Page 1

LonScanner™ FX Protocol
Analyzer User’s Guide
078-0305-01B
Page 2

Echelon, i.LON, LNS, LonMaker, LONMARK, LonTalk, LON WORKS,
Neuron, NodeBuilder, and the Echelon logo are trademarks
of Echelon Corporation registered in the United States and
other countries. LonScanner is a trademark of the Ech elon
Corporation.
Other brand and product names are trademarks or
registered trademarks of their respective holders.
Neuron Chips and other OEM Products were not designed
for use in equipment or systems, which involve danger to
human health or safety, or a risk of property damage and
Echelon assumes no responsibility or liability for use of the
Neuron Chips in such applications.
Parts manufactured by vendors other than Echelon and
referenced in this document have been described for
illustrative purposes only, and may not have been tested
by Echelon. It is the responsibility of the customer to
determine the suitability of these parts for each
application.
ECHELON MAKES AND YOU RECEIVE NO WARRANTIES OR
CONDITIONS, EXPRESS, IMPLIED, STATUTORY OR IN ANY
COMMUNICATION WITH YOU, AND ECHELON SP ECIFICALLY
DISCLAIMS A N Y IMPLIED WARR A N T Y O F M ER C H ANTABILITY
OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a
retrieval s ystem, or transmitted, in any form or by any means,
electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or
otherwise, without the prior written permission of Echelon
Corporation.
Printed in the United States of America.
Copyright © 1994, 2010 Echelon Corporation.
Echelon Corporation
www.echelon.com
Page 3
Welcome
The Echelon® LonScanner™ Protocol Analyzer is a software tool that you can use
to monitor, analyze, and diagnose the behavior of L
LonScanner Protocol Analyzer connects to IP-852 (ISO/IEC 14908-4) and native
ONWORKS (ISO/IEC 14908-1) channels, collects packets from those channels,
L
and stores information from the packets into log files. You can use the log files to
inspect and interpret the collected packets.
You can monitor up to 10 channels at once with the protocol analyzer. You can
view the logs created for each channel (called active logs) while the protocol
analyzer is monitoring the channel and collecting packets, and you can take
advantage of the filtering and statistical features that the tool provides to gather
the information that you want. You can also view logs that you have saved to
diagnose network problems that occurred when the log was created.
Audience
This document assumes that the reader has a good understanding of the
ONWORKS platform and of general analysis for network communications.
L
What’s New for LonScanner FX
The LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer is part of the LONWORKS 2.0 product
family. The LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer adds the following features to
those provided by Release 3 of the LonScanner Protocol Analyzer:
ONWORKS
®
networks. The
®
• Runs on Microsoft
2008. The LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer is designed for the 32-bit
versions of Windows, but is compatible with the x64 Editions.
• Provides multiuser licensing options.
Windows® 7, Windows Vista®, and Windows Server
Related Documentation
The following manuals are available from the Echelon Web site
www.echelon.com/docs) for products that are commonly used with the
(
LonScanner Protocol Analyzer:
i.LON SmartServer 2.0 User's Guide
•
describes how to configure the
applications to monitor and manage control networks.
Introduction to the LONW
•
provides an introduction to the ISO/IEC 14908-1 (ANSI/CEA-709.1 and
EN14908) Control Network Protocol, and provides a high-level
introduction to L
are used for developing, installing, operating, and maintaining them.
IP-852 Channel User's Guide
•
information you will need when creating an IP-852 channel with an
i
.LON SmartServer, i.LON 100 Internet Server, i.LON 600 LONWORKS/IP
Server, or an LNS Server. This includes instructions you can follow when
ONWORKS networks and the tools and components that
(078-0345-01E). This manual
i
.LON SmartServer and use its
ORKS
Platform
(078-0312-01A). This manual provides
(078-0183-01B). This manual
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide iii
Page 4

configuring the IP-852 channel with the Echelon L
ONWORKS/IP
Configuration Server, and guidelines to follow when using NAT, DNS, or
DHCP on the IP-852 channel.
LNS Programmer's Guide
•
(078-0177-01F). This manual describes how to
write LNS applications.
LonMaker User's Guide
•
(078-0333-01A). This manual describes how to
use the LonMaker Integration Tool to design, commission, monitor and
control, maintain, and manage a network.
•
LONM
®
ARK
Application Layer Interoperability Guidelines.
This manual
describes design guidelines for developing applications for open
interoperable L
Web site,
LONW
•
ORKS
ONWORKS devices, and is available from the LONMARK
www.lonmark.org.
PCC-10 PC Card User's Guide
(078-0155-01B). This manual
provides an overview of the PCC-10 card and software, including
installation details and configuration options. For developers and end
users of L
LONW
•
ONWORKS systems using the PCC-10 card.
ORKS
PCLTA-20 PCI LonTalk Adapter User's Guide
(078-017901C). This manual provides detailed technical specifications on the
electrical and mechanical interfaces and operating environment
characteristics for the PCLTA-20 adapter.
LONW
ORKS
•
PCLTA-21 PCI Interface User's Guide
(078-0271-01A). This
manual describes the mechanical characteristics and the hardware and
software driver installation for the Echelon PCLTA-21 Interface (Models
74501, 74502, 74503, 74504, and 74505).
LONW
ORKS
•
USB Network Interface User's Guide
(078-0296-01B). This
manual describes how to install and use Echelon's U10 and U20 USB
Network Interface products. The USB Network Interfaces are miniature,
high performance network interfaces that provide network connection
between USB-enabled PCs and Free Topology (TP/FT-10) or C-Band
Power Line (PL-20C or PL-20N) L
ONWORKS channels. The interfaces are
provided through a v1.1 and v2.0 compliant USB connection.
Mini FX User’s Guide
•
(078-0398-01A). This manual describes how to use
the Mini FX Evaluation Kit. You can use the Mini kit to develop a
prototype or production control system that requires networking, or to
evaluate the development of applications for such control networks using
ONWORKS platform.
the L
NodeBuilder® FX User’s Guide
•
how to develop a L
ShortStack FX User's Guide
•
ONWORKS device using the NodeBuilder tool.
to develop an application for a L
®
ShortStack
FX Micro Server. It describes the architecture of a
(078-0405-01A). This manual describes
(078-0365-01B). This manual describes how
ONWORKS device using Echelon’s
ShortStack device and how to develop a ShortStack device.
®
All of the Echelon documentation is available in Adobe
PDF format. To view the
PDF files, you must have a current version of the Adobe Reader
download from Adobe at:
www.adobe.com/products/acrobat/readstep2.html.
®
, which you can
iv
Page 5

Table of Contents
Welcome.........................................................................................................iii
Audience ........................................................................................................iii
What’s New for LonScanner FX...................................................................iii
Related Documentation ................................................................................iii
Chapter 1. Introduction to the LonScanner Protocol Analyzer........................ 1
Introduction.................................................................................................... 2
Software Requirements .................................................................................2
Installing the LonScanner Software............................................................. 2
Updating LonScanner 3.................................................................................3
Activating the LonScanner Software............................................................ 3
Transferring a LonScanner Activation ..................................................5
Viewing Activation Status ......................................................................7
Using the LonScanner Protocol Analyzer..................................................... 7
Monitoring a Network Channel.............................................................. 8
Opening an Existing Packet Log ............................................................ 9
Log Files Overview .................................................................................. 9
Using the LonScanner Window ............................................................ 11
LonScanner Menus .........................................................................11
LonScanner Toolbar........................................................................ 12
LonScanner Status Bar ..................................................................13
Using LonScanner with LNS Turbo Edition .............................................. 13
Chapter 2. Logging Data.................................................................................. 15
Configuring the LonScanner Protocol Analyzer ........................................ 16
Setting Logging Preferences ................................................................. 16
Filtering Packets ...................................................................................17
Configuring the Global and Device Filters....................................18
Importing Filter Settings from a Channel ....................................21
Saving Filter Settings for Later Use ............................................. 21
Setting the Capture and Monitor Modes ............................................. 22
Viewing Channel Statistics and Trend Graphs .........................................22
Viewing General Statistics ................................................................... 23
Viewing Bandwidth Utilization by Packet Type .................................24
Viewing Bandwidth Utilization History ..............................................24
Viewing Error Rate History .................................................................. 25
Setting Statistics Options ..................................................................... 26
Using Names ................................................................................................ 29
Importing Names...................................................................................30
Importing Names from an LNS Database..................................... 30
Importing Names from a Local Names File .................................. 34
Importing Names from a Channel ................................................. 35
Creating and Customizing Names ....................................................... 36
Creating Group Names...................................................................36
Creating Device Names .................................................................. 37
Creating Message Code Names...................................................... 38
Creating Domain Names ................................................................ 39
Managing Names Files.......................................................................... 41
Chapter 3. Analyzing Packet Log Details ....................................................... 43
Searching For Packet Log Entries .............................................................. 44
Searching By String ..............................................................................44
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide v
Page 6

Searching By Log Number .................................................................... 45
Bookmarking Packet Log Entries ............................................................... 45
Formatting the Packet Log.......................................................................... 47
Selecting Data Fields ............................................................................47
Formatting Data Field Columns ..........................................................48
Color-Coding the Packet Log ................................................................49
Printing Log Files ........................................................................................50
Exporting Log Files...................................................................................... 51
Chapter 4. Example Logs................................................................................. 53
Example Packet Logs...................................................................................54
Sample 1: Channel without Assigned Names...................................... 54
Sample 2: Channel with Names Imported from an LNS Database ... 55
Appendix A. Network Interfaces ..................................................................... 59
Network Interfaces Overview...................................................................... 60
PCC-10 and PCLTA-20/21 ....................................................................61
Appendix B. LonScanner FX Software License Agreement ........................... 63
vi
Page 7

1
Introduction to the LonScanner
Protocol Analyzer
This chapter introduces the LonScanner Protocol Analyzer.
It describes how to install and activate the LonScanner
software, and how to get started with the protocol analyzer.
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 1
Page 8

Introduction
The LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer is a software tool that you can use to
monitor, analyze, and diagnose the behavior of L
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer connects to IP-852 (ISO/IEC 14908-4) and
native ISO/IEC 14908-1 channels, collects packets from those channels, and
stores information from the packets into log files. You can use the log files to
inspect and interpret the collected packets.
You can monitor up to 10 channels at once with the protocol analyzer. You can
view the logs created for each channel (called active logs) while the protocol
analyzer is monitoring the channel and collecting packets, and you can take
advantage of the filtering and statistical features that the tool provides to gather
the information that you want. You can also view logs that you have saved to
diagnose network problems that occurred when the log was created.
ONWORKS networks. The
This manual refers to both IP-852 (ISO/IEC 14908-4) and L
channels as
channels, such as TP/FT-10 and PL-20 channels, as
IP-852 channels
. This manual refers to native ISO/IEC 14908-1
LONW
Software Requirements
To install and use the LonScanner software, your computer must meet the
following minimum requirements:
®
• Intel
• 128 MB RAM
• 32-bit version of Windows 7, Windows Vista, or Windows Server 2008
• 10 MB of available hard-disk space
• 1024x768 screen resolution
Pentium® III 800 MHz processor
Installing the LonScanner Software
To install the LonScanner software:
1. Start the installation program for the LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer by
performing one of the following steps:
ONWORKS/IP
ORKS
channels
.
a. Insert the Echelon LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer CD into a CD-
ROM or DVD-ROM drive. If the installation does not automatically
start after a few seconds, start the program manually. You can
start the installation by clicking the Windows Start button, clicking
Run, browsing to the setup application, and then clicking Open.
The main LonScanner installation window opens.
b. Double-click the LonScannerFX.exe file that you downloaded from
the Echelon Web site.
2. Click Install Products to continue. The Install Products window opens.
2 Introduction to the LonScanner Protocol Analyzer
Page 9

3. Click LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer to continue. The Welcome window
opens.
4. Click Next to continue. The License Agreement window opens.
5. Read the terms of the
agreement. If you agree to the terms of the license agreement, click I
Accept the Terms in the License Agreement. The User window opens.
Note: The LonScanner software license is included in this document as
B,
Appendix
Agreement
6. Enter your user name, organization and product serial number. Click Next
to continue.
7. If the L
prompt you to choose this path. You can change this setting as long as you
have not previously installed any other Echelon or L
OK to select the path.
8. On the next dialog, click Install to begin the installation. When the
installation has completed, a completion dialog appears.
You can also install the Adobe Reader or the NodeBuilder
software from the Install Products dialog (see step
SmartServer,
the U10 and U20 USB Network Interfaces are included with the main
LonScanner software installation.
You can use the NodeBuilder Resource Editor to browse the network variable
types available on your computer when configuring device names with the
protocol analyzer, as described in Chapter
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer Software License
, on page 63.
ONWORKS path has not been set for your computer, a dialog opens to
i.
LON 100 Internet Server, i.LON 600 LONWORKS/IP Server, and
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer software license
ONMARK software. Click
®
Resource Editor
2). Drivers for the i.LON
2,
Logging Data
, on page 15.
Updating LonScanner 3
You can install the LonScanner FX software over an existing LonScanner 3
installation by following the procedure described in
Software
FX software will automatically be activated. If you used the LonScanner 3 LNS
Turbo Edition, an LNS Turbo Server is still required to use the LonScanner FX
software. If you had the LonScanner 3 Professional Edition, an LNS Turbo
Server is not required, but can be used. If you had the LonScanner 3 Demo
Edition, you will have a LonScanner FX Demo Edition.
on page 2. If you activated the LonScanner 3 software, the LonScanner
Installing the LonScanner
Activating the LonScanner Software
After a successful installation, the protocol analyzer runs in demonstration mode
until you activate it. When operating in demonstration mode, the LonScanner
License Activation dialog (shown in
start the protocol analyzer.
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 3
Figure 1 on page 4) appears each time you
Page 10
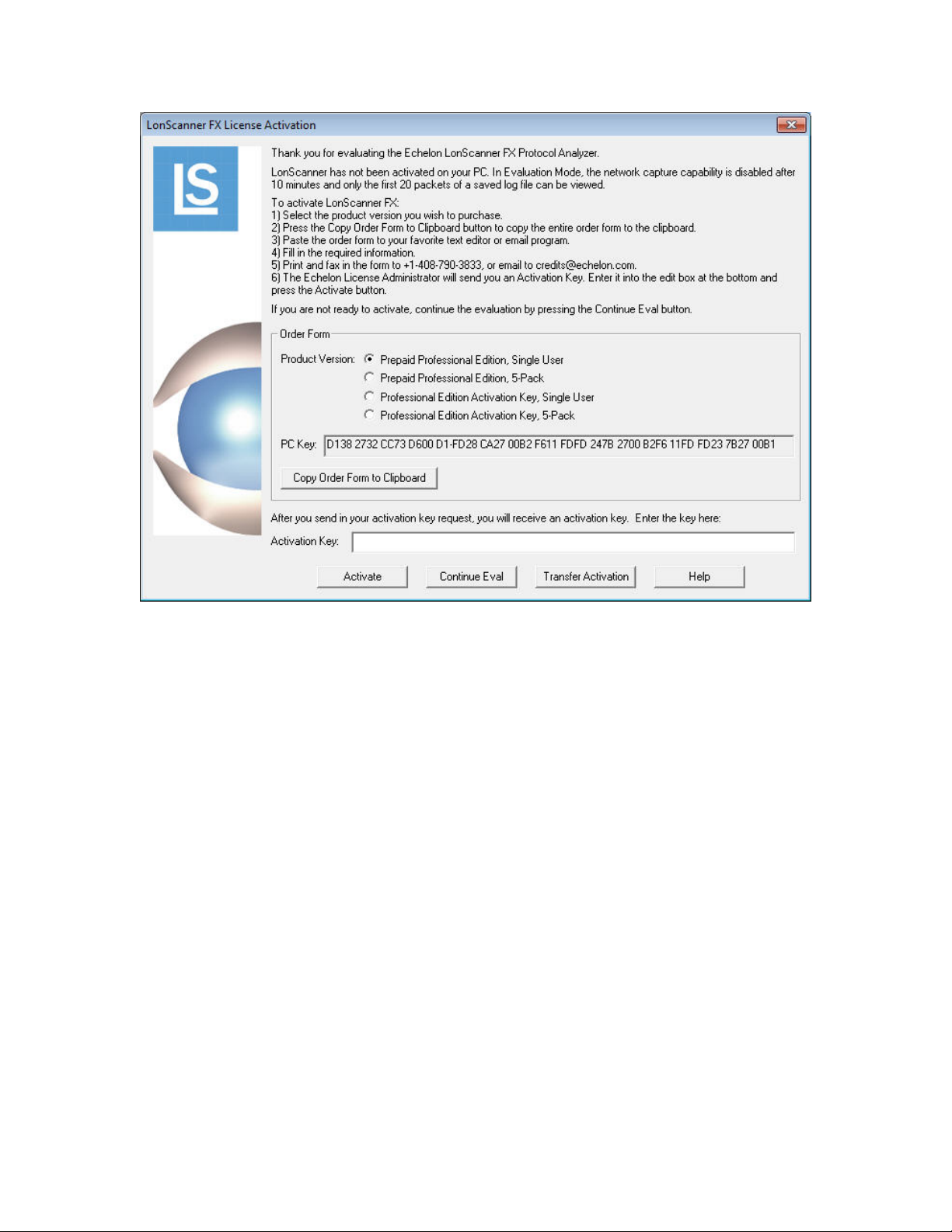
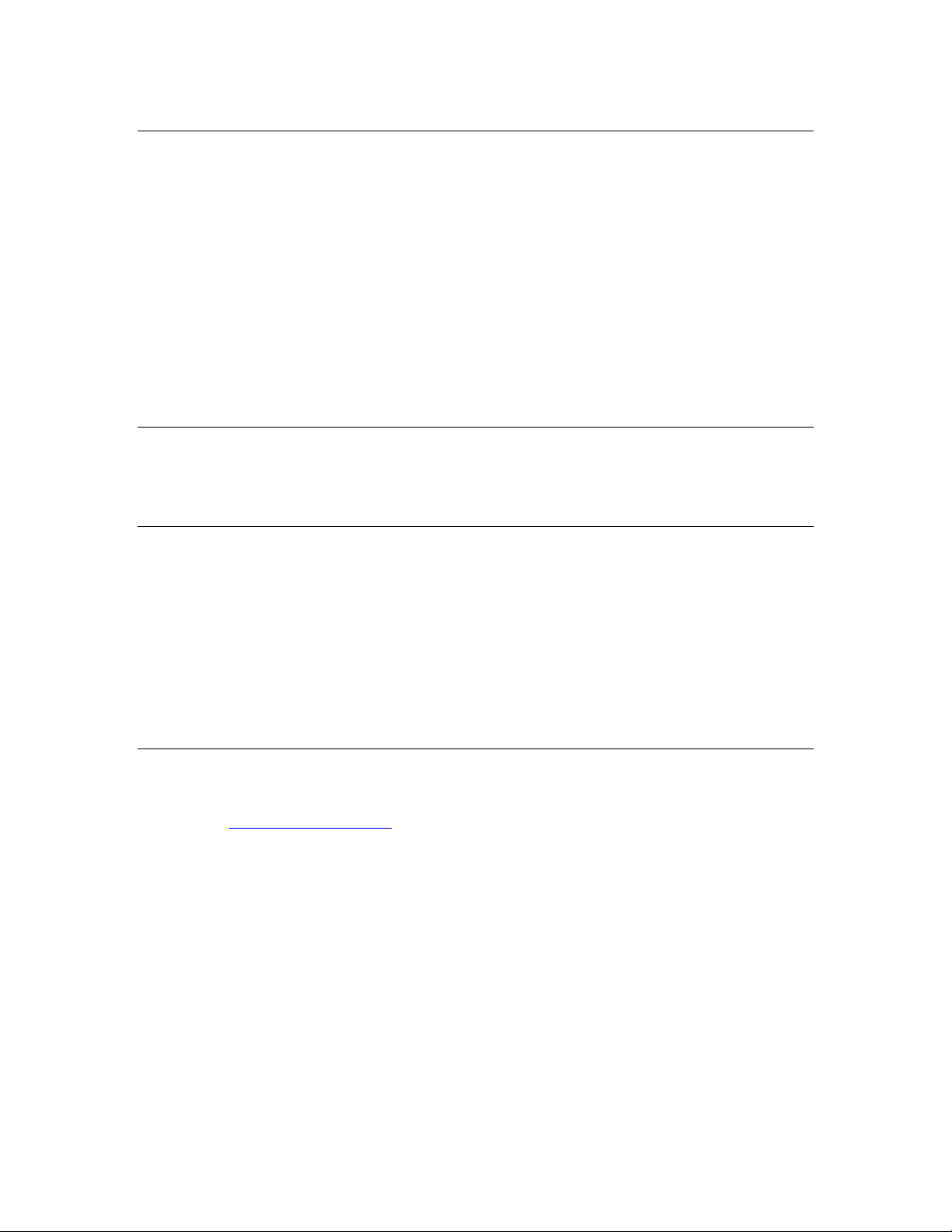
Figure 1. LonScanner License Activation Dialog
To continue running in demonstration mode, click Continue Eval. When
operating in demonstration mode, the protocol analyzer does not display every
captured packet and displays only the first 20 packets of a saved or imported log
file. After you activate the product, you will have access to all LonScanner
features.
If you choose to operate in demonstration mode, the LonScanner License
Activation dialog appears every time you open the protocol analyzer. You can
also access the LonScanner License Activation dialog and activate the
LonScanner software while running in demonstration mode by selecting Help →
Activate Product → Activate.
To activate the protocol analyzer from the LonScanner License Activation dialog,
select a product version from the list:
• Select Prepaid Professional Edition, Single User if you purchased a Model
33110-401 LonScanner FX Professional Edition with prepaid key. You
must supply the serial number supplied with your prepaid edition for
either of the prepaid editions.
• Select Prepaid Professional Edition, 5-Pack if you purchased a Model
33110-403 LonScanner FX Professional Edition with five prepaid keys.
You must supply the serial number supplied with your prepaid edition for
either of the prepaid editions. Repeat the activation process on up to five
primary computers and up to five secondary computers.
4 Introduction to the LonScanner Protocol Analyzer
Page 11

• Select Professional Edition Activation Key, Single User if you do not have
a prepaid key, and you are ordering a single activation key. You can use
this option to activate a LonScanner FX Demo Edition or to add an
additional user for a LonScanner FX Professional Edition.
• Select Professional Edition Activation Key, 5-Pack if you do not have a
prepaid key, and you are ordering a 5-pack with five activation keys. You
must repeat the activation process on up to five primary computers and
up to five secondary computers. You can use this option to either activate
a LonScanner FX Demo Edition on up to five computers or to add up to
five additional users for a LonScanner FX Professional Edition.
After you select a product version, click Copy Order Form to Clipboard. Paste the
order form that is copied to an e-mail message or text editor document, fill in the
blanks on the form, and then e-mail or fax the request to Echelon, using the email address or fax number on the form. Echelon will process the request and
send you an activation key.
After you receive the activation key, enter it in the Activation Key field, and click
Activate to activate the software.
Transferring a LonScanner Activation
You can transfer your LonScanner activation to another computer. This process
deactivates the protocol analyzer on your original computer, and then activates it
on the new computer.
To transfer activation, perform the following steps:
1. Select Help → Activate Product → Transfer Activation. The Transfer
Activation Wizard opens, as shown in
Figure 2 on page 6.
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 5
Page 12
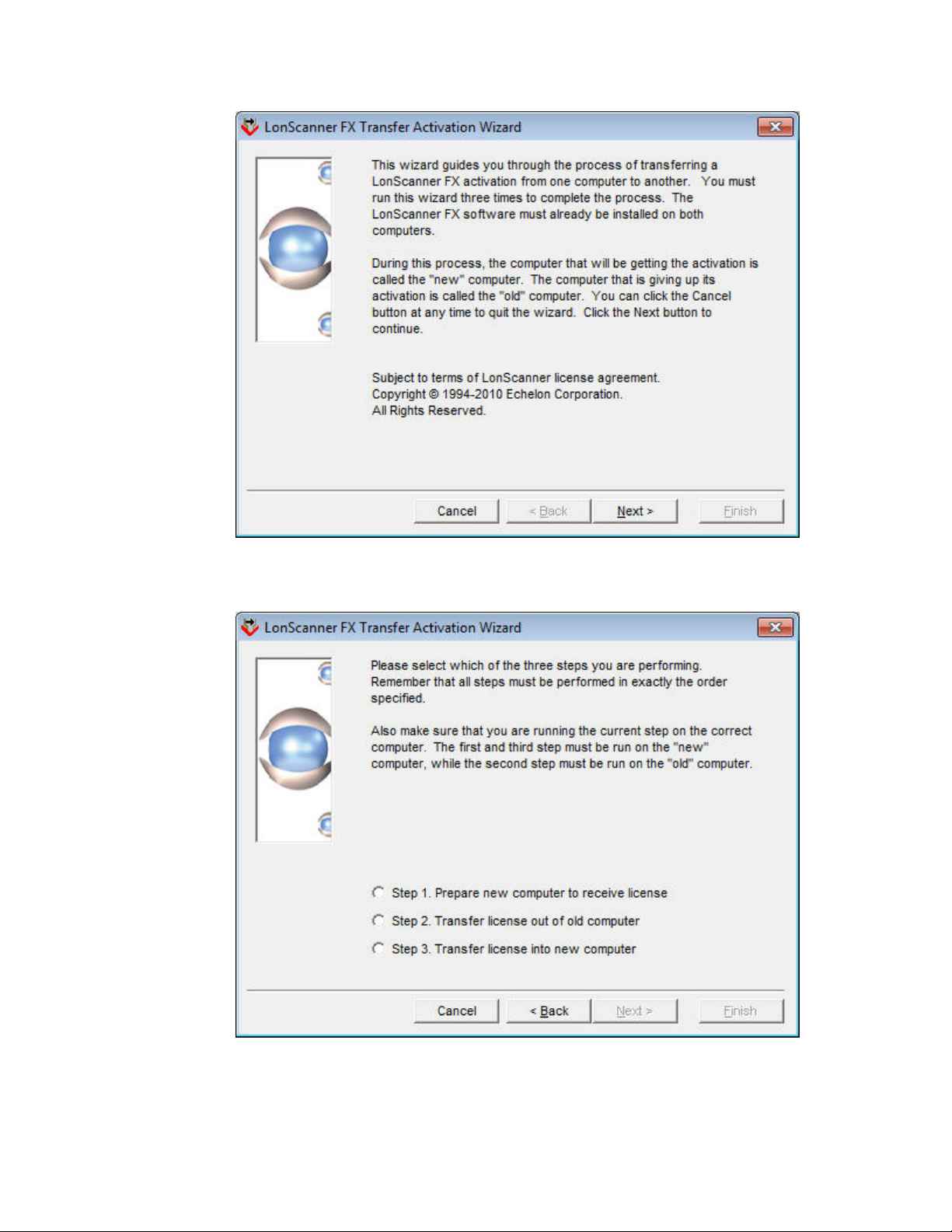
Figure 2. LonScanner Transfer Activation Wizard
2. Click Next to continue. The main window opens, as shown in
Figure 3. LonScanner Transfer Activation Wizard Main Window
Figure 3.
3. From the main window, you must perform all three steps:
6 Introduction to the LonScanner Protocol Analyzer
Page 13
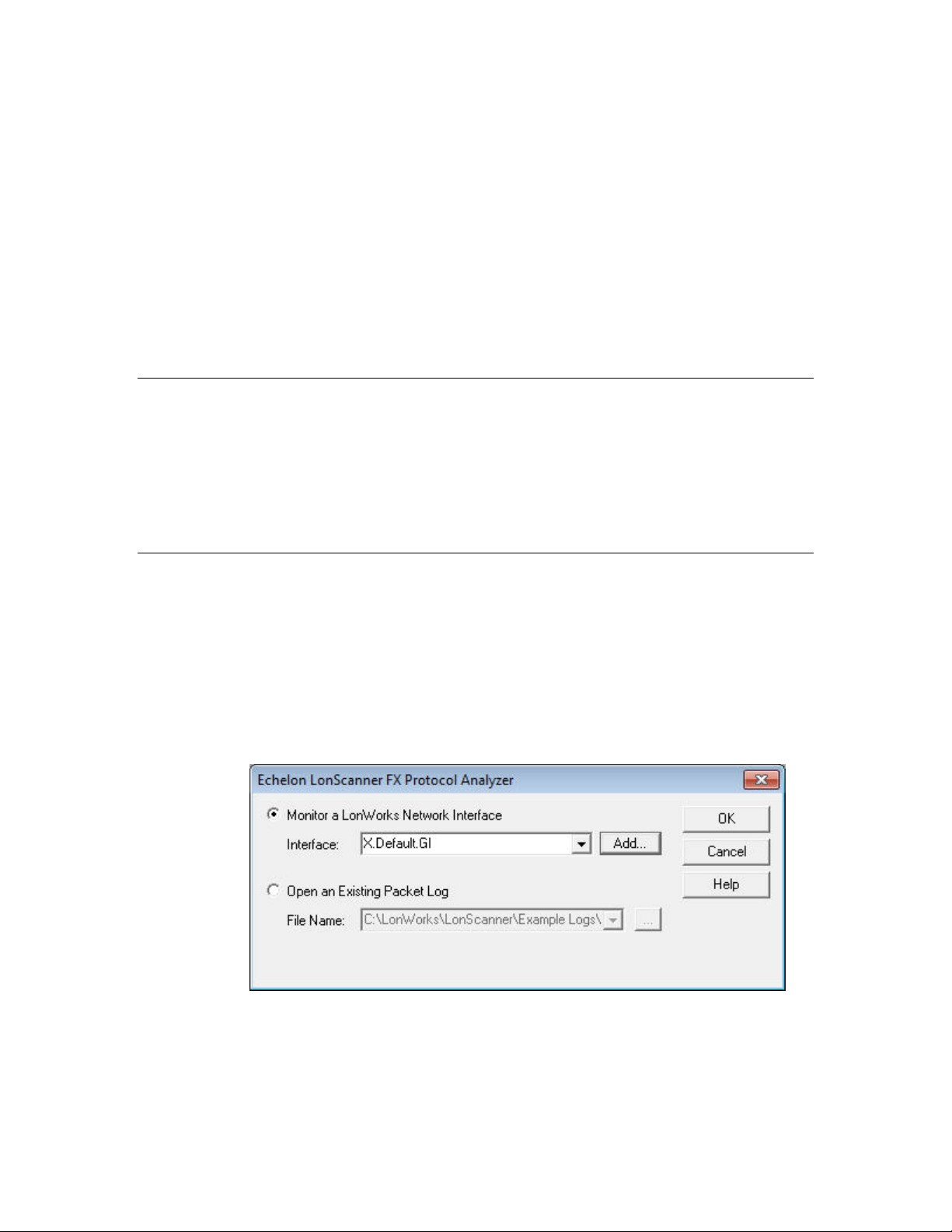
a. Step one must be performed on the target computer to which you
want to transfer the activation.
b. Step two must be performed on the computer that currently
contains the activation that you want to transfer. The
LonScanner software on this computer will no longer be activated
after the transfer is complete, and will run in demonstration
mode.
c. Step three must be performed on the target computer to which
you want to transfer the activation. This step completes the
transfer.
See the LonScanner online help for more information about these steps.
Viewing Activation Status
You can access information about your LonScanner software at any time by
selecting Help → About LonScanner Protocol Analyzer to open the About Echelon
LonScanner Protocol Analyzer dialog. This dialog displays the version number
and activation key of your LonScanner software. You can access additional
activation information by selecting Help → Activate Product → Display
Activation Status to open the Activation Status dialog.
Using the LonScanner Protocol Analyzer
After you install the LonScanner software, you can begin monitoring IP-852 and
ONWORKS channels with the protocol analyzer and analyzing the data that it
L
collects.
To start the protocol analyzer, select Programs → Echelon LonScanner Protocol
Analyzer → LonScanner Protocol Analyzer from the Windows Start menu. If you
have not yet activated the software, the LonScanner License Activation dialog
opens, as shown in
Continue Eval from the dialog), the Start-Up dialog opens, as shown in
Figure 1 on page 4. If the product is activated (or you click
Figure 4. Start-Up Dialog
Figure 4.
From the Start-Up dialog, you have two options to choose from:
•
Monitor a LonWorks Network Interface.
IP-852 or L
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 7
ONWORKS channel through a local or remote LONWORKS
Select this option to monitor an
Page 14

network interface. For more information, see
Channel
.
Monitoring a Network
Open an Existing Packet Log.
•
saved from a previous monitoring session. For more information, see
Select this option to view a packet log
Opening an Existing Packet Log
Monitoring a Network Channel
To monitor an IP-852 or LONWORKS channel, perform the following steps:
1. Select Monitor a LonWorks Network Interface on the Start-Up dialog
shown in
use from the Interface dropdown list box. This list box displays the
available network interfaces for your computer.
To add a new network interface, click Add to open the L
Interfaces application (from the Windows Control Panel). If you are
using an
ONWORKS/IP Server as your network interface, you must configure it
L
with the L
protocol analyzer.
From the LONWORKS Interfaces application, you can add a remote
network interface (RNI), an IP-852 network interface, or a USB network
interface:
Figure 4, and then select the network interface that you plan to
i
.LON SmartServer, i.LON 100 Internet Server or an i.LON 600
ONWORKS Interfaces application before you can use it with the
• To add an RNI, click Add to open the Add Network Interface
Wizard. On the first page of the wizard, enter a name for the
network interface, and click Next. On the second page, select
LonScanner as the Interface Type. Click Finish to add the
network interface and close the wizard.
on page 9.
ONWORKS
• To add an IP-852 network interface, click Add to open the
Network Interface Add dialog. Enter a name for the network
interface in the Name field, select (or enter) an IP address in the
IP Address dropdown list box, enter the IP port in the IP Port
field, select the appropriate channel timing type, and enter the
authentication key (if the device uses authentication) in the MD5
Authentication Key field. Click OK to add the network interface
and close the dialog.
• To add a USB network interface, plug an Echelon U10 or U20
network interface into to an available USB port on your
computer. The L
network interface automatically. Select the Show detached
interfaces checkbox to show previously configured USB network
interfaces that are not currently connected to your computer.
See the L
information.
No additional configuration is required to use an Echelon U10 or U20
USB Network Interface. For additional information about an
ONWORKS Interfaces application’s online help for more
ONWORKS Interfaces application should show the
i
.LON
8 Introduction to the LonScanner Protocol Analyzer
Page 15

SmartServer,
network interface see Appendix
2. Click OK to begin monitoring the selected channel. The main
LonScanner window opens. A log entry is added to the Packet Log tab for
each packet that the protocol analyzer receives from the channel. For an
overview of the Packet Log tab and the rest of the main LonScanner
window, see
3. To save the log file for later use, select File → Save Log As to open the
Save As dialog. After you save the log file, you can re-open the log file at
any time, as described in
4. To monitor additional channels, select File → New Connection, or click
New from the LonScanner toolbar. You can monitor up to 10 channels at
the same time.
See Chapter
the protocol analyzer to perform additional tasks, such as filtering
incoming data or controlling the packet log.
i
.LON 600 LONWORKS/IP Server, PCC-10, or PCLTA-20/21
A,
Network Interfaces
Log Files Overview
on page 9.
Opening an Existing Packet Log
2,
Logging Data
, on page 15, for a description of how to use
Opening an Existing Packet Log
To open a packet log saved from a previous LonScanner or LonManager Protocol
Analyzer session, select Open an Existing Packet Log on the Start-Up dialog
shown in
Name field, or click the browse button to open the Open dialog. LonScanner log
files have the .lsl extension, and LonManager log files have the .pal extension.
Figure 4 on page 7, and enter the log that you want to open in the File
, on page 59.
.
After you select a file, click OK to open the main LonScanner window. The log
that you selected is displayed in the Packet Log tab. For an overview of the
Packet Log tab and the rest of the main LonScanner window, see the
Overview
You can open additional packet logs after you start the protocol analyzer by
selecting File → Open Log or by clicking Open from the LonScanner toolbar.
section.
Log Files Overview
When you begin monitoring a channel or open a saved log file with the protocol
analyzer, the main LonScanner window opens, as shown in
Log Files
Figure 5 on page 10.
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 9
Page 16
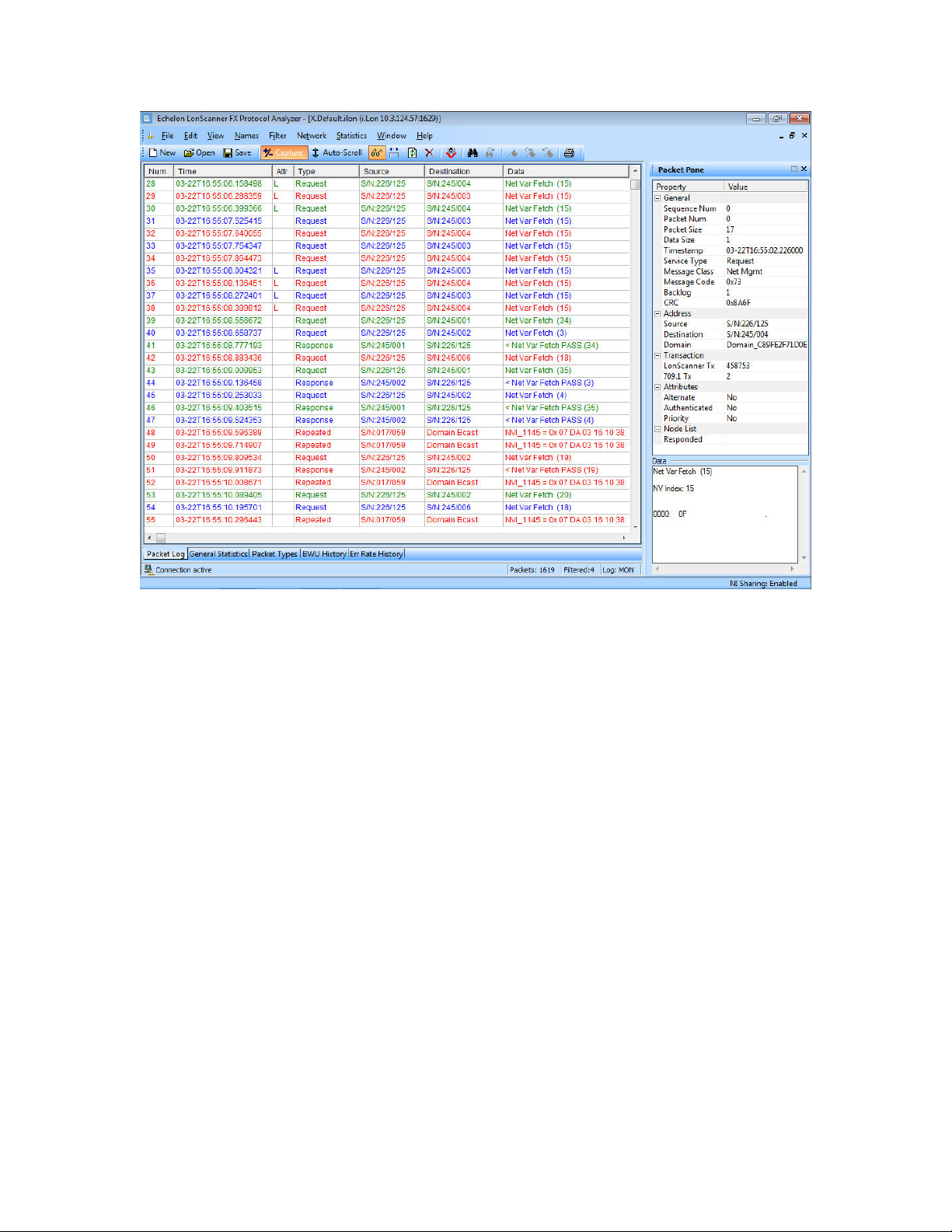
Figure 5. Main LonScanner Window
The main window includes the following three main areas:
• The Packet Log tab comprises the majority of the main LonScanner
window. The Packet Log tab contains a series of log entries, one for each
packet that the protocol analyzer collects from the channel. The log
entries are listed sequentially by timestamp. See the online help for
descriptions of the data fields listed for each packet.
While you are actively monitoring a channel, you can also select the
General Statistics, Packet Types, Bandwidth Utilization History, and
Error Rate History tabs at the bottom of the window to view statistics
collected from the channel during your log session. For more information
on these tabs, and for information about how you can configure the
protocol analyzer’s behavior during an active log session, see Chapter
Logging Data
• The Packet Detail pane to the right of the Packet Log tab lists detailed
information about the packet that is currently selected (if any) in the
Packet Log. Click a packet in the Packet Log to select it and view its
details in the Packet Detail pane. See the online help for descriptions of
the data fields listed for each packet in the Packet Detail pane.
• The menus and toolbar at the top of the window allow you to determine
how the protocol analyzer collects data from the channel and to organize
and analyze the data after it has been collected. For an overview of the
features provided by each menu, see
11.
page
, on page 15.
Using the LonScanner Window
2,
on
10 Introduction to the LonScanner Protocol Analyzer
Page 17
Using the LonScanner Window
This section provides a brief introduction to the features that you can access
using the main LonScanner window. These features are described in more detail
in later chapters, and in the LonScanner online help.
LonScanner Menus
Table 1 lists the LonScanner menus, and describes the functionality that is
provided by each menu. For detailed descriptions of each menu option, see
Chapters
Menu Description
File Use the File menu to open new connections to local and remote
2 and 3 of this document, and the LonScanner online help.
Table 1. LonScanner Menus
channels, and to open pre-existing log files. You can also use the
File menu to print and export log files, and to set the general logging
preferences that affect how the protocol analyzer creates and
manages log files.
Edit Use the Edit menu to search through log files, and to bookmark
specified log entries as being of interest.
View Use the View menu to format how the data in the Packet Log is
displayed (including selecting which data fields are displayed in the
Packet Log for each log entry, how each data field is formatted, and
what color and font is used to display each log entry). You can also
use the View menu to hide or display the LonScanner toolbar, status
bar, and Packet Detail pane.
Names Use the Names menu to import or edit device and network variable
names for the channel that you are monitoring.
Filter Use the Filter menu to create and activate LonScanner filters, which
you can use to select which packets the protocol analyzer stores into
a log file, and which ones it does not store.
Network When you are actively monitoring a channel with the protocol
analyzer, you can use the Network menu to enable and disable
capture mode and monitor mode, and to clear all data from the
currently selected log.
Statistics When you are actively monitoring a channel with the protocol
analyzer, you can use the Statistics menu to configure how the
protocol analyzer gathers and displays network statistics.
Window Use the Window menu to arrange the log files and windows that are
currently open.
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 11
Page 18
Menu Description
Help Use the Help menu to access information about the version and
activation status of the LonScanner software, and to access the
LonScanner online help. You can also access the LonScanner
Transfer Activation Wizard from this menu.
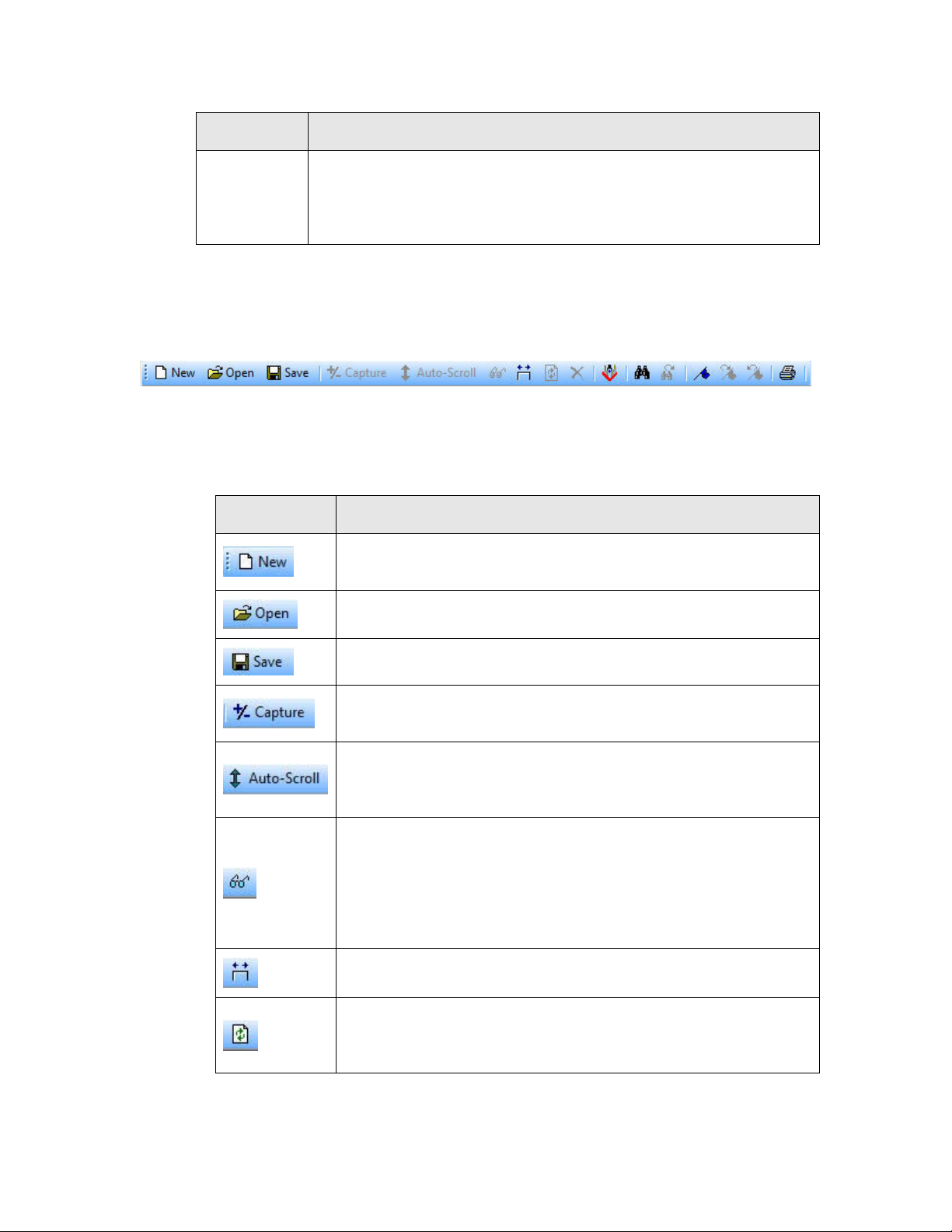
LonScanner Toolbar
The LonScanner toolbar provides quick access to commonly used menu options.
The LonScanner toolbar is shown in
Figure 6. LonScanner Toolbar
You can click a button on the toolbar to use the feature provided by that button.
Table 2 describes the buttons.
Table 2. LonScanner Toolbar Buttons
Button Description
Opens a new connection to a channel and starts a new Packet
Log.
Figure 6.
Opens an existing log file.
Saves the log file currently displayed in the Packet Log tab.
Enables or disables the recording of packets into the current log
file when LonScanner is actively monitoring a channel.
Enables or disables automatic scrolling of the Packet Log tab to
the most recently collected packets when you are actively
monitoring a channel and recording packets into a log file.
Enables or disables automatic refreshing of the Packet Log tab
when you are actively monitoring a channel and recording
packets into a log file. When disabled, you must manually
refresh the Packet Log by clicking the Refresh button, or by
selecting View → Refresh Display, to see the most recently
collected packets in the Packet Log tab.
Adjusts the column widths of the Packet Log tab.
Refreshes the information shown in the Packet Log and
Statistics tabs when you are actively monitoring a channel and
recording packets into a log file.
12 Introduction to the LonScanner Protocol Analyzer
Page 19

Clears all data from the log file currently shown in the Packet
Log tab.
Starts the LNS Names Import Wizard, which you can use to
import device and network variable names from an LNS
database.
Finds an occurrence of a string in the Packet Log tab.
Finds the next occurrence of a string in the Packet Log tab.
Creates a bookmark. You can use bookmarks to mark certain
log entries as being of interest.
Scrolls the Packet Log tab to the next bookmarked packet.
Scrolls the Packet Log tab to the previous bookmarked packet.
Prints the log file currently displayed in the Packet Log tab.
LonScanner Status Bar
The Status Bar is at the bottom of the LonScanner Protocol Analyzer window. It
provides the following information:
• A status message that provides a brief description of the currently selected
menu items and buttons.
• The total number of packets recorded into log file.
• The number of packets that have been filtered.
• The logging state of the currently selected active log.
• Whether or not network interface sharing is enabled or disabled.
Using LonScanner with LNS Turbo Edition
If you plan to use LonScanner FX Professional Edition with LONWORKS channels,
you do not need an LNS Turbo Edition Server. However, when used with the
protocol analyzer, an LNS Turbo Edition Server provides several additional
features, including importing device and network variable names, network
interface sharing, and monitoring of IP-852 channels.
With an LNS Turbo Edition Server, you can import device and network variable
names from an LNS network database into the current LonScanner active log.
2,
See Chapter
With LNS Turbo Edition Server installed, the protocol analyzer and the
LonMaker
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 13
Logging Data
Integration Tool (or any custom LNS application) can share a network
, on page 15, for more information.
Page 20
interface (that is, each tool can use the network interface at the same time).
i
Network interface sharing applies to PCC-10, PCLTA-20/21,
i.
LON 100 Internet Server, i.LON 600 LONWORKS/IP Server, and U10/U20 USB
Network Interfaces.
You can also run the protocol analyzer and the LonMaker tool (or any custom
LNS application) at the same time with the same network interface on a
i
computer with an LNS 3 Server if you use an
i.
Internet Server, or an
In addition, you can import device and network variable names from your LNS
database if you have an LNS 3 Server.
If you have an LNS Turbo Edition Server installed, you can use the protocol
analyzer to monitor IP-852 channels, as well as L
attempt to monitor an IP-852 channel without an LNS Turbo Edition Server
installed, the LonScanner Protocol Analyzer issues an error message (“Failed to
open channel via OpenLDV”).
LON 600 LONWORKS/IP Server as the network interface.
.LON SmartServer, i.LON 100
ONWORKS channels. If you
.LON SmartServer,
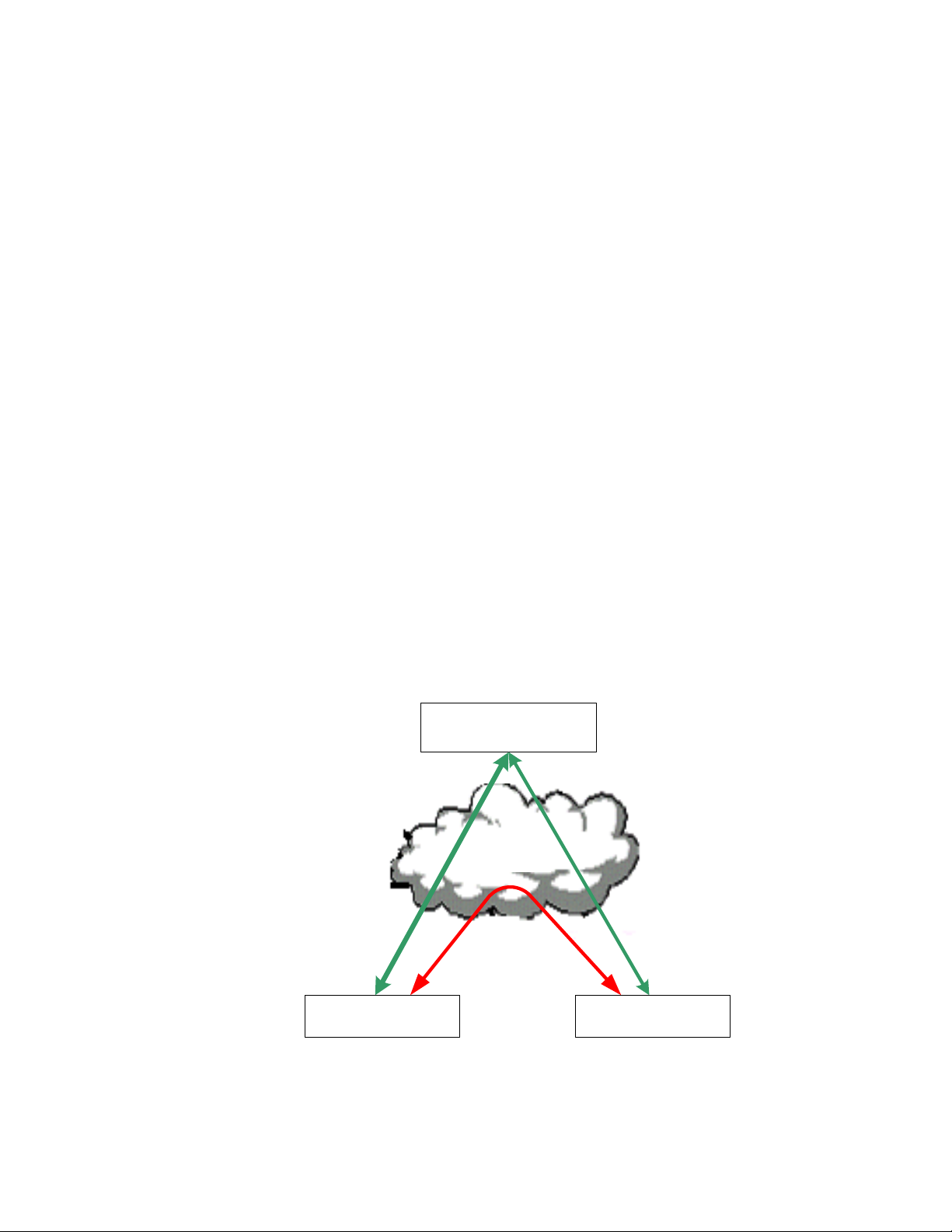
The IP-852 interface operates differently from L
interface of every device on a L
channel. But, Echelon’s IP-852 devices and routers do not automatically forward
packets to every other device and router on the channel. Instead, they selectively
forward packets directly to the intended destination devices and routers on the
channel. As a result, the protocol analyzer does not receive packets that are sent
on an IP-852 channel from one device or router to another if the source or
destination device is not the computer running the protocol analyzer.
Figure 7 demonstrates this behavior. In the figure, the protocol analyzer is
monitoring an IP-852 channel that contains two devices (named “IP-852 Device
1” and “IP-852 Device 2”). The protocol analyzer receives only those packets sent
between the IP-852 devices and the LonScanner computer (the network paths
displayed in green). The protocol analyzer does not receive packets sent between
IP Device 1 and IP Device 2 (the network path displayed in red).
ONWORKS channel receives every packet on the
LonScanner
Computer
ONWORKS channels. The layer 2
IP-852 Channel
IP-852 Device 2IP-852 Device 1
Figure 7. Using LonScanner to Monitor an IP-852 Channel
14 Introduction to the LonScanner Protocol Analyzer
Page 21

2
Logging Data
This chapter describes how you can log packets with the
protocol analyzer, and how you can view statistics related to
those packets. The first part of this chapter describes how
you can configure the behavior of the protocol analyzer while
it monitors a channel and collects packets, including topics
such as setting logging preferences, using the Capture and
Auto-Scroll features, and filtering packets.
The second part of this chapter describes how to access
statistics that are available when you monitor a channel
with the protocol analyzer, including data related to
bandwidth utilization, the types of packets traveling on the
network, and other network statistics.
This chapter also describes how you can use names to
identify the devices and network variables on the channel
that you are monitoring.
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 15
Page 22
Configuring the LonScanner Protocol Analyzer
You can configure the behavior of the protocol analyzer while it monitors a
channel, including:
• Setting logging preferences to control how the protocol analyzer collects
and record packets from a channel.
• Filtering packets to select which packet types are written to the log file.
• Setting the capture and monitor modes to determine whether the packets
collected from the channel are written to the log file, and whether the
protocol analyzer automatically refreshes the Packet Log display as data
is added to the log.
Setting Logging Preferences
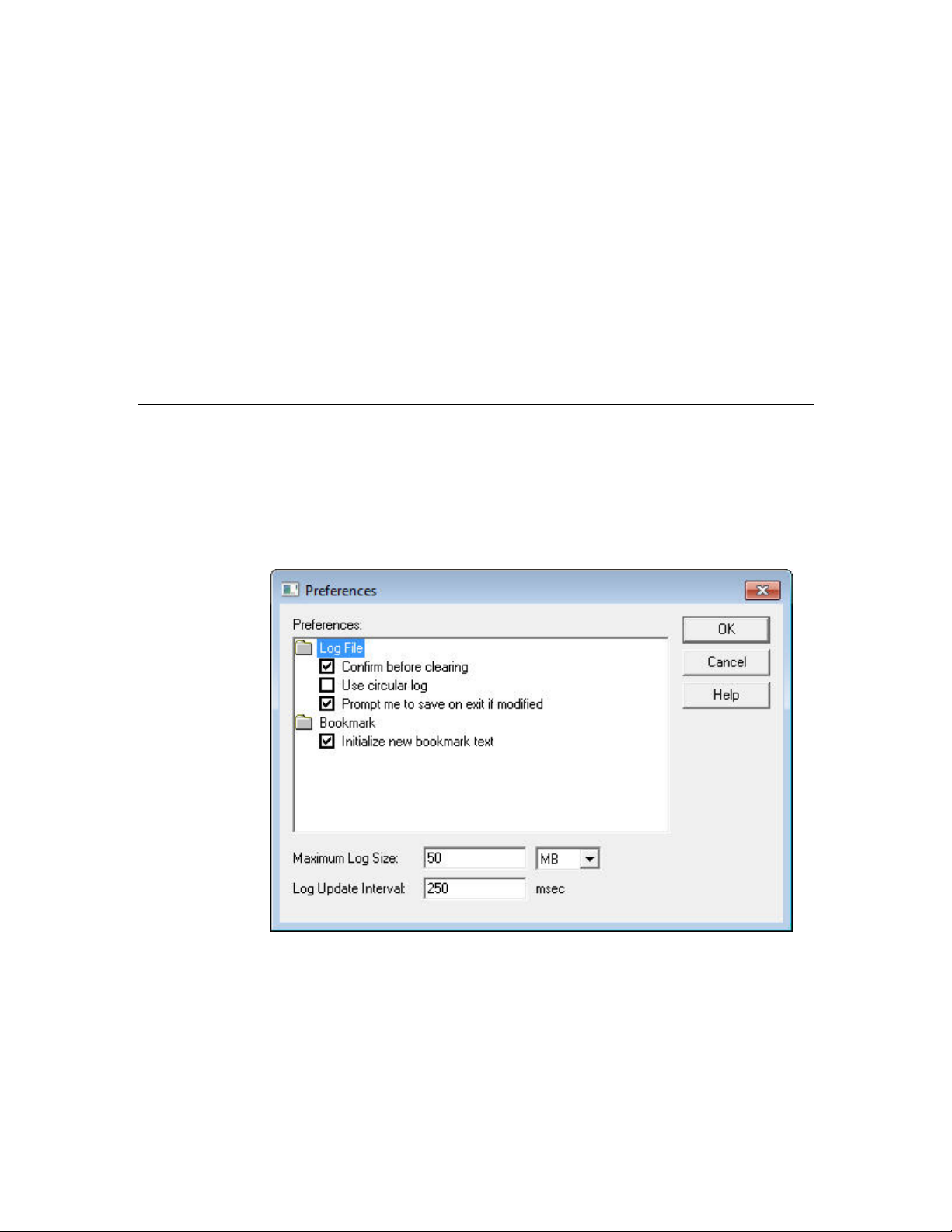
You can use the LonScanner Preferences dialog to determine how the protocol
analyzer collects and displays data during a monitoring session. To set logging
preferences, perform the following steps:
Select File → Preferences to open the Preferences dialog, as shown in
1.
Figure 8.
Figure 8. LonScanner Preferences Dialog
2.
Specify your preferences. See the online help for descriptions of the fields
in this dialog.
3.
Click OK to save your changes.
16 Logging Data
Page 23
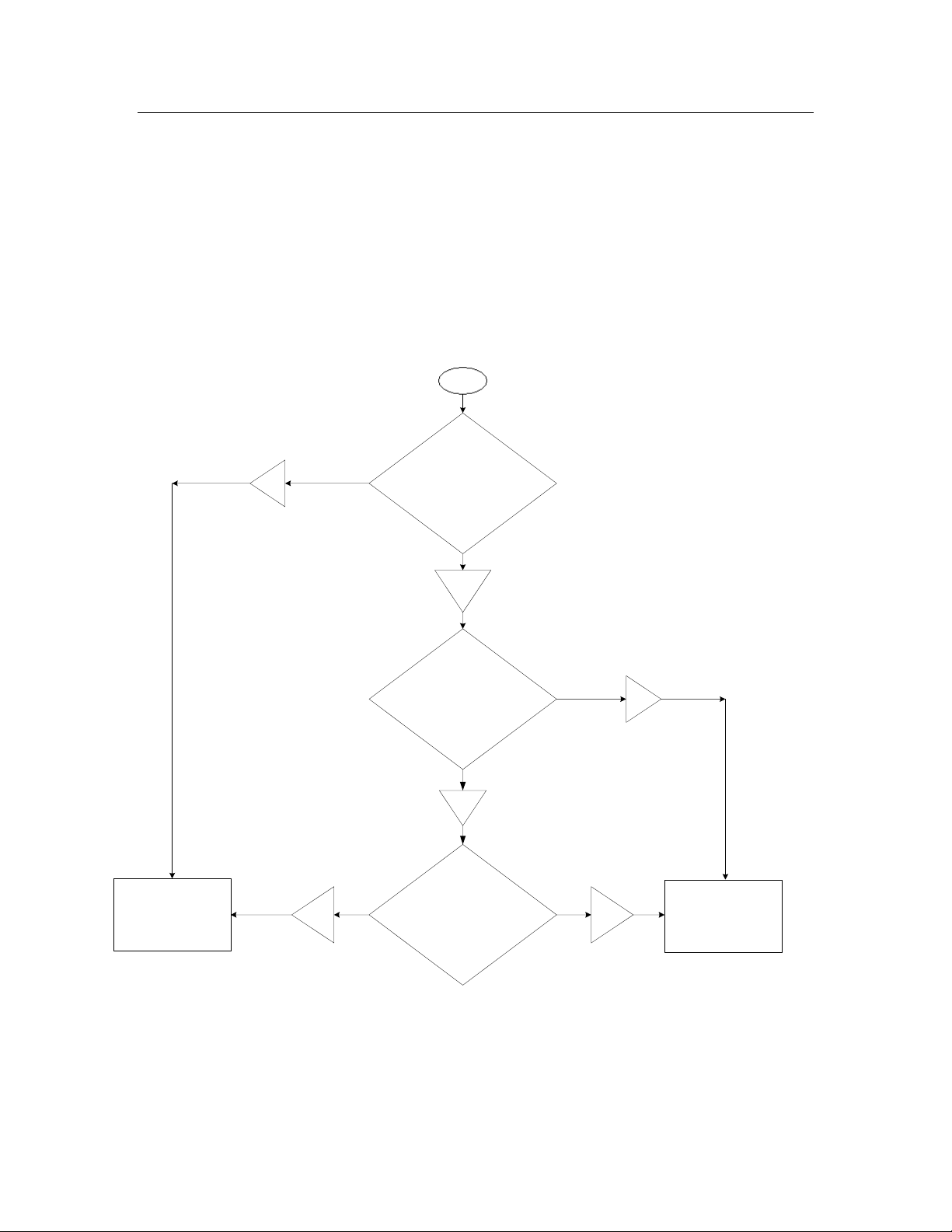
Filtering Packets
You can use filters to select the types of packets that are written to the log file.
You can use two types of filters:
• A
global filter
• A
device filter
the network
When the protocol analyzer receives a packet from the channel, it uses the global
and device filter to determine if the packet passes the filter requirements, as
described in
Figure 9.
that applies to all packets
that applies to packets sent to and from specific devices on
Start
The packet does not
pass the filter
requirements.
No
No
Does the packet pass the global
filter requirements?
Yes
Have any devices been defined
in the device filter?
Yes
Does the packet pass the device
filter requirements?
Yes
No
The packet passes the
filter requirements.
Figure 9. Filtering Packets
Important: Each time you modify the filter settings for a channel, the protocol
analyzer automatically saves those settings. Thus, every time you connect to a
channel, the protocol analyzer uses the last set of filter settings defined for the
channel.
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 17
Page 24

You can also filter packets with a custom filter file. To create and use a custom
filter file, modify the LsCustomFilter.cpp file in the LonScanner Example
Custom Filter directory.
Configuring the Global and Device Filters
To configure either the device filter or the global filter, perform the following
steps:
Select Filter → Edit Filters to open the Device Filter dialog, as shown in
1.
Figure 10.
Figure 10. Device Filter Dialog
To include all devices in the filter, skip to step 5. To filter packets
2.
addressed to or from a specific device, click New. The Select Device to
Add dialog opens, which lists all of the devices that are defined in the
current names file. Select a device to add to the filter, and click Add. For
more information on names files, see
After you select a device to filter, you return to the Device Filter dialog
and the newly added device is listed in the Device list.
3.
If you added a device to the filter in the previous step, all packets
addressed to or from the device pass the device filter by default. You can
refine the filter by specifying which packets pass the device filter: all
packets or network variable packets addressed to the device, or all
packets or network variable packets sent by the device.
To refine the filter, edit the filter configuration for the device by selecting
18 Logging Data
Using Names
on page 29.
Page 25

it in the Device Filters list, and then click one of the buttons at the
bottom of the Device Filter dialog:
• New opens the Select Device to Add dialog, as described in step 2.
• Delete removes the selected device from the device filter.
• Sel Input opens the Input Mode dialog. You can use this dialog to
to
specify whether or not packets sent
the device filter requirements.
• Sel Output opens the Output Mode dialog. You can use this dialog to
specify whether or not packets sent
pass the device filter requirements.
• Sel NVs opens the Select Network Variables dialog. You can use this
dialog to determine which network variable update messages sent to
and from the selected device should pass the device filter
requirements. You must define the network variable types in the
current names file before adding them to the device filter. For more
information on names files, see
• Sel Msg Codes opens the Select Message Codes dialog. You can use
this dialog to determine which message codes sent to and from the
selected device should pass the device filter. You must define the
message codes in the current names file before adding them to the
device filter. For more information on names files, see
on page
29.
the selected device should pass
from
the selected device should
Using Names
on page 29.
Using Names
See the online help for more information about each of these buttons and
dialogs. You can bypass these steps if you do not want to filter packets
based on their source or destination device.
4.
To include other devices in the filter, repeat steps 2 and 3 until the filter
includes all of the devices. Filter settings that you define for each device
apply only to that device, and not to the other devices in the filter.
5.
To define a global filter, click Global Filter to open the Global Filter
dialog, as shown in
global filter, skip to step
Figure 11 on page 20. If you do not want to define a
10.
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 19
Page 26

Figure 11. Global Filter Dialog
Under Mode, select Capture packets that pass the global and device
6.
filters to write packets that pass the requirements of the global and
device filters into the Packet Log. Select Discard packets that pass the
global and device filters to write packets that do not pass the
requirements into the Packet Log.
Select the Both source and destination must pass the device filter
7.
checkbox to verify that each packet meets the filter settings for both the
source device and the destination device. This setting allows you to filter
traffic between a specified pair of devices.
Under Good Packets, Bad Packets, and Address Mode, select which
8.
packet types should pass the global filter by selecting or clearing the
appropriate checkboxes. You can select all packet types by clicking Select
All, and clear all packet types by clicking Clear All. See the online help
for information about each of the packets types listed on the Global Filter
dialog.
20 Logging Data
Page 27

Click OK to save your changes and return to the Device Filter dialog.
9.
10.
Click OK on the Device Filter dialog. The protocol analyzer uses the
updated filter configuration to filter all incoming packets.
You can edit the configuration of the filter file again later by selecting Filter
Edit Filters, and repeating steps
You can select Filter
default filter settings.
→ Set to Defaults at any time to revert the filter to the
2 through 10.
→
Importing Filter Settings from a Channel
The protocol analyzer automatically saves the filter settings that you define for a
channel each time they are modified. When you modify the filter settings for a
channel, the protocol analyzer uses those settings the next time you connect to
the channel.
You can import the filter settings for a given channel into another channel. For
example, if you use multiple network interfaces to monitor a channel or group of
channels, and want them all to use the same filter settings, you can import the
filter settings from one network interface to the others.
To import filter settings:
1.
Select Filter → Import From Channel. A dialog box opens to remind you
that this action overwrites any filter settings defined for the channel.
Click Yes to continue. A dialog box opens from which you can select the
2.
network interface that you use to connect to the channel which contains
the filter settings that you want to import.
3.
Select the network interface from the Interface dropdown list box, or click
Add to add a new network interface, and then click OK.
A dialog box opens to inform you that the filter settings have been imported.
Click OK to close the dialog box. The protocol analyzer uses the imported filter
settings.
Saving Filter Settings for Later Use
You can save the global and device filter settings you create into a filter file so
that you can return to those settings later, without having to reconfigure the
filter and undo any subsequent changes later. To save the current global and
device filter settings into a filter file, select Filter
After you save a filter file, you can create or import new filter settings as
described in the previous sections, and then restore the saved filter settings at
any point. To restore your saved filter settings, select Filter
Filter File, and open your saved filter file. The protocol analyzer uses the filter
settings defined in the saved filter file. These settings overwrite any previously
defined filter settings for the channel.
You can save any number of filter files, and import them at any time.
→ Save Copy.
→ Import From
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 21
Page 28

Setting the Capture and Monitor Modes
You can use the Capture and Monitor modes to control whether the packets
collected from the channel are written to the log file, whether the Packet Log tab
is refreshed as packets are received, and whether the Packet Log tab is
automatically scrolled to display incoming packets.
To record packets collected from the network into the current log file, click the
Capture button on the LonScanner toolbar or select Network
To automatically update the Packet Log tab as packets are collected from the
channel, click the Monitor button on the LonScanner toolbar or select Network
Monitor Mode. When monitoring is disabled, you must manually refresh the
Packet Log tab whenever you want to see the most recently collected packets by
clicking the Refresh button on the LonScanner toolbar or by selecting View
Refresh Display.
You can check the status bar to determine whether Capture mode and Monitor
mode are enabled. For more information on the status bar, see
LonScanner Window
To automatically scroll the Packet Log tab to the most recently collected packets,
click the Auto-Scroll button on the LonScanner toolbar or select View
Scroll.
on page 11.
→ Capture Mode.
Using the
→ Auto-
Viewing Channel Statistics and Trend Graphs
→
→
You can view channel statistics and trend graphs while you are monitoring a
channel to assess overall channel health at a specific point in time, or over a
longer period of time. To view channel statistics or trend graphs, click the tabs at
the bottom of the main LonScanner window:
• General Statistics. Select the General Statistics tab to view channel
statistics, such as the total packets received during the log session, the
average packet size received, and the number of packets received per
second. The General Statistics tab also displays maximum and
cumulative statistics, such as the maximum and average bandwidth
utilization percentage and the maximum and average error rate during
the session.
• Packet Types. Select the Packet Types tab to view a breakdown of the
packet types collected from the monitored channel. For each packet
type, the total number of packets of that type that has been collected
from the monitored channel is listed, as well as the percentage of the
total packet count for each type.
• BWU History. Select the BWU History tab to view a trend graph
displaying the bandwidth utilization (by percentage) over time for the
monitored channel.
• Err Rate History. Select the Err Rate History tab to view a trend graph
displaying the percentage of invalid packets received from the monitored
channel over time.
These tabs are not available if you are viewing a saved packet log.
22 Logging Data
Page 29

Note: The data displayed on the statistics tabs is calculated based on the packets
that pass the global and device filters and are written to the current log file.
Packets that are discarded because they do not meet the current filter
requirements are not used in the statistics calculations.
Viewing General Statistics
Select the General Statistics tab to view a variety of network statistics, including
the total number of packets collected during the current session, the average
packet size, and the number of packets received per second. You can also view
maximum and cumulative information, such as the maximum and average
bandwidth utilization percentage and the maximum and average error rate
during the session. See the online help for descriptions of the data fields
displayed on the General Statistics tab.
Figure 12 shows the General Statistics tab with example data.
Figure 12. General Statistics Tab
You can control the rate at which the statistics on the display are updated by
setting the general update interval with the statistics options dialogs. See
Setting Statistics Options
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 23
on page 26 for more information.
Page 30

Viewing Bandwidth Utilization by Packet Type
Select the Packet Types tab to view a breakdown of the packet types collected
from the monitored channel. The packet types are grouped as good (valid) and
bad (invalid) packets. For each packet type, the total number of collected packets
of that type is listed. The percentage of the total packet count for each type is
also listed. See the online help for descriptions of the packet types listed on the
Packet Types tab.
Figure 13 shows the Packet Types tab with example data.
Figure 13. Packet Types Tab
In the figure, all the packets received during the current session have been valid
packets. The protocol analyzer adjusts the packet count and percentage figures
as additional packets are received from the channel. You can control the rate at
which the statistics on the display are updated by setting the general update
interval with the statistics options tabs. See
26 for more information.
Setting Statistics Options
on page
Viewing Bandwidth Utilization History
Select the BWU History tab to view a trend graph that displays the bandwidth
utilization (by percentage) of the monitored channel. A well-designed network
will not have any peaks in bandwidth utilization that are over 80%.
24 Logging Data
Page 31
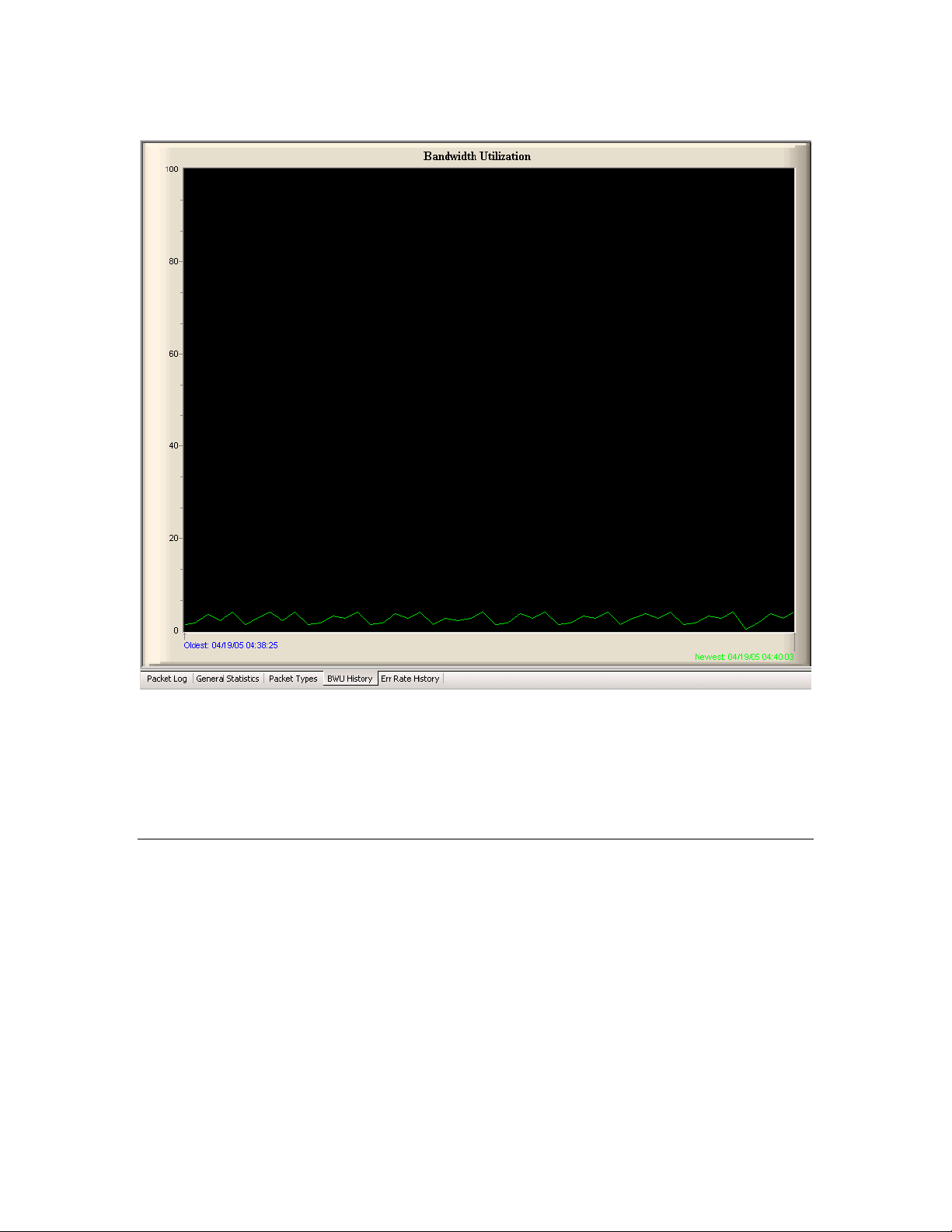
Figure 14 shows a bandwidth utilization trend graph with example data.
Figure 14. Bandwidth Utilization History Tab
The BWU History tab includes two timestamps: the timestamp for the oldest
and the newest update points on the trend graph. You can set the rate at which
this display is updated, as well as the number of points that are displayed on the
chart, with the statistics options dialogs. See
26 for more information.
Viewing Error Rate History
Select the Err Rate History tab to view a trend graph that displays the
percentage of invalid packets received from the monitored channel. A welldesigned network will not have any peaks in error rate over 4%.
Figure 15 on page 26 shows the Error Rate History tab with example data.
Setting Statistics Options
on page
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 25
Page 32

Figure 15. Error Rate History Tab
The Err Rate History tab includes two timestamps: the timestamp for the oldest
and the newest update points on the trend graph. You can set the rate at which
this display is updated, as well as the number of points that are displayed on the
chart, with the statistics options tabs. See
information.
Setting Statistics Options
You can configure the statistics options to control how the protocol analyzer
collects data from the network and how that data is displayed. To set the
statistics options, perform the following steps:
1.
Select Statistics → Statistics Options to open the Statistics Options
dialog, as shown in
Figure 16 on page 27. The General tab displays.
Setting Statistics Options
for more
26 Logging Data
Page 33

Figure 16. General Tab
Configure the settings on the General tab. These settings determine the
2.
interval at which the statistics display is updated, and the format that is
used to display the statistics. See the online help for descriptions of these
fields.
Select the Bandwidth Graph tab, as shown in Figure 17.
3.
Figure 17. Bandwidth Graph Tab
4.
Configure the settings on the Bandwidth Graph tab. These settings
determine the number of historical points that are displayed on the
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 27
Page 34

Bandwidth Utilization chart, whether logarithmic scaling should be used
for the chart, and the colors that are used to display the chart. See the
online help for descriptions of these fields.
Select the Error Graph tab, as shown in Figure 18.
5.
Figure 18. Error Graph Dialog
Configure the settings on the Error Graph tab. These settings determine
6.
the number of historical points that are displayed on the Error Rate
History chart, whether logarithmic scaling should be used for the chart,
and the colors that are used to display the chart. See the online help for
descriptions of these fields.
7.
Click OK to save your changes and close the dialog. Or, click Apply to
save your changes and continue editing the statistics options settings.
You can click Defaults at any time to return the settings to their default
values.
To choose the channel type that you are monitoring, select Statistics →
8.
Channel Type. The Channel Type dialog opens, as shown in
29.
page
Figure 19 on
28 Logging Data
Page 35

Select the channel type and bandwidth utilization options for the channel
9.
that you are monitoring and click OK. These settings are important for
calculating bandwidth utilization because the available bandwidth is
determined by the channel type.
When you begin monitoring a channel, the protocol analyzer attempts to
determine the channel type automatically. If the protocol analyzer cannot
determine the channel type, the Channel Type dialog opens to remind you to
select the correct channel type.
Using Names
You can assign names to devices, network variables, domains, groups, and
message codes on the channel that you are monitoring. The domain and group
assignments associated with a network are used to determine to which devices a
given packet should be sent, and to identify to which part of the network a device
belongs. For more information about domains, groups, and the rest of the
ISO/IEC 14908-1 control networking protocol, see the
ONWORKS
L
Platform
Figure 19. Channel Type Dialog
Introduction to the
.
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 29
Page 36

Names are not included in the packets sent over the network, nor are they saved
in log files. However, you can use names to identify the devices that are sending
or receiving messages on the channel that you are monitoring, to identify the
network variables that are being updated by these messages, or to identify the
domains and groups that exist on your network.
When you start a LonScanner session, you can import names from an LNS
database or from another channel. You can also manually add and customize
names. You can import and modify names at any time, for example, when you
are actively monitoring a channel or when you are viewing a saved log file.
When you import or create a set of names for a channel, the protocol analyzer
saves those names in a
open a connection to that channel, even after you have stopped and re-started the
protocol analyzer. The channel names file is updated and saved automatically
each time you modify the names that apply to a channel.
channel names file
. These names are used each time you
You can also save the names into a
import or create a set of names to use
file and use them at any time, for example, if you are using multiple network
interfaces to monitor the same network. You could define one names file that
contains all the names for the network, and then import the names from that file
whenever you start a LonScanner session with any of the network interfaces on
that network. You can also copy the local names file to another computer with
the protocol analyzer, and then import the names file on the second computer.
Importing Names
This section describes how to import names from an LNS database, a local names
file, or a channel names file.
Importing Names from an LNS Database
You can import the names that are stored an LNS database for your network.
The network database must be stored on the same computer as the protocol
analyzer, and you must have an LNS Turbo Edition Server or an LNS 3 Server
installed on the computer.
To import names from an LNS database, perform the following steps:
Select Names → Import from LNS Database to open the LNS Names
1.
Import Wizard, as shown in
local names file
.
You can import the names saved in the
Figure 20 on page 31.
on your computer after you
30 Logging Data
Page 37

Figure 20. LNS Names Import Wizard – Page One
Select the LNS database that contains the names that you want to import
2.
from the LNS Database Name dropdown list box, and click Next. The second
page of the wizard displays, as shown in
Figure 21 on page 32.
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 31
Page 38
Figure 21. LNS Names Import Wizard – Page Two
Select the subsystem (or subsystems) that contains the names that you want
3.
to import from the Available Subsystems list. Alternatively, you can click
Select All to select all subsystems, or click Select Subtree to select all
subsystems within the currently selected subsystem. Click Next to continue.
The third page of the wizard displays, as shown in
Figure 22 on page 33.
32 Logging Data
Page 39

Figure 22. LNS Names Import Wizard – Page Three
As the names are imported, it is possible that the names stored in the LNS
4.
database could conflict with names that you have previously imported or
assigned. These conflicts can occur under the following circumstances:
Two domains have the same ID.
Two devices or router sides in the same domain have the same Neuron
ID.
Two devices or router sides in the same domain have the same
subnet/node address.
Two network variables belonging to the same device have the same index.
Two network variables belonging to the same device have the same
direction and selector.
Select Use LNS Database Name or Use Original Name to automatically use
the name from the LNS database or from the current names file when a
conflict occurs. Select Prompt for Each Conflict to be prompted each time a
conflict is detected, allowing you to decide on a case-by-case basis.
Click Next. The fourth page of the wizard displays, as shown in
34.
page
Figure 23 on
®
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 33
Page 40

Figure 23. LNS Names Import Wizard – Page Four
Select a format for device and network variable names. Examples for each
5.
option are shown on the dialog.
6.
Click Next. The LonScanner software imports the names from the LNS
database. When it finishes the import, a completion dialog appears. Click
Finish to exit the wizard. You can also click Save from the completion dialog
to save the imported names into an .RTF file.
You can now use the imported names. You can also use the Names menu to
7.
add new names, or to customize the ones that you imported. See
and Customizing Names
on page 36 for more information.
Creating
Importing Names from a Local Names File
You can import names from a
contain predefined sets of names. You can create a names file by importing
names from an LNS database or from a network channel, and then saving them
to a file. You can also create a names file manually. See
on page
A names file can be useful if you are using multiple network interfaces to monitor
the same network. You could define one names file containing all the names for
the network, and then import the names from that file whenever you start a
LonScanner session with any of the network interfaces on that network.
To import names from a names file, perform the following steps:
34 Logging Data
41 for information about how to save names files.
local names file
on your computer. Names files
Managing Names Files
Page 41

Select Names → Import from Names File. A dialog opens to remind you that
1.
names that you are currently using will be overwritten.
Click Yes to continue. The Windows Open dialog opens.
2.
3.
Browse for the names file that you want to use, and click Open to import the
names.
You can now use the imported names. You can also use the Names menu to
4.
add new network object names or to customize the ones you imported. See
Creating and Customizing Names
on page 36 for more information.
Importing Names from a Channel
The protocol analyzer saves the names created for a channel as the default names
for that channel in a
automatically each time a name is added to or removed from a channel. The
names defined in the channel names file are used each time you open a
connection to that channel, even after you have stopped and re-started the
protocol analyzer.
You can import names from one channel to another, if you want multiple
channels to use the same set of names. When you import these names into a
channel, the protocol analyzer clears all the names currently being used for that
channel from memory.
channel names file
. The channel names file is updated
To import names from a channel names file, perform the following steps:
1.
Select Names → Import from Channel. A dialog opens to remind you that
the names that you are currently using will be overwritten.
2.
Click Yes to continue. The Select a Channel dialog opens, as shown in
Figure 24.
Figure 24. Select a Channel
3.
Select the network interface that you are using to connect to the channel
from which you want to import the names, and click OK to import the
names.
You can now use the imported names. You can also use the Names menu to save
the imported names file for later use, or to add new network object names and
customize the ones that you imported. For more information on this, see
Creating and Customizing Names
on page 36 for more information.
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 35
Page 42
Creating and Customizing Names
You can use the Names menu to create your own names, or to customize the
names that you already created.
Creating Group Names
You can create or change an ISO/IEC 14908-1 group name with the protocol
analyzer. To create a group name, perform the following steps:
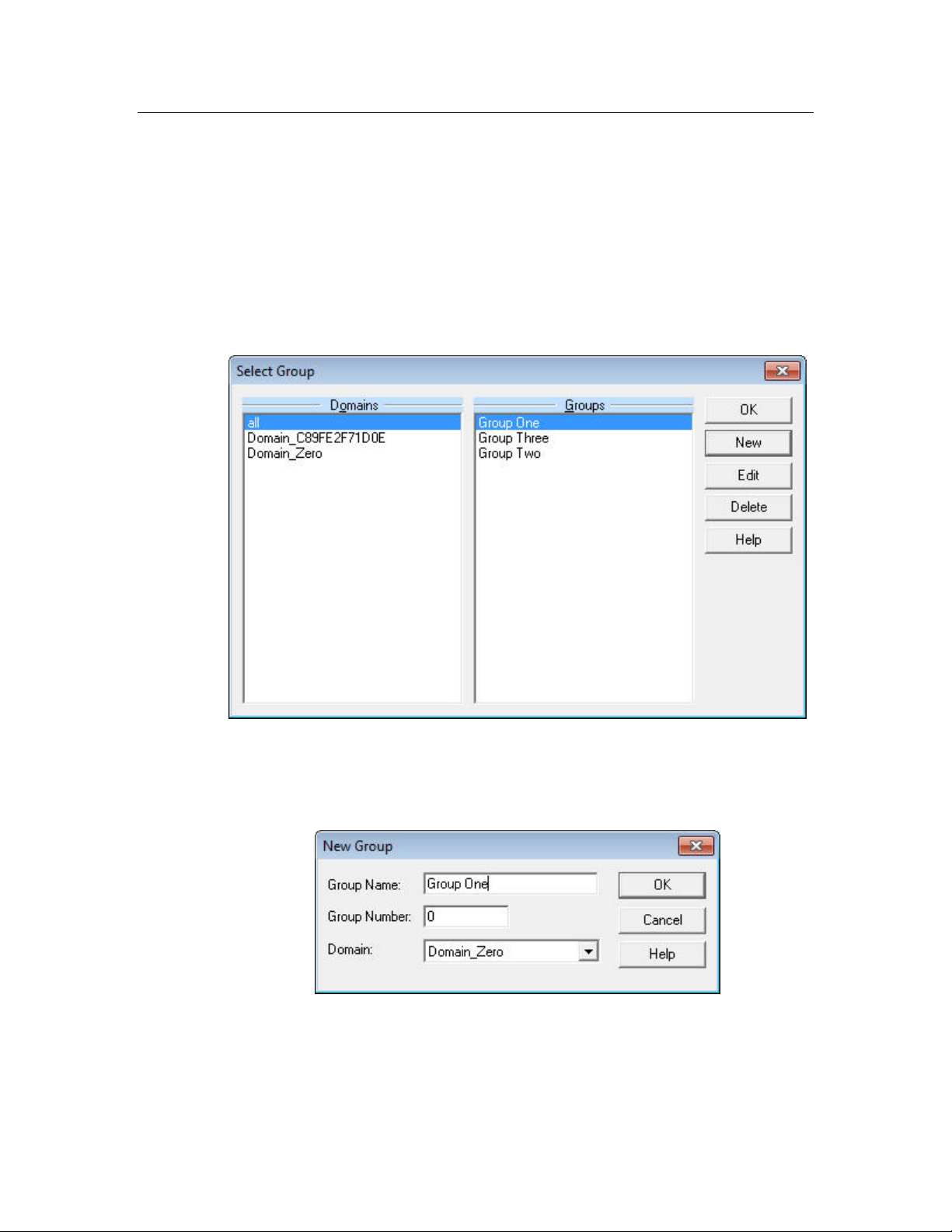
Select Names → Edit Groups to open the Select Group dialog, as shown in
1.
Figure 25.
Figure 25. Select Group Dialog
Select a domain from the Domains list. The groups that have been assigned
2.
names in that domain (if any) are listed in the Groups list. To create new
group name, click New. The New Group dialog opens, as shown in
Figure 26. New Group Dialog
3.
Select the domain that contains the group from the Domain dropdown list
box.
Figure 26.
36 Logging Data
Page 43

Enter the group ID for the group in the Group Number field, and enter the
4.
name for the group in the Group Name field.
Click OK to close the New Group dialog and return to the Select Group
5.
dialog.
The new group name is listed in the Groups list. You can edit the group
6.
name by selecting it and clicking Edit. You can delete the group name by
selecting it and clicking Delete.
7.
Click OK to close the dialog.
Creating Device Names
You can create or change a device name based on ISO/IEC 14908-1 subnet and
node IDs. To create or edit a device name, perform the following steps:
Select Names → Edit Devices to open the Select Device dialog, as shown in
1.
Figure 27.
Figure 27. Select Device Dialog
Select a domain from the Domains list. The devices that have been assigned
2.
names in that domain are listed in the Devices list. To add a new device
name, click New. The New Device Data dialog opens, as shown in
on page
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 37
38.
Figure 28
Page 44

Figure 28. New Device Data Dialog
3.
Enter the device’s name in the Device Name field, and then fill in the rest of
the fields in the New Device Data dialog. See the online help for information
about these fields.
4.
Click OK to close the New Device Data dialog and return to the Select Device
dialog. The new device name is listed in the Devices list. You can edit the
device name by selecting it and clicking Edit. You can delete the device name
by selecting it and clicking Delete.
5.
Click OK to close the dialog.
Creating Message Code Names
You can create or change an ISO/IEC 14908-1 message code name, and you can
optionally specify formatting for a message. To create message code names,
perform the following steps:
1.
Select Names → Edit Message Codes to open the Edit Message Codes dialog,
as shown in
Figure 29 on page 39.
38 Logging Data
Page 45

Figure 29. Edit Message Codes Dialog
2.
The Edit Message Codes dialog lists all currently defined message code
names. To create a new message code name, click New. The New Message
Code dialog opens, as shown in
Figure 30.
Figure 30. New Message Code Dialog
Enter the name of the message code, and the message code to which the new
3.
name should apply. See the online help for more information on these
settings.
4.
Click OK to close the New Message Code dialog and return to the Edit
Message Codes dialog. The new message code name is listed in the dialog.
You can edit the message code name by selecting it and clicking Edit. You
can delete the message code by selecting it and clicking Delete.
5.
Click OK to close the dialog.
Creating Domain Names
You can create or change an ISO/IEC 14908-1 domain name with the protocol
analyzer. To create domain names, perform the following steps:
Select Names → Edit Domains to open the Select Domain dialog, as shown in
1.
Figure 31 on page 40.
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 39
Page 46
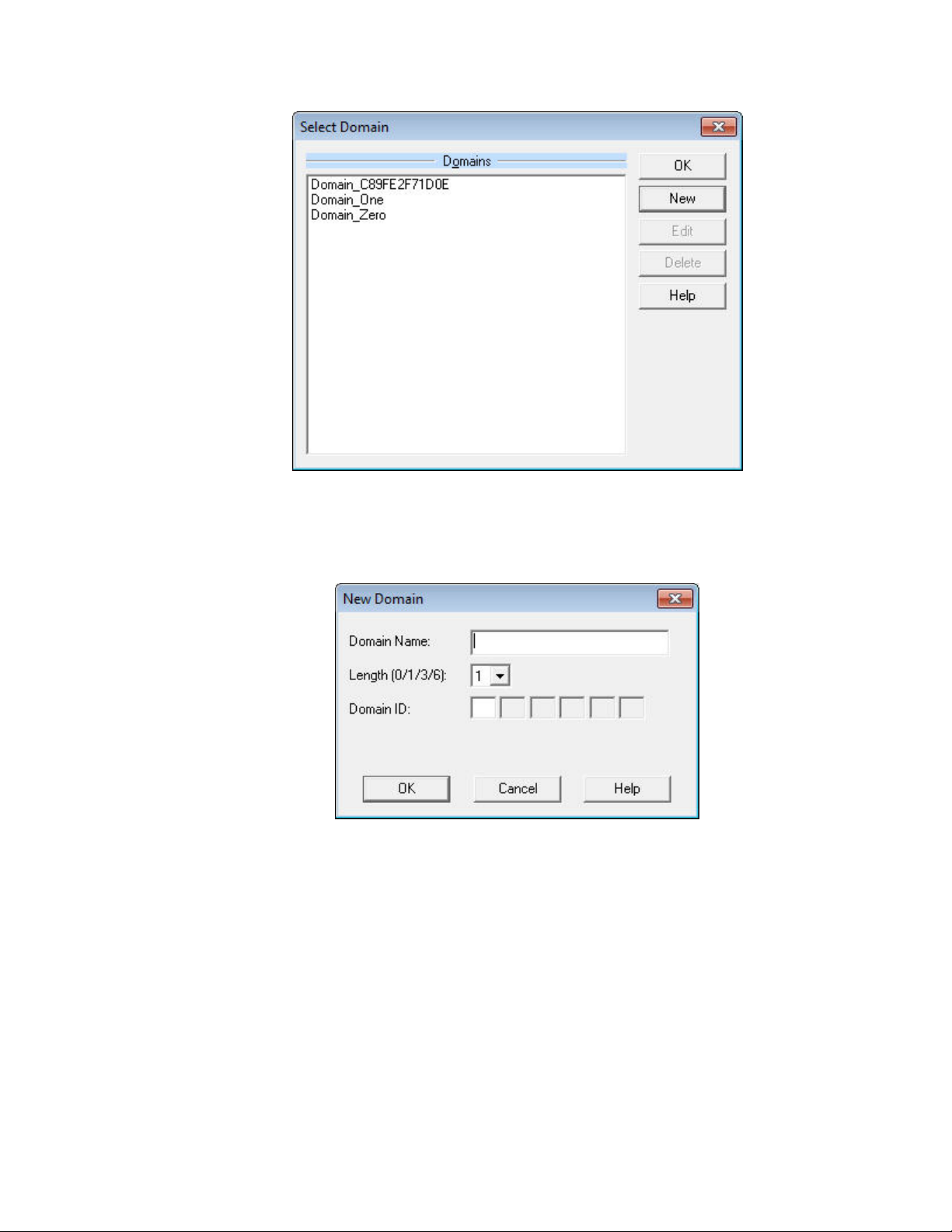
Figure 31. Select Domain Dialog
2.
The Select Domain dialog lists the domain names that are currently defined
in your network. To create a new domain name, click New. The New
Domain dialog opens, as shown in
Figure 32.
Figure 32. Edit Domain Dialog
3.
Enter a name for the domain in the Domain Name field, and set the domain
ID and length for the domain. See the online help for more information about
these fields.
4.
Click OK to close the New Domain dialog and return to the Select Domain
dialog. The new domain name is listed in the dialog. You can edit the
domain name by selecting it and clicking Edit. You can delete the domain
name by selecting it and clicking Delete.
Click OK to close the dialog.
5.
40 Logging Data
Page 47

Managing Names Files
You can save names that you have created, edited, or imported for later use by
saving them into a names file. When you create, edit, or import names, the
protocol analyzer starts using those names immediately. You can save the names
names file
to a
share them with other channels. You can also backup the names file for
safekeeping, and you can copy the names file to another computer that has the
LonScanner software installed so that you can interpret names within a packet
log on the second computer.
to prevent changing them in future LonScanner sessions or to
To manually save the names into a names file, select Names
open the Save File dialog, from which you can select the file name and directory
for the names file. After you save the names file, you can back it up, copy it to
another computer, or import it for use in future LonScanner sessions, as
described in
Importing Names from a Local Names File
→ Save Copy to
on page 30.
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 41
Page 48

Page 49

3
Analyzing Packet Log Details
This chapter describes how to organize and analyze the data
stored in your log files, including how to search a log file for
a specific packet, how to bookmark certain packets as being
of interest, and how to format the data in the Packet Log tab
for display. It also describes how to print and export log
files.
You can use the features described in this chapter when
viewing a saved log file, or when viewing an active log file.
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 43
Page 50

Searching For Packet Log Entries
You can quickly search a packet log to find a specific packet, even if your log file
contains log entries for hundreds or even thousands of packets. You can search a
log file for a string or for a specific packet number.
Searching By String
You can search any of the fields listed in the Packet Log tab for a specific string
by performing the following steps:
Select Edit → Find to open the Find String dialog, as shown in Figure 33.
1.
Figure 33. Find String Dialog
Enter the string you want to find in the Find String field.
2.
3.
Select the data fields that you want to search by selecting the appropriate
checkboxes in the Fields area. For example, select the Data checkbox to
search the data field of every packet in the log.
Click one of the Direction buttons to determine whether you want to search
upwards or downwards through the log. The search starts from the currently
selected log entry.
See the online help for descriptions of the fields in the dialog.
4.
Click Find Next to find the next occurrence of the string in the log file. Then,
you can use the Edit
additional occurrences of the same string with the same search conditions,
without having to use the Find String dialog.
You can highlight each log entry containing the string in the Packet Log by
clicking Highlight All. You can clear the highlights by clicking Clear
Highlights.
For an active log, you can turn off autoscrolling so that you can see the
highlighted log entry (or entries) that matches your find request.
→ Find Next and Edit → Find Prev commands to find
44 Analyzing Packet Log Details
Page 51

The LonScanner toolbar also includes buttons you can use to find a string,
and to move to the next occurrence of a string once you have begun a search.
For more information on the LonScanner toolbar, see
12.
page
Searching By Log Number
You can find a particular log entry by searching for its log packet number or its
arrival sequence number. The
assigned to the packet in the log. If you are using a circular log, this number
could change as log entries are added to and removed from the log. The
sequence number
analyzer collects it from the channel, and it does not change.
To search for a log entry by its log packet or arrival sequence number, perform
the following steps:
Select Edit → Go To to open the Go to Packet dialog, as shown in Figure 34.
1.
is a unique number assigned to the packet when the protocol
log packet number
LonScanner Toolbar
is the number currently
arrival
on
Figure 34. Go to Packet Dialog
2.
Select Log Packet Number to search for a packet by its log packet number.
Select Arrival Sequence Number to search for a packet by the sequence
number assigned to the packet when the protocol analyzer received it.
3.
Enter the packet or sequence number in the Number field, and click OK. The
Packet Log tab scrolls to the specified packet.
For an active log, you can turn off autoscrolling so that you can see the
highlighted log entry.
Bookmarking Packet Log Entries
You can use bookmarks to mark specific log entries as being of interest, so that
they are easier to find in the log. When you bookmark a log entry, that log entry
is highlighted in the Packet Log tab, so that it stands out. After you create a set
of bookmarks, you can scroll through the log from one bookmarked packet to the
next bookmarked packet.
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 45
Page 52

To use bookmarks, perform the following steps:
1.
Right-click the log entry in the Packet Log tab and click Toggle Bookmark
from the shortcut menu, or select Edit
Bookmark dialog, as shown in
For an active log, you can turn off autoscrolling so that you can see the
selected log entry.
Figure 35.
→ Toggle Bookmark, to open the Add
Figure 35. Add Bookmark Dialog
2.
Optional
optionally enter any descriptive text that you want to associate with the
bookmark in the Description text area. By default, the Description area
contains the message data associated with the log entry.
Click OK to save the bookmark and return the Packet Log tab. The packet
3.
appears highlighted in the Packet Log tab.
To scroll from bookmark to bookmark, use the Edit
→ Prev Bookmark commands. The LonScanner toolbar also includes buttons you
can use to scroll from bookmark to bookmark. For more information on the
LonScanner toolbar, see
To view all your bookmarks or delete any of your bookmarks, perform the
following steps:
46 Analyzing Packet Log Details
: Enter a name for the bookmark in the Name field. You can also
→ Next Bookmark and Edit
LonScanner Toolbar
on page 12.
Page 53

Select Edit → Bookmarks to open the Bookmarks dialog, as shown in Figure
1.
36.
Figure 36. Bookmarks Dialog
2.
The bookmarks are listed at the top of the dialog, sequentially by packet
number. Click a bookmark in the list to select that bookmark, and then click
Go To to scroll the Packet Log to that log entry. Or, click Delete to remove
the log entry from the log. To remove all packets at once, click Delete All.
Formatting the Packet Log
There are several ways to format the data that is displayed in the Packet Log tab.
You can select the fields to be displayed in the Packet Log, and you can change the
formatting for a field. You can also change the color that is used to highlight
bookmarked packets.
Selecting Data Fields
You can select the fields that are displayed in the Packet Log by performing the
following steps:
1.
Select View → Select Columns to open the Select Columns dialog, as shown
in
Figure 37 on page 48.
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 47
Page 54

Figure 37. Select Columns Dialog
The fields that are currently displayed in the Packet Log are listed in the
2.
Visible Fields list. See the online help for descriptions of these fields. To
change the column position of a field in the log, select the field and click Move
Up or Move Down to move the field. The top field is displayed on the left side
of the Packet Log, and the bottom field is displayed on the right side of the
Packet Log.
To remove a field from the Visible Fields list, select it and click Remove>>.
The field will move to the Hidden Fields list. To add a hidden field to the
Visible Fields list, select it and click <<Add.
Select the Apply to All New Windows checkbox to apply your changes to all
log files that you open during the current LonScanner session. The default is
for all data fields to be displayed.
3.
Click OK to save your changes and close the dialog.
Formatting Data Field Columns
You can change the formatting used to display the fields in the Packet Log tab by
performing the following steps:
1.
Select View → Format Columns to open the Format Columns dialog, as
shown in
48 Analyzing Packet Log Details
Figure 38 on page 49.
Page 55

Figure 38. Format Columns Dialog
The dialog defaults to the Packet Number tab, which you can use to format
2.
the Packet Number field. You can select the other tabs to format the other
data fields in the Packet Log window.
Fill in the fields on each tab, and then click OK to save your changes and
close the dialog. Or, click Apply to save your changes and continue
formatting data fields. See the online help for more information about how to
use each tab.
3.
To change the font used to display the fields in the Packet Log tab, select
→ Fonts. A Windows Font dialog opens. Select the font to use, and
View
click OK to save your changes.
Color-Coding the Packet Log
You can color-code certain log entries to make them stand out, including
bookmarked packets and messages that belong to certain transactions. For an
acknowledged message, a transaction includes the original message, all
acknowledgements from all receiving devices, all retries, and any challenge and
response messages. For a request/response message, a transaction includes the
request message, all response messages from all receiving devices, all retries, and
any challenge messages involved. When transaction color-coding is enabled, all
packets within the same transaction are colored the same color, so that it is
easier to find log entries for the packets involved in a particular transaction.
To use color-coding, perform the following steps:
1.
Select View → Colors to open the Colors dialog, as shown in Figure 39 on
page
50.
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 49
Page 56

2.
To enable transaction color-coding, select the Color Code Transactions
checkbox. When you enable this feature, the log entries for all the packets
involved a single transaction have the same color. Click the Transaction
Color 1, Transaction Color 2, and Transaction Color 3 buttons to select the
three transaction colors. The LonScanner tool uses transaction colors 1, 2,
and 3 in a rotation as new transactions begin.
To disable transaction color-coding, clear the Color Code Transactions
checkbox.
3.
To change the cell text or header text color in the Packet Log tab, click the
Cell Text Color or Header Text Color button in the Packet Window box.
To change the bookmark or highlight color, click the Bookmark Color or
4.
Highlight Color button in the Bookmark and Highlight area. The highlight
color is the color for packets highlighted by the Find String dialog.
To restore the default colors, click Defaults.
5.
6.
Click OK to save your settings and close the dialog.
Printing Log Files
Figure 39. Colors Dialog
To print a log file, perform the following steps:
1.
Select File → Print to open the Print Selection dialog, as shown in Figure 40
on page
50 Analyzing Packet Log Details
51.
Page 57

Figure 40. Print Selection Dialog
2.
Select the packets that you want to print and click OK. The Windows Print
dialog appears, from which you can select a printer and print the selected log
entries.
You can also print any of the statistics tabs described in
Statistics and Trend Graphs
the tab that you want to print, and select File
dialog.
Exporting Log Files
You can export the contents of a log file to a text or XML file. You can use the
XML file format to export packets to other applications.
To export a log file, perform the following steps:
Select File → Export to open the Packet Log Export dialog, as shown in
1.
Figure 41.
Viewing Channel
on page 22. To print one of the statistics tabs, select
→ Print to open the Windows Print
Figure 41. Packet Log Export Dialog
2.
Select the packets to be exported in the What to Export area.
3.
Use the options in the Format area to determine whether the selected log
entries will be exported into a text file or an XML file. If you select a text file,
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 51
Page 58

each log entry is written to the output file as a single line of plain ASCII text,
followed by an end-of-line terminator. If you are exporting a text file, choose
what character will be used to separate the fields of a single log entry from
the Delimiter options.
Enter the name of the file to contain the exported log in the Output file field.
By default, the file is created in the L
ONWORKS LonScanner directory. To
select a different directory, click Browse.
Click OK to export the selected log entries.
4.
52 Analyzing Packet Log Details
Page 59

4
Example Logs
This chapter describes the example log files that are
included with the LonScanner software.
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 53
Page 60

Example Packet Logs
Two example logs are included with the LonScanner software. One of the
example log files is taken from a channel without any names defined. The second
example log file is taken from a channel that has imported a set of names from an
LNS database.
Sample 1: Channel without Assigned Names
The first example log file is shown in Figure 42. There are no names defined for
this log file. This example shows how you can use a log file to find the log entry
for a request message, find the log entry for the response to the request, and
finally, how you can find the acknowledgement for the response.
Figure 42. Example Log File One – Packet 12 Selected
Figure 42, packet 12 is selected in the Packet Log. In this example, the
In
formats for the Num and the Time fields have been changed from their defaults.
Based on the data fields in the Packet Log, packet 12 is from a device with
subnet/node address 1/1 (Source field) that sent a Network Variable Fetch
request message to a device with subnet/node address 1/2 (Destination field).
From the information in the Packet Detail pane, you can determine that the
request message code is 0x73. For a complete list of network diagnostic
messages, see the
A network variable fetch retrieves the value of a network variable from a device
by its index in the device. Thus, a fetch can be used to poll the value of a network
54 Example Logs
ISO/IEC 14908-1 Control Network Protocol Specification.
Page 61

variable. In this example, the network variable index is 6. At packet 13, device
1/2 responds to device 1/1. The success response code is 0x33, and the returned
data is “0 0” in raw format.
Figure 43. Example Log File One – Packet 16 Selected
Figure 43, packet 16 is selected in the Packet Log. At packet number 16,
In
device 1/1 sends an acknowledgement to device 1/2. The Data field for packet 16
shows “NVO_848=51201,” which means that the network variable is an output
network variable with selector number 848. A selector is the number used by the
Neuron firmware to associate a network variable update message with a network
variable on the device. In this example, the network variable type is
SNVT_switch and the data sent is “C8 01” (hex) which is “200 1” in raw format.
51201 is the decimal display for 0xC801. Packet number 17 is the
acknowledgment.
Sample 2: Channel with Names Imported from an LNS Database
The second example log file is shown in Figure 44 on page 56. The names shown
in this log file have been imported from an LNS database. This example shows
how you can search a log for responses to a message sent using the acknowledged
messaging service.
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 55
Page 62

Figure 44. Example Log File Two – Packet 13 Selected
Figure 44, packet 13 is selected in the Packet Log. At packet number 13,
In
device DI-1 is sending out a group acknowledged network variable update
message (group number 0). The message data (Data field) is “100.0 1”, which is a
SNVT_switch structure. At packets 14 and 15, device DO-1 and LNS Network
Interface send acknowledgments back to device DI-1. These packets represent a
fan-out connection from device DI-1 to device DO-1 and an LNS Network
Interface.
At packet number 18, device DI-1 is sending a repeated network variable update
message to device DO-1. The retry count is 3 by default, and packets 19 to 21 are
the retry messages. Because this message was sent using the repeated
messaging service, no response is expected from the target device DO-1.
56 Example Logs
Page 63

Figure 45. Example Log File Two – Packet 24 Selected
At packet number 22, device DI-1 is sending out an acknowledged network
variable update message to device AO-1, but device AO-1 fails to respond.
Packets 23 through 25 are retry messages (see
path attribute is set on the last two attempts, packet number 24 and 25, of
an acknowledged transaction. This concept also applies to a
request/response transaction. If a host monitoring application fails to get
an update, check the log file to verify whether the target device fails to
respond to a network variable fetch message.
Figure 45). The alternate
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 57
Page 64

Page 65

A
Network Interfaces
This appendix lists the Echelon network interfaces that you
can use with the protocol analyzer, and describes any special
considerations for using each type of network interface.
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 59
Page 66

Network Interfaces Overview
You can use any of the following Echelon network interfaces with the
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer:
U10 USB Network Interface
ONWORKS network interfaces for any computer with a USB interface,
L
which includes most desktop, laptop, and embedded computers. These
network interfaces are ideal for use in applications that require a
computer to monitor, manage, or diagnose a network. The interfaces
feature support for TP/FT-10 channels (the U10) or PL-20 channels (the
U20), and provide simple plug-and-play installation. See the
USB Network Interface User's Guide
information about the USB network interfaces.
PCLTA-20/SMX PCI Network Interface
Interface
personal computers equipped with a 3V (PCLTA-21) or 5V (both PCLTA20 and PCLTA-21) 32-bit PCI interface. These network interfaces are
ideal for use in applications that require a desktop or embedded computer
to monitor, manage, or diagnose a network. There are four versions of
the PCLTA-21 card that include an onboard transceiver (TP/FT-10,
TP/XF-78, TP/XF-1250, or TP-RS485), and one version of the PCLTA-20
card that accepts a standard modular transceiver (SMX) which can be
used with any media type for which an SMX transceiver exists. Before
using either a PCLTA-20 or a PCLTA-21 with the protocol analyzer, you
must configure it to operate as a layer-2 network interface. For
instructions, see
— LONWORKS network interfaces for desktop and embedded
PCC-10 and PCLTA-20/21
and
U20 USB Network Interface
(078-0296-01B) for more
and
PCLTA-21 PCI Network
on page 61.
—
LonWorks
PCC-10 PC Card
equipped with a type II PC card (formerly PCMCIA) interface, which
includes most laptop computers. Includes an integral TP/FT-10
transceiver for use with TP/FT-10 channels. Other transceiver types can
be connected to the PCC-10 through external transceiver pods. Before
using a PCC-10 with the protocol analyzer, you must configure it to
operate as a layer-2 network interface. For instructions, see
PCLTA-20/21
i.LON SmartServer
network interface (RNI) that can be accessed through an Ethernet or
dial-up IP connection, with optional IP-852 routing support. This
network interface is ideal for use in applications requiring remote access
via a LAN or the Internet and allows you to remotely monitor a network
with the LonScanner tool. The LonScanner tool can either be used with
the remote network interface (RNI) capability of the
with an IP-852 channel created using the optional IP-852 routing of the
i
.LON products. LonScanner IP-852 support requires an LNS Turbo
Server. The LonScanner tool is also compatible with the original
SmartServer and all versions of the
i.LON SmartServer 2.0 User's Guide
information about the
as an RNI or an IP-852 router. If you are using an earlier version of the
i
.LON product, see the user’s guide for the version that you are using.
— LONWORKS network interface for any computer
on page 61.
— Controller, Web server, and LONWORKS remote
i
.LON products, or
i
.LON 100 Internet Servers. See the
(078-0345-01E) for more
i.
LON SmartServer, including how to configure it
PCC-10 and
i
.LON
60 Network Interfaces
Page 67

See the
information about creating an IP-852 channel with an
LNS server.
i.LON 600 LONW
remote network interface (RNI) that can be accessed through an Ethernet
or dial-up IP connection. You can use the IP-852 router to connect a
ONWORKS channel to an IP-852 backbone. The LonScanner tool can
L
either be used with an IP-852 channel created using the IP-852 routing of
the
the
Server. This router is ideal for use in large networks requiring an IP
backbone. See the
0272-01) for more information about the
to configure it as an RNI or an IP-852 router. See the
User's Guide
852 channel with an
See the Echelon Web site at
network interfaces.
IP-852 Channel User's Guide
ORKS
/IP Server
i
.LON 600, or with the remote network interface (RNI) capability of
i
.LON 600. LonScanner IP-852 support requires an LNS Turbo
i.LON 600 LonWorks/IP Server User's Guide
(078-0312-01A) for more information about creating an IP-
i
.LON 600 or an LNS server.
www.echelon.com for more information about these
PCC-10 and PCLTA-20/21
You can use a PCC-10, PCLTA-20, or PCLTA-21 with the protocol analyzer.
Before using one of these cards, you must configure the card to operate as a layer2 network interface with the L
the following steps:
ONWORKS Plug ‘n Play application, by performing
(078-0312-01A) for more
i
.LON server or an
—IP-852 router and a LONWORKS
(078-
i.
LON 600 router, including how
IP-852 Channel
Open the Windows Control Panel, and double-click the LONWORKS Plug
1.
‘n Play icon to open the LonWorks Plug ‘n Play dialog, as shown in
46.
Figure 46. L
ONWORKS Plug ‘n Play Application
Figure
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 61
Page 68

Select the network interface that you want to configure in the Device
2.
Selected dropdown list box.
For the NI Application dropdown list box:
3.
a.
If you are using a PCC-10, select PCC10VNI.
b.
If you are using a PCLTA-20 or a PCLTA-21, select PCL10VNI.
4.
Click OK to save your changes and close the dialog. You can now use
your PCC-10, PCLTA-20 or PCLTA-21 with the protocol analyzer.
See one of the following manuals for additional information:
•
LonWorks PCC-10 PC Card User's Guide
•
LonWorks PCLTA-20 PCI LonTalk Adapter User's Guide
•
LonWorks PCLTA-21 PCI Interface User's Guide
(078-0155-01B)
(078-0271-01A)
(078-0179-01C)
62 Network Interfaces
Page 69

LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer
Software License Agreement
To successfully install the LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer
software, you must agree to the terms of the software license
agreement. This appendix shows the agreement.
B
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 63
Page 70

LONSCANNER™ FX PROTOCOL ANALYZER
NOTICE
This is a legal agreement between you and Echelon Corporation (“Echelon”). YOU MUST READ
AND AGREE TO THE TERMS OF THIS SOFTWARE LICENSE AGREEMENT BEFORE ANY
LICENSED SOFTWARE CAN BE DOWNLOADED OR INSTALLED OR USED. BY CLICKING ON THE
“I AGREE” OR “I ACCEPT” BUTTON OF THIS SOFTWARE LICENSE AGREEMENT, OR
DOWNLOADING LICENSED SOFTWARE, OR INSTALLING LICENSED SOFTWARE, OR USING
LICENSED SOFTWARE, YOU ARE AGREEING TO BE BOUND BY THE TERMS AND CONDITIONS
OF THIS SOFTWARE LICENSE AGREEMENT. IF YOU DO NOT AGREE WITH THE TERMS AND
CONDITIONS OF THIS SOFTWARE LICENSE AGREEMENT, THEN YOU SHOULD EXIT THIS PAGE
AND DO NOT DOWNLOAD OR INSTALL OR USE ANY LICENSED SOFTWARE. BY DOING SO
YOU FOREGO ANY IMPLIED OR STATED RIGHTS TO DOWNLOAD OR INSTALL OR USE
LICENSED SOFTWARE.
LonScanner Software License Agreement
In consideration of Your agreement to the terms of this Agreement, Echelon grants You a
limited, non-exclusive, non-transferable license to use up to two (2) Activated copies of the
Licensed Software and Documentation for each Activation Key that You purchase according to
the terms set forth below. If the Licensed Software is being provided to You as an update or
upgrade to software which You have previously licensed, then You agree the Licensed
Software may be used and transferred only as part of a single product package and may not
be separated for use on more than two (2) computers per Activation Key as expressly
provided below.
DEFINITIONS
For purposes of this Agreement, the following terms shall have the following meanings:
• “Documentation” means the documentation included with the Licensed Software.
• “Licensed Software” means all computer software and associated media, printed materials,
and online or electronic documentation that accompany the LonScanner product;
including, without limitation, any and all executable files, add-ons, stencils, templates,
filters, tutorials, help files and other files, that accompany such software or are in the
accompanying documentation. The Licensed Software also includes any software updates,
add-on components, stencils, templates, shapes, SmartShapes symbols, Web services
and/or supplements that Echelon may provide to You or make available to You, or that
You obtain from the use of features or functionality of the Licensed Software, after the
date you obtain your initial copy of the Licensed Software (whether by delivery of a CD,
permitting downloading from the Internet or a dedicated Web site, or otherwise) to the
extent that such items are not accompanied by a separate license agreement or terms of
use.
• “Demonstration Mode” refers to a restricted mode of the Licensed Software where it will
operate without full functionality as described in the Documentation, including but not
limited to partial display of incoming packets.
• “Activation Key” refers to a software key provided by Echelon that activates a copy of the
Licensed Software on a particular computer such that the Licensed Software is no longer in
Demonstration Mode. An Activation Key may be purchased for a single computer, or may
be purchased in packs for multiple computers.
• “Activate(d)” refers to the process of entering an Activation Key into the Licensed Software
such that the Licensed Software is no longer running in Demonstration Mode.
64 LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer Software License Agreement
Page 71

• “You(r)” means Licensee, i.e. the company, entity or individual who has rightfully
acquired the Licensed Software.
LICENSE
You may:
(a) install and use the Licensed Software on any number of computers in Demonstration
Mode;
(b) Activate the Licensed Software on any number of primary computers (the “Primary
Computer”), provided that you have purchased and installed an Activation Key from
Echelon for each Activated Primary Computer;
(c) Activate a second copy of the Licensed Software on one (1) additional computer (the
“Additional Computer”) for each Primary Computer, for the exclusive use of the individual
who is the primary user of the Licensed Software installed on the Primary Computer,
provided that the Licensed Software may only be used on one of the two computers at a
time, and provided that such installation and use otherwise comply with all the terms and
conditions of this Agreement;
(d) physically transfer an Activation Key from one computer to another, provided that the
Licensed Software is no longer Activated on the computer on which it was previously used
and the Licensed Software is Activated on only one Primary Computer and one Additional
Computer per purchased Activation Key at a time;
(e) copy the Licensed Software as necessary for the uses expressly permitted above; and
(f) transfer Your rights under this Agreement to an end user of the Licensed Software;
provided that (i) You require the transferee to execute two copies of the Software License
Transfer Agreement included with the Licensed Software, (ii) You retain one (1) signed
original thereof and furnish Echelon with a copy of same upon request, and (iii) the
Licensed Software is Activated on only one Primary Computer and one Additional
Computer per purchased Activation Key at a time. This right of transfer is exercisable on
a one-time-only basis, and Your transferee shall have no right whatsoever to further
transfer any rights to the Licensed Software.
You may not, and shall not permit others to:
(a) Activate more than one Primary Computer and one Additional Computer at a time for each
Activation Key that You purchase;
(b) Activate the Licensed Software on a Primary Computer without purchasing an Activation
Key;
(c) Activate the Licensed Software on an Additional Computer without purchasing an
Activation Key for the associated Primary Computer;copy the Licensed Software (except as
expressly permitted above), or copy the Documentation;
(d) modify, translate, reverse engineer, decompile, disassemble or otherwise attempt (i) to
defeat, avoid, bypass, remove, deactivate, or otherwise circumvent any software
protection mechanisms in the Licensed Software, including without limitation any such
mechanism used to restrict or control the functionality of the Licensed Software, or (ii) to
derive the source code or the underlying ideas, algorithms, structure or organization from
the software from the Licensed Software (except to the extent that such activities may not
be prohibited under applicable law); or
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 65
Page 72

(e) except for the limited rights granted above, distribute, rent, loan, lease, transfer or grant
any rights in the Licensed Software or modifications thereof or accompanying
documentation in any form to any person without the prior written consent of Echelon.
This license is not a sale. Title, copyrights and all other rights to the Licensed Software,
Activation Key, Documentation, and any copy made by You remain with Echelon.
TERMINATION
This license will continue in effect until terminated. Unauthorized copying of the Licensed
Software, Activation Key, or the Documentation, or failure to comply with the terms and
conditions contained herein, will result in automatic termination of this license and will make
available to Echelon other legal remedies. This Agreement will terminate automatically
without notice, (i) upon the institution by or against You of insolvency, receivership or
bankruptcy proceedings or any other proceedings for the settlement of Your debts, (ii) upon
You making an assignment for the benefit of creditors, or (iii) in the event of Your dissolution
or insolvency. Upon termination of this license for any reason You shall destroy all copies of
the Licensed Software, and shall certify to Echelon in writing that all such copies are
destroyed.
TRADEMARKS
You may make appropriate and truthful reference to Echelon, Echelon products and technology
in Your company and product literature; provided that You properly attribute Echelon’s
trademarks and do not use the name of Echelon or any Echelon trademark in Your name or
product name. No license is granted, express or implied, under any Echelon trademarks,
trade names, trade dress, or service marks.
LIMITED WARRANTY AND DISCLAIMER
Echelon warrants that, for a period of ninety (90) days from the date of delivery or
transmission to You, the Licensed Software under normal use will perform substantially in
accordance with the Licensed Software specifications contained in the documentation
accompanying the Licensed Software. Echelon’s entire liability and Your exclusive remedy
under this warranty will be, at Echelon’s option, to use reasonable commercial efforts to
attempt to correct or work around errors, to replace the Licensed Software with functionally
equivalent Licensed Software, or to terminate this Agreement and accept return of the
Licensed Software and refund Your purchase price less a reasonable amount for use.
EXCEPT FOR THE ABOVE EXPRESS LIMITED WARRANTIES AND CONDITIONS GIVEN BY
ECHELON ABOVE, ECHELON AND ITS SUPPLIERS MAKE AND YOU RECEIVE NO OTHER
WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS, EXPRESS, IMPLIED, STATUTORY OR OTHERWISE OR IN ANY
COMMUNICATION WITH YOU, AND ECHELON AND ITS SUPPLIERS SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIM
ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY, SATISFACTORY QUALITY, FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR NONINFRINGEMENT AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS. Echelon does not
warrant that the operation of the Licensed Software will be uninterrupted or error free or that
the Licensed Software will meet Your specific requirements.
SOME STATES OR OTHER JURISDICTIONS DO NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OF IMPLIED
WARRANTIES, SO THE ABOVE EXCLUSIONS MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU. YOU MAY ALSO HAVE
OTHER RIGHTS THAT VARY FROM STATE TO STATE AND JURISDICTION TO JURISDICTION.
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY
IN NO EVENT WILL ECHELON OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR LOSS OF OR CORRUPTION
TO DATA, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OF CONTRACTS, COST OF PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE
PRODUCTS OR OTHER SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, PUNITIVE, CONSEQUENTIAL OR INDIRECT
66 LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer Software License Agreement
Page 73

DAMAGES, LOSSES, COSTS OR EXPENSES OF ANY KIND ARISING FROM THE SUPPLY OR USE
OF THE LICENSED SOFTWARE OR ACCOMPANYING DOCUMENTATION, HOWEVER CAUSED
AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY (INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION NEGLIGENCE). THIS
LIMITATION WILL APPLY EVEN IF ECHELON OR AN AUTHORIZED DISTRIBUTOR HAS BEEN
ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES AND NOTWITHSTANDING THE FAILURE OF
ESSENTIAL PURPOSE OF ANY LIMITED REMEDY. EXCEPT TO THE EXTENT THAT LIABILITY
MAY NOT BY LAW BE LIMITED OR EXCLUDED, IN NO EVENT SHALL ECHELON’S OR ITS
SUPPLIERS’ LIABILITY EXCEED THE AMOUNTS PAID FOR THE LICENSED SOFTWARE. YOU
ACKNOWLEDGE THAT THE AMOUNTS PAID BY YOU FOR THE LICENSED SOFTWARE REFLECT
THIS REASONABLE ALLOCATION OF RISK.
SOME STATES OR OTHER JURISDICTIONS DO NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OR LIMITATION
OF LIABILITY FOR INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, SO THE ABOVE LIMITATIONS
AND EXCLUSIONS MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU.
SAFE OPERATION
YOU ASSUME RESPONSIBILITY FOR, AND HEREBY AGREE TO USE YOUR BEST EFFORTS IN,
DESIGNING, MANUFACTURING, COMMISSIONING, AND RECOVERING LONWORKS® DEVICES
HEREUNDER TO PROVIDE FOR SAFE OPERATION THEREOF, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED
TO, COMPLIANCE OR QUALIFICATION WITH RESPECT TO ALL SAFETY LAWS, REGULATIONS
AND AGENCY APPROVALS, AS APPLICABLE. THE LICENSED SOFTWARE, SMART
TRANSCEIVER, NEURON
LONWORKS NETWORK INTERFACES ARE NOT DESIGNED OR INTENDED FOR USE AS
COMPONENTS IN EQUIPMENT INTENDED FOR SURGICAL IMPLANT INTO THE BODY, OR
OTHER APPLICATIONS INTENDED TO SUPPORT OR SUSTAIN LIFE, FOR USE IN FLIGHT
CONTROL OR ENGINE CONTROL EQUIPMENT WITHIN AN AIRCRAFT, OR FOR ANY OTHER
APPLICATION IN WHICH THE FAILURE THEREOF COULD CREATE A SITUATION IN WHICH
PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH MAY OCCUR, AND YOU SHALL HAVE NO RIGHTS HEREUNDER
FOR ANY SUCH APPLICATIONS.
LANGUAGE
The parties hereto confirm that it is their wish that this Agreement, as well as other
documents relating hereto, have been and shall be written in the English language only. Any
translations are provided for convenience only, and the English language version shall control.
Les parties aux présentes confirment leur volonté que cette convention de même que tous les
documents y compris tout avis qui s'y rattache, soient rédigés en langue anglaise.
COMPLIANCE WITH EXPORT CONTROL LAWS
You agree to comply with all applicable export and reexport control laws and regulations,
including the Export Administration Regulations ("EAR") maintained by the United States
Department of Commerce. Specifically, you covenant that You shall not—directly or
indirectly—sell, export, reexport, transfer, divert, or otherwise dispose of any software, source
code, or technology (including products derived from or based on such technology) received
from Echelon under this Agreement to any country (or national thereof) subject to
antiterrorism controls or U.S. embargo, or to any other person, entity, or destination
prohibited by the laws or regulations of the United States, without obtaining prior
authorization from the competent government authorities as required by those laws and
regulations. You agree to indemnify, to the fullest extent permitted by law, Echelon from and
against any fines or penalties that may arise as a result of your breach of this provision. This
export control clause shall survive termination or cancellation of this Agreement.
®
CHIP, LONTALK® PROTOCOL, NEURON CHIP FIRMWARE AND THE
LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer User’s Guide 67
Page 74

GENERAL
This Agreement shall not be governed by the 1980 U.N. Convention on Contracts for the
International Sale of Goods; rather, this Agreement shall be governed by the laws of the State
of California, including its Uniform Commercial Code, without reference to conflicts of laws
principles. This Agreement is the entire agreement between You and Echelon and supersedes
any other communications or advertising with respect to the Licensed Software and
accompanying documentation. If any provision of this Agreement is held invalid or
unenforceable, such provision shall be revised to the extent necessary to cure the invalidity or
unenforceability, and the remainder of the Agreement shall continue in full force and effect. If
You are acquiring the Licensed Software on behalf of any part of the U.S. Government, the
following provisions apply. The Licensed Software and accompanying documentation are
deemed to be “commercial computer software” and “commercial computer software
documentation”, respectively, pursuant to DFAR Section 227.7202 and FAR 12.212(b), as
applicable. Any use, modification, reproduction, release, performance, display or disclosure of
the Licensed Software and/or the accompanying documentation by the U.S. Government or
any of its agencies shall be governed solely by the terms of this Agreement and shall be
prohibited except to the extent expressly permitted by the terms of this Agreement. Any
technical data provided that is not covered by the above provisions is deemed to be “technical
data-commercial items” pursuant to DFAR Section 227.7015(a). Any use, modification,
reproduction, release, performance, display or disclosure of such technical data shall be
governed by the terms of DFAR Section 227.7015(b).
Echelon, LON, LonTalk, LonWorks, and Neuron are U.S. registered trademarks of Echelon
Corporation. LonScanner is a trademark of Echelon Corporation.
68 LonScanner FX Protocol Analyzer Software License Agreement
Page 75

www.echelon.com
 Loading...
Loading...