Page 1
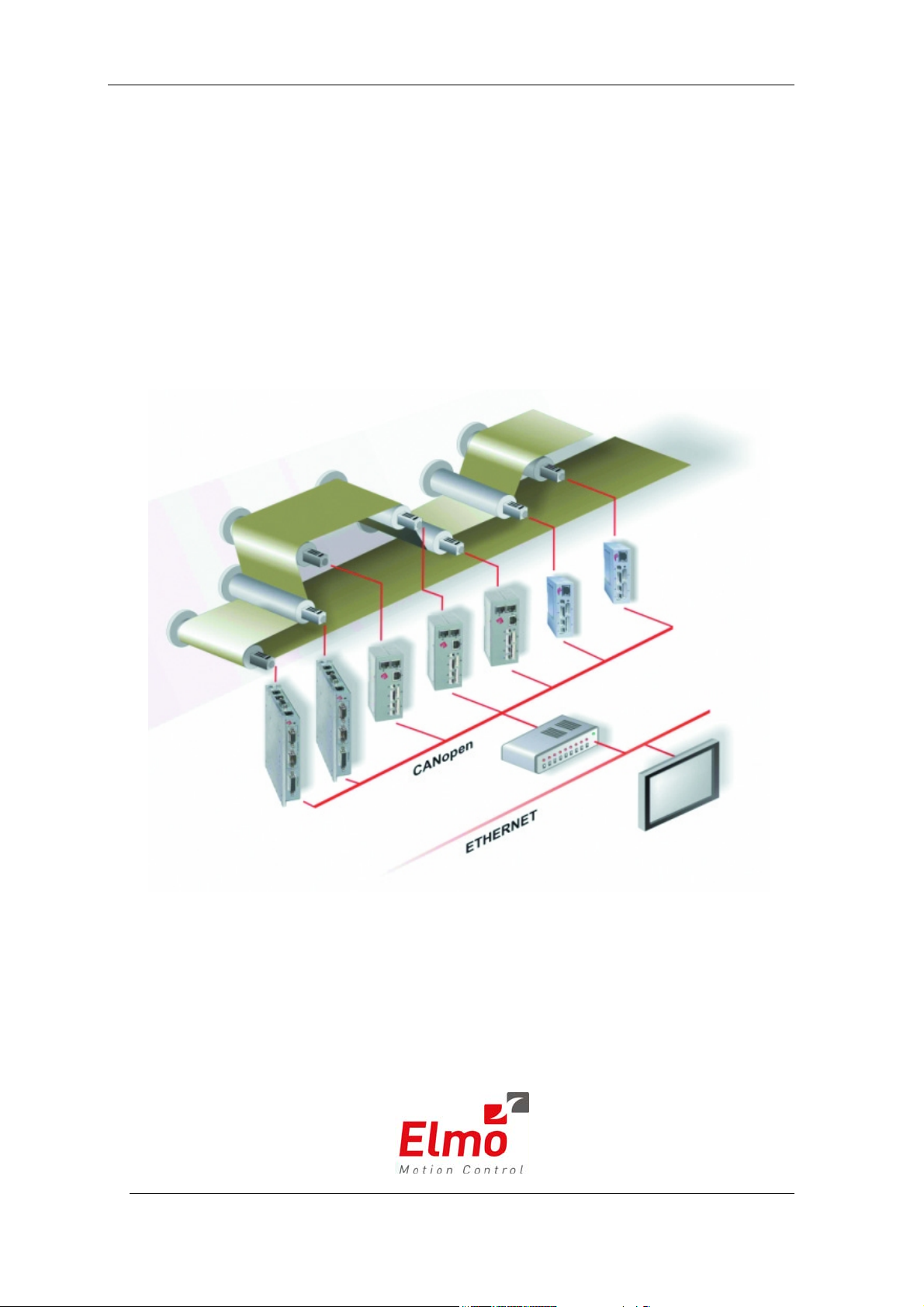
Elmo Motion Control
CANopen DSP 402
Implementation Guide
December 2004
Page 2

Important Notice
This guide is delivered subject to the following conditions and restrictions:
This guide contains proprietary information belonging to Elmo Motion Control Ltd.
Such information is supplied solely for the purpose of assisting users of
servo drives in implementing CANopen networking.
The text and graphics included in this manual are for the purpose of illustration and
reference only. The specifications on which they are based are subject to change
without notice.
Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Corporate and
individual names and data used in examples herein are fictitious unless otherwise
noted.
SimplIQ
Doc. No. MAN-
CAN402IG
Copyright © 2003, 2004
Elmo Motion Control Ltd.
All rights reserved.
Revision History
Ver. 1.2 Dec. 2004 References to Harmonica changed to SimplIQ (MAN-CAN402IG)
• New Profile Torque chapter
• Chapter on interpolation was modified
Ver. 1.1 Nov. 2003 mapping of the following objects modified: (MAN-CAN402IG)
0x6040,0x6060,0x607A,0x6081,0x6082,0x6083,0x6084,0x6089, 0x60C1,0x60C2
Ver. 1.0 Sept. 2003 Initial Release (HARCREN1102)
Elmo Motion Control Inc.
1 Park Drive, Suite 12
Westford, MA 01886
USA
Tel: +1 (978) 399-0034
Fax: +1 (978) 399-0035
Elmo Motion Control GmbH
Steinbeisstrasse 41
D-78056, Villingen-Schwenningen
Germany
Tel: +49 (07720) 8577-60
Fax: +49 (07720) 8577-70
www.elmomc.com
Page 3

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Contents
1: Introduction ............................................................................................................................ 1
1.1 Operating Principles......................................................................................................... 1
1.2 Abbreviations and Terms................................................................................................. 2
1.3 Elmo Documentation........................................................................................................ 3
2: The DSP 402 Object Dictionary ........................................................................................... 4
3: Emergencies ............................................................................................................................ 9
4: Predefinition........................................................................................................................... 9
Object 0x1000: Device type .............................................................................................. 9
Object 0x1001: Error register............................................................................................ 9
5: Common Entries....................................................................................................................12
5.1 Drive Error........................................................................................................................12
Object 0x6007: Abort connection option code.............................................................. 12
Object 0x603F: Error code .............................................................................................. 13
5.2 Motor Data........................................................................................................................13
Object 0x6402: Motor type.............................................................................................. 13
Object 0x6403: Motor catalog number .......................................................................... 14
Object 0x6404: Motor manufacturer.............................................................................. 15
Object 0x6406: Motor calibration data .......................................................................... 15
Object 0x6407: Motor service periods ........................................................................... 16
5.3 Drive Data.........................................................................................................................16
Object 0x6502: Supported drive modes ........................................................................ 17
Object 0x6504: Drive manufacturer............................................................................... 17
Object 0x6505: http drive catalog address.................................................................... 18
Object 0x60FD: Digital inputs........................................................................................ 18
6: Device Control.......................................................................................................................20
6.1 Objects...............................................................................................................................20
Object 0x6040: Controlword .......................................................................................... 26
Object 0x6041: Statusword............................................................................................. 28
6.2 Halt, Stop and Fault Objects...........................................................................................31
Object 0x605A: Quick stop option code........................................................................ 31
Object 0x605B: Shutdown option code ......................................................................... 32
Object 0x605C: Disable operation option code ............................................................ 33
Object 0x605D: Halt option code................................................................................... 34
Object 0x605E: Fault reaction option code ................................................................... 35
7: Modes of Operation..............................................................................................................36
7.1 Functional Description....................................................................................................36
7.2 Objects...............................................................................................................................36
Object 0x6060: Modes of operation ............................................................................... 36
Object 0x6061: Modes of operation display.................................................................. 37
Page 4

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
8: Factors .....................................................................................................................................38
8.1 Relationship between Physical and Internal Units.......................................................38
8.2 Functions and Limits.......................................................................................................38
8.3 Objects...............................................................................................................................39
Object 0x607E: Polarity................................................................................................... 39
Object 0x6089: Position notation index......................................................................... 40
Object 0x608A: Position dimension index.................................................................... 40
Object 0x608B: Velocity notation index ........................................................................ 41
Object 0x608C: Velocity dimension index.................................................................... 42
Object 0x608D: Acceleration notation index ................................................................ 42
Object 0x608E: Acceleration dimension index ............................................................. 43
Object 0x608F: Position encoder resolution ................................................................. 44
Object 0x6090: Velocity encoder resolution.................................................................. 45
Object 0x6093: Position factor........................................................................................ 46
Object 0x6094: Velocity encoder factor......................................................................... 47
Object 0x6095: Velocity factor 1..................................................................................... 48
Object 0x6096: Velocity factor 2..................................................................................... 49
Object 0x6097: Acceleration factor ................................................................................ 51
ii
9: Homing ...................................................................................................................................53
9.1 General Information ........................................................................................................53
9.2 Objects...............................................................................................................................55
Object 0x607C: Home offset........................................................................................... 55
Object 0x6098: Homing method .................................................................................... 56
Object 0x6099: Homing speeds...................................................................................... 57
Object 0x609A: Homing acceleration............................................................................ 58
9.3 Functional Description....................................................................................................58
9.4 DSP 402 Homing Methods..............................................................................................60
9.4.1 Method 1: Homing on the negative limit switch and index pulse.................60
9.4.2 Method 2: Homing on the positive limit switch and index pulse..................60
9.4.3 Methods 3 and 4: Homing on the positive home switch and index pulse ....61
9.4.4 Methods 5 and 6: Homing on the negative home switch and index pulse ...61
9.4.5 Methods 7 to 14: Homing on the home switch and index pulse....................62
9.4.6 Methods 15 and 16: Reserved ............................................................................63
9.4.7 Methods 17 to 30: Homing without an index pulse ........................................63
9.4.8 Methods 31 and 32: Reserved ............................................................................63
9.4.9 Methods 33 and 34: Homing on the index pulse .............................................63
9.4.10 Method 35: Homing on the current position....................................................63
10: Position Control Function..................................................................................................64
10.1 General Information ........................................................................................................64
10.2 Objects...............................................................................................................................65
Object 0x6062: Position demand value ......................................................................... 65
Object 0x6063: Position actual value............................................................................. 65
Object 0x6064: Position actual value............................................................................. 66
Object 0x6065: Following error window....................................................................... 66
Object 0x6066: Following error time out ...................................................................... 67
Object 0x6067: Position window.................................................................................... 68
Object 0x6068: Position window time........................................................................... 68
Object 0x60FC: Position demand value - increments.................................................. 69
Page 5

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
11: Profiled Position..................................................................................................................70
11.1 General Information ........................................................................................................70
11.2 Objects...............................................................................................................................72
Object 0x607A: Target position...................................................................................... 72
Object 0x607B: Position range limit............................................................................... 72
Object 0x607D: Software position limit ........................................................................ 74
Object 0x607F: Max profile velocity.............................................................................. 75
Object 0x6081: Profile velocity....................................................................................... 76
Object 0x6082: End velocity (not yet implemented).................................................... 76
Object 0x6083: Profile acceleration................................................................................ 77
Object 0x6084: Profile deceleration ............................................................................... 77
Object 0x6085: Quick stop deceleration........................................................................ 78
Object 0x6086: Motion profile type ............................................................................... 78
11.3 Functional Description ....................................................................................................79
12: Interpolated Position ..........................................................................................................81
12.1 General Information ........................................................................................................81
12.2 Objects...............................................................................................................................84
Object 0x60C0: Interpolation sub mode select ............................................................. 84
Object 0x60C1: Interpolation data record..................................................................... 85
Object 0x60C2: Interpolation time period .................................................................... 86
Object 0x60C3: Interpolation sync definition............................................................... 87
Object 0x60C4: Interpolation data configuration......................................................... 88
12.3 Functional Description ....................................................................................................91
12.3.1 Linear Interpolation............................................................................................92
12.3.2 Spline Interpolation ............................................................................................92
12.3.3 Motion Synchronization.....................................................................................93
iii
13: Profiled Velocity..................................................................................................................94
13.1 General Information ........................................................................................................94
13.2 Objects...............................................................................................................................96
Object 0x6069: Velocity sensor actual value................................................................. 96
Object 0x606A: Sensor selection code ........................................................................... 96
Object 0x606B: Velocity demand value......................................................................... 97
Object 0x606C: Velocity actual value............................................................................ 98
Object 0x606D: Velocity window .................................................................................. 98
Object 0x606E: Velocity window time .......................................................................... 99
Object 0x606F: Velocity threshold................................................................................. 99
Object 0x6070: Velocity threshold time....................................................................... 100
Object 0x60FF: Target velocity..................................................................................... 100
Page 6

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
14: Profiled Torque Mode......................................................................................................101
14.1 General Information ......................................................................................................101
14.1.1 Internal states ....................................................................................................102
Controlword of profile torque mode .......................................................................... 102
14.2 Objects dictionary entries..............................................................................................103
14.2.1 Objects defined in other chapters....................................................................103
14.2.2 Objects description............................................................................................103
Object 0x6071: Target torque ....................................................................................... 103
Object 0x6072: Max torque........................................................................................... 104
Object 0x6073: Max Current......................................................................................... 104
Object 0x6074: Torque Demand value ........................................................................ 105
Object 0x6075: Motor Rate Current............................................................................. 106
Object 0x6076: Motor Rate Torque .............................................................................. 106
Object 0x6077: Torque Actual value............................................................................ 107
Object 0x6078: Current Actual value .......................................................................... 107
Object 0x6087: Torque slope ........................................................................................ 108
Object 0x6088: Torque profile type ............................................................................. 108
iv
Appendix A: Dimension Index Table .................................................................................109
Appendix B: Notation Index Table......................................................................................110
Page 7

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
1
1: Introduction
This document describes the objects and operational modes of the Elmo DSP-based
motion controller implementation of the CiA DSP 402 protocol. The Elmo Harmonica
digital servo drive (part of the
example in this document.
Generally, the DSP 402 protocol refers only to the load behavior relating to the operation
of speed, position, limits and emergencies. It does not deal with control parameters such
as PI/P, scheduling and feed forward. The motor can be tuned and the plant parameters
set with the Elmo Composer, which may or may not use this protocol for settings. The
protocol offers methods in which a profiled reference can be given to the final load.
The DSP 402 implementation is applicable to Elmo position unit modes; that is
UM=4 or UM=5. This is assumed by the Elmo drive itself and it gives no other
indication.
SimplIQ family of digital servo drives ) is used as the main
The Elmo controller provides a number of different options for setting commands and
parameters, such as via the binary interpreter, OS interpreter, RS-232 interpreter and user
programs. When the user works with DSP 402, all relevant motion commands must be
given through this method only. Other command sources may prevent it from operating
properly according to the protocol.
Subsequently modifying controller states, modes and reference parameters using other
methods may lead to undefined states. For example, in a fault state, a FAULT_RESET
from the controlword must be given before enabling the motor again. But sending MO=1
through the OS interpreter may activate the motor and leave the status word of the
DSP 402 with an undefined status.
Other command sources are still useful for purposes not covered by the DSP 402
protocol. Examples include:
Monitoring the states of and inputs to the
Using the Composer to monitor
SimplIQ digital servo drive behavior through the RS-
SimplIQ digital servo drive.
232 port while the digital servo drive is under control of the CAN DSP 402 protocol.
Using the user program (or any of the interpreters) to program issues outside the
range of DSP 402 usage. For example, when the DSP 402 digital output command is
not used, the digital outputs can be operated freely by a user program.
1.1 Operating Principles
The CiA DSP 402 CANopen Device Profile for Drives and Motion Control is used to provide
drives in a CAN network with an understandable and consistent behavior. The profile is
built on top of a CAN communication profile, called CANopen, which describes the basic
communication mechanisms common to all devices in the CAN network.
Page 8

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
The purpose of the drive units is to connect axle controllers or other motion control
products to the CAN bus. They usually receive configuration information via service data
objects for I/O configurations, limit parameters for scaling, or application-specific
parameters. At run time, data ban be obtained from the drive unit via the CAN bus either
by polling or in event-driven mode (with properly-mapped TPDOs).
The motion control products use process-data object mapping for real-time operation,
which may be configured using service data objects (SDOs). This communication channel
is used to interchange real-time data-like set-points or actual values such as position
actual values.
The most important part of a device profile is the object dictionary description. The
object dictionary is essentially a grouping of objects accessible via the network in an
ordered pre-defined fashion. The DSP 402 standard objects of single-axis drives, like the
Harmonica, are all in the index range of 0x6000 to 0x67ff.
1.2 Abbreviations and Terms
2
The following terms are used in this document:
abs/rel Absolute and relative, which are indications of how to treat
the position reference command in relation to the actual
location.
Elmo Composer An Elmo software application used for controller setup,
application downloading and monitoring.
Hexadecimal Numbers marked with either “h” (such as 1000h) or “0x”
(such as 0x1000) refer to a hexadecimal value. Objects and
numbers may appear in either form in different CAN
documents.
hm Homing mode
ip Interpolated position mode
Load position What the position sensor measures, expressed in position
units (in contrast to position sensor increments).
Non-volatile The object data may be saved to the flash memory of a
device using the SV command, or by setting object 0x1010
(sub1).
Position sensor increments Units measured by the load position sensor. The speed is
derived from the position sensor.
pp Profiled position mode
tq Profiled torque mode
pv Profiled velocity mode
Reference Motion parameters can be specified in terms of
meters/second for speed, or encoder counts for position.
rfg The reference generator, which generates the trajectory for
velocity mode only.
Page 9
l
CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
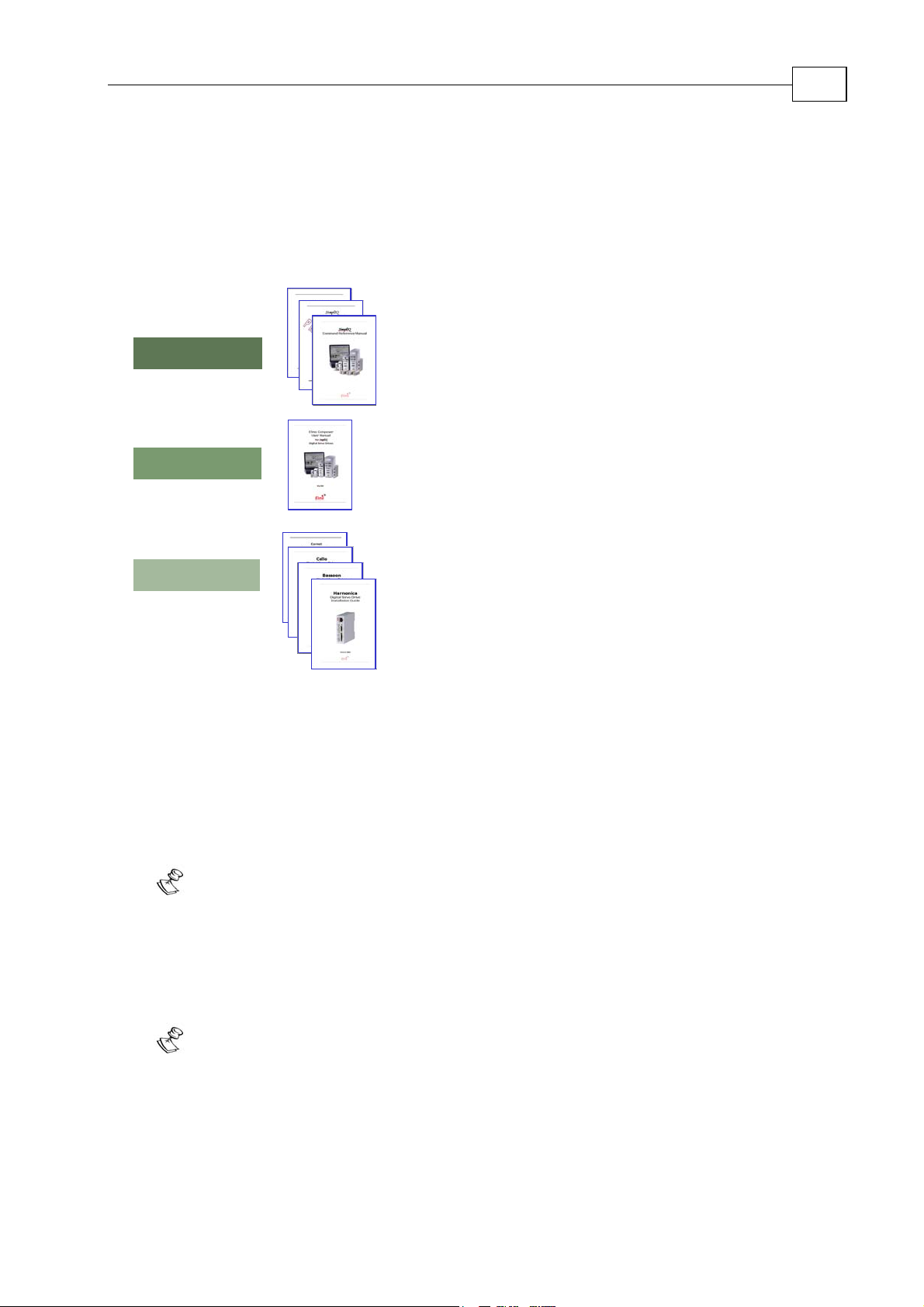
1.3 Elmo Documentation
This manual – included in the Elmo CANopen Implementation Guide – is part of the Elmo
SimplIQ digital servo drive documentation set, as outlined in the following diagram:
CANopen Implementation Guide
SimplIQ
SimplIQ
Programming
Composer User Manual
Setup
Software Manual
Command Reference Manua
3
SimplIQ Servo Drive
Installation
In addition to this document, the
The Harmonica, Cello and Bassoon Installation Guides, which provides full
instructions for installing a drive
The Composer User Manual, which includes explanations of all the software tools that
are a part of Elmo’s Composer software environment
The
The
The CANopen Implementation Guide, which explains how to implement CANopen DS
SimplIQ Software Manual, which describes the comprehensive software used with
the
SimplIQ line of line of line of digital servo drives
This is the main source of detailed explanations of all SimplIQ commands
mentioned in this manual.
SimplIQ Software Manual, which describes the comprehensive software used with
the
SimplIQ digital servo drive.
301-based communication with a
Installation Guides
SimplIQ documentation set includes:
SimplIQ digital servo drive.
SimplIQ drives are fully compliant with CiA’s DSP305 protocol for Layer Setting
Service (LSS).
Page 10
CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
4
2: The DSP 402 Object Dictionary
This section describes the objects related to the DSP 402 device specific functionality. For
more information about the object dictionary, refer to the Elmo
Implementation Guide.
Name Index Description Access Mappable?
SimplIQ CANopen DS 301
Abort
connection
0x6007 Function to perform on heartbeat
event. (Link)
R/W N
option code
Error code 0x603F Captures the last error R N
Controlword 0x6040 Allows changing of drive states. R/W Y
Statusword 0x6041 Indicates current drive status. R Y
Quick stop
0x605A Sets the quick stop option code. R/W N
option code
Shut down
0x605B Sets the shut down option code. R/W N
option code
Disable
0x605C Sets the disable operation option code. R/W N
operation option
code
Halt option code 0x605D Sets the Halt option code. R/W N
Fault reaction
0x605E Sets drive reaction when fault occurs. R/W N
option code
Modes of
0x6060 Sets mode of operation R/W Y
operation
Modes of
operation
display
Position
demand value
Actual position
internal unit
Position actual
value
Position
following error
window
Position
following error
window time
Position
window
0x6061 Displays actual mode of operation. R N
0x6062 Output of profiler. Position
R Y
command.
0x6063 Actual position taken from position
R Y
sensor, in increments.
0x6064 Actual position as taken from
R Y
position sensor, in user units.
0x6065 Defines a range of tolerated position
R/W N
values symmetrical to the position
demand value.
0x6066 Defines the timeout for the next error
R/W N
window to set the following error
indication.
0x6067 Defines a symmetrical position
R/W N
window for the target position for
target reached indication.
Page 11

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
5
Name Index Description Access Mappable?
Position
window time
Velocity sensor
actual value
Velocity sensor
selection code
Velocity
demand value
Velocity actual
sensor
Velocity
window
Velocity
window time
Velocity
threshold
Velocity
threshold time
0x6068 Defines the time in which the position
R/W N
within the position window indicates
target reached.
0x6069 Actual velocity as calculated from the
R Y
main velocity sensor, in increments.
0x606A Selects the velocity sensor reading
R/W N
from either the position or the
velocity sensor.
0x606B Demand value for velocity controller. R Y
0x606C Actual velocity from either position
R Y
or velocity sensor.
0x606D Monitors whether required target
R/W N
velocity was achieved.
0x606E Defines the time in which a target
R/W N
velocity is considered as reached.
0x606F Defines the value in which the
R/W N
velocity is considered to be 0.
0x6070 Defines (with object 0x607F) the time
R/W N
in which the velocity is considered to
be 0.
Target torque 0x6071 The input value for the torque
controller in profile torque mode.
Max torque
0x6072
The maximum permissible torque in
the motor.
Max current 0x6073 The maximum permissible torque
creating current in the motor.
Torque demand
value
Motor rated
current
Motor rated
torque
Torque actual
value
Current actual
value
Profiled target
position
0x6074 The maximum permissible torque
creating current in the motor.
0x6075 This value is taken from the motor
nameplate.
0x6076 This value is taken from the motor
name plate.
0x6077 The instantaneous torque in the drive
motor.
0x6078 The instantaneous current in the
drive motor.
0x607A Defines target position for absolute or
relative point-to-point motion.
R/W Y
R/W
N
R/W N
R N
R/W N
R/W N
R Y
R Y
R/W Y
Position range
limit
0x607B Sets the limits in which the position
numerical values are available.
R/W N
Page 12
CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
6
Name Index Description Access Mappable?
Homing offset 0x607C Defines offset from homing zero
position to application zero position.
Software
position limit
0x607D Defines limits for demand position
value and actual position value.
Polarity 0x607E Sets polarity for position or speed
command and actual value.
Max profile
velocity
0x607F Defines limit to which a profile
velocity speed is saturated.
Profile velocity 0x6081 Sets the speed for the profile position
motion.
Profile
acceleration
0x6083 Defines the acceleration for the
profile velocity and profile position
motion.
Profile
deceleration
0x6084 Defines deceleration for profile
velocity and profile position motion.
Quick stop
deceleration
0x6085 Sets the deceleration for a quick stop
state.
R/W N
R/W N
R/W Y
R/W N
R/W Y
R/W Y
R/W N
R/W N
Motion profile
type
0x6086 Defines method by which profile
motion is evaluated (linear or jerk)
R/W N
Torque slope 0x6087 the rate of change of torque R/W Y
Torque profile
type
0x6088 Used to select the type of torque
profile used to perform a torque
R/W N
change.
Position
0x6089 Used to scale position objects. R/W N
notation index
Position
dimension index
Velocity
notation index
Velocity
dimension index
Acceleration
notation index
0x608A This object defines the position
dimension index.
0x608B This is defined by the physical
dimensions and calculated by unit type.
0x608C This is used together with the velocity
notation index to define a unit.
0x608D The unit is defined by the physical
dimensions and calculated by unit
R/W N
R/W N
R/W N
R/W N
type and exponent
Acceleration
dimension index
0x608E This defines the acceleration
dimension index, which is used
R/W N
together with the acceleration
notation index (object 0x608D) to
define a unit
Page 13
CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
7
Name Index Description Access Mappable?
Position encoder
resolution
Velocity
encoder
0x608F Defines relation between motor
revolution and position increments.
0x6090 Defines ratio of encoder increments/
sec per motor revolutions/sec.
R/W N
R/W N
resolution
Position factor 0x6093 Converts position in user units to
R/W N
position in internal increments
Velocity
Encoder factor
Velocity factor 1 0x6095 Converts motor data into velocity
0x6094 Converts desired velocity in velocity
units into internal increments/sec.
R/W N
R/W N
data.
Velocity factor 2 0x6096 Converts encoder data for position
R/W N
into encoder data for velocity.
Acceleration
factor
Homing method 0x6098 Defines method by which homing
0x6097 Converts the acceleration from user
units to internal increments/sec.
R/W N
R/W N
procedure is performed.
Homing speed 0x6099 Sets speed for homing procedure. R/W N
Homing
acceleration
Interpolated
position sub
0x609A Sets acceleration for homing
sequence.
0x60C0 Sets sub-mode for interpolated
position algorithm.
mode
Interpolated
data record
Interpolated
position time
0x60C1 Sets data for interpolation position
trajectory.
0x60C2 Defines time for interpolation
position trajectory.
period
Interpolation
data
0x60C4 Defines method to store position data
record.
configuration
Position
demand value
0x60FC Reads position command in
increments as given to position
controller
Digital input 0x60FD Reads digital input according to DSP
402, and also reflects Elmo digital
input logical state.
R/W N
R/W N
R/W Y
R/W Y
R/W Y: buffer
position
N: all the
other
entries.
R Y
R Y
Target velocity 0x60FF Sets velocity reference for velocity
profiler.
R/W Y
Page 14

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
8
Name Index Description Access Mappable?
Motor type 0x6402 R/W N
Motor catalog
0x6403 32 characters. R/W N
number
Motor
0x6404 32 characters. R/W N
manufacturer
http motor
0x6405 R/W N
catalog address
Motor
0x6406 R/W N
calibration date
Motor service
0x6407 R/W N
period
Driver modes 0x6502 R/W N
Drive
0x6504 R N
manufacturer
Drive manu-
0x6505 R N
facturer web site
Page 15
CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
3: Emergencies
Emergency messages are detailed in the SimplIQ CANopen Implementation Guide.
4: Predefinition
Object 0x1000: Device type
The object at index 1000h describes the device type and functionality.
The SimplIQ returns 0x20192 for servo drive supporting DSP 402.
Object 0x1001: Error register
All bits are defined as in the
The device-specific bit in the error register is used by the DSP 402 protocol. The error code
can be read from the predefined error field at object 1003h and is compatible with device
profiles for drives available for other field bus systems from object 0x603F as well.
SimplIQ CANopen Implementation Manual and CiA DS-301.
9
The error register captures the latest emergency messages. SimplIQ servo drives
allow the user to block the transmission of an emergency according to object
0x2F20. Nevertheless, a blocked emergency message is captured in the relevant
entry of the error register.
PDO Mapping
The Elmo drive supports more than one operating mode of DSP 402. It also allows more
than one method to set and query commands. In addition, the use of more than one
standard PDO is predefined. With the Harmonica, four TPDOs and four RPDOs are free
for any mapping according to the Elmo object dictionary. At reset (power up, NMT
communication reset and NMT node reset), a default mapping is introduced according to
DSP 402. These default mapping can be later changed by the user.
Receive PDO 1 mapped to the controlword in the following manner:
Index Sub-index Name Default Value
1400h 0 Number of entries 2
1 COB-ID used by PDO 4000027Fh
2 Transmission type 255
Index Sub-index Name Default Value
1600h 0 Number of mapped entries 1
1 Controlword 6040 00 10h
Page 16
CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Transmit PDO 1 monitors the drive behavior by transmitting the statusword whenever it
changes (typically after reception of a controlword):
Index Sub-index Name Default Value
1800h 0 Number of entries 3
1 COB-ID used by PDO 400001FFh
2 Transmission type 255
3 Inhibit Time 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Event timer 0
Index Sub-index Name Default Value
10
1A00h 1 Number of entries 1
Statusword 6041 00 10h
Index Sub-index Name Default Value
2F20h 1 TPDO1 asynchronous
events
The asynchronous transmission of TPDO1 reflects changes performed
3 milliseconds prior to the transmission.
Receive PDO 2 is mapped to the binary interpreter by default. This is done for
compatibility reasons and to enable communication with the Elmo Composer.
Index Sub-index Name Default Value
1401h 0 Number of entries 2
1 COB-ID used by PDO 4000037Fh
0
2 Transmission type 254
Index Sub-index Name Default Value
1601h 0 Number of entries 1
1 Binary interpreter
command
2013 00 40h
Page 17
CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Transmit PDO 2 is mapped to the binary interpreter result object, transmitted each time
the binary interpreter completes its processing. The event behavior is set by object
0x2F20, defined in the
SimplIQ CANopen Implementation Manual.
Index Sub-index Name Default Value
1801h 0 Number of entries 3
1 COB-ID used by PDO 400002FFh
2 Transmission type 254
3 Inhibit time 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Event timer 0
11
Index Sub-index Name Default Value
1A01h 1 Number of entries 1
2 Binary interpreter result 2014 00 40h
Index Sub Name Default Value
2F20h 2 TPDO2 events 0x8000000
Page 18
CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
5: Common Entries
5.1 Drive Error
The drive functionality in case of an error is determined using the following objects:
6007h: defined according to the
603Fh: reflects the 16 lower bits of object 0x1003, which, together with this object, get the
emergency value regardless of the emergency message mask in object 2F21h.
Object 0x6007: Abort connection option code
This object details the motor control behavior after a heartbeat failure. It has no effect if
the motor is already off.
Object description:
Index 6007h
SimplIQ CANopen Implementation Manual.
12
Name Abort connection option code
Object code VAR
Data type INTEGER16
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read/Write
PDO mapping No
Value range -32,768…32,767
Default value 0
Data description:
(Command details are found in SimplIQ Command Reference Manual.)
Option
Code Meaning
0 No action
1 Malfunction Motor is off (MO=0) and motor failure code is
Details
0x800. The failure is reported and possibly
activates an AUTOERR routine similar to
other failures (MF command).
2 Device control
command
“Disable_voltage”
3 Device control
command “Quick_stop”
Motor is off (MO=0), but no failure indication
is set (MF=0).
ST command is executed. Its action depends
on unit mode (UM).
Page 19

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Object 0x603F: Error code
This object captures the code of the last error that occurred in the drive. It corresponds to
the value of the lower 16 bits of object 1003h, pre-defined error field.
Object description:
Index 603Fh
Name Error code
Object code VAR
Data type UNSIGNED16
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read only
PDO mapping No
13
Value range UNSIGNED16
Default value 0
5.2 Motor Data
Objects 6402h to 64FFh serve as a database for motor parameters. The values are typically
found on the motor nameplate or the manufacturer’s motor catalog and are used to
maintain a service database within the controlling device of the drive. Most of the entries
are typically entities from the manufacturer’s motor catalog. The Elmo DSP 402
implementation supports the following objects:
6402h: Motor type
6403h: Motor catalog number
6404h: Motor manufacturer
6405h: Http motor catalog address
6406h: Motor calibration date
6407h: Motor service period
Object 0x6402: Motor type
This object defines the type of motor driven by the controller. The values of this object are
represented in the following table:
Object values:
Value Motor Type
0 Non-standard motor
1 DC motor
9 Micro-step stepper motor
10 Sinusoidal PM brushless motor
11 Trapezoidal PM brushless motor
Page 20

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
This object contains information for the user only and does not convey the value of
the CA[28] command at the calibration procedure of a drive.
Object description:
Index 6402h
Name Motor type
Object code VAR
Data type UNSIGNED16
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read/Write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED16
14
Default value
Object 0x6403: Motor catalog number
This object describes the manufacturer’s motor catalog number (nameplate number). The
maximum length of this object is 32 characters.
Object description:
Index 6403h
Name Motor catalog number
Object code VAR
Data type VISIBLE_STRING
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read/Write
PDO mapping No
Value range
Default value
Page 21

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Object 0x6404: Motor manufacturer
This object gives the motor manufacturer’s name. The maximum length of this object is
32 characters.
Object description:
Index 6404h
Name Motor manufacturer
Object code VAR
Data type VISIBLE_STRING
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read/Write
PDO mapping No
Value range
15
Default value
Objects of data type VISIBLE_STRING have 32 characters.
Object 0x6406: Motor calibration d
ata
Date of the motor last inspection.
Object description:
Index 6406h
Name Motor calibration date
Object code VAR
Data type TIME_OF_DAY
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read/Write
PDO mapping No
Value range No
Default value No
Page 22
CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Object 0x6407: Motor service periods
Value, in hours, of the nominal motor lifetime. The motor needs servicing after this time.
Object description:
Index 6407h
Name Motor service period
Object code VAR
Data type UNSIGNED32
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read/Write
PDO mapping No
16
Value range Unsigned32
Default value No
5.3 Drive Data
Objects 6500h to 65FFh serve as a database for drive parameters. The Elmo DSP 402
implementation supports the following objects:
6502h: Supported drive modes:
Homing mode (hm), profiled position mode (pp), interpolated position mode (ip),
profiled velocity mode (pv), Profiled torque mode (tq).
6504h: Drive manufacturer
6505h: Http drive catalog address
60FDh: Drive digital input
These objects, except 6503h, are “read only” and are burnt into the drive as part of the
manufacturing process. Object 6503h is a non-volatile object, which serves as a database
for the user to enter the type of drive as appears in the nameplate (for example,
HAR A15/200CAN). The default value is 0.
The following objects provide more information about the drive:
1008h: Manufacturer device name
100Ah: Manufacturer software version
Page 23

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Object 0x6502: Supported drive modes
Object description:
Index 6502h
Name Supported drive modes
Object code VAR
Data type UNSIGNED32
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read only
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED32
17
Default value 0x65
Data description:
31 16 15 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Manufacturer
reserved ip hm reserved tq pv vl pp
specific
Object 0x6504: Drive manufacturer
This object gives the drive manufacturer’s name.
Object description:
Index 6504h
Name Drive manufacturer
Object code VAR
Data type VISIBLE_STRING
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read only
PDO mapping No
Value range
Default value Elmo Motion Control Ltd.
According to DSP 402, object 0x6504 has read/write access, although with the
Harmonica, it has read only access.
Page 24

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Object 0x6505: http drive catalog address
This object gives the Internet address of the drive manufacturer.
Object description:
Index 6505h
Name http drive catalog address
Object code VAR
Data type VISIBLE_STRING
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read only
PDO mapping No
Value range
Default value http:\\www.elmomc.com
18
According to DSP 402, object 0x6505 has read/write access, although with the
SimplIQ, it has read only access.
Object 0x60FD: Digital inputs
This object defines simple digital inputs for drives.
The reflected functions are:
• Negative limit switch – Similar to RLS
• Positive limit switch – Similar to FLS
• Home switch – As reflected in the IL[5] command
Object description:
Index 60FDh
Name Digital inputs
Object code VAR
Data type UNSIGNED32
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read only
PDO mapping Yes
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value 0
Page 25

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Data description:
31 22 21 16 15 4 3 2 1 0
Manufactu
rer specific
Digital
input 1…10
logic state
Reserved Interlock Home
switch
Positive
limit
switch
Negative
limit switch
MSB
The switch must be “active high.”
Notes:
The interlock is always 0.
“Active high” means that the bit is set to high when the switch is logically
active.
Bits 16 – 25 reflect the logic active state of the digital inputs, starting from 1.
Logic active means that the switch can be active in either high state or low state
according to the IL[N] definition. More information can be found in the
SimplIQ
Command Reference Manual.
19
Different SimplIQ drives support a different number of digital inputs. It is
advised to use only the relevant bits according to the specific drive.
This object is evaluated every 3 milliseconds.
When mapped as asynchronous, this object is transmitted at every change within the
calculation resolution period. Inhibit time can be used to prevent busload or to control
the time latency causing the same TPDO to be transmitted due to other asynchronous
events.
Page 26
CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
6: Device Control
6.1 Objects
6040h: controlword
6041h: statusword
The Device Control function block controls all functions of the device, categorized as:
Device control of the state machine
Operation mode functions
The state of the device is controlled by the controlword, while the status of the device is
indicated by the statusword.
The state machine is controlled externally by the controlword and external signals. Write
access to the controlword is always allowed. The SimplIQ is always in external mode,
thus the “Remote” indication in the statusword is always ‘1’. The state machine is also
controlled by internal signals such as faults and modes of operation.
20
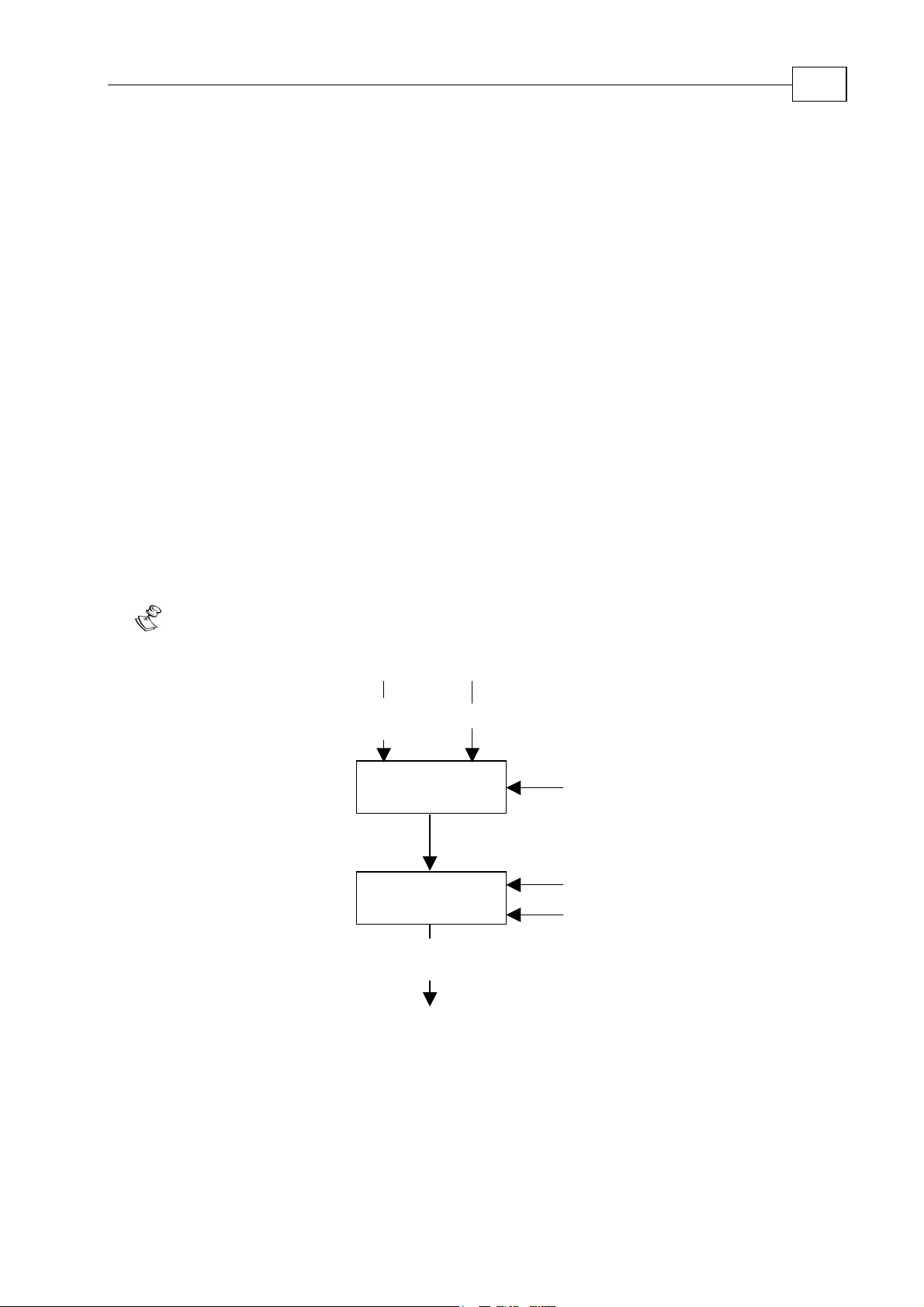
The following diagram illustrates the Device Control function.
The Elmo drive is always in remote mode; that is, it can be controlled only
externally by using the SDO and PDO.
controlword
controlword
(6040h)
(6040h)
Logical Operation
Logical OperationLogical Operation
State Machine
State MachineState Machine
Terminals
Terminals
statusword
statusword
(6041h)
(6041h)
Remote
Remote
Faults
Faults
Status of the Drive Function
Status of the Drive Function
Figure
6-1: Remote Mode
State Machine
The state machine describes the device status and the possible control sequence of the
drive. A single state represents a special internal or external behavior. The state of the
drive also determines which commands are accepted; for example, a point-to-point
motion can be started only when the drive is in OPERATION ENABLE state.
Page 27
CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
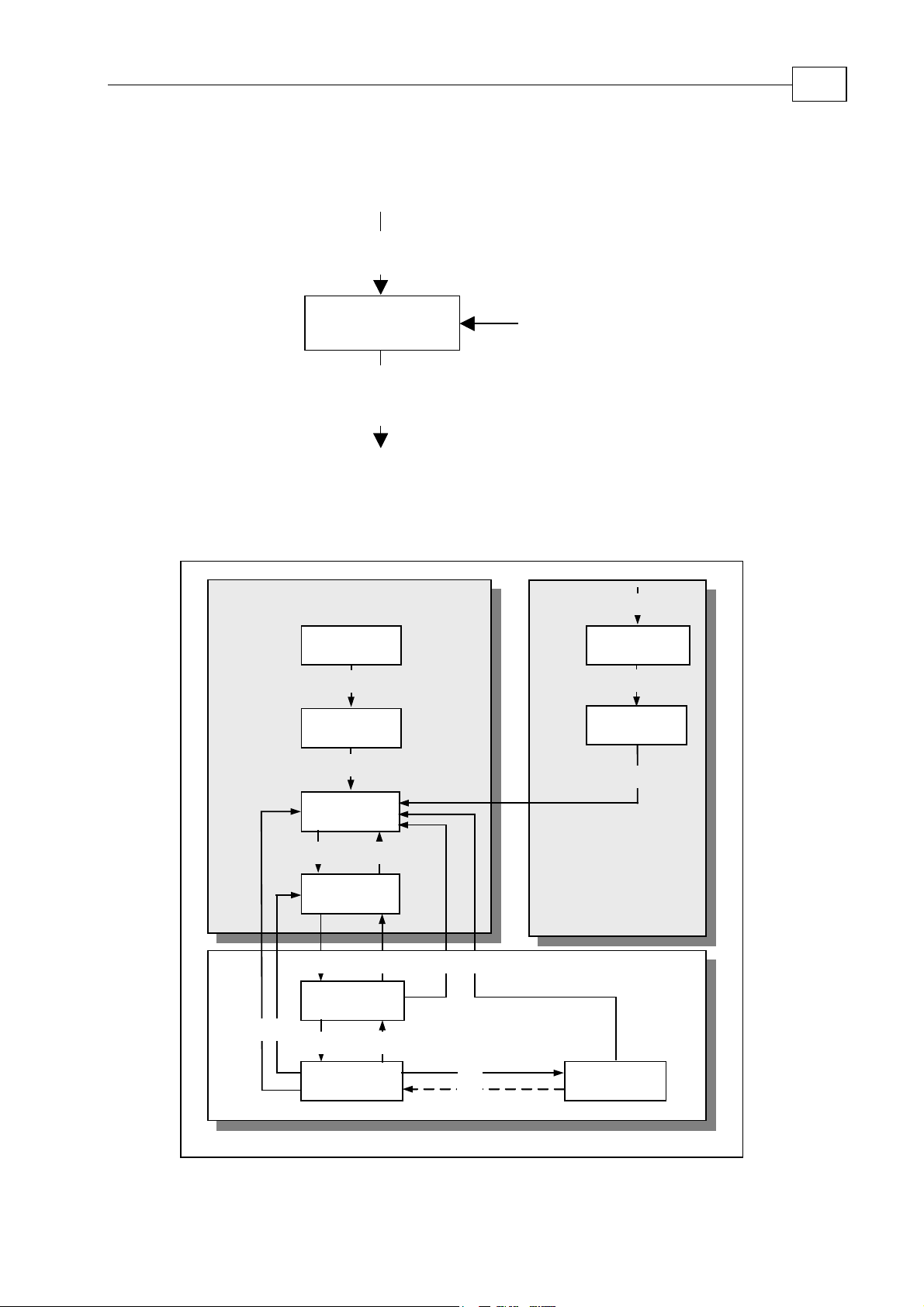
States may be changed using the controlword and/or according to internal events. The
current state can be read using the statusword.
controlword
controlword
(6040h)
(6040h)
Internal Events
State Machine
State MachineState Machine
statusword
statusword
(6041h)
(6041h)
Actions
Actions
Internal Events
Figure 6-2: State Machine in System Context
The device states and possible control sequence of the drive are described by the state
machine, as depicted in the following figure:
21
Power
Disabled
Power
Enabled
89
Start
0
NOT READY TO
SWITCH ON
1
SWITCH ON
DISABLED
72
READY TO
SWITCH ON
SWITCHED ON
Fault
63
54
1210
13
FAULT REACTION
ACTIVE
14
NOT READY TO
SWITCH ON
15
OPERATION
ENABLE
Figure
11
16
QUICK STOP
ACTIVE
6-3: State Machine Block Diagram
Page 28

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Drive States
The following states of the device are possible:
* NOT READY TO SWITCH ON:
Low-level power (24V) has been applied to the drive.
The drive is being initialized and is running the self test.
A brake output, if present, is applied in this state.
The drive function is disabled.
This state is an internal state in which communication is enabled only at the
end. The user can neither retrieve nor monitor this state.
* SWITCH ON DISABLED:
Drive initialization is complete.
The drive parameters have been set up.
Drive parameters may be changed.
High voltage may not be applied to the drive, (such as for safety reasons; refer to
following note).
The drive function is disabled.
22
Notes:
In this state, if high power is applied anyway, no indication of an error is
given. The application must be responsible for handling the state transition.
SWITCH ON DISABLED is the minimum state to which a user may switch.
* READY TO SWITCH ON:
High voltage may be applied to the drive.
The drive parameters may be changed.
The drive function is disabled.
* SWITCHED ON:
High voltage has been applied to the drive.
The power amplifier is ready.
The drive parameters may be changed.
The drive function is disabled.
No indication is given if the drive high voltage has not been applied.
* OPERATION ENABLE:
No faults have been detected.
The drive function is enabled and power is a
pplied to the motor.
The drive parameters may be changed.
(This corresponds to normal operation of the drive.)
In this state, a brake is automatically released according to the brake parameter
(BP[N]) timing.
Page 29

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
* QUICK STOP ACTIVE:
The drive parameters may be changed.
The quick stop function is being executed.
The drive function is enabled and power is applied to the motor.
According to the quick stop option code, the drive stops the motion and either
stays in quick stop or disables the motor. The term “drive stops” means that the
rfg completed the deceleration trajectory and not that the motor is stationary.
If the quick stop option code (object 0x605A) is 0 (disable drive function), the state
of the drive is SWITCH ON DISABLED.
* FAULT REACTION ACTIVE:
The drive parameters may be changed.
A fault has occurred in the drive.
The fault reaction function is being executed.
The drive function is disabled.
23
This parameter cannot be retrieved by the user. The drive automatically
switches to FAULT state.
* FAULT:
The drive parameters may be changed.
A fault has occurred in the drive.
High voltage switch-on/-off depends on the application.
The drive function is disabled.
State Transitions of the Drive Supervisor
State transitions are caused by internal events in the drive or by commands from the host
via the controlword.
State Transition 0: START => NOT READY TO SWITCH ON
Event: Reset.
Action: The drive self-tests and/or self-initializes.
State Transition 1: NOT READY TO SWITCH ON => SWITCH ON DISABLED
Event: The drive has self-tested and/or initialized successfully.
Action: Activate communication.
State Transition 2: SWITCH ON DISABLED => READY TO SWITCH ON
Event: Shutdown command received from host.
Action: None
State Transition 3: READY TO SWITCH ON => SWITCHED ON
Event: Switch On command received from host.
Action: The power section is switched on if it is not already on.
Page 30

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
State Transition 4: SWITCHED ON => OPERATION ENABLE
Event: Enable Operation command received from host.
Action: The drive function is enabled.
State Transition 5: OPERATION ENABLE => SWITCHED ON
Event: Disable Operation command received fro
m host.
Action: The drive operation is disabled.
State Transition 6: SWITCHED ON => READY TO SWITCH ON
Event: Shutdown command received from host.
Action: The pow
er section is switched off.
24
State Transition 7: READY TO SWITCH ON => SWITCH ON DISABLED
Event: Quick Stop and Disable Voltage command
s received from host.
Action: None.
State Transitio
n 8: OPERATION ENABLE => READY TO SWITCH ON
Event: Shutdown command received from host.
Action: The power section is switched off immediately,
and the motor is free to rotate
if not braked.
State Transitio
n 9: OPERATION ENABLE => SWITCH ON DISABLED
Event: Disable Voltage command received from host.
Action: The power section is switched off immediately, and the motor i
s free to rotate
if not braked.
State Transitio
n 10: SWITCHED ON =>SWITCH ON DISABLED
Event: Disable Voltage or Quick Stop command received from host.
Action: The power section is switched off immedia
tely, and the motor is free to rotate
if not braked.
State Transition 11: OPERATION ENABLE =>QUICK STOP ACTIVE
Event: Quick Stop command received from host.
Action: The quick stop function is executed.
State Transition 12: QUICK STOP ACTIVE=>SWITCH ON DISABLED
Event: Quick Stop completed or Disable Voltage command received from host.
This transition is possible if the quick stop option code is hig
her than 5 (stay in QUICK
STOP ACTIVE state).
Action: The profile generator finished the d
eceleration and the motor is disabled.
State Transition 13: All => FAULT REACTION ACTIVE
Event: A fault has occurred in the drive.
Action: Execute appropriate fault reaction.
State Transition 14: FAULT REACTION ACTIVE => FAU
LT
Event: The fault reaction is completed.
Action: The drive function is disabled. The power section may be switched
State
Transition 15: FAULT=>SWITCH ON DISABLED
Fault Reset command received from host.
Event:
Action:
The fault condition is reset if no fault currently exists in the drive.
off.
Page 31

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
After leaving FAULT state, the Fault Reset bit of the controlword must be
cleared by the host. The drive does not monitor this bit in other states. If this
bit is not cleared from a previous fault st
ate, when the next fault occurs, the
drive automatically enters SWITCH ON DISABLED state with no indications
or warn
ing.
25
State T
Event: En
the quick
Action: Th
ransition 16: QUICK STOP ACTIVE=>OPERATION ENABLE
able Operation command received from host. This transition is possible if
stop option code (object 0x605A) is 5, 6.
e drive function is enabled.
Notes:
This transition forces a “motion begin”; for example, if the controlword
forces transition 11 during a home seque nce, the motor will stop according
to the quick stop option code. If a new homing speed and homing acceleration are
set to the drive and the controlword
sets transition 16, the home sequence
will continue according to the method and with the new home parameters.
If the motor is turned off by an external source (such as the inter
during OPERATION ENABLE, the minimum state SWITCH ON ENABLE
will merge with no further notification.
Important Notes about State Transition:
If a command that causes a change of state i s received, it is processed completely
and the new state is attained before the next command is processed.
er up or at
The drive performs transitions 0 and 1 after initiation, either at pow
NMT node reset. From this state, it is up to the host to change the trans
according to the application needs.
preter)
itions
e
“Drive function is disabled” implies that no energy is being supplied to th
motor. Reference values are not processed.
“Drive function is enabled” implies that energy can be supplied to the motor.
The reference values (torque, velo
city and position) are processed.
“Fault occurred” implies that a fault has occurred in the drive during
“Operation Enable”. In this case, there is a transition to state FAULT
REACTION ACTIVE, during which the device executes a motor disab
function. After executing this fault reaction, the device switches to state FAUL
It is possible to leave this state only through the Fault Reset command, and only
if the fault is not active anymore.
If a fault occurs in OPERATION ENABLE state, an emergency message – if not
masked – is sent with the fault reason. The last 16 fault messages are latched and
can be retrieved later by uploading object 0x1003, defined in DS-301.
In a fault state, setting MO=1 through methods other than the controlword
activates the motor and leads to an ambiguous state of the DSP 402 protocol.
le
T.
Page 32

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Illegal Transition
After initiation of a drive by either power on or NMT node reset, the drive automatically
performs transitions 0 and 1 to the SWITCH ON DISABLED state. The controlword can
then be used to cause any of the transitions defined previously. If a transition is illegal
(such as requesting a QUICK STOP in a FAULT state), the controlword is rejected with
abort code 0609 0030, “Value range of parameter exceeded.” If an RPDO is used to
control the drive, an RPDO style emergency is transmitted with the error code. The
emergency structure and meaning is illustrated in the
SimplIQ CANopen Implementation
Manual. This emergency can be masked in accordance with object 2F21h. In case of an
illegal transition, bit 7 in the statusword (warning) is set for at least the next
transmission of this statusword. The bit is after a legal transition of the controlword.
The resolution for statusword transmission is approximately 3 milliseconds. Events
that are modified during this time are sensed and responded to, but no notification
of them is made by the statusword.
26
Object 0x6040: Controlword
The controlword contains bits for:
Controlling the state
Controlling operating modes
Manufacturer-specific options
Object description:
Index 6040h
Name Controlword
Object code VAR
Data type UNSIGNED16
Category Mandatory
Entry description:
Access Read/write
PDO mapping Possible
Value range UNSIGNED16
Default value No
Page 33

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Data description:
15 11 10 9 8 7 6 4 3 2 1 0
Manufacturer
specific
O O O M O M M M M
MSB LSB
O: Optional
M: Mandatory
Reserved Halt Fault
reset
Operation
mode specific
Enable
operation
Quick
stop
Enable
voltage
Switch on
Bits 0 – 3 and 7:
Device control commands are triggered by the following bit patterns in the
controlword:
27
Command
7 3 2 1 0
Fault
Reset
Bits of the controlword
Enable
Operation
Quick
Stop
Enable
Voltage
Transitions
Switch
On
Shutdown 0 X 1 1 0 2, 6, 8
Switch ON 0 0 1 1 1 3*
Switch ON 0 1 1 1 1 3**
Disable
0 X X 0 X 7, 9, 10, 12
Voltage
Quick Stop 0 X 0 1 X 7, 10, 11
Disable
0 0 1 1 1 5
Operation
Enable
0 1 1 1 1 4, 16
Operation
Fault Reset
X X X X 15
Device Control Command Triggers
Bits marked with X are not relevant.
* The drive executes the functionality of SWITCH_ON.
** The drive does nothing in this state, which is treated the same as in *.
Page 34

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Bits 4, 5, 6 and 8:
These bits are operation-mode specific. Their description is found in the chapter
about the special mode.
Velocity
Bit
Mode
4 rfg enable New set-point Reserved Reserved Homing
5 rfg unlock Change set
6 rfg use ref abs/rel Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
8 Halt Halt Halt Halt Halt Halt
Profile
Position
Mode
immediately
Operation Mode
Profile
Velocity
Mode
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
Profile
Torque
Mode
Homing
Mode
operation
start
Interpolation
Position
Mode
Enable ip
mode
Not all modes mentioned in the table are implemented in Elmo servo drives.
28
Bits 9 and 10:
These bits are reserved for future use. They are de-activated by setting them to 0. If
they have no special function, they are set to zero.
Bits 11, 12, 13, 14 and 15:
These bits are manufacturer specific.
Object 0x6041: Statusword
The statusword indicates the present state of the drive. No bits are latched. The statusword
contains bits for:
The current drive state
The operating state of the mode
Manufacturer-specific options
Object description:
Index 6041h
Name Statusword
Object code VAR
Data type UNSIGNED16
Category Mandatory
Page 35

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Entry description:
Access Read only
PDO mapping Yes
Value range UNSIGNED16
Default value No
Data description:
Bit Description
0 Ready to switch on
1 Switched on
2 Operation enabled
3 Fault
29
4 Voltage enabled
5 Quick stop
6 Switch on disabled
7 Warning
8 Manufacturer specific
9 Remote
10 Target reached
11 Internal limit active
12 - 13 Operation mode specific
14 - 15 Manufacturer specific
Bits 0 - 3, 5 and 6:
The following bits indicate the status of the device:
Value (binary) State
xxxx xxxx x0xx 0000 Not ready to switch on
xxxx xxxx x1xx 0000 Switch on disabled
xxxx xxxx x01x 0001 Ready to switch on
xxxx xxxx x01x 0011 Switch on
xxxx xxxx x01x 0111 Operation enabled
xxxx xxxx x00x 0111 Quick stop active
xxxx xxxx x0xx 1111 Fault reaction active
xxxx xxxx x0xx 1000 Fault
Page 36

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Bit 4: Voltage Enabled:
High voltage is applied to the drive when this bit is set to 1.
Bit 5: Quick Stop:
When reset, this bit indicates that the drive is reacting to a Quick Stop request. Bits 0,
1 and 2 of the statusword must be set to 1 to indicate that the drive is capable of
regenerating. The setting of the other bits indicates the status of the drive (for
example, the drive is performing a quick stop in reaction to a non-fatal fault. The
fault bit is set in addition to bits 0, 1 and 2).
Bit 7: Warning:
A drive warning is present if bit 7 is set. While no error has occurred, this state must
still be indicated; for example, job refused. The status of the drive does not change.
The cause of this warning may be found by reading the fault code parameter. This
bit is set when an illegal controlword is received and reset after at least one statusword
of this transition has been transmitted.
Bit 8:
This bit is reserved for the manufacturer. It is not used and is set to 0.
30
Bit 9: Remote:
If bit 9 is set, parameters may be modified via the CAN network, and the drive
executes the contents of a command message. If the bit remote is reset, the drive is in
local mode and does not execute the command message. The drive may transmit
messages containing actual valid values such as a position actual value, depending on
the actual drive configuration. The drive accepts accesses via SDO in local mode.
The Remote bit is always set by the Elmo servo drive.
Bit 10: Target Reached:
Bit 10 is set by the drive to indicate that a set-point has been reached. The set-point is
dependent on the operating mode. The relevant description is found in the chapter
about the special mode. The change of a target value by software alters this bit.
If the quick stop option code is 5 or 6, this bit is set when the quick stop operation is
finished and the drive is halted.
If a Halt occurs and the drive has halted, this bit is also set.
Bit 11: Internal Limit Active:
The drive can set this bit to indicate that an internal limitation is active (such as
software position limit).
Bits 12 and 13:
These bits are operation-mode specific. Their description is found in the chapter
about the special mode. The following table provides an overview of the bits:
Bit
vl pp pv tq hm ip
12 Reserved Set-point
acknowledge
13 Reserved Following
error
Operation Mode
Speed Reserved Homing
attained
Max slippage
error
Reserved Homing
error
ip mode
active
Reserved
Page 37

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Not all modes mentioned in the table are implemented in Elmo servo drives.
Bits 14 and 15:
These bits are reserved. They are not used and are set to 0.
31
6.2 Halt, Stop
and Fault Objects
605A: Quick stop option code
605B: Shutdown option c
605C: Disable operation mo
ode
de
605D: Halt option code
605E: Fault reaction code
Slow down ramp – DC value
uick stop ramp – SD value
Q
Disable drive – MO=0
Object 0x605A:
This parameter determi
Quick stop option code
nes which action should be taken if the Quick Stop function is
executed.
Object description:
Index 605Ah
Name Quick stop option code
Object code VAR
Data type INTEGER16
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range INTEGER16
Default value 2
Page 38

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Data description:
Value Description
-32,768…-1 Manufacturer specific
0 Disable drive function
1 Slow down on slow-down ramp and then disable the drive
2 Slow down on quick-stop ramp and then disable the drive
3 Slow down on current limit and than disable the drive (tq
mode only)
4 Not supported
5 Slow down on slow-down ramp and stay in QUICK STOP
7 Slow down on the current limit and stay in QUICK STOP
(tq mode only)
32
8 Not supported
9…32,767 Reserved
An attempt to set an unsupported value causes the transmission of abort code
0609 0030: Value exceeded.
Object 0x605B: Shutdown option code
This parameter determines which action should be taken in case of the transition:
OPERATION ENABLE => READY TO SWITCH ON.
Object description:
Index 605Bh
Name Shutdown option code
Object code VAR
Data type INTEGER16
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range INTEGER16
Default value 0
Page 39

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Data description:
Value Description
-32,768…-1 Manufacturer specific
0 Disable drive function
1 Slow down on slow-down ramp; disable drive function
2…32,767 Reserved
An attempt to set an unsupported value causes the transmission of abort code
0609 0030, value exceeded.
Object 0x605C: Disable operation option code
This parameter determines which action shou
ld be taken in case of the transition:
OPERATION ENABLE => SWITCHED ON.
Object description:
33
Index 605Ch
Name Disable operation option code
Object code VAR
Data type INTEGER16
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range INTEGER16
Default value 1
Data description:
Value Description
-32,768…-1 Manufacturer specific
0 Disable drive function
1 Slow down on slow-down ramp and then disable drive function
2…32,767 Reserved
An attempt to set an unsupported value causes the transmission of abort
code 0609 0030: Value exceeded.
Page 40
CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Object 0x605D: Halt option code
This parameter determines which action should be taken if bit 8 (halt) in the controlword
is active.
Object description:
Index 605Dh
Name Halt option code
Object code VAR
Data type INTEGER16
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read/write
34
PDO mapping No
Value range INTEGER16
Default value 1
Data description:
Value Description
-32,768…-1 Manufacturer specific
0 Disable drive function
1 Slow down on slow-down ramp
2 Slow down on quick-stop ramp
3 Slow down on current limit (only for tq mode)
3…32,767 Reserved
In Profile Position mode, the Halt option is not affected when this object is set.
Page 41

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Object 0x605E: Fault reaction option code
Object description:
Index 605Eh
Name Fault reaction option code
Object code VAR
Data type INTEGER16
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range INTEGER16
35
Default value 0
Data description:
Value Description
-32,768…-1 Manufacturer specific
0 Disable drive function
1…4 Not supported
1…32,767 Reserved
Notes:
An attempt to set an unsupported value causes the transmission of abort
code 0609 0030: Value exceeded.
All drive faults are considered fatal. When a fatal fault occurs, the drive is
no longer able to control the motor, requiring that the drive be switched-off
immediately.
Page 42

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
7: Modes of Operation
6060h: Modes of operation
6061h: Modes of operation display
7.1 Functional Description
The drive behavior depends on the activated modes of operation. Different modes can be
implemented, although not in parallel. Therefore, the user must activate the required
function by selecting a mode of operation. The modes-of-operation variables are
initialized at reset to “no mode” (value -1). Modes can be set in any state, including
OPERATION ENABLE. At OPERATION ENABLE, the motor stands still until an explicit
motion command is received via a control word. Bit 10 in the statusword (Target reached) is
set.
When switching modes in OPERATION ENABLE, the transition proceeds as if bit 8
(Halt) in the controlword has been set. The motion first stops according to object 605Dh.
The mode actually changes only after a complete stop, according to the definition of
target reached. The actual mode is reflected via object 6061h.
36
The statusword contains bits whose meaning depends on the mode of operation. When
switching modes, the “mode dependent” bits in the controlword and statusword must be
monitored.
7.2 Objects
Object 0x6060: Modes of operation
Object description:
Index 6060h
Name Modes of operation
Object code VAR
Data type INTEGER8
Category Mandatory
Entry description:
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range INTEGER8
Default value -1
Page 43

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Data description:
Value Description
-128…-2 Reserved
-1 No mode
0 Reserved
1 Profile position mode
2 Velocity (not supported)
3 Profiled velocity mode
4 Torque profiled mode
5 Reserved
6 Homing mode
7 Interpolated position mode
8…127 Reserved
37
Notes:
A read of this object shows only the value of modes of operation. The actual
mode of the drive is reflected in the modes o f operation display object. It may be
changed by writing to modes of operation.
ted mode causes the transmission of abort
An attempt to access an unsuppor
code 0609 0030: Value exceeded.
Object 0x6061: Modes of operation display
This object shows the current mode of operation. The meaning of the re
corresponds to that of the
modes of operation option code (index 6060h).
turned value
Object description:
Index 6061h
Name Modes of operation display
Object code VAR
Data type INTEGER8
Category Mandatory
Entry description:
only Access Read
PDO mapping No
Value range INTEGER8
Default value -1
Data description:
Similar to object 6060h, modes of operation.
The actual mode is reflected in the modes of operation display (index 6061h),
and not in modes of operation (index 6060h).
Page 44

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
8: Factors
607Eh: Polarity
6089h: Position notation index
608Ah: Position dimension index
608Bh: Velocity notation index
608Ch: Velocity dimension index
608Dh: Acceleration notation index
608Eh: Acceleration dimension index
608Fh: Position encoder resolution
6090h: Velocity encoder resolution
6093h: Position factor
6094h: Velocity encoder factor
6095h: Velocity factor 1
6096h: Velocity factor 2
38
6097h: Acceleration factor
Physical dimensions and sizes need to be converted into the device internal units,
requiring a number of different factors. This chapter describes how these factors
influence the system, how they are calculated and which data is needed to build them.
8.1 Relationship between Physical and Internal Units
The factors defined in the factor group determine a relationship between the Elmo drive
internal units and the application physical units. The factors are a result of the calculation
of two parameters – called dimension index and notation index – which are defined
Appendix A and Appendix B. One parameter indicates the physical dimensions, and the
other indicates the decimal exponent for the values. These factors are directly used to
normalize the physical values.
The application-specific parameters are used in the corresponding mode of operation to
build the described factors. Parameters that are commonly used are integrated in the
object dictionary without defining their junctions. This guarantees a common parameter
number for further use without the need for predefinition.
8.2 Functions and Limits
Factors cannot be set while the drive is in OPERATION ENABLE state.
Divisors cannot be set to 0. An abort message with abort code 0609 0030 will be
transmitted.
Values are truncated to the nearest integer.
Page 45

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
8.3 Objects
Object 0x607E: Polarity
Position demand value and position actual value are multiplied by 1 or -1, depending on the
value of the polarity flag.
Object description:
Index 607Eh
Name Polarity
Object code VAR
Data type UNSIGNED8
Category Optional
Entry description:
39
Access Read/write
PDO mapping Yes
Value range UNSIGNED8
Default value 0
Data Description
7 6 5 . . . 0
Position
polarity
Velocity
polarity
Reserved
Value Description
0 Multiply by 1
1 Multiply by -1
Page 46

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Object 0x6089: Position notation index
This index is used to scale position objects. The unit is defined by the physical
dimensions and calculated by unit type and exponent, declared in the dimension/
notation index tables (refer to Appendix A and Appendix B).
Notes:
The Elmo drive does not use this object; it is available for user convenience.
The object is not checked for value and consistency.
Object description:
Index 6089h
Name Position notation index
Object code VAR
Data type INTEGER8
40
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read/write
PDO mapping Yes
Value range INTEGER8
Default value 0
Object 0x608A: Position dimension index
This object defines the position dimension index, which is used together with the position
notation index (object 0x6089) to define a unit (refer to Appendix A).
Notes:
The Elmo drive does not use this object; it is available for user convenience.
The object is not checked for value and consistency.
This object is non-volatile.
Object description:
Index 608Ah
Name Position dimension index
Object code VAR
Data type UNSIGNED8
Category Optional
Page 47

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Entry description:
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED8
Default value —
Object 0x608B: Velocity notation index
This object defines the velocity notation index. The unit is defined by the physical
dimensions and calculated by unit type and exponent, declared in the dimension/
notation index tables (refer to Appendix A and Appendix B).
Notes:
The Elmo drive does not use this object; it is available for user convenience.
41
The object is not checked for value and consistency.
This object is non-volatile.
Object description:
Index 608Bh
Name Velocity notation index
Object code VAR
Data type INTEGER8
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range INTEGER8
Default value —
Page 48

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Object 0x608C: Velocity dimension index
This object defines the velocity dimension index, which is used together with the velocity
notation index (object 0x608B) to define a unit (refer to Appendix A and Appendix B).
Notes:
The Elmo drive does not use this object; it is available for user convenience.
The object is not checked for value and consistency.
This object is non-volatile.
Object description:
Index 608Ch
Name Velocity dimension index
Object code VAR
Data type UNSIGNED8
Category Optional
42
Entry description:
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED8
Default value —
Object 0x608D: Acceleration notation index
This object defines the acceleration notation index. The unit is defined by the physical
dimensions and calculated by unit type and exponent, declared in the dimension /
notation index tables (refer to Appendix A and Appendix B).
Notes:
The Elmo drive does not use this object; it is available for user convenience.
The object is not checked for value and consistency.
This object is non-volatile.
Object description:
Index 608Dh
Name Acceleration notation index
Object code VAR
Data type INTEGER8
Category Optional
Page 49

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Entry description:
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range INTEGER8
Default value —
Object 0x608E: Acceleration dimension index
This object defines the acceleration dimension index, which is used together with the
acceleration notation index (object 0x608D) to define a unit (refer to Appendix A).
Notes:
The Elmo drive does not use this object; it is available for user convenience.
The object is not checked for value and consistency.
This object is non-volatile.
43
Object description:
Index 608Eh
Name Acceleration dimension index
Object code VAR
Data type UNSIGNED8
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED8
Default value —
Page 50

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Object 0x608F: Position encoder resolution
This object defines the ratio of encoder increments per motor revolution:
_
resolutionencoderposition __ =
incrementsencoder
_
srevolutionmotor
Object description:
Index 608Fh
Name Position encoder resolution
Object code ARRAY
Data type UNSIGNED32
Category Optional
Entry description:
Sub-index 0
44
Description Number of entries
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read only
PDO mapping No
Value range 2
Default value 2
Sub-index 1
Description Encoder increments
Entry category Optional
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value 1
Sub-index 2
Description Motor revolutions
Entry category Optional
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value 1
Page 51

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Object 0x6090: Velocity encoder resolution
This object defines the ratio of encoder increments/second per motor revolutions/
second.
resolutionencodervelocity __ =
incrementsencoder
sec/_
sec/_
srevolutionmotor
Object description:
Index 6090h
Name Velocity encoder resolution
Object code ARRAY
Data type UNSIGNED32
Category Optional
Entry description:
45
Sub-index 0
Description Number of entries
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read only
PDO mapping No
Value range 2
Default value 2
Sub-index 1
Description Encoder increments per second
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value 1
Sub-index 2
Description Motor revolutions per second
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value 1
Page 52

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Object 0x6093: Position factor
This object converts the desired position (in position units) into the internal format (in
increments). The object entries are the numerator and the divisor.
Object description:
Index 6093h
Name Position factor
Object code ARRAY
Data type UNSIGNED32
Category Optional
Entry description:
Sub-index 0
Description Number of entries
46
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read only
PDO mapping No
Value range 2
Default value 2
Sub-index 1
Description Numerator
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value 1
Sub-index 2
Description Divisor
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value 1
Page 53

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Notes:
The position factor is calculated according to this object regardless of the setting
of any other objects, such as 0x608F (position encoder resolution).
The actual value range of the divisor may not exceed 16,383 due to numeric
overflow.
Object 0x6094: Velocity encoder factor
This object converts the desired velocity (in velocity units) into the internal format (in
increments/second).
Object description:
Index 6094h
Name Velocity encoder factor
47
Object code ARRAY
Data type UNSIGNED32
Category Optional
Entry description:
Sub-index 0
Description Number of entries
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read only
PDO mapping No
Value range 2
Default value 2
Sub-index 1
Description Numerator
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value 1
Page 54

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Sub-index 2
Description Divisor
Entry category Optional
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value 1
Notes:
The position factor is calculated according to this object regardless of the setting
of any other objects, such as 0x6090 (velocity encoder resolution).
The actual value range of the divisor may not exceed 16,383 due to numeric
overflow.
48
Object 0x6095: Velocity factor 1
This object is used to convert motor data (such as maximum motor revolutions) into
velocity data (such as maximum velocity) because the data items are based on different
physical dimensions.
Object description:
Index 6095h
Name Velocity factor 1
Object code ARRAY
Data type UNSIGNED32
Category Optional
Entry description:
Sub-index 0
Description Number of entries
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read only
PDO mapping No
Value range 2
Default value 2
Page 55

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Sub-index 1
Description Numerator
Entry category Optional
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value 1
Sub-index 2
Description Divisor
Entry category Optional
Access Read/write
49
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value 1
Notes:
The velocity factor 1 is calculated according to this object regardless of the setting
of any other objects, such as 0x6092 (feed constant).
The actual value range of the divisor may not exceed 16,383 due to numeric
overflow.
Object 0x6096: Velocity factor 2
This object is used to define the relationship between the velocity encoder data and the
position encoder data, because they are based on different dimensions.
Object description:
Index 6096h
Name Velocity factor 2
Object code ARRAY
Data type UNSIGNED32
Category Optional
Page 56

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Entry description:
Sub-index 0
Description Number of entries
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read only
PDO mapping No
Value range 2
Default value 2
Sub-index 1
Description Numerator
Entry category Optional
50
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value 1
Sub-index 2
Description Divisor
Entry category Optional
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value 1
Notes:
The velocity factor 2 is calculated according to this object regardless of the setting
of any other objects, such as 0x608F (position encoder resolution).
The actual value range of the divisor may not exceed 16,383 due to numeric
overflow.
Page 57

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Object 0x6097: Acceleration factor
This object converts the acceleration (in acceleration units/second
format (in increments/second
2
).
2
) into the internal
Object description:
Index 6097h
Name Acceleration factor
Object code ARRAY
Data type UNSIGNED32
Category Optional
Entry description:
Sub-index 0
Description Number of entries
51
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read only
PDO mapping No
Value range 2
Default value 2
Sub-index 1
Description Numerator
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value 1
Sub-index 2
Description Divisor
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value 1
Page 58

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Notes:
The acceleration factor is calculated according to this object regardless of the
setting of any other objects, such as 0x6094 (velocity encoder factor).
The actual value range of the divisor may not exceed 16,383 due to numeric
overflow.
52
Page 59

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
9: Homing
607Ch: Home offset
6098h: Homing method
6099h: Homing speeds
609Ah: Homing acceleration
9.1 General Information
This chapter describes the method by which a drive seeks the home position (also called
the datum, reference point or zero point). Homing can be performed using limit switches
at the ends of travel or a home switch (zero point switch) in mid-travel; most of the
methods also use the index (zero) pulse train from an incremental encoder.
Input Data
The user can specify the speeds, acceleration and method of homing. An additional
object, home offset, is used to displace zero in the user’s coordinate system from the home
position. There are two homing speeds: in a typical cycle the faster speed is used to find the
home switch and the slower speed is used to find the index pulse.
53
Output Data
There is no output data except for those bits in the statusword that return the status or
result of the homing process and the demand to the position control loops.
Internal States
The homing mode is controlled by the bits of the controlword and statusword
.
Homing Mode Controlword
Bit Function
0…3 Described in Device Control
4 Home operation start
5..6 Reserved
7 Described in Device Control
8 Halt
9..12 Described in Device Control
13..15 Described in Device Control
Page 60

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Name Value Description
54
Homing
operation start
0 Homing mode inactive.
0→1 Start homing mode.
1 Homing mode active.
1→0 Interrupt homing mode.
0 Execute the instruction of bit 4. Halt
1 Stop axle with homing deceleration.
Notes:
If homing is interrupted by setting bit 4 from “1” to “0”, the movement of the
motor is not interrupted; that is, the motor remains in its present state, either
moving or not. The home sequence is interrupted and the home target is not
attained. By setting the bit back to “1”, the homing mode begins again.
If a Halt occurs, the drive stops the homing method and halts the motor
according to object 609Ah. When this bit is set to “0” and bit 4 remains “1”, the
home method begins again.
Statusword of Homing Mode
Bit Function
0…9 Described in Device Control
10 Target reached
11 Described in Device Control
12 Homing attained
13 Homing error
14…15 Described in Device Control
Name Value Description
Target reached
0 Halt = 0: Homing position not reached
Halt = 1: Axle decelerates
1 Halt = 0: Homing position reached
Halt = 1: Velocity of axle is 0
0 Homing mode not yet completed. Homing attained
1 Homing mode carried out successfully.
0 No homing error. Homing error
1 Homing error occurred.
Homing mode carried out unsuccessfully.
Error cause found in error code.
During the homing process, no reference position limits are active. If no physical
limit exists — such as the limit switch — the load may travel indefinitely.
Page 61

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
9.2 Objects
Object 0x607C: Home offset
This object is the difference between the zero position for the application and the
machine home position (found during homing), measured in position units. During
homing, the machine home position is found. Once homing is completed, the zero
position is offset from the home position by adding the home offset to the home position.
All subsequent absolute moves are taken relative to this new zero position, as illustrated
in the following diagram.
55
Home
Home
Position
Position
home_offset
home_offset
By default, the home offset is 0.
Object description:
Index 607Ch
Name Home offset
Object code VAR
Data type INTEGER32
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Zero
Zero
Position
Position
Value range INTEGER32
Default value No
The zero position is determined after a successful homing sequence (home attain).
Internal position limits are taken relative to the zero position point.
Page 62

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Object 0x6098: Homing method
This object determines the method used during homing.
Object description:
Index 6098h
Name Homing method
Object code VAR
Data type INTEGER8
Category Mandatory
Entry description:
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
56
Value range INTEGER8
Default value 0
Data description:
Value Description
-128…-1 Manufacturer specific
0 No homing operation required
1…35 Methods 1 to 35 (see Functional
Description)
36…127 Reserved
Page 63

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Object 0x6099: Homing speeds
This entry in the object dictionary defines the speeds used during homing, in velocity
units. The value is normalized to increments by velocity code factor. Typically, a high
speed is used when searching for a home switch and the slow speed is used when
searching for the index.
Object description:
Index 6099h
Name Homing speeds
Object code ARRAY
Data type UNSIGNED32
Category Mandatory
Entry description:
57
Sub-index 0
Description Number of entries
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read only
PDO mapping No
Value range 2
Default value 2
Sub-index 1
Description Speed during search for switch
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value 0
Sub-index 2
Description Speed during search for zero
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value 0
Page 64

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
The speed is submitted to the maximum speed limit given by the user during
setup. Otherwise, an abort message with abort code 0609 0030, “Value range of
parameter exceeded” is activated. If the limits have been changed during the
process, the drive enters a fault state.
Object 0x609A: Homing acceleration
This object establishes the acceleration to be used for all accelerations and decelerations
with the standard homing modes, and is given in acceleration units.
Object description:
Index 609Ah
Name Homing acceleration
Object code VAR
58
Data type UNSIGNED32
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value No
Home deceleration is performed according to the SD value set during setup. The
user may use the binary interpreter to modify this value. Refer to the relevant
Command Reference Manual for the SD parameter information.
9.3 Functional Description
Choosing a method of homing by writing a value to homing method clearly establishes the:
Homing signal (positive limit switch, negative limit switch, home switch)
Direction of actuation
Position of the index pulse, where appropriate
Homing is performed on either the main position sensor (PX) or the auxiliary position
sensor (PY), depending on the unit mode — for position loop (UM=5) or dual loop
(UM=4) — respectively. The relevant source is selected when homing is activated by the
controlword.
The home position and zero position are offset by the home offset (see the home offset
definition for how this offset is used).
Page 65

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Various homing positions are illustrated in the diagrams that follow (section 9.4). A
circled number indicates the code for selecting the homing position. The direction of
movement is also indicated.
Additional homing methods are available with other modes of the Elmo drives,
such as the binary interpreter or the user program.
Four sources of homing signal are available: the negative and positive limit switches,
the home switch and, and the index pulse, which are handled by fast inputs. The
captured value is independent of drive sampling time. Limit switches must be
previously defined during the drive setup (using the IL[N] command).
In the homing sequence diagrams, the encoder count increases as the axle position moves
to the right. In other words, the left is the minimum position and the right is the
maximum position. In the SimplIQ drive, the user may select the configuration;
otherwise, it is determined according to the setup process.
Error Cases
Error cases are events in which the drive cannot reach the home method or operate the
home demand parameters, such as high speed. In cases where the limit is known in
advance — such as home speed higher than the speed limit — an abort message is
executed. In cases where a fault is hit during the operation of the home procedure —
such as an abort switch — the drive goes into a fault state. The homing error bit in the
statusword is set and an emergency message for motor fault, if not masked, is transmitted.
The error register can be monitored for the fault indication. In cases where a limit
prevents the home sequence from being finished, such as reaching a mechanical limit, no
special indication is given. It is up to the application to monitor or set a timeout sequence
for the home procedure.
59
Page 66

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
9.4 DSP 402 Homing Methods
The following sub-sections describe the details of how each homing mode functions. The
Elmo drives support each of these methods.
9.4.1 Method 1: Homing on the negative limit switch and
index pulse
Using this method, the initial direction of movement is leftward if the negative limit
switch is inactive (here shown as low). The home position is at the first index pulse to the
right of the position where the negative limit switch becomes inactive.
60
Figure 9-1: Homing on the negative limit switch and index pulse
9.4.2 Method 2: Homing on the positive limit switch and
index pulse
Using this method, the initial direction of movement is rightward if the positive limit
switch is inactive (here shown as low). The position of home is at the first index pulse to
the left of the position where the positive limit switch becomes inactive.
Figure 9-2: Homing on the positive limit switch and index pulse
Page 67

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
9.4.3 Methods 3 and 4: Homing on the positive home
switch and index pulse
Using methods 3 or 4, the initial direction of movement is dependent on the state of the
home switch. The home position is at the index pulse to either the left or right of the pint
where the home switch changes state. If the initial position is sited so that the direction of
movement must reverse during homing, the point at which the reversal takes place is
anywhere after a change of state of the home switch.
61
Figure 9-3: Homing on the positive home switch and index pulse
9.4.4 Methods 5 and 6: Homing on the negative home
switch and index pulse
Using methods 5 or 6, the initial direction of movement is dependent on the state of the
home switch. The home position is at the index pulse to either the left or the right of the
point where the home switch changes state. If the initial position is sited so that the
direction of movement must reverse during homing, the point at which the reversal takes
place is anywhere after a change of state of the home switch.
Figure 9-4: Homing on the negative home switch and index pulse
Page 68

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
62
9.4.5 Methods 7 to 14: Homing on the home switch an
d
index pulse
These methods use a home switch that is active over only a portion of the travel; in effec
the switch has a “momentary” action as the axle position sweeps past the switch.
Using methods 7 to 10, the initial direction of movement is to the right, and using
methods 11 to 14, the initial direction of movement is to the lef
switch is active at the start of motion. In this case, the initial direction of motion is
dependent on the edge being sought. The home position is at the index pulse on either
side of the rising or falling edges of the home switch, as shown in the following two
diagrams. If the initial direction of movement leads away from the home switch, the
drive must reverse on encountering the relevant limit switch.
t, except if the home
t,
Figure 9-5: Homing on the home switch and index pulse — positive initial move
Figure 9-6: Homing on the home switch and index pulse — negative initial move
Page 69

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
9.4.6 Methods 15 and 16: Reserved
These methods are reserved for future expansion of the homing mode.
9.4.7 Methods 17 to 30: Homing without an index pulse
These methods are similar to methods 1 to 14, except that the home position is not
dependent on the index pulse; it is dependent only on the relevant home or limit switch
transitions. For example, methods 19 and 20 are similar to methods 3 and 4, as shown in
the following diagram:
63
Figure 9-7: Homing on the positive home switch
9.4.8 Methods 31 and 32: Reserved
These methods are reserved for future expansion of the homing mode.
9. x pulse
4.9 Methods 33 and 34: Homing on the inde
Using methods 33 or 34, the direction of homing is negative or positive, respectively. The
home position is at the index pulse found in the selected direction.
Figure 9-8: Homing on the positive home switch
9.4.10 Method 35: Homing on the current position
In this method, the current position is taken to be the home position.
Page 70

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
10: Position Control Function
6062h: Position demand value in position units
6063h: Position actual value in increments
6064h: Position actual value
6065h: Following error window
6067h: Position window
6068h: Position window time out
60F4h: Following error actual value
60FAh: Position control effort
60FCh: Position demand value in increments
10.1 General Information
64
This chapter describes all parameters required for closed-loop position control. The
control loop is fed with the position demand value as one of the outputs of the trajectory
generator and with the output of the position detection unit (position actual value) as input
parameters. The behavior of the control is influenced by the control parameters. Position
control parameters (PI/P) may be set using the Composer Wizard during setup.
To ensure that the physical limits of a drive are not exceeded, an absolute limit function
is implemented for the position control effort. The Elmo drive implements a cascaded
control loop in which the position control effort is a velocity demand value for the velocity
control loop. For further information about tuning the position loop and using the
Composer Wizard, refer to the
SimplIQ Composer User Manual and the SimplIQ Software
Manual.
The following terms are used in this chapter:
Following error:
A position actual value outside the allowed range of the following error window around a
position demand value for longer than the following error timeout results in setting bit 13,
following error, in the statusword.
The position following error calculates each cycle of the position control. The
position demand value must be set lower than the setup value of the drive
following error ER[3]. When the position following error exceeds ER[3], the
motion aborts.
Position reached:
This function provides the option of defining a position range around a position
demand value to be regarded as valid. If a drive position is within this area for a
specified time — the position window time — the related control bit 10 target reached
in the statusword is set. Bit 10 is reset to 0 when the motor is off.
The position range in the Elmo servo drive is limited to ±1 * 109 regardless of the
DSP 402 maximum range.
Page 71

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
10.2 Objects
Object 0x6062: Position demand value
The value of this object is taken from the internal position command and is given in
position units after being converted by position factor.
Object description:
Index 6062h
Name Position demand value
Object code VAR
Data type INTEGER32
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read only
65
PDO mapping Yes
Value range INTEGER32
Default value 0
Object 0x6063: Position actual value
The actual value of the position measurement device is one of the two input values of the
closed loop position control. The data unit is defined as increments.
Object description:
Index 6063h
Name Position actual value - increments
Object code VAR
Data type INTEGER32
Category Mandatory
Entry description:
Access Read only
PDO mapping Yes
Value range INTEGER32
Default value 0
Notes:
Value range submits to the position range limits as defined in the specific drive.
9
For the Harmonica servo drive: ±1 * 10
This object has a write access when the motor is not enabled.
Page 72

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Object 0x6064: Position actual value
This object represents the actual value of the position measurement device, in userdefined units. When dual loop mode is active (UM=4), this object returns the value of the
position sensor as derived from the load feedback (PY command); in all single loop
modes (UM = 1,2,3,5), it returns the motor position feedback (PX command) value.
Object description:
Index 6064H
Name Position actual value
Object code VAR
Data type INTEGER32
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read only
PDO mapping Yes
66
Value range INTEGER32
Default value 0
Object 0x6065: Following error window
This object defines a range of tolerated position values symmetrical to the position demand
value. Because it is usually used with user-defined units, a transformation into increments
with the position factor is necessary. If the position actual value is out of the following error
window, a following error occurs. A following error may occur:
When a drive is blocked
When the profile velocity is unreachable
Due to wrong closed loop coefficients
If the value of the following error window is 2
32
-1, the following control is switched off.
The value of this object in increments is saturated to the maximum position range
allowed in the drive (1,000,000,000).
By default, this object is set internally to ER[3]/2 and then converted to user units by
position factor.
Object description:
Index 6065h
Name Following error window
Object code VAR
Data type UNSIGNED32
Category Optional
Page 73

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Entry description:
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value 0
Object 0x6066: Following error time out
When a following error occurs longer than the defined value of the timeout, given in
multiples of milliseconds, the corresponding bit 13 following error in the statusword is set
to 1. No further reaction is taken.
The Elmo drive setup parameter for position following error is ER[3]. When the
following error exceeds this value, the drive aborts the motion, the motor continues
to run through its own inertia and the DSP 402 status is “switch on disable.”
67
Object description:
Index 6066h
Name Following error time out
Object code VAR
Data type UNSIGNED16
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED16
Default value 0
Page 74

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Object 0x6067: Position window
This object defines a symmetrical range of accepted positions relative to the target
position. If the actual value of the position encoder is within the position window, this target
position is regarded as reached. Because the position window is usually specified in user-
defined units, the position factor must be used to transform this value into increments.
Before it can be used with this function, the target position must be handled in the same
manner as in the trajectory generator for limiting functions and transformation into
internal machine units.
The Elmo drive always checks the target position window in its own setup
parameters TR[1] and TR[2] at the real-time level. Therefore, the following points
must be taken into account:
The position error mechanism cannot be switched off.
The limits of the position window and the position window time (in internal units)
are 32,000 increments and 100 milliseconds, respectively.
Object description:
68
Index 6067h
Name Position window
Object code VAR
Data type UNSIGNED32
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value No
Object 0x6068: Position window time
When the actual position is within the position window during the defined position window
time — given in multiples of milliseconds — the corresponding bit 10 target reached in the
statusword is set to 1. Refer to the description in the position window object.
Object description:
Index 6068h
Name Position window time
Object code VAR
Data type UNSIGNED16
Category Optional
Page 75

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Entry description:
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED16 (note in object 6067h)
Default value 20
Object 0x60FC: Position demand value - increments
This output of the trajectory generator in profile position mode is an internal value using
increments.
Object description:
Index 60FCh
Name Position demand value - increments
69
Object code VAR
Data type INTEGER32
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read only
PDO mapping Yes
Value range INTEGER32
Default value 0
Page 76

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
11: Profiled Position
607Ah: Target position
607Bh: Position range limit
607Dh: Software position limit
607Fh: Maximum profile velocity
6081h: Profiled velocity
6082h: End velocity
6083h: Profiled acceleration
6084h: Profiled deceleration
6086h: Motion profile type
60C5h: Maximum acceleration
60C6h: Maximum deceleration
70
11.1 General Information
This chapter describes how to set a point-to-point (PTP) movement under a profiled
position where a target position is applied to the trajectory generator. It generates a
position demand value to the control loop. The trajectory generator input includes profiled
velocity, acceleration, deceleration, and selection of motion type, motion polarity and
stopping option. The inputs to the trajectory are given in user units and are limited
before being normalized to internal increments.
Notes:
Limits supported by the DSP 402 protocol may be submitted to internal limits
that protect the drive or support any previous behavior for compatibility
reasons.
The velocity, acceleration, deceleration is submitted to the limits according to
the relevant limit range.
C ontrolword of the profiled position mode:
Bit Function
0…3 Described in Device Control
4 Set new point
5 Change set immediately
6 Absolute/relative movement
7 Described in Device Control
8 Halt
9..12 Described in Device Control
13 New point is buffered
14..15 Described in Device Control
Page 77

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Name Value Description
0 Does not assume target position. New set-point
1 Assumes target position.
0 Finish actual positioning and then start next positioning. Change set
immediately
1 Interrupt actual positioning and start next positioning.
0 Target position is an absolute value. abs\rel
1 Target position is a relative value.
0 Execute positioning. Halt
1 Stop axle with profile acceleration.
0 New set point is not buffered. New buffered
point
1 New set point is buffered.
71
Statusword of the profiled position mode:
Bit Function
0…9 Described in Device Control
10 Target reached
11 Described in Device Control
12 Set new point acknowledge
13 Following error
12…15 Described in Device Control
Name Value Description
Target reached
0 Halt = 0: Target position not reached.
Halt = 1: Axle decelerates.
1 Halt = 0: Target position reached.
Halt = 1: Velocity of axle is 0.
Set new point
acknowledge
0 Trajectory generator has not assumed the
positioning values (yet).
1 Trajectory generator has assumed the
positioning values.
0 Following error
1 Following error.
Page 78

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
11.2 Objects
Object 0x607A: Target position
The target position is the position to which the drive should move in position profile
mode, using the current settings of motion control parameters such as velocity,
acceleration, deceleration and motion profile type. The target position is given in userdefined position units. It is converted to position increments using the position factor. The
target position is interpreted as absolute or relative, depending on the Abs/Rel flag in the
controlword.
Object description:
Index 607Ah
Name Profile target position
Object code VAR
Data type INTEGER32
72
Category Mandatory
Entry description:
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range INTEGER32
Default value No
Object 0x607B: Position range limit
This object contains two sub-parameters that limit the numerical range of the input value:
min position range limit and max position range limit. On reaching or exceeding these limits,
the input value automatically wraps to the other end of the range. Wrap-around of the
input value can be prevented by setting software position limits.
Notes:
The high position range limit and the low position range limit must be even.
This object cannot be set while in OPERATION ENABLE or QUICK STOP state.
Object description:
Index 607Bh
Name Position range limit
Object code ARRAY
Data type INTEGER32
Category Mandatory
Page 79

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Entry description:
Sub-index 0
Description Number of entries
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read only
PDO mapping No
Value range 2
Default value 2
Sub-index 1
Description Min position range limit
Entry category Mandatory
73
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range INTEGER32
Default value No
Sub-index 2
Description Max position range limit
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range INTEGER32
Default value No
The value of the position range limit is reflected in the XM[1] and XM[2] commands,
to which the range and restrictions are ultimately submitted (refer to the
SimplIQ
Command Reference Manual).
Page 80

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Object 0x607D: Software position limit
This object contains the sub-parameters min position limit and max position limit, which
define the absolute position limits for the position demand value and the position actual
value. Every new target position must be checked against these limits. The position limits
are specified in position units (same as target position) and are always relative to the
machine home position.
Before being compared with the target position, the position limit must be corrected
internally by the home offset, as follows:
Internal correct minimum position limit = min position limit - home offset
Internal corrected maximum position limit = max position limit - home offset
This calculation is performed when home offset or software position limit is changed.
Object description:
Index 607Dh
Name Software position limit
74
Object code ARRAY
Data type INTEGER32
Category Mandatory
Entry description:
Sub-index 0
Description Number of entries
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read only
PDO mapping No
Value range 2
Default value 2
Sub-index 1
Description Min position limit
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range INTEGER32
Default value No
Page 81

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Sub-index 2
Description Max position limit
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range INTEGER32
Default value No
The value of the software position limit is reflected in the VH[3] and VL[3]
commands, to which the range and restrictions are ultimately submitted (refer to
the
SimplIQ Command Reference Manual).
Object 0x607F: Max profile velocity
The max profile velocity is the maximum speed allowed in either direction during a
profiled move. It is given in the same units as profile velocity.
75
Object description:
Index 607Fh
Name Max profile velocity
Object code VAR
Data type UNSIGNED32
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value No
The value of this object is limited internally to the maximum allowed velocity
as reflected in VH[2] and VL[2].
Page 82

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Object 0x6081: Profile velocity
This object is the velocity normally attained at the end of the acceleration ramp during a
profiled move and is valid for both directions of motion. The profile velocity is given in
user-defined speed units. It is converted to position increments per second using the
velocity encoder factor.
Object description:
Index 6081h
Name Profile velocity
Object code VAR
Data type UNSIGNED32
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read/write
76
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value No
The value and default value of the profile velocity is reflected in the SP command, to
which the range and restrictions are ultimately submitted (refer to the
SimplIQ
Command Reference Manual).
Object 0x6082: End velocity (not yet implemented)
The end velocity defines the velocity required by the drive upon reaching the target
position. Normally, the drive stops at the target position; that is, the end velocity = 0. The
end velocity is given in the same units as profile velocity.
Object description:
Index 6082h
Name End velocity
Object code VAR
Data type UNSIGNED32
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value 0
Page 83

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Object 0x6083: Profile acceleration
The profile acceleration is given in user-defined acceleration units. It is converted to
position increments per second
2
using the normalizing factors.
Object description:
Index 6083h
Name Profile acceleration
Object code VAR
Data type UNSIGNED32
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
77
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value No
The value of the profile acceleration is reflected in the AC command, to which the
range and restrictions are ultimately submitted (refer to the
SimplIQ Command
Reference Manual).
Object 0x6084: Profile deceleration
The profile deceleration is given in the same units as profile acceleration. If the end velocity
(object 0x6082) is different than 0, this object is not valid and the profiled deceleration is
considered to be similar to the profiled acceleration.
Object description:
Index 6084h
Name Profile deceleration
Object code VAR
Data type UNSIGNED32
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value No
Page 84

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
The value of the profile deceleration is reflected in the DC command, to which the
range and restrictions are ultimately submitted (refer to the
SimplIQ Command
Reference Manual).
Object 0x6085: Quick stop deceleration
The quick stop deceleration is the deceleration used to stop the motor if the Quick Stop
command is given and the quick stop option code (see 605Ah) is set to 2. The quick stop
deceleration is given in the same units as the profile acceleration.
Object description:
Index 6085h
Name Quick stop deceleration
Object code VAR
Data type UNSIGNED32
78
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value 0
Object 0x6086: Motion profile type
This object is used to select the type of motion profile used to perform a profile move.
Object description:
Index 6086h
Name Motion profile type
Object code VAR
Data type INTEGER16
Category Mandatory
Entry description:
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range INTEGER16
Default value 0
Page 85

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Data description:
Value Description
-32,768…-1 Manufacturer specific
0 Linear ramp (trapezoidal profile)
1 Not supported
2 Not supported
3 Not supported
4…32,767 Reserved
11.3 Functional Description
Two different means of applying target positions to a drive are supported by this device
profile:
79
Set of set-points:
After reaching the target position, the drive unit immediately processes the next target
position that results in a move in which the velocity of the drive is not normally
reduced to zero after achieving a set-point.
Single set-point:
After reaching the target position, the drive unit signals this status to a host computer
and then receives a new set-point. After reaching a target position, the velocity is
normally reduced to zero before starting a move to the next set-point.
The two modes are controlled by the timing of the bits “new set-point” and “change set
immediately” in the controlword, and “set-point acknowledge” in the statusword. These bits
allow a request-response mechanism to be set up in order to prepare a set of set-points
while another set is still being processed in the drive unit. This minimizes reaction times
within a control program on a host computer.
The Elmo drive introduces a buffered mode (bit 13 in the controlword), in which up to 16
subsequent profiled motions can be programmed. The programmed profiles are executed
when the previous motion is target reached. In buffered motion, set-point acknowledge
behaves in a manner similar to non-buffered mode, whereby the bit is reset when new
data can be buffered. Using change set immediately interrupts the buffered motion. In this
case, the buffer is reset and the last programmed motion is executed immediately.
The sequence of a set new point is:
1. The host sends the trajectory data and validates it by setting the new set point.
2. The Elmo drive acknowledges reception and buffering of the new data by setting
set-point acknowledge.
3. The host sends a command to start the first motion by resetting the new set point.
4. The motion begins. If the drive can accept more set points, the set-point acknowledge
resets.
Page 86

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
5. Unless it was interrupted by a change set immediately, the next trajectory is executed
as soon as a target reached is set.
Notes:
A target position can be programmed at any status but can be executed only in
ENABLE OPERATION state. Otherwise, an emergency message is transmitted.
The amount of buffered data can be received by object 0x2F15.
80
Page 87

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
12: Interpolated Position
60C0h: Interpolation sub mode select
60C1h: Interpolation data record
60C2h: Interpolation time period
60C3h: Interpolation sync definition
60C4h: Interpolation data configuration
12.1 General Information
Interpolated Position mode is used to control multiple coordinated axles or a single axle
with the need for time-interpolation of set-point data. The mode normally uses time
synchronization mechanisms like the sync object for a time coordination of the related
drive units.
81
The interpolation data record contains the interpolation data; the data type and the data
size of the sub-indices of this structure are according to the sub-mode, as described in
object 0x60C0. For all cases of motion, the interpolation cycle time is defined by the object
interpolation time period. Time synchronization can be performed by the Sync message
defined in DS301 (refer to the Elmo CANopen Implementation Guide).
Interpolated Position mode allows a host controller to transmit a stream of interpolation
data with an explicit time reference to the drive. The Elmo drive supports an input buffer
that allows the interpolation data to be sent in bursts rather than continuously in real
time. The actually available and the maximum size of the input buffer can be requested
by the host using the interpolation data configuration. The buffer size is the number of
interpolation data records that may be sent to a drive to fill the input buffer; it is not the size
in bytes.
The interpolation algorithm is defined in the interpolation sub mode select. Linear
interpolation is the default interpolation method. For each interpolation cycle, the drive
calculates a position demand value by interpolating interpolation data over a period of
time.
Limit functions of speed acceleration deceleration and position are applied to the
interpolation data.
Internal states
The interpolated position mode is controlled by the bits of the controlword and statusword
.
Page 88

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
82
Interpolation inactive
The state entered when the device is in OPERATION ENABLED state and
Interpolated Position mode is selected and displayed (object 0x6061). The drive unit
accepts input data and buffers it for interpolation calculations, but does not move the
axles.
Interpolation active
The state entered when the device is in OPERATION ENABLED state, the
interpolated position mode is selected and it is enabled. The drive unit accepts input
data and moves the axles.
Buffer reset
Buffer points start from the first entry. The interpolation buffer is reset in the
following cases:
Entering Interpolated Position mode
Modifying Interpolation sub-mode.
Entering INTERPOLATION INACTIVE state
Setting buffer clear state in object 0x60C4
Motion is halted
Page 89

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Controlword of Interpolated Position mode:
Name Value Description
0 Interpolated position mode is inactive. Enable ip mode
1 Interpolated position mode is active.
0 Execute the instruction of bit 4. Halt
1 Stop axle according to halt option code.
Notes:
If the interpolation is interrupted by setting bit 4 from 1 to 0, the drive stops at
quick stop deceleration (object 0x6085) and is treated similarly to axis halted. In this
case, the buffer is cleared; that is, the actual buffer size is the maximum buffer
size.
Setting bit 4 to 1 always starts the interpolation from the first data record. It is up
to the user to ensure consistency of the trajectory.
83
In case of a Halt, the drive stops the interpolation and stops the motor according
to object 0x605D. This case is treated similarly to interpolation interrupted
described previously.
In case the motor is stopped due to an internal fault or controlword command, the
interpolation is disabled, even if bit 4 is 1. Interpolation can be enabled again
only after the device enters the OPERATION_ENABLE state and bit 4 is set to 1.
Statusword of Interpolated Position mode:
Bit Function
0…9 Described in Device Control
10 Target reached
11 Described in Device Control
12 Ip mode active.
13 Reserved
14…15 Described in Device Control
Name Value Description
Target reached
0
Halt = 0: Position not reached.
Halt = 1: Axle decelerates.
1
Halt = 0: Position reached.
Halt = 1: Velocity of axle is 0.
0 Interpolation mode not active. IP mode active
1 Interpolation mode active.
Setting bit 4 from 0 to 1 starts the interpolation from the first entry of the interpolation
buffer.
Page 90

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
12.2 Objects
Object 0x60C0: Interpolation sub mode select
This object reflects or changes the actual chosen interpolation mode, selected by the user.
The interpolation sub-modes can be changed only when the interpolated mode is
inactive.
When modifying the interpolation mode, a new mapping (if needed) of object 0x60C1
must be made after the sub mode is modified. Failing to do so may cause unpredictable
results.
Object description:
Index 60C0h
Name Interpolated sub mode select
Object code VAR
84
Data type INTEGER16
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read/write
PDO mapping No
Value range -1...0
Default value 0 (linear interpolation)
Data description:
Value Description
-32768..-2 Reserved
-1 Cubic spline (PV)
0 Linear interpolation
1…32767 Reserved
For more details, refer to section Error! Reference source not found.
Page 91

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Object 0x60C1: Interpolation data record
This object is the data words, which are necessary for performing the interpolation
algorithm. The interpretation of the data words may vary with the different possible
interpolation modes as set by 60C0h.
Object description:
Index 60C1h
Name Interpolation data record
Object code ARRAY
Data type 60C0h = -1 : DSP402 PV data record (0x44)
60C0h = 0 : INTEGER32
60C0h > 0 : not defined
Category Optional
Entry description:
85
Sub-index 0
Description Number of entries
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read only
PDO mapping Yes
Value range 1
Default value 1
Sub-index 1
Description Parameter of the IP function
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read/Write
PDO mapping Yes
Value range 60C0h = -1 : DSP 402 PV data record
(0x44)
60C0h = 0 : INTEGER32
60C0h > 0 : not defined
Default value No
Page 92

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Object 0x60C2: Interpolation time period
This object is used to define the relative time taken between two set points for the
interpolation position modes. The interpolation time unit is given in 10
interpolation time index
seconds.
The interpolation time period can be changed only when the interpolated mode is
inactive.
Object description:
Index 60C2h
Name Interpolation time period
Object code RECORD
Data type Interpolation time period (object 0x80)
Category Optional
Entry description:
Sub-index 0
Description Number of entries
86
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read only
PDO mapping Yes
Value range 2
Default value 2
Sub-index 1
Description Interpolation time unit
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read/Write
PDO mapping Yes
Value range 1..255 msec
Default value 1
Sub-index 2
Description Interpolation time index
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read only
PDO mapping No
Value range -3 , -4 (refer to Appendix B)
Default value -3
The interpolated time period is always in milliseconds (10
sub-index 2, Interpolation time index.
-3
seconds) regardless of
Page 93

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Object 0x60C3: Interpolation sync definition
Devices in the interpolation position mode often interact with other devices. Therefore it
is necessary to define a communication object, which is used to synchronize these
interactions. This can be done by the general Sync as described in /3/, or a specific
group-sync-signal. Each reception of this trigger-signal or a specified number of
occurrences of the trigger-signal can synchronize the devices.
Description of synchronize on group:
Value Description
0 General Sync is used
1…255 Reserved
Object description:
Index 60C3h
Name Interpolation sync definition
Object code ARRAY
Data type UNSIGNED8
Category Optional
87
Entry description:
Sub-index 0
Description Number of entries
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read only
PDO mapping No
Value range 2
Default value 2
Sub-index 1
Description Synchronize on group
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read only
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED8
Default value 0
Sub-index 2
Description IP sync every n event
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read/Write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED8
Default value 1
Page 94

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Object 0x60C4: Interpolation data configuration
The interpolation data configuration enables the user to get information about the buffer
size and set the buffer configuration and strategy.
Type of buffer organization:
Value Description
0 FIFO buffer
1 Ring buffer
2…255 Reserved
Description of buffer clear values:
Value Description
0
Clear input buffer
Access disabled
Clear all Ip data records
1
Enable access to input buffer for drive
functions
2…255 Reserved
88
Object description:
Index 60C4h
Name Interpolated data configuration
Object code RECORD
Data type Interpolated data configuration record
(object 0x81)
Category Optional
Entry description:
Access Read/Write
PDO mapping Yes
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value No
Sub-index 0
Description Number of entries
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read only
PDO mapping No
Value range 6
Default value 6
Page 95

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Sub-index 1
Description Maximum buffer size
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read only
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value 1
Sub-index 2
Description Actual buffer size
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read/Write
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED32
Default value 0
Sub-index 3
Description Buffer organization
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read/Write
PDO mapping No
Value range 0…1 (described on following pages)
Default value 0
Sub-index 4
Description Buffer position
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read/Write
PDO mapping Yes
Value range UNSIGNED16
Default value 1
Sub-index 5
Description Size of data record
Entry category Mandatory
Access Read only
PDO mapping No
Value range
60C0h = -1 : 8 bytes
60C0h = 0: 4 bytes
Default value INTEGER32
89
Page 96

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
Sub-index 6
Description Buffer clear
Entry category Mandatory
Access Write only
PDO mapping No
Value range UNSIGNED8 (described below)
Default value 0
Notes:
The maximum and actual buffer size are the number of interpolated data records
that may be sent to the drive to fill the input buffer. They are not the size in
bytes. The actual buffer size may be between max buffer size to.
The buffer position has an effect when the ring buffer is selected.
The buffer organization may change only when interpolated mode is not active.
Reorganization of the buffer clears the input buffer.
90
Buffer can be clear by sub-index 6 only if interpolation is not active.
Buffer strategies
The contents of the buffer items can only be accessed via the interpolation data record. The
maximum buffer size is given in object 0x60C4 is used by the host to determine the actual
buffer size.
Commonly, first-in-first-out (FIFO) structures or ring buffers are used as input buffers.
FIFO:
If the buffer is organized as FIFO, every new received interpolation data record is
placed at the end of the queue, and the drive takes the next data record from the top
of the queue. When the last item of a data record is stored, the buffer pointer is
incremented in order to point to the next buffer position. With this buffer principle,
the object buffer position has no affect. The FIFO buffer is organized as a cyclic buffer
so that after the last buffer entry is updated (entry of max buffer size), the first entry
may be available again depending on actual buffer size. When the buffer is full, an
emergency is transmitted and the last message is discarded.
If buffer is empty interpolation is disabled and emergency may be transmitted if
o CANopen Implementation Guide). defined so by object 0x2F21 (refer to the Elm
Ring buffer:
If the buffer is structured as a ring, the host can place an interpolation data record into
any valid position in the ring by changing the pointer defined in buffer position.
Without changing the buffer position, all data records are written at the same location.
The drive reads the next entry out of the buffer by an internal ring pointer. It is set to
the first data record with buffer clear, after the reorganization of the input buffer. The
user cannot exceed the max buffer
Page 97

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
∆
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
12.3 Functional Description
In Interpolated Position mode, the drive executes a time-synchronized motion path. The
user specifies the value of the reference signal at an initial time, and at fixed-time
intervals from then on (as in the following figure).
P4
P3
P1
P0
P2
T∆ T∆ T∆ T∆
91
TimeT sta rt
Figure 9: Interpolated Motion
is set by the object 0x60c2, in milliseconds. The data
In the figure, the time interval
T∆
records P0,P1,P2,… (object 0x60C1) to define the motion path data relating to the times
,,2
TT T+∆ + ∆,...
start start start
The motion path is synchronized to the CAN microsecond timer, as set and corrected by
the SYNC-Time stamp mechanism.
The user must specify the data records P0,P1,P2,…fast enough – at an average rate of at
least one record per
T
. The drive can store up to 64 records, so that the path may be
programmed in bursts in order to relax the feeding real-time requirements.
In order to enter IP mode, use the controlword (0x6040) to start the motor, and then use
the modes of operation(0x6060) object to select IP mode.
You can monitor the mode using the statusword (0x6041) and modes of operation display
(0x6061).
The interpolation sub-mode in object 0x60C0 determines the type of interpolation
performed.
The Elmo drive supports two types of interpolation:
Linear interpolation (default)
Cubic spline interpolation
The structure of the 0x60C1 object depends on the interpolation sub-modes. Refer to the
definition of 0x60C1 to learn more about sub-mode switching.
Page 98

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
12.3.1 Linear Interpolation
Linear interpolation requires only the position specified in data record object 0x60C1. The
structure of the position data is according to data type 0x41 (refer to the Elmo CANopen
Implementation Guide). The velocity at each time point is calculated by finding the
difference between the corresponding position and the position of the previous point, as
in the following figure.
P3
92
P0
P1
P2
T∆ T∆ T∆ T∆
T sta rt
Figure 10: Linear IP
In the linear interpolation, two set points can be given in one message and thereby save
on busload and real time requirements.
12.3.2 Spline Interpolation
In cubic spline interpolation, the user specifies both the position and the speed at each
time point. The record data type is 0x44 (refer to the Elmo CANopen Implementation
Guide). The drive constructs the motion path to be at the given time, at the given position,
with the given speed, as in the following figure. Spline interpolation can yield a more
accurate path specification with fewer time points, but it requires the care in constructing
the speed data.
Time
P1
P0
T∆ T∆ T∆ T∆
T sta rt
Figure 11: Spline IP
Time
P3
P2
Page 99

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
12.3.3 Motion Synchronization
The IP mode enables the synchronized motion of multiple axes. The motions of several
slave axes are synchronized if they all run IP, and they all being the IP at the same time.
Synchronization can proceed continuously using the SYNC-Time stamp mechanism.
In order to start several axes synchronously, map the controlword to a synchronous RPDO,
and then use the mapped controlword to enable interpolation for all axes. Nothing will
happen until the next SYNC. Then, all drives will enable interpolated motion at once,
setting the SYNC arrival time as the “zero” time of the path specification.
If the axes have been previously synchronized by SYNCs and Time stamps, the moving
axes will be relatively synchronized to the precision of microseconds.
93
Page 100

CANopen DSP 402 Implementation Guide
MAN-CAN402IG (Ver. 1.2)
13: Profiled Velocity
6069h: Velocity sensor actual value
6060h: Velocity window
606Ah: Sensor selection code
606Bh: Velocity demand value
606Ch: Velocity actual value
606Dh: Velocity window
606Eh: Velocity window time
606Fh: Velocity threshold
6070h: Velocity threshold time
60FFh: Target velocity
94
13.1 General Information
Profile Velocity mode includes the following sub-functions:
Demand value input via trajectory generator
Velocity capture using the position sensor or velocity sensor
Velocity control function with the appropriate input and output signals
Monitoring of the profile velocity using a window function
Monitoring of the velocity actual value using a threshold
The input parameters of the reference value generator are:
Profile velocity
Profile acceleration
Profile deceleration
Emergency stop
Motion profile type
These parameters and the operation of the reference value generator are described in
section
The velocity controller calculates a torque variable. When a different target position
arrives, it is executed immediately.
11:.
Notes:
A target velocity can be executed only in OPERATION ENABLED state.
Otherwise, the process aborts with an emergency message.
The velocity, acceleration and deceleration are submitted to the limits according
to the relevant limit range.
 Loading...
Loading...