
or a single entity) and the mentioned author and copyright holder (Lightjams inc.) and
distributor (Enttec LLC) of this Software for the software product identified above, which
includes computer software and may include associated media, printed materials, and “online”
or electronic documentation (“SOFTWARE PRODUCT”).
By installing, copying, or otherwise using the SOFTWARE PRODUCT, you agree to be bounded
by the terms of this EULA.
If you do not agree to the terms of this EULA, do not install or use the SOFTWARE PRODUCT.
SOFTWARE PRODUCT LICENSE
1. GRANT OF LICENSE. This EULA grants you the following rights: Installation and Use. Each
license is registered to one person and covers the use of the SOFTWARE PRODUCT on one or
multiple computers depending on the license type, so long as multiple computers are not used
at the same time. The license is locked to the computer’s CPU and motherboard.
2. DESCRIPTION OF OTHER RIGHTS AND LIMITATIONS.
Limitations exist on Reverse Engineering, Decompilation, Disassembly and changing
(adding,deleting or modifying) the resources in the compiled assembly of the SOFTWARE
PRODUCT. You may not reverse engineer, decompile, or disassemble the SOFTWARE PRODUCT,
except and only to the extent that such activity is expressly permitted by applicable law
notwithstanding this limitation.
Updates and Maintenance
ELM updatess are FREE of charge.
Separation of Components.
The SOFTWARE PRODUCT is licensed as a single product. Its component parts may not be
separated for use on more than one computer.
Software Transfer.
You may not rent, lease or sublicense the SOFTWARE PRODUCT on a temporary or permanent
basis.

Effortless LED Mapping by Enttec
ELM User Manual rev 1.42
52
Termination.
Without prejudice to any other rights, the Author of this Software may terminate this EULA if
you fail to comply with the terms and conditions of this EULA. In such event, you must destroy
all copies of the SOFTWARE PRODUCT and all of its component parts.
3. COPYRIGHT.
All title and copyrights in and to the SOFTWARE PRODUCT (including but not limited to any
images, photographs, clipart, libraries, and examples incorporated into the SOFTWARE
PRODUCT), the accompanying printed materials, and any copies of the SOFTWARE PRODUCT
are owned by the Author of this Software (Lightjams inc). The SOFTWARE PRODUCT is protected
by copyright laws and international treaty provisions. Therefore, you must treat the SOFTWARE
PRODUCT like any other copyrighted material.
LIMITED WARRANTY
NO WARRANTIES.
The Author of this Software expressly disclaims any warranty for the SOFTWARE PRODUCT. The
SOFTWARE PRODUCT and any related documentation is provided “as is” without warranty of
any kind, either express or implied, including, without limitation, the implied warranties of
merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose, or noninfringement. The entire risk arising out
of use or performance of the SOFTWARE PRODUCT remains with you.
NO LIABILITY FOR DAMAGES.
In no event shall the author of this Software be liable for any special, consequential, incidental or
indirect damages whatsoever (including, without limitation, damages for loss of business profits,
business interruption, loss of business information, or any other pecuniary loss) arising out of
the use of or inability to use this product, even if the Author of this Software is aware of the
possibility of such damages and known defects.
 Loading...
Loading...