Page 1

1
11N Long Range Multi-Function Client Bridge / Access Point
ECB150
11 N Long Range Multi-Function Client Bridge / Access Point
V1.0
Page 2

1
Table of Contents
1 Introduction ....................................................................................................................................................................... 6
1.1 Features and Benefits.........................................................................................................................................................................................6
1.2 Package Contents ................................................................................................................................................................................................7
1.3 System Requirements.........................................................................................................................................................................................8
1.4 Applications............................................................................................................................................................................................................8
2 Before you Begin............................................................................................................................................................. 10
2.1 Considerations for Wireless Installation .................................................................................................................................................. 10
2.2 Computer Settings (Windows XP/Windows Vista/Windows 7)...................................................................................................... 11
2.3 Apple Mac X OS................................................................................................................................................................................................. 14
2.4 Hardware Installation ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 15
3 Configuring Your Client Bridge ..................................................................................................................................... 17
3.1 Default Settings ................................................................................................................................................................................................. 17
3.2 Web Configuration........................................................................................................................................................................................... 18
4 Building a Wireless Network ......................................................................................................................................... 20
4.1 Client Bridge Mode .......................................................................................................................................................................................... 20
4.2 Access Point Mode........................................................................................................................................................................................... 21
4.3 WDS AP Mode.................................................................................................................................................................................................... 22
4.4 WDS Bridge Mode............................................................................................................................................................................................ 23
4.5 Router Mode....................................................................................................................................................................................................... 24
4.6 Repeater Mode .................................................................................................................................................................................................. 25
5 System .............................................................................................................................................................................. 26
5.1 Operation Mode................................................................................................................................................................................................
5.2 Status .....................................................................................................................................................................................................................
26
28
Page 3

2
5.3 DHCP...................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 32
5.4 Schedule ............................................................................................................................................................................................................... 34
5.5 Event Log.............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 36
5.6 Monitor ................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 37
6 Wireless ............................................................................................................................................................................ 38
6.1 Status ..................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 38
6.2 Basic........................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 40
6.3 Site Survey ........................................................................................................................................................................................................... 44
6.4 Advanced.............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 48
6.5 Security.................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 52
6.6 Filter........................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 58
6.7 WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup)........................................................................................................................................................................ 60
6.8 Client List.............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 62
6.9 VLAN ...................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 63
6.10 AP Profile.............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 64
7 Network............................................................................................................................................................................ 66
7.1 Status ..................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 66
7.2 LAN ......................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 67
7.3 Spanning Tree .................................................................................................................................................................................................... 70
7.4 WAN (Router mode)........................................................................................................................................................................................ 71
7.4.1 Static IP Address....................................................................................................................................................................................... 71
7.4.2 Dynamic IP Address................................................................................................................................................................................ 72
7.4.3 PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE)................................................................................................................................................................... 73
7.4.4 Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)...................................................................................................................................... 74
8 Firewall .............................................................................................................................................................................
8.1 Enable ....................................................................................................................................................................................................................
76
76
Page 4

3
8.2 DMZ........................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 77
8.3 DoS.......................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 78
8.4 MAC Filter............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 79
8.5 IP Filter................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 80
8.6 URL Filter .............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 82
9 Advanced.......................................................................................................................................................................... 83
9.1 Network Address Translation (NAT).......................................................................................................................................................... 83
9.2 Port Mapping...................................................................................................................................................................................................... 84
9.3 Port Forwarding................................................................................................................................................................................................. 85
9.4 Port Triggering................................................................................................................................................................................................... 86
9.5 Application Layer Gateway (ALG) ............................................................................................................................................................... 87
9.6 Universal Plug and Play (UPnP)................................................................................................................................................................... 88
9.7 Quality of Service (QoS) ................................................................................................................................................................................. 89
9.8 Static Routing ..................................................................................................................................................................................................... 92
9.9 Dynamic Routing............................................................................................................................................................................................... 93
9.10 Routing Table ..................................................................................................................................................................................................... 94
10 Management ................................................................................................................................................................ 95
10.1 Admin .................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 95
10.2 SNMP ..................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 97
10.3 Firmware Upgrade............................................................................................................................................................................................ 99
10.4 Configure............................................................................................................................................................................................................102
10.5 Reset.....................................................................................................................................................................................................................103
11 Tools ............................................................................................................................................................................ 104
11.1 Time Setting......................................................................................................................................................................................................104
11.2 Diagnosis............................................................................................................................................................................................................
12 Logout.........................................................................................................................................................................
105
106
Page 5

4
Appendix A – FCC Interference Statement ........................................................................................................................ 107
Appendix B – IC Interference Statement ........................................................................................................................... 108
Appendix C – CE Interference Statement........................................................................................................................... 110
5
Page 6

Revision History
Version Date Notes
1.0 Feb. 15, 2012 First Release
Page 7

6
1 Introduction
The ECB150 is a multi-function 802.11b/g/n product with 6 major multi-functions. The ECB150 is designed to operate in
every working environment including enterprises.
The ECB150 is a Wireless Network device that delivers up to 3x faster speeds and 7x extended coverage than 802.11b/g
devices. The ECB150 supports use in the home network with superior throughput, performance, and significant wireless
range.
To protect data during wireless transmissions, the ECB150 encrypts all wireless transmissions through WEP data encryption
and supports WPA/WPA2 encryption. The ECB150 has MAC address filtering to allow users to select differing stations to
access the network. The ECB150 is an ideal product to ensure network safety for both home and enterprise environments.
1.1 Features and Benefits
Features Benefits
High Speed Data Rate Up to 150 Mbps Capable of handling heavy data payloads such as HD multimedia
streaming.
10/100 Fast Ethernet Support up to 100Mbps networking speed.
IEEE 802.11n Draft Compliant and Backwards
Compatible with 802.11b/g devices
Multi-Function Allowing users to select Access Point, Client Bridge, WDS AP, WDS
Point-to-Point or Point-to-Multipoint
Wireless Connectivity
Fully compatible with IEEE 802.11b/g/n devices.
Bridge, Router or Universal Repeater mode in various applications.
Allows transfer of data from building to building.
Page 8

7
Support Multiple SSID in AP mode (up to 4) Allow clients to access different networks through a single access
point and assign different policies and functions for each SSID
through the built in software.
WPA/WPA2/IEEE 802.1x Support Powerful data security.
MAC Address Filtering in AP Mode Ensure a secure network connection.
User Isolation Support (AP mode) Protect the private network between client users.
Power-over-Ethernet (IEEE802.3af) Flexible Access Point locations.
Save User Settings Firmware upgrade does not delete user settings.
SNMP Remote Configuration Management Allows remote connection to configure or manage the ECB150
easily.
QoS (WMM) support Enhanced user performance and density.
1.2 Package Contents
The ECB150 package contains the following items (all items must be in package to issue a refund):
ECB150 Wireless Long Range Multi-Function Client Bridge / Access Point
12V/1A 100V~240V Power Adapter
RJ-45 Ethernet Cable
Detachable Antenna
CD with User’s Manual
Quick Installation Guide
Page 9

8
1.3 System Requirements
The following are the minimum system requirements in order configure the device.
Computer with an Ethernet interface or Wireless Network.
Windows, Mac OS, or Linux based operating systems.
Web-Browsing Application (example: Internet Explorer, FireFox, Safari, or other similar software)
1.4 Applications
Wireless LAN products are easy to install and highly efficient. The following list describes some of the many applications
made possible through the power and flexibility of wireless LANs:
a) Difficult-to-Wire Environments
There are many situations where wires cannot be laid easily or cannot be hidden from view. Older buildings, sites with
multiple buildings, and/or areas make the installation of a Wired LAN impossible, impractical, and/or expensive.
b) Temporary Workgroups
Create temporary workgroups/networks in open areas such as parks, athletic arenas, exhibition centers, temporary
offices, and construction sites where one wants a temporary Wireless LAN established and easily removed.
c) The Ability to Access Real-Time Information
Doctors/Nurses, Point-of-Sale Employees, and/or Warehouse Workers can access real-time information while dealing
with patients, serving customers, and/or processing information.
d) Frequently Changing Environments
Set up networks in environments that change frequently (i.e.: Show Rooms, Exhibits, etc.).
e) Small Office and Home Office (SOHO) Networks
SOHO users need a cost-effective, easy and quick installation of a small network.
Page 10

9
f) Wireless Extensions to Ethernet Networks
Extend network coverage where the network cannot reach (i.e.: There is no wired internet connection to reach certain
location of the environment).
g) Wired LAN Backup
Implement wireless LANs to provide backup for mission-critical applications running on wired networks.
h) Training/Educational Facilities
Training sites at corporations and students at universities use wireless connectivity to ease access to information,
information exchanges, and learning.
Page 11

10
2 Before you Begin
This section will guide you through the installation process. Placement of the ENGENIUS ECB150 is essential to maximize
the ECB150’s performance. Avoid placing the ECB150 in an enclosed space such as a closet, cabinet, or wardrobe.
2.1 Considerations for Wireless Installation
The operating distance of all wireless devices cannot be pre-determined due to a number of unknown obstacles in the
environment that the device is deployed in. These could be the number, thickness, and location of walls, ceilings, or other
objects that the ECB150’s wireless signals must pass through. Here are some key guidelines to allow the ECB150 to have
optimal wireless range.
Keep the number of walls and/or ceilings between the ECB150 and other network devices to a minimum. Each wall
and/or ceiling can reduce the signal strength, resulting in lower signal strength.
Building materials makes a difference. A solid metal door and/or aluminum stubs may have a significant negative effect
on the signal strength of the ECB150. Locate your wireless devices carefully so the signal can pass through a drywall
and/or open doorways. Materials such as glass, steel, metal, concrete, water (example: fish tanks), mirrors, file cabinets,
and/or brick can also lower your wireless signal strength.
Interferences can also come from other electrical devices and/or appliances that generate RF noise. The most usual
types are microwaves and cordless phones.
Page 12
11
2.2 Computer Settings (Windows XP/Windows Vista/Windows 7)
In order to use the ECB150, you must first configure the TCP/IPv4 connection of your computer system.
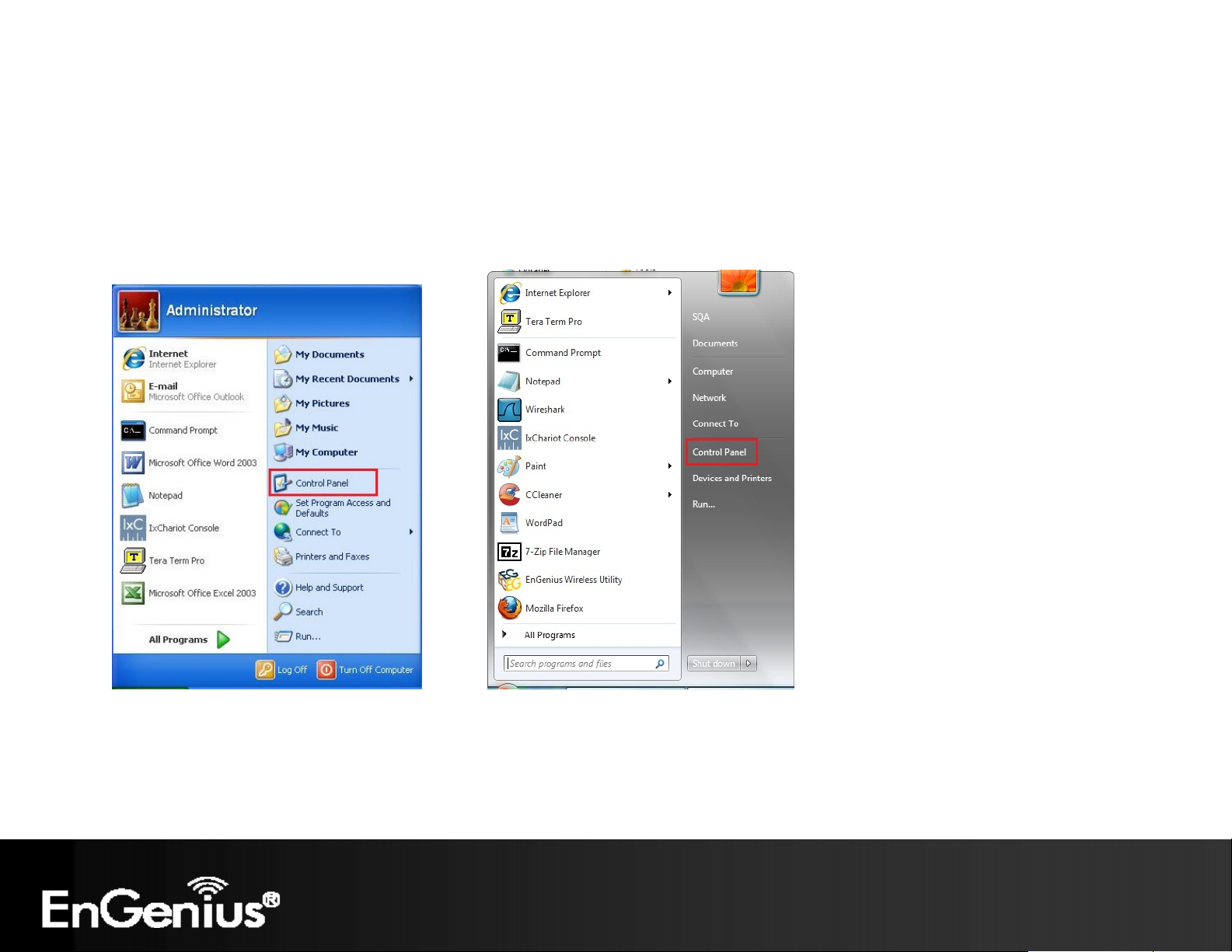
Click Start button and select Control Panel.
Windows XP Windows Vista/Windows 7
Page 13
12
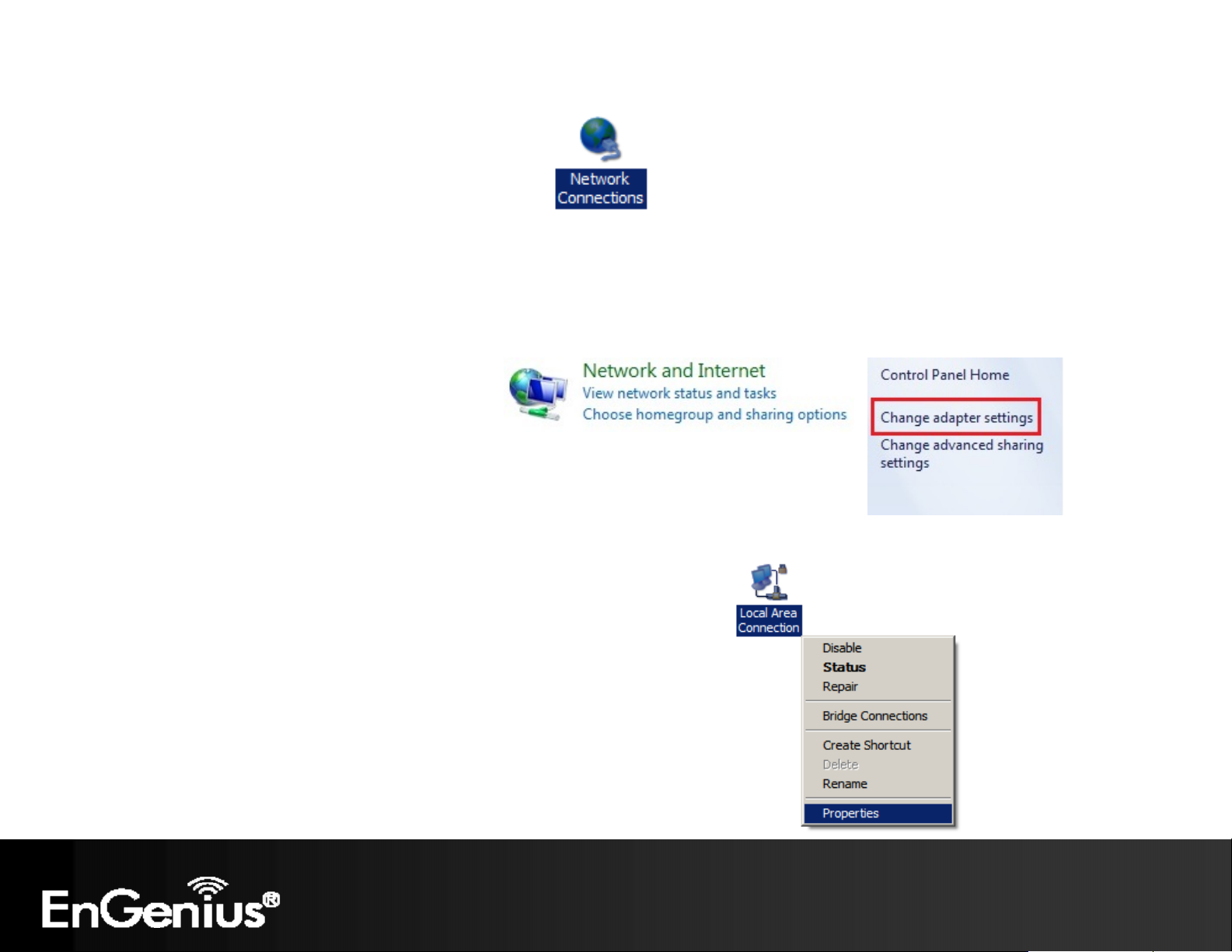
In Windows XP, click Network Connections
In Windows 7, click View Network Status and Tasks in the Network and Internet section, then select Change
Adapter Settings
Right click on Local Area Connection and select Properties
Page 14
13
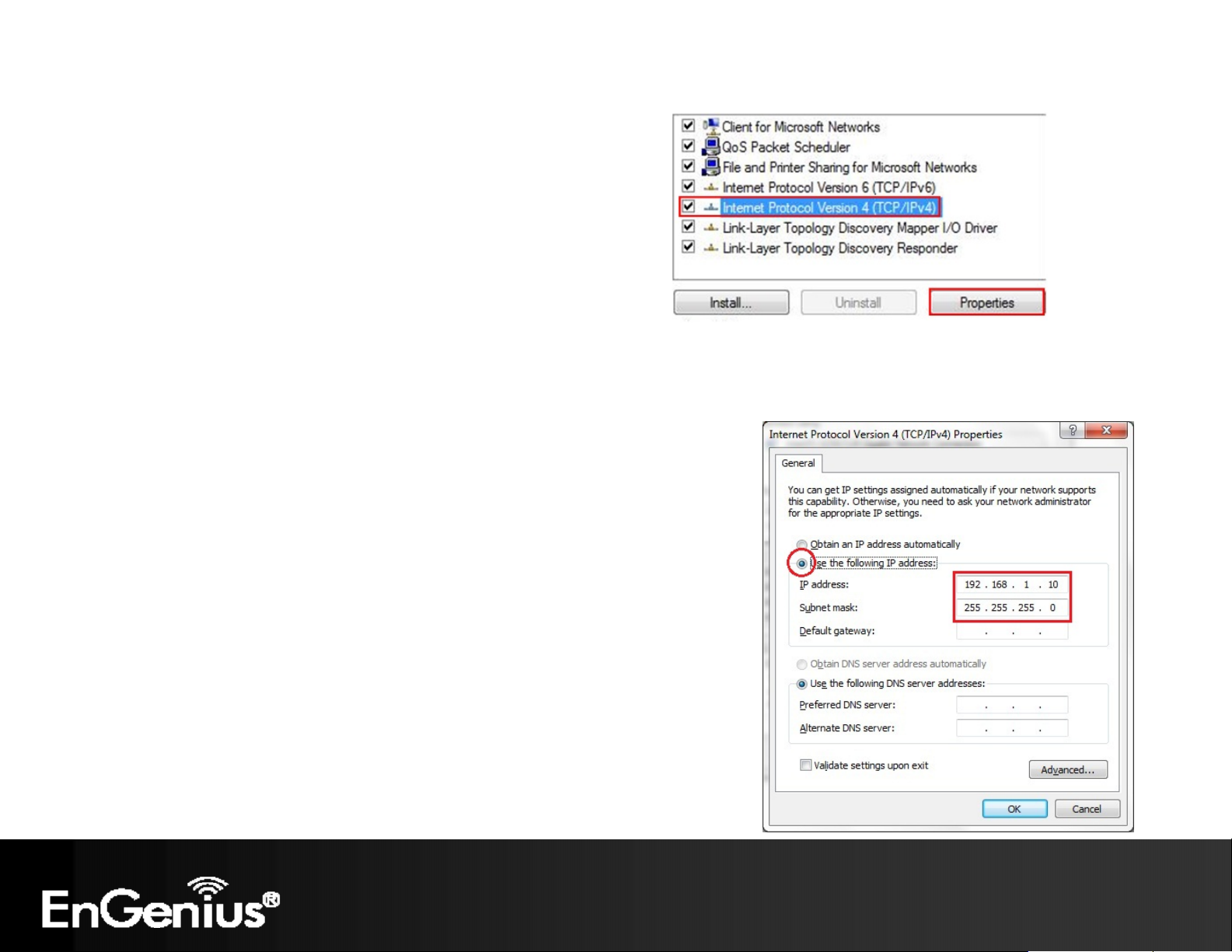
Highlight Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and select
Properties
Select Use the following IP address and enter IP address and subnet
mask then press OK.
Note: Ensure that the IP address and subnet mask are on the same
subnet as the device.
For example: Device IP address: 192.168.1.1
PC IP address: 192.168.1.2 - 192.168.1.254
PC subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
Page 15
14
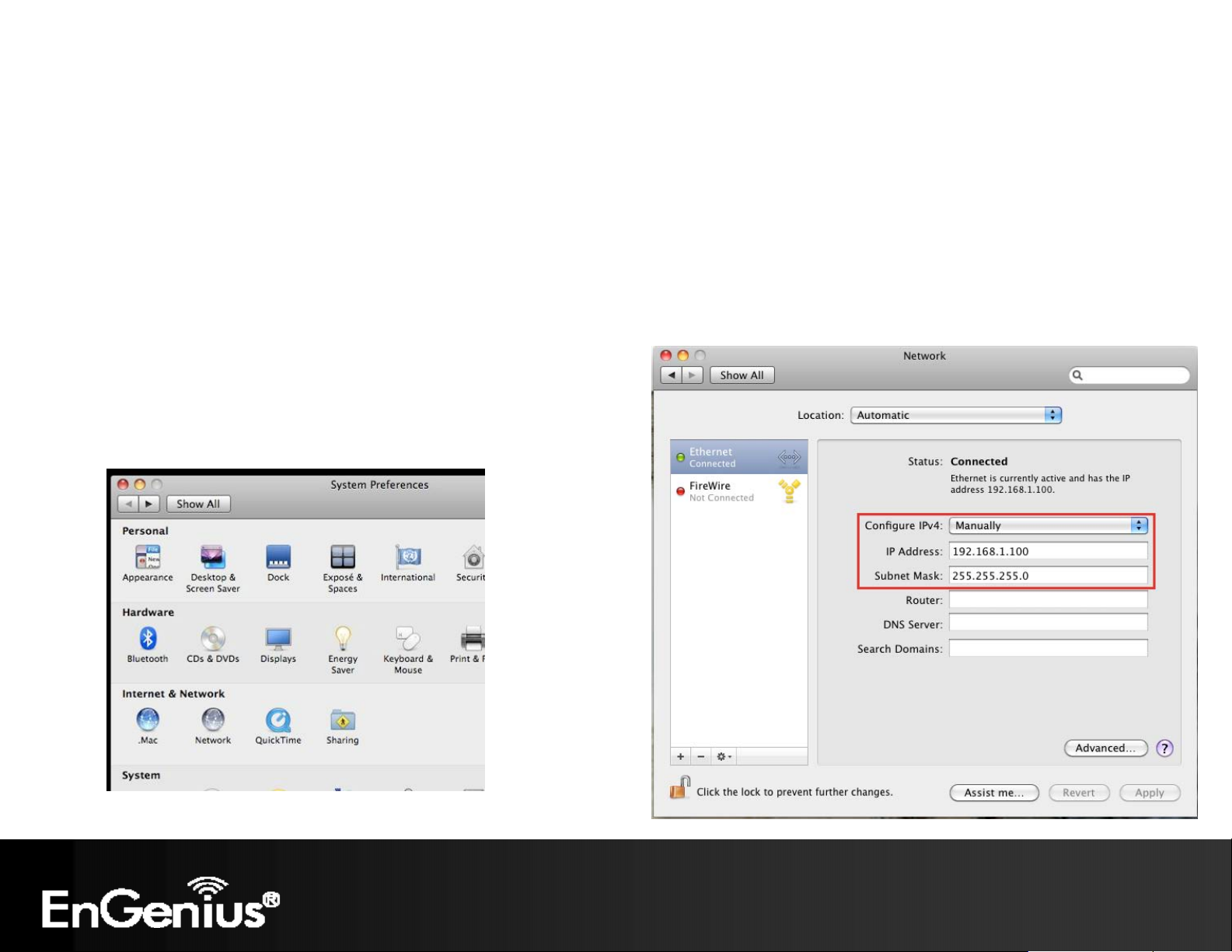
2.3 Apple Mac X OS
Open the System Preferences (can be opened in the Applications folder or selecting it in the Apple Menu)
Select Network in the Internet & Network section
Highlight Ethernet
In Configure IPv4, select Manually
Enter IP address and subnet mask then press OK.
Note: Ensure that the IP address and subnet mask are on the same subnet as the device.
For example: Device IP address: 192.168.1.1
PC IP address: 192.168.1.2 - 192.168.1.254
PC subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
Click Apply when done.
Page 16
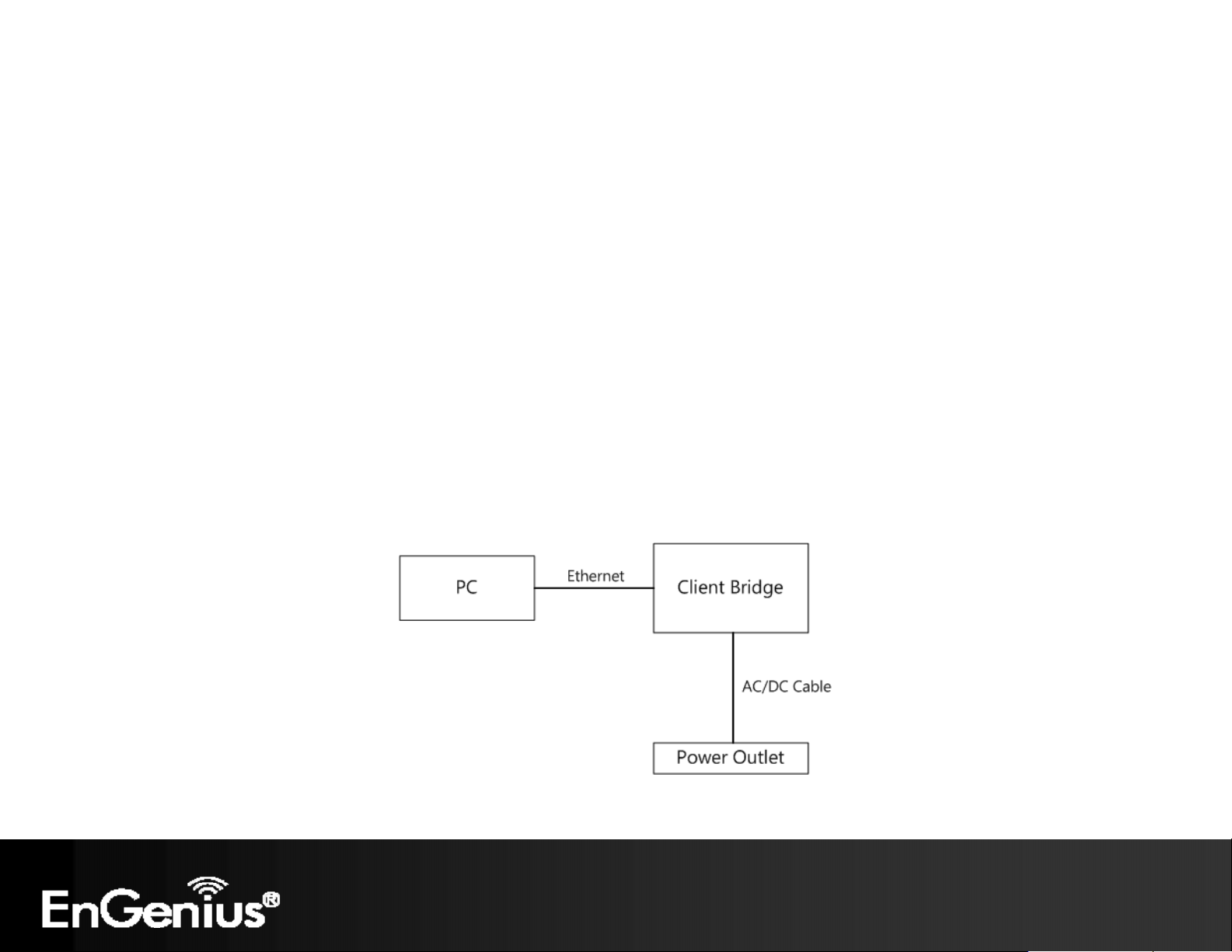
15
2.4 Hardware Installation
1) Ensure that the computer in use has an Ethernet Card (RJ-45 Ethernet Port). For more information, verify with our
computer user manual.
2) Connect one end of the Category 5 Ethernet cable into RJ-45 port of the ECB150 and the other end to the RJ-45 port
on the computer that will use the ECB150. Ensure that the cable is securely connected to both the ECB150 and the
Computer.
3) Connect the Power Adaptor DC Inlet to the DC-IN port of the ECB150 and the Power Adaptor to the electrical out.
Once both connections are secure, verify the following:
a) Ensure that the Power light is on (it will be blue).
b) Ensure that the Wireless light is on (it will be blue).
c) Ensure that the LAN (Computer/ECB150 Connection) light is on (it will be blue).
d) Once all three lights are on, proceed to setting up the computer.
This diagram depicts the hardware configuration.
Page 17
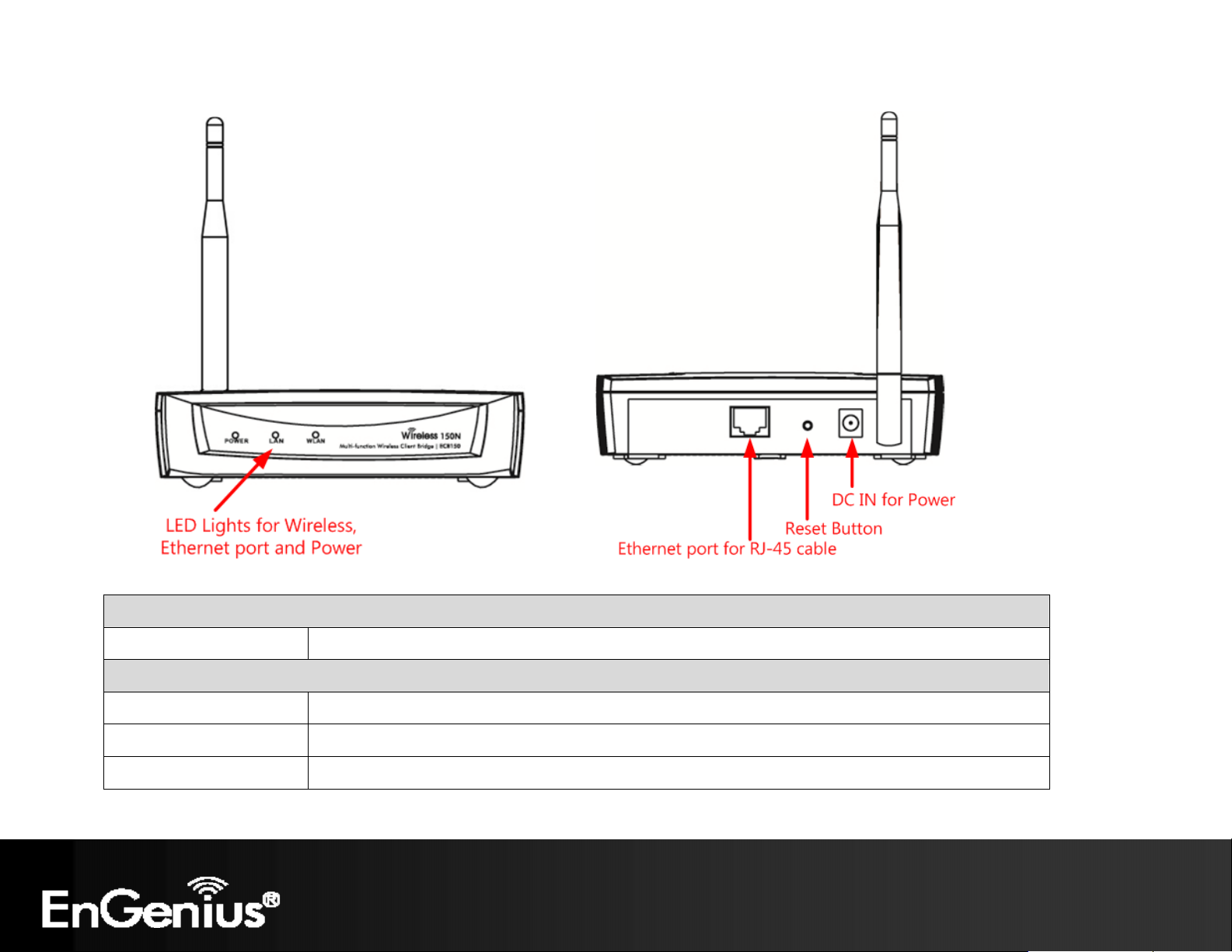
16
Front Panel Rear Panel
Front Panel
LED Lights LED lights for Wireless, Ethernet port and Power.
Rear Panel
DC IN DC IN for Power.
Reset Button One click for reset the device. Press over 10 seconds for reset to factory default.
Ethernet port for RJ-45 cable. Ethernet Port
Page 18
17
3 Configuring Your Client Bridge
This section will show you how to configure the device using the web-based configuration interface.
3.1 Default Settings
Please use your Ethernet port or wireless network adapter to connect the Client Bridge.
Default Settings
IP Address 192.168.1.1
Username / Password admin / admin
Operation Mode Client Bridge
Page 19
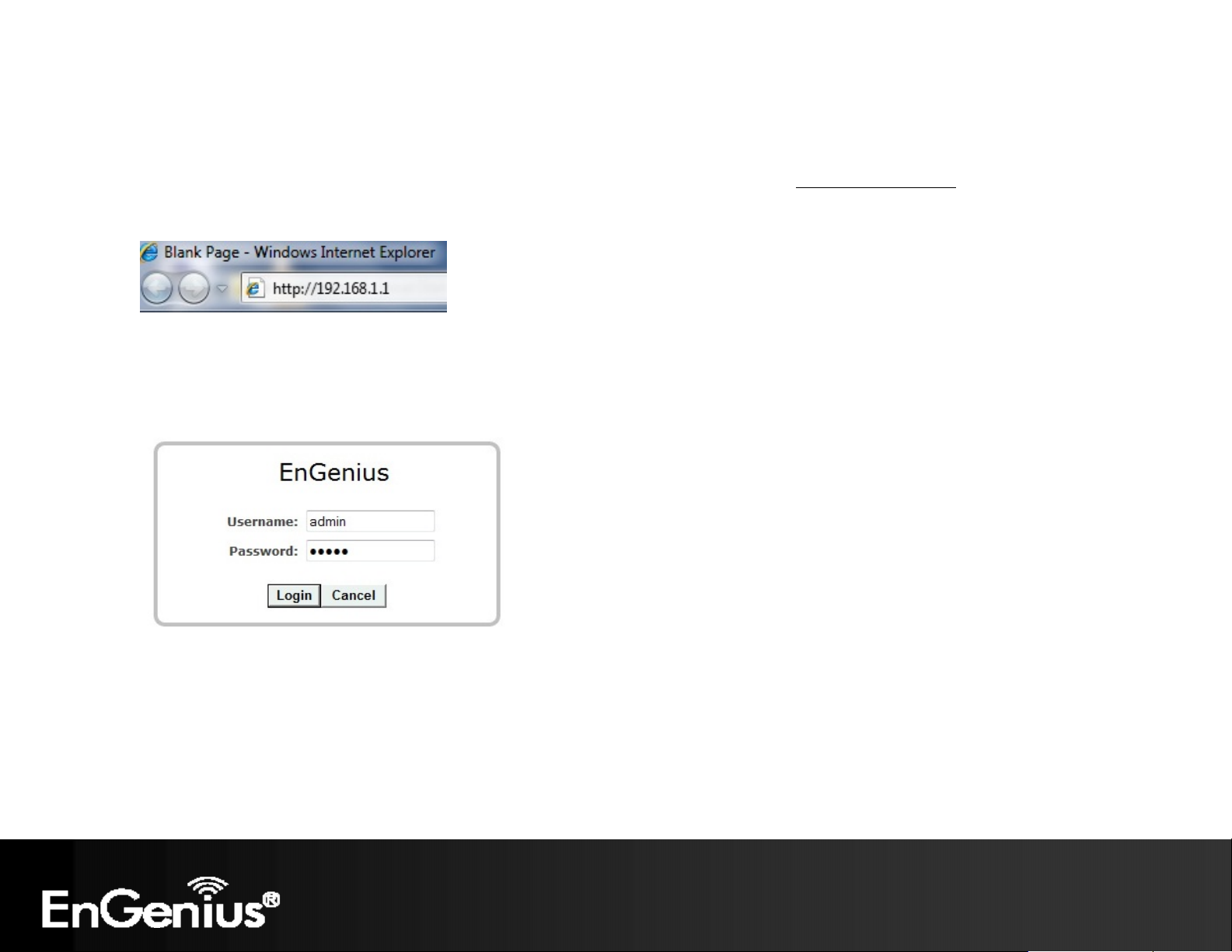
18
3.2 Web Configuration
Open a web browser (Internet Explorer/Firefox/Safari) and enter the IP Address: http://192.168.1.1
Note: If you have changed the default LAN IP Address of the Access Point, ensure you enter the correct IP Address.
The default username and password are admin. Once you have entered the correct username and password, click the
Login button to open the web-base configuration page.
Page 20

19
If successful, you will be logging in and see the ECB150 User Menu
Page 21
20
4 Building a Wireless Network
The ECB150 has the ability to operate in various operating modes. The ECB150 is the ideal device in which you can build
your WLAN. This chapter describes how to build a WLAN around your ECB150 using the operating modes of the ECB150.
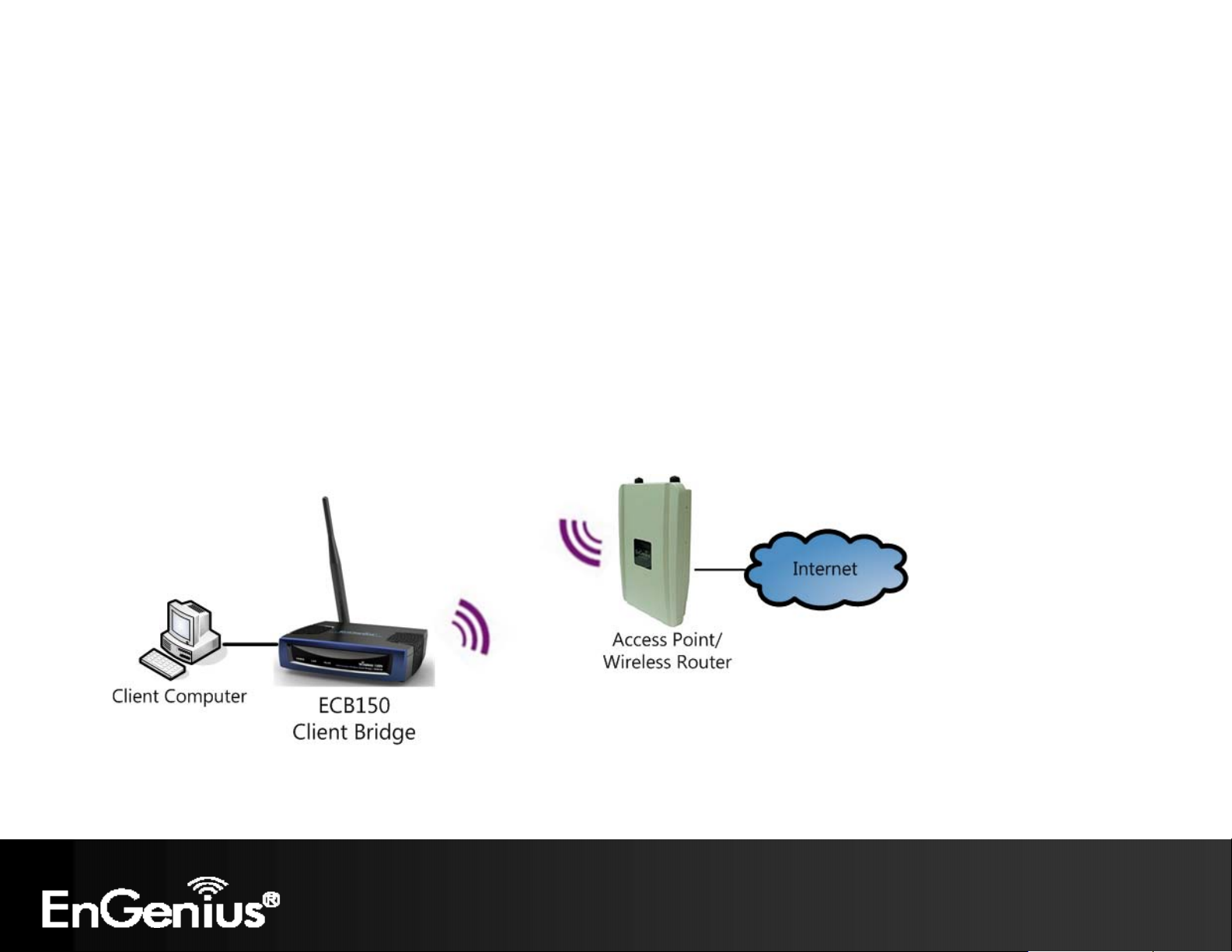
4.1 Client Bridge Mode
In Client Bridge Mode, the ECB150 acts as a wireless dongle that connects to an Access Point to allow a system wireless
access to the network. This mode requires you to connect the Ethernet port on your PC to the ECB150 LAN port.
If you use the client bridge operating mode, use the ECB150 Site Survey feature to scan for Access Points within range.
When you find an Access Point, configure the ECB150 to use the same SSID and Security Password as the Access Point to
associate with it.
Page 22
21
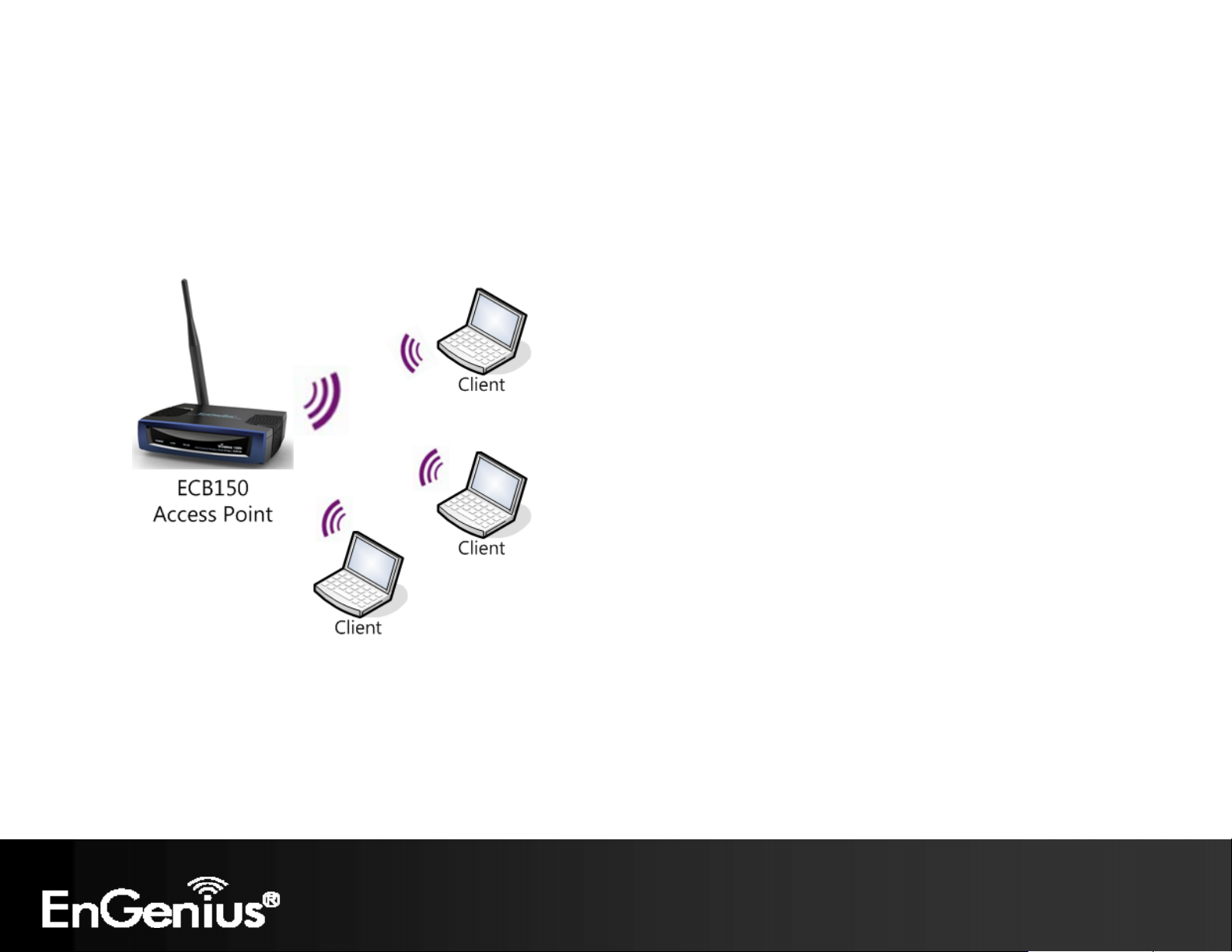
4.2 Access Point Mode
In Access Point Mode, ECB150 behaves likes a central connection for stations or clients that support IEEE 802.11b/g/n
networks. The stations and clients must be configured to use the same SSID and security password to associate with the
ECB150. The ECB150 supports up to four SSIDs at the same time for secure guest access.
Page 23

22
4.3 WDS AP Mode
The ECB150 also supports WDS AP mode. This operating mode allows wireless connections to the ECB150 using WDS
technology. In this mode, configure the MAC addresses in both Access Points to enlarge the wireless area by enabling
WDS Link settings. WDS supports four AP MAC addresses.
Page 24
23
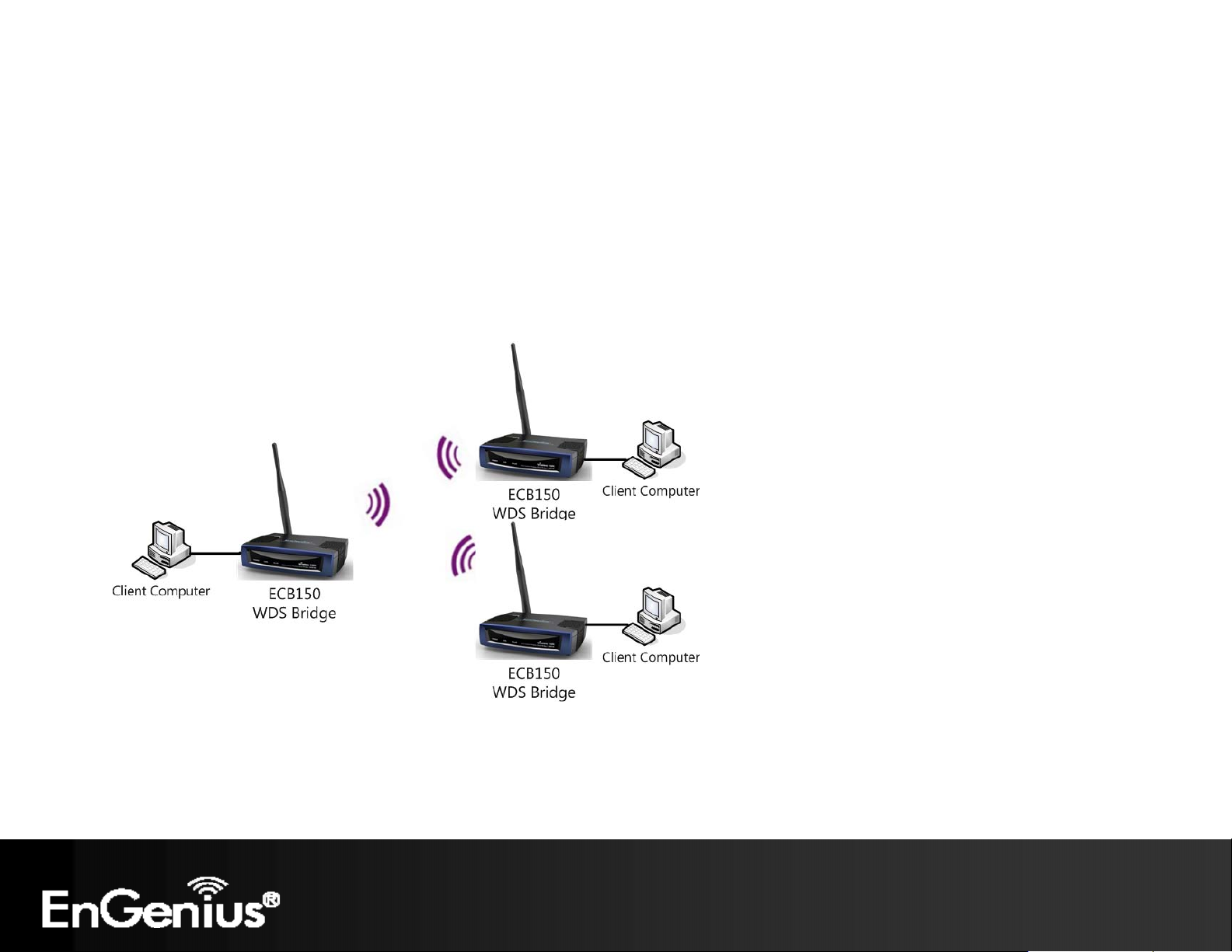
4.4 WDS Bridge Mode
In WDS Bridge Mode, the ECB150 can wirelessly connect different LANs by configuring the MAC address and security
settings of each ECB150 device. Use this mode when two wired LANs located a small distance apart want to communicate
with each other. The best solution is to use the ECB150 to wirelessly connect two wired LANs, as shown in the following
figure.
WDS Bridge Mode can establish four WDS links, creating a star-like network.
Note: WDS Bridge Mode does not act as an Access Point. Access Points linked by WDS are using the same frequency channel. More Access
Points connected together may lower throughput. Please be aware to avoid loops in your wireless connection, otherwise enable Spanning
Tree Function.
Page 25
24
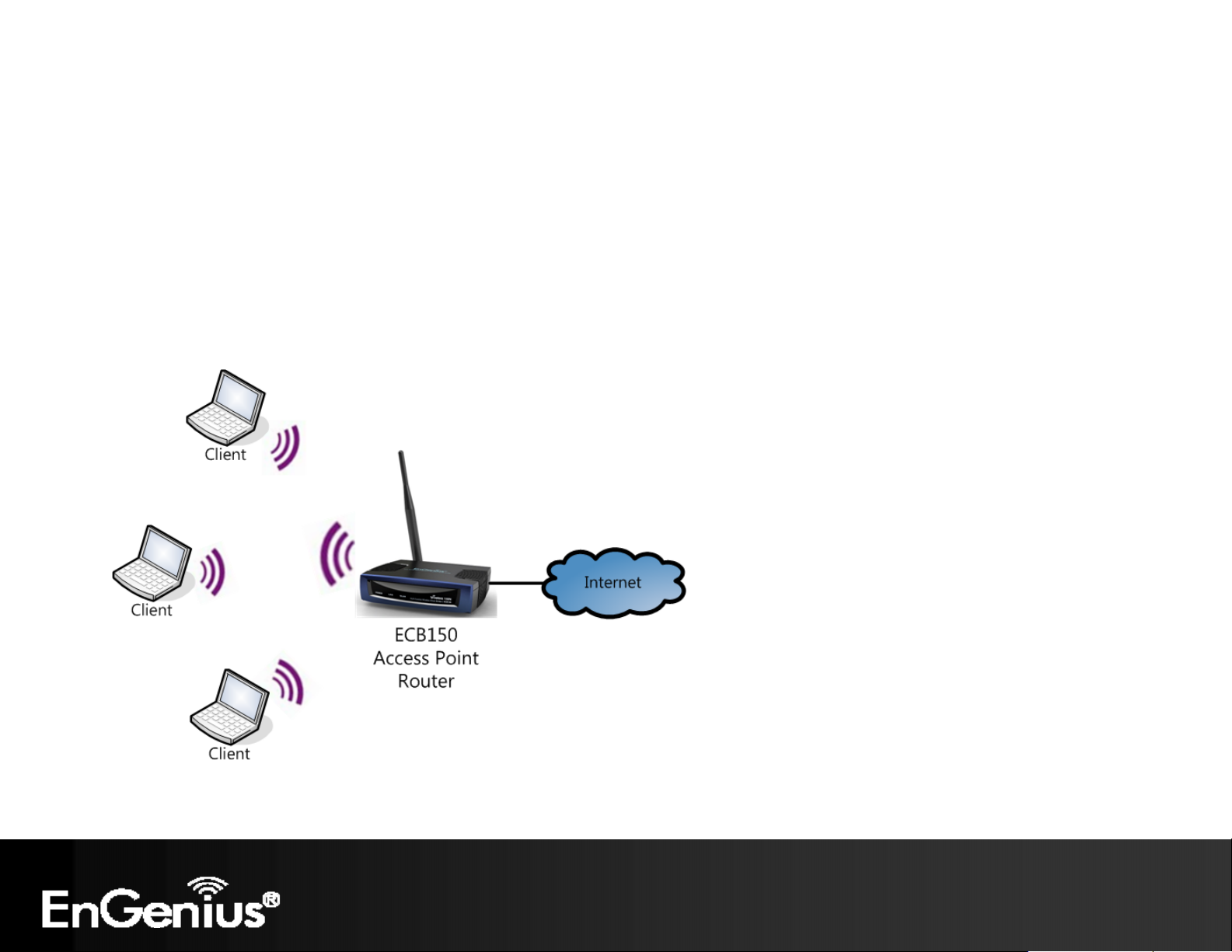
4.5 Router Mode
In Access Point Router Mode, ECB150 grants Internet access to multiple wireless clients. In this mode, the ECB150’s internal
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server automatically allocates ranges of IP addresses to each wireless client
that will access the Internet through the ECB150.
This mode requires you to connect the ECB150’s Ethernet port to a modem or router. And the wireless clients must be
configured to use the same SSID and security password to associate with the ECB150. The ECB150 supports up to four
SSIDs at the same time for secure guest access.
Page 26
25
4.6 Repeater Mode
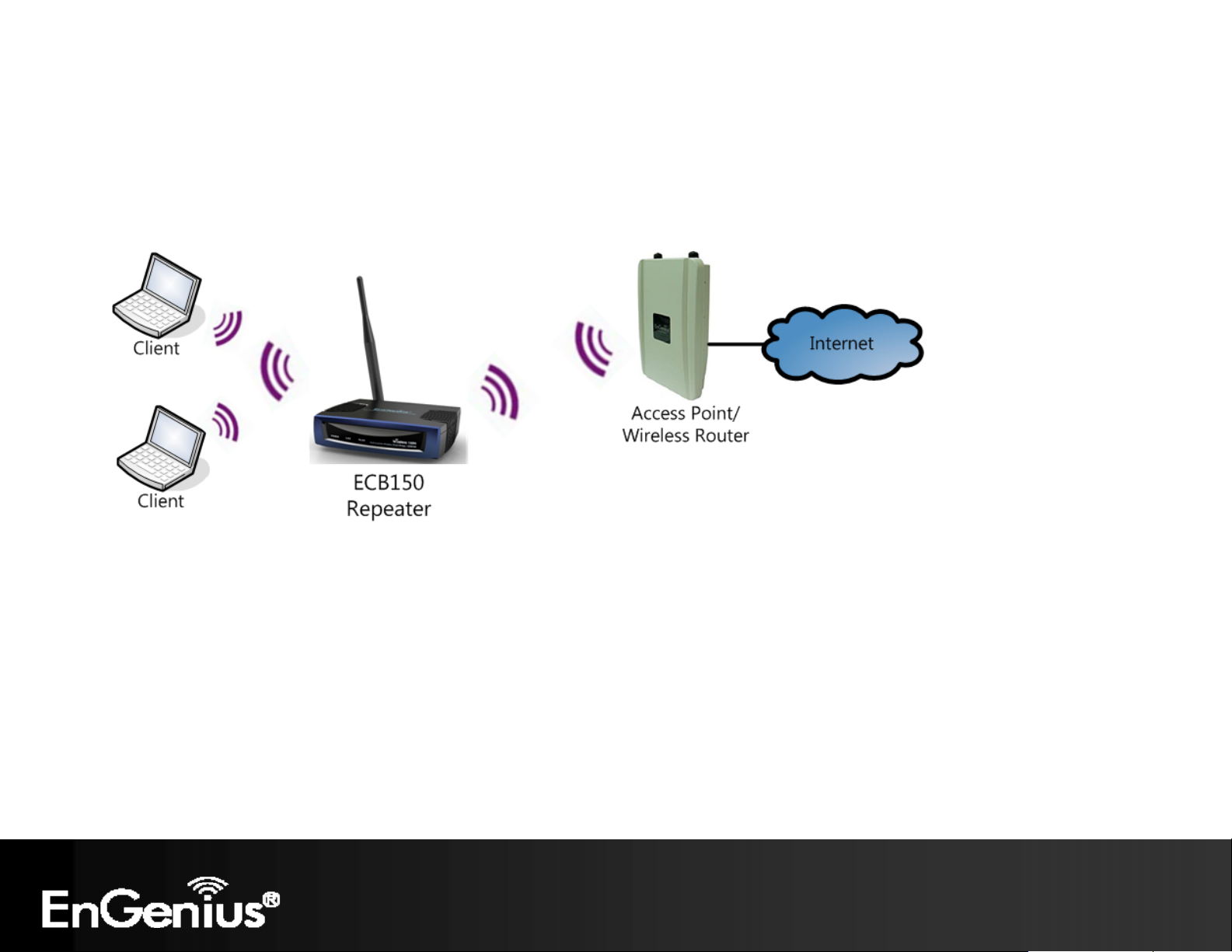
Repeater is used to regenerate or replicate signals that are weakened or distorted by transmission over long distances and
through areas with high levels of electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Page 27
26
5 System
5.1 Operation Mode
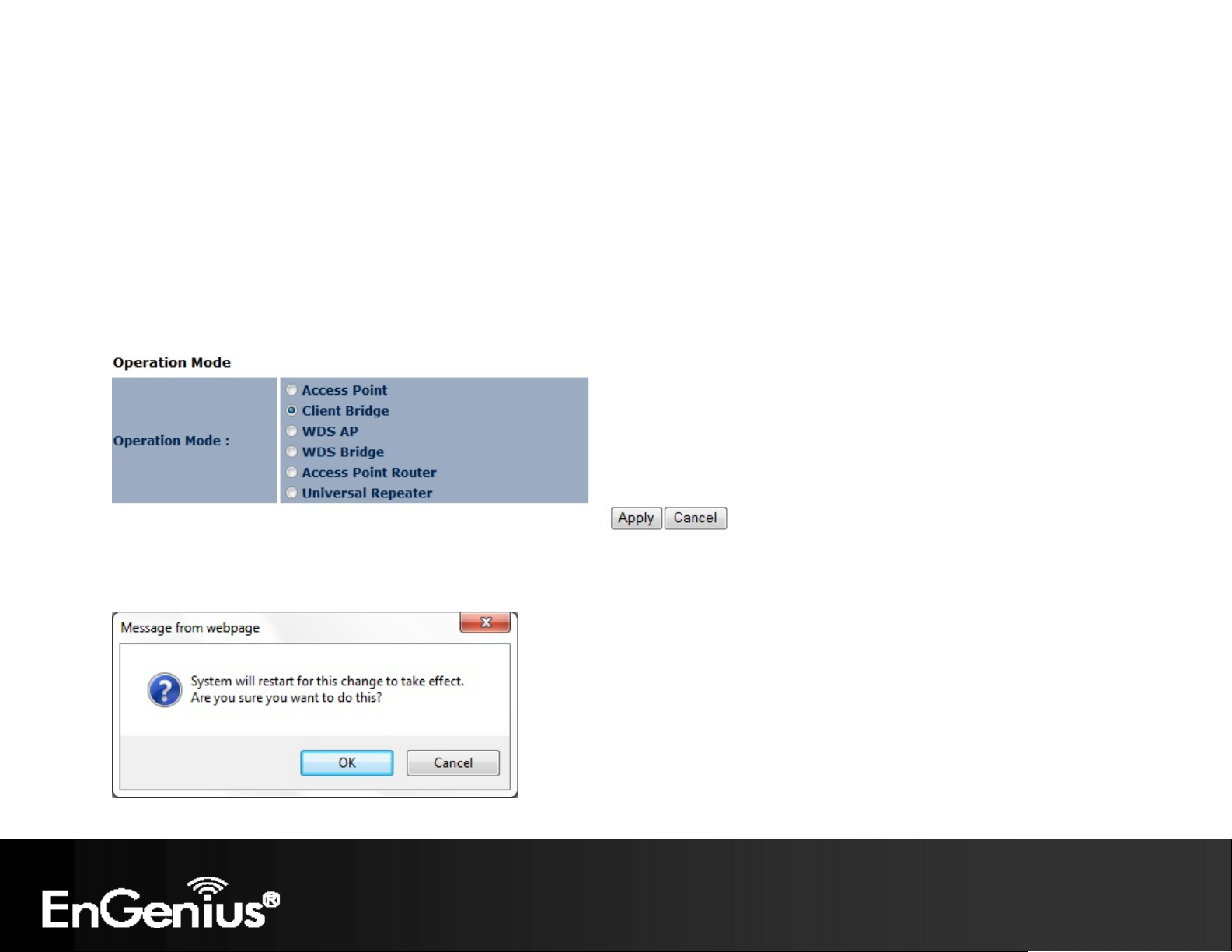
Each operating mode offers different features. In order to switch the operating mode, select it from the Operation Mode
from the System Menu. There are six operation modes: Access Point, Client Bridge, WDS AP, WDS Bridge, Access
Point Router and Universal Repeater.
A dialog box will appear to notify you that the system will restart in order for the changes to take effect. Click on the OK
button to continue.
Page 28
27
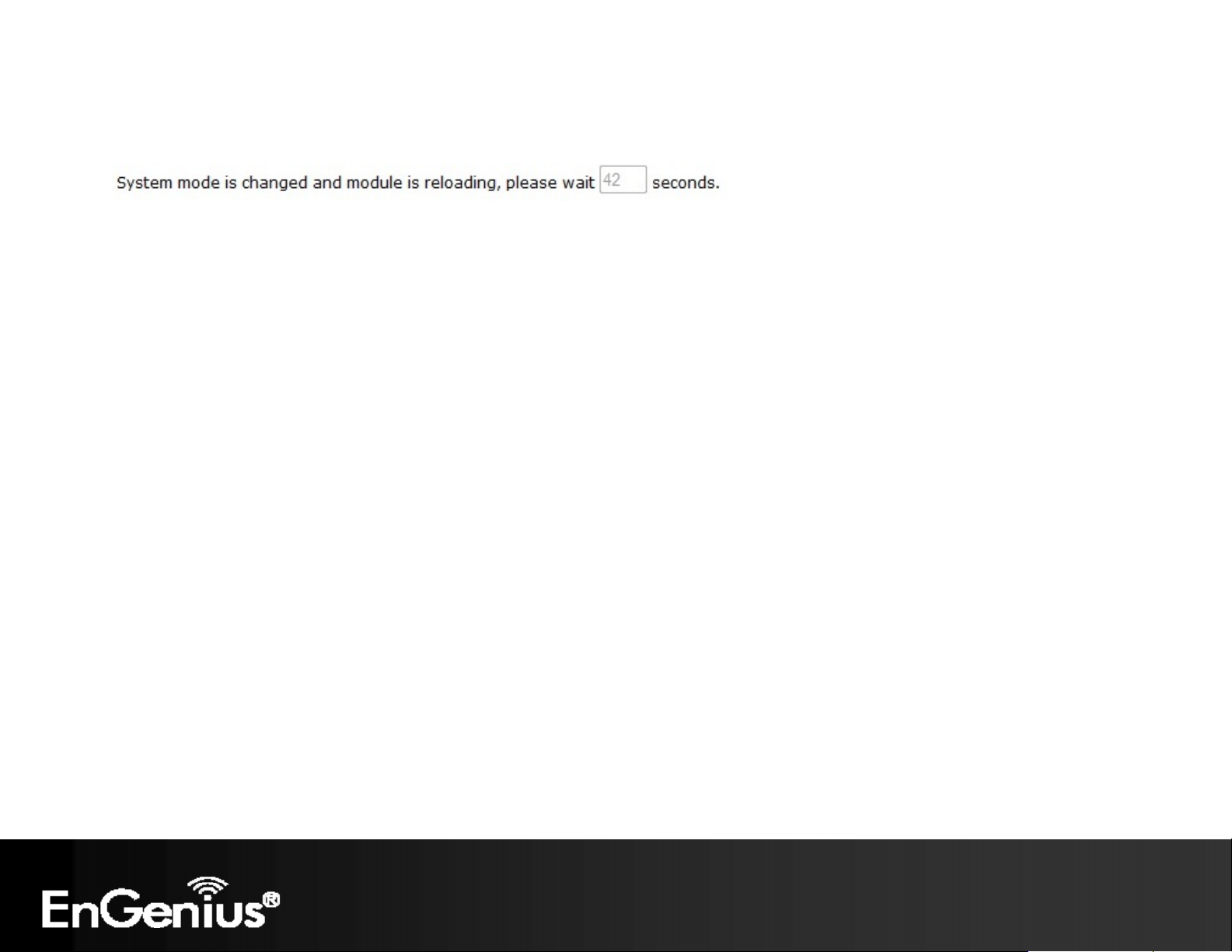
The ECB150 will display how much time it will take to restart the device in the new operating mode as shown below.
Page 29
28
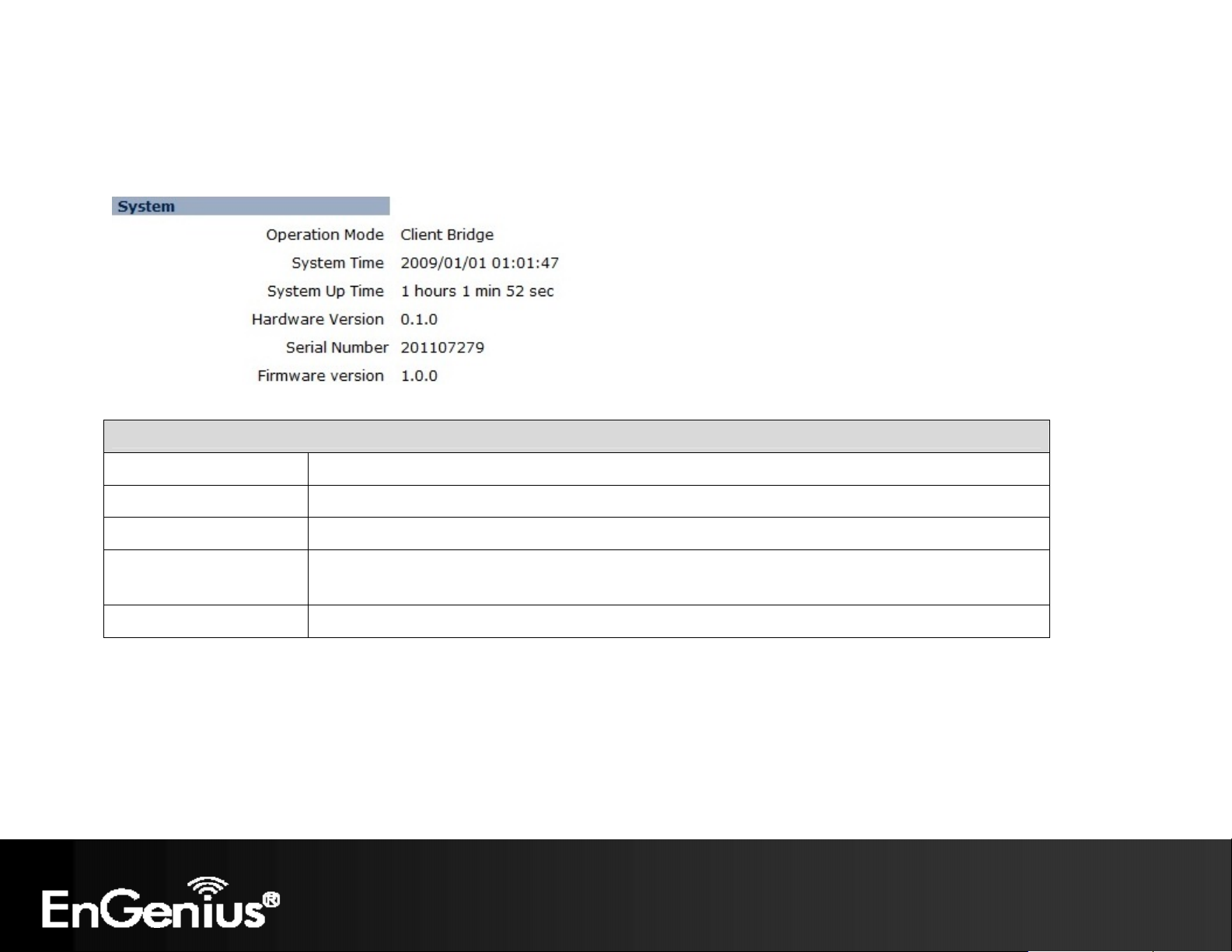
5.2 Status
This page will display status of the device.
System
Operation Mode Displays the current mode of operation of the ECB150.
System Time Displays the current time of the ECB150.
System Up Time The elapsed time of operation of the ECB150.
Hardware Version and
Serial Number
Firmware Version The current firmware version of the ECB150.
Hardware information of the ECB150.
Page 30
29
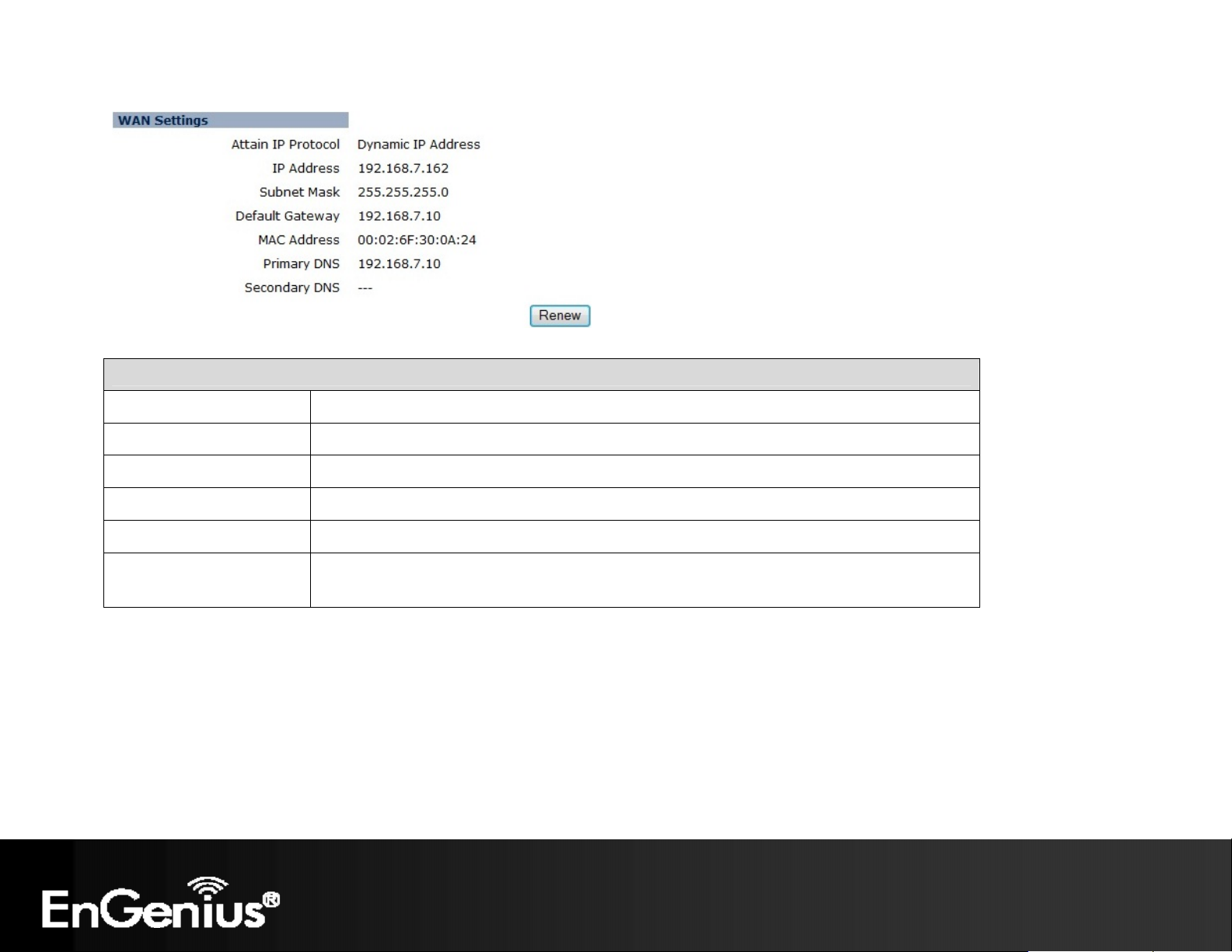
WAN Settings (Router mode)
Attain IP Protocol Method used to connect to the Internet. This is your WAN connection type.
IP Address The WAN IP address of the Router.
Subnet Mask The WAN subnet mask of the Router.
Default Gateway The default gateway of the Router.
MAC Address The WAN MAC address of the Router.
Primary and Secondary
DNS
The IP addresses of the Primary and Secondary DNS servers assigned to the WAN
connection.
Page 31

30
WLAN Station Information (Client Bridge mode)
Connection Status The connection status: Successful or Fail.
Channel The wireless channel in use.
ESSID The SSID (Network Name) of the wireless network which ECB150 connected.
Security The wireless encryption in use.
BSSID The MAC address of this SSID which ECB150 connected.
WLAN Repeater Information (Repeater mode)
Connection Status The connection status: Successful or Fail.
Channel The wireless channel in use.
ESSID The SSID (Network Name) of the wireless network.
Page 32

31
Security Wireless encryption for this SSID.
BSSID The MAC address of this SSID.
WLAN Settings (Access Point / WDS AP / Repeater / Router mode)
Channel Displays the current Wireless Channel in use by the ECB150.
ESSID The SSID (Network Name) of the wireless network (up to 4 SSIDs supported).
Security Current wireless encryption for the corresponding SSID.
The MAC address of the corresponding SSID. BSSID
Page 33

32
5.3 DHCP
The DHCP option in the System menu displays the client IP address assigned by the DHCP Server. You can also set the IP
Addresses of the connected devices manually.
Note: Only in Access Point / Router mode.
Page 34

33
The DHCP Client Table shows the LAN clients that have been allocated an IP address from the DHCP Server.
DHCP Client Table
IP address Displays the IP Address of the client on the LAN.
MAC address Displays the MAC Address of the client on the LAN.
Expiration Time Displays the time of expiration of the IP Address of the client.
Click this button to update the DHCP Client Table. Refresh
Page 35

34
5.4 Schedule
The Schedule option of the System menu allows you to set a schedule when the ECB150’s Wireless is active.
The Schedule Table will display:
NO.: The entry number of the schedule.
Description: The name given to the schedule.
Service: Displays whether the wireless service will be activate or not during the scheduled time.
Schedule: Displays when the schedule will execute.
You will also be able to Add new schedules (at most 10), Edit schedules, Delete Selected schedules, or Delete All
schedules.
Page 36

35
After selecting Add or Edit, the following form will show up. Fill in the form to set the schedule you want.
Schedule
Schedule Description Assign a name to the schedule.
Service The service provided for the schedule.
Days Set which days the schedule will be active.
Set what time of the selected days the schedule will be active. Time of day
Page 37

36
5.5 Event Log
The Event Log of the System menu displays the system events and actions of the ECB150. When powered down or
rebooted, the Event Log will be cleared.
Event Log
Save Save the log to a .txt file.
Clear Clear the log.
Refresh Update the log.
Page 38

37
5.6 Monitor
The Monitor option of the System menu displays 2 histogram graphs. The histograms represent the bandwidth usage of
both the daily use of the Ethernet and the daily use of the WLAN. If you click on Detail, a new browser window will open
with 4 additional histograms (6 total). In the new browser window, you will be able to view the weekly and monthly
bandwidth usage for both the Ethernet and WLAN.
Page 39

38
6 Wireless
6.1 Status
The Status of the Wireless menu displays the current status of the ECB150's wireless configuration.
Client Bridge mode:
Access Point / Router mode:
Page 40

39
Repeater mode:
Page 41

40
6.2 Basic
The Basic option of the Wireless menu displays the basic wireless options of the ECB150.
Client Bridge:
Basic (Client Bridge mode)
Radio Enable or Disable the device’s wireless signal.
Band Select the types of wireless clients that the device will accept.
Site Survey Click on [Site Survey] to search the existing AP.
Page 42

41
Access Point / Router mode:
Basic (Access Point / Router mode)
Radio Enable or Disable the ECB150’s wireless signal.
Mode Select between Access Point or Wireless Distribution System (WDS) modes.
Band Select the types of wireless clients that the device will accept.
Enable SSID# Select the number of SSID’s (Wireless Network names) you would like (up to 4).
SSID# Enter the name of your wireless network. You can use up to 32 characters.
Auto Channel When enabled, the device will scan the wireless signals around your area and select the channel
with the least interference.
Channel Manually select which channel the wireless signal will use.
Page 43

42
Check Channel Time When Auto Channel is Enabled, you can specify the period of device will scan the wireless
signals around your area.
WDS AP / WDS Bridge mode:
Wireless Distribution System (WDS)
Using a WDS to connect Access Points wirelessly extends a wired
infrastructure to locations where cabling is not possible or inefficient
to implement.
Note: Compatibility between different brands and models of Access
Points is not guaranteed. It is recommended that a WDS network be
created using the same Access Point models for maximum
compatibility.
Also, all Access Points in the WDS network need to use the same
Channel and Security settings.
To create a WDS network, please enter the MAC addresses of the Access
Points that you want included in the WDS. There can be a maximum of
four access points.
Page 44

43
Repeater mode:
Basic (Repeater mode)
Radio Enable or Disable the device’s wireless signal.
Band Select the types of wireless clients that the device will accept.
eg: 2.4 Ghz (B+G)
Only 802.11b and 11g clients will be allowed.
ESSID1 Enter the name of your wireless network. You can use up to 32 characters.
Click on [Site Survey] to search the existing AP. Site Survey
Page 45

44
6.3 Site Survey
Client Bridge mode:
1. AP list after site survey.
2. Select an AP and click on [Add to AP Profile].
Page 46

45
3. Enter the correct security setting.
4. Add AP profile successfully, click on [Close] to close the browser.
5. The AP profile is added in AP Profile Table.
Page 47

46
Repeater mode:
1. AP list after site survey.
2. Select an AP and click on [Connect].
3. Enter the correct security setting.
Page 48

47
4. Connect AP successfully, click on [Close] to close the browser.
5. You can see the Connection Status in Status WEB page.
Page 49

48
6.4 Advanced
The Advanced option of the Wireless menu displays the advanced wireless options of the ECB150.
It is recommended that the ECB150’s default settings are used unless the user has experience with advanced networking.
Client Bridge mode:
Advanced (Client Bridge mode)
Fragment Threshold Specifies the maximum size of the packet per fragment. This function can reduce the chance of
packet collision.
However, when the fragment threshold is set too low, there will be increased overhead resulting in
poor performance.
RTS Threshold When the packet size is smaller than the RTS Threshold, the packet will be sent without an
RTS/CTS handshake, which may result in incorrect transmission.
Page 50

49
Access Point / WDS AP / Router / Repeater mode:
Advanced (Access Point / WDS AP / Router / Repeater mode)
Fragment Threshold Specifies the maximum size of the packet per fragment. This function can reduce the chance of
packet collision.
However, when the fragment threshold is set too low, there will be increased overhead resulting in
poor performance.
RTS Threshold When the packet size is smaller than the RTS Threshold, the packet will be sent without an
RTS/CTS handshake, which may result in incorrect transmission.
Beacon Interval The time interval that the device broadcasts a beacon. This beacon is used to synchronize all
wireless clients on the network.
Page 51

50
DTIM Period A Delivery Traffic Indication Message (DTIM) informs all wireless clients that the access point
will be transmitting Multi-casted data.
N Data Rate You can limit the transfer rates between the device and wireless clients. Each Modulation Coding
Scheme (MCS) refers to a specific transfer speed.
Channel Bandwidth Set whether each channel uses 20Mhz or 40Mhz transmission frequency. To achieve 11n speeds,
40Mhz channels must be used.
Preamble Type A preamble is a message that helps access points synchronize with the client.
Long Preamble is standard based so increases compatibility.
Short Preamble is non-standard, resulting in decreased compatibility, but increased performance.
Tx Power Set the power output of the wireless signal.
WDS Bridge mode:
Page 52

51
Advanced (WDS Bridge mode)
Fragment Threshold Specifies the maximum size of the packet per fragment. This function can reduce the chance of
packet collision.
However, when the fragment threshold is set too low, there will be increased overhead resulting in
poor performance.
RTS Threshold When the packet size is smaller than the RTS Threshold, the packet will be sent without an
RTS/CTS handshake, which may result in incorrect transmission.
N Data Rate You can limit the transfer rates between the device and wireless clients. Each Modulation Coding
Scheme (MCS) refers to a specific transfer speed.
Channel Bandwidth Set whether each channel uses 20Mhz or 40Mhz transmission frequency. To achieve 11n speeds,
40Mhz channels must be used.
Preamble Type A preamble is a message that helps access points synchronize with the client.
Long Preamble is standard based so increases compatibility.
Short Preamble is non-standard, resulting in decreased compatibility, but increased performance.
Tx Power Set the power output of the wireless signal.
Page 53

52
6.5 Security
The Security option in the Wireless menu allows you to set the wireless security settings.
Note: Only in Access Point / WDS AP / Router and Repeater mode.
Security (Access Point / WDS AP / Router / Repeater mode)
SSID Selection Select the SSID that the corresponding security settings will apply to.
Separate Separating the SSID from each other (or use of STA) prevents communication and data sharing
between wireless stations associated with the SSIDs.
Broadcast SSID If Disabled, the ECB150 will not broadcast the SSID. It will be invisible to the clients.
WMM Wi-Fi Multi-Media is a Quality of Service protocol which prioritizes traffic in the order according
to voice, video, best effort, and background.
Note: In certain situations, WMM needs to be enabled to achieve 11n transfer speeds.
Page 54

53
Encryption The encryption method to be used on the corresponding SSID.
You can choose between WEP, WPA Pre-Shared Key, or WPA RADIUS.
Disabled - No data encryption is used.
WEP - Data is encrypted using the WEP standard. WEP is the Wired Equivalent Privacy
security over a wireless network.
WPA-PSK - Data is encrypted using the WPA-PSK standard. This is a later standard than WEP,
and provides much better security than WEP. WPA-PSK is Wi-Fi Protected Access using a
Pre-Shared Key. This is the equivalent of password protecting your wireless network.
WPA2-PSK - This is a further development of WPA-PSK, and offers even greater security,
using the AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) method of encryption.
WPA-RADIUS - This version of WPA requires a Radius Server on your LAN to provide the
client authentication according to the 802.1x standard. Data transmissions are encrypted using
the WPA standard.
If this option is selected:
This Access Point must have a Client Login on the Radius Server.
Each user must have a User Login on the Radius Server.
Each user's wireless client must support 802.1x and provide the login data when required.
All data transmission is encrypted using the WPA standard. Keys are automatically
generated, so no key input is required.
IEEE 802.1x is an authentication protocol. Every user must use a valid account to login to this Access Point before accessing the
wireless LAN. The authentication is then processed by a RADIUS server. This mode only authenticates users by IEEE 802.1x, but it does
not encrypt the data during communication.
Page 55

54
802.1x Authentication
RADIUS Server IP
The IP Address of the RADIUS Server.
Address
RADIUS Server port The port number of the RADIUS Server.
RADIUS Server
The RADIUS Server password.
password
Page 56

55
WEP Encryption:
WEP Encryption
Authentication Type Please ensure that your wireless clients use the same authentication type.
Key type ASCII: Using characters from the ASCII standard (recommended)
HEX: Uses hexadecimal characters.
Key Length The amount of bits the WEP key will use.
64 Bit - data is encrypted, using the default key, before being transmitted. You must enter
at least the default key. For 64 Bit Encryption, the key size is 10 chars in HEX (0~9 and A~F).
128 Bit - data is encrypted, using the default key, before being transmitted. You must enter
at least the default key. For 128 Bit Encryption, the key size is 26 chars in HEX (0~9 and A~F).
Default Key Select the key you wish to be the default. Transmitted data is ALWAYS encrypted using the
Default Key; the other Keys are for decryption only.
You must enter a Key Value for the Default Key.
Encryption Key # Enter the key value or values you wish to use. Only the Key selected as Default is required. The
others are optional.
Page 57

56
WPA Pre-Shared Key Encryption:
WPA Pre-Shared Key Encryption
WPA type Select the WPA encryption you would like.
Please ensure that your wireless clients use the same settings.
WPA(TKIP): Uses a Pre-Shared Key with a dynamically generated key for each 128-bit
packet.
WPA2(AES): Government standard of WPA2 encryption.
WPA2 Mixed: Allows the use of both WPA and WPA2 clients on the network.
Pre-shared Key Type Pre-Shared Key format (ASCII or Hexadecimal).
Pre-shared Key Wireless clients must use the same key to associate the device to the ECB150.
If using passphrase format, the Key must be from 8 to 63 characters in length.
Page 58

57
WPA RADIUS Encryption:
WPA RADIUS Encryption
WPA type Select the WPA encryption you would like.
Please ensure that your wireless clients use the same settings.
WPA(TKIP): Uses a Pre-Shared Key with a dynamically generated key for each 128-bit
packet.
WPA2(AES): Government standard of WPA2 encryption.
WPA2 Mixed: Allows the use of both WPA and WPA2 clients on the network.
RADIUS Server IP
address
RADIUS Server Port Enter the port number used for connections to the RADIUS server.
password
Enter the IP address of the RADIUS Server.
Enter the password required to connect to the RADIUS server. RADIUS Server
Page 59

58
6.6 Filter
The Filter option in the Wireless menu allows users to allow clients with specific MAC Addresses to join the SSID.
Note: Only in Access Point / WDS AP / Router and Repeater mode.
Wireless MAC Filter (Access Point / WDS AP / Router / Repeater mode)
Enable Wireless Access
Control
Description Enter a name or description for this entry.
MAC Address Enter the MAC address of the wireless client that you wish to allow connection.
Enable Wireless Access Control.
When Enabled, only wireless clients on the Filtering Table will be allowed.
Page 60

59
Add Click this button to add the entry.
Reset Click this button if you have made a mistake and want to reset the MAC address and
Description fields.
MAC Address Filtering Table
Only clients listed in this table will be allowed access to the wireless network.
Delete Selected Delete the selected entries.
Delete All Delete all entries.
Reset Deselect all entries.
Page 61

60
6.7 WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup)
The WPS feature in the Wireless menu follows the Wi-Fi Alliance WPS standard. It eases the set up of security-enabled
Wi-Fi networks in homes and/or small office environments.
It reduces the user steps required to configure a network and supports two methods that are familiar to most consumers
to configure a network and enable security.
Note: Only in Access Point / WDS AP and Router mode.
Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS)
WPS Check to Enable the WPS feature.
Wi-Fi Protected Setup Information
WPS Current Status Shows whether the WPS function is Configured or Un-configured.
Configured means that WPS has been used to authorize connection between the ECB150 and
the wireless clients.
Page 62

61
SSID The SSID (network name) used when connecting using WPS.
Authentication Mode Shows the encryption method used by the WPS process. This is set as the mode selected in the
Security option in the Wireless menu.
Passphrase Key This is the passphrase key that is randomly generated during the WPS process. It is required if
wireless clients that do not support WPS attempts to connect to the wireless network.
WPS Via Push Button Activate WPS using a push button.
WPS Via PIN Activate WPS using the PIN code from the WPS device.
Page 63

62
6.8 Client List
The Client List option of the Wireless menu shows all the wireless clients that are currently connected to the ECB150.
Note: Only in Access Point / WDS AP / Router and Repeater mode.
Page 64

63
6.9 VLAN
The VLAN option of the Wireless menu allows you to configure the VLAN (Virtual LAN).
Note: Only in Access Point mode.
VLAN (Access Point and WDS AP mode)
Virtual LAN Choose to Enable or Disable the VLAN feature.
SSID# Tag Specify the VLAN tag for each SSID.
LAN VLAN MGMT Choose to Enable or Disable the LAN VLAN MGMT feature.
MGMT Tag Specify the VLAN tag for the LAN.
Page 65

64
6.10 AP Profile
This page allows you to configure the profile of the Client Bridge including Security Setting exactly the same as the Access
Point. You can save three AP profiles at most.
Note: Only in Client Bridge mode.
AP Profile Table (Client Bridge mode)
Add / Edit Select a profile to add or edit.
Move Up / Move Down Select a profile to move up or move down.
Delete Selected Delete the selected entries.
Delete All Delete all entries
Connect Select a profile to connect.
Page 66

65
AP Profile Settings
Network Name (SSID) Enter the SSID (Network Name) of the wireless network which ERB9260 want to connect.
Encryption The encryption method to be applied.
You can choose from Disable, WEP, WPA pre-shared key and RADIUS.
Please select the correct security type.
Page 67

66
7 Network
7.1 Status
The Status option of the Network menu shows the current status of the ECB150’s LAN and WAN (Router mode)
connection.
Page 68

67
7.2 LAN
The LAN option of the Network menu allows you to modify the device's LAN settings.
The LAN setting in Router mode:
There is additional setting Default Gateway in Access Point / Client Bridge / WDS AP / WDS Bridge and Repeater mode.
Page 69

68
LAN IP
Bridge Type Select the Bridge type of the LAN.
Static IP: Manually specify an IP address and subnet mask for the ECB150 to use.
Dynamic IP: The IP address is received automatically from the external DHCP server.
Note: The option: Dynamic IP is only in Access Point and WDS AP mode.
IP Address The LAN IP Address of this device.
IP Subnet Mask The LAN Subnet Mask of this device.
Default Gateway The Default Gateway of the device. Leave empty for default setting.
Note: The option: Dynamic IP is only in Access Point / Client Bridge / WDS AP / WDS Bridge
and Repeater mode.
DNS Type Select the DNS type of the LAN.
Static: Manually specify the DNS of the ECB150.
Dynamic: The DNS is received automatically from the external DNS server.
Note: The option: Dynamic is only in Access Point and WDS AP mode.
First / Second DNS
Address
The first / second DNS address for this device.
Page 70

69
The DHCP Server feature is only available in Access Point and Router mode.
DHCP Server (Access Point / Router mode)
DHCP Server Enable or disable DHCP feature. The DHCP Server automatically allocates IP addresses to your
LAN device. Disabled as default.
Lease Time The duration of the DHCP server allocates each IP address to a LAN device.
Start / End IP The range of IP addresses of the DHCP server will allocate to LAN device.
Domain name The domain name for this LAN network.
The first / second DNS address for this LAN network. First / Second DNS
Address
Page 71

70
7.3 Spanning Tree
The Spanning Tree option of the Network menu allows you to set the ECB150 to use the Spanning Tree Protocol.
Enabling Spanning Tree Protocol will prevent network loops in your LAN network.
Note: Only in Access Point / Client Bridge / WDS AP / WDS Bridge and Repeater mode.
Spanning Tree Settings
Spanning Tree Status Enable or disable the Spanning Tree Protocol.
Bridge Hello Time The duration of the initial connection between two access points.
Bridge Max Age The maximum amount of time the bridge is connected when transmitting.
Bridge Forward Delay The delay between transmissions between access points.
Bridge Priority The priority port of the Spanning Tree Protocol.
Page 72

71
7.4 WAN (Router mode)
The WAN section allows you to manually set the WAN type connection and its related settings.
Note: Only in Router mode.
7.4.1 Static IP Address
If your ISP Provider has assigned you a fixed IP address, enter the assigned IP address, Subnet mask, Default Gateway IP
address, and Primary DNS and Secondary DNS (if available) of your ISP provider.
Static IP Address
IP Address Assign an IP address Manually.
IP Subnet Mask Specify an IP address’s subnet mask.
Default Gateway Specify the gateway of your network.
Primary DNS Specify the primary DNS server’s IP address.
Secondary DNS Specify the second DNS server’s IP address.
Page 73

72
7.4.2 Dynamic IP Address
The IP Address is allocated automatically. However some ISP’s will also recognize the MAC address and will reject
connections if the MAC address does not match.
If your ISP has recorded the MAC address of your computer’s Ethernet LAN card, please connect only the computer with
the authorized MAC address, and click the Clone MAC button.
Note: This will replace the WAN MAC address to the computer MAC address. The correct MAC address is used to initiate the connection to the ISP.
Dynamic IP Address
Hostname This is optional. Only required if specified by ISP
MAC Address The MAC Address that is used to connect to the ISP.
Page 74

73
7.4.3 PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE)
This protocol is used by most DSL services worldwide.
Select this option if you have a DSL connection.
Enter the username and password provided by your ISP.
PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE)
Login Username assigned to you by the ISP
Password Password for this username.
Service Name You can assign a name for this service. (Optional)
MTU The maximum size of packets.
Do not change unless mentioned by the ISP.
Type You can choose the method that the router maintains connection with the ISP.
Keep Connection: The device will maintain a constant connection with the ISP.
Automatic Connection: The device will only initiate connection to the ISP when there is an
Internet connection request made from a LAN device.
Manual Connection: The user will need to manually connect to the ISP by clicking the Connect
button.
Idle Timeout: When the connection type is Automatic Connection, when Internet traffic is idle, then the
device will automatically disconnect from the ISP.
Please specify the Idle time in minutes.
Page 75

74
7.4.4 Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)
PPTP is used by very few ISPs.
Page 76

75
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)
WAN Interface Type Select whether the ISP is set to Static IP or will allocate Dynamic IP address.
Hostname This is optional. Only required if specified by ISP
MAC address The MAC Address that is used to connect to the ISP.
Login Username assigned to you by the ISP
Password Password for this username.
Service IP Address The IP Address of the PPTP server.
Connection ID This is optional. Only required if specified by ISP
MTU The maximum size of packets.
Do not change unless mentioned by the ISP.
Type You can choose the method that the router maintains connection with the ISP.
Keep Connection: The device will maintain a constant connection with the ISP.
Automatic Connection: The device will only initiate connection to the ISP when there is an
Internet connection request made from a LAN device.
Manual Connection: The user will need to manually connect to the ISP by clicking the Connect
button.
Idle Timeout: When the connection type is Automatic Connection, when Internet traffic is idle, then the
device will automatically disconnect from the ISP.
Please specify the Idle time in minutes.
Page 77

76
8 Firewall
The Firewall section allows you to set the access control and Firewall settings.
Note: Only in Router mode.
8.1 Enable
This page allows you to Enable / Disable the Firewall features.
If enabled Firewall service, the Denial of Service (DoS) and SPI (Stateful Packet Inspection) features will also be enabled.
Page 78

77
8.2 DMZ
If enabled this feature, allows the DMZ computer on your LAN to be exposed to all users on the Internet.
This allows almost any application to be used on the server.
The “DMZ PC” will receive all Unknown connections and data.
If the DMZ feature is enabled, please enter the IP address of the PC to be used as the “DMZ PC”
Note: The “DMZ PC” is effectively outside the Firewall, making it more vulnerable to attacks. For this reason, you should only enable the DMZ
feature when required.
Page 79

78
8.3 DoS
Denial of Service (Denial of Service) is a type of Internet attack that sends a high amount of data to you with the intent to
overload your Internet connection.
Enable the DoS firewall feature to automatically detect and block these DoS attacks.
Page 80

79
8.4 MAC Filter
You can choose whether to Deny or only Allow those computers listed in the MAC Filtering table to access the Internet.
MAC Filter
Enable MAC filtering Tick this box to Enable the MAC filtering feature.
Deny all clients with MAC addresses
listed below to access the network
Allow all clients with MAC addresses
listed below to access the network
When selected, the computers listed in the MAC Filtering table will be Denied
access to the Internet.
When selected, only the computers listed in the MAC Filtering table will be
Allowed access to the Internet.
Page 81

80
8.5 IP Filter
You can choose whether to Deny or only Allow, computer with those IP Addresses from accessing certain Ports.
This can be used to control which Internet applications the computers can access.
You may need to have certain knowledge of what Internet ports the applications use.
Page 82

81
IP Filter
Enable IP filtering Tick this box to Enable the IP filtering feature.
Deny all clients with IP addresses
listed below to access the network
Allow all clients with IP addresses
listed below to access the network
When selected, the computers with IP addresses specified will be Denied access to
the indicated Internet ports.
When selected, the computers with IP addresses specified will be Allowed access
only to the indicated Internet ports.
Page 83

82
8.6 URL Filter
You can deny access to certain websites by blocking keywords in the URL web address.
For example, “gamer” has been added to the URL Blocking Table. Any web address that includes “gamer” will be blocked.
Page 84

83
9 Advanced
The Advanced section allows you to configure the Advanced settings of the router.
Note: Only in Access Point Client Router mode.
9.1 Network Address Translation (NAT)
This page allows you to Enable / Disable the Network Address Translation (NAT) feature. The NAT is required to share one
Internet account with multiple LAN users.
Page 85

84
9.2 Port Mapping
Port Mapping allows you to redirect a particular range of
ports to a computer on your LAN network. This helps you
host servers behind the NAT and Firewall.
In the example below, there is a FTP Server that requires
ports 21 to 22.
When there is a connection from the Internet on those
ports, it will be redirected to the FTP Server at IP address
192.168.1.100.
Port Mapping
Enable Port Mapping Check this box to enable the Port Mapping feature.
Description Enter a name or description for this entry.
Local IP The local IP address of the computer the server is hosted on.
Protocol Select to apply the feature to TCP, UDP or Both types of packet transmissions.
Port Range The range of ports that this feature will be applied to.
Page 86

85
9.3 Port Forwarding
Port Forwarding allows you to redirect a particular public
port to a computer on your LAN network. This helps you
host servers behind the NAT and Firewall.
In the example below, there is a Web Server running on port
80 on the LAN.
For security reasons, the Administrator would like to provide
this server to Internet connection on port 100.
Therefore when there is a connection from the Internet on
port 100, it will be forwarded to the computer with the IP
address 192.168.1.150 and changed to port 80.
Port Forwarding
Enable Port Forwarding Check this box to enable the Port Forwarding feature.
Description Enter a name or description for this entry.
Local IP The local IP address of the computer the server is hosted on.
Protocol Select to apply the feature to TCP, UDP or Both types of packet transmissions.
Local Port The port that the server is running on the local computer.
Forwarded Port When a connection from the Internet is on this port, it will be forwarded to the indicated local IP
address.
Page 87

86
9.4 Port Triggering
If you use Internet applications which use non-standard
connections or port numbers, you may find that they do not
function correctly because they are blocked by the Wireless
Router's firewall. Port Triggering will be required for these
applications to work.
Port Triggering
Enable Port Triggering Check this box to enable the Port Trigger feature.
Popular Applications This is a list of some common applications with preset settings.
Select the application and click Add to automatically enter the settings.
Trigger Port This is the outgoing (outbound) port numbers for this application.
Trigger Type Select whether the application uses TCP, UDP or Both types of protocols for outbound
transmissions.
Forwarded Port These are the inbound (incoming) ports for this application.
Public Type Select whether the application uses TCP, UDP or Both types of protocols for inbound transmissions.
Page 88

87
9.5 Application Layer Gateway (ALG)
Certain applications may require the use of the ALG feature to function correctly. If you use any of the applications listed
on the table below, select the feature and click Apply.
Page 89

88
9.6 Universal Plug and Play (UPnP)
The UPnP function allows automatic discovery and configuration of UPnP enabled devices on your network. It also
provides automatic port forwarding for supported applications to seamlessly bypass the Firewall.
Page 90

89
9.7 Quality of Service (QoS)
QoS allows you to control the priority that the data is transmitted over the Internet, or to reserve a specific amount of
Internet bandwidth. This is to ensure that applications get enough Internet bandwidth for a good user experience.
QoS
Priority Queue Sets the QoS method to Priority Queue.
Bandwidth Allocation Sets the QoS method to Bandwidth Allocation.
Disabled Disables the QoS feature.
Page 91

90
Priority Queue Method
Bandwidth priority is set to either High or Low. The
data transmissions in the High Priority queues will
be processed first.
Unlimited Priority Queue
IP Address The computer with this IP Address will not be bound by the QoS rules.
High / Low Priority Queue
Protocol The type of network protocol.
High / Low Priority Sets the protocol to High or Low priority.
Specific Port Each protocol uses a specific port range.
Please specify the ports used by this protocol.
Page 92

91
Bandwidth Allocation Method
You can set the maximum amount of bandwidth a
certain protocol will use at one time. Or you can
set a minimum amount of bandwidth that will be
guaranteed to a certain protocol.
Bandwidth Allocation
Type Set whether the QoS rules apply to transmission that are Download, Upload or Both directions.
IP range Enter the IP address range of the computers that you would like the QoS rules to apply to.
Protocol Select from this list of protocols to automatically set the related port numbers.
Port Range Each protocol uses a specific port range. Specify the ports used by this protocol.
Policy
Choose whether this rule is to set a limit on the Maximum amount of bandwidth allocated to the
specified protocol, or to set the guaranteed Minimum amount of bandwidth for the protocol.
Page 93

92
9.8 Static Routing
If your wireless router is connected to a network
with different subnets, this feature will allow the
different subnets to communicate with each
other.
Note: The NAT function needs to be disabled for the
Routing feature to be enabled.
Static Routing
Enable Static Routing Check this box to enable the Static Router feature.
Destination LAN IP Enter the IP address of the destination LAN.
Subnet Mask Enter the Subnet Mask of the destination LAN IP address
Default Gateway Enter the IP address of the Default Gateway for this destination IP and Subnet.
Page 94

93
9.9 Dynamic Routing
Dynamic routing allows routing tables in routers to change as the possible routes change. This device use RIP to support
dynamic routing.
Page 95

94
9.10 Routing Table
This page allows you to observe the current routing table.
Page 96

95
10 Management
10.1 Admin
The Admin section of the Management menu allows you to change the ECB150 default password and to configure
remote management (Router mode). By default, the password is: admin. The password can contain 0 to 12 alphanumeric
characters and is case sensitive.
Change Password
Old Password Enter the current password.
New Password Enter your new password.
Confirm Password Re-enter your new password.
Idle Timeout Enter Administration Page timeout time (minutes).
Page 97

96
There is additional setting Remote Management in Router mode.
Remote Management (Router mode)
Host Address
Port Enter the port number you want to accept remote management connections.
You can only perform remote management from the specified IP address. Leave blank to allow any
host to perform remote management.
Tick to Enable the remote management feature. Enable
Page 98

97
10.2 SNMP
The SNMP section of the Management menu allows you to assign the contact details, location, community name, and
trap settings for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). The SNMP is a networking management protocol
used to monitor network-attached devices. SNMP allows messages (called protocol data units) to be sent to various parts
of a network. Upon receiving these messages, SNMP-compatible devices (Agents) return data stored in their Management
Information Bases.
Page 99

98
SNMP
SNMP Active Enable or disable the SNMP feature.
SNMP Version You may select the SNMP version you want to deploy.
All: Interoperability between SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c devices.
v1: The standard SNMP version.
v2c: Improvement in performance and security of SNMPv1.
Read Community Specify the password for access the SNMP community for read only access.
Set Community Specify the password for access to the SNMP community with read/write access.
System Location Specify the location of the device.
System Contact Specify the contact details of the device
Trap
Trap Active Enable or disable SNMP trapping feature.
Trap Manager IP Specify the IP address of the computer that will receive the SNMP traps.
Trap Community Specify the password for the SNMP trap community.
Page 100

99
10.3 Firmware Upgrade
The Firmware Upgrade section of the Management allows you to upgrade the ECB150's firmware.
To perform the Firmware Upgrade:
1. Download the firmware version that you want to install into the ECB150 and place it in a known location.
2. Click the Browse button and navigate to the location of the firmware upgrade file.
3. Select the firmware upgrade file. Its name will appear in the Upgrade File field.
4. Click the Apply button to commence the firmware upgrade.
Note: The device is unavailable during the upgrade process, and must restart when the upgrade is completed. Any connections to or through the
device will be lost.
 Loading...
Loading...