Page 1

Instruction Manual
Form 5347
August 2009
Type Y692
Type Y692 Low-Pressure Gas Blanketing Regulator
WARNING
!
Failure to follow these instructions or
to properly install and maintain this
equipment could result in an explosion,
re and/or chemical contamination
causing property damage and personal
injury or death.
Fisher® regulators must be installed,
operated, and maintained in accordance
with federal, state, and local codes,
rules and regulations, and Emerson
Process Management Regulator
Technologies Inc. instructions.
If the regulator vents gas or a leak
develops in the system, service to the unit
may be required. Failure to correct trouble
could result in a hazardous condition.
Installation, operation, and maintenance
procedures performed by unqualied
personnel may result in improper
adjustment and unsafe operation. Either
condition may result in equipment
damage or personal injury. Use qualied
personnel when installing, operating,
and maintaining the Type Y692 LowPressure Gas Blanketing Regulator.
Introduction
Scope of the Manual
This instruction manual provides installation, startup,
maintenance, and parts ordering information for the
Type Y692 Low-Pressure Gas Blanketing Regulator.
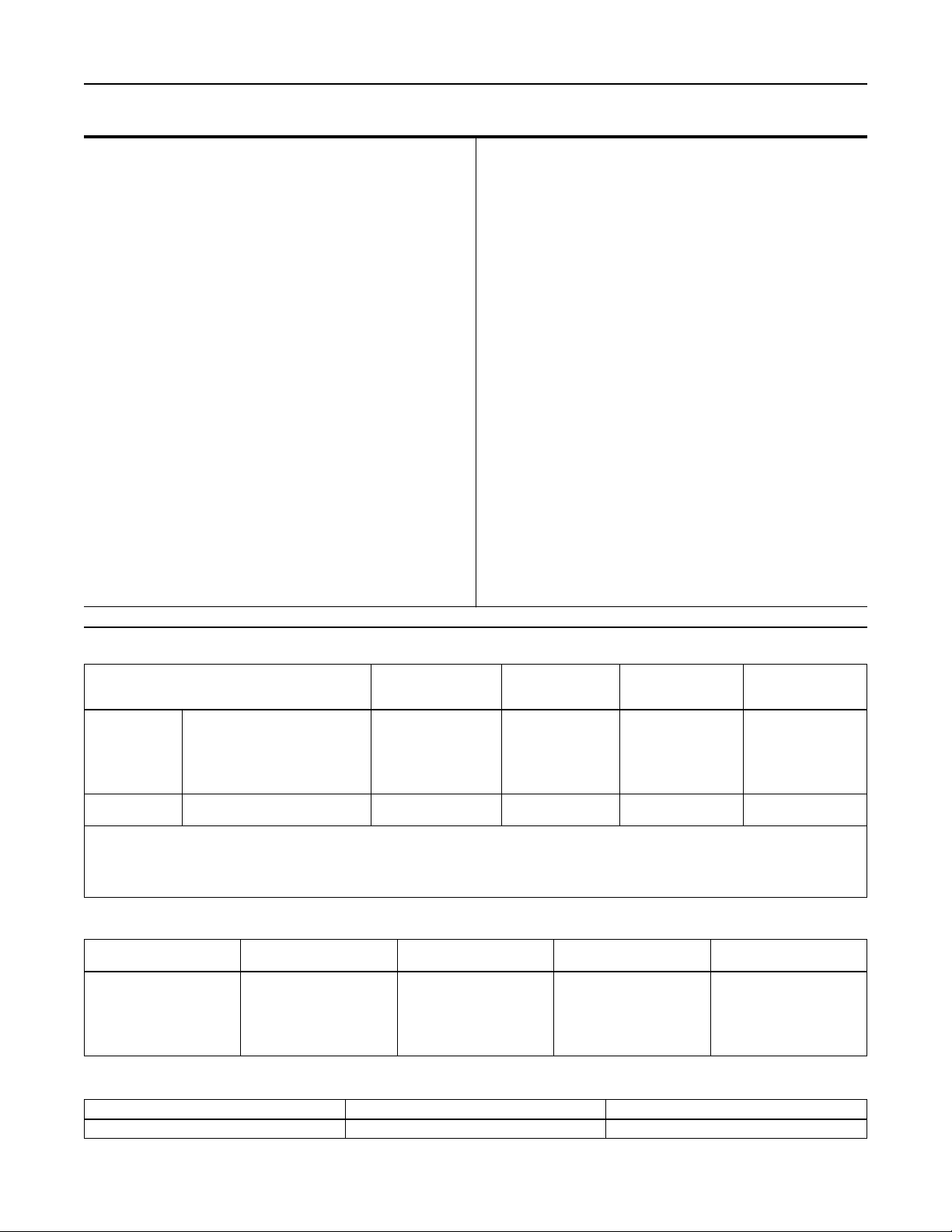
W5930
Figure 1. Type Y692 Low-Pressure Gas Blanketing Regulators
operated regulator with internal registration or external
pressure registration. It is used for accurate pressure
control on very low-pressure blanketing systems.
Blanketing with low-pressure gas helps prevent
corrosion, helps control emissions from the blanketed
product and helps protect against any contamination to
the blanketed product by atmospheric conditions.
The regulator will maintain a positive vessel
pressure reducing the possibility of vessel wall
collapse. The Type Y692 is available in NPS 1-1/2
and 2 (DN 40 and 50) body sizes.
Type Y692 with external pressure registration
regulators have a stem seal with O-rings and a
1/2 NPT control line connection in the diaphragm
case. The control line can be used to more accurately
control the pressure in the tank if the regulator is
mounted an extended distance from the control point.
The stem seal separates the body outlet pressure from
the diaphragm case.
Specications
Product Description
The Accu-Pressure™ Type Y692 Gas Blanketing
Regulator (Figure 1) is a pressure reducing direct-
www.emersonprocess.com/regulators
The Specications section lists specications for
Type Y692 Gas Blanketing Regulator. Specications
for a given regulator as it originally comes from the
factory are stamped on the spring case nameplate.
D102031X012
Page 2
Type Y692
Specications
Available Congurations
Direct-operated pressure reducing regulator with
external or internal pressure registration with
seven outlet (control) pressure ranges from
1-inch w.c. to 7 psig (2 mbar to 0,48 bar).
Available in NPS 1-1/2 and 2 (DN 40 and 50)
body sizes.
Body Sizes and End Connection Styles
(1)(2)
Cast Iron: NPS 1-1/2 (DN 40), NPT
NPS 2 (DN 50), NPT or CL125 FF
Steel: NPS 1-1/2 or 2 (DN 40 or 50), NPT, SWE,
CL150 RF, CL300 RF, or PN 16/25/40
Stainless Steel: NPS 1-1/2 or 2 (DN 40 or 50), NPT,
CL150 RF, CL300 RF, or PN 16/25/40
Maximum Allowable Inlet Pressure
(1)
150 psig (10,3 bar) or body rating limit
Maximum Control (Casing) Pressure
(1)
15 psig (1,0 bar)
Control Pressure Ranges
(1)
See Table 1
Orices Sizes and Flow Coefcients
See Table 2
IEC Sizing Coefcients
See Table 3
Pressure Registration
Internal (standard) or External
Maximum Operating Control Pressure to Avoid
Internal Part Damage
(1)
3 psig (0,21 bar) above control pressure setting
Temperature Capabilities
(1)
Nitrile (NBR): -20° to 180°F (-29° to 82°C)
Fluorocarbon (FKM): 0° to 300°F (-18° to 149°C)
Ethylenepropylene (EPDM):-20° to 275°F
(-29° to 135°C)
Peruoroelastomer (FFKM): -20° to 300°F
(-29° to 149°C)
Spring Case Connection
1/4 NPT
Approximate Weights
Cast Iron Body: 45 pounds (20 kg)
Steel/Stainless Steel Body: 57 pounds (26 kg)
1. The pressure/temperature limits in this Instruction Manual and any applicable standard limitation should not be exceeded.
Table 1. Control Pressure Ranges
CONTROL PRESSURE RANGES WITH
CASE BARREL POINTED DOWN
1 to 3-inches w.c. (2 to 7 mbar)
3 to 11-inches w.c. (7 to 27 mbar)
Light Spring
Assembly
Heavy spring
Assembly
1. Install with spring case pointing down to achieve low setpoints in these spring ranges.
2. Do not use uorocarbon (FKM) diaphragm with these springs at diaphragm temperature lower than 60°F (16°C).
3. Installation with spring case pointing up will change outlet (control) pressure range to 3 to 5-inches w.c. (7 to 12 mbar).
4. Installation with spring case pointing up will change outlet (control) pressure range to 5.75 to 14-inches w.c. (14 to 35 mbar).
5. Installation with spring case pointing up will change outlet (control) pressure range to 7.5-inches w.c. to 1.3 psig (19 to 90 mbar).
6.5-inches w.c. to 1.2 psig (16 mbar to
0.7 to 2 psig (0,05 to 0,14 bar)
1 to 3.2 psig (0,07 to 0,22 bar)
2 to 5.5 psig (0,14 to 0,38 bar)
4 to 7 psig (0,28 to 0,48 bar)
0,08 bar)
(5)
CONTROL SPRING
COLOR CODE
(2)(3)
(2)(4)
Metallic with green stripe
Metallic (silver)
Brown
Iridite
Green
Blue
Orange
CONTROL SPRING
PART NUMBER
1D892527022
0B019727052
0B019427052
0B019627032
0A081127202
0Y066427022
1H802427032
SPRING WIRE
DIAMETER,
INCHES (mm)
0.109 (2,77)
0.148 (3,76)
0.187 (4,75)
0.225 (5,71)
0.250 (6,35)
0.363 (9,22)
0.406 (10,3)
Table 2. Orice Sizes and Flow Coefcients
BODY SIZES, NPS (DN)
1-1/2 and 2 (40 and 50)
ORIFICE SIZES,
INCHES (mm)
1/4
(6,4)
3/8
(9,5)
1/2
(13)
3/4
(19)
1
(25)
1-3/16
(30)
WIDE-OPEN C
1.51
3.14
5.43
11.9
20
26
V
WIDE-OPEN C
53.0
111.0
190.0
415.0
700.0
910.0
g
SPRING FREE
LENGTH,
INCHES (mm)
6.12 (155)
6.00 (152)
6.00 (152)
6.00 (152)
6.00 (152)
6.00 (152)
6.00 (152)
C
1
35
Table 3. IEC Sizing Coefcients
X
T
0.775 0.50 0.89
2
F
D
F
L
Page 3
Type Y692
M1042
INLET PRESSURE
OUTLET PRESSURE
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
July 2007
Type Y692
BLOCK
Type Y692
M1042
INLET PRESSURE
OUTLET PRESSURE
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
July 2007
Type Y692
VALVE
SUPPLY
PRESSURE
VENT
VALVE
BLOCK
VALVE
SUPPLY
PRESSURE
VENT
VALVE
Type Y692
A6340
INLET PRESSURE
CONTROL PRESSURE
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
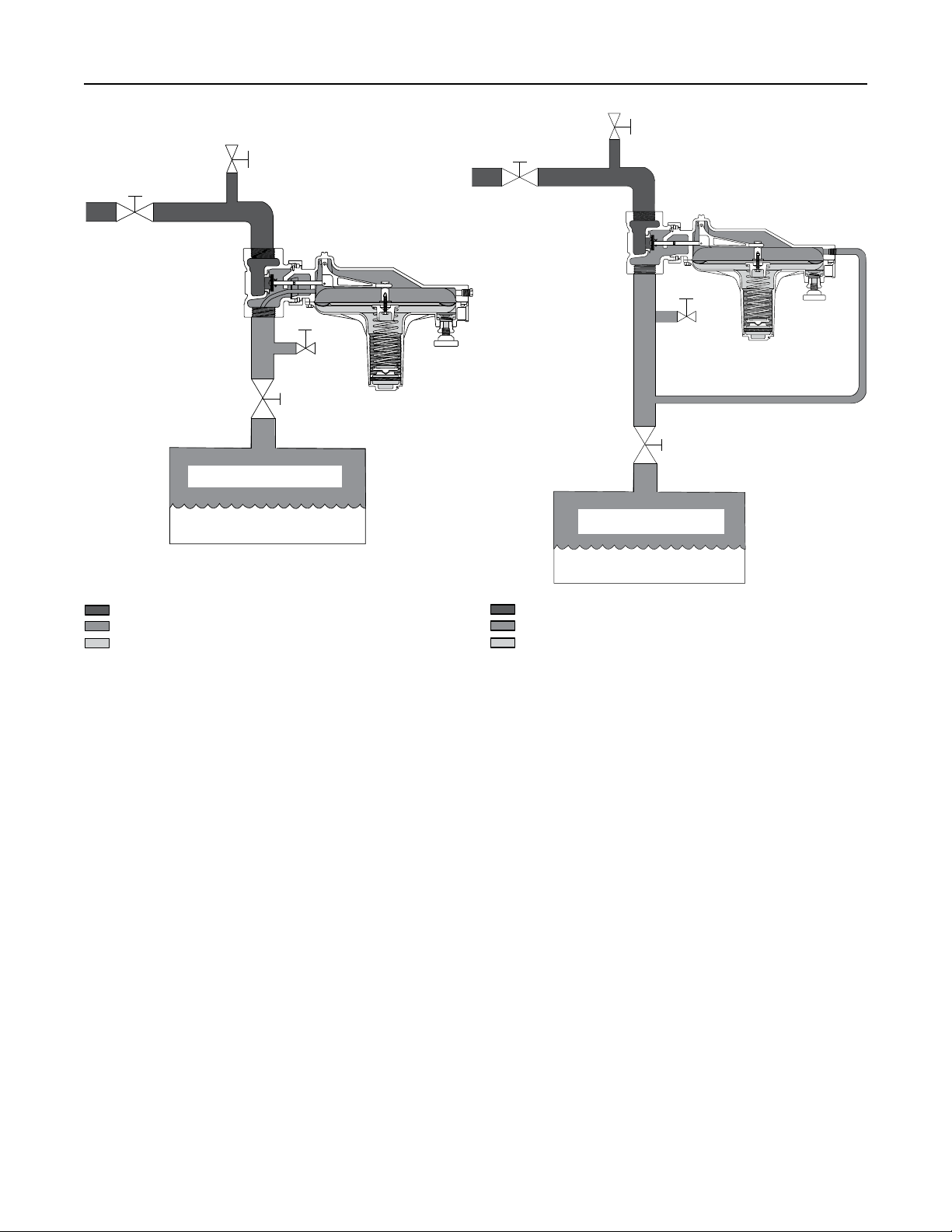
Figure 2. Type Y692 with Internal Registration
Principle of Operation
The Type Y692 Gas Blanketing Regulator reduces a
high-pressure gas to maintain a positive low-pressure
of blanket gas over a stored liquid when the liquid is
being pumped out of the vessel (see Figures 2 and
3). Also when the vessel (or tank) is suddenly cooled,
causing vapors to contract, the regulator replaces
the volume of contracting vapors with a volume of
blanketing gas to prevent the internal vessel pressure
from decreasing. In both cases, a positive vessel
pressure prevents outside air from entering the vessel
and reduces the possibility of atmospheric pressure
collapsing the vessel.
Gas blanketing regulators respond to a slight decrease
in internal vessel pressure by throttling open to
increase the ow rate of gas into the vessel. When the
vessel’s liquid level has been lowered to the desired
point and the vapor pressure re-established, the
regulator throttles closed.
VENT
VALVE
BLOCK
VALVE
GAS BLANKETING PRESSURE
LIQUID
Operational Schematic
VENT
POINTED
DOWNWARD
VENT
VALVE
BLOCK
VALVE
GAS BLANKETING PRESSURE
LIQUID
INLET PRESSURE
CONTROL PRESSURE
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
Figure 3. Type Y692 with External Registration
Operational Schematic
VENT
POINTED
DOWNWARD
When the liquid level drops and vessel pressure
decreases below the setting of the control spring,
the spring force on the diaphragm opens the disk
assembly to supply the required ow of gas to the
vessel. When vessel pressure has been satised,
control pressure tends to increase slightly, acting on
the diaphragm. When the control (vessel) pressure
exceeds the control spring setting, the diaphragm
moves to close the disk assembly.
The Type Y692 Gas Blanketing Regulator provides
a constant set pressure for accurate gas blanketing.
When vessel pressure decreases below the control
spring setpoint, the force of the spring moves the disk
away from the orice allowing gas to ow into the
vessel. As the vessel pressure increases, the increase
is sensed by the diaphragm through the pitot tube or
control line. This movement of the diaphragm causes
the disk to move toward the orice, decreasing the
ow of blanketing gas. When the vessel pressure
reaches the system setpoint, the disk will seat against
the orice shutting off the ow of gas.
3
Page 4
Type Y692
Installation
WARNING
!
Personal injury, equipment damage, or
leakage due to escaping accumulated
gas or bursting of pressure-containing
parts may result if the gas blanketing
regulator is overpressured or installed
where service conditions could exceed
the limits given in Specications
section, or where conditions exceed
any ratings of the adjacent piping or
piping connections. To avoid such
injury or damage, provide pressurerelieving or pressure-limiting devices
(as required by Title 49, Part 192, of the
U.S. Code of Federal Regulations, by
the National Fuel Gas Code Title 54 of
the National Fire Codes of the National
Fire Protection Association, or by other
applicable codes) to prevent service
conditions from exceeding those limits.
Additionally, physical damage to the
gas blanketing regulator could result in
personal injury and property damage
due to escaping accumulated gas. To
avoid such injury and damage, install
the gas blanketing regulator in a safe
and well ventilated location.
1. Use qualied personnel when installing, operating,
and maintaining the regulator. Before installing,
inspect the regulator for any shipment damage
or foreign material that may have collected during
crating and shipment. Make certain the body
interior is clean and the pipelines are free of
foreign material. Apply pipe compound only to the
external pipe threads.
2. To achieve the published capacities, install the
regulator as close as possible to the blanketed
vessel using a straight run of pipe the same size
or larger as the regulator body. Flow through the
regulator body is indicated by the ow arrow cast
on the body. If a block valve is required, install a full
ow valve between the regulator and the blanketed
vessel. For proper operation, the regulator
must be installed with the spring case barrel
pointed down (as shown in Figures 2 and 3).
Key numbers referenced in this section are shown
in Figure 6.
WARNING
!
If the regulator vents some gas or a leak
develops in the system, it indicates that
service is required. Failure to take the
regulator out of service immediately
may create a hazardous condition. In
hazardous or ammable gas service,
vented gas may accumulate, and cause
personal injury, death, or property damage
due to re or explosion. Vent a regulator
in hazardous gas service to a remote,
safe location away from air intakes or
any hazardous location. The vent line or
stack opening must be protected against
condensation or clogging.
3. To keep the spring case vent from being plugged
or the spring case from collecting moisture,
corrosive chemicals, or other foreign material,
point the vent down or otherwise protect it.
4. To remotely vent the regulator, remove the vent
(key 56) and install obstruction-free tubing or
piping into the 1/4 NPT vent tapping. Provide
protection on a remote vent by installing a
screened vent cap into the remote end of the
vent pipe.
5. If continuous operation of the system is required
during inspection or maintenance, install a parallel
run with a three-valve bypass around the regulator.
For Types with external pressure registration which
require a downstream control line, be sure to install the
control line before putting the regulator into operation.
The control line pipe should be at least 1/2-inch
(13 mm) in diameter and connected to a straight
section of outlet piping 5 to 10 pipe diameters
downstream of the regulator. If turbulence exists, a
hand valve can be installed in a straight section of the
control line. This hand valve can be throttled down to
dampen out pulsations which may cause instability or
cycling of the regulator. If a block valve is required,
install a full ow valve between the regulator and the
blanketed vessel.
Startup and Adjustment
WARNING
!
To avoid personal injury, property
damage, or equipment damage caused
4
Page 5

Type Y692
by bursting of pressure containing parts
or explosion of accumulated gas, never
adjust the control spring to produce a
control pressure higher than the upper
limit of the control pressure range or
that particular spring (see Specications
section). If the desired control pressure
is not within the range of the control
spring, install a spring of the proper
range according to the Diaphragm
and Spring Case Area section of the
Maintenance procedure.
With installation completed, the regulator can be
placed in operation by slowly opening the upstream
and downstream block valves, if used, while using
gauges to monitor pressure. The regulator takes
control when downstream pressure is established.
The regulator has been adjusted at the factory to
provide approximately the control pressure requested.
To ensure the correct pressure setting always use a
pressure gauge to verify the pressure setting. The
range of allowable pressure settings is stamped on the
spring casing nameplate. If a pressure setting beyond
the stamped range is required, install a spring with the
desired range by following the procedures for changing
the spring and diaphragm in the Maintenance section.
To adjust the pressure setting, perform the following
steps (key numbers are referenced in Figure 6):
in response to the decreasing downstream pressure.
If vent valves are not installed, safely bleed off both
inlet and outlet pressures, and check that the regulator
contains no pressure.
Maintenance
Regulator parts are subject to normal wear and
must be inspected and replaced as necessary. The
frequency of inspection and replacement of parts
depends upon the severity of service conditions or the
requirements of local, state, and federal regulations.
Due to care Emerson Process Management Regulator
Technologies, Inc. takes in meeting all manufacturing
requirements (heat treating, dimensional tolerances,
etc.), use only replacement parts manufactured
or furnished by Emerson Process Management
Regulator Technologies, Inc.
WARNING
!
To avoid personal injury, property
damage, or equipment damage caused
by sudden release of pressure, isolate the
regulator from all pressure and cautiously
release trapped pressure from the
regulator before attempting disassembly.
Key numbers are referenced in Figure 6.
1. Remove the closing cap (key 3, if required).
2. Turn the adjusting screw (key 2) either clockwise
to increase control pressure or counterclockwise
to decrease control pressure. The regulator will
go into immediate operation. To ensure correct
operation always use a pressure gauge to monitor
the blanket pressure when making adjustments.
3. Replace the closing cap (key 3, if required).
Shutdown
Installation arrangements vary, but in any installation
it is important to open and close valves slowly and
to close the upstream block valve rst when shutting
down the system.
First, close the nearest upstream block valve and then,
close the nearest downstream block valve to vent the
regulator properly. Next, open the vent valve between
the regulator and the downstream block valve nearest
to it. Then, open the upstream vent valve and the
vent valve in the control line. All pressure between
these block valves is released through the open vent
valves, since a gas blanketing regulator remains open
Body Area
This procedure is for gaining access to the disk
assembly, orice, body gasket, split ring, and pitot
tube if used. All pressure must be released from the
regulator, before these steps can be performed.
1. Unscrew the union nut (key 19) from the body
(key 28) and remove the lower casing assembly
(key 20) and split ring (key 17). The lower casing
assembly (key 20) must be tipped toward the
body outlet to allow removal clearance for the
pitot tube (key 74).
2. Inspect and replace the orice (key 27) if
necessary. Lubricate the threads of the
replacement orice with a good grade of
pipe thread sealant. Install the orice with
75 to 100 foot-pounds (102 to 136 N•m)
of torque.
3. Remove the cotter pin (key 14) if it is necessary to
replace the disk assembly (key 25).
4. To replace the pitot tube (key 74) on units with
internal pressure registration, remove the
ared end connection and press a new pitot tube
5
Page 6

Type Y692
into the pitot tube hole and secure by aring the
end. Rotate the pitot tube so that it points into the
outlet of the body (key 28) after the lower casing
assembly (key 20) is installed.
5. Install the disk assembly (key 25) and secure it
with the cotter pin (key 14).
6. If necessary, install a replacement body gasket
(key 16) into the body (key 28).
7. Slide the union nut (key 19) as far as it will go
onto the lower casing assembly (key 20). Install
both halves of the split ring (key 17) into the slots
of the lower casing assembly (key 20) and secure
them by sliding the union nut down on the split ring.
8. Install the lower casing assembly (key 20) with the
attached split ring (key 17) and union nut (key 19)
so that the pitot tube ts into the outlet of the body.
9. Tighten the union nut (key 19) until the lower
casing assembly (key 20) is secure on the
body (key 28).
Diaphragm and Spring Case Area
This procedure is for gaining access to the spring,
diaphragm, and lever assembly. All pressure must be
released from the diaphragm case assembly before
these steps can be performed.
To Change the Control Spring:
1. Remove the closing cap (key 3, if required), and
turn the adjusting screw (key 2) counterclockwise
until all compression is removed from the control
spring (key 1).
2. Remove the adjusting screw (key 2) and spring
seats (keys 4 and 44). Change the control spring
to match the desired spring range.
3. Replace the spring seats (keys 4 and 44) and the
adjusting screw (key 2).
4. Install a replacement closing cap gasket (key 35),
if necessary, and reinstall the closing cap
(key 3, if used).
5. If the spring range was changed, be sure to
change the stamped spring range on the nameplate.
To Disassemble and Reassemble
Diaphragm Parts:
Key numbers are referenced in Figure 6.
1. Remove the closing cap (key 3, if required), and
turn the adjusting screw (key 2) counterclockwise
to remove the adjusting screw (key 2) and the
control spring (key 1).
2. Remove the hex nuts (key 22), cap screws
(key 21) and spring case (key 23).
3. In a regulator with a light control spring (see
Figure 4): Lift the upper spring seat (key 44), lower
spring seat (key 4), and control spring (key 1) off
the diaphragm and plate assembly (key 5).
In a regulator with a heavy control spring (see
Figure 5): Lift the two spring seats (key 4) and
control spring (key 1) off the diaphragm and plate
assembly (key 5).
4. Remove the diaphragm and plate assembly
(key 5) by tilting them so that the pusher post (key 8)
slips off the lever assembly (key 9).
5. To separate the diaphragm assembly (key 5) from
the attached parts, unscrew the diaphragm cap
screw (key 30) from the pusher post (key 8).
6. To replace the lever assembly (key 9), remove
the machine screws (key 11). To replace the
stem (key 13) or access the stem seal O-ring
(key 15, for Types with external pressure
Registration) perform body area maintenance
procedure steps 1 and 3, and pull the stem
(key 13) out of the lower casing assembly (key 20).
7. Inspect the stem (key 13) and replace if required.
Install the stem into the lower casing assembly
(key 20) and perform body area maintenance
procedure steps 5 through 9 as necessary.
8. Install the lever assembly (key 9) into the stem
(key 13) and secure the lever assembly (key 9)
with the machine screws (key 11).
9. During the assembly procedure, use lubricants
on parts as indicated in Figure 6 and replace parts
as required.
10. Install the parts on the pusher post (key 8) in the
order listed below:
• Diaphragm plate gasket (key 7)
• Lower diaphragm plate (key 6)
• Diaphragm and plate assembly (key 5) pattern
side up
• Lower spring seat (key 4)
11. Insert and tighten the diaphragm cap screw
(key 30) to secure the diaphragm parts to the
pusher post (key 8). Carefully tighten to a torque
of 7 to 9 foot-pounds (9 to 12 N•m).
12. Install the assembled parts in the lower casing
(key 20). Make sure that the lever (key 9) ts in
6
Page 7

Type Y692
the pusher post (key 8) and that the holes in the
diaphragm align with the holes in the lower casing.
13. Install the spring case (key 23) on the lower
casing assembly (key 20) so that the vent
assembly (key 56) is correctly oriented, and
secure with the cap screws (key 21) and hex nuts
(key 22) nger tight only.
14. In a regulator with a light control spring (see
Figure 4): Insert the lower control spring
(key 1) into the spring case (key 23), followed by
the upper spring seat (key 44) and the adjusting
screw (key 2).
In a regulator with a heavy control spring (see
Figure 5): Insert the lower spring seat (key 4), and
the control spring (key 1), into the spring case
(key 23), followed by the upper spring seat (key 4)
and the adjusting screw (key 2).
15. Turn the adjusting screw (key 2) clockwise
until there is enough control spring (key 1) force
to provide proper slack to the diaphragm (key 5).
Using a crisscross pattern, nish tightening the cap
screws (key 21) and hex nuts (key 22) to 15 to
20 foot-pounds (20 to 27 N•m) of torque. To adjust
the control pressure to the desired setting, refer to
the Startup and Adjustment section.
16. Install a replacement closing cap gasket
(key 35) if necessary, and then install the closing
cap (key 3, if used).
Parts Ordering
When corresponding with your local Sales Ofce
about this equipment, always reference the
equipment serial number or FS number that can be
found on the nameplate.
When ordering replacement parts, reference the key
number of each needed part as found in the following
parts list. Separate kits containing all recommended
spare parts are available.
Parts List
Note
In this parts list, parts marked NACE
are intended for corrosion-resistant
service as detailed in the NACE
International Standard MR0175
and/or MR0103.
Type Y692 Regulator (Figure 6)
Key Description Part Number
Type Y692 Parts Kit
For 1/4, 3/8, and 1/2-inch (6,4; 9,5; 13 mm) Orice Sizes
(includes keys 5, 7, 14, 16, 25,and 35) RY692X00012
For 3/4, 1, and 1-3/16-inch (19; 25; 30 mm) Orice Sizes
(includes keys 5, 7, 14, 16, 25, 35, 46, and 47) RY692X00022
1 Control Spring, Plated steel See Table 1
2 Adjusting Screw See Table 4
3 Closing Cap See Table 4
4 Lower Spring Seat See Table 4
5* Diaphragm and Plate Assembly
Nitrile (NBR) 1N9722X0012
Fluorocarbon (FKM) 1N9722X0022
Ethylenepropylene (EPDM) 1N9722X0052
Silicone (VMQ) 1N9722X0062
6 Lower Diaphragm Plate
Stainless steel 0V003935032
Stainless steel (NACE) 0V0039X0022
7 Diaphragm Plate Gasket, Composition 1A348704022
8 Pusher Post
Stainless steel (also NACE) 0Y096435072
9 Lever Assembly
Stainless steel (also NACE) 1E3409X0052
11 Machine Screw (2 required)
Stainless steel 1A866935032
Stainless steel (NACE) 1A8669X0012
12 Stem Bushing, 303 Stainless steel 1F513035032
13 Stem
Stainless steel 1E767635032
Stainless steel (NACE) 1E7676X0012
14* Cotter Pin
Stainless steel 1A866537022
Stainless steel (NACE) 1A8665X00A2
15 Stem Seal (O-Ring)
Nitrile (NBR) 1E472706992
Fluorocarbon (FKM) 1N430406382
Peruoroelastomer (FFKM) 1D6875X0082
Ethylenepropylene (EPDM) 1D6875X0032
16* Body Gasket, Composition 1A348004032
17 Split Ring, Zinc-plated steel 0Y095828982
19 Union Nut
Malleable iron 0Z0176X0032
Stainless steel 0Z017624092
Stainless steel (NACE) 0Z0176X0012
20 Lower Casing
For Internal Registration
Cast iron 3B973519012
Steel 3F191622012
Steel (NACE) 3F1916X0022
Stainless steel 3F191633092
For External Registration
Cast iron 3E767819012
Steel 39A7502X022
Stainless steel 39A7502X012
21 Diaphragm Case Cap Screw (12 required)
Zinc-plated steel 1B136324052
Stainless steel 1B136338992
*Recommended Spare Parts
7
Page 8

Type Y692
Key Description Part Number
22 Hex Nut (12 required)
Zinc-plated steel 1A309324122
Stainless steel 1A309338992
23 Spring Case
Cast Iron 2B155719042
Steel 34B2157X012
Stainless steel 34B2157X042
Aluminum (setpoint under 1.2 psi (0,08 bar)) AE6180X0012
Aluminum (setpoint over 1.2 psi (0,08 bar)) AE6180X0032
25* Disk Assembly
Stainless steel disk holder with
Nitrile (NBR) disk
1/2-inch (13 mm) orice and smaller 1A8431000B2
3/4-inch (19 mm) orice and larger 1C7831X0072
Fluorocarbon (FKM) disk
1/2-inch (13 mm) orice and smaller 1A8431X0072
3/4-inch (19 mm) orice and larger 1C7831X0092
Polytetrauoroethylene (PTFE) disk
1/2-inch (13 mm) orice and smaller 1A8431X0092
3/4-inch (19 mm) orice and larger 1C7831X0112
Ethylenepropylene (EPDM) disk
1/2-inch (13 mm) orice and smaller 1A8431X0182
Stainless steel disk holder with
Neoprene (CR) disk (NACE)
1/2-inch (13 mm) orice and smaller 1A8431X0132
3/4-inch (19 mm) orice and larger 1C7831X0152
Stainless steel disk holder with
Fluorocarbon (FKM) disk (NACE)
1/2-inch (13 mm) orice and smaller 1A8431X0142
3/4-inch (19 mm) orice and larger 1C7831X0162
Stainless steel disk holder with FFKM disk (NACE)
1/2-inch (13 mm) orice and smaller 1A8431X0162
3/4-inch (19 mm) orice and larger 1C7831X0202
Stainless steel disk holder with PTFE disk (NACE)
1/2-inch (13 mm) orice and smaller 1A8431X0192
3/4-inch (19 mm) orice and larger 1C7831X0212
Stainless steel disk holder with EPDM disk (NACE)
1/2-inch (13 mm) orice and smaller 1A8431X0202
3/4-inch (19 mm) orice and larger 1C7831X0222
27 Orice
Stainless Steel
1/4-inch (6,4 mm) 0L087835032
3/8-inch (9,5 mm) 0H082535072
1/2-inch (13 mm) 0L040135032
3/4-inch (19 mm) 1A832335072
1-inch (25 mm) 1A832435072
1-3/16-inch (30 mm) 1C783435072
Stainless steel (NACE)
1/4-inch (6,4 mm) 0L0878X0012
3/8-inch (9,5 mm) 0H0825X0012
1/2-inch (13 mm) 0L0401X0012
3/4-inch (19 mm) 1A8323X0012
1-inch (25 mm) 1A8324X0012
1-3/16-inch (30 mm) 1C7834X0012
28 Body
NPT
Cast iron
NPS 1-1/2-inch (DN 40) size 1B403619012
NPS 2-inch (DN 50) size 1B403719012
Key Description Part Number
28 Body (continued)
Steel
NPS 1-1/2-inch (DN 40) size 2L244522012
NPS 2-inch (DN 50) size 2L243322012
Stainless steel
NPS 1-1/2-inch (DN 40) size 2L244533092
NPS 2-inch (DN 50) size 2L2433X00A2
Socket Weld End
NPS 1-1/2 (DN 40) size 2E2291X0012
NPS 2 (DN 50) size 2H562322012
CL150 RF Flanged
Steel
NPS 1-1/2-inch (DN 40) size 14B3208X262
NPS 2-inch (DN 50) size 14B3208X012
NPS 1-1/2 (DN 40) size (NACE) 14B3208X252
NPS 2 (DN 50) size (NACE) 14B3208X202
Stainless steel
NPS 1-1/2-inch (DN 40) size 14B3208X272
NPS 2-inch (DN 50) size 14B3208X042
CL300 RF Flanged
Steel
NPS 1-1/2-inch (DN 40) size 14B3208X022
NPS 2-inch (DN 50) size 14B3208X032
NPS 1-1/2 (DN 40) size (NACE) 14B3208X242
NPS 2 (DN 50) size (NACE) 14B3208X162
CL300 RF Flanged
Stainless steel
NPS 1-1/2-inch (DN 40) size 14B3208X052
NPS 2-inch (DN 50) size 14B3208X062
EN PN 16/25/40RF
Steel
NPS 1-1/2-inch (DN 40) size 14B3208X072
NPS 2-inch (DN 50) size 14B3208X082
NPS 1-1/2 (DN 40) size (NACE) 14B3208X222
NPS 2 (DN 50) size (NACE) 14B3208X232
Stainless steel
NPS 1-1/2-inch (DN 40) size 14B3208X092
NPS 2-inch (DN 50) size 14B3208X102
29 Pipe Plug See Table 4
30 Diaphragm Cap Screw See Table 4
35* Closing Cap Gasket, Neoprene (CR) 1N446206992
44 Upper Spring Seat See Table 4
46 Valve Disk Washer
3/4-inch (19 mm) orice and over only
Stainless steel 0X014635032
Stainless steel (NACE) 0X0146X0012
47 Machine Screw
3/4-inch (19 mm) orice and over only
Stainless steel (also NACE) 19A7151X022
51 Drive Screws (4 required) - - - - - - - - - - 56 Vent Assembly, Plastic
Type Y602-1 for down-pointing
Spring case 17A6570X012
71 Bushing, Steel 1A3424X0042
74 Pitot Tube, Stainless steel (also NACE) 1C947138082
80 Lubricant, Dow Corning 33, 10 oz. tube - - - - - - - - - - -
93 Hex Nut (see Figure 5) See Table 4
*Recommended Spare Parts
8
Page 9

Type Y692
3
2
44
1
4
34B4869-A
Figure 4. Type Y692 with a Light Control Spring Assembly
35
23
30
5
3
35
2
1
93
4
23
30
4
5
34B4832-B
Figure 5. Type Y692 with a Heavy Control Spring Assembly
Table 4. Additional Part Numbers
KEY
NUMBER
2 Adjusting Screw
3 Closing Cap
4 Lower Spring Seat
29 Pipe Plug
30 Cap Screw
44 Upper Spring Seat
93 Hex Head Nut - - - - - - - -
DESCRIPTION
FOR CONTROL SPRINGS EXCEPT 2 TO 5.5 AND 4 TO 7 PSIG
(0,14 to 0,38 and 0,28 to 0,48 bar) SPRINGS
Standard Trim Stainless Steel Trim Standard Trim Stainless Steel Trim
1L928608012
Aluminum
1A589544022
Steel
14B4240X012
Aluminum
1C333528992
Steel
1B720924052
Plated steel
0Y095644012
Aluminum
1L928608012
Aluminum
1J880124092
Steel
14B4240X012
Aluminum
1C3335X0012
Stainless steel
1B720924052
Plated steel
0Y095644012
Aluminum
FOR 2 TO 5.5 AND 4 TO 7 PSIG
(0,14 to 0,38 and 0,28 to 0,48 bar)
CONTROL SPRINGS ONLY
1A500528982
Plated steel
1H798714012
Brass
1H7974X0012
Plated steel
1C333528992
Steel
1E4539X0012
Plated steel
- - - - - - - -
1A3524X0082
Plated steel
1A500528982
1J8801X0022
1H7974X0012
1C3335X0012
Stainless steel
1E4539X0012
1A3524X0082
Plated steel
Brass
Plated steel
Plated steel
Plated steel
9
Page 10

Type Y692
TYPE
ORIFICE
SPRING
RANGE
DATE MFGD
FISHER CONTROLS CO.
MARSHALLTOWN IOWA, USA
7
9
13
19
16
14
27
21
22
6
8
20
11
17
28
25
46
5
4
44
3
2
35
1
30
23
74
47
APPLY LUB /SEAL/ADH
43B0674-B
INTERNAL REGISTRATION
Figure 6. Type Y692 Regulator Assembly
10
Page 11

Type Y692
TYPE
ORIFICE
SPRING
RANGE
DATE MFGD
FISHER CONTROLS CO.
MARSHALLTOWN IOWA, USA
7
9
13
19
16
14
27
21
22
6
8
20
11
17
28
25
46
5
4
3
2
35
1
30
23
15
A
A
29
50
51
56
APPLY LUB /SEAL/ADH
4343B0674-C
47
71
SECTION A - A
EXTERNAL REGISTRATION
Figure 6. Type Y692 Regulator Assembly (continued)
11
Page 12

Type Y692
Industrial Regulators
Emerson Process Management
Regulator Technologies, Inc.
USA - Headquarters
McKinney, Texas 75069-1872 USA
Tel: 1-800-558-5853
Outside U.S. 1-972-548-3574
Asia-Pacic
Shanghai, China 201206
Tel: +86 21 2892 9000
Europe
Bologna, Italy 40013
Tel: +39 051 4190611
Middle East and Africa
Dubai, United Arab Emirates
Tel: +971 4811 8100
For further information visit www.emersonprocess.com/regulators
The Emerson logo is a trademark and service mark of Emerson Electric Co. All other marks are the property of their prospective owners. Fisher is a mark owned by Fisher Controls, Inc., a
business of Emerson Process Management.
The contents of this publication are presented for informational purposes only, and while every effort has been made to ensure their accuracy, they are not to be construed as warranties or
guarantees, express or implied, regarding the products or services described herein or their use or applicability. We reserve the right to modify or improve the designs or specications of such
products at any time without notice.
Emerson Process Management does not assume responsibility for the selection, use or maintenance of any product. Responsibility for proper selection, use and maintenance of any Emerson
Process Management product remains solely with the purchaser.
Natural Gas Technologies
Emerson Process Management
Regulator Technologies, Inc.
USA - Headquarters
McKinney, Texas 75069-1872 USA
Tel: 1-800-558-5853
Outside U.S. 1-972-548-3574
Asia-Pacic
Singapore, Singapore 128461
Tel: +65 6777 8211
Europe
Bologna, Italy 40013
Tel: +39 051 4190611
Gallardon, France 28320
Tel: +33 (0)2 37 33 47 00
TESCOM
Emerson Process Management
Tescom Corporation
USA - Headquarters
Elk River, Minnesota 55330-2445 USA
Tel: 1-763-241-3238
Europe
Selmsdorf, Germany 23923
Tel: +49 (0) 38823 31 0
©Emerson Process Management Regulator Technologies, Inc., 1994, 2009; All Rights Reserved
 Loading...
Loading...