Page 1

DuPont™ Suva
refrigerants
Technical Information
P–HP
®
DuPont™
®
Suva
HP
Refrigerants
Properties, Uses,
Storage, and Handling
DuPont™ Suva® HP80 (R-402A) refrigerant
®
DuPont™ Suva
DuPont™ Suva
HP81 (R-402B) refrigerant
®
404A (HP62) refrigerant
Page 2

DuPont™ Suva® HP Refrigerants
Proper ties, Uses, Stora ge, and Handling
Table of Contents
Page
Introduction ................................................................................................................. 1
Background................................................................................................................ 1
Suva® HP Refrigerants ............................................................................................... 1
Uses ............................................................................................................................. 1
Physical Properties ..................................................................................................... 2
Chemical/Thermal Stability ........................................................................................ 2
Stability with Metals .................................................................................................... 2
Thermal Decomposition ............................................................................................10
Compatibility Concerns if R-502 and Suva® HP Refrigerants Are Mixed ...................10
Materials Compatibility ............................................................................................10
Elastomers ................................................................................................................10
Motor Materials .........................................................................................................12
Desiccants ................................................................................................................13
Refrigeration Lubricants ............................................................................................13
Safety ...........................................................................................................................13
Inhalation Toxicity......................................................................................................13
Cardiac Sensitization.................................................................................................15
Skin and Eye Contact................................................................................................15
Spills or Leaks........................................................................................................... 15
Combustibility of Suva® HP Refrigerants ...................................................................15
Air Monitors and Leak Detection ..............................................................................16
Types of Detectors ....................................................................................................16
Nonselective Detectors..........................................................................................17
Halogen-Selective Detectors .................................................................................17
Compound-Specific Detectors ...............................................................................17
Fluorescent Additives ............................................................................................17
Storage and Handling ................................................................................................17
Shipping Containers in the U.S..................................................................................17
Bulk Storage Systems ...............................................................................................18
Converting Bulk Storage Tanks from R-502 to Suva® HP Refrigerants..................19
Material Compatibility Concerns ............................................................................19
Handling Precautions for Suva® HP Refrigerant Shipping Containers .......................19
Recovery, Recycle, Reclamation and Disposal .......................................................20
Recovery ...................................................................................................................21
Recycle .....................................................................................................................21
Reclamation ..............................................................................................................21
Disposal ....................................................................................................................21
Page 3

Introduction
Background
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), which were developed over 60 years ago, have many unique properties. They are low in toxicity, nonflammable,
noncorrosive, and compatible with other materials.
In addition, they offer the thermodynamic and
physical properties that make them ideal for a
variety of uses. CFCs are used as refrigerants; as
blowing agents in the manufacture of insulation,
packaging, and cushioning foams; as cleaning
agents for metal and electronic components; and
in many other applications.
However, the stability of these compounds, coupled
with their chlorine content, has linked them to
depletion of the earth’s protective ozone layer. As
a result, DuPont has phased out production of CFCs
and introduced environmentally acceptable alternatives, such as the DuPont™ Suva
family.
®
HP refrigerant
In addition, DuPont has formulated a mixture based
on all-HFC refrigerants, which results in no ozone
depletion factor. This refrigerant is called Suva
®
404A (HP62), and its composition is:
HFC-125 HFC-143a HFC-134a
®
404A
Suva
(HP62), wt% 44 52 4
The individual components of the three mixtures
are listed in Table 1 to show their chemical names
and formulae. In addition, the physical properties
of the Suva
®
HP refrigerants are listed in Table 3.
Uses
The Suva® HP refrigerants can be used in virtually
all R-502-based applications, either as a result of
retrofiting existing equipment that uses R-502 or
following development of new equipment designed
to use the Suva
®
HP products.
Suva® HP Refrigerants
The products designated as Suva® HP refrigerants
are intended as replacements for R-502 in mediumand low-temperature refrigeration systems. The
®
Suva
HP refrigerant family contains two different
types of refrigerants. Both types involve the use of
refrigerant blends to achieve alternatives that will
act very much like R-502 in refrigeration systems.
The first type of blends incorporate the following
refrigerants in two compositions to optimize different performance characteristics:
HCFC-22 HFC-125 Propane
Suva® HP80
(R-402A), wt% 38 60 2
Suva® HP81
(R-402B), wt% 60 38 2
R-502 currently serves a wide range of applications
in the refrigeration industry. It is used widely in
supermarket applications, in food service and warehousing, for transport refrigeration, in cascade systems for very low temperatures, and other assorted
applications. It offers good capacity and efficiency
without suffering from the high compressor discharge temperatures that can be seen with HCFC22 single-stage equipment.
Suva® HP80 and HP81, which contain HCFC-22,
are each formulated to optimize different performance characteristics.
®
HP80 offers compressor discharge temper-
Suva
atures equivalent to R-502, with improved capacity versus R-502, and slightly lower theoretical
efficiency.
Table 1
Refrigerant Information
Refrigerant Chemical Name Formula CAS No. Molecular Wt.
HCFC-22 Chlorodifluoromethane CF2HCl 75-45-6 86.47
HFC-125 Pentafluoroethane CF
HFC-134a 1,1,1,2-Tetrafluoroethane CF
HFC-143a 1,1,1-Trifluoroethane CF
HC-290 Propane C3H
CHF
3
2
F 811-97-2 102.0
3CH2
3CH3
8
354-33-6 120.02
420-46-2 84.08
74-98-6 44.1
The DuPont Oval Logo, DuPont™, The miracles of science™, and
Suva® are trademarks or registered trademarks of E. I. du Pont de
Nemours and Company.
1
Page 4

Suva® HP81 offers the highest efficiency versus
R-502, with slightly better capacity. However, the
higher HCFC-22 content results in compressor
discharge temperatures in the range of 14°C (25°F)
higher than that of R-502, which makes Suva
®
HP81 most suited for medium-temperature systems
such as ice machines.
®
Suva
404A (HP62) offers the best overall properties when compared with R-502. Capacity and efficiency values should be equivalent to R-502, and
compressor discharge temperatures may be up to
9°C (14°F) lower than R-502, which may equate to
longer compressor life and better lubricant stability.
In addition, the heat transfer characteristics of
®
all the Suva
HP products appear to be better than
R-502, so any loss of compression efficiency may
be offset by improvements in heat transfer.
Due to the differences in operating characteristics
described above, Suva
cally selected for different applications. Suva
®
HP80 and HP81are typi-
®
HP81 is preferred where higher energy efficiency
and capacity are needed and where the higher discharge temperatures will not create operating diffi-
®
culties. Both Suva
are full-range R-502 replacements, with Suva
HP80 and Suva® 404A (HP62)
®
HP80 preferred for retrofitting of existing systems,
®
and Suva
ment. Suva
404A (HP62) preferred for new equip-
®
404A (HP62) can also be used for
retrofitting existing equipment where HFCs are
desired. Table 2 shows markets that currently use
each of these refrigerants.
Thermodynamic tables in English and SI units are
available in Bulletins T-HP80-ENG, T-HP80-SI,
T-HP81-ENG, T-HP81-SI, T-HP62-ENG, and
®
T-HP62-SI for Suva
®
Suva
404A (HP62).
HP80, Suva® HP81, and
Chemical/Thermal Stability
Stability with Metals
Stability tests for refrigerant with metals are typically performed in the presence of refrigeration
lubricants. Results of sealed tube stability tests
available for R-502/mineral oil and alkylbenzene
lubricants have shown long-term stability in contact
with copper, steel, and aluminum in actual refrigeration systems. Mineral oils, alkylbenzene, mixtures of mineral oil/alkylbenzene and polyol esters
(POE) are all possible candidates for use with
®
Suva
HP80 and HP81; POE are proposed lubri-
cants for use with Suva
The method followed was generally the same as
ASHRAE 97 with several minor modifications. A
3-mL volume of refrigerant/lubricant solution was
heated in the presence of copper, steel, and aluminum coupons in an oven for 14 days at 175°C
(347°F). Both the neat lubricant and a mixture of
lubricant and refrigerant (50/50 volume ratio) were
tested. Visual ratings were obtained on both the
liquid solutions and the metal coupons after the
designated exposure time. The visual ratings range
from 0 to 5, with 0 being best.
®
404A (HP62).
Table 2
DuPont™ Suva® HP Refrigerant
Market Applications
Product Medium Temperature Low Temperature
Suva® HP81 Ice Machines To Be Determined
®
HP80 Supermarket Supermarket
Suva
®
404A
Suva
(HP62) All
Food Service
Vending
Supermarket
Transport Transport
Food Service
Physical Properties
General physical properties of the Suva® HP refrigerants are shown in Table 3. Pressure-enthalpy diagrams for the Suva
Figures 1–6.
Additional physical property data may be found
in other DuPont publications. Bulletin ART-18
contains viscosity, thermal conductivity, and heat
capacity data for saturated liquid and both saturated
and superheated vapor. ART-18 also contains heat
capacity ratios for saturated and superheated vapor.
®
HP refrigerants are shown in
After the visual ratings were obtained, sample tubes
were opened and the lubricant and refrigerant (if
present) were analyzed. The lubricant was typically
checked for halide content and viscosity, while the
refrigerant was examined for the presence of decomposition products. Table 4 summarizes typical
data for Suva
®
HP refrigerants. Visual ratings are
listed for the neat lubricant, the lubricant/refrigerant solution, and the three metals that were present
in the lubricant/refrigerant solutions. Viscosity was
determined on the unused lubricant, the tested neat
lubricant, and the lubricant tested in the presence
of refrigerant. Decomposition products were determined in some cases. Typical measurements for
decomposition products is in the low parts per
million (ppm) range.
®
Suva
HP81 tests with various lubricants indicate it
has adequate chemical stability with these lubricants. In addition, we believe that HP80 will have
similar behavior due to the same refrigerants being
used in the formulation. Suva
®
404A (HP62) tests
with common POE lubricants indicate that chemical stability of Suva
®
404A (HP62) with common
metals used in refrigeration systems is acceptable.
2
Page 5

Table 3
General Property Information
Physical Property Unit (R-402A) (R-402B) (HP62)
Molecular Wt, avg. g/mol 101.55 94.71 97.6
Boiling Point, 1 atm °C –49.2 –47.4 –46.5
°F –56.5 –53.2 –51.6
Freezing Point °C n/a n/a n/a
°F
Critical Temperature °C 75.5 82.6 72.1
°F 167.9 180.7 161.7
Critical Pressure kPa 4135 4445 3732
psia 599.7 644.8 541.2
lb/ft
lb/ft
3
3
3
3
3
3
Critical Density kg/m
Liquid Density at 25°C (77°F) kg/m
Density, Saturated Vapor kg/m
at –15°C (5°F) lb/ft
Specific Heat at 25°C (77°F)
Liquid kJ/kg•K 1.37 1.34 1.53
Btu/lb•°F 0.328 0.320 0.367
Vapor, 1 atm kJ/kg•K 0.755 0.725 0.870
Btu/lb•°F 0.181 0.173 0.207
Vapor Pressure at 25°C (77°F) kPa 1337 1254 1255
psia 194.0 181.9 182.0
Heat of Vaporization kJ/kg 194.0 210.0 202.1
at Boiling Point Btu/lb 83.5 90.3 87.0
Thermal Conductivity at 25°C (77°F)
Liquid W/m•K 6.91E-2 7.35E-2 6.83E-2
Btu/hr•ft•°F 4.00E-2 4.25E-2 3.94E-2
Vapor, 1 atm W/m•K 1.266E-2 1.205E-2 1.346E-2
Btu/hr•ft•°F 7.32E-3 6.96E-3 7.78E-3
Viscosity at 25°C
(77°F)
Liquid Pa•s 1.38E-4 1.45E-4 1.28E-4
Vapor, 1 atm Pa•s 1.29E-5 1.28E-5 1.22E-5
Flammability Limit vol% None None None
in Air, 1 atm
Ozone-Depletion Potential (CFC-12 = 1) 0.02 0.03 0.0
Halocarbon Global (CFC-11 = 1) 0.63 0.52 0.94
Warming Potential
TSCA Inventory Status Reported/Included? Yes Yes Yes
Inhalation Exposure Limit AEL* ppm 1000 1000 1000
(8- and 12-hr TWA)
Suva® HP80 Suva® HP81 Suva® 404A
541.7 530.7 484.5
33.82 33.13 30.23
1151 1156 1048
71.86 72.14 65.45
19.93 16.90 18.20
1.24 1.05 1.14
* AEL (acceptable exposure limit) is an airborne inhalation exposure limit established by DuPont which specifies time-weighted
average concentrations to which nearly all workers may be repeatedly exposed without adverse effects.
3
Page 6
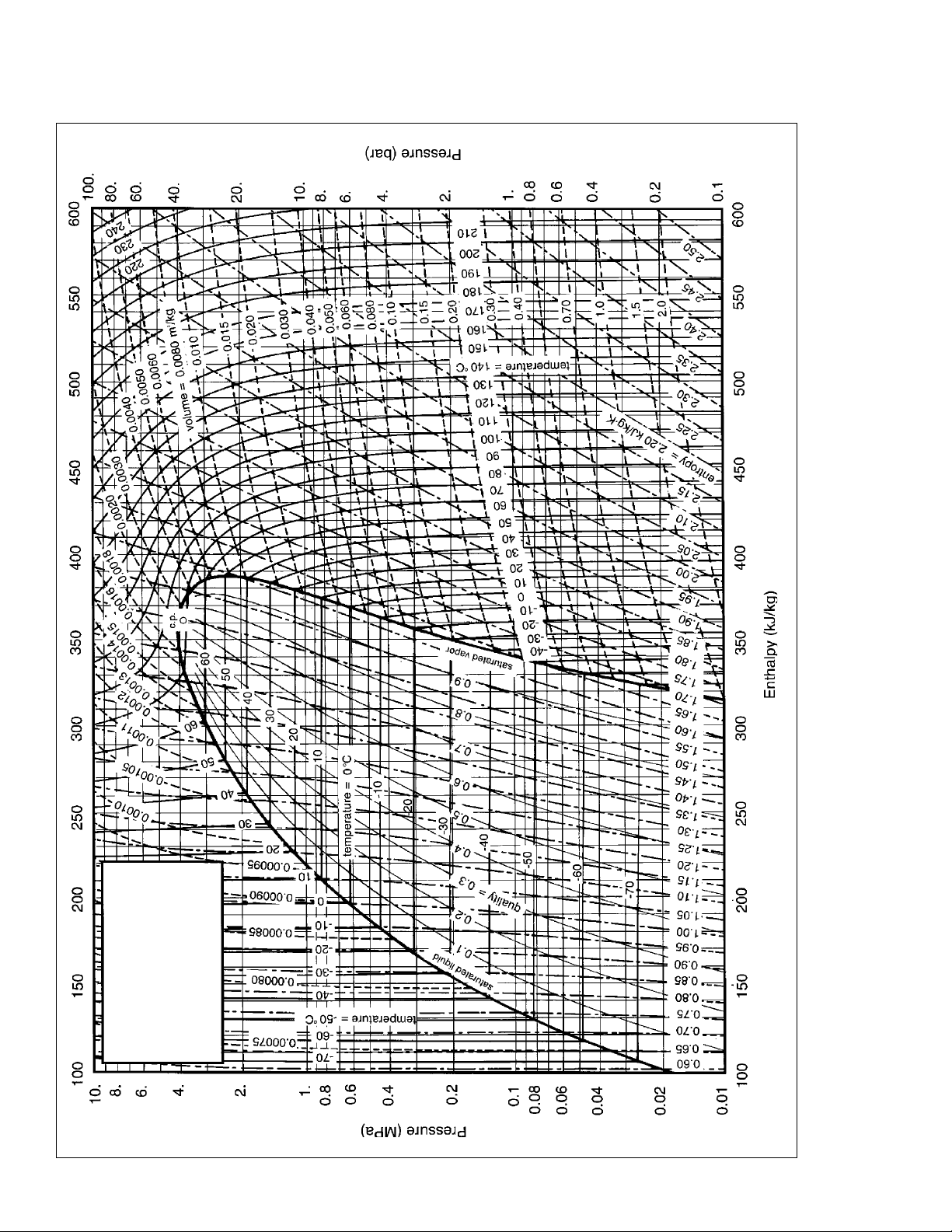
Figure 1. DuPont™ Suva® 404A (HP62) Pressure–Enthalpy Diagram (SI Units)
404A (HP62)
®
DuPont™
Suva
Pressure-Enthalpy Diagram
(SI Units)
4
Page 7
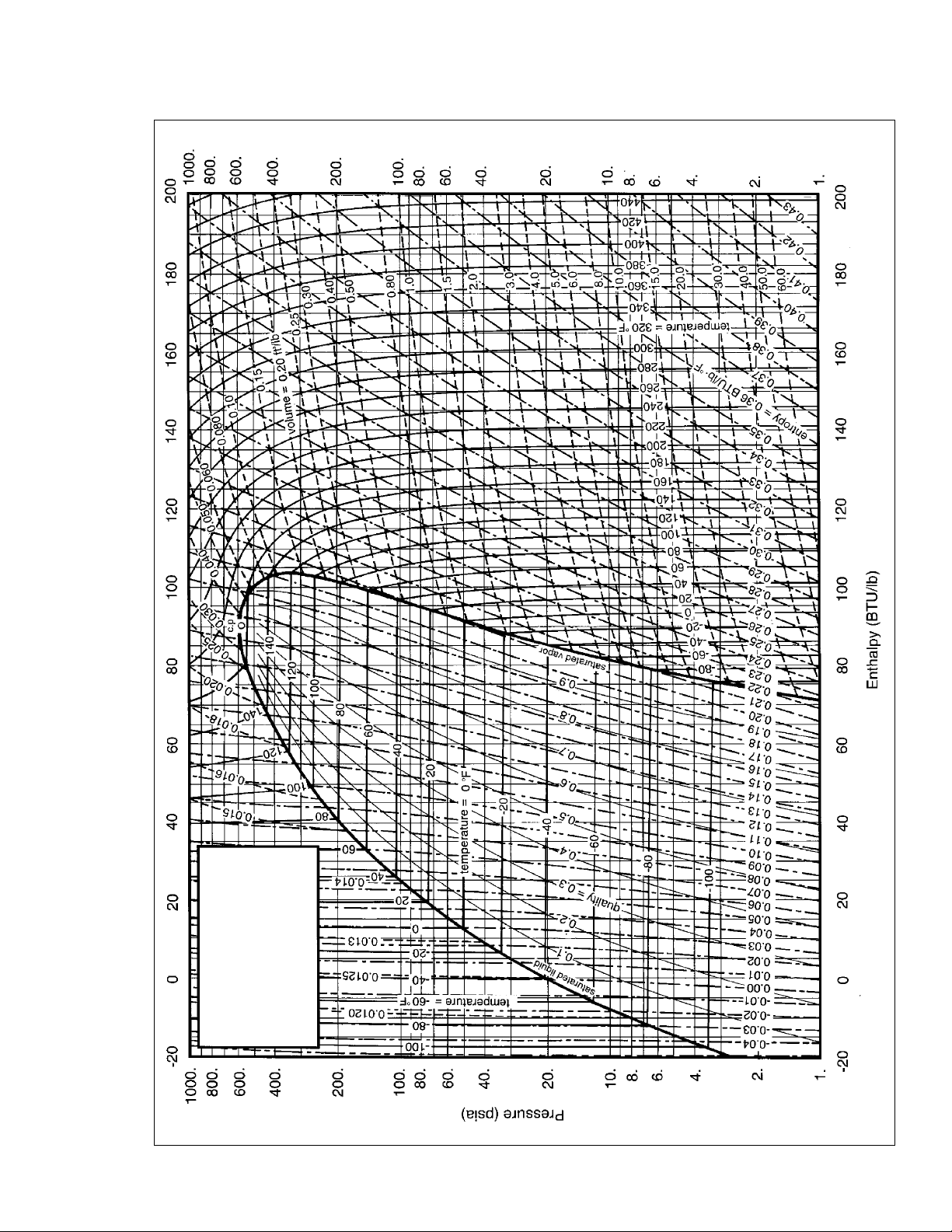
Figure 2. DuPont™ Suva® 404A (HP62) Pressure–Enthalpy Diagram (English Units)
404A (HP62)
®
DuPont™
Suva
Pressure-Enthalpy Diagram
(English Units)
5
Page 8
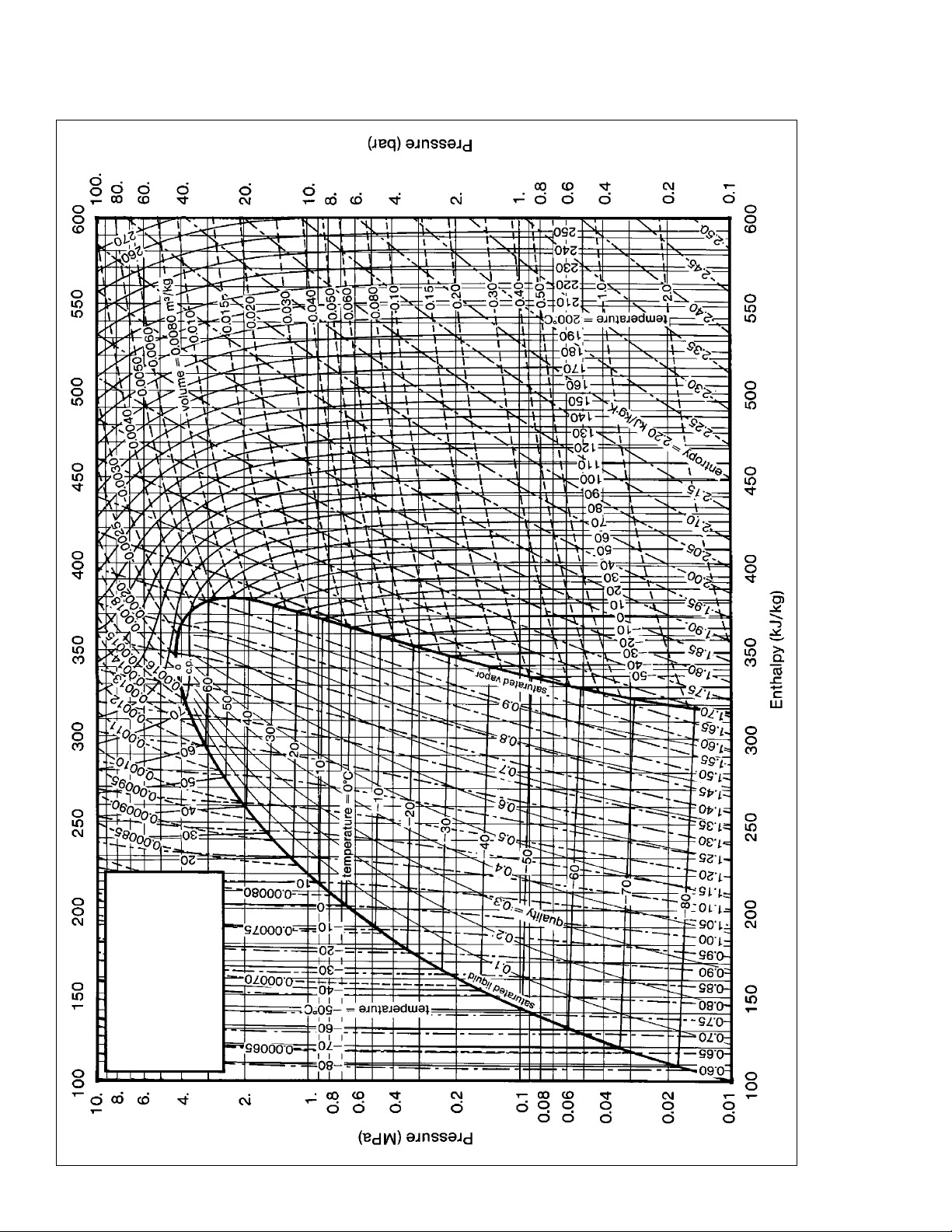
Figure 3. DuPont™ Suva® HP80 (R-402A) Pressure–Enthalpy Diagram (SI Units)
HP80 (R-402A)
®
DuPont™
Suva
Pressure-Enthalpy Diagram
(SI Units)
6
Page 9

Figure 4. DuPont™ Suva® HP80 (R-402A) Pressure–Enthalpy Diagram (English Units)
HP80 (R-402A)
®
DuPont™
Suva
Pressure-Enthalpy Diagram
(English Units)
7
Page 10

Figure 5. DuPont™ Suva® HP81 (R-402B) Pressure–Enthalpy Diagram (SI Units)
HP81 (R-402B)
®
DuPont™
Suva
Pressure-Enthalpy Diagram
(SI Units)
8
Page 11

Figure 6. DuPont™ Suva® HP81 (R-402B) Pressure–Enthalpy Diagram (English Units)
HP81 (R-402B)
®
DuPont™
Suva
Pressure-Enthalpy Diagram
(English Units)
9
Page 12

Note: Lubricant/refrigerant combinations shown
throughout this report are for the purposes of comparing the stability and compatibility of different
lubricants with the Suva
®
HP products. No recommendation is made or implied that these combinations will operate successfully in refrigeration
systems.
Thermal Decomposition
Like R-502, Suva® HP refrigerants will decompose
when exposed to high temperature or flame
sources. Decomposition may produce toxic and
irritating compounds, such as hydrogen chloride
and hydrogen fluoride. The decomposition products
released will irritate the nose and throat. Therefore,
it is important to prevent decomposition by following DuPont Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS)
recommendations for handling and use.
Compatibility Concerns if R-502 and
Suva® HP Refrigerants Are Mixed
R-502 and Suva® HP refrigerants are chemically
compatible with each other; this means that they
do not react with each other and form other compounds. However, when the different refrigerants
are mixed by accident or deliberately, they will
form mixtures that can be very difficult to separate.
Therefore, mixtures of R-502 and Suva
®
HP
refrigerants cannot be separated in on-site recycle
machines or in the typical facilities of an off-site
reclaimer. These mixtures will have to be disposed
of by incineration.
Also, mixtures of R-502 and Suva® HP refrigerants
will have performance properties different from
either refrigerant alone. These properties may not
be acceptable for your systems. Therefore, we do
not recommend mixing R-502 and Suva
®
HP refrigerants in any systems. First remove the R-502 properly (see page 21 for recovery discussion) and then
charge the new refrigerant.
Materials Compatibility
Because the Suva® HP refrigerants will be used in
many different applications, it is important to review materials of construction for compatibility
when designing new equipment, retrofitting existing equipment, or preparing storage and handling
facilities. Because the Suva
been designed as refrigerants, the compatibility
data summarized here will include materials
commonly used in refrigeration applications.
®
HP products have
Elastomers
Compatibility results for Suva® HP81 and Suva
404A (HP62) were developed with five different
polymer and lubricant combinations. It was assumed that Suva
®
HP80 compatibility would be
similar to HP81.
Recognize that these data reflect compatibility in
sealed tube tests, and that refrigerant compatibility
in real systems can be influenced by the actual operating conditions, the nature of the polymers used,
compounding formulations of the polymers, and the
curing or vulcanization processes used to create the
polymer. Polymers should always be tested under
actual operating conditions before reaching final
conclusions about their suitability.
The rankings shown in Table 5 are based on duplicate samples of each polymer subjected to aging
at 150°C (302°F) for 30 days in various lubricant/
refrigerant combinations. Physical properties of the
test samples were determined before and after aging. The resulting ratings are based on 1 being best
and 5 being worst for the purposes of comparison.
The factors included in the overall assessment of
compatibility included:
• visual observations of material changes due
to aging
• changes in weight and volume of the samples
due to aging
• changes in hardness of the samples due to aging
• changes in flexural properties of the samples
due to aging
• recovery of weight and flexural properties after
refrigerant evaporation
The compounds tested were:
• PTFE (Teflon
®
, commercial-grade skived sheet,
from Tex-O-Lon Mfg. Co.)
• Neoprene W (from Precision Rubber Co.)
• HNBR (hydrogenated nitrile butadiene, N1195
from Parker Seal Co.)
• EPDM (ethylene propylene diene, commercial
grade, Kirkhill Rubber Co.)
• NBR (BUNA N, nitrile butadiene, from Parker
Seal Co.)
Lubricants tested:
• Mineral Oil, Suniso 3GS, Witco Corporation
• Alkylbenzene, Zerol 150 TD, Shrieve Chemical
Products Inc.
• Polyol Ester, Icematic SW32, Castrol
• Polyol Ester, Arctic EAL22, Mobil
Chemical
®
10
Page 13

Table 4
Stability of HP Refrigerants with Metals and Lubricants
Suva® HP81 with various lubricants
HP81 with HP81 with
Mineral Oil, Alkylbenzene, HP81 with
Property 3GS 150 TD Icematic SW32
Suniso Zerol Polyol Ester, Castrol
Viscosity of Neat
Oil at 40°C (104°F), (mm)
2
/s (cSt) ND ND 29.6
Stability Tests
Visual Ratings
Neat Oil 0 ND 1,H
Oil/Refrig 1,G,H 2,P 0
Copper 0 2,T 0
Iron 0 0 1,T
Aluminum 0 0 0
Viscosity Change
% Change Neat ND ND 5.0
% Change w/ Refrig ND ND –13.3
Decomposition Analysis
[F-], ppm ND ND 7
[Cl-], ppm ND ND 7
(values for Suva® HP80 assumed to be comparable)
Suva® 404A (HP62) with various lubricants
®
404A (HP62) Suva® 404A (HP62) Suva® 404A (HP62) Suva® 404A (HP62)
Suva
with Mineral Oil, with Alkylbenzene, with with
Suniso Zerol Polyol Ester, Castrol Polyol Ester, Mobil
Property 3GS 150 TD Icematic SW32 Arctic EAL22
Viscosity of Neat
Oil at 40°C (104°F), (mm)
2
/s (cSt) ND ND 29.6 23.7
Stability Tests
Visual Ratings
Neat Oil 0 0 1,H 0
Oil/Refrig. 1,G 2,P,G,H 0,G 1,G
Copper 0 2,T 0 0
Iron 0 1,T 1,T,P 0
Aluminum 0 0 0 0
Viscosity Change
% Change Neat ND ND 5.0 ND
% Change w/ Refrig. ND ND ND ND
Visual Ratings: Stability Ratings: 0 to 5
ND = Not Determined 0 = Best
G = Gel 3 = Failed
T = Tarnish 5 = Coked
H = Haze
P = Precipitate
11
Page 14

Table 5
Relative Ranking of Polymer/Refrigerant/Lubricant Compatibility
Polymer
Refrigerant/Lubricant PTFE HNBR Neoprene W EPDM NBR
R-502 neat 24221
R-502/Mineral Oil 24452
R-502/Alkylbenzene 24252
HP81 neat 24222
HP81/Mineral Oil 24452
HP81/Alkylbenzene 24252
HP81/Castrol Ester 24225
HP81/Mobil Ester 24215
404A (HP62) neat 21121
404A (HP62)/Mineral Oil 22452
404A (HP62)/Alkylbenzene 22352
404A (HP62)/Castrol Ester 24215
404A (HP62)/Mobil Ester 24215
(1 → 5; best → worst)
Motor Materials
In hermetic and semihermetic compressors, the
compressor motor is normally cooled by direct
contact with refrigerant returning from the evaporator. As a result, the motor must be compatible with
the refrigerants and lubricants used in the refrigeration system.
Accelerated aging tests were conducted with
combinations of refrigerants, lubricants, and motor
materials using sealed tube tests prepared according
to ANSI/ASHRAE 97-1989. After aging, the materials in the tubes were inspected visually and microscopically and tested physically and chemically to
determine property changes.
Materials tested, and a summary of test results, are
described below.
PET (polyethylene terephthalate,
Mylar
PET film is used as phase and slot insulation in
hermetic motors. Visual inspection of sealed tubes
after aging in refrigerant environments revealed no
extracts with refrigerant alone [R-502, Suva
or Suva
cloudiness and light precipitates when lubricants
were present.
PET weight change on aging was small (<5%) and
occurred with R-502/lubricant and HP81/lubricant
combinations. Weight gain with Suva® 404A
(HP62) /ester lubricants was 2% or less.
PET flexibility after aging was determined by a
bend test. The results show excellent retention of
flexibility on aging at 135°C (275°F). There is
®
)
®
404A (HP62)], but varying degrees of
®
HP81,
definite loss of flexibility when PET is aged in
R-502/mineral oil or R-502/alkylbenzene at 150°C
(302°F). This loss of flexibility does not occur
when PET is aged in HP81 or Suva
®
404A (HP62)
with ester lubricants at 150°C (302°F).
Polyesterimide Enameled Motor Wire,
amide-imide overcoated (NEMA NW
35C)
No extracts or precipitates were observed on
aging the enameled wire in any of the lubricant/
refrigerant combinations. No blistering, crazing, or
cracking was observed after aging. Retention of
flexibility was confirmed by 1x bend tests of the
wire after aging.
Dacron
®
/Mylar®/Dacron® lead wire
(Belden 14 AWG)
After aging of D-M-D samples in refrigerant/
lubricant environments, contents of the tubes
were inspected for particulates, the tubes were
cooled and opened, and the lead wire samples
were subjected to bend tests. Minimal particulates
or extracts were observed after aging. PET
embrittlement, ranging from slight loss of
flexibility to shattering, was observed when
specimens were bent 135 degrees. The degree
of embrittlement appeared to be a factor of the
lubricant, rather than the refrigerant. All D-M-D
samples were embrittled in the presence of mineral
oil or alkylbenzene lubricants. Good flexibility was
seen after aging with polyol esters in the presence
of all refrigerants.
12
Page 15

Summary
In summary, ester-based lubricants appear to cause
much less effect on common motor materials than
mineral oils or alkylbenzene lubricants. In all cases,
the results appeared to be better than R-502 with
lubricants commonly used with R-502.
Desiccants
In refrigeration systems, keeping the refrigerant
and lubricant free of moisture is very important.
Dryers filled with moisture-absorbing desiccant are
typically used to prevent moisture accumulation. A
desiccant used with R-502, UOP’s (formerly Union
Carbide Molecular Sieve) 4A-XH-5, is not generally compatible with highly fluorinated refrigerants
such as the Suva
®
HP products. However, compatible molecular sieve desiccants, such as XH-9, have
been developed. For loose-filled and solid core
dryers, new desiccants are available that are also
compatible with the new refrigerants and lubricants. Be sure to tell your parts wholesaler what
refrigerants you plan to use when specifying the
dryer for your system.
Refrigeration Lubricants
Most compressors require a lubricant to protect
internal moving parts. The compressor manufacturer usually recommends the type of lubricant(s)
and proper viscosity that should be used to ensure
acceptable operation and equipment durability.
Recommendations are based on several criteria,
which can include lubricity, miscibility, compatibility with materials of construction, thermal stability,
and compatibility with other lubricants. It is important to follow the manufacturers’ recommendations
for lubricants to be used with their equipment.
Current lubricants used with R-502 have at least
partial miscibility with R-502, which eases the
problems of designing systems to allow lubricant
return back to the compressor. Many refrigeration
systems take advantage of this miscibility when
considering lubricant return.
Note: Field experience has shown that Suva
works successfully with mineral oil in many small
hermetic systems where oil return is not a concern.
®
Refrigerants such as the Suva
HP products, with
little or no chlorine present in them, may exhibit
less miscibility with common lubricants used with
R-502. Although many R-502 systems operating
at low temperatures allow for reduced miscibility
with the lubricant, it is important to know that the
lubricants used with the Suva
®
HP refrigerants will
return to the compressor using existing equipment
designs.
®
HP81
Different compressor and equipment manufacturers
will recommend lubricants to use with their equipment and the Suva
®
HP products. It would be difficult to summarize all possible lubricant candidates
that may be screened by various equipment manufacturers. In addition, there will be continuing research and development of new lubricants that we
may not have tested because the market for alternative refrigerants continues to stimulate other market
areas. Review your system needs with the equipment manufacturer, DuPont distributor, certified
refrigeration service contractor, or other qualified
party. Never assume the current lubricant in your
refrigeration system will be acceptable with the
®
Suva
HP refrigerant you intend to use. Always
review system components for compatibility with
the new refrigerant and possibly a new lubricant.
Table 6 shows a summary of miscibility tests done
with a 50/50 volume mixture of refrigerant and
lubricant over a wide range of temperatures, with
visual inspection for phase separation as the tubes
are slowly warmed. This table does not show that
any refrigerant/lubricant combination is acceptable,
only whether the two appear to be miscible at the
conditions shown.
Safety
Users must have and understand the applicable
®
Suva
HP refrigerant Material Safety Data Sheets.
Inhalation Toxicity
Suva® HP refrigerants pose no acute or chronic
hazard when they are handled in accordance with
DuPont recommendations and when exposures are
maintained below recommended exposure limits,
such as the DuPont acceptable exposure limit
(AEL) of 1,000 ppm, 8- or 12-hour time-weighted
average (TWA).
An AEL is an airborne exposure limit established
by DuPont that specifies time-weighted average for
airborne concentrations to which nearly all workers
may be repeatedly exposed without adverse effects.
The AEL for the Suva
level as the threshold limit value (TLV) established
for HCFC-22 and calculated for R-502 based on
the TLVs for the components.
However, like R-502, exposure above the recommended exposure limit to the vapors of Suva® HP
refrigerants by inhalation may cause human health
effects that can include temporary nervous system
depression with anesthetic effects such as dizziness,
headache, confusion, loss of coordination, and even
®
HP refrigerants is the same
13
Page 16

R-502
w/mineral oil
w/alkylbenzene
®
HP81
Suva
w/mineral oil
w/alkylbenzene
w/polyol ester
®
HP80
Suva
w/mineral oil
w/alkylbenzene
w/polyol ester
Table 6
Miscibility Summary
–60 +73 +80
2 phases 2 phases
(inversion)
–60 –27 +80
2 phases 1 phase
–60 +68 +80
2 phases 2 phases
(inversion)
–60 +16 +80
2 phases 1 phase
–60 +80
1 phase
–50 +65 +72
2 phases 2 phases
(inversion)
–50 +66 +72
2 phases 2 phases
(inversion)
–50 +72
1 phase
®
404A (HP62)
Suva
w/mineral oil
w/alkylbenzene
w/polyol ester
Note: All temperatures in °C
–60 +52 +80
2 phases 2 phases
(inversion)
–60 +57 +80
2 phases 2 phases
(inversion)
–60 +80
1 phase
14
Page 17

loss of consciousness. Higher exposures to the vapors may cause temporary alteration of the heart’s
electrical activity with irregular pulse, palpitations,
or inadequate circulation. Death can occur from
gross overexposure. Intentional misuse or deliberate inhalation of Suva
®
HP refrigerant vapors may
cause death without warning. This practice is extremely dangerous.
A person experiencing any of the initial symptoms
should be moved to fresh air and kept calm. If
breathing is difficult, administer oxygen. If not
breathing, administer artificial respiration. Call
a physician.
Cardiac Sensitization
As with many other halocarbons and hydrocarbons,
inhalation of Suva
intravenous injection of epinephrine, to simulate
human stress reactions, results in a cardiac sensitization response. In humans, this can lead to cardiac
irregularities and even cardiac arrest. The likelihood of these cardiac problems increases if you are
under physical or emotional stress. The Suva
refrigerants can cause these responses well above
the AEL, but the effect level varies with people,
and has not been fully determined.
If you are exposed to very high concentrations of
Suva® HP refrigerants, move immediately from the
area, and seek medical attention as a precaution.
Do not attempt to remain in the area to fix a leak or
perform other duties—the effects of overexposure
can be very sudden.
Medical attention must be given immediately if
someone is having symptoms of overexposure to
®
Suva
HP refrigerants. Do not treat the patient with
drugs such as epinephrine. These drugs could increase the risk of cardiac problems. If the person is
having trouble breathing, administer oxygen. If
breathing has stopped, administer artificial respiration. Call a physician.
®
HP refrigerants followed by
®
HP
Skin and Eye Contact
At room temperature, Suva® HP refrigerant vapors
have little or no effect on the skin or eyes. However, in liquid form, they can freeze skin or eyes
on contact, causing frostbite. If contact with liquid
does occur, soak the exposed areas in lukewarm
water, not cold or hot. In all cases, seek medical
attention immediately.
Always wear protective clothing when there is
a risk of exposure to liquid refrigerants. Where
splashing of refrigerant may occur, always wear
eye protection and a face shield.
Spills or Leaks
If a large release of vapor occurs, such as from
a large spill or leak, the vapors may concentrate
near the floor or in low elevation areas, which can
displace the oxygen needed for life, resulting in
suffocation.
Evacuate everyone until the area has been well
ventilated. Re-enter the area only while using
self-contained breathing apparatus. Use blowers
or fans to circulate the air at floor or low levels.
Always use self-contained breathing apparatus or
an air-line respirator when entering tanks or other
areas where vapors might exist. Use the buddy system (a second employee stationed outside the tank)
and a lifeline. Refer to the Material Safety Data
Sheet for the specific Suva
®
HP refrigerant you
plan to use.
®
HP refrigerants have virtually no odor, and
Suva
therefore can be extremely difficult to detect in
enclosed areas. Frequent leak checks and the installation of permanent leak detectors may be necessary for enclosed areas or machinery rooms. Refer
to ASHRAE Standards 15 and 34 for machinery
room requirements.
To ensure safety when using Suva
®
HP refrigerants
in enclosed areas:
1. Route relief and purge vent piping outdoors,
away from air intakes.
2. Make certain the area is well ventilated at all
times; use auxiliary ventilation, if necessary, to
remove vapors.
3. Make sure the work area is free of vapors prior
to beginning any work.
4. Install air monitoring equipment to detect leaks.
Combustibility of Suva® HP
Refrigerants
Suva® 404A (HP62), HP80 and HP81 are not flammable in air at temperatures up to 100°C (212°F) at
atmospheric pressure. However, mixtures of HP62,
HP80 or HP81 with high concentrations of air at
elevated pressure and/or temperature can become
combustible in the presence of an ignition source.
®
Suva
404A (HP62), HP80 and HP81 can also become combustible in an oxygen enriched environment (oxygen concentrations greater than that in
air). Whether a mixture containing Suva
(HP62), HP80 or HP81 and air, or Suva
(HP62), HP80 or HP81 in an oxygen enriched
atmosphere becomes combustible depends on the
inter-relationship of 1) the temperature 2) the
pressure, and 3) the proportion of oxygen in the
®
404A
®
404A
15
Page 18

mixture. In general, Suva® 404A (HP62), HP80 or
HP81 should not be allowed to exist with air above
atmospheric pressure or at high temperatures; or in
an oxygen enriched environment. For example:
HP62, HP80 or HP81 should NOT be mixed
with air under pressure for leak testing or other
purposes.
Refrigerants should not be exposed to open flames
or electrical heating elements. High temperatures
and flames can cause the refrigerants to decompose,
releasing toxic and irritating fumes. In addition, a
torch flame can become dramatically larger or
change color if used in high concentrations of many
refrigerants including R-500 or R-22, as well as
many alternative refrigerants. This flame enhancement can cause surprise or even injury. Always
recover refrigerants, evacuate equipment, and ventilate work areas properly before using any open
flames.
Based on the above information, the following
operating practices are recommended.
• Refrigerant Recovery Systems
Efficient recovery of refrigerant from equipment
or containers requires evacuation at the end of
the recovery cycle. Suction lines to a recovery
compressor should be periodically checked for
leaks to prevent compressing air into the recovery
cylinder during evacuation. In addition, the
recovery cylinder pressure should be monitored,
and evacuation stopped in the event of a rapid
pressure rise indicating the presence of air. The
recovery cylinder contents should then be analyzed for NAG, and the recovery system leak
checked if air is present. Do not continue to
evacuate a refrigeration system that has a
major leak.
• Combustibility With Chlorine
Experimental data have also been reported
which indicate combustibility of HCFC-22 (a
component of HP80 and HP81) in the presence
of chlorine.
• Do Not Mix With Air For Leak Testing
– Equipment should never be leak tested with a
pressurized mixture of HP62, HP80 or HP81
and air. Pressurized mixtures of dry nitrogen
and HP62, HP80 or HP81 can be used for leak
testing.
• Bulk Delivery and Storage
– Tanks should be evacuated prior to initial
filling, and should never be filled while under
positive air pressure.
– Tank pressure should never be allowed to
exceed the tank manufacturer’s maximum
allowable working pressure when filling with
HP62, HP80 or HP81. Relief devices on either
the tanks or the supply system should be
present and in good operating condition.
– Tank pressures should be monitored routinely.
– Air lines should never be connected to storage
tanks.
• Filling and Charging Operations
– Before evacuating cylinders or refrigeration
equipment, any remaining refrigerant should
be removed by a recovery system.
– Vacuum pump discharge lines should be free
of restrictions that could increase discharge
pressures and result in the formation of com-
bustible mixtures.
– Cylinders or refrigeration equipment should
be evacuated at the start of filling, and
should never be filled while under positive
air pressure.
– Filled cylinders should periodically be analyzed
for air (nonabsorbable gas or NAG).
Air Monitors and Leak Detection
Service personnel have used leak detection equipment for years when servicing equipment. Leak
detectors exist not only for pinpointing specific
leaks, but also for monitoring an entire room on a
continual basis. There are several reasons for leak
pinpointing or area monitoring, including:
• conservation of refrigerant
• protection of employees
• detection of fugitive or small emissions
• protection of equipment
Leak detectors can be placed into two broad cate-
gories: leak pinpointers and area monitors. Before
purchasing a monitor or pinpointer, several criteria
should be considered, which include sensitivity,
detection limits, and selectivity.
Types of Detectors
Using selectivity as a criterion, leak detectors can
be placed into one of three categories: nonselective,
halogen selective, or compound specific. In general,
as the specificity of the monitor increases, so will
the complexity and cost.
A different technology that can be employed to
find leaks is by using a dye or other additive that
is placed in the refrigeration system and is emitted
with the leaking refrigerant and lubricant.
A detailed discussion of leak detection, along with
a list of manufacturers of leak detection equipment,
can be found in DuPont bulletin ARTD-27.
16
Page 19

Nonselective Detectors
Nonselective detectors are those which will detect
any type of emission or vapor present, regardless
of its chemical composition. These detectors are
typically quite simple to use, very rugged, inexpensive, and almost always portable. However, their
inability to be calibrated, long-term drift, lack of
selectivity, and lack of sensitivity limit their use
for area monitoring.
Some nonselective detectors designed for use with
R-502 may have a much lower sensitivity when
used with Suva
®
HP refrigerants. However, newly
designed detectors with good sensitivity for HFCs
are now available. Be sure to consult with the
manufacturer before selecting or using a nonselective detector with Suva
®
HP refrigerants.
Halogen-Selective Detectors
Halogen-selective detectors use a specialized sensor that allows the monitor to detect compounds
containing fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine
without interference from other species. The major
advantage of such a detector is a reduction in the
number of nuisance alarms—false alarms caused by
the presence of some compound in the area
other than the target compound.
With Suva
®
HP refrigerants, using compoundspecific detectors may be difficult because the
different mixtures often contain similar types of
compounds. In an area where different refrigerant
mixtures are used, these detectors may offer more
specificity than is needed for normal leak management. Discuss these issues with the equipment
manufacturers before making a purchase decision.
Fluorescent Additives
Fluorescent additives have been used in refrigeration systems for several years. These additives,
invisible under ordinary lighting, but visible under
ultraviolet (UV) light, are used to pinpoint leaks in
systems. The additives are typically placed into the
refrigeration lubricant when the system is serviced
or charged. Leaks are detected by using a UV light
to search for additive that has escaped from the
system.
Recent innovations in dye technology have allowed
fluorescent additives to be used with HFCs and new
refrigerant mixtures. However, before adding additives to a system, the compatibility of the specific
dye with the lubricant and refrigerant should be
tested.
These detectors are typically easy to use, feature
higher sensitivity than the nonselective detectors
(detection limits are typically <5 ppm when used
as an area monitor and <1.4 g/yr [<0.05 oz/yr]
when used as a leak pinpointer) and are very
durable. In addition, due to the partial specificity
of the detector, these instruments can be easily
calibrated.
Compound-Specific Detectors
The most complex detectors, which are also the
Storage and Handling
Shipping Containers in the U.S.
Suva® HP refrigerants are liquefied compressed
gases. According to the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) a nonflammable compressed gas
is defined as a nonflammable material having an
absolute pressure greater than 40 psia at 21°C
(70°F) and/or an absolute pressure greater than
104 psia at 54°C (130°F). See Table 7 for the
appropriate DOT designation.
most expensive, are compound-specific detectors.
These units are typically capable of detecting the
presence of a single compound without interference
from other compounds.
Table 7
DOT Designations
DOT Proper Shipping Name (HP80/81) Compressed Gas N.O.S. (Contains
Pentafluoroethane and Chlorodifluoromethane)
[404A (HP62)] Compressed Gas N.O.S. (Contains
Hazard Class (All) Nonflammable Gas
DOT/IMO Hazard Class (HP80/81) 2
[404A (HP62)] 2.2
UN/NA Number (All) UN 3163
DOT Labels (All) Nonflammable Gas
DOT Placard (All) Nonflammable Gas
Pentafluoroethane and Trifluoroethane)
17
Page 20

A list of the different types of containers that can
be used to ship Suva
®
HP refrigerants in the United
States, along with their water capacities, dimensions, DOT specifications, and net weights, are
provided in Table 8. All pressure relief devices
used on the containers must be in compliance with
the corresponding Compressed Gas Association
(CGA) Standards for compressed gas cylinders,
cargo, and portable tanks.
The 15-lb, 30-lb, and 123-lb cylinders designed for
refrigerant applications will be painted the colors
shown in Table 8, with labels that bear the name
of the product in the same color. For clarification,
the colors are:
®
Suva
HP80 PMS 461 Light brown
®
Suva
HP81 PMS 385 Green brown
®
Suva
404A (HP62) PMS 021 Orange
Disposable cylinders, known as a Dispos-A-Can
®
(or DAC), fit into a box with the measurements
given in Table 8. When used to ship Suva
®
HP
refrigerants to the stationary refrigeration market,
the cylinders will have the same outlet fittings as
cylinders of R-502.
The 123-lb cylinders are equipped with a nonrefillable liquid vapor CGA-660 valve. With this twoway valve, refrigerant can be removed from the
cylinder as either vapor or liquid, without inverting
the cylinder. The vapor valve handwheel is located
on the top of the valve assembly. The liquid
handwheel is on the side of the valve and attached
to a dip tube extending to the bottom of the cylinder. Each is clearly identified as vapor or liquid.
The 4,400-gal cylinder is known as an ISO tank.
The dimensions referenced in Table 8 represent the
frame in which the container is shipped. The tank
itself has the same length of 20 ft and an outside
diameter of approximately 86 in. ISO tanks are
used for export shipments of refrigerants from the
United States.
The general construction of a one-ton returnable
container is shown in Figure 7. Note that one end
of the container is fitted with two valves. When the
container is turned so that the valves are lined up
vertically, the top valve will discharge vapor and
the bottom valve will discharge liquid. The valves
are protected by a dome cover. The valves are Superior Type 660-X1-B1.
One-ton containers are equipped with two fusible
plugs in each end. The fusible metal in the plugs
is designed to start melting at 69°C (157°F) and
completely melt at 74°C (165°F). Containers
should never be heated to temperatures higher than
52°C (125°F). One spring-loaded pressure relief
valve is also located in each end of the container.
Bulk Storage Systems
DuPont sells storage systems, at cost, to their refrigeration customers. The systems are prefabricated, tested, and ready to install on site. The units
are designed to optimize economy, efficiency
and safety in the storage and dispensing of DuPont
refrigerants. The delivered systems include all
components, such as storage tank, pumps, piping,
valves, motors, and instrumentation as an integrated
unit. All systems are equipped with dual pumps
to provide an installed spare. The units are skidmounted and require only placement on a concrete pad and connection to electrical and process
systems.
Table 8
Specifications of Shipping Containers for DuPont™ Suva® HP Refrigerants
Container Dimensions DOT Spec. Net Weight (lb) Color Code
15 lb Dispos-A-Can
30 lb Dispos-A-Can
123 lb Cylinder 55" H x 10" OD 4BA300 (HP81) 110
1,682 lb ton Cylinder 82" L x 30" OD 110A500W
5,000 gal Tank Truck MC-330 or -331 40,000
4,400 gal ISO 8' x 8.5' x 20' (frame) 51
170,000 lb Rail Car 114A340W
* Dispos-A-Can is a registered trademark of the DuPont Company.
®
* 7.5" x 7.5" x 14.5" 39 (HP81 Only) 13 PMS 385
®
10" x 10" x 17" 39 (HP80) 27 PMS 461
[404A (HP62)] 24 PMS 021
[404A (HP62)] 100
4BA400 (HP80) 110
18
Page 21

Figure 7. One-Ton Returnable Container
A typical bulk storage system is shown in Figure 8.
Your DuPont marketing representative can arrange
for guidance on site selection, purchase, installation, start-up, and maintenance.
Converting Bulk Storage Tanks from
R-502 to Suva
®
HP Refrigerants
Before switching any R-502 storage system to
®
HP refrigerants, the existing storage equip-
Suva
ment must be checked to verify that it is adequate.
Storage tanks built to the specifications of the
American Society of Mechanical Engineers
(ASME) Pressure Vessel Code are required to have
a metal nameplate indicating each tank’s maximum
allowable working pressure (MAWP). This rating
must be 320 psig or higher for use with all Suva
®
HP refrigerants. In addition, the set pressure of the
tank relief device must also be checked and
changed if necessary. This relief setting cannot be
higher than the maximum working pressure listed
on the nameplate, however.
We recommend that storage tanks be completely
emptied of all R-502 liquid and vapor before introducing the HP refrigerant. In general, converting a
storage tank to HP refrigerant requires:
1. Removing all R-502 from the storage tank,
lines, and equipment.
2. Evacuating the storage tank to 25–29 in of
vacuum and purging with compressed dry
nitrogen gas.
3. Making necessary repairs to the tank after
initial evacuation and purging.
4. Repeating step 2 until R-502 and moisture
levels are within acceptable limits.
®
5. Refilling the system with Suva
HP refrigerant.
This is a simplified outline of what is actually a
lengthy procedure. Your DuPont marketing representative can assist in obtaining the equipment,
instrumentation, and technical assistance to safely
and effectively make the conversion.
Material Compatibility Concerns
Most metal components suitable for use with R-502
are also compatible with Suva
®
HP refrigerants.
These include standard grades of carbon steel,
aluminum, and copper. Some elastomeric or nonmetallic components suitable for R-502 may not be
adequate with the new refrigerants. Therefore, all
elastomeric or nonmetallic components throughout
the system must be identified and their compatibility with Suva
®
HP refrigerants verified. For complete reliability, any component that cannot be
properly identified should be replaced.
In a fluorocarbon storage system, elastomers are
most commonly found in:
• Packing and seats of manual valves
• Pressure relief device seats
• Flange and manway gaskets
• Mechanical pump seals
• Wet-end pump gaskets and O-rings
• Filter O-rings
• Sight-glass gaskets
• Back-pressure regulator diaphragms and O-rings
Handling Precautions for Suva® HP
Refrigerant Shipping Containers
The following rules for handling HP refrigerant
containers are strongly recommended:
• Use personal protective equipment such as side
shield safety glasses, gloves, and safety shoes
when handling refrigerant containers.
19
Page 22

Figure 8. Typical Bulk Storage System
Pressure
Gauge
Liquid Level
Gauge
Tank
Internal Safety
Relief Valves
Manway
Excess Flow Valves
Vapor
Equalizing
Line
Relief Valves
Liquid Fill Line
FEED System
Flow Indicator
Check Valve
• Avoid skin contact with refrigerants, as they
may cause frostbite.
• Never heat a container to temperatures higher
than 52°C (125°F).
• Never apply direct flame or live steam to a
container or valve.
• Never refill disposable cylinders with anything.
The shipment of refilled disposable cylinders is
prohibited by DOT regulations.
• Never refill returnable cylinders without DuPont
consent. DOT regulations forbid transportation
of returnable cylinders refilled without DuPont
authorization.
• Never use a lifting magnet or sling (rope or
chain) when handling containers. A crane may
be used when a safe cradle or platform is used
to hold the container.
• Never use containers as rollers, supports, or for
any purpose other than to carry refrigerant.
• Protect containers from any object that will result
in a cut or other abrasion in the surface of the
metal.
• Never tamper with the safety devices in the
valves or containers.
• Never attempt to repair or alter containers or
valves.
Ball Valve
Back
Pressure
Regulator
1" Pipe
Filter
Flange
To Service
Thermometer
2" Pipe
Pump
Motor
• Never force connections that do not fit. Make
sure the threads on the regulators or other auxiliary equipment are the same as those on the
container valve outlets.
• Keep valves tightly closed and valve caps and
hoods in place when the containers are not in use.
• Store containers under a roof to protect them
from weather extremes.
• Use a vapor recovery system to collect refrigerant
vapors from lines after unloading.
Recovery, Recycle,
Reclamation and Disposal
Responsible use of Suva® HP refrigerants requires
that the product be recovered for re-use or disposal
whenever possible. DuPont purchases used refrigerant for reclamation through its distributor networks in the United States, Canada and Europe.
In the United States, all Suva
be accepted as part of this program. Recovery and
re-use of refrigerant makes sense from an environmental and economic standpoint. In addition, the
U.S. Clean Air Act prohibits known venting of
CFC, HCFC, and HFC refrigerants during the
maintenance, servicing or disposal of refrigeration
equipment.
®
HP products will
20
Page 23

Recovery
Recovery refers to the removal of refrigerant from
equipment and collection in an appropriate container. As defined by the Air Conditioning and
Refrigeration Institute (ARI), recovery does not
involve processing or analysis of the refrigerants.
®
Suva
HP refrigerants may be recovered from refrigeration equipment using permanent on-site
equipment or many of the portable recovery devices
now available in the marketplace. The portable
devices contain a small compressor and an aircooled condenser, and may be used for vapor (and
in some cases, liquid) recovery. At the end of the
recovery cycle, the system is evacuated thoroughly
to remove vapors. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) sets standards for
recovery equipment. Before purchasing a specific
recovery unit, check with the manufacturer to be
sure that it contains proper materials of construction and lubricant for the refrigerants you intend to
recover.
Due to the fact that Suva
®
HP products are not
azeotropes, it is important that all refrigerant is
removed from a system during recovery or recycle.
It is always recommended that refrigerant transfers
be made liquid phase whenever possible to minimize composition changes in the products.
Recycle
Refrigerant recycle refers to reducing the contaminant levels in used refrigerants by passing the refrigerants through devices that separate out or
reduce the amount of lubricant, water, acidity and
particulates. Recycle is usually a field or shop procedure with no analytical testing of refrigerant.
®
Suva
HP refrigerants may be recycled using many
of the devices now available. In the United States,
the EPA sets standards for these devices. Recycle
is already standard practice in many portions of
the commercial refrigeration industry. Consult with
the manufacturer before specifying a recycle device
for any refrigerant.
®
If you routinely recycle Suva
HP refrigerants
through several cycles, we recommend that you
have the composition of the refrigerant checked
periodically. This will prevent loss of performance
in the unlikely event that the composition has
shifted.
Reclamation
Reclamation refers to the reprocessing of used refrigerant to new product specifications. Quality of
the reclaimed product is verified by chemical analysis. In the United States, Suva
®
HP refrigerants are
included in DuPont’s refrigerant reclamation program. Contact DuPont or one of our authorized
distributors for further information.
Reclamation offers advantages over on-site refrigerant recycling procedures because recycling systems cannot guarantee complete removal of all
contaminants. Putting refrigerants that do not meet
new product specifications into expensive equipment may cause damage.
Disposal
Disposal refers to the destruction of used refrigerant. Disposal may be necessary when the refrigerant has become badly contaminated with other
products and no longer meets the acceptance specifications of DuPont or other reclaimers. Although
DuPont does not presently accept severely contaminated refrigerant for disposal, licensed waste disposal firms are available. Be sure to check the
qualifications of any firm before sending them
used refrigerants.
21
Page 24

For Further Information:
DuPont Fluorochemicals
Wilmington, DE 19880-0711
(800) 235-SUVA
www.suva.dupont.com
Europe
DuPont de Nemours
International S.A.
2 Chemin du Pavillon
P.O. Box 50
CH-1218 Le Grand-Saconnex
Geneva, Switzerland
41-22-717-5111
Canada
DuPont Canada, Inc.
P.O. Box 2200, Streetsville
Mississauga, Ontario
Canada
L5M 2H3
(905) 821-3300
Mexico
DuPont, S.A. de C.V.
Homero 206
Col. Chapultepec Morales
C.P. 11570 Mexico, D.F.
52-5-722-1100
South America
DuPont do Brasil S.A.
Alameda Itapecuru, 506
Alphaville 06454-080 Barueri
São Paulo, Brazil
55-11-7266-8263
DuPont Argentina S.A.
Casilla Correo 1888
Correo Central
1000 Buenos Aires, Argentina
54-1-311-8167
Pacific
DuPont Australia
P.O. Box 930
North Sydney, NSW 2060
Australia
61-2-99236111
Japan
Mitsui DuPont Fluorochemicals
Co., Ltd.
Chiyoda Honsha Bldg.
5-18, 1-Chome Sarugakucho
Chiyoda-Ku, Tokyo 101-0064 Japan
81-3-5281-5805
Asia
DuPont Taiwan
P.O. Box 81-777
Taipei, Taiwan
886-2-514-4400
DuPont China Limited
P.O. Box TST 98851
1122 New World Office Bldg.
(East Wing)
Tsim Sha Tsui
Kowloon, Hong Kong
Phone: 852-734-5398
Fax: 852-236-83516
DuPont Thailand Ltd.
9-11 Floor, Yada Bldg.
56 Silom Road
Suriyawongse, Bankrak
Bangkok 10500
Phone: 66-2-238-0026
Fax: 66-2-238-4396
DuPont China Ltd.
Rm. 1704, Union Bldg.
100 Yenan Rd. East
Shanghai, PR China 200 002
Phone: 86-21-328-3738
Telex: 33448 DCLSH CN
Fax: 86-21-320-2304
DuPont Far East Inc.
6th Floor Bangunan Samudra
No. 1 JLN. Kontraktor U1/14, SEK U1
Hicom-Glenmarie Industrial Park
40150 Shah Alam, Selangor Malaysia
Phone 60-3-517-2534
DuPont Korea Inc.
4/5th Floor, Asia Tower
#726, Yeoksam-dong, Kangnam-ku
Seoul, 135-082, Korea
82-2-721-5114
DuPont Singapore Pte. Ltd.
1 Maritime Square #07 01
World Trade Centre
Singapore 0409
65-273-2244
DuPont Far East, Philippines
8th Floor, Solid Bank Bldg.
777 Paseo de Roxas
Makati, Metro Manila
Philippines
Phone: 63-2-818-9911
Fax: 63-2-818-9659
DuPont Far East Inc.
7A Murray’s Gate Road
Alwarpet
Madras, 600 018, India
91-44-454-029
DuPont Far East Inc.—Pakistan
9 Khayaban-E-Shaheen
Defence Phase 5
Karachi, Pakistan
92-21-533-350
DuPont Far East Inc.
P.O. Box 2553/Jkt
Jakarta 10001, Indonesia
62-21-517-800
The information contained herein is based on technical data and tests which we believe to be reliable and is intended for use by persons having technical
skill, at their own discretion and risk. Because conditions of use are outside of DuPont control, we can assume no liability for results obtained or damages
incurred through the application of the data presented.
© 2004. E. I. du PONT de NEMOURS AND COMPANY. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
NO PART OF THIS MATERIAL MAY BE REPRODUCED, STORED IN A RETRIEVAL SYSTEM OR TRANSMITTED IN ANY FORM OR BY
ANY MEANS ELECTRONIC, MECHANICAL, PHOTOCOPYING, RECORDING, OR OTHERWISE WITHOUT THE PRIOR WRITTEN PERMISSION OF DUPONT.
(7/04) 235091D Printed in U.S.A.
[Replaces: H-47122-4]
Reorder No.: H-47122-5
 Loading...
Loading...