Page 1
AP3154A
120mA HIGH EFFICIENCY WHITE LED DRIVER
Features
• Up to 88% Max power efficiency
• Wide input voltage range: 2.7V ~ 5.5V
• 1x, 1.5x, and 2x charge-pump modes
• Drive up to 4 white LEDs
• Default maximum current setting: 20mA each channel
• 120mA maximum output current through 4 channels
• Programmable switching frequency, default 1.2MHz
• Spread Spectrum Control with 10% frequency deviatio n
• 1-wire Serial Digital Interface (SDI) or PWM for dimming
control
• Soft-start during power-up and mode switching
• Soft-stop during s hutdown
• Short-circuit protection
• Over-voltage protection and under-voltage lockout
• Low shutdown curr ent < 6
• Industry-leading low profile package
• Lead Free package: DFN3030-12
• DFN3030-12: Available in “Green” Molding Compound
(No Br, Sb)
• Lead Free Finish / RoHS Compliant (Note 1)
µA
Applications
• Mobile Phone
• PDA (Personal Digital Assistant)
• White LED Backlighting
• Camera Flash LED Lighting
• LCD Modules
• Portable Devices
General Description
The AP3154A is a high efficiency charge-pump white LED driver
with 1x, 1.5x, 2x operating modes. The AP3154A operates on
power supplies from 2.7v to 5.5v. It drives up to four channels of
white LEDs while the intensity of each channel is configured by
varying the respective current levels. Each channel can supply up
to 30mA current. Up to four channels can be ganged together to
provide maximum load current of 120mA. By default, all
4 channels are set to the minimum current level after the chip is
enabled or back from shutdown mode.
The Serial Digital Interface (SDI) provides the capability to
configure the current for each LED channel. Some other key
features, such as Up Spread Spectrum Control, different
charge-pump switching frequencies (0.6MHz/1.2MHz/1.8MHz),
and PWM dimming control, can also be programmed through the
interface.
The AP3154A has a built-in soft-start circuit to minimize the inrush
current during power-up and mode switching. Various protections
such as short-circuit, over-voltage, under-voltage, and thermal
shutdown are integrated to ensure system reliability. The
quiescent current of AP3154A during shutdown is less than 6
µA.
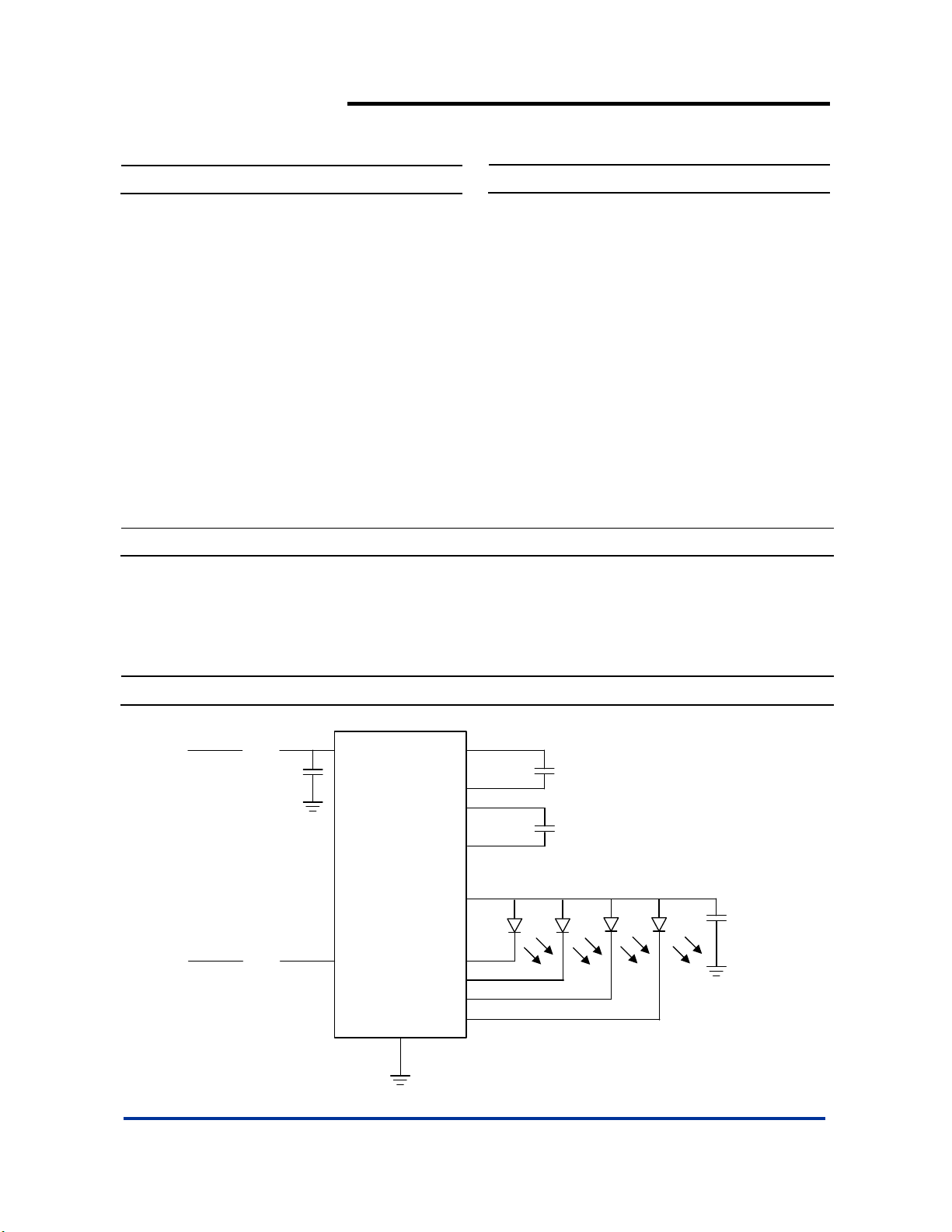
Typical Application Circuit
8
V
IN
V
IN
1uF
C
IN
AP3154A
2
SDI
SDI
GND
9
AP3154A Rev. 1 1 of 14 AUGUST 2009
www.diodes.com © Diodes Incorporated
V
C2
C2
C1
C1
OUT
D4
D3
D2
D1
6
P
N
P
N
1uF
C
7
2
3
1uF
C
4
1
5
D4
LED
D3
LED
D2
LED
D1
LED
1uF
C
OUT
1
12
11
10
Page 2
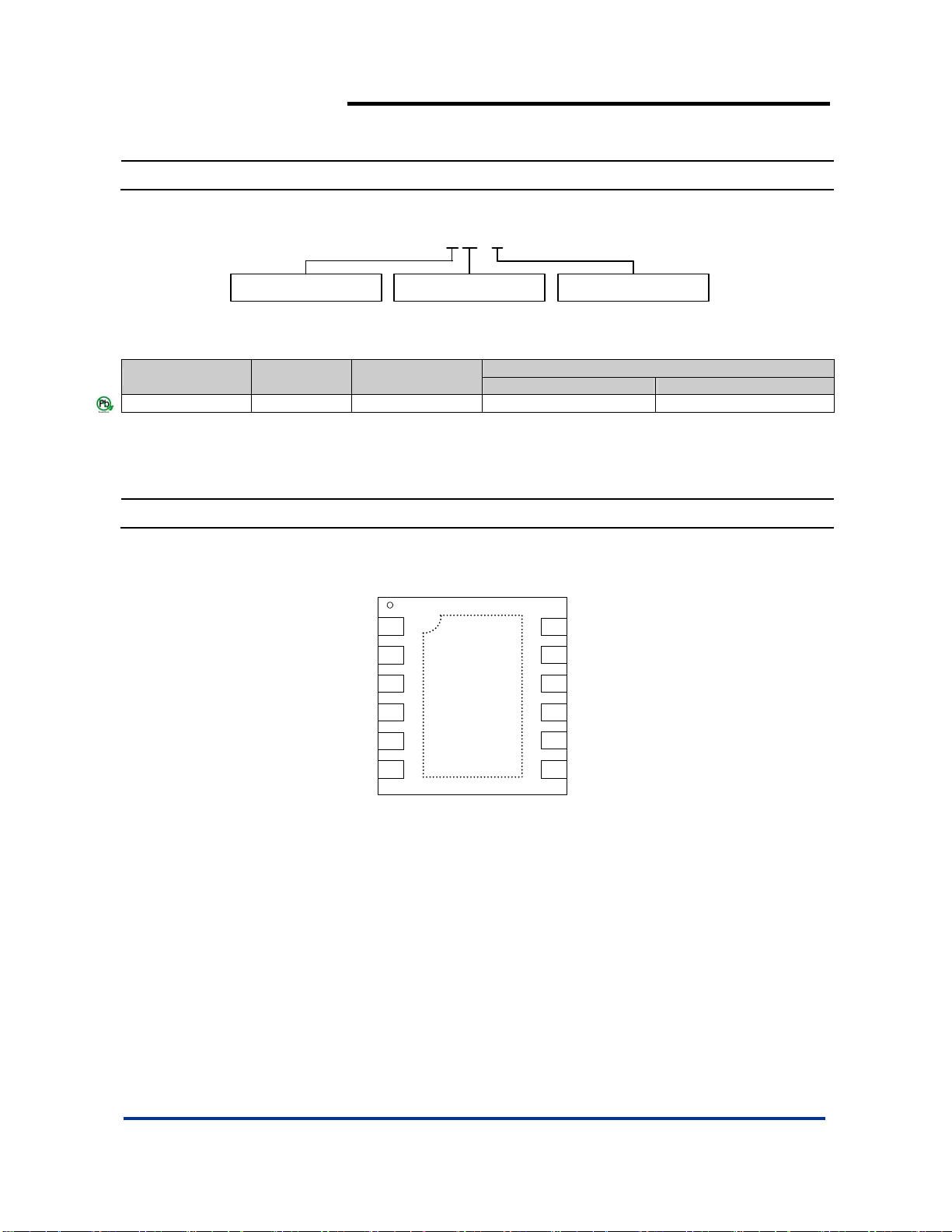
Ordering Information
AP3154A
120mA HIGH EFFICIENCY WHITE LED DRIVER
AP 3154 A F G - 7
Package
F : DFN3030-12
Green
G : Green
Packing
7 : Tape & Reel
Device
Package
Code
Packaging
(Note 2)
Quantity Part Number Suffix
7” Tape and Reel
AP3154AFG-7 F DFN3030-12 3000/Tape & Reel -7
Notes: 1. EU Directi ve 2 002/95/EC (RoHS). All applicable RoHS exemptions applied. Please visit our website at
http://www.diodes.com/datasheets/ap02001.pdf.
http://www.diodes.com/products/lead_free.html
2. Pad layout as shown on Diodes Inc. suggested pad layout document AP02001, which can be found on our website at
Pin Assignment
( Top View )
V
D4
C1
C1
OUT
C2
1
2
3
P
4
N
5
P
Exposed
Pad
12
D3
11
D2SDI
10
D1
9
GND
8
V
IN
76
C2
N
DFN3030-12
AP3154A Rev. 1 2 of 14 AUGUST 2009
www.diodes.com © Diodes Incorporated
Page 3
AP3154A
120mA HIGH EFFICIENCY WHITE LED DRIVER
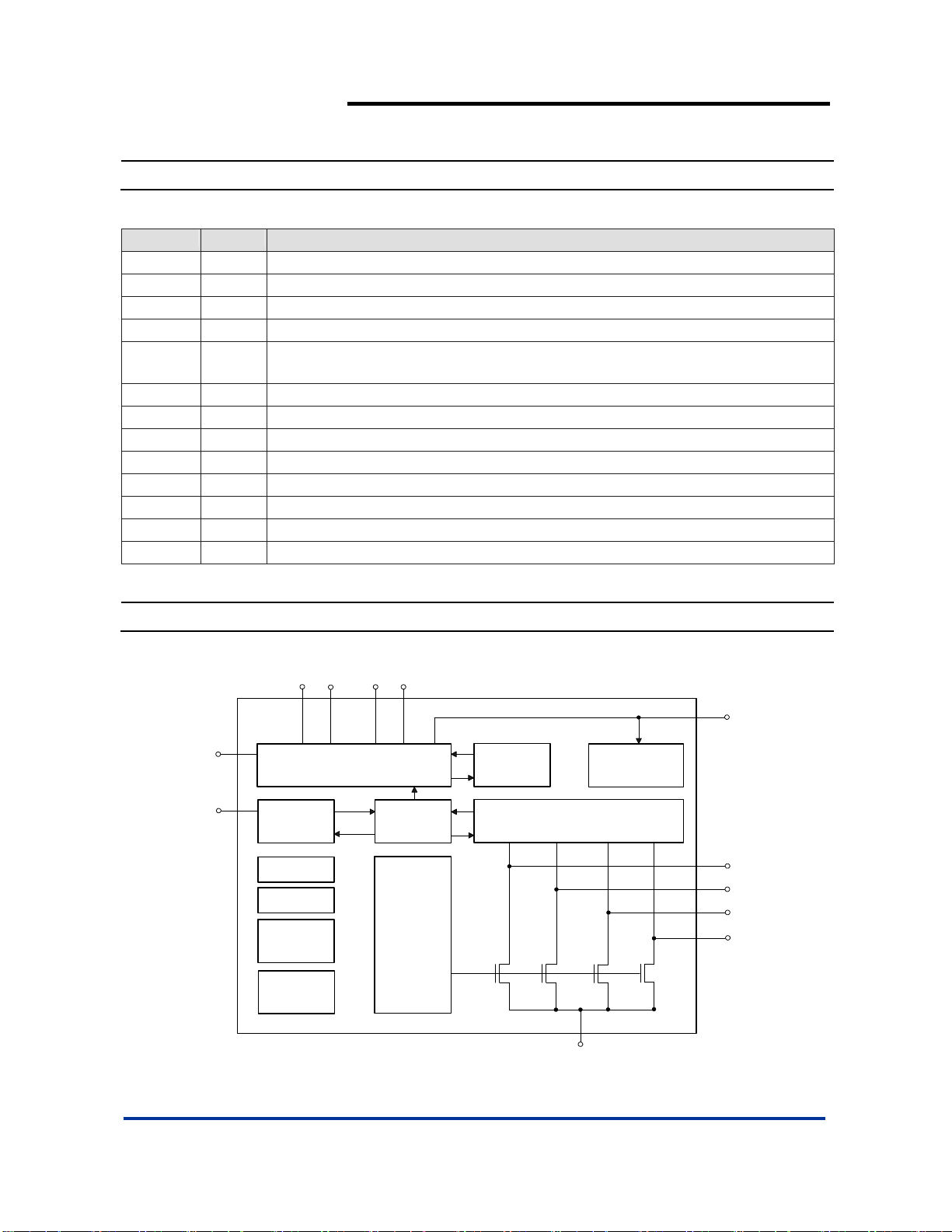
Pin Descriptions
Pin Name Pin # Description
D4 1 Current Sink Input #4. Connect to V
SDI 2 1-wire Serial Digital Interface Input / PWM input
C1P 3 Positive Terminal of Flying Capacitor. Connect a 1µF capacitor between C1P and C1N.
C1N 4 Negative Terminal of Flying Capacitor.
V
OUT
5
The charge pump output voltage to drive load circuit. Connect a 1µF capacitor
between this pin and ground.
C2P 6 Positive Terminal of Flying Capacitor. Connect a 1µF capa citor between C2P and C2N.
C2N 7 Negative Terminal of Flying Capacitor.
VIN 8 Input Power Source. Connect a 1µF capacitor between this pin and ground.
GND 9 Ground.
D1 10 Current Sink Input #1. Connect to V
D2 11 Current Sink Input #2. Connect to V
D3 12 Current Sink Input #3. Connect to V
GND
EP PAD
Exposed Pad (bottom). Connect to groun d u n d e r n ea th t he package.
when un-used.
OUT
when un-used.
OUT
when un-used.
OUT
when un-used.
OUT
Block Diagram
V
IN
SDI
C2
P
SERIAL
DIGITAL
INTERFACE
BANDGAP
OSCILLATOR
OVER
TEMPERATURE
PROTECTION
UNDER
VOLTAGE
LOCKOUT
C1
C2
N
CHARGE PUMP
SWITCHES
C1
P
DIGITAL
CONTROL
BLOCK
CURRENT
CONTROL
N
V
OUT
SHORT
CIRCUIT
PROTECTION
OUTPUT VOLTAGE REGULATION
LED SHORT CIRCUIT DETECTION
&
GND
OVER
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
D1
D2
D3
D4
AP3154A Rev. 1 3 of 14 AUGUST 2009
www.diodes.com © Diodes Incorporated
Page 4
AP3154A
120mA HIGH EFFICIENCY WHITE LED DRIVER
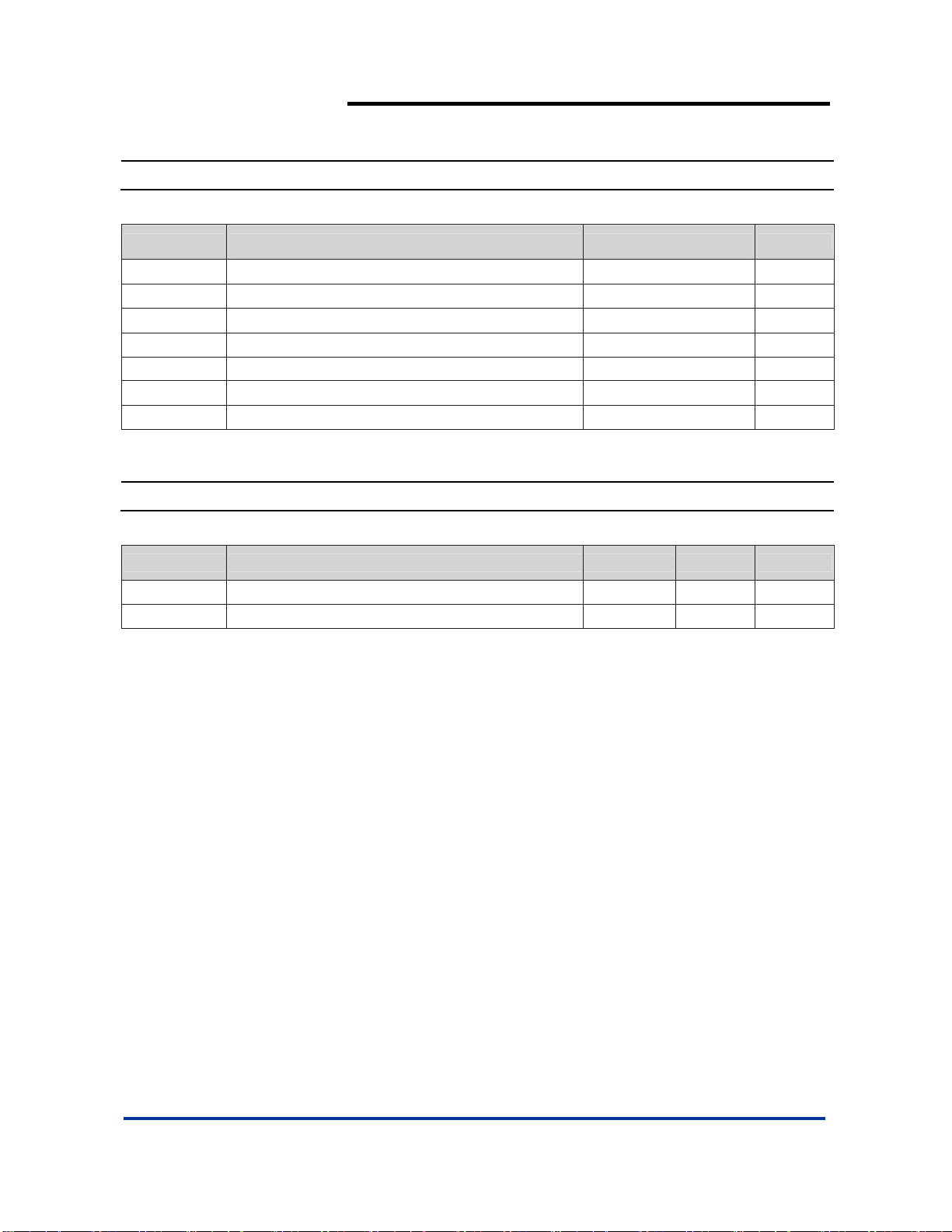
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Notes 3)
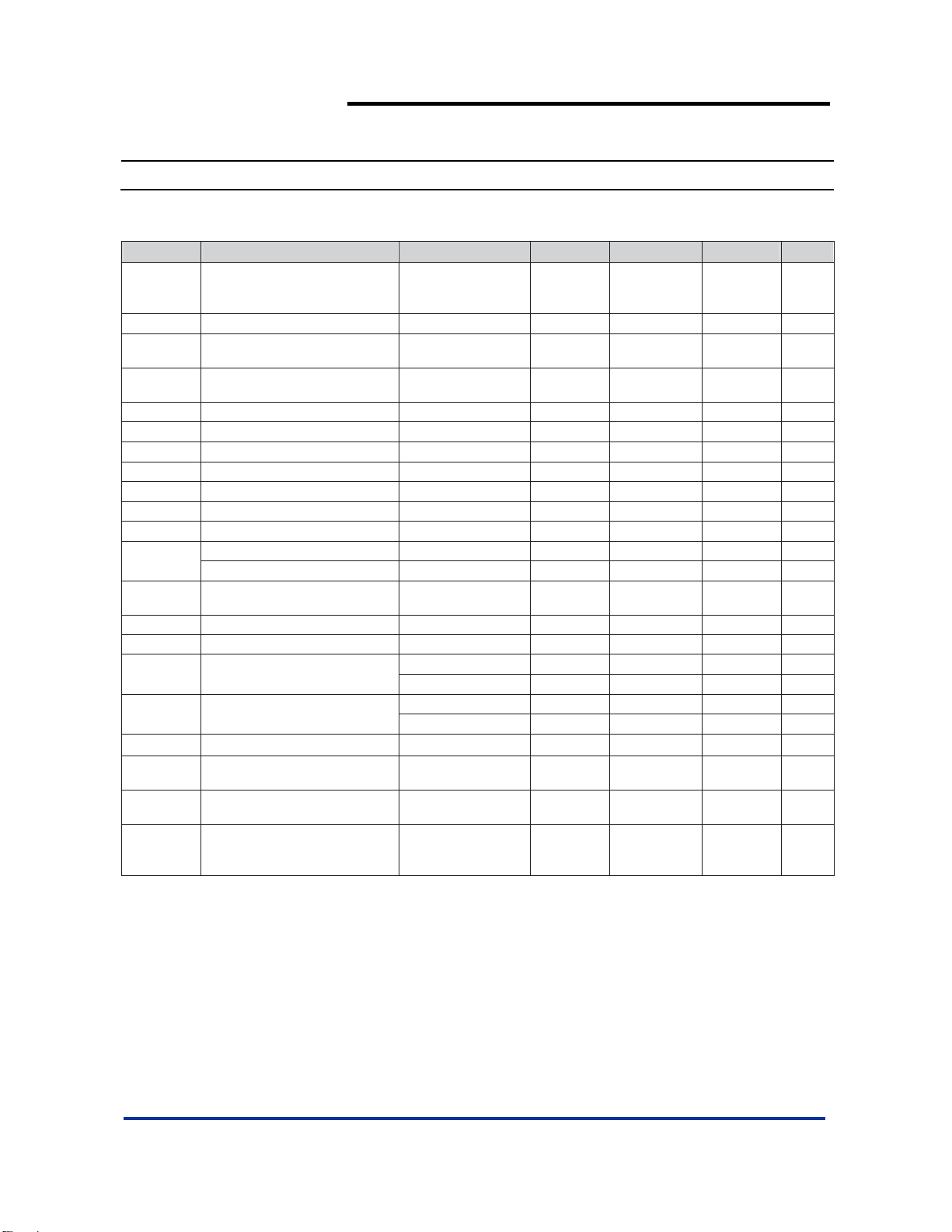
Symbol Description Value Units
ESD HBM Human Body Model ESD Protection
ESD MM Machine Model ESD Protection 200 V
V
IN
VSDI SDI to GND Voltage -0.3 to VIN + 0.3 V
I
OUT
PD Maximum Power Dissipation 0.85 W
TJ Operating Junction Temperature Range -40 to 150 °C
Notes: 3. Exceeding Absolute Maximum Ratings will cause permanent damage to the device.
Input Voltage -0.3 to 6 V
Maximum DC Output Current 150 mA
2
Recommended Operating Conditions
Symbol Parameter Min Max Units
VIN
TA
Input Voltage 2.7 5.5 V
Operating Ambient Temperature
-40 85 °C
KV
AP3154A Rev. 1 4 of 14 AUGUST 2009
www.diodes.com © Diodes Incorporated
Page 5
AP3154A
120mA HIGH EFFICIENCY WHITE LED DRIVER
Electrical Characteristics
= C
C
IN
Symbol Description Conditions Min Typ. Max Units
I
V
V
Notes: 4. Determined by the average current levels of all active channels.
= C1 = C2 = 1.0µF; TA = 25°C, VIN = 3.5V. Unless otherwise stated.
OUT
1X Mode
IQ Quiescent Current
Fosc=1.2MHz,
1.2 mA
SDI=HIGH, no load
I
Shutd own Current SDI = 0 0.3 6 µA
SHDN
I
Current Accuracy
IDX
D-Match
SINK
(Note 4)
Current Matching
(Note 5)
= 20mA -10 10 %
I
SINK
V
: D1=D2=D3=D4
F
I
= 2, 20mA
D
5 %
TSS Soft-start Time 1 ms
F
Switching Clock Frequency 0.6/1.2/1.8 MHz
CLK
F
Spread Spectrum Enabled +10 %
SSP
SDI Threshold Low VIN = 2.7V to 5.5V 0.4 V
SDI(L)
SDI Threshold High VIN = 2.7V to 5.5V 1.6 V
SDI(H)
T
SDI Low Time 0.05 50 µs
SLO
T
SDI High Time 0.05 50 µs
SHI
f
T
T
T
T
T
I
PWM
PWM
PLO
OFF
SEP
I
SDI
SCP
θ
θ
PWM Frequency (Range 1) 0.2 1.5 KHz
PWM Frequency (Range 2) 20 30 KHz
PWM Signal Period
PWM Signal Lo w (LED off) 1 T
PWM Signal High (LED on) 1 T
PHI
Chip Disable (held low)
Interval betw ee n S D I
sequences (held high)
PWM 65 100 ms
No PWM 512 800 µs
PWM 65 100 ms
No PWM 512 800 µs
f
PWM
1/
-Max
1/ f
-Min µs
PWM
– 1 µs
PWM
– 1 µs
PWM
SDI Input Leakage -1 1 µA
Short to GND hold
V
OUT
Current
Thermal Resistance1 –
JA
Junction to Ambient
Maximum Thermal
Resistance1 –
JC
Junction to Case
5. Defined as the deviation of any sink current from the average of all active current channels.
6. Device mounted on FR-4 substrate PC board, 2oz copper, with minimum recommended pad layout.
500 mA
DFN3030-12
(Note 6)
DFN3030-12
(Note 6)
160 °C/W
21 °C/W
AP3154A Rev. 1 5 of 14 AUGUST 2009
www.diodes.com © Diodes Incorporated
Page 6

120mA HIGH EFFICIENCY WHITE LED DRIVER
Typical Performance Characteristics
Efficienc y vs. Suppl y Vo l tage
AP3154A
Turn-On to 1X Mode
= 4.2V; 20mA Load)
(V
IN
Turn-On from 1.5X Mode
= 3.5V; 20mA Load)
(V
IN
Turn-Off from 1.5X Mode
= 3.5V; 20mA Load)
(V
IN
Turn-On to 2X Mode
= 2.7V; 20mA Load)
(V
IN
Current Matching vs. Temperature
AP3154A Rev. 1 6 of 14 AUGUST 2009
www.diodes.com © Diodes Incorporated
Page 7

120mA HIGH EFFICIENCY WHITE LED DRIVER
Typical Performance Characteristics (Continued)
Load Characteristics
= 3.5V; 1.5X Mo de; 14mA Load)
(V
IN
= 2.7V; 2X Mode; 14mA Load)
(V
IN
AP3154A
Load Characteristics
Load Characteristics
= 3.5V; 1.5X Mo de; 20mA Load)
(V
IN
Load Characteristics
= 2.7V; 2X Mode; 20mA Load)
(V
IN
Load Characteristics
= 3.5V; 1.5X Mo de; 30mA Load)
(V
IN
Load Characteristics
= 3.1V; 2X Mode; 30mA Load)
(V
IN
AP3154A Rev. 1 7 of 14 AUGUST 2009
www.diodes.com © Diodes Incorporated
Page 8

120mA HIGH EFFICIENCY WHITE LED DRIVER
Typical Performance Characteristics (Continued)
Enable Threshold High vs. Input Voltage
Enable Threshold Low vs. Input Voltage
AP3154A
PWM Dimming Operation
= 3.5V; 20mA Lo ad; Duty=1:1; f=1KHz)
(V
IN
PWM Dimming Operation
= 3.5V; 20mA L oad; Duty=1:11; f=1KHz)
(V
IN
PWM Dimming Operation
= 3.5V; 20mA L oad; Duty=11:1; f=1KHz)
(V
IN
AP3154A Rev. 1 8 of 14 AUGUST 2009
www.diodes.com © Diodes Incorporated
Page 9

)
)
)
,
)
)
)
)
120mA HIGH EFFICIENCY WHITE LED DRIVER
Functional Description
General Functional Description
The AP3154A is designed for white LED applications. An
internal comparator circuit compares the voltage at each constan t
current sink input against a reference voltage. To ensure
maximum power efficiency, the most appropriate switching mode
(x1, x1.5, x2) is automatically selected.
In applications, only four external components are required: two
1µF ceramic flying capacitors (C
capacitor each for input and output (C
AP3154A drives up to four white LEDs with a maximum current of
30mA each. A total of 120mA is provided to the four channels.
Through SDI, the current into each channel can be configured in
accordance to specific protocol and pre-defined values.
Maximum output current can be set to one of the four possible
scales: 2mA, 14mA, 20mA, 30mA. Among these, the ‘2mA’
setting is called “low current mode”. This would be useful for
applications which require very low operating current, e.g.
transmissive LCD panels.
For each maximum output current scale, there are 16 current
level settings separated from one another by approximately
1dB. While level-16 corresponds to maximum current output,
level-1 corresponds to zero output current. As the current level
varies logarithmically, intensity of the LED changes in a linear
fashion.
By default, all 4 channels are set to current level 1 (minimum
current level) after the chip is enabled or back from shutdown
mode.
The current level at the individual channels is config ured via SDI
which supports data rate up to 10MHz. It allows the main
controller in the system to be offloaded to perform more
mission-critical functions.
Serial Digital Interface
SDI is a general purpose 1-wire digital interface designed to
transport digital controls for power management ICs such as
AP3154A. The current levels of the four channels can be
configured either together or individ ually. Up to 16 current
levels are allowed. A generic system controller can easily
support the SDI protocol via bit-banging over its general
purpose I/Os.
The SDI protocol is simple yet flexible enough to
accommodate different switching clock frequencies. Any
sequence of negative-edged pulses of 63 or less ( see tab le 1),
separated by T
a channel configuration event. In the future, the number of
pulses can be extended to support additional commands.
In addition to th e SDI protocol, dimmi ng control can also be
achieved by presenting a timing-specific PWM signaling a t the
SDI pin.
at the SDI pin is interpreted by AP3154A as
SEP
and C2), one 1µF ceramic
1
, C
).
IN
OUT
AP3154A
Number
of Falling
Edges
1 Current level step up (1 up to level 16)
2 Current level step down (16 down to level 1
3 Current level set to 16 (maximum current level
4 Current level set to 1 (minimum current level
5 All 4 Channels in dimming control
6CH2
7 CH1 and CH2 in dimming control
8 CH3 and CH4 in dimming control
9 CH1 in dimming control
10 CH2 in dimming control
11 CH3 in dimming control
12 CH4 in dimming control
13 Low-Current Mode (Maximum Current set to 2mA
14 Maximum Current set to 14mA (All channels
15 Maximum Current set to 20mA (All channels
16 Maximum Current set to 30mA (All channels
17 10% Up Spread Spectrum Control Enable/Disable
19 Switching Frequency set to 1.2Mhz
20 Switching Frequency set to 1.8Mhz
21~62 Reserved
63 PWM Dimming Control Enable/Disable
Dimming Control Current Level Setting
AP3154A supports four maximum output current scales including
30mA, 20mA, 14mA, and 2mA low-current scales. For each
maximum current scale, there are 16 current level settings
separated from one ano the r b y appr omi mat el y 1dB (s ee tab le 2).
By default, maximu m current scale is set to 20mA and dimming
control current level is set to maximum (level 16).
Through SDI, certain channels or all four channels can be
selected, and dimming control level for these ch a nnels can be set
to maximum (level 16), minimum (l evel1), up from minimum to
maximum or down from maximum to minimum (see table 1).
Dimming
Control
Current
Levels
16 20.0 30.0 14.0 2.0
15 17.8 26.7 12.5 1.78
14 15.9 23.8 11.1 1.59
13 14.3 21.4 10.0 1.43
12 12.7 19.0 8.9 1.27
11 11.1 16.7 7.8 1.11
10 10.2 15.2 7.1 1.02
9 8.9 13.3 6.2 0.89
8 7.9 11.9 5.6 0.79
7 7.0 10.5 4.9 0.70
6 6.3 9.5 4.4 0.63
5 5.7 8.6 4.0 0.57
4 5.1 7.6 3.5 0.51
3 4.4 6.7 3.1 0.44
2 4.1 6.2 2.9 0.41
1 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05
I
out
(20mA)
Table 2: Dimming Control Current Level
Command Description
CH3 and CH4 in dimming control
I
out
(30mA)
I
out
(14mA)
Low-Current
(2mA)
AP3154A Rev. 1 9 of 14 AUGUST 2009
www.diodes.com © Diodes Incorporated
Page 10

AP3154A
120mA HIGH EFFICIENCY WHITE LED DRIVER
Functional Description (Continued)
Disabled Current Sinks
Unused current channels must be disabled by connecting the
sinks to V
disabled channel.
Soft-Start and Soft-Stop
Soft-start and Soft-stop function are incorporated to prevent
excessive inrush current during power-up, mode switching,
power-down, transition out of stand-by mode.
Short-Circuit Prote ction
Short-circuit protection function is incorporated to prevent
excessive load current when either flying cap terminals or output
pin electrically tied to a very low voltage or ground.
Over-Voltage Protection
Over-voltage protection function is incorporated to limit the
output voltage under a safe value to avoid on-chip device
breakdown.
Under-Voltage Lockout
Under-voltage lockout feature disables the device when the
input voltage drops below UVLO threshold.
with only a small sense current flowing through the
OUT
Serial Digital Interface
SDI Command Timing
For an SDI command to be successfully receiv ed by th e AP3154A , all SDI timing sp ecifications sh ould b e satisfied. When no command is
being sent the SDI pin should be held high. If the SD I pin go es low and stays low for a time length o f be tween TSLO(min) and T SLO(max)
and then goes high and stays high for between TSHI(min) and TSHI(max), one falling edge is registered by the AP3154A. The total
number of falling edges registered before the SDI pin is held high for longer than the maximum separation time TSEP(max) identifies the
command that has been received by the AP3154A. The next series of falling edges before another separation time TSEP represents the
next command. In other words, the AP3154A counts the number of consecutive falling edges on the SDI pin and a different number
represents a different command.
Each command is executed after it is successfully received. If at any time the SDI pin is held low for longer than the maxi mum chip
disable time TOFF(max), the AP3154A is disabled and enters the shutdown mode. All internal registers are reset to default. Setting
the SDI pin high again will re-enable the AP3154A and bring it out of the shutdown mode.
The AP3154A enters the SDI mode by default when it is first powered up. The first SDI command 63 (63 falling edges) will put the
AP3154A into the PWM mode, where a high level on the SDI pin turns the LEDs on, a low level turns the LEDs off and the duty cycle
determines the average LED brightness. The next SDI command 63 will put the AP3154A back into the SDI mode. It should be pointed
out that the PWM mode is for dimming control only and configuration settings have to be done in the SDI mode.
Channel Configuration Example
The following timing diagram is a dimming control example. In this example, the first command (command 10) selects Channel 2 as the
configuration target and the second command (command 2) sets the Channel 2 current level to one step lower while the other channels
remain unchanged.
Thermal Shutdown
When the die temperature exceeds the thermal limit, the device
will be disabled and enter stand-by mode. The operation will be
resumed whenever the die cools off sufficiently.
Switching Frequency
By default, AP3154A is working at 1.2Mhz switching frequency.
It can also work at 0.6MHz or 1.8MHz switching frequency set
through SDI. User can choose the appropriate switching
frequency with consideration of noise immunity, input/output
voltage ripple requirement, and capacitor selection etc.
Up Spread Spectrum Control
When this feature is enabled through SDI, the switching
frequency periodically varies between 100% and 110% of
nominal frequency. It flattens the peak energy on nominal
frequency over a range of frequency band so that EMI effect is
significantly reduced.
PWM Dimming Control
The AP3154A provides flexible dimming control with either
16-level SDI protocol control or PWM dimming control through
SDI pin. When PWM dimming control is enabled, the sink
current is adjusted by the duty cycle of the signal applied on SDI
pin.
AP3154A Rev. 1 10 of 14 AUGUST 2009
www.diodes.com © Diodes Incorporated
Page 11

Serial Digital Interface (Continued)
AP3154A
120mA HIGH EFFICIENCY WHITE LED DRIVER
Marking Information
(1) DFN3030-12
Part Number Package Identification Code
AP3154A DFN3030-12 F9
( Top View )
XX
X
Y
W
: F9 : AP3154A
XX
Y
: Year : 0~9
: Week : A~Z : 1~26 week;
W
a~z : 27~52 week;
z : represents 52 and 53
: A~Z : Green
X
AP3154A Rev. 1 11 of 14 AUGUST 2009
www.diodes.com © Diodes Incorporated
Page 12

120mA HIGH EFFICIENCY WHITE LED DRIVER
Package Information (All Dimensions in mm)
(1) Package type: DFN3030-12
0.57/0.63
0.10 C
AP3154A
2x-
0.08 C
0.25 B
B
2.9 / 3.1
2x
0/0.05
R
0
1.5 / 1.7
0.45typ
A
0.25
.
3
2.9 / 3.1
2.3 / 2.5
0.18/0.28
Bottom View
Seating plane
C
0.15max.
A
0.25/0.55
0.10
M C A B
AP3154A Rev. 1 12 of 14 AUGUST 2009
www.diodes.com © Diodes Incorporated
Page 13

Taping Orientation
AP3154A
120mA HIGH EFFICIENCY WHITE LED DRIVER
Notes: 7. The taping orientation of the other package type can be found on our website at http://www.diodes.com/datasheets/ap02007.pdf
AP3154A Rev. 1 13 of 14 AUGUST 2009
www.diodes.com © Diodes Incorporated
Page 14

AP3154A
120mA HIGH EFFICIENCY WHITE LED DRIVER
IMPORTANT NOTICE
DIODES INCORPORATED MAKES NO WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, WITH REGARDS TO THIS
DOCUMENT, INCLUDING, BU T NOT LIMI TED TO, T HE IMPLIE D WARRANT IES OF ME RCHANTABILIT Y AND FI TNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS OF ANY JURISDICTION).
Diodes Incorporated and its subsidiaries reserve the right to make modifications, enhancements, improvements, corrections or other
changes without further notice to t his document and any product described herein. Diodes Incorporated does not assume any
liability arisi ng out of the application or use of this document or any product descr ibed herein; neither does Diode s Incorporated
convey any license under its patent or trademark rig hts, nor the rights of othe rs. Any Customer or user of this docume nt or products
described herein in such applications shall assume all risks of such use and will agree to hold Diodes Incorporated and all the
companies whose products are represented on Diodes Incorporated website, harmless against all damages.
Diodes Incorporat ed does not warrant or accept a ny liabil ity whatsoeve r in respect of any p roducts purc hase d through unau thori zed
sales channel.
Should Customers purch ase or use Diodes Incorpo rated products for an y unintended or unau thorized applic ation, Customers sh all
indemnify and hold Dio des Inc orporated and its re presen tatives harmle ss against all cla ims, d amages, expens es, a nd attor ney fees
arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim of personal injury or death associated with such unintended or unauthorized
application.
Products described here in may be covered by one or more Unit ed States, i nternationa l or foreign patents p ending. Product n ames
and markings noted herein may also be covered by one or more United States, i nte rn ational or foreign trademarks.
LIFE SUPPORT
Diodes Incorporated products are specifically not authorized for use as critical components in life support devices or systems
without the express written approval of the Chief Execut i ve Off icer of Diodes Incorporate d. As us e d herei n:
A. Life support devices or systems are devices or systems which:
1. are intended to implant into t he body, or
2. support or sustain life and whose failure to perform when properly used in accordance wi th instructions for use provided
in the labeling can be reasonably expected to result in significant injury to the user.
B. A critical component is any c omponent in a life sup port devic e or system whose f ailure to perform c an be reasona bly expect ed
to cause the failure of the life support device or to affect its safety or effectiveness.
Customers repres ent that th ey have all necessar y expertis e in th e safety a nd regul ator y ramific ations of t heir lif e support devic es or
systems, and acknowledge and agree that they are solely responsible for all legal, regulatory and safety-related requirements
concerning their products and any use of Diodes Incorporated products in such safety-critical, life support devices or systems,
notwithstandin g a ny de vices- or systems-related information or support that may be provided by Diodes Inc orporated. Further,
Customers must full y indemnify Diode s Incorporat ed and its represent atives ag ainst any damages ari sing out of th e use of Diodes
Incorporated products in suc h safety-critical, life support devices or sys tems.
Copyright © 2009, Diodes Incorporated
www.diodes.com
AP3154A Rev. 1 14 of 14 AUGUST 2009
www.diodes.com © Diodes Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...