Page 1

Instruction Manual
Form 589
April 2008
Type 99 Pressure Reducing Regulators
Introduction
Scope of the Manual
This manual describes and provides instructions and
parts lists for Type 99 pressure reducing regulators
complete with standard P590 Series integral lter.
However, complete instructions and parts listing for the
Type 1301F pilot supply regulator, and other Fisher®
equipment, such as monitoring pilots will be found in
separate instruction manuals.
Description
The Type 99 gas regulators provide a broad capacity
for controlled pressure ranges and capacities
in a wide variety of distribution, industrial, and
commercial applications.
Type 99
A Type 99 regulator has a Type 61L (low pressure),
Type 61H (high pressure), or a Type 61HP (extra
high pressure) pilot integrally mounted to the actuator
casing as shown in Figure 1. The Type 99 regulator
can handle up to 1000 psig (69,0 bar) inlet pressures
(the 1000 psig (69,0 bar) regulator requires a
Type 1301F pilot supply regulator and a Type H110 pop
relief valve). The pilot supply regulator reduces inlet
pressure to a usable 200 psig (13,8 bar) for the extra
high pressure pilot. This regulator comes standard with
O-ring seals on the guide bushing and valve carrier
(key 26, Figure 7) to keep main valve body outlet
pressure from interfering with outlet pressure in the
lower casing assembly (key 29, Figure 9).
Specications
WARNING
!
Since a pilot-operated regulator is
constructed of both a pilot and a main
valve, care should be used not to exceed
W2676
Figure 1. Type 99 Regulator with Type 61H (high pressure) Pilot
the maximum inlet pressure shown on
the nameplate of either unit. When inlet
pressure exceeds the pilot limitation, a
pilot supply reducing regulator and/or
relief valve will be required.
Specications and ratings for various Type 99
constructions are listed in the Specications section
on page 2. Some specications for a given regulator
as it originally comes from the factory are stamped
on nameplates located on the pilot and actuator
spring cases. A tag (key 159, Parts List) additionally
may be installed on the pilot to indicate a regulator
with O-ring stem seal. These regulators and their
installations should be checked for compliance with
applicable codes.
www.emersonprocess.com/regulators
D100260X012
Page 2
Type 99
Specications
Body Size and End Connection Styles
2-inch (DN 50) body with NPT; CL125, CL150,
CL250, or CL300 anged; or SWE
Maximum Allowable Inlet Pressure
(1)
160 psig (11,0 bar): When using Type 61LD pilot
400 psig (27,6 bar): When using Types 61L/
61H pilots
600 psig (41,4 bar): Type 61HP pilot
Maximum Actuator Pressures
Operating: 100 psig (6,90 bar)
Emergency: 110 psig (7,58 bar)
Maximum Pilot Spring Case Pressure for
Pressure Loading
Types 61L, 61LD
(1, 2)
(3)
with special steel closing cap
Types 61H and 61HP: 100 psi (6,90 bar)
(5/8-inch (15,9 mm) orice maximum)
1000 psig (69,0 bar): Type 61HP pilot, along with
Type 1301F pilot supply regulator and Type H110
relief valve (1/2-inch (12,7 mm) orice only)
Outlet (Control) Pressure Ranges
See Table 1
Approximate Proportional Bands
See Table 2
Maximum Allowable Pressure Drop
(1)
See Table 3
Minimum Differential Pressure Required for
Full Stroke
See Table 3
Maximum Rated Travel
1/4-inch (6,35 mm)
Temperature Capabilities
With Nitrile (NBR) / Neoprene (CR):
-20° to 180°F (-29° to 82°C)
With Fluorocarbon (FKM):
0° to 300°F (-18° to 149°C)
1. The pressure/temperature limits in this Instruction manual and any applicable standard or code limitation should not be exceeded.
2. For stability or overpressure protection, a pilot supply regulator may be installed in the pilot supply tubing between the main valve and pilot.
3. Type 61LD construction has narrower proportional band than does the standard Type 61L pilot.
4. Type 61LE construction has broader proportional band than does the standard Type 61L pilot.
(1)
, and 61LE
(1)
(4)
: 50 psi (3,45 bar)
Table 1. Outlet Pressure Ranges
PILOT
TYPE
61L 400 (27,6)
61LD
61LE
61H 400 (27,6) 10 to 65 psig (0,69 to 4,48 bar) 0Y0664000A2 Green stripe 0.363 (0,92) 6 (15,2)
61HP 600 (41,4) 35 to 100 psig (2,41 to 6,90 bar) 1D387227022 Blue 0.200 (0,51) 1-11/16 (4,29)
1. Type 61LD construction has narrower proportional band than does the standard Type 61L Pilot.
2. Type 61LE construction has broader proportional band than does the standard Type 61L Pilot.
MAXIMUM PILOT
SUPPLY PRESSURE,
PSIG (bar)
(1)
(2)
160 (11,0)
400 (27,6)
OUTLET (CONTROL)
PRESSURE RANGES
2 to 4-inches w.c.
3 to 12-inches w.c.
0.25 to 2 psig
1 to 5 psig
2 to 10 psig
5 to 15 psig
10 to 20 psig
(5 to 10 mbar)
(7 to 30 mbar)
(0,02 to 0,14 bar)
(0,07 to 0,34 bar)
(0,14 to 0,69 bar)
(0,34 to 1,03 bar)
(0,69 to 1,38 bar)
Part Number Color Code
1B558527052
1C680627222
1B886327022
1J857827022
1B886427022
1J857927142
1B886527022
PILOT CONTROL SPRING
Wire Diameter,
Inches (cm)
Orange
Unpainted
Red
Yellow
Blue
Brown
Green
0.075
0.080
0.109
0.142
0.172
0.187
0.363
(0,19)
(0,20)
(0,28)
(0,36)
(0,44)
(0,47)
(0,92)
Free Length,
Inches (cm)
4-1/8
3-1/4
2-3/4
2-3/4
2-7/8
2-7/8
3-1/8
Table 2. Proportional Bands
PILOT TYPES
61LD
61L 1B886327022 Red 0.109 (0,28) 2-3/4 (7,00) 1 to 2-inches w.c. (2 to 5 mbar)
61LD 1B886327022 Red 0.109 (0,28) 2-3/4 (7,00) 0.25 to 1-inch w.c. (0,62 to 2 mbar)
61LE 1B886327022 Red 0.109 (0,28) 2-3/4 (7,00) 5 to 8-inches w.c. (12 to 20 mbar)
61L, 61LD, 61LE
61H 0Y0664000A2 Green stripe 0.363 (0,92) 6 (15,2) 0.1 to 0.3 psi (0,007 to 0,02 bar)
61HP 1D387227022 Blue 0.200 (0,51) 1-11/16 (4,29) 1 to 2 psi (0,069 to 0,14 bar)
Part Number Color Code
1B558527052
1C680627222
1B886527022
1J857927142
1B886427022
1J857827022
PILOT CONTROL SPRING
Wire Diameter,
Inches (cm)
Orange
Unpainted
Green
Brown
Blue
Yellow
0.075 (0,19)
0.080 (0,20)
0.207 (0,53)
0.187 (0,47)
0.172 (0,44)
0.142 (0,36)
Free Length,
Inches (cm)
4-1/8 (10,5)
3-1/4 (8,26)
3-1/8 (7,94)
2-7/8 (7,30)
2-7/8 (7,30)
2-3/4 (7,00)
PROPORTIONAL BANDS
0.1 to 0.5-inch w.c. (0,25 to 1,0 mbar)
0.1 to 0.3 psi (0,007 to 0,02 bar)
(10,5)
(8,26)
(7,00)
(7,00)
(7,30)
(7,30)
(7,94)
2
Page 3
Type 99
A6469
Type 99
Type 99
A6469
January 2008
Type 99
INLET PRESSURE
OUTLET PRESSURE
LOADING PRESSURE
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
A6814
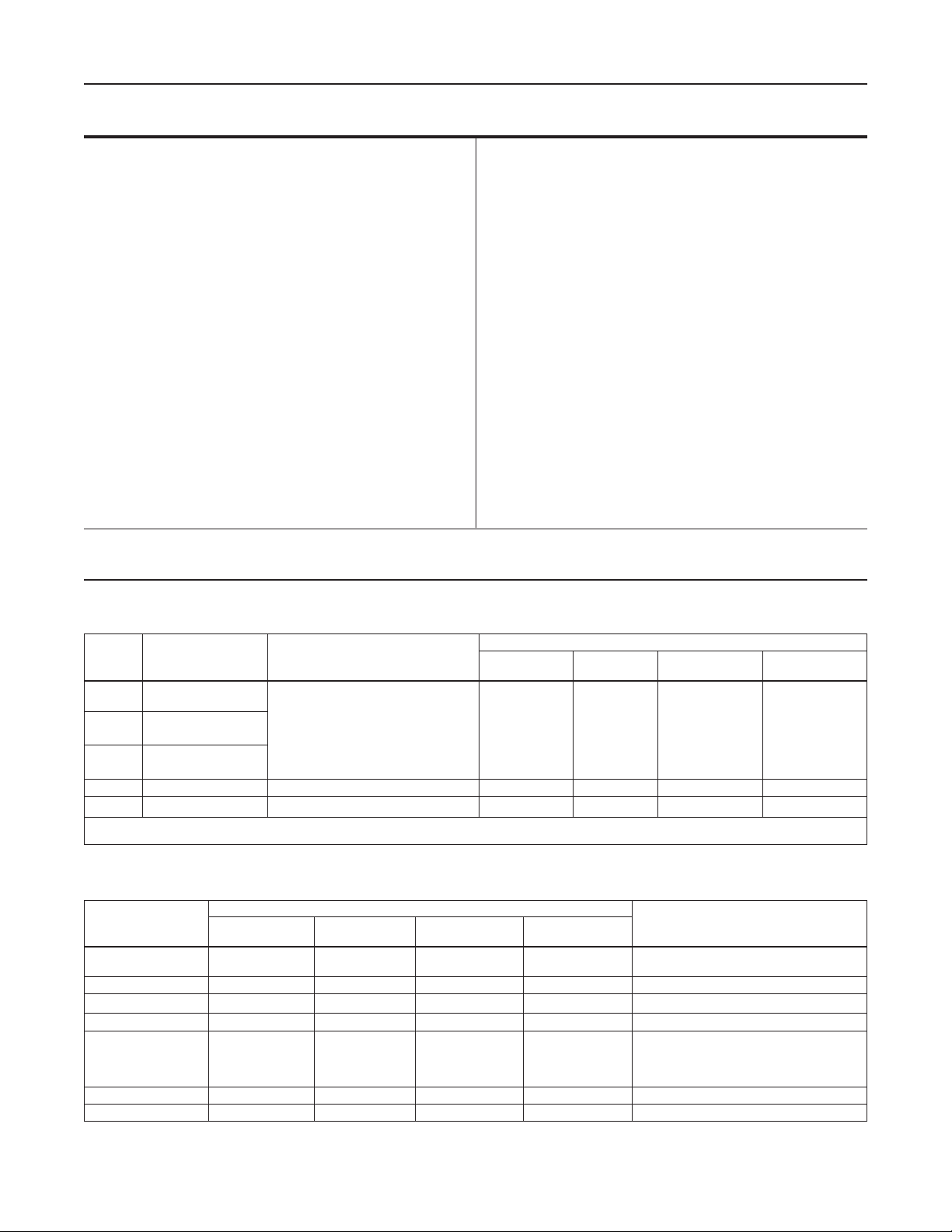
Principle of Operation
The key to the operation of a Type 99 regulator is the
yoked double-diaphragm pilot (letter keys in this section
refer to both Figures 2 and 3 unless otherwise noted).
Fast response and accuracy are made possible by the
amplifying effect of the pressure-balanced pilot and
by the two-path control system. The function of the
pilot is to sense change in the controlled pressure and
amplify it into a larger change in the loading pressure.
Any changes in outlet pressure act quickly on both the
actuator diaphragm and the loading pilot, thus providing
the precise pressure control that is characteristic of a
two-path system.
INLET PRESSURE
OUTLET PRESSURE
LOADING PRESSURE
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
H
B
E
K
F
G
Figure 2. Schematic of Type 99 Regulator with Type 61L (Low Pressure) Pilot
C
A
D
OUTLET PIPE
INLET
In operation, assume the outlet pressure is less
than the setting of pilot control spring (A). The top
side of pilot diaphragm assembly (F) will have a
lower pressure than the setting of spring (A). Spring
(A) forces the diaphragm head assembly upward,
opening the relay or inlet orice (C). Additional loading
pressure is supplied to the pilot body and to the top
side of main diaphragm (E).
This creates a higher pressure on the top side of the
main diaphragm (E) than on the bottom side, forcing
the diaphragm downward. This motion is transmitted
through a lever, which pulls the valve disk open,
allowing more gas to ow through the valve.
A typical pilot has an approximate gain of 20, which
means the outlet pressure needs to droop only 1/20 as
much as a self-operated regulator in order to obtain the
same pressure differences across the main diaphragm.
Advantages of a pilot operated regulator are high
accuracy and high capacity.
Upstream or inlet pressure is utilized as the operating
medium, which is reduced through pilot operation to
load the main diaphragm chamber. Tubing connects
the inlet pressure to the pilot through a lter assembly.
Downstream or outlet pressure registers underneath the
main diaphragm (E) through the downstream control line.
When the gas demand in the downstream system
has been satised, the outlet pressure increases.
The increased pressure is transmitted through the
downstream control line and acts on top of the
pilot diaphragm head assembly (F). This pressure
exceeds the pilot spring setting and forces the head
assembly down, closing orice (C). The loading
pressure acting on the main diaphragm (E) bleeds to
the downstream system through a small slot between
the pilot bleed valve (D) and the bleed orice (H).
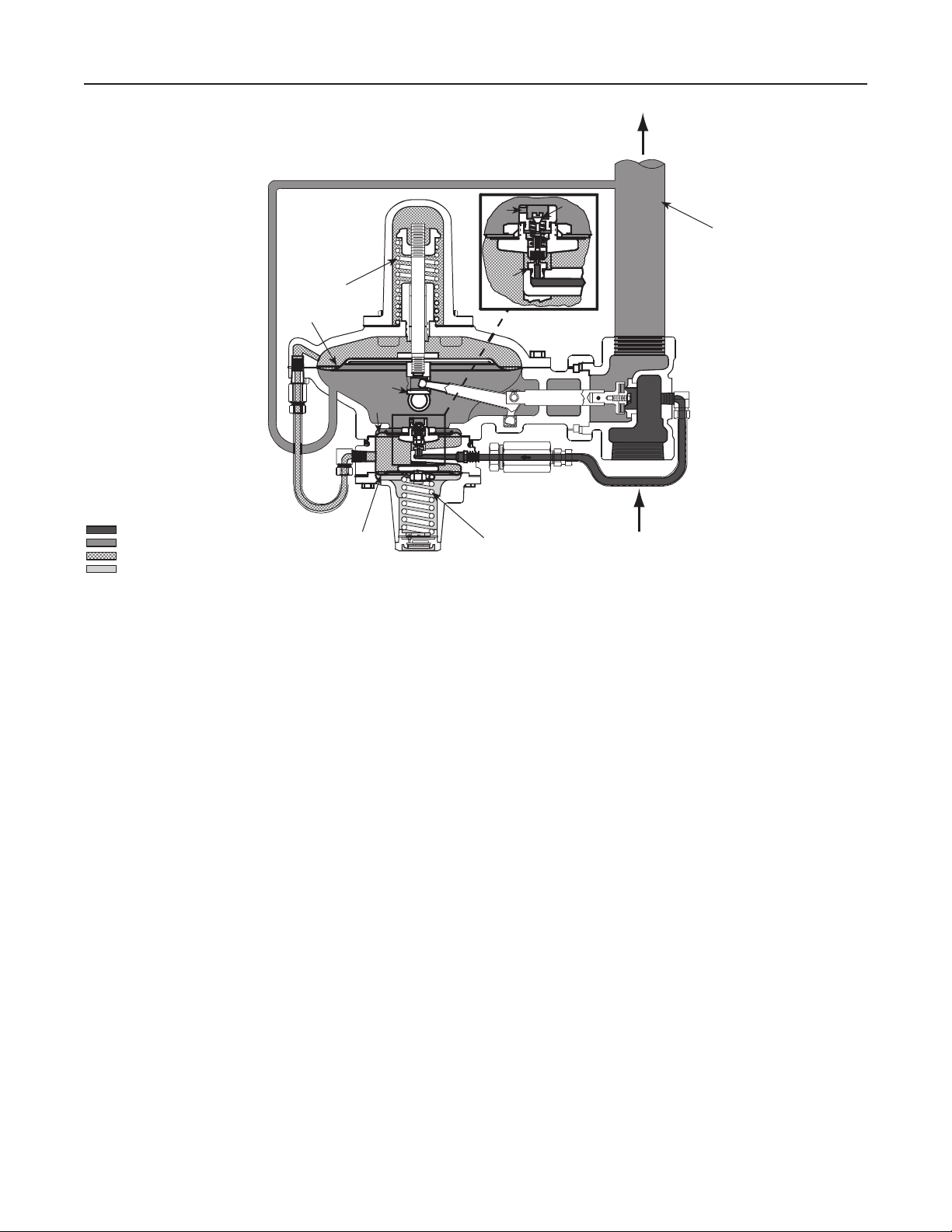
Normally, excess loading pressure slowly escapes
downstream around bleed valve (D) (Figure 3) or
3
Page 4
Type 99
A2505
Type 99
Type 99
A6469
January 2008
Type 99
INLET PRESSURE
OUTLET PRESSURE
LOADING PRESSURE
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
DOWNSTREAM
CONTROL LINE
B
RELIEF
VALVE
CAP
through the relief valve body (J) (Figure 4). Since
loading pressure needs to exceed outlet pressure
only moderately to stroke the main valve fully open,
a continued increase in loading pressure differential
extends the main diaphragm (E) and the pusher
post assembly (K) far enough to separate the bleed
valve (D) and the bleed orice (H). This permits
quick dumping of excess loading pressure into the
downstream system.
With a decrease in loading pressure on top of the
main diaphragm (E), the main spring (B) exerts an
upward force on the diaphragm rod connected to the
main diaphragm (E), pulling it upward. This moves
the main valve toward its seat, decreasing ow to the
downstream system.
Diaphragm (G) in the pilot valve acts as a sealing
member for the loading chamber and as a balancing
member to diaphragm (F). These two diaphragms are
connected by a yoke so any pressure change in the
pilot chamber has little effect on the position of the pilot
valve. Therefore, the active diaphragm in the pilot is
(F) and the pressure on the top side of this diaphragm
opposes the force of the pilot control spring (A).
INLET PRESSURE
OUTLET PRESSURE
LOADING PRESSURE
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
54A2767-a
A2505
E
K
YOKE
LEG
FLANGE
ADAPTOR
G
Figure 3. Schematic of Type 99 Regulator with Type 61HP (Extra High Pressure) Pilot
INLET PRESSURE
TUBING CONNECTION
A
YOKE
CAP
YOKE
CAP
H
D
J
RELAY
VALVE
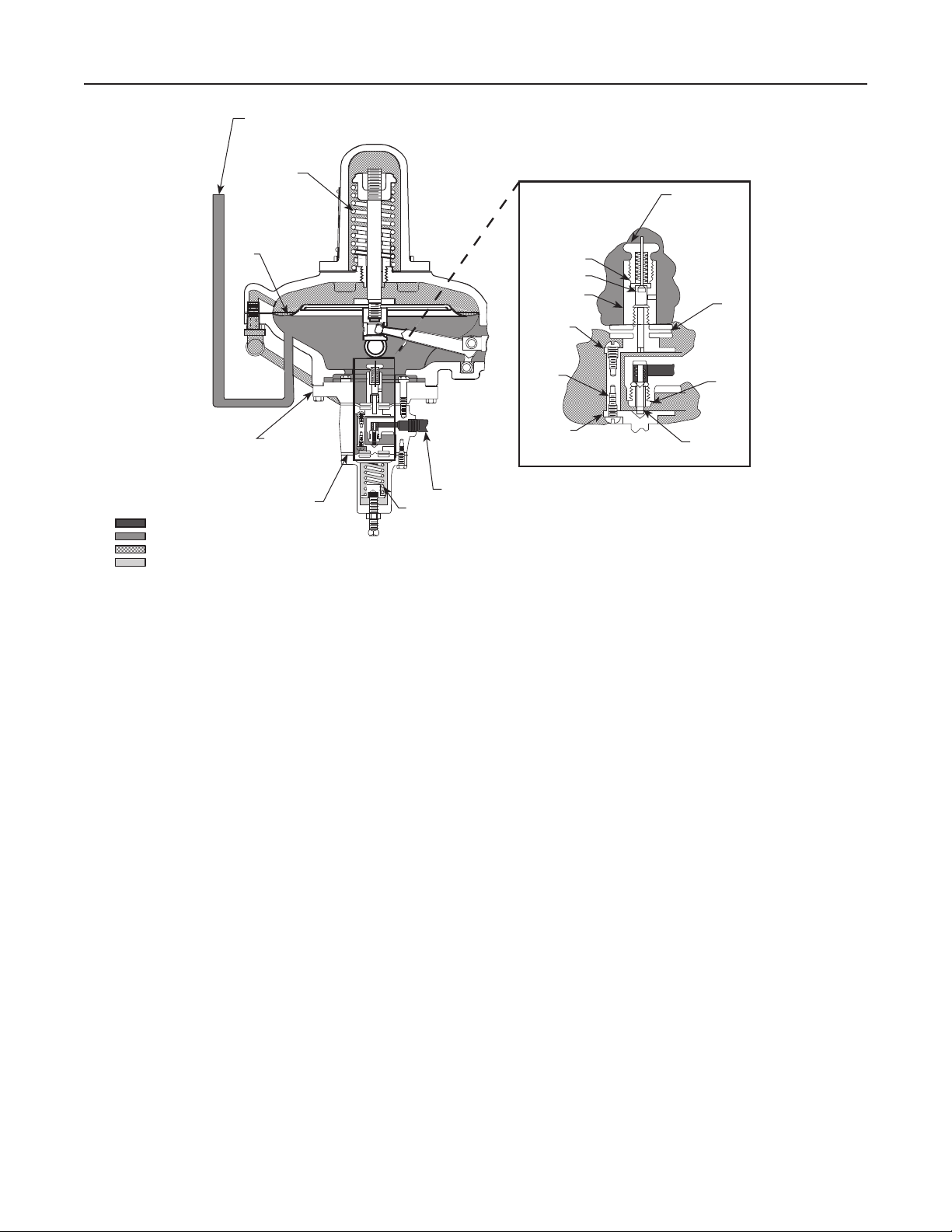
Monitoring Systems
Monitoring regulators serve as overpressure protection
devices to limit system pressure in the event of open
failure of a working regulator feeding the system. Two
methods of using Type 99 regulators in monitoring
systems are as follows:
Working Monitor
On a working monitor installation (Figure 4), the
control line of the monitoring pilot is connected
downstream of the working regulator. During
normal operation, distribution pressure causes
the monitoring pilot to stand wide open. Full pilot
supply pressure enters the working monitor pilot and
permits the working monitor regulator to control at its
intermediate pressure setting.
Open failure of the working regulator increases
distribution pressure as the working regulator goes
wide-open. Intermediate pressure is then ignored by
the monitoring regulator, which controls downstream
pressure at its own pressure setting (slightly higher
than the normal control pressure).
F
C
4
Page 5
TYPE 161AYW MONITORING
PILOT (ALSO REPRESENTATIVE
OF TYPE 627-109)
PILOT SUPPLY LINE
WORKING
MONITOR PILOT
DISTRIBUTION PRESSURE
CONTROL LINE
INTERMEDIATE PRESSURE
CONTROL LINE
Type 99
LOADING
PRESSURE
OPTIONAL
PILOT SUPPLY
REGULATOR
UPSTREAM
PRESSURE
20A1389-A
B2484
Figure 4. Working Monitor Installation
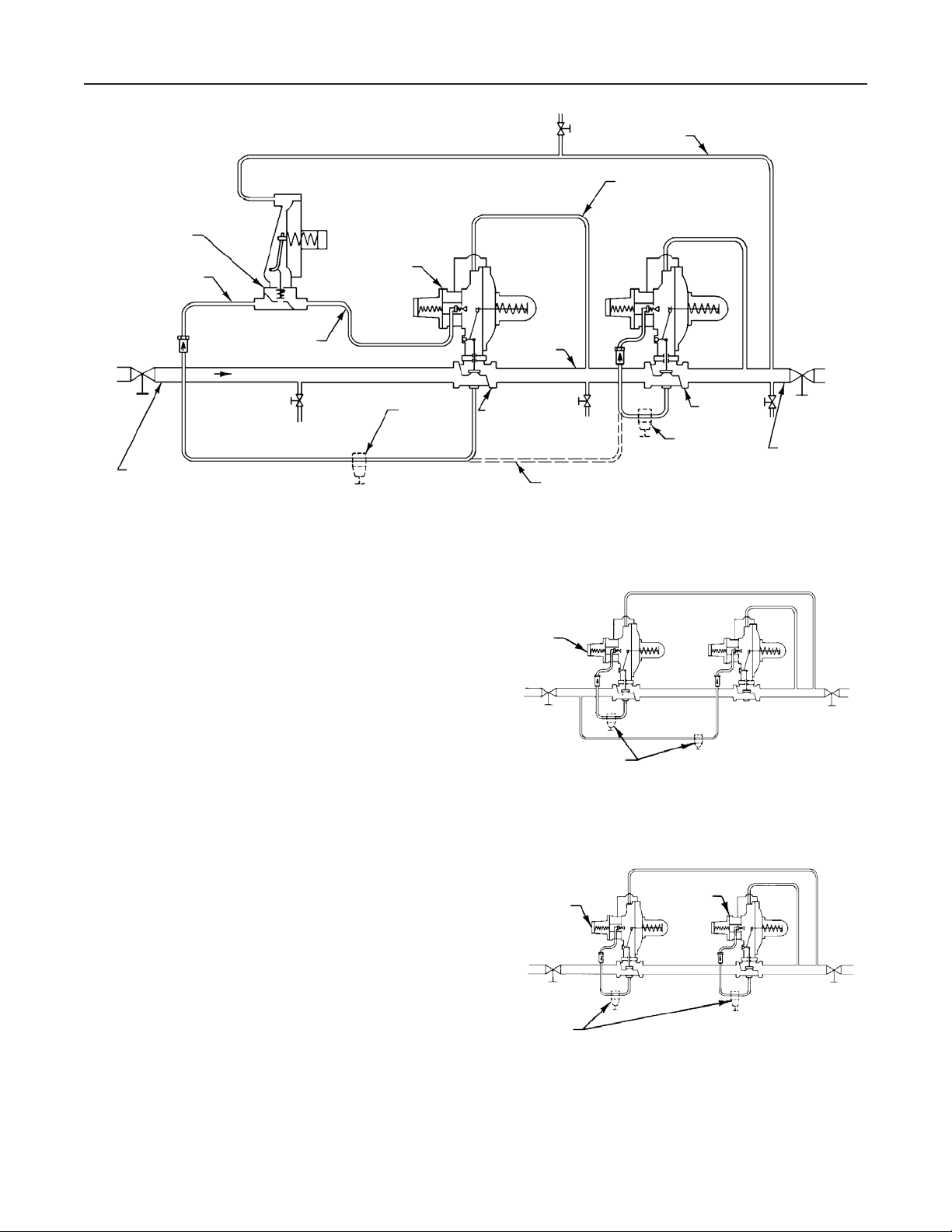
The monitoring pilot should be upstream of the working
monitor regulator. This enables a closer setpoint
between the working regulator and the monitoring
pilot. Special Types 161AYW and 627-109 monitoring
pilots with quick-bleed operation have been designed
to give faster response to abnormal downstream
conditions. Table 4 gives the spread between normal
distribution pressure and the minimum pressure at
which the working monitor regulator can be set to take
over if the working regulator fails open.
INTERMEDIATE
PRESSURE
WORKING
MONITOR
REGULATOR
PILOT SUPPLY PIPING FOR WORKING REGULATOR
WHEN PILOT IS REQUIRED TO BE SUPPLIED FROM
UPSTREAM PRESSURE
UPSTREAM
REGULATOR
(REQUIRES O-RING
STEM SEAL)
10A1388-A
A2504
OPTIONAL PILOT
SUPPLY REGULATOR
FLEXIBLE ARRANGEMENT THAT PERMITS WIDE-OPEN
MONITOR TO BE EITHER UPSTREAM OR DOWNSTREAM
WORKING
REGULATOR
OPTIONAL
PILOT SUPPLY
REGULATOR
DISTRIBUTION
PRESSURE
Wide-Open Monitor
The control line of the upstream regulator is
connected downstream of the second regulator
(Figure 5), so that during normal operation the
monitoring regulator is standing wide open with the
reduction to distribution pressure being taken across
the working regulator. Only in case of open failure of
the working regulator does the wide-open monitoring
regulator take control at its slightly higher setting.
The upstream regulator must have an O-ring seal on
the valve carrier assembly. This seals off the leak
path that otherwise would let line pressure ahead of
the working regulator inlet try to close the wide-open
monitoring regulator.
UPSTREAM
REGULATOR
(REQUIRES O-RING
STEM SEAL)
10A1386-A
A2503
OPTIONAL PILOT
SUPPLY REGULATOR
FLEXIBLE ARRANGEMENT THAT PERMITS WIDE-OPEN
MONITOR TO BE EITHER UPSTREAM OR DOWNSTREAM
WORKING
REGULATOR
Figure 5. Typical Wide-Open Monitor Installations
5
Page 6
Type 99
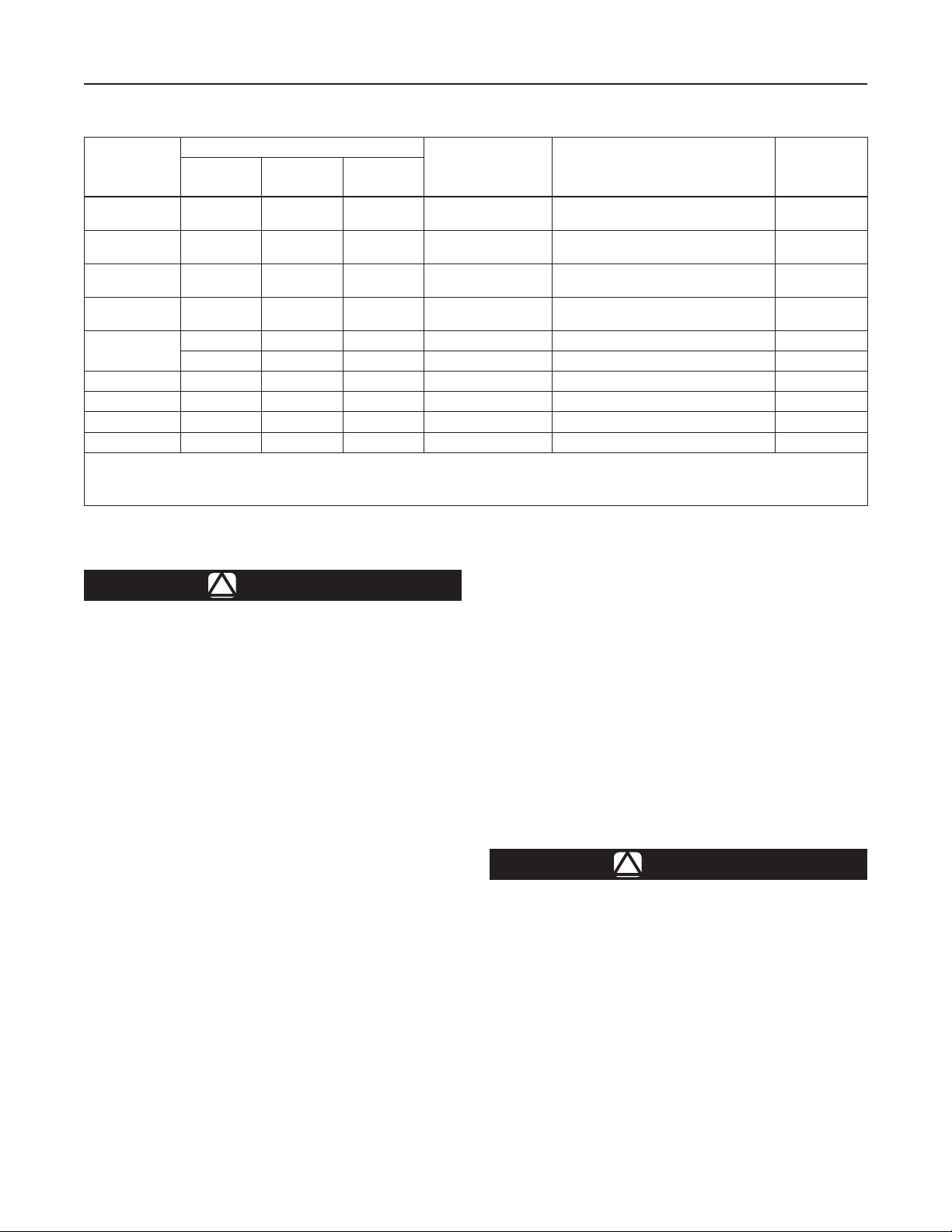
Table 3. Maximum Allowable Drop and Minimum Differential Pressures
MAXIMUM
ALLOWABLE
PRESSURE
DROP, PSIG (bar)
25 (1,72) 1C277127022 0.148 (0,38) 6 (15,2) 0.75 (0,05)
50 (3,45) 1N801927022 0.156 (0,40) 7-1/8 (18,1) 1.5 (0,10)
150 (10,3) 1B883327022 0.187 (0,47) 6-5/8 (16,8) 3 (0,21)
175 (12,1) 1B883327022 0.187 (0,47) 6-5/8 (16,8) 3 (0,21)
250 (17,2)
300 (20,7) 0W019127022 0.281 (0,71) 6 (15,2) 10 (0,69) Nylon (PA) 1-1/8 (28,6)
400 (27,6) 0W019127022 0.281 (0,71) 6 (15,2) 10 (0,69) Nylon (PA) 7/8 (22,2)
600 (41,4) 0W019127022 0.281 (0,71) 6 (15,2) 10 (0,69) Nylon (PA) 5/8 (15,9)
1000 (69,0) 0W019127022 0.281 (0,71) 6 (15,2) 10 (0,69) Nylon (PA) 1/2 (12,7)
1. Can use all port diameters up to maximum size listed.
2. CL125 FF anged body only.
3. O-ring seat only.
4. 1/2-inch (12,7 mm) is the only orice available for 1000 psig (69,0 bar) maximum inlet pressure regulator.
1B883327022 0.187 (0,47) 6-5/8 (16,8) 3 (0,21) Nitrile (NBR), Fluorocarbon (FKM) 7/8 (22,2)
0W019127022 0.281 (0,71) 6 (15,2) 10 (0,69) Nitrile (NBR)
Installation
MAIN VALVE SPRING MINIMUM
Part
Number
Wire Diameter,
Inches (cm)
Free Length,
Inches (cm)
DIFFERENTIAL
PRESSURE FOR FULL
STROKE, PSIG (bar)
Like most regulators, the Type 99 regulator has a outlet
SEAT MATERIAL
Nitrile (NBR), Neoprene (CR),
Fluorocarbon (FKM)
Nitrile (NBR), Neoprene (CR),
Fluorocarbon (FKM)
Nitrile (NBR), Neoprene (CR),
Fluorocarbon (FKM)
Nitrile (NBR)
(2)
, Neoprene (CR)
Fluorocarbon (FKM)
(3)
, Fluorocarbon (FKM)
(2)
(2)
,
(3)
MAXIMUM PORT
DIAMETER
INCHES (mm)
1-1/8 (28,6)
1-1/8 (28,6)
1-1/8 (28,6)
7/8 (22,2)
1-1/8 (28,6)
pressure rating lower than its inlet pressure rating.
WARNING
!
Complete downstream overpressure protection is
needed if the actual inlet pressure can exceed the
• Personal injury, equipment damage, or
leakage due to escaping gas or
bursting of pressure-containing
parts might result if this regulator
is overpressured or is installed where
service conditions could exceed
the limits for which the regulator was
designed, or where conditions exceed
any ratings of the adjacent piping or
piping connections. To avoid such
injury or damage, provide pressure-
regulator outlet pressure rating or the pressure ratings
of any downstream equipment. Although the Type H110
relief valve provides sufcient relief capacity to protect
the extra high pressure pilot of the 1000 psig (69,0 bar)
maximum inlet regulator in case the Type 1301F supply
regulator fails open, this protection is insufcient if the
main valve body fails open. Regulator operation within
ratings does not preclude the possibility of damage from
external sources or from debris in the lines. A regulator
should be inspected for damage periodically and after
any overpressure condition.
relieving or pressure-limiting devices
(as required by the appropriate code,
WARNING
regulation, or standard) to prevent
!
service conditions from exceeding
those limits.
• A regulator may vent some gas to the
atmosphere in hazardous or ammable
gas service, vented gas might
accumulate and cause personal injury,
death or property damage due to re or
explosion. Vent a regulator in
hazardous gas service to a remote,
safe location away from air intakes or
any hazardous location. The vent
line or stack opening must be
protected against condensation
or clogging.
The 1000 psig (69,0 bar) maximum
inlet regulator must not be used on
hazardous gas service unless the
Type H110 relief valve can be vented
into a safe area. If vented gas can
accumulate and become a hazard in
enclosed conditions such as in a pit,
underground, or indoors, the relief valve
must be repiped to carry the gas to a
safe location.
A repiped vent line or stack must be
located to avoid venting gas near
buildings, air intakes, or any hazardous
(1)
,
(4)
6
Page 7

Table 4. Working Monitor Performance
Type 99
MONITORING PILOT INFORMATION
Construction Spring Range
Type 161AYW with 1/8-inch
(3,18 mm) port diameter and
150 psig (10,3 bar) maximum
allowable inlet pressure
Type 627-109 with 1/8-inch
(3,18 mm) port diameter and
150 psig (10,3 bar) maximum
allowable inlet pressure for cast
iron body or 750 psig (51,7 bar)
maximum allowable inlet pressure
for malleable iron body
1. With large diaphragm plate.
2. With small diaphragm plate.
5 to 15-inches w.c. (12 to 37 mbar)
11 to 28-inches w.c. (27 to 70 mbar)
1 to 2.5 psig (0,069 to 0,17 bar)
2.25 to 4.5 psig (0,16 to 0,31 bar)
4.5 to 7 psig (0,31 to 0,48 bar)
5 to 15 psig (0,34 to 1,03 bar)
10 to 25 psig (0,69 to 1,72 bar)
20 to 35 psig (1,38 to 2,41 bar)
25 to 60 psig (1,72 to 4,14 bar)
40 to 80 psig (2,76 to 5,52 bar)
80 to 150 psig (5,52 to 10,3 bar)
130 to 200 psig (9,00 to 13,8 bar)
location. The line or stack opening must
be protected against condensation,
freezing, and clogging.
Clean out all pipelines before installation and check
to be sure the regulator has not been damaged or
collected foreign material during shipping.
Apply pipe compound to the male pipe threads only with
a screwed body, or use suitable line gaskets and good
bolting practices with a anged body. This regulator
may be installed in any position desired as long as the
ow through the body is in the direction indicated by the
arrow on the body. Install a three-valve bypass around
the regulator if continuous operation is necessary during
maintenance or inspection.
Although the standard orientation of the actuator and
pilot to the main valve body is as shown in Figure 1, this
orientation may be changed as far as the inlet tubing
(key 24, Figure 9 or 11) will permit by loosening the
union nut (key 14, Figure 9), rotating the actuator lower
casing (key 29, Figure 9) as desired, and tightening
the union nut. To keep the pilot spring case from being
plugged or the spring case from collecting moisture,
corrosive chemicals, or other foreign material, the vent
must be pointed down, oriented to the lowest possible
point on the spring case, or otherwise protected. Vent
orientation may be changed by rotating the spring
case with respect to the pilot body, or on the extra
high pressure pilot with optional tapped spring case by
rotating the vent with respect to the spring case.
To remotely vent a low pressure pilot, install the vent
line in place of the pressed-in vent assembly (key 60,
Figure 9). Install obstruction-free tubing or piping
MINIMUM PRESSURE
AT WHICH WORKING
MONITOR REGULATOR
CAN BE SET
3-inches w.c. (7 mbar)
over normal
distribution pressure
0.5 psi (0,03 bar)
over normal
distribution pressure
3.0 psi (0,21 bar)
over normal
distribution pressure
5.0 psi (0,34 bar)
over normal
distribution pressure
Part Number
1B653927022
1B537027052
1B537127022
1B537227022
1B537327052
1D892327022
1D751527022
1D665927022
1D755527142
1E543627142
1P901327142
1P901327142
Pilot Spring
Wire Diameter,
Inches (cm)
0.105 (0,27)
0.114 (0,29)
0.156 (0,40)
0.187 (0,47)
0.218 (0,55)
0.168 (0,43)
0.187 (0,47)
0.218 (0,55)
0.500 (1,27)
0.283 (0,72)
(1)
0.240 (0,61)
(2)
0.240 (0,61)
Free Length,
Inches (cm)
3-3/4 (9,52)
4-5/16 (11,0)
4-1/8 (10,5)
3-15/16 (10,0)
4-1/8 (10,5)
2-15/16 (7,46)
2-13/16 (7,14)
2-15/32 (6,27)
9-1/4 (23,5)
2-15/16 (7,46)
2-5/8 (6,67)
2-5/8 (6,67)
into the 1/4-inch (6,35 mm) vent tapping. Provide
protection on a remote vent by installing a screened
vent cap into the remote end of the vent pipe.
To remotely vent a high pressure pilot, or an extra high
pressure pilot with optional tapped spring case, remove
the screwed-in vent assembly (key 72, Figure 9) from
the high pressure pilot spring case or the pressed-in
vent assembly from the extra high pressure pilot
spring case and install obstruction-free tubing or piping
into the 1/4-inch (6,35 mm) vent tapping. Provide
protection on a remote vent by installing a screened
vent cap into the remote end of the vent pipe.
An upstream pilot supply line is not required because
of the integral pilot supply tubing (key 24, Figure 9
or 11). However, as long as the 1/4-inch NPT
tapping in the main valve body is plugged, this
tubing may be disconnected from both the main
valve and lter assembly (key 75, Figure 9) in order
to install a pilot supply line from a desired remote
location into the lter.
If the maximum pilot inlet pressure will be exceeded
by main valve pressure, install a separate reducing
regulator (if not already provided) in the pilot supply line.
A Type 99 regulator has two 1/2-inch threaded NPT
control line pressure taps on opposite sides of the
lower casing (key 29, Figure 9). The regulator normally
comes from the factory with the tap closest to the
regulator outlet left unplugged for the downstream
control line as shown in Figure 1, and with opposite
tap plugged.
Attach the control line from the unplugged tap 2 to
3 feet (0,61 to 0,91 meter) downstream of the regulator
in a straight run of pipe. If impossible to comply with
7
Page 8

Type 99
this recommendation due to the pipe arrangement, it
may be better to make the control line tap nearer the
regulator outlet rather than downstream of a block
valve. Do not make the tap near any elbow, swage, or
nipple which might cause turbulence.
In many instances, it will be necessary to enlarge the
downstream piping to keep ow velocities within good
engineering practices. Expand the piping as close to
the regulator outlet as possible.
WARNING
!
Adjustment of the pilot control spring to
produce an outlet pressure higher than
the upper limit of the outlet pressure
range for that particular spring can cause
personal injury or equipment damage
due to bursting of pressure-containing
parts or the dangerous accumulation
of gases if the maximum actuator
emergency casing pressure in the
Specications section is exceeded. If the
desired outlet pressure is not within the
range of the pilot control spring, install a
spring of the proper range according to
the Maintenance section.
The only adjustment on the regulator is the reduced
pressure setting affected by the pilot control spring
(key 43, Figure 9 or 11). Remove the closing cap
assembly (key 46, Figure 9) and turn the adjusting
screw (key 45, Figure 9 or 11). Turning the adjusting
screw clockwise into the spring case increases the
controlled or reduced pressure setting. Turning
the screw counterclockwise decreases the reduced
pressure setting. Always replace the closing cap, if
used, after making the adjustment.
Shutdown
Isolate the regulator from the system. Vent the
downstream pressure rst; then vent inlet pressure to
release any remaining pressure in the regulator.
Maintenance
Regulator parts are subject to normal wear and must be
inspected and replaced as necessary. The frequency
of inspection and replacement of parts depends on the
severity of service conditions or the requirements of
local, state, and federal rules and regulations.
WARNING
!
Each regulator is factory-set for the pressure setting
specied on the order. If no setting was specied, outlet
pressure was factory-set at the midrange of the pilot
control spring. In all cases, check the control spring
setting to make sure it is correct for the application.
Startup
Key numbers are referenced in Figure 9 for a low or
high pressure pilot and in Figure 12 for an extra high
pressure pilot. With proper installation completed and
downstream equipment properly adjusted, perform the
following procedure while using pressure gauges to
monitor pressure.
1. Very slowly open the upstream block valve.
2. Slowly open the hand valve (if used) in the control
line. The unit will control downstream pressure
at the pilot control spring setting. See the
adjustment paragraph following these numbered
steps if changes in the setting are necessary during
the startup procedure.
3. Slowly open the downstream block valve.
4. Slowly close the bypass valve, if any.
5. Check all connections for leaks.
Avoid personal injury or damage to
property from sudden release of pressure
or uncontrolled gas or other process uid.
Before starting to disassemble, isolate
the pilot or regulator from all pressure
and cautiously release trapped pressure
from the pilot or regulator. Use gauges to
monitor inlet, loading, and outlet pressures
while releasing these pressures.
On reassembly of the regulator, it is recommended
that a pipe thread sealant be applied to pressure
connections and ttings as indicated in Figures 7
and 9 and lubricant be applied to sliding and bearing
surfaces as indicated in Figures 7 and 9, and that an
anti-seize compound be applied to adjusting screw
threads and other areas indicated Figures 9 and 11.
Actuator and Standard P590 Series Filter
This procedure is to be performed if changing the main
spring and spring seat for those of a different range,
or if inspecting, cleaning, or replacing any other parts.
Unless otherwise indicated, part key numbers for a
Type 99 regulator with low or high pressure pilot and
8
Page 9

Type 99
disk or O-ring seat are referenced in Figure 9, part key
numbers unique to the 1000 psig (69,0 bar) maximum
inlet regulator are referenced in Figure 11, and part
key numbers for a Type 61HP (extra high pressure)
pilot is referenced in Figure 12.
1. Access to all internal actuator parts can be gained
without removing the main valve body from the
line. Disconnect the loading tubing from the
upper casing.
CAUTION
If the regulator has an indicator
assembly, perform the following step
carefully to avoid bending the travel
indicator stem (key 103, Figure 6).
Note
The O-rings and gaskets (keys 111 and
108, Figure 6) in the indicator assembly
are static seals and need not be
disturbed, unless they are leaking.
2. Remove the four cap screws (key 58, Figure 9) and
lift off the spring case (key 1, Figure 9). Remove
the travel indicator stem, if any, by unscrewing the
indicator stem adapter (key 101, Figure 6).
3. Remove the main spring seat (key 2, Figure 9)
and main spring (key 3, Figure 9).
4. Remove the 12 cap screws (key 12, Figure 9)
and hex nuts (key 13, Figure 9), and lift off the
upper casing.
5. Remove the diaphragm (key 11, Figure 9) and
diaphragm plate (key 10, Figure 9) by tipping it so
that the lever (key 9, Figure 9) slips out of the
pusher post (key 8, Figure 9).
6. Separate the diaphragm and diaphragm plate by
unscrewing the diaphragm rod (key 4, Figure 9)
from the pusher post. Inspect the diaphragm
(key 11, Figure 9) and pusher post gasket (key 7,
Figure 9). Either part must be replaced if it is
damaged or no longer pliable.
7. If the unit has a stem seal O-ring (key 64,
Figure 7 or 11), this O-ring may be replaced by
removing the retaining ring or cotter pin (key 28,
Figure 9) and disconnecting the lever from the
valve carrier (key 26, Figure 9 or 11), removing
the union nut (key 14, Figure 9 or 11),
disconnecting the pilot supply tubing (key 24,
Figure 9 or 11), and sliding the lower casing
(key 29, Figure 9) away from the valve body
(key 17, Figure 9), with a disk or O-ring seat, the
valve carrier must be pulled out of the lower
casing to gain access to the O-ring. Another
O-ring, held captive by the pressed-in bushing, is
part of the lower casing assembly on a stem seal
unit and normally does not require replacement.
8. If clogging is suspected in the upstream regulator
passages, disconnect the pilot supply tubing
(key 24, Figure 9 or 11), remove the lter assembly
(key 75, Figure 9), and blow through it to check
for lter clogging. If necessary, to clean or replace
lter parts in a standard P590 Series lter
assembly, remove the following as shown in
Figure 10: lter body (key 1), machine screw
(key 4), spring washer (key 6), gasket (key 7),
washer (key 5), and lter element (key 2). Upon
reassembly, one of the at washers must go
between the lter element and lter head (key 3)
and the other must go between the lter element
and gasket.
9. If the lower casing was removed, install a new body
gasket (key 16, Figure 9) and, with a disk or O-ring
seat, slide the valve carrier into the casing. Then
slide the entire assembly into the valve body (disk
or O-ring seat) and secure with the union nut.
Secure the lever to the valve carrier with the
retaining ring or cotter pin.
10. Loosely reassemble the diaphragm and
diaphragm plate so that the bolt holes and
loading connection hole in the diaphragm can
be properly aligned with the corresponding
holes in the casing when the lever is tted
properly into the pusher post. When this
orientation is made, install the collar (key 6,
Figure 9) and tighten the diaphragm rod into the
pusher post (key 8, Figure 9).
11. In order for the regulator to operate properly, the
assembled collar, diaphragm, diaphragm plate,
pusher post, and diaphragm rod must be
mounted on the ball of the lever so that the
pusher post (key 8, Figure 9) orientation is as
shown in Figure 9.
12. Install the upper casing and secure it to the
lower casing with the twelve cap screws torque
580 to 920 inch-pounds (65,5 to 104 N•m) and hex
nuts. Put lower casing back on body and install
union nut.
9
Page 10

Type 99
CAUTION
To avoid part damage due to over
compressing the main spring seat, always
use main spring seat 1E242724092 with
main spring 0W019127022.
13. Install the main spring and main spring seat,
turning the main spring seat until its bottom
shoulder is even with the bottom thread of the
diaphragm rod.
14. Install a new spring case gasket (key 57,
Figure 9), the spring case, and the four cap
screws with 340 to 420 inch-pounds (38,4 to
47,5 N•m) of torque, making sure the indicator
stem, O-ring, and gaskets (keys 103, 111, and
108, Figure 6) are installed If used.
15. Connect the loading tubing, then refer to the
Startup section for putting the regulator
into operation.
Type 61L, 61LD, 61LE (Low), or 61H
(High Pressure) Pilots
This procedure is to be performed if changing the
control spring for one of a different range, or if
inspecting, cleaning or replacing any other pilot parts.
Key numbers are referenced in Figure 9.
1. Remove the closing cap (key 46) if used and
unscrew the adjusting screw (key 45) to relieve
control spring compression.
2. Disconnect the loading tubing (key 53) and pilot
supply tubing (key 24).
3. Unscrew the eight cap screws (key 47) and remove
the pilot assembly from the lower casing (key 29).
4. Use the projecting prong in the relay valve body
(key 39) as the restraining member and remove
the diaphragm nuts (keys 13 and 51). Separate
the parts and inspect the diaphragms (keys 30
and 40) and O-ring seal (key 33). Replace if worn
or damaged.
Note
Before putting the relay spring case over
the diaphragm, make certain the yoke is
square with respect to the prong in the
relay body. (The yoke can bind on the
prong if it is not square.)
7. Use care in reassembly to be sure the edges of
the diaphragms slip properly into the recess on
the lower casing and relay valve body. With the
pilot in place, check to see if it can be rocked. If
it does not rock, it is in place and the diaphragm
is free of wrinkles. With both diaphragms rmly
in place, install the cap screws using torque
150 inch-pounds (16,9 N•m) of torque. Tighten
using a crisscross pattern to avoid placing a
strain on the unit. Set the pilot control spring
(key 43) according to the adjustment information
in the Startup section.
8. Reinstall the closing cap (key 46, if used). If you
have a plastic closing cap, be sure that you have
a vent (key 60) in place of the pipe plug installed in
the low pressure pilot spring case.
Type 61HP (Extra High Pressure) Pilot
This procedure is to be performed if changing the
control spring for one of a different range, or if
inspecting, cleaning, or replacing any other pilot parts.
Key numbers are referenced in Figure 12.
1. Unscrew the adjusting screw (key 45) to relieve
control spring compression.
2. Disconnect the loading tubing and pilot supply tubing.
3. Remove the six cap screws (key 123) which fasten
the spring case (key 44) spring seat (key 68) and
control spring (key 43) to the pilot body.
4. Unscrew the diaphragm nut (key 128) and remove
a diaphragm plate (key 41), diaphragm (key 40),
and another diaphragm plate.
5. Unscrew the eight cap screws and remove the
pilot body (key 39) and gasket. Remove six cap
screws, seal washers and the ange adapter.
5. Unscrew the bleed orice (key 52) from the yoke
(key 37). Also removed with the bleed orice are
the relay disk assembly (key 48) and bleed valve
(key 50). These parts can be unscrewed for
inspection and replacement, if necessary.
6. When reassembling the pilot, the relay disk holder
assembly and both diaphragms should be
tightened on the yoke after it is placed in the body.
10
6. Unscrew the relief valve body (key 119) and remove
a diaphragm plate, diaphragm, and another
diaphragm plate. Inspect the diaphragm inserts
(key 150) and both diaphragms. Replace if worn
or damaged.
7. The relief valve assembly can be further
disassembled for inspection by unscrewing the
relief valve cap (key 118).
Page 11

Type 99
8. Four machine screws (key 130) hold both yoke
caps (keys 37 and 116) to the yoke legs (key 31).
Separate these parts to expose the pilot valve.
9. Unscrew the inlet orice (key 38) to inspect its
seat, the inlet valve plug (key 117), and valve
spring (key 124).
Note
Make certain that the yoke assembly is
square with respect to the cross member
of the body casting so that it will not
bind on the body.
10. When reassembling, screw in the inlet orice all
the way and secure the yoke caps to the yoke
legs. Replace two diaphragm plates, the
diaphragms, and inserts, two more diaphragm
plates, the hex nut, and the relief valve assembly.
11. Assemble the control spring and spring seat
into the body and spring case, being careful
that the diaphragms are free of wrinkles and
properly in place, and evenly installing the cap
screws in a crisscross pattern to avoid placing a
strain on the unit. Install the body ange adapter
with seal washers and cap screws. Install a new
gasket and secure the pilot to the lower casing
with eight cap screws. Set the control spring
according to the adjustment information in the
Startup section.
low to high pressure pilot or vice versa, everything below
the lower pilot diaphragm (key 40, Figure 9) except the
cap screws and the hex nut (keys 47 and 13, Figure 9)
will need to be replaced. Actuator and main valve parts
may remain unchanged unless a change in service
conditions requires a change in seat construction, main
spring, or main spring seat. See the Parts List sections
for obtaining the appropriate conversion parts.
Main Valve Trim with Disk or O-ring Seat
This procedure is to be performed if inspecting,
cleaning, or replacing trim parts. Part key numbers
for a Type 99 regulator with disk or O-ring seat are
referenced in Figure 9, and part key numbers for
the disk seat unique to the 1000 psig (69,0 bar)
maximum inlet regulator are referenced in Figure 11.
Note
All trim maintenance may be performed
with the valve body (key 17, Figure 9
or 11) in the line and with the elbow
(key 23, Figure 9 or 11), pilot supply
tubing (key 24, Figure 9 or 11), and pilot
supply regulator (key 155, Figure 11, if
used) attached to the valve body unless
the valve body itself will be replaced.
1. Disconnect the pilot supply tubing and downstream
control line.
Converting the Pilot
Note
A complete pilot assembly rather than
individual parts may be ordered for
the following conversion procedure.
When a low pressure pilot is ordered
for eld conversion of a high pressure
pilot or vice versa, the replacement pilot
assembly comes complete with a pilot
cover (key 132, Figure 9). Remove this
cover before installing replacement pilot
on the existing regulator. The cover can
then be installed on the removed pilot
to form a complete Type 61 (low or high
pressure) pilot for use elsewhere.
When changing one pilot construction (low pressure, high
pressure, or extra high pressure) for another, all parts
attached to the lower casing (key 29, Figure 9) may need
to be replaced with those appropriate for the desired
construction. At the very least, when changing from a
2. Loosen the union nut (key 14, Figure 9) and
remove the lower casing (key 29, Figure 9) with
the cap screw (key 22, Figure 9) or disk and
holder assembly (key 18, Figure 11) on
disassembly or reassembly. A thin-walled socket
may be used to remove the orice.
3. Access to the disk or O-ring (key 19, Figure 9) can
be gained by removing the cap screw and retainer
(key 21, Figure 9), while on the 1000 psig
(69,0 bar) maximum inlet regulator the entire
disk and holder assembly is removed as a unit.
If necessary, the holder (key 18, Figure 9 or 11) or
adapter (key 157, Figure 11) can be removed by
taking out the cotter pin (key 25, Figure 9 or 11).
4. Install a new body gasket (key 16, Figure 9) and
a new disk, O-ring, or disk and holder assembly
as necessary. Then slide the entire assembly into
the valve body and secure with the union nut.
5. Connect the pilot supply tubing and downstream
control line, then refer to the Startup section for
putting the regulator into operation.
11
Page 12

Type 99
20A7146-B
Figure 6. Travel Indicator Assembly
Parts Ordering
A serial number is assigned to each regulator, and it
is stamped on both the actuator and pilot nameplates.
If the pilot is replaced, the new pilot will have its own
serial number different from the main valve serial
number. Always indicate one or both serial numbers
when communicating with your local Sales Ofce.
When ordering a replacement part, be sure to include
the complete eleven-character part number.
Parts List
Key Description Part Number
Repair kits include parts for regulator with composition
trim only, key numbers 7, 11, 16, 19, 20, and 57. Also
included are parts for pilot, key numbers 30, 33, 38, 40,
48, 49, 50, 52, 71, 117, 126, 129, 150, 153, and
P590 Series lter, key numbers 2 and 7.
With low pressure pilot
7/8-inch (22,2 mm) orice R99LX000012
1-1/8-inch (28,6 mm) orice R99LX000022
With high pressure pilot
7/8-inch (22,2 mm) orice R99HX000012
1-1/8-inch (28,6 mm) orice R99HX000022
With extra high pressure pilot
7/8-inch (22,2 mm) orice R99HPX00012
1-1/8-inch (28,6 mm) orice R99HPX00022
*Recommended Spare Parts
Travel Indicator Assembly (Figure 6)
Key Description Part Number
Complete Assembly (includes individual parts
listed below) 20A7146X0C2
1 Spring Case, Cast iron 2L296219012
101 Indicator Stem Adaptor, Aluminum 1R395909012
102 Indicator Cap, Aluminum 1L290809012
103 Indicator Stem, Aluminum 1L296509022
104 Disk Nut, Plastic 1F730506992
105 Machine Screw Nut, Plated steel (2 required) 1A342024152
106 Retainer, Aluminum 1L291009012
107 Indicator Window, Glass 1L296706992
108* Gasket, Neoprene (CR) (2 required) 1L291103012
109* Indicator Cover, Plastic (2 required) 1L296405032
110 Machine Screw, Plated steel (8 required) 1A899028982
111* O-ring, Nitrile (NBR) (2 required) 1E591406992
112 Indicator Scale, Stainless steel 1J511638982
Actuator and Main Body Assembly
(Figures 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, and 11)
Key Description Part Number
1 Standard Spring Case without travel
indicator, Cast iron 1B883119012
2 Main Spring Seat, Plated steel
250 psid (17,2 bar d) maximum
allowable pressure drop, Cast iron 1B883219042
1000 psid (69,0 bar d) maximum allowable
pressure drop 1E242724092
12
Page 13

Type 99
64
LUBRICANT
SEALANT
20A7148-B
26
SEALANT
LUBRICANT
Figure 7. O-ring Stem Seal Figure 8. O-ring Sealed Handwheel
Key Description Part Number
3 Main Spring, Plated steel
25 psid (1,72 bar d) maximum allowable
pressure drop 1C277127022
50 psid (3,45 bar d) maximum allowable
pressure drop 1N801927022
250 psid (17,2 bar d) maximum
allowable pressure drop 1B883327022
1000 psid (69,0 bar d) maximum allowable
pressure drop–requires main spring
seat 1E242724092 0W019127022
4 Diaphragm Rod, 416 Stainless steel 1B883435232
5 Diaphragm Rod Guide Assembly
Brass with bronze insert 1D9712000A2
316 Stainless steel 1B883535072
6 Collar
Brass 1B883614012
316 Stainless steel 1B883635072
7* Pusher Post Gasket
Composition - for standard construction 1B883704022
Fluorocarbon (FKM) - for oxygen service 1N430306382
8 Pusher Post Assembly
Brass with bronze insert 1D9714000A2
316 Stainless steel 1B883835072
316 Stainless steel - for oxygen service 14B1320X012
9 Lever, Steel 2F823423072
10 Diaphragm Plate, Plated steel 1B989225072
11* Diaphragm
Nitrile (NBR) 1B884102052
Fluorocarbon (FKM) 1N378902312
12 Cap Screw, Plated steel (12 required) 1B884224052
13 Hex Nut, Plated steel (13 required) 1A340324122
14 Union Nut, Iron 0Z0176X0032
15 Body Snap Ring, Plated steel 0Y095828982
16* Body Gasket
Composition 1A348004032
Graphite - for oxygen service 1A3480X0022
17 Valve Body
2-inch NPT
Cast iron 1C254619012
Steel 2N153522012
Brass 1C254612012
Brass - for oxygen service 1C2546X0012
2-inch (DN 50) CL125 FF anged, Cast iron 2D986519012
2-inch (DN 50) CL250 RF anged, Cast iron 2D986619012
A6802
Key Description Part Number
17 Valve Body (continued)
2-inch (DN 50) CL150 RF anged
Steel 2E275622012
2-inch (DN 50) CL300 RF anged
Steel 2E275722012
18 Holder for Type 99 regulator
Disk seat
Brass 1B884314012
316 Stainless steel 1B884335072
O-ring Seat
7/8-inch (22,2 mm) orice
Brass 1E603214012
316 Stainless steel 1E603235072
1-1/8-inch (28,6 mm) orice
Brass 1E342414012
316 Stainless steel 1E342435072
18* Disk and Holder Assembly for 1000 psig
(69,0 bar) maximum inlet regulator, Nylon (PA)/
316 Stainless steel 1C1860000B2
19 Disk for Type 99 Regulator
250 psid (17,2 bar d) maximum
allowable pressure drop
Neoprene (CR) 1C997403032
Nitrile (NBR) 1C158703332
Fluorocarbon (FKM) 1C9974X0012
400 psid (27,6 bar d) maximum
allowable pressure drop
Nylon (PA) 1E480603152
Polytetrauoroethylene (PTFE) 1C997406242
19* O-ring
7/8-inch (22,2 mm) orice
Nitrile (NBR) 1D237506992
Fluorocarbon (FKM) 1D237506382
1-1/8-inch (28,6 mm) orice
Nitrile (NBR) 1H8498X0012
Fluorocarbon (FKM) 1H8498X0032
20* Orice
Disk seat for all regulators
3/8-inch (9,52 mm) orice, 416 Stainless steel 19A7390X012
1/2-inch (12,7 mm) orice, 416 Stainless steel 14A8410X012
5/8-inch (15,9 mm) orice, 416 Stainless steel 19A7391X012
7/8-inch x 3/8-inch (22,2 x 9,52 mm) orice
Brass 1N878114012
316 Stainless steel 1N8781X0012
*Recommended Spare Parts
13
Page 14

Type 99
AS – APPLY ANTI-SEIZE COMPOUND
PTS – APPLY PIPE THREAD SEALANT
LUB – APPLY LUBRICANT
PTS
AS
O-RING SET DETAIL
AS
AS
PTS
CONTROL
LINE TAP
(OTHER TAP
180° OPPOSITE)
DJ6642
PTS
AS
LUB
PTS
PTS
1/4-INCH (6,35 mm) VENT SHOWN 90°
COUNTERCLOCKWISE FROM NORMAL
PTS
COMPLETE REGULATOR SHOWING TYPE 61L PILOT AND DISK SEAT
14
DJ6642_B
PILOT RELAY ASSEMBLY
Figure 9. Type 99 Regulator with Type 61L (Low) or 61H (High Pressure) Pilot
Page 15

Type 99
30A6800
HIGH PRESSURE PILOT PARTS
C0289-1C
PILOT RELAY AND COVER ASSEMBLY
Figure 9. Type 99 Regulator with Type 61L (Low) or 61H (High Pressure) Pilot (continued)
15
Page 16

Type 99
Actuator and Main Body Assembly
(Figures 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, and 11) (continued)
Key Description Part Number
20* Orice (continued)
Disk seat for all regulators
7/8-inch x 1/2-inch (22,2 x 12,7 mm) orice
Brass 1C942314012
316 Stainless steel 1C942335072
7/8-inch x 5/8-inch (22,2 x 15,9 mm) orice
Brass 1C942414012
316 Stainless steel 1C9424X0012
3/4-inch (19,1 mm) orice
Brass 1C780414012
316 Stainless steel 1C780435072
7/8-inch (22,2 mm) orice
Brass 1C394714012
316 Stainless steel 1C394735072
1-inch (25,4 mm) orice, Brass 13A5017X012
1-1/8-inch (28,6 mm) orice
Brass 1B884414012
316 Stainless steel 1B884435072
1/2-inch (12,7 mm) disk seat for
1000 psig (69,0 bar) maximum inlet regulator,
416 Stainless steel 14A8410X012
O-ring seat for all regulators
7/8-inch (22,2 mm) orice
Brass 1E603014012
316 Stainless steel 1E603035072
1-1/8-inch (28,6 mm) orice
Brass 1E342514012
316 Stainless steel 1E342535072
21 Retainer
Disk seat 3/4-inch (19,1 mm)
All except 3/4-inch (19,1 mm) or
1-1/8-inch (28,6 mm) orice or
1000 psig (69,0 bar) maximum inlet regulator
Brass 1C394814012
303 Stainless steel 1C394835032
3/4-inch (19,1 mm) orice
Brass 1C780314012
316 Stainless steel 1C7803X0012
1-1/8-inch (28,6 mm) orice
Brass 1B884514012
316 Stainless steel 1B884535072
O-ring seat for all regulators
7/8-inch (22,2 mm) orice
Brass 1E603114012
316 Stainless steel 1E603135072
1-1/8-inch (28,6 mm) orice
Brass 1E342614012
316 Stainless steel 1E342635072
22 Cap Screw, Plated steel 1A391724052
25 Cotter Pin, 316 Stainless steel 1B108438992
26 Valve Carrier
Brass 1E597114072
416 Stainless steel 1E597135132
27 Lever Pin
316 Stainless steel 1B884935162
303 Stainless steel 1C911635032
28 Retaining Ring for brass trim,
Plated steel (2 required) 1B8850X0012
Cotter Pin for Stainless steel trim,
316 Stainless steel (2 required) 1A866537022
PIPE THREAD
SEALANT
AJ5004-A
A2135/IL
Figure 10. Standard P590 Series Filter Assembly
Key Description Part Number
29 Lower Casing, Cast iron
Standard 4B983719012
For use with optional protector, spring washer,
and machine screw (keys 61, 62, and 63) 2N379419012
Lower Casing Assembly for use with O-ring stem
seal, Cast iron with SST guide bushing
Complete with Nitrile (NBR) O-ring 2R7230000A2
Complete with Fluorocarbon (FKM) O-ring 2R7230X0022
32 Nameplate, Aluminum - - - - - - - - - - 56 Upper Casing, Cast iron 3B887619012
57* Spring Case Gasket
Composition 1B8877X0012
Graphite - for oxygen service 1B8877X0022
58 Cap Screw, Plated steel (4 required) 1A675124052
(1)
61
Lower casing protector (not shown), Brass 1N379514012
(1)
62
Optional Spring Washer (not shown)
Plated brass (2 required) 1N339518992
(1)
63
Optional Machine Screw (not shown)
Plated brass (2 required) 1H340518992
64* O-ring (for use only with O-ring stem seal)
Nitrile (NBR) 1E220206992
Fluorocarbon (FKM) 1R620106382
73 Pipe plug, Plated steel (not shown) 1A767524662
75 Standard P590 Series Filter Assembly
(parts listed under separate heading)
Type P594-1, Brass FSP594-1
Type P593-1, Aluminum FSP593-1
133 Pipe Elbow, Plated steel 1B860828992
134 Pipe Nipple, Plated steel 1B218826232
152 Drive Screw, 18-8 Stainless steel
(4 required for low pressure pilot and
6 required for high pressure pilot) 1A368228982
155 Type 1301F Pilot Supply Regulator
only with extra high pressure pilot) See footnote 2
156 Type H110 Pop Relief Valve, (for use only
with extra high pressure pilot) brass with
Nitrile (NBR) disk and 316 Stainless steel spring Consult Factory
159 Tag (for use only with O-ring stem seal and extra
high pressure pilot) alloy 1100 (not shown) 16A0957X012
(2)
(for use
*Recommended Spare Parts
1. Required with lower casing 2N379419012
2. Pilot supply regulator parts are found in Types 1301F and 1301G Instruction manual.
16
Page 17

Type 99
A6803
Figure 11. 1000 Psig (69,0 bar) Maximum Inlet Regulator Partial Detail
Standard P590 Series Filter Assembly
(Figure 10)
Key Description Part Number
1 Filter Body
Type P594-1, Brass 1E312414012
Type P593-1, Aluminum 1E3124X0022
2* Filter Element, Cellulose 1E312606992
3 Filter Head
Type P594-1, Brass 1E312514012
Type P593-1, Aluminum 1E3125X0022
4 Machine Screw
Type P594-1, Brass 1J500218992
Type P593-1, Aluminum 1J500209012
5 Washer (2 required)
Type P594-1, Brass 1J500018992
Type P593-1, Aluminum 1J500010062
6 Spring Washer, Plated carbon steel 1H885128982
7* Gasket, Composition 1F826804022
*Recommended Spare Parts
3. An entire pilot assembly may be ordered from your local Sales Ofce.
by specifying a Type 61L, a 61H, or a 61HP pilot for eld conversion.
Pilot and Tubing Parts
(3)
Low or High
Pressure Pilot (Figure 9)
Key Description Part Number
13 Hex Nut, Plated steel (13 required) 1A340324122
23 Elbow (2 required)
Brass 15A6002X292
316 Stainless steel 15A6002X612
24 Pilot Supply Tubing, disk or O-ring main valve seat
Copper 1D8793000A2
Copper - for oxygen service 0500201701W
316 Stainless steel 0500213809W
30* Upper Relay Diaphragm
Nitrile (NBR) 1B885202052
Fluorocarbon (FKM) 1N162802332
31 Upper Relay Diaphragm Plate, Plated steel
For use with all low pressure pilots except LE 1B989225072
For use with all high pressure pilots and LE
low pressure pilot 1D558425072
17
Page 18

Type 99
Pilot and Tubing Parts
(3)
Low or High
Pressure Pilot (Figure 9) (continued)
Key Description Part Number
33* O-ring Seal
Nitrile (NBR) 1B885506992
Fluorocarbon (FKM) 1B8855X0012
34 Connector
Brass 1D692214012
316 Stainless steel 15A6002X602
37 Yoke
Zinc 1D662544012
38* Relay Orice, Stainless steel
For use with 25 psi (1,72 bar) maximum allowable
pressure drop actuator main spring 1D373735032
For use with all other main springs 1C520135032
For use with oxygen service 1N162314042
39 Relay Valve Body, Cast iron 2J581919012
40* Lower Relay Diaphragm
Low pressure pilot
Nitrile (NBR) 1B886002052
Fluorocarbon (FKM) 1N536102332
High pressure pilot
Nitrile (NBR) 1B894202192
Fluorocarbon (FKM) 1N162702302
41 Lower Relay Diaphragm Plate, Plated steel
Low pressure pilot 1B989425072
High pressure pilot 1D558325072
42 Spring Seat, Plated steel
Low pressure pilot 1B886225072
High pressure pilot 1D558525072
43 Control Spring, Plated steel
For use only with LD low pressure pilot
0 to 4-inches w.c. (0 to 10 mbar), Orange 1B558527052
3 to 12-inches w.c. (7 to 30 mbar), Silver 1C680627222
For use with all low pressure pilots
0.25 to 2 psig (0,02 to 0,14 bar), Red 1B886327022
1 to 5 psig (0,07 to 0,34 bar), Yellow 1J857827022
2 to 10 psig (0,14 to 0,69 bar), Blue 1B886427022
5 to 15 psig (0,34 to 1,03 bar), Brown 1J857927142
10 to 20 psig (0,69 to 1,38 bar), Green 1B886527022
For use with high pressure pilot, Green stripe 0Y066427022
44 Spring Case, Cast iron
Low pressure pilot 1B983919012
High pressure pilot, Standard 1B984119012
For use with closing cap (not shown) 1H232619012
45 Adjusting Screw
Low pressure pilot, Standard, Zinc 1B537944012
Handwheel-style, Plated steel 1J496428982
O-ring seated handwheel assembly 1R759414012
High pressure pilot, Standard, Plated steel 1A279128982
For use with closing cap 1H236514012 1J881524102
46 Closing Cap
For use with standard low pressure pilot, Plastic T11069X0012
For use with handwheel-style low pressure
pilot, Brass (not shown) 1A926114012
For use with O-ring sealed handwheel 1R759314012
For use with high pressure pilot with spring
case 1H232619012, Brass (not shown) 1H236514012
47 Cap Screw, Plated steel (8 required) 1B989624052
48* Relay Disk Assembly
Brass/Nitrile (NBR) 1B8868000A2
303 Stainless steel/Nitrile (NBR) 1B8868000B2
Key Description Part Number
48* Relay Disk Assembly (continued)
Brass/Fluorocarbon (FKM) 1B8868X0012
303 Stainless steel/Fluorocarbon (FKM) 1B8868X0022
49* Bleed Valve Spring, Stainless steel
For use with low pressure pilot with relay orice
1D373735032 or bleed valve 1H951635132 1E643637022
For use with all low and high pressure pilots
Inlet pressure up to 250 psig (17,2 bar) 1C911537022
Inlet pressure over 250 psig (17,2 bar) 1N859137022
50* Bleed Valve, Stainless steel
For use with LD low pressure pilot with bleed
valve spring 1E643637022 1H951635132
For use with all low and high pressure pilots 1D986735132
51 Diaphragm Nut
Brass 1B989514012
316 Stainless steel 1B989535072
52* Bleed Orice, 316 Stainless steel 1B887335032
53 Loading Tubing
Copper 1J4928000A2
316 Stainless steel 0500213809W
54 Connector
Brass 1H628114012
316 Stainless steel 15A6002X992
55 Pipe Nipple
Plated steel (1 required with copper tubing
and 2 required with aluminum tubing) 1C488226232
316 Stainless steel 1C488238982
59 Pipe plug, Steel (not shown) 1A369224492
60 Type Y602-1 Vent Assembly 27A5516X012
68 Spring Seat
Handwheel-style low pressure pilot,
Steel, (not shown) 1J618124092
High pressure pilot, Zinc 16A9812X012
71* Closing Cap Gasket (for use only with
low pressure pilot), Neoprene (CR) 1P753306992
72 Type Y602-1 Vent Assembly (for use only with
standard high pressure pilot spring case),
Zinc/18-8 Stainless steel 17A6570X012
78 Handwheel (for use only with handwheel-style
low pressure pilot), Zinc 1J496144012
79 Machine Screw (for use only with handwheel-style
low pressure pilot), Plated steel 16A5763X012
80 Lockwasher (for use only with handwheel-style
low pressure pilot), Steel 1A352332992
81 O-ring (for use only with O-ring sealed
handwheel assembly) 1D541506992
82 Hex nut
For use only with O-ring sealed
handwheel assembly 1A351124122
For use with high pressure pilot, Plated steel 1A352224122
114* Gasket (for use only with high pressure pilot
with spring case 1H232619012), Steel/
Composition (not shown) 1B487099202
115 Adaptor (for use only with high pressure pilot with
spring case 1H232619012), Steel (not shown) 1J881624092
132 Pilot Cover (used only with complete replacement
pilot assembly for eld conversion), Cast iron 2C518619012
152 Drive Screw, 18-8 Stainless steel
(4 required for low pressure pilot and
6 required for high pressure pilot) 1A368228982
154 Drive Screw (for use only with low pressure
pilot), 18-8 Stainless steel (2 required) 1A368228982
*Recommended Spare Parts
3. An entire pilot assembly may be ordered from your local Sales Ofce.
by specifying a Type 61L, a 61H, or a 61HP pilot for eld conversion.
18
Page 19

A.S. – APPLY ANTI-SEIZE COMPOUND
Type 99
A6804
Figure 12. Type 61HP (Extra High Pilot) Pilot
Type 61HP (Extra High Pressure) Pilot
(Figure 12)
Key Description Part Number
23 Elbow
For use with all standard regulators
Brass 15A6002X292
316 Stainless steel 15A6002X202
For use with 1000 psig (69,0 bar) maximum inlet
regulator, Steel 1J139628982
24 Pilot Supply Tubing
For use with all standard regulators
Copper 1D7703000A2
316 Stainless steel 0500213809W
For use with 1000 psig (69,0 bar) maximum inlet
regulator, Steel 0500213809W
30* Diaphragm
Neoprene (CR) 13A9840X012
Fluorocarbon (FKM)/Dacron® 13A9840X022
31 Yoke Leg, 416 Stainless steel (2 required) 13A9838X012
Key Description Part Number
34 Connector (3 required)
For use with all standard regulators
Brass 1D692214012
316 Stainless steel 15A6002X602
For use with 1000 psig (69,0 bar) maximum
inlet regulator, Steel 15A6002XW22
35 Cap Screw, Plated steel (6 required) 1A930424052
36 Elbow, Plated steel 1B860828992
37 Yoke Cap, 416 Stainless steel 13A9837X012
38 Inlet Orice
303 Stainless steel 1D318135032
39 Pilot Body, Cast iron 33A9845X012
40* Diaphragm
Neoprene (CR) 13A9841X022
Fluorocarbon (FKM)/Dacron
41 Diaphragm Plate,
416 Stainless steel (4 required) 13A9839X012
43 Control Spring, Plated steel (blue) 1D387227022
44 Spring Case, Cast iron
Standard 2P969419012
(4)
13A9841X012
*Recommended Spare Parts
4. Dacron® is a mark owned by E.I. du Pont de Nemours and Co.
19
Page 20

Type 99
Type 61HP (Extra High Pressure) Pilot
(Figure 12) (continued)
Key Description Part Number
45 Adjusting Screw, Plated carbon steel
Standard 1C216032992
47 Cap Screw, Plated steel (8 required) 1B787724052
49 Relief Valve Spring, 316 Stainless steel 1C374037022
50 Relief Valve Plug, 316 Stainless steel 1K377535162
52 Bleed Orice
Brass 1B329014012
53 Loading Tubing
For use with all standard regulators
Copper 1D7702000A2
317 Stainless steel 0500213809W
For use with 1000 psig (69,0 bar) maximum
inlet regulator, Steel 1K5466X0042
55 Pipe Nipple, Plated steel (2 required) 1C488226232
60 Pipe plug, Steel (not shown) 1A649528982
68 Spring Seat, Plated steel 10A3963X012
72 Type Y602-12 Vent Assembly (for use only
with tapped spring case 20A4735X012),
Zinc with 18-8 Stainless steel screen 27A5516X012
82 Locknut, Plated steel 1A352224122
116 Yoke Cap, 416 Stainless steel 13A9836X012
117* Inlet Valve Plug
304 Stainless steel/Nitrile (NBR) 1D5604000B2
304 Stainless steel/Fluorocarbon (FKM) 1N3798000C2
Key Description Part Number
118 Relief Valve Cap
Brass 1D904914012
303 Stainless steel 1D904935072
119 Relief Valve Body
Brass 1D904814012
316 Stainless steel 1D904835072
120 Spring Seat
Brass 1K377718992
316 Stainless steel 1K377735072
121 Spring Seat Washer
Brass 1B495118992
316 Stainless steel 1K377835072
122 Pipe Bushing, Carbon-plated steel 1C379026232
123 Cap Screw, Plated steel (6 required) 1P327028982
124 Valve Spring, 316 Stainless steel 1B797937022
125 Flange Adaptor, Steel 23A9846X012
126* Gasket, Composition 0U0365X0032
128 Diaphragm Nut, Plated steel 1A346524122
129* Valve Spring Seat, Aluminum 1L251135072
130 Machine Screw, 303 Stainless
steel (4 required) 1A866935032
131 Pipe plug, Steel (not shown) 1A369224492
150 Diaphragm Insert (2 required)
Nitrile (NBR) 13A9842X012
Fluorocarbon (FKM) 13A9842X022
152 Drive Screw, 18-8 Stainless
steel (2 required) 1A368228982
153 Seal Washer, Nitrile (NBR)/Plated
steel (6 required) 13A9849X012
*Recommended Spare Parts
Industrial Regulators
Regulator Division
Emerson Process Management
USA - Headquarters
McKinney, Texas 75070 USA
Tel: 1-800-558-5853
Outside U.S. 1-972-548-3574
Asia-Pacic
Shanghai, China 201206
Tel: +86 21 2892 9000
Europe
Bologna, Italy 40013
Tel: +39 051 4190611
For further information visit www.emersonprocess.com/regulators
The Emerson logo is a trademark and service mark of Emerson Electric Co. All other marks are the property of their prospective owners. Fisher is a mark owned by Fisher Controls, Inc., a
business of Emerson Process Management.
The contents of this publication are presented for informational purposes only, and while every effort has been made to ensure their accuracy, they are not to be construed as warranties or
guarantees, express or implied, regarding the products or services described herein or their use or applicability. We reserve the right to modify or improve the designs or specications of such
products at any time without notice.
Emerson Process Management does not assume responsibility for the selection, use or maintenance of any product. Responsibility for proper selection, use and maintenance of any Emerson
Process Management product remains solely with the purchaser.
Natural Gas Technologies
Regulator Division
Emerson Process Management
USA - Headquarters
McKinney, Texas 75070
Tel: 1-800-558-5853
Outside U.S. 1-972-548-3574
Asia-Pacic
Singapore, Singapore 128461
Tel: +65 6777 8211
Europe
Bologna, Italy 40013
Tel: +39 051 4190611
Gallardon, France 28320
Tel: +33 (0)2 37 33 47 00
TESCOM
Regulator Division
Emerson Process Management
USA - Headquarters
Elk River, Minnesota 55330 USA
Tel: 1-763-241-3238
Europe
Selmsdorf, Germany 23923
Tel: +49 (0) 38823 31 0
©Fis her C ontr ols Intern ational, In c., 1979, 2008; All Rights Reserved
 Loading...
Loading...