Page 1

Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
Installer/User Guide
Page 2

For important safety information, visit:
www.emersonnetworkpower.com/ComplianceRegulatoryInfo
Emerson, Emerson Network Power and the Emerson Network Power logo are trademarks or service marks of Emerson Electric
Co. Avocent, the Avocent logo and Cyclades are trademarks or service marks ofAvocent Corporation or its affiliates in the U.S. and
other countries. Liebert is a trademark and service mark of Liebert Corporation. Allother marks are the property of their respective
owners. This document may contain confidential and/or proprietary information of Avocent Corporation, and its receipt or
possession does not convey any right to reproduce, disclose its contents, or to manufacture or sell anything that it may describe.
Reproduction, disclosure, or use without specific authorization from Avocent Corporation is strictly prohibited. ©2014 Avocent
Corporation. Allrights reserved.
NOTE: This document supports versions up to and including release 3.0
Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
i
Introduction
Features and Benefits
Access options
Web manager
IPv4 and IPv6 support
Flexible users and groups
Security
Authentication
VPN based on IPSec with NAT traversal
Packet filtering
SNMP
Data logging, notifications, alarms and data buffering
Power management
Auto discovery
FIPS module
Configuration Example
Installation
Getting Started
Supplied with the console server
Additional items needed
Rack Mounting
Connecting the Hardware
Console server connectors
Connecting device consoles or modems to serial ports
Turning On the Console Server
AC power
DC power
Configuring a Console Server
Using Telnet or SSH
Accessing the Console Server via the Web Manager
Web Manager Overview for Administrators
Wizard Mode
Expert Mode
Access
System Tools
System
Security
Date and Time
Help and Language
General
Boot Configuration
1
1
1
2
2
3
3
3
3
3
4
4
4
4
4
4
7
7
7
7
7
8
8
10
11
11
12
13
13
17
17
18
20
20
21
22
22
26
27
27
28
Page 4

ii.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
Information
Usage
Network
Settings
Devices
IPv4 and IPv6 static routes
Hosts
Firewall
IPSec(VPN)
SNMP Configuration
Ports
Serial ports
Auxiliary ports
CAS Profile
Dial-in Profile
Dial-out Profile
Pluggable Devices
Device configuration
Authentication
Appliance authentication
Authentication servers
Users Accounts and User Groups
Local accounts
User groups
DSView software access rights
Event Notifications
Event List
Event Destinations
Trap Forward
Data Buffering
Appliance logging
Sensors
Power Management
PDUs
Login
Outlet Groups
Network PDUs
Active Sessions
Monitoring
Change Password
Web Manager Overview for Regular Users
Appendices
Technical Specifications
28
29
29
29
29
30
30
31
33
34
35
35
42
42
45
47
48
49
49
50
51
53
53
54
61
61
61
62
62
63
63
64
64
65
67
67
68
68
69
69
70
71
71
Page 5

.....iii
Recovering a Console Server's Password
Port Information for Communication with the DSView Software
Accessing a Console Server with a DSView Software Installation via Dial-up
Installing DSView software with an OOB back door
Configuring dial-up for a console server
Internal Modem
AT+MS modulation selection
Set telephone extension option
AT S registers
Basic modem result codes
Digital line guard
Sleep mode operation
Disconnecting a call
Selecting country codes
Using caller ID
Technical Support
72
73
74
74
74
77
80
81
81
82
82
83
83
83
84
86
Page 6

Page 7

Introduction
The Avocent® ACS 6000 advanced console server is a 1U appliance that serves as a single point
for access and administration of connected devices, such as target device consoles, modems and
power devices. Console servers support secure remote data center management and out-of-band
management of IT assets from any location worldwide.
NOTE: Unless noted, references to a console server refer to all models in the 60XX series.
Console servers provide secure local (console port) and remote (IP and dial-up) access. The
console servers run the Linux®operating system with a persistent file system in Flash memory, and
can be upgraded from either FTP or a DSView™4 management software server.
NOTE: Unless otherwise noted, all references to DSView software in this document refer to version 4 or
greater.
Multiple administrators can be logged into the console server at the same time and can use the web
manager, the Command Line Interface (CLI utility) or DSView software to access and configure the
console server.
Some models feature two PC card/slots to support modem, Ethernet, fast Ethernet (fiber optic) and
storage PC cards (16 bit and 32 bit). One USB port supports modem (V.92 and Wireles), storage
devices and USB hubs. Two fast Ethernet ports support connections to more than one network or
configuration of Ethernet bonding (failover) for redundancy and greater reliability. For dial-in and
secure dial-back with Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP), optional internal modems can be factory
installed, or you can use external modems or wireless modem CardBus devices.
Features and Benefits
Access options
Secure access is available through the following local (analog console port) and remote (digital IP
and dial-up) options:
• LAN/WAN IP network connection.
• Dial-up to a factory-configured internal modem (optional), a modem connected either to a
serial port or the AUX port (which is only possible when an internal modem is not installed), or
to a PC phone card installed in one of the PC card slots (if applicable)or in the USB port or a
wireless modem.
Page 8

2.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
• Target device connection. An authorized user can make a Telnet, SSH v1, SSH v2 or Raw
connection to a target device. For Telnet or SSH to be used for target device connections, the
Telnet or SSH service must be configured in the Security Profile that is in effect.
• Console server console connection. An administrator can log in either from a local terminal or
from a computer with a terminal emulation program that is connected to the console port and
can use the CLI utility. The CLI utility prompt (--|- cli>) displays at login.
More than one administrator can log into the console server and have an active CLI or web
manager session. All sessions receive the following warning message when the configuration is
changed by another administrator or by the system: The appliance configuration has been altered
from outside of your session. Upon receipt of this message, each administrator needs to verify that
changes made during the session were saved.
Web manager
Users and administrators can perform most tasks through the web manager (accessed with HTTP
or HTTPS). The web manager runs in Microsoft®Internet Explorer®, Mozilla®Firefox®, and
Apple®Safari®on any supported computer that has network access to the console server. The list
of supported client browsers and their versions are available in the release notes.
IPv4 and IPv6 support
The console server supports dual stack IPv4 and IPv6 protocols. The administrator can use the
web manager or CLI to configure support for IPv4 addresses only or for both IPv4 and IPv6
addresses. The following list describes the IPv6 support provided in the console server:
• DHCP
• Dial-in and dial-out sessions (PPP links)
• DSView software integration
• eth0 and eth1 Ethernet interfaces
• Firewall (IP tables)
• HTTP/HTTPs
• Linux kernel
• Remote authentication: Radius, Tacacs+, LDAP and Kerberos servers
• SNMP
• SSH and Telnet access
• Syslog server
NOTE: Remote authentication NFS, NIS and IPSec are not supported with IPv6.
Page 9

Introduction.....3
Flexible users and groups
An account can be defined for each user on the console server or on an authentication server. The
admin and root users have accounts by default, and either can add and configure other user
accounts. Access to ports can be optionally restricted based on authorizations an administrator can
assign to custom user groups. For more information, see Users Accounts and User Groups on
page 53.
Security
Security profiles determine which network services are enabled on the console server.
Administrators can either allow all users to access enabled ports or allow the configuration of group
authorizations to restrict access. You can also select a security profile, which defines which
services (FTP, ICMP, IPSec and Telnet) are enabled and SSH and HTTP/HTTPS access. The
administrator can select either a preconfigured security profile or create a custom profile. For more
information, see Security on page 22.
Authentication
Authentication can be performed locally, with One Time Passwords (OTP), a remote Kerberos,
LDAP, NIS, RADIUS, TACACS+ authentication server or a DSView server. The console server
also supports remote group authorizations for the LDAP, RADIUS and TACACS+ authentication
methods. Fallback mechanisms are also available.
Any authentication method configured for the console server or the ports is used for authentication
of any user who attempts to log in through Telnet, SSH or the web manager. For more information,
see Authentication on page 49.
VPN based on IPSec with NAT traversal
If IPSec is enabled in the selected security profile, an administrator can use the VPN feature to
enable secure connections. IPSec encryption with optional NAT traversal (which is configured by
default) creates a secure tunnel for dedicated communications between the console server and
other computers that have IPSec installed. ESP and AH authentication protocols, RSA Public Keys
and Shared Secret aresupported. For more information, see IPSec(VPN) on page 33.
Packet filtering
An administrator can configure a console server to filter packets like a firewall. Packet filtering is
controlled by chains, which are named profiles with user-defined rules. The console server filter
table contains a number of built-in chains that can be modified but not deleted. An administrator
can also create and configure new chains.
Page 10

4.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
SNMP
If SNMP is enabled in the selected security profile, an administrator can configure the Simple
Network Management Protocol (SNMP) agent on the console server to answer requests sent by an
SNMP management application.
The console server SNMP agent supports SNMP v1/v2 and v3, MIB-II and Enterprise MIB. For
more information, see SNMP Configuration on page 34.
NOTE: The text files with the Enterprise MIB (ACS6000-MIB.asn) and the TRAP MIB (ACS6000-TRAP-
MIB.asn) are available in the appliance under the /usr/local/mibs directory.
Data logging, notifications, alarms and data buffering
An administrator can set up data logging, notifications and alarms to alert administrators of
problems with email, SMS, SNMP trap or DSView software notifications. An administrator can also
store buffered data locally, remotely or with DSView management software. Messages about the
console server and connected servers or devices can also be sent to syslog servers.
Power management
The console server enables users who are authorized for power management to turn power on,
turn power off and reset devices plugged into a connected power distribution unit (PDU). The
power devices can be connected to any serial port or to the AUX/Modem port (if an internal modem
is not installed). For more information, see Power Management on page 64.
Auto discovery
An administrator can enable auto discovery to find the hostname of a target connected to a serial
port. Auto discovery’s default probe and answer strings have a broad range. An administrator can
configure site-specific probe and answer strings. Auto discovery can also be configured through
the DSView software.
FIPS module
The 140 series of Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) are U.S. government
computer security standards that specify requirements for cryptography modules.
The console server uses an embedded FIPS 140-2 validated cryptographic module (Certificate No.
1747)running on a Linux PPCplatform per FIPS 140-2 Implementation Guidance section G.5
guidelines. For more information, see FIPS module on page 23.
Configuration Example
The following graphic and table illustrate a typical ACS 6000 console server configuration.
Page 11

Typical ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server Configuration
Introduction.....5
Typical ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server Configuration Descriptions
Number Description Number Description
1 ACS 6000 advanced console server 8 Phone line
2 Target devices 9
3 PDU (one or more) 10
4 Serial port connection 11 LAN firewall
5
6 Either AUX/Modem or any serial port 13
7
PC card (modem, Ethernet or storage - not available on all
models)
Modem ordered and configured internally at the factory -orexternal modem (on a device in one of the PC card slots or USB
port, or connected to a serial port or the AUX port)
12
14
Remote dial-in
client
Local Area
Network (LAN)
Remote
authentication
server
DSView
client/server
Remote/local
Windows/Linux
computer
Page 12

Introduction.....6
Page 13

Installation
Getting Started
Before installing your ACS 6000 console server, refer to the following list to ensure you have all
items that shipped with it , as well as other items necessary for proper installation.
Supplied with the console server
• Quick InstallationGuide (QIG)
• Power Cord
• RJ-45 to RJ-45 straight-through CAT 5cable
• RJ-45 to DB-9F cross adaptor
• DB-25 loop-back plug
• RJ-45 to DB-25M cross adaptor
• RJ-45 to DB-25F cross adaptor
• RJ-45 to DM-25M straight-through cable
• Mounting brackets, screws and cord retention clips
• Keyhole mounting kit
• Software License Agreement
• Safety Sheet
Additional items needed
If you are configuring the console server in a standalone configuration, you will also need the
following items:
• One or more RJ-45 to RJ-45 CAT 5 straight-through cables
• An RJ-45 to DB-9F straight-through adaptor
• A PC running a terminal emulation program
Rack Mounting
You can mount the console server in a rack or cabinet, or place it on a desktop or other flat surface.
For rack or cabinet mounting, two mounting brackets are supplied.
To rack mount a console server:
Page 14

8.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
1. Install the brackets at the front or back edges of the console server with the screws provided
with the mounting kit.
2. Mount the console server in a secure position.
Bracket Connections for Front Mount Configuration
Connecting the Hardware
Console server connectors
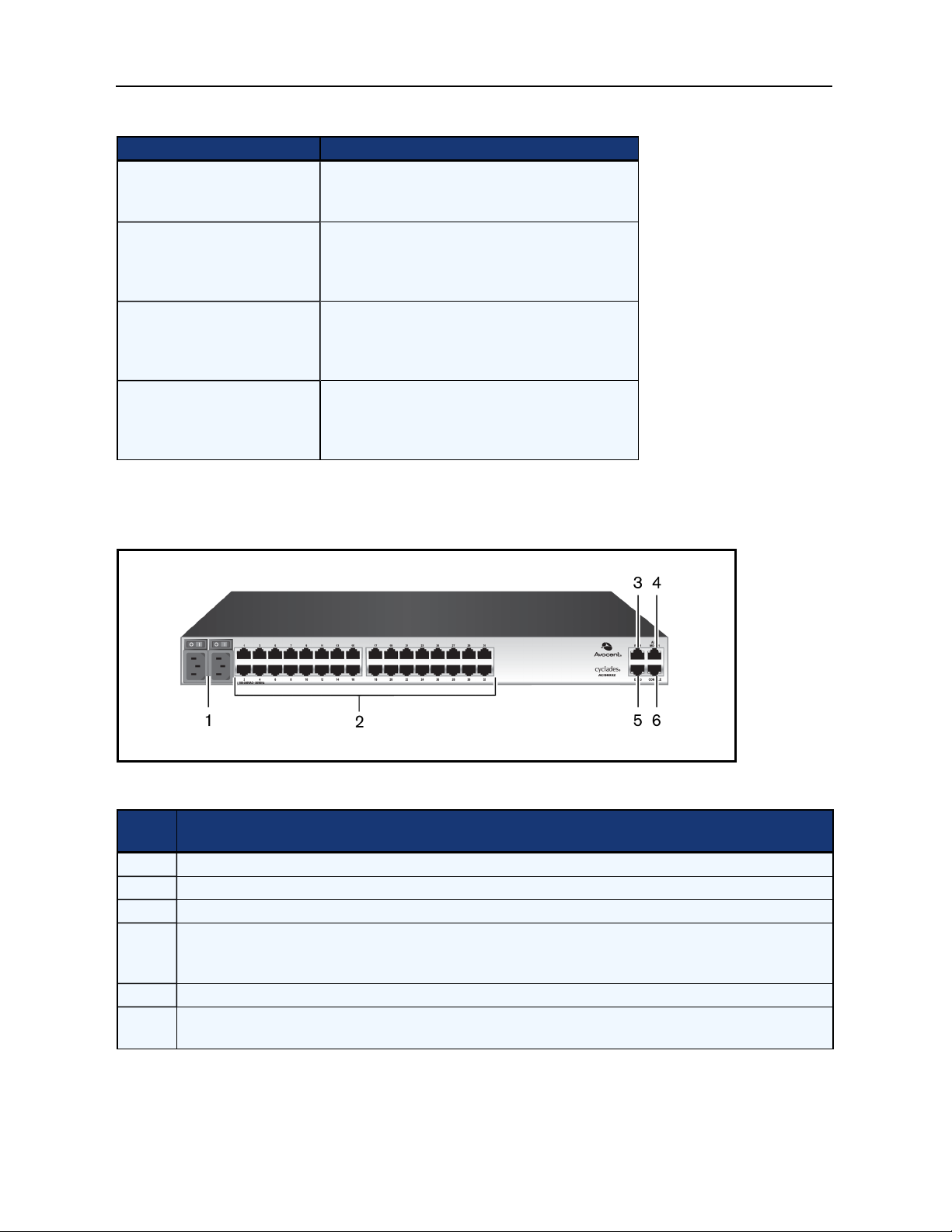
The following figure shows the connectors on the front of the ACS 6000 console server.
Front of the Console Server (ACS 6032 Console Server Shown)
Connectors on the Console Server Front
Number Descr iption
1 USB connector
2 LEDs
3 PC card slots (not available on all models)
Page 15
LEDs on the Console Server Front
Label Descr iption
• Blue Blinks - During unit boot
PWR/CPU
ETH 0/ETH 1
AUX/MODEM
[One LED for each serial port]
• Solid - During operation
• Off - Power is off
• Amber - Link at 10BaseT speed
• Yellow - Link at 100BaseT speed
• Green - Link at 1000BaseT speed
• Off - No link/cable disconnected/Ethernet fault
Dual LED: Yellow on top, green on bottom
• Yellow - DTR/DCD activity
• Green - TXD and RXD activity
• Off - No activity
Green
• Blinks - Ready, with activity
• Solid - Ready
• Off - Not ready
The following figure shows the rear connectors on the console server.
Installation.....9
Rear of the Console Server (ACS 6032 Console Server Shown)
Connectors on the Console Server Rear
Number
1 Power supplies (dual AC shown).
2 Serial ports (32 ports shown). Models come with 4, 8, 16, 32 or 48 serial ports.
3 ETH 1 10/100M/1G Ethernet port. Can be connected to a second network or used for failover.
4
5 ETH0 10/100M/1G Ethernet port for remote IP access.
6
Descr iption
AUX/Modem port. If an optional internal modem is ordered, this port is defined as a V.92 modem at
the factory; otherwise, the port is factory-defined as RS-232 with an RJ-45 ACS console server
pinout and can be used to connect either an external modem or a power device.
Console port. Allows for local administration and access to connected devices through a terminal or
a computer with a terminal emulator.
Page 16

10.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
Connecting device consoles or modems to serial ports
Use CAT 5 or greater cables and DB-9 or DB-25 console adaptors as needed to connect target
device consoles or modems to the serial ports on the console server.
The console server supports the Cisco®serial port pinout configuration, which is disabled by
default. If a Cisco cable is connected to a port, an administrator must enable the Cisco pinout for the
port. An administrator can select Expert - Ports - Serial Ports - (SetCAS or SetPower) - Physical to
open the Physical Settings screen, then check Enable Cisco RJ Pin-Out.
The following tables show serial port pinout information.
ACS Console Server Serial Port Pinout
Pin No. Signal Name Input/Output
1 RTS OUT
2 DTR OUT
3 TxD OUT
4 GND N/A
5 CTS IN
6 RxD IN
7 DCD/DSR IN
8 Not Used N/A
Cisco Serial Port Pinout
Pin No. Signal Name Input/Output
1 CTS IN
2 DCD/DSR IN
3 RxD IN
4 GND N/A
5 Not Used N/A
6 TxD OUT
7 DTR OUT
8 RTS OUT
To connect devices, modems and PDUs to serial ports:
Make sure the crossover cable used to connect a device has the same pinout type that is
configured in the software for the port (either Cyclades or Cisco).
1. Make sure the devices to be connected are turned off.
2. Use CAT 5 or greater crossover cables to connect the devices to the console server, using an
adaptor, if necessary.
Page 17
Installation.....11
3. To connect modems, use straight-through CAT 5 or greater cables, with an appropriate
connector or adaptor (USB, DB-9 or DB-25) for the modem.
NOTE: To comply with EMC requirements, use shielded cables for all port connections.
WARNING: Do not turn on the power on the connected devices until after the console server is turned on.
To daisy chain PDUs to a console server:
This procedure assumes that you have one PDU connected to a serial port on a console server.
NOTE: Daisy chaining is not possible with SPC PDUs. ServerTech PDUs will allow only one level (Master
and Slave) of daisy chaining.
1. Connect one end of a UTP cable with RJ-45 connectors to the OUT port of the connected
PDU.
2. Connect the other end of the cable to the IN port of the chained PDU. Repeat both steps until
you have connected the desired number of PDUs.
NOTE: For performance reasons, Avocent recommends connecting no more than 128 outlets per serial
port.
Turning On the Console Server
The console server is supplied with single or dual AC or DC power supplies.
WARNING: Always execute the shutdown command through the web manager, CLI or DSView software
under the Overview/Tools node before turning the console server off, then on again. This will ensure the
reset doesn't occur while the file system in Flash is being accessed, and it helps avoiding Flash memory
corruptions.
AC power
To turn on a console server with AC power:
1. Make sure the console server is turned off.
2. Plug the power cable into the console server and into a power source.
3. Turn the console server on.
4. Turn on the power switches of the connected devices.
Page 18

12.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
DC power
DC power is connected to DC-powered console servers by way of three wires: Return (RTN),
Ground (GND) and -48 VDC.
WARNING: It is critical that the power source supports the DC power requirements of your console server.
Make sure that your power source is the correct type and that your DC power cables are in good condition
before proceeding. Failure to do so could result in personal injury or damage to the equipment.
The following diagram shows the connector configuration for DC power.
DC Power Connection Terminal Block
DC Power Connection Details
Number Descr iption Number Descr iption
1 Power switch 3 GND (Ground)
2 RTN (Return) 4 -48 VDC
To turn on a console server with DC power:
1. Make sure the console server is turned off.
2. Make sure DC power cables are not connected to a power source.
3. Remove the protective cover from the DC power block by sliding it to the left or right.
4. Loosen all three DC power connection terminal screws.
5. Connect your return lead to the RTN terminal, your ground lead to the GND terminal and your
-48 VDC lead to the -48 VDC terminal and tighten the screws.
6. Slide the protective cover back into place over the DC terminal block.
7. If your console server has dual-input DC terminals, repeat steps 3-6 for the second terminal.
8. Connect the DC power cables to the DC power source and turn on the DC power source.
9. Turn on the console server.
Page 19

Installation.....13
10. Turn on the power switches of the connected devices.
Configuring a Console Server
A console server may be configured at the appliance level through the command line interface
accessed through the CONSOLE or Ethernet port. All terminal commands are accessed through a
terminal or PC running terminal emulation software.
NOTE: To configure using DSView software, see the DSView Software Installer/User Guide. To configure
using the console server’s web manager, see Chapter 3. To configure using Telnet or SSH, see the ACS
6000 Command Reference Guide.
To connect a terminal to the console server:
1. Using a null modem cable, connect a terminal or a PC that is running terminal emulation
software (such as HyperTerminal®) to the CONSOLE port on the back panel of the console
server. An RJ-45 to DB9 (female) cross adaptor is provided.
The terminal settings are 9600 bits per second (bps), 8 bits, 1 stop bit, no parity and no flow
control.
2. Turn on the console server. When the console server completes initialization, the terminal will
display the login banner plus the login prompt.
Using Telnet or SSH
An authorized user can use a Telnet or SSH client to make a connection directly to the console of a
device if all of the following are true:
The Telnet or SSH:
• protocol is enabled in the selected security profile
• protocol is configured for the port
• client is available, and it is enabled on the computer from which the connection is made
To use Telnet to connect to a device through a serial port:
For this procedure, you need the username configured to access the serial port, the port name (for
example, 14-35-60-p-1), device name (for example, ttyS1), TCP port alias (for example, 7001) or
IP port alias (for example, 100.0.0.100) and the hostname of the console server or its IP address.
To use a Telnet client, enter the information in the dialog boxes of the client.
-or-
To use Telnet in a shell, enter the following command:
Page 20

14.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
# telnet [hostname | IP_address]
login: username:[portname | device_name]
-or-
# telnet [hostname | IP_address] TCP_Port_Alias
login: username
-or-
# telnet IP_Port_Alias
login: username
To close a Telnet session:
Enter the Telnet hotkey defined for the client. The default is Ctrl ] + q to quit, or enter the text
session hotkey for the CLI prompt and then enter quit.
To use SSH to connect to a device through a serial port:
For this procedure, you need the username configured to access the serial port, the port name (for
example, 14-35-60-p-1), TCP port alias (for example, 7001), device name (for example, ttyS1),
and the hostname of the console server, IP address or IP Port alias (for example, 100.0.0.100).
To use an SSH client, enter the information in the dialog boxes of the client.
-or-
To use SSH in a shell, enter the following command:
ssh -l username:port_name [hostname | IP_address]
-or-
ssh -l username:device_name [hostname | IP_address]
-or-
ssh -l username:TCP_Port_Alias [hostname | IP_address]
-or-
ssh -l username IP_Port_Alias
To close an SSH session:
Page 21

Installation.....15
At the beginning of a line, enter the hotkey defined for the SSH client followed by a period. The
default is ~. Or, enter the text session hotkey for the CLI prompt and then enter quit.
Page 22

Installation.....16
Page 23
Accessing the Console Server via the Web Manager
Once you’ve connected your ACS 6000 console server to a network, you can access the console
server with its web manager. The web manager provides direct access to the console server via a
graphical user interface instead of a command-based interface.
NOTE: For instructions on accessing the console server via the CLI or DSView software see the Cyclades
ACS 6000 Command Reference Guide or the DSView Software Installer/User Guide.
Web Manager Overview for Administrators
NOTE: For an overview of the web manager for regular users, see Web Manager Overview for Regular
Users on page 70.
To log into the web manager:
1. Open a web browser and enter the console server IP address in the address field.
2. Log in as either admin with the password avocent or as root with the password linux.
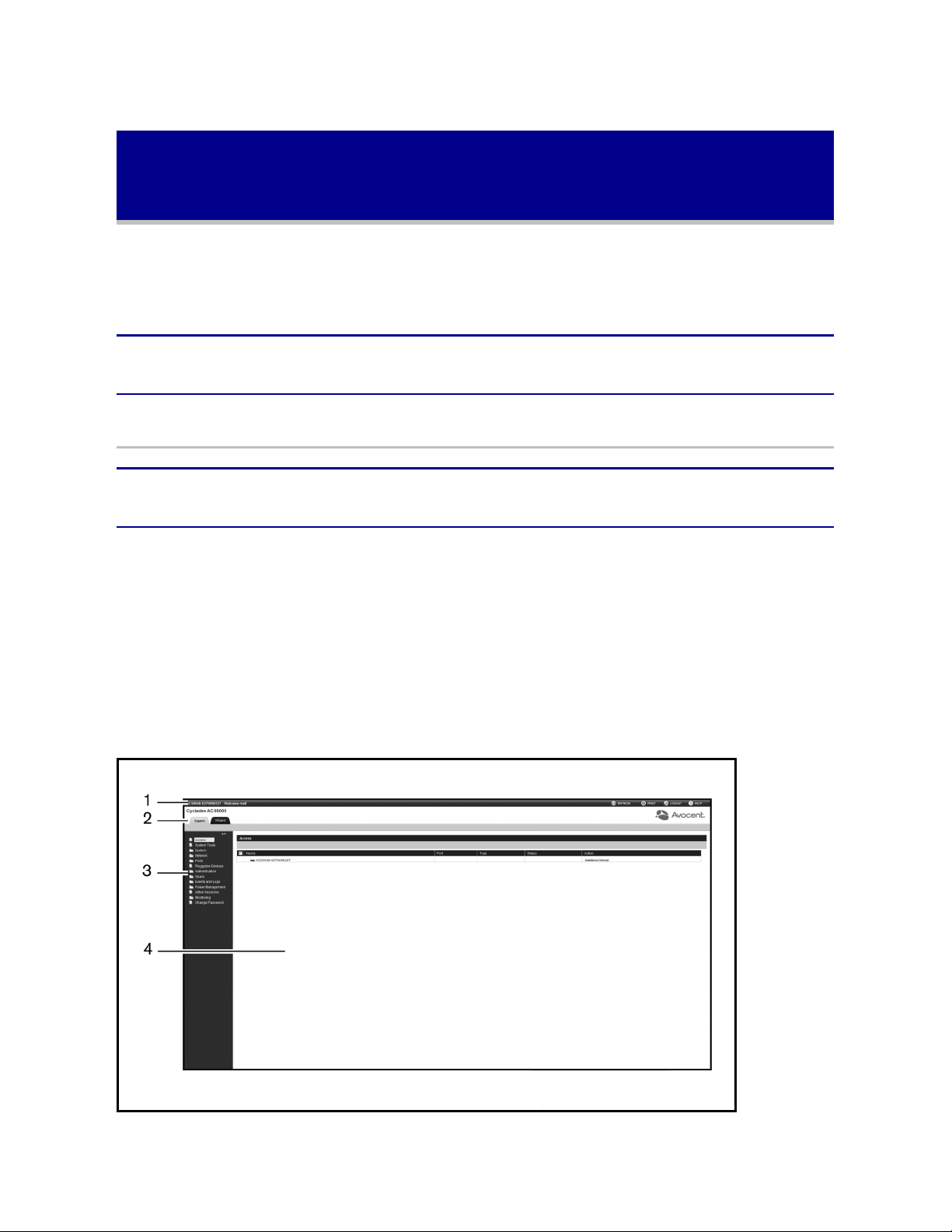
Figure 3.1 shows a typical web manager screen for an administrator and descriptions follow in
Table 3.1.
Administrator Web Manager Screen
Page 24

18.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
Web Manager Screen Areas
Number
Descr iption
1
2 Tab bar. Displays whether the admin is in Expert or Wizard mode.
3
4 Content area. Contents change based on the options selected in the side navigation bar.
Top option bar. The name of the appliance and of the logged in user appear on the left side.
Refresh, Print, Logout and Help buttons appear on the right.
Side navigation bar. Menu options for configuration, viewing of system information and access to
devices. The options change based on user rights.
Wizard Mode
The Wizard mode is designed to simplify the setup and configuration process by guiding an
administrator through the configuration steps. An administrator can configure all ports in the CAS
Profile and set the Security Profile, Network and Users Settings using the Wizard.
By default, the first time an administrator accesses the console server through the web manager,
the Wizard will be displayed. Subsequent log-ins will open in Expert mode, and once the console
server has been configured, Expert mode becomes the default mode. An administrator can toggle
between Expert and Wizard modes by clicking the tab bar on the web manager administrator
screen.
Figure 3.2 shows a typical screen when an administrator is in Wizard mode.
Wizard Screen
The following procedures describe how to configure the console server from the Wizard.
To configure security parameters and select a Security Profile:
1. Select the Security link in the content area.
Page 25

Accessing the Console Server via the Web Manager.....19
2. Select the desired Security Profile. If using a Custom Security Profile, click the checkboxes
and enter values as needed to configure the services, SSH and HTTP and HTTPS options to
conform with your site security policy.
3. Under the Bootp Configuration Retrieval heading, uncheck the box(es)to disable Bootp
configuration retrieval and/or live configuration retrieval.
4. If you are not using DSView software to manage the appliance, uncheck the Allow Appliance
to be Managed by DSView box.
5. Click Next to configure the Network or click the Network, Ports or Users link to open the
appropriate screen.
To configure network parameters:
1. Select the Network link in the content area.
2. Enter the Hostname, Primary DNS and Domain in the appropriate fields.
3. Select the IPv4 or IPv6 method for the ETH0 interface. If using Static, enter the Address,
Mask and Gateway in the appropriate fields.
4. Enable or disable IPv6 support.
5. Click Next to configure ports or click on the Security, Ports or Users link to open the
appropriate screen.
To configure Ports:
1. Select the Ports link in the content area.
2. Check the box(es) to enable all ports and/or to enable Cisco RJ45 Pin-Out to change the pin-
out when a Cisco cable is connected.
3. Use the appropriate drop-down menus to select the values for Speed, Parity, Data Bits, Stop
Bits, Flow Control, Protocol, Authentication Type and Data Buffering Status.
4. Select the Data Buffering Type. If using NFS, enter the NFS Server and NFS Path information
in the appropriate fields.
5. Click Next to configure users or click on the Network, Security or Users link to open the
appropriate screen.
To configure users and change the default user passwords:
WARNING: For security reasons, it is recommended you change the default password for both root and
admin users immediately.
1. Select the Users link in the content area.
2. Click a username (admin or root) and enter the new password in the Password and Confirm
Password fields.
Page 26

20.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
-or-
Click Add to add a user. Enter the new username and password in the appropriate fields.
3. (Optional) To force the user to change the default password, select the User must change
password at next login checkbox.
4. Assign the user to one or more groups.
5. (Optional) Configure account expiration and password expiration.
6. Click Next.
7. Repeat steps 3-7 as needed to configure new user accounts and assign them to default
groups.
NOTE: By default, all configured users can access all enabled ports. Additional configuration is needed if
your site security policy requires you to restrict user access to ports.
8. Click Save, then click Finish.
Expert Mode
The following tabs are available in the side navigation bar of the web manager when an
administrator is in Expert mode.
Access
Click Access to view all the devices connected to the console server.
To view and connect to devices using the web manager:
1. Select Access in the side navigation bar. The content area displays the name of the console
server and a list of names or aliases for all installed and configured devices the user is
authorized to access.
2. Select Serial Viewer from the Action column. A Java®applet viewer appears. In a gray area at
the top of the viewer, the Connected to message shows the IP address of the console server
followed by the default port number or alias.
3. Log in if prompted.
The following table describes the available buttons in the Java applet.
Java Applet Buttons for Connecting to the
Button Purpose
SendBreak
To send a break to the terminal
Page 27
Accessing the Console Server via the Web Manager.....21
Button Purpose
Disconnect
To disconnect from the Java applet
Select the left icon to reconnect to the server or device; or select the right icon to end the session
and disconnect from the Java applet
System Tools
Click System Tools to display icons which can be clicked to reboot or shut down the console server,
upgrade the console server’s firmware, save or restore its configuration or open a terminal session
with the console server.
To upgrade a console server's firmware:
1. From http://www.avocent.com, browse to the product updates section and find the firmware
for your console server.
2. Save the new firmware to an FTPserver or to your desktop.
3. From the sidebar of the console server's web manager, click System Tools, then click
Upgrade Firmware.
4. Download the file from an FTPserver by selecting FTPserver.
a. In the FTPsite field, enter theaddress of the FTPserver where you saved the firmware.
b. Enter the username and password for the FTPserver in the appropriate fields.
c. Enter the file directory where the firmware is saved and the filename for the firmware in
the appropriate fields.
-or-
Download the file from your desktop by selecting My Computer.
a. Type the filename for the new firmware or click Browse to open a window to browse to
the file.
5. Click Download. The console server will download the firmware from the specified site and will
display a message when the download is complete.
6. Click Install.
7. Once the new firmware is installed, reboot the console server.
NOTE: If the page after installation displays empty or blank values, there was not enough memory to
upgrade the firmware. Reboot the console server and upgrade the firmware again.
Page 28
22.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
System
Click System to display information about the console server and allow an administrator to
configure the console server’s system parameters. The following tabs are listed under System in
the side navigation bar.
Security
Security Profile
ASecurity Profile determines which network services are enabled on the console server.
During initial configuration, the console server administrator must configure security parameters to
conform with the site security policy. The following security features can be configured either in the
web manager, CLI or the DSView software:
• Configure the session idle time-out
• Enable or disable RPC
• Ability to configure access for all users, or allow the configuration of group authorizations to
restrict access
• Select a Security Profile, which defines:
• Enabled services (FTP, ICMP, IPSec and Telnet)
• SSH and HTTP/HTTPS access
• Enable or disable Bootp Configuration retrieval
The administrator can select either a preconfigured Security Profile or create a custom profile.
All the services and the SSH and HTTP/HTTPS configuration options that are enabled and
disabled for each Security Profile are shown in the Wizard - Security and the System - Security -
Security Profile pages.
To configure a Security Profile:
1. Select System - Security - Security Profile.
2. In the Idle Timeout field, enter the number of minutes before the console server times out
open sessions.
NOTE: This value applies to any user session to the appliance via HTTP, HTTPS, SSH, Telnet or
CONSOLE port. It will not overwrite the value configured for the user's authorization group. The new idle
time-out will be applied to new sessions only.
3. Under the Enabled Services section, enable or disable the RCP checkbox.
Page 29

Accessing the Console Server via the Web Manager.....23
4. Under the Serial Devices heading, select whether port access is controlled by user group
authorization or configure port access settings to apply to all users.
5. Under Bootp Configuration retrieval, enable or disable the service.
6. Select the checkbox for Custom, Moderate, Open or Secure under the Security Profile
heading.
7. Enable/disable SSH authentication via username/password.
8. Click Save.
DSView software security
You can also configure DSView software security settings. When the console server is managed by
the DSView software, the DSView server will supply the certificate to the console server. Under
normal conditions, the DSView software will manage the certificate to clear and replace it with a
new certificate as needed. If communication with the DSView software is lost, the DSView server
will be unable to clear the certificate and the console server cannot be used. Click the Clear
DSView Certificate button to configure the console server in Trust All mode.
To configure DSView software security settings:
1. Select System - Security - DSView.
2. Click the Allow appliance to be managed by DSView checkbox and click Save.
FIPS module
The console server has embedded the FIPS-capable OpenSSL that is the combination of the FIPS
Object Module (the FIPS 140-2 validated module) along with a FIPS-compatible OpenSSL (it is a
version of the OpenSSL product that is designed for compatibility with the FIPS Object Module
API).
If an administrator enables the FIPS module, the console server will use the FIPS Object Module to
perform encryption operations. The FIPS module is disabled by default.
When the FIPS module is enabled, the Monitoring - FIPS mode page will show what service
(SSHv2, HTTPS, SNMPv3 and ADSAP2) is in FIPS mode. All security functions and cryptographic
algorithms used by the service are performed in FIPS 140-2 Approved mode.
To enable the FIPS module:
1. Select System - Security - FIPS140.
2. Check the box to Enable the FIPS140-2 Module and click Save.
The console server will automatically reboot. During the reboot, the console server will erase
SSHkeys, update the configuration of HTTPD, SSHD, ADSAP2d and SNMPD files and test the
Page 30

24.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
integrity of the FIPSObject Module. Once the reboot is complete, the console server will accept
SSH and HTTPSconnections using only FIPS-approved ciphers.
When FIPS is enabled the following restrictions apply:
For SSH sessions:
Protocol version 1 will be disabled.
Triple-DES CBS and AES 128/192/256 are the only encryption ciphers that will be accepted.
HMAC-SHA1 and HMAC-SHA1-96 are the only message integrity algorithms that will be accepted.
Only RSAkeys 1024 to 16384 bits will be accepted.
HTTPSsessions will accept only the SSL v 3.1(TLSv1) protocol to establish the SSLtunnel
with one of the following encryption ciphers:
AES-256-SHA
AES-128-SHA
Triple DESSHA (DES-CBC3-SHA)
SNMPversion 3 requests will be accepted when authentication is SHAand the encryption
cipher is AES.
HTTPS Certificate
You can generate a new self-signed certificate or download a signed certificate to the appliance
from an FTP server or from your desktop.
To generate a new self-signed certificate:
1. Select System – Security – HTTPS Certificate.
2. Check the radio button next to Generate Self-Signed Certificate.
3. Enter the desired information in the self-signed certificate fields: Country, State/Province,
City/Locality, Organization, Organization Unit, Common Name, Email Address and Netscape
Comment.
4. Click Generate/Download. The generated certificate's information will be displayed.
5. Click Install. The certificate will be saved and the browser server will restart to use the new
certificate.
To download a signed certificate:
1. Select System – Security – HTTPS Certificate.
Page 31

Accessing the Console Server via the Web Manager.....25
2. Check the radio button next to Download Certificate from FTP Server to download the file from
the FTP server.
3. Enter all information about the FTP server: FTP site (IP address), Username, Password, File
Directory and File Name
-or-
Check the radio button next to Download Certificate from My Computer to download the file
from your desktop.
4. Enter the filename's path or click Browser to browse to the file.
5. Click Generate/Download. The generated certificate's information will be displayed.
6. Click Install. The certificate will be saved and the browser server will restart to use the new
certificate.
NOTE: The browser server will restart to use the new certificate, all http/https sessions will close and user
needs to re-establish the connection.
Bootp Configuration Retrieval
You can set your consoleserver to be reconfigured during boot or at IPrenewal.
To generate configuration to be retrieved:
1. Click System Tools - Save Configuration and save the configuration to either an FTPsite or
locally.
-or-
Use the list_configuration command to get the CLItemplate scripts, edit the configuration of
the console server and save it as a text file.
-or-
Edit a file with CLI commands and save it.
2. Transfer the saved file to a DHCPserver.
3. Configure the DHCP server to transfer the configuration file to the console server.
To reconfigure a console server with bootp:
1. Click System - Security - Security Profile. Under the Bootp Configuration Retrieval heading,
ensure the box next to Enabled is checked.
Page 32

26.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
2. Uncheck the box next to Enable Live Configuration. The saved configuration will be retrieved
and applied on the next reboot.
-or-
Ensure the box next to Enable Live Configuration is checked. The saved configuration will be
retrieved and applied on the next IPrenewal.
NOTE: You must configure your DHCPserver in order to transfer the configuration file to your console
server.
Date and Time
The console server provides two options for setting the date and time. It can retrieve the date and
time from a network time protocol (NTP) server, or you can set the date and time manually so that
the console server’s internal clock is used to provide time and date information.
NOTE: The Current Time displayed in the Date & Time screen shows only the time when the screen was
opened. It does not continue to update in real time.
To set the time and date using NTP:
1. Click System - Date And Time.
2. Select Enable network time protocol.
3. Enter the NTP server site of your choice and click Save.
To set the time and date manually:
1. Click System - Date And Time.
2. Select Set manually.
3. Using the drop-down menus, select the required date and time and click Save.
To set the time zone using a predefined time zone:
1. Click System - Date And Time - Time Zone.
2. Select Predefined.
3. Select the required time zone from the drop-down menu and click Save.
To define custom time zone settings:
1. Click System- Date And Time - Time Zone.
2. Select Define Time Zone.
3. Enter the Time Zone Name and Standard Time Acronym of your choice.
Page 33

Accessing the Console Server via the Web Manager.....27
4. Enter the GMT Offset.
5. Select Enable daylight savings time if needed.
6. Select or enter the required values for daylight savings time settings and click Save.
Help and Language
Click System - Help And Language and use the drop-down menu to select the console server’s
language. Enter the full URL of the online help, ending in /index.html, on the local web server in the
Online Help URL field. Click Save.
Online help
When the online help feature is configured for your console server, clicking the Help button from
any form on the web manager opens a new window and redirects its content to the configured path
for the online help product documentation.
NOTE: Using the online help feature from the Avocent/Cyclades server is not always possible due to
firewall configurations, nor is it recommended. It is generally advisable for you to use the online help system
provided with the product or download the online help .zip file and run it from a local server.
The system administrator can download the online help from Avocent. For more information on
downloading the online help, contact Technical Support.
Once the online help file is obtained (in zip format), the files must be extracted and put in to a user-
selected directory under the web server’s root directory. The web server must be publicly
accessible.
NOTE: The default URL for online help is http://global.avocent.com/us/olh/acs6000/v_3.0.0/en/index.html.
General
An administrator can configure a login banner to display when a user begins a SSHv2, Telnet,
Console or web manager session.
To create a login banner:
1. Click System - General in the side navigation bar.
2. Check the box to enable the login banner.
3. Enter the text you want displayed upon login in the Login Banner field and click Save.
Page 34

28.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
Boot Configuration
Boot configuration defines the location from which the console server loads the operating system.
The console server can boot from its internal firmware or from the network. By default, the console
server boots from Flash memory. Clicking System- Boot Configuration will display the Boot
Configuration screen.
If you need to boot from the network, make sure the following prerequisites are met:
• A TFTP or BootP server must be available on the network
• An upgraded console server boot image file must be downloaded from Avocent and made
available on the TFTP or BootP server
• The console server must be configured with a fixed IP address
• The boot filename and the IP address of the TFTP or BootP server is known
To configure boot configuration:
1. Click System - Boot Configuration.
2. Under Boot Mode, select From Flash, and select Image 1 or Image 2.
-or-
Select From Network and enter the following information:
• Appliance IP Address: Enter the fixed IP address or a DHCP assigned IP address to the
console server.
• TFTP Server IP: Enter the IP address of the TFTP boot server.
• Filename: Enter the filename of the boot firmware.
3. Using the drop-down menu, select whether the Watchdog Timer is enabled. If the Watchdog
Timer is enabled, the console server reboots if the software crashes.
4. Using the drop-down menu, select one of the following speeds for both Ethernet 0 Mode and
Ethernet 1 Mode: 100BT full, 100BT half, 10BT full, 10BT half or Auto.
5. Using the drop-down menu, select the console port speed and click Save.
NOTE: Ethernet Mode will be affected after saving. The rest of the configuration will be applied after
rebooting.
Information
Click System - Information to view the console server’s identity, versions, power and CPU
information.
Page 35

Accessing the Console Server via the Web Manager.....29
Usage
Click System - Usage to view memory and Flash usage.
Network
Click Network to view and configure the network options for Hostname, DNS, IPv6, Bonding, IPv4
and IPv6 static routes, Hosts, Firewall, IPSec (VPN) and SNMP.
Settings
Click Network - Settings to make changes to the configured network settings: Hostname, DNS,
Bonding, IPv4 Multiple Routing Table.
NOTE: IPv4 Multiple Routing Table allow administrator to configure two networks one for each interface
(EHT0 and ETH1) with its own default gateway.
Devices
An administrator can select, enable and configure the IP addresses assigned to the network
interfaces and view the MAC address. Besides the two standard Ethernet interfaces, the list of
network interfaces includes entries for any Ethernet PC cards that may be installed.
To configure a network device:
1. Select Network - Devices. The Devices screen appears with a list of network interfaces and
their status (enabled or disabled).
2. Click the name of the network device to configure.
3. Select the status (either Enabled or Disabled) from the drop-down menu.
4. Select one of the following IPv4 method options:
• Select DHCP to have the IPv4 IP address set by the DHCP server.
• Select Static to enter the IPv4 IP address, subnet mask and gateway address manually.
• Select IPv4 address unconfigured to disable IPv4.
5. Select one of the following IPv6 method options:
• Select Stateless if the link is restricted to the local IP address.
• Select DHCPv6 to have the IPv6 IP address set by the DHCP server.
• Select Static to enter the IPv6 IP address and prefix length manually.
• Select IPv6 address unconfigured to disable IPv6.
6. Select the Ethernet Mode for the built-in interface (ETH0 and ETH1).
Page 36

30.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
NOTE: The MAC Address for the device will be displayed after this option.
IPv4 and IPv6 static routes
To add static routes:
1. Select Network - IPv4 Static Routes or IPv6 Static Routes. Any existing static routes are listed
with their Destination IP/Mask, Gateway, Interface and Metric values shown.
2. Click Add.
3. Select Default to configure the default route.
-or-
Select Host IP Or Network to enter custom settings for Destination IP/Mask.
Enter the required Destination IP/Mask Bits with the syntax <destination IP>/<CIDR> in the
Destination IP/Mask Bits field.
4. Enter the IP address of the gateway in the Gateway field.
5. Enter the interface name (Eth0, Eth1 or PPPx) in the Interface field when the route is by
interface.
6. Enter the number of hops to the destination in the Metric field, then click Save
Hosts
An administrator can configure a table of host names, IP addresses and host aliases for the local
network.
To add a host:
1. Select Network - Hosts.
2. Click Add to add a new host.
3. Enter the IP address, hostname and alias of the host you want to add, then click Save.
To edit a host:
1. Select Network - Hosts.
2. Click on the IP address of the hostname you want to edit.
3. Enter a new hostname and alias, if applicable, then click Save.
Page 37

Accessing the Console Server via the Web Manager.....31
Firewall
Administrators can configure the console server to act as a firewall. By default, three built-in chains
accept all INPUT, FORWARD and OUTPUT packets. Select the Add, Delete or Change Policy
buttons to add a user chain, delete user-added chains and to change the built-in chains policy.
Default chains can have their policy changed (Change Policy) to accept or drop, but cannot be
deleted. Clicking on the Chain Name allows you to configure rules for chains.
Firewall configuration is available by clicking on Network - Firewall. Separate but identical
configuration screens are available from either the IPv4 Filter Table or IPv6 Filter Table menu
options.
Only the policy can be edited for a default chain; default chain policy options are ACCEPT and
DROP.
When a chain is added, only a named entry for the chain is created. One or more rules must be
configured for a chain after it is added.
Configuring the firewall
For each rule, an action (either ACCEPT, DROP, RETURN, LOG or REJECT ) must be selected
from the Target pull-down menu. The selected action is performed on an IP packet that matches all
the criteria specified in the rule.
If LOG is selected from the Target pull-down menu, the administrator can configure a Log Level, a
Log Prefix and whether the TCP sequence, TCP options and IP options are logged in the Log
Options Section.
If REJECT is selected from the Target pull-down menu, the administrator can select an option from
the Reject with pull-down menu; the packet is dropped and a reply packet of the selected type is
sent.
Protocol options
Different fields are activated for each option in the Protocol pull-down menu.
If Numeric is selected from the Protocol menu, enter a Protocol Number in the text field.
If TCP is selected from the Protocol menu, a TCP Options Section is activated for entering source
and destination ports and TCP flags.
If UDP is selected from the Protocol menu, the UDP section is activated for entering source and
destination ports.
Page 38

32.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
Firewall Configuration - TCP and UDP Options Fields
Field/Menu
Option
Source Port - or
- Destination
Port
TCP Flags
Definition
A single IP address or a range of IP addresses.
[TCP only] SYN (synchronize), ACK (acknowledge), FIN (finish), RST (reset), URG (urgent)
and PSH (push). The conditions in the pull-down menu for each flag are: Any, Set or Unset.
If ICMP is selected from the Protocol menu, the ICMP Type pull-down menu is activated.
If an administrator enters the Ethernet interface (eth0 or eth1) in the input or output interface fields
and selects an option (2nd and further packets, All packets and fragments or Unfragmented
packets and 1st packets) from the Fragments pull-down menu, the target action is performed on
packets from or to the specified interface if they meet the criteria in the selected Fragments menu
option.
To add a chain:
1. Select Network - Firewall.
2. Select either IPv4 Filter Table or IPv6 Filter Table as needed.
3. Click Add.
4. Enter the name of the chain to be added.
5. Click Save.
NOTE: Spaces are not allowed in the chain name.
6. Add one or more rules to complete the chain configuration.
To change the policy for a default chain:
NOTE: User-defined chains cannot be edited. To rename a user-added chain, delete it and create a new
one.
1. Select Network - Firewall.
2. Select either IPv4 Filter Table or IPv6 Filter Table as needed.
3. Select the checkbox next to the name of the chain you want to change (FORWARD, INPUT,
OUTPUT).
4. Click Change Policy and select Accept or Drop from the drop-down menu.
5. Click Save.
To add a rule:
Page 39

Accessing the Console Server via the Web Manager.....33
1. Select Network - Firewall.
2. Select either IPv4 Filter Table or IPv6 Filter Table as needed.
3. From the chain list, click the name of the chain you want to add a rule to.
4. Click Add and configure the rule as needed, then click Save.
To edit a rule:
1. Select Network - Firewall.
2. Select either IPv4 Filter Table or IPv6 Filter Table as needed.
3. From the chain list, click the name of the chain with the rule you want to edit.
4. Select the rule you want to edit and click Edit.
5. Modify the rule as needed and click Save.
IPSec(VPN)
Virtual Private Network (VPN) enables a secure communication between the console server and a
remote network by utilizing a gateway and creating a secured connection between the console
server and the gateway. The IPSec protocol is used to construct the secure tunnel and provides
encryption and authentication services at the IP level of the protocol stack.
NOTE: IPSec(VPN) is not supported with IPv6.
When Network - IPSec(VPN) is selected, the IPSec(VPN) screen is displayed.
Use the Add button to add a VPN connection or click on an existing connection name to edit one
already in the list. Click the Delete button to delete an existing connection. If NAT settings need to
be changed, click the Configure NAT button.
When you click the Add button, the IPSec(VPN) - Add screen is displayed.
NOTE: To run IPSec (VPN), you must enable IPSec under the custom Security Profile.
The remote gateway is referred to as the remote or right host and the console server is referred to
as the local or left host. If left and right are not directly connected, then you must also specify a
NextHop IP address.
The next hop for the remote or right host is the IP address of the router to which the remote host or
gateway running IPSec sends packets when delivering them to the left host. The next hop for the
left host is the IP address of the router to which the console server sends packets to for delivery to
the right host.
Page 40

34.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
A Fully Qualified Domain Name should be indicated in the ID fields for both the Local (Left) host and
the Remote (Right) host where the IPSec negotiation takes place.
The following table describes the fields and options on the IPSec(VPN) - Add screen. The
information must match exactly on both ends for local and remote.
Field and Menu Options for Configuring IPSec(VPN)
Field Name Definition
Connection
Name
Authentication
Protocol
Boot Action
Authentication
Method
Remote
(Right) Side and - Local
(Left) Side
RSA Key (If
RSA Key
selected)
Pre-Shared
Secret (If
Secret is
selected)
Any descriptive name you wish to use to identify this connection.
The authentication protocol used, either ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload) or AH
(Authentication Header).
The boot action configured for the host, either
Authentication method used, either RSA Public Keys or Shared Secret.
Enter the required address or text for each of the four fields for both Remote Side and Local
Side: ID: This is the hostname that a local system and a remote system use for IPSec
negotiation and authentication. It can be a fully qualified domain name preceded by @. For
example, hostname@xyz.com IP Address: The IP address of the host. NextHop: The router
through which the console server (on the left side) or the remote host (on the right side) sends
packets to the host on the other side. SubNet: The netmask of the subnetwork where the host
resides. Use CIDR notation. The IP number followed by a slash and the number of ‘one’ bits in
the binary notation of the netmask. For example, 192.168.0.0/24 indicates an IP address
where the first 24 bits are used as the network address. This is the same as 255.255.255.0.
For IPSec(VPN) authentication, you need to generate a public key for the console server and
is
find out the key used on the remote gateway. Copy and paste for copying the RSA key from
another source is supported.
Pre-shared password between left and right users.
Ignore,AddorStart
.
SNMP Configuration
An administrator can configure SNMP, which is needed if notifications are to be sent to an SNMP
management application.
NOTE: The Avocent ACS 6000 Enterprise MIB text file is available in the appliance at:
/usr/local/mibs/ACS6000-MIB.asn. The Avocent ACS 6000 Enterprise TRAP MIB text file is available in
the appliance at: /usr/local/mibs/ACS6000-TRAP-MIB.asn. Both files are also available at
www.avocent.com.
To configure SNMP:
1. Click Network - SNMP.
2. Click the System button.
Page 41

Accessing the Console Server via the Web Manager.....35
a. Enter the SysContact information (email address of the console server’s administrator,
for example, acs6000_admin@avocent.com).
b. Enter the SysLocation information (physical location of the console server, for example,
Cyclades_ACS6000), then click Save to go back to the SNMP screen.
3. Click Add to add a new community or v3 user.
4. Enter the community name for SNMP v1/v2 or the user name for SNMP v3 in the Name field
and enter the OID.
5. Select the desired permission from the pull-down menu. Choices are Read and Write or Read
Only.
6. If the required SNMP version is v1 or v2, click the Version v1, v2 button, then enter the source
(valid entry is the subnet address).
-or-
If the required SNMP version is v1 or v2 using an IPv6 network, click the Version v1,v2 for
IPv6 network button, then enter the source (valid entry is the subnet address).
-or-
If the required SNMP version is v3, click the Version v3 button, then select the Authentication
Type (MD5 or SHA), enter the authentication passphrase or password, select the Encryption
Method (DES or AES), enter the privacy passphrase and select the Minimum Authentication
Level (NoAuthNoPriv, AuthNoPriv, AuthPriv).
7. Click Save.
NOTE: For SNMP v1/v2c, the console server will allow an administrator to configure the same community
name with different sources (filters) to have access to specific object identifiers (OIDs).
Ports
An administrator can enable and configure serial ports, auxiliary ports, the CAS Profile and the
Dial-in Profile from the Ports tab in the side navigation bar. On the auxiliary ports screen, you can
enable the auxiliary port and configure it based on the type of connected device.
Serial ports
On the Serial Ports table, you can specify the connection profile (CAS, Dial-In, Power, Dial-Out or
Socket Client) based on the type of connected device and you can clone the port, reset to factory
defaults and enable/disable ports.
To enable or disable one or more serial ports:
Page 42

36.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
1. Select Ports - Serial Ports.
2. Click the checkbox for each port you want to enable or disable.
3. Click the Enabled or Disabled button.
To configure or edit one or more serial ports with the CAS Profile:
1. Select Ports - Serial Ports.
2. Click the checkbox for each port you want to configure.
3. Click the Set CAS button.
a. To change the default pinout when a Cisco cable is connected to the selected port(s),
select the Enable Cisco from the RJ-45 pinout checkbox.
b. Use the drop-down menus to enable or disable the port and set the speed, parity, data
bits, stop bits and flow control.
4. Click Next or click the CAS link.
a. Enter the port name (when only one port was selected) or the port name prefix (when
more than one port were selected). The port name will be <port name prefix>-p-<port
number>.
b. Check the box to enable auto discovery. In this case, the port name will be used when
auto discovery fails to discover the server name.
c. Check the box to enable speed auto detection.
NOTE: Auto speed detection requires additional configuration in the CAS Profile-Auto Discovery Settings
screen.
d. Use the appropriate drop-down menus to set the protocol and authentication type.
e. Enter the text session hotkey and power session hotkey in the appropriate fields.
f. Enter the TCP port alias for each protocol type (Telnet, SSH and Raw Mode) in the
appropriate field.
g. Enter the IPv4 or IPv6 alias and its interface in the appropriate field.
h. To allow a session only if DCD is on and to enable auto answer, check the appropriate
boxes.
i. Use the drop-down menu to select the DTR mode and enter the DTR off interval.
j. Use the drop-down menus to enable or disable line feed suppression and NULL after CR
suppression.
k. Enter the transmission interval, break sequence and break interval in the appropriate
fields.
Page 43

Accessing the Console Server via the Web Manager.....37
l. Use the drop-down menus to enable or disable log in/out multisession notification and
informational message notification.
5. Click Next or click the Data Buffering link and use the drop-down menus to enable and
configure data buffering.
6. Click Next or click the Alerts link.
a. Click Enable Alerts to enable detection of alerts.
b. Click Add to add an alert string. In the Alerts String field, enter the string. In the Script
field, enter the shell script that will run when the match happens. Click Next to return to
the Alerts screen.
NOTE: The console server allows an administrator to associate one shell script to the alert string. When
there is a match with the alert string, the console server will call the script passing the port number and the
line where the match occurs as arguments.
c. Check the box next to an existing alert and click Delete to delete the string.
d. Click Delete Any to delete all strings whether selected or not.
NOTE: Clicking Delete Any will delete all alert strings. Selecting all the alert strings and clicking Delete is
not the same functon as it will not delete alert strings not shown in the table.
7. Click Next or click the Power link.
a. Click Add to add a new outlet. Click Selected PDU and select a PDU from the list of
detected PDUs. Enter the outlet(s) in the Outlets field, and click Next.
b. Check the box next to an existing merged outlet and click Delete to delete it.
NOTE: Power is only available when a single serial port is selected.
8. Click Save.
CAS Profile Parameters
Parameter Descr iption
Physical
Enable Cisco
RJ-45 Pin-Out Defines the serial port pinout. Default: Disabled.
Status Defines the status of the serial port as either enabled or disabled. Default: Disabled.
Speed
Parity Defines the parity as either Even, Odd or None. Default: None.
Data Bits Defines the data bits as either 5, 6, 7 or 8. Default: 8.
Stop Bits Defines the stop bits as either 1 or 2. Default: 1.
Defines the speed as 300, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200 or 230400.
Default: 9600.
Page 44

38.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
Parameter Descr iption
Flow Control
Defines the flow control as none, hardware, software, RxON software or TxON software.
Default: None.
CAS
Port Name
Enable Auto
Discovery
Enable Speed
Auto
Detection
Protocol
Authentication
Type
Text Session
Hot Key
Power
Session Hot
Key
TCP Port
Alias
Port
IPv4/IPv6
Alias
Port
IPv4/IPv6
Alias Interface
Name associated with the serial port (as an alias). Default: <appliance mac address>-p-<port
number>.
The target name will be discovered and will be associated with this serial port. If it fails, the
Port Name will be used. Default: Disabled.
Tries to discover the speed of the serial port. This feature requires additional configuration
under the CAS Profile / Auto Discovery / Settings page. Default: Disabled.
The protocol that will be used by authorized users to access the serial port/target. The console
server accepts three protocols for connection to the target: Telnet for telnet connection, SSH
for secure connection and Raw Mode for raw socket connection. An administrator can
configure the port to accept one, two or all three types. NOTE: Raw protocol requires the
configuration of the Raw Mode Port Alias. Default value: Telnet/SSH.
Authentication type that will be used to authenticate the user during target session. Default:
Local.
Hotkey to suspend the target session and go to the CLI prompt. Not available for Raw.
Default: Ctrl-Z.
Note:The default escape character for ts_menu is Ctrl-X.
Hotkey to suspend the target session and display Power Management Menu to control the
outlets merged to the target. Not available for Raw. Default: Ctrl-P.
NOTE:The default escape character for ts_menu is Ctrl-X.
Telnet Port Alias: TCP port to connect directly to a serial port using Telnet protocol for the
connection. SSH Port Alias: TCP port to connect directly to a serial port using SSH protocol
for the connection/ Raw Mode Port Alias: TCP port to connect directly to a serial port using
raw socket for the connection.
IPv4/IPv6 address used to connect directly to a serial port. Default: not configured (empty).
Interface (ETH0/ETH1) associated with the IPv4/IPv6 alias. Default: ETH0.
Allow Session
Only if DCD is
On
Enable Auto
Answer
DTR Mode
DTR Off
Interval
Line Feed
Suppression
Null After CR
Suppression
When the DCD is OFF, the appliance will deny access for this serial port. Default: Disabled
(allow access if DCD is OFF).
When the input data matches one input string configured in Auto Answer, the output string will
be transmitted to the serial port. Default: Disabled.
DTR Mode can be set to the following: Always On. Normal - the DTR status will depend on the
existence of a CAS session. Off Interval - when the a CAS session is closed, the DTR will stay
down during this interval. Default: Normal.
Interval in seconds used by DTR Mode Off Interval in milliseconds. Default: 100.
Enables the suppression of the LF character after the CR character. Default: Disabled.
Enables the suppression of the NULL character after the CR character. Default: Disabled.
Page 45

Accessing the Console Server via the Web Manager.....39
Parameter Descr iption
Transmission
Interval
Break
Sequence
Break Interval Interval for the break signal in milliseconds. Not available for Raw. Default: 500.
Log In/Out
Multi Session
Notification
Informational
Message
Notification
The interval the port waits to send data to a remote client in milliseconds. Default: 20.
An administrator can configure the control key as the break sequence, entering ^ before the
letter. Not available for Raw. Default: ~break.
Enables the notification to multi-session users when a new user logs in or a user logs out. Not
available for Raw. Default: Disabled.
Displays an information message when a target session is opened. Not available for Raw.
Default: Enabled.
Data
Buffering
Status Enables or disables data buffering. Default: Disabled.
Displays the type of data buffering: Local - stores the data buffering file in the local file
Type
Time Stamp
Log-in/out
Message
Serial Session
Logging
system. NFS - stores the data buffering file in the NFS server. Syslog - sends the data to the
syslog server. DSView - sends the data to the DSView software. Default: Local.
When enabled, adds the time stamp to the data buffering line for a Local or NFS database.
Default: Disabled.
Includes special notification for logins and logouts in data buffering. Default: Disabled.
Enabled - stores data at all times. Disabled - stores data when a CAS session is not opened.
Default: Enabled.
Alerts
Status
Alert Strings Strings used to generate event notifications. Default: Empty.
Scripts
A special event notification will be generated when input data matches one of the alert strings.
Default: Disabled.
Name of shell script that will be called when there is match of the alert string in the line. The
script will be called with two arguments: the port number and the line where the match
happened.
To configure the Dial-in Profile for a serial port with a connected modem:
1. Select Ports - Serial Ports.
2. Click the checkbox for a serial port with a connected modem.
3. Click the Set Dial button and use the drop-down menus to configure the dial-in settings.
4. Configure the PPP parameters (address, authentication and so on) and click Save.
Dial-in Parameters
Parameter Descr iption
Status Enables or disables the port. Default: Disabled.
Speed The speed that will be used by mgetty to configure the serial device. Default: 38400 bps.
Init Chat Chat for modem initialization. Default: "" \d\d\d+++\d\d\dATZ OK.
PPP Address
Configures the local and the remote IP address for the the PPP link. If
from Remote Peer
remote) during negotiation. Default: No Address.
is selected, the remote peer should send both IP addresses (local and
Accept Configuration
Page 46

40.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
Parameter Descr iption
Local
IPv4/IPv6
Address
Remote
IPv4/IPv6
Address
PPP
Authentication
Protocol
CHAP
PPP Idle
Timeout
Configures the local IPv4/IPv6 address for this PPP connection.
Configures the remote IPv4/IPv6 address for this PPP connection.
Uses the radio button to select: none, PAP, CHAP or EAP.
None - no authentication.
• PAP - use PAP protocol and the authentication type configured in the PPP authentication
type (it is configured in the Authentication / Unit Authentication page).
• CHAP - use CHAP protocol. The configuration of the CHAP secrets should be done while
editing the file /etc/ppp/chap-secrets.
• EAP - use EAP protocol. Available authentications: CHAP, SRP-SHA1 and TLS. The
configuration of the secrets for CHAP should be done while editing the file /etc/ppp/chapsecrets. The configuration of the secrets for SRP-SHA1 should be done while editing the file
/etc/ppp/srp-secrets.
Default: None.
Configure the CHAP-interval, CHAP-max-challenge and CHAP-restart. Default values:
• CHAP Interval = 0.
• CHAP Max Challenge = 10.
• CHAP Restart = 3.
Number of seconds being idle before PPP times out. Default: 0 (no time-out).
To configure or to edit one or more serial ports with a connected PDU:
1. Select Ports - Serial Ports.
2. Click the checkbox for one or more serial ports with a connected PDU.
3. Click the Set Power button and use the drop-down menus to configure the physical settings.
4. Click Next or click the Power link.
a. Use the drop-down menu to select the PDU type.
b. Check the box to enable speed auto detection.
c. Configure the polling rate.
d. For Avocent/Cyclades PDUs, enter the power cycle interval and then use the drop-down
menus to enable or disable Syslog, Buzzer and SW Overcurrent Protection.
5. Click Save.
Power Parameters
Parameter Descr iption
Physical
Enable Cisco RJ-45 PinOut
Status
Defines the serial port pinout. Default: Disabled.
Defines the status of the serial port as either enabled or disabled. Default:
Disabled.
Page 47

Accessing the Console Server via the Web Manager.....41
Parameter Descr iption
Speed
Parity Defines the parity as either Even, Odd or None. Default: None.
Data Bits
Stop Bits Defines the stop bits as either 1 or 2. Default: 1.
Flow Control
Defines the speed as 300, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600 or
115200. Default: 9600.
Defines the data bits as either 5, 6, 7 or 8. Default: 8.
Defines the flow control as none, hardware, software, RxON software or TxON
sofware. Default: None.
Power
Defines the type or vendor of the PDU connected to the serial port.
• Auto - the vendor will be detected.
PDU Type
Enable Speed Auto
Detection
Pooling Rate The interval in seconds to update information from the PDU. Default: 20.
• Avocent-Cyclades - Avocent-Cyclades PM PDU family.
• SPC - SPC power control device family.
• Server Tech - Server Tech family.
Default: Auto.
When enabled, detects the speed of the port. Default: Disabled.
For Avocent/Cyclades
PDUs
Power Cycle Interval
Syslog
Buzzer Enables or disables the PDU’s buzzer. Default: Enabled.
SW Overcurrent
Protection
The interval in seconds between Off and On actions for the power cycle command.
Default: 15.
When enabled, the PDU will send syslog messages to the appliance. Default:
Enabled.
When enabled, the software’s overcurrent protection is on. Default: Disabled.
To copy/clone the configuration of one port to other ports:
1. Select Ports - Serial Ports.
2. Click the checkbox for the serial port you want to clone.
3. Click the Clone button.
4. Enter the serial port(s) to be configured in the Copy Configuration To field and click Save.
NOTE: If the selected port is configured as a CAS Profile, the following parameters will not be copied: Port
Name, TCP Port Alias, IPv4 Port Alias, IPv6 Port Alias and Power (merged outlets).
To reset one or more serial ports to their factory configuration:
1. Select Ports - Serial Ports.
2. Click the checkbox for one or more serial ports you want to reset to their factory configuration,
then click the Reset To Factory button.
NOTE: Serial ports are set to the CAS Profile and disabled in the factory configuration.
Page 48

42.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
Auxiliary ports
On the Auxiliary Ports screen, you can enable the auxiliary port and configure it based on the type
of connected device.
To configure or edit auxiliary port with connected PDU:
1. Select Ports - Auxiliary Ports.
2. Click the Set Power button and use the drop-down menus to configure the physical settings.
3. Click Next or click the Power link.
a. Use the drop-down menu to select the PDU type.
b. Check the box to enable speed auto detection.
c. Configure the polling rate.
d. For Avocent/Cyclades PDUs, enter the power cycle interval and then use the drop-down
menus to enable or disable Syslog, Buzzer and SW Overcurrent Protection.
4. Click Save.
To configure or edit auxiliary port with a connected or internal modem:
1. Select Ports - Auxiliary Ports.
2. Click the Set Dial-In or Set Dial-Out button and use the drop-down menus to configure the
Dial-in settings.
3. Configure the PPP parameters (address, authentication, and so on).
4. Click Save.
CAS Profile
An administrator can configure settings for auto discovery and for auto answer features.
Auto discovery
The auto discovery feature will discover the target name of the server connected to the serial port.
This name will be used as the alias of the serial port.
When auto discovery is active for a certain serial device, upon target connection (DCD ON event),
the appliance will send probe strings and start analyzing target device answers using regular
expressions. There will be predefined probe and match strings as well as customer-defined ones.
For each probe string sent, all regular expressions defined by the match strings will be tested. After
the last cycle, the sequence restarts. This procedure will run for a certain period (given by the auto
discovery time-out parameter) or until the target is successfully detected. If auto discovery fails, the
Page 49

Accessing the Console Server via the Web Manager.....43
target name will be reset to the configured target name or to the corresponding unique default
target name.
NOTE: The configured target name will be used only after the auto discovery process fails.
NOTE: The auto discovery process starts when there is variation in the DCD signal from OFF to ON
(disconnect/connect the target's cable, turn off/on the target) and when the configuration of the serial port
goes from disabled to enabled and there is a target connected in the port.
The probe strings will be used to stimulate the server (such as “\n”: a single newline).
The match strings are regular expressions where “%H” is a placeholder for the target name you
want to detect, such as:
“\\(.*\\)(%H)\\(.*\\)” or just “xxx%Hyyy”.
The first one will extract target name from things such as:
nanana(myTarget): à results: myTarget
jhdsgjhas(tg2)kjafja à results: tg2
And the second one from things such as:
hsagdfjhagfxxxTARGETyyyyyy à resulting: TARGET
To configure the strings for probe/match used by auto discovery:
Perform this procedure to change the default settings or the probe or match strings used in auto
discovery.
1. Select Ports - CAS Profile - Auto Discovery. The Settings, Probe Strings and Match Strings
options appear in the side navigation bar.
2. To change the default auto discovery time-out or probe time-out, perform the following steps.
a. Select Settings.
b. Enter a new value in the Auto Discovery Timeout and Probe Timeout fields.
c. Select a speed from the Default Speed on Auto Discovery Failure drop-down menu and
Probe Speed List.
d. Click Save.
3. To add a new probe or match string or delete an existing string, perform the following steps.
a. Select Probe Strings or Match Strings.
Page 50

44.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
b. To add a string, click Add, enter a new string in the New Probe String or New Match
String field and click Save.
c. To delete a string, select the checkbox for the string and click Delete.
4. Click Save.
To configure the input/output strings used by auto answer:
1. Select Ports - CAS Profile - Auto Answer.
2. To add an auto answer input and output string, click Add. Enter a new string in the Input String
or Output String fields and click Save.
-or-
To delete an auto input and output string, select the checkbox next to the string you want to
delete. Click Delete, then click Save.
Pool of CAS ports
An administrator can create a pool of serial ports where each serial port in the pool shares a pool
name, Telnet Port Alias, SSH Port Alias, Raw Mode Port Alias, IPv4 Alias and IPv6 Alias. The first
available port in the pool is used as the serial port for connection.
NOTE: The multiple session access right does not have any effect when using a pool of CAS ports. When
all ports in the pool are taken, the connection to the pool is denied.
NOTE: All ports in the pool must share the same CAS protocol. The protocol is validated during the
connection to the serial port. If the protocol does not match, the connection will be denied.
To configure a pool of CAS ports:
1. Click Ports - Pool of CAS Ports.
2. To create a pool, click the Add button.
- or -
To edit an existing pool, click the name of the pool you want to edit.
- or -
To delete a pool, check the box next to the pool you want to delete and click the Delete button.
3. Enter the parameters for the pool in the appropriate fields.
4. In the left side of the Pool Members field, select the ports to be added to the pool and click
Add.
Page 51

Accessing the Console Server via the Web Manager.....45
- or -
In the right side of the Pool Members field, select the ports to be removed from the pool and
click Remove.
5. Click Save.
NOTE: A serial port can only belong to one pool at a time, but a user can create an empty pool and add
ports to it later.
Pool of CAS Ports Parameters
Parameter Description
Pool Name
The name of the pool. The pool name is mandatory and should follow hostname guidelines,
not exceed 64 characters and start with a letter.
The Port Alias where the pool responds for each protocol.
Port Alias
Pool IPv4 Alias The IPv4 address used by the pool. This parameter is optional.
Pool IPv4 Alias
Interface
Pool IPv6 Alias The IPv6 address used by the pool. This parameter is optional.
Pool IPv6 Alias
Interface
l Telnet Port Alias for telnet protocol. It is optional.
l SSH Port Alias for ssh protocol. It is optional.
l Raw Mode Port Alias for raw mode protocol.
l It is mandatory when Raw Mode is configured as protocol for the ports.
The interface used by the IPv4 Alias. Default: Eth0.
The interface used by the IPv6 Alias. Default: Eth0.
Dial-in Profile
An administrator can configure secure dial-in settings such as OTP login, PPP connections,
PPP/PAP authentication, callback and OTP users for PPP connections.
NOTE: If pluggable devices are being used for dial-out, dial-in should be disabled.
To configure secure dial-in settings for ports with the Dial-in Profile:
1. Select Ports - Dial-In Profile - Settings.
2. To enable logging in to the console server through the modem and select a condition for which
logging in is allowed, perform the following steps.
a. To allow callback connections only, select Callback.
b. To allow any connection, select Enable.
3. To enable OTP authentication, select Enable from the OTP Login Authentication menu.
4. To enable and select a condition for PPP connections, perform the following steps.
a. To allow PPP callback connections only, select Callback.
Page 52

46.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
b. To allow any connection, select Enable.
5. When the PAP authentication protocol is configured for the port, select the authentication type
from the PPP/PAP Authentication menu.
6. Click Save.
To configure callback users and phone numbers for ports with the Dial-in Profile:
1. Select Ports - Dial-In Profile - Secure Dial-In - Callback Users.
2. Click Add.
3. Enter the name and phone number used to perform the callback in the appropriate fields and
click Save.
To configure PPP OTP users for ports with the Dial-in Profile:
1. Select Ports - Dial-In Profile - Secure Dial-In - PPP OTP Users.
2. Click Add.
3. Enter the username and passphrase in the appropriate fields and click Save.
NOTE: This PPP OPT user will establish PPP connection after being successfully authenticated.
To configure EAP-TLS as PPP authentication for ports with the Dial-in Profile:
1. Select Ports - Serial Ports.
-or-
Select Ports - Auxiliary Ports.
2. Check the box next to the port where the modem is connected and click Set Dial-In.
NOTE: If using an auxiliary port, the modem can be internal.
3. Configure the PPP Address settings. For example, set the PPP Address to Local
Configuration using 10.0.0.1 as the Local IPv4 Address and 10.0.0.2 as the Remote IPv4
Address.
4. For PPP Authenticaion, select the button next to By Appliance, and then select the button
next to EAP for the protocol. Click Save.
5. Select Ports - Dial-In Profile - Settings.
6. Use the drop-down menu to enable the PPP Connection and click Save.
Page 53

Accessing the Console Server via the Web Manager.....47
7. Copy the certificates and keys to the /etc/ppp/cert file. They must be named server.crt (the
ACS 6000 console server certificate), ca.crt (the Certificate Authority’s certificate) and
server.key (the ACS 6000 console server asymmetric key).
Dial-out Profile
To configure the Dial-out Profile for a serial port with a connected modem:
1. Select Ports – Serial Ports.
2. Click the checkbox for a serial port with a connected modem.
3. Click the Set Dial-out button.
4. Use the drop-down to enable/disable the port.
5. Configure the phone number to dial on-demand in the field Phone No.
6. Use the drop-down to configure the modem speed.
7. Configure the initial chat with modem in the Init Chat field.
8. Configure the PPP parameters (address, authentication and so on) and click Save.
NOTE: The Dial-out profile will work only to establish PPP link on-demand. The administrator must
configure static route to have packages routed to the PPP interface.
Dial-out Parameters
Parameter Descr iption
Status Enables or disables the port. Default:Disabled.
Phone No. The phone number to dial to.
Speed
Init Chat Chat for modem initialization.
Local IPv4/IPv6 Address
Remote IPv4/IPv6 Address
PPPAuthentication Protocol
PPP Idle Timeout
CHAP
The speed that will be used to configure the serial
device and communicate with the connected modem.
Configures the local IPv4/IPv6 address for this
PPPconnection. If empty, PPPwill accept the
address from the remote peer.
Configures the remote IPv4/IPv6 address for this
PPPconnection. If empty, PPPwill accept the
address from the remote peer.
Number of seconds being idle before PPPtimes out.
Default:0 (no time-out).
To configure the Socket Client Profile for a serial port with a connected device:
1. Select Ports - Serial Ports.
2. Click the checkbox for a serial port with a connected device.
Page 54

48.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
3. Click Set Socket Client and use the drop-down menus to configure the physical settings.
4. Configure the Socket Client Settings (remote server address, TCP port and event trigger) and
click Save.
Socket Client Parameters
Parameter Descr iption
Enable Cisco RJ-45 Pin-Out Defines the serial port pinout.
Status
Speed
Parity Defines the parity as Even, Odd or None. Default:None.
Data Bits Defines the data bits as 5, 6, 7 or 8. Default:8.
Stop Bits Defines the stop bits as 1 or 2. Default:1.
Flow Control
Remote Server IPv4 or IPv6 address of the remote server.
Remote TCPPort
Establish Connection
Defines the status of the serial port as either enabled or
disabled. Default:Disabled.
Defines the speed as 300, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600,
19200, 38400, 57600, 115200 or 230400. Default:9600.
Defines the flow control as none, hardware, software,
RxON software or TxON software. Default: None.
TCPport to be used to establish a connection with a
remote server.
Configure the event that will trigger the establishment of
the connection:DCDRegards or Always.
Pluggable Devices
The console server supports a variety of pluggable devices connected to its USBports. Some
models also support PCcards connected to the PCMCIAslots on the front of the console server.
For more information, go to http://emersonnetworkpower.com/en-us/products, then select
Infrastructure Management-Serial Consoles-Avocent ACS6000 Advanced Console Server. From
the product page, click the PCMCIACards tab to see the list of supported devices.
NOTE: When a pluggable device is not in the current list of supported pluggable devices, the console server
may attempt to configure the device with standard settings, allowing it to work normally. Also, when a
pluggable device is not listed in the internal database, the Device Info column may show no text at all or
show different text based on the type of card. One example is Unknown device f024 (rev 01).
To install and detect a pluggable device:
1. From the side navigation bar, select Pluggable Devices.
2. Click Enable Pluggable Device Detection to detect connected pluggable devices.
3. Connect a device to a USBport on the console server.
-or-
Page 55

Accessing the Console Server via the Web Manager.....49
If supported by the console server, insert a PC card into a PCMCIAslot.
4. The Pluggable Devices table displays all detected pluggable devices.
NOTE: To disable pluggable device detection, click Disable Pluggable Device Detection.
To eject or delete a pluggable device:
1. From the side navigation bar, select Pluggable Devices.
2. Select the checkbox next to the pluggable device you want to eject, rename or delete.
3. Click Eject, Rename or Delete as desired. If renaming a device, enter the new name in
Rename field. Click Save.
NOTE: Always eject a pluggable device from the web manager. Any other method may cause a kernel
panic.
Device configuration
Storage devices are automatically mounted and configured once detected by the console server.
Ethernet cards and modems must be configured.
NOTE: Configuration of wireless devices takes effect only after the device is ejected and re-inserted.
To configure a pluggable device:
1. From the side navigation bar, click Pluggable Devices.
2. For a network device, click its name to configure its network parameters.
3. -or-
4. For a modem (V.92 or wireless), click the box next to its name and then click either Set Dial-In
or Set Dial-Out to configure its dial-in or dial-out parameters.
Authentication
Authentication can be performed locally, with OTP, or on a remote Kerberos, LDAP, NIS, Radius or
TACACS+ authentication server. If the console server is managed by a DSView server, DSView
authentication is also supported. The console server also supports remote group authorizations for
the LDAP, Radius and TACACS+ authentication methods.
Fallback mechanisms of the following types are available:
Page 56

50.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
Local authentication can be tried first, followed by remote, if the local authentication fails
(Local/Remote_Method).
-or-
Remote authentication may be tried first, followed by local (Remote_Method/Local).
-or-
Local authentication may be tried only if a remote authentication server is down (Remote_Method_
Down_Local).
An administrator can configure authentication using the CLI utility and the web manager. The
default authentication method for the console server and the serial ports is Local. Any
authentication method that is configured for the console server or the ports is used for
authentication of any user who attempts to log in through Telnet, SSH or the web manager.
Appliance authentication
The console server authenticates for the console server and the ports, either in groups or
individually.
NOTE: It is advised when using group authorization that you use the same authentication for both the
console server and all serial ports, or use Single Sign-on Authentication to facilitate group authorization.
When Single Sign-on Authentication is disabled, the console server uses the individual
configuration based in the destination of the access: the console server itself or each serial port.
Users must use their password each time they access an individual port. If enabled, Single Sign-on
Authentication will use the authentication server you choose from the pull-down menu for all access
and no further authentication will be needed.
NOTE: Selecting unconfigured from the pull-down menu will allow the ports to continue to use individual
authentication servers, and will require your password the first time you access any port. After that, the port
will not require password authentication if Single Sign-on Authentication is enabled.
To set authentication for the console server:
1. Click Authentication - Appliance Authentication.
2. Select the desired authentication server from the Authentication Type drop-down menu.
3. Select Enable fallback to Local type for root user in appliance console port when the remote
authentication fails and an administrator wants to access the appliance via console port as the
root user.
Page 57

Accessing the Console Server via the Web Manager.....51
4. Select Enable single sign-on to enable single sign-on authentication, and select the desired
authentication server from the Authentication Type drop-down menu.
5. Click Save.
Authentication servers
When using an authentication server, you must configure its IP address and in most cases other
parameters before it can be used. The following authentication servers require configuration:
RADIUS, TACACS+, LDAP(S)|AD, Kerberos, NIS and DSView servers.
To configure a RADIUS authentication server:
1. Select Authentication - Authentication Servers - RADIUS.
2. Enter the IP addresses of the First Authentication Server and First Accounting Server.
3. If used, enter the IP addresses for the Second Authentication Server and Second Accounting
Server.
4. Enter your secret word or passphrase in the Secret field (applies to both first and second
authentication and accounting servers), then re-enter the secret word or passphrase in the
Confirm Secret field.
5. Enter the desired number of seconds for server time-out in the Timeout field.
6. Enter the desired number of retries in the Retries field.
7. If you select the Enable Service-Type attribute to specify the authorization group checkbox,
enter the authorization group name for each of the following Service Types: Login, Framed,
Callback Login, Callback Framed, Outbound and Administrative.
8. Click Save.
To configure a TACACS+ authentication server:
1. Select Authentication - Authentication Servers - TACACS+.
2. Enter the IP addresses for the First Authentication Server and First Accounting Server.
3. If used, enter the IP addresses of the Second Authentication Server and Second Accounting
Server.
4. Select the desired service (PPP or raccess) from the Service drop-down menu.
5. Enter your secret word or passphrase in the Secret field (applies to both first and second
authentication and accounting servers), then re-enter the secret word or passphrase in the
Confirm Secret field.
6. Enter the desired number of seconds for server time-out in the Timeout field.
7. Enter the desired number of retries in the Retries field.
Page 58

52.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
8. If you select the Enable User-Level attribute to specify the authorization group checkbox,
enter the authorization group name for up to 15 User-Levels.
9. Click Save.
To configure an LDAP(S)|AD authentication server:
1. Select Authentication - Authentication Servers - LDAP(S)|AD.
2. Enter the IP address of the server.
3. Enter the Base.
4. At the Secure drop-down menu, select Off, On or Start_TLS.
5. Enter the Database User Name.
6. Enter your Database Password, then re-type the database password in the Confirm
Password field.
7. Enter your desired Login Attributes.
8. Click Save.
To configure a Kerberos authentication server:
1. Select Authentication - Authentication Servers - Kerberos.
2. Enter the IP address (Realm) of the server.
3. Enter the Realm Domain Name (example: avocent.com).
4. Enter the Domain Name (example: avocent.com).
5. Click Save.
To configure an NIS authentication server:
1. Select Authentication - Authentication Servers - NIS.
2. Enter the NIS Domain Name of the server (example: corp.avocent.com).
3. Enter the NIS Server Address or broadcast (default is broadcast).
4. Click Save.
To configure a DSView authentication server:
1. Select Authentication - Authentication Servers - DSView.
2. Enter IP Address 1 - 4 for the DSView servers in the relevant fields.
3. Click Save.
Page 59

Accessing the Console Server via the Web Manager.....53
Users Accounts and User Groups
Access to ports can be optionally restricted, based on authorizations that an administrator can
assign to custom user groups. Groups can also be authorized to manage power while connected to
devices. The console server has two default users (admin and root) and four pre-defined user
groups: admin, appliance-admin, shell-login-profile and user.
A user account must be defined for each user on the console server or on an authentication server.
The admin and root users have accounts by default, and either administrator can add and
configure other user accounts. Each local user account is assigned to one or more of the user
groups.
CAUTION: Change the default passwords for root and admin before you put the console server into
operation.
Local accounts
The admin and root are equivalent users but named differently to address users familiar with
either Avocent equipment or the Cyclades families of console servers. Regular users can be
granted permissions by administrators at any time. The console server has two local user accounts
by factory default.
• admin: Performs the initial network configuration. The factory default password for admin is
avocent. The admin user is a member of the admin group and can configure the console
server and ports as well as user and group authorizations.
• root: Has the same permissions as the admin user. The factory default password for root is
linux. The root user is a member of the admin and shell-login-profile groups. When a root
user logs in via the CONSOLE port, SSH or telnet, the session is pre-defined by the login
profile to go directly to shell. The login profile can be customized so that it does not go directly
to shell.
To add new users:
1. Click Users - Local Accounts - User Names. The User Names screen is displayed with a list of
all users.
2. Click Add. The Local User Information screen is displayed.
3. Enter the new username and enter a password, then confirm the password.
4. Select or deselect User must change password at the next login checkbox.
5. To add the user to an available user group, select the user group name in the box on the left
and click Add (user is the default group). You can remove a user group from the box at right by
selecting it and clicking Remove.
6. Enter the desired parameters for Password Expiration.
Page 60

54.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
• Min Days: Enter the minimum number of days allowed between password changes.
Password changes attempted sooner will be rejected. If not specified, -1 is the default
which disables the restriction.
• Max Days: Enter the maximum number of days a password is valid. After this period, a
password change will be forced. If not specified, -1 is the default which disables the
restriction.
• Warning Days: Enter the number of days that a warning is issued to the user prior to
expiration. Entering 0 will cause the warning to be issued on the expiration day. A
negative value or no value means that no warning will be issued.
7. Enter the desired Account Expiration date (YYYY-MM-DD).
8. Click Save.
To configure password rules:
1. Click Users - Local Accounts - Password Rules.
2. If password complexity is desired (recommended), make sure Check Password Complexity is
selected.
3. If password complexity is enabled, enter the desired values for password complexity.
4. Enter the desired values for Default Expiration.
5. Click Save.
User groups
User groups are given access and authorizations either by default or as assigned by an
administrator. Administrators can alter the permissions and access rights of users belonging to the
appliance-admin or user groups or create additional groups with custom permissions and access
rights. Administrators can add, delete or modify permissions and access rights for users from any
group at any time.
If an administrator configures the console server to restrict user access to ports, the administrator
can assign users to groups that are authorized for port access. The administrator can also
authorize groups for power management and data buffer management.
This document and the software refer to users whose accounts are configured on remote
authentication servers as remote users. Remote users do not need local accounts.
Radius, TACACS+ and LDAP authentication services allow group configuration. If a remote user is
configured as a member of a remote group, the authentication server provides the group name to
the console server when it authenticates the user. A local group by the same name must also be
configured on the console server. If an authentication server authenticates a remote user but does
not return a group, then the remote user is, by default, assigned to the user group.
Page 61

Accessing the Console Server via the Web Manager.....55
admin group
Members of the admin group have full administrative privileges that cannot be changed, the same
access and configuration authorizations as the default admin user. Administrators can configure
ports, add users and manage power devices connected to the console server.
NOTE: The only configuration allowed for the admin group is adding or deleting members.
To view admin Appliance Access Rights:
1. Click Users - Authorization - Groups. The Group Names screen is displayed, showing the
three default user groups along with any groups that have been created.
2. Click on admin under the Group Name heading. The content area will display the Members
screen listing all members belonging to the admin group (default members are admin and root
users).
NOTE: When any Group Name is selected, both the content area and side navigation bar change. The side
navigation bar will display specific menu options for Members and Access Rights (which include Serial,
Power and Appliance rights).
3. In the side navigation bar, click Access Rights - Serial or Access Rights - Power to access the
screens displaying the fixed access rights and permissions for members of the admin group
pertaining to serial ports and power management.
NOTE: The Serial and Power screens are read-only and cannot be changed.
4. In the side navigation bar, click on Access Rights - Appliance. The Appliance Access Rights
screen appears and lists all access rights available to a member belonging to the admin
group. All appliance access rights are shown enabled (checked). Available appliance access
rights are:
• View Appliance Information
• Disconnect Sessions and Reboot Appliance
• Appliance Flash Upgrade and Reboot Appliance
• Configure Appliance Settings
• Configure User Accounts
• Backup/Restore Configuration
• Shell Access
• Transfer Files
Page 62

56.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
NOTE: The Appliance Access Rights screen for the admin and appliance-admin user groups is read-only
and cannot be changed. Unchecking any box and clicking Save will result in an error message. The console
server will maintain all rights selected.
appliance-admin group
Members of the appliance-admin group have access restricted to tasks for managing only the
appliance. Appliance-admin user group members have no access to the serial ports or power
management options, and share all of the appliance access rights as admin except for Configure
User Accounts and Shell Access, which are permanently disabled for this group.
user group
Members of the user group have access to target devices unless they are restricted by an
administrator but have no access rights for the console server. Administrators can add appliance
access rights and permissions and can add users to custom user groups to add permissions and
access rights as needed. By default, all selections on the Appliance Access Rights screen will be
disabled.
NOTE: The Appliance Access Rights screen for the user group can be changed at any time by an
administrator. This will change the access rights for all members of the console server’s user group.
shell-login-profile
Members of the shell-login-profile group have access to the shell after logging in. By default, the
root user belongs to this group. This is not a protected group and can be deleted.
Managing user groups
Administrators and members of the admin group can create custom user groups that contain any
users. Permissions and access for custom user groups will be determined by the top-level user
group permissions.
To create a custom user group:
1. Click Users - Authorization - Groups. The Groups screen is displayed and contains a list of the
three default user groups and any additional custom user groups that have been created.
2. Click Add in the content area.
3. Enter the name of the new user group you are creating.
4. Click Save.
To add members to a user group:
1. Click Users - Authorization - Groups.
Page 63

Accessing the Console Server via the Web Manager.....57
2. Click the user group name.
3. Click Add. The Members Assignment screen is displayed showing a list of available users in
the left box and an empty box on the right.
4. Move users from the Available Users box on the left to the box on the right by double-clicking
on the username, or by selecting the name and clicking the Add button. You can remove any
names from the box on the right by double-clicking on the name or by selecting the name and
clicking the Remove button.
5. If you want to add remote users to the new user group (these must be valid names in your
remote authentication server), add them in the New Remote Users field.
6. Click Save.
To remove members from a user group:
1. Click Users - Authorization - Groups.
2. Click the user group name.
3. Check the box(es) of the member(s) you want to remove. Click Delete to delete the selected
members.
To configure a session idle time-out and/or login profile for a group:
1. Click Users - Authorization - Groups.
2. Click on the name of the group whose session idle time-out and/or login profile you want to set.
In the side navigation bar, click Login Profile.
3. Select the radio button to use either the global settings for the Session Timeout or to use
custom settings for the user group. If using custom settings, enter the custom session timeout
(in seconds) in the field.
4. Check the Enable Log-In Profile box.
5. Click ts_menu to use the ts_menu application when a member of the selected user group
opens a session in the console server. Enter the ts-menu options in the Options field.
-or-
Click CLI to use CLI when opening a session. Enter the CLI command in the CLI cmd field and
check the box if you want to exit after executing the command.
6. Click Save.
NOTE: If the user belongs to multiple groups, the login profile used will be the first enabled login profile
based on alphabetical order of the group.
Page 64

58.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
ts_menu Options
Command Description
-p Displays TCP port
-i Displays local IPv4 assigned to the serial port
-i6 Displays local IPv6 assigned to the serial port
-u <name> Username to be used in the target session
-e <[^]char>
-l Sorted lists ports and exit
-ro Read-Only mode
<portname> Connect directly to a serial port
-t Idle time-out in seconds to choose the target
Escape character used to close the target session. Default value: Ctrl-X
To add access to serial ports for a user group:
1. Click Users - Authorization - Groups.
2. Click the new user group name.
3. In the side navigation bar, click Access Rights.
4. In the content area, click Add.
5. Move serial target devices from the Available Target box on the left to the box on the right by
double-clicking on the serial target name, or by selecting the target and clicking the Add
button. You can remove any targets from the box on the right by double-clicking on the target
or by selecting the target and clicking the Remove button.
6. Select the desired access rights.
7. Click Save. The Serial screen will appear and show the serial target devices you have
authorized for use by the user group with configured permission(s).
8. Edit the access rights by selecting the checkbox next to one or more of the target names in the
list as needed and click Edit. The Target Access Rights screen is displayed with the access
rights. Select the desired access rights and click Save.
To assign PDU access for a user group:
NOTE: Assigning PDU access to a user group gives them full access to all power management functions for
that PDU. If you want the user group to have access to outlets only, use the procedure To assign outlet
access for a new custom user group below.
1. Click on Users - Authorization - Groups.
2. Click on the user group name.
3. In the side navigation bar, click Access Rights - Power.
4. In the content area, click Add. The PDU Assignment screen appears with the list of available
PDUs in the left box.
Page 65

Accessing the Console Server via the Web Manager.....59
5. Move PDU devices from the Available PDU box on the left to the box on the right by doubleclicking on the PDU name, or by selecting the PDU and clicking the Add button. You can
remove any PDUs from the box on the right by double-clicking on the PDU name or by
selecting the PDU and clicking the Remove button.
6. You can specify a custom PDU ID in the field at bottom and assign it a custom PDU ID.
NOTE: The custom PDU ID is for assigning user group authorization to manage PDUs that have not yet
been connected to the console server.
7. Click Save.
To assign outlet access for a new custom user group:
NOTE: Assigning outlet access to user groups allows group members to turn outlets on or off, and enable
locking and power cycle capabilities on compatible PDUs.
1. Click Users - Authorization - Groups.
2. Click on the new user group name.
3. In the side navigation bar, click Access Rights - Power - Outlets.
4. Click Add. The Add Outlet screen is displayed.
5. For connected PDUs, click the Select PDU button to activate the Connected PDUs and
Outlets fields.
6. Select Connected PDU from the pull-down menu.
7. Enter the outlets assigned to the user group.
NOTE: Outlets can be specified individually, (for example 1,3,6,8) or as a range (for example 1-4) or a
combination of both, (for example 1-4,6,8 which assigns access to outlets 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 and 8).
8. If a custom PDU ID has been created for future use, and you want to pre-assign outlets, click
the Custom button to enter the custom PDU ID name and specify the outlets.
9. Click Save.
To assign appliance access rights for custom user groups:
1. Click Users - Authorization - Groups.
2. Click the new user group name.
3. In the side navigation bar, click Access Rights - Appliance.
4. Select the desired appliance access rights and click Save.
To configure a group in a TACACS+ authentication server:
Page 66

60.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
1. On the server, add raccess service to the user configuration.
2. Define which group(s) the user belongs to in the raccess service following this syntax:
group_name = <Group1>[,<Group2,...,GroupN>];
For example:
In the console server, configure a new authorization group TACACS_1 , and configure the access
rights for this group. In the TACACS+ server, configure the user regina with the following attribute:
raccess = group_name=TACACS_1;
Then, configure the user special with the following attribute: raccess = group_name=admin;
During the authentication phase, the console server will receive the attribute raccess from the
TACACS+ server. The user regina belongs to the authorization group TACACS_1 and the user
special belongs to the authorization group admin.
To configure a group in a RADIUS authentication server:
Define which group(s) the user belongs to in the attribute FRAMED_FILTER_ID with the following
syntax:
[:group_name=]<acs6000_group1>[,<acs6000_group2>];
NOTE: The group names should be separated by a comma and end with a semi-colon.
NOTE: The ACS 6000 console server accepts multiple FRAMED_FILTER_ID attributes.
For example:
In the console server, configure new authorization groups RADIUS_1 and RADIUS_2, and
configure the access rights for these groups. In the Radius server, configure the user regina with
the following attribute:
FramedFilterID = group_name=RADIUS_1,RADIUS_2;
-or-
FramedFilterID = RADIUS_1,RADIUS_2;
-or-
FramedFilterID = RADIUS_1;
FramedFilterID += RADIUS_2;
Then, configure the user special with the following attribute:
Page 67

Accessing the Console Server via the Web Manager.....61
FramedFilterID = group_name=admin;
During the authentication phase, the console server will receive the attribute FramedFilterID from
the RADIUS server. The user regina belongs to authorization group RADIUS_1 and RADIUS_2.
and the user special belongs to authorization group admin.
To configure group an LDAP authentication server:
On the LDAP server, edit the info attribute for the user and add the following syntax.
info: group_name=<Group1>[,<Group2>,...,<GroupN>];
DSView software access rights
An administrator can configure how the DSView software's viewer session rights will be mapped to
the console server's access rights when a user accesses a target via the DSView software's serial
viewer.
To configure the map of DSView software access rights to console server access rights:
1. Click Users – Authorization – DSView Access Rights.
2. Select the desired access rights and click Save.
Event Notifications
The console server will generate notifications for a variety of events. You can configure the console
server to direct or store those event notifications to various destinations for immediate use or for
analysis later.
Event List
The Event List screen lists console server events, each of which can be configured for SNMP
Traps, Syslog, DSView software, Email and SMS.
To configure Events:
1. Click Events and Logs - Events.
2. Locate the events for which you want notification sent and select the checkbox(es) next to the
event number(s).
3. Click Edit.
4. If you want an event notification sent for any configured event destination type, click its
associated Send checkbox.
5. Click Save. The Events page appears with an X in the column below the destination type if the
Send box was checked on the Events Settings screen.
Page 68

62.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
Event Destinations
The console server will generate notifications for a variety of events. You can configure the console
server to direct or store event notifications to various destinations for immediate use or for analysis
later.
To configure Event Destinations:
1. Click on Event and Logs - Event Destinations.
2. Under the Syslog heading, use the drop-down menu to select the Facility.
Select Remote Server - IPv4 to enable syslog messages to be sent to one or more remote
IPv4 syslog servers, and enter the IPv4 Address or Hostname and the UPDport for each
remote syslog server.
-or-
Select Remote Server - IPv6 to enable syslog messages to be sent to one or more remote
IPv6 syslog servers, and enter the IPv6 Address or Hostname and the UPDport for each
remote syslog server.
3. Select Appliance Console to send messages to the console server’s console.
4. Select Root Session to send syslog messages to all sessions where you are logged in as root
user.
5. Under the SNMP Trap heading, enter the name of the community defined in one or more of
the SNMP trap servers in the Community field then enter the IP addresses of up to five
servers in the server fields.
6. Under the SMS heading, enter the SMS Server, Port and Pager Number information in the
appropriate fields.
7. Under the Email heading, enter the Server, Port and Destination Email information in the
appropriate fields.
8. Under the DSView heading, enter the IP address of the DSView server where event
notifications will be sent in the DSView server field. Enter the syslog server port number for the
DSView server, the SSH information and the buffer warning information in the appropiate
fields.
9. Click Save.
Trap Forward
The console server will receive SNMP traps and forward them to a remote SNMP trap server.
To add a SNMP trap server to forward traps:
Page 69

Accessing the Console Server via the Web Manager.....63
1. Click Events and Logs – Trap Forward.
2. Click Add.
3. Enter the IP address of the remote server and the UDP port.
4. Enter the OID to filter traps to send to this server (optional).
To edit SNMP trap server configuration:
1. Click Events and Logs – Trap Forward.
2. Click the index of the server to be edited.
3. Update the UDP port and/or the OID and click Save.
Data Buffering
To configure Data Buffering:
1. Select Events and Logs - Data Buffering.
2. Enter the segment size in kilobytes and spare segments in the Local Data Buffering Settings
section.
3. In the NFS Data Buffering Settings section, enter the following information: NFS Server, NFS
Path, Segment Size (Kbytes) and Spare Segments.
NOTE: RPC service must be enabled in the Security Profile screen before configuring NFS Data Buffering
Settings. NFS does not support IPv6.
4. To segment data buffering files every day based in hour, enter the time in the Close Log Files
and Open New Ones at Time (HH:MM) field. This will be valid for local and NFS data buffering.
5. To configure data buffer storage on a syslog server in the Syslog Data Buffering Settings
section; select a facility number from the drop-down menu: Log Local 0, Log Local 1, Log
Local 2, Log Local 3, Log Local 4 or Log Local 5.
6. Click Save.
Appliance logging
To configure appliance logging:
1. Click Enable appliance session data logging.
a. Select the destination for appliance session data logs from the pull-down menu. Choices
are Local, NFS, Syslog and DSView.
b. Enable or disable timestamping the appliance session data logs.
2. Click Enable appliance session data logging alerts.
3. Enter the desired alert strings (up to ten) in the fields provided.
Page 70

64.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
4. Click Save.
Sensors
The console server has sensors that monitor the internal temperature. You can specify an
operating range for the console server that fits its environment.
CAUTION: Do not use values that exceed the maximum and minimum temperatures. Technical
Specifications on page 71.
To configure the temperature sensors:
1. Click Events and Logs - Sensors.
2. In the Maximum Temperature field, enter the temperature in degrees Celsius that, if
exceeded, will generate an event notification.
3. In the Maximum Temperature Threshold field, enter the temperature threshold in degrees
Celsius below the maximum temperature.
NOTE: The Maximum Temperature Threshold field will define a region around the maximum temperature.
When the temperature exceeds the Maximum Temperature plus Threshold, an event notification will be
generated. When the temperature falls below the Maximum Temperature minus Threshold, an even
notification that the console server has returned to normal operating temperature will be generated. This is
also true for setting the minimum temperature threshold.
4. In the Minimum Temperature field, enter the temperature in degrees Celsius that, if the
console server’s temperature falls below, will generate an event notification.
5. In the Minimum Temperature Threshold field, enter the temperature threshold in degrees
Celsius above the minimum temperature.
6. Click Save.
Power Management
Connected power devices can be used for remote power management. The console server
enables users who are authorized for power management to turn power on, turn power off and
reset devices that are plugged into a connected PDU.
The following types of power devices can be connected to any serial port or to the AUX/Modem port
(if an internal modem is not installed):
• Avocent Power Management Power Distribution Unit (PM PDU).
• Emerson Network Power MPH2 rack Power Distribution Units (PDUs) as well as MPX and
MPH rack PDUs with RPC2 cards installed.
Page 71

Accessing the Console Server via the Web Manager.....65
• Cyclades PM Intelligent Power Distribution Units (IPDUs) - With Cyclades PM IPDUs, up to
128 outlets can be daisy-chained and managed from a single serial port.
• Avocent SPC power control devices.
• Server Technology Sentry™ family of Switched Cabinet Power Distribution Units (CDUs),
Smart Cabinet Power Distribution Units (Smart CDUs) and switched CDU Expansion Module
(CW/CX) power devices. One additional level of power devices can be daisy-chained with
ServerTech Expansion modules.
• Server Technology Sentry Power Tower XL™ (PTXL) and Power Tower Expansion Module
(PTXM) power devices.
NOTE: The term PDU refers to any of these types of power devices.
The console server automatically recognizes and supports Liebert RPC2 cards, Avocent PM
PDUs, Cyclades PM PDUs or Avocent SPC devices when the corresponding serial port is
configured for power management.
PDUs
To manage a PDU:
1. Select Power Management - PDUs.
2. Select the checkbox next to the PDU you want to manage.
3. Click On, Off, Cycle, Reboot PDU, Reset HW Overcurrent Protection or Factory Defaults if
desired. A confirmation appears. Click OK.
NOTE: The power controls (On, Off and Cycle) will be applied to all outlets of the PDU.
4. To change the PDU ID, click Rename and enter the name in the New PDU ID field.
5. Click Save.
To upgrade firmware:
1. Select the checkbox next to the PDU you want to upgrade and click the Upgrade Firmware
button.
2. Fill all fields with correct information and click Download to download the firmware to the
console server.
3. When the download finishes, the Install PM Firmware screen appears. If the version
information is correct, click Upgrade Now to start the upgrade of the firmware in the PDU.
4. When the upgrade finishes, the Finish Upgrade screen appears with the result of the upgrade
action. Click Finish.
Page 72

66.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
NOTE: You can upgrade the firmware for multiple PDUs at the same time for Avocent PM PDUs only.
To view a PDU’s information and manage outlets:
1. Select Power Management - PDUs.
2. Click the name of the PDU you want to view or manage.
3. The Outlet Table with power controls window appears and the side navigation bar displays a
list of options.
4. To manage outlets of PDU:
a. Check the box(es) of the outlet number(s) you want to manage.
b. Click On, Off, Cycle, Lock or Unlock to perform that function for the selected outlet(s).
5. Click Information in the side navigation bar to view a PDU’s information.
6. Click Overview in the side navigation bar to view data monitoring information.
7. Click Current, Voltage, Power Consumption, Energy Consumption or Environment in the side
navigation bar to view a table with appropriate information. Click Reset Values to clear Max,
Min and Average values.
To configure a PDU:
1. Click Settings to expand the side navigation bar.
2. Click Outlets.
3. Click on an outlet number to change its settings. Click Save, then click Close.
-or-
Check two or more boxes next to the outlets for which you want to change settings. Click Edit
to change the settings for the outlets you selected. Click Save.
4. Click PDU to view and configure PDU settings. Click Save when finished.
5. Click Phases or Banks.
a. Click on the name of a phase or bank to change its settings, or click one or more boxes
next to the phase(s) or bank(s) you want to change.
b. Click Save to save the settings and click Close to return to the Phase screen.
NOTE: The PDU model defines available parameters in the Settings window.
Page 73

Accessing the Console Server via the Web Manager.....67
Login
An administrator can change the login password for a supported PDU type. This password is used
by the console server to communicate with the PDU. (Only one password is supported for all PDUs
of the same type.)
To change a PDU password:
1. Select Power Management - Login.
2. To change the password for an Avocent or Cyclades PDU, an Avocent SPC power control
device or a Server Tech PDU, enter the password in the appropriately labeled section.
3. Click Save.
Outlet Groups
By selecting the Outlet Groups tab, you can view status, outlet and power consumption for outlet
groups, as well as configure them. You can also turn on, turn off or cycle selected outlet groups.
To manage outlet groups:
1. Select Power Management - Outlet Groups.
2. Check the box next to the name of the Outlet Group you want to manage.
3. Click the On, Off or Cycle radio button, if desired.
-or-
4. Click Add to add an outlet group. The Add Group screen appears. Enter the name in the
Group Name field.
5. Click Save.
To view and change outlet group information:
1. Select Power Management - Outlet Groups.
2. Click the name of the outlet group you want to view or manage.
3. To add outlets, click Add to add a new outlet to the group. Fill the fields and click Save to return
to the Outlet Group Details table.
4. To delete outlets, check one or more boxes next to the outlet(s) you want to remove from the
group. Click Delete, then click Close when finished.
Page 74

68.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
Network PDUs
Power devices connected to the network with SNMP (read/write) enabled can be used for remote
power management. The console server enables authorized users to turn power on and turn power
off in devices that are plugged into the network PDU.
The following type of power devices are support via network connection:
• Avocent Power Management Power Distribution Unit (PM PDU).
• Emerson Network Power MPH2 rack Power Distribution Units (PDUs) as well as MPX and
MPH rack PDUs with RPC2 cards installed.
• Server Technology Sentry™ family of Switched Cabinet Power Distribution Units (CDUs) and
switched CDU Expansion Module (CW/CX) power devices.
NOTE: SNMP needs to be enabled and have one community with write permission enabled in the PDU.
By selecting the Network PDUs node, an administrator can add new Network PDUs or edit
configuration of current ones.
The following functionalities are supported for Network PDUs:Power Control (turn on, turn off and
cycle/reboot) outlets, rename the PDU and rename the outlets
To add a network PDU
1. Select Power Management – Network PDUs.
2. Click Add.
3. Enter the IP address of the network PDU.
4. Select the PDU type: Net-ServerTech or Net-MPH/MPX.
5. Enter the interval to poll the PDU for the status of the outlets.
6. Enter the community name that has write permission in the PDU.
NOTE: The support for network PDUs is restricted to power operations (turn on, turn off, cycle outlets),
rename PDU and rename outlets.
Active Sessions
The console server allows multiple users to log in and run sessions simultaneously. The Active
Sessions feature allows you to view all active sessions and kill any unwanted sessions. Click Active
Sessions to view all open sessions on the console server.
Page 75

Accessing the Console Server via the Web Manager.....69
NOTE: If you start another session with the console server while viewing this screen, it will not be visible
until you click Refresh at the top of the web manager window.
To kill an active session:
1. Click Active Sessions. The Active Sessions screen appears and lists all open sessions to the
console server by the user’s workstation IP.
2. Select the checkbox next to the session you want to kill, then click the Kill button. After a few
seconds, the Active Session screen will redisplay the open sessions, minus the one you killed.
Monitoring
When you click Monitoring, a variety of network and console port information is available for
viewing. The screens are only for viewing and have no interactivity with the user. The following table
shows the types of information available.
Monitoring Screens
Screen
Name
Network Devices
Network IPv4 Routing
Table
Network IPv6 Routing
Table
Serial Ports
Fips Mode Shows Service Name and Mode Indication.
Definition
Shows Ethernet ports and PC card Device Name, Status (enabled/disabled), IPv4 Address,
IPv4 Mask and IPv6 Address (not available on all models).
Shows Destination, Gateway, Genmask, Flags, Metric, Ref, Use and lface.
Shows Destination, NextHop, Flags, Metric, Ref, Use and lface.
Shows Device Name, Profile, Settings, Signals, TX Bytes, RX Bytes, Frame Error, Parity
Error, Break and Overrun. The Reset Counter button allows administrators to reset the statistic
counters for selected ports.
Change Password
An administrator or user can change their own password from this screen.
To change your own password:
1. Select Change Password.
2. Enter the old password and new password in the appropriate fields.
3. Confirm the new password, then click Save.
Page 76

70.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
Web Manager Overview for Regular Users
The following figure shows features of the web manager for a regular user.
Web Manager Regular User Screen
Web Manager Regular Users Screen Functional Areas
Number Descr iption
1
2 Side navigation bar. Menu options appear that are available for regular users.
3 Content area. Contents change based on the options selected in the side navigation bar.
Top option bar. The name of the appliance and the name of the logged in user appears on the left
side and Refresh, Print, Logout and Help buttons appear on the right.
Web Manager Options for Regular Users
Menu Option Descr iption
Access
Power
Management
PDUs Outlet
Groups
Change
Password
Displays all the devices the user can access. Click on
column to launch a terminal session with that device.
Click
PDUs
to turn on, turn off, cycle, reboot, reset the HW overcurrent protection, returnt to
factory defaults or rename PDUs connected to the console server. Click
manage groups of outlets on connected PDUs.
Change your own password.
Serial Viewer
in a device’s Action
Outlet Groups
to
Page 77

Appendices
Technical Specifications
Technical Specifications for the ACS 6000 Console Server Hardware
Category Value
General Information
CPU PPC440EPx @ 533 MHz (PowerPC with Security Acceleration Engine)
Memory 256 MB DDR-2 / 128 MB NAND Flash (embedded ICs on motherboard)
2 Ethernet 10/100/1000BT on RJ-45 1 RS232 Console on RJ-45 1 AUX RS232 on RJ-45 or
Interfaces
Power Information
Power
Supply
Power
Consumption
Ambient Atmospheric Condition Ratings
Operating
Temperature
Storage
Temperature
Humidity 20% to 80% relative humidity (non-condensing) across the operating temperature range
Dimensions
Height x
Width x
Depth
Weight 6-7 pounds (2.722- 3.175 kg) depending on the model
Certifications
internal MODEM V.92 on RJ-45 (RJ11 compatible) RS232 Serial Ports on RJ-45 1 USB 2.0
Host on Type A connector 2 PC Card / CardBus with ejector (dual Type II or single Type III)
Internal 100-240 VAC, 50/60 HzOptional Dual entry, redundant power supplies-48 VDC option
available
Nominal voltage 120 VAC: Typical 0.17 A, 20 W Maximum 0.25 A, 30 W
Nominal voltage 230 VAC: Typical 0.1 A, 23 W Maximum 0.15 A, 35 W
Nominal voltage -48 VDC (20% tolerance) Typical 0.5 A
32oF to 122oF (0oC to 50oC)
-4oF to 158oF (-20oC to 70oC)
1.715 x 17.250 x 9.50 in (4.3561 x 43.815 x 24.13 cm)
Emissions and Immunity: FCC Class A (USA), CE Class A (EU), ICES-003 (Canada), VCCI
(Japan), C-Tick (Australia, no internal modem), A-Tick (Australia), KCC (Korea) Safety: UL
60950-1 (USA), cUL (Canada), EN-60950-1 (EU), CB, GS, GOSTR (Russia)
Page 78

72.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
Recovering a Console Server's Password
To recover the console server's root password:
1. Connect directly to the console server’s CONSOLE port.
2. Turn the console server off, then on again.
3. Press the Spacebar to access the uboot prompt.
4. Type hw_boot single and press Enter.
5. The console server will boot into single-user mode. Type passwd and press Enter.
6. Enter the new password and confirm.
7. Type reboot and let the console server boot normally.
Page 79

Appendices.....73
Port Information for Communication with the DSView Software
The following ports on an ACS 6000 advanced console server can accept connections from the
DSView management software:
• TCP port 3502 (https)
• TCP port 3871 (adsap2)
• UDP port 3211 (aidp)
• TCP port 22 (sshd)
The following ports in the DSView software can accept connections from the ACS 6000 advanced
console server:
• TCP port 4122 (default: SSH server)
• TCP port 4514 (default: data logging or Syslog server)
Page 80

74.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
Accessing a Console Server with a DSView Software Installation via Dial-up
When a DSView software user establishes a serial session, the following events occur:
• The user selects a serial port to access.
• A viewer is downloaded from the DSView server to the user's workstation.
• The DSView software passes information to the viewer, such as an authorization key, the
console server's IP address and serial port.
• The viewer then accesses the console server's serial port through an SSH session by
passing the authorization key obtained from the DSView server.
• The serial session begins.
To ensure constant connectivity, a DSView server can be configured with an out of band (OOB)
“back door” that will allow it to call a console server via modem in the event of a network or Internet
failure.
Installing DSView software with an OOB back door
The DSView server must be running on hardware that has a connected modem, and the console
server must have a built-in modem or access to a modem via a PCMCIA card, USB or serial port.
For this installation, the DSView server must be the central point of reception of both the packets
leaving the downloaded viewer and the console server. To ensure this, Proxy mode must be
configured within the DSView software. The viewer will then point to the DSView server (not the
console server) to establish the SSH connection. The DSView server would then route the packets
by changing both the source and destination IP addresses and act as a middle point of
communication.
Under normal operating conditions, packets received from the Video Viewer would route through
the DSView server via Ethernet. In an error state, the DSView server would detect that the normal
path to the console server was interrupted and would dial out to the console server, pass
authentication and establish a PPP connection. Packets that would normally pass via Ethernet
would instead be routed via PPP.
Because of the speed differences between Ethernet and dial-up, performance would be notably
slower, but still present. Multiuser connections would further degrade performance and are not
recommended. For this reason, dial-up backup is recommended as an emergency backup feature
only.
Configuring dial-up for a console server
To configure dial-up to a console server within the DSView software:
Page 81

Appendices.....75
1. In a Units view window containing appliances, select the ACS 6000 console server you want to
configure. For dial-in with callback, you must first select DSView Server - Properties -
DSView Modem Sessions under the System tab and enter the the phone number assigned to
the DSView server in the Analog Phone Number field.
2. Select DSView Settings - Dial-up, and click Enable Dial-up.
3. Select Modem Type - Analog.
4. Enter the phone number for the console server you want to use.
5. Enter the PPP User and select the PPP Auth Protocol in the appropriate fields.
6. For dial-in with callback, enable the dial-back checkbox.
7. Select DSView Settings - Dial-up - PPP Password, then enter and confirm the password
needed to access the ACS 6000 console server.
8. Select DSView Settings - Dial-up - IP Addresses.
9. Click Generate Automatically to set the IP address automatically, or enter the PPP Local IP
address and Appliance IP address manually.
10. Select DSView Settings - Dial-up and click Save.
11. To configure a console server to receive the dial-up connection within the DSView software:
12. In a Units view window containing appliances, select the ACS 6000 console server you want to
configure.
13. For a modem attached to a serial port, select Ports - Serial Ports, then select the port that
contains the attached modem. Click Set Dial-In.
-or-
For a modem attached to an auxiliary port, select Ports - Auxiliary Ports, then select the port.
Click Set Dial-In.
-or-
For an internal modem, select Ports - Auxiliary Ports and select the modem.
-or-
For a pluggable device modem, select Pluggable Devices, select the modem and click Save.
14. Select DSView Settings - Dial-up and click Push Configuration.
NOTE: The following step is only required if CHAP was selected in the PPP Auth Protocol field in the
DSView software Settings Dial-up window.
Page 82

76.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
15. Log in to the console server’s CLI and access the Linux shell. Edit the /etc/ppp/chap-secrets
and add a line in the format, where the first column should have the PPP user and the third
column should have the PPP password as is shown in the following example:
pppuser * "ppppassword" *
Page 83

Appendices.....77
Internal Modem
Some models of the ACS 6000 console server come equipped with an internal modem. This
modem is used to originate and answer phone calls and establish communication with other
modems to transmit data.
Controlling the modem’s functions is done by using the “AT” commands. These commands are
used to instruct the modem to perform functions such as dialing or answering calls and are normally
automatically issued by communication software. However, for some applications, custom software
may have to be written due to the absence of a normal operating system.
The modem will automatically accept and process AT commands at most standard DTE (Data
Terminal Equipment) speeds and parity settings. For each command issued, the modem will
respond with a result code to inform you of the modem’s status. The format of a basic AT command
and result code is as follows:
AT<Command><CR>
OK
AT = Attention.
<Command> = any valid command
<CR> = Carriage Return or Enter key
OK = Result Code
Sample Command String
Command Description
ATDT7678900<CR>
ATS0=2<CR>
Instructs the modem to dial the number 7678900 and attempt to connect to the remote
device.
Enables auto answer option. When the modem detects a ring, it will attempt to answer
after two rings.
Basic AT Commands
Command Description
ATA/ Repeat the previous command.
ATA Answer.
ATB0 CCITT operation at 300 or 1200 bps.
ATB1 Bell operation at 300 or 1200 bps (default).
ATD Dial.
ATD0-9 Dial the DTMF digits 0 to 9.
Page 84

78.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
Command Description
ATDA-D Dial the DTMF digits A, B, C and D.
ATDP Select pulse dialing; effects current and subsequent dialing.
ATDT Select tone dialing; effects current and subsequent dialing.
ATD! Flash: go on-hook by time defined by S29.
Wait for dial tone detection before dialing a number. If no dial tone is detected within the time
ATDW
ATD@
ATD,
ATD; Return to the command mode after processing the command.
ATE0 Disables the command echo.
ATE1 Enables the command echo (default).
ATH0 Hang up.
ATH1 Forces the modem off-hook.
ATI0 Reports product code.
ATI2 Reports OK (for software compatibility).
ATI3 Reports the firmware version of the modem. Example: CX810801-V90.
ATL0 Sets the speaker volume off.
ATL1 Sets the speaker volume low (default).
ATL2 Sets the speaker volume medium.
ATL3 Sets the speaker volume high.
ATM0 Speaker is always off.
ATM1 Speaker is on during call establishment but goes off when carrier is detected (default).
ATM2 Speaker is always on.
ATM3 Speaker if off during dialing and when receiving carrier but on during answering.
ATQ0 Enables result codes to the DTE (default).
ATQ1 Disables result codes to the DTE.
ATSr Establishes S-register “r” as the default register.
ATSr=n Sets S-register “r” to the value “n.”
ATSr? Reports the value of S-register “r.”
ATV0 Enables short-form result codes.
ATV1 Enables long-form result codes.
ATW0
ATW1
ATW2
ATX0
ATX1
specified by S7, the modem aborts the rest of the sequence, goes on-hook and generates an error
message.
Wait for five seconds of silence before proceeding with next dialing string and then complete
handshake sequence.
Pause. The modem pauses for a time specified by S8 before dialing the number. Most often used
when dialing an outside line through a PBX.
Upon connection, the modem reports only the DTE speed (for example, CONNECT 9600).
Subsequent responses are disabled (default).
Upon connection, the modem reports the modulation type, line speed, the error correction protocol
and the DTE speed. Subsequent responses are disabled.
Upon connection, the modem reports DCE speed (for example, CONNECT 2400). Subsequent
responses are disabled.
Ignores dial and busy tone. Sends CONNECT message when a connection is established by blind
dialing.
Disables monitoring of busy tones. Sends only OK, CONNECT, RING, NO CARRIER and
ERROR messages. If busy tone detection is enforced and busy tone is detected, NO CARRIER
will be reported instead of BUSY. If dial tone detection is enforced or selected and dial tone is not
Page 85

Appendices.....79
Command Description
detected, NO CARRIER will be reported instead of NO DIALTONE.
Disables monitoring of busy tones. Sends only OK, CONNECT, RING, NO CARRIER, ERROR,
ATX2
NO DIALTONE and CONNECT XXXX. If busy tone detection is enforced and busy tone is
detected, NO CARRIER, will be reported instead of BUSY. If dial tone detection is enforced or
selected and dial tone is not detected, NO CARRIER will be reported instead of NO DIALTONE.
Enables monitoring of busy tones. Sends only OK, CONNECT, RING, NO CARRIER, ERROR,
ATX3
NO DIALTONE and CONNECT or CARRIER XXXX. If dial tone detection is enforced and dial
tone is not detected, NO CARRIER will be reported.
ATX4 Enables monitoring of busy tones. Sends all messages (default).
ATZ0 Soft reset.
AT&C0 DCD remains on at all times.
AT&C1 DCD follows the state of the carrier (default).
AT&D0 Ignores DTR.
AT&D1 Enters the escape mode when ON-to-OFF transition is detected on DTR.
AT&D2
AT&D3
Hangs up, assumes command state and disables auto answer upon detecting ON-to-OFF
transition of DTR (default).
ON-to-OFF transition causes the modem to perform a soft reset. It is the same as if an ATZ
command is issued.
AT&F Restores factory configuration.
AT&G0 Disables guard tone (default).
AT&G1 Enables 550-Hz guard tone.
AT&G2 Enables 1800-Hz guard tone.
AT&K0 Disables flow control.
AT&K3 Enables RTS/CTS flow control (default for data modes).
AT&K4 Enables XON/XOFF flow control.
AT&K5 Supports transparent XON/XOFF flow control.
AT&P0 39/61 make/break ratio at 10 pulses per second (default).
AT&P1 33/67 make/break ratio at 10 pulses per second.
AT&P2 39/61 make/break ratio at 20 pulses per second.
AT&P3 33/67 make/break ratio at 20 pulses per second.
AT&Q0 Selects direct asynchronous operation.
AT&Q5 Modem will try an error-corrected link.
AT&Q6
AT&V
Selects asynchronous operation in normal mode (allows speed buffering and flow control but no
error correction).
Displays modem’s current configuration. When this command is entered, the modem will display
its current command and register settings.
AT%C0 Disables data compression.
AT%C1 Enables MNP 5 data compression.
AT%C2 Enables V.42 bis data compression (sets S46 bit 1).
AT%C3 Enables V.42 bis and MNP 5 data compression (default).
AT%E0 Disables line quality monitor and auto-retrain.
AT%E1 Enables line quality monitor and auto-retrain.
AT%E2 Enables line quality monitor and fallback/fall-forward (default).
AT%L Line signal level. Returns a value that indicates the received signal level. Example, 009 = -9dBM.
Page 86

80.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
Command Description
Line signal quality. Reports line signal quality (DAA-dependent). Returns higher order byte of the
AT%Q
AT+MS Select/force modulation.
EQM value. Based on EQM value, retrain or fallback/fall-forward may be iniated if enabled with
AT%E1 or AT%E2 commands.
AT+MS modulation selection
This extended-format compound parameter controls the manner of operation of the modulation
capabilities in the modem. It accepts six sub-parameters:
+MS=<carrier>, <automode>, <min_tx_rate>, <max_tx_rate>, <min_rx_rate), <max_rx_
rate><CR>.
To read the current settings, enter AT+MS?<CR>
+MS Command Supported Rates
Modulation Carrier Description
Bell 103 B103 300
Bell 212 B212 1200
V.21 V21 300
V.22 V22 1200
V.22 bis V22 2400 or 1200
V.23 V23C 1200rx/75tx or 75rx/1200tx
V.32 V32 9600 or 4800
V.32 bis V32B 14400, 12000, 9600, 7200 or 4800
V.34 V34 33600, 31200, 28800, 26400, 19200, 16800, 14400, 12000, 9600, 7200, 4800 or 2400
V.90 V90
K56flex K56
V92
downstream
V92
upstream
V92
V92
56000, 54667, 53333, 52000, 50667, 49333, 48000, 46667, 45333, 42667, 41333,,
40000, 38667, 37333, 36000, 34667, 33333, 32000, 30667, 29333, 28000
56000, 54000, 52000, 50000, 48000, 46000, 44000, 42000, 40000, 38000, 36000,
34000, 32000
56000, 54667, 53333, 52000, 50667, 49333, 48000, 46667, 45333, 42667, 41333,,
40000, 38667, 37333, 36000, 34667, 33333, 32000, 30667, 29333, 28000
48000, 46667, 45333, 42667, 41333,, 40000, 38667, 37333, 36000, 34667, 33333,
32000, 30667, 29333, 28000, 26667, 25333, 24000
Page 87

.....81
Set telephone extension option
This command enables/disables “line-in-use” and “extension pickup” options.
Set Telephone Extension Options
-STE=n Value Extension Pickup Line-In-Use
0 (default) Disabled Disabled
1 Disabled Enabled
2 Enabled Disabled
3 Enabled Enabled
If the line is in use and the modem receives an ATDT command to dial out, the modem will not go
off hook and will display the “LINE-IN-USE” result code. If the modem is off hook and the extension
is picked up, the modem will drop the connection and display the “OFF-HOOK INTRUSION” result
code.
AT S registers
The S registers use the following format: ATSr=n<CR> where the “r” is the S register number and
“n” is the parameter to set it to. To read the current contents of an S register, issue an ATSr?<CR>
command where “r” is the register in question. The modem will then display the value of the S
register.
AT S Registers
Register Range Units Default Description
S0 0-255 Rings 0
S1 0-255 Rings 0 Number of rings counted.
S2 0-127 ASCII 43 Escape code character.
S3 0-127 ASCII 13 Command terminator<CR>.
S4 0-127 ASCII 10 Line feed character.
S5 0-127 ASCII 8 Backspace character.
S6 2-255 Seconds 2 Wait time for dial-tone detection.
S7 1-255 Seconds 50 Wait time for carrier.
S8 0-255 Seconds 2 Pause time for coma in dial string.
S10 1-255 .1sec 14 Loss of carrier to hang up delay.
S11 50-255 .01sec 85 DTMF tone duration.
S12 0-127 1/50 sec 50 Escape code guard time.
S24 0-255 1sec 0 Sleep mode inactivity timer.
S29 0-255 10mS 70 Hook flash dial modifier time.
S30 0-255 10Sec 0 Inactivity disconnect timer.
S95 0 Result code control.
Ring to answer on. ATS0=1<CR> means answer call on first ring
detected.
Page 88

82.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
Basic modem result codes
There are basic codes the modem will issue in response to processing an AT command. Result
codes may be displayed either in word (V1) or numeric (V0) format by using the Vn command. The
Qn command controls if result codes are issued (Q0) or not issued (Q1). The Xn, Wn commands
and register S95 determines which result code format the modem will display to indicate the type of
connection established. There are more than 300 codes. The most commonly used are listed in the
table below.
Basic Result Code Listing
Numeric Verbose Description
0 OK The modem has received and acknowledged the command.
1 CONNECT Connection made at 300bps or extended result codes are off (X0).
2 RING An incoming ring signal has been detected.
3 NO CARRIER
4 ERROR An invalid command was issued to the modem.
5
6 NO DIALTONE
7 BUSY The modem has detected a busy tone.
8 NO ANSWER After S7 time has elapsed, the remote server never answered.
10
12
15
16
17
18
CONNECT
1200
CONNECT
2400
CONNECT
9600
CONNECT
14400
CONNECT
19200
CONNECT
38400
CONNECT
57600
This result code reflects either an intended disconnect or a failure to complete a
connection.
Indicates a 1200bps line or DTE connection.
Line speed or DTE connection at 2400bps.
Line speed or DTE connection at 9600bps.
Line speed or DTE connection at 14400bps.
Line speed or DTE connection at 19200bps.
Line speed or DTE connection at 38400bps.
Line speed or DTE connection at 57600bps.
Digital line guard
The modem has an optional Digital Line Guard Circuit that automatically detects an over current
situation on the Tip and Ring pins. When the modem goes off hook, it will immediately check the
current on the Tip and Ring pins. If the current exceeds 150 mA, the modem will display the
“DIGITAL LINE DETECTED” result code and then go back on hook. The modem will continue to
display this result code until normal current is detected on the Tip and Ring pins during an off hook
condition. The DLG feature will protect the modem in case it is accidentally connected to a Digital
Telephone Line.
Page 89

.....83
Sleep mode operation
The modem can be set to enter the low power sleep mode by setting ATS24=n. In this case, “n” is
time, in seconds, that the modem will operate in normal mode with no detected telephone line or
DTE line activity before entering low power sleep mode. The timer is reset upon any DTE or
telephone line activity. If S24 is set to zero, the modem will never enter the low power sleep mode.
Disconnecting a call
There are several ways to disconnect a call. Below are the choices.
Resetting the modem’s power or toggling the Reset Line (Pin #12) will disconnect and put the
modem back into the OFF line state.
An ON to OFF transition of the DTR signal (Pin #4) will also disconnect the modem. If you use this
method, check to make sure that the DTR command is set to &D2 or &D3 and not forced (&D0).
The remote device can also cause the modem to disconnect. If the remote modem disconnects
your modem will automatically sense the loss of the carrier signal and return to the OFF line state.
The ATH or ATZ commands can also be used to disconnect a call. In order to issue a command to
the modem when it is On Line, the modem must be placed into the On Line Command State. This is
accomplished by issuing a special escape sequence. The default value of this three digit escape
sequence is the “+” character (see S2 to change). The “+++” is protected by a one-second delay
before and after it is sent (see S12 to change the time) When the modem detects the escape
sequence, the OK result Result code will be displayed and the modem is in the On Line Command
State. The ATH or ATZ command can now be issued to disconnect the call.
Selecting country codes
Setting the modem’s country code is done by with the +GCI command. To change to one of the 30
available countries, issue the AT+GCI=n command where “n” is one of the two digit country codes.
This command must be issued each the modem is turned on. It will not automatically store or save
this setting. It should be part of the Initialization string.
Example: AT+GCI=00<CR> Meaning: Change country code to Japan.
OK Meaning: The modem has accepted the command and is
now configured to operate in Japan
AT+GCI?<CR> Meaning: Display current country code
+GCI:00 Meaning: (Japan is the current country selected).
OK
Page 90

84.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
To view which countries are available in the modems firmware, enter AT+GCI=?<CR>.
The modem will display all of the possible two digit country codes available.
Country Codes List
Country Code Country Code Country Code
Australia 09 Hong Kong 50 Poland 8A
Austria 0A India 53 Portugal 8B
Belgium 0F Ireland 57 South Africa 9F
Brazil 16 Italy 59 Singapore 9C
China 26 Japan 00 Spain A0
Denmark 31 Korea 61 Sweden A5
Finland 3C Mexico 73 Switzerland A6
France 3D Netherlands 7B Taiwan Fe
Germany 42 Norway 82 TBR21 FD
United States B5 United Kingdom B4
Using caller ID
The modem can be used to display certain information about incoming telephone calls. The
modem can inform you of the date, time, telephone number and name associated with incoming
calls. When the CID option is enabled, information will be displayed between the first and second
incoming “RING.” In order for this feature to work properly, the telephone line connected to the
modem must subscribe to caller ID service offered by the local telephone company. A sample of the
displayed information is shown below:
RING
DATE = 0513
TIME = 1346
NMBR = 408 767 8900
NAME = RADICOM RESEARCH
RING
The CID information can either be presented formatted as shown previously or unformatted. The
+VCID and +VRID commands control the modem CID option.
Caller ID Information
Command Parameter Description
+VCID? NA Display current +VCID setting (0-2)
+VCID= 0 Disable caller ID reporting (default).
+VCID= 1 Enable caller ID with formatted presentation to the DTE.
Page 91

Command Parameter Description
+VCID+ 2 Enable caller ID with unformatted presentation to the DTE.
+VRID= 0 Displays the formatted caller ID of the last received call.
+VRID+ 1 Displays the unformatted caller ID of the last received call.
.....85
Page 92

86.....Avocent® ACS 6000 Advanced Console Server
Technical Support
Our Technical Support staff is ready to assist you with any installation or operational issues you
encounter with your Avocent product. If an issue should develop, follow the steps below for the
fastest possible service.
To resolve an issue:
1. Check the pertinent section of this manual to see if the issue can be resolved by following the
procedures outlined.
2. Visit www.avocent.com/support and use one of the following resources:
Search the knowledge base or use the online service request
-or-
Select Technical Support Contacts to find the Avocent Technical Support location nearest
you.
Page 93

About Emerson Network Power
Emerson Network Power, a business of Emerson (NYSE:EMR), delivers software, hardware and services that maximize
availability, capacity and efficiency for data centers, healthcare and industrial facilities. A trusted industry leader in smart
infrastructure technologies, Emerson Network Power provides innovative data center infrastructure management solutions
that bridgethe gap betweenIT and facility management and deliver efficiency and uncompromised availability regardless of
capacity demands. Our solutions are supported globally by localEmerson Network Power service technicians. Learn more
about Emerson Network Power products and services at www.EmersonNetworkPower.com.
590-767-501G
 Loading...
Loading...