Page 1
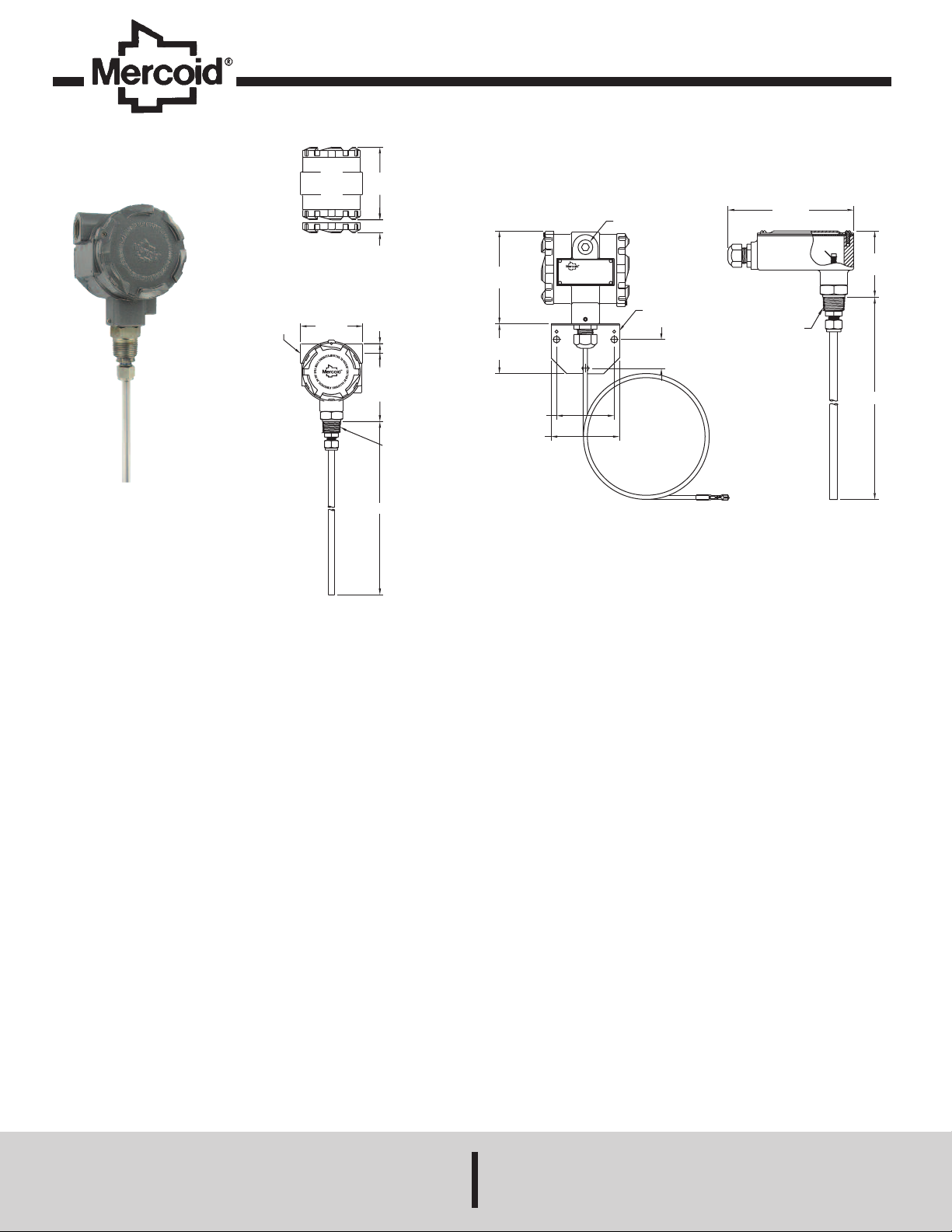
Series CRF2 Capacitive Level Transmitter
2X 1/2 FEMALE NPT
CONDUIT CONNECTION
3-19/32
(91.28)
4-1/2
(114.30)
3/4 MALE
NPT
PROCESS
CONNECTION
9/16
(14.29)
4-3/16
(106.36)
2X 3/4 (19.05)
CLEARANCE FOR
COVER REMOVAL
“L”
CONTINUOUS LEVEL TRANSMITTER
MOD CRF2
SERIAL:
INDUSTRIAL CONTROL EQUIPMENT
A DIVISION O F
DWYER INSTRU MEN TS, INC .
MICHIGAN CIT Y, I N 46 360 , U .S.A .
2X 1/2 FEMALE NPT
CONDUIT CONNECTION
4-7/16
(112.7)
2-3/8
(
60.3)
MOUNTING
BRACKET
1-3/8
(34.9)
2-3/4
(70.0)
3-1/4
(82.6)
3
-5/32
(
80.2)
6
(152.4)
3/4 MALE NPT
PROCESS CONNECTION
“L”
Specifications - Installation and Operating Instructions
Bulletin L-36
The Series CRF2 is a level transmitter providing a two-wire 4 to 20 mA
output to indicate level of liquids, powders and bulk materials. State of
the art sensing technology in the CRF2, using impulse RF admittance
measurement provides excellent accuracy and stability. The CRF2
senses capacitance changes resulting from the height of the material in
the tank between the probe and the tank wall. In non-metallic tanks or
tanks that do not have the wall parallel to the probe a ground reference
must be used.
The CRF2 comes with either a rigid or flexible probe depending on
application installation need and probe length required. Featured in the
CRF2 is easy push button calibration of zero and span. Custom order
the CRF2 to any length probe that you need for your application. FEP
covered probe is ideal for use with corrosive media.
MERCOID DIVISION
DWYER INSTRUMENTS, INC.
P.O. BOX 258 • MICHIGAN CITY, IN 46360 U.S. A.
SPECIFICATIONS
Service: Liquids, powders, and
bulk materials compatible with
wetted materials.
Wetted Materials: Standard:
rod/cable: FEP; connection: 316
SS. Ground Option: rod/cable
and connection: 316 SS; cable
spacers: PVC. Flange Option:
material of flange.
Capacitance Range: 0 to 2000
pF.
Sensitivity: 0.15 pF.
Minimum Span: 8 pF.
Accuracy: ±0.5 pF or ±0.25% of
span, whichever is greater.
Repeatability: ±0.25 pF or
±0.1% of span, whichever is
greater.
Temperature Limits: Ambient: 40 to 185°F (-40 to 85°C);
Process: -40 to 250°F (-40 to
121°C).
Pressure Limit: 100 psi (6.9
bar).
Power Requirements: 12 to 35
VDC.
Output Signal: 4 to 20 mA or 20
to 4 mA, 2 wire.
Response Time: 0.5 seconds.
Electrical Connection: Screw
terminal.
Conduit Connection: 1/2˝ NPT
female.
Process Connection: Standard:
3/4˝ NPT male. Optional: See
model chart.
Enclosure Rating: NEMA 4X
(IP66) weather-tight/corrosion
resistant.
Spark/Static Protection: 106Ω
dissipation resistance with spark
gap. Surge current to 100A max.
Calibration: Zero, Span, 4 mA,
20 mA.
Mounting Orientation: Vertical.
Weight: 6 ft rod type: 3.6 lb (1.63
kg).
Phone: 219/879-8000 www.dwyer-inst.com
Fax: 219/872-9057 e-mail: info@dwyer-inst.com
Page 2
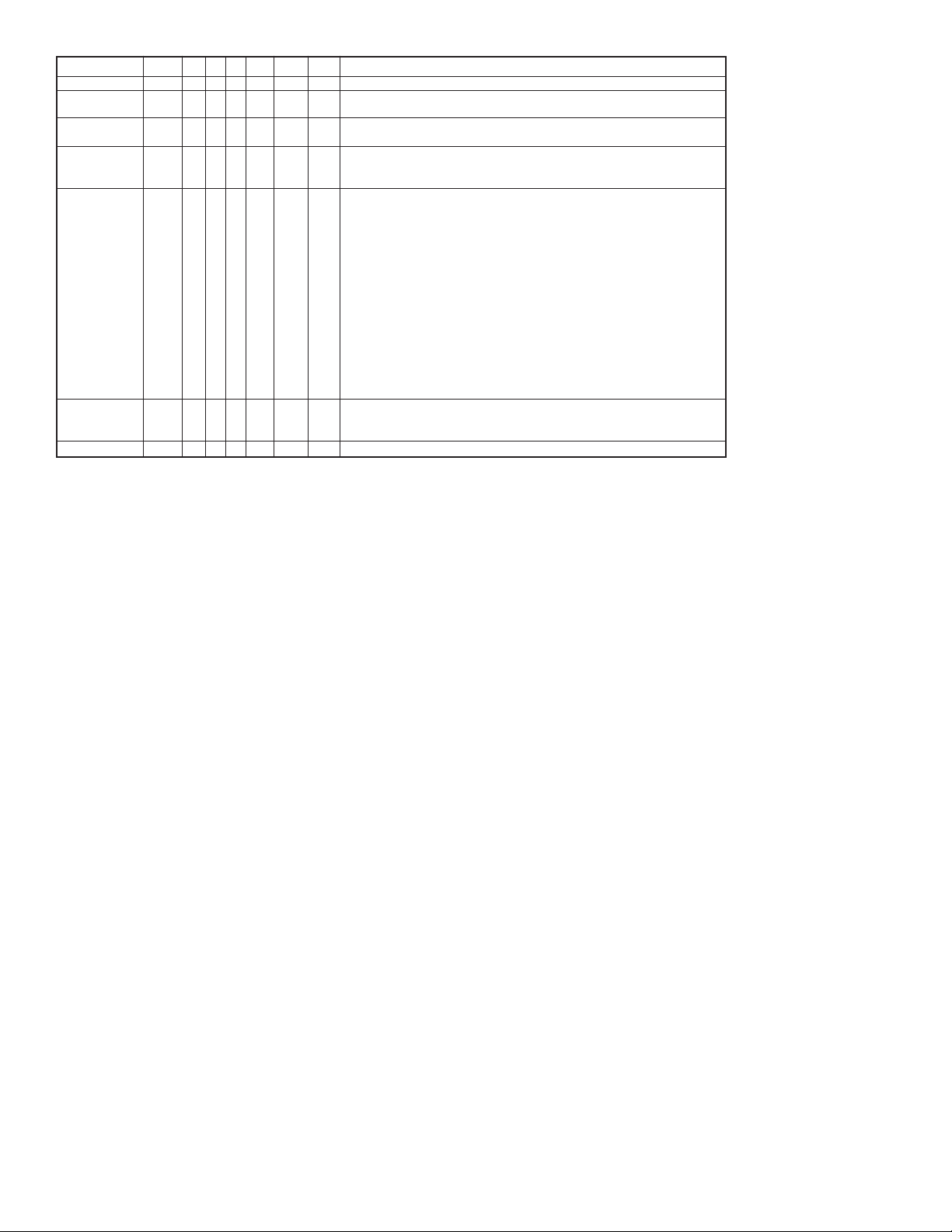
Example
Series
Enclosure
Probe Type
Ground
Process
Connection
Probe Length
Options
CRF2
CRF2
W
R
0
1T
048
M20
CRF2-WR01T-048-M20
W
R
R
C
0
A
U
1T
2T
3T
1B
2B
3B
1S
2S
3S
1F
2F
3F
4F
5F
6F
XXX
Capacitive Level Transmitter
Weatherproof
Remote Mount Weatherproof Housing
Rod
Cable
None Included
Attached ground rod (3˝ or 4˝ flange process connection types only)
Unattached ground rod
3/4˝ NPT male
1˝ NPT male
1-1/2˝ NPT male
3/4˝ BSPT
1˝ BSPT
1-1/2˝ BSPT
1˝ sanitary clamp
1-1/2˝ sanitary clamp
2˝ sanitary clamp
2˝ 150# flange, 316 SS
2˝ 150# flange, PVC
3˝ 150# flange, 316 SS
3˝ 150# flange, PVC
4˝ 150# flange, 316 SS
4˝ 150# flange, PVC
Insertion length in inches. Example 048 is 48˝ length.
Rod Type: minimum: 24˝, maximum: 144˝
Cable Type: minimum: 24˝, maximum: 360˝
M20
M20 conduit connection with cable gland
OPERATING PRINCIPLE
Capacitance and Dielectrics
Capacitance is the property of two or more conductors to store a charge
when there is a voltage difference between the conductors. In other
words capacitance relates the voltage between two conductors and the
amount of charge that can be held on the conductors (i.e., the number
of electrons). Capacitance is measured in Farads. Since a Farad of
capacitance represents a very large charge storage capacity, most
capacitance encountered is generally measured in microFarads (µF, 10-
6) or picoFarads (pF, 10-12). Capacitances encountered in level sensing
applications are generally in the 10’s or 100’s of pico Farads range.
The material between the conductors affects the capacitance also.
Insulating materials do not allow free movement of electrons, however
in an electric field the molecules of these materials will tend to align with
the field thus storing energy. This is called the dielectric effect and these
materials are often referred to as dielectrics. When placed between two
conductors the energy storage capability of these dielectrics will allow
more charge to be stored on the conductors for a given voltage
difference thus increasing the capacitance between the conductors. The
ratio of capacitance change caused by these dielectrics is referred to as
the dielectric constant. Different materials have differing dielectric
constants and will consequently change the capacitance between two
conductors more or less depending on the value of this constant. This
value ranges from 1.0 for a vacuum to over 100 for certain materials.
The dielectric constant for air is very close to 1.0 and usually assumed
to be exactly 1.0.
Capacitive level sensors determine the level of material by changes in
probe capacitance resulting from the movement of dielectric materials
between the probe and the reference ground electrode such as a tank
wall. Since measuring very small capacitance changes (less than 1 pF)
can be problematic in industrial environments, capacitance level sensing
tends to be most effective for materials with a dielectric constant greater
than 1.2. Since the difference in capacitance is being measured, it is
also possible to detect the level of two immiscible liquids that have
different dielectric constants such as oil and water.
Measurement
The CRF2 uses an impulse RF admittance measurement technique to
measure the probe capacitance. The impulse admittance measurement
offers advantages over other techniques in that it produces minimal
emissions to interfere with other communication or instrumentation
systems. The CRF2 continuously measures the probe capacitance.
Using this capacitance measurement, it computes a linear value with 0%
at the zero calibration value and 100% at the span calibration value.
From this the output current is computed and generated. Since no
assumptions are made regarding the relative value of the zero and span
calibration capacitances, the output can be set to measure from low to
high capacitance or high to low capacitance.
INSTALLATION
Unpacking
Remove the CRF2 from the shipping carton and inspect for damage. If
damage is found, notify the carrier immediately.
Materials
The CRF2 may be used to detect level of a variety of materials.
Conductive materials such as water require an insulated probe for
proper operation. When used with a conductive material, the material
itself must be grounded to the reference ground of the CRF2. This may
be done through a conductive tank wall or using an optional reference
ground electrode. Dry non-conductive materials may use either an
insulated or uninsulated probe. Capacitance level measurement is best
applied when the material dielectric constant is greater than 1.2. With
non-conductive materials, particularly low dielectric materials, the probe
should be spaced more closely to the reference ground to increase the
base capacitance and ensure reasonable sensitivity. The limiting factor
for spacing will be to ensure that material buildup around the probe is
avoided. For conductive materials this will be less of a concern since the
dielectric insulator around the probe is the predominant factor in the
capacitance changes with level.
Page 3

Mounting Location
SUPPORTS
6
(152.40)
MAX
1
(25.40)
MIN
7-1/16
(179.39)
DEAD AREA
“L”
• The process temperature and ambient temperature must be
within the specified limits.
• The probe must be located away from tank inlets or chutes
where material may fall on the probe during filling or emptying.
• Avoid placing the probe close to agitators or other such
devices.
• When used with high density bulk material, the probe must be
protected from material shifts that would bend or shift the
probe.
• If a cable probe is used, make sure that shifting bulk material will
not exert too much strain on the cable connections.
The accuracy of the CRF2 is very dependent on the installation of the
probe. The probe must be installed vertically and parallel to the
reference ground, particularly for non-conductive materials. The
reference ground may be a conductive tank wall or other internal parallel
metallic structure. If these are unavailable then a reference electrode
must be installed with the probe (See Figure 1). Support for the probe
and reference electrode must be provided to ensure these components
maintain their parallelism.
In nonmetallic tanks a ground reference must be provided. If the probe
is near the wall of the tank an adhesive backed metallic sheet may be
applied to the outside tank wall nearest to the probe. Other metallic
objects may be used also if they are in close proximity to the tank wall.
If the probe is located further than 6 inches from the wall, an internal
conductor must be provided parallel to and within 6 inches of the probe.
Maintain a minimum of 1 inch spacing between the probe and the
reference conductor. These conductors must be connected to the case
ground of the sensor. An internal ground clamp is provided for this if
other grounding is not available.
If turbulence or material movement within the tank could cause probe
movement, the probe must be supported appropriately with nonconductive material to minimize this movement (See Figure 2).
Electrical Connection (See Figure 3)
CAUTION
esigned for AC voltage operation .
d
Do not exceed the specified supply voltage rating. Permanent
amage not covered by the warranty may result. This unit is not
d
NOTE: Installation must be made in accordance with local codes and
regulations. When fishing wire through the conduit connection do not
allow the wire to touch or press on components on the boards. Damage
to the circuitry may result. Make sure that the wire is routed so it will not
interfere with the calibration switches.
The CRF2 provides a 1/2˝ NPT female port for conduit connection. The
conduit connection must be made such that condensation is not allowed
to enter the sensor housing. If necessary install a conduit breather drain
in a separate conduit body to prevent buildup of moisture. If nonmetallic
conduit is used the protective ground may be connected to the internal
ground connection screw.
The CRF2 transmitter is designed as a two wire 4 to 20 mA device.
Connection to the board is through a two pin terminal block. The circuitry
is non-polarized so the positive and negative leads may be connected to
either pin. It is recommended that shielded twisted pair wire be used if
the potential exists for interference from external noise sources. Ground
the shield at the case using the internal ground screw and leave the
other end of the shield open. Do not use the shield as one of the current
loop conductors.
The body of the CRF2 must be grounded to the tank or other earth
ground using the internal ground screw provided. If the tank is nonconductive then a reference electrode must be provided. This reference
electrode must be connected to the case ground.
Power Supply
The transmitter requires a minimum of 10 Volts DC at its connection for
proper operation, and a maximum of 35 Volts. Choose a power supply
with a voltage and current rating sufficient to meet this power
specification under all operational conditions. If the supply is
unregulated, make sure that the output voltage remains within the
required voltage range under all power line conditions. Ripple on the
supply should not exceed 100 mV.
Figure 1: Attached Ground
Rod Option
Figure 2: Supports to
Tank Side Wall
When installing a unit that has a Remote Mount Housing, the probe
should be installed before the coaxial cable is connected. This will
prevent twisting of the cable and possible damage to the unit. The
housing can be mounted in any position using the bracket provided,
being careful to prevent kinking or pulling the cable. The cable should be
connected to probe by inserting the cable through the cable gland on the
probe’s conduit enclosure and pushing the quick connect onto the spade
terminal provided. Be sure to replace the enclosure cover and tighten the
cable gland to protect and seal the connections.
Loop Resistance
The maximum allowable loop resistance is dependent on the power
supply voltage. The maximum loop voltage drop must not reduce the
transmitter voltage below the 10 Volt minimum. The maximum loop
resistance can be calculated using the following equation:
V
- 10.0
R
MAX
Where V
PS
=
20mA
is the power supply voltage.
ps
Page 4

P
OWER
S
UPPLY
R
ECEIVER/
R
EADOUT
––++
Z
ERO/
4
-MA
S
PAN/
2
0-MA
OUTPUT
Figure 3: Electrical Wiring Diagram
SETUP & CALIBRATION
Two multi-function buttons are provided for all calibration operations.
With these you can set the zero and span points, adjust the 4 and 20 mA
calibration points, or reset the 4 and 20 mA calibration points to the
factory settings. All settings are stored in nonvolatile memory so they will
not be lost if the power is removed.
Zero and Span Calibration
The zero and span calibration is done with the CRF2 installed in the
measured tank or vessel. Calibrating zero or span can be done in either
order as these settings are independent of one another. The calibration
can be done such that the output can go from 4 to 20 mA or from 20 to
4 mA depending on the desired measurement for full and empty
conditions.
The span or zero calibration is activated by pressing and holding the
corresponding ˝Zero˝ or ˝Span˝ button for three seconds. Set the tank
level to one endpoint (i.e., full or empty), then press and hold either the
Zero or Span button corresponding to the desired endpoint. Set the tank
to the other endpoint then press and hold the opposite Span or Zero
button. Calibration is now complete.
NOTE: Be careful to press the buttons only once within 3 seconds.
Double clicking the switches within 3 seconds will place the unit in
current calibration mode. If this happens press both buttons
simultaneously to exit the current calibration mode. If the calibration was
accidentally changed, the factory calibration can be restored as
described later in ˝Restore Factory Calibration˝.
Current Calibration
The 4 and 20 mA points of the CRF2 have been calibrated at the factory
and generally will not need to be recalibrated, but if needed the points
may be recalibrated. To do this you will need a milliammeter connected
in the current loop.
To calibrate the 4 mA calibration point, ˝double click˝ the Zero/4 mA
button by pressing it twice within 1.5 seconds. The milliammeter will
indicate approximately 4.00 mA. Adjust the 4 mA set point by pressing
the Zero/4 mA button to decrease the current and the Span/20 mA button
to increase the current. When complete, press both the Zero/4 mA and
Span/20 mA buttons simultaneously to exit the calibration mode.
To calibrate the 20 mA calibration point, ˝double click˝ the Span/20 mA
button by pressing it twice within 1.5 seconds. The milliammeter will
indicate approximately 20.00 mA. Adjust the 20 mA set point by pressing
the Zero/4 mA button to decrease the current and the Span/20 mA button
to increase the current. When complete, press both the Zero/4 mA and
Span/20 mA buttons simultaneously to exit the calibration mode.
NOTE: If the buttons are not pressed for approximately 4 minutes in
calibrate mode, the CRF2 will automatically revert to the normal
operation mode.
Restore Factory Calibration
The factory 4 and 20 mA calibration points may be restored by pressing
and holding both the Zero/4 mA and Span/20 mA buttons simultaneously
for 3 seconds. This must be done in the normal operation mode.
MAINTENANCE & REPAIR
Other than the controls mentioned in this manual there are no user
maintenance adjustments or routine servicing required for this product.
The unit is not field repairable and should be returned to the factory if
service is required. Disassembly or modifications made by the user will
void the warrantee and could impair the continued safety of the product.
If repair is required obtain a Returned Goods Authorization (RGA)
number and send the unit, freight prepaid, to the address below. Please
include a detailed description of the problem and conditions under which
the problem was encountered.
When the CLS2 with Sanitary Process Connection is to be used in a
sanitary or hygenic application, the unit must be cleaned and/or
sanitized in accordance with appropriate guidelines prior to installation.
The CLS2 with Sanitary Process Connection is suitable for “Clean In
Place” methods.
Dwyer Instruments Inc.
Attn: Repair Department
102 Highway 212
Michigan City, IN 46360
©Copyright 2012 Dwyer Instruments, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. 11/12 FR# M1-443559-00 Rev. 6
MERCOID DIVISION
DWYER INSTRUMENTS, INC.
Phone: 219/879-8000 www.dwyer-inst.com
Fax: 219/872-9057 e-mail: info@dwyer-inst.com
P.O. BOX 258 • MICHIGAN CITY, IN 46360 U.S. A.
 Loading...
Loading...