Page 1
Revision
Date
Comment
A.00
11/27/2013
Initial release
A.01
9/3/2014
Minor update
A.02
3/22/2016
Updated section 7.1 (Command Line Interface)
A.03
4/4/2017
Correction in console login
Epsilon-12G2 User Manual
Managed 14-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Part Number 7460440
Copyright 2016
FOR TECHNICAL SUPPORT Diamond Systems Corporation
PLEASE CONTACT: 158 Commercial Street
Sunnyvale, CA 94086 USA
support@diamondsystems.com Tel 1-650-810-2500
Fax 1-650-810-2525
www.diamondsystems.com
Page 2

CONTENTS
1. Important Safe Handling Information .............................................................................................................3
2. Introduction .......................................................................................................................................................4
2.1 Main Feature List ...........................................................................................................................................4
2.2 Mechanical and Environmental .....................................................................................................................5
2.3 Products .........................................................................................................................................................5
2.4 Cable List .......................................................................................................................................................5
3. Functional Overview .........................................................................................................................................6
4. Board Outline and Layout ................................................................................................................................7
5. Connector and Jumper List .............................................................................................................................8
5.1 Connector List ................................................................................................................................................8
5.2 Jumper Block .................................................................................................................................................8
6. Connector Pinout and Pin Description ...........................................................................................................9
6.1 Ethernet (J1-J12) ...........................................................................................................................................9
6.2 Serial Interface (J13) .....................................................................................................................................9
6.3 SFP Socket (J15)...........................................................................................................................................9
6.4 LED Status Signals (J17) ........................................................................................................................... 10
6.5 Input Power (J18) ....................................................................................................................................... 11
7. Software Interfaces ........................................................................................................................................ 11
7.1 Command Line Interface ............................................................................................................................ 11
7.1.1 Making an Initial Connection .......................................................................................................... 11
7.1.2 General Command Groups ................................................................................................................ 12
7.1.3 IP Commands .................................................................................................................................... 12
7.1.4 MAC Commands ................................................................................................................................ 13
7.1.5 VLAN/PVLAN Commands ................................................................................................................. 13
7.1.6 dot1x (IEEE Standard for port-based Network Access Control) ........................................................ 13
7.1.7 LACP Commands .............................................................................................................................. 14
7.1.8 LLDP Commands ............................................................................................................................... 14
7.1.9 Access Management Commands ...................................................................................................... 14
7.1.10 Logging Commands ........................................................................................................................... 14
7.1.11 Spanning-tree Commands ................................................................................................................. 14
7.1.12 Green-Ethernet Commands ............................................................................................................... 15
7.1.13 Thermal-protect Commands .............................................................................................................. 15
7.1.14 Loop-protect Commands ................................................................................................................... 15
7.1.15 QoS Commands ................................................................................................................................ 15
7.1.16 Privilege Commands .......................................................................................................................... 15
7.1.17 SNMP Commands ............................................................................................................................. 16
7.1.18 SNTP Commands (config)# sntp ....................................................................................................... 16
7.1.19 Radius Server Commands ................................................................................................................. 16
7.1.20 Banner Commands (Defines a login banner) .................................................................................... 17
7.1.21 Terminal Commands .......................................................................................................................... 17
7.1.22 Reload ................................................................................................................................................ 17
7.1.23 Firmware Commands ......................................................................................................................... 17
7.1.24 Ping Commands ................................................................................................................................ 17
7.1.25 Debug Commands ............................................................................................................................. 17
7.1.26 Security Commands ........................................................................................................................... 17
7.1.27 Monitor ............................................................................................................................................... 18
7.2 Examples .................................................................................................................................................... 18
7.2.1 IP Configuration ................................................................................................................................. 18
7.2.2 Port Configuration .............................................................................................................................. 18
7.2.3 Change Switch Password .................................................................................................................. 19
7.2.4 Set up VLANs .................................................................................................................................... 19
7.2.5 SNMP configuration ........................................................................................................................... 19
7.2.6 Mirroring ............................................................................................................................................. 20
7.2.7 Setup QoS ......................................................................................................................................... 20
7.2.8 Factory defaults ................................................................................................................................. 20
7.3 Web Interface ............................................................................................................................................. 21
7.3.1 Web Interface Activation / Deactivation ............................................................................................. 22
8. Specifications ................................................................................................................................................. 23
Appendix A Supported MIBs ........................................................................................................................... 24
Epsilon-12G2 User Manual Revision A.02 www.diamondsystems.com Page 2
Page 3

WARNING!
ESD-Sensitive Electronic Equipment
Observe ESD-safe handling procedures when working with this product.
Always use this product in a properly grounded work area and wear appropriate
ESD-preventive clothing and/or accessories.
Always store this product in ESD-protective packaging when not in use.
1. IMPORTANT SAFE HANDLING INFORMATION
Safe Handling Precautions
The Epsilon-12G2 board contains a high density connector with many connections to sensitive electronic
components. This creates many opportunities for accidental damage during handling, installation and connection
to other equipment. The list here describes common causes of failure found on boards returned to Diamond
Systems for repair. This information is provided as a source of advice to help you prevent damaging your
Diamond (or any vendor’s) boards.
ESD damage – This type of damage is usually almost impossible to detect, because there is no visual sign of
failure or damage. The symptom is that the board eventually simply stops working, because some component
becomes defective. Usually the failure can be identified and the chip can be replaced. To prevent ESD damage,
always follow proper ESD-prevention practices when handling computer boards.
Damage during handling or storage – On some boards we have noticed physical damage from mishandling. A
common observation is that a screwdriver slipped while installing the board, causing a gouge in the PCB surface
and cutting signal traces or damaging components.
Another common observation is damaged board corners, indicating the board was dropped. This may or may not
cause damage to the circuitry, depending on what is near the corner. Most of our boards are designed with at
least 25 mils clearance between the board edge and any component pad, and ground / power planes are at least
20 mils from the edge to avoid possible shorting from this type of damage. However these design rules are not
sufficient to prevent damage in all situations.
A third cause of failure is when a metal screwdriver tip slips, or a screw drops onto the board while it is powered
on, causing a short between a power pin and a signal pin on a component. This can cause overvoltage / power
supply problems described below. To avoid this type of failure, only perform assembly operations when the
system is powered off.
Sometimes boards are stored in racks with slots that grip the edge of the board. This is a common practice for
board manufacturers. However our boards are generally very dense, and if the board has components very close
to the board edge, they can be damaged or even knocked off the board when the board tilts back in the rack.
Diamond recommends that all our boards be stored only in individual ESD-safe packaging. If multiple boards are
stored together, they should be contained in bins with dividers between boards. Do not pile boards on top of each
other or cram too many boards into a small location. This can cause damage to connector pins or fragile
components.
Power supply wired backwards – Our power supplies and boards are not designed to withstand a reverse
power supply connection. This will destroy each IC that is connected to the power supply (i.e. almost all ICs). In
this case the board will most likely will be unrepairable and must be replaced. A chip destroyed by reverse power
or by excessive power will often have a visible hole on the top or show some deformation on the top surface due
to vaporization inside the package. Check twice before applying power!
Overvoltage on analog input – If a voltage applied to an analog input exceeds the design specification of the
board, the input multiplexor and/or parts behind it can be damaged. Most of our boards will withstand an
erroneous connection of up to 35V on the analog inputs, even when the board is powered off, but not all boards,
and not in all conditions.
Overvoltage on analog output – If an analog output is accidentally connected to another output signal or a
power supply voltage, the output can be damaged. On most of our boards, a short circuit to ground on an analog
output will not cause trouble.
Overvoltage on digital I/O line – If a digital I/O signal is connected to a voltage above the maximum specified
voltage, the digital circuitry can be damaged. On most of our boards the acceptable range of voltages connected
to digital I/O signals is 0-5V, and they can withstand about 0.5V beyond that (-0.5 to 5.5V) before being damaged.
However logic signals at 12V and even 24V are common, and if one of these is connected to a 5V logic chip, the
chip will be damaged, and the damage could even extend past that chip to others in the circuit.
Epsilon-12G2 User Manual Revision A.02 www.diamondsystems.com Page 3
Page 4

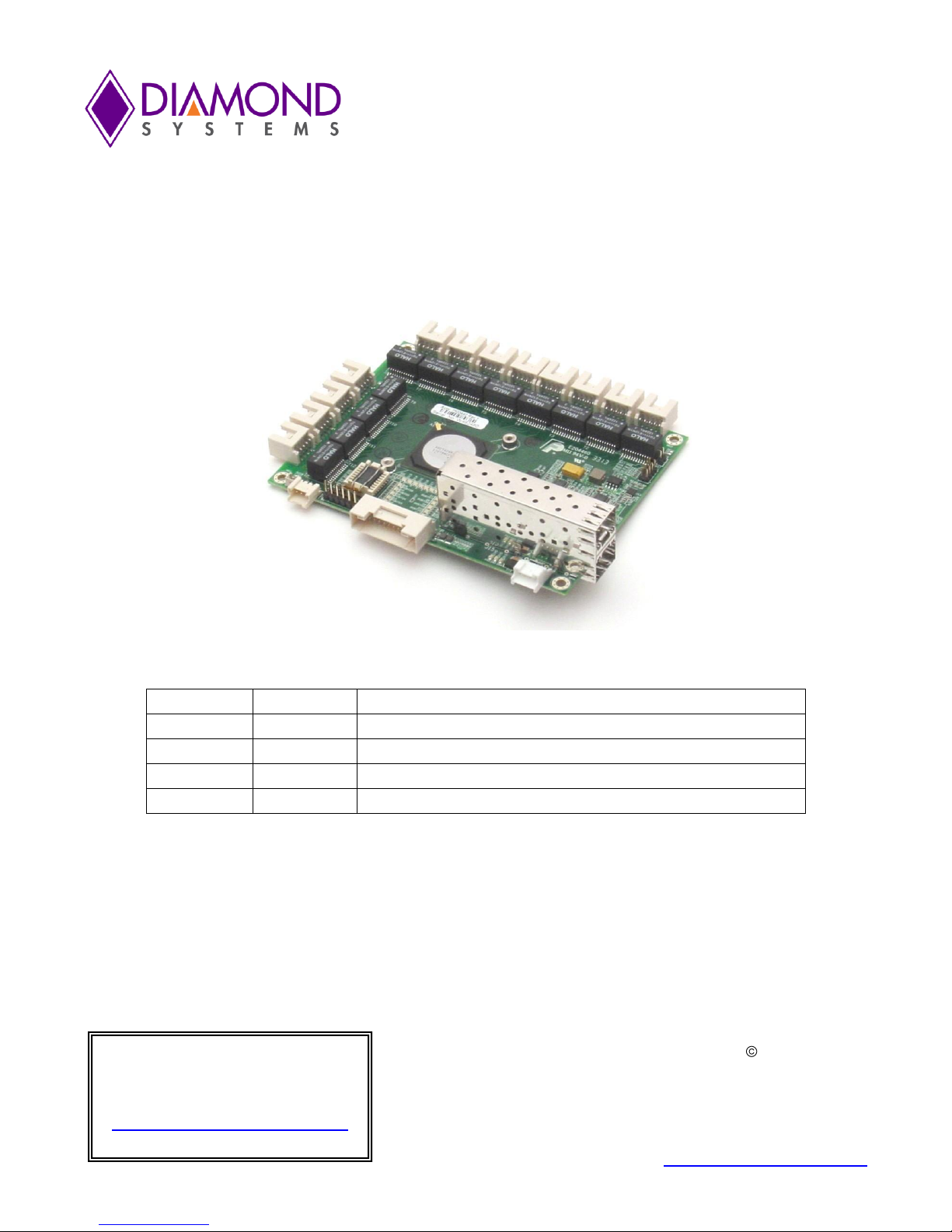
2. INTRODUCTION
Epsilon-12G2 is a managed, 14-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch with wide power supply voltage input and a serial
management port. Epsilon-12G2 offers twelve 10/100/1000Mbps copper twisted pair ports, one 1G SFP socket,
and one 2.5G SFP socket on a COM Express format board. The board is standalone, so no bus connectors are
required. An RS-232 interface is provided to enable communication between the on-board management
microcontroller and a host processor through a command line interface (CLI). A wide-range DC power supply is
built into the board to allow it to be used with industrial power sources as well as the typical embedded +5V
supply.
Highly Advanced Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Epsilon-12G2 is a standalone 14-port Gigabit Ethernet managed switch in the COM Express form factor. It delivers
a comprehensive, end-to-end carrier Ethernet solution supporting MEF service delivery and timing over packet
solutions for IEEE 1588 and synchronous Ethernet.
Layer 2+ Managed Switch
Epsilon-12G2’s Ethernet switch chip includes a built-in microcontroller for configuration and management. It can
be accessed either through the on-board RS-232 port or one of the Ethernet ports.
Wide Power DC/DC Power Supply
Epsilon-12G2 can be powered through a wide voltage +5-40V DC/DC power supply input.
Rugged Design
Extended temperature operation of -40°C to +85°C is tested and guaranteed. Epsilon-12G2 was designed with
harsh applications in mind. Latching connectors provide increased reliability.
Software Support
The Epsilon-12G2 switch is ready to plug into your application without any driver installation or firmware
upgrades. An intuitive GUI web interface and a command line interface provide means for configuring and
managing the switch.
2.1 Main Feature List
12 10/100/1000Mbps copper Ethernet ports with nonblocking wire-speed performance
1 1G SFP socket and 1 2.5G SFP socket
Dual leaky bucket policers with remarking and statistics
Jumbo frame support at all speeds
8K MAC addresses and 4K VLANs (IEEE 802.1Q), as well as 8K IPv4 and IPv6 multicast group support
Flexible link aggregation support based on Layer-2 through Layer-4 information (IEEE 802.3ad)
Multicast and broadcast storm control, as well as flooding control
RSTP and MSTP
8 priorities and 8 QoS queues per port with scheduling
Shaping/policing per queue and per port
Multiple protocol support: IEEE 802.1d, IEEE 802.1w, IEEE 802.1s, and IEEE 802.1X
Built-in 416MHz MIPS 24KEC microcontroller for configuration and management
RS-232 serial port provides out-of-band management interface
Can operate autonomously or in conjunction with a host SBC
Wide input voltage range: +5-40VDC input
COM Express form factor (95 x 125mm)
Epsilon-12G2 User Manual Revision A.02 www.diamondsystems.com Page 4
Page 5
Model Number
Description
EPS-12G2
14-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch, COM Express form factor,
-40°C to +85°C operating temperature
CK-EPS12G2
Epsilon-12G2 Cable Kit
Number
Part Number
Quantity
Description
1
6981050
1
Serial cable
2
6981052
12
Ethernet cable (1 per port)
3
6981053
1
Power cable
2.2 Mechanical and Environmental
COM Express compliant form factor including:
Board dimensions
Mounting holes
Component height
-40°C to +85°C ambient operating temperature
2.3 Products
The table below lists the model number and description for the Epsilon-12G2 and its associated cable kit.
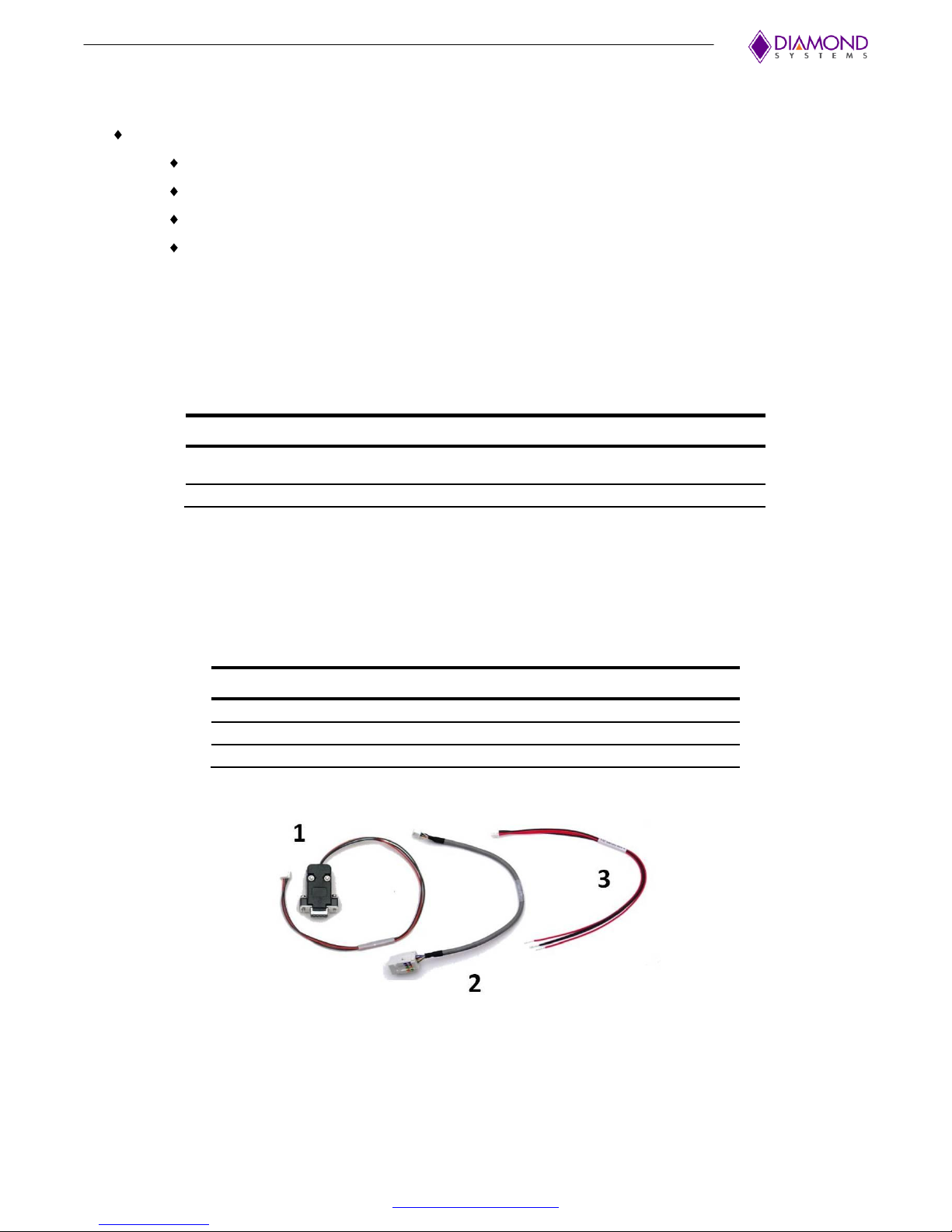
2.4 Cable List
The contents of the Epsilon-12G2 Cable Kit, CK-EPS12G2, are shown below.
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Epsilon-12G2 User Manual Revision A.02 www.diamondsystems.com Page 5
Page 6
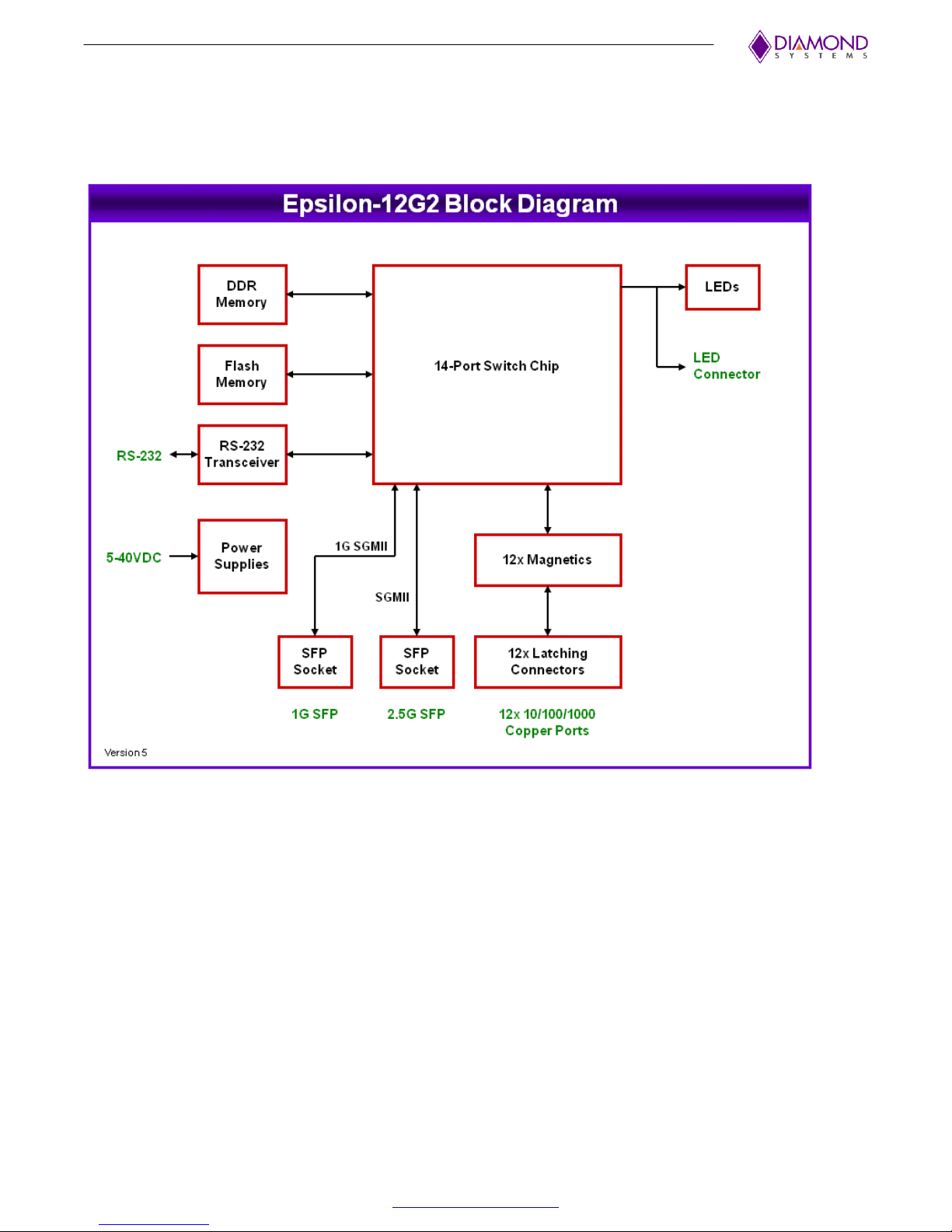
3. FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW
Functional Block Diagram
Epsilon-12G2 is an 14-Port managed Gigabit Ethernet switch module offering 10/100/1000Mbps copper twisted
pair ports, one 1G SFP socket, and one 2.5G SFP socket on a COM Express form factor board. Epsilon-12G2
operates standalone, requiring no connection to a single board computer in the stack.
Epsilon-12G2 is a Layer 2+ managed Ethernet switch with built-in microcontroller and memory for configuration
and management. The Flash memory holds dual application images along with the boot code, The SRAM is used
for program execution and storing the MAC addresses. The EEPROM holds the configuration parameters. .
An RS-232 interface is provided to enable communication between the on-board management microcontroller
and a host processor through a CLI interface. The microcontroller is also accessible through one of the Ethernet
ports via a web management interface.
Power is provided through the +5-40VDC wide-range DC power supply built into the board, enabling use with
industrial power sources.
Epsilon-12G2 User Manual Revision A.02 www.diamondsystems.com Page 6
Figure 1. Functional Block Diagram
Page 7

J12
J13
J17
J15
J11
J10
J9
J8
J7
J6
J5
J4
J3
J2
J1
J18
J19
4. BOARD OUTLINE AND LAYOUT
The following image shows the locations for all connectors and jumpers which are described in the next sections.
Figure 2. Epsilon-12G2 (Connectors and Jumpers)
Epsilon-12G2 User Manual Revision A.02 www.diamondsystems.com Page 7
Page 8
Connector
Function
J1-J12
Gigabit Ethernet (x12)
J13
RS-232 Serial Interface
J15
Dual SFP Ethernet sockets
J17
LED Status Signals and Resets
J18
Power In
Jumper
J19 Pins
Function
1&2
Reset: Install jumper and apply power to reset the switch
5. CONNECTOR AND JUMPER LIST
5.1 Connector List
The following table summarizes the functions of Epsilon-12G2’s interface connectors. Refer to the Figure 2 for the
locations of these connectors on Epsilon-12G2. Signal functions relating to all of Epsilon-12G2’s interface
connectors are discussed in greater detail in Section 6 of this document. Other connectors and jumper blocks on
Epsilon-12G2 are reserved for Diamond Systems’ use only.
5.2 Jumper Block
The following table summarizes the functions of Epsilon-12G2’s jumper block, J19. Refer to the drawing in
Section 4 for the location of this jumper block on Epsilon-12G2.
Epsilon-12G2 User Manual Revision A.02 www.diamondsystems.com Page 8
Page 9

DD+
1
2
DD-
DC+
3
4
DC-
DB+
5
6
DB-
DA+
7
8
DA-
Ground
9
10
Ground
1
Ground
2
TxD Out
3
RxD In
6. CONNECTOR PINOUT AND PIN DESCRIPTION
6.1 Ethernet (J1-J12)
Epsilon-12G2 contains twelve right-angle, locking pin headers for the twelve Ethernet ports. Each port has the
same style and pinout. Each signal is associated with a particular color inside of the Diamond Systems’ cable
part number 6981502. The color coding for this cable follows the TIA/EIA 568B standard.
Connector Type: 2mm dual row right-angle, locking pin header with tin plating
Mating Connector: JST Sales America PUDP-10V-S housing with SPUD-002T-P0.5 terminals
6.2 Serial Interface (J13)
Epsilon-12G2 contains an RS-232 connector, J12 that connects the on-board MIPS 24KEC microcontroller to an
external serial port.
Connector Type: 2mm single row right-angle, locking pin header with tin plating
Mating Connector: Molex Connector 35507-0300 housing with 50212-8100 terminals
6.3 SFP Socket (J15)
Connector J15 offers one dual SFP stacking socket. This socket provides two industry standard SerDes
interfaces for two additional 1G or 2.5G copper or optical SFP Ethernet ports. The 1G port is the top port in the
socket and the 2.5G port is the bottom port.
Epsilon-12G2 User Manual Revision A.02 www.diamondsystems.com Page 9
Page 10

Port0_LED1
1 2 Port0_LED2
Port1_LED1
3 4 Port1_LED2
Port2_LED1
5 6 Port2_LED2
Port3_LED1
7 8 Port3_LED2
Port4_LED1
9
10
Port4_LED2
Port5_LED1
11
12
Port5_LED2
Port6_LED1
13
14
Port6_LED2
Port7_LED1
15
16
Port7_LED2
Port8_LED1
17
18
Port8_LED2
Port9_LED1
19
20
Port9_LED2
Port10_LED1
21
22
Port10_LED2
Port11_LED1
23
24
Port11_LED2
+3.3V
25
26
GND
6.4 LED Status Signals (J17)
Connector J17 provides access to the Ethernet LED signals for each of the twelve ports. LEDs may be directly
connected to these signals without requiring any current-limiting resistors. The 3.3V supply required for the LEDs
is also provided by the connector. The control signals pull the LED pin low to turn it on. To use J17 to operate an
LED externally to Epsilon-12G2, connect the LED’s anode (+) to the 3.3V pin (J17 pin 25). Connect the LED’s
cathode (-) to the corresponding control signal on connector J17.
The on board activity LED is a green LED (LTST-C190GKT) with a typical forward voltage of 2.1V and a
maximum of 2.6V with a 20mA If. The on board speed LED is a Yellow LED (LTST-C190YKT) with the same
characteristics. The control signal is capable of sinking a maximum of 18mA. The series resistor is 330 ohms,
which gives an If of about 3.6mA. When an LED is connected to connector J17, it is in parallel with the on board
LED. If the external LED has about the same forward voltage, the current will be cut in half. If the external LED
has a lower forward voltage, it will dominate the on-board LED and be brighter. Therefore, if the external LED is
not bright enough use an external LED with a lower forward voltage.
Connector Type: 2mm dual row right-angle, locking pin header with tin plating
Mating Connector: JST Sales America PUDP-26V-S housing with SPUD-002T-P0.5 terminals
Following is a diagram illustrating how to wire J17 to external LEDs.
Epsilon-12G2 User Manual Revision A.02 www.diamondsystems.com Page 10
Page 11

1
+Vin
2
+Vin
3
Ground
4
Ground
Username: admin
Password: {none}
# configure terminal
(config)# interface vlan 1
(config-if-vlan)# ip address dhcp
(config-if-vlan)# end
# configure terminal
(config)# interface vlan 1
(config-if-vlan)# ip address 192.0.2.1 255.255.255.0
(config-if-vlan)# end
6.5 Input Power (J18)
Input power is supplied through connector J18. Epsilon-12G2 has a +5V to +40VDC wide voltage input. The
pinout for J14 is:
Connector Type: 2mm single row right-angle, locking pin header with tin plating
Mating Connector: JST Sales America PAP-04V-S housing with SPHD-001T-P0.5 terminals
7. SOFTWARE INTERFACES
7.1 Command Line Interface
The command line interface (CLI) is a modal, line-based interface with no screen editing features where
commands are executed immediately upon end-of-line. Privilege levels can be implemented for certain
operations where users have to have a certain privilege in order to exercise that operation. The CLI can be
accessed directly via the serial connection. The user must log in before CLI commands can be executed.
7.1.1 Making an Initial Connection
Serial line configuration:
115200 baud
8 bit data
No parity
1 stop bit
Login information
The IP address, mask and gateway must be set according to your environment or you can enable IP and DHCP if
your environment includes a DHCP server. For example:
Below example depicts configuration of static IP address,
Epsilon-12G2 User Manual Revision A.02 www.diamondsystems.com Page 11
Page 12

# show ip interface brief
Vlan Address Method Status
---- -------------------- -------- ----- 1 192.0.2.1 Manual UP
#
# ?
clear Reset functions
configure Enter configuration mode
copy Copy from source to destination
debug Debugging functions
delete Delete one file in flash: file system
dir Directory of all files in flash: file system
disable Turn off privileged commands
do To run exec commands in config mode
dot1x IEEE Standard for port-based Network Access Control
enable Turn on privileged commands
exit Exit from EXEC mode
firmware Firmware upgrade/swap
help Description of the interactive help system
ip IPv4 commands
logout Exit from EXEC mode
more Display file
no Negate a command or set its defaults
ping Send ICMP echo messages
reload Reload system.
send Send a message to other tty lines
show Show running system information
terminal Set terminal line parameters
#
Display the IP address to confirm:
7.1.2 General Command Groups
The following groups of general commands are available in the command line interface (CLI).
You may get help by pressing the ? key or entering help. The help info depends on the context:
At top level, a list of command groups is displayed.
At group level, a list of the command syntaxes for the current group is displayed.
If the help command is issued for a specific command, the command syntax and a description of the
command are shown
7.1.3 IP Commands
(config)# ip http secure-redirect
(config)# ip http secure-server
(config)# ip igmp snooping
(config)# ip igmp snooping vlan <v_vlan_list>
(config)# ip igmp unknown-flooding
(config)# ip route <v_ipv4_addr> <v_ipv4_netmask> <v_ipv4_gw>
(config)# ip dhcp retry interface vlan <vlan_id>
(config)# no ip http secure-redirect
(config)# no ip http secure-server
(config)# no ip igmp snooping
(config)# no ip igmp snooping vlan [ <v_vlan_list> ]
Epsilon-12G2 User Manual Revision A.02 www.diamondsystems.com Page 12
Page 13

(config)# no ip igmp unknown-flooding
(config)# no ip route <v_ipv4_addr> <v_ipv4_netmask> <v_ipv4_gw>
# clear ip arp
# clear ip igmp snooping [ vlan <v_vlan_list> ] statistics
# clear ip statistics [ system ] [ interface vlan <v_vlan_list> ] [ icmp ] [ icmp-msg <type> ]
# show ip arp
# show ip http server secure status
# show ip igmp snooping [ vlan <v_vlan_list> ] [ group-database [ interface ( <port_type> [ <v_port_type_list> ] ) ] [
sfm-information ] ] [ detail ]
# show ip igmp snooping mrouter [ detail ]
# show ip interface brief
# show ip route
# show ip statistics [ system ] [ interface vlan <v_vlan_list> ] [ icmp ] [ icmp-msg <type> ]
7.1.4 MAC Commands
(config)# mac address-table aging-time <v_0_10_to_1000000>
(config)# mac address-table static <v_mac_addr> vlan <v_vlan_id> interface ( <port_type> [
<v_port_type_list> ] )
(config)# no mac address-table aging-time
(config)# no mac address-table aging-time <v_0_10_to_1000000>
(config)# no mac address-table static <v_mac_addr> vlan <v_vlan_id> interface ( <port_type> [
<v_port_type_list> ] )
# clear mac address-table
# show mac address-table [ conf | static | aging-time | { { learning | count } [ interface ( <port_type> [
<v_port_type_list> ] ) ] } | { address <v_mac_addr> [ vlan <v_vlan_id> ] } | vlan <v_vlan_id_1> | interface (
<port_type> [ <v_port_type_list_1> ] ) ]
7.1.5 VLAN/PVLAN Commands
(config)# interface vlan <vlist>
(config)# no interface vlan <vlist>
(config)# no vlan { { ethertype s-custom-port } | <vlan_list> }
(config)# vlan <vlist>
(config)# vlan ethertype s-custom-port <etype>
# show interface vlan [ <vlist> ]
# show pvlan [ <pvlan_list> ]
# show pvlan isolation [ interface ( <port_type> [ <plist> ] ) ]
# show vlan [ id <vlan_list> | name <name> | brief ]
# show vlan status [ interface ( <port_type> [ <plist> ] ) ] [ combined | admin | nas | mvr | voice-vlan | mstp | erps |
vcl | evc | gvrp | all | conflicts ]
7.1.6 dot1x (IEEE Standard for port-based Network Access Control)
(config)# dot1x authentication timer inactivity <v_10_to_100000>
(config)# dot1x authentication timer re-authenticate <v_1_to_3600>
(config)# dot1x re-authentication
(config)# dot1x system-auth-control
(config)# dot1x timeout quiet-period <v_10_to_1000000>
(config)# dot1x timeout tx-period <v_1_to_65535>
(config)# no dot1x authentication timer inactivity
(config)# no dot1x authentication timer re-authenticate
(config)# no dot1x re-authentication
(config)# no dot1x system-auth-control
(config)# no dot1x timeout quiet-period
(config)# no dot1x timeout tx-period
# clear dot1x statistics [ interface ( <port_type> [ <v_port_type_list> ] ) ]
# dot1x initialize [ interface ( <port_type> [ <plist> ] ) ]
# show dot1x statistics { eapol | radius | all } [ interface ( <port_type> [ <v_port_type_list> ] ) ]
Epsilon-12G2 User Manual Revision A.02 www.diamondsystems.com Page 13
Page 14

# show dot1x status [ interface ( <port_type> [ <v_port_type_list> ] ) ] [ brief ]
7.1.7 LACP Commands
(config)# lacp system-priority <v_1_to_65535>
(config)# no lacp system-priority <v_1_to_65535>
# clear lacp statistics
# show lacp { internal | statistics | system-id | neighbour }
7.1.8 LLDP Commands
(config)# lldp holdtime <val>
(config)# lldp reinit <val>
(config)# lldp timer <val>
(config)# lldp transmission-delay <val>
(config)# no lldp holdtime
(config)# no lldp reinit
(config)# no lldp timer
(config)# no lldp transmission-delay
# clear lldp statistics
# show lldp eee [ interface ( <port_type> [ <v_port_type_list> ] ) ]
# show lldp neighbors [ interface ( <port_type> [ <v_port_type_list> ] ) ]
# show lldp statistics [ interface ( <port_type> [ <v_port_type_list> ] ) ]
7.1.9 Access Management Commands
(config)# access management <access_id> <access_vid> <start_addr> [ to <end_addr> ] { [ web ] [ snmp ] | all }
(config)# no access management
(config)# no access management <access_id_list>
# clear access management statistics
# show access management [ statistics | <access_id_list> ]
6.5.8 Access-list Commands
(config)# access-list rate-limiter [ <rate_limiter_list> ] { pps <pps_rate> | 100pps <pps100_rate> | kpps
<kpps_rate> | 100kbps <kpbs100_rate> }
(config)# default access-list rate-limiter [ <rate_limiter_list> ]
(config)# no access-list ace <ace_list>
# clear access-list ace statistics
# show access-list [ interface [ ( <port_type> [ <v_port_type_list> ] ) ] ] [ rate-limiter [ <rate_limiter_list> ] ] [ ace
statistics [ <ace_list> ] ]
# show access-list ace-status [ static ] [ link-oam ] [ loop-protect ] [ dhcp ] [ ptp ] [ upnp ] [ arp-inspection ] [ evc ] [
mep ] [ ipmc ] [ ip-source-guard ] [ ip-mgmt ] [ conflicts ] [ switch <switch_list> ]
7.1.10 Logging Commands
(config)# logging host <v_word45>
(config)# logging level { info | warning | error }
(config)# logging on
(config)# no logging host
(config)# no logging on
# clear logging [ info ] [ warning ] [ error ] [ switch <switch_list> ]
# show logging <log_id> [ switch <switch_list> ]
# show logging [ info ] [ warning ] [ error ] [ switch <switch_list> ]
7.1.11 Spanning-tree Commands
(config)# spanning-tree aggregation
(config)# spanning-tree edge bpdu-filter
Epsilon-12G2 User Manual Revision A.02 www.diamondsystems.com Page 14
Page 15

(config)# spanning-tree edge bpdu-guard
(config)# spanning-tree mode { stp | rstp | mstp }
(config)# spanning-tree recovery interval <interval>
(config)# spanning-tree transmit hold-count <holdcount>
(config)# no spanning-tree edge bpdu-filter
(config)# no spanning-tree edge bpdu-guard
(config)# no spanning-tree mode
(config)# no spanning-tree recovery interval
(config)# no spanning-tree transmit hold-count
# clear spanning-tree { { statistics [ interface ( <port_type> [ <v_port_type_list> ] ) ] } | { detected-protocols [
interface ( <port_type> [ <v_port_type_list_1> ] ) ] } }
# show spanning-tree [ summary | active | { interface ( <port_type> [ <v_port_type_list> ] ) } | { detailed [ interface
( <port_type> [ <v_port_type_list_1> ] ) ] } | { mst [ configuration | { <instance> [ interface ( <port_type> [
<v_port_type_list_2> ] ) ] } ] } ]
7.1.12 Green-Ethernet Commands
(config)# green-ethernet eee optimize-for-power
(config)# green-ethernet led interval <v_0_to_24> intensity <v_0_to_100>
(config)# green-ethernet led on-event { [ link-change <v_0_to_65535> ] [ error ] }*1
(config)# no green-ethernet eee optimize-for-power
(config)# no green-ethernet led interval <0~24>
(config)# no green-ethernet led on-event [ link-change ] [ error ]
# show green-ethernet [ interface ( <port_type> [ <port_list> ] ) ]
# show green-ethernet eee [ interface ( <port_type> [ <port_list> ] ) ]
# show green-ethernet energy-detect [ interface ( <port_type> [ <port_list> ] ) ]
# show green-ethernet short-reach [ interface ( <port_type> [ <port_list> ] ) ]
7.1.13 Thermal-protect Commands
(config)# no thermal-protect prio <prio_list>
(config)# thermal-protect prio <prio_list> temperature <new_temp>
# show thermal-protect [ interface ( <port_type> [ <port_list> ] ) ]
7.1.14 Loop-protect Commands
(config)# loop-protect
(config)# loop-protect shutdown-time <t>
(config)# loop-protect transmit-time <t>
(config)# no loop-protect
(config)# no loop-protect shutdown-time
(config)# no loop-protect transmit-time
# show loop-protect [ interface ( <port_type> [ <plist> ] ) ]
7.1.15 QoS Commands
(config)# no qos qce <qce_id_range>
(config)# no qos storm { unicast | multicast | broadcast }
(config)# qos storm { unicast | multicast | broadcast } { { <rate> [ kfps ] } | { 1024 kfps } }
# show qos [ { interface [ ( <port_type> [ <port> ] ) ] } | wred | { maps [ dscp-cos ] [ dscp-ingress-translation ] [
dscp-classify ] [ cos-dscp ] [ dscp-egress-translation ] } | storm | { qce [ <qce> ] } ]
7.1.16 Privilege Commands
(config)# privilege { exec | configure | config-vlan | line | interface | if-vlan | ipmc-profile | snmps-host | stp-aggr |
dhcp-pool | rfc2544-profile } level <privilege> <cmd>
(config)# no privilege { exec | configure | config-vlan | line | interface | if-vlan | ipmc-profile | snmps-host | stp-aggr |
dhcp-pool | rfc2544-profile } level <0-15> <cmd>
# show privilege
Epsilon-12G2 User Manual Revision A.02 www.diamondsystems.com Page 15
Page 16

7.1.17 SNMP Commands
(config)# snmp-server
(config)# snmp-server access <group_name> model { v1 | v2c | v3 | any } level { auth | noauth | priv } [ read
(config)# <view_name> ] [ write <write_name> ]
(config)# snmp-server community v2c <comm> [ ro | rw ]
(config)# snmp-server community v3 <v3_comm> [ <v_ipv4_addr> <v_ipv4_netmask> ]
(config)# snmp-server contact <v_line255>
(config)# snmp-server engine-id local <engineID>
(config)# snmp-server host <conf_name>
(config)# snmp-server location <v_line255>
(config)# snmp-server security-to-group model { v1 | v2c | v3 } name <security_name> group <group_name>
(config)# snmp-server trap
(config)# snmp-server user <username> engine-id <engineID> [ { md5 <md5_passwd> | sha <sha_passwd> } [
priv { des | aes } <priv_passwd> ] ]
(config)# snmp-server version { v1 | v2c | v3 }
(config)# snmp-server view <view_name> <oid_subtree> { include | exclude }
(config)# no snmp-server
(config)# no snmp-server access <group_name> model { v1 | v2c | v3 | any } level { auth | noauth | priv }
(config)# no snmp-server community v2c
(config)# no snmp-server community v3 <community>
(config)# no snmp-server contact
(config)# no snmp-server engined-id local
(config)# no snmp-server host <conf_name>
(config)# no snmp-server location
(config)# no snmp-server security-to-group model { v1 | v2c | v3 } name <security_name>
(config)# no snmp-server trap
(config)# no snmp-server user <username> engine-id <engineID>
(config)# no snmp-server version
(config)# no snmp-server view <view_name> <oid_subtree>
# show snmp
# show snmp access [ <group_name> { v1 | v2c | v3 | any } { auth | noauth | priv } ]
# show snmp community v3 [ <community> ]
# show snmp host [ <conf_name> ] [ system ] [ switch ] [ interface ] [ aaa ]
# show snmp mib context
# show snmp mib ifmib ifIndex
# show snmp security-to-group [ { v1 | v2c | v3 } <security_name> ]
# show snmp user [ <username> <engineID> ]
# show snmp view [ <view_name> <oid_subtree> ]
7.1.18 SNTP Commands (config)# sntp
(config)# sntp server ip-address { <ipv4_var> }
(config)# no sntp
(config)# no sntp server
# show sntp status
7.1.19 Radius Server Commands
(config)# radius-server attribute 32 <id>
(config)# radius-server attribute 4 <ipv4>
(config)# radius-server deadtime <minutes>
(config)# radius-server host <host_name> [ auth-port <auth_port> ] [ acct-port <acct_port>] [ timeout <seconds> ]
[ retransmit <retries> ] [ key <key> ]
(config)# radius-server key <key>
(config)# radius-server retransmit <retries>
(config)# radius-server timeout <seconds>
(config)# no radius-server attribute 32
Epsilon-12G2 User Manual Revision A.02 www.diamondsystems.com Page 16
Page 17

(config)# no radius-server attribute 4
(config)# no radius-server deadtime
(config)# no radius-server host <host_name> [ auth-port <auth_port> ] [ acct-port <acct_port> ]
(config)# no radius-server key
(config)# no radius-server retransmit
(config)# no radius-server timeout
# show radius-server [ statistics ]
# show running-config [ all-defaults ]
# show running-config feature <feature_name> [ all-defaults ]
# show running-config interface ( <port_type> [ <list> ] ) [ all-defaults ]
# show running-config interface vlan <list> [ all-defaults ]
# show running-config line { console | vty } <list> [ all-defaults ]
# show running-config vlan <list> [ all-defaults ]
7.1.20 Banner Commands (Defines a login banner)
(config)# banner [ motd ] <banner>
(config)# banner exec <banner>
(config)# banner login <banner>
(config)# no banner [ motd ]
(config)# no banner exec
(config)# no banner login
7.1.21 Terminal Commands
(# no terminal editing
# no terminal exec-timeout
# no terminal history size
# no terminal length
# no terminal width
# terminal editing
# terminal exec-timeout <min> [ <sec> ]
# terminal help
# terminal history size <history_size>
# terminal length <lines>
# terminal width <width>
7.1.22 Reload
# reload { { { cold | warm } [ sid <usid> ] } | { defaults [ keep-ip ] } }
7.1.23 Firmware Commands
# firmware swap
# firmware upgrade <tftpserver_path_file>
7.1.24 Ping Commands
# ping ip <v_ip_addr> [ repeat <count> ] [ size <size> ] [ interval <seconds> ]
7.1.25 Debug Commands
(config)# line { <0~16> | console 0 | vty <0~15> }
# no debug prompt
# debug prompt <debug_prompt>
7.1.26 Security Commands
(config)# no aaa authentication login {console | http}
Epsilon-12G2 User Manual Revision A.02 www.diamondsystems.com Page 17
Page 18

# configure terminal
(config)# interface vlan 1
(config-if-vlan)# ip address 166.20.234.1 255.255.0.0
(config-if-vlan)# end
# show ip interface brief
Vlan Address Method Status
---- -------------------- -------- ----- 1 166.20.234.1 Manual UP
#
# configure terminal
(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 1/1
(config-if)# speed ?
10 10Mbps
100 100Mbps
1000 1Gbps
auto Auto negotiation
(config-if)# speed 100
(config-if)# end
(config)# password encrypted <encry_password>
(config)# password none
(config)# password unencrypted <password>
(config)# enable password [ level <priv> ] <password>
(config)# enable secret { 0 | 5 } [ level <priv> ] <password>
(config)# no enable password [ level <priv> ]
(config)# no enable secret { [ 0 | 5 ] } [ level <priv> ]
# show aaa
# show port-security port [ interface ( <port_type> [ <v_port_type_list> ] ) ]
# show port-security switch [ interface ( <port_type> [ <v_port_type_list> ] ) ]
(config)# aaa authentication login {console | http} {{local | radius} [ {local | radius}]}
7.1.27 Monitor
(config)# monitor destination interface <port_type> <in_port_type>
(config)# monitor source { { interface ( <port_type> [ <v_port_type_list> ] ) } | { cpu [<cpu_switch_range> ] } } {
both | rx | tx }
(config)# no monitor destination
(config)# no monitor source { { interface ( <port_type> [ <v_port_type_list> ] ) } | { cpu [ <cpu_switch_range> ] } }
7.2 Examples
7.2.1 IP Configuration
Below example depicts configuration of static IP address,
Display the IP address to confirm:
7.2.2 Port Configuration
Individual ports can be configured to different speed. Following example shows configuring speed as 100 Mbps
for port 1.
Epsilon-12G2 User Manual Revision A.02 www.diamondsystems.com Page 18
Page 19

#
# configure terminal
(config)# password unencrypted <password>
(config)# exit
#
#configure terminal
(config)# vlan 2
(config)# vlan 3
#configure terminal
(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 1/2
(Config-if)# switchport mode access
(Config-if)# switchport access vlan 2
(config)# exit
(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 1/3
(Config-if)# switchport mode access
(Config-if)# switchport access vlan 3
(config)# exit
# show vlan
VLAN Name Interfaces
---- -------------------------------- ---------1 default Gi 1/1,4-6
2 VLAN0002 Gi 1/2
3 VLAN0003 Gi 1/3
# configure terminal
(config)# snmp-server
(config)# exit
#
7.2.3 Change Switch Password
Following example shows setting of new password,
7.2.4 Set up VLANs
Virtual LANs (VLANs) are used to divide the network into separate logical areas. VLANs can also be considered
as broadcast domains.
Following example shows setting up VLAN2 and VLAN3 with switch port mode set to access.
Set access port, in this case it’s assumed that port 1~3 are connected to PC. The PVID of each port is different.
To verify created VLAN
As shown above, VLAN2 is created with the name VLAN0002 and a port 2 assigned to VLAN2. Similarly port 3
assigned to VLAN0003. Remaining ports 1 & 4 to 6 are by default assigned to VLAN 1
7.2.5 SNMP configuration
Following example depicts the configuration of SNMP,
To enable the SNMP mode operation
Epsilon-12G2 User Manual Revision A.02 www.diamondsystems.com Page 19
Page 20

# configure terminal
(config)# snmp-server host Example
(config-snmp-host)# host 166.20.234.20
(config-snmp-host)# exit
(config)# exit
#
# configure terminal
(config)# monitor destination interface GigabitEthernet 1/1
(config)# monitor source interface GigabitEthernet 1/2-3 rx
(config)# monitor source interface GigabitEthernet 1/4-6 tx
# configure terminal
(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 1/1
(config-if)# qos cos 2
(config-if)# qos pcp 1
(config-if)# end
# reload defaults
#
SNMP Trap configuration,
7.2.6 Mirroring
For debugging network problems or monitoring network traffic, the switch system can be configured to mirror
frame from multiple ports to a mirror port. Following example depicts Mirror traffic of Port 2 and 3 (Rx) & 4 to 6
(Rx) to Port 1.
7.2.7 Setup QoS
Quality of Service (QoS) refers to the capability of a network to provide better service to selected network traffic
over various technologies, including Frame Relay, Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM), Ethernet and 802.1
networks, SONET, and IP-routed networks that may use any or all of these underlying technologies.
Following example shows setting up the QoS, all traffic coming on port 1 is mapped to QoS class (CoS) 2 and
PCP is set as 1.
7.2.8 Factory defaults
User can reset the configuration of the switch by below command. Only the IP configuration is retained.
Epsilon-12G2 User Manual Revision A.02 www.diamondsystems.com Page 20
Page 21

7.3 Web Interface
The web interface offers an alternate user interface to the CLI. The web interface is in-band and requires use of
one of the Ethernet ports. This port provides simultaneous web management and normal usage. The same
commands with the same functionality can be accessed via either interface.
From the WEB interface it is possible to, among other things:
Set port mode
Enable/disable flow control
Configure simple port-based VLAN
Configure aggregation groups
Configure LACP parameters
Configure RSTP parameters
Configure QoS
Read and clear statistics counters
Monitor LACP status
Monitor RSTP status
Configure and monitor 802.1X
Configure and monitor IGMP snooping (if defined for switch device)
Configure source-IP address and DHCP server filter
Upgrade software
All operations are password protected. The password must be entered at login. The password is the same as is
being used in the command line interface.
The IP mode is disabled in the factory default configuration. To be able to use the WEB interface, the IP must be
enabled and configured via the command line interface. The IP address, mask and gateway must be set
according to your environment or you can enable IP and DHCP if your environment include a DHCP server.
Example of enabling the WEB interface via the command line interface:
>ip setup 10.10.129.189 255.255.252.0 10.10.128.14 1
>ip mode enable
There is an extensive on-line help facility available in the web interface that describes each command, what it
does and how to use it.
Epsilon-12G2 User Manual Revision A.02 www.diamondsystems.com Page 21
Page 22

7.3.1 Web Interface Activation / Deactivation
The web interface can be activated and deactivated through either the command line interface or the web Control
Panel.
Using the Control Panel, in the Configuration/Security/Switch/Access Management Configuration screen, first
ensure the mode is set to Disabled as shown below. This is the default mode. If it is not set to Disabled, set it as
Disabled and click Save.
This configuration should be stored on the switch with the following CLI command:
#copy startup-config flash:{filename}
To disable web access of the switch, in the Control Panel navigate to the Configuration/Security/Switch/Access
Management Configuration screen, change the mode to Enabled and click Save.
Now there is no access to the switch using the web interface. To store this configuration in flash as the standard
configuration on startup, enter the following command in the CLI:
#copy running-config startup-config
To allow web access of the switch in the future, enter the following commands in the CLI:
#copy startup-config flash:backup_config
#copy flash:{filename} startup-config
Then reboot the switch.
Epsilon-12G2 User Manual Revision A.02 www.diamondsystems.com Page 22
Page 23

Ethernet switch
14-port, layer 2+ switch
Built-in 416MGz MIPS 24KEC microcontroller for configuration and management
Number of ports
12 10/100/1000Mbps copper Ethernet ports with non-blocking wire-speed performance
1 1G SFP socket
1 2.5G SFP socket
On-board memory
4Mb packet memory
Shared memory buffer with per-port and CoS memory management
MEF
Hierarchical MEF compliant policing and scheduling
MEF E-Lane, E-Line, and E-Tree services
Frame buffer
Jumbo frame support at all speeds
VLAN
IEEE 802.1Q VLAN switch with 8K MACs and 4K VLANs
Push/pop up to two VLAN tags
Independent and shared VLAN learning (IVL, SVL)
Multicast
IPv4 and IPv6 multicast group support
Remarking
Dual leaky bucket policers with remarking and statistics
Classifier
8 priorities and 8 CoS queues per port with strict or deficit-weighted round robin
scheduling
Shaping/policing per queue and per port
Storm control
Policing with storm control and MC/BC protection
Link aggregation
IEEE 802.3ad
Security
Advanced security and prioritization available though multistage TCAM engine
RSTP
Rapid spanning tree protocol (IEEE 802.1W) and MTSP
Power management
ActiPHY and PerfectReach power management; VeriPHY cable diagnostics
Serial port
1 RS-232 for host interface
Indicator LEDs
28 status LEDs, 2 per port
2 GPIO
Standalone Capable
Can operate as a standalone network switch or in combination with a host computer
Power Input
+5-40V DC/DC power supply
Power consumption
9.2W maximum with all ports active, approximately 0.26W less for each inactive port
Form factor
COM Express (95mm x 125mm)
Operating temp
-40°C to +85°C (-40°F to +185°F)
Weight
4.9oz (138.9g) with heatsink
RoHS
Compliant
Time to Login and alive LED flashing after power-on, power cycle, or reboot
8 sec
Time for ports to reconnect after power-on, power cycle, or reboot
15 sec
Time for all ports to start passing data after power-on, power cycle, or reboot
<30 sec. (typical 24-26 sec)
Time for all ports to start passing data after restoring factory defaults
8 sec
8. SPECIFICATIONS
The specifications for Epsilon-12G2 are summarized in the following table.
The timing specifications for the board are summarized in the following table.
Epsilon-12G2 User Manual Revision A.02 www.diamondsystems.com Page 23
Page 24

APPENDIX A SUPPORTED MIBS
Epsilon-12G2 supports the following management information bases (MIBs). Each MIB contains definitions and
information regarding the properties of managed resources and the services that the agents support. Epsilon12G2 supports both WebStaX and CEServices MIBs as shown below.
WebStax 3.40 MIBs:
LLDP
RFC1213 Interfaces
RFC1213 IP
RFC1213 SNMP
RFC1213 System
RFC1213 TCP
RFC1213 UDP
RFC3635 Transmission
RFC4188 Dot1D
CEServices 3.40 MIBs:
IEEE 802.1X
LACP
LLDP
LLDP-MED
RFC1213 Interfaces
RFC1213 IP
RFC1213 SNMP
RFC1213 System
RFC1213 TCP
RFC1213 UDP
RFC2819 RMON Alarm
RFC2819 RMON Event
RFC2819 RMON History
RFC2819 RMON Statistics
RFC2863 IF
RFC3414 USMSTATS
RFC3414 USMUSER
RFC3415 VACMACCESSTABLE
RFC3415 VACMCONTEXTTABLE
RFC3415 VACMMIBVIEWS
RFC3415 VACMSECURITYTOGROUPTABLE
RFC3635 Transmission
RFC3636 MAU
RFC4133 ENTITY
RFC4188 Dot1D
RFC4668 RADIUS
RFC4670 RADIUS
RFC4878 LINK OAM
RFC5519 MGMD
Epsilon-12G2 User Manual Revision A.02 www.diamondsystems.com Page 24
 Loading...
Loading...