DFI LANPARTY UT 915P-T12 User Manual

82520436
System Board
User’s Manual

Copyright
This publication contains information that is protected by copyright.
No part of it may be reproduced in any form or by any means or
used to make any transformation/adaptation without the prior
written permission from the copyright holders.
This publication is provided for informational purposes only. The
manufacturer makes no representations or warranties with respect to
the contents or use of this manual and specifically disclaims any
express or implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for any
particular purpose. The user will assume the entire risk of the use or
the results of the use of this document. Fur ther, the manufacturer
reserves the right to revise this publication and make changes to its
contents at any time, without obligation to notify any person or
entity of such revisions or changes.
© 2004. All Rights Reserved.
Trademarks
Windows® 2000, Windows NT® 4.0 and Windows® XP are
registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Intel® and Pentium
®
4 are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation. Award is a
registered trademark of Award Software, Inc. Other trademarks and
registered trademarks of products appearing in this manual are the
properties of their respective holders.
Caution
To avoid damage to the system:
• Use the correct AC input voltage range
..
..
.
To reduce the risk of electric shock:
• Unplug the power cord before removing the system chassis
cover for installation or servicing. After installation or servicing,
cover the system chassis before plugging the power cord.

Battery:
• Danger of explosion if battery incorrectly replaced.
• Replace only with the same or equivalent type recommend
by
the manufacturer.
• Dispose of used batteries according to the battery
manufacturer’s
instructions.
FCC and DOC Statement on Class B
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits
for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules.
These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against
harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with
the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference
will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause
harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is
encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the
following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from
that to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio TV technician for
help.
Notice:
1. The changes or modifications not expressly approved by the
party responsible for compliance could void the user's authority
to operate the equipment.
2. Shielded interface cables must be used in order to comply with
the emission limits.

About this Manual
This user’s manual contains detailed information about the system
board. If, in some cases, some information doesn’t match those
shown in the multilingual manual, the multilingual manual should always be regarded as the most updated version. The multilingual
manual is included in the system board package.
To view the user’s manual, insert the CD into a CD-ROM drive. The
autorun screen (Mainboard Utility CD) will appear. Click the
“TOOLS” icon then click “Manual” on the main menu.
Notice
The system board and accessories you receive in the package may
not come similar to the information stated in this manual. This may
differ in accordance to the sales region or models in which it was
sold. For more information about the standard package in your
region, please contact your dealer or sales representative.

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 - Introduction
1.1 Specifications......................................................................................................................
1.2 Special Features of the System Board.....................................................
1.3 Package Checklist.........................................................................................................
Chapter 2 - Hardware Installation
2.1 System Board Layout ...........................................................................................
2.2 System Memory...........................................................................................................
2.3 CPU........................................................................................................................................
2.4 Jumper Settings.............................................................................................................
2.5 Rear Panel I/O Ports..............................................................................................
2.6 I/O Connectors...........................................................................................................
Chapter 3 - Award BIOS Setup Utility
3.1 The Basic Input/Output System.....................................................................
3.2 Updating the BIOS.....................................................................................................
Chapter 4 - Supported Softwares
4.1 Desktop Management Interface.................................................................
4.2 Drivers, Utilities and Software Applications.....................................
4.3 Installation Notes......................................................................................................
7
10
15
16
17
20
26
31
41
57
102
104
107
116

Introduction
1
6
Appendix A - Enabling the Hyper-Threading
Technology
A.1 Enabling the Hyper-Threading Technology...........................................
Appendix B - System Error Messages
B.1 POST Beep....................................................................................................................
B.2 Error Messages...........................................................................................................
Appendix C - Troubleshooting
C.1 Troubleshooting Checklist.................................................................................
117
120
120
122
1
Introduction
7
Chapter 1 - Introduction
1.1 Specifications
Processor
• Intel® Pentium® 4 Prescott processor
- Hyper-Threading Technology
- 533MT/s and 800MT/s (200MHz) system bus interface
• Socket LGA 775 (LAN Grid Array)
Chipset
• Intel
®
915P chipset
- Intel® 915P Memory Controller Hub (MCH)
- Intel® 82801FB I/O Controller Hub (ICH6)
System Memory
• Two 240-pin DDR2 DIMM sockets that support DDR2 400
and DDR2 533 DIMMs
• Two 184-pin DDR1 DIMM sockets that support PC2700
(DDR333) and PC3200 (DDR400) DIMMs
• Supports dual channel (128-bit wide) memory interface
• Supports up to 2GB system memory
• Supports non-ECC x8 and x16 DIMMs
• Supports 256Mb and 512Mb DRAM densities
• Supports unbuffered DIMMs
Important:
Use either DDR1 or DDR2. Do not use both at the
same time.
BIOS
• Award BIOS, Windows
®
2000/XP Plug and Play compatible
• Genie BIOS provides:
- CPU/DRAM overclocking
- CPU/NB/DRAM overvoltage
• Supports SCSI sequential boot-up
• Supports DMI 2.0 function
• 4Mbit flash memory

Introduction
1
8
Energy Efficient Design
• Supports ACPI specification and OS Directed Power
Management
• Supports ACPI STR (Suspend to RAM) function
• Wake-On-Events include:
- Wake-On-PS/2 Keyboard/Mouse
- Wake-On-USB Keyboard/Mouse
- Wake-On-Ring (external modem)
- Wake-On-LAN
- RTC timer to power-on the system
• AC power failure recovery
Hardware Monitor
• Monitors CPU/system temperature and overheat alarm
• Monitors 12V/5V/3.3V/Vcore/Vbat/5Vsb/3.3Vsb voltages
• Monitors the speed of the CPU/system fan
• CPU Overheat Protection function monitors CPU temperature
and fan during system boot-up - automatic shutdown upon
system overheat
Onboard Audio Features
• Azalia audio codec with independent variable sampling rate
• True stereo line level outputs
• S/PDIF-in/out interface
• 8-channel audio output
Onboard LAN Features
• Gigabit ethernet controllers - Marvell 88E8053 PCI Express and
Marvell 88E8001 PCI
• Integrated power management functions
• Full duplex support at both 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps and 1Gbps
• Supports IEEE 802.3u auto-negotiation
• Supports wire for management
Serial ATA Interface
• Supports four SATA (Serial ATA) interfaces which are compliant
with SATA 1.0 specification (1.5Gbps interface)
IEEE 1394 Interface
• Supports two 100/200/400 Mb/sec ports

1
Introduction
9
IDE Interface
• Supports ATA/33, ATA/66 and ATA/100 hard drives
Rear Panel I/O Ports
• 1 mini-DIN-6 PS/2 mouse port
• 1 mini-DIN-6 PS/2 keyboard port
• 2 S/PDIF RCA jacks (S/PDIF-in and S/PDIF-out)
• Karajan audio card (6 audio jacks)
• 1 IEEE 1394 port
• 2 RJ45 LAN ports
• 6 USB 2.0/1.1 ports
I/O Connectors
• 1 connector for 2 additional external USB 2.0/1.1 ports
• 1 connector for 1 external IEEE 1394 por t
• 1 connector for 1 external serial port
• 1 front audio connector for external line-out and mic-in jacks
• 1 CD-in internal audio connector
• 1 S/PDIF connector for optical cable connection
• 1 IR connector
• 1 CIR connector
• 4 Serial ATA connectors
• 1 IDE connector
• 1 floppy connector
• 2 ATX power supply connectors
• 5 fan connectors
• 4 diagnostic LEDs
• 1 diagnostic LED connector for external 4 diagnostic LEDs
display
• EZ touch switches (power switch and reset switch)
Expansion Slots
• 1 PCI Express x16 slot
• 3 PCI Express x1 slots
• 3 PCI slots
Compatibility
• PCI 2.2 and Azalia compliant
PCB
• 6 layers, ATX form factor
• 24.5cm (9.64") x 30.5cm (12")

Introduction
1
10
1.2 Special Features of the System Board
PCI Express
PCI Express is a high bandwidth I/O infrastructure that possesses
the ability to scale speeds by forming multiple lanes. The system
board currently supports the physical layer of x1 and x16 lane
widths.
The x1 PCI Express lane supports transfer rate of 2.5 Gigabytes
(250MBbps) per second. The PCI Express architecture also provides
a high performance graphics infrastructure by doubling the capability
of the existing AGP 8x designs over a x16 PCI Express lane that
provides 4 Gigabytes per second transfer rate.
Hyper-Threading Technology Functionality Requirements
The system board supports Intel processors with Hyper-Threading
Technology. Enabling the functionality of Hyper-Threading Technology
for your computer system requires ALL of the following platforms.
Components:
• CPU - an Intel
®
Pentium® 4 Processor with HT Technology
• Chipset - an Intel® chipset that supports HT Technology
• BIOS - a BIOS that supports HT Technology and has it enabled
• OS - an operating system that includes optimizations for HT
Technology
Please refer to Appendix A for information about enabling the
functionality of the Hyper-Threading Technology. For more information
on Hyper-Threading Technology, go to: www.intel.com/info/
hyperthreading.

1
Introduction
11
CPU Overheat Protection
CPU Overheat Protection has the capability of monitoring the CPU’s
temperature during system boot up. Once the CPU’s temperature
exceeded the temperature limit pre-defined by the CPU, the system
will automatically shutdown. This preventive measure has been added
to protect the CPU from damage and insure a safe computing
environment.
DDR2
DDR2 is a higher performance DDR technology whose data transfer
rate delivers bandwidth of 4.3 GB per second and beyond. That is
twice the speed of the conventional DDR without increasing its
power consumption. DDR2 SDRAM modules work at 1.8V supply
compared to 2.6V memory voltage for DDR modules. DDR2 also
incorporates new innovations such as the On-Die Termination (ODT)
as well as larger 4-bit pre-fetch against DDR which fetches 2 bits
per clock cycle.
DDR1
DDR1 (Double Data Rate) is a type of SDRAM that doubles the
data rate through reading and writing at both the rising and falling
edge of each clock. This effectively doubles the speed of operation
therefore providing two times faster data transfer.
CMOS Reloaded
CMOS Reloaded is a technology that allows storing multiple userdefined BIOS settings by using the BIOS utility to save, load and
name the settings. This is especially useful to overclockers who
require saving a variety of overclocked settings and being able to
conveniently switch between these settings simultaneously.
Karajan Audio Card
The Karajan audio add-in card at the rear I/O panel supports 8channel audio output via the audio jacks on the card.

Introduction
1
12
S/PDIF
S/PDIF is a standard audio file transfer format that transfers digital
audio signals to a device without having to be converted first to an
analog format. This prevents the quality of the audio signal from
degrading whenever it is converted to analog. S/PDIF is usually
found on digital audio equipment such as a DAT machine or audio
processing device. The S/PDIF connector on the system board sends
surround sound and 3D audio signal outputs to amplifiers and
speakers and to digital recording devices like CD recorders.
Serial ATA Interface
Serial ATA is a storage interface that is compliant with SATA 1.0
specification. With speed of up to 1.5Gbps, it improves hard drive
performance faster than the standard parallel ATA whose data
transfer rate is 100MB/s.
IEEE 1394 Interface
IEEE 1394 is fully compliant with the 1394 OHCI (Open Host
Controller Interface) 1.1 specification. It supports up to 63 devices
that can run simultaneously on a system. 1394 is a fast external bus
standard that supports data transfer rates of up to 400Mbps. In
addition to its high speed, it also supports isochronous data transfer
which is ideal for video devices that need to transfer high levels of
data in real-time. 1394 supports both Plug-and-Play and hot
plugging.
IrDA Interface
The system board is equipped with an IrDA connector for wireless
connectivity between your computer and peripheral devices. The
IRDA (Infrared Data Association) specification supports data
transfers of 115K baud at a distance of 1 meter.
USB Ports
The system board supports USB 2.0 and USB 1.1 ports. USB 1.1
supports 12Mb/second bandwidth while USB 2.0 supports 480Mb/
second bandwidth providing a marked improvement in device
transfer speeds between your computer and a wide range of
simultaneously accessible external Plug and Play peripherals.

1
Introduction
13
Dual Function Power Button
Depending on the setting in the “Soft-Off By PWR-BTTN” field of
the Power Management Setup, this switch will allow the system to
enter the Soft-Off or Suspend mode.
Wake-On-Ring
This feature allows the system that is in the Suspend mode or Soft
Power Off mode to wake-up/power-on to respond to calls coming
from an external modem or respond to calls from a modem PCI
card that uses the PCI PME (Power Management Event) signal to
remotely wake up the PC.
Important:
If you are using a modem add-in card, the 5VSB power source
of your power supply must support a minimum of ≥720mA.
Wake-On-LAN
This feature allows the network to remotely wake up a Soft Power
Down (Soft-Off) PC. It is supported via the onboard LAN port or
via a PCI LAN card that uses the PCI PME (Power Management
Event) signal. However, if your system is in the Suspend mode, you
can power-on the system only through an IRQ or DMA interrupt.
Important:
The 5VSB power source of your power supply must support
≥
720mA.
Wake-On-PS/2 Keyboard/Mouse
This function allows you to use the PS/2 keyboard or PS/2 mouse
to power-on the system.
Important:
The 5VSB power source of your power supply must support
≥
720mA.

Introduction
1
14
Wake-On-USB Keyboard/Mouse
This function allows you to use a USB keyboard or USB mouse to
wake up a system from the S3 (STR - Suspend To RAM) state.
Important:
• If you are using the Wake-On-USB Keyboard/Mouse
function for 2 USB ports, the 5VSB power source of your
power supply must support ≥1.5A.
• If you are using the Wake-On-USB Keyboard/Mouse
function for 3 or more USB ports, the 5VSB power source
of your power supply must support ≥2A.
RTC Timer to Power-on the System
The RTC installed on the system board allows your system to
automatically power-on on the set date and time.
ACPI STR
The system board is designed to meet the ACPI (Advanced
Configuration and Power Interface) specification. ACPI has energy
saving features that enables PCs to implement Power Management
and Plug-and-Play with operating systems that support OS Direct
Power Management. Currently, only Windows
®®
®®
®
2000/XP supports
the ACPI function. ACPI when enabled in the Power Management
Setup will allow you to use the Suspend to RAM function.
With the Suspend to RAM function enabled, you can power-off the
system at once by pressing the power button or selecting “Standby”
when you shut down Windows
®®
®®
®
2000/XP without having to go
through the sometimes tiresome process of closing files, applications
and operating system. This is because the system is capable of
storing all programs and data files during the entire operating session
into RAM (Random Access Memory) when it powers-off. The
operating session will resume exactly where you left off the next time
you power-on the system.
Important:
The 5VSB power source of your power supply must support
≥
1A.

1
Introduction
15
AC Power Failure Recovery
When power returns after an AC power failure, you may choose to
either power-on the system manually, let the system power-on
automatically or return to the state where you left off before power
failure occurs.
1.3 Package Checklist
; One LANPARTY UT 915P-T12 system board
; One Karajan audio card
; One Serial ATA to Parallel ATA adapter module
; One Serial ATA power cable for the adapter module
; One IDE round cable
; One floppy round cable
; Two Serial ATA data cables
; One Serial ATA power cable
; One card-edge bracket mounted with a DB-9 serial port
; One I/O shield
; One “Mainboard Utility” CD
; One LANPARTY UT 915P-T12 User’s Manual
; One CMOS Reloaded User Guide
If any of these items are missing or damaged, please contact your
dealer or sales representative for assistance.
16
2
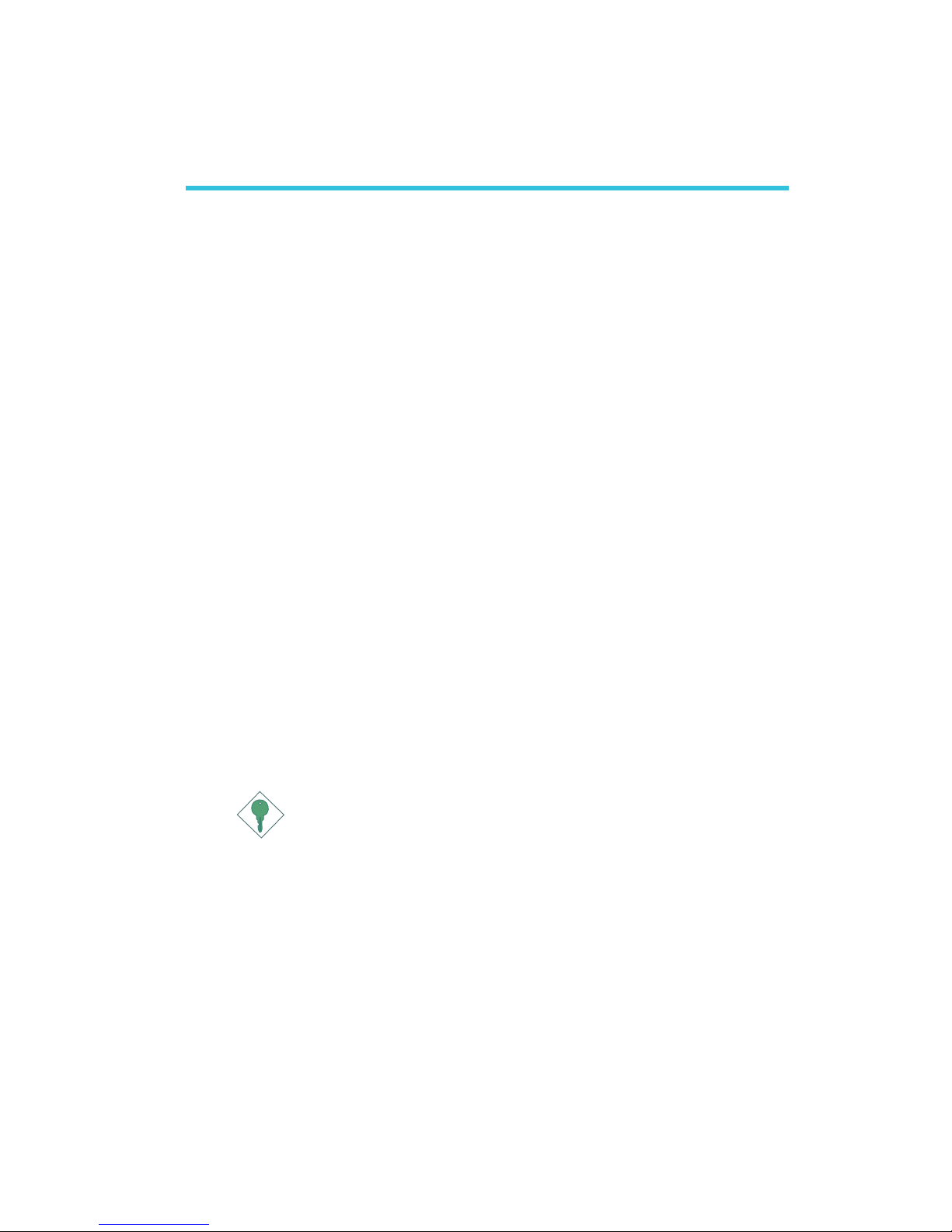
Hardware Installation
2.1 System Board Layout
Chapter 2 - Hardware Installation
JP8
1
S/PDIF-in
S/PDIF-out
S/PDIF
PS/2 power
select (JP1)
1
USB 1-6 power
select (JP2)
1
KB
Mouse
1
Audio
Line-in,
Mic-in,
1394_1
USB 1
USB 2
LAN 1
USB 3
USB 4
(PCI Express x1)
LAN 2 (PCI)
USB 5
USB 6
1
Fan 5
1
Fan 2
1
Fan 4
1
Fan 3
1
CPU fan
1
+12V power
DDR2_1
DDR1_1
DDR2_2
DDR1_2
LGA 775 CPU Socket
Intel
915P
Intel
ICH6
VIA
VT6307
I/O
chip
1
1
1
1394_2
ATX
power
1
Diagnostic LED
IDE
Standby Power LED
DRAM Power LED
LED 1
LED 3
LED 2
LED 4
BIOS
1
USB 7-8
USB 7-8 power
select (JP3)
1
1
Clear CMOS (JP4)
1
FDD
1
Speaker
On/Off (JP8)
1
SATA 4
1
1
1
SATA 3
SATA 2
SATA 1
Battery
CIR
IR
Reset
Power
HD-LED
RESET
SPEAKER
PCI 1
PCI 2
PCI 3
1
COM
PCIEX1 1
PCIEX1 3
PCIEX1 2
PCIEX16
Marvell
88E8053
Rear R/L
Front R/L,
Side R/L
Center/
Subwoofer
Marvell
88E8001
PWR-LED
ATX-SW
1
17
2
Hardware Installation
JP8
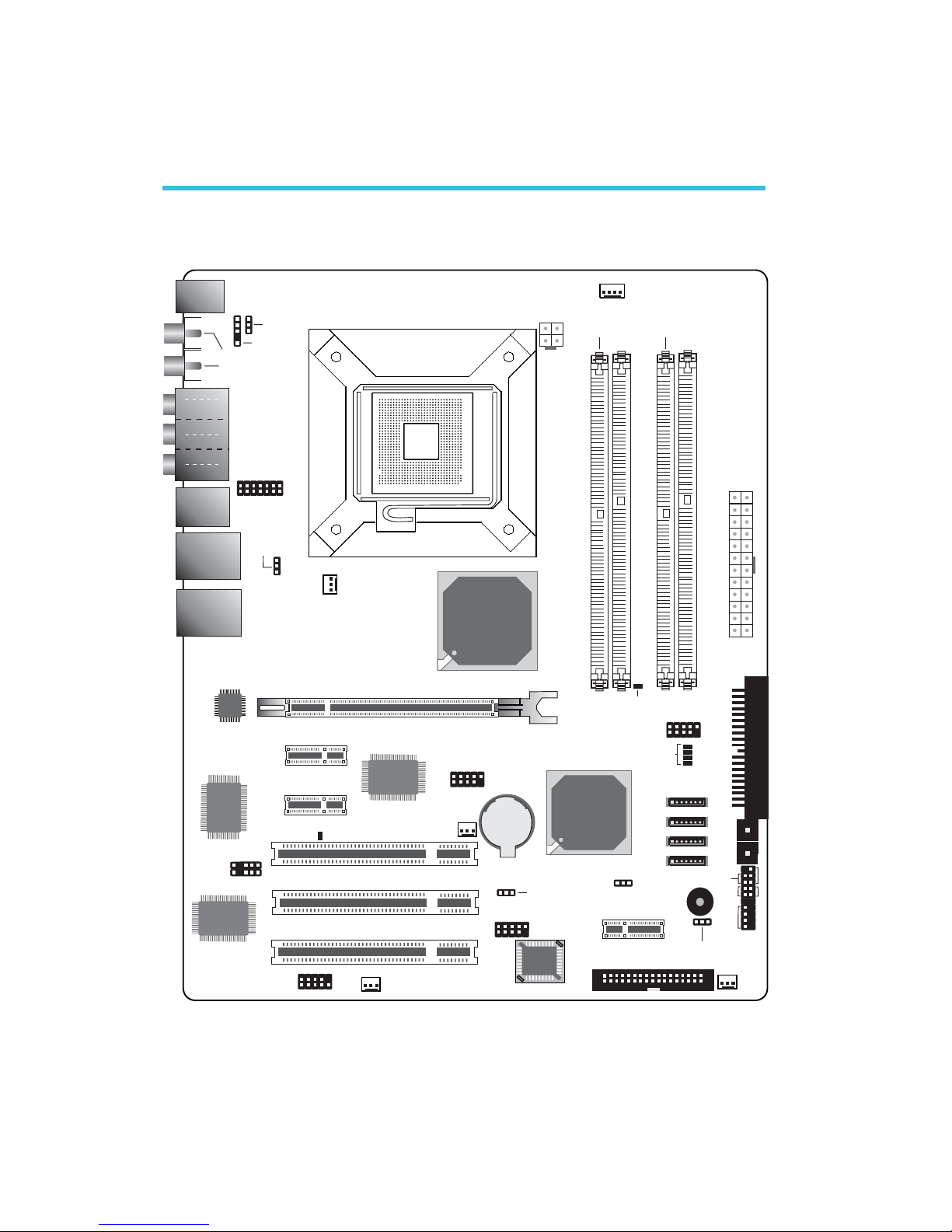
2.2 System Memory
Warning:
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can damage your system board,
processor, disk drives, add-in boards, and other components. Perform
the upgrade instruction procedures described at an ESD workstation
only. If such a station is not available, you can provide some ESD
protection by wearing an antistatic wrist strap and attaching it to a
metal part of the system chassis. If a wrist strap is unavailable,
establish and maintain contact with the system chassis throughout
any procedures requiring ESD protection.
The system board supports two 240-pin DDR2 DIMM sockets
and two 184-pin DDR1 DIMM sockets. Both types suppor t dual
channel.
Note:
Use either DDR1 or DDR2. Do not use both at the same
time.
The system board supports the following memory interface.
Single Channel (SC)
Data will be accessed in chunks of 64 bits (8B) from the memory
channels.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
DDR2_1
DDR1_1
DDR2_2
DDR1_2

18
2
Hardware Installation
Virtual Single Channel (VSC)
If both channels are populated with different memory configurations,
the MCH defaults to Virtual Single Channel.
Dual Channel (DC)
Dual channel provides better system performance because it doubles
the data transfer rate.
BIOS Setting
Configure the system memory in the Advanced Chipset Features
submenu of the BIOS.
Only one socket is populated with
DIMM.
The two DIMM sockets are populated
with different memory configurations.
The two DIMM sockets are populated
with identical memory configurations.
Single Channel
Virtual Single Channel
Dual Channel

19
2
Hardware Installation
2.2.1 Installing the DIM Module
A DIM module simply snaps into a DIMM socket on the system
board. Pin 1 of the DIM module must correspond with Pin 1 of the
socket.
1. Pull the “tabs” which are at the ends of the socket to the side.
2. Position the DIMM above the socket with the “notch” in the
module aligned with the “key” on the socket.
3. Seat the module vertically into the socket. Make sure it is
completely seated. The tabs will hold the DIMM in place.
Pin 1
Notch
Key
Tab
Tab
20
2
Hardware Installation
JP8
2.3 CPU
2.3.1 Overview
The system board is equipped with a surface mount LGA 775
socket. This socket is exclusively designed for installing a LGA 775
packaged Prescott CPU.
2.3.2 Installing the CPU
1. Make sure the PC and all other peripheral devices connected to
it has been powered down.
2. Disconnect all power cords and cables.
3. Locate the LGA 775 CPU socket on the system board.
X
Important:
The CPU socket must not come in contact with anything
other than the CPU. Avoid unnecessary exposure. Remove
the protective cap only when you are about to install the
CPU.
21
2
Hardware Installation
4. The CPU socket comes with a cover that is attached with a
removable protective cap. The cap is used to protect the CPU
socket against dust and harmful particles. Remove the protective
cap only when you are about to install the CPU.
Protective cap
Lever
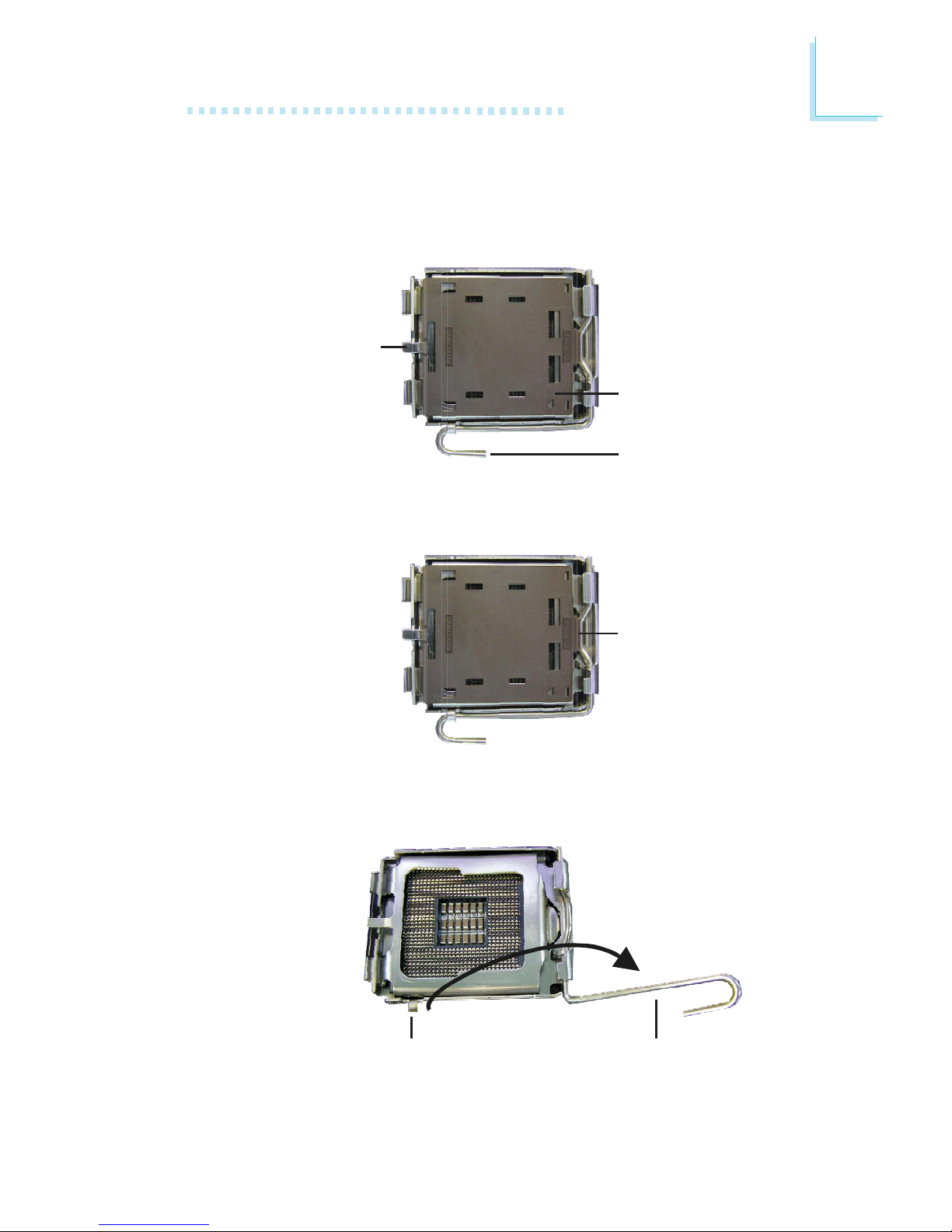
6. Unlock the socket by pushing the lever down, moving it away from
the side tab of the socket, then lifting it up.
Cover
Lift this part up
Lever lifted
5. Lift the protective cap from the location pointed below to detach
the cap from the cover.
Ta b

22
2
Hardware Installation
7. Now lift the cover.
8. Position the CPU above the socket. The gold mark on the CPU
must align with pin 1 of the CPU socket.
Important:
Handle the CPU by its edges and avoid touching the pins.
Cover
Pin 1 of the socket
Gold mark
23
2
Hardware Installation
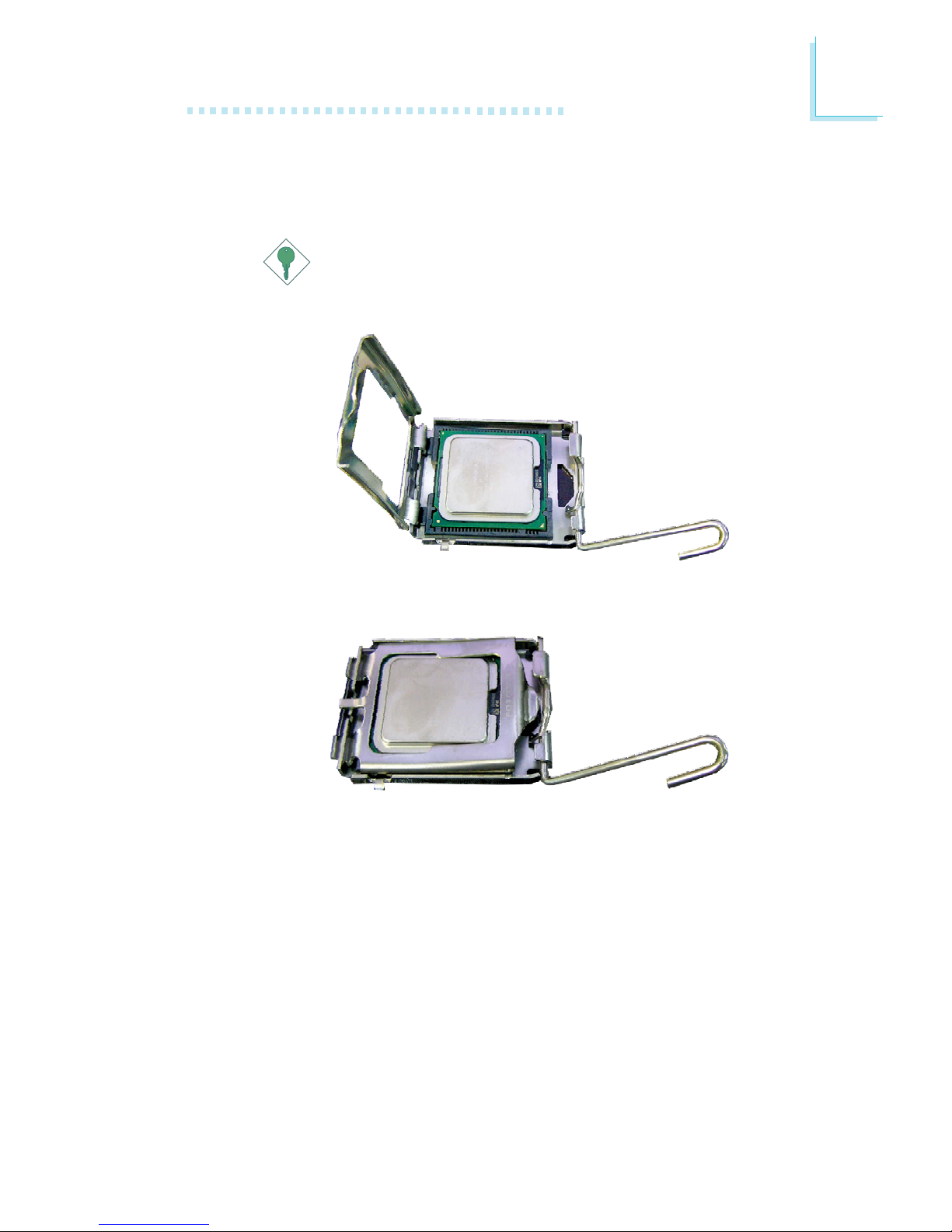
9. Insert the CPU into the socket until it is seated in place. The
CPU will fit in only one orientation and can easily be inserted
without exerting any force.
Important:
Do not force the CPU into the socket. Forcing the CPU into
the socket may bend the pins and damage the CPU.
10. Once the CPU is in place, move the cover down.

24
2
Hardware Installation
2.3.3 Installing the Fan and Heat Sink
The CPU must be kept cool by using a CPU fan with heat sink.
Without sufficient air circulation across the CPU and heat sink, the
CPU will overheat damaging both the CPU and system board.
Note:
• Use only certified fan and heat sink.
• The fan and heat sink package usually contains the fan and
heat sink assembly, and an installation guide. If the
installation procedure in the installation guide differs from
the one in this section, please follow the installation guide in
the package.
1. Before you install the fan / heat sink, you must apply a thermal
paste onto the top of the CPU. The thermal paste is usually
supplied when you purchase the CPU or fan heat sink assembly.
Do not spread the paste all over the surface. When you later
place the heat sink on top of the CPU, the compound will
disperse evenly.
Do not apply the paste if the fan / heat sink already has a patch
of thermal paste on its underside. Peel the strip that covers the
paste before you place the fan / heat sink on top of the CPU.
11. Push the lever down to lock the socket. The lever should hook
onto the side tab to indicate that the CPU is completely
secured in the socket.
25
2
Hardware Installation
JP8
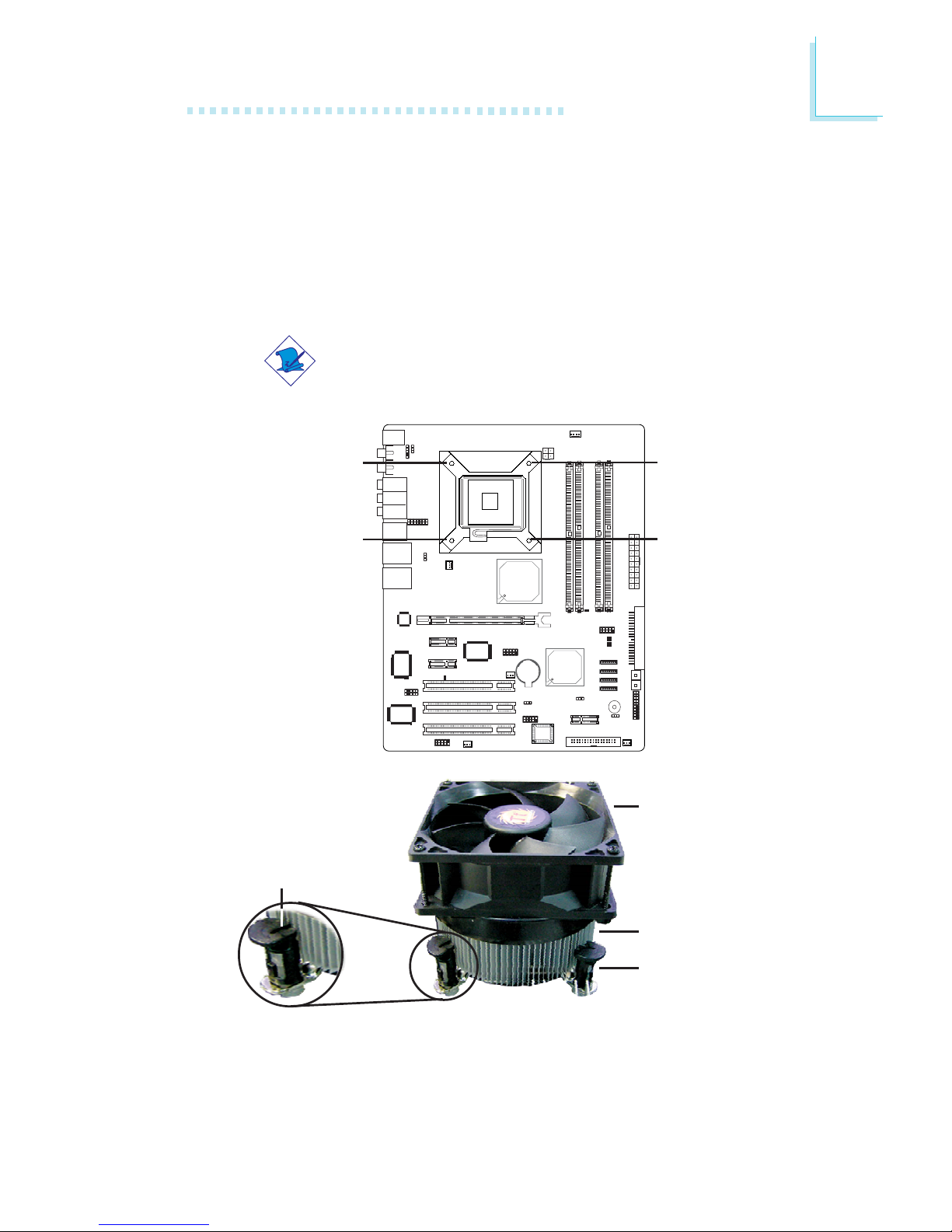
2. Place the heat sink on top of the CPU. The 4 studs around the
heat sink which are used to secure the heat sink onto the
system board must match the 4 mounting holes around the
socket.
Position each stud so that the groove faces the heat sink then
push it down firmly until it clicks into place.
Note:
You will not be able to secure the fan and heat sink
assembly in place if the groove is not facing the heat sink.
Heat sink
Fan
Stud
Groove
Mounting holes
Mounting holes
Mounting holes
Mounting holes
3. Connect the CPU fan’s cable connector to the CPU fan connector on the system board.
26
2
Hardware Installation
JP8
2.4 Jumper Settings
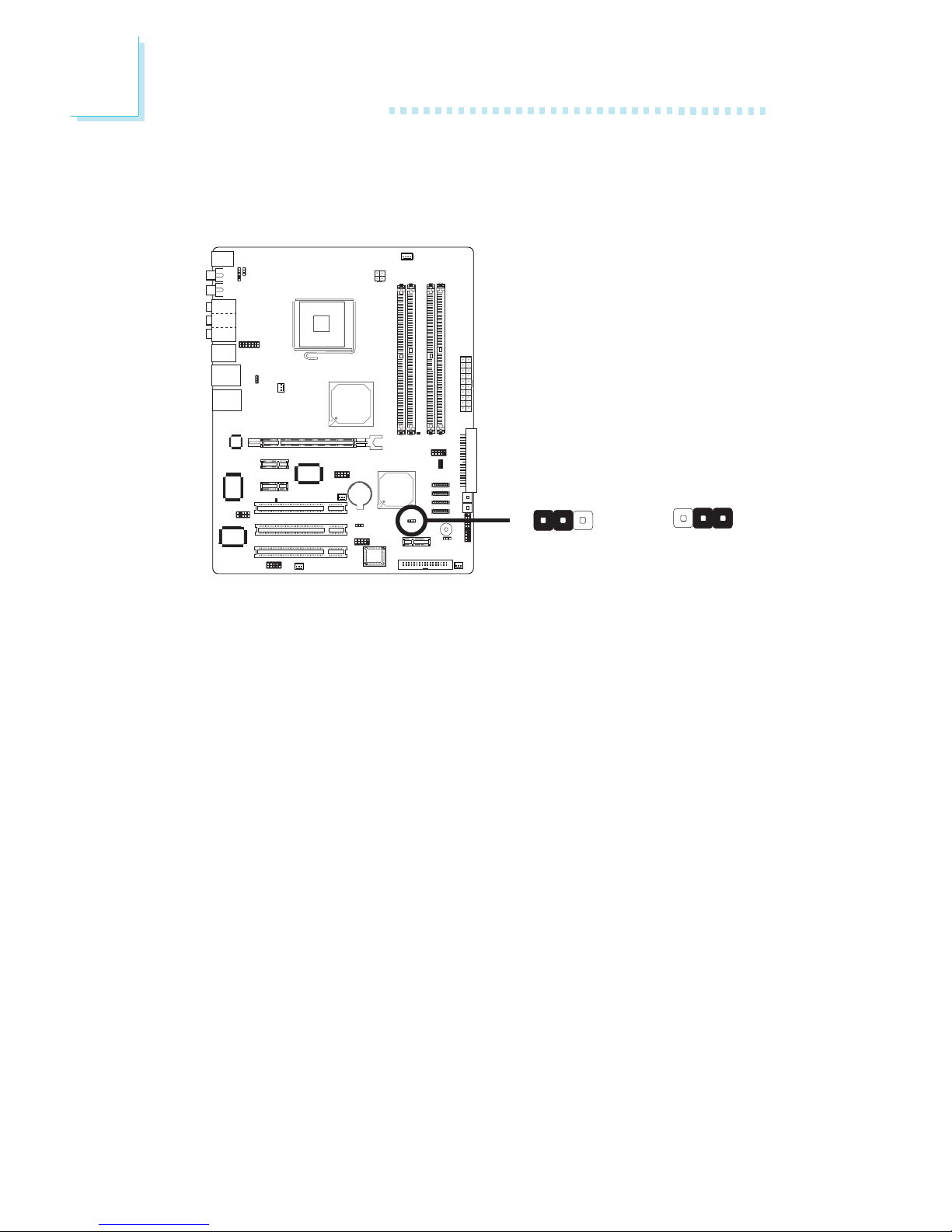
2.4.1 Clear CMOS Data
If you encounter the following,
a) CMOS data becomes corrupted.
b) You forgot the supervisor or user password.
c) You are unable to boot-up the computer system because the
processor’s ratio/clock was incorrectly set in the BIOS.
you can reconfigure the system with the default values stored in the
ROM BIOS.
To load the default values stored in the ROM BIOS, please follow
the steps below.
1. Power-off the system.
2. Set JP4 pins 2 and 3 to On. Wait for a few seconds and set JP4
back to its default setting, pins 1 and 2 On.
3. Now power-on the system.
If your reason for clearing the CMOS data is due to incorrect
setting of the processor’s ratio/clock in the BIOS, please proceed
to step 4.
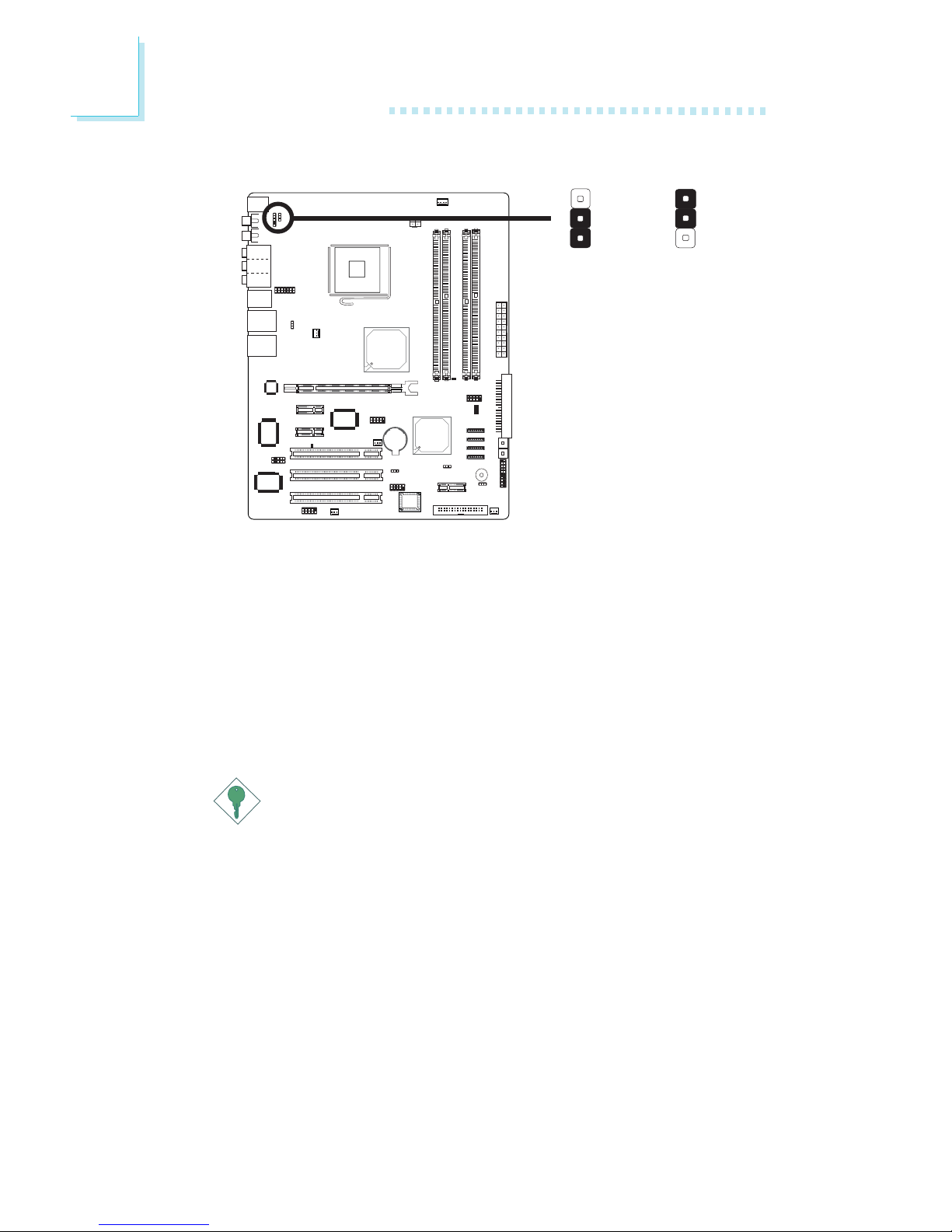
2-3 On:
Clear CMOS Data
1-2 On: Normal
(default)
X
JP4
312
312

27
2
Hardware Installation
4. After powering-on the system, press <Del> to enter the main
menu of the BIOS.
5. Select the Genie BIOS Setting submenu and press <Enter>.
6. Set the “CPU Clock” or “Multiplier Factor” field to its default
setting or an appropriate bus clock or multiplier factor. Refer to
the Genie BIOS Setting section in chapter 3 for more
information.
7. Press <Esc> to return to the main menu of the BIOS setup
utility. Select “Save & Exit Setup” and press <Enter>.
8. Type <Y> and press <Enter>.
28
2
Hardware Installation
JP8
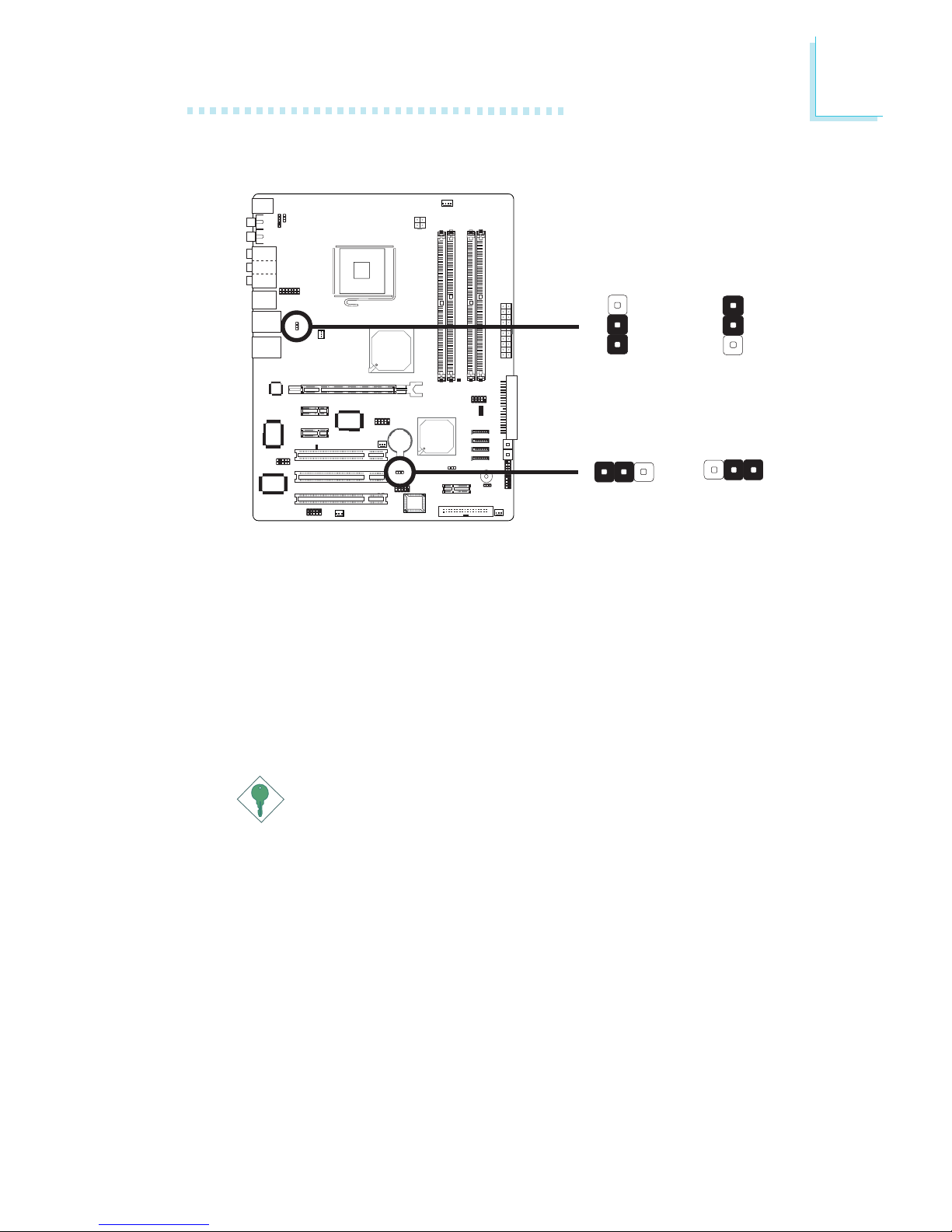
2.4.2 PS/2 Power Select
X
JP1
2-3 On: 5VSB
1-2 On: 5V
(default)
3
1
2
3
1
2
JP1 is used to select the power of the PS/2 keyboard/mouse port.
Selecting 5VSB will allow you to use the PS/2 keyboard or PS/2
mouse to wake up the system.
BIOS Setting
Configure the PS/2 keyboard/mouse wake up function in the
Integrated Peripherals submenu (“Super IO Device” section) of the
BIOS. Refer to chapter 3 for more information.
Important:
The 5VSB power source of your power supply must support
≥
720mA.
29
2
Hardware Installation
JP8
2.4.3 USB Power Select
X
USB 1-6
(JP2)
3
1
2
3
1
2
2-3 On: 5VSB1-2 On: 5V
(default)
312
312
2-3 On: 5VSB
1-2 On: 5V
(default)
X
USB 7-8
(JP3)
JP2 and JP3 are used to select the power of the USB ports.
Selecting 5VSB will allow you to use the USB keyboard or USB
mouse to wake up the system.
BIOS Setting
“USB KB Wake-Up From S3” in the Power Management Setup
submenu of the BIOS must be set to Enabled. Refer to chapter 3
for more information.
Important:
• If you are using the Wake-On-USB Keyboard/Mouse
function for 2 USB ports, the 5VSB power source of your
power supply must support ≥1.5A.
• If you are using the Wake-On-USB Keyboard/Mouse
function for 3 or more USB ports, the 5VSB power source
of your power supply must support ≥2A.
30
2
Hardware Installation
JP8
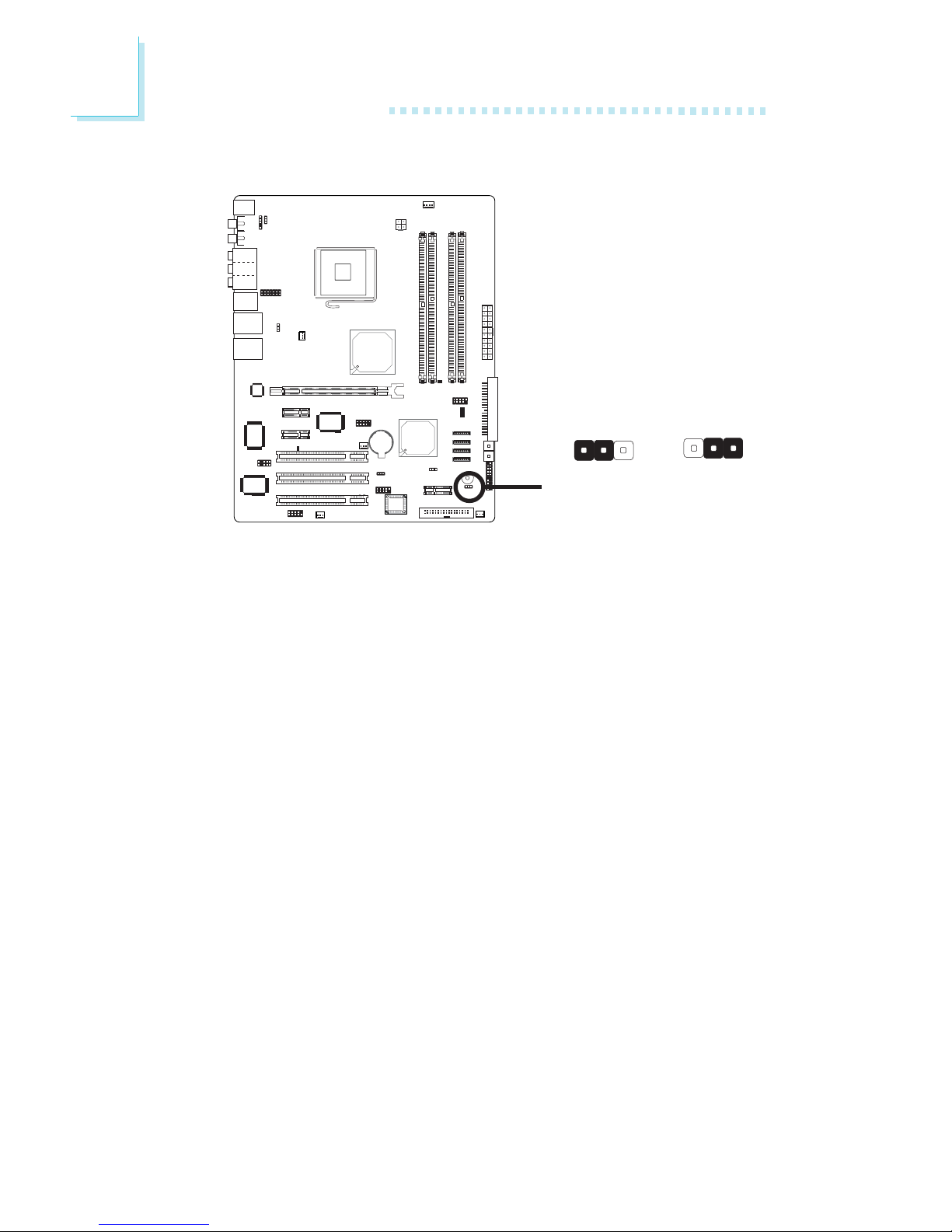
JP8 is used to turn on or off the PC’s speaker. Turning on the
speaker will allow you to hear the system’s beep messages and
warnings.
2.4.3 Speaker On/Off Select
X
JP8
312
312
2-3 On:
Speaker On
(default)
1-2 On:
Speaker Off
 Loading...
Loading...