Page 1
AH5798
SINGLE PHASE HALL EFFECT LATCH SMART
FAN MOTOR CONTROLLER
Description
The AH5798 is a single chip solution for driving single-coil
brushless direct current (BLDC) fans and motors. The
integrated full-bridge driver output stage uses soft switching
to minimize audible switching noise and electromagnetic
interference (EMI) providing a low noise solution.
To help protect the motor coil, the AH5798 provides Rotor
Lock Protection which shuts down output drive if rotor lock is
detected. The device automatically re-starts when the rotor
lock is removed. Over temperature shutdown provides
thermal protection for the device.
A Tachometer output is provided by open-drain Frequency
Generator (FG) Pin which allows external interface to monitor
motor rotation or speed. The FG output is the magnetic
change frequency.
The AH5798 is available in space saving SOT89-5L and
thinner TSOT25 packages.
Features
• Supports single-coil full-wave DC fan drivers
• Built-in Hall sensor and input amplifier
• Operating Voltage: 1.8V to 5.5V
• Soft switching for low noise DC fan motor applications
• Rotor Lock Protection (Lock detection, output shutdown
and automatic re-start)
• Thermal protection
• Tachometer (FG) output
• No external timing capacitor - Reduces the numbers of
external components required
• Low profile packages: SOT89-5L and TSOT25
• “Green” Molding Compound
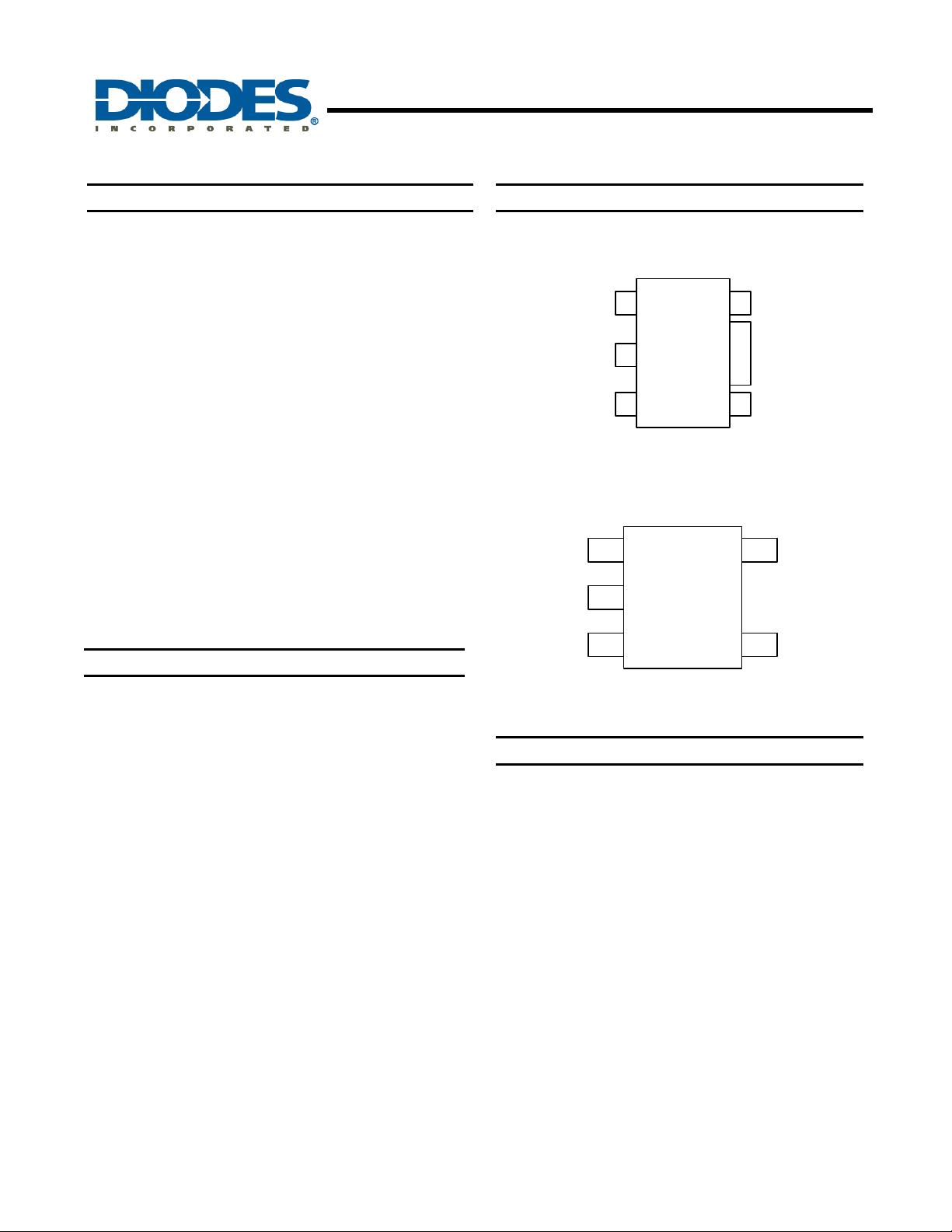
Pin Assignments
( Top View )
Vdd
1
2
Vss
3 7
O1
SOT89-5L
( Top View)
FG
Vss
1
2
O2
TSOT25
Applications
• 3.3V / 5V Min. BLDC Cooling Fans
• Netbook/ Notebook BLDC fans
• Low Voltage/ Low Power BLDC Motors
FG
5
NC
4
O2
5
Vdd
43
O1
AH5798
Document number: DS32001 Rev. 2 - 2
1 of 11
www.diodes.com
June 2010
© Diodes Incorporated
Page 2
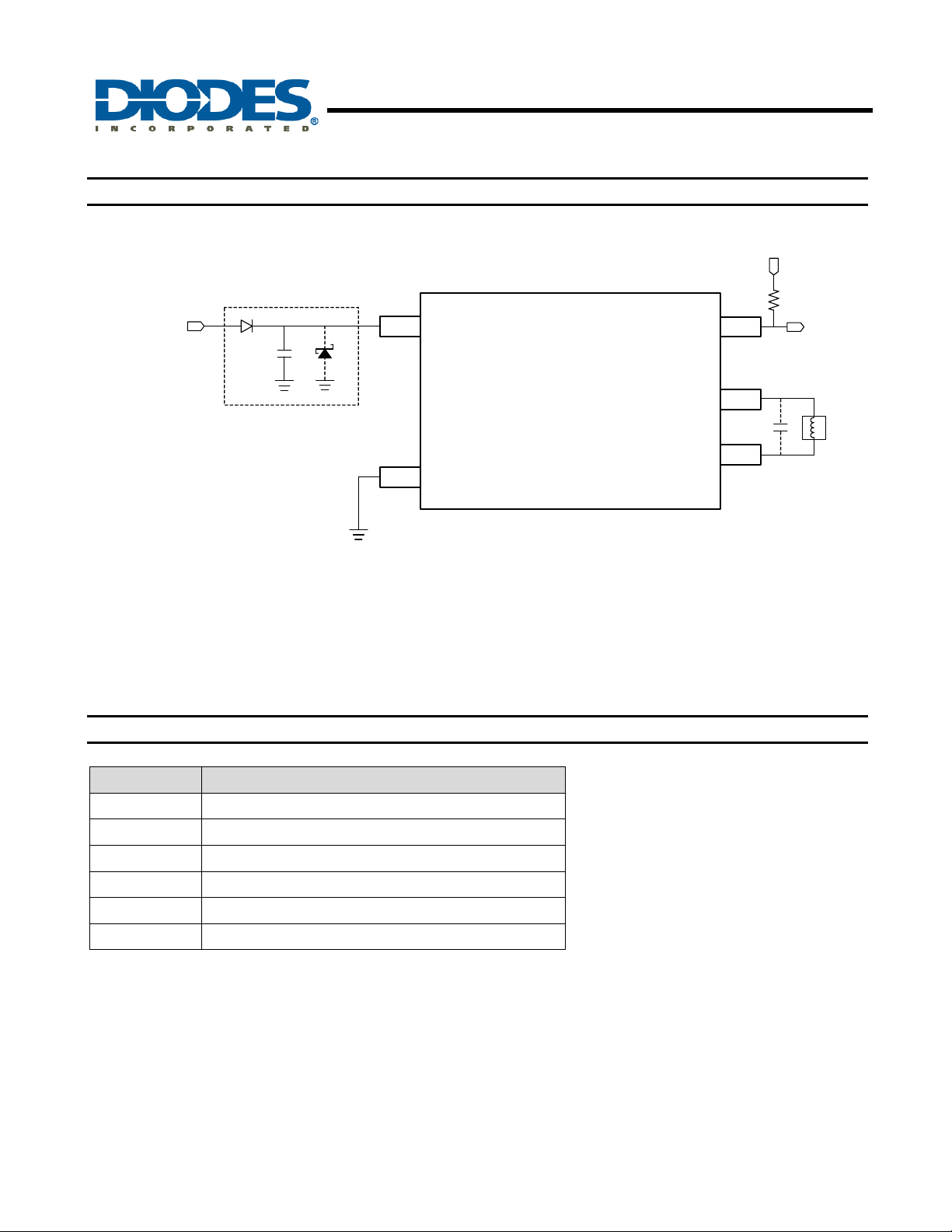
Typical Application Circuit
SYSTEM
POWER
D1
C1
Dz
AH5798
SINGLE PHASE HALL EFFECT LATCH SMART
FAN MOTOR CONTROLLER
SYSTEM
POWER
10Kohm
V
dd
FG
FG
AH5798
V
SS
O1
O2
* Reverse connection of power supply may damage the device. To prevent reverse power damage, a protection (reverse blocking)
Diode D1 is needed between power supply and Vdd terminal. If a reverse power protection diode D1 is used, there
is no current return path to power supply, so it is necessary to follow measures such as below.
- Connect Dz (Zener diode) between Vdd and Vss terminal, to prevent voltage exceeding the absolute maximum rating of the device.
- Connect a capacitor C1 between Vdd and Vss terminal, to complete the current return path to power supply.
The AH5798 has an open-drain tachometer FG output that follows the magnetic change frequency. Typically, a pull-up resistor of 10kΩ is
recommended from FG pin to the supply voltage.
Pin Descriptions
Pin Name Description
Vdd Power Supply Pin
Vss Ground Pin
O1 Output Driving & Sinking Pin 1
O2 Output Driving & Sinking Pin 2
NC No Connection
FG Frequency Generator (Note 1)
Notes: 1. The FG is the same as the magnetic change frequency.
AH5798
Document number: DS32001 Rev. 2 - 2
2 of 11
www.diodes.com
June 2010
© Diodes Incorporated
Page 3
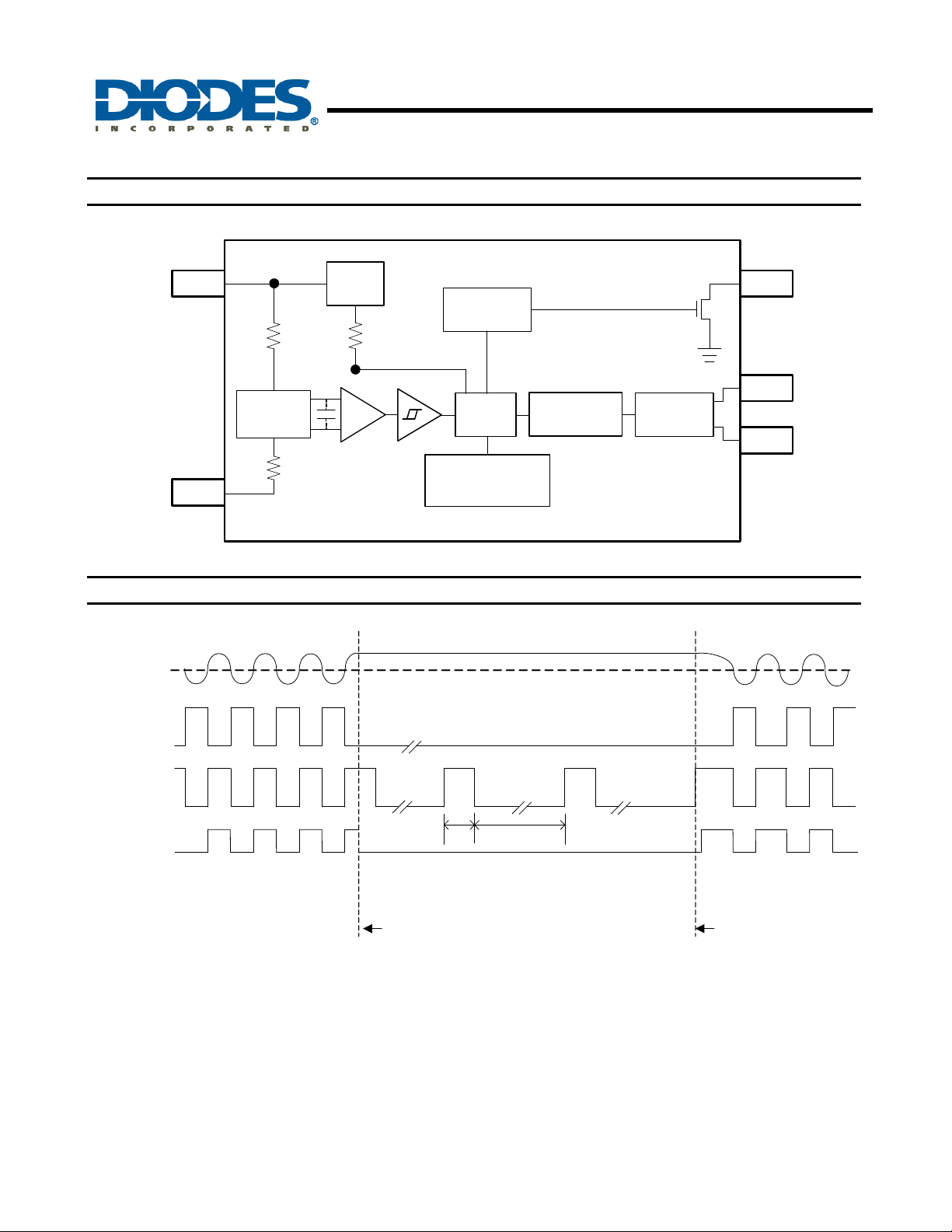
Functional Block Diagram
AH5798
SINGLE PHASE HALL EFFECT LATCH SMART
FAN MOTOR CONTROLLER
Operating
Magentic
S
N
Vdd
Vss
Hall
Sensor
Power
AMP
Frequency
Generator
Control
Logic
Lock detect,
Shoutdown and
Automatic re-start
Soft Switching
Control
FG
O1
Full Bridge
Driver
O2
O2
O1
FG
Ton
Normal spinning
motor locked detected
Toff
Mechanical lock
“Re-start spinning”
motor locked cleared
Notes: 2. In “Normal spinning”, the FG changes its state at each rising edge of O1.
3. When the motor locks with South pole at the Hall element, O2 is kept on “L” and O1 is a clock with Ton/Toff ratio. When motor
locks with North pole at the Hall element, O1 is kept on “L”, O2 is a clock with Ton/Toff ratio.
4. When “Re-start spinning” occurs, the motor speed ramps up to the “Normal Spinning” speed from zero. Speed ramp-up profile
depends on motor characteristics.
AH5798
Document number: DS32001 Rev. 2 - 2
3 of 11
www.diodes.com
June 2010
© Diodes Incorporated
Page 4
AH5798
θJAθ
SINGLE PHASE HALL EFFECT LATCH SMART
FAN MOTOR CONTROLLER
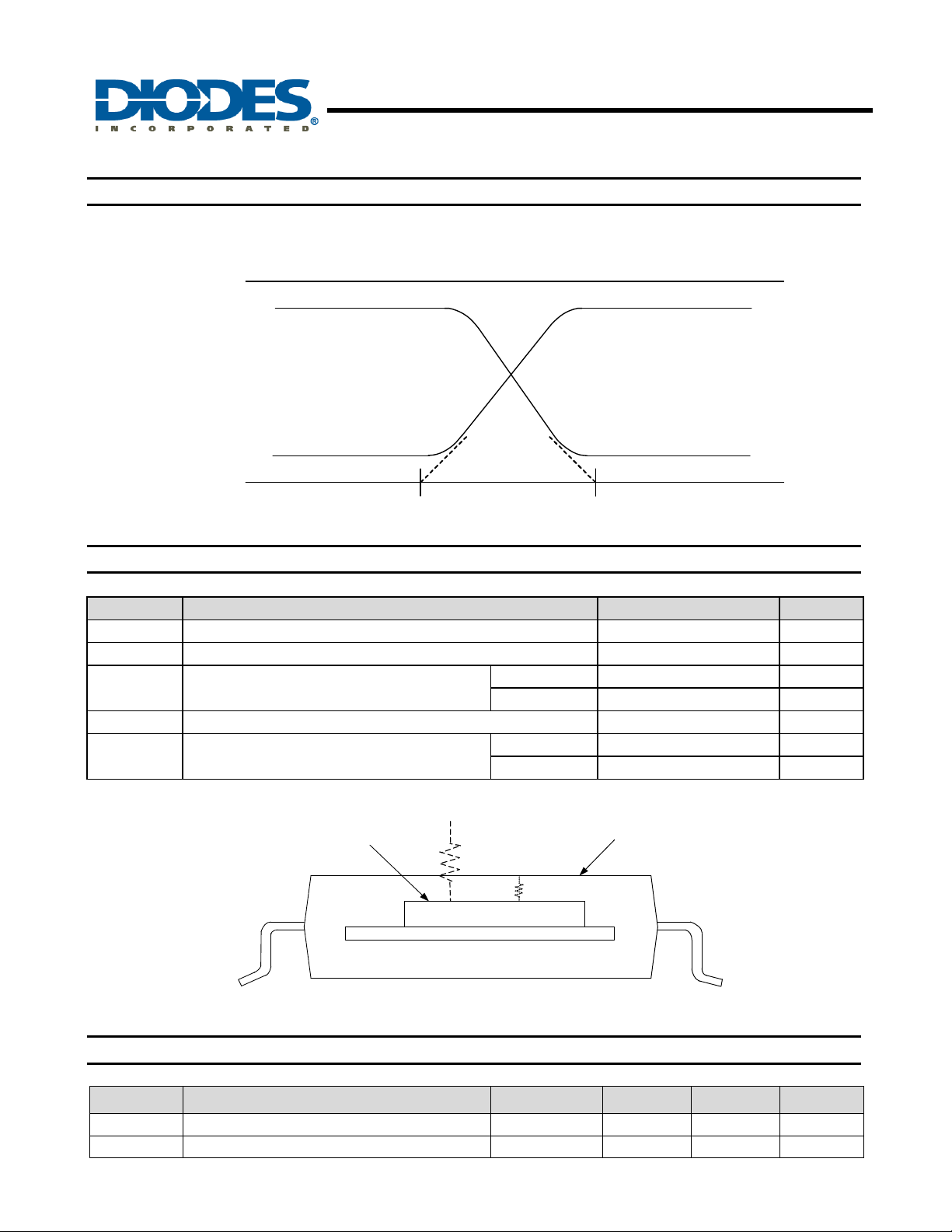
Soft Switching
AH5798 employs soft switching of output drive at commutation to reduce audible noise and EMI for low noise
applications.
Vdd
Vout 1
Vout 2
GND
100µs typ.
Absolute Maximum Ratings (T
= 25°C, unless otherwise noted)
A
Symbol Parameter Rating Unit
Vdd Supply voltage 6 V
I
Maximum Output Current (Peak) 800 mA
O(PEAK)
PD Power Dissipation
TST Storage Temperature Range -65 ~ 150
θ
JA
Notes: 5. θJA should be confirmed with heat sink thermal resistance. If there is no heat sink contact, θJA will almost be the same as θJC.
Thermal Resistance Junction-to-Ambient
(Note 5)
TJ
TA
SOT89-5L 800 mW
TSOT25 520 mW
o
C
o
SOT89-5L 156
C/W
TSOT25 240 oC/W
Tc
JC
Recommended Operating Conditions (T
Symbol
Parameter Conditions Min Max Unit
= 25°C)
A
Vdd Supply Voltage Operating 1.8 5.5 °C
TA Operating Ambient Temperature Range Operating -40 105 V
AH5798
Document number: DS32001 Rev. 2 - 2
4 of 11
www.diodes.com
June 2010
© Diodes Incorporated
Page 5

AH5798
SINGLE PHASE HALL EFFECT LATCH SMART
FAN MOTOR CONTROLLER
Electrical Characteristics (T
Symbol Parameter Test Conditions Min Typ. Max Unit
Idd Supply Current No Load - 5 - mA
VOH Output Voltage High I
VOL Output Voltage Low I
TSW Output Switching Slope Duration 50Ω load on out1/out2 - 100 - μs
I
FG Output Leakage Current - - 5 μA
LEAK
V
FG Output Voltage Low I
FGOL
TON On Time 350 500 650 ms
RDR Duty Ratio T
= 25°C, Vdd = 5V)
A
= 300mA 4.4 4.65 - V
OUT
= 300mA - 0.35 0.6 V
OUT
= 5mA - - 0.4 V
FG
/ TON - 10 -
OFF
Magnetic Characteristics (T
= 25°C, Vdd = 1.8V~5V, Note 6)
A
(1mT = 10 G)
Symbol
Parameter
Min Typ. Max Unit
Bop Operate Point 10 25 50 G
Brp Release Point -50 -25 -10 G
Bhy Hysteresis - 50 - G
Notes: 6. The magnetic characteristics may vary with supply voltage, operating temperature and after soldering.
AH5798
Document number: DS32001 Rev. 2 - 2
5 of 11
www.diodes.com
June 2010
© Diodes Incorporated
Page 6

Operating Characteristics
O1
AH5798
SINGLE PHASE HALL EFFECT LATCH SMART
FAN MOTOR CONTROLLER
O2
V
OH
OFF
OP
OFF
RP
Output Voltage in Volts
V
OL
V
OL
BopBrp 0BopBrp 0
Magnetic Flux Density in GaussMagnetic Flux Density in Gauss
OP
ON
Output Voltage in Volts
RP
ON
V
OH
S
Marking side
N
Marking side
(SOT89-5L)
AH5798
Document number: DS32001 Rev. 2 - 2
N
6 of 11
www.diodes.com
S
(TSOT25)
June 2010
© Diodes Incorporated
Page 7

Performance Characteristics
(1) SOT89-5L
TA (°C)
PD (mW) 800 640 576 512 480 448 416 384 352 320
TA (°C)
PD (mW) 288 256 224 192 160 128 96 64 32 0
P
(m W)
D
25 50 60 70 75 80 85 90 95 100
105 110 115 120 125 130 135 140 145 150
900
800
700
600
500
400
300
200
100
0
0 25 50 75 100 125 150
-4 0
AH5798
SINGLE PHASE HALL EFFECT LATCH SMART
FAN MOTOR CONTROLLER
Power Dissipation Curve
105
TA (°C)
(2) TSOT25
TA (°C)
25 50 60 70 75 80 85 90 95 100
PD (mW) 520 417 375 333 313 292 271 250 230 208
TA (°C)
105 110 115 120 125 130 135 140 145 150
PD (mW) 188 167 146 125 104 83 63 42 21 0
P
(mW)
D
600
520
500
400
300
200
100
0
0 255075100125150
-4 0
Power Dissipation Curve
105
TA (°C)
AH5798
Document number: DS32001 Rev. 2 - 2
7 of 11
www.diodes.com
June 2010
© Diodes Incorporated
Page 8

Ordering Information
AH5798
SINGLE PHASE HALL EFFECT LATCH SMART
FAN MOTOR CONTROLLER
AH 5798 - XX G - X
Package
Y : SOT89-5L
Green
G : Green 7/13 : Tape & Reel
WT : TSOT25
Device
AH5798-YG-13 Y SOT89-5L 2500/Tape & Reel -13
AH5798-WTG-7 WT TSOT25 3000/Tape & Reel -7
Notes: 7. Pad layout as shown on Diodes Inc. suggested pad layout document AP02001, which can be found on our website at
http://www.diodes.com/datasheets/ap02001.pdf
8. EU Directive 2002/95/EC (RoHS). All applicable RoHS exemptions applied. Please visit our website at
http://www.diodes.com/products/lead_free.html
Package
Code
Packaging
(Note 7 & 8)
Quantity Part Number Suffix
7”/13” Tape and Reel
Packing
Marking Information
(1) SOT89-5L
(Top View)
5
Y W X
XX
4
7
: Identification code
XX
Y
: Year : 0~9
W
: Week : A~Z : 1~26 week;
a~z : 27~52 week;
z represents 52 and 53 week
: Internal code
X
1 2 3
A~Z : Green
Part Number Package Identification Code
AH5798-YG SOT89-5L K4
(2) TSOT25
AH5798
Document number: DS32001 Rev. 2 - 2
(Top View)
5
4
7
XX : Identification code
: Year 0~9
Y
XX Y
W X
W
: Week : A~Z : 1~26 week;
a~z : 27~52 week;
z represents 52 and 53 week
: A~Z : Green
1 2 3
Part Number Package Identification Code
AH5798-WTG TSOT25 K4
www.diodes.com
X
8 of 11
June 2010
© Diodes Incorporated
Page 9

SINGLE PHASE HALL EFFECT LATCH SMART
Package Outline Dimensions (All Dimensions in mm)
(1) Package type: SOT89-5L
AH5798
FAN MOTOR CONTROLLER
Sensor Location
AH5798
Document number: DS32001 Rev. 2 - 2
9 of 11
www.diodes.com
© Diodes Incorporated
June 2010
Page 10

Package Outline Dimensions (Continued)
(2) Package type: TSOT25
AH5798
SINGLE PHASE HALL EFFECT LATCH SMART
FAN MOTOR CONTROLLER
AH5798
Document number: DS32001 Rev. 2 - 2
Sensor Location
10 of 11
www.diodes.com
June 2010
© Diodes Incorporated
Page 11

AH5798
SINGLE PHASE HALL EFFECT LATCH SMART
FAN MOTOR CONTROLLER
IMPORTANT NOTICE
DIODES INCORPORATED MAKES NO WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, WITH REGARDS TO THIS
DOCUMENT, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS OF ANY JURISDICTION).
Diodes Incorporated and its subsidiaries reserve the right to make modifications, enhancements, improvements, corrections or other
changes without further notice to this document and any product described herein. Diodes Incorporated does not assume any liability
arising out of the application or use of this document or any product described herein; neither does Diodes In corporated convey any
license under its patent or trademark rights, nor the rights of others. Any Customer or user of this documen t or products described
herein in such applications shall assume all risks of such use and will agree to hold Diodes Incorporated and all the companies
whose products are represented on Diodes Incorporated website, harmless against all damages.
Diodes Incorporated does not warrant or accept any liability whatsoever in respect of any products purchased through unauthorized
sales channel.
Should Customers purchase or use Diodes Incorporated products for any unintended or unauthorized application, Customers shall
indemnify and hold Diodes Incorporated and its representatives harmless against all claims, damages, expenses, and attorney fees
arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim of personal injury or death associated with such unintended or unauthorized application.
Products described herein may be covered by one or more United States, international or foreign p atents pending. Product names
and markings noted herein may also be covered by one or more United States, international or foreign trademarks.
LIFE SUPPORT
Diodes Incorporated products are specifically not authorized for use as critical components in life support devices or systems without
the express written approval of the Chief Executive Officer of Diodes Incorporated. As used herein:
A. Life support devices or systems are devices or systems which:
1. are intended to implant into the body, or
2. support or sustain life and whose failure to perform when properly used in accordance with instructions for use provided
in the labeling can be reasonably expected to result in significant injury to the user.
B. A critical component is an y component in a life support device or system whose failure to perform can be reasonably expected
to cause the failure of the life support device or to affect its safety or effectiveness.
Customers represent that they have all necessary expertise in the safety and regulatory ramifications of their life support dev ices or
systems, and acknowledge and agree that they are solely responsible for all legal, regulatory and safety-related requirements
concerning their products and any use of Diodes Incorporated products in such safety-critical, life support devices or systems,
notwithstanding any devices- or systems-related information or support that may be provided by Diodes Incorporated. Further,
Customers must fully indemnify Diodes Incorporated and its representatives against any damages arising out of the use of Diodes
Incorporated products in such safety-critical, life support devices or systems.
Copyright © 2010, Diodes Incorporated
www.diodes.com
AH5798
Document number: DS32001 Rev. 2 - 2
11 of 11
www.diodes.com
June 2010
© Diodes Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...