Page 1

User Guide
Digi TS Family
Digi One TS, Digi One TS Wireless, Digi One RealPort, Digi One RealPort Wireless, PortServer TS 2/4,
PortServer TS 2/4 MEI, PortServer TS 2/4 Wireless, PortServer TS 1/3 + Modem, and PortServer TS 8/16
90000583_A
Page 2

Digi International Inc. 2004. All Rights Reserved.
The Digi logo, PortServer, Connectware, Digi One, and RealPort are trademarks or registered trademarks of Digi
International, Inc.
90000583_A
Page 3

Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction
About This Guide...................................................................................7
Purpose .............................................................................................................. 7
Audience............................................................................................................. 7
Scope ................................................................................................................. 7
Other Documents in the Library.............................................................7
Quick Start Guide ............................................................................................... 7
Digi Command Reference .................................................................................. 7
RealPort Setup Guides....................................................................................... 7
Online Help for the Web UI................................................................................. 7
Setup Overview.....................................................................................8
Step A: Plan........................................................................................................ 8
Step B: Set Up the Hardware ............................................................................. 8
Step C: Install and Setup Digi Port Authority-Remote........................................ 8
Step D: Configure an IP Address ....................................................................... 8
Step E: Configure Ports...................................................................................... 8
Step F: Configure Other Features as Required.................................................. 9
Supported Devices................................................................................ 9
About Configuration Methods................................................................9
Configure the Digi Device with the Wizard ......................................................... 9
Configure the Digi Device from an Attached Terminal ....................................... 9
Configure the Digi Device from a Telnet Session............................................... 9
Configure the Digi Device from the Web Interface ............................................. 9
Downloading a Configuration File..................................................................... 10
Accessing the Configuration from the Web Interface..........................10
Quick Find Table.................................................................................10
Chapter 2 Configuring the IP Address
Options for Configuring the IP Address and Mask..............................13
Device Support: Digi Port Authority-Remote and ARP-Ping for IP Address
Configuration .................................................................................................... 13
Configuring the IP Address with Digi Port Authority-Remote ..............14
Assumptions..................................................................................................... 14
Procedure......................................................................................................... 14
Configuring the IP Address Using ARP-Ping.......................................14
Assumptions..................................................................................................... 14
Procedure......................................................................................................... 15
Configuring an IP Address using DHCP and RARP............................15
About DHCP and RARP................................................................................... 15
Procedure......................................................................................................... 15
Accessing the Digi Device...................................................................15
Chapter 3 Configuration
Network Settings.................................................................................17
Procedure for Using a Name Server ................................................................ 18
Configuring the Serial Ports.................................................................19
Contents 3
Page 4

Port Profiles.........................................................................................21
RealPort............................................................................................................ 21
Console Management ...................................................................................... 21
TCP Sockets . ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... .................................... 22
UDP Sockets .................................................................................................... 22
Serial Bridging .................................................................................................. 23
Printer............................................................................................................... 24
Terminal............................................................................................................ 24
Industrial Automation........................................................................................ 25
Modem Profiles................................................................................................. 25
Modem Emulation............................................................................................. 26
Modem.............................................................................................................. 26
Power Management ......................................................................................... 27
Custom ............................................................................................................. 28
User Configuration...............................................................................29
Common User Features ................................................................................... 29
Security Configuration.........................................................................30
Procedure......................................................................................................... 30
System Configuration..........................................................................31
PPP Settings ...... ....... ...................................... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... .......... 31
About Autoconnection.........................................................................33
Configuring a Port for Autoconnection.................................................33
Configuring a User for Autoconnection................................................34
Chapter 4 Setting Up RealPort
About RealPort....................................................................................35
What is RealPort?............................................................................................. 35
RealPort Advantages........................................................................................ 35
Configuring the RealPort Software................................................................... 35
Chapter 5 Special Features: Wireless
Configuration Considerations..............................................................37
Using Ethernet.................................................................................................. 37
Chapter 6 Special Features: Embedded Modem
Embedded Modem..............................................................................41
Installing the PortServer TS 1/3 + Modem........................................................ 41
Configuring the PortServer TS 1/3 + Modem ................................................... 41
Chapter 7 Special Features: Modem Emulation
Modem Emulation................................................................................43
Modem Emulation Cable Signals........................................................44
Scenarios for Modem Emulation............................................. ..... .... ...45
Outgoing Modem Emulation Connection.......................................................... 45
Incoming Modem Emulation Connection.......................................................... 45
Modem Emulation Pooling................................................................................ 45
Modem Emulation Bridge ................................................................................. 45
Originating, Answering, and Disconnecting Calls................................45
Disconnecting Calls-Digi Device Server........................................................... 46
Modem Emulation AT Command Set..................................................46
4 Contents
Page 5

S-Registers..........................................................................................52
Result Codes.......................................................................................57
Chapter 8 Special Features: Power Over the Serial Ports
Serial Power Feature...........................................................................59
Configuring RI Power..........................................................................59
RI Power In....................................................................................................... 59
RI Power Out.................................................................................................... 60
Configuring DTR Power.......................................................................60
Power Out......................................................................................................... 60
Serial Power Table..............................................................................61
Chapter 9 Special Features: IA (Industrial Automation)
Configuring Industrial Automation with Modbus..................................63
Chapter 10 Special Features: SNMP
About SNMP and the Device Server Agent.........................................65
Network Management Components................................................................. 65
SNMP Management Agent..................................... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... .......... 65
SNMP Traps.................... ....... ...... ...... ....................................... ....... ...... ....... ... 65
MIB Support...................................................................................................... 65
Message Support ............................................................................................. 66
Supported Traps............................................................................................... 66
Configuration Procedure: Web Interface.............................................66
Chapter 11 Configuration Management
Upgrading the Firmware......................................................................67
HTTP or TFTP Upgrade Procedure.................................................................. 67
Copying the Configuration to and from a Remote Host.......................67
When To Use Remote Configuration................................................................ 67
Download Procedure ........................................................................................ 67
TFTP Procedure............................................................................................... 68
Resetting Configuration to Defaults.....................................................68
Chapter 12 Reference and Certifications
Interpreting the LEDs...........................................................................69
LEDs................................................................................................................. 69
LED Diagnostics............................................................................................... 69
Device EIA 232/422/485 Switch Settings ......................................................... 70
RJ-45 Pinouts................................................................................................... 70
Safety Statements...............................................................................70
PortServer TS 8/16........................................................................................... 70
Rack Mounting Installation (PortServer TS 16 Rack and DC Rack)................. 71
PortServer TS 1/3 + Modem............... ....... ...... ....................................... ....... ... 71
Specifications......................................................................................72
PortServer TS 8/16........................................................................................... 72
Digi One TS Wireless, PortServer TS 2/4 Wireless.......................................... 73
PortServer TS 2/4 MEI, Digi One TS.. ....... ...... ....... ...... .................................... 74
PortServer TS 2/4............................................................................................. 74
PortServer TS 1/3 + Modem............... ....... ...... ....................................... ....... ... 75
Contents 5
Page 6

Regulatory Notices..............................................................................76
Certifications........................................................................................78
FCC Part 15 Class A (PortServer TS 8).......................................................... 78
Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) (FCC 15.105) .......................................... 78
Labeling Requirements (FCC 15.19)................................................................ 78
Modifications (FCC 15.21)................................................................................ 78
Cables (FCC 15.27).......................................................................................... 78
ICES 003 Class B ( Digi One TS, Digi One TS Wireless, PortServer TS 2/4,
PortServer TS 2/4 MEI, PortServer TS 2/4 Wireless,
PortServer TS 16).............................................................. 78
Antennae (Wireless only) .......................... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....... ................ 78
Maximum Permissible Exposure (Wireless only) ............................................. 79
Declaration of Conformity................................................................................. 79
Digi Contact Information......................................................................80
6 Contents
Page 7

Chapter 1
About This Guide
Introduction
Purpose
This user guide provides the following:
• Configuration and administration procedures
• Configuration examples
Audience
This guide is intended for the person responsible for configuring and
administering device server. It assumes that this person has experience
configuring network devices and is familiar with networking concepts.
Scope
This guide provides step-by-st ep instructions for configuring and
administering your Digi device’s main features. It focuses on performing
these tasks through the Web user interface. It does not address how to
configure ever y option, provide complete inf ormation on commands, or
discuss hardware installation. These topics are covered in other
documents in the Digi library.
Other Documents in the Library
Related documents in the library include:
Quick Start Guide
The guide that comes in the package with the Digi device coverin g t he first
steps necessary to get your device up and running.
Digi Command Reference
This online manual, available on the Software and Documentation CD,
provides complete information on commands.
RealPort Setup Guides
These online manuals provide information on setting up servers for
RealPort software.
Online Help for the Web UI
This context-sensitive online help provides information on configuration
fields used wi th web browser co nfiguration int erface.
Chapter 1 Introduction 7
Page 8

Setup Overview
Following is an overview of the process for setting up a device in the Digi
TS family of devices for use. The rest of this guide provides details on each
step of the process.
Step A: Plan
Before beginning setup, consider the following:
• How to assign an IP address to the Digi device’s Et hern et i nt erface ,
which can be accomplished in a number o f ways. See "Configuring
the IP Address" on page 13.
• How to configure serial ports. A key consideration is whether to use
RealPort. Other considerations include the type of peripheral t hat
will connect to the port and the peripheral’s cabling requirements.
See "Setting Up RealPo r t" on p a ge 35 and the online RealPort
driver documentation and Cable Guide, both of which are on the
Software and Documentation CD.
• The various ways in which your Digi device can be configured. See
"About Configuration Methods" on page 9 for more information.
Step B: Set Up the Hardware
1. If the Digi device supports multiple serial port interfaces (EIA-232,
EIA-422/485), set the interface with the dip switches on the device.
2. Connect the device to the network.
3. Connect peripherals to serial ports. See the Cable Guide on the
Software and Documentation CD.
4. Connect the power supply to the Digi device.
Step C: Install and Setup Digi Port Authority-Remote
Digi Port Authority-Remote is a utility that provides one of the ways to
configure an IP address and also provides port monitoring.
Step D: Configure an IP Address
There are a number of ways to configure an IP address. See "Configuring
the IP Address" on page 13 for more information.
Step E: Configure Ports
See the following for mo re information:
• "Setting Up RealPort" on page 35
• "Network Settings" on page 17
8 Chapter 1 Introduction
Page 9

Supported Devices
Step F: Configure Other Features as Required
See the following for information on setting up other features:
• "PPP Settings" on page 31
• "Configuring Autoconnection" on page 43
• "Configuring IP Routing" on page 47
• "Configuring S ec urity Features" on page 49
• "Special Features:Domain Name Sy stem (DNS)" on page 63
This manual prov ides information on the following Digi devices:
• Digi One TS, Digi One TS H (high temperature), and Digi One TS
Wireless
• PortServer TS 1/3 + Modem
• PortServer TS 2/4, PortServer TS 2/4 MEI, PortServer TS 2/4 H,
PortServer TS 2/4 MEI H, and PortServ er 2/4 Wireless
• PortServer TS 8/16, PortServer TS 16 Rack, PortServer TS 16 DC
Rack
About Configuration Methods
Use this section to learn about the different configuration methods.
Configure the Digi Device with the Wizard
Simply follow the prompts and choose your configuration with the wizard.
Choose either a Microsoft Windows or Unix platform.
Configure the Digi Device from an Attached Terminal
With this method, you cable a terminal or PC running terminal emulation
software to a device server port and then use the command line to enter
commands. This method allows you to configure a ll features. It requires,
however, that you and the device server be in the same location. Some
users find it advantageous to configure the device server IP address this
way and then u se one of the othe r met hods for t he rest of the configu ration .
Configure the Digi Device from a Telnet Session
With this method, you Telnet to the device server and use the command
line to complete configuration tasks. The only disadvantage to this method
is that you have to configure the device server with an IP address before
you can Telnet to it.
Configure the Digi Device from the Web Interface
The great advantage to this method is ease of use. This method requires
that you configure the IP address before you can access the configuration
from the web interface, however, some features cannot be configured this
way.
Chapter 1 Introduction 9
Page 10

Downloading a Configuration File
With this method, you configure a Digi device and then do the following:
1. Download an existing configuration file to a host system.
2. Edit the file with specific configuration using a text editor.
3. Upload the file to the device server.
This an excellent method for maintaining highly similar configuration files
for multiple Digi devices. The disadvantage is that the device server
requires some configuration steps, such as the IP address, to be
completed before it can be used.
Accessing the Configuration from the Web Interface
To access the configuration from the web interface, follow these steps.
This procedure assumes that you have configured the Digi device with an
IP address already. See "Configuring the IP Address" on page 13.
1. Access the Digi device from a web browser by specifying the device
server’s IP address in the URL window.
2. Log on as root. The default password is dbps.
Quick Find Table
The following table is a quick reference for specific features and where to
find the web interface configuration procedures.
The Digi TS Family includes the following devices:
• Digi One TS (and high temperature models )
• Digi One TS Wireless
• PortServer TS 2 (and high temperature models)
• PortServer TS 4 (and high temperature models)
• PortServer TS 2 MEI (and high temperature models)
• PortServer TS 4 MEI (and high temperature models)
• PortServer TS 2 Wi reless
• PortServer TS 4 Wi reless
• PortServer TS 1 + Modem
• PortServer TS 3 + Modem
• PortServer TS 8
• PortServer TS 16 (and Rack models)
Feature Products Availability Configuration Details
RealPort Digi TS Family
Serial Port > Por t Profile >
RealPort
Digi One TS Wireless
Wireless
10 Chapter 1 Introduction
Digi One RealPort Wireless
PortServer TS 2/4 Wireless
Network > Wireless LAN
Settings
Page 11

Feature Products Availability Configuration Details
Digi One TS
PortServer TS 2/4 MEI
Modem Emulation
PortServer TS 2/4 Wireless
PortServer TS 1 + Modem
PortServer TS 3 + Modem
PortServer TS 8/16
Serial Port > Por t Profile >
Modem Emulation
Embedded Modem
AutoConnection Digi TS Family
IP Routing PortServer TS 8/16
Access Control Digi TS Family
DNS Digi TS Family System > System Name
Industrial
Automation (IA)
Power Over Serial
Port
PortServer TS 1 + Modem
PortServer TS 3 + Modem
Digi One TS
PortServer TS 2/4 MEI
PortServer TS 2/4 Wireless
PortServer TS 1 + Modem
PortServer TS 3 + Modem
PortServer TS 8/16
Digi One TS Wireless
Digi One RealPort Wireless
PortServer TS 2/4 Wireless
PortServer TS 2/4 MEI
Serial Port > Por t Profile >
Internal Modem
Serial Port > Por t Profile
>TCP Sockets
Serial Port > Port Pr ofile > IA
> Serial Master > Packet
Routing
User > New User >
determine access
Serial Port > Por t Profile
>Industrial Automation
See "Special Features:
Power Over the Serial Ports"
on page 59
PPP Digi TS Family System > PPP
SSH V ersion 2
TCP Socket
Communication
UDP Multicast
Communication
RADIUS PortServer TS 8/16 Security > RADIUS
Power Management
Chapter 1 Introduction 11
PortServer TS 2/4 MEI
PortServer TS 8/16
Digi TS Family
Digi TS Family
PortServer TS 2/4 MEI
PortServer TS 2/4 Wireless
PortServer TS 8/16
Network > Security >
Custom
Serial Port > Por t Profile
>TCP Sockets
Serial Port > Por t Profile
>UDP Sockets
Serial Port > Por t Profile
>Power Management
Page 12

12 Chapter 1 Introduction
Page 13

Chapter 2
Configuring the IP Address
The next step in the device configuration process is to configure an IP
address and access the device for more advanced configurations. You
must set the initial IP before you can use the web interface. Once the IP is
set, the device can be accessed through the web interface and any
changes made including cha ngin g the IP add ress.
Options for Configuring the IP Address and Mask
The device server IP address can be configured using the following
methods:
• With the Wizard from the Software and Documentation CD. (Insert
the CD and the wizar d auto mati cally po p s up f or Micr osof t Window s
systems. If you have a UNIX system see the back of the quick start
guide for mounting instructions.)
• With Digi Port Authority-Remote, a Digi utility on the Software and
Documentation CD.
• From the command line, using the set config command. See the
Digi Command Reference for more details.
• By updating the ARP table on a server and then pinging the Digi
device (called ARP-Ping, see "Configuring the IP Address Using
ARP-Ping" on page 14).
• Using a DHCP server ("Configuring an IP Address using DHCP and
RARP" on page 15.)
• Using a RARP server ("Configuring an IP Address using DHCP and
RARP" on page 15.)
The IP address and mask can also be changed using the web interface,
but not for initial IP address configuration.
Device Support: Digi Port Authority-Remote and ARP-Ping for IP Address Configuration
Not all Digi devices can use Digi Port Authority-Remote and ARP-Ping for
IP address configuration. To determine if you can use these features, find
the hardware label on your Digi device and then use the table below to
determine whether this feature is available:
Device Part Number Revision Required
Digi One IA RealPort 50000764-01 F or higher
Digi One RealPort 50000723-01 J or higher
PortServer TS 2 50000723-02 J or higher
PortServer TS 4 50000723-03 G or higher
Chapter 2 Configuring the IP Address 13
Page 14

Configuring the IP Address with Digi Port Authority-Remote
Use this section to configu re an initial IP add ress, subnet mask, and defau lt
gateway using Digi Por t Autho rit y-Re mote. Thi s proce dure cannot b e used
to change the IP address, but only to assign the initial IP address. It also
cannot be used if a DHCP server is act i ve.
Assumptions
This procedure assumes the following:
• That your Digi device supports this feature. See "Device Support:
Digi Port Authority-Remote and ARP-Ping for IP Address
Configuration" on page 13.
• That your Dig i device is connected to the Ethernet network.
• That the Digi device has DHCP client turned on. This is the default
setting and it will be on unless it was turned off.
• That you do not have a DHCP server to serve IP ad dress. If you d o,
use the DHCP procedure. See "Configuring an IP Address using
DHCP and RARP" on page 15.
• That you have installed Digi Port Authority-Remote version 2.01.11
or later. Click the Help button on the tool bar in Digi Port AuthorityRemote to check the version number.
Procedure
1. Run Digi Port Authority-Remote.
2. Click Discover. A list of Digi devices appears. Systems with IP
addresses of 0.0.0.0 nee d IP addresses.
3. Select a device from the list and then click Configure.
4. Supply an IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway and then
choose OK.
Digi Port Authority-Remote configures the IP address, subnet mask,
and default gateway.
Configuring the IP Address Using ARP-Ping
An IP address can be configured by manually updating a server’s ARP
table and then pinging the Digi device.
Note: The ARP-Ping command assigns the IP address you designate but also
assigns default subnet mask and gateway addresses. It is necessary to
change the subnet mask and gateway addresses.
Assumptions
This procedure assumes the following:
• That your Digi device supports this feature. See "Device Support:
Digi Port Authority-Remote and ARP-Ping for IP Address
Configuration" on page 13.
• That your Dig i device is connected to the Ethernet network
14 Chapter 2 Configuring the IP Address
Page 15

Procedure
1. Record the MAC address of th e Digi device. The MAC addr ess is on the
back of the unit.
2. Access a server on the same subnet as the Digi device.
3. Manually updat e the server’s ARP table using the Digi device’s MAC
address and the IP address you want assigned to the Digi device. The
following is an example of how this is done on a Windows NT 4.0
system:
arp -s 143.191.2.1 00-00-9d-22-23-60
4. Ping the Digi device using the IP address just assigned. The following is
an example:
ping 143.191.2.1
The ping will probably time out before there is a response from the Digi
device.
5. Wait several seconds and then ping the Digi device again.
The Digi device replies to the ping, indicating that the IP address has
been configured.
Configuring an IP Address using DHCP and RARP
About DHCP and RARP
When the device server boots, it transmits a DHCP request and a RARP
request. This continues until an address is assigned.
Procedure
To use RARP or DHCP follow these steps:
1. Set up an entry for an address on a DHCP or RARP server. If you
intend to use RealPort, do the following:
• Reserve a permanent IP address.
• Record the IP address. You will need it when you configure the
2. Power on the device server.
The DHCP or RARP server assigns the device server an IP address.
Accessing the Digi Devi ce
1. Enter the IP address in the URL bar of your browser.
2. Enter your login name (root) and password (dbps).
Note: The following screen appears allowing you to configure the device for your
RealPort driver.
specific needs. A tutorial is available to guide you in your decisions. The Help
Chapter 2 Configuring the IP Address 15
Page 16

button in the upper right corner is also available.
From the web interface, you make any changes you need for your
configuration. Remember to click Apply to save your changes and Reboot
when you are ready for the changes to take effect.
16 Chapter 2 Configuring the IP Address
Page 17

Chapter 3
Network Settings
Configuration
The next step in the device setup process is to configure the network and
serial port settings. In order t o access the web in te rfa c e an IP addre ss
must be assigned. It is assumed you have logged onto the web interface
using the username, root and password, dbps in order to make any
changes or additional configuration assignments. However, it is important
to note that if you have used the wizard, your configuration is complete and
you do not additional changes.
1. Click Network to view the IP settings or make any changes to the IP
address.
2. Click Advance Network Settings.
Chapter 3 Configuration 17
Page 18

Adjust the network settings to fit your configuration needs. If you need
additional information use the Help button on the top right hand corner of
the configuration screen.
3. Click Apply to save any changes you make.
4. Click Reboot for changes to take effect.
Procedure for Using a Name Server
To configure a DNS server, follow these steps:
1. Click Network and select Use the following IP address.
2. Enter the IP address for the DNS server in the Name Server box. The
DNS server maps names (MyDeviceName.mycompany.com) to IP
addresses (192.105.1.2).
3. Enter a name for a group of network devices.
4. Enter the domain name that this device will live in and is tied to the DNS
server address assigned in step 2. This name can be used by other
network devices to talk to it, instead of using the its IP address. Get this
name from the network administrator, because it must be entered in the
DNS server to work properly.
5. Enter the Base Socket. The base socket is the incoming port number
which remote devices need to use to access the device using the
named protocols.
Note: Base Socket
This determines which network port (socket) on this Digi terminal server
another network device (such as another Digi terminal server or a PC) uses to
communicate using certain services. Most applications can leave this value
unchanged. To calculate these settings:
Telnet port = Base Socket + Serial Port Number
Raw port = Base Socket + 100 + Serial Port Number
18 Chapter 3 Configuration
Page 19
raw (TCP or UDP) 2000 2101
6. Click Apply.
7. Click Reboot for changes to take effect.
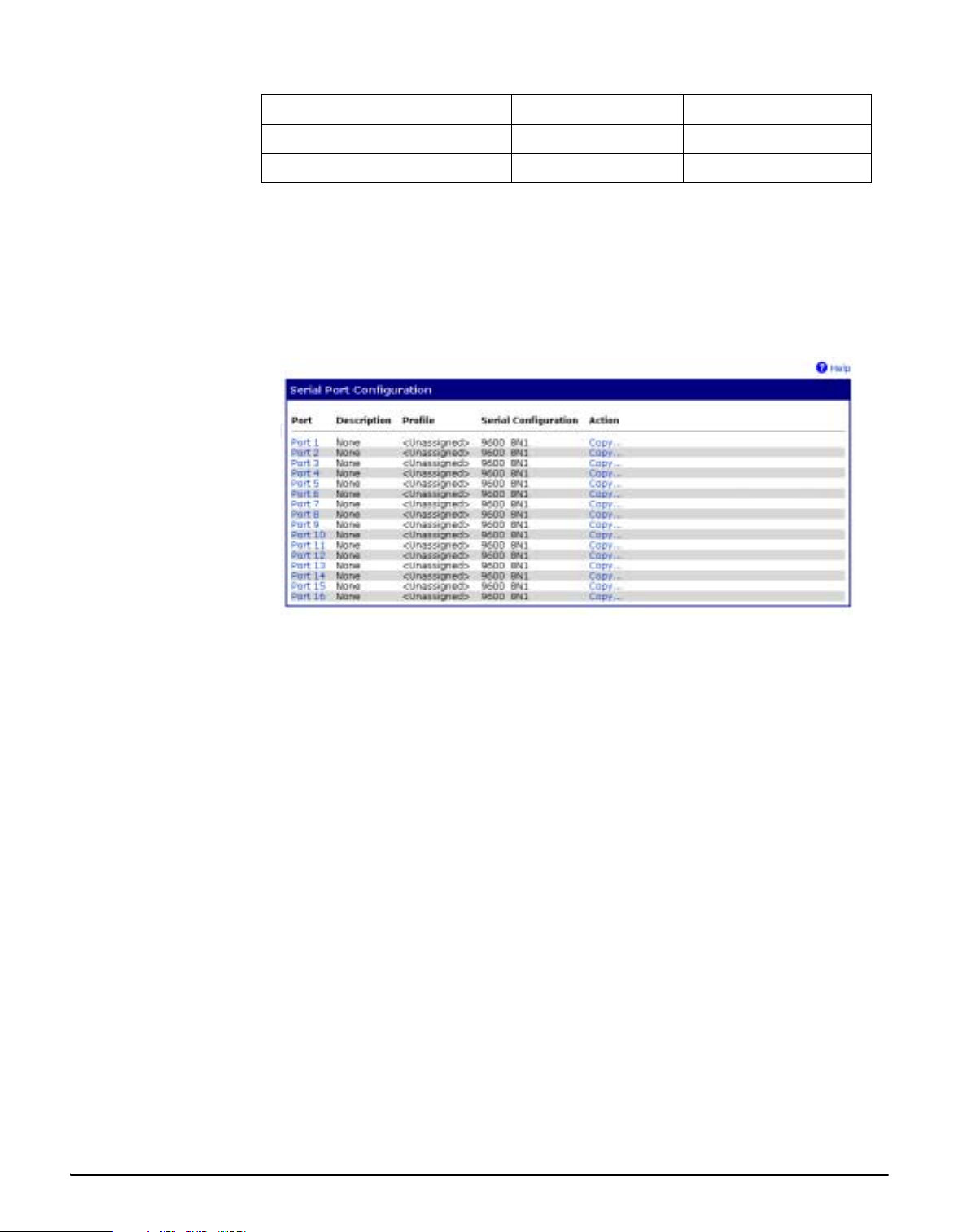
Configuring the Serial Ports
1. Click Serial Ports under Configuration.
Service Ba se Sock et Network Port
telnet 2000 2001
2. Click the port number that you want to configure.
3. Click Change Profile and select a profile based on the device you have
connected to your port.
Note: The following section shows the settings available for each profile.
Chapter 3 Configuration 19
Page 20

Note: The ‘More’ link will describe the profiles with additional information.
Note: Profiles appear depending on your device. Naturally, if you do not have a
device capable of a specific profile such as Power Management or Wireless,
you will not have that particular profile available.
4. Click Apply to save the profile. The interface will determine any
additional settings and advise you what tab to click next. See "Port
Profiles" on page 21 or click Help for additional information.
5. A port profile or port options page will come up and ask for additional
parameters if needed. Enter the appropriate parameters and click Apply.
6. Click Reboot for changes to take effect.
20 Chapter 3 Configuration
Page 21

Port Profiles
Each port profile determines the setti ngs nee de d. The fol low i ng
screenshots of each profile show the port settings. For a complete
description of each profile click the Help button.
RealPort
Installed on a network-based PC, Rea l Port emulates a serial port. That is,
the application “t hinks” it is working with a real serial port, such as COM1.
When the applicatio n sends dat a to this serial port, RealPor t ship s the data
across the network to the device server which in turn routes it to the serial
device. This is also referred to as COM Port Redirection. The network is
transparent to both the application and the device.
Console Management
Access a device's console port over a network connection. Most network
devices such as routers, switches, and servers offer serial port(s) for
management. Instead of connecting a terminal to the console port, ca ble
the console port to the serial port of your Digi device. Then using TCP/IP
utilities like reverse telnet, network administrators can access these
consoled serial ports from the L AN.
Chapter 3 Configuration 21
Page 22
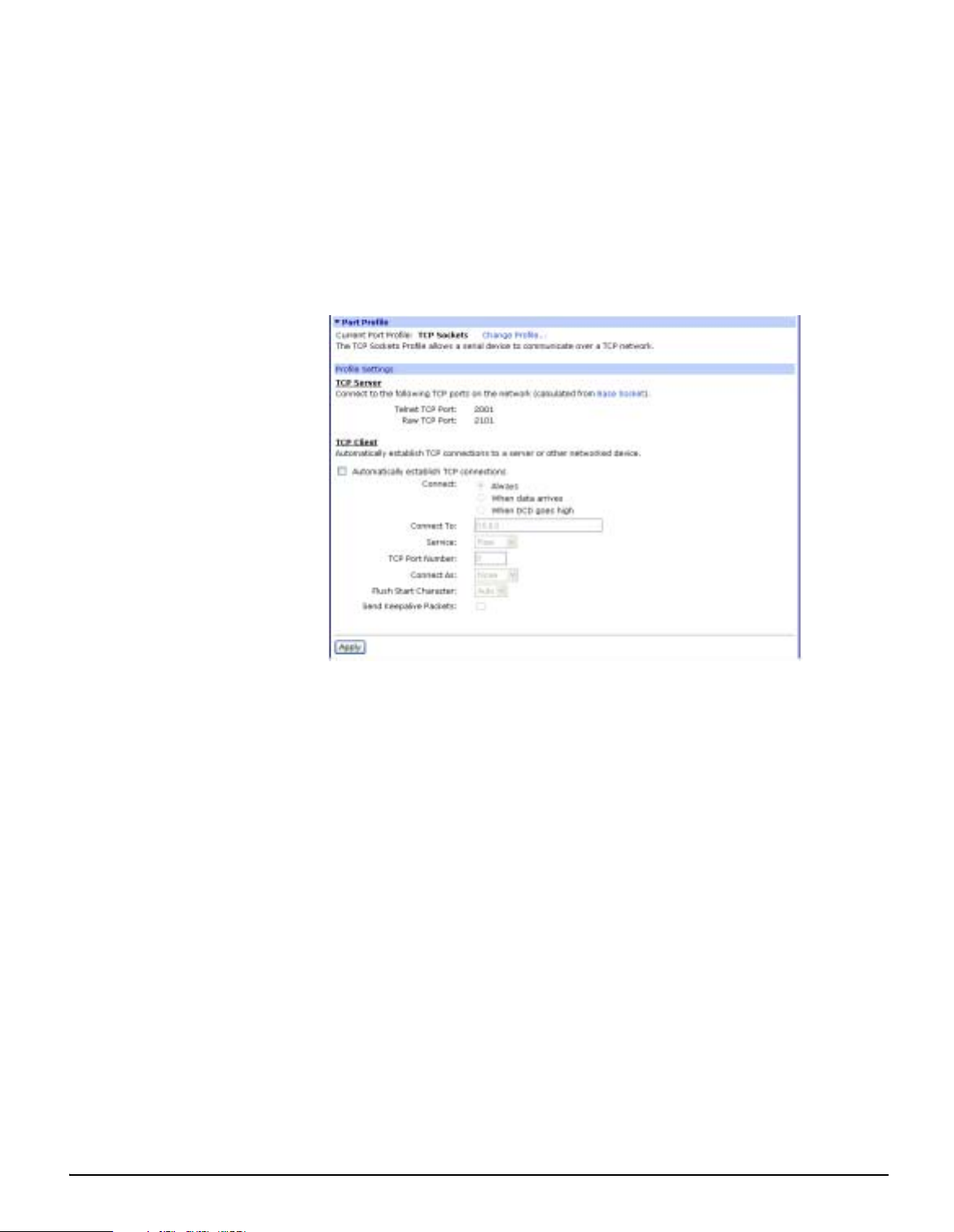
TCP Sockets
TCP socket communication enables serial devices to communicate with
each other over an Ethernet network as though they were connected by a
serial cable.
Configuring TCP socket communications involves configuring the Digi
device for the following types of c onnections:
• Inbound connections, that is, connections that are initiated by the
device on th e other side of the network.
• Outbound connection, that is, connections that are initiated by the
device connected to the serial port.
Note: TCP Sockets profile is also the profile to use for Autoconnection. See "Click
UDP Sockets
Reboot for changes to take effect." on page 33 for more information.
The Digi TS Family devices are capable of UDP multicast. UDP multicast is
used to send serial dat a over an Et hernet cable to one or many host s at the
same time. UDP is a ‘connectionless’ protocol, meaning UDP does not
need a protoc ol , b ut i s se nding data wi thout any form of acknowledgement
or error correction. Up to 64 devices can receive a UDP multicast at one
time. Both the transmitting and receiving devices must be configured
properly for UDP multicast to work.
Configuring UDP multicast communications involves configuring the D i gi
device for the following types of c onnections:
• Inbound connections, that is, connections that are initiated by the
device on th e other side of the network.
• Outbound connection, that is, connections that are initiated by the
device connected to the serial port.
22 Chapter 3 Configuration
Page 23

Note: The serial parameters for two connecting devices must match meaning if one
device is set for 9600 bps, the other device must be set for the same rate.
Serial Bridging
A serial bridge is a network connection between two serial devices, each of
which uses a device server. The serial devices “think” they are
communicating wit h each other across a serial cable using serial
communication techniques. There is no need to reconfigure the server or
the serial device. Neither is aware of the intervening network.
This profile configures each side of the bridge separately. Repeat the
configuration for the secon d Dig i device se rve r o f the bridge sp eci fyi ng the
IP address of the first Digi device server.
Chapter 3 Configuration 23
Page 24

Printer
This profile allows you to con nect a printer to a serial port. Use this profile i f
you intend to print using the lpd protocol on your UNIX system.
Note: Refer to your UNIX User Guide for tips on configuring the print spooler on
your UNIX system.
Terminal
This profile allows you to connect to a terminal to the serial port.
24 Chapter 3 Configuration
Page 25

Industrial Automation
The Industrial Autom ation (IA) Profile all ows you to co nnect IA device s and
PLCs to the serial port in order to network-enable the devices. Use this
profile if you need to communicate over the network with an IA device or
PLC that only uses serial protocols. This profile may also be used to add
routing capabilities to IA devices or PLCs that act as serial masters and
send packets to various systems or devices on the network. Industrial
Automation enhances the IA device or PLC connected to the serial port.
Modem Profiles
There are 3 types of modem profiles :
• Modem Emulation
Modem Emulation allows the Digi device to function as a modem. A
short description follow the modem profiles listed below. For more
specific informat ion about Mo dem Emulat ion see "Special Features:
Modem Emulatio n" on page 43, including AT commands specific to
this function.
• Modem
The Modem profile configures the Digi device for attaching a modem
to a serial port. For more specific information about the modem
profile use the H elp button in the upper right corner on the profile
page of the web inter f a c e.
• Internal Mode m
The Internal Modem profile (not liste d in the graphic) is specific to
the PortServer TS 1/3+Modem devices. The fully functioning
Chapter 3 Configuration 25
Page 26

modem is embedded in port one and uses the standard AT
command set. See the Documentation on the Digi CD for the
complete AT Command Reference.
Modem Emulation
Modem Emulation allows you to configure the serial port to act as a
modem. The Digi device emulates modem responses to a serial device
and seamlessly sends an d receiv es dat a ov er an Eth ernet ne twork i nstea d
of a PSTN (Public Swit ched Telephone Net work). The advan tage f or a user
is the ability to retain legacy software applications without modification and
use a less expensive Ethernet network in place of public telephone lines.
Modem
Modem allows you to attach modem devices to the serial port in order to
establish or receive connections from other systems and modems.
Note: Click the PPP Configuration link to set up incoming, outgoing or advanced
PPP settings if the attached modem uses PPP connections. See "System
Configuration" on page 31 for more information about PPP settings.
26 Chapter 3 Configuration
Page 27

Power Management
The Power Controller feature allows the administrators of the Digi CM to
use console management to control power function s. Power control
consists of three basic functions: on, off, and reboot (power cycle).There
are two typical scenarios when using a power controller. The simplest
scenario is a non-serial device connected to a power controller (for
example, an environmental sensor controller or a tape backup device).
Note: Power controller settings can be automatically detected or configured
Chapter 3 Configuration 27
manually.
Page 28

Custom
This profile allows you to see all settings and set them accor dingly . Use this
profile only if your application doe s not fit into any of the predefined port
profiles.
28 Chapter 3 Configuration
Page 29

User Configuration
Although it is not required, the device server is often configured to
accommodate the requirements of particular users. Typical configurable
user attributes include:
• Whether the user is required to supply a password.
• Autoconnection attributes, such as the system to which the user
should be automatically connec ted at login.
• The interface the device presents the user, such as a menu or
command line.
• Whether th e user has access to outbound ports.
Note: For information on configuring PPP users, see "PPP Settings" on page 31.
Common User Features
Feature Description
Automatically connects the user to the host specified on the autohost
autoconnect
Default
access type
Menu
access
Port access
PPP Defines PPP-related parameters for the user.
Routing
updates
field using the service (TCP port) defined on the autoport or
autoservice fields.
Autoconnection can also be implemented by port instead of by user.
Defines the type of access the user is restricted to. Menu, command
line, autoconnect, and outgoing and netservice are the types.
Defines the menu that is to be presented to a user with menu
access.
Defines the number of outbound ports a user connected over the
LAN can access at one time.
This feature is not configurable from the web interface.
Defines whether RIP routing updates are forwarded over the link to
this user.
1. Click Users > New User
2. Enter the Username, password, and password confirmation and click
Next.
3. Select the profile that fits the user’s environment/needs and click Next.
Chapter 3 Configuration 29
Page 30

4. Select the Ports to manage or the Autoconnect function if needed and
5. Review settings and click Finish.
The Advanced tab under User allows you to set Escape characters for
Connect, Telnet, Rlogin, and Kill a s well as an SSH Public Key. Click Apply
to save the settings.
6. Click Reboot for changes to take effect.
Security Configuration
Security settings allow the administrator to set passwords, security levels,
and authentication via RADIUS server.Some services, such as Telnet and
Rlogin, can be disabled for inboun d users. This means that the users
cannot access the Digi device using those services. This feature allows
you to turn off individual services or to specify a security level, which
means that all services not included in that level are turned off. The
following services can be turned off.
click Next.
• HTTP
• RealPort
•Reverse TCP
• Reverse Telnet
• Remote login
• Remote shell
•SNMP
•SSH
• Telnet
Procedure
1. Click Security > and enter a new password for the root administrator.
2. Enter the confirmati on password and click Apply.
3. Click Network Security and select the security level appropriate to your
environment and click Apply.
Note: Secure Access Levels -
Secure: SSH is the only service available to inbound users.
High: SSH, HTTP, SNMP, and RealPort services are available to inbound
30 Chapter 3 Configuration
Page 31

4. Click RADIUS and select Authenticate users via RADIUS server.
5. Enter the appropriate IP address and secret and clic k Apply. The secret
6. Click Reboot for changes to take effect.
System Configuration
System settings allow you to set the bandwidth (throughput or latency) the
date and time, PPP connections, and SNMP traps.
1. Click System and enter the System Des cription (network name
users.
Normal: all services are available.
Custom, which means you can select services to turn off.
The default service level is Normal.
is the passwo rd use d for encryp tion of me ssages b etwe en the RAD IUS
server and the Digi device.
assigned to the Digi devic e), Contact (SNMP contact person -often the
network administrator), Location (text des cription of the physical
location of the Digi device), and Optimization (bandwidth used on the
network) and click Apply
Note: Latency - Allows fast access to time-sensitive devices. Requires more
network bandwidth.
Throughput - Allows better network performance at higher throughput.
2. Click Date/Time
3. Enter the date and time information and click Apply.
4. Click Reboot for changes to take effect.
PPP Settings
Under System Configuration, users can set the PPP (Point-to-Point
Protocol) options to enable or disable the dynamic IP address pool. The
dynamic IP address pool is a set of reserved IP addresses unique to the
network that are assigned to the incoming connections. Users set the first
IP address to use and th e number o f sequential a ddresses (pl us one) to b e
reserved for assignment.
1. Click PPP.
2. If you are using PPP select Enable Dynamic IP Address Pool for
Incoming Connections.
3. Enter the fi rst re served IP add ress of the incom ing connec tions and the
number of addresses to use and click Apply.
4. Click Incoming Connections > New Connection
Chapter 3 Configuration 31
Page 32

5. Enter the appropriate parameters and click Apply.
6. Click Reboot for changes to take effect.
For outgoing connections, CHAP or PAP authentication, password
configuration, follow the procedure for Outgoing Connections.
1. Click Outgoing Connections
Note: CHAP authentication can be used to restrict PPP user access to outbound
ports.
2. Enter the appropriate parameters and click Apply.
3. Click Reboot for changes to take effect.
For dynamic routing or proxy ARP settings follow the procedure for
Advanced PPP settings.
4. Click Advanced PPP settings.
32 Chapter 3 Configuration
Page 33

5. Select Enable Dynamic Routing (RIPv1)
6. Select the passive or active route setting.
7. Select the Process ARP reque sts if appropriate.
8. Click Apply.
9. Click Reboot for changes to take effect.
About Autoconnection
The autoconnection feature allows you to configure a user to access the
device server and then be automatically connected to a host on the LAN.
You can implement autoconnection in the following ways:
• By port, where all port users are automatically connected to the
same host. The device server is completely transparent to them.
• By user, where a user is required to log on and may be required to
supply a password. Once the user is authenticated, an automatic
connection to a host is made.
Configuring a Port for Autoconnection
1. Select Serial Port s under Configuration.
2. Click the TCP Sockets Port Profile.
Note: TCP Sockets is the Autoconnection profile.
3. Click Apply.
4. Select Automatically establish TCP connections and the appropriate
parameters. Use the Help button for addtional information.
5. Click Apply.
6. Click Reboot for changes to take effect.
Note: To return to the main Ports menu, choose Ports from the Menu again.
Chapter 3 Configuration 33
Page 34

Configuring a User for Autoconnection
1. Click Users from the menu.
2. Choose New User.
3. Enter a username and then click Next.
4. Select the “Terminal/Terminal Emulation” user profile and click Next
5. Select Automatically connect to a ...
Be sure to specify the following:
• Hostname or IP address that will be the destinatio n
•Service
• Destination TCP port number, which determines the type of
connection for this user (such as 23 for Telnet)
6. Click Next and Verify the settings.
7. Click Finish to save settings.
34 Chapter 3 Configuration
Page 35

Chapter 4
About RealPort
Setting Up RealPort
The next step in the device setup process is to configure RealPort. This
section provides a brief introduction to RealPort. If you use the wizard,
follow the steps in the pop-up after selecting the Incoming scenario.
What is RealPort?
RealPort is a feature that allows network-based host systems to use the
ports of the device server as though they were the host system’s own ports,
appearing and behaving as local ports to the network-based host.
RealPort Advantages
RealPort provides the following advantages:
• It expands the number of ports available to the host system.
• It enables device server ports to be treated as if they were directly
connected to the host, whi ch mean s they use al l st andar d opera ting
system interfaces that control baud rate, parity, stop bits, and flow
control.
• It enables host administrators to do most of the required
configuration on the host, the syst em with which th e administrator is
most familiar.
• It dramatically reduces host CPU overhead because multiple
terminal or printer sessions are multiplexed over the same TCP/IP
connection.
Configuring the RealPort Software
You must install and configure RealPort software on each host that will use
RealPort ports. See the RealPort documentation for more information.
1. From the CD, click Software. (If the wizard pops up, click cancel.)
Chapter 4 Setting Up RealPort 35
Page 36

2. From the Control Pa nel, click Add new ha rdware and follo w the prompts
listed above.
The files are located in the drivers\windows\win2k\realport folder.
If you use the wizard, follow the steps in the pop-up after selecting the
Incoming scenario.
36 Chapter 4 Setting Up RealPort
Page 37

Chapter 5
Use this chapter for the initial configuration of your Digi Wirele ss de vice.
After the initial configuration, the device can be configured using the same
methods as the other Digi TS family products.
Configuration Considerations
The Digi wireless devices work ONL Y with the antennae provided. You can
use the wizard to configure your wireless device available on the Software
and Document ation CD . You will need an E thernet cable and a netwo rk PC
to configure the wireless Digi device. After assigning the IP address,
access the device from your br owser by enter ing the IP address in the URL
address bar.
Special Features: Wireless
Using Ethernet
1. Connect serial cable, Ethernet cable, and power supply.
2. Insert the CD in the drive. The configurat ion wizard will automatically
start. Follow the steps in the wizard (either for Microsoft Windows or
Unix) to configure the device.
Or:
If you do not want to use the wizard, click Cancel and follow the
remaining procedure steps to s et up the IP address and config ure the
device through the web interface.
3. Select Discover Digi Device (from the CD).
4. Select the wireless device and assign the IP address.
5. Click Set IP.
6. Enter the IP address, Subnet, and Gateway mask and click OK.
Chapter 5 Special Features: Wireless 37
Page 38

7. Select the device and click Configure to launch your browser.
8. Enter the username root and password dbps and click OK.
The home screen appears.
9. Click Network > Wireless LAN
38 Chapter 5 Special Fe atures: Wireless
Page 39

10..Enter parameters, click Apply to save.
11. Click Reboot for changes to take effect.
12.Click Advanced Network Settings, enter any additional par ameters neede d
and click Apply to save..
13.Unplug the Ethernet cable from the Digi device, disconnect the power,
and power the unit up (reboot).
Configuration is complete.
Chapter 5 Special Features: Wireless 39
Page 40

40 Chapter 5 Special Fe atures: Wireless
Page 41

Chapter 6
Embedded Modem
Special Features: Embedded Modem
The PortServer TS 1+ M ode m and Po rtServer TS 3 + Mode m functions as
both terminal serve r and mo dem. The e mbedded m odem can be used wit h
PPP, dial-out, or auto answer and conforms to the standard AT command
interface.
The PortServer TS 1 + Modem and PortServer TS 3 + Modem allow
• remote monitoring
• diagnostics
• data collection
• dial-up, wireless, or Ethernet connectivity
For a complete AT command reference see the AT Command reference
from the CD under Documentation.
The remaining ports can be configured the same as any Digi TS Family
product, eith er through the web interface or command line.
Installing the PortServer TS 1/3 + Modem
The PortServer TS 1/3 + Modem comes with a bi-directional cable for
connecting the modem (port 1) to the phone line.
1. Plug the cable with the ferrite end into the modem port.
2. Plug other end into phone line.
3. Connect Ethernet.
4. Connect power supply.
Configuring the PortServer TS 1/3 + Modem
1. Follow the setup wizard from the CD to assign an IP.
2. If the wizard scenar ios need addi tional confi guration, logi n to the device
IP from the URL.
3. Select Serial Ports > Change profile
4. Select the appropriate profile (Custom shows all options)
Chapter 6 Special Features: Embedded Modem 41
Page 42

5. Enter the appropriate parameters and click Apply to save.
6. Click Reboot for changes to apply.
42 Chapter 6 Special Features: Embedded Modem
Page 43
Chapter 7
Modem Emulation
Special Features: Modem Emulation
The following Digi TS Family products include Modem emulation:
• Digi One TS
• Digi One TS Wireless
• PortServer TS 2/4 MEI
• PortServer TS 2/4 Wireless
• PortServer TS 1/3 + Modem
Note: Port one on the PortServer TS 1/3 + Modem is an actual embedded modem.
The remaining ports are capable of emulating a modem.
• PortServer 8/16
Modem emulation enables a system administrator to configure a
networked Digi device to act as a modem. The Digi device emulates
modem responses to a serial device and seamlessly sends and receives
data over an Ethernet network instead of a PSTN (Public Switched
Telephone Network) . The adva ntag e for a user is th e abil ity to reta in lega cy
software applications without modification and use a less expensive
Ethernet network in place of pub lic tele phone lines.
To use a Digi device for modem emulation, do the following:
• Use a cable with the correct wiring pinouts (see "Modem Emulation
Cable Signals" on page 44)
• Configure the serial ports and device type with the Web Interface
serial port profile - Modem Emulation
Note: Before AT commands are accepted, DSR must go high on the Digi device-
Common User Scenarios
The Digi device in modem emulation mode allows for the easy replacement
of modems in almost any environment where there is a LAN or WAN.
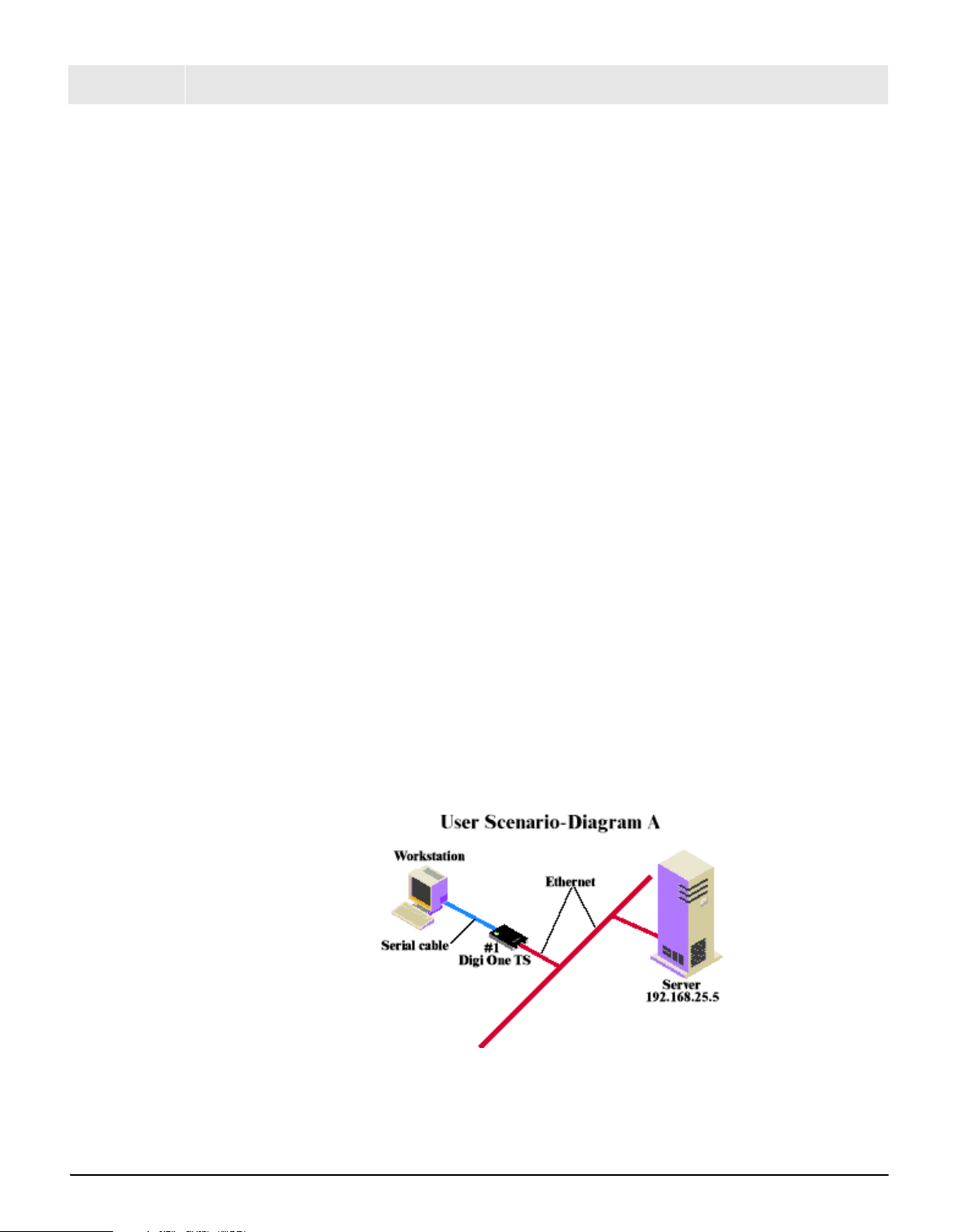
In Diagram A, the Digi One TS repla ces a modem connected to a
workstation running an application. The Digi One TS allows for the use of
software applications without modification by responding to all the AT
commands configured in the workstation application. The Digi One TS
Chapter 7 Special Features: Modem Emulation 43
Page 44
connects to the IP Address of the server when an
ATDT ipaddress:port (ATDT 192.168.25.5:50001)
command is issued. Once the remote device establishes the TCP
connection, a CONNECT message is sent to the serial port and only then
does the Digi device switch from AT command mode to data mode. Using
the modem escape sequence or dropping DTR on either side terminates
the connection. A DISCONNECT message will be sent to the application if
the remote side closes the TCP connection.
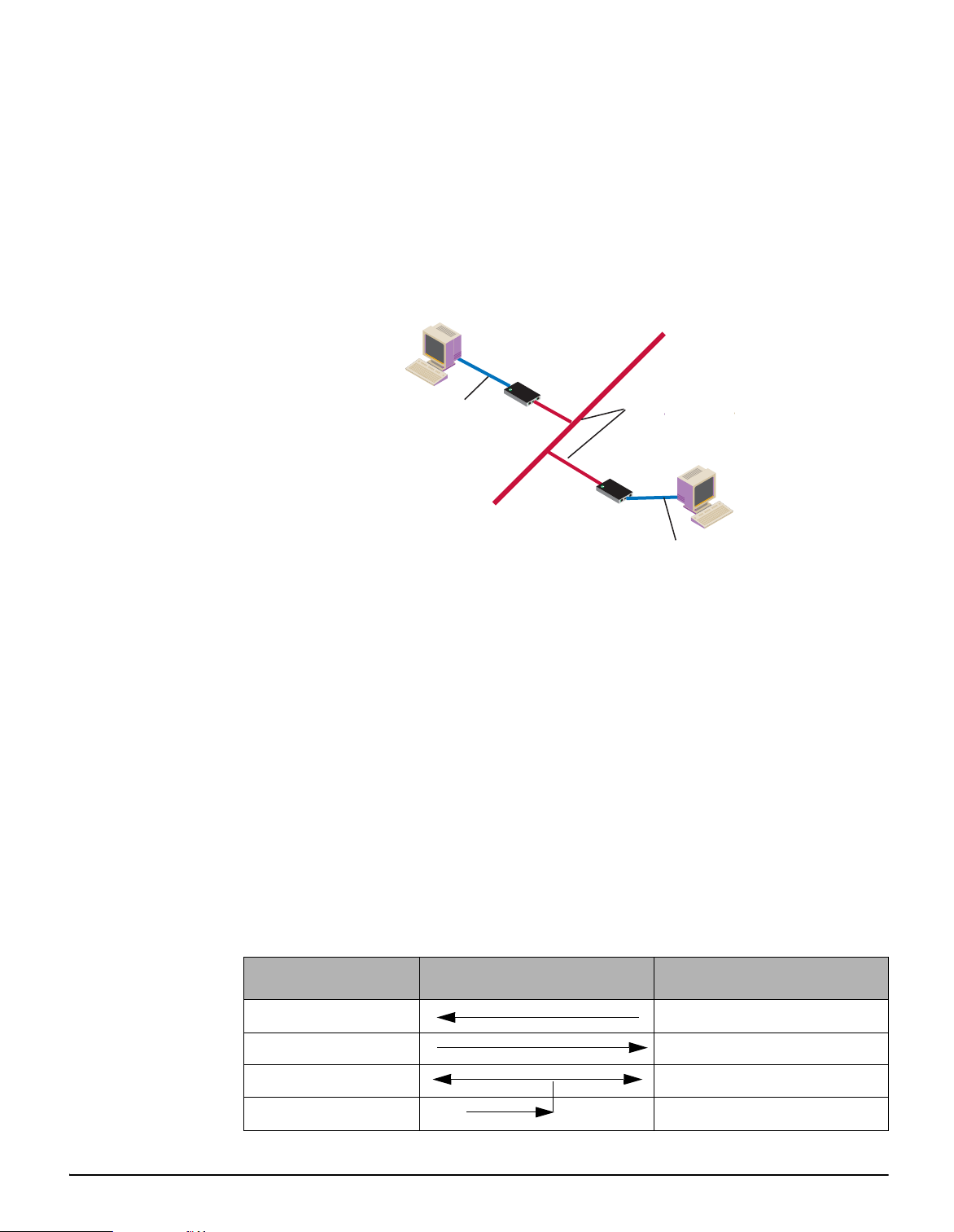
User Scenario-Diagram B
Workstation
S
T
E
N
O
I
G
I
Serial cable
Digi One TS
#1
D
Ethernet
S
T
E
N
O
I
G
I
D
#2
Digi One TS
192.168.25.30
Serial cable
Workstation
In Diagram B, two Digi devices will replace modems on both sides of the
connection. The initiation of the connection occurs with either of the Digi
devices. If both ends are Digi devices, the TCP listening port number is
50001 for port 1. An example of the connection command is ATDT
192.168.25.30:50001. Upon establishing a successful TCP
connection, a CONNECT message is sent to the serial port and only then
does the Digi device server switch from AT command mode to data mode.
After the CONNECT is received, the transmi ssion of data begins. Using
the modem escape sequence or dropping DTR on either side terminates
the connection.
Modem emulation has the ability to communicate to an infinite number of
other devices.
Modem Emulation Cable Signals
Use the following signal assignments to make a cable connecting the Digi
device to a serial device.
Serial Device Digi Device
CTS (in) RTS (out)
RTS (out) CTS (in)
DSR (in) DSR (in)
DTR (out)
44 Chapter 7 Special Features: Modem Emulation
Page 45

Serial Device Digi Device
DCD (in) DTR (out)
TX (out) RX (in)
RX (in) TX (out)
GND GND
DSR and DTR on the serial device side are connected to the DSR signal of
the Digi device.
Scenarios for Modem Emulation
Outgoing Modem Emulation Connection
Serial device sends ATDx.x.x.x:y command, which triggers the device
server to establish a telnet connection to destination IP=x.x.x.x, port=y.
Incoming Modem Emulation Connection
A device on the network telnets to port 50001 (50000+1 = 1st serial port).
This incoming conn ection trig gers the device ser ver to gen erate a R ING on
the serial port. The device attached to the serial port will answer the RING
and the connection is established.
Modem Emulation Pooling
This is a combination of Incoming Modem Emulation Connection and a
hunt group. A device on the network telnets to port 50000. The device
server checks if a serial port configured for modem emulation is available.
If so, it connects to the port, otherwise returns an error.
Modem Emulation Bridge
A combination of Outgoing and Incoming Modem Emulation Connections,
in which both serial devices requir e to talk to a modem. The first serial
device telnets to the second device using ATDx.x.x.x:y, the second device
gets a RING and accepts the incoming telnet connect ion.
Originating, Answering, and Disconnecting Calls
In the following table, an application requests a TCP session with the Digi
device. The table displays the responses of the Digi device and application
as they negotiate a TCP connection.
Application AT Com-
mand
AT&F OK.
ATDT ipaddress:TCPport#
<P>+++<P> OK
Digi Device Server Response Notes
Receives request to start a
TCP session. CONNECT
115200.
AT command request to restore defaults to factory settings-Digi device server responds OK.
Request to start TCP session with IP address and TCP
port number of the Digi de vice serv er-Digi devi ce server
starts a TCP session
Escape sequence is sent <P> is Pause in seconds with
“+++” being the escape seq uen ce in ASCII c har acters Digi device server switches from AT command to data
mode
Chapter 7 Special Features: Modem Emulation 45
Page 46

Application AT Com-
mand
ATH NO CARRIER response sent
Digi Device Server Response Notes
Disconnect AT command is sent-Digi device server
responds with NO CARRIER
In the following table, the Digi device server receives a request for a
connection.
AT Command Digi Device Server Res pon se Notes
RING The Digi device server sends a Call Notification
Manual (ATA) or Auto Answer (ATS0=n) response-the
ATA (or ATS0=n) CONNECT 115200
NO CARRIER
Digi device server sends a CONNECT message when
the TCP session is started
The Digi device serve r sends a N O CARRIER me ssage
when the remote disconnects
Originating Calls
To send data to a Digi device server, enter the following information for
your application replacing the telephone number with the Digi device
server’s IP address and TCP port number. Enter the following command:
ATDT ipaddress:tcp_port#
an example is ATDT 146.135.13.5:50001
Answering Calls
The Digi device server listens on a pre-defined TCP port to receive data.
When the Digi device server receives a call notification (RING) through a
serial port to begin a TCP connection, it needs to reply with an ATA or a
pre-configured Auto-Answer to answer the call.
Note: The TCP ports assigned to the serial ports are as follows:
Serial port 1 listens on TCP port 50001
Serial port 2 listens on TCP port 50002
Serial port 3 listens on TCP port 50003
Serial port 4 listens on TCP port 50004
Disconnecting Calls
The TCP connection d isconn ects by either dropping the DTR si gn al o n the
serial port or sending the escape sequence <P>+++<P> to the Digi device
server. <P> represents a one se cond pause.
Disconnecting Calls-Digi Device Server
The Digi device sends a NO CARRIER response to the serial port when
the network connection is dropped.
Modem Emulation AT Command Set
AT
Command
ATA
46 Chapter 7 Special Features: Modem Emulation
Answer command: The Digi Device Server will go off hook and answer a
TCP connection request.
Function
Result
Code
Page 47

AT
Command
ATD<IP>:
<TCP
PORT>
Function
This command directs the Digi Device Server to go on-line, dial according to
the IP address entered as follow 191.1.2.3:12 and attempt to establish a
TCP connection. If no dial string is supplied, the Digi Device Server will
respond no dial tone.
Note: If the ATD command is issued before the S1 register has cleared, the
modem will respond with the NO CARRIER result code.
Dial Modifiers. The valid dial string parameters are described below. Punctuation characters may be used for clarity with parentheses, hyphen, and
spaces being ignored.
Result
Code
ATEn
ATH
ATIn
Command echo. The Digi Device Server enables or disables the echo of
characters to the DTE according to the parameter supplied. The parameter
value, if valid, is written to S14 bit 1.
E0 : Disables command echo
E1 : Enables command echo
Disconnect (Hang up) command
This command initiates a hang up sequence.
H0 : Disconnect the TCP session if the modem is currently on line.
H1 : If on-hook, the Digi Device Server will go off-hook and enter command
mode.
Identification command
I0 reports product code. Example: Digi Device server
I1 reports 255
I2 reports “OK”
I3 reports “OK”
I4 reports DIGI DS_TS
I5 reports “OK”
I6 reports “OK”
I7 reports “OK”
I8 reports “ERROR”
I9 reports “ERROR”
OK n=0 or 1
ERROR
Otherwise
OK n=0 or 1
ERROR
Otherwise
OK n=0 or 9
ERROR
Otherwise
Chapter 7 Special Features: Modem Emulation 47
Page 48

AT
Command
Function
ATLn Accepted but ignored.
ATMn Accepted but ignored.
ATNn Accepted but ignored.
Return to On-Line Data Mode.
This command determines how the modem will enter the on-line data mode.
If the modem is in the on-line command mode, the modem enters the online data mode. If the modem is in the off-line command mode (no connec-
ATOn
tion), ERROR is reported.
O0Enters on-line data mode. Handling is determined by the Call Establish-
ment task. Generally, if a connection exists, this command connects the
DTE back to the remote modem after an escape (+++).
O1Same as above
ATP Accepted but ignored.
Quiet Results Codes Control command.
The command enables or disables the sending of the result codes to the
ATQn
DTE according to the parameter supplied. The parameter value, if valid, is
written to S14 bit 2.
Q0 Enables result code to the DTE (Default).
Q1 Disables result code to the DTE
Read/Write S- Register.
ATSn
n Establishes S-register n as the last register accessed
n=v Sets S-Register n to the value v.
n? Reports the value of S-Register n.
ATT Accepted but ignored. .
Result Code Form. This command selects the sending of short-form or longform codes to the DTE. The parameter, if valid, is written to S14 bit 3.
ATVn
V0 Enables short-form (terse) result codes. Line feed is not issues before a
short-form result.
V1 Enables long-form (verbose) results codes (Default).
ATWn Accepted but ign ored.
ATXn A ccep ted but ign or ed.
ATYn A ccep ted but ign or ed.
ATZn Accepted but ignored. (Soft Reset and restore Profile).
DCD Option. The Digi Device Server controls the DCD output in accordance with the parameter supplied. The parameter value, if valid is written
AT&Cn
to S21 bit 5.
&C0 DCD remains ON at all times.
&C1 DCD follows the state of the connection
Result
Code
OK n=0 or 3
ERROR
Otherwise
OK n=0 or 3
ERROR
Otherwise
OK n=0 or 1
ERROR
Otherwise
OKn = 0 or 1 and
a connection
exists.
ERROR
Otherwise or if
not connected.
OK
OK n=0 or 1
ERROR
Otherwise
OK
OK n=0 or 1
ERROR
Otherwise
OK n=0 to 3
ERROR
Otherwise
OK n=0 to 3
ERROR
Otherwise
OK n=0 or 1
ERROR
Otherwise
OK n=0 or 1
ERROR
Otherwise
OK n=0 or 1
ERROR
Otherwise
48 Chapter 7 Special Features: Modem Emulation
Page 49

AT
Command
DTR Option. This command interprets the ON to OFF transition of the DTR
signal from the DT E in ac cord anc e wit h th e par am eter supp lie d. Th e p aram eter value, if valid, is written to S21 bits 3 and 4. Also see S25.
&D0 -DTR is ignored (assumed ON). Allows operation with DTEs which
do not provide DSR.
AT&Dn
AT&Fn
AT&Jn Accepted but ignored.
AT&Gn Accepted but ignored.
AT&Jn Accepted but ignored.
AT&Kn
AT&Ln Accepted but ignored.
AT&Mn Accepted but ignored.
AT&Pn Accepted but ignor ed.
AT&Qn Accepted but ignored.
&D1DTR drop is interpreted by the modem as if the asynchronous escape
sequence had been entered. The modem returns to asynchronous command state without disconnecting.
&D2DTR drop causes the modem to hang up. Auto-answer is inhibited.
(Default.)
&D3DTR drop causes the modem to perform a soft reset as if the Z command were received. The &Y setting determines which profile is loaded.
Restore Factory Configuration (Profile)
The Device Server loads the factory default configuration (profile). The fac-
tory defaults are identified for each command and in the S-Register descriptions. A configuration (profile) consists of a subset of S-Registers.
&F0Restore factory configuration 0.
&F1Restore factory configuration 1.
Flow control. This command defines the DTE/DCE flow control mechanism.
The parameter value, if valid, is written to S39 bits 0, 1, and 2.
&K0 Disables flow control
&K3 Enables RTS/CTS flow control (Default)
&K4 Enables XON/XOFF flow control
&K5 Enables transparent XON/XOFF flow control
&K6 Enables both RTS/CTS and XON/XOFF flow control.
Function
Result
Code
OK n=0 to 3
ERROR
Otherwise
OK n=0 or 1
ERROR
Otherwise
OK n=0 or 1
ERROR
Otherwise
OK n=0 or 1
ERROR
Otherwise
OK n=0 or 1
ERROR
Otherwise
OK n=0,3,4,5,or 6
ERROR
Otherwise
OK n=0, 1, 2
ERROR
Otherwise
OK n=0, 1, 2
ERROR
Otherwise
OK n=0, 1, 2
ERROR
Otherwise
OK n=0 to 8
ERROR
Otherwise
Chapter 7 Special Features: Modem Emulation 49
Page 50

AT
Command
Function
RTS/CTS Option
This selects how the Digi Device Server controls CTS. CTS is modified if
hardware flow control is selected (see &K command). The parameter value,
if valid, is written to S21 bit2.
&R0CTS reflects the ability of the modem to transmit data. For example,
AT&Rn
CTS will drop during retrains. In sync mode, CTS tracks the state of RTS;
the RTS-to-CTS delay is defined by S26. In async mode, CTS is normally
ON and will turn OFF only if required by flow control.
&R1CTS forced on (default). In sync mode, CTS is always ON (RTS transitions are ignored). tracks the state of RTS. In async mode, CTS is normally
ON and will turn OFF only if required by flow control.
&R2CTS follows RTS.
DSR Override
This command selects how the modem will control DSR. The parameter
AT&Sn
value, if valid, is written to S21 bit 6.
&S0DSR will remain ON at all times. (Default.)
&S1DSR will become active after answer tone has been detected and inac-
tive after the carrier has been lost.
AT&Tn Accepted but ignored.
AT&V
Display Current Configuration and Stored Profiles
There is no NVRAM support currently.
AT&Vn Accepted but ignor ed.
AT&V6 Display current IP settings of the Device Server
AT&Wn Accepted but ignored.
AT&Xn Accepted but ignor ed.
AT&Yn Accepted but ignor ed.
AT&Zn
&Zn=x - Store Telephone Number.
Currently not supported
AT\An Accepted but ign or ed.
AT\Gn Accepted but ignored.
AT\Kn Accepted but ign or ed.
Result
Code
OK n=0 or 1
ERROR
Otherwise
OK n=0 or 1
ERROR
Otherwise
OK n= 0
ERROR
Otherwise
OK
OK n=0 to 5
ERROR
Otherwise
OK
OK n=0 or 1
ERROR
Otherwise
OK n=0 or 1
ERROR
Otherwise
OK n=0 or 1
ERROR Otherwise
OK n=0 or 3
ERROR
Otherwise
OK n=0 to 3
ERROR
Otherwise
OK n=0 or 1
ERROR
Otherwise
OK n=0 to 5
ERROR
Otherwise
50 Chapter 7 Special Features: Modem Emulation
Page 51

AT
Command
Operating Mode
This command controls the preferred error correcting mode to be negotiated
in a subsequent data connection.
\N0 Selects normal speed buffered mode
AT\Nn
AT\Vn Accepted but ign or ed.
AT+MS Accepted but ignored.
AT+MI Accepted but ign or ed.
AT%Cn Accepted but ignored.
\N1 Serial interface selected - Selects direct mode
\N2 Accepted but ignored.
\N3 Accepted but ignored.
\N4 Accepted but ignored.
\N5 Accepted but ignored.
Function
Result
Code
OK n=0 to 5
ERROR
Otherwise
OK n=0 or 1
ERROR
Otherwise
OK
OK
OK n=0 to 3
ERROR
Otherwise
Chapter 7 Special Features: Modem Emulation 51
Page 52

S-Registers
Register Function Range Units Saved Default
Rings to Auto-Answer
S0
S1
S2
S3
S4
S5
S6 Accepted but ignored. 2-255 s * 2
S7 Accepted but ignored. 1-255 s * 50
S8 Accepted but ignored. 0-255 s * 2
S9 Accepted but ignored. 1-255 0.1 s * 6
S10 Accepted but ignored. 1-255 0.1 s * 14
S11 Accepted but ignored. 50-255 0.001 s * 95
S12
Sets the number of rings required before the
Digi Device Server automatically answers a
call. Setting this register to Zero disables autoanswer mode.
Ring Counter
S1 is incremented each time the modem
detects a ring signal on the telephone line. S1
is cleared if no rings occur over an eight second interval.
Escape Character
S2 holds the decimal value of the ASCII char-
acter used as the escape character. The
default value corresponds to an ASCII ’+’. A
value over 127 disables the escape process,
i.e., no escape character will be recognized.
Carriage Return Character
Sets the command line and result code termi-
nator character. Pertains to asynchronous
operation only.
Line Feed Character
Sets the character recognized as a line feed.
Pertains to asynchronous operation only. The
Line Feed control character is output after the
Carriage Return control character if verbose
result codes are used.
Backspace Character
Sets the character recognized as a backspace.
Pertains to asynchronous operation only. The
modem will not recognize the Backspace character if it is set to a value that is greater than 32
ASCII. This character can be used to edit a
command line. When the echo command is
enabled, the modem echoes back to the local
DTE the Backspace character, an ASCII space
character and a second Backspace character;
this means a total of three characters are transmitted each time the modem processes the
Backspace character.
Escape Prompt Delay
Defines the maximum period, in fiftieths of a
second, allowed between receipt of the last
character of the three escape character
sequence from the DTE and sending of the OK
result code to the DTE. If any characters are
detected during this time, the OK will not be
sent. Note that sending of the OK result code
does not affect entry into command mode.
0-255 Rings * 0
0-255 Rings 0
0-255 ASCII * 43
0-127 ASCII 13
0-127 ASCII 10
0-32 ASCII 8
0-255 0.02 s * 50
52 Chapter 7 Special Features: Modem Emulation
Page 53

Register Function Range Units Saved Default
S13 Reserved - - -
General Bit Mapped Options Status
Indicates the status of command options.
Default:138 (8Ah) (10001010b)
Bit 0This bit is ignored.
Bit 1Command echo (En)
0 =Disabled (E0)
1 =Enabled (E1) (Default.)
Bit 2Quiet mode (Qn)
0 =Send result codes (Q0) (Default.)
1 =Do not send result codes (Q1)
S14
S15 Reserved - - S16 Accepted but ignored. - - 0
S17 Reserved - - S18 Accepted but ignored. 0-255 s * 0
S19 Accepted but ignored. - - 0
S20 Accepted but ignored. 0-255 - * 0
Bit 3Result codes (Vn)
0 =Numeric (V0)
1 =Verbose (V1) (Default.)
Bit 4Reserved
Bit 5Tone (T)/Pulse (P)
0 =Tone (T) (Default.)
1 =Pulse (P)
Bit 6Reserved
Bit 7Originate/Answer
0 =Answer
1 =Originate (Default.)
*
138
(8Ah)
Chapter 7 Special Features: Modem Emulation 53
Page 54

Register Function Range Units Saved Default
General Bit Mapped Options Status
Indicates the status of command options.
Default:52 (34h) (00110100b)
Bit 0Set by &Jn command but ignored otherwise.
0 =&J0 (Default.)
1 =&J1
Bit 1Reserved
Bit 2CTS behavior (&Rn)
0 =CTS tracks RTS (&R0)
1 =CTS always on (&R1) (Default.)
Bits 3-4DTR behavior (&Dn)
S21
S22 Accepted but ignored. - - *
0 =&D0 selected
1 =&D1 selected
2 =&D2 selected (Default.)
3 =&D3 selected
Bit 5RLSD (DCD) behavior (&Cn)
0 =&C0 selected
1 =&C1 selected (Default.)
Bit 6DSR behavior (&Sn)
0 =&S0 selected (Default.)
1 =&S1 selected
Bit 7Long space disconnect (Yn)
0 =Y0 (Default.)
1 =Y1
- - * 52 (34h)
117
(75h)
54 Chapter 7 Special Features: Modem Emulation
Page 55
Register Function Range Units Saved Default
General Bit Mapped Options Status
Indicates the status of command options.
Default:62 (3Dh) (00111110b)
Bit 0Grant RDL
0 =RDL not allowed (&T5) (Default.)
1 =RDL allowed (&T4)
Bits 1-3DTE Rate
0 =0 - 300 bps
1 =600 bps
2 =1200 bps
S23
S24 Accepted but ignored. 0-255 s * 0
S25
S26
S27 General Bit Mapped Options Status - - * 73 (49h)
S28 Accepted but ignored. - - * 0
S29 Accepted but ignored. 0-255 10 ms 70
S30 Accepted but ignored. 0-255 10 s 0
S31 Accepted but ignored. - - *
S32 XON Character 0-255 ASCII 17 (11h)
S33 XOFF Character 0-255 A SCII 19 (13h)
S34 S35 Reserved - - S36 Accepted but ignored. - - * 7
3 =2400 bps
4 =4800 bps
5 =9600 bps
6 =19200 bps
7 =38400 bps or higher (Default.)
Bits 4-5Assumed DTE parity
0 =even
1 =not used
2 =odd
3 =none (Default.)
Bits 6-7not action applied
Delay to DTR Off
Sets the length of time that the modem will
ignore DTR for taking the action specified by
&Dn. Its units are seconds for synchronous
modes and one hundredths of a second for
other modes
RTS-to-CTS Delay
Sets the time delay, in hundredths of a second,
before the modem turns CTS ON after detecting an OFF-to-ON transition on RTS when &R0
is commanded. Pertains to synchronous operation only.
0-255
0-255 0.01 s 1
s or
0.01 s
*
5
62
(3Dh)
194
(C2h)
Chapter 7 Special Features: Modem Emulation 55
Page 56
Register Function Range Units Saved Default
General Bit Mapped Options Status
Telnet support for modem emulation.
Default:0
Bit 0-1 Send TCP transmit data timer
0 = 100ms
1 = 200 ms
2 = 300 ms
3 = 500 ms
Bits 2-3 Service TCP transmit data watermark
0 = 256
1 = 512
2 =768
S37
3 =1024
Bits 4-5 Se rvice TCP receive dat a watermark
0 = 256
1 = 512
2 =768
3 =1024
Bits 6-7 Telnet support (RFC 2217)
0 = Disabled
1 = Receive Telnet support enabled
2 = Transmit Telnet support enabled
3 = Receive and Transmit Telnet support
enabled
--*0
S38 Accepted but ignored. 0-255 s 20
Flow Control Bit Mapped Options Status
Default:3 (00000011b)
Bits 0-2Status of command options
0 =No flow control
S39
S40 Accepted but ignored. - - *
S41 Accepted but ignored. - - *
S42 - S45 Reserved - - -
S46 Accepted but ignored. - - * 138
S48 Accepted but ignored. - - * 7
S82 Accepted but ignored. - -
S86 Accepted but ignored. 0-255 - -
3 =RTS/CTS (&K3) (Default.)
4 =XON/XOFF (&K4)
5 =Transparent XON (&K5)
6 =Both methods (&K6)
Bits 3-7Reserved
--*3
104
(68h)
195
(C3h)
128(40h)
56 Chapter 7 Special Features: Modem Emulation
Page 57

Register Function Range Units Saved Default
10
S91 Accepted but ignored. 0-15 dBm
S92 Accepted but ignored. 0-15 dBm
S95 Accepted but ignored. - - * 0
* Register value may be stored in one of two user profiles with the &W command.
(Country
dependent)
10
(Country
dependent)
Result Codes
Short Long Form Short Long Form Short Long Form
0OK 13
1CONNECT
2RING
3 N O CARRIER
4 ERROR
5
6 N O DIALTONE
7BUSY
8 NO ANSWER
9
10
11
12
CONNECT
1200
CONNECT
0600
CONNECT
2400
CONNECT
4800
CONNECT
9600
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
59
61
62
63
64
CONNECT
7200
CONNECT
12000
CONNECT
14400
CONNECT
19200
CONNECT
38400
CONNECT
57600
CONNECT
115200
CONNECT
230400
CONNECT
16800
CONNECT
21600
CONNECT
24000
CONNECT
26400
CONNECT
28800
84
91
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
CONNECT
33600
CONNECT
31200
CONNECT
32000
CONNECT
34000
CONNECT
36000
CONNECT
38000
CONNECT
40000
CONNECT
42000
CONNECT
44000
CONNECT
46000
CONNECT
48000
CONNECT
50000
Chapter 7 Special Features: Modem Emulation 57
Page 58

58 Chapter 7 Special Features: Modem Emulation
Page 59

Chapter 8
Serial Power Feature
Special Features: Power Over the Serial
The Serial Power feature available for the Digi One TS, PortServer TS 2
MEI, and PortServer TS 4 MEI allows the Digi device to power a serial
device (power out) or use a serial device to power the Digi device (power
in). The advantage of this feature is to eliminate an external power supply.
Power out is available on all ports through Ring Indicator (RI) or Data
Terminal Ready (DTR). Power in is availab le only through RI and only on
port one (1). The Seri al Power fe ature is ac tive on a spec ific port whe n that
port is configured for RS 232 operation.
Ports
• The power out budget equals one (1) watt (the total amount of
power available). The available pow er c an be divided in any combination between the ports but the following rules must be observed:
— RI = 5 volts @ up to 200 mA (max)
— DTR = 9 volts @ up to 100 mA (max)
— You may use DTR or RI as the source of power (power out) on
any port but you may not use bot h DTR a nd RI on the same po rt.
• Pinout information
Configuring RI Power
RI Power In
Ring Indicator (RI) power in accepts power into the Digi device server only
on port one. Power in is availabl e using the RI pin . The Digi device r equires
power in the range of 9-30 VDC @ 525mA (max). Ports 2, 3, and 4 can still
supply power to a serial device through the RI or DTR pins for each port.
When using power in through the RI, the external power supplies (both
powered Ethernet and the barrel connector power supply) are inoperative.
Altpin will not work for RI power in.
— RI is pin 1
—DTR is pin 9
• RI signaling is lost when the pin is used for power
Chapter 8 Special Features: Power Over the Serial Ports 59
Page 60

1. Open the device unit enclosure and move the black jumper to the
ill
following settings:
P-6 jumper on pins 1 and 2
Note: When the jumper is
placed correctly for
power in, the jumper w
set on the pins closest
to the edge of the
board. The left arrow
indicates the open pin
and the right arrow is
pointing to the jumper.
2. Close the device unit enclosure.
RI Power Out
Ring Indicator (RI) power out is available on all ports. The total power
budget for this featu re is one (1 ) watt not to exceed 5 volt s @ up to 200mA
on any single port. The following procedure assumes the unit will only be
used for RI power out.
1. Set the port DIP switches to the following place s: sw i tch 1 an d 3 are up
and 2 and 4 are do wn (see "Serial Power Table" on page 61 for
illustration).
2. Enable the RI power through the web interface.
3. Connect power su pply with the bar rel-connect or power sup ply provid ed
with the device or use powered Ethernet.
Note: If the unit will be used with RI power in (port 1 only), set the jumper to the
Configuring DTR Power
Power Out
Data Terminal Ready (DTR) power out is the factory default on the Digi
device server. Total power budget for th is feature is one w att no t to exce ed
9 volts @ up to 100mA to any single port.
1. Set the port DIP switches to EIA 232 (switch 1 is up, 2,3, and 4 are
down) to enable DTR power.
following setting:
P-6 jumper on pins 1and 2
and do not use an external power source. Port 1 cannot be used for both
power in and power out.
60 Chapter 8 Special Features: Power Over the Serial Ports
Page 61

2. Open the port and set DTR high.
Note Here are the pins to verify
the jumper position. The
default position has the
jumper on the two pins
furthest from the edge. DO
NOT MOVE THE JUMPER
FROM THE DEFAULT
UNLESS USING RI POWER
IN.
Serial Power Table
If you are havi ng trouble with your unit after using the Power over port
feature, you may have tripped the circuit breaker in the unit. You can
identify this by the RI or DTR signal indicators found in the System
Information under Administrat i on on the main menu in the web interface.
Click the port number using serial power. (Remember serial power out is
unavailable if the MEI settings are not 232.)
Under serial power will be a message if the breaker is tripped. Follow the
instructions to reset.
From the command line use the two examples below for additional
information.
display circuitbreaker
Display the status of the circuit breaker
set configuration circuitbreaker=reset
Reset the circuit breaker
Note: set configuration print will also give the status of the circuitbreaker state.
Use this table for summary information for a serial power setup.
Chapter 8 Special Features: Power Over the Serial Ports 61
Page 62

.
Quick Summary
Table for Setup of
Serial Power
Switch Settings
DTR setting DTR ON DTR OFF DTR OFF
Ports Allowed 1, 2, 3, 4
Jumper Pin Settings
Power Budget
DTR Power RI Power
OUT OUT IN
1*, 2, 3, 4
*unless port 1 is used
for power in
P-6 jumper on pins
2 & 3
(Factory Default)
9v @ up to 100mA
one watt
P-6 jumper on pins
2 & 3
(Factory Default)
5v @ up to 200 mA
one watt
1
P-6 jumper on pins
1 & 2
9 -30 v @ up to
525mA (max)
62 Chapter 8 Special Features: Power Over the Serial Ports
Page 63

Chapter 9
Special Features: IA (Industrial
Automation)
Industrial Automation (IA) uses the Modbus protocol that defines how
devices in an IA environment communicate. It specifies that a controlling
unit, called a master, manages one or more units, called slaves. Only the
master may initiate communication, and slaves may only respond.
Some of the element s of communication between devices that are defin ed
by the Modbus protocol include:
• The structure of Modbus messages
• How the mast er requests infor m ation from the slave or specifies an
action for the slave to ta ke
• How the sla ve is to respond
• Addressi ng conventions
• Handling of many of th e other det ails req uired for communicati on to
occur.
Modbus defines two encod ing schemes: M odbus AS CII an d Modb us RT U.
Each Modbus device uses one or the other.
Designed to function over a serial commu nication cab le, Modbus ha s been
extended in rec ent years to fu nction over an Ethernet network using
Modbus/TCP, which defines a method of encapsulating Modbus ASCII or
Modbus RTU messages in IP packets for transport over the network.
The extermely flexible Digi implementation includes support for Modbus
ASCII, Modbus RTU, Modbus/TCP, and two other methods of transport
over a network, TCP socket and UDP socket communication. The
implementation enables multiple net w ork-based masters to concurrently
initiate communica tion w ith se r ial -b ase d sl a ves u si ng an y of th e su pp or ted
network prot ocols.
Configuring Industrial Automation with Modbus
1. Click Serial Port > Change profile and select Industrial Automation.
2. Click Apply.
3. Under Profile settings, click change protocol.
4. Select the protocol that be st matches your environment (master or
slave) Use the Help button for additonal information.
5. Enter the User defined protocol settings (Start delimiter, end delimiter,
Message timeout, and Process ANSI escape characters) and click
Apply.
6. Click Packet Routing > Add.
7. Enter the packet routing information. Click the Help button for additional
information.
Note: Configure the serial port for the serial communication parameters (baud rate,
Chapter 9 Special Features: IA (Industrial Automation) 63
data bits, parity and stop bits) required by the connected IA device. If you
configure the port for a slave, you do not have to configure a network-based
master. Communication with the master just works. (If the master is
Page 64

connected to a serial port, it must be configured, however.) If you configure a
port for a master and the slaves are located on the network, TCP sockets,
UDP sockets, and Modbus/TCP are all supported. Use the protocol required
by the master.
64 Chapter 9 Special Features: IA (Industrial Automation)
Page 65

Chapter 10
This chapter describes the configuring SNMP, the network management
protocol that governs the exchange between nodes and stations.
About SNMP and the Device Server Agent
This section introduces SNMP and network management in TCP/IP
networks and it describes the d evice server agent. It discusses the
following:
• Network management components
• SNMP agent
•SNMP traps
• MIB support of the device server agent
• Support traps of the device server agent
Network Management Components
The TCP/IP network management architecture contains the following
components:
• Managed nodes such as host systems, routers, terminal and com-
munications servers (such as device server) and other network
devices.
Special Features: SNMP
• One or more network manager s (also called network manag ement
stations), which are the points from which the network is m anaged
• Agents that reside on managed nodes and retr ieve management
information and communicate this information to network managers.
• The network management protocol, SNMP, which governs the
exchange of inf ormation between the nodes and stations.
• Management information, which is the database of information
about managed objects. This database is called the management
information base (MIB ).
SNMP Management Agent
Each managed node contains at least one agent—a component that
responds to requests from the network manager—that retrieves network
management information from its node and notifies the manager when
significant events occur.
SNMP Traps
A mechanism defin ed by SNMP i s called a tr ap, which is a report or “a larm”
from a managed node to an SNMP manager that a significant event has
occurred.
MIB Support
The SNMP management agent supports the following MIBs:
Chapter 10 Special Features: SNMP 65
Page 66

• Read-write for MIB II (RFC 1213), which is an Internet-standard
MIB, consisting of managed ob jects from the systems, inte rfaces, IP,
ICMP, TCP, UDP, transmission, and SNMP group
• Read-write for the characte r-st ream d evice s usi ng SMIv2 MIB (RFC
1658)
• Read-write for the RS-232-like hardware devices MIB (RFC 1659)
• Read-write for the device server IP Network Control Protocol of the
Point-to-Point Protocol MIB (RFC 1473)
Message Support
The SNMP agent supports the Set, Get, GetNext, and Trap messages as
defined in RFC 1157. These messages are used as follows:
• Set, which means set the value of a specific object from one of the
supported MIBs
• Get, which means retrieve the value of a specific object form one of
the supported MIBs
• GetNext, which means retrieve the value of the next object in the
MIB
• Trap, which means send traps to the manager when a particular
type of significant event occurs
Supported Traps
The agent can send traps when any of the following occur:
• Cold starts (d evi ce ser ver initi a lizes)
• Authentication failures
• Login attempts
Configuration Procedure: Web Interface
1. Click SNMP under System from the menu.
2. Fill in the configuration fields and click Apply to save settings.
3. Click Reboot for changes to take effect.
66 Chapter 10 Special Features: SNMP
Page 67

Chapter 11
This chapter describes configuration-management activities, including
firmware upgrades and restoring the device configuration to defaults.
Upgrading the Firmware
Firmware upgrades can be performed from the web interface, using HTTP
or FTP.
HTTP or TFTP Upgrade Procedure
If your hardware is okay, make sure you are running the latest firmware
version available. Check the Digi Support site for the latest firmware and/or
POST updates for your device:
http://ftp.digi.com/support/firmware
1. Download a copy of the firmware file.
2. Access the Digi device server’s web interface by entering the Digi
device server’s IP address in a browser’s URL window and log on (User
Name root, Password dbps).
3. Choose Update Firmware under Administration from the main menu.
4. Browse to the location on your system where the firmware has been
saved, select the correct file, and click Update.
Do not leave
your
browser until
you are
prompted to
reboot.
5. Reboot the device when prompted.
6. Access the Digi device server’s web interface and verify on the
Information Page that the Firmware version has been successfully
updated.
Configuration Management
Copying the Configuration to and from a Remote Host
You can copy the configuration to a remote host and from a remote host,
which means you can configure the Digi device remotely by entering
commands in a text file and then copying the file to the Digi device.
When To Use Remote Configuration
Typically, you use remote configuration when you have several device
servers with simila r configura tions and w ant to ke ep a mas ter configu ration
on a remote host, from which you can easily create variations for
downloading to individual device servers.
Download Procedure
1. Access the web interface by entering the device server IP address in a
browser’s URL window.
2. Log on to the device server as root. The default password is dbps.
3. From the main menu, choose Backup/Restore > Backup File.
4. Enter the location to save the file and click Save.
5. Access the device to configur e.
6. Click Backup/Restore > Restore.
Chapter 11 Configuration Management 67
Page 68

7. Enter the location of the configuration file saved in step 4 and click Open.
TFTP Procedure
1. Ensure that TFTP is running on the remote host.
2. Access the web interface by entering the device server IP address in a
browser’s URL window.
3. Log on to the device server as root. The default password is dbps.
4. From the main menu, choose Backup/Restore >
5. Enter the name of the file and the IP address of the TFTP server and
click Backup (to save the file) or Restore to apply the file.
Resetting Configuration to Defaults
To reset the configuration to defaults, follow these steps:
Note: The reset procedure causes the Digi device to lose all configuration changes.
If you have a complex configuration, contact Digi before performing for
information on saving your configuration. See "Reference and Certifications"
on page 69 for information.
1. Use a pen, the point of a paper clip, or some other device to press the
recessed button on the front panel.
2. While holding down the button, power on the Digi dev i ce.
3. When the 1-5-1 LED pattern is displayed, release the button.
Note: It may take approximately two minutes for the device to boot up.
The device boots up.
TFTP Server.
68 Chapter 11 Configuration Management
Page 69

Chapter 12
Interpreting the LEDs
LEDs
Reference and Certifications
LED Color St ate Indicates
On Power detected
Waiting for an IP
address
Starting the TFTP
process
Configuration returned
to factory defaults
Signal strength relates
to brightn ess or
dimness of the light
Physical network
detected
No physical network
detected
Power
Radio
Signal
Strength
Status
(Link)
ACT Yellow
Green
(labeled PWR)
Yellow Varying brightness
Green
Steady blinking
Blinking 1-1-1 Starting the EOS
Blinking 1-3-1
Blinking 1-5-1
Off No power detected
On
Off
On Bad initialization
Off Ready
Blinking Network activity
LED Diagnostics
LED Activity Indication
1-1-1 pattern Starting the EOS.
1-3-1 pattern TFTP boot process started.
1-5-1 pattern
9-1-1 pattern
Steady blinking Device seeking an IP address from DHCP server.
Solid
Tells you that configuration has been return to the factory
configuration. See "Configuration Management" on page
67.
Contact Tech Support for help.
1-952-912-3444 or outside the U.S. (+011) 952-912-3444
On Digi One RealPort and PortServer TS 2/4 devices, this
means the boot completed sucessfully.
Chapter 12 Reference and Certifications 69
Page 70

Device EIA 232/422/485 Switch Settings
Note: MEI Switch settings apply only to Digi One TS, PortServer TS 2/4 MEI, and
EIA-232 Up Down Down Down
EIA-422/485 Full-duplex Down Up Down If up, termination.
EIA-485 half-duplex Down Down Up
RJ-45 Pinouts
the Wireless Family.
Switch Settings
Function
1 2 3 4
If down,
no termination
Safety Statements
RJ-45
Pin
1 RI TxD- TxD2 DSR RxD- RxD3RTS RTS+ NA
4 GND GND GND
5 TxD TxD+ TxD+
6 RxD RxD+ RxD+
7SG SG SG
8CTS CTS+ NA
9DTR RTS- NA
10 DCD CTS- NA
PortServer TS 8/16
EIA-232
EIA-422/485
Full-Duplex
EIA-485 Half-
Duplex
WARNING: To prevent electric shock, do not remove the cover of this
module while unit is powered up. There are no user-serviceable parts
inside. Refer servicing to qualified personnel.
CAUTION: This unit has two power inputs. For total isolation from electrical
shock and energy hazard, disconnect both power inputs. The device is
intended to be mounted in an indoor only type system.
70 Chapter 12 Reference and Certifications
Page 71

Rack Mounting Installation (PortServer TS 16 Rack and DC Rack)
• Distribute weight evenly in the rack to avoid overloading.
• Ensure proper venti l atio n w ith at least 12 inches ( 30 cen ti mete rs) o f
clearance on all sides.
• Check equipment nameplate ratings before connecting to the supply
circuit to avoid over loads which may dama ge over-current protection
devices and supply wiring.
• Maintain reliable earthing for rack-mounting equipment, especially
for supply connections.
• Install equipment in Restricted Access Areas only (dedicated
equipment rooms/closets) in accordance with Articles 110-16,
110-17, and 110-18 of the National Electrical Code, ANSI/NFPA 70.
• Connect equipment to a DC supply source (reliably earthed) that is
electrically isolated from the AC source.
• Directly connect the equipment chassis to the DC supply system-
grounding electrode conductor or a bonding jumper from a
grounding terminal bar (or bus) th at is connected to the DC supply
system grounding electrode conductor.
• Contain equipment that has a connection between the grounded
conductor of the same DC supply circuit, the grounding conductor,
and also the point of grounding of the DC system in the same
immediate area. Do not ground the equipment elsewhere.
• Locate the DC supply source within the same premises as the
equipment.
• Route away and secure all DC input wiring from sharp edges to
prevent chaffing as well as provide strain relief.
Provide a readily accessible dis connect device and protective device a
fixed wiring for a DC power supply suitable for the specified rated voltage
and current. Disconnect and protective devices to be rated 2A Amps
maximum.
PortServer TS 1/3 + Modem
To avoid contact with electrical current:
• Never install electrical wiring during an electrical storm.
• Never install telephone jacks in wet locations unless that jack is
specifically designed for wet locations.
• Use caution when installing or modifying telephone lines.
• Use a screwdriver and other tools with insu lated handles.
• You and those around you should wear safety glasses or goggles.
• Do not place telephone wiring or connections in any conduit, outlet
or junction box containing electrical wiring.
Chapter 12 Reference and Certifications 71
Page 72

Do not work on your telephone wiring if you wear a
Important!
pacemaker. Telephone lines carry electrical current.
• Installation of inside wire may bring you close to electrical wire,
conduit, terminals and other electrical facilities. Extreme caution
must be used to avoid el ectrical shock from su ch facilitie s. You must
avoid contact with all such facilities.
• Telephone wiring must be at least 6 feet fr om bare power wirin g or
lightning rods and associated wires, and at least 6 inches from other
wire (antenna wires, door bell wires, wires fr om transformers to ne on
signs), steam or hot water pipes, and heating ducts.
• Before working with existing inside wiring, check all electrical outlets
for a square telephone dial light transformer and unplug it from the
electrical outlet. Failure to unplug all telephone transformers can
cause electrical shock.
• Do not place a jack where it would allow a person to use the
telephone while in a bathtub, shower, swimming pool, or similar
hazardous location.
• Protectors and grounding wire placed by the service provider must
not be connected to, removed, or modified by the customer.
Specifications
PortServer TS 8/16
2-contact barrel
connector
Environmental PortServer TS 8 PortServer TS 16
Ambient
temperature
Relative
humidity
Do not touch uninsulated telephone wiring if lightning is
likely!
External Wiring
Any external communication s wiring you may insta ll needs to
be constructed to all relevant electrical codes. In the United
States this is the National Electrical Code Article 800.
Contact a licensed electrician for details.
Power Requirements
(Standard Models)
+9 to +30 VDC 525 mA (max) external power
supply
0 to 50° Celsius
32 to 131° Fahrenheit
5% to 90% non-condensing
72 Chapter 12 Reference and Certifications
Page 73

Altitude
Mechanical PortServer TS 8 PortServer TS 16
0 to 12,000 feet
0 to 3,658 meters
Length
Width
Height
Weight
Digi One TS Wireless, PortServer TS 2/4 Wireless
2-contact barrel
connector
Ambient
temperature
Relative
humidity
21.08 centimeters
8.3 inches
9.4 centimeters
3.7 inches
2.54 centimeters
1 inches
.227 Kilos
3.05 lbs
Power Requirements
(Standard Models)
+9 to +30 VDC 525 mA (max)
external power supply
Environmental
0 to 50° Celsius
32 to 131° Fahrenheit
5% to 90% non-condensing
34.04 centimenters
13.4 inc hes
16.76 centimenters
6.6 inches
4.06 centimenters
1.6 inches
2.4 Kilos
5.3 lbs
Altitude
Length
Width
Height
Weight
0 to 12,000 feet
0 to 3,658 meters
Mechanical
13.31 centimeters
5.42 inches
8.46 centimeters
3.3 inches
2.42 centimeters
.952 inches
64 grams
2.25 ounces
Chapter 12 Reference and Certifications 73
Page 74

PortServer TS 2/4 MEI, Digi One TS
Power Requirements
(Standard Models)
2-contact barrel
connector
+9 to +30 VDC 525 mA (max)
external power supply
Environmental
Ambient
temperature
Ambient
temperature for
TS H models
Relative
humidity
Altitude
Length
Width
Height
Weight
0 to 50° Celsius
32 to 122° Fahrenheit
-35 to 70° Celsius
-31 to 158° Fahrenheit
5% to 90% non-condensing
0 to 12,000 feet
0 to 3,658 meters
Mechanical
13.31 centimeters
5.42 inches
8.46 centimeters
3.3 inches
2.42 centimeters
.952 inches
64 grams
2.25 ounces
PortServer TS 2/4
Power Requirements
(Standard Models)
2-contact barrel
connector
Ambient
temperature
Ambient
temperature for
TS H models
Relative
humidity
74 Chapter 12 Reference and Certifications
+9 to +30 VDC 525 mA (max)
external power supply
Environmental
10 to 55° Celsius
50 to 131° Fahrenheit
-25 to 70° Celsius
-13 to 158
5% to 90% non-condensing
Page 75

Altitude
0 to 12,000 feet
0 to 3,658 meters
Mechanical
Length
Width
Height
Weight
PortServer TS 1/3 + Modem
13.31 centimeters
5.42 inches
8.46 centimeters
3.3 inches
2.42 centimeters
.952 inches
64 grams
2.25 ounces
• ITU-T V.92/V.90/56K (-92 build option)
• V.3 4/V.33. 6 (-34 build option
• V.32 bis/14.4K (-32 build option)
• V.22 bis/2400 baud (-22 build option)
•V.22
•V.23
•V.21
• Bell 212A and Bell 103
• V.44 Error Correction
• V.42 LAP M, MNP 2-4 Error Correction
• V.42 bis and MNP Class 5 data compression
Chapter 12 Reference and Certifications 75
Page 76
Regulatory Notices
PortServer 1/3 + Modem
Electromagnetic
Emissions
• FCC Part 15 Subpart B, Class B
• EN55022 Class B
• AS /NZS 3548
• VCCI
• EN61000-3-2
• EN61000-3-3
Electromagnetic
Immunity
Safety
Power Supply • 9-30 Vdc 50/60 Hz @ 15 W
Digi One RealPort, Digi One TS, PortServer TS 2/4,
PortServer TS 2/4 MEI, PortServer TS 16
Emission
Immunity • EN55024:1998
Safety
• EN55024:1998
• UL/CUL 60950-1
• IEC60950
• EN60950
• FCC P15 Subpart B, Class B
• ICES-003, Class B
• EN55022:1994, Class B
• AS/NZS 3548
•VCCI
• EN61000-3,2:2000
• EN61000-3-3:1995
• UL60950-1
• CSA 22.2 No. 60950-1-03
• IEC60950
• EN60950
Power Supply • 9-30 Vdc 50/60 Hz @ 15 W
Digi One TS Wireless, PortServer TS 2/4 Wireless
• FCC P15 Subpart B, Class B
• ICES-003, Class B
• EN55022:1994, Class B
Emission
Immunity
76 Chapter 12 Reference and Certifications
• AS/NZS 3548
•VCCI
• EN61000-3,2:2000
• EN61000-3-3:1995
• EN55024:1998
• EN 301 489-3
Page 77

Digi One TS Wireless, PortServer TS 2/4 Wireless
• UL60950-1
Safety
Power Supply • 9-30 Vdc 50/60 Hz @ 15 W
Emission
Immunity • EN55024:1998
Safety
• CSA 22.2 No. 60950-1-03
• IEC60950
• EN60950
PortServer TS 8
• FCC P15 Subpart B, Class A
• ICES-003, Class A
• EN55022:1994, Class A
• AS/NZS 3548
•VCCI
• EN61000-3,2:2000
• EN61000-3-3:1995
• UL60950-1
• CSA 22.2 No. 60950-1-03
• IEC60950
• EN60950
Power Supply • 9-30 Vdc 50/60 Hz @ 15 W
Digi One TS, PortServer TS 2/4, PortServer TS 2/4 MEI,
PortServer TS 16
• FCC P15 Subpart B, Class B
• ICES-003, Class B
• EN55022:1994, Class B
Emission
Immunity • EN55024:1998
Safety
Power Supply • 9-30 Vdc 50/60 Hz @ 15 W
• AS/NZS 3548
•VCCI
• EN61000-3,2:2000
• EN61000-3-3:1995
• UL60950-1
• CSA 22.2 No. 60950-1-03
• IEC60950
• EN60950
Chapter 12 Reference and Certifications 77
Page 78

Certifications
FCC Part 15 Class A (PortServer TS 8)
Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) (FCC 15.105)
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for
Class A digital devic es pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Th ese limits
are designed to provide r easonab le pro tection a gainst har mful in terfere nce
in a residential environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio freq uency e nergy, and if not installed and used in accor dance
with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interf erence to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not
occur in a particular ins tallation. If this equi pment does cause harmful
interference to radi o or television reception, whic h can be deter m ined by
turning the equip m ent off and on, the user is encourage d to t ry an d correct
the interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that
to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Labeling Requirements (FCC 15.19)
This device complies with Part 15 of FC C rul e s. Op er at ion is subject to the
following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful
interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired operation.
Modifications (FCC 15.21)
Changes or modification s to this equipment no t expressly approved by Digi
may void the user's authority to operate this equipment.
Cables (FCC 15.27)
Shielded cables must be used to remain within the Class A limitations.
ICES 003 Class B ( Digi One TS, Digi One TS Wireless, PortServer TS 2/4, PortServer TS 2/4 MEI, PortServer TS 2/4 Wireless, PortServer TS 16)
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class B limits for radio noise
emissions from digital apparatus set out in the Radio Interference
Regulations of the Canadian Department of Communications.
Le present appareil numerique n'emet pas de bruits radioelect riques
depassant les limites applicables aux appareils numeriqu es de la class B
prescrites dans le Regl e me nt sur l e brouillage radioel ect ri qu e e di cte par le
ministere des Communications du Canada.
Antennae (Wireless only)
Digi Wireless products can only use the Digi antennae provided in the box.
78 Chapter 12 Reference and Certifications
Page 79

Maximum Pe rmissible Exposure (Wireless only)
To comply with Maximum Permissible Exposure requirements, antennas
must be installed to provide at least 20 cm of separation from all persons
per FCC 47 CFR 2.1091.
Declaration of Conformity
(in accordance with FCC Dockets 96-208 and 95-19)
Digi International declares, that the product:
Manufacturer’s Name: Corporate Headquarters : Manufacturing Headquarters :
Digi International
Digi One TS
Digi One TS (High temperature model)
PortServer TS 2 (High temperature model)
PortServer TS 4 (High temperature model)
PortServer TS 2
PortServer TS 4
PortServer TS 2 MEI
PortServer TS 4 MEI
PortServer TS 1+Modem
PortServer TS 3+Modem
Digi One TS Wireless
PortServer TS 2 Wireless
PortServer TS 4 Wireless
PortServer TS 16
PortServer TS 16 Rack
PortServer TS 16 DC Rack
11001 Bren Road East
Minnetonka MN 55343
Product Name: Model Numbers:
10000 West 76th Street
Eden Prairie MN 55344
50000836-01
50000837-01
50000837-02
50000837-03
50000723-02
50000723-03
50000836-02
50000836-03
50000836-05
50000836-06
50000836-10
50000836-11
50000836-12
50001207-01
50000854-01
50000722-01
to which this declar ation relates, meets the requirements specified by the
Federal Communications Commission as detailed in the following
specifications:
• Part 15, Subpart B, for Class B Equi pment
• FCC Docket 96-208 as it applies to C l ass B personal
• Computers and Peripherals
The product listed above has been tested at an External Test Laboratory
certified per FCC rules and has been found to meet the FCC, Part 15,
Class B, Emission Limits. Documentation is on file and available from the
Digi International Homologation Department.
Chapter 12 Reference and Certifications 79
Page 80

Digi Contact Information
Digi International
11001 Bren Road East
Minnetonka, MN 55343
U.S.A.
World Wide Web: http://digi.com
email digi.info@digi.com
Telephone (U.S.) 1-952-912-3444
Telephone (other locations) (+011) 952-912-3444
Digi Contacts
80 Chapter 12 Reference and Certifications
 Loading...
Loading...