Page 1

Bulletin 74.2:Y695A
Y695A Series Vapor Recovery Regulators
January 2010
W7381
Figure 1. Y695A Series Vapor Recovery Regulators
Features
• Precision Control—Large diaphragm area
provides very accurate throttling control at low
pressure settings.
• Easy Conversion—Changes easily from the
Type Y695A to the Type Y695AM with two O-rings
and a machine screw.
• Rugged Construction—Heavy duty casings and
internal parts are designed to reduce vibration and
shock and give this regulator the ability to
withstand 150 psig (10,3 bar) inlet pressure with
no internal parts damage.
• Simplicity—Direct-operated, straightforward stem
and lever design minimizes the number of parts
while providing excellent regulation of pressure.
Introduction
The Y695A Series are direct-operated vapor recovery
regulators. These regulators are used to sense an
increase in vessel pressure and vent excessive internal
tank pressure to an appropriate vapor recovery disposal
or reclamation system. They may also be used as
backpressure regulators or relief valves.
www.sherregulators.com
D102595X012
Page 2
Bulletin 74.2:Y695A
Specications
Available Congurations
Type Y695A: Direct-operated vapor
recovery regulator.
Type Y695AM: Direct-operated vapor recovery
regulator equipped with a blocked throat and O-ring
stem seal. The lower diaphragm casing is tapped
1/2 NPT for control line connection.
Body Sizes
NPS 3/4 or 1 (DN 20 or 25)
End Connection Styles
See Table 1
Maximum Allowable Inlet (Casing) Pressure
(1)
150 psig (10,3 bar)
Maximum Outlet Pressure
(1)
150 psig (10,3 bar)
Maximum Emergency Inlet Pressure to Avoid
Internal Parts Damage
150 psig (10,3 bar)
Control Pressure Ranges
(1)
See Table 2
Flow Coefcients with Fully Open Disk
Cg: 120, CV: 3.43, C1: 35
Flow Capacities
See Table 4
Orice Size
7/16-inch (11 mm)
Construction Materials
See Table 3
Material Temperature Capabilities
Nitrile:
-20° to 180°F (-29° to 82°C)
Fluorocarbon (FKM):
40° to 300°F (4° to 149°C)
Peruoroelastomer (FFKM):
-20° to 300°F (-29° to 149°C)
Ethylenepropylene (EPDM):
-20° to 300°F (-29° to 149°C)
Pressure Setting Adjustment
Adjusting Screw
Spring Case Vent Connection
1/4 NPT
Diaphragm Case Connection
1/2 NPT
Approximate Weight
19 pounds (9 kg)
(1)
1. The pressure/temperature limits in this bulletin and any applicable standard or code limitation should not be exceeded.
Table 1. End Connection Styles
BODY SIZES,
NPS (DN)
3/4 or 1 (20 or 25) NPT
1. All anges have 14-inches (356 mm) face-to-face.
Ductile Iron
END CONNECTION STYLES
CF8M
Stainless Steel
NPT, ANSI Class 150 RF,
ANSI Class 300 RF, or PN 16/25/40
(1)
Table 2. Control Pressure Ranges
RELIEF SET PRESSURE RANGE
2 to 7-inches w.c.
3 to 13-inches w.c.
10 to 26-inches w.c.
0.9 to 2.5 psig
1.3 to 4.5 psig
3.8 to 7 psig
1. Spring ranges based on spring case installed pointed down. When installed pointing up, the spring ranges increase by 2-inches w.c. (5 mbar).
2. Do not use Fluorocarbon (FKM) diaphragm with these springs at diaphragm temperatures lower than 60°F (16°C).
(5 to 17 mbar)
(7 to 32 mbar)
(25 to 65 mbar)
(0,06 to 0,17 bar)
(0,09 to 0,31 bar)
(0,26 to 0,48 bar)
(1)(2)
(1)(2)
SPRING PART
NUMBER
1B653827052
1B653927022
1B537027052
1B537127022
1B537227022
1B537327052
SPRING COLOR SPRING WIRE DIAMETER FREE LENGTH
Red
Olive drab
Yellow
Light green
Light blue
Black
0.085-inch
0.105-inch
0.114-inch
0.156-inch
0.187-inch
0.218-inch
(2,2 mm)
(2,7 mm)
(2,9 mm)
(4,0 mm)
(4,8 mm)
(5,5 mm)
Hastelloy® C
ANSI Class 150 RF
3.625-inches
3.75-inches
4.188-inches
4.060-inches
3.938-inches
3.980-inches
(92,1 mm)
(95,2 mm)
(106 mm)
(103 mm)
(100 mm)
(101 mm)
2
Page 3
Bulletin 74.2:Y695A
Type Y695A
Type Y695A
MXXXX
January 2010
Type Y695A
INLET PRESSURE
OUTLET PRESSURE
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
Table 3. Construction Materials
BODY SPRING CASE DIAPHRAGM CASE DISK HOLDER DIAPHRAGM DISK
Ductile iron,
CF8M Stainless steel,
or Hastelloy C
Ductile iron or
CF8M Stainless
steel
Table 4. Y695A Series Capacities
SPRING RANGE,
PART NUMBER, AND COLOR
2 to 7-inches w.c. (5 to 17 mbar)
1B653827052
Red
3 to 13-inches w.c. (7 to 32 mbar)
10 to 26-inches w.c. (25 to 65 mbar)
1B653927022
Olive drab
1B537027052
Yellow
0.9 to 2.5 psig (0,06 to 0,17 bar)
1B537127022
Light green
1.3 to 4.5 psig (0,09 to 0,31 bar)
1B537227022
Light blue
3.8 to 7 psig (0,26 to 0,48 bar)
1B537327052
Black
Ductile iron,
CF8M Stainless steel, or
Hastelloy C
SET PRESSURE
2-inches w.c.
(5 mbar)
4-inches w.c.
(10 mbar)
10-inches w.c.
(25 mbar)
15-inches w.c.
(37 mbar)
1 psig
(0,07 bar)
2 psig
(0,14 bar)
5 psig
(0,34 bar)
316 Stainless steel
or Hastelloy C
MINIMUM BUILDUP TO
WIDE-OPEN
1.5-inches w.c.
(3,7 mbar)
1.5-inches w.c.
(3,7 mbar)
2.3-inches w.c.
(5,7 mbar)
3.4-inches w.c.
(8,5 mbar)
0.40 psig
(0,03 bar)
0.88 psig
(0,06 bar)
1.66 psig
(0,11 bar)
VACUUM OUTLET
Nitrile (NBR),
Fluorocarbon (FKM), or
Nitrile (NBR) with bonded
Teon (PTFE)
PRESSURE
0 psig
(0 bar)
2.5 psig
(0,17 bar)
5 psig
(0,34 bar)
0 psig
(0 bar)
2.5 psig
(0,17 bar)
5 psig
(0,34 bar)
0 psig
(0 bar)
2.5 psig
(0,17 bar)
5 psig
(0,34 bar)
0 psig
(0 bar)
2.5 psig
(0,17 bar)
5 psig
(0,34 bar)
0 psig
(0 bar)
2.5 psig
(0,17 bar)
5 psig
(0,34 bar)
0 psig
(0 bar)
2.5 psig
(0,17 bar)
5 psig
(0,34 bar)
0 psig
(0 bar)
2.5 psig
(0,17 bar)
5 psig
(0,34 bar)
SPECIFIC GRAVITY NITROGEN
Nitrile (NBR),
Fluorocarbon (FKM),
Peruoroelastomer (FFKM),
Teon (PTFE), or
Ethylenepropylene (EPDM)
CAPACITIES IN
SCFH (Nm3/h) OF 0.97
280
(7,50)
1180
(31,6)
1520
(40,7)
350
(9,38)
1200
(32,2)
1530
(41,0)
520
(13,9)
1250
(33,5)
1570
(42,1)
640
(17,2)
1300
(34,8)
1600
(42,9)
940
(25,2)
1450
(38,9)
1720
(46,1)
1360
(36,4)
1730
(46,4)
1940
(52,0)
2110
(56,5)
2330
(62,4)
2470
(66,2)
INLET PRESSURE
OUTLET PRESSURE
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
B2648
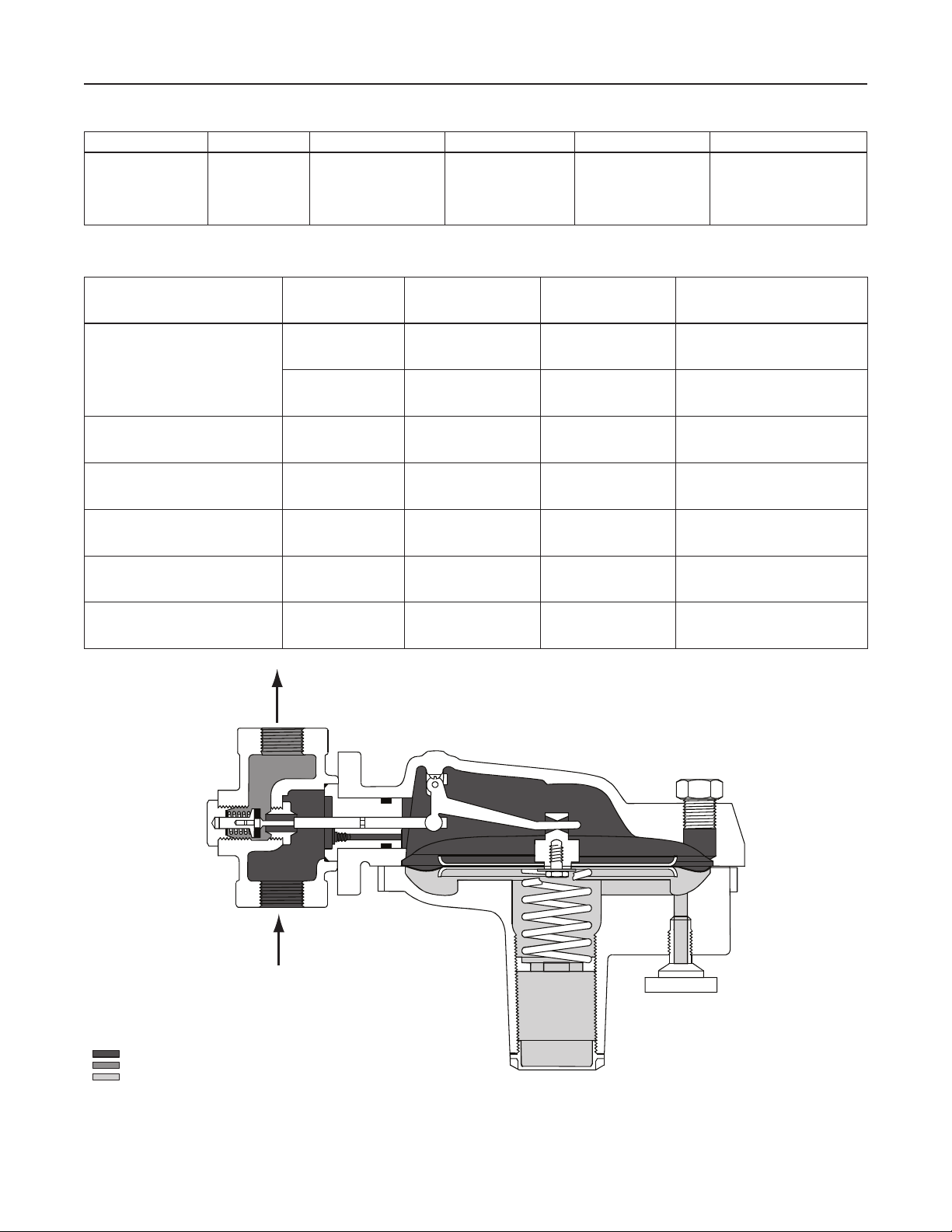
Figure 2. Y695A Series Operational Schematic
3
Page 4

Bulletin 74.2:Y695A
Table 5. Materials Compatibility
Material
CORROSION INFORMATION
Material
Fluid
Cast or
Ductile Iron
Carbon Steel
Acetic Acid (Air Free)
Acetic Acid Vapors
Acetone
Acetylene
Alcohols
Aluminum Sulfate
Ammonia
Ammonium Chloride
Ammonium Nitrate
Ammonium Sulfate
Ammonium Sulte
Beer
Benzene (Benzol)
Benzoic Acid
Boric Acid
Butane
Calcium Chloride (Alkaline)
Carbon Dioxide (Dry)
Carbon Dioxide (Wet)
Carbon Disulde
Carbon Tetrachloride
Carbonic Acid
Chlorine Gas (Dry)
Chlorine Gas (Wet)
Chlorine (Liquid)
Chromic Acid
Citric Acid
Coke Oven Gas
Copper Sulfate
Ether
Ethyl Chloride
Ethylene
Ethylene Glycol
Formaldehyde
Formic Acid
Freon (Wet)
Freon (Dry)
Gasoline (Rened)
Glucose
Hydrochloric Acid (Aerated)
1. Monel is a trademark of International Nickel Co.
2. Hastelloy is a trademark of Stelite Div., Cabot Corp.
I.L.
I.L.
C
C
C
C
A
A
A
A
A
A
C
C
A
A
C
C
A
C
C
C
C
C
B
B
A
A
C
C
C
C
A
A
B
B
A
A
C
C
A
A
B
B
C
C
A
A
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
A
A
C
C
B
B
C
C
A
A
A
A
B
B
C
B
B
B
B
A
A
A
A
C
C
S41600
Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel
CF8M or S31600
S30200 or S30400
B
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
C
A
A
A
B
B
B
C
C
C
B
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
B
B
A
A
A
C
C
A
C
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
C
A
A
B
C
A
C
A
C
A
B
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
B
C
A
A
A
A
A
B
B
C
B
A
B
C
C
C
C
C
B
C
A
B
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
C
A
I.L.
A
I.L.
A
A
A
A
C
C
(2)
C
(1)
®
®
Monel
Stainless Steel
Hastelloy
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
B
A
C
A
A
A
C
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
C
B
C
A
A
A
B
A
B
A
C
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
I.L.
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
C
B
Fluid
Cast or
Carbon Steel
Hydrochloric Acid (Air free)
Hydrogen
Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydrogen Sulde (Liquid)
Magnesium Hydroxide
Methanol
Methyl Ethyl Ketone
Natural Gas
Nitric Acid
Petroleum Oils (Rened)
Phosphoric Acid (Air Free)
Phosphoric Acid Vapors
Potassium Chloride
Potassium Hydroxide
Propane
Silver Nitrate
Sodium Acetate
Sodium Carbonate
Sodium Chloride
Sodium Chromate
Sodium Hydroxide
Stearic Acid
Sulfur
Sulfur Dioxide (Dry)
Sulfur Trioxide (Dry)
Sulfuric Acid (Aerated)
Sulfuric Acid (Air Free)
Sulfurous Acid
Trichloroethylene
Water (Boiler Feed)
Water (Distilled)
Water (Sea)
Zinc Chloride
Zinc Sulfate
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
A+--Best possible selection
A--Recommended
B--Minor to moderate effect. Proceed with caution.
C--Unsatisfactory
I.L.--Information lacking
I.L.
C
C
A
A
A
C
C
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
C
C
A
A
C
C
C
C
B
B
B
B
A
A
C
C
A
A
A
A
C
C
A
A
A
A
A
C
A
A
A
A
A
A
C
C
C
C
C
C
B
B
B
C
A
A
B
B
C
C
C
C
Ductile Iron
Stainless Steel
CF8M or S31600
S30200 or S30400
C
C
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
B
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
C
C
C
C
B
B
B
A
A
A
A
A
B
B
C
C
A
A
®(1)
S41600
Monel
Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel
C
C
A
A
B
A
C
C
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
C
C
A
A
C
B
C
C
C
B
B
A
A
A
B
C
A
A
B
A
B
A
A
A
B
A
B
B
A
A
B
A
B
A
C
C
C
B
C
C
B
A
B
A
B
A
C
A
C
C
B
A
(2)
C
®
Hastelloy
B
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
I.L.
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
- continued -
Principle of Operation
Y695A Series vapor recovery regulators are used to
maintain a constant blanket (inlet) pressure or vessel
pressure with the outlet owing to a system whose
pressure is lower than the inlet (see Figure 2).
4
When vessel pressure increases above the setpoint
of the regulator due to pumping in or thermal heating,
the force of the control spring is overcome by pressure
acting on the diaphragm. This moves the disk away
from the orice, allowing gas to ow from the vessel
to the vapor recovery system. As vessel pressure is
Page 5

Table 5. Materials Compatibility (continued)
Fluid
Acetic Acid (30%)
Acetone
Alcohol (Ethyl)
Alcohol (Methyl)
Ammonia (Anhydrous)
Ammonia (Gas, Hot)
Benzene
Brine (Calcium Chloride)
Butadiene Gas
Butane (Gas)
Butane (Liquid)
Carbon Tetrachloride
Chlorine (Dry)
Chlorine (Wet)
Coke Oven Gas
Ethyl Acetate
Ethylene Glycol
Freon 11
Freon 12
Freon 22
Freon 114
Gasoline
Hydrogen Gas
Hydrogen Sulde (Dry)
Hydrogen Sulde (Wet)
Jet Fuel (JP-4)
Natural Gas
Natural Gas + H2S (Sour Gas)
Nitric Acid (20%)
Nitric Acid (50 to 100%)
Nitrogen
Oil (Fuel)
Propane
Sulfur Dioxide
Sulfuric Acid (to 50%)
Sulfuric Acid (50 to 100%)
Water (Ambient)
Water [at 200°F (93°C)]
Water (Sea)
A+--Best possible selection
A--Recommended
B--Minor to moderate effect. Proceed with caution.
C--Unsatisfactory
I.L.--Information lacking
Neoprene
(CR)
C
B
A
A+
A
B
C
A
B
A
B
C
C
C
C
C
A
B
A+
A+
A
B
A
A
B
C
A
A
B
C
A
B
A
B
A
B
C
A
C
FLUID INFORMATION
Nitrile
(NBR)
B
C
A
A
C
C
C
A
C
A+
A
C
C
C
B
C
A
A
A
C
A
A+
A
C
C
A
A+
B
C
C
A
A+
A
A
C
C
C
A
B
Material
Fluorocarbon
(FKM)
B
C
B
C
C
C
A
B
B
A
A
A
A
A
A+
C
A
A+
B
C
B
A
A
C
C
A
A
C
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
Bulletin 74.2:Y695A
Peruoroelastomer
(FFKM)
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
Ethylenepropylene
(EPDM)
A
A
A
A
A
B
C
A
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
B
A
C
B
A
A
C
A
A
A
I.L.
C
C
C
C
A
C
C
A
A
B
B
A
A
reduced, the force of the back disk spring causes the
disk to move toward the orice, decreasing the ow of
gas out of the vessel. As vessel pressure drops below
the setpoint of the regulator, the disk will seat against
the orice, shutting off the ow of gas.
Sizing Vapor Recovery Systems
To determine the capacity required, you must consider
the amount of blanketing gas that must be displaced
from the tank when either lling the vessel with liquid
(pump-in) or the expansion of tank vapors during
atmospheric thermal heating.
Using the established procedures from American
Petroleum Institute Standard 2000 (API 2000),
determine the required ow rate for outbreathing.
For liquids with a ash point below 100°F (38°C) or a
normal boiling point below 300°F (149°C), multiply the
calculated outbreathing requirements in Table 6 by 2.0
as indicated in footnote 1 from Table 6.
5
Page 6

Bulletin 74.2:Y695A
Table 6. Flow Rate Conversions (Gas ow required to displace
blanketing gas with pump-in of liquid.)
MULTIPLY MAXIMUM
PUMP RATE IN
U.S. GPM
U.S. GPH
Barrels/hour
Barrels/day
1. For liquids with a ash point below 100°F (38°C) or normal boiling point below 300°F
(149°C), multiply the above calculated outbreathing requirement by 2.0.
2. To convert to Nm³/h multiply SCFH by 0.0268.
BY TO OBTAIN
8.021
0.1337
5.615
0.2340
SCFH air
required
(1)(2)
1. Determine the ow rate of blanketing gas displaced
when liquid is being pumped in (see Table 6).
2. Determine the gas ow rate due to “outbreathing”
caused by atmospheric thermal heating (see
Table 7).
3. Add the requirements of steps 1 and 2 and select
a vapor recovery regulator size based on total
capacity required from Table 4.
Sample sizing problem for vapor
recovery applications:
Vessel capacity . . . . . . 1000 barrels (42,000 gal)(159 000 liters)
Pump in capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20 GPM (75,7 l/min)
Inlet pressure source . . . . . . . . 60 psig (4,14 bar) nitrogen
Desired blanket setpoint . . . . . . . . 0.5-inches w.c. (1 mbar)
Desired vapor recovery setpoint . . . 2-inches w.c. (5 mbar)
Vapor recovery vacuum source . . . 5-inches Hg (169 mbar)
Fluid . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Hexane
Boiling point . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155°F (68°C)
1. From Table 6 the desired air ow rate due to pump
in equals 20 GPM (75,7 l/min) x 8.021 x 2 = 321
SCFH (8,60 Nm3/h) air.
Table 7. Gas Flow Required for Thermal Heating (Outbreathing)
per API 2000 (Interpolate for intermediate sizes.)
VESSEL CAPACITY
Barrels Gallons Liters
60
100
500
1000
2000
3000
4000
5000
10,000
15,000
20,000
25,000
30,000
35,000
40,000
45,000
50,000
60,000
70,000
80,000
90,000
100,000
120,000
140,000
160,000
180,000 7,560,000 28 616 000 54,000 (1447) 90,000 (2412)
2500
4200
21,000
42,000
84,000
126,000
168,000
210,000
420,000
630,000
840,000
1,050,000
1,260,000
1,470,000
1,680,000
1,890,000
2,100,000
2,520,000
2,940,000
3,360,000
3,780,000
4,200,000
5,040,000
5,880,000
6,720,000
9500
15 000
79 500
159 000
318 000
477 000
636 000
795 000
1 590 000
2 385 000
3 180 000
3 975 000
4 769 000
5 564 000
6 359 000
7 154 000
7 949 000
9 539 000
11 129 000
12 718 000
14 308 000
15 898 000
19 078 000
22 257 000
25 437 000
SCFH (Nm³/h) AIR FLOW
RATE REQUIRED
Flash point is equal
to or above 100°F
(38°C) or normal
boiling point is
equal to or above
300°F (149°C)
40 (1,07)
60 (1,61)
300 (8,04)
600 (16,1)
1200 (32,2)
1800 (48,2)
2400 (64,3)
3000 (80,4)
6000 (161)
9000 (241)
12,000 (322)
15,000 (402)
17,000 (456)
19,000 (509)
21,000 (563)
23,000 (616)
24,000 (643)
27,000 (724)
29,000 (777)
31,000 (831)
34,000 (911)
36,000 (965)
41,000 (1099)
45,000 (1206)
50,000 (1340)
Flash point is
below 100°F
(38°C) or
normal boiling
point is below
300°F (149°C)
60 (1,61)
100 (2,68)
500 (13,4)
1000 (26,8)
2000 (53,6)
3000 (80,4)
4000 (107)
5000 (134)
10,000 (268)
15,000 (402)
20,000 (536)
24,000 (643)
28,000 (750)
31,000 (831)
34,000 (911)
37,000 (992)
40,000 (1072)
44,000 (1179)
48,000 (1286)
52,000 (1394)
56,000 (1501)
60,000 (1608)
68,000 (1822)
75,000 (2010)
82,000 (2198)
given capacity of nitrogen by 0.985, and divide by the
square root of the appropriate specic gravity of the
gas required. To determine regulating capacities at
pressure settings not given or to determine wide-open
ow capacities, use the following formula:
2. From Table 7 the desired air ow rate = 1000 SCFH
(26,8 Nm3/h) air due to thermal heating.
3. Total required ow rate = 1000 SCFH (26,8 Nm3/h)
air + 320 SCFH (8,58 Nm3/h) = 1320 SCFH
(35,4 Nm3/h) air. This converts to nitrogen
requirements of 1340 SCFH (35,9 Nm3/h).
Capacity Information
Table 4 gives typical nitrogen regulating capacities at
selected inlet pressures and outlet pressure settings.
Flows are in SCFH at 60°F and 14.7 psia and Nm³/h at
0°C and 1,01325 bar of 0.97 specic gravity nitrogen.
For gases of other specic gravities, multiply the
6
520
Q = CgP1SIN
GT
3417
C
∆P
Deg.
P
1
1
Where:
Cg = gas sizing coefcient from Specications
C1 = Cg/CV or 35 from Specications
G = gas specic gravity (air = 1.0)
P
= inlet pressure, psia (add 14.7 psi to gauge inlet
1abs
pressure to obtain absolute inlet pressure)
Q = ow rate, SCFH
T = absolute temperature in °Rankine of gas at inlet
(°Rankine = °F + 460)
∆P = Pressure differential across the valve,
psig (P1 - P2)
Page 7

Installation
Bulletin 74.2:Y695A
Install the regulator using a straight run of pipe the
same size or larger as the regulator body. Flow
through the regulator body is indicated by the ow
arrow on the body. If a block valve is required, install a
B
14
(356)
B2441
INCHES
(mm)
A
5.56
(141)
full ow valve between the regulator and the blanketed
vessel. For proper operation at low setpoint ranges,
the regulators should be installed with the spring case
pointed down.
G F
D
8.38
(213)
DIAMETER
DIMENSIONS, INCHES (mm)
BODY SIZE,
NPS (DN)
3/4,1 (20, 25) 4.0 (102) 4.12 (105) 2.12 (54) 2.25 (57) 6.19 (157) 6.19 (157) 10.38 (264) 10.38 (264) 1.69 (43) 1.69 (43)
A B D F G
Iron
Stainless
Steel or
Hastelloy® C
Ductile
Iron
Stainless
Steel or
Hastelloy® C
Ductile
Iron
Stainless
Steel or
Hastelloy® C
Ductile
Iron
Stainless
Steel or
Hastelloy® C
Ductile
Iron
Stainless
Steel or
Hastelloy® C
Figure 3. Dimensions
7
Page 8

Bulletin 74.2:Y695A
Ordering information
When ordering, specify:
Application
1. Type of gas being controlled (natural gas, air, etc.);
list any factors such as impurities in the gas that
may affect compatibility of gas with the regulator
trim parts.
2. Specic gravity of the gas.
3. Temperature of the gas.
4. Range of owing inlet pressures to regulator.
5. Flow rates
a) Minimum controlled ow
b) Normal ow
c) Maximum ow
6. Line size and end connection size of adjacent piping.
Regulator
Refer to the Specications table on page 2. Carefully
review the description of each specication and make
the desired selection wherever there is a choice.
Always specify the type number.
Industrial Regulators
Emerson Process Management
Regulator Technologies, Inc.
USA - Headquarters
McKinney, Texas 75069-1872 USA
Tel: 1-800-558-5853
Outside U.S. 1-972-548-3574
Asia-Pacic
Shanghai, China 201206
Tel: +86 21 2892 9000
Europe
Bologna, Italy 40013
Tel: +39 051 4190611
Middle East and Africa
Dubai, United Arab Emirates
Tel: +971 4811 8100
For further information visit www.sherregulators.com
The Emerson logo is a trademark and service mark of Emerson Electric Co. All other marks are the property of their prospective owners. Fisher is a mark owned by Fisher Controls, Inc., a
business of Emerson Process Management.
The contents of this publication are presented for informational purposes only, and while every effort has been made to ensure their accuracy, they are not to be construed as warranties or
guarantees, express or implied, regarding the products or services described herein or their use or applicability. We reserve the right to modify or improve the designs or specications of such
products at any time without notice.
Emerson Process Management does not assume responsibility for the selection, use or maintenance of any product. Responsibility for proper selection, use and maintenance of any Emerson
Process Management product remains solely with the purchaser.
Natural Gas Technologies
Emerson Process Management
Regulator Technologies, Inc.
USA - Headquarters
McKinney, Texas 75069-1872 USA
Tel: 1-800-558-5853
Outside U.S. 1-972-548-3574
Asia-Pacic
Singapore, Singapore 128461
Tel: +65 6777 8211
Europe
Bologna, Italy 40013
Tel: +39 051 4190611
Gallardon, France 28320
Tel: +33 (0)2 37 33 47 00
TESCOM
Emerson Process Management
Tescom Corporation
USA - Headquarters
Elk River, Minnesota 55330-2445 USA
Tel: 1-763-241-3238
Europe
Selmsdorf, Germany 23923
Tel: +49 (0) 38823 31 0
©Emerson Process Management Regulator Technologies, Inc., 1999, 2010; All Rights Reserved
 Loading...
Loading...