
A
A
b
b
a
a
c
c
u
u
s jj
s
u
u
nii
n
orr
o
A
A
A
A
Hematology Analyzer
b
b
b
b
a
a
a
a
c
u
u
u
u
s jj
s
s jj
s
3.0 release
c
c
c
Service Manual
u
u
u
u
nii
n
nii
n
orr
o
orr
o
v
ett
v
e
B
B
DIATRON Messtechnik Ges.m.B.H.
A-1141 Wien, Ameisgasse 49-51/2. AUSTRIA
Tel.: (431) 914-85-00, 911-38-48
Fax: 914-85-07-15
Web: www.diatron.com
E-mail: support@diatron.com

Abacus junior /vet / B Service Manual
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. INTRODUCTION......................................................................................................................................4
1.1. NAME AND SERIAL NUMBER..................................................................................................................4
1.2. INTENDED USE ......................................................................................................................................4
1.3. INTEGRATED SOFTWARE .......................................................................................................................5
2. FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION...............................................................................................................6
2.1. MAIN ELECTRONIC PARTS OF THE ANALYZERS...................................................................................... 6
2.1.1. Counting chamber with electrodes and measuring aperture......................................................8
2.1.2. HGB Head................................................................................................................................... 8
2.1.3. Cell counter Amplifier Board......................................................................................................9
2.1.4. Control and Measurement Board (COMB) with Dimm-PC core - AJ/AJvet............................10
2.1.5. Dimm-PC* Module – AJ/AJvet.................................................................................................11
2.1.6. Configuration and ID E2PROM board (IDEPROM) - AJ/AJvet............................................... 11
2.1.7. Pneumatic and Power Board (PPB) - AJ/AJvet........................................................................12
2.1.8. Opto-boards for stepper motors................................................................................................ 12
2.1.9. Valve boards ............................................................................................................................. 13
2.1.10. Pressure Sensor.........................................................................................................................14
2.1.11. Digital Reagent Sensor Board .................................................................................................. 14
2.1.12. LCD Display Module with High Voltage Board of AJ/AJvet....................................................15
2.1.13. LCD Display Module with High Voltage Board of Abacus Junior B ....................................... 16
2.1.14. Keypad of Abacus junior/Abacus junior vet..............................................................................17
2.1.15. Keypad of Abacus junior B .......................................................................................................18
2.1.16. Floppy Disk Drive and CD-ROM Drive - AJ/AJvet..................................................................18
2.1.17. External Power Supply.............................................................................................................. 19
2.1.18. MAIN board - AJB .................................................................................................................... 19
2.2. MAIN MECHANIC AND FLUIDIC PARTS OF THE ANALYZER................................................................... 21
2.2.1. Sample rotor..............................................................................................................................22
2.2.2. Sampling needle........................................................................................................................22
2.2.3. Washing head............................................................................................................................22
2.2.4. H&V moving unit......................................................................................................................23
2.2.5. Main Dilutor .............................................................................................................................24
2.2.6. Micro Dilutor............................................................................................................................25
2.2.7. Puffer reservoir......................................................................................................................... 25
2.2.8. Pump .........................................................................................................................................25
2.3. ASSEMBLED ANALYZER .....................................................................................................................26
2.3.1. Abacus junior / Abacus junior vet.............................................................................................26
2.3.2. Abacus junior B.........................................................................................................................29
1
3. OPERATION OF THE FLUIDIC SYSTEM.........................................................................................32
3.1. FLOW DIAGRAM OF MEASUREMENT .................................................................................................... 33
3.2. INITIALIZATION OF THE FLUIDIC SYSTEM ...........................................................................................36
3.3. SAMPLING PROCESS ............................................................................................................................36
3.4. NEEDLE WASHING PROCESS ................................................................................................................37
3.5. DILUTING PROCESS ............................................................................................................................. 38
3.6. LYSING PROCESS................................................................................................................................. 39
3.7. COUNTING PROCESS............................................................................................................................ 40
3.8. CHAMBER DRAINING PROCESS ............................................................................................................41
3.9. CLEANING PROCESS............................................................................................................................ 42
3.10. SHUTDOWN PROCESS ..........................................................................................................................42
4. ADJUSTMENT.........................................................................................................................................43
4.1. MECHANICAL SETTINGS...................................................................................................................... 43
4.1.1. Opto wheel setting..................................................................................................................... 43
4.1.2. Sampling needle setting.............................................................................................................44
4.2. HARDWARE SETTINGS......................................................................................................................... 44
4.2.1. Amplifier offset setting .............................................................................................................. 44

2
Diatron Ltd. 2004
5. CHECKING THE PROPER OPERATION ..........................................................................................45
5.1. SELF TEST OF ABACUS JUNIOR AND VET .............................................................................................45
5.1.1. Self test Screens (AJ/AJvet) .......................................................................................................45
5.1.2. Normal range of Self Test parameters (AJ/AJvet).....................................................................46
5.1.3. Troubleshooting Guide for Self test...........................................................................................46
5.2. SELF TEST OF ABACUS JUNIOR B........................................................................................................47
5.2.1. Self Test Menu...........................................................................................................................47
5.2.2. Normal range of Self Test parameters (AJB) ............................................................................49
5.3. SERVICE MENU - AJ/AJVET................................................................................................................50
5.3.1. Entering to Service Menu..........................................................................................................50
5.3.2. Main Service Menu....................................................................................................................50
5.3.3. Edit service contact ...................................................................................................................50
5.3.4. Device Information ....................................................................................................................50
5.3.5. Service Calibration....................................................................................................................51
5.3.6. Software Settings.......................................................................................................................51
5.3.7. Service Testing Menu ................................................................................................................53
5.3.8. Valve Test Menu........................................................................................................................53
5.3.9. Display and Keyboard Test.......................................................................................................53
5.3.10. Stress Mode ...............................................................................................................................53
5.3.11. Miscellaneous Settings..............................................................................................................54
5.3.12. Multi-user Rescue Code ............................................................................................................54
5.4. SERVICE MENU (AJB).........................................................................................................................55
5.4.1. MAIN Service Menu ..................................................................................................................55
5.4.2. Service Calibration of Abacus Junior B....................................................................................56
6. SERVICE OPERATION .........................................................................................................................57
6.1. OPENING THE INSTRUMENT.................................................................................................................57
6.2. MDA (MONOCHROME DISPLAY ADAPTER) EMULATION MODE – AJ/AJVET ......................................57
6.3. KEY BIOS SETTINGS FOR CORRECT OPERATION – AJ/AJVET..............................................................58
6.4. CHECKING THE BIOS SETUP – AJ/AJVET ...........................................................................................59
6.5. BIOS-DESCRIPTION – AJ/AJVET........................................................................................................59
6.6. DOS FUNCTIONS ON THE INSTRUMENT – AJ/AJVET ...........................................................................61
6.7. ERROR MESSAGES – AJ/AJVET ...........................................................................................................61
6.7.1. Abacus Junior / Abacus Junior Vet error code list ...................................................................62
6.7.2. Abacus Junior / Abacus Junior Vet message code list ..............................................................65
6.8. WARNINGS AND ERROR CODES FOR ABACUS JUNIOR B......................................................................66
6.9. POSSIBLE CAUSES OF NOISE................................................................................................................68
6.9.1. Contaminated reagent............................................................................................................68
6.9.2. Bad earth grounding..............................................................................................................68
6.9.3. External electrical noise............................................................................................................69
6.9.4. Internal noise sources............................................................................................................69
7. MAINTENANCE......................................................................................................................................71
7.1. WEEKLY MAINTENANCE BY USER ......................................................................................................71
7.1.1. Cleaning the washing head .......................................................................................................71
7.2. PERIODIC MAINTENANCE BY SERVICE ................................................................................................71
7.2.1. Check Self test and Device statistics..........................................................................................71
7.2.2. Cleaning and Greasing Dilutor Block.......................................................................................71
7.2.3. Checking and Lubricating Dilutor Piston Tips.........................................................................71
7.2.4. Cleaning and Lubricating Needle Moving Mechanics..............................................................71
7.2.5. Checking and Replacing Washing Head...................................................................................71
7.2.6. Checking and Replacing Peristaltic Pump Tube.......................................................................71
7.2.7. Checking of the Power Supply...................................................................................................72
7.2.8. Bleaching of Fluidic System......................................................................................................72
8. SPARE PARTS.........................................................................................................................................73

Abacus junior /vet / B Service Manual
9. APPENDICES...........................................................................................................................................76
9.1. WARNING FLAGS - AJ/AJVET ONLY.................................................................................................... 76
9.2. SERIAL COMMUNICATION PROTOCOL.................................................................................................77
9.2.1. General Description.................................................................................................................. 77
9.2.2. Format of Packages Sent .......................................................................................................... 78
9.2.3. Format of Acknowledge of the Receiver ...................................................................................78
9.2.4. Detailed Description of Packages............................................................................................. 78
9.3. UPLOADER: SOFTWARE UPGRADING TOOL FOR ABACUS JUNIOR B.................................................82
9.3.1. Process of SW download (AJB).................................................................................................83
9.3.2. Troubleshooting of SW download (AJB)................................................................................... 86
9.4. ABACUS JUNIOR CABLING DIAGRAM - AJ/AJVET ............................................................................... 87
9.5. ABACUS JUNIOR B CABLING DIAGRAM - AJB..................................................................................... 88
9.6. ABACUS JUNIOR / ABACUS JUNIOR B TUBING SCHEMATICS - AJ/AJB................................................89
9.7. ABACUS JUNIOR VET TUBING SCHEMATICS - AJVET...........................................................................90
9.8. RECOMMENDED KIT OF TOOLS ............................................................................................................91
9.9. ELECTRONIC SCHEMATICS ..................................................................................................................91
3

4
Diatron Ltd. 2004
1. INTRODUCTION
Since Abacus junior / Abacus junior vet / Abacus junior B have so much common
characteristics, we issue a common Service Manual covering all instruments.
Information herein applies for all instruments unless otherwise noted.
To be well up in the instruments, please read this manual carefully to have the
knowledge for servicing the instruments perfectly and avoid extra costs and wasting
precious time.
In this manual, we are using the following conventions:
AJ – stands for Abacus junior
AJvet – stands for Abacus junior vet
AJB – stands for Abacus junior B
This Abacus junior / Abacus junior vet / Abacus junior B Service Manual contains the
functional descriptions of all analyzers, operation of the fluidic systems, adjustments and
settings, and very important information for the Service Personnel about the service
operations and possible problems.
1.1. Name and serial number
Name: Abacus junior / Abacus junior vet / Abacus junior B Hematology Analyzer
Serial No.: Every instrument has its own serial number, which is printed on the rear panel
label and it can be read out from Device Information or from the self test
submenu. This identity number is write-protected by DIATRON.
1.2. Intended use
Abacus junior / Abacus junior vet / Abacus junior B hematology analyzers are fully
automated cell counters for in vitro diagnostic use. The compact instruments were developed
for small clinics, point-of-cares and vet offices.
Abacus junior can process 30, Abacus junior vet can process 20-25 samples per hour and
they are intended to determine the following 18 hematology parameters from a 25µl whole
blood sample:
• WBC - LYM# - MID# - GRA# - LYM% - MID% - GRA% (
• HGB - RBC - HCT - MCV - RDW - MCH - MCHC
• PLT - MPV - PCT – PDW
Abacus junior B
12 hematology parameters from a 25µl whole blood sample:
can process 30 samples per hour and intended to determine the following
three-part WBC differential)
• WBC
• HGB - RBC - HCT - MCV – RDW-cv - MCH – MCHC
• PLT - MPV - PCT – PDW-cv

Abacus junior /vet / B Service Manual
5
1.3. Integrated software
The integrated software controls the instrument operations, displays, stores, recalls data, and
allows the user to perform QC and calibration procedures and modify the user settings. The
software version number can be read out from the Device Information or from the Self test
submenu.
Software is absolutely “Plug and Play”, it can read out and detect the type and the serial
number of the instrument, therefore it will run the correct program for the hardware, without
any user or service help. Every Abacus junior / Abacus junior vet software version is
upgradeable (using a floppy disk) by the latest program developed by DIATRON.
Software upgrade of Abacus Junior B requires a special SW downloading application (more
about this in Section 9.3) running on a separate PC, a standard null-modem serial cable –
with 9-pin connector, and an upgrade SW from web page of DIATRON:
www.diatron.com
Diatron Ltd. 2004
6
2. FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
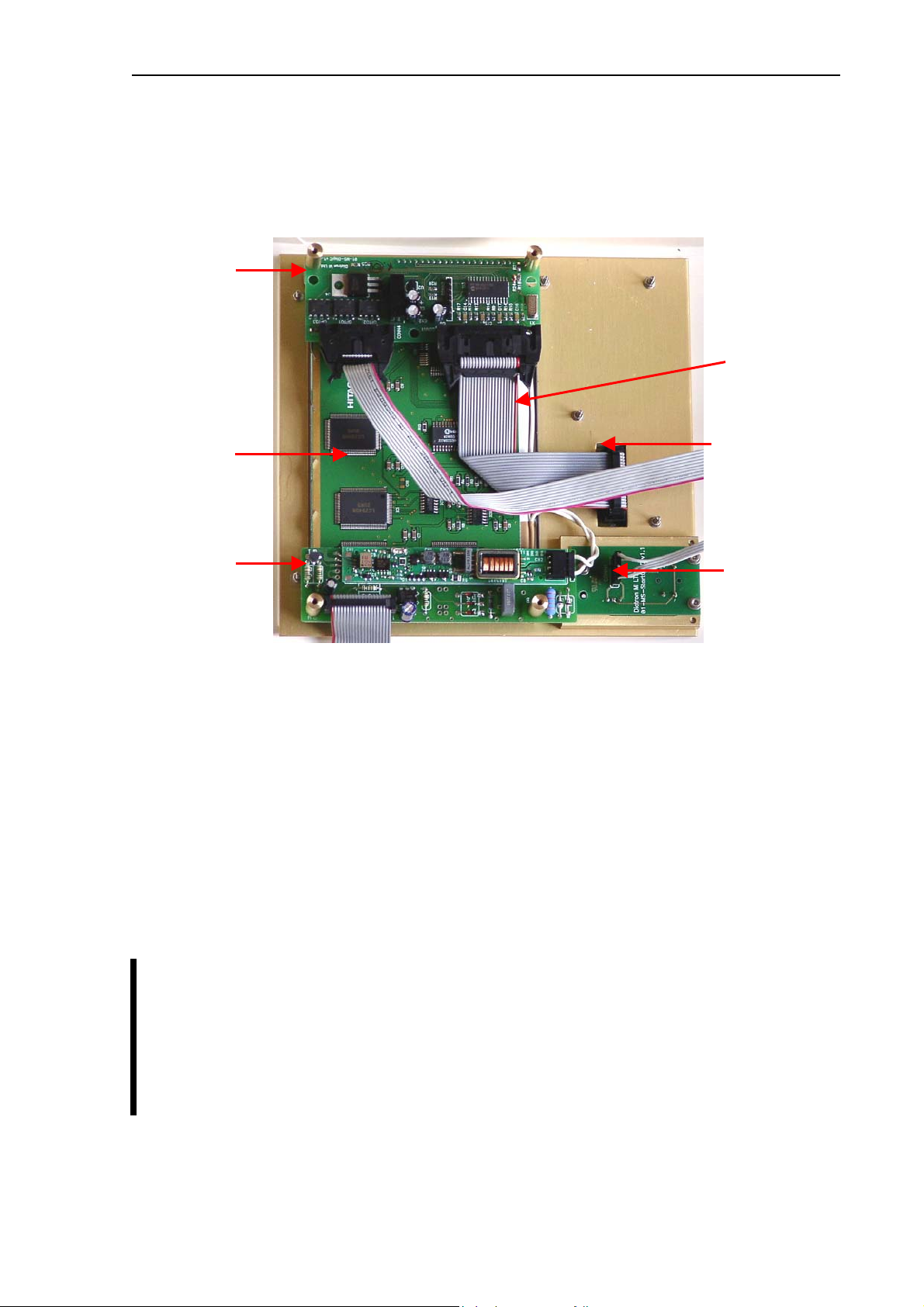
2.1. Main electronic parts of the analyzers
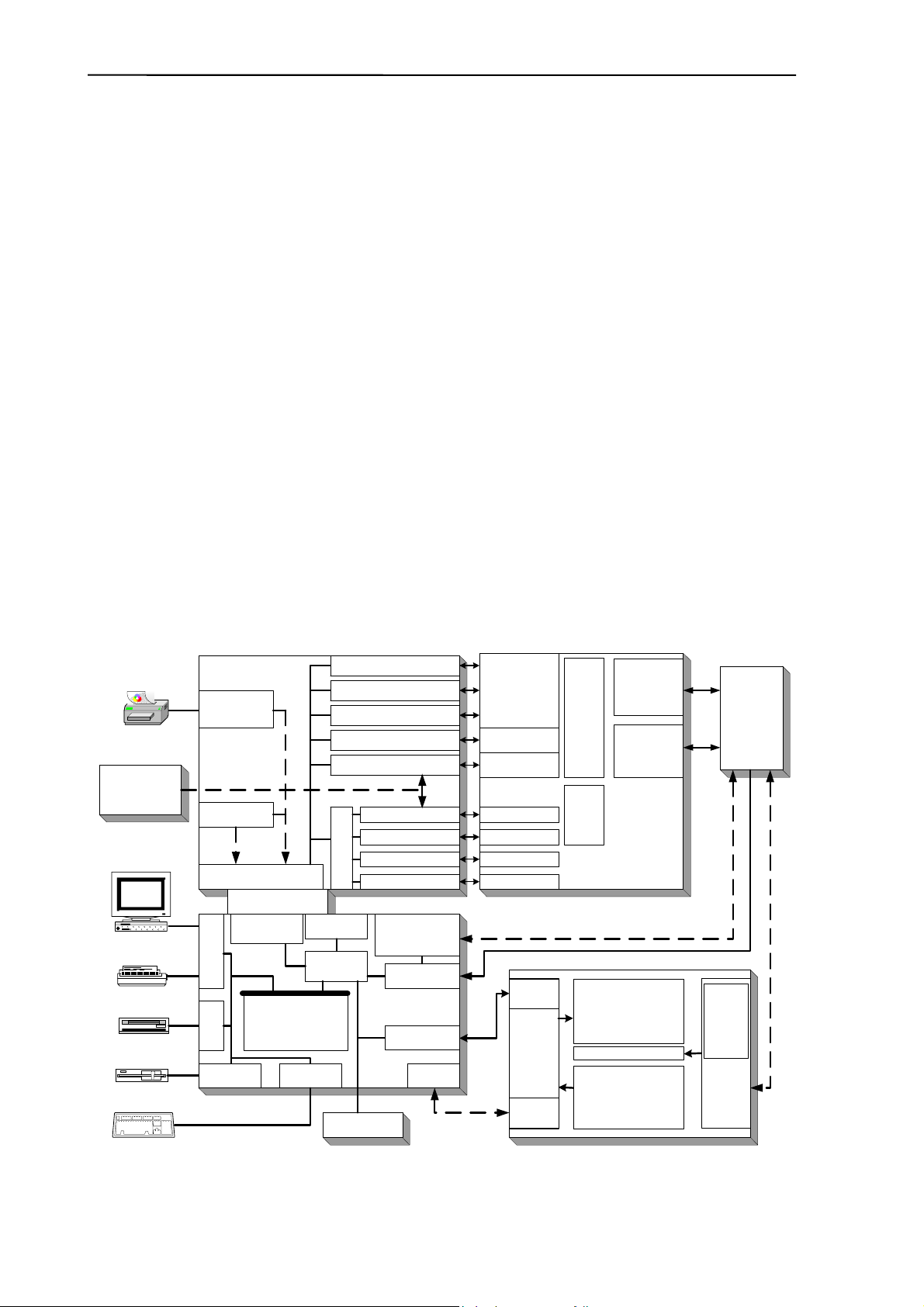
Abacus junior / Abacus junior vet contains the following electronic parts:
1. Counting chamber with electrodes and measuring aperture
2. HGB Measuring Head
3. Cell Counter Amplifier Board (behind the chamber)
4. CPU Board with Dimm-PC and measurement processing unit (COMB Board)
5. Safe configuration E
6. Pneumatic and Power Board with 6 motor controllers, valve & pneumatic controller,
pump driver and power supply for internal printer (+8V) and digital circuitry (+5V)
7. Motors with common opto-board of needle moving motors (H/V) and sample rotor
8. Main dilutor block with opto-board for diluent, lyse and rinse (AJVet)
9. Micro-dilutor block with opto-board for sampling
10. Valve boards (set of 5 and max. 7)
11. Peristaltic Pump
12. Pressure Sensor
13. Digital Reagent Sensor Board
14. Floppy Disk Drive and CD-ROM Drive (optional)
15. Graphic LCD Display Module with High Voltage Board
16. LCD and Keyboard controller and Keyboard Panel
17. Internal Printer
2
PROM board connecting CPU board and PPB
Internal Printer
12Vdc External
Power Supply
Ext. Computer
Ext.Printer
CD-ROM Drive
Floppy drive
Ext. Keyboard
Internal printer
power and I/F
+8V
Digital power
+5V
Power Board Interface
+5V, +12V, Pneum I
Serial No.
Config. Data
Configuration
microcontroller
Legacy I/O I/F
Dimm-PC
AMD Elan
IDE I/F
Floppy I/F
SC-520
Keyboard I/F
Pneumatic and Power Board
Motor controller/driver #1
Motor controller/driver #2
C bus
Motor controller/driver #3
2
Motor controller/driver #4&5
Motor controller/driver #6
Pneumatic I
Valve drivers
Pump driver
Reagent sensor I/F
2
C
Pneum I/F
converter
+12V, -12V
Pressure sensor I/F
Valve controller
IDEPROM
DC/DC
FPGA
START button
Status LEDs
CPU Board
DC/DC converter
+12V / -12V
analog power
A/D converter
LCD I/F
12Vdc
Opto board of
needle moving
motors H/V and
sample rotor
Opto board of
main dilutor
Opto board of
microdilutor
Valve blocks
Pump
Reagent sensors
Pressure sensor
Optical
isolation
LCD and
Keypad
controller
DC/DC
converter
Motors
Valves
Fluidic System
Counting
chamber with
electrodes
HGB
measuring
head
Display Assembly
LCD
LCD Lamp
Keypad
High
Voltage
Inverter
300V
High
Voltage
Board
+50V
+150V
Amplifier
Cell
counter
amplifier
HGB I/F
AC
Abacus junior / Abacus junior vet Electronic Functional Block Diagram

Abacus junior /vet / B Service Manual
7
Abacus junior B contains the following electronic parts:
1. Counting chamber with electrodes and measuring aperture
2. HGB Measuring Head
3. Cell Counter Amplifier Board (behind the chamber)
4. Motors with common opto-board of needle moving motors (H/V) and sample rotor
5. Main dilutor block with opto-board for diluent and lyse
6. Micro-dilutor block with opto-board for sampling
7. Valve boards (set of 5)
8. Peristaltic Pump
9. Pressure Sensor
10. Digital Reagent Sensor Board
11. Alphanumeric LCD Display Module with High Voltage Board
12. Keyboard Panel
13. Internal Printer
14. MAIN board
Fluidic System
Counting
chamber with
electrodes
Motors
HGB
measuring
head
Valves
Internal Printer
12Vdc External
Power Supply
Internal printer
power and I/F
+8V
Power regulating
and filtering
+3.3V, +5V,
+8V, +12V,
Serial No.
Config. Data
Real Time Clock
Battery
MAIN Board
Motor driver #1
Motor driver #2
Motor driver #3
Motor driver #4 & #5
Motor driver #6
Valve drivers
Pump driver
Reagent sensor I/F
Pressure sensor I/F
Opto board of
needle moving
motors H/V and
sample rotor
Opto board of
main dilutor
Opto board of
microdilutor
Valve blocks
Pump
Reagent sensors
Pressure sensor
Amplifier
Cell
counter
amplifier
HGB I/F
Ext. Computer
(SW Uploader)
RS-232
Microcontroller,
CPLD and
some digital chips
START button
Status LEDs
Measurement
processing unit
and control I/F
LCD I/F
Keyboard I/F
(backlig ht internally
controlled)
Abacus junior B Electronic Functional Block Diagram
LCD
Keypad
Display Assembly
High
Voltage
Board
+50V
+150V
Diatron Ltd. 2004
8
A
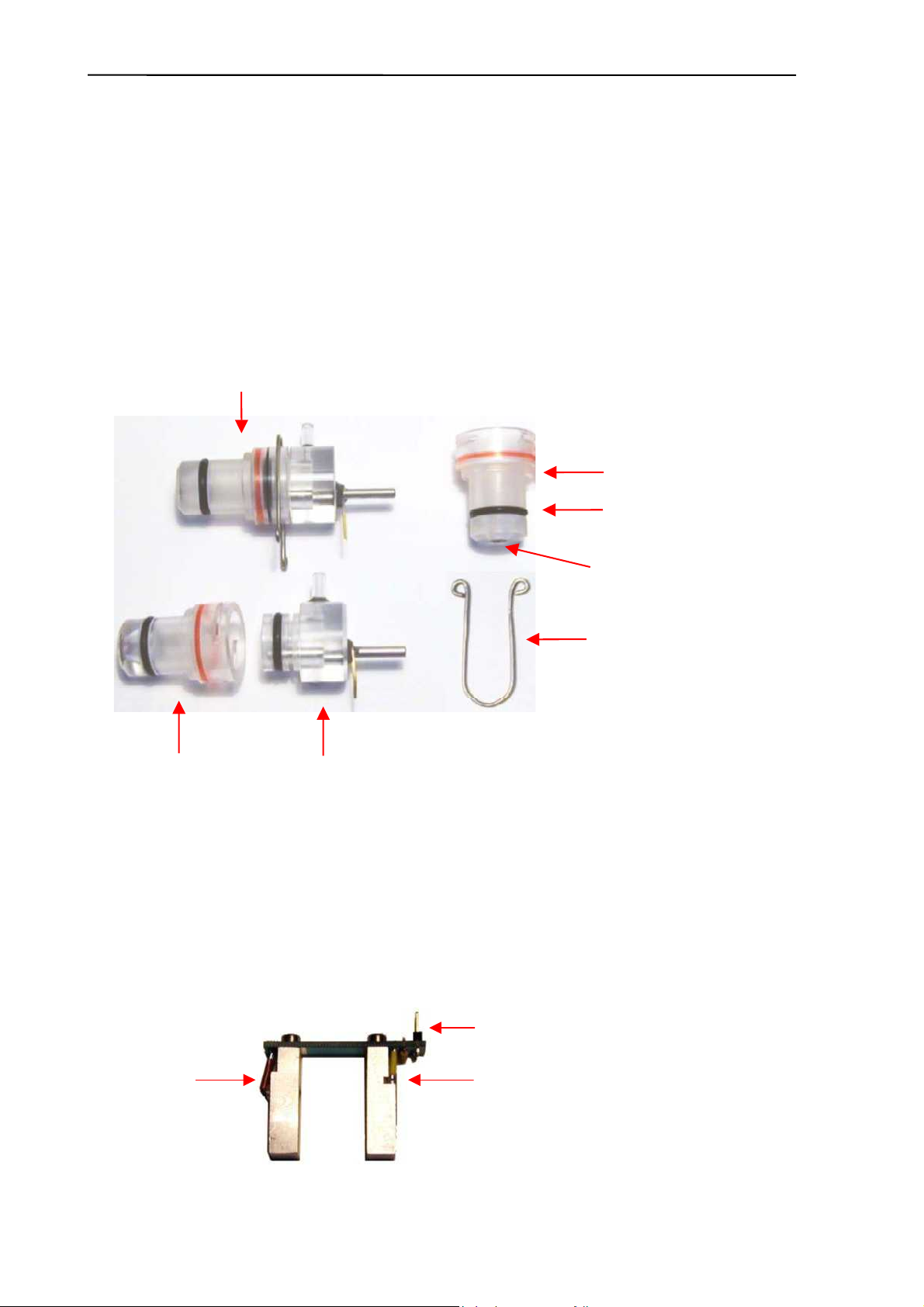
2.1.1. Counting chamber with electrodes and measuring aperture
Impedance method is used for determination of volume and number of cells. In this method a
known volume of dilution is drawn through a small aperture. Constant current is passed
through the aperture from one side to the other. When a cell passes through the aperture, it
causes a change in resistance, which generates a voltage pulse.
The amplitude of the voltage pulse is proportional to the ratio of cell volume per aperture
volume. This is used to determine the volume of cells. The number of cells can be obtained
by counting the pulses.
In the instruments there is one cell-counter probe: the aperture size is 80 µm and has a
reference electrode assembly and U-shaped metal fixing as it is shown in the figure below.
ssembled Cell-counter Probe
Measuring tube
O-ring
Aperture (80µm)
U-shaped metal fixing
Measuring tube
Reference electrode
The aperture is made of ruby and it is molded into the measuring tube.
2.1.2. HGB Head
Hemoglobin head is placed around the measuring chamber in all instruments.
It contains: light source (LED) at 540 nm wavelength and Photo Detector (TSL235). The
Photo Detector converts the light to frequency. The HGB concentration is a logarithmic
function of this frequency measured by
• the FPGA circuit of the COMB card in AJ/AJvet
• the micro-controller of the MAIN board in AJB
Connection to the amplifier
LED
TSL235
Abacus junior /vet / B Service Manual
9
The analyzers perform enhanced Hemoglobin measurement technology for HGB
measurement. The output of HGB head is frequency (TSL235 detector is light to frequency
converter). This signal is counted by a digital counter in the FPGA circuit/micro-controller.
This counter counts up while the LED is on and counts down while the LED is off, the LED
and the counter directions are switched with a 100 Hz signal. This method provides “real time
backlight correction”, which makes the HGB measurement more precise in changing
backlight environment situation as well.
There are two kinds of HGB measurements:
• Sample measurement (before RBC counting)
• Diluent measurement (in WBC washing phase)
The HGB result is calculated from these measurements by:
HGB ≅ log (CNT
diluent light
Due to enhanced HGB
/ CNT
technology, junior is less sensitive to incident light changes.
sample light
)
It is recommended to keep side door closed during measurements.
2.1.3. Cell counter Amplifier Board
Amplifier board includes its own voltage regulator, connection interfaces to HGB head, to
high voltage board and to COMB in AJ/AJvet (to MAIN in AJB). In this board there is a
current generator circuit, which works from 50V measuring voltage (generated by High
Voltage Board) and the probe voltage (DC) is amplified with a voltage follower (output: ELV).
Nominal measuring current is 870 µA.
Amplifier board includes one input connector for the chamber (measuring electrode). There
are two opto switches (U1, U3) to connect high voltage to the probe with HSW signal and
isolate the input of the amplifier. Test circuit makes possible to generate test pulses (with
TEST and PLS signals through FETs) for checking the proper operation of the amplifier
channel.
Connection to:
CSA1 on COMB (AJ/AJvet)
CS_IMP on MAIN (AJB)
Connection
to HVB
CSA1 on COMB (AJ/AJvet)
CS_ANALOG on MAIN (AJB)
Connection to:
Amplifier board includes a 3-stage main amplifier channel, which gains input signal to the
0...5 V range (this is the input range of the A/D converter, which is placed on the COMB
card). The RSW signal changes the gain (RBC, WBC) in the feedback of the second
amplifier stage with U2 (MAX319) analog switch. There is an offset potentiometer, P1 in the
third amplifier stage, manufacturer sets the correct offset voltage.
Adjust the offset voltage only in case it is out of the +/- 5mV range.
1
0
Diatron Ltd. 2004
DHON signal (from the COMB board - AJ/AJvet; from the MAIN board - AJB) switches on
the LED and the MVON signal – which is active during counting – switches off the Photo
Detector in the HGB head, to prevent noise generated by the HGB detector.
The other side of the amplifier board contains special connectors for the chamber and the
HGB head (JP4).
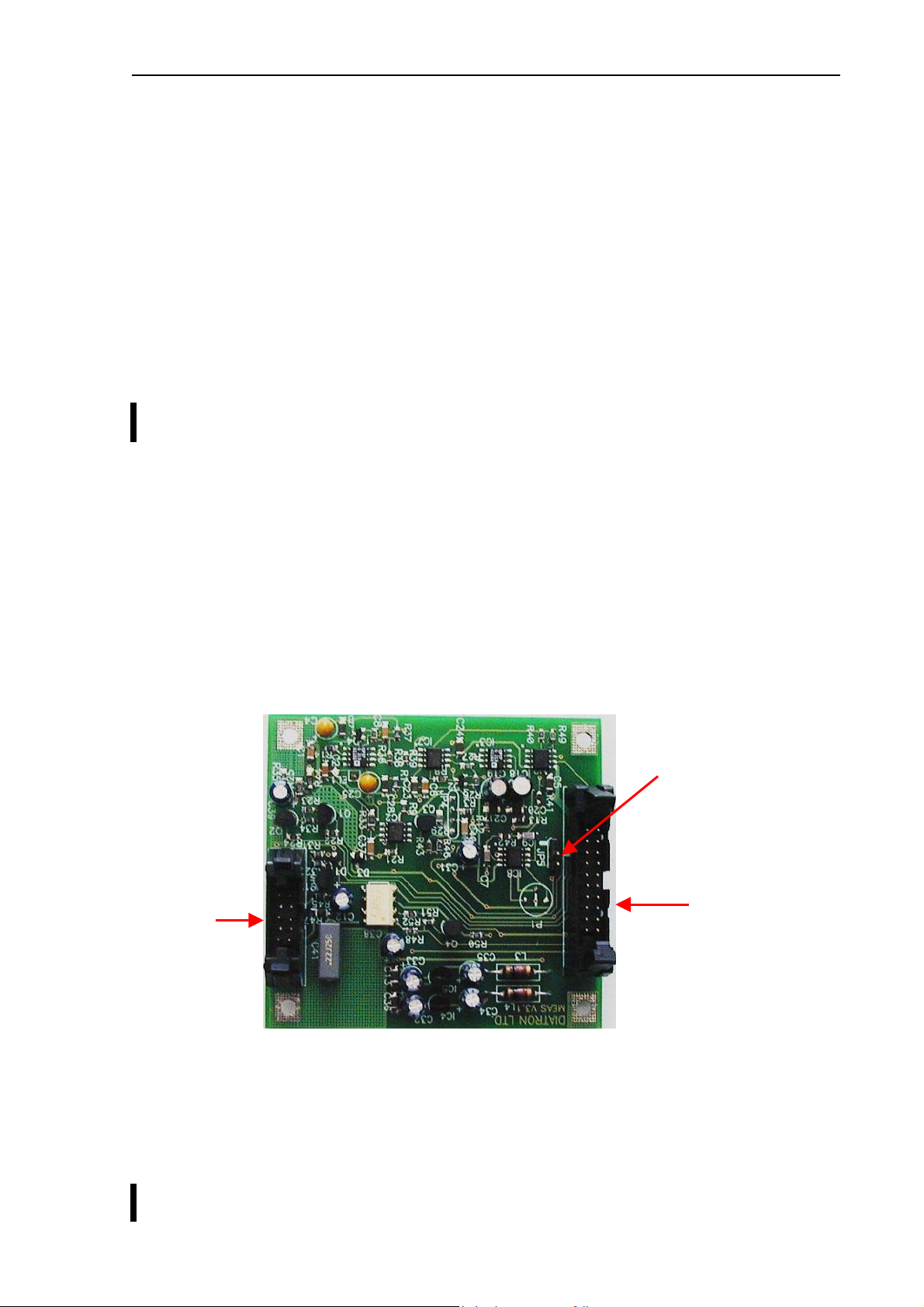
2.1.4. Control and Measurement Board (COMB) with Dimm-PC core - AJ/AJvet
The compact COMB incorporates a single PC and its environmental functions, as well as the
specific measurement processing functions in one board.
Speaker
connection
CD-ROM
connection
CSDIGIO
CSA1
Amplifier
connections
LPT port
COM port USB port
PS2 port
keyboard
CSINTCON
ID board
connection
CSHEAT
Reagent
heater
connection
CSD
Keyboard & Display and
Start key/LED connection
CSFLOPPY
Floppy
connection
CSHVBP
High voltage
board connection
PC system of the COMB board is based on the Dimm-PC module, which is a credit card size
PC with AMD Elan SC520 133 MHz micro-controller. Dimm-PC itself contains 16 or 32Mbyte
RAM and same size of SanDisk that acts like a hard disk. Dimm-PC module is easily
replaceable as it has an open socket (it has also a screw for safe fixing). COMB card
contains single ICs and some drivers/protection-circuits for the interfaces such as LPT,
COM1, PS2, USB, IDE, Floppy and Speaker.
Measurement processing is based on FPGA circuit. After power on, FPGA holds the DimmPC in wait state (with
IDEPROM (status LED is red during configuration). After that the FPGA controls the entire
pneumatic system through the Pneumatic I
–IOCHRDY signal) until the PIC configures the FPGA circuit from the
2
C bus, the Keyboard and Display module with
video RAM for MDA (Monochrome Display Adapter) emulation, and Start button & status
LED. FPGA circuit also performs measurement data acquisition by using the 10-bit A/D chip.
FPGA makes digital data processing and stores the results in the internal FIFO memory. Cell
parameters are sent to the Dimm-PC by single DMA cycles.
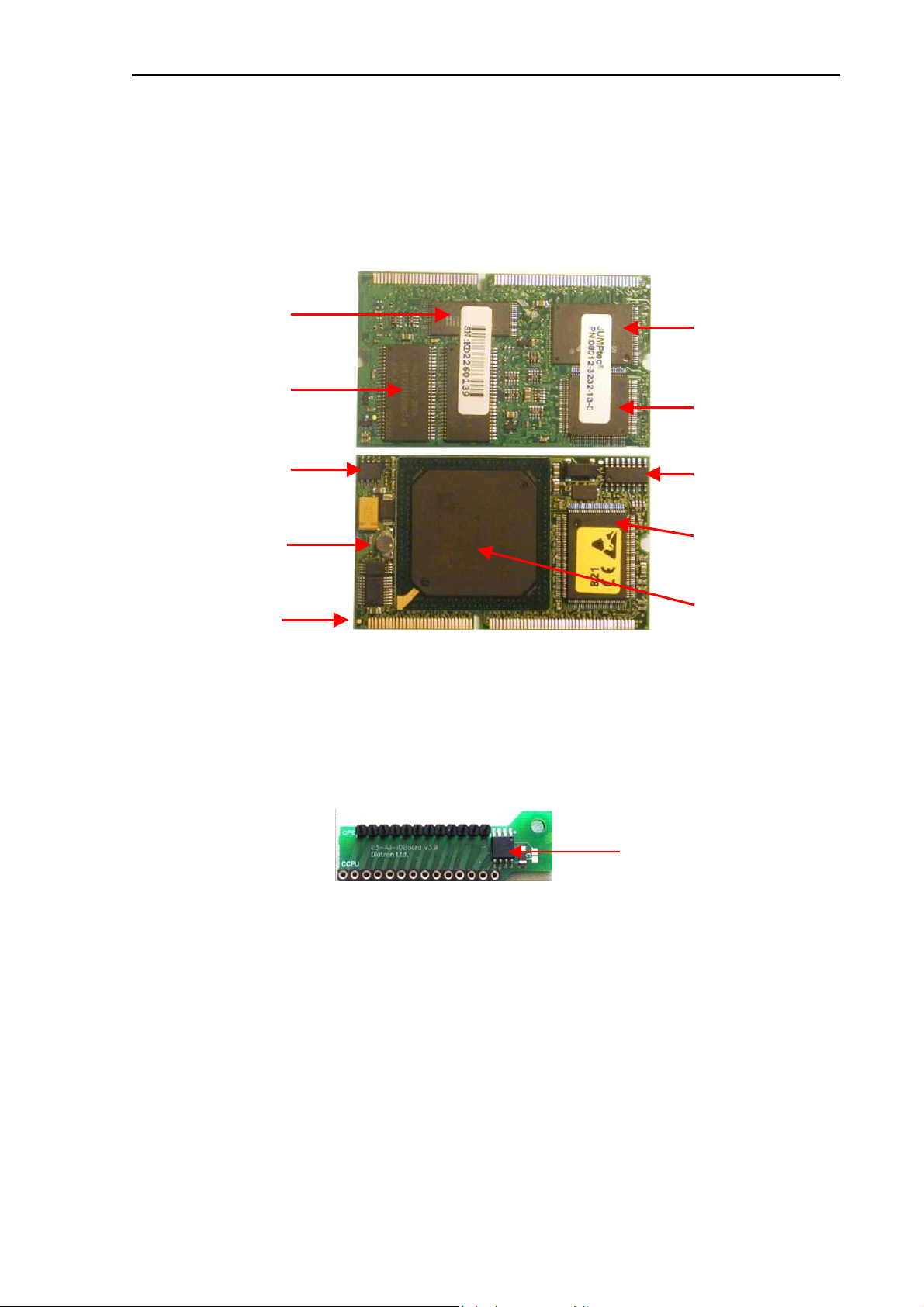
Abacus junior /vet / B Service Manual
11
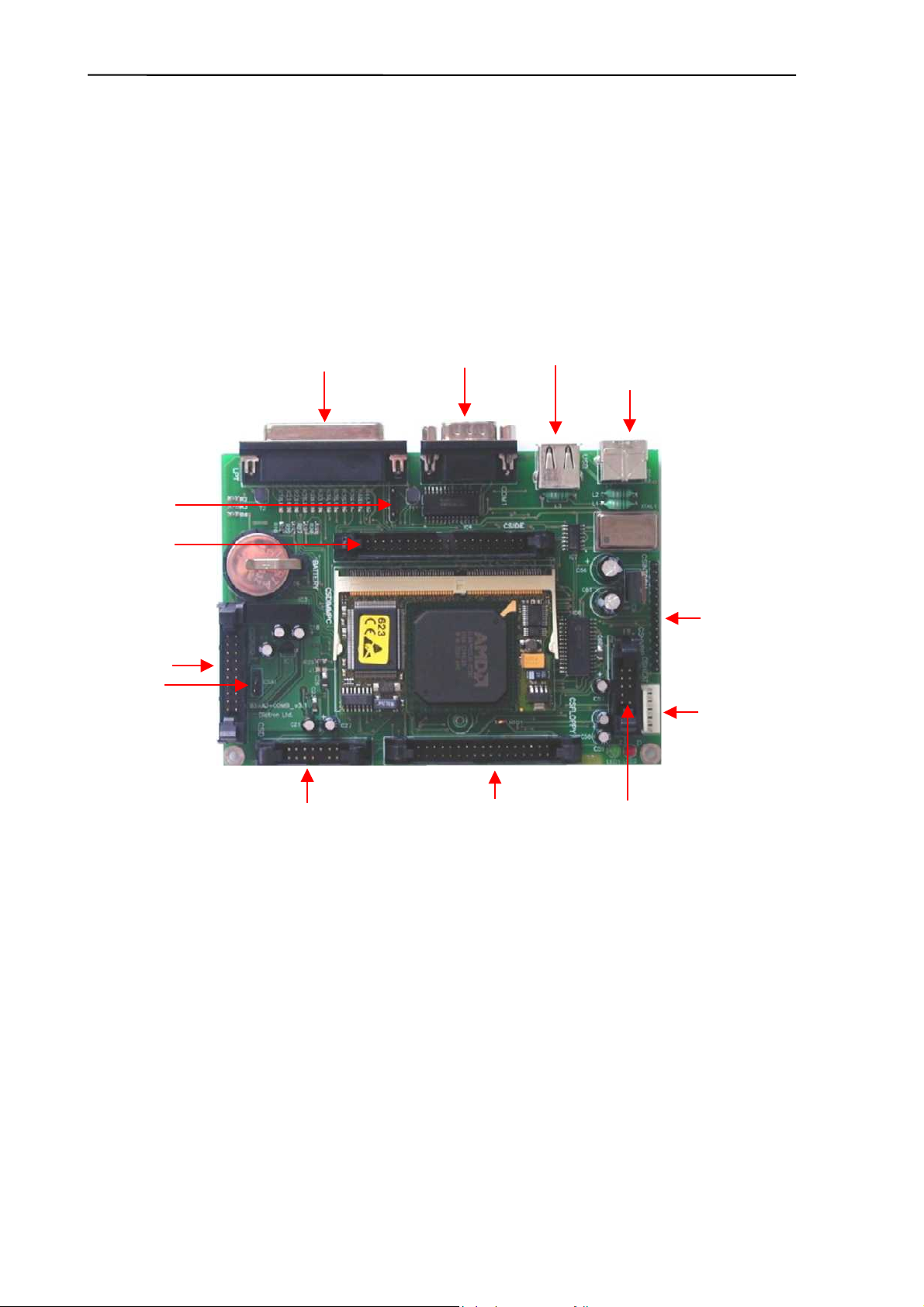
2.1.5. Dimm-PC* Module – AJ/AJvet
The MB4 board incorporates a credit-card sized PC, named Dimm-PC*. The processor on
the Dimm-PC is a 133MHz Pentium-class core, with 32Mbytes on-board RAM, and 32Mbytes
on-board SanDisk. This is the HDD (hard disk drive) of the analyzer, so instrument software
with all user settings, calibration, database, etc. is stored on the Dimm-PC.
* DimmPC® is the Trade Mark of Kontron Embedded Modules GmbH
Flash BIOS
Hard Disk
(SanDisk)
32 Mbytes RAM
SanDisk
controller
CMOS EEPROM
On-board SMPS
Real-time clock
Super I/O
AMD Elan
Edge connector
SC520 CPU
2.1.6. Configuration and ID E2PROM board (IDEPROM) - AJ/AJvet
This board is the interconnection between COMB and PPB cards: Pneumatic I2C bus, power
lines and internal printer signals are connected through this card. The board also contains a
24FC256 serial E
information of the instrument (Serial Number, OEM, model, etc.).
2
PROM, which stores the FPGA’s configuration data and identity
E2PROM
Keeping the hardware identity information (write-protected), IDEPROM makes possible to
run the correct software (Human or Vet).
12
Diatron Ltd. 2004
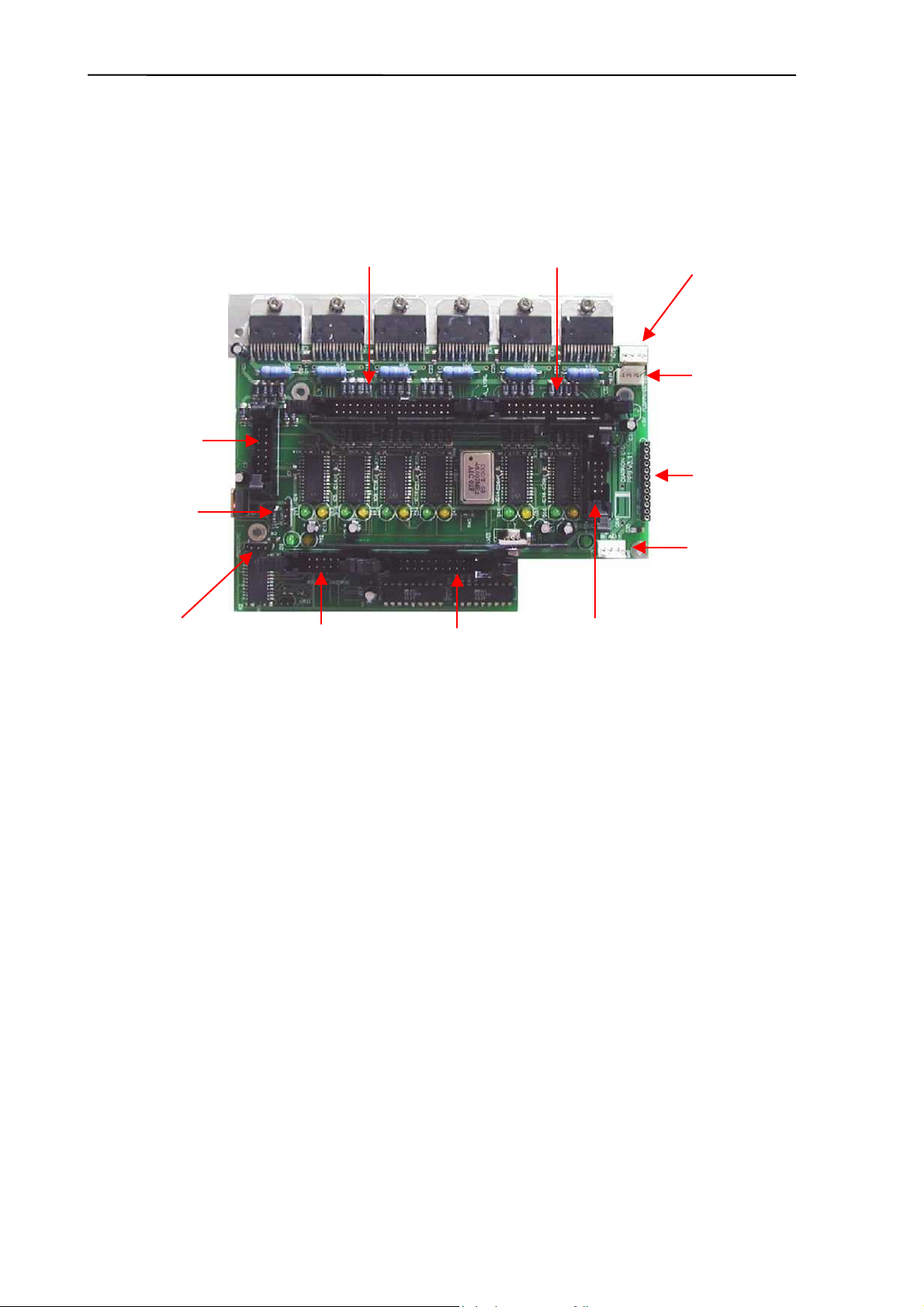
2.1.7. Pneumatic and Power Board (PPB) - AJ/AJvet
PPB card contains the main power regulator circuits, valve and motor driver circuits and
other connections for the fluidic and pneumatic system’s parts.
MDIL
Micro dilutor
connection
PUMP
Peristaltic pump
connection
PRESSURE
Pressure sensor
connection
X_Y_SR
Horizontal, Vertical & Sample
rotor connection
REAGENT_SENSOR
Reagent sensor
connection
Valves connection
VALVES
DIL_MDIL
Main Dilutor
connection
PRINTER
Internal printer
connection
5V voltage
regulator
(on chassis)
FLOPPY/CD
Power to
Floppy/CD
I_PCB_CONN
ID board
connection
+12V_IN
Power input
Power system generates +5V (Digital power), +8V (Printer power) and +12V (Motor and
valve power) from the single +12V DC input signal.
Motor driver part consists of six separated PIC micro-controllers with power drivers.
Horizontal, Vertical and Sample rotor motors have one combined ribbon cable connection.
Main Dilutor (with two motors) and Micro-dilutor have separated connectors.
Valve driver section is based on the valve driver PIC micro-controller and two 8-bit, powered
output shift registers (with built in protection diodes) and there is one common ribbon cable
connection for the valve boards. The peristaltic pump has a separated Darlington driver
circuit for more reliable operation.
2.1.8. Opto-boards for stepper motors
There are six stepper motors in the system: Horizontal and Vertical motors, which make the
movements of the sampling needle; the main Dilutor motors (2), which move the syringes
(macro, lyse, rinse); the micro Dilutor motor, which drives the sampling phase and the motor
moving the sample rotor. The stepper motor opto boards make the connections between the
motor driver ICs and motors, and have opto switches for the motor’s home and end
positions. The actual status of the stepper motor’s optos is indicated by two LEDs on each
stepper motor opto boards.
Dilutor and Micro-dilutor have its own separated opto-board, located directly in the units.
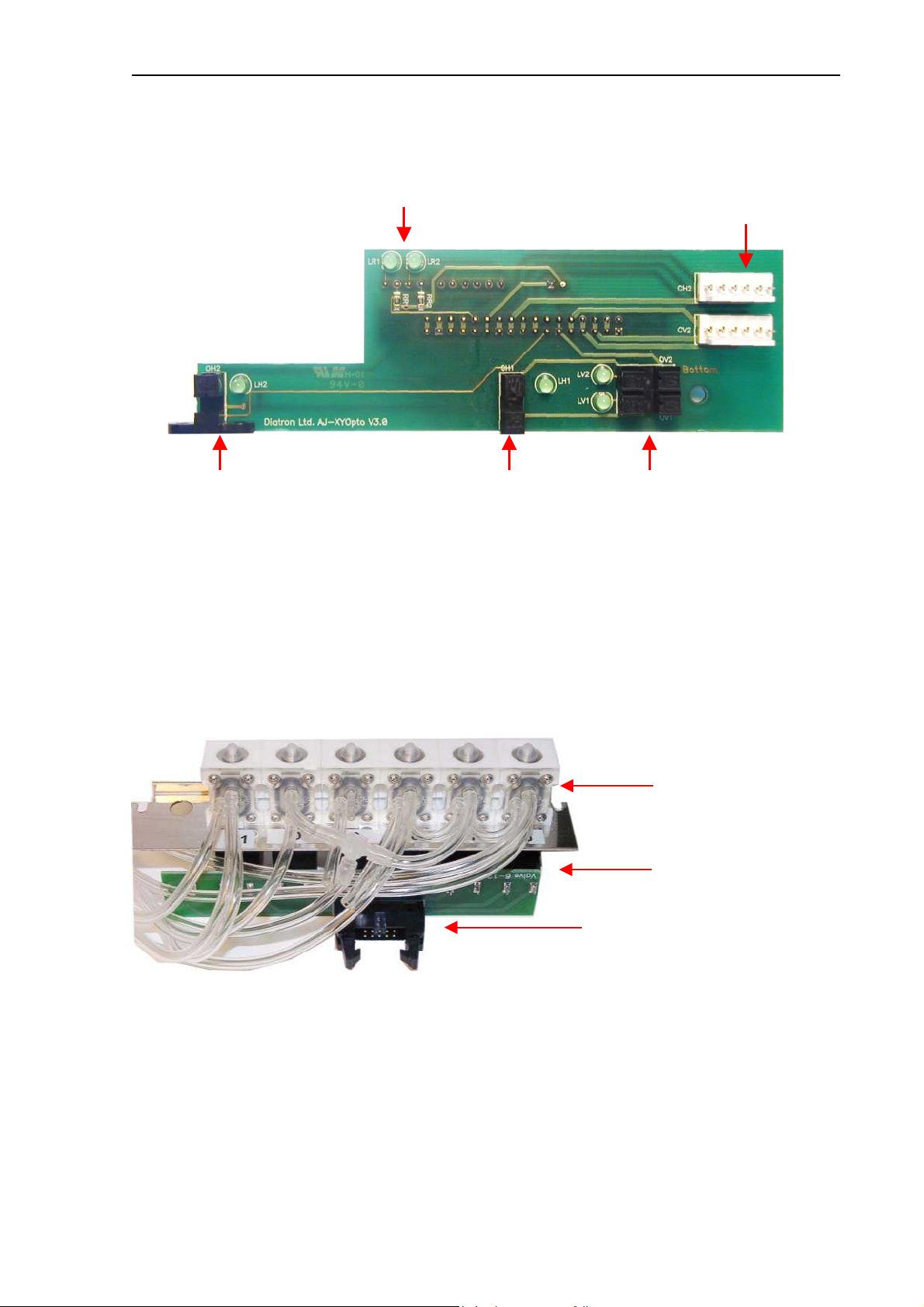
Abacus junior /vet / B Service Manual
Horizontal and Vertical motors and the sample rotor unit have a common Opto-board, called
XYOpto Board:
LEDs for Sample rotor Connections for Hoirizontal &
Vertical motors
13
Opto switches & LEDs for Horizontal motor
The other side of the board contains the connection for the Sample rotor and a ribbon cable
connection to the COMB (AJ/AJvet) or to the MAIN board (AJB).
Opto switches & LEDs for Vertical motor
2.1.9. Valve boards
There are two kinds of valve boards: Valve board 1-5 and Valve board 6-12.
AJ
and AJB have 5 valves, while AJvet has 6 valves in Valve board 6-12 module. The
valve boards are connected to controller and driver chips are located on the PPB.
Valves
Valve Board
Connection to PPB
14
Diatron Ltd. 2004
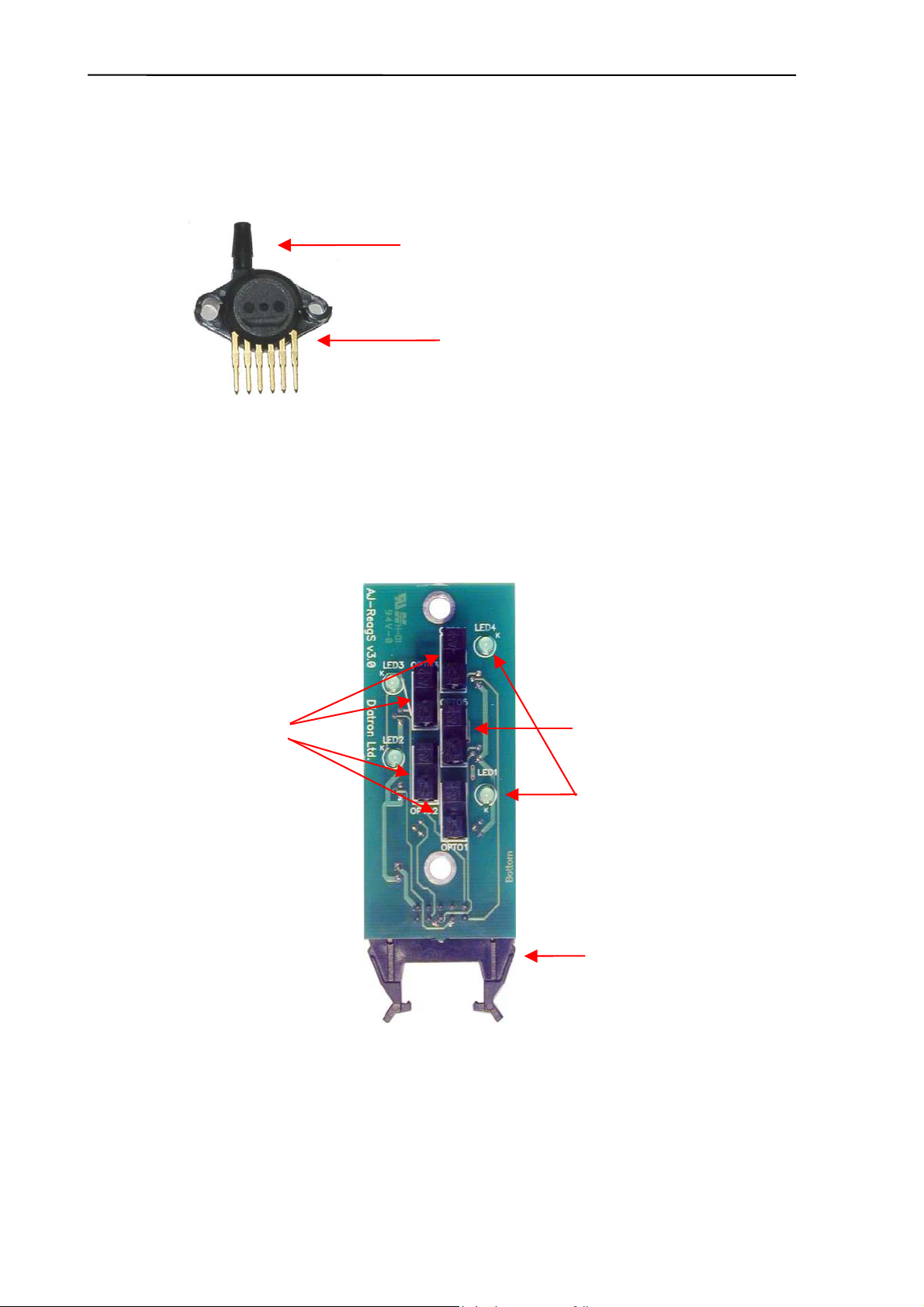
2.1.10. Pressure Sensor
This is an MPX5100AP calibrated pressure sensor, which can measure the required air
pressure and vacuum. The Pressure Sensor is connected directly to the PPB card (AJ/Ajvet)
or to the MAIN board (AJB).
Connection to Puffer reservoir
Connection to:
PPB (AJ/Ajvet)
MAIN (AJB)
The pressure sensor can operate from +5V only. It is a calibrated sensor with 0-1.1 Bar input
range. Do not apply more than 1.5 Bar to it, because it can ruin the pressure sensor.
2.1.11. Digital Reagent Sensor Board
This board contains four liquid detector opto-detectors (optos) and a reference opto for
automatic temperature and stray light compensation. The reference opto is located in the
middle and it has the same temperature and backlight conditions as the sensing ones.
Reagent detectors
Reference detector
Control LEDs
Connection to:
PPB (AJ/Ajvet)
MAIN (AJB)
The Reagent Sensor Board is connected to the PPB card in AJ/AJvet, and the valve driver
micro-controller makes the sensing and compensating operations. In AJB,
this board is
connected to the MAIN board and the micro-controller controls the operation of the Reagent
Sensor Board.
Instrument makes automatic initialization – called calibration – of reagent sensors during
priming phase of fluidics.
Abacus junior /vet / B Service Manual
5
2.1.12. LCD Display Module with High Voltage Board of AJ/AJvet
LCD &
Keypad
controller
LCD backlight
lamp
1
LCD module
HVB with
inverter
Keypad connector
Start key and
status LED board
Display assembly contains the 240x128 dots graphics LCD display and the high voltage
board. LCD has a high voltage backlight lamp (high voltage board generates the required
voltage).
There is a special temperature compensation circuit in the display module, which makes
possible to use the LCD module in wide temperature ranges with the adjusted contrast.
High Voltage Board (HVB) generates LCD backlight voltage (300V), aperture cleaning
voltage (150V), and measuring voltage (50V). The high voltage board is connected to the
system through the amplifier board and the COMB card. This unit contains INVC191 inverter,
which is a high voltage, high frequency circuit producing suitable voltage for CCFL (cold
cathode fluorescent lamp) of the LCD.
The CFSW digital signal (from the COMB card) controls HVB: logical LOW turns inverter on.
The MVON digital signal (from the COMB card) switches the measuring voltage (50 V) on/off
by O1 opto switch.
Warning! Be careful with servicing this board in active state, because the high
voltage (300V) at LCD lamp connector can cause damages or electric shock.
Never operate the analyzer without the LCD backlight connected to the HVB,
because the over-voltage on the output of the HVB can damage the HVB board and
the amplifier.
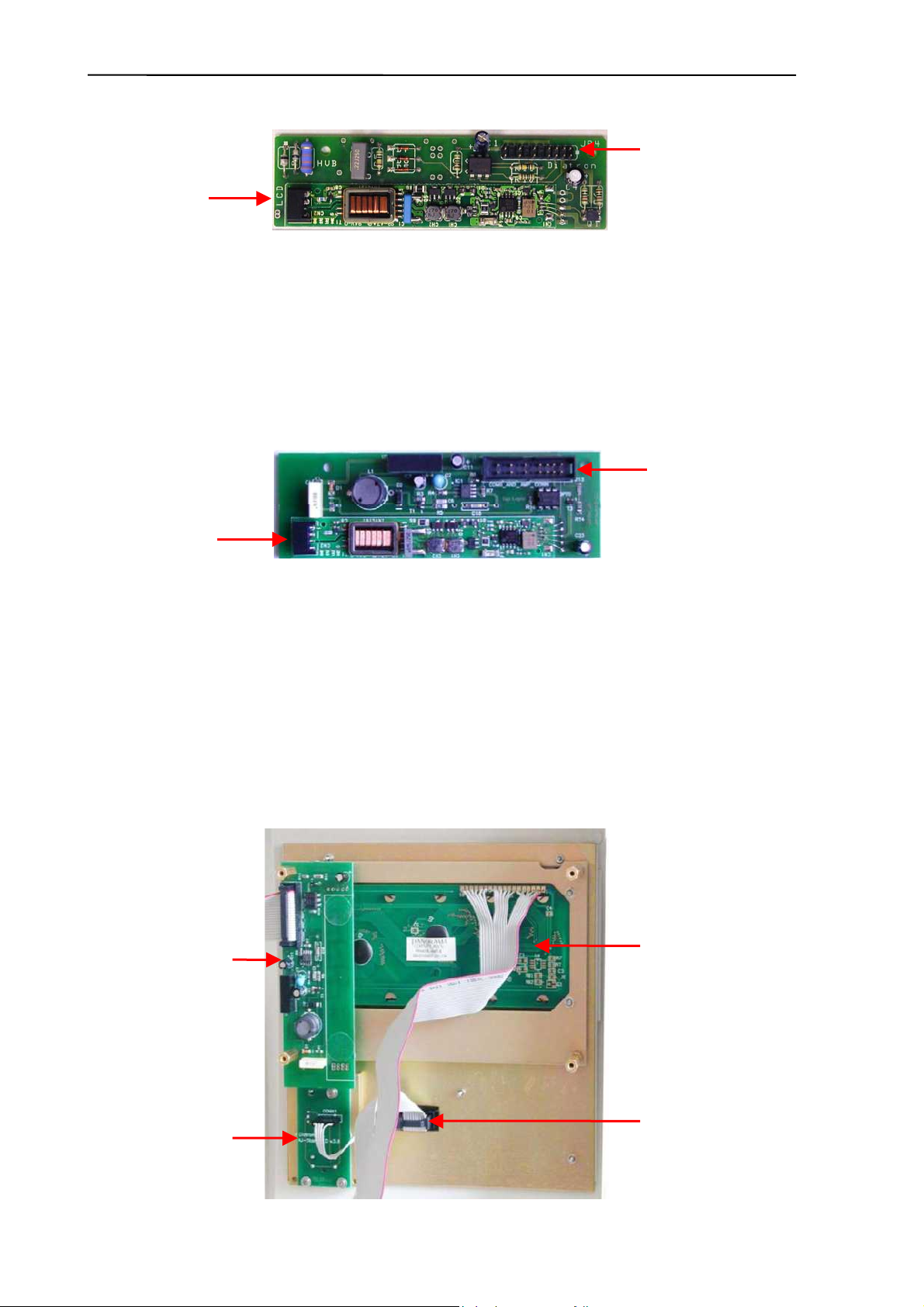
1
6
Diatron Ltd. 2004
Connection to
COMB and
amplifier
Connection
to LCD lamp
In Abacus Junior B, we needed a new high voltage board, because in this instrument there’s
no need for the inverter on the previous HVB (the alphanumeric display has no CCFL
backlight), but the measuring and cleaning voltage generation based on the inverter’s high
voltage. That’s why we developed HVB v2.1, which is still capable to carry and feed the
inverter, but the board has its own high voltage generation circuitry, so can be used without
the inverter placed on it.
HVB v2.1:
Connection to
COMB and
amplifier
Connection
to LCD lamp
Start key is a micro-switch, connected to the COMB card (through the Display ribbon cable).
The status LED indicates the actual status of the analyzer and it has three colors: red, green
and amber (See User’s Manual). The LED has three pins and the actual color depends on
the controlled pins. Start key and status LED are controlled by COMB.
2.1.13. LCD Display Module with High Voltage Board of Abacus Junior B
The display assembly in Abacus Junior B contains a 4x20 characters alphanumeric display,
a high voltage board, a Start key and status LED board. The alphanumeric display has
internal LED based backlight, which is driven and controlled by the MAIN board.
HVB
without inverter
Alphanumeric LCD
Start key and status
LED board
Keypad connector
Abacus junior /vet / B Service Manual
7
1
High Voltage Board (HVB) generates the aperture cleaning voltage (150V), and measuring
voltage (50V). The high voltage board is connected to the system through the amplifier board
and the MAIN board.
Connection to
MAIN board
Uninstalled
inverter board
CFSW signal (from MAIN board) controls HVB: logical LOW turns inverter on. MVON signal
(from MAIN board) switches the measuring voltage (50 V) on/off by O1 opto switch.
Warning! Be careful with servicing this board in active state, because the high
voltage can make damages or electric shock!
Start key is a micro-switch, connected to the MAIN board (through the Display ribbon cable).
The status LED indicates the actual status of the analyzer and it has three colors: red, green
and amber (See User’s Manual). The LED has three pins and the actual color depends on
the controlled pins. The MAIN board controls start key and status LED.
In Abacus Junior B the LCD controlling and keypad reading are handled by the microcontroller of the MAIN board via some interface circuitry.
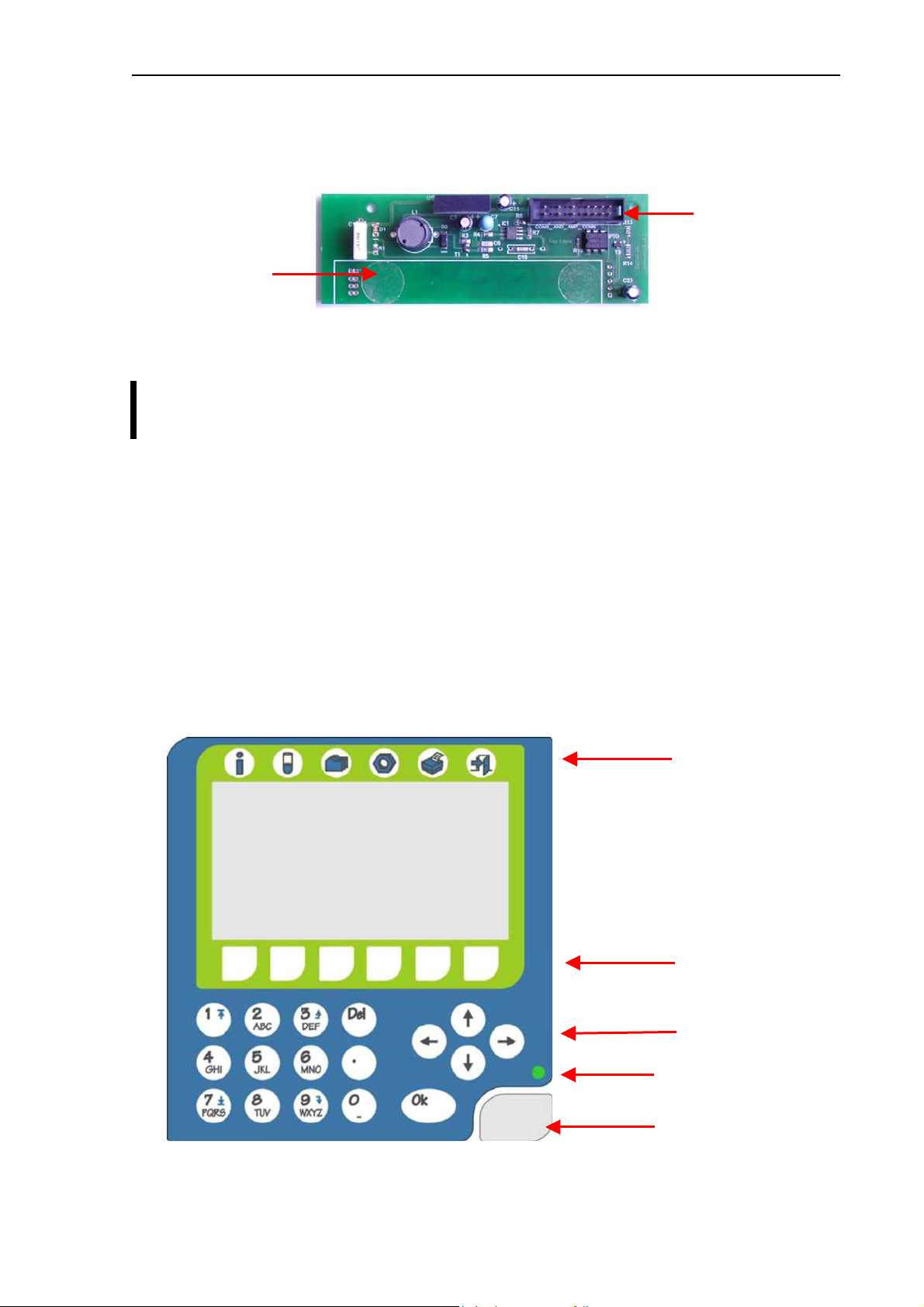
2.1.14. Keypad of Abacus junior/Abacus junior vet
The analyzer has a 29-button foil keypad including numerical keypad (0-9, “.”), cursor
moving, OK and Del buttons, and 6-6 function buttons, above and under the LCD display as
it is shown in the picture below:
Function buttons
Function buttons
Cursor buttons
Status LED
START button

1
8
Diatron Ltd. 2004
2.1.15. Keypad of Abacus junior B
The analyzer has a 21-button foil keypad including numerical keypad (0-9, “.”), OK and Del
buttons, and 4-4 function buttons, above and under the LCD display as it is shown in the
picture below:
2.1.16. Floppy Disk Drive and CD-ROM Drive - AJ/AJvet
Function buttons
Function buttons
Status LED
Start button
The built-in Floppy Disk Drive makes possible to save data on floppy disks, and to install (or
upgrade) the software. The optional CD-ROM drive can be used to install software (only read
actions from CD-ROM, as write operations are not supported by the instrument’s operating
system). Both units are connected to COMB card: CD-ROM to IDE interface, FDD to Floppy
interface.
CD-ROM
Drive
Floppy Disk
Drive
Abacus junior /vet / B Service Manual
19
2.1.17. External Power Supply
The analyzer works with an external power supply. The next figure shows the power supply
unit generating 12VDC.
115V or 230V
AC inlet
12V DC outlet
The power supply modules have an auto range input, which makes possible to use them with
230V or 115V mains outlet and it has the CE and UL safety certification. The input socket of
the power supply is a standard 3-terminal plug, with power cable connection; the output is a
special, lockable socket as it is shown in the picture.
2.1.18. MAIN board - AJB
MAIN board is responsible to control the instrument: contains the main power regulator
circuits, valve and motor driver circuits and other connections for the fluidic and pneumatic
system’s parts, responsible for the specific measurement processing functions.
The board also contains two 24FC256 serial E
information of the instrument (Serial Number, OEM, model, etc.) and the measurement
database.
The central micro-controller with a CPLD and with several other digital chips (buffers,
decoder, multiplexer) handles the pneumatic system, displaying, measurement and data
management.
Power system: filtering the +12V Input and generates +3.3V (CPLD), +5V (Digital power),
+8V (Printer power). Filtered +12V is used for the power of motors and valves.
Motor drivers: 6 power drivers; Horizontal, Vertical and Sample rotor motors have one
combined ribbon cable connection. Main Dilutor (with two motors) and Micro-dilutor have
separated connectors.
Valve driver: consists two 8-bit, powered output shift registers (with built in protection diodes)
and there is one common ribbon cable connection for the valve boards. The peristaltic pump
has a separated Darlington driver circuit for more reliable operation.
Real Time Clock: for TIME/DATE functions; powered by Battery at switched off state.
2
PROMs, which store the settings and identity
Measurement processing: the A/D conversion made by the micro-controller itself, but several
preprocessing steps (time limits, noise handling, pulse integration) taken by the external
analog circuitry.
External communication through RS232 makes possible to update the firmware of the microcontroller with an external PC.

2
0
Diatron Ltd. 2004
Micro
dilutor
connection
Horizontal, Vertical & Sample
rotor connection
Pressure
sensor
connection
Peristaltic
Pump
connection
Reagent
Sensor
connection
Valves
connection
+12V
Power Input
High Voltage
Board
connection
Speaker
connection
Main Dilutor
connection
+5V voltage
regulator
(on chassis)
Printer
connection
COM port
LCD, Keypad and
Startkey/LED
connection
CS_ANALOG and CS_IMP
amplifier connections
Abacus junior /vet / B Service Manual
21
2.2. Main mechanic and fluidic parts of the Analyzer
Abacus junior / Abacus junior vet / Abacus junior B Hematology Analyzers consist of the
following mechanic and fluidic parts:
1. Sample rotor
2. Sampling needle
3. Washing head
4. H&V moving unit
5. Micro Dilutor
6. Dilutor
7. Chamber
8. Cell-counter probe
9. Puffer reservoir
10.Pump
11.Valves
12.Tubing
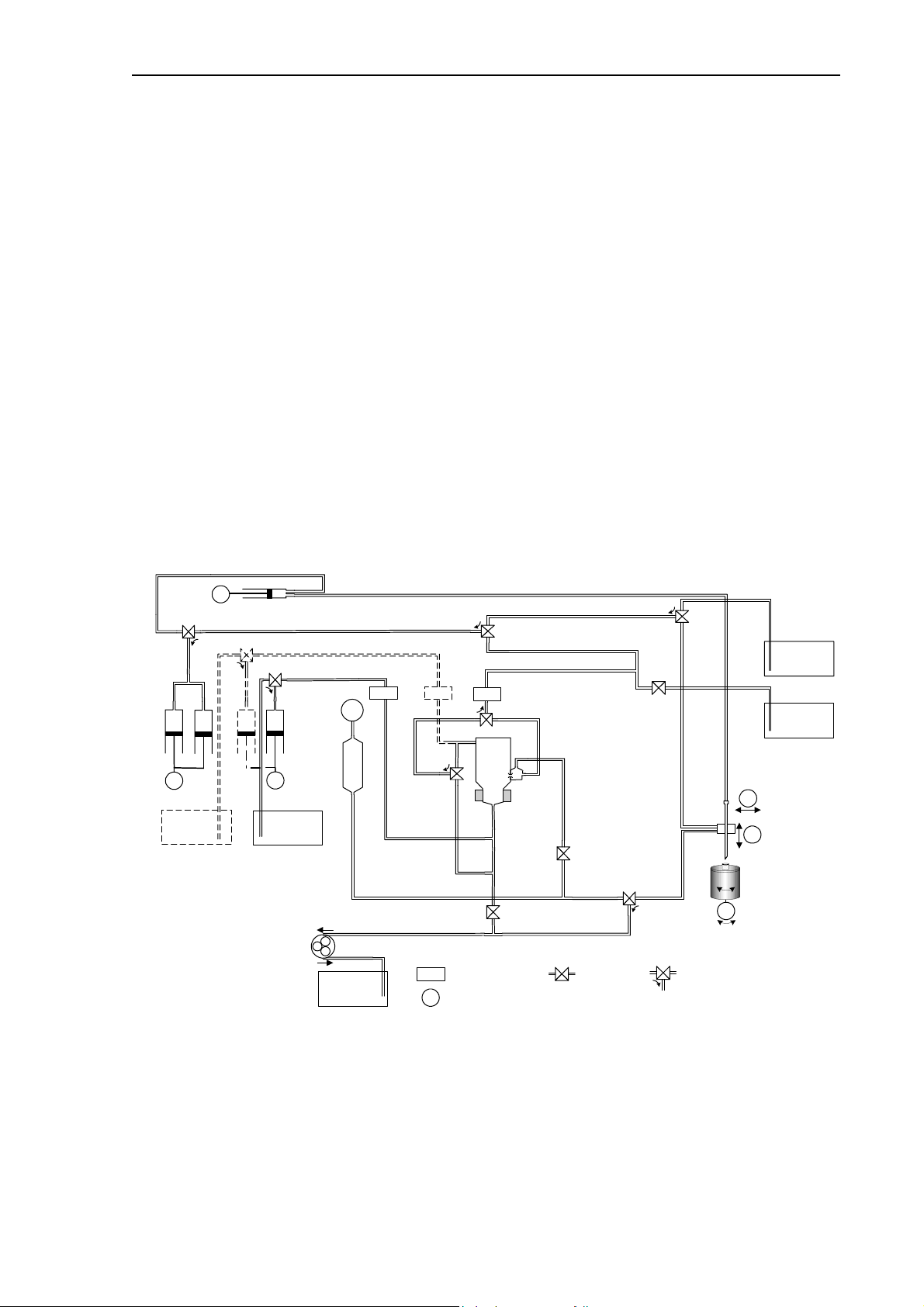
Main
dilutor
V8 DilNeedle
2
3
Dil
M3
RINSE
Abacus junior & Abacus junior vet
&
Abacus junior
B
Fluidic Schematics
Version 2.1
M4
Micro-dilutor
1
V11Rinse
1
2
3
V9LyseWbc
1
2
Pressure
3
Meter
Lyse
Sensor
V7 DilChamber
LDRLDL
P
Puffer
Reservoir
M6
Lyse
V3 Bubble
Rinse
Rinse
Sensor
3
3
LDD
1
1
2
HGB
1
2
Diluent & Cleaner
Sensor
3
V4 DilAperture
2
RBC
WBC
V10 Cleaner
LYSE
V2 DrainAperture
V5 DrainPuffer
1
2
3
2-way Valve
Closed = Off
Open = On
Pump
WASTE
LDx
M1
V1 DrainChamber
Liquid Detector
Stepper Motor
V6 DilWash
12
3
3
1
2
3-way
Valve
1-3 = Off
2-3 = On
M5
M1
Hor
M2
Ver
Sample
rotor
DILUENT
CLEANER
The main fluidic schematics are almost the same for the three models. The only exception is
the Rinse reagent and the corresponding Rinse syringe and Rinse valve (V11), which is
present for the AJvet model only.
22
Diatron Ltd. 2004
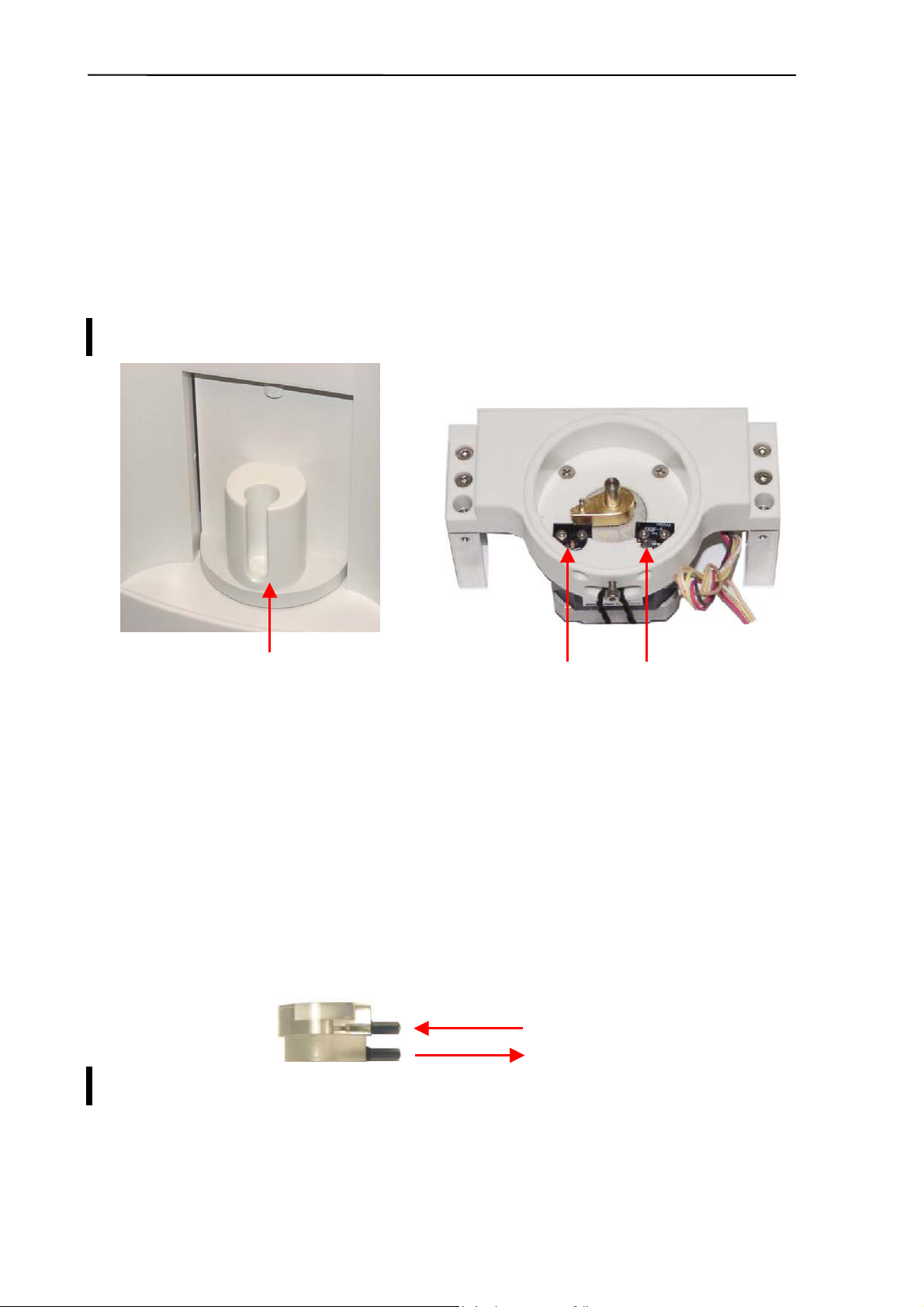
2.2.1. Sample rotor
Abacus junior / Abacus junior vet / Abacus junior B hematology Analyzers has a sample
rotor for safety and more precise sample handling. Commonly used sample tubes are
supported by replaceable tube adapters.
The Sample rotor unit uses a stepper motor, connected to the PPB (AJ/AJvet) or to the
MAIN board (AJB), through the XY opto board. The rotor has micro switches for positioning.
The unit blocks itself in the home and end position with mechanical parts and has a special
cap that prevents the damage of the electronic and mechanic parts caused by any fluid.
Sample rotor is maintenance-free.
Replaceable tube adapter Micro switches for positioning
2.2.2. Sampling needle
Sampling needle is assembled in the H&V moving unit and it makes the sample aspirations.
Correct setting of sampling needle is necessary and very important (see Chapter
Adjustments).
2.2.3. Washing head
Washing head is located at the bottom of the H&V moving unit and it is for cleaning the outer
surface of the sampling needle. This washing process is made with diluent reagent and the
fluid is drained by the pump. The arrows on the picture show the direction of diluent flow
during sampling needle washing.
Clean diluent
Pump to waste
Clean or replace washing head yearly, or after 10 000 measurements.
Abacus junior /vet / B Service Manual
23
2.2.4. H&V moving unit
All three instruments use the same H&V moving unit.
This unit contains slides to move the sample sampling needle in Horizontal and Vertical
directions, two stepper motors, XYR opto board, opto wheel, washing head and the sampling
needle. It moves the needle to the desired position: from sampling position, to washing head,
and to the measuring chamber.
Sampling needle
holder
XYR opto board
Sampling needle
Washing head
Horizontal
motor
Vertical opto wheel
Vertical
motor
Both stepper motors have optical end-switch sensors for detecting these positions. These
are required for correct initialization and error detection. All sensors have status LEDs to
show actual conditions.
The Vertical motor works with a special opto wheel for detecting home & end positions. See
the Adjustment section of this manual to place this wheel to the proper position.
Greasing of the horizontal/vertical guiding rods should be done regularly using
“Photorub”, a PTFE-based thin lubricant.
It is recommended to check and repeat greasing of guiding rods every year, or after
10000 measurements.
24
(
Diatron Ltd. 2004
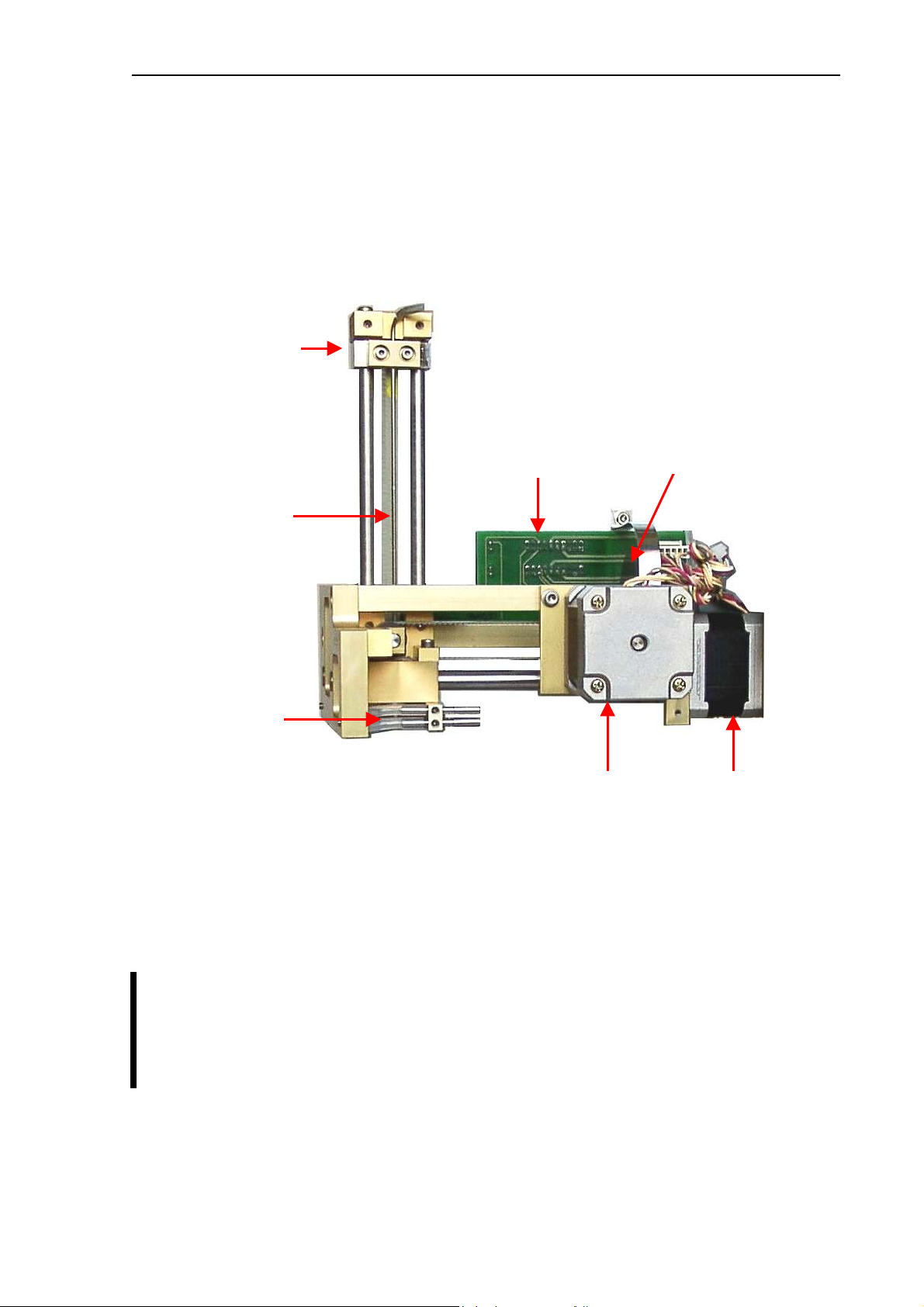
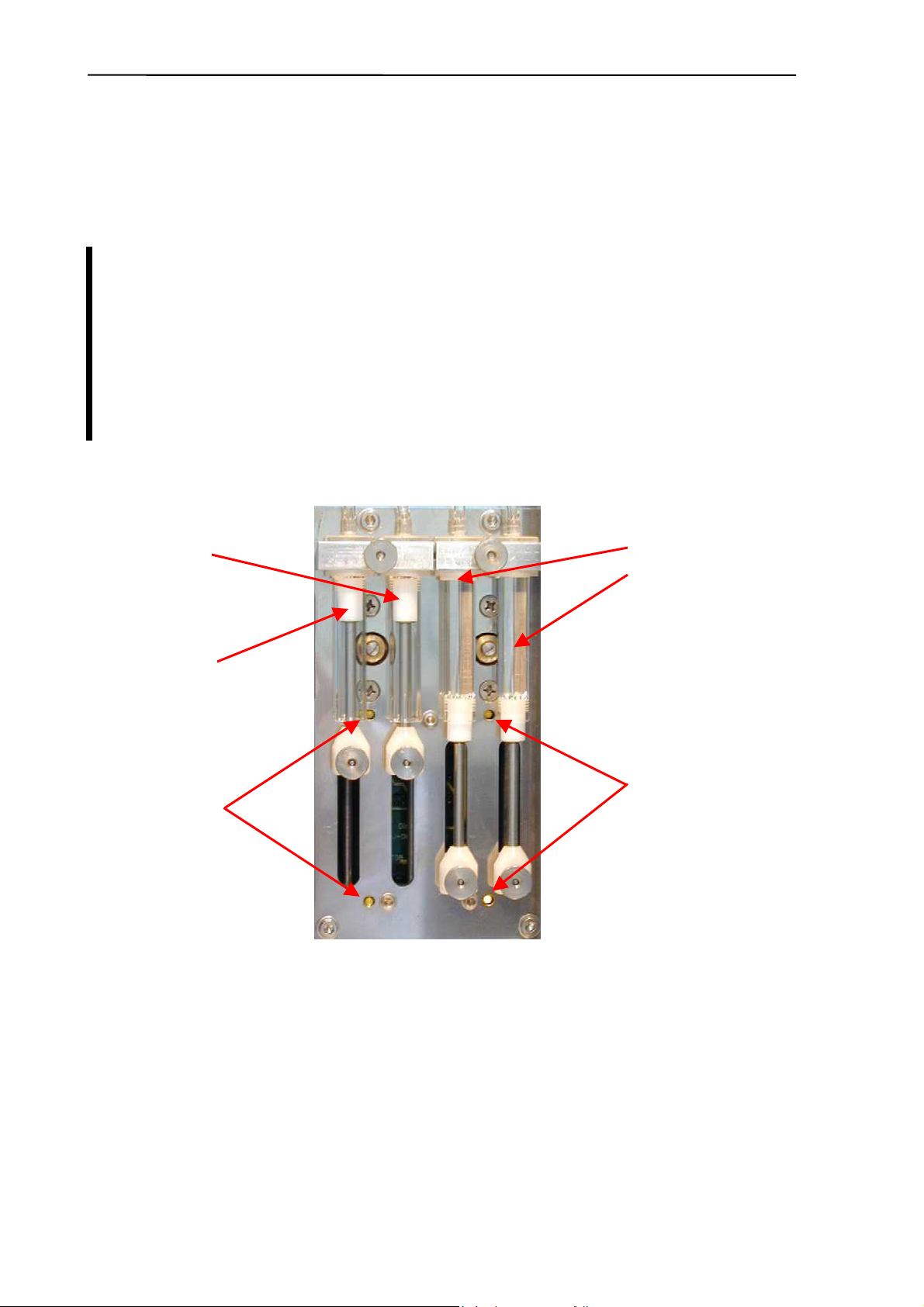
2.2.5. Main Dilutor
In case of AJ and AJB this unit includes two dilutor channels – one for diluent, and another
one for lyse reagents. (There’s another channel for Rinse in the AJvet model). There are two
stepper motors, a common motor opto board, three (AJ/AJB) or four (AJvet) syringes and
piston rods with gear transmission.
Maintenance should be provided to the piston tips, by applying neutral silicon
grease to the cogged end of the Macro and Lyse pistons, between the syringe and
the tip itself. This will ensure optimum sealing and longer lifetime of piston tips.
Greasing of the cogged transmission parts (cogwheel and cogged bar) should be
done regularly using machine grease.
It is recommended to check and repeat greasing of piston tips, and transmission
gear every year, or after 10000 measurements.
Rinse
piston
AJvet)
Diluent
syringes
Lyse
piston
Control
LEDs
Control
LEDs
Abacus junior /vet / B Service Manual
5
2
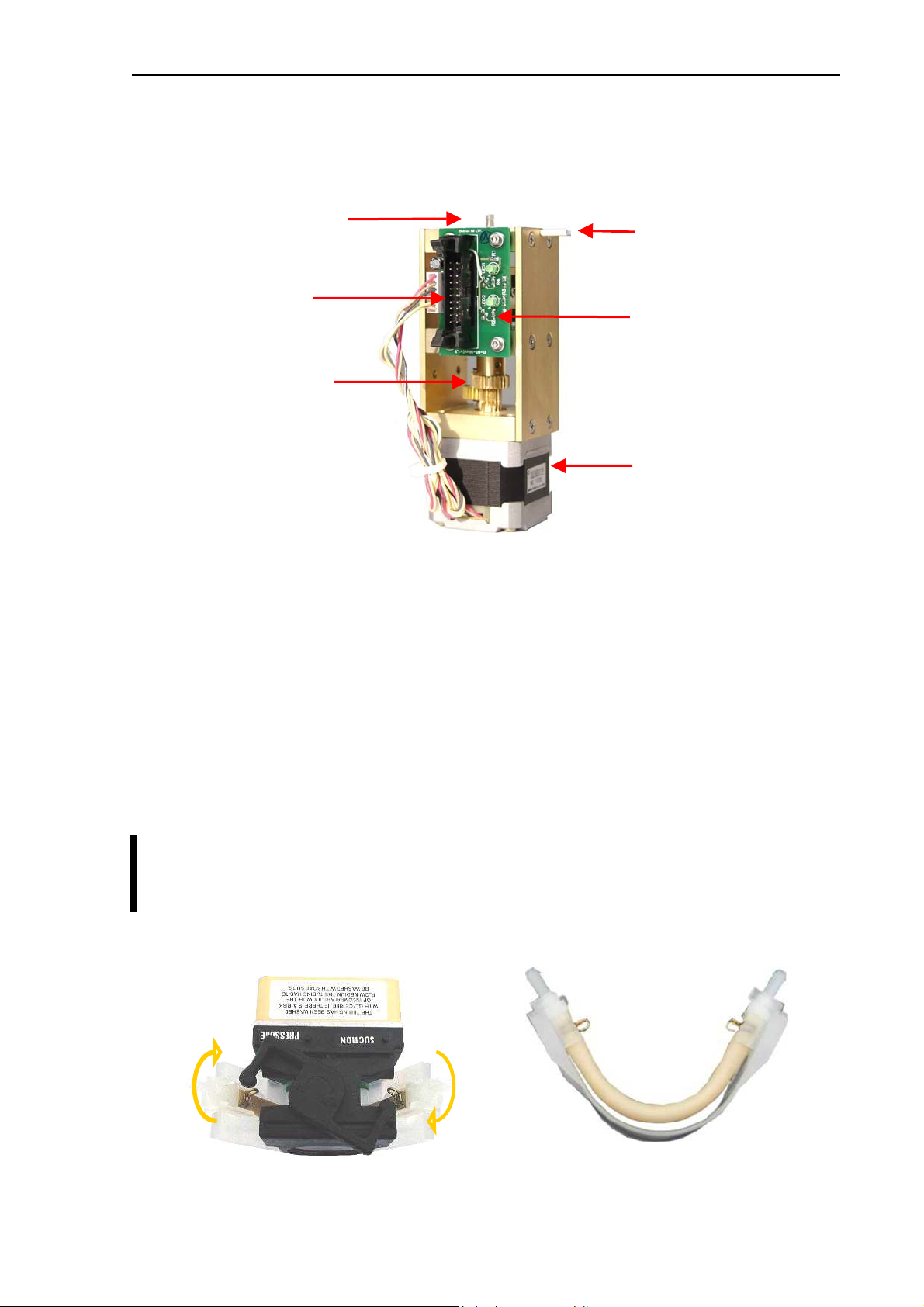
2.2.6. Micro Dilutor
Micro dilutor is taking the precise sample (25 or 50µl) into the sampling needle. It includes a stepper
motor, a motor opto board and the micro syringe.
Connection to Valve
Connection to
PPB (AJ/AJvet)
MAIN board (AJB)
Transmission gear
Connection to needle
Motor opto board
Stepper motor
2.2.7. Puffer reservoir
The glass puffer reservoir is directly connected to the pressure sensor.
During measurement, there is no pump activity, so the puffer reservoir maintains measuring
vacuum stable. The instrument measures atmospheric pressure and adjusts measuring
vacuum according to it.
2.2.8. Pump
Pump generates regulated vacuum and drains the fluidic system. It is connected to the PPB
(AJ/AJvet) or to the MAIN board (AJB) and it has its own driver circuit (Darlington).
If the tube of the peristaltic pump becomes worn, it can be broken, causing Pressure error.
It is recommended to check the state of the tube, and replace it every 2 years, or
after 20 000 measurements. Always replace the peristaltic pump tube to the same
PharMed® type, with the same length.
For servicing the tube of the pump, open the peristaltic pump from its top (see picture) and
remove the tube together with the white plastic side wall (see picture):
In case of damaged tubes, it can be replaced by a new one by opening the two metal locks
located at the two ends of the tube (see picture).

2
6
Diatron Ltd. 2004
2.3. Assembled Analyzer
2.3.1. Abacus junior / Abacus junior vet
Front Panel (note display logo: it is an Abacus Junior model; and missing optional CD-ROM
drive module):
Built-in thermal
printer (optional)
240x128 dots
Graphic LCD
Function keys
Foil keypad
START button
Sample tube
adapters
Sample rotor
Floppy drive
Rear panel (note reagent inlets: it is an Abacus Junior model as there is no Rinse
connection):
Back door to
access pump and
main dilutor
Reagent inlets
Power switch
Keyboard
Serial Port
Printer Port

Abacus junior /vet / B Service Manual
7
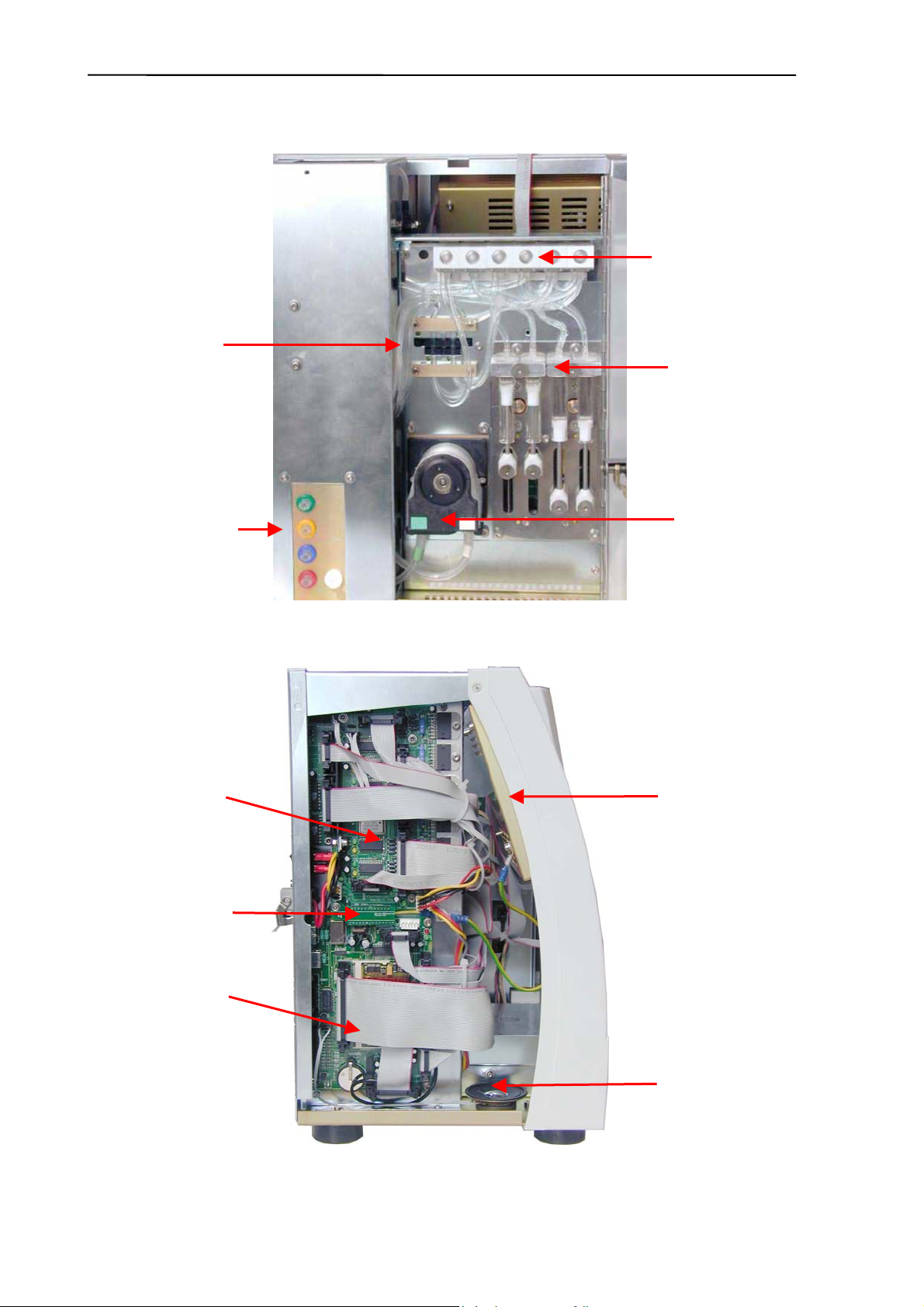
Construction – front (note optional CD-ROM drive):
Pressure
sensor
Valve block
Electronic
block
Sample rotor
2
Speaker
CD-ROM, FDD
Construction – right side (note white reagent inlet for Rinse: it is an Abacus Junior Vet
model):
Washing head
Chamber and
aperture
Adapter
Needle
moving
mechanics
Micro dilutor
Amplifier
assembly
Reagent
inlets
Sample rotor
Valve block
2
8
(
Diatron Ltd. 2004
Construction – back (note white reagent inlet for Rinse, main dilutor and valve block with 6
valves: it is an Abacus Junior Vet model):
Valve block
Reagent
sensors
Main Dilutor
Reagent
connectors
Construction – left side (note connected IDE ribbon cable):
Pneumatic
and Power
Board (PPB)
ID Eprom Board
IDEPROM)
Peristaltic
pump
Display
assembly
Control and
Measurement
Board (COMB)
Speaker

Abacus junior /vet / B Service Manual
2.3.2. Abacus junior B
Front panel (note missing floppy and CD-ROM drives):
Built-in thermal
printer
4x20 character
Alphanumeric LCD
Function keys
29
Foil keypad
Rear panel (note Serial Port as the only interface):
START
Sample rotor
button
Sample tube
adapters
Back door to
access pump and
main dilutor
Reagent inlets
Power switch
Serial Port
 Loading...
Loading...