Page 1

D-Link DBT-122
Bluetooth USB Adapter
Manual
Version 2.0
(23 June 2006)
Page 2

Contents
Package Contents ................................................................ 4
System Requirements .......................................................... 4
Introduction ........................................................................... 5
Installing the Bluetooth Software .......................................... 6
Using the Bluetooth Conguration Wizard.......................... 10
Introduction to the Bluetooth Software ............................... 13
Bluetooth Tray....................................................... 13
Access My Bluetooth Places ................................ 13
Icons Used for Bluetooth Devices and Services ... 14
Bluetooth Software Basic Operations ................................. 17
Start or Stop Bluetooth ......................................... 17
Create a Connection ............................................. 17
Find Bluetooth Devices ......................................... 18
Find A Service....................................................... 19
Bluetooth Connection Status ................................ 20
Send to Bluetooth ................................................. 21
Bluetooth Conguration ...................................................... 22
Access the Bluetooth Conguration Panel ........... 22
Bluetooth Services versus Bluetooth Applications 22
Bluetooth Exchange Folder .................................. 22
Bluetooth Applications Overview .......................... 23
Applications > Human Interface Device (HID) ...... 24
Applications > HID, Audio Gateway ...................... 25
Applications > Serial Port ..................................... 26
2
Page 3

Contents (cont’d)
Bluetooth Conguration (cont’d)
Applications > Dial-up Networking ........................ 27
Applications > Fax, Headset ................................. 28
Applications > Headset ......................................... 29
Applications > Headset, File Transfer ................... 30
Applications > Network Access ............................ 32
Applications > PIM ................................................ 33
Applications > My Headset / Audio Gateway ........ 36
Applications > Printer ............................................ 38
Bluetooth Services ................................................ 40
Services > Notications ........................................ 41
Services > Audio Gateway Service ...................... 42
Services > Bluetooth Serial Port Service .............. 43
Services > Dial-up, Fax, File Transfer Service ..... 44
Services > Headset .............................................. 45
Services > Network Access ................................. 46
Services > PIM ..................................................... 47
Hardware Settings ................................................ 51
Advanced Settings ................................................ 52
Accessibility Settings ............................................ 53
Discovery Settings ................................................ 54
Security............................................................................... 56
Troubleshooting .................................................................. 58
Copyright and Emissions Statements................................. 61
Contacting Technical Support ............................................. 62
3
Page 4

Package Contents
These items are included with your purchase:
D-Link DBT-122 USB Bluetooth Adapter
•
USB Extension Cable
•
Installation CD with Driver, Manual, Quick Installation Guide, & Bluetooth
•
Software
If any of the above items are missing, please contact your reseller.
System Requirements
Windows XP/Me/2000/98SE
•
One Available USB Port
•
CD-ROM Drive
•
4
Page 5

Introduction
Introduction to Bluetooth
The term “Bluetooth” refers to a worldwide standard for the wireless
exchange of data between two devices within a Personal Area Network.
In order to exchange data, two Bluetooth devices must establish a
connection. Before a connection is established, one device must request a
connection with another, where the second device accepts (or rejects) the
connection. The originator of the request is known as the client. The device
that accepts (or rejects) the request is known as the server. Many Bluetooth
devices can act as both client and server. A client Bluetooth device runs a
software program that requests a connection to another device as part of
its normal operation. For example, the program may request a connection
to a remote computer, a printer, or a modem.
Becoming a Bluetooth client normally requires an action by the device
operator, such as an attempt to browse a remote computer, print a le,
or dial out on a modem. Every Bluetooth device that provides a service
must be prepared to respond to a connection request. Bluetooth software
is always running in the background on the server, ready to respond to
connection requests.
Introduction to the DBT-122 Bluetooth USB Adapter
The D-Link Bluetooth USB Adapter is the perfect wireless solution for quick
and easy access to Bluetooth enabled devices. It is a class 2/3 low power
device and is bundled with Bluetooth Software which allows you to connect
to several Bluetooth devices at once. The wireless transmission range of
the D-Link DBT-122 Bluetooth USB Adapter is about 10 meters (30 feet). A
PC congured as the Bluetooth server can support up to seven Bluetooth
client devices with IP addresses being automatically assigned upon a
successful connection. The Bluetooth Software also provides Internet
sharing and security access between the server and clients.
After nishing the steps outlined in this manual, you will have the ability
to share information, obtain network access, and take full advantage of a
wireless connected environment.
5
Page 6

Installing the Bluetooth Software
Uninstalling a previous version of the Bluetooth
software:
If you are installing the Bluetooth software for the rst time, please skip this
section.
Any previous versions of the Bluetooth software must be uninstalled before installing
an upgraded version.
Please uninstall the software by completing these steps:
1) Close any open programs and insert the Driver CD into your CD-ROM Drive.
2) The Autorun screen will appear. Click on Install Bluetooth Software.
3) The Welcome screen will indicate the previous version of BTW that is
currently installed. Click on the Next button to continue.
4) Click on the Remove button from the Remove the Program screen.
5) When the les have been removed, you will be presented with a screen
informing of its completion.
a. Click on the Finish button
b. Click on the Yes button when the pop-up dialog box appears on the
screen to reboot your PC.
You have now removed the previous version of the Bluetooth software.
Installing the Bluetooth Software
Install the driver and software located on the D-Link CD that came with your
purchase BEFORE installing the DBT-122 USB Bluetooth Adapter into your
computer.
Insert the D-Link PersonalAir DBT-122 Driver CD in the CD-ROM drive.
If this Autorun screen does not
automatically appear, click on Start >
Run, enter “D:\Autorun.exe” and click
OK. “D” represents the letter of your
CD-ROM drive.
Click Install
Driver
6
Page 7

Installing the Bluetooth Software (cont’d)
Click Next
Click Accept
Click Next
Click Next
7
Page 8
Installing the Bluetooth Software (cont’d)
Click Install
Only Windows XP and
Windows 2000 Users will
see this screen.
Click OK
8
Page 9
Installing the Bluetooth Software (cont’d)
When this screen appears,
connect the DBT-122 to an
available USB port on your
USB host adapter or USB hub.
Click OK
9
Page 10
Installing the Bluetooth Software (cont’d)
Click Finish
Only Windows 2000,
Windows Me, and Windows
98SE Users will see this
screen.
Click Yes
Using the Bluetooth Configuration Wizard
After you have completed the driver and software installation and reboot your
computer, a Bluetooth icon will appear on your desktop and in the bottom right hand
corner of your desktop screen (systray). The Bluetooth icon gives you access to My
Bluetooth Places, for conguring your Bluetooth settings.
Double-click the Bluetooth icon for access to
My Bluetooth Places.
10
Page 11
Using the Bluetooth Configuration Wizard (cont’d)
The Bluetooth Conguration
Wizard launches the rst time that
you double click on My Bluetooth
Places.
Click Next
Type a unique name for
your Computer. Select
Desktop or Laptop
Click Next
Click Next
11
Page 12
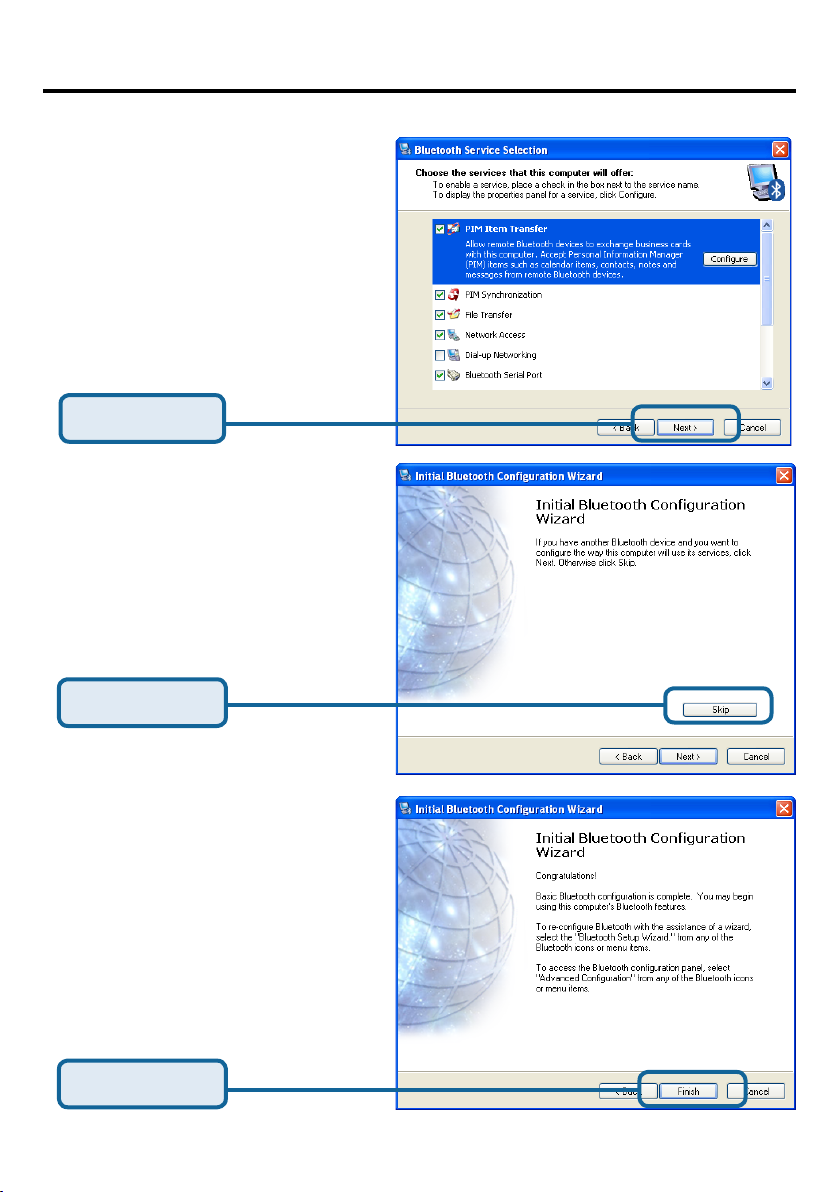
Using the Bluetooth Configuration Wizard (cont’d)
Select the Services that your DBT122 will provide to other Bluetooth
products.
Click Next
You can choose to congure your
other Bluetooth devices at this point.
Otherwise, click Skip to nish the
conguration for your DBT-122.
Click Skip
Click Finish
12
Page 13

Introduction to the Bluetooth Software
Bluetooth Tray
The Bluetooth tray resides in the Windows system tray, which is normally located in
the lower-right corner of the screen. The Bluetooth tray provides fast access to most
Bluetooth operations.
From the Bluetooth tray you can:
· Access My Bluetooth Places—double-click the Bluetooth icon, or
right-click the Bluetooth icon and then select Explore My Bluetooth
Places.
· Access the Bluetooth Setup Wizard. This wizard will help you:
• Congure how this computer accesses a service on another
Bluetooth device
• Locate remote Bluetooth devices
• Congure the way that this computer provides services to
remote Bluetooth devices
• Set the name and type of this Bluetooth device, e.g., “John’s
PC” and “Desktop.”
• Access the Bluetooth Conguration Panel—right-click the
Bluetooth icon, and then select Advanced Conguration.
• Access the Quick Connect option—right-click the Bluetooth icon,
select Quick Connect, and then select the type of service to which
you wish to connect.
• Start/Stop Bluetooth on this computer.
Access My Bluetooth Places
My Bluetooth Places is part of Windows Explorer.
There are multiple ways to access My Bluetooth Places:
• In the Windows system tray
• Right-click the Bluetooth icon and select Explore My Bluetooth
Places
or
• Double-click the Bluetooth icon
• On the desktop, double-click the Bluetooth icon
• Open Windows Explorer and select My Bluetooth Places in the
Folders pane or from the Address shortcut menu.
13
Page 14

Introduction to the Bluetooth Software (cont’d)
Icons Used for Bluetooth Devices and Services
Bluetooth icons provide at-a-glance feedback about a device or service’s status by
changing appearance.
The Bluetooth icon in the Windows system tray provides feedback about Bluetooth
status.
Figure 1: Bluetooth Icon
Bluetooth Icon Indicates Bluetooth Status
Enabled
Connected
Blue with White
Figure 2: Device Icons for Windows 98SE, Me and 2K
Device Icons for Windows 9x, Me and 2K
Name
Audio Gateway
Desktop
Headset
Human Interface Device
Laptop
Modem
Network Access Point
Personal Digital Assistant
Printer
Blue with Red
Normal
Blue with Green
Connected
Paired
Telephone
Unknown
14
Page 15
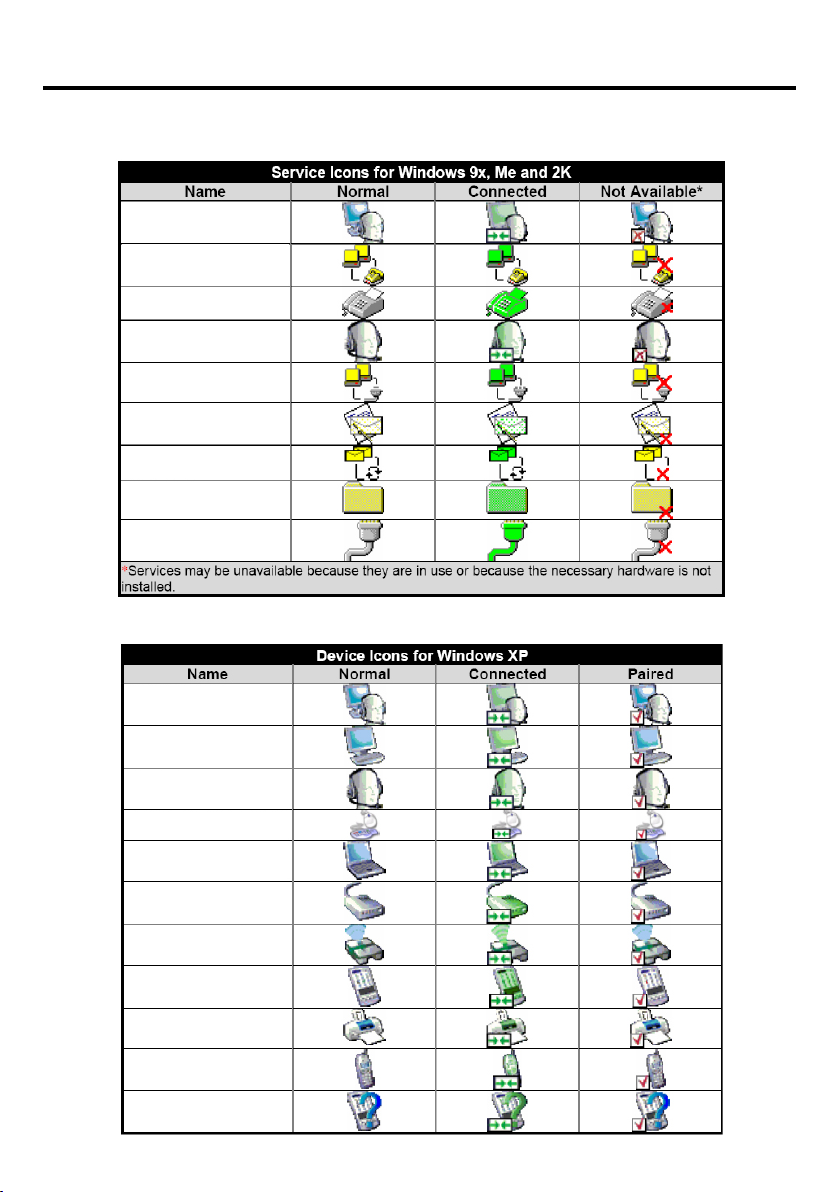
Introduction to the Bluetooth Software (cont’d)
Icons Used for Bluetooth Devices and Services
Figure 3: Service Icons for Windows 98SE, Me and 2K
Audio Gateway
Dial-up Networking
Fax
Headset
Network Access
PIM Item Transfer
PIM Synchronization
Public Folder
Serial Port
Figure 4: Device Icons for Windows XP
Audio Gateway
(cont’d)
Desktop
Headset
Human Interface Device
Laptop
Modem
Network Access Point
Personal Digital
Assistant
Printer
Telephone
Unknown Device
15
Page 16
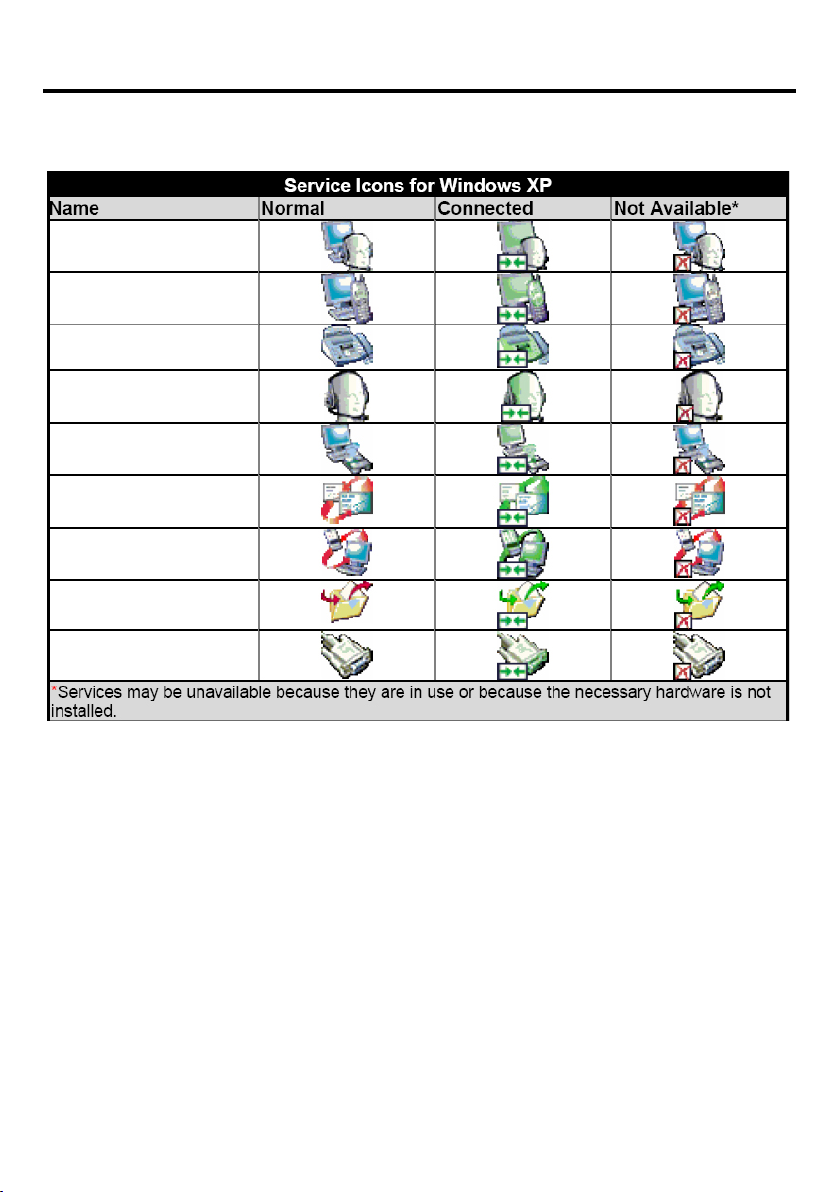
Introduction to the Bluetooth Software (cont’d)
Icons Used for Bluetooth Devices and Services
Figure 5: Service Icons for Windows XP
Audio Gateway
Dial-up Networking
Fax
Headset
Network Access
PIM Item Transfer
PIM Synchronization
Public Folder
Serial Port
(cont’d)
16
Page 17

Bluetooth Software Basic Operations
Start or Stop Bluetooth
To start Bluetooth: in the Windows system tray, right-click the Bluetooth
icon and select Start the Bluetooth Device. The Bluetooth icon is blue in
color with a white insert when Bluetooth is running.
To stop Bluetooth: in the Windows system tray, right-click the Bluetooth
icon and select Stop the Bluetooth Device. The Bluetooth icon is blue in color
with a red insert when Bluetooth is stopped.
Create a Connection
From the Bluetooth Icon in the System Tray
In the Windows system tray, right-click the Bluetooth icon, select Quick
Connect and then the Bluetooth service that you wish to use.
If this computer has created a connection to the desired type of service in
the past, the options on the shortcut menu are:
• The name(s) of any device(s) with which prior connections to this
type of service have been established. Select a name from the list to
re-establish connection.
• Other Devices…Select this option to search for additional devices
that potentially provide the desired service, select a device from the
list, and then click Connect.
If this computer has never created a connection to this type of service, the
only option on the shortcut menu is “Find Devices….” Select this option
to search for devices that potentially provide the desired service, select a
device from the list, and then click Connect.
Using the Bluetooth Setup Wizard
• From the Folders pane of Windows Explorer, right-click My
Bluetooth Places and select Bluetooth Setup Wizard
or
• In Windows Explorer, with My Bluetooth Places selected, from
the Bluetooth menu, select Bluetooth Setup Wizard
or
• From the Windows system tray: right-click the Bluetooth icon
and select Bluetooth Setup Wizard.
Follow the wizard’s on-screen instructions.
17
Page 18

Bluetooth Software Basic Operations (cont’d)
From Entire Bluetooth Neighborhood
From Windows Explorer:
• In the Folders pane, select Entire Bluetooth Neighborhood, right-
click a device name and select “Connect …” the desired service.
or
• In the Folders pane, expand Entire Bluetooth Neighborhood, select
a device, and then, in the right pane, right-click a service provided by
that device and select “Connect to…”
Find Bluetooth Devices
Search for Devices looks for Bluetooth devices in the vicinity and displays
the devices that it nds in My Bluetooth Places.
To start a search for devices, in the Folders pane of My Bluetooth Places,
select Entire Bluetooth Neighborhood, and then, from the Bluetooth menu,
select Search for Devices.
NOTE: The Bluetooth menu is only visible when My Bluetooth Places is
active.
Periodic Search for Devices
Bluetooth can be congured to automatically search for devices on a regular
basis (Bluetooth Conguration Panel > Discovery tab).
One of the advantages of Bluetooth is the mobility that the wireless
connections allow. However, mobility means that devices may move in or out
of connection range during the time between the automatic updates
performed by Bluetooth. To be certain that the displayed list of devices in the
neighborhood is current, or if automatic periodic inquiry is not enabled, force
an update of the device list using the technique described in Search for
Devices, above.
Some devices within connection range may not show up in the list of
devices found because:
• Your device is congured to report only specic types or classes of
devices (Bluetooth Conguration Panel > Discovery tab, on your
device).
• The unlisted device is congured to be non-discoverable (Bluetooth
Conguration Panel > Accessibility tab, on the un-listed device).
18
Page 19

Bluetooth Software Basic Operations (cont’d)
Find A Service
The process of determining the services that a device provides is called
Service Discovery.
To initiate a Service Discovery, in the Folders pane of My Bluetooth
Places, right-click a device name and select Discover Available Services
from the shortcut menu.
Bluetooth services are those things that this computer can do for remote
Bluetooth devices. For example, if this computer allows a remote Bluetooth
device to send a fax using a fax modem that is physically attached to this
computer, then this computer is providing the Bluetooth fax service.
Some services are hardware dependant; this computer cannot provide the
fax service unless it has a physical fax modem, for example.
Some Bluetooth services use virtual “hardware.” The Bluetooth Serial Port
service, for example, does not use a physical port on this computer. Instead,
it creates virtual serial ports that Windows applications can see and use as if
they were actual physical ports.
Each Bluetooth service that this computer is capable of providing can be
started automatically when Bluetooth starts. Each service can be setup to
require security measures before allowing a remote Bluetooth device to
connect.
Bluetooth services require a Bluetooth application on the remote device;
services and applications usually have coinciding names; i.e., there is a
Bluetooth Fax Service and a Bluetooth Fax Application.
The services supported by Bluetooth are:
• Bluetooth Serial Port—a wireless connection between two devices.
This connection can be used by applications as though a physical
serial cable connected the devices.
• Dial-up Networking—allows a device to use a modem that is
physically attached to another Bluetooth device.
• Fax—allows a device to send a fax using a remote Bluetooth cell
phone, modem, or computer.
• File Transfer—allows a device to perform le system operations on
another Bluetooth device; browse, open, copy, etc.
• Headset—allows a Bluetooth headset to be used as the audio input/
output mechanism for another Bluetooth device, such as a computer
or cell phone.
• PIM Item Transfer—allows two Bluetooth devices to exchange
Personal Information Manager data such as business cards,
calendar items, email messages, and notes.
19
Page 20

Bluetooth Software Basic Operations (cont’d)
• PIM Synchronization—allows two Bluetooth devices to synchronize
Personal Information Manager data.
• Network Access—allows a device to access a Local Area Network
via a second Bluetooth device that is physically connected to the
network or allows a remote device to become part of an ad hoc
network provided by the Bluetooth server.
• Audio Gateway—allows the microphone/speakers on Bluetooth
device (typically a computer) to be used as the audio input/output
mechanism for a remote Bluetooth device, such as a cell phone.
All Bluetooth servers do not necessarily provide all of these services. For
example, network gateways may provide only the Network Access service.
Bluetooth Connection Status
The Bluetooth Connection Status dialog box displays information about the
state of a connection and provides a means to disconnect an active
connection.
Display the Connection Status dialog box: in My Bluetooth Places, from
the Folders pane, select a device, and then, in the right pane of My Bluetooth
Places, right-click a service name and select Status from the shortcut menu.
The Information provided is:
• Status: “Connected” or “Not Connected”
• Device Name: the name of the device to which this computer is
connected.
• Duration: the length of time that this connection has been
established, displayed in hours, minutes and seconds. Depending on
the service, the connection may time out (automatically disconnect)
after a specic period of inactivity.
• Activity: the number of bytes sent and received over the connection.
• Signal Strength: a graphic indicator that ranges from Too Weak
through Good to Too Strong.
NOTE: To change the power transmission level of this computer: from the Bluetooth
Conguration Panel, Hardware tab, click the Advanced button, and then change the
setting in the Maximum Power Transmission drop-down list. The Advanced button is
not available in all countries.
The controls in the Bluetooth Connection Status dialog box are
• Properties button: displays the Bluetooth Properties dialog box for
this connection.
• Disconnect button: closes this connection.
• Close button: closes the Bluetooth Connection Status dialog box.
20
Page 21

Bluetooth Software Basic Operations (cont’d)
Send to Bluetooth
This feature is used to send information to another Bluetooth device. Data
types include:
• Files from Windows Explorer
• Documents from Microsoft Ofce applications, including:
• Word
• Excel
• Access
• PowerPoint.
• Microsoft Outlook items, including:
• Contacts
• Appointments
• Tasks
• Messages
• Notes.
To use Send to Bluetooth
1. In the application:
a) Windows Explorer—select one or more les to be transferred.
Folders cannot be transferred.
b) Microsoft Ofce—only the document in the active window can be
transferred.
c) Microsoft Outlook—select one or more items to be transferred.
2. From the application’s File menu, select Send To, and then select
Bluetooth from the shortcut menu.
Select a device from the shortcut menu to send the data
or
Select Other..., choose a device from the list, and then click OK to
send the data.
21
Page 22

Bluetooth Configuration
Access the Bluetooth Conguration Panel
The Bluetooth Conguration Panel provides access to settings for Bluetooth
services, client applications, hardware, security, discovery, accessibility,
default paths, event notication and other Bluetooth related items.
To Open the Bluetooth Conguration Panel
• From the Windows Control Panel, select Bluetooth Conguration
or
• In the Windows System Tray, right-click the Bluetooth icon, and
select Advanced Conguration from the shortcut menu.
Bluetooth Services versus Bluetooth Applications
Bluetooth Services are services that this computer provides to remote
Bluetooth devices. The Bluetooth services on this computer are referred to
collectively in the Bluetooth conguration panel as “Local Services.”
Bluetooth Applications are software applications on this computer that
allow this computer to use the Bluetooth services that are provided by
remote devices. The Bluetooth applications on this computer are referred to
collectively in the Bluetooth conguration panel as “Client Applications.”
Bluetooth Services and Bluetooth Applications usually have coinciding
names; e.g., there is a File Transfer service and a File Transfer client
application.
How this computer provides a service to remote devices is congured on the
Local Services tab of the Bluetooth conguration panel.
How this computer uses a service that is provided by a remote device is
congured on the Client Applications tab of the Bluetooth conguration
panel.
Bluetooth Exchange Folder
This is the highest-level directory on this computer to which a remote
Bluetooth device has access.
Devices that have been granted access to this computer’s Bluetooth
Exchange Folder also have access to all sub-folders contained within that
folder and all les in those sub-folders.
NOTE: The Bluetooth Exchange Folder is shared by the PIM Item
Transfer and the File Transfer services and can be congured from
the Properties page of either of those services. When the Bluetooth
Exchange Folder is re-congured for either of these services, the other
service will be updated to use the new location.
22
Page 23

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Applications > Overview
General Conguration Settings
General Conguration Settings
The settings on the General tab of the Bluetooth Conguration Panel
determine information that is displayed to remote devices.
Identity
• Computer Name-enter a unique name to identify this computer to
other Bluetooth devices in the vicinity; this eld cannot be left blank.
• Computer type-select either Desktop or Laptop from the shortcut
menu to set the type of icon remote devices will use to represent this
computer.
Bluetooth Applications Overview
Some built-in Bluetooth applications provide full functionality
for a specic task, such as locating other Bluetooth devices or
synchronizing two Personal Information Managers.
Other built-in Bluetooth applications provide a way for standard Windows
applications to accomplish their tasks wirelessly. For example, a Bluetooth
application may create a wireless serial connection between computers or
provide wireless access to the Internet.
The difference between Bluetooth Applications and Bluetooth Services
• Bluetooth Applications are software programs on this computer
that allow this computer to use the Bluetooth services that are
provided by other devices. In the Bluetooth conguration panel,
these programs are referred to collectively as “Client Applications.”
• Bluetooth Services are software programs on this computer that
provide a service to other devices. In the Bluetooth conguration
panel, these programs are referred to collectively as “Local
Services.”
Note: Client Applications and Local Services usually have coinciding names;
e.g., there is a Fax service and a Fax application.
23
Page 24

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Applications > Human Interface Device (HID)
General Conguration
All of the built-in Bluetooth applications allow you to rename the application
and to require a secure connection when using the application.
To access the conguration properties page for a built-in Bluetooth
application:
• In the Windows system tray, right-click the Bluetooth icon and select
Advanced Conguration from the shortcut menu
or
• From the Windows control panel select Bluetooth Conguration
or
• From Windows Explorer, right-click Entire Bluetooth Neighborhood
and select Properties from the shortcut menu.
In the Bluetooth conguration panel, Client Applications tab, highlight the
application to be congured, and then click Properties (or double-click the
application).
Human Interface Device
Overview
The Human Interface Device (HID) Application allows this computer to
wirelessly use one or more remote Bluetooth HIDs as input/output devices.
For example, the HID Application allows this computer to use a Bluetooth
keyboard and a Bluetooth mouse. Important Note: The DBT-122 should work
with most HID devices.
Create a Bluetooth HID connection
NOTE: Some HIDs have multiple modes. Before establishing a connection, be
sure the HID is in the desired mode. For example, in the case of an HID
that can function as both a mouse and a laser pointer, be sure the mode
switch is set to “Mouse” before attempting to connect.
Open a connection to a Bluetooth Human Interface Device using one of
these techniques:
• From My Bluetooth Places
• Using the Bluetooth Setup Wizard
Once an HID connection is established, that connection will persist. If the
computer is shut down, when the computer is turned on again the connection
will re-establish automatically.
24
Page 25

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Applications > HID, Audio Gateway
NOTE: HIDs usually have a button, which is sometimes difcult to nd, that must
be pressed before other Bluetooth devices can locate the HID. Even after
the button is pressed, the HID can only be discovered for a limited time,
and then the button must be pressed again. The time period can be as
short as 30 seconds or as long as 180 seconds. Read the documentation
that accompanies the HID before you attempt to connect to the device.
Close an HID connection
Under normal circumstances, there is no reason to close an HID connection;
once established the connection is maintained automatically, even during the
power off and power on processes.
If, for some reason, the connection must be closed: from My Bluetooth
Places, right-click the service name and select Disconnect.
When an HID connection is closed manually by the operator, the
connection’s “persistence” is broken. The connection must be re-established
manually, after which the connection will again persist until broken manually.
Congure
No conguration is necessary.
Audio Gateway
Overview
The Audio Gateway Application allows a remote Bluetooth device to use this
computer’s microphone and speakers as the remote device’s audio input
and output devices.
Create a Bluetooth Audio Gateway connection
Open a connection to the Audio Gateway service that is provided by another
Bluetooth device using one of these techniques:
• Windows system tray, Bluetooth icon
• From My Bluetooth Places
• Using the Bluetooth Setup Wizard
Close an audio gateway connection:
If the connection was established via the Bluetooth icon in the Windows
system tray; click the Bluetooth icon, select Quick Connect, Audio Gateway
and then select the device that is providing the service (active connections
have a checkmark in front of them).
or
No matter how the connection was created, in My Bluetooth Places, right click the service name and select Disconnect.
25
Page 26

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Applications > Serial Port
Congure
The Bluetooth Conguration Panel > Client Applications > Audio Gateway >
General tab provides options to congure:
• The application name—to change it, highlight the existing name and
enter the new name.
• Enable or disable secure connection. To enable secure connection,
place a checkmark in the box.
Bluetooth Serial Port
The Bluetooth Serial Port application allows this computer to establish a
wireless serial connection with a remote Bluetooth device.
The applications on both this computer and the remote device must be
congured to send and receive data to and from the respective
communications port (COM port) assigned to the Bluetooth serial port. The
wireless serial connection may then be used by the applications as though a
physical serial cable connected the devices.
Create a Bluetooth Serial Port connection
Establish a connection using one of these techniques
• Windows system tray, Bluetooth icon
• From My Bluetooth Places
• Using the Bluetooth Setup Wizard
Close a Bluetooth Serial Port connection
• If the connection was established via the Bluetooth icon in the
Windows system tray; click the Bluetooth icon, select Quick
Connect, Bluetooth Serial Port and then select the device that is
providing the service (active connections have a checkmark in front
of them).
or
• No matter how the connection was created, In My Bluetooth Places,
right-click the service name and select Disconnect.
Congure
The Bluetooth Conguration Panel > Client Applications > Bluetooth Serial
Port > General tab provides options to congure:
• The application name—to change it, highlight the existing name and
enter the new name.
• Enable or disable secure connection. To enable secure connection,
place a checkmark in the box.
• The communications port (COM port) to be used.
NOTE: Unless you have a specic reason to do so, DO NOT CHANGE the default COM Port
setting.
26
Page 27

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Applications > Dial-up Networking
Dial-up Networking
Overview
The Bluetooth Dial-up Networking application allows this computer to use a
modem that is physically connected to a remote device to access the
Internet, and log on to a remote network.
Open a connection to the Dial-up Networking service that is provided by
another Bluetooth device using one of these techniques:
• Windows system tray, Bluetooth icon
• From My Bluetooth Places
• Using the Bluetooth Setup Wizard
After the Bluetooth dial-up networking connection is established it can be
used the same way as any other networking connection. For example,
you can open a browser and explore the World Wide Web, if the remote
computer has Internet access.
Close a Dial-up Networking connection
• If the connection was established via the Bluetooth icon in the
Windows system tray; click the Bluetooth icon, select Quick
Connect, Dial-up Networking and then select the device that is
providing the service (active connections have a checkmark in front
of them).
or
• No matter how the connection was created, In My Bluetooth Places,
right-click the service name and select Disconnect.
Congure
The Bluetooth Conguration Panel > Client Applications > Dial-up
Networking > General tab provides options to congure:
• The application name—to change it, highlight the existing name and
enter the new name.
• Enable or disable secure connection. To enable secure connection,
place a checkmark in the box.
• The Bluetooth virtual device to be used.
NOTE: Unless you have a specic reason to do so, DO NOT CHANGE the
default Bluetooth device or alter the device’s conguration.
27
Page 28

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Applications > Fax, Headset
Fax
Overview
The Bluetooth Fax service allows this computer to send a fax using a Fax/
Modem that is physically connected to a remote device.
To Send a Fax
1. Open a connection to the Fax service that is provided by another
Bluetooth device, using one of these techniques:
• Windows system tray, Bluetooth icon
• From My Bluetooth Places
• Using the Bluetooth Setup Wizard
2. Open or create the document to be faxed and select the “Print,”
“Send to Fax Recipient” or similar command that is available in most
applications.
Close a Fax Connection
Fax connections close automatically when the Fax transmission is complete.
Congure
The Bluetooth Conguration Panel > Client Applications > Fax > General tab
provides options to congure:
• The application name—to change it, highlight the existing name and
enter the new name.
• Enable or disable secure connection. To enable secure connection,
place a checkmark in the box.
Headset
Overview
The Headset application allows this computer to use a Bluetooth headset (or
any other device that offers the Bluetooth headset service) as the audio input
and output device for this computer.
Possible uses include:
• If this computer has on-board telephone hardware, a Bluetooth
headset might be used as the audio input/output device to make/
receive telephone calls.
• If this computer has voice recognition capabilities, a Bluetooth
headset might be used as the audio input device.
Any other scenario that requires audio input/output can potentially take
advantage of a Bluetooth headset to replace a hardwired microphone and/or
speakers.
28
Page 29

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Applications > Headset
Hands-Free Prole (HFP)
Overview
The Hands-Free Prole (HFP) denes how two devices that support HFP will
interact on a point-to-point basis. With HFP, a headset or any other Hands-
Free embedded unit can connect wirelessly to a cellular phone to act as the
cellular phone’s audio input and output mechanism. HFP applied in this way
also allows typical telephone functions to be performed without the need to
access the actual phone. The Hands-Free AG (Audio Gateway) role can be
used as the source side of the HFP connection. It can be used to connect
with a Hands-Free device, like a Bluetooth headset.
Two roles are dened for this application:
An Audio Gateway (AG) is a device that is the source of the audio, both for
input and output. Cellular phones are a typical AG role device.
A Hands-Free (HF) unit is a device acting as an Audio Gateway’s remote
audio input and output mechanism. Units in an HF role also provide some
remote control capabilities over AG devices.
Create a Headset connection
Establish a connection using one of these techniques:
• Windows system tray, Bluetooth icon
• From My Bluetooth Places
• Using the Bluetooth Setup Wizard
NOTE: Most Bluetooth headsets “ring” when a connection is
attempted; answer the ring to complete the connection and begin using
the headest as the audio input/output device for this computer.
Close a Headset connection
• If the connection was established via the Bluetooth icon in
the Windows system tray; click the Bluetooth icon, select
Quick Connect, Headset and then select the device that is
providing the service (active connections have a checkmark
in front of them). OR
• No matter how the connection was created, in My Bluetooth
Places, right-click the service name and select Disconnect.
29
Page 30

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Applications > Headset, File Transfer
Congure
The Bluetooth Conguration Panel > Client Applications > Headset >
General tab provides options to congure:
• The application name—to change it, highlight the existing name and
enter the new name.
• Enable or disable secure connection. To enable secure connection,
place a checkmark in the box.
NOTE: Using A2DP and HFP, a user can listen to music playing on a PC
without missing VoIP phone calls received by the same PC. When a
VoIP phone call comes in, music will be paused automatically while the
user answers the phone call using the Bluetooth stereo headset. The
music stream will then resume automatically after the VoIP phone call
is completed.
File Transfer
Overview
The Bluetooth File Transfer application allows this computer to perform le
operations on the Bluetooth Exchange Folder (and the folders and les it
contains) of a remote device.
Copy to/from a remote device
In the Folders pane of Windows Explorer, from the Entire Bluetooth
Neighborhood branch, select a device and expand that branch to view the
Bluetooth Exchange Folder of the remote device.
NOTE: If “Public Folder” is not available, the remote device is not
congured to allow remote le operations.
30
Page 31

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Applications > File Transfer
Use drag-and-drop to copy any le or folder contained in the Public Folder of
the remote device to the desired folder on this computer.
You can also drag-and-drop les or folders from this computer to the Public
Folder (and its sub-folders) of the remote device.
Other le operations
Right-click a le or folder in the remote device’s Public Folder for a context
sensitive menu. All potential menu options may not be available at all times.
Potential menu options include:
(cont’d)
• Open—opens the selected le on this computer, using the default
application for this type of le.
• Print—sends the selected le to this computer’s default printer.
• Send To
• 3 ½ oppy (A)—the 3 ½ inch oppy drive on this computer
• Bluetooth Exchange Folder—the Bluetooth Exchange Folder on this
computer.
• Rename—applies only to empty folders; le names and the names
of folders that contain objects cannot be changed using this
technique.
• Cut, Copy, Paste, Delete, Refresh, View & New—standard Windows
functions.
Congure
The Bluetooth Conguration Panel > Client Applications > File Transfer >
General tab provides options to congure:
• The application name—to change it, highlight the existing name and
enter the new name.
• Enable or disable secure connection. To enable secure connection,
place a checkmark in the box.
31
Page 32

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Applications > Network Access
Network Access
Overview
The Bluetooth Network Access application makes it possible for this
computer:
• To connect to a Local Area Network via a physical connection on a
remote Bluetooth device.
or
• To connect to an ad hoc network provided by a remote Bluetooth
device.
The type of network connection that is available is determined by the
conguration of the remote Bluetooth device.
Create a Network Access connection
Establish a connection using one of these techniques
• Windows system tray, Bluetooth icon
• From My Bluetooth Places
• Using the Bluetooth Setup Wizard
Close a Network Access connection
• If the connection was established via the Bluetooth icon in the
Windows system tray; click the Bluetooth icon, select Quick
Connect, Network Access and then select the device that is
providing the service (active connections have a checkmark in front
of them).
or
• No matter how the connection was created, In My Bluetooth Places,
right-click the service name and select Disconnect.
Congure
The Bluetooth Conguration Panel > Client Applications > Network Access >
General tab provides options to congure:
• The application name—to change it, highlight the existing name and
enter the new name.
• Enable or disable secure connection. To enable secure connection,
place a checkmark in the box.
32
Page 33

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Applications > PIM
PIM Synchronization
Overview
The PIM Synchronization Application is used to synchronize the Personal
Information Manager (PIM) database of this computer with the PIM database
of a remote Bluetooth device.
The supported PIMs are:
• Microsoft Outlook
• Microsoft Outlook Express
• Lotus Notes.
The supported data types are:
• Business cards
• Calendar items
• Email (with or without attachments)
• Notes.
Congure PIM Synchronization
The Bluetooth Conguration Panel > Client Applications > PIM
Synchronization > General tab provides options to congure:
• The application name—to change it, highlight the existing name and
enter the new name.
• Enable or disable secure connection. To enable secure connection,
place a checkmark in the box.
• The PIM items to be synchronized and the PIM on this computer
NOTE: If synchronization is enabled for a specic item type, but is not enabled
for that item type on the remote device, synchronization WILL NOT take
place for that item.
• The data item types which can be synchronized are:
• Business cards
• Calendar items
• Email (with or without attachments-see below)
• Notes
Possible synchronization options for each of these data item types include:
• Do Not Synchronize-this item type will not be synchronized
33
Page 34

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Applications > PIM
(cont’d)
• Synchronize Microsoft Outlook-this item type will be synced
with its matching entry in Microsoft Outlook, regardless of the
PIM that contains this entry on the remote device. If a matching
Outlook entry does not exist, it will be created
• Synchronize Outlook-Express-this item type will be synced
with its matching entry in Express, regardless of the PIM that
contains this entry on the remote device. If a matching Express
entry does not exist, it will be created
• Synchronize Lotus Notes-this item type will be synced with
its matching entry in Lotus Notes, regardless of the PIM that
contains this entry on the remote device. If a matching Notes
entry does not exist, it will be created.
NOTE: All choices are not available for all items. For example, “Note” items
can only be synchronized in Microsoft Outlook, therefore Lotus Notes
and Outlook Express do not appear as options in the “Notes” item
shortcut menu. Personal Information Managers that are not installed
on this computer do not appear as options in the shortcut menus.
• Email attachments. The only option is include or do not include
attachments with email that is sent or received on this computer
using this service.
PIM Item Transfer
Overview
The Bluetooth PIM Item Transfer application allows this computer to send
and receive Personal Information Manager items to-and-from a remote
Bluetooth device. Item transfer can be accomplished several ways:
To send, receive or exchange business cards:
1. From Windows Explorer, My Bluetooth Places, right-click the PIM
Item Transfer service on a remote device and select the appropriate
option.
or
In the Windows system tray, right-click the Bluetooth icon, select
Quick Connect > Business Card Exchange, select a device from the
list, select the appropriate option from the shortcut menu, and then
click OK.
34
Page 35

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Applications > PIM
2. From Windows Explorer, My Bluetooth Places, highlight the PIM
Item Transfer service on a remote device, and then, from the
Bluetooth menu on the Windows menu bar, select the appropriate
action.
In addition to the business card options listed above, you can also
send Notes (*.vnt), Email (*.vmg) and Calendar (*.vcs) items from
this menu.
3. From within a supported Personal Information Manager, select one
or more items and then, from the PIM’s File menu, select Send to
Bluetooth.
Whether sent items are accepted by the remote device is determined by how
the remote device’s PIM Item Transfer service is congured.
Close a PIM Item Transfer Connection
This application closes the open connection automatically when its task is
complete.
Congure PIM Item Transfer
The Bluetooth Conguration Panel > Client Applications > PIM Item Transfer
> General tab provides options to congure:
(cont’d)
• The application name—to change it, highlight the existing name and
enter the new name.
• Enable or disable secure connection. To enable secure connection,
place a checkmark in the box.
• How your business card is handled when it is requested by a remote
device. The Send My Business Card options are:
Choose a business card as needed-each time a remote device requests
your business card you must select a card from your PIM. If you
ignore the request the remote device will receive a timeout notice.
Always send the same business card-when this option is selected a dialog
appears that allows you to set a default business card, which will be
sent automatically when requests are received.
• Where to store received business cards. The Received
Business Cards options are:
• Microsoft Outlook
• Outlook Express
• Lotus Notes
• Email attachments (only option is to include or not include)
35
Page 36

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Applications > PIM
NOTE: The selected Received Business Cards option does not inuence the
settings on other PIM-related property pages.
For example, even if the PIM Item Transfer service business card
option on this computer is congured to “Do Not Accept,” the PIM Item
Transfer application will still accept business cards that the application
has specically requested via its “Receive” or “Exchange” functions.
(cont’d)
Applications > My Headset / Audio Gateway
Advanced Audio Distribution Prole (A2DP)
Overview
The Bluetooth Advanced Audio Distribution Prole (A2DP) application allows
a computer to use Bluetooth for distribution of high quality audio content
in mono or stereo on ACL channels. A typical application of A2DP is for
streaming music content from a stereo music player or PC to headphones or
speakers. Users can enjoy high-quality music on a Bluetooth stereo headset
receiving streaming music from the DBT-122 dongle via a PC.
A2DP denes the protocol for audio streaming while the Video Distribution
Prole (VDP) denes video streaming. So, to gain both high quality audio
and video, you need Bluetooth devices which support both A2DP and VDP.
Two roles are dened for this application:
An A2DP Source is a device, such as a Bluetooth MP3 or PDA, providing
the source of a digital audio stream for delivery to an A2DP Sink.
An A2DP Sink is a device, such as a Bluetooth headset or stereo speakers,
receiving a digital audio stream provided by an A2DP Source.
Some devices can operate in both roles, although not simultaneously. For
example, the speakers on a PC can be used as an A2DP Sink to play music
transmitted from an A2DP Source such as a Bluetooth MP3 player.
36
Page 37

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Applications > My Headset / Audio Gateway
Conversely, a PC can also be used as an A2DP Source to, for example,
transmit music to a Bluetooth headset.
Congure
The Bluetooth Conguration Panel > Client Applications > My Headset /
Audio Gateway > General tab provides options to congure:
• The application name—to change it, highlight the existing name and
enter the new name.
• Enable or disable secure connection. To enable a secure
connection, place a check mark in the box.
Video Distribution Prole (VDP)
Overview
The Bluetooth Video Distribution Prole (VDP) application denes how a
Bluetooth enabled device streams video content using ACL channels. A
typical application of VDP is for streaming stored video playback from a PC
media center to a portable player or streaming from a digital video camera to
a TV. Users can watch streaming video playback using the DBT-122 dongle
via a PC.
VDP denes the protocol for video streaming while A2DP denes high quality
audio streaming. So, for high quality audio and video, your Bluetooth devices
should support both VDP and A2DP.
(cont’d)
Two roles are dened for this application:
A VDP Source is a device, such as a Bluetooth enabled digital video
camera, providing the source of a digital video stream for delivery to a VDP
Sink.
A VDP Sink is a device, such as a Bluetooth enabled PC, receiving a digital
audio stream provided by an VDP Source.
Congure
The Bluetooth Conguration Panel > Client Applications > My Headset /
Audio Gateway > General tab provides options to congure:
• The application name—to change it, highlight the existing name and
enter the new name.
• Enable or disable secure connection. To enable a secure connection,
37
Page 38

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Applications > Printer
Basic Printing Prole (BPP)
Overview
The Basic Printing Prole (BPP) denes how a Bluetooth device can send
print job requests to a Bluetooth enabled printer without the need for device-
specic printer drivers. Common applications of BPP include printing e-mail
messages, short messages (SMS), and formatted documents. Optional
support for the printing of structured data objects such as vCard and
vCalendar entries is also dened, as well as methods for negotiating the use
of other formats supported by the printer.
The Basic Printing Prole allows a Bluetooth enabled printer to act as a print
server to accept objects pushed by a sender, for example a PDA or a mobile
phone, and print out the result.
Two roles are dened for this application:
A Printer is a server device used as an object exchange server.
A Sender is the client device that pushes an object to the Printer
BPP also species two types of print service: Direct Printing and Reference
Printing. For Direct Printing jobs or services, the content to be printed is
stored on the Sender. For Reference Printing jobs or services, the content to
be printed is stored on the network and referenced by the Sender in queuing
a print request. The Printer’s main task is to accept a print request of either
type from a Sender, queue it, and print the content.
Congure
The Bluetooth Conguration Panel > Client Applications > My Printer >
General tab provides options to congure:
• The application name—to change it, highlight the existing name and
enter the new name.
• Enable or disable secure connection. To enable a secure connection,
place a check mark in the box.
38
Page 39

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Applications > Printer
(cont’d)
Printer
Overview
The Bluetooth Printer application allows this computer to use a Bluetooth
printer. Once a Bluetooth printer has been properly installed, it can be used
from this computer in the same way as any other printer would be.
Congure
The Bluetooth Conguration Panel > Client Applications > Printer > General
tab provides options to congure:
• The application name—to change it, highlight the existing name and
enter the new name.
• Enable or disable secure connection. To enable secure connection,
place a checkmark in the box.
Install a Bluetooth Printer
Option One:
1. Perform a search for devices and then, from Entire Bluetooth
Neighborhood, right-click a Bluetooth printer, select Add Printer from
the shortcut menu and follow the on-screen instructions.
2. When the wizard asks you to select a printer make and model, do
so.
If your printer is not in the list of options, click Have Disk…, insert
the driver disk for the printer, and then navigate to the drive and
directory that contains the driver initiation le (*.inf) for the printer.
3. To complete the installation, follow the on-screen instructions.
Option Two:
1. From the Windows Control Panel, select Printers > Add Printer >
Next > Local printer > Next.
2. On the Select the Printer Port screen of the wizard:
a) Select Create a new port
b) In the Type shortcut menu, select Bluetooth Printer Port, and
3. On the next screen, select the printer by name, and then click
Connect.
then click Next.
39
Page 40

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Applications > Printer
Option Two (continued):
4. Install the driver: when asked to select a printer make and model, do
so.
If your printer is not in the list of options, click Have Disk…, insert
the driver disk for the printer, and then navigate to the drive and
directory that contain the driver initiation le (*.inf) for the printer.
5. To complete the installation, follow the on-screen instructions.
Delete a printer:
Click Start > Settings > Printers, right-click the printer to be deleted, and then
select Delete from the shortcut menu.
Or
In Entire Bluetooth Neighborhood, right-click an installed Bluetooth printer
and select Delete Printer from the shortcut menu.
Bluetooth Services
(cont’d)
Service Common Conguration Settings
These properties can be set individually for each Bluetooth service:
• Service Name-the default name of each service can be changed.
• Secure Connection-requires that remote devices provide proof of
identity and that all data be encrypted.
• Startup Automatically-starts the service automatically when
Bluetooth is started.
• Notications-provides visual and/or audio notication that a remote
device is attempting to connect (or has connected) to a service on
this computer.
40
Page 41

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Services > Notications
Notications
Overview
There are three types of notication:
• Authentication request, also called a PIN code request—this
notication appears automatically in a balloon over the Windows
system tray if a Personal Identication Code is required before a
connection can proceed. An audio le can also be associated with
the notication.
• Authorization request, also called a connection request—this type of
notication can be visual, audio, or both. It noties you of attempts to
access a Bluetooth service on this computer; the connection will not
proceed until you click the balloon that appears over the Windows
system tray. If the notication balloon is ignored, the connection
request will time out and fail.
• Notication only—this type of notication does not effect access in
any way; it is solely for information purposes to let you know that a
connection has been established.
Example
Both Authentication and Authorization request notications are controlled by
whether Secure Connection is enabled for an individual service.
An example of how notications might work when a remote device attempts
to access a service on this computer, if all notications are enabled:
1. Authentication: a balloon notication (audio optional) appears to
prompt for a PIN code. If the PIN code does not match the code
entered on the remote device, the connection will not be allowed.
Once the remote device has been authenticated this notication will
not appear again, unless the paired relationship is broken and the
devices must re-pair.
2. Authorization: a balloon notication appears and/or a sound le
provides audio notication that a remote device is attempting to
access a Bluetooth service on this computer. Click the balloon to
proceed. A dialog box appears that offers the option of letting the
connection proceed this time only or to always allow this particular
remote device to use the service it is attempting to access.
3. Once a connection has been authorized, an additional visual and/or
audio notication may appear (if enabled). This notication is for
information only to inform the operator that a connection has been
established.
41
Page 42

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Services > Audio Gateway Service
After two devices are paired (step 1, above), the authentication notication
will no longer appear when a connection is attempted.
If “Always allow…” is enabled during the authorization process (step 2,
above), the authorization notication will not appear on future connection
attempts.
Connection notication (step 3, above) only happens if it has been enabled
Service Access Notication
“Notications” lets you associate a sound (Windows *.wav le) and/or a
visual indication with access attempts by remote devices.
A different notication sound can be associated with each local Bluetooth
service.
Associate a sound with service access
From the Bluetooth Conguration Panel, Local Services tab:
1. Double-click a service name and then select the Notications tab.
2. Check the desired options; visual and sound may both be selected
for a single event.
3. Choose a sound; click the Browse button and navigate to the sound
le (*.wav) to be used for notication.
Audio Gateway
The Bluetooth Audio Gateway service allows this computer to use a remote
Bluetooth device’s microphone and speakers as this computer’s input and
output devices.
For example, if this computer has voice recognition capabilities, a Bluetooth
headset might be used as the audio input device.
Hardware Requirements
• The Bluetooth radio on both this computer and the remote device
must support audio.
• The remote device handles both audio input and output for this
computer; therefore, this computer does not require a sound card,
microphone, or speakers.
Congure the Audio Gateway Service
From the Windows system tray, right-click the Bluetooth icon, select
Advanced Conguration > Local Services, and then double-click the Audio
Gateway service.
Set the common conguration properties of the service, and then click OK.
42
Page 43

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Services > Bluetooth Serial Port Service
Bluetooth Serial Port
The Bluetooth Serial Port service allows a remote Bluetooth device to
establish a wireless serial connection with this computer. The wireless serial
connection may be used by applications as though a physical serial cable
connected the devices.
To establish a Bluetooth Serial Port connection
The connection must be initiated from the remote device by the Bluetooth
Serial Port application.
Determine the communications port being used by this computer for
the Bluetooth Serial Port
In the Windows system tray, right-click the Bluetooth icon, select Advanced
Conguration, and then the Local Services tab. The COM port assigned to
this service is the last item in the Bluetooth Serial Port service row. Congure
the application on this computer that will use this service to send its data to
this COM.
Add a Bluetooth Serial Port
The Bluetooth Serial Port service has one pre-congured Bluetooth Serial
Port, but additional Bluetooth Serial Ports can be added as needed.
To add a port
1. From the Bluetooth Conguration Panel, Local Services tab, click
Add Serial Service.
2. In the properties dialog box, modify the properties.
3. Enter a unique name (less than 99 alphanumeric characters).
4. Select secure connection, if desired.
5. Select Startup Automatically, if desired.
6. From the COM Port shortcut menu select a communications port
that is not assigned to any other service.
7. Click OK.
To remove a Bluetooth Serial Port
From the Bluetooth Conguration Panel, Local Services tab, select the port
to be removed and then click Delete.
NOTE: The Delete button is only available when a Bluetooth Serial
Port is selected.
43
Page 44

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Services > Dial-up, Fax, File Transfer Service Dial-up Networking Service
The Bluetooth Dial-up Networking service makes it possible for a remote
Bluetooth device to use a modem that is physically connected to this
computer. The remote device can then access the Internet or log on to a
remote network.
Congure the Dial-up Networking service:
From the Windows system tray, right-click the Bluetooth icon, select
Advanced Conguration > Local Services, and then double-click the Dial-up
Networking service.
• Select the physical modem to be used from the Modems: shortcut
menu.
• Set the common conguration properties of the service, and then
click OK.
Fax Service
The Fax service allows a remote Bluetooth device to send a Fax via a
modem that is physically attached to this computer.
Congure the Fax service:
From the Windows system tray, right-click the Bluetooth icon, select
Advanced Conguration > Local Services, and then double-click the Fax
service.
• Select the physical modem to be used from the Modems: shortcut
menu.
• Set the common conguration properties of the service, and then
click OK.
File Transfer Service
The File Transfer service allows this computer to perform le operations on
the Bluetooth Exchange Folder (and the folders and les it contains) of a
remote device.
Basic setup procedure
Right-click the Bluetooth icon and select Explore My Bluetooth Places.
Congure Windows Explorer so that the Folders pane is visible (View >
Explorer Bar > Folders).
In the Folders pane, select Entire Bluetooth Neighborhood and then, on the
menu bar, select Bluetooth > Search For Devices.
In the Folders pane, expand Entire Bluetooth Neighborhood to show the
devices in the vicinity.
Copy to/from a remote device
In the Folders pane of Windows Explorer, from the Entire Bluetooth
Neighborhood branch, select a device and expand that branch to view the
Bluetooth Exchange Folder of the remote device.
44
Page 45

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Services > Headset
NOTE: “Public Folder” is not available, the remote device is not congured to
allow remote le operations.
Use drag-and-drop to copy any le or folder contained in the Public Folder of
the remote device to the desired folder on this computer.
You can also drag-and-drop les or folders from this computer to the Public
Folder (and its sub-folders) of the remote device.
Other le operations
Right-click a le or folder in the remote device’s Public Folder for a context
sensitive menu. All potential menu options may not be available at all times.
Potential menu options include:
• Open—opens the selected le on this computer, using the default
application for this type of le.
• Print—sends the selected le to this computer’s default printer.
• Send To
• 3 ½ oppy (A)—the 3 ½ inch oppy drive on this computer
• Public Folder on My Device—the Public Folder on this computer.
• Rename—applies only to empty folders; le names and the names
of folders that contain objects cannot be changed using this
technique.
• Cut, Copy, Paste, Delete, Refresh, View & New—standard Windows
functions.
Headset Service
The Bluetooth Headset Service allows this computer to provide audio input/
output for remote Bluetooth devices.
For example, if the remote device is a Bluetooth telephone, this computer’s
microphone and speakers can be used as speakerphone input and output for
that device.
Hardware Requirements
• This computer must have a sound card, microphone, and speakers
installed.
• The Bluetooth radio on both on this computer and the remote device
must support audio.
Congure the Headset Service
• From the Windows system tray, right-click the Bluetooth icon, select
Advanced Conguration > Local Services, and then double-click the
Headset service.
• Set the common conguration properties of the service, and then
click OK.
45
Page 46

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Services > Network Access Network Access
The Bluetooth Network Access service makes it possible for a remote
Bluetooth device to access a Local Area Network that is physically attached
to this computer or allows a remote device to become part of an ad hoc
network provided by this computer.
After this computer has been congured to provide the Network Access
service to other Bluetooth devices, it will not be able to use the Bluetooth
Network Access service provided by another Bluetooth device without being
re-congured. Put another way, this computer cannot be both a Bluetooth
Network Access server and a Bluetooth Network Access client at the same
time.
Setup for Windows 98SE & Windows Me
NOTE: Internet Protocol routing software is required on Windows 98SE and
Windows Me servers.
Install and congure the routing software as instructed by the
software’s manufacturer.
Congure the server:
1. From the Windows Control Panel, double-click the Network icon.
2. On the Conguration tab, select TCP/IP-> Bluetooth LAN Access
Server Driver (scroll down if necessary).
3. Click Properties and select the IP Address tab.
a) Select Specify an IP address
b) Enter an IP Address (suggested value—192.168.1.1)
c) Enter a Subnet Mask (suggested value—255.255.255.0)
4. Click OK twice to close the dialog boxes and then click YES to
restart the computer.
Setup for Windows 2000 and Windows XP
If Internet Connection sharing was previously enabled (before BTW was
installed) it must be disabled and then re-enabled before the Bluetooth
network adapter can use it.
Congure for Network Access:
1. From the Windows system tray, right-click the Bluetooth icon and
select Advanced Conguration from the shortcut menu.
2. In the Bluetooth conguration panel, select the Local Services tab,
Network Access and then click Properties....
3. From the Network Access, General properties page, in the Type of
service shortcut menu, select “Allow other devices to access the
Internet/LAN via this computer,” and then click Congure Connection
Sharing.
46
Page 47

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Services > Network Access, PIM
4. Right-click Local Area Connection, select Properties and then select
the Sharing tab.
5. Select Enable Internet Connection Sharing for this connection, click
OK, and then click YES in the conrmation dialog box.
Congure for Group Ad Hoc Networking:
1. From the Windows system tray, right-click the Bluetooth icon and
select Advanced Conguration from the shortcut menu.
2. In the Bluetooth conguration panel, select the Local Services tab,
Network Access and then click Properties....
3. From the Network Access, General properties page, in the Type of
service shortcut menu, select “Allow other devices to create a private
network with this computer.”
4. Click OK.
PIM Item Transfer
Overview
The PIM Item Transfer service allows Personal Information Manager items to
be transferred between this computer and a remote Bluetooth device.
Four data types are supported:
• Business Cards
• Calendar Items
• Email Messages
• Notes
Each data type can be saved in any of the supported and installed PIMs.
NOTE: PIMs which are not installed on this computer will not appear in the
shortcut menus.
When the PIM that is associated with an individual data type is changed on
the PIM Item Transfer page, that data type is also changed for the PIM
Synchronization service.
(Continued on the next page)
47
Page 48

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Services > PIM
Congure
In addition to the conguration options common to all Bluetooth services, this
service also has settings that determine:
(cont’d)
• How business card requests are handled. The options are:
• Never send my business card—ignore the request.
• Choose a business card as needed—when prompted, select a
business card to be sent to the requester.
• Always send the same business card—when a request is
received always send the same business card. When this option
is selected, a dialog box appears from within which an installed
Personal Information Manager (if more than one is installed on
this computer) and an existing business card can be selected.
NOTE: Previously sent business card additions to the menu are limited to ten,
after which the oldest contact will be replaced.
• Previously sent business cards—once a card is selected using
the “Always send the same business card” option, above, that
card will be added to the shortcut menu as an option.
• Where to store inbound data items, on an individual basis. Options
include (not all options apply to all items):
• Do Not Accept
• Any of the installed PIMs on this computer
• Save to Folder
• The Bluetooth Exchange Folder location—the directory on this
computer where inbound items that are not to be saved in a PIM will
be kept.
NOTE: This is also the folder where the File Transfer service stores inbound
items. If this folder is recongured here, it will also be recongured in
that service automatically.
• Whether to send/receive attachments with email. Check or clear this
option, as appropriate.
Close a PIM Item Transfer connection
PIM Item Transfer connections close automatically when the data transfer is
complete.
48
Page 49

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Services > PIM
Default Business Card Selection
When the “Always send the same business card” option is selected, a dialog
box appears to allow the selection of a default business card.
The rst time the dialog box appears it provides a way to choose the Personal
Information Manager that stores the default business card. Click the down-
arrow in the PIM shortcut menu and select the PIM to be used.
On subsequent appearances of this dialog box, the PIM selection option is
not available.
Change the selected PIM
On the PIM Item Transfer properties page, “Received items” section, there is
a Business Cards shortcut menu. When a PIM was selected during initial
setup the selected item in this menu was set to the same PIM. To change
the PIM used for the default business card, open this shortcut menu and
select a new PIM.
NOTE: A new default business card must be selected from the database
of the newly selected PIM.
Choose a default business card
1. In the Select a Bluetooth Business Card dialog box that appears
when “Always send the same business card” is selected, highlight
the card.
(cont’d)
NOTE: Once a card is highlighted, if you “hover” the mouse pointer over that
selection, a balloon appears with additional information about that
contact.
2. Click OK to choose a highlighted business card and return to the PIM
Item Transfer Properties page. The chosen contact now appears in,
and is selected in, the “Business card requests” shortcut menu.
If the “Always send the same business card” option is selected again, and a
different contact chosen, the properties page will display both contacts in the
shortcut menu.
NOTE: In addition to the default menu options, the shortcut menu can hold up
to ten contact names.
49
Page 50

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Services > PIM
(cont’d)
PIM Synchronization
The PIM Synchronization service can be used by a remote device to
synchronize its Personal Information Manager (PIM) database with
the PIM database of this computer.
Four data types are supported:
• Business cards
• Calendar items
• Email messages
• Notes
Whether an individual item is accepted and where it is stored, when
accepted, is congured in the PIM Item Transfer service. If that
service is not congured to store a particular data type in Outlook,
then that data type cannot be synchronized.
NOTE: Data types that will be synchronized must be saved in the PIM
database (this is congured in the PIM Item Transfer service);
otherwise, that data type will not be available for selection (it will be
grayed out) in the PIM Synchronization conguration settings.
Microsoft Outlook permits duplicate entries, so all duplicates may not
be exchanged in the synchronization process.
NOTE: Only Outlook’s default contacts folder is synchronized. Items in sub folders are not synchronized. Items that are moved from the default
folder to a sub-folder will appear to have been deleted the next time
synchronization takes place.
50
Page 51

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Hardware Settings
The Hardware tab of the Bluetooth Conguration Panel provides basic
information about the Bluetooth hardware installed on this computer and
access to the Advanced Settings dialog box, if required:
• Devices:
• Name: the name of the device, e.g., WIDCOMM Bluetooth
Device
• Type: the type of device, e.g., USB.
• Device Properties:
• Device status: indicates that the device is operating properly or
that there is a problem/conict.
• Manufacturer: the name of the company that manufactured the
device selected in the Devices section of this dialog box.
• Firmware Revision: the manufacturer’s rmware version
number.
• Device Address: the Bluetooth Device Address (BDA or BD_
Addr) assigned to this device when it was manufactured.
• HCI Version: the version number of the Bluetooth Specication
that the Host Controller Interface complies with.
• HCI Revision: the revision number of the Bluetooth
Specication that the Host Controller Interface complies with.
• LMP Version: the version number of the Bluetooth Specication
that the Link Manager Protocol complies with.
• LMP Sub Version: the sub-version number of the Bluetooth
Specication that the Link Manager Protocol complies with.
• The Advanced button: displays the Advanced Settings dialog box,
which allows you to select the country code and transmission power
settings. This option is not available on all systems.
51
Page 52

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Advanced Settings
When available, this dialog box is reached from the Hardware tab of the
Bluetooth Conguration Panel.
NOTE: Depending on the country in which the hardware is sold and/or in
which it will be used, the Advanced button may not be present.
From this dialog box you can set the:
• Country Code:
• North America, Europe (except France), and Japan
• France and China
• Maximum Transmission Power:
• High
• Medium
• Low
Click Apply to implement the changes. A dialog box appears
with notication that the Bluetooth device attached to this
computer must be reset before the change(s) will take effect.
Click Yes to reset the Bluetooth device now—all open Bluetooth
connections will be closed.
Click No to save the changes—the changes will be applied the
next time the Bluetooth device is reset or restarted.
52
Page 53

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Accessibility Settings
The Accessibility tab of the Bluetooth Conguration Panel lets you specify
whether remote devices may access this computer, which remote devices
have access, and whether an audio warning is played when a Personal
Identication Number (PIN code) is required.
Allow other devices to discover this computer
Select “Let other Bluetooth devices discover this computer” to permit remote
Bluetooth devices to nd and report this computer.
If “Allow No devices” (below) is selected, this option is not available.
Control the types of devices that are allowed to connect to this
computer
From the “Devices allowed to connect to this computer” shortcut-menu,
select:
• No devices—no remote devices are permitted to initiate a
connection with this computer. However, this computer can still
initiate connections with remote Bluetooth devices.
• All devices—all remote devices are permitted to connect to this
computer.
Connections are subject to additional security restrictions, such
as authentication and authorization, that may be required by the
individual services provided by this computer.
• Only paired devices—only devices that have been paired with this
computer are allowed to connect to it.
• Only devices listed below—only the listed devices are allowed
to connect to this computer (see Accessibility, adding and deleting
devices).
Choose an audio notication le
When Secure Connection is enabled for any of the Bluetooth Services on his
computer a PIN code is required before that service can be accessed. To
chose a notication sound that will play when a remote device attempts to
access a service that requires a secure connection, click Select audio le...
and select the sound (*.wav) le to be played.
Limit access to this computer to specic remote devices
From the Bluetooth Conguration Panel, Accessibility tab, in the Allow
shortcut menu, select “Only devices listed below”.
53
Page 54

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Accessibility Settings
Add a device to the list
1. Click Add Device.
2. In the Devices with access... dialog box select the desired device(s)
and click OK.
NOTE: Multiple devices may be selected using SHIFT + click and/or CTRL +
click.
Delete a device from the list
In the list of devices allowed to access this computer, select the device to be
removed from the list, and then click Delete.
(cont’d)
Discovery Settings
The settings on the Discovery tab of the Bluetooth Conguration Panel
determine whether this computer looks for other Bluetooth devices
automatically, how often it looks and what type of devices it looks for.
Periodic Search for Devices
When “Look for other Bluetooth devices” is selected, Bluetooth automatically
searches for devices every X minutes. X is an whole number between 1 and
60. To change the time between auto inquiries, highlight the existing time
and enter the new time.
NOTE: When My Bluetooth Places is rst opened it performs an initial
automatic search for devices even if “Look for other Bluetooth
devices” is not enabled.
Determine the devices that will be reported
Bluetooth can screen out devices that you do not need access to.
The options are:
• Report all Bluetooth devices.
• Report only selected Bluetooth devices (see Discovery, Adding
Specic Devices and Discovery, Deleting Specic Devices).
• Select the desired option from the drop-down list.
54
Page 55

Bluetooth Configuration (cont’d)
Discovery Settings
Discover Specic Devices
The type of device(s) that this computer looks for and reports when it is
searching for other Bluetooth devices can be limited.
Limit the remote devices reported
Bluetooth can report only specic devices, specic class(es) of device(s), or
specic type(s) of device(s) within a class.
(cont’d)
• Specic devices: an individual computer or Bluetooth cellular
telephone are examples of specic devices.
• Specic class of device: “computer” is an example of a class of
devices.
• Specic type of device within a class: “laptop” is an example of a
specic type of device within the “computer” class of devices.
The devices to be discovered can be mixed-and-matched; you can discover
one or more specic devices, classes of devices and types of devices within
a class at the same time.
Remove a device from the list of devices to be discovered
In the Bluetooth Conguration Panel, from the Discovery tab, select the
device to be removed and click the Delete button.
NOTE: If “Report only selected Bluetooth devices” is not selected the Delete
button will not be available.
Temporarily override the discovery of specic devices
In the Bluetooth Conguration Panel, from the Discovery tab, select “Report
all Bluetooth devices.” The specically selected devices will be discovered
along with all other devices.
To re-enable specic device discovery re-select “Report only selected
Bluetooth devices.”
NOTE: When all devices are deleted an error message will appear if “Report all
bluetooth devices” is not selected.
55
Page 56

Security
Authentication
Authentication is used to verify identity; it requires a passkey or link key from
the remote device. When a remote device attempts access, a visual and/or
audio warning noties the local operator.
If the notication is ignored, access is denied after a preset timeout.
When devices are “paired,” those devices automatically exchange a link key
and Authentication is carried out without operator intervention.
Authorization
Authorization is Yes-or-No security that requires operator intervention to
avoid having the connection time out and fail.
Authorization is limited to:
• Yes, you may connect (click the balloon to proceed).
• No, you may not connect (ignore the balloon prompt and the
connection will fail).
Bluetooth Device Identity
Every Bluetooth device has a unique Bluetooth Device Address (BDA)
assigned to it during the manufacturing process. This address cannot be
changed by the end-user.
A device’s BDA is usually displayed in hexadecimal format;
00:D0:B7:03:2E:9F is a valid BDA.
Each Bluetooth device also has an operator-congurable, user-friendly
name to help distinguish it from other devices. The user-friendly name may
be up to 99 alphanumeric characters in length and may contain spaces. My
Personal Computer is a valid user-friendly name.
Encryption
Encrypting data translates it into an unreadable format using a secret key or
password. Decrypting the data requires the same key or password that was
used to encrypt it.
Link Key
A unique, internally generated, access code based on a passkey, the
Bluetooth Device Address and an internally generated random number. Link
keys are generated automatically when devices Pair.
After a link key is generated, manual entry of the passkey is not required.
56
Page 57

Security (cont’d)
Pairing Devices
Pairing allows you to avoid entering access information each time a
connection is attempted. Paired devices share a unique link key, which they
exchange each time they connect.
NOTE: The mate of a pair always appears in My Bluetooth Places, even if the
mate is not turned on or is out of connection range.
Paired devices remain paired even when
• One of the devices is not on
• A service connection is interrupted or the service stopped
• One or both devices are rebooted.
To Pair with another device
If Secure Connection is enabled, devices will pair automatically the rst time
they connect (a passkey must be successfully exchanged).
To pair with a device manually:
In the Folders pane of My Bluetooth Places, right-click a device, select Pair
Device from the shortcut menu, and then follow the on-screen instructions.
Remove Pairing
In the Folders pane of My Bluetooth Places, right-click a paired device and
select Unpair Device from the shortcut menu.
Passkey
An alphanumeric string up to 16 characters in length. Passkeys are also
called Personal Identication Numbers, or PIN codes.
A passkey may be required if the Secure Connection option is enabled for a
Bluetooth service or application.
Secure Connection
A passkey or link key is required each time a connection is attempted.
All data exchanged over the Bluetooth connection is encrypted.
Depending on other conguration options, authorization may also be
required.
Security Request Dialog Box
A Bluetooth passkey request and/or Bluetooth Authorization request balloon
may appear over the Windows system tray when a connection is attempted if
Secure Connection is enabled.
Click the balloon to proceed.
57
Page 58

Troubleshooting
Cannot connect to a paired device
Paired devices are always displayed in My Bluetooth Places, even if the
remote device is out of range or not powered up.
Verify that the remote member of the pair is within radio range, and powered
up, and then attempt the connection again.
Cannot discover services on an unpaired
remote device
The remote device may not be powered up or may be out of range.
• Verify that the remote device is powered up.
• Verify that the remote device is in Connectable mode (Bluetooth
Conguration Panel > Accessibility tab).
• Perform a Search for Devices to verify that the device is within range.
Dial-up Networking service does not start
The Dial-up Networking service will not start unless a properly congured
modem is attached to the server.
• Verify that the modem is usable as a local device on the computer to
which it is attached.
• In the Bluetooth Conguration Panel, Local Services tab,
double-click the Dial-up Networking service.
• Click the down arrow in the Modem eld and select the modem
that will be used to dial out.
• Click the OK button.
• Click the OK button to close the Bluetooth Conguration Panel.
58
Page 59

Troubleshooting (cont’d)
Determine the Bluetooth Device Address (BDA) of
my hardware device
In the Bluetooth Conguration Panel, on the Hardware tab, in the Devices
section, select the device you want to determine the address of. In the
Device Properties section of the dialog box, the fourth entry, Device Address,
is the BDA of the selected Bluetooth device.
Determine the version of the Host Controller
Interface (HCI)
In the Bluetooth Conguration Panel, on the Hardware tab, in the Device
Properties section, the fth entry provides Bluetooth Specication
compliance information for the Host Controller Interface.
The sixth entry contains the Specication Revision information for the Host
Controller Interface, if appropriate.
Determine the version of the Link Manager
Protocol (LMP)
In the Bluetooth Conguration Panel, on the Hardware tab, in the Device
Properties section, the seventh entry provides Link Manager Protocol
version number information. The eighth entry contains the Link Manager
Protocol sub-version number information, if appropriate.
Find information about the Bluetooth hardware
attached to my computer
In the Bluetooth Conguration Panel, select the Hardware tab.
Internet Connection Sharing Does Not Work
This occurs because Internet Connection Sharing was enabled when
Bluetooth was installed (this is a Microsoft Windows behavior and is
considered proper operation).
To resolve the “problem”:
1. Disable Sharing for the Ethernet adapter:
a) Windows Control Panel > Network and Dial-up Connections.
b) Right-click “Local Area Connection,” select Properties, and then
select the Sharing tab.
c) Clear (uncheck) the box for “Enable Internet Connection Sharing
for this connection” and click OK.
59
Page 60

Troubleshooting (cont’d)
Internet Connection Sharing Does Not Work
2. Re-enable Sharing for the Ethernet adapter; repeat Step 1.c.), and
select (check) the sharing box.
If offered an option to select an adapter, select “Bluetooth network adapter.”
(This option will not appear unless more than one adapter is available.)
If asked to reboot the computer, do so.
Test a Network Access connection
If the client is hardwired to the LAN, unplug the hardwired connection to
ensure that the test checks the wireless connection rather than the hardwired
connection. If the server has access to the Internet, open a browser on the
client and connect to the World Wide Web.
You may also Ping the server from the DOS prompt.
Unknown Port message when using a Bluetooth
Serial Port
The “Unknown Port” error message usually means an attempt was made to
connect a port that was in use.
Additional Bluetooth Serial Ports can be added if they are required.
Bluetooth Headset Doesn’t Always Function
Under WIN 98
Windows 98 cannot convert audio les with the extension m3u (e.g.,
myle.m3u) into the Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) audio format used by
Bluetooth headsets; this is a limitation of Windows 98.
Other versions of Windows (2000, ME and XP) can translate m3u audio les
into the PCM format.
Possible solutions are:
• Upgrade to a newer version of Windows.
• Use an m3u-to-mp3 conversion utility to convert the le(s) into a
format that is supported by Windows 98. (Conversion utilities are
available as freeware or shareware on the Internet.)
60
Page 61

© 2006 D-Link Corporation. All rights reserved.
Reproduction in any manner whatsoever without the written permission of
D-Link Corporation is strictly forbidden.
Trademarks used in this text: D-Link and the D-Link logo are trademarks of D-Link
Corporation/D-Link Systems Inc.; Other trademarks and trade names may be used
in this document to refer to either the entities claiming the marks and names or their
products. D-Link Corporation disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and
trade names other than its own.
Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
FCC Warning
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and,
if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful
interference to radio communication. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful
interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the
equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one
or more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
•
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
•
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which
•
the receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
•
FCC Caution: To assure continued compliance, any changes or modications not
expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate this equipment. (Example - use only shielded interface cables when
connecting to computer or peripheral devices). This device complies with Part 15 of
the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
(1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and
(2) This device must accept any interference received, including interference
that may cause undesired operation.
CE Mark Warning
This is a Class B product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio
interference in which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
61
Page 62

IC Radiation Exposure Statement
Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
1) This device may not cause interference and
2) This device must accept any interference, including interference that may
cause undesired operation of the device.
Important Note: This equipment complies with IC radiation exposure limits set forth
for an uncontrolled environment. End users must follow the specic operating instructions for satisfying RF exposure compliance. This equipment should be installed
and operated with a minimum distance of 20cm between the radiator and your body.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other
antenna or transmitter.
62
Page 63

Technical Support
You can nd software updates and user documentation on the D-Link website.
D-Link provides free technical support for customers within the United States and
within Canada for the duration of the warranty period on this product.
U.S. and Canadian customers can contact D-Link technical support through our
website, or by phone.
Tech Support for customers within the United States:
D-Link Technical Support over the Telephone:
(877) 453-5465
24 hours a day, seven days a week
D-Link Technical Support over the Internet:
http://support.dlink.com
email:support@dlink.com
Tech Support for customers within Canada:
D-Link Technical Support over the Telephone:
(800) 361-5265
Monday to Friday 7:30am to 12:00am EST
D-Link Technical Support over the Internet:
http://support.dlink.ca
email:support@dlink.ca
Tech Support for customers within
the United Kingdom & Ireland:
D-Link UK & Ireland Technical Support over the Telephone:
+44 (0)845 612 0003 (United Kingdom)
+353 (0)12 421 061 (Ireland)
Monday to Friday 8:00 am to 10:00 pm
D-Link Technical Support over the Internet:
http://www.dlink.co.uk
 Loading...
Loading...