Page 1

K6XV3+
Rev. A+
System Board
Users Manual
38700901
Page 2

Copyright
This publication contains information that is protected by copyright. No
part of it may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to
make any transformation/adaptation without the prior written permission
from the copyright holders.
This publication is provided for informational purposes only. The
manufacturer makes no representations or warranties with respect to
the contents or use of this manual and specifically disclaims any express
or implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose.
The user will assume the entire risk of the use or the results of the use of
this document. Fur ther, the manufacturer reserves the right to revise this
publication and make changes to its contents at any time, without obligation
to notify any person or entity of such revisions or changes.
All Rights Reserved. © 1999
Trademarks
Microsoft® MS-DOS®, WindowsTM ,Windows® 95 and Windows® 98
are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Intel and Pentium
are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation. Cyrix 6x86, 6x86L,
6x86MX and M II are registered trademarks of Cyrix Corporation. AMD
K5, K6 and K6-2 are registered trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices,
Inc. IBM is a registered trademark of International Business Machine
Corporation. IDT C6 and WINCHIP2 are registered trademarks of IDT
Corporation. Award is a registered trademark of Award Software, Inc.
Other trademarks and registered trademarks of products appearing in
this manual are the properties of their respective holders.
Caution:
Danger of explosion if battery incorrectly replaced.
Replace only with the same or equivalent type recommended by the
manufacturer.
Dispose of used batteries according to the battery manufacturers
instructions.
Page 3

FCC and DOC Statement on Class B
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits
for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules.
These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against
harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with
the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference
will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause
harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is
encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the
following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from
that to which the receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio TV technician for
help.
Notice:
1. The changes or modifications not expressly approved by the
party responsible for compliance could void the user's authority
to operate the equipment.
2. Shielded interface cables must be used in order to comply with
the emission limits.
Page 4

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 - Introduction
1.1 Features and Specifications ......................................................................
1.2 Package Checklist .........................................................................................
Chapter 2 - Hardware Installation
2.1 System Board Layout .................................................................................
2.2 System Memory .............................................................................................
2.3 DIP Switch Settings of the Processors ............................................
2.4 Jumper Settings for Clearing CMOS Data. ...................................
2.5 Jumper Settings for SDRAM Clock (DIMM) ................................
2.6 Connecting the Ribbon Cables and Wires of the Ports
and Connectors .............................................................................................
Chapter 3 - Award BIOS Setup Utility
3.1 The Basic Input/Output System ...........................................................
3.1.1 Standard CMOS Setup.............................................................
3.1.2 BIOS Features Setup..................................................................
3.1.3 Chipset Features Setup.............................................................
3.1.4 Power Management Setup ......................................................
3.1.5 PNP/PCI Configuration .............................................................
3.1.6 Load Fail-Safe Settings ...............................................................
3.1.7 Load Optimal Settings ..............................................................
3.1.8 Integrated Peripherals .................................................................
3.1.9 Supervisor Password ..................................................................
3.1.10 User Password...............................................................................
3.1.11 IDE HDD Auto Detection .....................................................
3.1.12 Save & Exit Setup ........................................................................
3.1.13 Exit Without Saving .....................................................................
6
10
28
28
32
36
38
41
43
43
43
47
47
48
49
49
11
12
12
17
18
19
Page 5

57
57
59
Chapter 4 - Supported Softwares
4.1 Desktop Management Interface .........................................................
4.2 System Health Monitor Utility ...............................................................
4.3 Drivers ...............................................................................................................
Appendix A - Identifying Processors
A.1 Intel Processors.............................................................................................
A.2 Cyrix Processors ..........................................................................................
A.3 IBM Processors .............................................................................................
A.4 AMD Processors .........................................................................................
A.5 IDT Processors .............................................................................................
Appendix B - System Error Messages
B.1 POST Beep .....................................................................................................
B.2 Error Messages..............................................................................................
Appendix C - Troubleshooting
C.1 Troubleshooting Checklist ........................................................................
50
53
54
55
55
56
56
56
Page 6

6
1.1 Features and Specifications
1.1.1 Features
Chipset
VIA Apollo MVP3 AGP system chipset
Processor
The system board is equipped with a switching voltage regulator
that supports 2.0V to 3.5V core voltage for various processors.
Intel Pentium 90/100/120/133/150/166/200MHz and Intel
Pentium processor with MMXTM technology-166/200/233MHz
Cyrix 6x86L PR150+/PR166+/PR200+, 6x86MX-PR166/
PR200/PR233/PR266 and M II-300/333/350/400
IBM 6x86MX-PR200/PR233/PR266/PR300/PR333
AMD K5 PR90/PR100/PR120/PR133/PR166, K6-166/200/233/
266/300 and K6-2/250/266/300/333/350/366/380/400
IDT C6-180/200/225/240 and WINCHIP2-200/225/240/266/
300
System Memory
16MB to 384MB memory using unbuffered DIMMs
Three 168-pin DIMM sockets using x64 or x72 SDRAM, 3.3V
PC-100 SDRAM DIMM for 100MHz external system bus clock
processors
ECC supported (uses x72 PC SDRAM DIMM)
Chapter 1 - Introduction
DIMMs
2MBx64/x72
4MBx64/x72
8MBx64/x72
16MBx64/x72
Memory Size
16MB
32MB
64MB
128MB
Page 7

7
1
Introduction
Level 2 Cache Memory
512KB or 1MB pipeline burst, direct map write-back cache
installed on the system board.
Expansion Slots
The system board is equipped with 1 dedicated AGP slot, 3
dedicated PCI slots, 2 dedicated 16-bit ISA slots and 1 shared PCI/
ISA slot. All PCI and ISA slots are bus masters.
Desktop Management Interface (DMI)
The system board comes with a DMI 2.0 built into the BIOS. The
DMI utility in the BIOS automatically records various information
about your system configuration and stores these information in the
DMI pool, which is a part of the system board's Plug and Play
BIOS. DMI, along with the appropriately networked software, is
designed to make inventory, maintenance and troubleshooting of
computer systems easier. Refer to Chapter 4 for instructions on
using the DMI utility.
ATX Double Deck Ports
2 USB ports
2 DB-9 serial ports
1 DB-25 parallel port
1 PS/2 mouse port
1 PS/2 keyboard port
Connectors
1 connector for IrDA interface
2 IDE connectors
1 floppy connector
1 20-pin ATX power supply connector
2 fan connectors for CPU and AGP fans
PCI Bus Master IDE Controller
Two PCI IDE interfaces support up to four IDE devices
Ultra DMA/33 supported (Synchronous Ultra DMA mode -
data transfer rate up to a maximum of 33MB/sec.)
Page 8

8
Introduction
1
PIO Mode 3 and Mode 4 Enhanced IDE (data transfer rate up
to 16.6MB/sec.)
Bus mastering reduces CPU utilization during disk transfer
ATAPI CD-ROM, LS-120 and ZIP supported
IrDA Interface
The system board is equipped with an IrDA connector for wireless
connectivity between your computer and peripheral devices. It
supports infrared peripheral devices that meet the ASKIR or HPSIR
standard.
USB Ports
The system board is equipped with two USB ports. USB allows
data exchange between your computer and a wide range of
simultaneously accessible external Plug and Play peripherals.
BIOS
Award BIOS, Windows 95 Plug and Play compatible
Flash EPROM for easy BIOS upgrades
1.1.2 Intelligence
Monitors Processor Temperature and Overheat Alarm
The system board is able to detect the temperature of the
processor. An alarm will sound in case of processor overheat.
Monitors Processor/AGP Fan Speed and Failure Alarm
The system board is able to detect the fan speed (RPM-Revolutions
Per Minute) of the processor and AGP fans, and alerts you to attend
to any irregularity that may damage your system.
Monitors Power Voltages and Failure Alarm
The system board is able to detect the output voltage of the power
supply. An alarm will sound warning you of voltage irregularity.
Page 9

9
1
Introduction
Automatic Fan Control
With the systems power switched on, the processors fan will rotate
only if the temperature of the processor is over 25oC.
Dual Function Power Button
Depending on the setting in the BIOS setup, this switch will allow
your system to enter the Soft-Off or Suspend mode.
External Modem Ring-on
The Modem Ring-on feature allows the system that is in the
Suspend mode or Soft Power Off mode to wake-up/power-on to
respond to incoming calls.
Note:
This feature supports external modem only. If you are using
this function, make sure to turn on the power of the modem
prior to powering-off the system.
RTC Timer to Power-on the System
The RTC installed on the system board allows your system to
automatically power-on on the set date and time.
ACPI
The system board is designed to meet the ACPI (Advanced
Configuration and Power Interface) specification. ACPI has energy
saving features that enables PCs to implement Power Management
and Plug-and-Play with operating systems that support OS Direct
Power Management.
Virus Protection
Most viruses today destroy data stored in hard drives. The system
board is designed to protect the boot sector and partition table of
your hard disk drive.
Page 10

10
Introduction
1
1.2 Package Checklist
The system board package contains the following items:
þ The system board
þ A users manual
þ One 40-pin IDE hard disk cable
þ One 34-pin floppy disk drive cable
þ One CD
If any of these items are missing or damaged, please contact your
dealer or sales representative for assistance.
Page 11
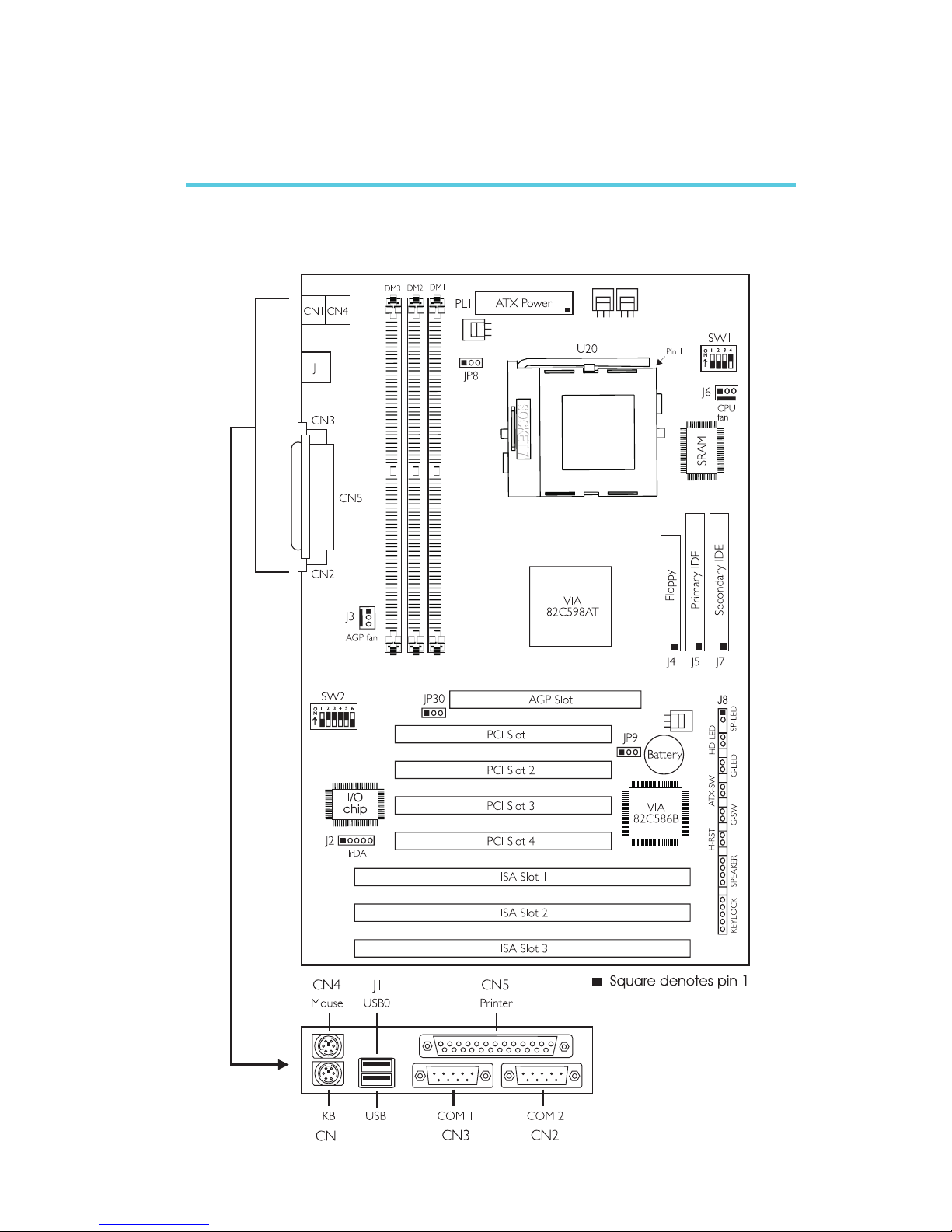
11
2.1 System Board Layout
Chapter 2 - Hardware Installation
Page 12
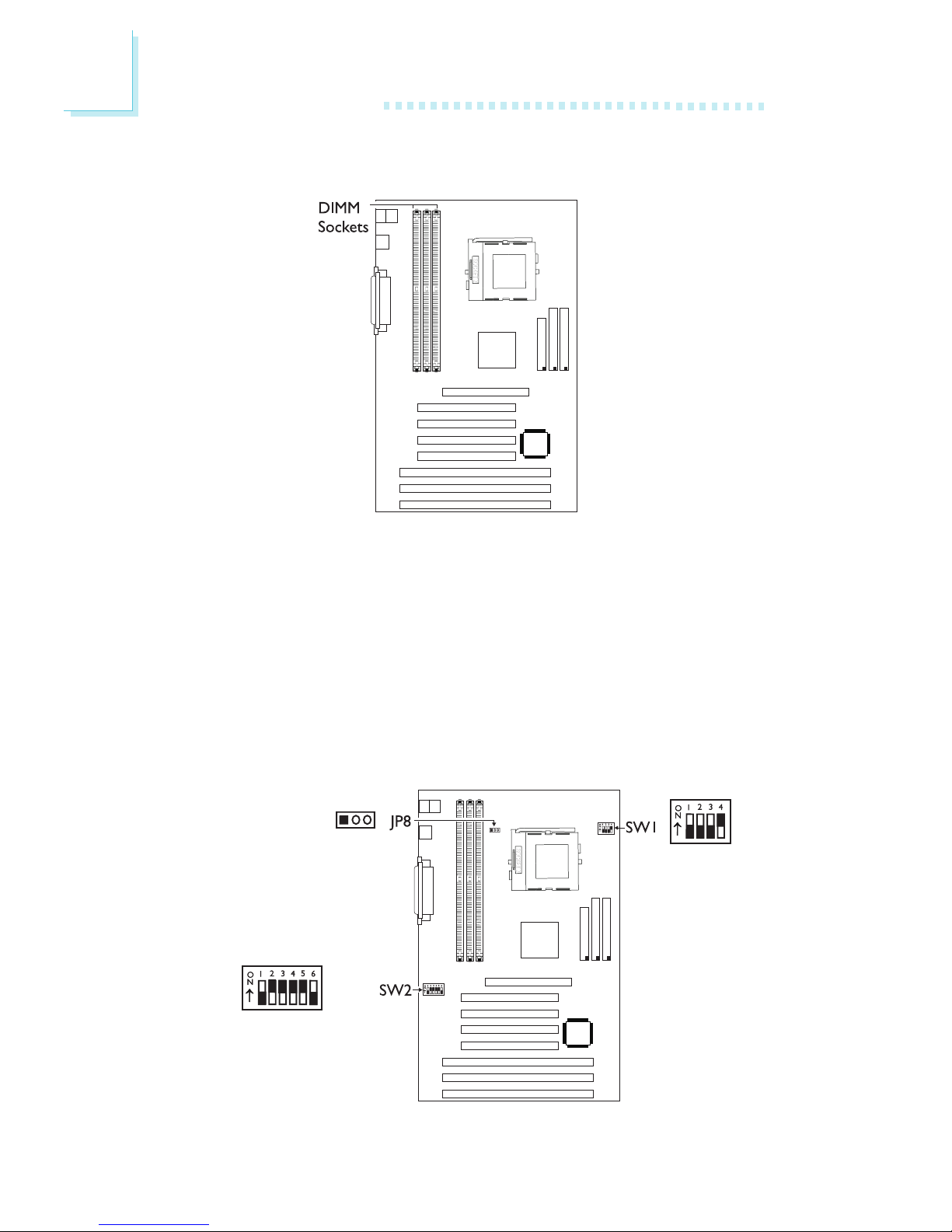
12
2
Hardware Installation
2.2 System Memory
2.3 DIP Switch and Jumper Settings of the
Processors
Make sure SW1, SW2 and JP8 are set correctly before applying
power or you may damage the processor or system board. There
are 4 switches on SW1 and 6 switches on SW2. The black rectangle
in the diagram denotes the part that is protruding, the adjustable
switch.
In the example above:
Switch 1: Off Switch 4: On
Switch 2: On Switch 5: On
Switch 3: On Switch 6: Off
Page 13
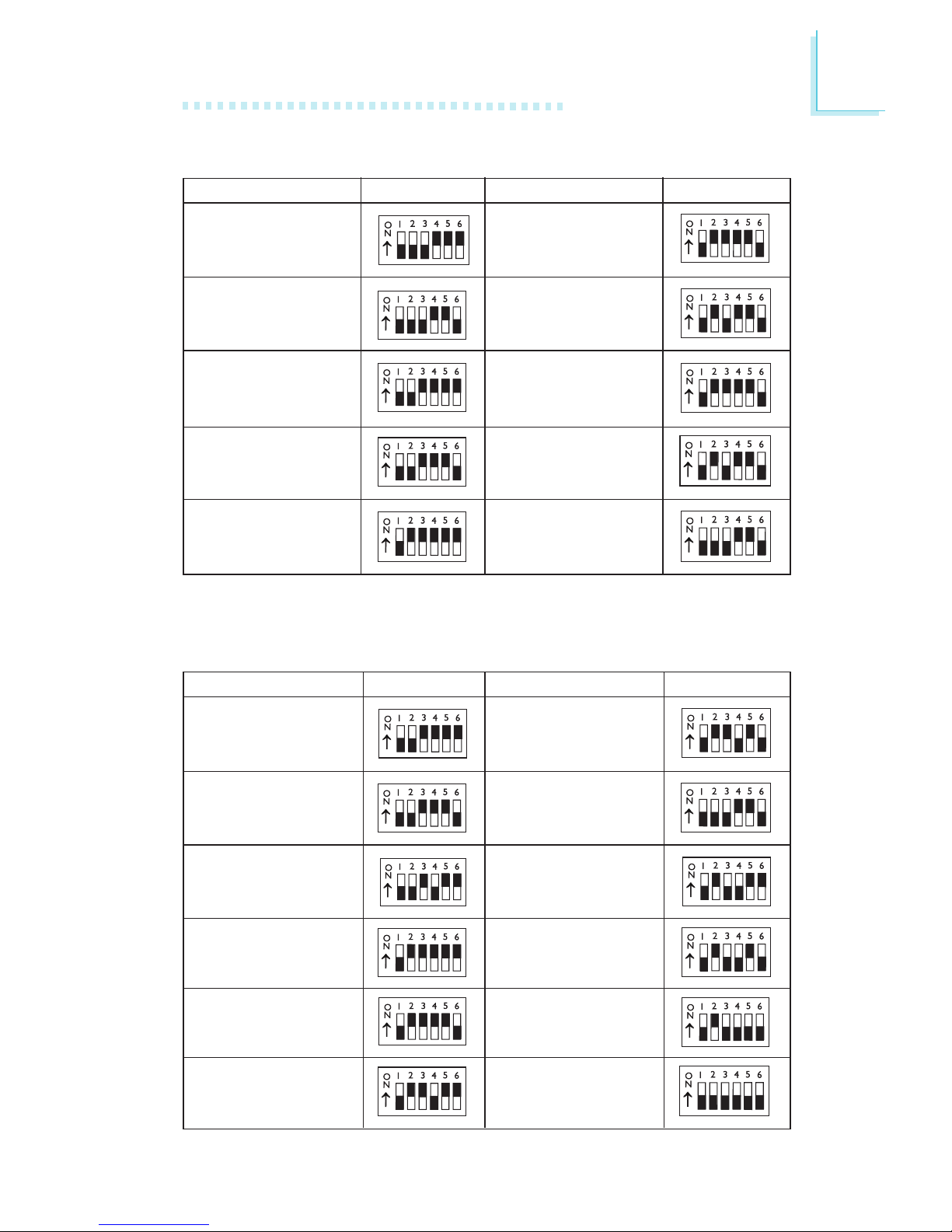
13
2
Hardware Installation
DIP Switch Settings for Cyrix Processors
DIP Switch Settings for Intel Processors
Cyrix Processors
SW2: 1-6
Cyrix Processors SW2: 1-6
6x86MX-PR200 66MHz - 2.5x
6x86MX-PR233 75MHz - 2.5x
6x86MX-PR266 83MHz - 2.5x
M II-300 75MHz - 3x
M II-333 83MHz - 3x
M II-350 100MHz - 3x
M II-400 100MHz - 3.5x
M II-300 66MHz - 3.5x
6x86L PR150+ 60MHz - 2x
6x86L PR166+ 66MHz - 2x
6x86MX-PR166 60MHz - 2.5x
6x86L PR200+ 75MHz - 2x
Intel Processors SW2: 1-6
90MHz 60MHz - 1.5x
100MHz 66MHz - 1.5x
120MHz 60MHz - 2x
133MHz 66MHz - 2x
150MHz 60MHz - 2.5x
166MHz 66MHz - 2.5x
200MHz 66MHz - 3x
MMX166MHz* 66MHz - 2.5x
MMX200MHz 66MHz - 3x
MMX233MHz 66MHz - 3.5x
Intel Processors
SW2: 1-6
* Default
Page 14
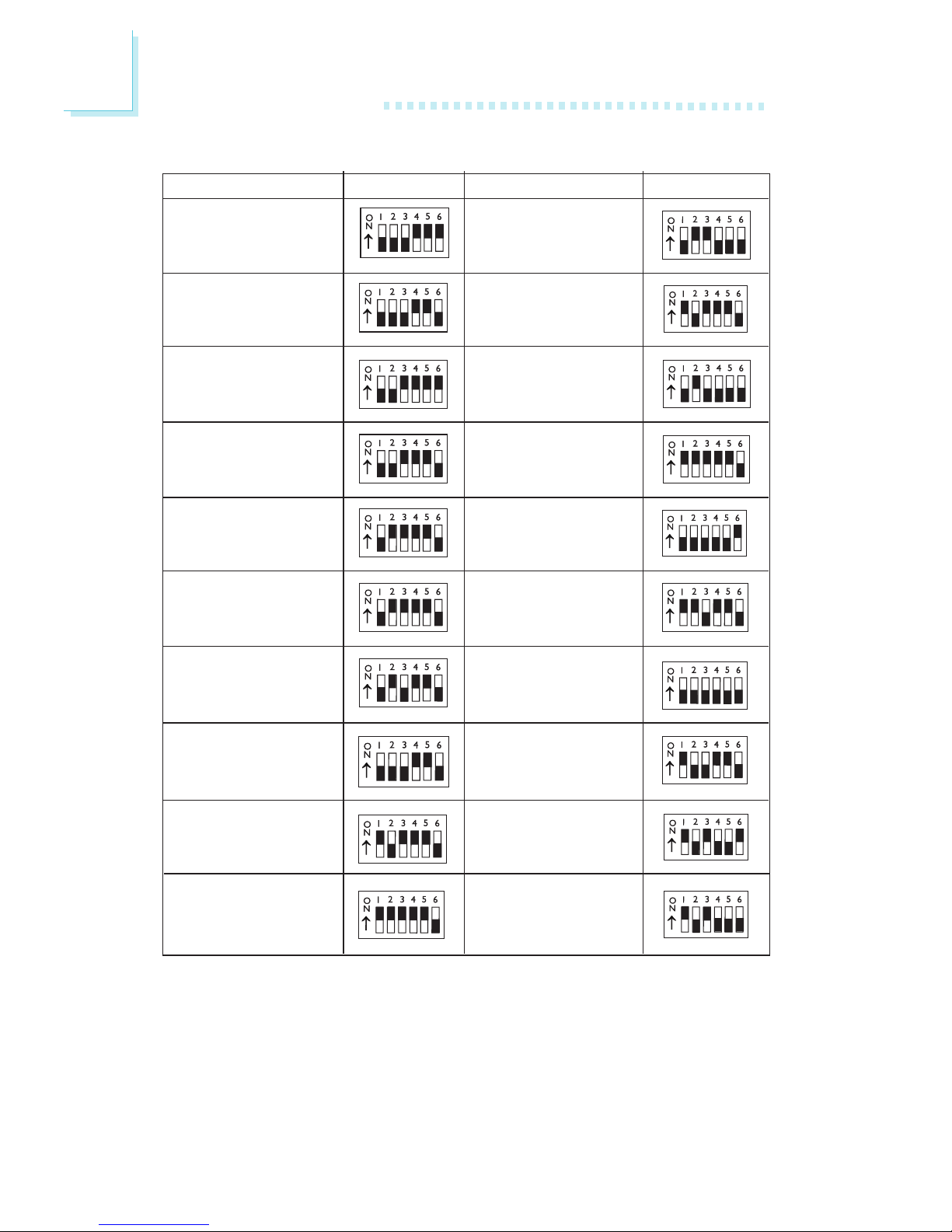
14
2
Hardware Installation
DIP Switch Settings for AMD Processors
AMD Processors
SW2: 1-6
AMD Processors SW2: 1-6
K6-200 66MHz - 3x
K6-233 66MHz - 3.5x
K6-2/250 100MHz - 2.5x
K6-2/266 66MHz - 4x
K5 PR90 60MHz - 1.5x
K5 PR100 66MHz - 1.5x
K5 PR120 60MHz - 2x
K5 PR133 66MHz - 2x
K5 PR166 66MHz - 2.5x
K6-166 66MHz - 2.5x
K6-266 66MHz - 4x
K6-2/400 100MHz - 4x
K6-2/380 95MHz - 4x
K6-2/366 66MHz - 5.5x
K6-2/350 100MHz - 3.5x
K6-2/333 95MHz - 3.5x
K6-2/300 100MHz - 3x
K6-2/333 66MHz - 5x
K6-300 66MHz - 4.5x
K6-2/300 66MHz - 4.5x
Page 15
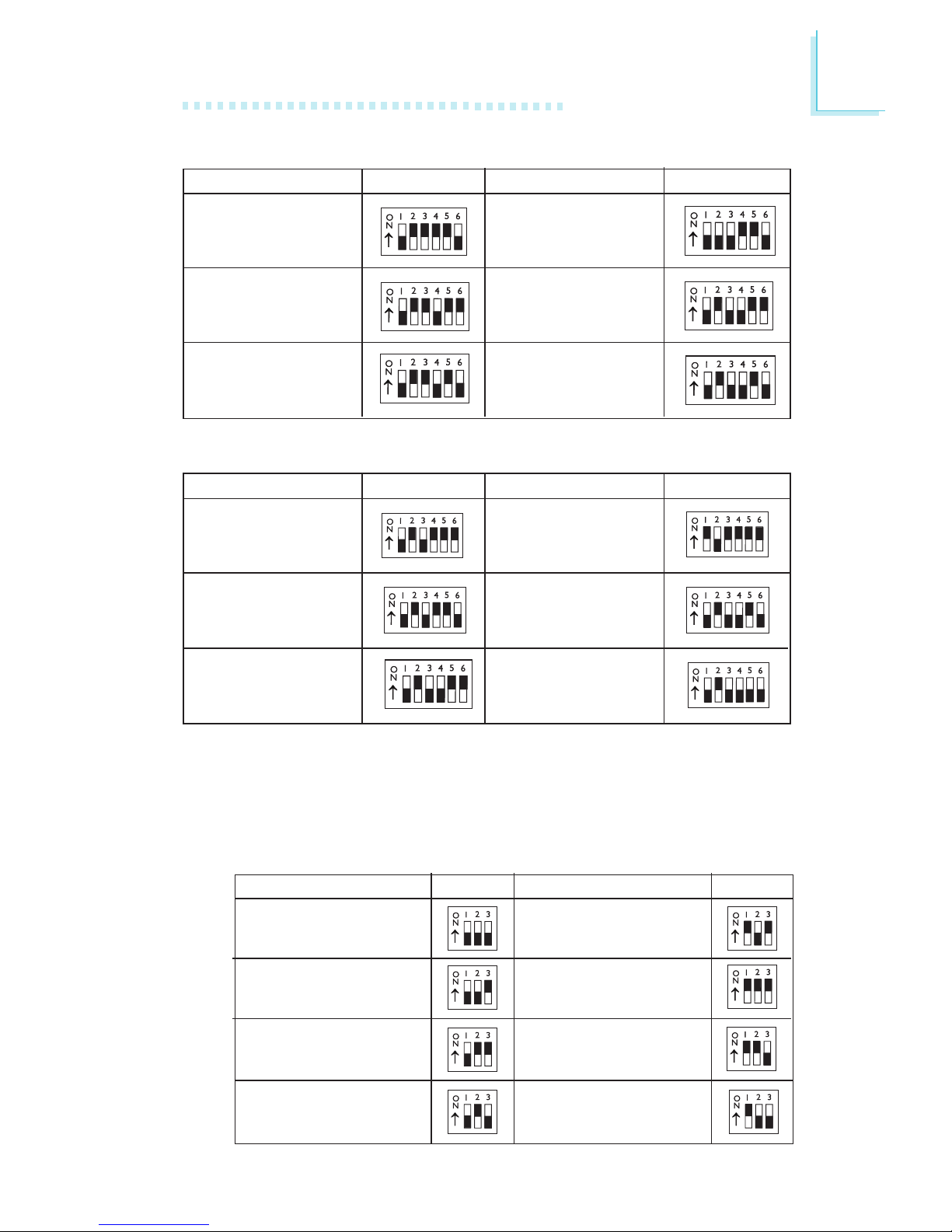
15
2
Hardware Installation
External System Bus Clock / Frequency Ratio - DIP Switch Settings
If the processor you are using is not included in the previous
tables, please refer to the tables below and set SW2 according
to the external system bus clock and frequency ratio of your
processor.
Frequency Ratio
SW2: 1-3
1.5x / 3.5x
Frequency Ratio
SW2: 1-3
2x
2.5x
4x
4.5x
5x
3x
5.5x
DIP Switch Settings for IDT Processors
C6-180 - 60MHz - 3x
C6-200 - 66MHz - 3x
WINCHIP2-200 66MHz - 3x
IDT Processors
SW2: 1-6 IDT Processors SW2: 1-6
C6-225 - 75MHz - 3x
WINCHIP2-225 75MHz - 3x
WINCHIP2-266 83MHz - 3x
C6-240 - 60MHz - 4x
WINCHIP2-240 60MHz - 4x
WINCHIP2-300 100MHz - 3x
DIP Switch Settings for IBM Processors
IBM Processors SW2: 1-6
IBM Processors
SW2: 1-6
6x86MX-PR200 66MHz - 2.5x
6x86MX-PR233 75MHz - 2.5x
6x86MX-PR266 83MHz - 2.5x
6x86MX-PR300 75MHz - 3x
6x86MX-PR333 83MHz - 3x
6x86MX-PR300 66MHz - 3.5x
Page 16
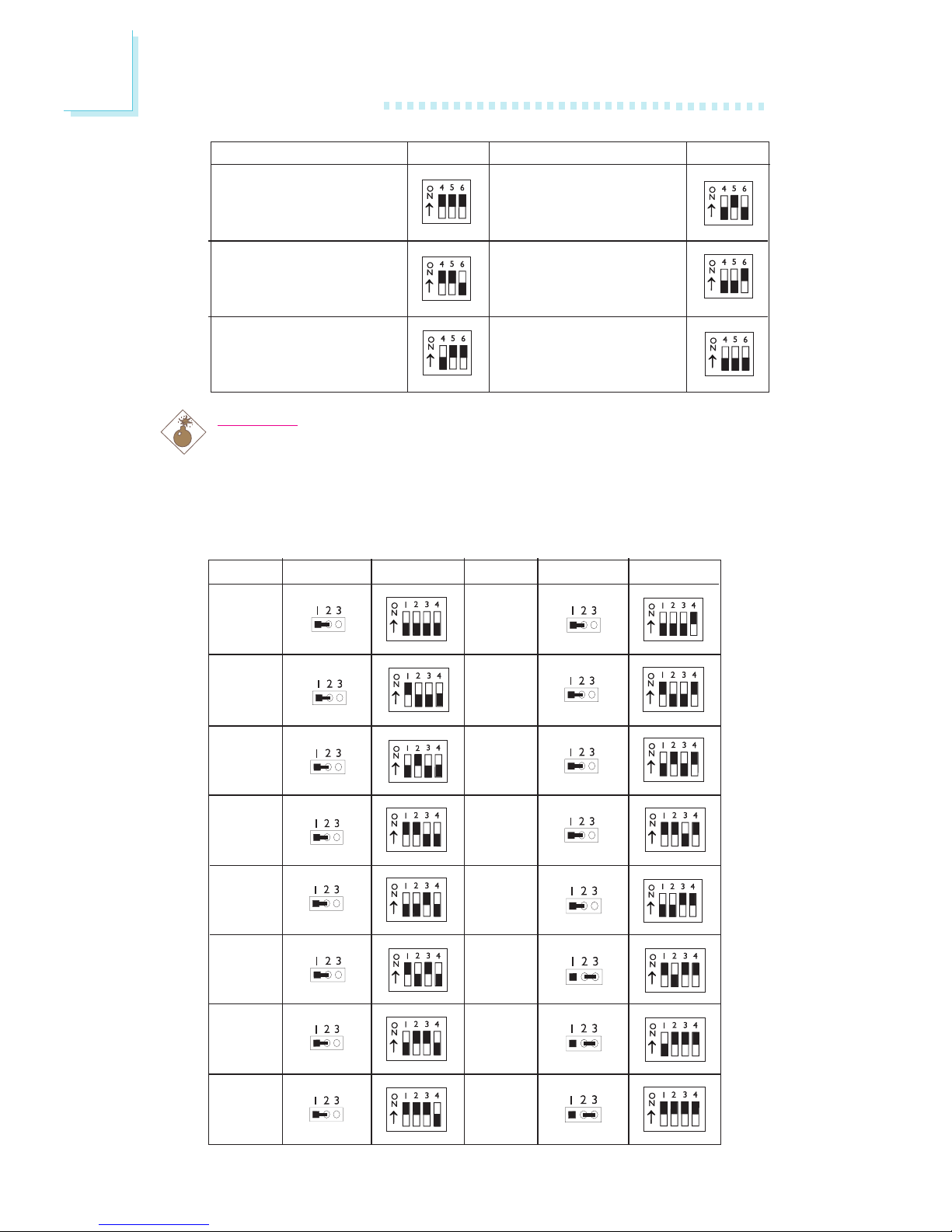
16
2
Hardware Installation
DIP Switch and Jumper Settings for Core Voltage
External System Bus Clock SW2: 4-6 External System Bus Clock SW2: 4-6
60MHz
83MHz
66MHz
95MHz
75MHz 100MHz
Voltage JP8 SW1
2.8V
2.0V
2.1V
2.9V
3.0V
3.1V
Voltage JP8 SW1
2.2V
2.3V
2.4V
2.5V
2.6V
2.7V
3.2V
3.3V
3.4V
3.5V
Warning:
We do not guarantee that 75MHz, 83MHz, 95MHz and 100MHz
external system bus clock processors will work with all types of add-in
cards, DIMM modules or other devices.
Page 17
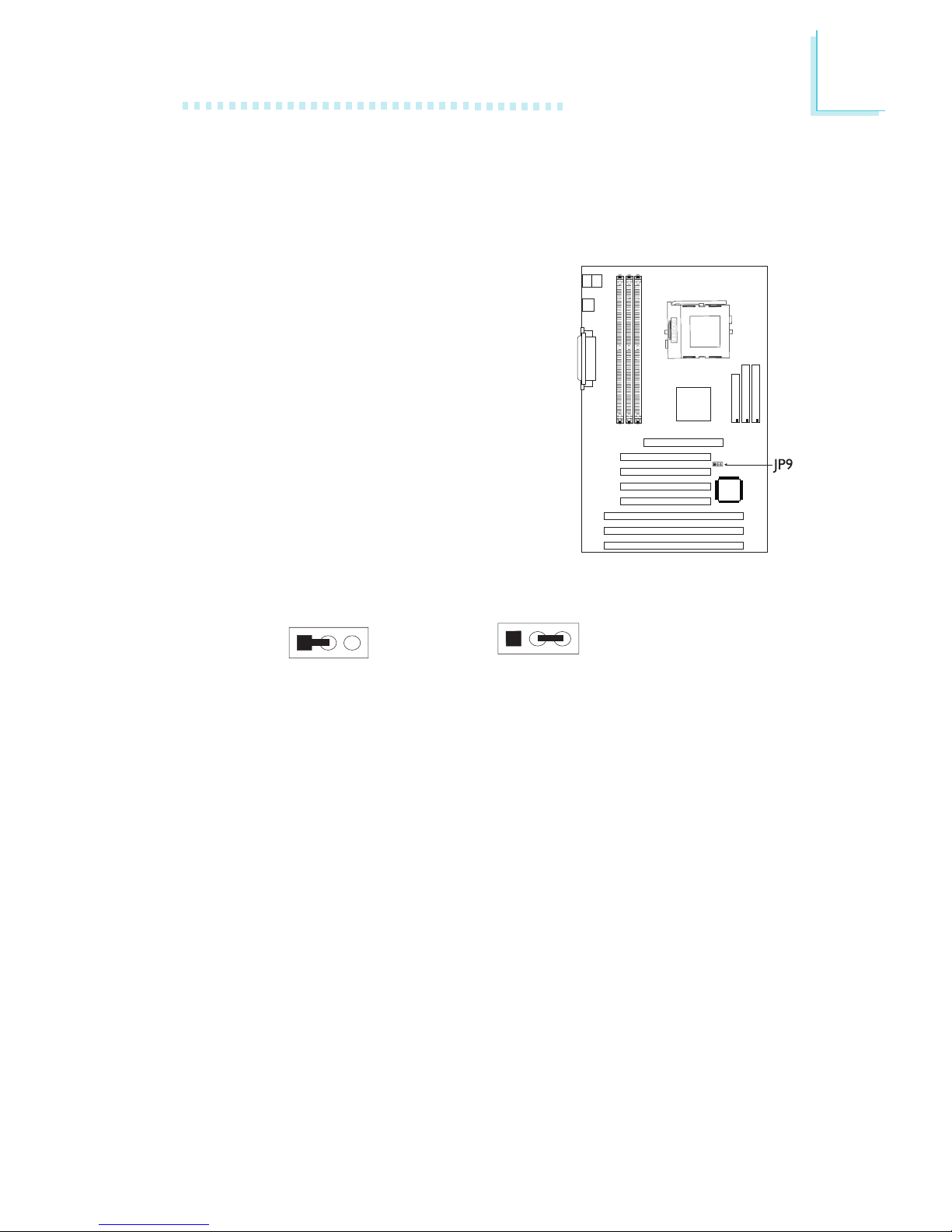
17
2
Hardware Installation
2-3 On:
Normal (default)
1-2 On:
Clear CMOS Data
2.4 Jumper Settings for Clearing CMOS Data
Jumper JP9
Clear CMOS Data
If, for some reason, the CMOS data
becomes corrupted, the system can be
reconfigured with the default values
stored in the ROM BIOS. To load the
default values, power off your system
and unplug the power cord. Set JP9
pins 1 and 2 to On. Wait for a few
seconds and set JP9 back to its default
setting, pins 2 and 3 On. You may now
plug the power cord and power-on
your system.
123123
Page 18

18
2
Hardware Installation
2.5 Jumper Settings for SDRAM Clock (DIMM)
Jumper JP30
SDRAM Clock
JP30 is used to set the SDRAMs clock
according to the CPU clock or AGP
clock. If you are using PC-100 SDRAM
DIMMs, it is recommended that you
set the SDRAM clock according to the
CPU clock (2-3 On). This setting will
provide better system performance
specially when used with 75/83/95/
100MHz processors. However, if you
encounter compatibility problems with
PC-100 SDRAM DIMMs or you are
using EDO/PC-66 SDRAM DIMMs, set
the SDRAM clock according to the
AGP clock (1-2 On).
2-3 On:
SDRAM CLK = CPU CLK
1-2 On:
SDRAM CLK = AGP CLK
(default)
123123
CPU CLK
60MHz
66MHz
75MHz
83MHz
95MHz
100MHz
SDRAM CLK
60MHz
66MHz
60MHz
66MHz
66MHz
66MHz
AGP CLK
60MHz
66MHz
60MHz
66MHz
66MHz
66MHz
CPU CLK
60MHz
66MHz
75MHz
83MHz
95MHz
100MHz
SDRAM CLK
60MHz
66MHz
75MHz
83MHz
95MHz
100MHz
AGP CLK
60MHz
66MHz
60MHz
66MHz
66MHz
66MHz
Page 19
19
2
Hardware Installation
2.6 Connecting the Ribbon Cables and Wires
of the Ports and Connectors
2.6.1 Serial Ports
The built-in serial ports are RS-232C
asynchronous communication ports
with 16C550A-compatible UARTs
that can be used with modems, serial
printers, remote display terminals, and
other serial devices. You can set the
serial ports I/O address in the
Integrated Peripherals setup of the
Award BIOS.
2.6.2 PS/2 Mouse Port
The PS/2 mouse port uses IRQ12. If
a mouse is not connected to this
port, the system will reserve IRQ12
for other expansion cards.
Warning:
Make sure to turn off your
computer prior to connecting
or disconnecting a mouse or
keyboard. Failure to do so may
damage the system board.
Page 20

20
2
Hardware Installation
2.6.3 Parallel Port
The system board has a standard
printer port for interfacing your PC
to a parallel printer. It supports
SPP, ECP and EPP modes. You can
set the ports mode in the
Integrated Peripherals setup of the
Award BIOS.
1. Install the 34-pin header connector
into the shrouded floppy disk header
(J4) on the system board. The
colored edge of the ribbon should
be aligned with pin 1 of J4.
2. Install the other 34-pin header
connector(s) into the disk drive(s).
Align the colored edge of the daisy
chained ribbon cable with pin 1 of
the drive edge connector(s). The endmost connector should be attached
to the drive you want to designate
as Drive A.
2.6.4 Floppy Disk Drive Controller
Page 21

21
2
Hardware Installation
Adding a Second IDE Hard Drive
When using two IDE drives, one must be set as the master and the
other as the slave. Follow the instructions provided by the drive
manufacturer for setting the jumpers and/or switches on the drives.
We recommend that you use Enhanced IDE or ATA-2, ATA-3 and
Ultra DMA hard drives be from the same manufacturer. In a few
cases, drives from two different manufacturers will not function
properly when used together. The problem lies in the hard drives, not
the system board.
Important:
If you encountered problems while using an ATAPI CD-ROM
drive that is set in Master mode, please set the CD-ROM drive
to Slave mode. Some ATAPI CD-ROMs may not be recognized
and cannot be used if incorrectly set in Master mode.
2.6.5 IDE Hard Disk Interface
1. If you are connecting two hard
drives, install the 40-pin connector of
the IDE cable into the primary
shrouded IDE header (connector J5).
If you are adding a third or fourth
IDE device, install the 40-pin
connector of the other IDE cable
into the secondary shrouded IDE
header (connector J7).
2. Install the other 40-pin header
connector(s) into the device with the
colored edge of the ribbon cable
aligned with pin 1 of the drive edge
connector(s).
Note:
Refer to your disk drive users manual for information about
selecting proper drive switch settings.
Page 22

22
2
Hardware Installation
2.6.6 Universal Serial Bus Ports
You must have the proper drivers
installed in your operating system to
use these ports. Refer to your
operating systems manual or
documentation.
2.6.7 IrDA Connector
The system board is equipped with an IrDA connector for wireless
connectivity between your computer and peripheral devices. Connect
your IrDA cable to connector J2 on the system board. Make sure
Onboard UART 2 Mode in the Integrated Peripherals setup of the
Award BIOS (Chapter 3) is set to the type of IrDA standard
supported by your IrDA peripheral/device.
You must have the proper drivers installed in your operating system
to use this connector. Refer to your operating systems manual or
documentation.
Pin
1
2
3
4
5
Function
IRTX
GND
IRRX
IRR3
VCC
Page 23

23
2
Hardware Installation
2.6.9 AGP Fan Connector
The system board is equipped with an AGP fan connector. If the
system board is installed with an AGP add-on card and you wish to
install a fan on the add-on card, connect the fans connector to
location J3 on the system board. Refer to the add-on cards manual
for instructions on installing the fan.
Pin
1
2
3
Function
GND
+12V
Sense
2.6.8 CPU Fan Connector
The processor must be kept cool by using a fan with heatsink.
Connect the CPU fan to the 3-pin fan connector at location J6 on
the system board.
Pin
1
2
3
Function
GND
+12V
Sense
Page 24

24
2
Hardware Installation
2.6.10 J8 (LEDs and Switches)
Pin
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
Pin Assignment
SP-LED
(ATX power LED)
HD-LED
(Primary/Secondary IDE LED)
G-LED
(Green LED)
ATX-SW
(ATX power switch)
G-SW
(Green switch)
H-RST
(Reset switch)
ATX Power
Ground
Open
HDD
HDD LED Power
Open
Green LED Power
Green
Open
PWRBT
Ground
Open
SMI
Ground
Open
H/W Reset
Ground
Open
Page 25

25
2
Hardware Installation
SP-LED - ATX 5VSB Standby LED
This LED will light when the 5VSB power is active.
HD-LED - Primary/Secondary IDE LED
This LED will light when the hard drive is being accessed.
G-LED - Green LED
This LED will light when the system is in the Suspend mode.
ATX-SW - ATX Power Switch
Depending on the setting in the BIOS setup, this switch is a dual
function power button that will allow your system to enter the SoftOff or Suspend mode. Refer to Soft-Off By PWRBTN in the Power
Management Setup (Chapter 3).
G-SW - Green Switch
This switch will allow your system to enter the Suspend mode. To
wake up the system, PM Events in the Power Management Setup
(Chapter 3) must be enabled so that access to the specified IRQ
will allow the system to wake up completely from the Suspend
mode.
Pin
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
Pin Assignment
SPEAKER
(Speaker connector)
KEYLOCK
(Keylock Connector)
Speaker Power
Ground
N. C.
Speaker
Open
LED Power
N.C.
Ground
Keylock
Ground
Use pins 24 to 26
for the Power LED.
Page 26

26
2
Hardware Installation
H-RST - Reset Switch
This switch allows you to reboot without having to power off the
system thus prolonging the life of the power supply or system.
SPEAKER - Speaker Connector
This connects to the speaker installed in the system chassis.
KEYLOCK - Keylock Connector and Power LED Connector
This is used to connect to the keyboard lock for locking the
keyboard. Use pins 24 to 26 to connect to the Power LED.
Page 27

27
2
Hardware Installation
2.6.11 Power Supply Connector
The system board is equipped with an ATX power connector at
location PL1 of the system board.
Pin
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Function
3.3V/14A
3.3V/14A
COM
+5V
COM
+5V
COM
PW-OK
5VSB
+12V
Pin
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
Function
3.3V/14A
-12V
COM
PS-ON
COM
COM
COM
-5V
+5V
+5V
Important:
Your power supply must meet the ATX specification supporting 3.3V/14A (minimum), otherwise your system will not
boot properly.
Page 28

28
3.1 The Basic Input/Output System
The Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) is a program that takes care
of the basic level of communication between the processor and
peripherals. In addition, the BIOS also contain codes for various
advanced features found in this system board. This chapter explains
the Setup Utility for the Award BIOS.
After you power up your system, the BIOS message appears on
your screen and the memory count begins. After the memory test,
the following message will appear on the screen:
Press DEL to enter setup
If the message disappears before you respond, restart your system
or press the Reset button. You may also restart the system by
pressing the <Ctrl> <Alt> and <Del> keys simultaneously.
When you press <Del>, the main program screen will appear.
3.1.1 Standard CMOS Setup
Use the arrow keys to highlight Standard CMOS Setup and press
<Enter>. A screen similar to the one on the next page will appear.
ROM PCI/ISA BIOS
CMOS SETUP UTILITY
AWARD SOFTWARE, INC.
STANDARD CMOS SETUP
BIOS FEATURES SETUP
CHIPSET FEATURES SETUP
POWER MANAGEMENT SETUP
PNP/PCI CONFIGURATION
LOAD FAIL-SAFE SETTINGS
LOAD OPTIMAL SETTINGS
INTEGRATED PERIPHERALS
SUPERVISOR PASSWORD
USER PASSWORD
IDE HDD AUTO DETECTION
SAVE & EXIT SETUP
EXIT WITHOUT SAVING
Esc
F10
: Quit
: Save & Exit Setup
↑↓→←
(Shift) F2
: Select Item
: Change Color
Chapter 3 - Award BIOS Setup Utility
Page 29

29
3
Award BIOS Setup Utility
Date
The date format is <day>, <month>, <date>, <year>. Day displays
a day, from Sunday to Saturday. Month displays the month, from
January to December. Date displays the date, from 1 to 31. Year
displays the year, from 1994 to 2079.
Time
The time format is <hour>, <minute>, <second>. The time is based
on the 24-hour military-time clock. For example, 1 p.m. is 13:00:00.
Hour displays hours from 00 to 23. Minute displays minutes from
00 to 59. Second displays seconds from 00 to 59.
Primary Master, Primary Slave, Secondary Master and Secondary Slave
These categories allow you to enter the appropriate specifications for
the type of hard disk drive(s) installed in your system. Press <PgUp>
or <PgDn> to select a numbered hard disk type or type the number
and press <Enter>. The hard disk will not work properly if you enter
improper information for this category. You can use Type User to
define your own drive type manually. This information should be included
in the documentation from your hard disk vendor. If you select Type
Auto, the BIOS will auto-detect the HDD & CD-ROM drive at the
POST stage and show the IDE for the HDD & CD-ROM drive. If a
hard disk has not been installed, select None and press <Enter>.
The settings on the screen are for reference only. Your version may not be
identical to this one.
ROM PCI/ISA BIOS
STANDARD CMOS SETUP
AWARD SOFTWARE, INC.
Date (mm:dd:yy) : Fri, Jul 17 1998
Time (hh:mm:ss) : 13: 27: 50
HARD DISKS
Primary Master
Primary Slave
Secondary Master
Secondary Slave
TYPE
Auto
Auto
Auto
Auto
SIZE
0
0
0
0
CYLS
0
0
0
0
HEAD
0
0
0
0
PRECOMP
0
0
0
0
LANDZ
0
0
0
0
SECTOR
0
0
0
0
MODE
Auto
Auto
Auto
Auto
Drive A : 1.44M, 3.5 in.
Drive B : None
Video : EGA/VGA
Halt on : All Errors
Base Memory : 640K
Extended Memory : 64512K
Other Memory : 384K
Total Memory : 65536K
PU/PD/+/- : Modify
↑↓→←
: Select Item
: Change(Shift)F2
:
:
:
:
Esc
F10
: Quit
: Save & Exit Setup
Page 30

30
3
Award BIOS Setup Utility
Drive A and Drive B
These categories identify the types of floppy disk drives installed.
None No floppy drive is installed
360K, 5.25 in. 5-1/4 in. standard drive; 360KB capacity
1.2M, 5.25 in. 5-1/4 in. AT-type high-density drive; 1.2MB
capacity
720K, 3.5 in. 3-1/2 in. double-sided drive; 720KB capacity
1.44M, 3.5 in. 3-1/2 in. double-sided drive; 1.44MB capacity
2.88M, 3.5 in. 3-1/2 in. double-sided drive; 2.88MB capacity
Video
This category selects the type of video adapter used for the primary
system monitor. Although secondary monitors are supported, you
do not have to select the type in Setup. The default setting is EGA/
VGA (BIOS default, Setup default).
EGA/VGA Enhanced Graphics Adapter/Video Graphics Array. For
EGA, VGA, SVGA and PGA monitor adapters.
CGA 40 Color Graphics Adapter. Power up in 40-column
mode.
CGA 80 Color Graphics Adapter. Power up in 80-column
mode.
Mono Monochrome adapter. Includes high resolution
monochrome adapters.
Halt On
This category determines whether the system will stop if an error is
detected during power up. The default setting is All Errors (BIOS
default, Setup default).
No Errors The system boot will not stop for any errors detected.
All Errors The system boot will stop whenever the BIOS detects
a non-fatal error.
All, But Keyboard The system boot will not stop for a keyboard
error; it will stop for all other errors.
All, But Diskette The system boot will not stop for a disk error;
it will stop for all other errors.
All, But Disk/Key The system boot will not stop for a disk or
keyboard error; it will stop for all other errors.
Page 31

31
3
Award BIOS Setup Utility
Memory
The base memory size, extended memory size and the other memory
size cannot be altered; your computer automatically detects and displays
them.
Base Memory The POST will determine the amount of base (or
conventional) memory installed in the system. The
value of the base memory is typically 512K for
systems with 512K memory installed on the
motherboard or 640K for systems with 640K or
more memory installed on the motherboard.
Extended Memory The BIOS determines how much extended
memory is present during the POST. This is
the amount of memory located above 1MB
in the CPUs memory address map.
Other Memory This refers to the memory located in the 640K
to 1024K address space. This is the memory that
can be used for different applications. DOS uses
this area to load device drivers in an effort to
keep as much base memory free for application
programs. The BIOS is the most frequent user of
this RAM area since this is where it shadows the
ROM.
Page 32

32
3
Award BIOS Setup Utility
3.1.2 BIOS Features Setup
The BIOS Features Setup allows you to configure your system for
basic operation. Some entries are defaults required by the system
board, while others, if enabled, will improve the performance of your
system or let you set some features according to your preference.
The settings on the screen are for reference only. Your version may not be
identical to this one.
Virus Warning
This category protects the boot sector and partition table of your hard
disk drive. When this item is enabled, the Award BIOS will monitor the
boot sector and partition table of the hard disk drive. If an attempt
is made to write to the boot sector or partition table of the hard disk
drive, the BIOS will halt the system and an error message will appear.
After seeing the error message, if necessary, you will be able to run
an anti-virus program to locate and remove the problem before any
damage is done.
Many disk diagnostic programs which attempt to access the boot
sector table will cause the warning message to appear. If you are
running such a program, we recommend that you first disable this
category. Also, disable this category if you are installing or running
certain operating systems like Windows® 95 or the operating system
may not install nor work.
ROM PCI/ISA BIOS
BIOS FEATURES SETUP
AWARD SOFTWARE, INC.
Virus Warning
CPU Internal Cache
External Cache
Quick Power On Self Test
Boot Sequence
Swap Floppy Drive
Boot Up Floppy Seek
Boot Up NumLock Status
Typematic Rate Setting
Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec)
T ypematic Delay (Msec)
Security Option
PCI/VGA Palette Snoop
OS Select For DRAM > 64MB
HDD S.M.A.R.T. Capability
: Disabled
: Enabled
: Enabled
: Enabled
: A, C, SCSI
: Disabled
: Disabled
:On
: Disabled
:6
: 250
: Setup
: Disabled
: Non-OS2
: Disabled
Video BIOS Shadow
C8000-CBFFF Shadow
CC000-CFFFF Shadow
D0000-D3FFF Shadow
D4000-D7FFF Shadow
D8000-DBFFF Shadow
DC000-DFFFF Shadow
: Enabled
: Disabled
: Disabled
: Disabled
: Disabled
: Disabled
: Disabled
ESC
F1
F5
F6
F7
: Quit
: Help
: Old Values
: Load Fail-Safe Settings
: Load Optimal Settings
↑↓→←
PU/PD/+/(Shift) F2
: Select Item
: Modify
: Color
Page 33

33
3
Award BIOS Setup Utility
CPU Internal Cache and External Cache
These categories speed up the memory access. The default value is
enabled. Enable the External Cache for better performance.
Quick Power On Self Test
This category speeds up Power On Self Test (POST) after you power
on your system. When Enabled, the BIOS will shorten or skip some
check items during POST.
Boot Sequence
This category determines which drive to search first for the disk
operating system. The default is A, C, SCSI. The options are:
A, C, SCSI; C, A, SCSI; C, CDROM, A; CDROM, C, A;
D, A, SCSI; E, A, SCSI; F, A, SCSI; SCSI, A, C;
SCSI, C, A; C only; LS/ZIP, C.
Swap Floppy Drive
When this option is enabled and the system is booting from the floppy
drive, the system will boot from drive B instead of drive A. When this
option is disabled and the system is booting from the floppy drive, the
system will boot from drive A. You must have two floppy drives to
use this function.
Boot Up Floppy Seek
When enabled, the BIOS will check whether the floppy disk drive installed
is 40 or 80 tracks. Note that the BIOS cannot distinguish between 720K,
1.2M, 1.44M and 2.88M drive types as they are all 80 tracks. When
disabled, the BIOS will not search for the type of floppy disk drive by
track number. Note that there will not be any warning message if the drive
installed is 360KB.
Boot Up NumLock Status
This allows you to determine the default state of the numeric keypad.
By default, the system boots up with NumLock on wherein the function
of the numeric keypad is the number keys. When set to Off, the
function of the numeric keypad is the arrow keys.
Page 34

34
3
Award BIOS Setup Utility
Typematic Rate Setting
When disabled, continually holding down a key on your keyboard will
cause the BIOS to report that the key is down. When the typematic
rate is enabled, the BIOS will not only report that the key is down,
but will first wait for a moment, and, if the key is still down, it will begin
to report that the key has been depressed repeatedly. For example,
you would use such a feature to accelerate cursor movements with
the arrow keys.
Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec)
This selection allows you to select the rate at which the keys are
accelerated.
Typematic Delay (Msec)
This selection allows you to select the delay between when the key
was first depressed and when the acceleration begins.
Security Option
System The system will not boot and access to Setup will be
denied if the correct password is not entered at the
prompt.
Setup The system will boot, but access to Setup will be denied
if the correct password is not entered at the prompt.
PCI/VGA Palette Snoop
It determines whether the MPEG ISA/VESA VGA Cards can work with
PCI/VGA or not. The default value is Disabled.
Enabled PCI/VGA working with MPEG ISA/VESA VGA cards.
Disabled PCI/VGA not working with MPEG ISA/VESA VGA
cards.
OS Select for DRAM > 64MB
This item allows you to access the memory that is over 64MB in
OS/2. The options are: Non-OS/2 and OS/2.
Page 35

35
3
Award BIOS Setup Utility
HDD S.M.A.R.T. Capability
The system board supports SMART (Self-Monitoring, Analysis and
Reporting Technology) hard drives. SMART is a reliability prediction
technology for ATA/IDE and SCSI drives. The drive will provide
sufficient notice to the system or user to backup data prior to the
drives failure. The default is Disabled. If you are using hard drives
that support S.M.A.R.T., set this field to Enabled. SMART is
supported in ATA-3 or later hard drives.
Video BIOS Shadow
Determines whether video BIOS will be copied to RAM. Video Shadow
will increase the video speed. Note that some graphics boards require
that this option be disabled. The default value is Enabled.
Enabled Video shadow is enabled.
Disabled Video shadow is disabled.
C8000-CBFFF Shadow to DC000-DFFFF Shadow
These categories determine whether option ROMs will be copied to
RAM.
Enabled Optional shadow is enabled.
Disabled Optional shadow is disabled.
Page 36

36
3
Award BIOS Setup Utility
The settings on the screen are for reference only. Your version may not be identical
to this one.
3.1.3 Chipset Features Setup
This section gives you functions to configure the system based on
the specific features of the chipset. The chipset manages bus speeds
and access to system memory resources. It also coordinates
communications between the conventional ISA bus and the PCI bus.
These items should not be altered unless necessary. Depending on
your add-in cards, you may not or should not enable some of those
features. The default settings have been chosen because they provide
the best operating conditions for your system. The only time you
might consider making any changes would be if you discovered
some incompatibility or that data was being lost while using your
system.
Note:
The system board comes with a System Health Monitor utility.
Once this utility is installed, the system will ignore the settings in
the System Health Monitor field of the Chipset Features Setup.
If you are using Windows 95 or Windows NT 4.0, you may
select between using the utility and the Chipset Features Setup.
For other operating systems, you may only use the Chipset
Features Setup. Refer to the System Health Monitor Utility
section (Chapter 4) for more information.
: Normal
: Normal
: Normal
:3
: Disabled
: Enabled
: Enabled
: Enabled
: Enabled
: Enabled
: Disabled
:64
: Enabled
: Enabled
: Enabled
: Enabled
: Enabled
: Enabled
: Disabled
: Disabled
ROM PCI/ISA BIOS
CHIPSET FEATURES SETUP
AWARD SOFTWARE, INC.
DIMM 1 DRAM Timing
DIMM 2 DRAM Timing
DIMM 3 DRAM Timing
SDRAM CAS Latency
SDRAM Bank Interleave
DRAM Read Pipeline
Sustained 3T Write
Cache Pipeline
Video BIOS Cacheable
System BIOS Cacheable
Memory Hole at 15M-16M
AGP Aperture Size (MB)
AGP-2X Mode
CPU to PCI Write Buffer
PCI Dynamic Bursting
PCI Master 0 WS Write
PCI Delay Transaction
PCI Master Read Prefetch
PCI#2 Access #1 Retry
AGP Master 1 WS Write
↑ ↓ → ←ESC
F1
F5
F6
F7
: Quit
: Help
: Old Values
: Load Fail-Safe Settings
: Load Optimal Settings
PU/PD/+/(Shift) F2
: Select Item
: Modify
: Color
**** System Health Monitor ****
Current CPU Temperature
Current CPU Fan Speed
Current AGP Fan Speed
CPU Temperature Limit
CPU Fan Speed Limit
AGP Fan Speed Limit
+3.3V Voltage
+12V Voltage
+5V Voltage
:27
o
C/80oF
: 4285 RPM
: 4137 RPM
: Ignore
: Ignore
: Ignore
: Ignore
: Ignore
: Ignore
AGP Master 1 WS Read : Disabled
Page 37

37
3
Award BIOS Setup Utility
Current CPU Temperature, Current CPU Fan Speed and Current
AGP Fan Speed
These fields show the current temperature of the processor, and the
current fan speed of the CPU and AGP fans in RPM (Revolutions Per
Minute).
CPU Temperature Limit
This field allows you to manually set a limit to the processors
temperature. If the temperature of the processor is over the
temperature set in this field (70oC/158oF recommended), an alarm
will sound warning you of system overheat. The sound of the alarm
is continuous low to high beeps. Some of the most common causes
leading to high temperature are:
- The fan is not functioning normally or has stopped. Turn off your
system and replace the fan.
- The space clearance of the processor, fan and heat sink is
inadequate to maintain proper airflow and heat dissipation.
- The chassis or cabinet has poor ventilation.
CPU Fan Speed Limit and AGP Fan Speed Limit
These fields allow you to manually set a limit to the speed of the CPU
and AGP fans. If the CPU/AGP fan speed is under the speed set in
these fields, an alarm will sound informing you to attend to any issue
that may damage your system. The sound of the alarm resembles that
of the siren of an ambulance. The failure detection circuit requires a
fan to operate at greater than 3600 RPM.
+3.3V, +5V and +12V Voltages
Set these fields to Monitor if you want the system board to detect
the output voltage of the power supply. If the output voltage is over
or under +3.3V/+5V/+12V (±10%), an alarm will sound warning
you of voltage issue. The sound of the alarm is continuous low to
high beeps but shorter than the temperature alarm. Some of the
most common causes leading to unstable output voltage of a power
supply are:
- The power supply is not functioning normally. Turn off your
system and replace the power supply.
Page 38

38
3
Award BIOS Setup Utility
3.1.4 Power Management Setup
The Power Management Setup allows you to configure your system to
most effectively save energy. If you like to use the soft power down
feature of Windows 95, you must enable the Power Management field
below. Select Min. Power, Max. Power or User Defined. Either one can
be used as long as it is NOT disabled.
The settings on the screen are for reference only. Your version may not be
identical to this one.
Power Management
This category allows you to select the type (or degree) of power saving
by changing the length of idle time that elapses before the Standby
mode and Suspend mode are activated.
Disable No power management. Disables the Standby and
Suspend modes.
Min. Power Saving Minimum power management. Standby Mode
= 1 hr., and Suspend Mode = 1 hr.
Max. Power Saving Maximum power management. Standby Mode
= 1 min., and Suspend Mode = 1 min.
User Defined Allows you to set each mode individually. When
enabled, each option ranges from 1 min. to 1 hr.
ROM PCI/ISA BIOS
POWER MANAGEMENT SETUP
AWARD SOFTWARE, INC.
Power Management
PM Control by APM
Video Of f Method
V ideo Off After
Standby Mode
Suspend Mode
HDD Power Down
Soft-Off by PWRBTN
Resume on Ring
Resume on Alarm
: User Define
:Yes
: DPMS
: Suspend
: Disabled
: Disabled
: Disabled
: Instant-Off
: Disabled
: Disabled
ESC
F1
F5
F6
F7
: Quit
: Help
: Old Values
: Load Fail-Safe Settings
: Load Optimal Settings
PU/PD/+/(Shift) F2
: Select Item
: Modify
: Color
↑ ↓ → ←
** PM Events **
IRQ3 (COM 2)
IRQ4 (COM 1)
IRQ5 (LPT 2)
IRQ6 (Floppy Disk)
IRQ7 (LPT 1)
IRQ8 (RTC Alarm)
IRQ9 (IRQ2 Redir)
IRQ10 (Reserved)
IRQ11 (Reserved)
IRQ12 (PS2 Mouse)
IRQ13 (Coprocessor)
IRQ14 (Hard Disk)
IRQ15 (Reserved)
: Primary
: Primary
: Primary
: Primary
: Primary
: Disabled
: Secondary
: Secondary
: Secondary
: Secondary
: Primary
: Primary
: Disabled
- The AC input from the power outlet to your system is unstable.
Please consult your MIS department or an electrician.
Page 39

39
3
Award BIOS Setup Utility
PM Control by APM
Yes An Advanced Power Management device will be activated to
enhance the Max. Power Saving mode and stop the CPUs internal clock. Use this option in Windows® 95. (default)
No The system BIOS will ignore APM when initiating the Power
Management mode.
Video Off Method
This determines the manner in which the monitor is blanked.
V/H SYNC + Blank This selection will cause the system to turn off
the vertical and horizontal synchronization
ports and write blanks to the video buffer.
Blank Screen This option only writes blanks to the video
buffer.
DPMS Initializes display power management signaling.
Use this option if your video board supports
it.
Video Off After
N/A The system BIOS will never turn off the screen.
Suspend The screen is off when the system is in the Suspend
mode.
Standby The screen is off when the system is in the Standby
mode.
Standby Mode
This is user configurable only when the Power Management category
is set to User Defined. When enabled and after the set time of
system inactivity, the CPU clock will run at a slower speed (1/2 of full
speed) while all other devices still operate at full speed.
Suspend Mode
This is user configurable only when the Power Management category
is set to User Defined. When enabled and after the set time of system
inactivity, the CPU and onboard peripherals will be shut off.
Page 40

40
3
Award BIOS Setup Utility
HDD Power Down
This is user configurable only when the Power Management categor y
is set to User Defined. When enabled and after the set time of system
inactivity, the hard disk drive will be powered down while all other
devices remain active.
Soft-Off by PWRBTN
This category allows you to select the method of powering off your
system.
Hold 4 Sec. Regardless of whether the Power Management field
is enabled or disabled, if the power button is pushed
and released in less than 4 sec, the system enters
the Suspend mode. The purpose of this function is
to prevent the system from powering off in case
you accidentally hit or pushed the power button.
Pushing the power button for more than 4 seconds
will power off the system.
Instant-Off Pressing and then releasing the power button at
once will immediately power off your system.
Resume On Ring
Enabled Enables the Modem Ring-on feature. This allows your
system to power-on to respond to incoming calls.
Disabled Disables the Modem Ring-on feature. Your system will not
respond to incoming calls.
Resume On Alarm
Enabled When Enabled, you can set the date and time you would
like the Soft Power Down (Soft-Off) PC to power-on.
Date (of Month) and Timer (hh:mm:ss) will appear
right below this field.
Disabled Disables the automatic power-on function. (default)
Page 41

41
3
Award BIOS Setup Utility
Date (of Month)
0 The system will power-on everyday according to the time
set in the Timer (hh:mm:ss) field.
1-31 Select a date you would like the system to power-on.
The system will power-on on the set date, and time set
in the Timer (hh:mm:ss) field.
Timer (hh:mm:ss)
This is used to set the time you would like the system to power-on.
If you want the system to power-on everyday as set in the Date (of
Month) field, the time set in this field must be later than the CMOS
RTCs time.
PM Events
When enabled, access to the specified IRQ will cause the system to
wake up completely from the power management mode. When
disabled, the system will not wake up from the power management
mode despite access to the specified IRQ.
The settings on the screen are for reference only. Your version may not be
identical to this one.
3.1.5 PNP/PCI Configuration
This section describes configuring the PCI bus system. It covers some
very technical items and it is strongly recommended that only
experienced users should make any changes to the default settings.
ROM PCI/ISA BIOS
PNP/PCI CONFIGURATION
AWARD SOFTWARE, INC.
Resources Controlled By
Reset Configuration Data
: Auto
: Disabled
PCI IRQ Actived By
Assign IRQ for VGA
PCI Slot 1 Use IRQ
PCI Slot 2 Use IRQ
PCI Slot 3 Use IRQ
PCI Slot 4 Use IRQ
: Level
: Enabled
: Auto
: Auto
: Auto
: Auto
ESC
F1
F5
F6
F7
: Quit
: Help
: Old Values
: Load Fail-Safe Settings
: Load Optimal Settings
PU/PD/+/(Shift) F2
: Select Item
: Modify
: Color
↑ ↓ → ←
Page 42

42
3
Award BIOS Setup Utility
Resources Controlled By
The Award Plug and Play BIOS has the capability to automatically
configure all of the boot and Plug and Play compatible devices.
Auto The system will automatically detect the settings for you.
The categories that follow will not be shown on the
screen.
Manual This will allow you to set the IRQ/DMA (you have
assigned your add-in card) to Legacy ISA or PCI/ISA
PnP. For non-PnP ISA cards, select Legacy ISA. For PnP
ISA or PCI cards, select PCI/ISA PnP.
Reset Configuration Data
Enabled The BIOS will reset the configuration data once
automatically. It will then recreate a new set of
configuration data.
Disabled The BIOS will not reset the configuration data.
PCI IRQ Actived By
This category is used to set the method by which the PCI bus
recognizes that an IRQ service is being requested by a device. Under
all circumstances, you should retain the default configuration unless
a different setting is needed.
Assign IRQ for VGA
When Enabled, the system automatically assigns an IRQ for the VGA
card installed. Your VGA card will need an IRQ only when using the
video capture function of the card. If you are not using this function
and a new device requires an IRQ, you can set this function to
Disabled. The IRQ (previously occupied by the VGA card) will be
available for your new device.
Note:
When Disabled, a Yellow mark will appear in Windows 95s
Device Manager.
PCI Slot 1 Use IRQ to PCI Slot 4 Use IRQ
By default, an IRQ will automatically be assigned to each PCI slot.
You may manually assign an IRQ to these slots by selecting one of
the available options.
Page 43

43
3
Award BIOS Setup Utility
3.1.8 Integrated Peripherals
The settings on the screen are for reference only. Your version may not be
identical to this one.
ROM PCI/ISA BIOS
INTEGRATED PERIPHERALS
AWARD SOFTWARE, INC.
Onboard Primary PCI IDE
Onboard Secondary PCI IDE
IDE Prefetch Mode
IDE HDD Block Mode
IDE Primary Master PIO
IDE Primary Slave PIO
IDE Secondary Master PIO
IDE Secondary Slave PIO
IDE Primary Master UDMA
IDE Primary Slave UDMA
IDE Secondary Master UDMA
IDE Secondary Slave UDMA
USB Controller
USB Keyboard Support
: Enabled
: Enabled
: Enabled
: Enabled
: Auto
: Auto
: Auto
: Auto
: Auto
: Auto
: Auto
: Auto
: Enabled
: Disabled
ESC
F1
F5
F6
F7
: Quit
: Help
: Old Values
: Load Fail-Safe Settings
: Load Optimal Settings
PU/PD/+/(Shift) F2
: Select Item
: Modify
: Color
↑ ↓ → ←
Onboard FDC Controller
Onboard UART 1
Onboard UART 2
Onboard UART 2 Mode
Onboard Parallel Port
Parallel Port Mode
ECP Mode Use DMA
Parallel Port EPP Type
: Enabled
: 3F8/IRQ4
: 2F8/IRQ3
: Standard
: 378/IRQ7
: ECP+EPP
:3
: EPP1.7
3.1.6 Load Fail-Safe Settings
The Load Fail-Safe Settings option loads the troubleshooting default
values permanently stored in the ROM chips. These settings are not
optimal and turn off all high performance features. You should use
these values only if you have hardware problems. Highlight this
option on the main menu and press <Enter>. The message below
will appear.
Load Fail-Safe Settings (Y/N)? N
If you want to proceed, type <Y> and press <Enter>. The default
settings will be loaded.
3.1.7 Load Optimal Settings
The Load Optimal Settings option loads optimized settings from the
BIOS ROM. Use the Setup default values as standard values for your
system. Highlight this option on the main menu and press <Enter>.
The message below will appear.
Load Optimal Settings (Y/N)? N
Type <Y> and press <Enter> to load the Setup default values.
Page 44

44
3
Award BIOS Setup Utility
Onboard Primary PCI IDE and Onboard Secondary PCI IDE
These categories allow you to enable or disable the primary and
secondary IDE controller. The default is Enabled. Select Disabled if
you want to add a different hard drive controller.
IDE Prefetch Mode
This allows data and addresses to be stored in the internal buffer of
the chip, thus reducing access time. Enable this field to achieve better
performance.
IDE HDD Block Mode
Enabled The IDE HDD uses the block mode. The system BIOS
will check the hard disk drive for the maximum block
size the system can transfer. The block size will depend
on the type of hard disk drive.
Disabled The IDE HDD uses the standard mode.
IDE Primary Master/Slave PIO and IDE Secondary Master/Slave PIO
PIO means Programmed Input/Output. Rather than have the BIOS
issue a series of commands to effect a transfer to or from the disk
drive, PIO allows the BIOS to tell the controller what it wants and
then let the controller and the CPU perform the complete task by
themselves. Your system supports five modes, 0 (default) to 4, which
primarily differ in timing. When Auto is selected, the BIOS will select
the best available mode after checking your drive.
Auto The BIOS will automatically set the system according to
your hard disk drives timing.
0-4 You can select a mode that matches your hard disk drives
timing. Caution: Do not use the wrong setting or you will
have drive errors.
IDE Primary Master/Slave UDMA and IDE Secondary Master/Slave
UDMA
These categories allow you to set the Ultra DMA in use. When Auto
is selected, the BIOS will select the best available option after
checking your hard drive or CD-ROM.
Page 45

45
3
Award BIOS Setup Utility
Auto The BIOS will automatically detect the settings for you.
Disabled The BIOS will not detect these categories.
USB Controller
We recommend that you leave this field in its default setting - Enabled.
USB Keyboard Support
By default, this field is Disabled. If you are using a USB keyboard, please
enable this function.
Onboard FDC Controller
Enabled Enables the onboard floppy disk controller.
Disabled Disables the onboard floppy disk controller.
Onboard UART 1 and Onboard UART 2
Auto The system will automatically select an I/O address for the
onboard serial port 1 and serial port 2.
3F8/IRQ4, 2F8/IRQ3, 3E8/IRQ4, 2E8/IRQ3 Allows you to
manually select an I/O address for the onboard serial
port 1 and serial port 2.
Disabled Disables the onboard serial port 1 and/or serial port
2.
Onboard UART 2 Mode
The system board supports IrDA function for wireless connectivity
between your computer and peripheral devices. You may not use
IrDA (J2) and the COM 2 serial port (CN2) at the same time. If you
are using the COM 2 serial port, make sure Onboard UART 2
Mode is set to Standard.
To use the IrDA function, follow the steps below.
1. Connect your IrDA cable to connector J2 on the system
board.
2. Set Onboard UART 2 Mode to the type of IrDA standard
supported by your IrDA peripheral/device (HPSIR or
ASKIR).
Page 46

46
3
Award BIOS Setup Utility
3. The following will appear right below Onboard UART 2
Mode.
IR Duplex Mode
Half Data is completely transmitted before receiving data.
Full Transmits and receives data simultaneously.
Use IR Pins
Set this field according to the IR pins of your IrDA peripheral/
device.
Onboard Parallel Port
378H/IRQ7, 3BCH/IRQ7, 278H/IRQ5 Selects the I/O address and
IRQ for the onboard parallel port.
Disabled Disables the onboard parallel port.
Parallel Port Mode
Parallel Por t Mode will appear only if you selected an I/O address and
IRQ in the Onboard Parallel Port field. This option applies to a
standard specification and will depend on the type and speed of your
device. Refer to your peripherals manual for the best option. Select the
parallel port mode according to the type of printer device connected
to your onboard parallel port.
The parallel modes are Normal, EPP, ECP and ECP+EPP. The default
is ECP+EPP. Both ECP Mode Use DMA and Parallel Port EPP
Type will appear on the screen.
If you selected EPP, Parallel Port EPP Type will appear. This field
applies to standard specification. The options are EPP1.9 and EPP1.7.
Default setting: EPP1.7.
If you selected ECP, ECP Mode Use DMA will appear. This is used
to select a DMA channel for the parallel port. The options are 1
and 3. Default setting: 3.
Page 47

47
3
Award BIOS Setup Utility
3.1.9 Supervisor Password
If you want to protect your system and setup from unauthorized entry,
set a supervisors password with the System option selected in the
BIOS Features Setup. If you want to protect access to setup only, but
not your system, set a supervisors password with the Setup option
selected in the BIOS Features Setup. You will not be prompted for a
password when you cold boot the system.
Use the arrow keys to highlight the Supervisor Password option and
press <Enter>. The message below will appear.
Enter Password:
Type in the password. You are limited to eight characters. When done,
the message below will appear:
Confirm Password:
You are asked to verify the password. Type in exactly the same
password. If you type in a wrong password, you will be prompted
to enter the correct password again. To delete or disable the
password function, highlight Supervisor Password and press
<Enter>, instead of typing in a new password. Press the <Esc> key
to return to the main menu.
3.1.10 User Password
If you want another user to have access only to your system but not
to setup, set a users password with the System option selected in
the BIOS Features Setup. If you want a user to enter a password when
trying to access setup, set a users password with the Setup option
selected in the BIOS Features Setup. Using users password to enter
Setup allows a user to access only the User Password option that
appears on the main screen. Access to all other options is denied. To
set, confirm, verify, disable or delete a users password, follow the
procedures described in the section Supervisor Password. If you
forget your password, refer to the procedure described in the same
section.
Page 48

48
3
Award BIOS Setup Utility
3.1.11 IDE HDD Auto Detection
Use this option to detect the parameters for the hard disk drives
installed in your system. These parameters will then be automatically
entered into the "Standard CMOS Setup". The IDE HDD Auto
Detection screen displays the following categories of information:
Size, Cylinders, Heads, Precomp, LandZone, Sectors and Mode.
For hard drives larger than 528MB, you would typically select the
LBA type. Certain operating systems require that you select Normal
or Large. Please check your operating systems manual or Help desk
on which one to select.
ROM PCI/ISA BIOS
CMOS SETUP UTILITY
AWARD SOFTWARE, INC.
HARD DISKS TYPE SIZE CYLS HEAD RECOMP LANDZ SECTOR MODE
Primary Master:
Select Primary Master Option (N=Skip): N
OPTIONS SIZE CYLS HEAD RECOMP LANDZ SECTOR MODE
2 (Y) 853 827 32 0 1653 63 LBA
1 853 1654 16 65535 1653 63 Normal
3 853 827 32 65536 1653 63 Large
Note: Some OS (like SCO-UNIX) must be “NORMAL” for installation
ESC: Skip
The settings on the screen are for reference only. Your version may not be
identical to this one.
Page 49

49
3
Award BIOS Setup Utility
3.1.12 Save & Exit Setup
When all the changes have been made, highlight Save & Exit Setup
and press <Enter>. The message below will appear:
Save to CMOS and Exit (Y/N)? N
Type Y and press <Enter>. The modifications you have made will
be written into the CMOS memory, and the system will reboot. You
will once again see the initial diagnostics on the screen. If you wish
to make additional changes to the setup, press <Ctrl> <Alt> <Esc>
simultaneously or <Del> after memory testing is done.
3.1.13 Exit Without Saving
When you do not want to save the changes you have made, highlight
Exit Without Saving and press <Enter>. The message below will
appear:
Quit Without Saving (Y/N)? N
Type Y and press <Enter>. The system will reboot and you will once
again see the initial diagnostics on the screen. If you wish to make any
changes to the setup, press <Ctrl> <Alt> <Esc> simultaneously or
<Del> after memory testing is done.
Page 50

50
4.1 Desktop Management Interface (DMI)
The system board comes with a DMI built into the BIOS. DMI, along
with the appropriately networked software, is designed to make
inventory, maintenance and troubleshooting of computer systems easier.
With DMI, a network administrator or MIS engineer can remotely
access some information about a particular computer system without
physically going to it. Quite often a service call may be unnecessary as
the problem can be solved remotely.
The DMI utility in the BIOS automatically records various information
about your system configuration. Information about the type and speed
of CPU, type and amount of memory for each memory slot, BIOS
revision level, types of add-in PCI boards and components, certain
revision numbers of hardware installed, etc. are automatically detected
and stored in the DMI pool, which is a part of the system board's
Plug and Play BIOS. Additional information, such as ISA based
peripherals, which may not be automatically detected, can be manually
recorded in the DMI pool by using the Add DMI menu. The DMI pool
data is then verified or updated whenever the system hardware or
setup is altered.
4.1.1 Running the DMI Utility
To run the DMI utility, type: DMICFG.EXE. You can download this utility
from ftp.dfiusa.com - /utilities/DMI directory.
The DMI utility must run in real mode with at least 180K of base
memory. Memory managers like HIMEM.SYS (required by Windows)
must not be installed. You may do this by using one of the 3 methods
listed below.
1. Boot up from a system diskette without the AUTOEXEC.BAT and
CONFIG.SYS files,
2. REM HIMEM.SYS in the CONFIG.SYS, or
3. Press <F5> during bootup to bypass your AUTOEXEC .BAT and
CONFIG.SYS files.
Chapter 4 - Supported Softwares
Page 51

51
4
Supported Softwares
4.1.2 Using the DMI Utility
The four menus located on top of the DMI Configuration Utility screen
are Edit DMI, Add DMI, Load DMI File and Save DMI File. Use the
← or → (left or right) arrow keys to select a menu from the Menu
bar.
On the left side of the screen is a list of the system configuration items.
Use the ↑ or ↓ (up or down) arrow keys to select an item.
The commands at the bottom of the screen will allow you to navigate
through the various setup menus.
Edit DMI
1. Use the ← or → arrow keys to select the Edit DMI menu.
2. Highlight the item on the left screen that you would like to edit
by using the ↑ or ↓ arrow keys, then press <Enter>.
3. The cursor will move to the screen you select allowing you to edit
information. The screen will also display the auto-detected
information.
4. Press <F10> to update the edited information into the flash ROM.
▲▲
▲▲
▲
■■
■■
■
Move cursor ENTER-Accept DEL-Delete ESC-Abort&Exit
↑ ↓ ↑ ↓
↑ ↓ ↑ ↓
↑ ↓
←←
←←
←
→→
→→
→
Award DMI Configuration Utility Copyright Award Software Inc, 1996
[Edit DMI] [Add DMI] [Load DMI File] [Save DMI File]
▲▲
▲▲
▲
BIOS
System
Enclosure/Chassis
Processor
Memory Controller
Memory Module
Memory Module
Memory Module
Memory Module
Cache
Cache
Port Connector
Port Connector
Port Connector
Port Connector
Port Connector
Port Connector
Port Connector
System Slots
*** BIOS Auto Detect ***
Type : BIOS Information
Handle : 0000
Vendor Name :
BIOS Version :
BIOS Starting Address Segment : F000
BIOS Build Date :
BIOS Characteristics :
Size of BIOS ROM : 0128K
Page 52

52
4
Supported Softwares
Add DMI
1. Use the ← or → arrow keys to select the Add DMI menu.
2. Highlight the item on the left screen that you would like to add
by using the ↑ or ↓ arrow keys, then press <Enter>.
3. The cursor will move to the screen you select allowing you to enter
information about the added item.
4. Press <F10> to save information into the flash ROM.
To view information about the added items, go to the Edit DMI menu.
Load DMI File
1. Use the ← or → arrow keys to select the Load DMI File menu.
2. The following message will appear.
Press [Enter] to select DMI file for load
Press <Enter>.
3. The DMI files will appear on the screen. Select the file you would
like to load and press <Enter>.
4. The following message will appear.
Do you want to execute? (Y/N)
Type <Y>. All previous DMI structures will be destroyed and the
new file will be saved into the flash ROM.
Save DMI File
1. Use the ← or → arrow keys to select the Save DMI File menu.
2. The following message will appear.
Press [Enter] to select DMI file for save
Press <Enter>.
3. Enter the directory and filename under which you would like the
DMI file saved.
Page 53

53
4
Supported Softwares
4.2 System Health Monitor Utility
The system board comes with a System Health Monitor utility
contained in the provided CD. This utility shows the current
temperature of the processor, power voltages, and CPU/AGP fan
speed.
The utility also allows you to manually set the range of the
processors temperature, power voltages, and CPU/AGP fan
speed. If the settings/values are over or under the set range, an
error message will pop-up and an alarm will sound. There are
three types of sound for the three different failure alarms
(temperature, voltage and fan). Refer to the Chipset Features
Setup (Chapter 3) section for details.
When you hear a failure alarm, you must power off your
computer and check the following: processor fan/heatsink, AGP fan
and power supply. We recommend that you use the Default
Setting which is the ideal setting that would keep the system in
good working condition.
Genesys Logic System Health Monitor Rev.A (for VIA)
The time
interval for
monitoring
the system
User Setting
Quit
Update w/o Save
Default Setting
Update and Save
Polling Interval:
T emperature
CPU Over-Heat T emperature:
4 Seconds
80
CPU Hysterisis Temperature: 75
CPU Temperature: 29
Celsius
Fahrenheit
Voltage (V)
High Limit: Low Limit:Current Voltage:
3.3V Values
3.60
12V Values
13.20
5V Values
5.50
3.35
12.91
5.08
3.00
10.80
4.50
Minimize when Startup
Alarm when
CPU Over Heat
3.3V Abnormal
12V Abnormal
5V Abnormal
Fan (RPM)
Low Limit:
2000
2000
CPU Fan
AGP Fan
Current Speed:
5454
3287
CPU Fan Abnormal
AGP Fan Abnormal
CPU
temperature
limit
Current
temperature
of the CPU
Output
voltage
limit
CPU/AGP
fan speed
limit
When
enabled,
this screen
will minimize
and display a
histogram
icon after
boot-up
These
items when
enabled will
alert you in
case of
detected
failure
Page 54

54
4
Supported Softwares
Important:
Once this utility is installed, the system will ignore the settings in
the System Health Monitor field of the Chipset Features Setup.
If you are using Windows 95 or Windows NT 4.0, you may
select between using the utility and the Chipset Features Setup.
For other operating systems, you may only use the Chipset
Features Setup.
4.2.1 Installing the Utility
Insert the CD that came with the system board into a CD-ROM
drive. The autorun screen (Main Board Utility) will appear. Click
System Health Monitor Utility. After completing installation, you will
find this utility in StartUp under Programs of Windows 95/
NT4.0. Please refer to the Readme file for details on using the
utility.
4.3 Drivers
The system board package comes with drivers contained in the
provided CD. To install the drivers, please refer to the readme file
in the CD. All steps or procedures to install software drivers are
subject to change without notice as the softwares are occassionally
updated. Please refer to the readme files for the latest information.
Installing Windows® 98 on a VIA Chipset-Based System
1. Before installing Windows® 98, make sure your system is installed
with a graphics card only. Take note - DO NOT install any addin cards other than the graphics card into any of the expansion
slots yet.
2. Boot your system and install the Windows® 98 operating system.
3. Now install the VIA IrQ routing miniport driver.
4. Install the VIA AGP driver.
5. After installing these drivers, turn off your system. You may now
install other add-in cards and their corresponding drivers.
Note:
The VIA IrQ routing miniport driver and VIA AGP driver are
included in the CD that came with the system board package.
Page 55

55
SXXXX/RSS
R (voltage range)
V for VRE voltage range
S for Standard voltage range
SXXXX/KLM
K = V for VRE voltage range, S for Standard voltage range
L = M for min valid MD timings, S for min valid standard
timings
M = U is not tested for DP, S is tested for DP, UP and MP
A.1 Intel Processors
A.2 Cyrix Processors
Appendix A - Identifying Processors
6x86MX-PR166
Product
name
P-rating
60MHz Bus 2.5x
Processor
clock
speed
2.9V
Core
voltage
(or as
marked)
M II-300GP
Product
name
75MHz Bus 3x
Processor
clock
speed
Core
voltage
(or as
marked)
2.9V
6x86L-PR200+GP
Product
name
P-rating
Grid-array
package
150MHz
Processor
clock
speed
2.8V
Core
voltage
Page 56

A
56
Identifying Processors
A.4 AMD Processors
A.3 IBM Processor
6x86MX-PR266
Product
name
P-rating
2.5x 83MHz-2.9V CORE
Processor
clock
speed
Core
voltage
A.5 IDT Processors
C6-PSME200GA
Product
name
Processor clock speed
3.52Vcc (66MHz clock)
Processor
voltage
External system bus clock
AMD-K5-PR166ABX
K5 = Processor core
PR166 = Performance rating
A = Package type: Type A = CPGA
B = Operating voltage:
B: 3.45V-3.60V H: 2.76V-3.0V/3.3V (core/IO)
C: 3.30V-3.465V J: 2.57V-2.84V/3.3V (core/IO)
F: 3.135V-3.465V K: 2.38V-2.63V/3.3V (core/IO)
X =Case temperature
W: 55
o
C R: 70oC Q: 65oC Y: 75oC X: 65oC Z: 85oC
AMD-K6-233ANR
K6 = Processor core
233 = Performance rating
A = Package type: Type A = CPGA
B = Operating voltage:
N: 3.1V-3.3V (core)/3.135V-3.6V (I/O)
L: 2.755V-3.045V (core)/3.135V-3.6V (I/O)
X =Case temperature
W: 55
o
C R: 70oC Q: 65oC
Y: 75
o
C X: 65oC Z: 85oC
Page 57

57
When the BIOS encounters an error that requires the user to
correct something, either a beep code will sound or a message will
be displayed in a box in the middle of the screen and the message,
PRESS F1 TO CONTINUE, CTRL-ALT-ESC or DEL TO ENTER
SETUP, will be shown in the information box at the bottom. Enter
Setup to correct the error.
B.1 POST Beep
There are two kinds of beep codes in the BIOS. One code indicates
that a video error has occured and the BIOS cannot initialize the
video screen to display any additional information. This beep code
consists of a single long beep followed by three short beeps. The
other code indicates that a DRAM error has occured. This beep
code consists of a single long beep.
B.2 Error Messages
One or more of the following messages may be displayed if the
BIOS detects an error during the POST. This list indicates the error
messages for all Awards BIOSes:
CMOS BATTERY HAS FAILED
The CMOS battery is no longer functional. It should be replaced.
Caution:
Danger of explosion if battery incorrectly replaced. Replace only
with the same or equivalent type recommended by the
manufacturer. Dispose of used batteries according to the
battery manufacturers instructions.
CMOS CHECKSUM ERROR
Checksum of CMOS is incorrect. This can indicate that CMOS has
become corrupt. This error may have been caused by a weak
battery. Check the battery and replace if necessary.
DISPLAY SWITCH IS SET INCORRECTLY
The display switch on the motherboard can be set to either
monochrome or color. This indicates the switch is set to a different
Appendix B - System Error Message
Page 58

B
58
System Error Message
setting than indicated in Setup. Determine which setting is correct,
either turn off the system and change the jumper or enter Setup
and change the VIDEO selection.
FLOPPY DISK(S) fail (80)
Unable to reset floppy subsystem.
FLOPPY DISK(S) fail (40)
Floppy type mismatch.
Hard Disk(s) fail (80)
HDD reset failed.
Hard Disk(s) fail (40)
HDD controller diagnostics failed.
Hard Disk(s) fail (20)
HDD initialization error.
Hard Disk(s) fail (10)
Unable to recalibrate fixed disk.
Hard Disk(s) fail (08)
Sector Verify failed.
Keyboard is locked out - Unlock the key
The BIOS detects that the keyboard is locked. Keyboard controller
is pulled low.
Keyboard error or no keyboard present
Cannot initialize the keyboard. Make sure the keyboard is attached
correctly and no keys are being pressed during the boot.
Manufacturing POST loop
System will repeat POST procedure infinitely while the keyboard
controller is pull low. This is also used for the M/B burn in test at
the factory.
BIOS ROM checksum error - System halted
The checksum of ROM address F0000H-FFFFFH is bad.
Memory test fail
The BIOS reports memory test fail if the memory has error(s).
Page 59

59
C.1 Troubleshooting Checklist
This chapter of the manual is designed to help you with problems
that you may encounter with your personal computer. To efficiently
troubleshoot your system, treat each problem individually. This is to
ensure an accurate diagnosis of the problem in case a problem has
multiple causes.
Some of the most common things to check when you encounter
problems while using your system are listed below.
1. The power switch of each peripheral device is turned on.
2. All cables and power cords are tightly connected.
3. The electrical outlet to which your peripheral devices are
connected is working. Test the outlet by plugging in a lamp or
other electrical device.
4. The monitor is turned on.
5. The displays brightness and contrast controls are adjusted
properly.
6. All add-in boards in the expansion slots are seated securely.
7. Any add-in board you have installed is designed for your system
and is set up correctly.
Monitor/Display
If the display screen remains dark after the system is turned on:
1. Make sure that the monitors power switch is on.
2. Check that one end of the monitors power cord is properly
attached to the monitor and the other end is plugged into a
working AC outlet. If necessary, try another outlet.
3. Check that the video input cable is properly attached to the
monitor and the systems display adapter.
4. Adjust the brightness of the display by turning the monitors
brightness control knob.
Appendix C - Troubleshooting
Page 60

C
60
Troubleshooting
The picture seems to be constantly moving.
1. The monitor has lost its vertical sync. Adjust the monitors vertical
sync.
2. Move away any objects, such as another monitor or fan, that
may be creating a magnetic field around the display.
3. Make sure your video cards output frequencies are supported
by this monitor.
The screen seems to be constantly wavering.
1. If the monitor is close to another monitor, the adjacent monitor
may need to be turned off. Fluorescent lights adjacent to the
monitor may also cause screen wavering.
Power Supply
When the computer is turned on, nothing happens.
1. Check that one end of the AC power cord is plugged into a live
outlet and the other end properly plugged into the back of the
system.
2. Make sure that the voltage selection switch on the back panel is
set for the correct type of voltage you are using.
3. The power cord may have a shor t or open. Inspect the cord
and install a new one if necessary.
Floppy Drive
The computer cannot access the floppy drive.
1. The floppy diskette may not be formatted. Format the diskette
and try again.
2. The diskette may be write-protected. Use a diskette that is not
write-protected.
3. You may be writing to the wrong drive. Check the path
statement to make sure you are writing to the targeted drive.
4. There is not enough space left on the diskette. Use another
diskette with adequate storage space.
Page 61

C
Troubleshooting
61
Hard Drive
Hard disk failure.
1. Make sure the correct drive type for the hard disk drive has
been entered in the BIOS.
2. If the system is configured with two hard drives, make sure the
bootable (first) hard drive is configured as Master and the
second hard drive is configured as Slave. The master hard drive
must have an active/bootable partition.
Excessively long formatting period.
1. If your hard drive takes an excessively long period of time to
format, it is likely a cable connection problem. However, if your
hard drive has a large capacity, it will take a longer time to
format.
Parallel Port
The parallel printer doesnt respond when you try to print.
1. Make sure that your printer is turned on and that the printer is
on-line.
2. Make sure your software is configured for the right type of
printer attached.
3. Verify that the onboard LPT ports I/O address and IRQ settings
are configured correctly.
4. Verify that the attached device works by attaching it to a parallel
port that is working and configured correctly. If it works, the
printer can be assumed to be in good condition. If the printer
remains inoperative, replace the printer cable and try again.
Page 62

C
62
Troubleshooting
Serial Port
The serial device (modem, printer) doesnt output anything or is
outputting garbled characters.
1. Make sure that the serial devices power is turned on and that
the device is on-line.
2. Verify that the device is plugged into the correct serial port on
the rear of the computer.
3. Verify that the attached serial device works by attaching it to a
serial port that is working and configured correctly. If the serial
device does not work, either the cable or the serial device has a
problem. If the serial device works, the problem may be due to
the onboard I/O or the address setting.
4. Make sure the COM settings and I/O address are configured
correctly.
Keyboard
Nothing happens when a key on the keyboard was pressed.
1. Make sure the keyboard is properly connected.
2. Make sure there are no objects resting on the keyboard and
that no keys are pressed during the booting process.
System Board
1. Make sure the add-in card is seated securely in the expansion
slot. If the add-in card is loose, power off the system, re-install
the card and power up the system.
2. Check the jumper settings to ensure that the jumpers are
properly set.
3. Verify that all memor y modules are seated securely into the
memory sockets.
4. Make sure the memory modules are in the correct locations.
5. If the board fails to function, place the board on a flat surface
and seat all socketed components. Gently press each component
into the socket.
6. If you made changes to the BIOS settings, re-enter setup and
load the BIOS defaults.
 Loading...
Loading...