Page 1

ENTERPRISE WIRELESS CLIENT/BRIDGE
Model: ENH210
User Manual
Version: 1.0
Page 2

Table of Contents
1 PRODUCT OVERVIEW................................................................................................................................................6
1.1 FEATURES...............................................................................................................................................................6
1.2 BENEFITS................................................................................................................................................................8
1.3 PACKAGE CONTENTS................................................................................................................................................9
1.4 SYSTEM REQUIREMENT ............................................................................................................................................9
1.5 HARDWARE OVERVIEW ............................................................................................................................................9
1.6 UNDERSTANDING THE ENH210 LEDS.....................................................................................................................10
2 ENGENIUS ZONECONTROLLER..............................................................................................................................11
2.1 ZONECONTROLLER OVERVIEW................................................................................................................................11
2.2 ZONECONTROLLER FEATURE LIST ............................................................................................................................13
2.3 ZONECONTROLLER, ADDITIONAL INFORMATION.......................................................................................................15
3 INSTALLATION .........................................................................................................................................................16
3.1 PRE-INSTALLATION GUIDELINES ..............................................................................................................................16
3.2 INSTALLING THE ENH210......................................................................................................................................17
4 WIRELESS NETWORK MODES................................................................................................................................18
4.1 ACCESS POINT MODE............................................................................................................................................18
4.2 ACCESS POINT WITH WDS FUNCTION MODE...........................................................................................................18
4.3 CLIENT BRIDGE MODE ...........................................................................................................................................19
4.4 WDS BRIDGE MODE.............................................................................................................................................20
4.5 CLIENT ROUTER MODE ..........................................................................................................................................21
5 CONFIGURING YOUR COMPUTER FOR TCP/IP ...................................................................................................23
5.1 CONFIGURING MICROSOFT® WINDOWS 7..............................................................................................................23
5.2 CONFIGURING MICROSOFT® WINDOWS VISTA........................................................................................................25
5.3 CONFIGURING MICROSOFT® WINDOWS XP............................................................................................................26
5.4 CONFIGURING APPLE® MAC OS X.........................................................................................................................27
5.5 LOGGING INTO THE ENH210.................................................................................................................................28
6 STATUS ......................................................................................................................................................................30
6.1 SAVE / LOAD ........................................................................................................................................................30
6.2 MAIN ..................................................................................................................................................................31
6.3 WIRELESS CLIENT LIST ...........................................................................................................................................32
6.4 SYSTEM LOG.........................................................................................................................................................32
6.5 CONNECTION STATUS............................................................................................................................................33
6.6 DHCP CLIENT TABLE.............................................................................................................................................33
7 SYSTEM......................................................................................................................................................................34
7.1 SWITCHING THE OPERATION MODE.........................................................................................................................34
Page 3

8 WIRELESS CONFIGURATION ..................................................................................................................................35
8.1 WIRELESS SETTINGS ..............................................................................................................................................35
8.1.1 Access Point Mode...................................................................................................................................35
8.1.2 Client Bridge Mode..................................................................................................................................38
8.1.3 WDS Bridge Mode...................................................................................................................................40
8.1.4 Client Router Mode.................................................................................................................................42
8.2 WIRELESS SECURITY SETTINGS ................................................................................................................................44
8.2.1 WEP.........................................................................................................................................................44
8.2.2 WPA-PSK.................................................................................................................................................45
8.2.3 WPA2-PSK...............................................................................................................................................46
8.2.4 WPA-PSK Mixed......................................................................................................................................47
8.2.5 WPA.........................................................................................................................................................48
8.2.6 WPA2.......................................................................................................................................................49
8.2.7 WPA Mixed..............................................................................................................................................50
8.3 WIRELESS ADVANCED SETTINGS..............................................................................................................................51
8.4 WIRELESS MAC FILTER..........................................................................................................................................53
8.5 WDS LINK SETTINGS.............................................................................................................................................54
9 LAN SETUP................................................................................................................................................................55
9.1 IP SETTINGS .........................................................................................................................................................55
9.2 SPANNING TREE SETTINGS .....................................................................................................................................56
10 ROUTER SETTINGS................................................................................................................................................57
10.1 WAN SETTINGS..................................................................................................................................................57
10.1.1 Static IP.................................................................................................................................................57
10.1.2 DHCP (Dynamic IP)...............................................................................................................................59
10.1.3 PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet).....................................................................................61
10.1.4 PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol)............................................................................................63
10.2 LAN SETTINGS (ROUTER MODE)..........................................................................................................................65
10.3 VPN PASS THROUGH ..........................................................................................................................................66
10.4 PORT FORWARDING ............................................................................................................................................67
10.5 DMZ................................................................................................................................................................68
11 MANAGEMENT SETTINGS....................................................................................................................................69
11.1 ADMINISTRATION................................................................................................................................................69
11.2 MANAGEMENT VLAN.........................................................................................................................................70
11.3 SNMP SETTINGS................................................................................................................................................71
11.4 BACKUP/RESTORE SETTINGS.................................................................................................................................72
11.5 FIRMWARE UPGRADE...........................................................................................................................................72
11.6 TIME SETTINGS ...................................................................................................................................................73
11.7 LOG...................................................................................................................................................................74
11.8 DIAGNOSTICS.....................................................................................................................................................75
Page 4

12 NETWORK CONFIGURATION EXAMPLES...........................................................................................................76
12.1 ACCESS POINT....................................................................................................................................................76
12.2 CLIENT BRIDGE MODE .........................................................................................................................................77
12.3 WDS BRIDGE MODE...........................................................................................................................................78
12.4 CLIENT ROUTER MODE ........................................................................................................................................79
APPENDIX A – TROUBLESHOOTING........................................................................................................................80
A.1 PROBLEM SOLVING...............................................................................................................................................80
A.2 CONTACTING TECHNICAL SUPPORT.........................................................................................................................81
APPENDIX B – SPECIFICATIONS................................................................................................................................82
APPENDIX C – GLOSSARY..........................................................................................................................................83
APPENDIX D – STATEMENTS OF CONFORMITY.....................................................................................................88
D.1 – FEDERAL COMMUNICATION COMMISSION INTERFERENCE STATEMENT ......................................................................88
D.2 – INDUSTRY CANADA STATEMENT ...........................................................................................................................89
D.3 – EUROPE DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY...............................................................................................................90
Page 5

About This Document
This document is written by EnGenius Inc. EnGenius Inc. the reserves the right to change this
document without notice and all rights are reserved. This document can only be used for the
configuration of EnGenius products.
This document is to characterize the EnGenius ENH210 Wireless Client Bridge. Please read
the document carefully before setting up the ENH210. Any damage which is caused by
inappropriate use will not be covered under the warranty.
Formats
This document uses following symbols to indicate and highlight special messages.
Caution: This symbol represents a vital message and it is critical for the device
or settings.
Note: This symbol represents an important message for the settings.
Tip: This symbol represents an alternative choice that can save time or
resources.
Before you start__________________________________________________
The following equipment is required to setup the ENH210:
1. (1) Computer/Notebook and Internet access.
2. (2) Ethernet cables.
3. (1) EnGenius ENH210.
The equipment listed above is only for configuration of the ENH210. You will
need additional equipment to connect to the Internet, and configuration will depend on your
current network infrastructure. Please refer to Chapter 2 for more information.
Page 6

1 Product Overview
Thank you for using the ENH210. It is a powerful and enhanced Enterprise class outdoor
point-to-point bridge with 4 multi-functions: Client Bridge, WDS, Access Point, and Client
Router.
EnGenius’ ENH210 uses the latest wireless standard, 802.11n, which allows for faster wireless
throughput. The ENH210 affords a great advantage to minimize the time and cost which is
required to expand your network. It operates at 2.4GHz and is also backwards compatible with
802.11b/g networking equipment.
The ENH210 is easy to install almost anywhere with included standard/proprietary Power over
Ethernet adapter for quick outdoor installation. In addition, the ENH210 can manage power
level control, and it features narrow bandwidth selection and traffic shaping. The ENH210 fully
supports wireless encryption including Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK),
(64/128/152)-bit WEP Encryption, and IEEE 802.1x with RADIUS. Additionally, the ENH210 is
the ideal choice to pair with the ENH210 in an Access Point – Client Bridge or WDS Bridge –
WDS Bridge topology.
The ENH210 provides a proprietary PoE adapter. Please only use the
supplied PoE adapter. ENH210 also supports standard 802.3af/at PoE supplier.
Damage may occur if other proprietary PoE adapter is used.
1.1 Features
The following list describes the design and scope of the ENH210 made possible through the
power and flexibility of wireless LANs:
a) Difficult-to-wire environments
There are many situations where wires cannot be laid easily. For example, historic
and older buildings or use ENH210 in conjunction with ENH210 or ENH202 to
replace traditional wired connections between different buildings. Also as well as
open areas and cross-street architectures to save cost and time instead of trenching
or lease expensive circuits.
b) Temporary workgroups
Consider situations in parks, athletic arenas, exhibition centers, disaster-recovery,
temporary offices and construction sites where one wants a temporary WLAN
established and removed at a future date. The ENH210 is easy to place into and
remove from production.
Page 7
c) The ability to access real-time information
Doctors and nurses, point-of-sale employees, and warehouse workers can access
real-time information while dealing with patients, serving customers, and
processing information.
d) Frequently altered environments
Show rooms, meeting rooms, retail stores, and manufacturing sites are prime
examples where frequently rearranged workplaces are suited for wireless LANs.
e) Wireless extensions of Ethernet networks
Network managers in dynamic environments can minimize the overhead caused by
moves, extensions to networks, and other changes by utilizing wireless LANs.
f) Wired LAN backup
Network managers may implement wireless LANs to provide redundancy for
mission-critical applications which are implemented on wired networks.
g) Training and educational facilities
Training sites at corporations and students at universities use wireless connectivity
to afford access to information, information exchanges, and learning.
Features
High Speed Data Rate
Up to 300 Mbps
High Output Power up to 29 dBm
IEEE 802.11b/g/n
Compliant
Capable of handling heavy data payloads such as HD video
streaming
Extended range and excellent coverage
Fully interoperable with IEEE 802.11 b/g/n compliant devices
Multi-Function Users can use different modes in various environments
Support RSSI
Indicator (CB mode)
Power-over-Ethernet
Support Multi-SSID
function (8 SSID) in
AP mode
WPA2/WPA/ WEP/
IEEE 802.1x support
MAC address filtering
in AP mode
Users can select the best signal to connect with AP efficiently
Flexible Access Point locations and cost savings (Note: The
ENH210 includes a proprietary PoE adapter.)
Allow clients to access different networks through a single
access point and assign different policies and functions for each
SSID
Full support for all types of current wireless security standards
Ensure secure network by enforcing network access control lists
PPPoE/PPTP function
support (AP
Easy to access Internet via ISP service authentication
Router/CR mode)
SNMP Remote
Configuration
Management
Allow administrators to remotely configure or manage the
Access Point.
QoS (WMM) support Enhance user performance and density
Page 8

1.2 Benefits
Access Point Mode This is considered the main application the device is designed for.
Use this feature to setup the access point’s configuration
information. It supports transmit power and channel adjustments.
Clients can access the network with different regulatory settings
and automatically change to the local regulations.
Client Bridge Mode Use this feature to connect to an Access Point, enabling WAN
sharing.
WDS Mode Use this feature to link multiple APs in a network; All associated
clients from any AP can communicate with each other like in
ad-hoc mode.
Client Router Mode Clients connect wirelessly to an AP and transmit data through AP
to access the Internet.
Multiple SSIDs ENH210 supports up to 4 SSIDs on your access point. The
following options can be set to each SSID:
- Public or private SSID
- Authentication
- VLAN identifier
- RADIUS accounting identifier
- Profile isolation for infrastructure network
VLAN Specify a VLAN number for each SSID to separate the services
among clients.
QoS Use this feature to limit the incoming or outgoing throughput.
Wi-Fi Protected Access Wi-Fi Protect Access is a standard-based interoperable security
enhancement that increases the level of data protection and
access control for existing and future wireless LAN systems. It is
compatible with IEEE 802.11i standard. WPA leverages TKIP and
802.1X for authenticated key management.
Page 9

1.3 Package Contents
Open the package carefully, and make sure that none of the items listed below are missing.
Do not discard the packing materials; in case of return, the unit must be shipped in its original
packaging.
1 x Wireless Access Point / Client Bridge (ENH210)
1 x 48V/380mA Power Adapter
1 x PoE Injector (EPE-48GR)
1 x Mounting Kit with Bracket-Mount Special Screw Set
1 x Mounting Installation Guide
1 x QIG
1 x CD (User Manual)
Using a power adapter other than the one included with the ENH210 may
cause damage to the device.
1.4 System Requirement
The following conditions are the minimum system requirements.
A computer with an Ethernet interface and operating under Windows XP, Vista, 7 or
Linux.
An Internet browser that supports HTTP and JavaScript.
1.5 Hardware Overview
Physical Interface - 1 x 10/100/1000 LAN Port with PoE support
- 1 x 10/100/1000 LAN port
- 2 x N-type Connector
Maximum Wireless Data rate - 300 Mbps
LEDs status - Power Status
- LAN1 (10/100/1000Mbps)
- LAN2 (10/100/1000Mbps)
- WLAN (Wireless is enabled)
- 3 x Link Quality (Client Bridge mode)
Page 10
1.6 Understanding the ENH210 LEDs
The rear of the ENH210 has two groups of LEDs. One group, labeled INDICATORS, shows the
status of the device. The second group, LINK QUALITY, shows the strength of the link
between the ENH210 and the network. The following table describes the ENH210 LEDs.
LED Color Mode Status
Power
LAN1
LAN2
WLAN
Link Quality
Green
Green(Main)
Orange(Secondary)
Green
See Status column
OFF= ENH210 is not receiving power.
ON= ENH210 is receiving power.
OFF = ENH210 is not connected to the network.
ON = ENH210 is connected to the network, but not sending or
receiving data.
Blink = ENH210 is sending or receiving data.
Access Point
or Client
Bridge Mode
Access Point
or Client
Bridge Mode
OFF = ENH210 radio is off and the device is not
sending or receiving data over the wireless LAN.
ON = ENH210 radio is on, and the device is not
sending or receiving data over the wireless LAN.
Blink = ENH210 radio is on, and the device is
sending or receiving data over the wireless LAN.
Shows the strength of the link between the
ENH210 and the network.
G = good quality (green).
Y = medium quality (yellow).
R = poor or no link (red).
Page 11

2 EnGenius ZoneController
This chapter describes the purpose and functionality of the ZoneController software which is
included with the ENH210.
2.1 ZoneController Overview
In enhancing the real-time functionality of a network,
applying the best network management software tool is
necessary. With an aggressive network management tool
you can perform monitoring, controlling, deploying and
allocating of data that are being transmitted to different
units/systems in a network. This application ensures the
entire network will typically run without faults and
interruptions.
Real-time monitoring means that the requests made by the
software tool to different units in a network must be
executed with precision and manage simultaneously. Such
equipment includes access points, client bridges, AP routers
and so forth for indoor or outdoor environment.
If you are someone who must meet with the growing
demand of performance related results from service
providers or someone involved in a small-scale enterprise,
you need to utilize a coherent platform to make it
successful. With geographical boundaries becoming
immaterial in business management, your network
management software tool must possess effective and
practical functions, like the EnGenius ZONECONTROLLER
software.
Page 12

Key Feature List Description
SNMP v1, v2c
Compliance
Simple configuration and discover the active SNMP device around
Network Monitoring
the network. Repeat the discovery process in a pre-defined time
interval to keep track of the status of the nodes
Allow super level user to create lower level user to perform
User Administration
monitoring job only
Block List Block certain node from being monitored
Image file imported by user and as a map. Map is zoomable, and its
Import Map
transparency level is configurable
Set actual scale on the map, which will be use for radio coverage
Map Scaling
plotting
Radio Coverage
Plotting
Base on some assumption along with the transmission power, plots
the radio coverage area. The assumption variables are configurable
Labeling Can display the unit on the map with MAC, IP or user-defined alias
System Log
User can save the running map's setting as a profile and apply it to
Map Profile
another new Map or ZONECONTROLLER
AP Stats
Read and save the up/download bytes data into database and can
be loaded in graph form
AP Stats (Old Record) The old data can be retrieve by select the desired date
Tabulated AP Unit The discovered AP unit will be display in a sortable table form
Reboot AP Unit *Only on recognized unit
Search and Locate perform search and locate unit in the AP table
Firmware Upgrade *Only on recognized unit
Tabulated Associated
User to The AP Unit
The users that associated to any discovered AP unit will be display in
a sortable table form
Block / Unblock User Move user to the MAC filter list of the recognized unit
Able to perform configurations to multiple nodes (must be same
Bulk Configuration
model). Only several selected parameters are configurable
View Properties Load selected unit properties data (general info, radio and users)
Perform configuration on selected node (Only applicable to
Configuration Tools
recognized model, and only selected parameter)
Launch Web GUI
Launch the web config page for more advanced settings
Configuration Page
Page 13
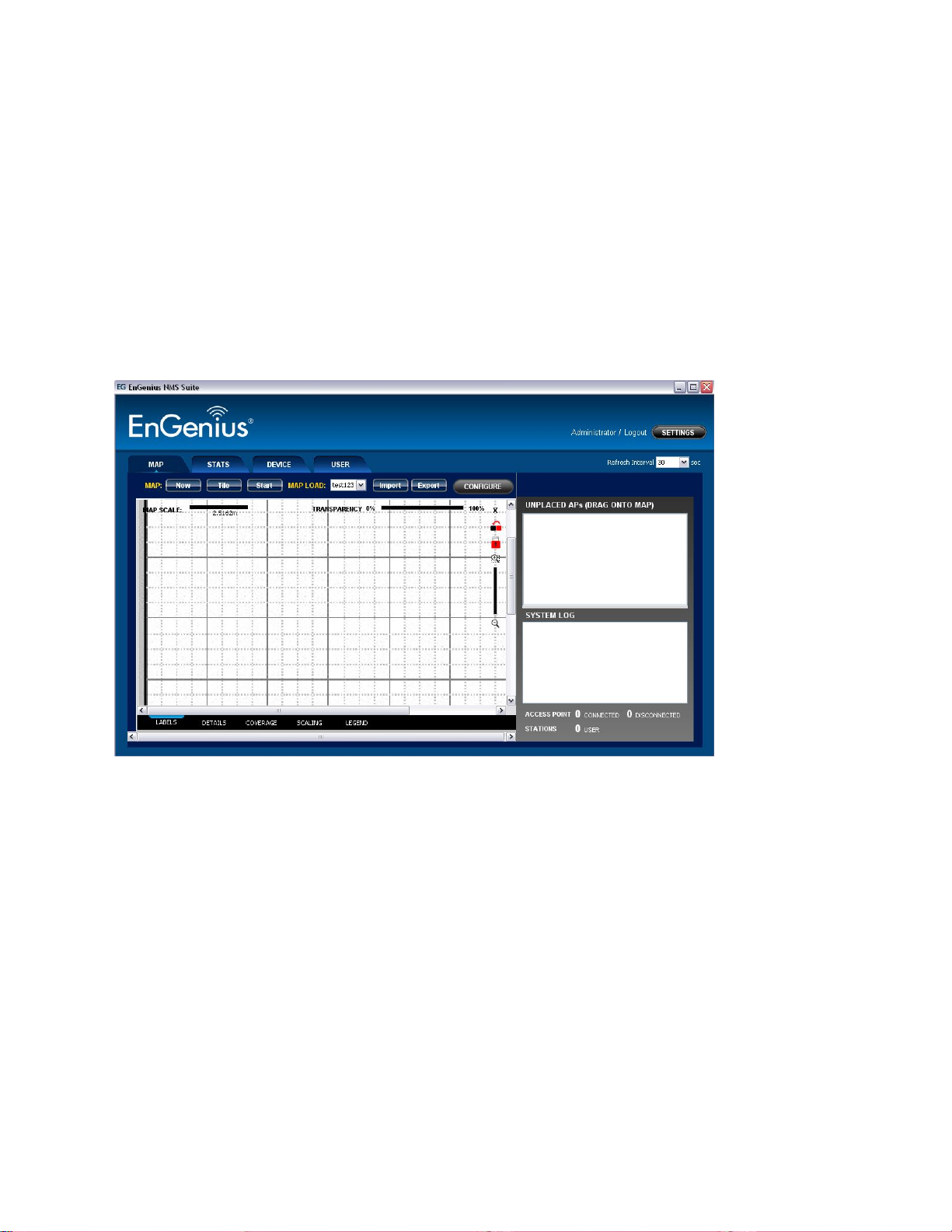
2.2 ZoneController Feature List
Upon logging into the ZONECONTROLLER Software, the user is presented with four different
functional panels. Users can switch to each panel by selecting the tab button at the top of
the suite. The four panels are Map, Stats, Device and User.
The Map panel is to geographically display the live status of the managed network.
Discovered units will be plotted on the map area at the left panel. All new located devices
will be added to the Unplaced APs columns before dragged to the map by the user.
Page 14
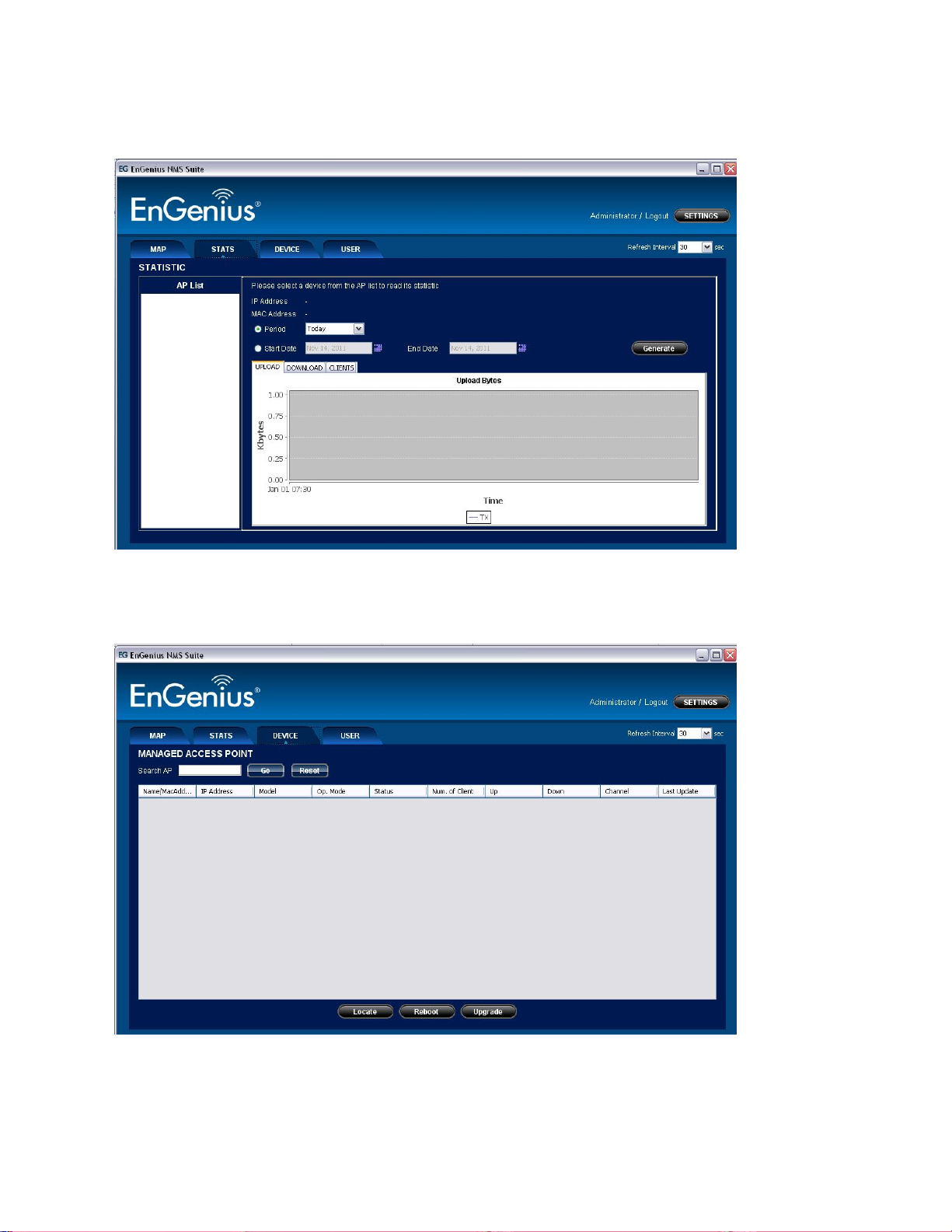
The Stats tab is to monitor the statistics of the nodes that are managed by the software.
Users can view the history of the bandwidth utilization in bytes of the node by utilizing the
available options.
The Device list, meanwhile, lists the discovered node units with their current data. Users can
reboot or upgrade firmware of the selected unit at this panel.
Page 15
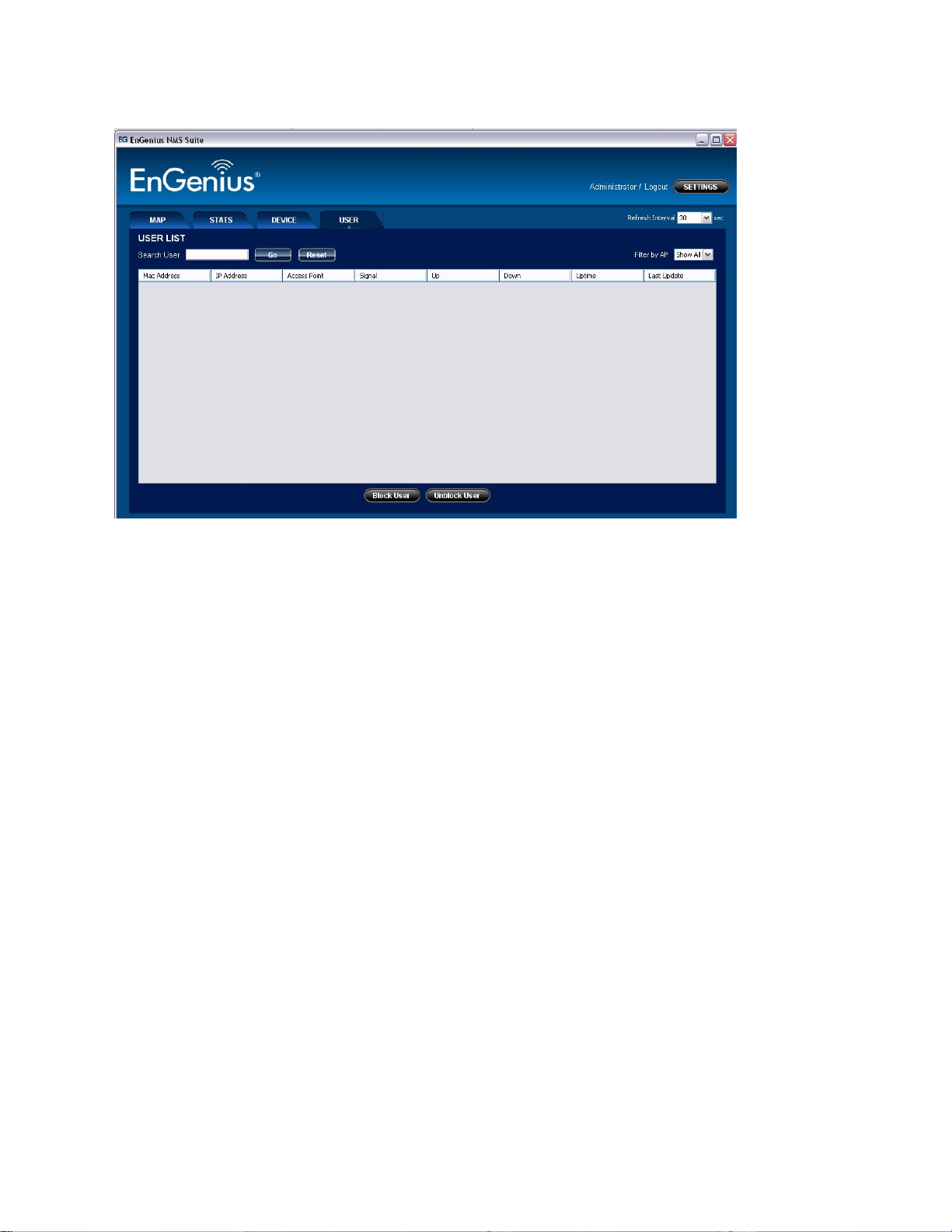
The User list tabulates the information of the clients that are currently connected to the nodes
which are monitored by the ZoneController.
2.3 ZoneController, Additional Information
The ZoneController Software contains a plethora of features which afford network
administrators the ability to effectively manage complex networks. Additional information
regarding the installation and features of the suite are available in the EnGenius
ZoneController User Manual.
Page 16

3 Installation
This chapter describes how to install the ENH210.
Only experienced installation professionals who are familiar with local building
and safety codes and, wherever applicable, are licensed by the appropriate government
regulatory authorities should install the ENH210.
3.1 Pre-installation Guidelines
Select the optimal locations for the equipment using the following guidelines:
- The ENH210 should be mounted on a 1"- 2" pole or wall. Its location should enable easy
access to the unit and its connectors for installation and testing.
- The higher the placement of the antennas, the better the achievable link quality.
- The antennas should be installed to provide a direct or near line of sight link with the base
station antenna.
Page 17
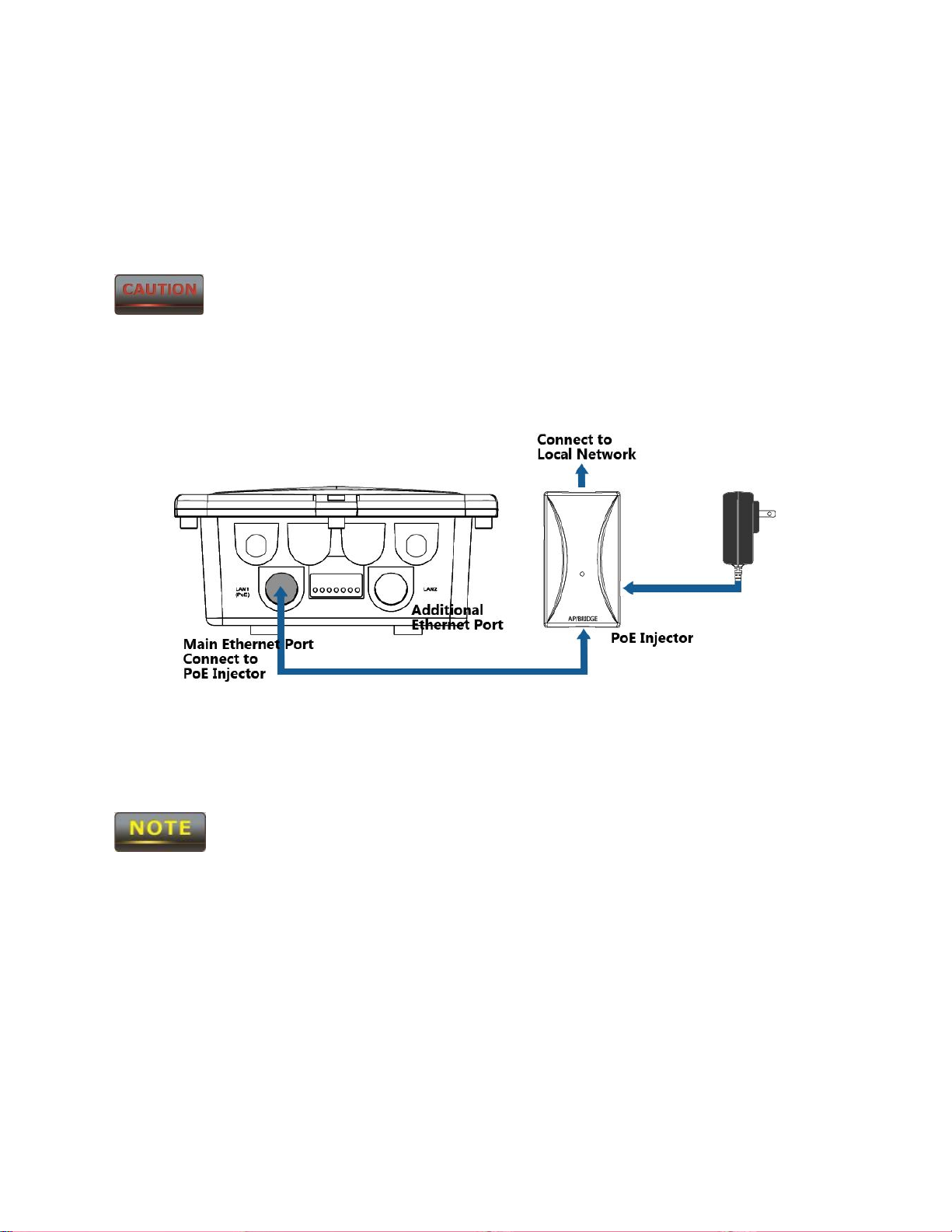
3.2 Installing the ENH210
To install the ENH210, use the following procedure to mount the device on a pole and refer to
the figure below.
1. Insert a standard Ethernet cable into the RJ-45 port labeled LAN1 (PoE).
2. Plug the power cord into the DC port of the PoE injector.
Only use the power adapter supplied with the ENH210. Using a different
power adapter might damage the ENH210.
3. Plug the other end of the Ethernet cable in Step 1 into the PoE port of the PoE
injector. When you finish Step 3, the installation will resemble the following picture.
4. Follow Mounting Installation Guide in order to mount ENH210, after selecting a
suitable mounting method.
This note is a tip only when you encounter difficulties to connect Ethernet cable
to the Ethernet port. The recommended method for the connection is to have Ethernet cable
(without connector) goes through the rubber ring and plastic holders then use crimping tools
to crimp the connector to the cable; If the crimping tool is not available, the installer can use a
x-acto knife to slice one opening on the rubber ring and place the cable through the cut then
use the plastic holder to hold the cable tightly for the connection.
This completes the installation procedure.
Page 18

4 Wireless Network Modes
4.1 Access Point Mode
In the Access Point Mode, the ENH210 functions like a central connection for any stations or
clients that support the IEEE 802.11b/g/n standards. Stations and clients must utilize the same
SSID and Security Password to associate while within range. The most suitable topology for
this mode is to have one ENH210 as an AP and the second one as a Client-Bridge.
4.2 Access Point with WDS Function Mode
The ENH210 also supports WDS functionality while in Access Point Mode. Simply configure
other Access Points and the associated MAC addresses in order to enlarge the wireless area by
enabling WDS Link Settings. WDS functionality can support up to 8 different AP MAC
addresses. Consequently, the wireless clients need to be located within range of the
ENH210’s antennas in order to send signal back to the ENH210.
Page 19
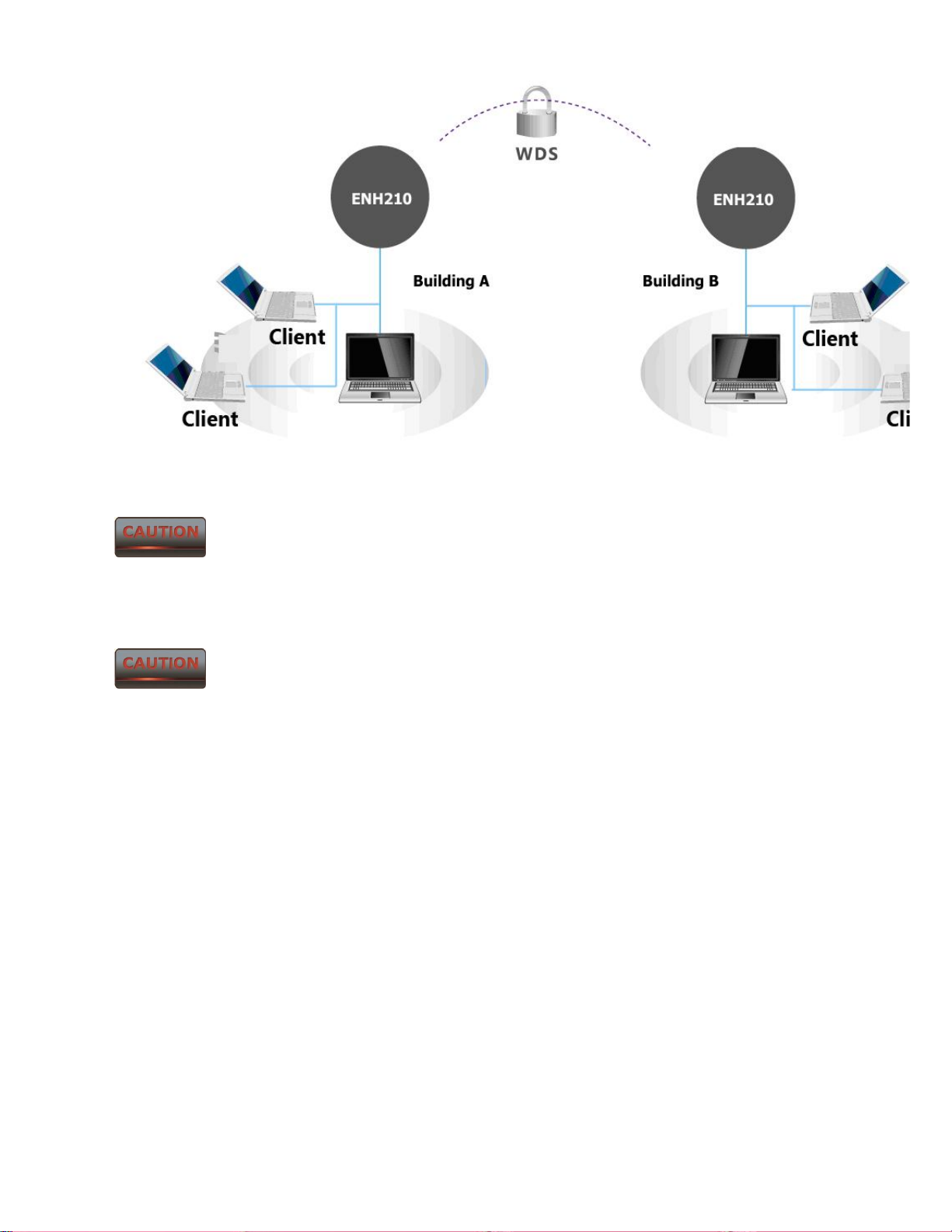
Not every Access Point supports WDS in Access Point Mode. WDS is not
part of the IEEE 802.11 standard. It is recommended to use only ENH210s if you would
like to utilize this functionality.
WDS in Access Point mode normally results in less wireless network
performance and is not recommended for bandwidth intensive applications.
4.3 Client Bridge Mode
In the Client Bridge Mode, the ENH210 functions like a wireless client, connecting to an
Access Point wirelessly and enabling Internet connectivity wherever you want. Use Site Survey
function to scan all of the Access Points within range and configure the SSID and Security
Password to associate with it. With Client Bridge Mode, the ENH210 functions as a long
range 2.4GHz wireless-Ethernet Bridge in order to provide a 2.4GHZ link between the access
point and networked clients.
Page 20

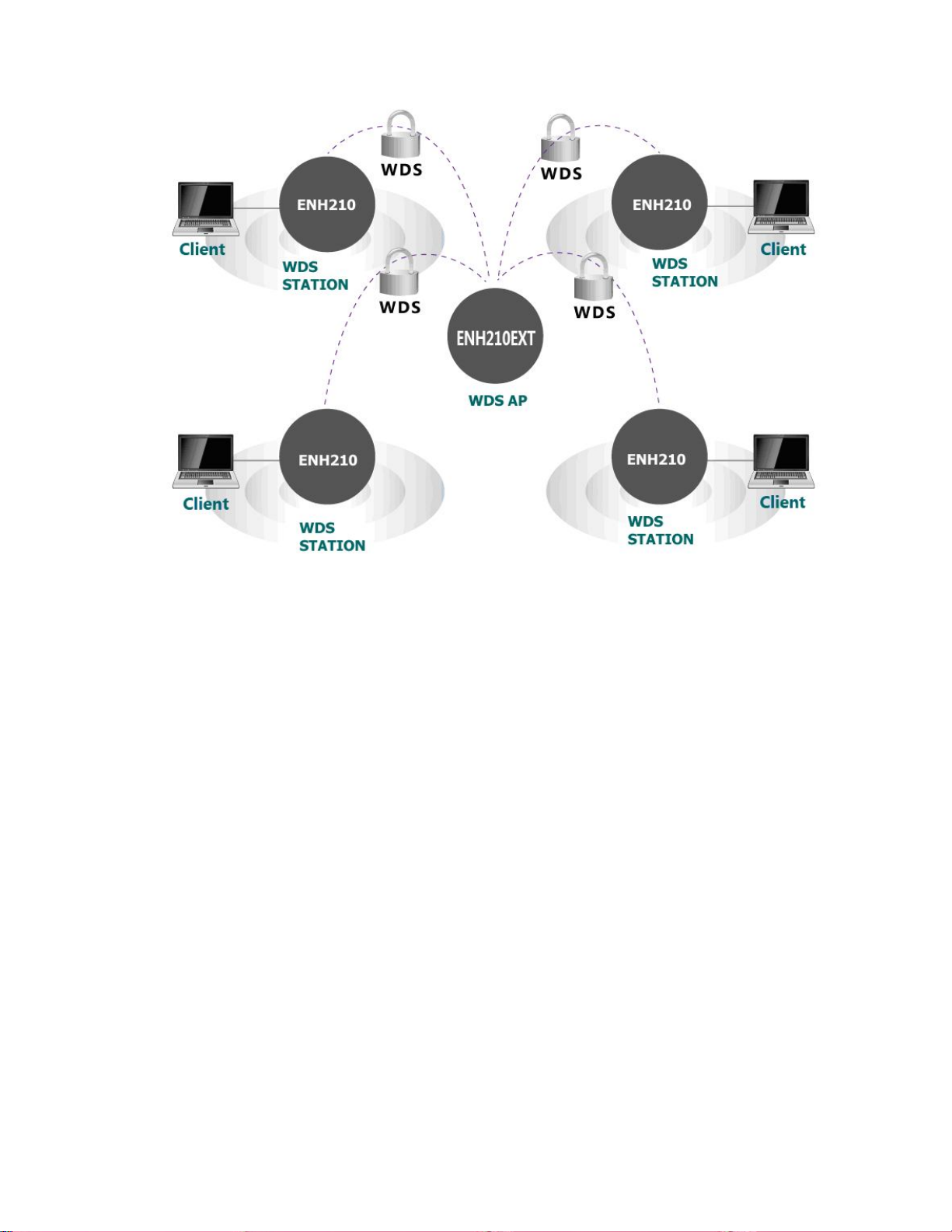
4.4 WDS Bridge Mode
In the WDS Bridge Mode, the ENH210 can wirelessly connect different local area networks by
configuring each device’s MAC address and security settings. The WDS Bridge Mode can
bridge up to four local wired networks together as one logical network. Every computer on
this logical network can see each other, sharing files as if they are in the same location. With
800mW output power and MIMO antenna technology, the connection distance can extend
beyond 1000 feet with good performance, assuming the antennas are within line of sight. The
WDS bridge network is a MAC-based network that provides transparent bridging.
Page 21
4.5 Client Router Mode
In Client Router Mode, the ENH210 provides two functions: 1) acting as a wireless-Ethernet
Bridge in order to relay signal from the access point; 2) acting as an active DHCP server that
allows WLAN clients to share the same wireless network connection. Ideally, have clients
wirelessly connect to an AP/WISP and connect to LANs via Ethernet. Client Router Mode is
Page 22

different from the AP Router Mode. It is not a common application; however, it is useful when
connecting to WISP APs.
Page 23
5 Configuring Your Computer for TCP/IP
This chapter describes how to configure the TCP/IP settings on a computer that will be used
to configure the ENH210. Because the default operating mode is Client Bridge, an IP address
will not be assigned to the computer/notebook. Therefore, follow the steps below to assign
an IP address to a client’s Ethernet adapter.
5.1 Configuring Microsoft® Windows 7
Use the following procedure to configure a computer running Microsoft® Windows 7.
1. In the Start menu search box, type: ncpa.cpl
2. When the Network Connections List appears, right-click the Local Area Connection icon
and click Properties.
Page 24
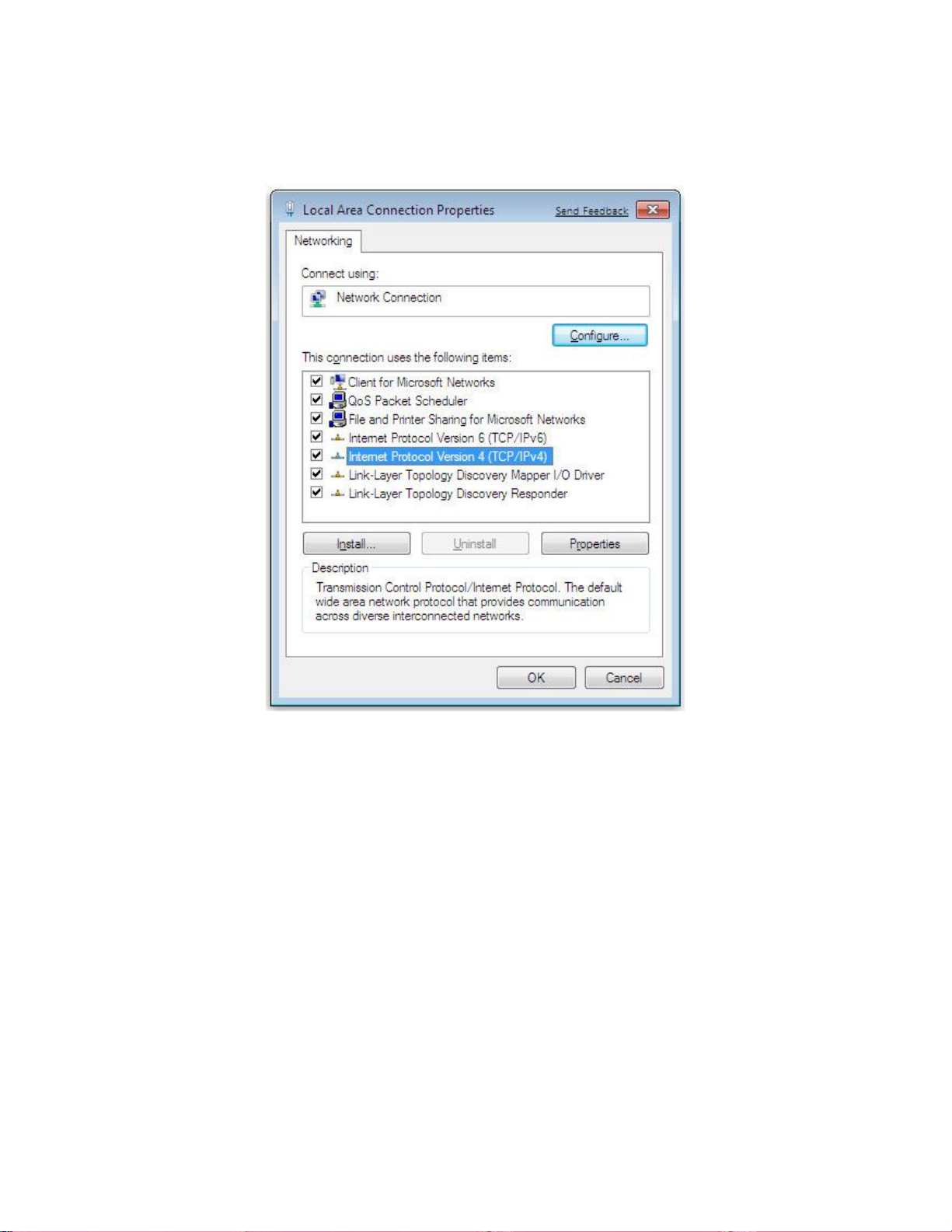
3. In the Networking tab, click Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4), and then click
Properties.
4. In the properties dialog box, click Use the following IP address: to configure your
computer for Static TCP/IP. Enter an IP address (i.e. 192.168.1.10), the subnet mask of the
ENH210, and the default gateway which is the ENH210’s IP address, 192.168.1.1. Note: the
subnet mask must match that of the ENH210 and the IP address must be on that subnet.
5. Click the OK button to save your changes and close the dialog box.
6. Click the OK button again to save your changes.
Page 25
5.2 Configuring Microsoft® Windows Vista
Use the following procedure to configure a computer running Microsoft® Windows Vista with
the default Windows interface.
1. On the Windows taskbar, click Start, click Control Panel, and then select the Network
and Internet icon.
2. Click View Network Status and tasks and then click Manage Networks Connections.
3. Right‐click the Local Area Connection icon and click Properties.
4. Click Continue. The Local Area Connection Properties dialog box appears.
5. In the Local Area Connection Properties dialog box, verify that Internet Protocol
(TCP/IPv4) is checked. Then select Internet Protocol (TCP/IPv4) and click the Properties
button. The Internet Protocol Version 4 Properties dialog box appears.
Page 26
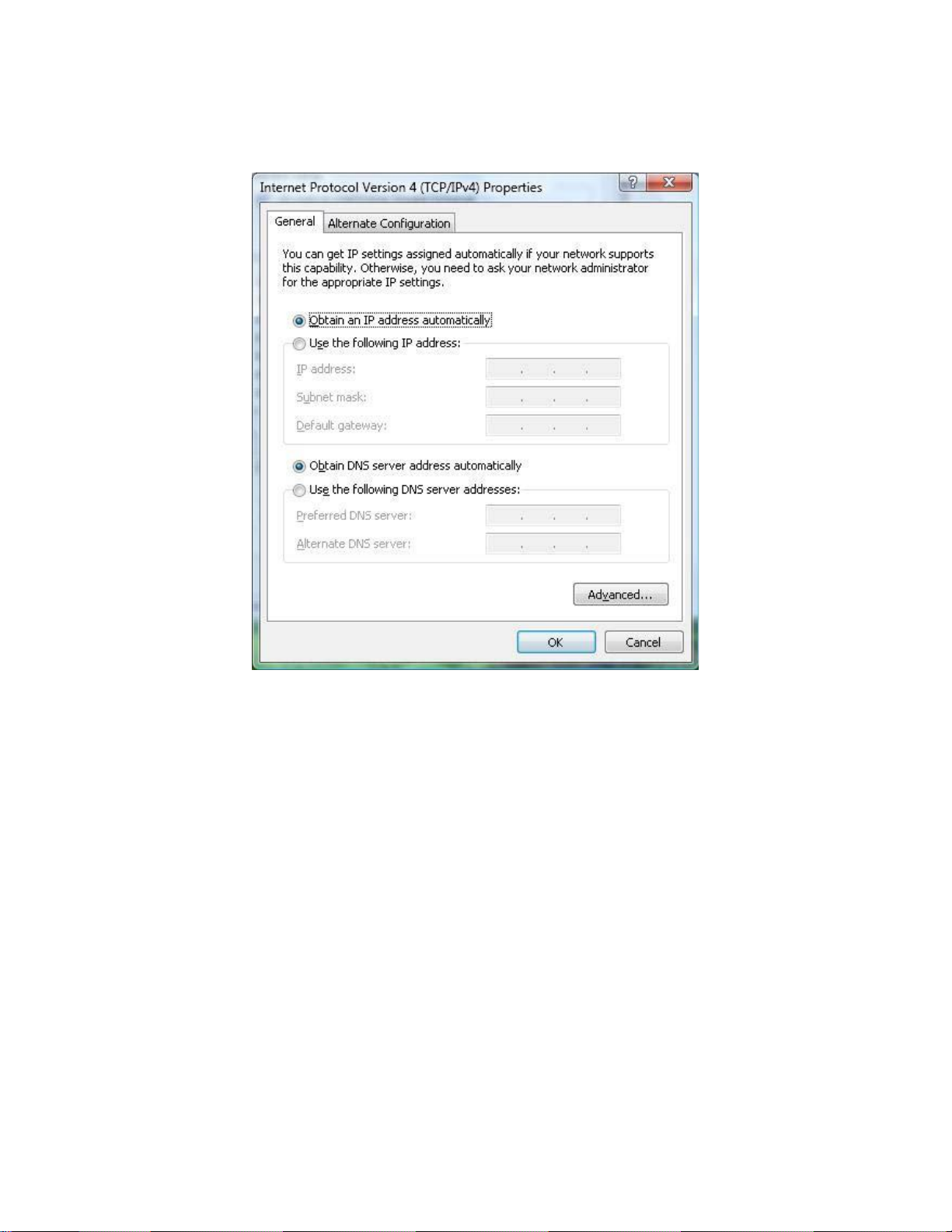
6. In the properties dialog box, click Use the following IP address: to configure your
computer for Static TCP/IP. Enter an IP address (i.e. 192.168.1.10), the subnet mask of the
ENH210, and the default gateway which is the ENH210’s IP address, 192.168.1.1. Note: the
subnet mask must match that of the ENH210 and the IP address must be on that subnet.
7. Click the OK button to save your changes and close the dialog box.
8. Click the OK button again to save your changes.
5.3 Configuring Microsoft® Windows XP
Use the following procedure to configure a computer running Microsoft® Windows XP with
the default Windows interface.
Page 27
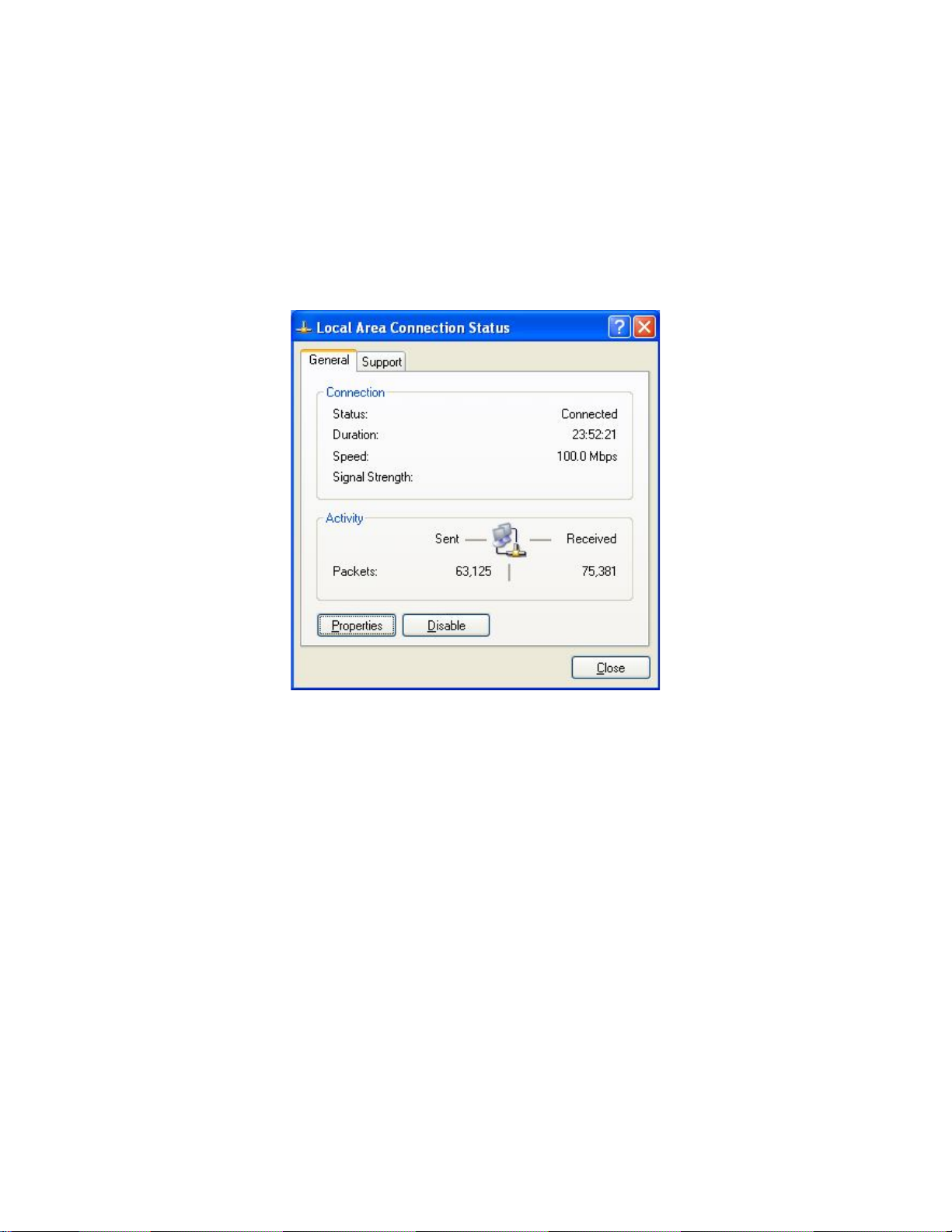
1. On the Windows taskbar, click Start, click Control Panel, and then click Network and
Internet Connections.
2. Click the Network Connections icon.
3. Click Local Area Connection for the Ethernet adapter connected to the ENH210. The
Local Area Connection Status dialog box appears.
4. In the Local Area Connection Status dialog box, click the Properties button. The Local
Area Connection Properties dialog box appears.
5. In the Local Area Connection Properties dialog box, verify that Internet Protocol
(TCP/IP) is checked. Then select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click the Properties button.
The Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box appears.
6. In the properties dialog box, click Use the following IP address: to configure your
computer for Static TCP/IP. Enter an IP address (i.e. 192.168.1.10), the subnet mask of the
ENH210, and the default gateway which is the ENH210’s IP address, 192.168.1.1. Note: the
subnet mask must match that of the ENH210 and the IP address must be on that subnet.
7. Click the OK button to save your changes and close the dialog box.
8. Click the OK button again to save your changes.
5.4 Configuring Apple® Mac OS X
The following procedure describes how to configure TCP/IP on an Apple® Macintosh running
Mac OS X 10.2 or later. Note: The menu titles and placement vary in each OS X (10.x)
operating system but are similar.
Page 28
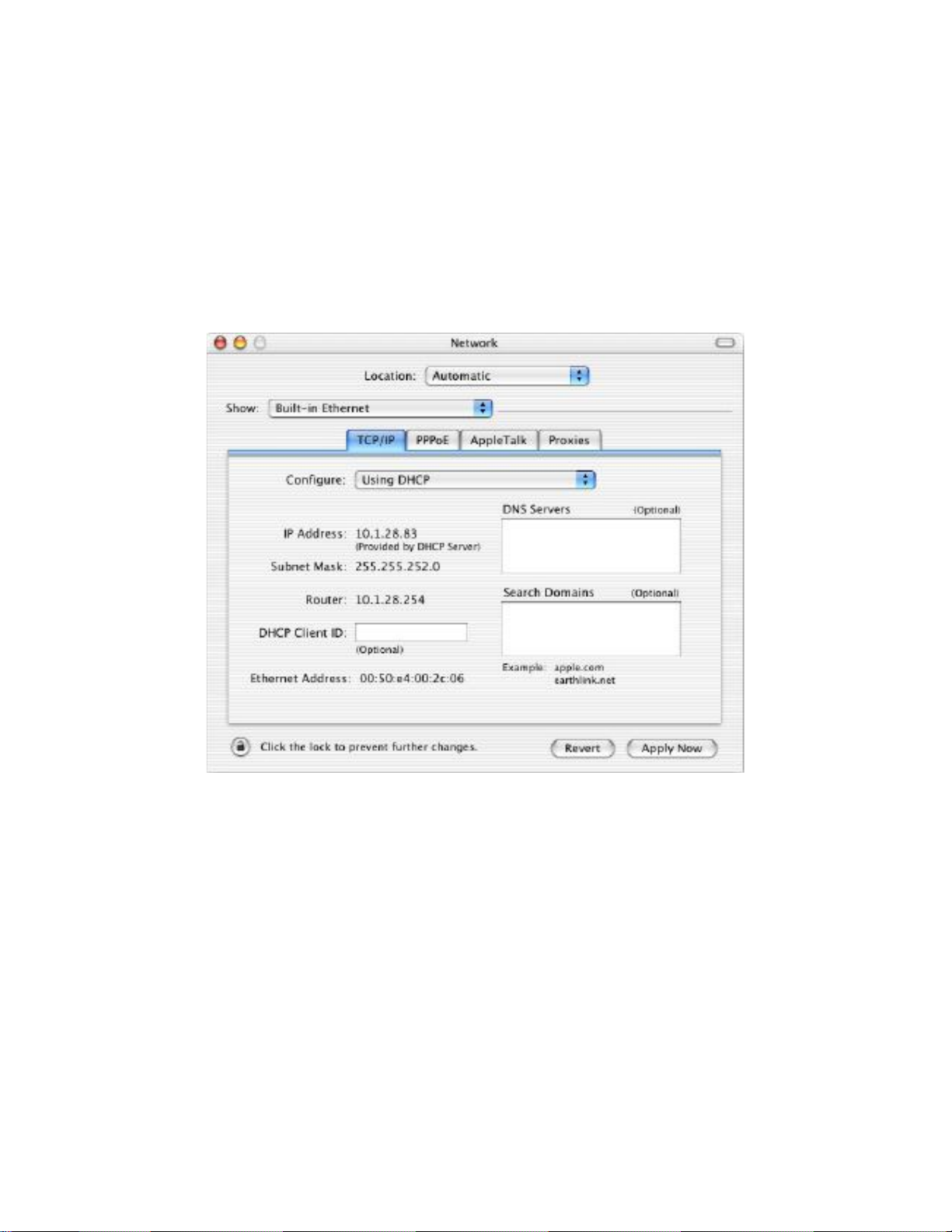
1. Pull down the Apple Menu, click System Preferences, and select Network.
2. Verify that the NIC connected to the ENH210 is selected in the Show field.
3. In the Configure field on the TCP/IP tab, select Manually.
4. Click Apply Now to apply your settings and close the TCP/IP dialog box.
5. Enter an IP address (i.e. 192.168.1.10), the subnet mask of the ENH210, and the Router
which is the ENH210’s IP address, 192.168.1.1. Note: the subnet mask must match that of
the ENH210 and the IP address must be on that subnet.
6. Click Apply Now to apply your settings and close the TCP/IP dialog box.
5.5 Logging into the ENH210
After completing the TCP/IP settings from the beginning of the Chapter, you can now access
the web-based configuration menu.
Page 29

1. Open your web browser.
2. Enter IP 192.168.1.1 into your address bar.
If you have changed the ENH210 LAN IP address, make sure to enter the
correct IP Address.
3. After successfully connecting to the ENH210, a browser pop-up with a Windows Security
notice will appear. Please enter the correct Username and Password.
4. The default Username and Password are both admin.
If you have changed the Username and Password, please enter the correct
Username and Password.
Page 30

6 Status
The Status section is on the navigation side-bar menu. Selecting it, you will then see four
options: Save/Reload, Main, Wireless Client List, and System Log. Each option is described in
detail below.
6.1 Save / Load
This page allows viewing of the modified settings. The changes will show in the Unsaved
changes list. You can decide to cancel (Revert) all the changes or to Save & Apply the new
settings.
Please make note of the following:
1. You cannot cancel specific settings. You can only save all of the settings or revert to the
previously saved state.
2. You need to use the Save/Reload page to commit your configurations by clicking the “Save
& Apply” button.
Page 31

6.2 Main
Click on the Main link under the Status side-bar menu or click Home from the top-right of
the webpage. The status that is displayed corresponds with the operating mode that is
selected. Information such as operating mode, system up-time, firmware version, serial
number, kernel version, and application version are displayed in the System section. LAN IP
address, subnet mask, and MAC address are displayed in the LAN section. In the Wireless
section, the frequency and channel are displayed. Since this device supports multiple-SSIDs,
the details of each SSID, such as ESSID and its security settings are displayed.
Page 32

6.3 Wireless Client List
Click on the Wireless Client List link under the Status side-bar menu. This page displays the
list of Clients that are associated to the ENH210. The MAC addresses and signal strength for
each client is displayed. Click on the Refresh button to refresh the client list.
6.4 System Log
Click on the System Log link under the Status side-bar menu. The device automatically
records events in its internal memory. When there is not enough internal memory for all of
the most recent events, events are deleted in descending chronological order so that the
latest events may be retained.
Page 33

6.5 Connection Status
Click on the Connection Status link under the Status side-bar menu. This page displays the
current status of the network, including Network Type, SSID, BSSID, Connection Status,
Wireless Mode, Current Channel, Security, Data Rate, Current noise level, and Signal strength.
6.6 DHCP Client Table
Click on the DHCP Client List link under the Status side-bar menu. This page displays the list
of Clients that are associated to the ENH210 through DHCP. The MAC addresses and signal
strength for each client is displayed. Click on the Refresh button to refresh the client list.
Page 34

7 System
7.1 Switching the Operation Mode
The ENH210 supports 4 modes: Access Point, Client Bridge, WDS Bridge, and Client Router. In
order to switch between the operating modes, please go to System -> Operation mode.
To begin, view System Properties under System Section.
Device Name: Specify a name for the device. It is not the broadcast SSID; this will be
shown in SNMP management.
Country/Region: Select a Country/Region to conform to local regulations.
Operation Mode: Select an operation mode via a Radio Button.
Click Accept to confirm the changes.
Clicking Accept does not apply the changes – you must go to Status ->
Save / Load to apply the new settings. Please refer to Chapter 6.1 for more information.
If you would like to use Access Point with WDS Function mode, please select
Access Point Mode and then enable WDS function in the Wireless Network section. The
scenario requiring this functionality, WDS and AP, is rare.
Page 35

8 Wireless Configuration
This section will guide you through all of the wireless settings. Please read the instructions
carefully. Inappropriate settings could lower the performance or affect the stability of your
network. Before continuing, please make sure you have chosen the correct operating mode.
8.1 Wireless Settings
This section contains the basic wireless settings. Please read the description carefully and
consult Chapter 10 for more detailed information.
8.1.1 Access Point Mode
While in Access Point mode, the ENH210 functions as a base-station - capable of providing up
to 8 SSIDs for wireless client connectivity.
Page 36

Wireless Mode The wireless mode supports 802.11b/g/n mixed operation.
Channel HT Mode The default channel bandwidth is 40 MHz. A larger channel can
provide better transmit quality and speed, while 20 MHz channel
bandwidth affords higher stability at farther distances.
Extension Channel When operating with a 40 MHz channel, this specifies which
additional wireless channel is to be used. Selecting Auto allows
the device to select the optimum channel.
Channel / Frequency The channel availability is determined by the United State’s law to
ensure compliance with FCC regulation. The device operates in
the 2.4GHz spectrum. Please select “United States”.
AP Detection AP Detection can help to select a best channel by scanning the
nearby area for other access points and the channels that they
are broadcasting on.
Current Profile Configure up to eight different SSIDs; it allows for the division of
clients into separate groups to access the network. Press Edit to
configure the profile and place a check to enable an additional
SSID.
Profile Isolation Restrict client communications with different VID by selecting the
Radio button.
Accept / Cancel Press Accept to confirm the changes or Cancel to return to the
previous settings.
Accept does not apply the changes – you must go to Status -> Save / Load
to apply the new settings. Please refer to Chapter 6.1 for more information.
Page 37

SSID Specify the SSID for current profile. This is the wireless network
name that wireless clients will use to connect to the AP.
VLAN ID Specify the VLAN tag for current profile. Only use if configuring
multiple SSIDs. Must be using VLAN enabled switches on the
network.
Suppressed SSID Place a check to hide the SSID. Clients will not be able to see the
broadcast SSID in Site Survey.
Station Separation Select enable to prevent clients associated to the same AP from
communicating with one another.
Wireless Security Please refer to the Wireless Security section.
Save / Cancel Press Save to save the changes or Cancel to return previous
settings.
Page 38

8.1.2 Client Bridge Mode
Wireless Mode The wireless mode supports 802.11b/g/n mixed operation. It is
compatible with the most common known wireless bands.
SSID Specify the SSID if known. The SSID text box will be automatically
filled in when an AP in the Site Survey is selected.
Site Survey Use Site Survey to scan nearby APs, and then select the AP to
establish a connection.
Prefer BSSID Specify the MAC address, if known. The Prefer BSSID check box
will be automatically filled in when an AP in the Site Survey is
selected. Used when multiple access points in a wireless
network broadcast the same SSID.
WDS Client Select a Radio button to Enable / Disable WDS Client.
Wireless Security Please refer to Chapter 6.2 for details.
Accept / Cancel Press Accept to confirm the changes or Cancel to return
previous settings.
Accept does not apply the changes – you must go to Status -> Save / Load
to apply the new settings. Please refer to Chapter 6.1 for more information.
Page 39

Profile After Site Survey, the webpage will display all of the nearby
Access Points. Click the BSSID if you would like to connect with it.
Wireless Security Please refer to the Wireless Security section.
Refresh Press Refresh to scan again.
If the Access Point is suppressing its own SSID, the SSID section will be blank; the
SSID must be entered manually.
Page 40

8.1.3 WDS Bridge Mode
Wireless Mode The wireless mode supports 802.11b/g/n mixed modes. It is
compatible with the most common wireless bands.
Channel HT Mode The default channel bandwidth is 40 MHz. A larger channel can
provide better transmit quality and speed, while 20 MHz channel
bandwidth affords higher stability at farther distances.
Extension Channel Specify the upper channel or lower channel selection. It may
influence the Auto channel function
Channel / Frequency The channel availability is determined by the country’s
regulations.
Accept / Cancel Press Accept to confirm the changes or Cancel to return to the
previous settings.
Accept does not apply the changes – you must go to Status -> Save / Load
to apply the new settings. Please refer to Chapter 6.1 for more information.
Page 41

MAC Address Enter the Access Point’s MAC address that you would like to
extend the wireless coverage of into the MAC address filter.
Mode Select Disable or Enable from the drop down list.
Accept / Cancel Press Accept to confirm the changes or Cancel to return to the
previous settings.
Please make note of the following:
1. Accept does not apply the changes – you must go to Status -> Save / Load to apply
the new settings. Please refer to Chapter 6.1 for more information.
2. You must enter the MAC address of the Access Point whose wireless coverage you
would like to extend. Not all Access Point supports this feature.
Page 42

8.1.4 Client Router Mode
Wireless Mode The wireless mode supports 802.11b/g/n mixed operation. It is
compatible with the most common wireless bands.
SSID Specify the SSID, if known. The SSID text box will be automatically
filled in if an AP in the Site Survey is selected.
Site Survey Use Site Survey to scan nearby APs, and then select the AP to
establish a connection.
Prefer BSSID Specify the MAC address, if known. Prefer BSSID text box will be
automatically filled in when an AP in the Site Survey is selected.
Used when multiple access points in a wireless network broadcast
the same SSID.
Wireless Security Please refer to Chapter 8.2 for details.
Accept / Cancel Press Accept to confirm the changes or Cancel to return to the
previous settings.
Accept does not apply the changes – you must go to Status -> Save / Load
to apply the new settings. Please refer to Chapter 6.1 for more information.
Page 43

Profile After Site Survey, the webpage will display all nearby Access
Points. Click the BSSID if you would like to connect with an AP.
Wireless Security Please refer to the Wireless Security section, Chapter 8.2.
Refresh Press Refresh to scan again.
If the Access Point is suppressing its own SSID, the SSID section will be blank;
the SSID must be entered manually.
Page 44

8.2 Wireless Security Settings
Wireless Security Settings section will guide you through the Security configurations: WEP,
WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK, WPA-PSK Mixed, WPA, WPA2, and WPA Mixed. We strongly
recommend the use of WPA2-PSK as your security setting.
8.2.1 WEP
Security Mode Select WEP from the drop down list.
Auth Type Select Auth Type in Open System or Shared.
Input Type Select Input Type in Hex or ASCII.
Key Length Select Key Length in 64/128/152 bit password length.
Default Key Select the default index key for wireless security.
Key1 Specify password for security key index No.1.
Key2 Specify password for security key index No.2.
Key3 Specify password for security key index No.3.
Key4 Specify password for security key index No.4.
The IEEE 802.11n standard does not include WEP/WPA-PSK/WPA-PSK TKIP
security mode. To comply with the standard, when you use the above encryptions, the
wireless transmit mode will drop from 802.11n to 802.11g.
Page 45

8.2.2 WPA-PSK
Security Mode Select WPA-PSK from the drop down list.
Encryption Select Both, TKIP or AES for encryption type.
Passphrase Specify the security password.
Group Key Update
Interval
The IEEE 802.11n standard does not include WEP/WPA-PSK/WPA-PSK TKIP
security mode. To comply with the standard, when you use the above encryptions, the
wireless transmit mode will drop from 802.11n to 802.11g.
Specify Group Key Update Interval time.
Page 46

8.2.3 WPA2-PSK
Security Mode Select WPA2-PSK from the drop down list.
Encryption Select Both, TKIP or AES for encryption type.
Passphrase Specify the security password.
Group Key Update
Interval
The IEEE 802.11n standard does not include WEP/WPA-PSK/WPA-PSK TKIP
security mode. To comply with the standard, when you use the above encryptions, the
wireless transmit mode will drop from 802.11n to 802.11g.
Specify Group Key Update Interval time.
Page 47

8.2.4 WPA-PSK Mixed
Security Mode Select WPA-PSK Mixed from the drop down list.
Encryption Select Both, TKIP or AES for encryption type.
Passphrase Specify the security password.
Group Key Update
Interval
Using WPA-PSK Mixed can allow multiple security modes at the same time.
The IEEE 802.11n standard does not include WEP/WPA-PSK/WPA-PSK TKIP
security mode. To comply with the standard, when you use the above encryptions, the
wireless transmit mode will drop from 802.11n to 802.11g.
Specify Group Key Update Interval time.
Page 48

8.2.5 WPA
Security Mode Select WPA from the drop down list. Only for Enterprise level
security and requires a RADIUS server for authentication.
Encryption Select Both, TKIP or AES for Encryption type.
Radius Server Specify Radius Server IP address.
Radius Port Specify Radius Port number, the default port is 1812.
Radius Secret Specify Radius Secret that is given by the Radius Server.
Group Key Update
Interval
The IEEE 802.11n standard does not include WEP/WPA-PSK/WPA-PSK TKIP
security mode. To comply with the standard, when you use the above encryptions, the
wireless transmit mode will drop from 802.11n to 802.11g.
Specify Group Key Update Interval time.
Page 49

8.2.6 WPA2
Security Mode Select WPA2 from the drop down list. Only for Enterprise level
security and requires a RADIUS server for authentication.
Encryption Select Both, TKIP or AES for encryption type.
Radius Server Specify Radius Server IP Address.
Radius Port Specify Radius Port number, the default port is 1812.
Radius Secret Specify Radius Secret that is given by the Radius Server.
Group Key Update
Interval
The IEEE 802.11n standard does not include WEP/WPA-PSK/WPA-PSK TKIP
security mode. To comply with the standard, when you use the above encryptions, the
wireless transmit mode will drop from 802.11n to 802.11g.
Specify Group Key Update Interval time.
Page 50

8.2.7 WPA Mixed
Security Mode Select WPA Mixed from the drop down list.
Encryption Select Both, TKIP or AES for encryption type.
Radius Server Specify Radius Server IP Address.
Radius Port Specify Radius Port number, the default port is 1812.
Radius Secret Specify Radius Secret that is given by the Radius Server.
Group Key Update
Interval
The IEEE 802.11n standard does not include WEP/WPA-PSK/WPA-PSK TKIP
security mode. To comply with the standard, when you use the above encryptions, the
wireless transmit mode will drop from 802.11n to 802.11g.
Specify Group Key Update Interval time.
Page 51

8.3 Wireless Advanced Settings
Data Rate Select Data Rate from the drop down list. Data rate will affect the
efficiency of the throughput. A lower data rate will allow for
transmissions to travel longer distances.
Transmit Power Select Transmit Power to increase or decrease the transmit power.
Altering the transmit power will change the wireless coverage
area correspondingly; however, setting the Transmit Power to an
extreme level may cause issues for wireless connectivity. Default
transmit power is 20. The maximum transmit power setting is
29
RTS/CTS Threshold Specify Threshold package size for RTC/CTS. Smaller thresholds
will cause RTS/CTS packets to be sent more often, consuming
more of the available bandwidth. In addition, if heavy traffic
occurs, the wireless network is more robust in the event of
interference or collisions.
Distance Specify distance range between AP and Clients. Farther distances
may utilize lower connection speeds. Intended for use with long
range point-to-point applications of 2 KM or longer.
Short GI Short GI is an improvement of 802.11n and 802.11b/g. It can
Page 52

increase performance by 10% during the data transmission. For
s.
example, if the 802.11b/g’s GI is 800μs, the short GI will be 400μ
The shorter guard interval results in a higher packet collision rate
when the delay-spread of the channel exceeds the guard interval
or if timing synchronization between the transmitter and receiver
is not precise.
Aggregation Aggregation is used to merge multiple packets together into a
large specified value. It is effective for scenarios with frequent
packets of small data size.
Wireless Traffic
Shaping
Place a check to enable Wireless Traffic Shaping function. This
function limits the throughput to each wireless client.
Incoming Traffic Limit Specify the wireless transmission speed for incoming traffic.
Outgoing Traffic Limit Specify the wireless transmission speed for outgoing traffic.
Accept / Cancel Press Accept to confirm the changes or Cancel to return
previous settings.
Please make note of the following:
1. Accept does not apply the changes – you must go to Status -> Save / Load to apply
the new settings. Please refer to Chapter 6.1 for more information.
2. Changing Wireless Advanced Settings may lower the wireless connection quality.
Please keep all settings as default unless you understand the modifications which you
have made.
Page 53

8.4 Wireless MAC Filter
Wireless MAC Filter is used to allow or deny wireless clients, by their MAC addresses, from
accessing the network. You can manually add a MAC address to restrict the access
permission’s of the client. The default setting is Disable Wireless MAC Filters.
0.
ACL Mode ACL Mode can deny or allow specific clients to access the
network. Select Disable, Deny MAC in the list, or Allow MAC in
the list from the drop down list.
MAC Address Filter Specify the MAC address, manually.
Add Press Add to add the MAC address in the table.
Apply Press Apply to apply the changes.
Page 54

8.5 WDS Link Settings
WDS Link Settings is used to establish a connection between Access Points without forgoing
Access Point functionality. APs with WDS functionality can extend the wireless coverage and
allow LANs to communicate with each other.
MAC Address Enter the Access Point’s MAC address that you would like to
extend the wireless coverage of into the MAC address filter.
Mode Select Disable or Enable from the drop down list.
Accept / Cancel Press Accept to confirm the changes or Cancel to return
previous settings.
Accept does not apply the changes – you must go to Status -> Save / Load
to apply the new settings. Please refer to Chapter 6.1 for more information.
The MAC address of the AP that you would like to extend the wireless coverage
of must be entered. Not all Access Points supports this feature.
Page 55

9 LAN Setup
This section will guide you to setup the Local Area Network (LAN) settings.
9.1 IP Settings
This section is only available for Non-Router Mode. IP Settings allows you to configure the IP
settings of the ENH210.
IP Network Setting Select Radio button for Obtain an IP address automatically or
Specify an IP address.
IP Address Specify LAN port IP address.
IP Subnet Mask Specify Subnet Mask.
Default Gateway Specify Default Gateway.
Primary DNS Specify Primary DNS.
Secondary DNS Specify Secondary DNS.
Accept / Cancel Press Accept to confirm the changes or Cancel to return
previous settings.
Please make note of the following:
1. Obtain an IP address automatically is not a DHCP server. This setting allows the
ENH210 to automatically request an IP address when it is connected to a device which
has a DHCP server.
2. Changing LAN IP Address will change LAN Interface IP address. The webpage will
automatically redirect to the new IP address after Apply is selected.
Page 56

9.2 Spanning Tree Settings
Spanning Tree Status Select the Radio button to On or Off to toggle the Spanning Tree
function. Spanning Tree may prevent loops in a network when
there may be multiple paths that data may travel.
Bridge Hello Time Specify Bridge Hello Time in seconds.
Bridge Max Age Specify Bridge Max Age in seconds.
Bridge Forward Delay Specify Bridge Forward Delay in seconds.
Priority Specify the Priority number; smaller numbers have greater
priority.
Accept / Cancel Press Accept to confirm the changes or Cancel to return
previous settings.
Accept does not apply the changes – you must go to Status -> Save / Load
to apply the new settings. Please refer to Chapter 6.1 for more information.
Page 57

10 Router Settings
This section is only available for AP Router Mode and Client Router Mode.
10.1 WAN Settings
There are four different types of WAN connections: Static IP, DHCP, PPPoE, and PPTP. Please
contact your ISP to determine the connection type.
10.1.1 Static IP
Select Static IP in WAN connection if your ISP gives all the of the necessary information about
IP address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway, Primary DNS and Secondary DNS.
Page 58

Internet Connection
Type
Account Name Specify Account Name that is provided by ISP.
Domain Name Specify Domain Name that is provided by ISP.
MTU Specify the Maximum Transmit Unit size. EnGenius recommends
IP Address Specify WAN port IP address.
IP Subnet Mask Specify WAN IP Subnet Mask.
Gateway IP Address Specify WAN Gateway IP address.
Primary DNS Specify Primary DNS IP.
Secondary DNS Specify Secondary DNS IP.
Discard Ping on WAN Place a check to Enable or Disable ping from WAN.
Accept / Cancel Press Accept to confirm the changes or Cancel to return
Select Static IP to begin configuration of the Static IP connection.
that it remains in Auto.
previous settings.
Accept does not apply the changes – you must go to Status -> Save / Load
to apply the new settings. Please refer to Chapter 6.1 for more information.
If the router's MTU is set too high, downstream packets will be fragmented. If
the router's MTU is set too low, the router will fragment packets unnecessarily and, in extreme
cases, may be unable to establish connections. In either case, network performance can suffer.
Page 59

10.1.2 DHCP (Dynamic IP)
Select DHCP as your WAN connection type to obtain the IP address automatically. You will
need to enter Account Name as your hostname and DNS addresses (Optional).
Internet Connection Type Select DHCP to begin configuration of the DHCP connection.
Account Name Specify Account Name which is provided by ISP.
Domain Name Specify Domain Name which is provided by ISP.
MTU Specify the Maximum Transmit Unit size. EnGenius recommends
that it remains in Auto.
Get Automatically From
ISP
Use These DNS Servers Select the Radio button to setup the Primary DNS and
Select the Radio button for the DNS servers to be obtained
automatically from the DHCP server.
Page 60

Secondary DNS servers manually.
Discard Ping on WAN Place a check to Enable or Disable ping from WAN.
Accept / Cancel Press Accept to confirm the changes or Cancel to return
previous settings.
Accept does not apply the changes – you must go to Status -> Save / Load
to apply the new settings. Please refer to Chapter 6.1 for more information.
If the router's MTU is set too high, downstream packets will be fragmented. If
the router's MTU is set too low, the router will fragment packets unnecessarily and, in extreme
cases, may be unable to establish connections. In either case, network performance can suffer.
Page 61

10.1.3 PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet)
Select PPPoE as your WAN connection type if your ISP provides a Username and Password. If
the PPPoE is a DSL service, please remove the PPPoE software from your computer as the
software is not necessary with the use of the ENH210.
Internet Connection
Type
MTU Specify the Maximum Transmit Unit size. EnGenius recommends
Login Specify the Username that is given by your ISP.
Password Specify the Password that is given by your ISP.
Service Name Specify the Service Name that is given by your ISP.
Select PPPoE to begin configuration of the PPPoE connection.
that it remains in Auto.
Page 62

Connect on Demand Select the Radio button to specify the maximum idle time. The
Internet will disconnect when it reaches the maximum idle time;
however, it will automatically connect when a client tries to access
the network.
Keep Alive Select the Radio button to keep internet connection always on.
Specify the redial period for once the Internet connection is lost.
Get Automatically
From ISP
Use These DNS Servers Select the Radio button for setup the Primary DNS and
Discard Ping on WAN Place a check to Enable or Disable ping from WAN.
Accept / Cancel Press Accept to confirm the changes or Cancel to return
Accept does not apply the changes – you must go to Status -> Save / Load
to apply the new settings. Please refer to Chapter 6.1 for more information.
If the router's MTU is set too high, downstream packets will be fragmented. If
the router's MTU is set too low, the router will fragment packets unnecessarily and, in extreme
cases, may be unable to establish connections. In either case, network performance can suffer.
Select the Radio button for the DNS servers to be obtained
automatically from the DHCP server.
Secondary DNS servers manually.
previous settings.
Page 63

10.1.4 PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol)
Select PPTP as your WAN connection type if your ISP provides information regarding: IP
Address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway (Optional), DNS (Optional), Server IP, Username, and
Password.
Page 64

Internet Connection
Type
MTU Specify the Maximum Transmit Unit size. EnGenius recommends
IP Address Specify WAN port IP address.
IP Subnet Mask Specify WAN IP Subnet Mask.
Gateway IP Address Specify WAN Gateway IP address.
PPTP Server Specify PPTP Server IP address.
Username Specify the Username that is given by your ISP.
Password Specify the Password that is given by your ISP.
Connect on Demand Select the Radio button to specify the maximum idle time. The
Keep Alive Select the Radio button to keep internet connection always on.
Select PPTP to begin configuration of the PPTP connection.
that it remains in Auto.
Internet will disconnect when it reaches the maximum idle time;
however, it will automatically connect when a client tries to access
the network.
Specify the redial period once the internet lose connection.
Get Automatically
From ISP
Use These DNS Servers Select the Radio button for setup the Primary DNS and
Discard Ping on WAN Place a check to Enable or Disable ping from WAN.
Accept / Cancel Press Accept to confirm the changes or Cancel to return
Accept does not apply the changes – you must go to Status -> Save / Load
to apply the new settings. Please refer to Chapter 6.1 for more information.
If the router's MTU is set too high, downstream packets will be fragmented. If
the router's MTU is set too low, the router will fragment packets unnecessarily and, in extreme
cases, may be unable to establish connections. In either case, network performance can suffer.
Select the Radio button for the DNS servers to be obtained
automatically from the DHCP server.
Secondary DNS servers manually.
previous settings.
Page 65

10.2 LAN Settings (Router Mode)
IP Address Specify LAN port IP address.
IP Subnet Mask Specify LAN IP Subnet Mask.
WINS Server IP Specify WINS Server IP.
Use Router As DHCP
Server
Starting IP Address Specify DHCP server starting IP address.
Ending IP Address Specify DHCP server ending IP address.
WINS Server IP Specify the WINS Server IP address.
Accept / Cancel Press Accept to confirm the changes or Cancel to return
Accept does not apply the changes – you must go to Status -> Save / Load
to apply the new settings. Please refer to Chapter 6.1 for more information.
Place a check to enable the DHCP server.
previous settings.
Page 66

10.3 VPN Pass Through
VPN Pass Through is used to allow certain protocols to be tunneled through an IP network
such as PPTP and L2TP, or to implement a secure exchange of packets at the IP Layer such as
IPSec.
PPTP Pass Through Place a check to enable PPTP protocol passes through WAN.
L2TP Pass Through Place a check to enable L2TP protocol passes through WAN.
IPSec Pass Through Place a check to enable IPSec protocol passes through WAN.
Accept / Cancel Press Accept to confirm the changes or Cancel to return
previous settings.
Accept does not apply the changes – you must go to Status -> Save / Load
to apply the new settings. Please refer to Chapter 6.1 for more information.
Page 67

10.4 Port Forwarding
Port Forwarding is used to allow public services such as Web Server, Mail Server, or FTP server
to be set up. For example: Set up a Web Server on your computer with port number 8080. A
visitor on the Internet can access your Web Server by entering WAN Port IP with port
number 8080. If the WAN Port IP address is 192.168.5.1, then visitors must enter
http://192.168.5.1:8080. To find out more about common port numbers please consult the
Internet.
Add Entry Press Add Entry to add a rule of Port Forwarding.
Accept Press Accept to confirm the changes.
Accept does not apply the changes – you must go to Status -> Save / Load
to apply the new settings. Please refer to Chapter 6.1 for more information.
Service Name Specify a name for current Port Forwarding rule.
Protocol Select a protocol from drop down list: Both, TCP, or UDP.
Starting Port Specify Starting Port number.
Ending Port Specify Ending Port number.
IP Address Specify IP address.
Save / Cancel Press Save to confirm the changes or Cancel to return previous
settings.
Page 68

10.5 DMZ
Enabling DMZ will expose the computer which is in the DMZ to the Internet. This feature may
be used in scenarios such as Internet Gaming or Video Conferencing. DMZ will forward all the
ports to one PC simultaneously. This PC will be vulnerable to any incoming traffic, including
unsolicited or malicious traffic, because DMZ opens all of the ports.
DMZ Hosting Select Enable or Disable DMZ from drop down list.
DMZ Address Specify an IP address of DMZ.
Accept / Cancel Press Accept to confirm the changes or Cancel to return
previous settings.
Accept does not apply the changes – you must go to Status -> Save / Load
to apply the new settings. Please refer to Chapter 6.1 for more information.
Page 69

11 Management Settings
The Management section is on the navigation side-bar menu. You will see seven options:
Administration, Management VLAN, SNMP Settings, Backup / Restore Settings, Firmware
Upgrade, Time Settings, and Log. Each option is described below.
11.1 Administration
Click on the Administration link under the Management menu. This option allows you to
create a username and password for the device. By default, this device is configured with a
username and password of admin. For security reasons it is highly recommended that you
create a new username and password.
Name Specify Username for login.
Password Specify a Password for login
Confirm Password Re-enter the Password for confirmation.
Remote Management Select the Radio button to Enable or Disable Remote
Management.
Remote Upgrade Select the Radio button to Enable or Disable Remote Upgrade.
Remote Management Specify the Port number for Remote Management. For example:
Page 70

Port if you specify the Port number is 8080, then you will need to enter
the following http://IPaddress:8080 to access the web interface.
Save / Apply / Cancel Press Save / Apply to confirm the changes or Cancel to return
previous settings.
Pressing Save / Apply will change the settings immediately. It is not
reversible unless the settings are changed again or the device is reset.
11.2 Management VLAN
Click on the Management VLAN link under the Management menu. This option allows you
to assign a VLAN tag to packets. A VLAN is a group of computers on a network whose
software has been configured so that they behave as if they were on a separate Local Area
Network (LAN). Computers on a VLAN do not have to be physically located next to one
another on the LAN.
Management VLAN ID If your network includes VLANs and if tagged packets need to
pass through the Access Point, specify the VLAN ID in this field. If
not, select the No VLAN tag radio button.
Accept / Cancel Press Accept to confirm the changes or Cancel to return
previous settings.
Please make note of the following:
1. Accept does not apply the changes – you must go to Status -> Save / Load to apply
the new settings. Please refer to Chapter 6.1 for more information.
2. If you reconfigure the Management VLAN ID, you may lose connection to the
ENH210. Verify the DHCP server can support the reconfigured VLAN ID, and then
re-connect to the new IP address.
Page 71

11.3 SNMP Settings
Click on the SNMP Settings link under the Management menu. This is a networking
management protocol used to monitor network-attached devices. SNMP allows messages
[called protocol data units] to be sent to various parts of a network. Upon receiving these
messages, SNMP-compatible devices [called agents] return data stored in their Management
Information Databases.
SNMP Enable/Disable Select the Radio button to Enable or Disable SNMP function.
Contact Specify the contact details of the device.
Location Specify the location of the device.
Community Name Specify the password for access the SNMP community for read
only access.
Community Name Specify the password for access the SNMP community for read
and write access.
Trap Destination IP
Address
Trap Destination
Community Name
Save / Apply / Cancel Press Save / Apply to confirm the changes or Cancel to return
Accept does not apply the changes – you must go to Status -> Save / Load
to apply the new settings. Please refer to Chapter 6.1 for more information.
Specify the IP address that will receive the SNMP trap.
Specify the password of the SNMP trap community.
previous settings.
Page 72

11.4 Backup/Restore Settings
Click on the Backup/Restore Setting link under the Management menu. This option is used
to save the current settings of the device in a file on a storage device, or to load settings on to
the device from storage device. This feature is very useful for administrators who have several
devices that need to be configured with the same settings.
Save A Copy of
Current Settings
Restore Saved Settings
from a File
Revert to Factory
Default Settings
Click on Backup to save current configured settings.
ENH210 can restore a previous setting that has been saved. Click
on Browse to select the file and Restore.
Click on Factory Default button to reset all the settings to the
factory default values.
11.5 Firmware Upgrade
Click on the Firmware Upgrade link under the Management menu. This page is used to
upgrade the firmware of the device. Make sure that to download the appropriate firmware
from EnGenius.
The upgrade process may take few minutes. Please do not power off the
device as this may cause the device to crash or become unusable. The ENH210 will
restart automatically once the upgrade is complete.
Page 73

11.6 Time Settings
Click on the Time Settings link under the Management menu. This page allows you to
configure the time on the device. You may do this manually or by connecting to a NTP server.
Manually Set Date and
Time
Automatically Get
Date and Time
Save / Apply / Cancel Press Save / Apply to confirm the changes or Cancel to return
Pressing Save / Apply will change the settings immediately. It is not
reversible unless the settings are changed again or the device is reset.
Manually setup the date and time.
Specify the Time Zone from the drop down list and Place a
check to specify the IP address of the NTP Server manually or use
the default NTP Server.
previous settings.
Page 74

11.7 Log
Click on the Log link under the Management menu. This page displays a list of events that
are triggered on the Ethernet and Wireless interface. This log can be referred to when an error
occurs on the system or when a report needs to be sent to the technical support department
for debugging purposes.
Syslog Select Enable or Disable Syslog function from the drop down list.
Log Server IP Address Specify the Log Server IP address.
Local Log Select Enable or Disable Local Log service.
Save/Apply / Cancel Press Save / Apply to confirm the changes or Cancel to return
previous settings.
Pressing Save / Apply will change the settings immediately. It is not
reversible unless the settings are changed again or the device is reset.
Page 75

11.8 Diagnostics
Click on the Diagnostics link under the Management menu. This function allows you to
detect connection quality and trace the routing table to the target.
Target IP Specify the IP address you would like to search.
Ping Packet Size Specify the packet size of each ping.
Number of Pings Specify the number of pings.
Start Ping Press Start Ping to begin.
Traceroute Target Specify an IP address or Domain name that you want to trace.
Start Traceroute Press Start Traceroute to begin.
Page 76

12 Network Configuration Examples
This chapter describes the role of the ENH210 with 4 modes. The Access Point mode’s default
configuration is a central unit of the wireless network or as a root device of the wired
environment. Repeater Mode requires additional configuration.
12.1 Access Point
Access Point
Step 1 Login to the web-based configuration interface with default IP
Step 2 Select your country or region’s regulation.
Step 3 Use site survey to scan channels of the nearby area.
Step 4 Select a channel with less interference.
Step 5
Step 6 Verify VLAN identifier in order to separate services among clients
Step 7 Setup the authentication settings.
Step 8 Select Apply to process all of the configurations.
For more advanced settings, please refer to the previous chapters.
Wireless Client
Step 1 Select the Wireless Mode you would like to associate with.
192.168.1.1
Specify the SSID for your broadcast SSID and you can also
configure multiple SSID at the same time.
Use Site Survey to scan for nearby Access Points and select the
Step 2
Step 3 Configure VLAN ID in your wireless device if available.
Step 4 Select the correct authentication type and password.
AP that you would like to connect with or enter the SSID
manually.
Page 77

The ENH210’s Access Point Mode does not provide a DHCP server so the
Wireless Client IP address must be configured manually in Local Area Network Settings.
12.2 Client Bridge Mode
Client Bridge Mode functions like a wireless client. It must connect to an Access Point/AP
Router to join the network.
Please refer to the last section to check the Access Point’s configuration.
Client Bridge
Step 1 Login to the web-based configuration interface with the default
Step 2 Select your country or region’s regulation.
Step 3 Select Operation Mode to Client Bridge from System
Step 4 Use site survey to scan channels of the nearby area.
Step 5 Select the AP that you would like to associate with.
Step 6
Step 7 Select Apply to process all of the configurations.
The Client-Bridge’s IP settings must match the Access Point’s settings.
IP: 192.168.1.1
Properties.
Setup the authentication settings that match to the Access Point’s
settings.
Page 78

12.3 WDS Bridge Mode
Use this feature to link multiple APs together in a network. All clients associated with any of
the APs can communicate with each other similar to an ad-hoc mode. The following
configuration shows four ENH210’s running on WDS Bridge Mode, which are connected to a
main ENH210 that is providing Internet access, also running on WDS Bridge Mode. This is a
bridged network; therefore, all nodes on the network can be in the same network IP block. All
computers are viewable as if they are in the same location and on the same Ethernet network.
WDS Bridge
Step 1 Login to the web-based configuration interface with default IP
192.168.1.1
Step 2 Select your country or region’s regulation.
Step 3 Change Operation Mode to WDS Bridge under System
Properties.
Step 4 Set the device’s IP settings under System -> IP Settings
Step 5 Set the WLAN settings under Wireless Network.
Step 6 Configure WDS Link Settings under Wireless.
Step 7 Specify the MAC address of the AP which you would like to
connect with.
Step 8 Press Apply under Save / Reload to process all of the
configurations.
Step 9 Verify the device’s settings by browsing to Status -> Main.
View the WDS link status.
Each WDS bridge device must use the same Subnet, Wireless Mode,
Wireless Channel, and Security Setting.
Page 79

12.4 Client Router Mode
In the Client Router Mode, the ENH210 has a DHCP Server that allows multiple devices to
share the same Internet connection. Connect to an AP/WISP wirelessly and connect to LANs
via wired. Client Router Mode is functionally opposite to the AP Router Mode.
Please refer to the last section to check Access point’s configuration.
Client Router
Step 1 Login to the web-based configuration interface with default IP
192.168.1.1
Step 2 Select your country or region’s regulation.
Step 3 Select Operation Mode to Client Router from System
Properties.
Step 4 Change your Local Area Network setting to Obtain an IP
Address Automatically.
Step 5 Use site survey to scan channels of the nearby area.
Step 6 Select the AP that you would like to associate with.
Step 7
Step 8 Configure your WAN connection type which is given by your
Step 9 Press Apply to process all of the configurations.
The Client Router’s IP settings must match those of the Access Point’s.
Setup the authentication settings that match the Access Point’s
settings.
Internet Service Provider on the WAN Settings.
Page 80

Appendix A – Troubleshooting
This appendix provides problem-solving information you may find useful in case
you need to troubleshoot your ENH210. It also includes information about
contacting technical support.
A.1 Problem Solving
Question Answer
How do I reset the ENH210? There are two ways to reset the ENH210, a
hardware method and a software method.
Both methods return the ENH210 to its
factory default configuration.
To use the hardware method, press reset
button behind the hole of the PoE injector
for 10 seconds.
To use the software method, click Restore
to Factory Default in the Management
What is the default IP address of the
ENH210?
I plugged the PoE to the Ethernet port on
the back of ENH210 but the unit is not on,
how come?
When I install the PoE connection to the
ENH210, what kind of PoE should I use?
menu.
The default IP address is 192.168.1.1
You need to plug the Ethernet cable
connect to PoE injector, and connect the
power adapter comes with the package to
the “DC IN” port on the PoE injector
The ENH210 uses a proprietary PoE injector
and is also workable with standard
802.3af/at-compliant PoE switches.
Page 81

A.2 Contacting Technical Support
If you encounter issues that cannot be resolved using this manual, please contact your vendor
where you purchase the device. If you cannot contact your vendor, you may also contact
EnGenius Customer Service department in the region where you purchased the device.
Before you contact your local EnGenius office, please prepare the following information:
Product model name and serial number
The place where you purchased the product
Warranty information
The date when you received the product
A brief description about the issue and the attempts you tried to resolve it
To contact EnGenius Customer Service office in the United States, please use either of the following methods:
� Email: Support@EnGeniustech.com
� Telephone: 1-888-735-7888
Page 82

Appendix B – Specifications
MCU: Atheros AR7242
RF: Atheros AR9283
Memory: 64 MB
Flash: 16 MB
Standard: 802.11 b/g/n
Physical Interface: - 1x LAN Port with PoE support
- 1x LAN Port
- 2 x N-type Connector
Max. Data rate: 300 Mbps
LEDs status: - Power Status
- LAN1/LAN2 (10/100Mbps)
- WLAN (Wireless is up)
- 3 x Link Quality (Client Bridge mode)
Security: - WEP Encryption-64/128/152 bit
- WPA/WPA2 Personal (WPA-PSK using TKIP or AES)
- WPA/WPA2 Enterprise (WPA-EAP using TKIP)
- 802.1x Authenticator
- Hide SSID in beacons
- MAC address filtering, up to 50 field
- Wireless STA (Client) connected list
Power Requirements: - Active Ethernet (Power over Ethernet)
- Standard 802.3af/at PoE design
- Power Adapter 48VAC / 380mA
Antenna: - Internal Directional 14dBi
Package Contents: - Wireless Long Range 11N AP/CB (ENH210)
- PoE Injector (EPE-48GR)
- Power Adaptor
- 5dBi Omni Antenna
- CD with User’s Manual
- QIG
- Mounting Set, - Special Screw Set
Certifications: FCC, CE, IC
ENVIRONMENT & MECHANICAL
Temperature Range:
Humidity (non-condensing):
Operating -20°C ~ 70°C (-4°F to 158° F)
Storage -30°C ~ 80°C (-22° F to 176°F)
0%~90% typical
Page 83

Waterproof: IP67
Appendix C – Glossary
Access Point
A base station in a WLAN that act as a central transmitter and receiver of WLAN radio signals.
Ad Hoc Network
A short-term WLAN framework created between two or more WLAN adapters, without going
through an Access Point. An ad hoc network lets computers send data directly to and from
one another. For an ad hoc network to work, each computer on the network needs a WLAN
card installed configured for Ad Hoc mode.
Antenna
A device that sends and receives radio-frequency (RF) signals. Often camouflaged on existing
buildings, trees, water towers or other tall structures, the size and shape of antennas are
generally determined by the frequency of the signal they manage.
Authentication
A process that verifies the identity of a wireless device or end-user. A common form of
authentication is to verify identities by checking a user name and password to allow network
access.
Backbone
A high-speed line or series of connections that form a major pathway within a network.
Bandwidth
The part of the frequency spectrum required to transmit desired information. Each radio
channel has a center frequency and additional frequencies above and below this carrier
frequency that carry the transmitted information. The range of frequencies from the lowest to
the highest used is called the bandwidth.
Bridge
A wireless device that connects multiple networks that are physically separate or use different
media, but which use similar standards.
Bridge Mode
An Access Pointy in bridge mode can operate as a WLAN bridge that connects two wired
network segments. The peer device also must be in bridge mode. This wireless bridge
connection is equivalent to a Wireless Distribution System (WDS).
CHAP
Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol. An alternative protocol that uses a
challenge/response technique instead of sending passwords over the wire.
Collision
Interference resulting from two network devices sending data at the same time. The network
detects the collision of the two transmitted packets and discards both of them.
Coverage
The region within which a paging receiver can reliably receive the transmission of paging
Page 84

signals.
Coverage Area
The geographical area that can be served by a mobile communications network or system.
Coverage Hole
An area within the radio coverage footprint of a wireless system where the RF signal level is
below the design threshold. Physical obstructions such as buildings, foliage, hills, tunnels, and
indoor parking garages are usually the cause of coverage holes.
Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC)
A common technique for detecting data transmission errors.
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
A protocol that assigns temporary IP addresses automatically to client stations logging onto
an IP network, so the IP addresses do not have to be assigned manually. The ENH210 contains
an internal DHCP server that automatically allocates IP address using a user-defined range of
IP addresses.
Dead Spot
An area within the coverage area of a WLAN where there is no coverage or transmission
falling off. Electronic interference or physical barriers such as hills, tunnels, and indoor parking
garages are usually the cause of dead spots. See also coverage area.
802.11
A category of WLAN standards defined by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
(IEEE).
802.11a
An IEEE standard for WLANs that operate at 5 GHz, with data rates up to 54 Mbps.
802.11n
An IEEE standard for WLANs that operates at 2.4 GHz, with data rate of 300 Mbps. The new
standard also raises the encryption bar to WPA2. The 40 HT option can be added to increase
the data rate.
Encryption
Translates data into a secret code to achieve data security. To read an encrypted file, you must
have a secret key or password for decryption. Unencrypted data is referred to as plain text;
encrypted data is referred to as cipher text
ESS ID
The unique identifier for an ESS. All Access Points and their associated wireless stations in the
same group must have the same ESSID.
Footprint
Geographical areas where an entity is licensed to broadcast its signal.
Gateway
A computer system or other device that acts as a translator between two systems that use
different communication protocols, data formatting structures, languages, and/or
architecture.
Page 85

HT mode
In the 802.11n system, two new formats, called High Throughput (HT), are defined for the
Physical Layer, Mixed Mode, and Green Field. If a system runs 40 HT, two adjacent 20 MHz
channels are used. The larger 40 MHz bandwidth can provide better transmit quality and
speed.
Keys
Like passwords, keys open (decrypt) and close (encrypt) messages. While many encryption
algorithms are commonly known and public, the key must be kept secret.
Local-Area Network (LAN)
A small data network covering a limited area, such as a building or group of buildings. Most
LANs connect workstations or personal computers. LANs let many users share devices such as
printers as well as data. LANs also facilitate communication through e-mail or chat sessions.
Media Access Control (MAC) Address
Address associated with every hardware device on the network. Every 802.11 wireless device
has its own specific MAC address. This unique identifier is hard-coded into the device and can
be used to provide security for WLANs. When a network uses a MAC table, only the 802.11
radios that have their MAC addresses added to that network's MAC table can access the
network.
Network Address Translation (NAT)
An Internet standard that lets a LAN use one set of IP addresses for internal traffic and a
second set of addresses for external traffic.
Network Time Protocol (NTP)
A protocol that lets devices synchronize their time with a time server. NTP uses TCP or UDP
port 123 by default.
Passphrase
A text string that automatically generates WEP keys on wireless client adapters.
Power Over Ethernet (PoE)
A PoE provides power to PoE-enabled devices using an 8-pin CAT 5 Ethernet cable,
eliminating the need for a power source.
Preamble
Synchronizes transmissions in a WLAN. The preamble type defines the length of the Cyclic
Redundancy Check block for communication between a device and roaming wireless stations.
Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol (PEAP)
Authentication protocol of IEEE 802.1x used to send authentication data and passwords over
802.11 WLANs.
Quality of Service (QoS)
A network’s ability to deliver data with minimum delay. QoS also refers to the networking
methods used to provide bandwidth for real-time multimedia applications.
Page 86

Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS)
Networking protocol that provides centralized authentication, authorization, and accounting
management for computers to connect and use a network service. Because of its broad
support and ubiquitous nature, the RADIUS protocol is often used by ISPs and enterprises to
manage access to the Internet or internal networks, WLANs, and integrated e-mail services.
Service Set Identifier (SSID)
Name of a WLAN. All wireless devices on a WLAN must use the same SSID to communicate
with each other.
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
An Internet-standard protocol for managing devices on IP networks.
Snooping
Passively watching a network for data, such as passwords, that can be used to benefit a
hacker.
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP)
An encryption protocol that uses 128-bit keys. Keys are dynamically generated and
distributed by the authentication server. TKIP regularly changes and rotates encryption keys,
with an encryption key never being used twice.
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
A protocol that allows communications over and between networks. TCP/IP is the basis for
Internet communications.
Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ)
WFQ services queues are based on priority and queue weight. Queues with larger weights get
more service than queues with smaller weights. This highly efficient queuing mechanism
divides available bandwidth across different traffic queues.
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
Security protocol that provides a WLAN with a level of security and privacy comparable to that
of a wired LAN. WEP encrypts data sent between wired and WLANs to keep transmissions
private.
Wireless Local-Area Network (WLAN)
WLANs use RF technology to send and receive data wirelessly in a certain area. This lets users
in a small zone send data and share resources such as printers without using cables to
physically connect each computer.
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA )
A subset of the IEEE 802.11i standard. WPA applies IEEE 802.1x and Extensible Authentication
Protocol (EAP) to authenticate wireless clients using an external RADIUS database. WPA uses
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP), Message Integrity Check (MIC), and IEEE 802.1x to
encrypt data. See also WPA-PSK (WPA -Pre-Shared Key).
Wi-Fi MultiMedia (WMM)
Part of the IEEE 802.11e QoS enhancement to the Wi-Fi standard that ensures quality of
Page 87

service for multimedia applications in WLANs.
Wireless Client Supplicants
Software that runs on an operating system, instructing the wireless client how to use WPA.
WPA -Pre-Shared Key (WPA-PSK)
WPA-PSK requires a single (identical) password entered into each Access Point, wireless
gateway, and wireless client. A client is granted access to a WLAN if the passwords match.
WPA2
A wireless security standard that defines stronger encryption, authentication, and key
management than WPA. It includes two data encryption algorithms, Temporal Key Integrity
Protocol (TKIP) and Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), in the Counter mode with Cipher
block chaining Message authentication Code Protocol (CCMP).
Wireless Distribution System (WDS)
A technology that lets Access Points communicate with one another to extend the range of a
WLAN.
Page 88

Appendix D – Statements of Conformity
D.1 – Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This
equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user
is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one of the following measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible
for compliance could void the user's authority to operate this equipment.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept
any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm
between the radiator & your body.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or
transmitter.
Note: Country selection is not available in the US model.
Page 89

D.2 – Industry Canada Statement
This device complies with RSS-210 of the Industry Canada Rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this
device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
Ce dispositif est conforme à la norme CNR-210 d'Industrie Canada applicable aux appareils
radio exempts de licence. Son fonctionnement est sujet aux deux conditions suivantes: (1) le
dispositif ne doit pas produire de brouillage préjudiciable, et (2) ce dispositif doit accepter
tout brouillage reçu, y compris un brouillage susceptible de provoquer un fonctionnement
indésirable.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with IC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm
between the radiator & your body.
NOTE IMPORTANTE: (Pour l'utilisation de dispositifs mobiles):
Déclaration d'exposition aux radiations:
Cet équipement est conforme aux limites d'exposition aux rayonnements IC établies pour un
environnement non contrôlé. Cet équipement doit être installé et utilisé avec un minimum de
20 cm de distance entre la source de rayonnement et votre corps.
Page 90

D.3 – Europe Declaration of Conformity
This device complies with the essential requirements of the R&TTE Directive 1999/5/EC. The following
test methods have been applied in order to prove presumption of conformity with the essential
requirements of the R&TTE Directive 1999/5/EC:
- EN60950-1:2006 A11:2009
Safety of Information Technology Equipment
- EN50385 : 2002
- Generic standard to demonstrate the compliance of electronic and electrical apparatus with the
basic restrictions related to human exposure to electromagnetic fields (0 Hz - 300 GHz)
- EN 300 328 V1.7.1: 2006-10
- Electromagnetic compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Wideband Transmission
systems; Data transmission equipment operating in the 2,4 GHz ISM band and using spread
spectrum modulation techniques; Harmonized EN covering essential requirements under article
3.2 of the R&TTE Directive
-
EN 301 489-1 V1.8.1: 2008-04
Electromagnetic compatibility and Radio Spectrum Matters (ERM); ElectroMagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 1: Common technical requirements
EN 301 489-17 V2.1.1 2009-05
Electromagnetic compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); ElectroMagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 17: Specific conditions for 2,4 GHz wideband
transmission systems and 5 GHz high performance RLAN equipment
This device is a 2.4 GHz wideband transmission system (transceiver), intended for use in all EU
member states and EFTA countries, except in France and Italy where restrictive use applies.
In Italy the end-user should apply for a license at the national spectrum authorities in order to obtain
authorization to use the device for setting up outdoor radio links and/or for supplying public access to
telecommunications and/or network services.
This device may not be used for setting up outdoor radio links in France and in some areas the RF
output power may be limited to 10 mW EIRP in the frequency range of 2454 – 2483.5 MHz. For
detailed information the end-user should contact the national spectrum authority in France.
Page 91

0560
Česky
[Czech]
Dansk
[Danish]
[Jméno výrobce] tímto prohlašuje, že tento [typ zařízení] je ve shodě se základními
požadavky a dalšími příslušnými ustanoveními směrnice 1999/5/ES.
Undertegnede [fabrikantens navn] erklærer herved, at følgende udstyr [udstyrets
typebetegnelse] overholder de væsentlige krav og øvrige relevante krav i direktiv
1999/5/EF.
Deutsch
[German]
Hiermit erklärt [Name des Herstellers], dass sich das Gerät [Gerätetyp] in
Übereinstimmung mit den grundlegenden Anforderungen und den übrigen einschlägigen
Bestimmungen der Richtlinie 1999/5/EG befindet.
Eesti
[Estonian]
Käesolevaga kinnitab [tootja nimi = name of manufacturer] seadme [seadme tüüp =
type of equipment] vastavust direktiivi 1999/5/EÜ põhinõuetele ja nimetatud direktiivist
tulenevatele teistele asjakohastele sätetele.
English Hereby, [name of manufacturer], declares that this [type of equipment] is in compliance
with the essential requirements and other relevant provisions of Directive 1999/5/EC.
Español
[Spanish]
Por medio de la presente [nombre del fabricante] declara que el [clase de equipo]
cumple con los requisitos esenciales y cualesquiera otras disposiciones aplicables o
exigibles de la Directiva 1999/5/CE.
Ελληνική
[Greek]
ΜΕ ΤΗΝ ΠΑΡΟΥΣΑ [name of manufacturer] ΔΗΛΩΝΕΙ ΟΤΙ [type of equipment]
ΣΥΜΜΟΡΦΩΝΕΤΑΙ ΠΡΟΣ ΤΙΣ ΟΥΣΙΩΔΕΙΣ ΑΠΑΙΤΗΣΕΙΣ ΚΑΙ ΤΙΣ ΛΟΙΠΕΣ
Français
[French]
Italiano
[Italian]
Latviski
[Latvian]
Lietuvių
[Lithuanian]
Nederland
s [Dutch]
Malti
[Maltese]
ΣΧΕΤΙΚΕΣ ΔΙΑΤΑΞΕΙΣ ΤΗΣ ΟΔΗΓΙΑΣ 1999/5/ΕΚ.
Par la présente [nom du fabricant] déclare que l'appareil [type d'appareil] est conforme
aux exigences essentielles et aux autres dispositions pertinentes de la directive
1999/5/CE.
Con la presente [nome del costruttore] dichiara che questo [tipo di apparecchio] è
conforme ai requisiti essenziali ed alle altre disposizioni pertinenti stabilite dalla
direttiva 1999/5/CE.
Ar šo [name of manufacturer / izgatavotāja nosaukums] deklarē, ka [type of equipment
/ iekārtas tips] atbilst Direktīvas 1999/5/EK būtiskajām prasībām un citiem ar to
saistītajiem noteikumiem.
Šiuo [manufacturer name] deklaruoja, kad šis [equipment type] atitinka esminius
reikalavimus ir kitas 1999/5/EB Direktyvos nuostatas.
Hierbij verklaart [naam van de fabrikant] dat het toestel [type van toestel] in
overeenstemming is met de essentiële eisen en de andere relevante bepalingen van
richtlijn 1999/5/EG.
Hawnhekk, [isem tal-manifattur], jiddikjara li dan [il-mudel tal-prodott] jikkonforma
mal-ħtiġijiet essenzjali u ma provvedimenti oħrajn relevanti li hemm fid-Dirrettiva
1999/5/EC.
Page 92

Magyar
[Hungarian]
Alulírott, [gyártó neve] nyilatkozom, hogy a [... típus] megfelel a vonatkozó alapvetõ
követelményeknek és az 1999/5/EC irányelv egyéb elõírásainak.
Polski
[Polish]
Português
[Portuguese]
Slovensko
[Slovenian]
Slovensky
[Slovak]
Suomi
[Finnish]
Svenska
[Swedish]
Niniejszym [nazwa producenta] oświadcza, że [nazwa wyrobu] jest zgodny z
zasadniczymi wymogami oraz pozostałymi stosownymi postanowieniami Dyrektywy
1999/5/EC.
[Nome do fabricante] declara que este [tipo de equipamento] está conforme com os
requisitos essenciais e outras disposições da Directiva 1999/5/CE.
[Ime proizvajalca] izjavlja, da je ta [tip opreme] v skladu z bistvenimi zahtevami in
ostalimi relevantnimi določili direktive 1999/5/ES.
[Meno výrobcu] týmto vyhlasuje, že [typ zariadenia] spĺňa základné požiadavky a
všetky príslušné ustanovenia Smernice 1999/5/ES.
[Valmistaja = manufacturer] vakuuttaa täten että [type of equipment = laitteen
tyyppimerkintä] tyyppinen laite on direktiivin 1999/5/EY oleellisten vaatimusten ja sitä
koskevien direktiivin muiden ehtojen mukainen.
Härmed intygar [företag] att denna [utrustningstyp] står I överensstämmelse med de
väsentliga egenskapskrav och övriga relevanta bestämmelser som framgår av direktiv
1999/5/EG.
 Loading...
Loading...