Page 1

CHA PTER
2
Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
This chapter provides step-by-step procedures for setting up BBSM Hotspot. After you complete the
procedures in this chapter, your BBSM Hotspot server should be fully operational.
The following two chapters, Chapter 3, “Advanced Configuration Options,” and Chapter 4, “System
Operation,”, provide more detailed information and advanced options for configuring and using BBSM
Hotspot.
Read the Before You Start section, then follow the step-by-step procedures to set up your BBSM
Hotspot.
• Before You Start, page 2-1
• Running the Setup Wizard, page 2-2
• Changing the Default Security Passwords, page 2-23
• Configuring Windows for Multinet, page 2-26
• Configuring DNS Forwarding, page 2-30
• Feature Considerations, page 2-32
Before You Start
This section describes the prerequisites that you need to complete or check before setting up the
software. After running the Setup Wizard in this chapter, you perform all operations from the Dashboard.
Before you configure BBSM, make sure that you complete the following tasks:
• First, read the ReadMeFirst web page, which launches the first time you start your BBSM Hotspot
server.
• Then, read the first chapter to this guide, and the cautions below to avoid costly problems.
• From your BBSM Hotspot server desktop, open the BBSM Hotspot Configuration Requirements
Checklist and complete it to make sure that you have all of the networking information you need to
configure your server.
• Assemble the BBSM Hotspot server using the instructions in the Cisco BBSM Hotspot Hardware
Assembly Guide. For information on obtaining this guide and other Cisco documentation, refer to
the Obtaining Documentation section in the preface to this user guide.
• If you will be using secured (https) pages, obtain and install a Certificate Authority (third-party
SSL). (Refer to Appendix B, “Installing an SSL Certificate.”)
78-15293-01
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
2-1
Page 2

Running the Setup Wizard
Caution Do not change the Windows 2000 computer name of your BBSM Hotspot server, because the BBSM
Caution We recommend using the latest version of Internet Explorer to perform functions accessed through the
Caution When running the wizards, making any changes to BBSM Hotspot, or rebooting the BBSM Hotspot
Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
• Before beginning the basic configuration of your BBSM Hotspot server, be sure to determine if any
service packs or patches need to be installed. We recommend that you install all available service
packs and patches to maximize the functionality of your BBSM Hotspot server. For instructions on
performing these installations, refer to Chapter 4, “System Operation.”
Hotspot MSDE database has the name embedded in the application. Changing the name breaks MSDE
functionality, and you will see SQL server errors reported on your BBSM Hotspot server. This problem
is a Microsoft issue and not one that the Cisco software team can change.
BBSM Hotspot Dashboard.
server, make sure that there are no active sessions. The Client Deactivation tool, located on the
Dashboard, can be used to deactivate any active sessions.
Running the Setup Wizard
This section explains how to configure the BBSM Hotspot server by using the Setup Wizard. This wizard
prompts you for your server’s basic configuration parameters and then configures the server with these
settings.
It also prompts you to decide if you would like to create a custom web page at this time:
• If you decide to use a custom web page, the Custom Web Page Wizard launches after the Setup
Wizard completes.
• If you decide not to create a custom web page, the first time you run the Setup Wizard, it applies the
FreeAccess web page to all ports. If you run the Setup Wizard again at a later time, it will not change
the port settings.
Note the following configuration and custom web page options that you can use:
• To configure your server using the Address Change Wizard and Switch Discovery Wizard, refer to
Appendix A, “Advanced Wizards.”
• To configure your server manually on a per-port basis or change your configurations after the initial
setup, refer to Configuring Your Server (Hotspot Configuration), page 3-1.
• To change your port settings after the initial setup, refer to Configuring Ports (Port Configuration),
page 3-27.
• To create a custom web page after the initial setup, refer to Adding Custom Web Pages to BBSM
Hotspot, page 3-24.
2-2
Note Be sure to complete the BBSM Hotspot Configuration Requirements Checklist before running the Setup
Wizard.
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
78-15293-01
Page 3
Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Caution Be sure to disconnect all active end-user sessions before running any BBSM Hotspot wizard, including
the Setup Wizard. Refer to the “Deactivating Client Sessions” section on page 4-21.
Follow these steps to run the wizard.
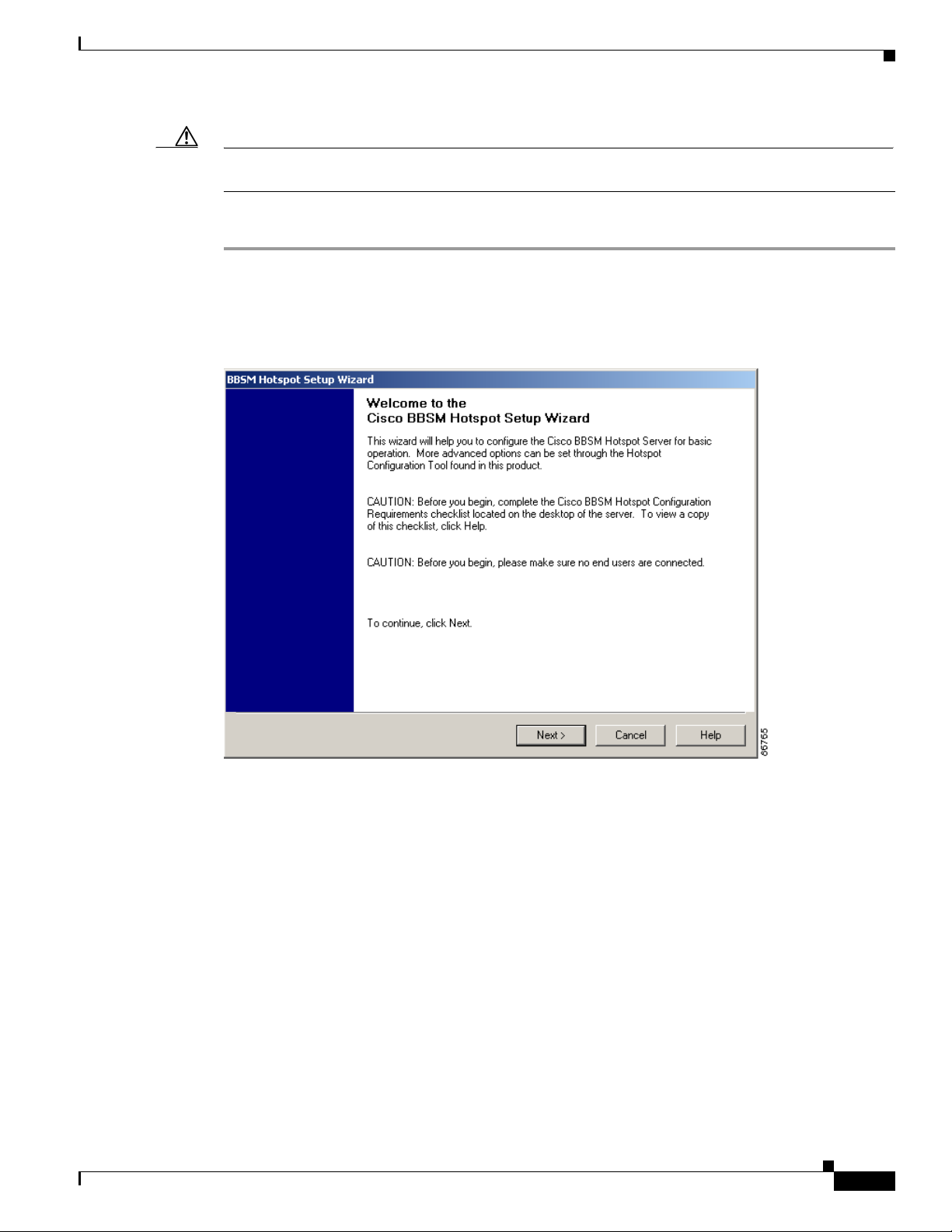
Step 1 From the Windows desktop, double-click the BBSM Hotspot Setup Wizard icon. (From the Windows
desktop, you can also choose Start > BBSM Hotspot Wizards > BBSM Hotspot Setup Wizard.) The
BBSM Hotspot Setup Wizard Welcome window appears. (See Figure 2-1.)
Figure 2-1 BBSM Hotspot Setup Wizard Welcome Window
Running the Setup Wizard
78-15293-01
Step 2
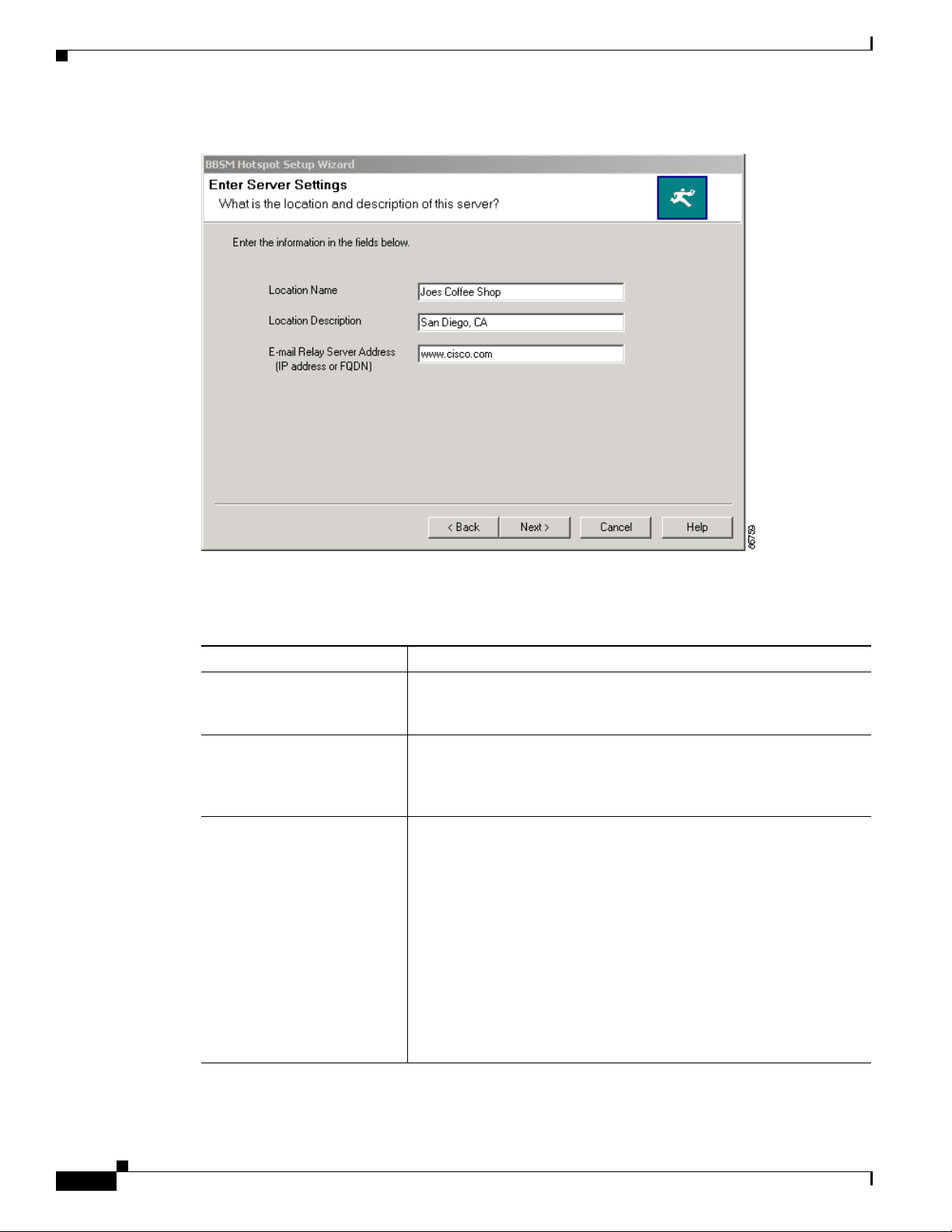
Click Next. The Enter Server Settings window appears. This window lets you enter location information
and the server address for relaying e-mail messages sent out through BBSM Hotspot. (See Figure 2-2.)
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
2-3
Page 4
Running the Setup Wizard
Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Figure 2-2 Enter Server Settings Window
Step 3
Enter the field data, as described in Table 2-1. This location data is used globally by BBSM Hotspot.
Table 2-1 Enter Server Settings Field Descriptions
Field Description
Location Name Enter a specific property name. Use up to 50 alphanumeric characters,
such as “Joes Coffee Shop” or “2nd Level Conference Rooms.” This
field is required.
Location Description Enter descriptive text for the location, such as the city or address. You
can use any alphanumeric word or phrase to a maximum of
100 characters, such as “San Diego, CA,” or “Guest cubicles in the
northeast annex.” This field is optional.
E-mail Relay Server Address
(IP address or FQDN)
Enter the IP address or the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) for
the e-mail relay server that is used by your Internet service provider
(ISP) to forward non–web-based e-mail, such as Microsoft Outlook or
Eudora mail programs, from public locations. An example FQDN is
www.ispemail.com. The FQDN can contain a maximum of
100 characters.
This field is optional. Use it only if you want to provide your end users
with e-mail support.
Typical e-mail servers block traffic from unknown sources for security
purposes. The BBSM Hotspot server, as with any public location, is
considered an unknown source that requires an e-mail relay server to
forward end-user mail.
2-4
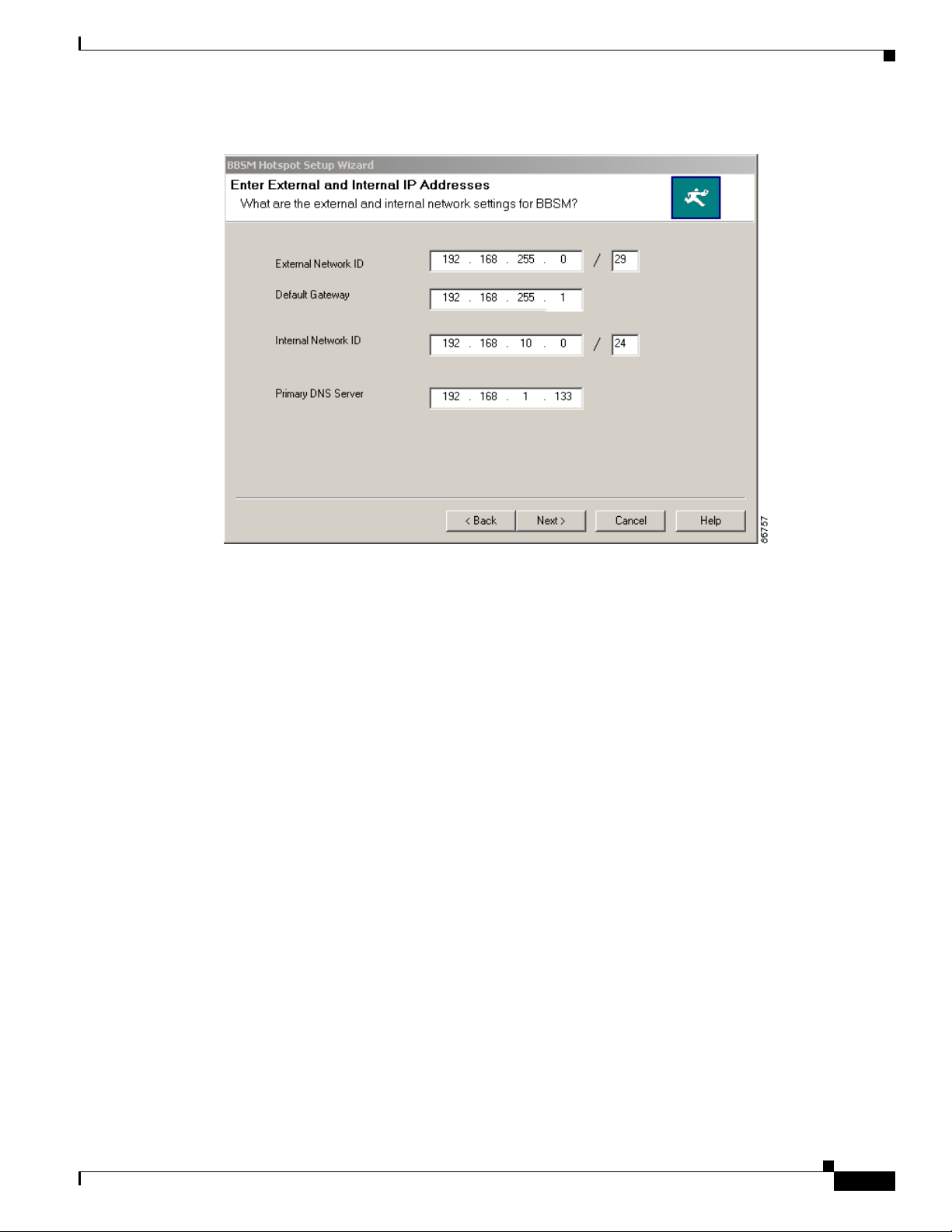
Step 4 Click Next. The Enter External and Internal IP Addresses window appears. (See Figure 2-3.)
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
78-15293-01
Page 5
Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Figure 2-3 Enter External and Internal IP Addresses Window
Running the Setup Wizard
Step 5
Enter the IP addresses, as described in Tab le 2-2. The wizard uses this data to determine BBSM Hotspot
external and internal NIC addresses, the router address, and allocation of the network device, static, and
DHCP client address pools. Note that the wizard requests the external and internal network IDs and
subnet masks and then calculates the external and internal IP addresses automatically. Obtain the
network IDs from your ISP. (An internal network of size Class C or smaller is supported.)
Table 2-3 shows the number of IP addresses available to you based on the subnet code number you enter
after the slash. The table shows the subnet codes that you would most likely use.
78-15293-01
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
2-5
Page 6
Running the Setup Wizard
Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
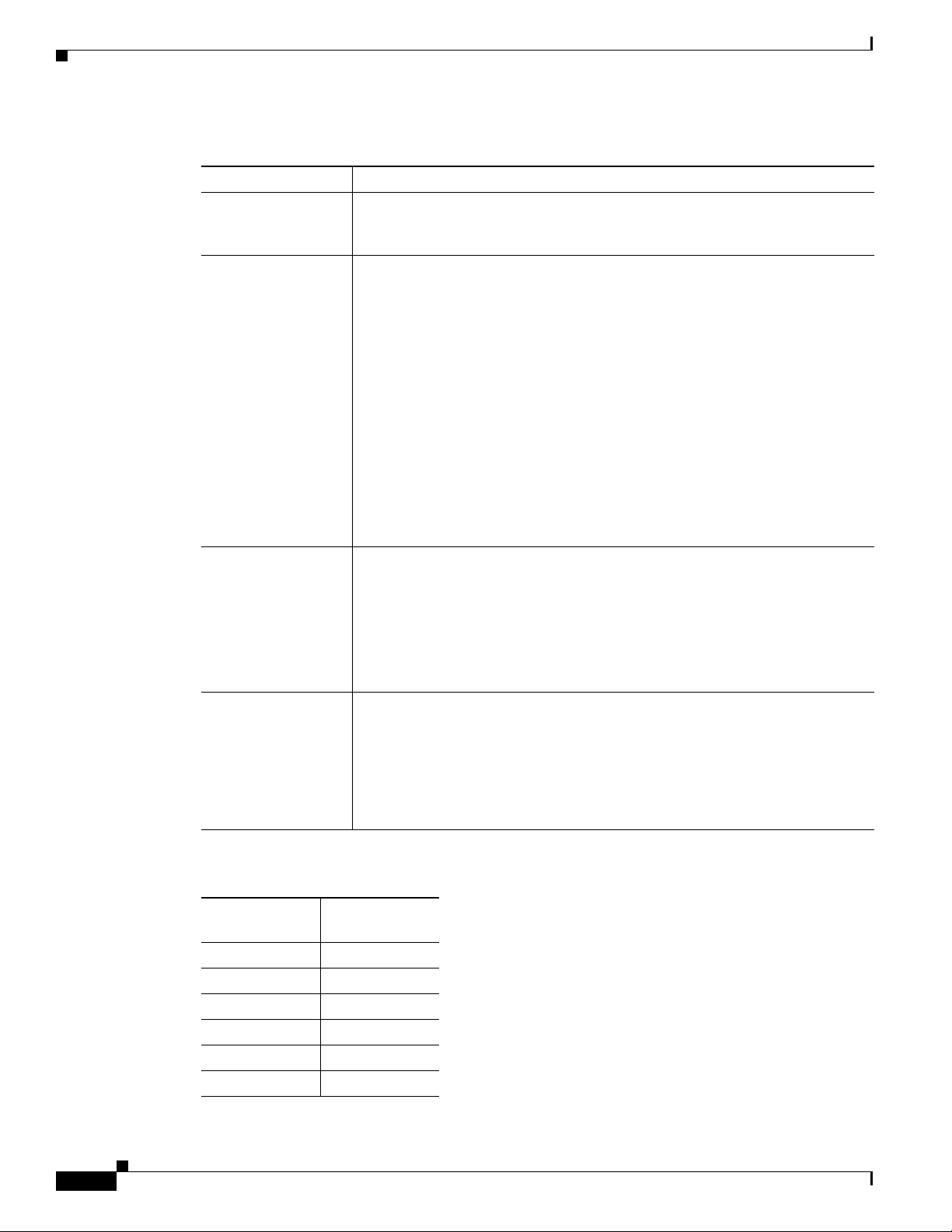
Table 2-2 Enter External and Internal IP Addresses Field Descriptions
Field Description
External Network ID Enter the external network IP address block assigned by your ISP. The number
after the slash is the subnet code for the number of IP addresses available in the
block.
Default Gateway This IP address is automatically generated based on the external network ID
that you entered. You cannot change the first three sets of numbers in this
address. This IP address is the address of the gateway (router) assigned by the
ISP and used to access the Internet. Here’s what can and cannot be changed in
this field:
• You cannot change the first three sets of numbers in the IP address.
• The fourth set defaults to the number 1. You can change this fourth octet
after the Setup Wizard populates the Default Gateway based on the
External Network ID.
Your router needs to be configured for the internal network to point to the
external NIC of the BBSM Hotspot server. If you are using a private IP address,
you will also need to create a network address translation (NAT) pool for end
users and one-to-one NAT statements for remote access to internal network
devices.
Internal Network ID This is the Network ID for the subnet that end users use to connect to the BBSM
Hotspot network and, through it, the Internet. The internal subnet consists of the
network devices, end-user clients (such as laptops and PDAs), and the BBSM
Hotspot internal NIC. The number after the slash is the subnet code for the
number of IP addresses available in the block.
You can enter your own private network ID, or you can input a public network
ID.
Primary DNS Server Enter the IP address for the primary domain name system (DNS) server
provided by your ISP. Because BBSM Hotspot is not configured as a DNS
server, DNS forwarding is enabled to forward all DNS requests to a remote
DNS server. BBSM Hotspot acts as a DNS forwarder for end-user DNS requests
as well as its own DNS requests. These requests, such as www.cisco.com, are
resolved into IP addresses so the Internet routers can locate the web server with
the content.
2-6
Table 2-3 Subnet Code Conversions
Subnet Code
/29 6
/28 14
/27 30
/26 62
/25 126
/24 254
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
Number of
IP Addresses
78-15293-01
Page 7
Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
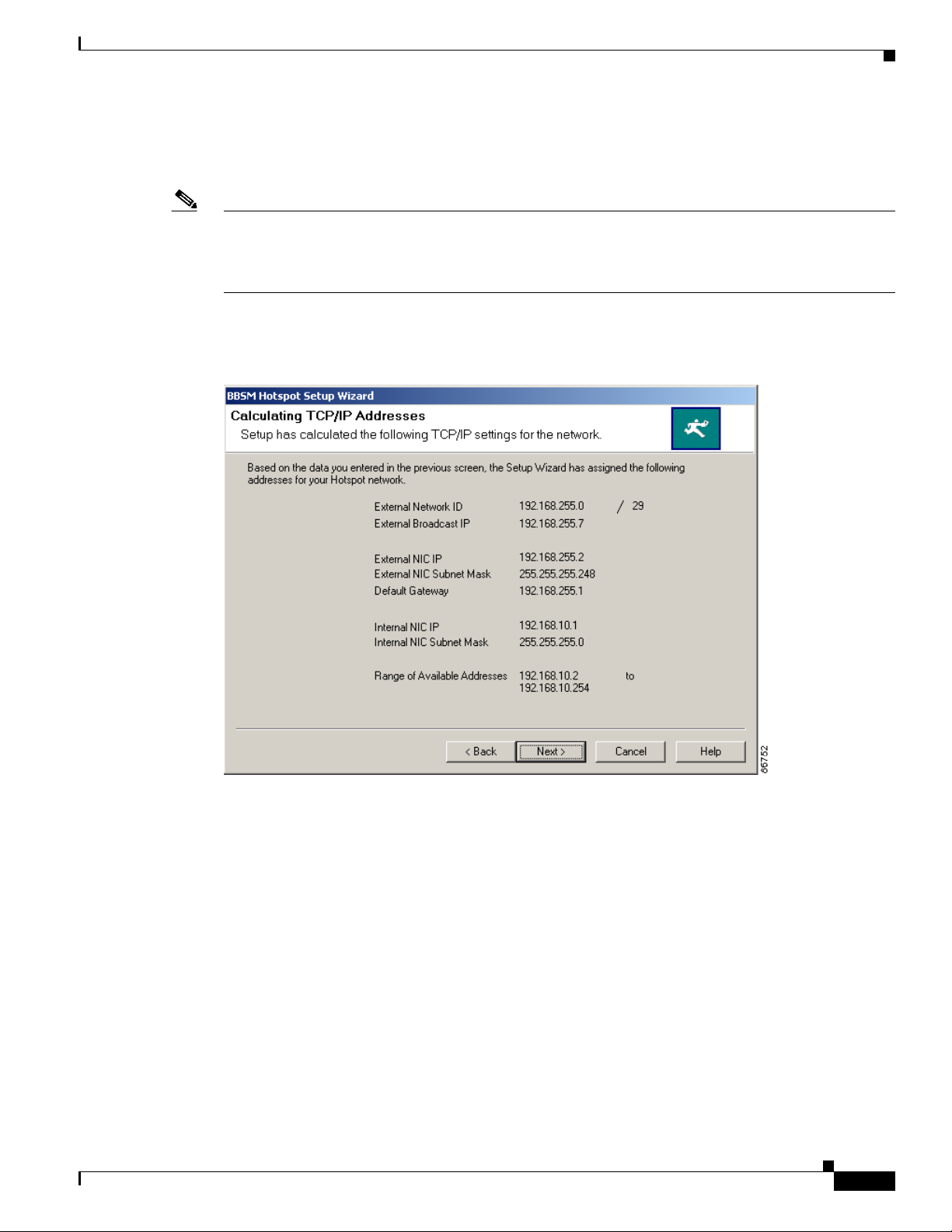
Step 6 Click Next. The Calculating TCP/IP Addresses window appears. BBSM Hotspot uses the information
provided in the Enter External and Internal IP Addresses window to calculate TCP/IP addresses for the
server.
Note If you need to change the IP addresses of the NICs from the defaults generated by the Setup Wizard, you
must use the Address Change Wizard to make these changes. Continue with and complete the Setup
Wizard, then use the Address Change Wizard to change the NIC addresses to the desired settings. Refer
to the “Running the Address Change Wizard” section on page A-1.
(See Figure 2-4 and Tabl e 2 -4 for field descriptions.)
Figure 2-4 Calculating TCP/IP Addresses Window
Running the Setup Wizard
78-15293-01
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
2-7
Page 8

Running the Setup Wizard
Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Table 2-4 BBSM Hotspot Setup Wizard, Calculating TCP/IP Addresses Field Descriptions
Field Description
External Network ID The network ID used for your BBSM external network.
External Broadcast IP The IP address used to broadcast data within the external network.
External NIC IP The IP address of the external NIC on BBSM Hotspot. BBSM Hotspot
assigns the first host address that is not the default gateway, as
calculated from the External Network ID field in Step 5.
External NIC Subnet Mask The subnet mask calculated from the External Network ID subnet code
(after the slash) in Step 5.
Default Gateway The default gateway address entered in the Default Gateway field in
Step 5.
Internal NIC IP The IP address on the internal NIC on BBSM Hotspot, as calculated
from the Internal Network ID in Step 5. It is set to the first host address
calculated from the Internal Network ID.
Internal NIC Subnet Mask The subnet mask on the internal NIC, as calculated from the Internal
Network ID subnet code (after the slash) in Step 5.
Range of Available Addresses The range of IP addresses available for internal network devices and
end-user connections on the internal network. The range is from the
second host ID through the last host ID calculated.
Step 7 Click Next. The Restart Computer dialog box appears on top of the Setup Wizard. This dialog box gives
you the option to restart BBSM now or cancel. (See Figure 2-5.) You must restart or reboot for the
IP address settings to take place. If you do not restart, you cannot continue with the setup.
Caution Restarting the BBSM Hotspot server at this point will save all of the settings entered for your server up
to this point. Click No to close the dialog box, which returns you to the Calculating TCP/IP Addresses
window. If you click Cancel at any point after the restart, the server settings and IP addresses that you
have entered at this time will be retained, while settings entered after the restart will be cancelled. If you
run the Setup Wizard a second time and do not change the IP address settings (a reboot is unnecessary),
if you click Cancel, all settings entered at that time, including the server settings, will be cancelled.
Figure 2-5 Restart Computer Dialog Box
Step 8
For the IP address configuration settings to take effect, click Yes . The BBSM Hotspot server configures
the new settings, then restarts. After you log in to BBSM Hotspot as Administrator, the Welcome Back
window appears. (See Figure 2-6.)
2-8
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
78-15293-01
Page 9
Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Figure 2-6 Welcome Back Window
Running the Setup Wizard
Caution Before continuing, make sure that your router is configured and connected to the Internet.
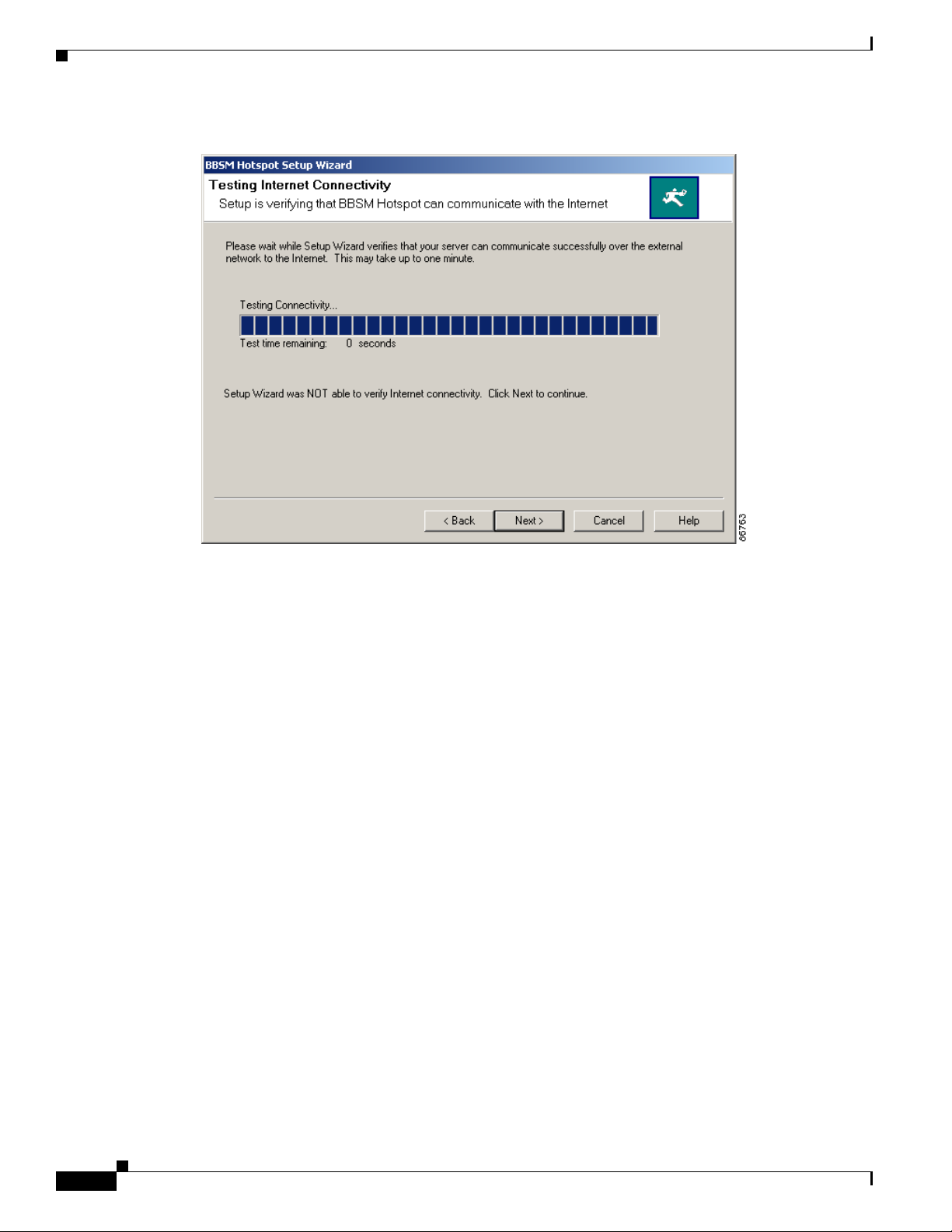
Step 9 Click Next. The Testing Internet Connectivity window appears and begins testing the connection from
BBSM Hotspot through the router to the Internet. A progress bar shows the test time remaining. The test
should take less than a minute. The Back and Next buttons are disabled until the test is complete.
(See Figure 2-7.)
• If the test is successful, a Test Success window pops up with a message telling you that the
connection test was successful. Click OK to close the window, then go to Step 11.
• If the test was unsuccessful, this message appears on the Testing Internet Connectivity web page:
“Setup Wizard was NOT able to verify Internet connectivity. Click Next to continue.” Go to Step 10.
78-15293-01
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
2-9
Page 10
Running the Setup Wizard
Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Figure 2-7 BBSM Hotspot Setup Wizard, Testing Internet Connectivity Window
Step 10
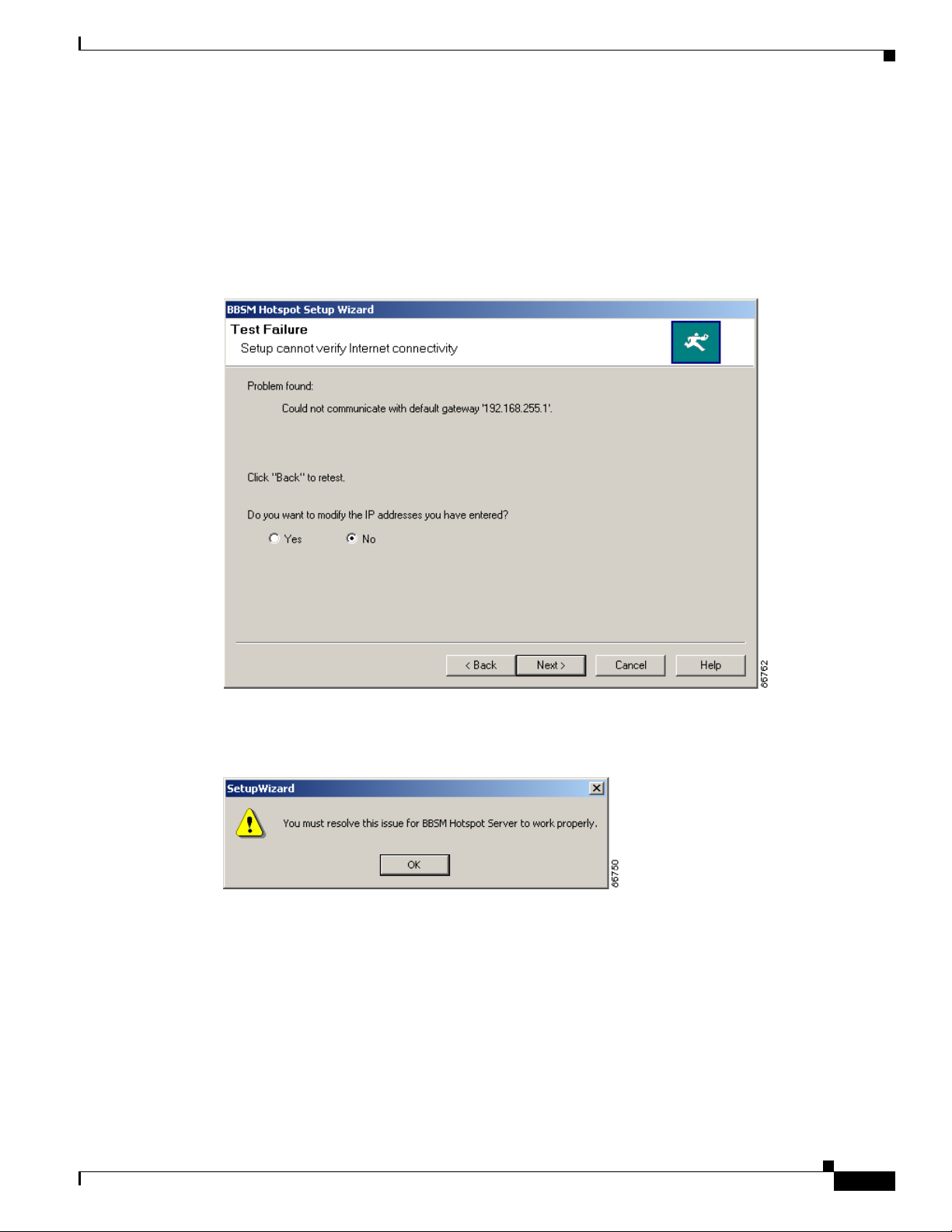
Click Next. The Test Failure window appears (Figure 2-8) and provides you with options. Note the
following reasons that the test may have failed and the options for correcting errors:
• Failure to communicate with the default gateway IP address:
–
Verify the physical connection from BBSM Hotspot to the router.
–
Make sure that a cross-over cable has been used.
–
Verify that the link status light is on for both the internal connection of the router and the BBSM
Hotspot external NIC.
–
Verify that the router IP address was configured correctly. You may need to contact your ISP so
they can verify this setting.
• Failure to communicate with the DNS server IP address:
–
Verify the physical connection from the router to the Internet.
–
Verify that the link status light is on for the external connection of the router.
–
Verify that the ISP provided the correct DNS address and that it was entered correctly.
–
Contact the ISP to verify this address.
• Failure to resolve the DNS name: www.yahoo.com—Contact the ISP to verify that the DNS is
operational.
The following are the options available to you from the Test Failure window:
–
Check your physical connections. Then click Back to rerun the test.
–
After the question asking if you want to change your IP addresses, click Yes. Then click Next
to continue. You are returned to the Enter External and Internal IP Addresses window where you
can enter new IP addresses. Then continue with the setup.
2-10
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
78-15293-01
Page 11
Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
–
–
Figure 2-8 Test Failure Window
Running the Setup Wizard
After the question asking if you want to change your IP addresses, click No to ignore the
connectivity issues and continue with the setup. A warning message pops up to tell you that you
must resolve the IP address issue for BBSM Hotspot to work properly. (See Figure 2-9.) You
are then taken to the Enter Network Device Configuration Parameters window.
(See Figure 2-10.)
Click Cancel to stop the setup.
78-15293-01
Step 11
Figure 2-9 You Must Resolve This Issue Dialog Box
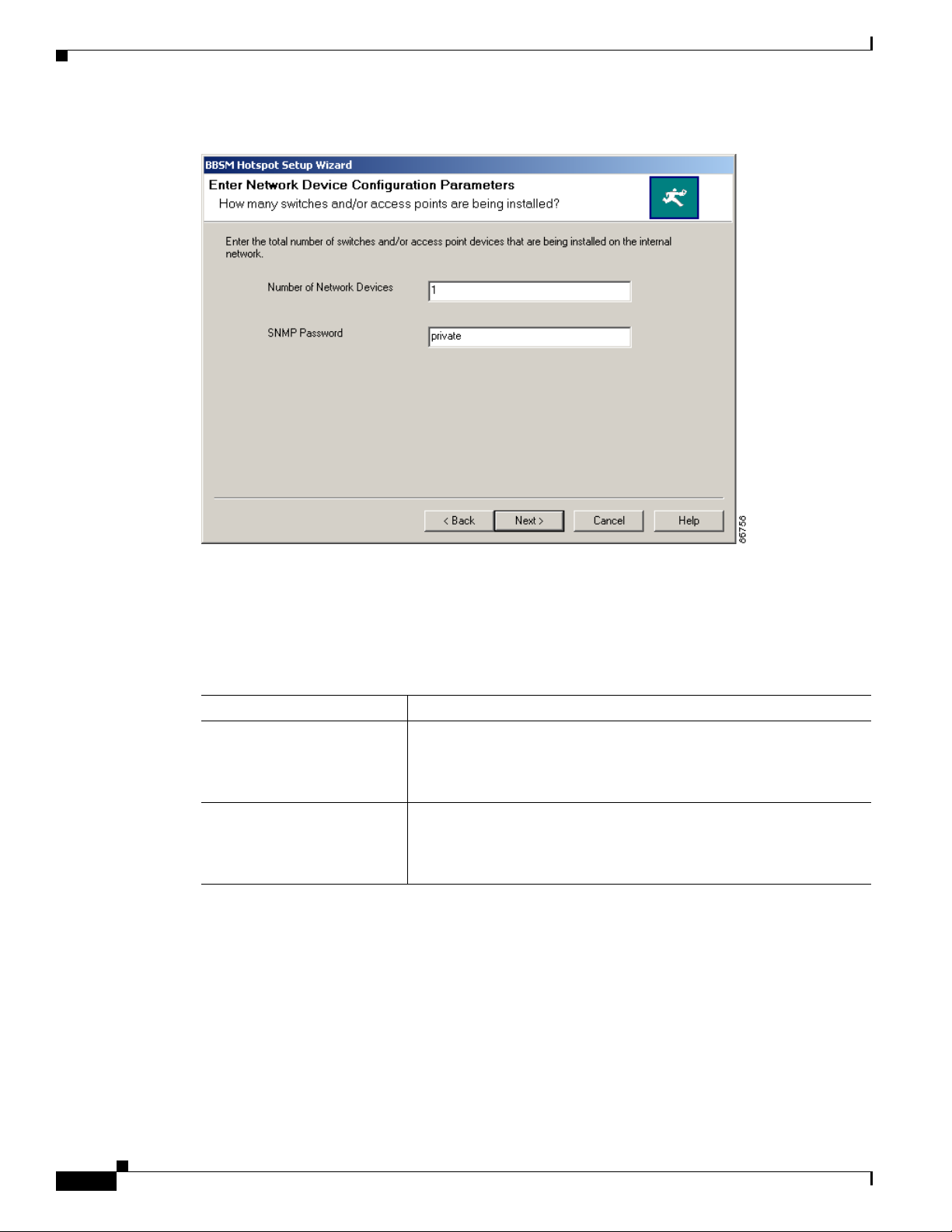
Click Next. The Enter Network Device Configuration Parameters window appears. (See Figure 2-10.)
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
2-11
Page 12
Running the Setup Wizard
Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Figure 2-10 Enter Network Device Configuration Parameters Window
Step 12 Enter the network device parameters, as described in Ta ble 2-5. The wizard uses this data to determine
the number of IP addresses to allocate to the network device range. (This may have been familiar to
current BBSM customers as the “Management Range.”) This information will also be used in the switch
discovery part of the wizard.
Table 2-5 Enter Network Device Configuration Descriptions
Field Description
Number of Network Devices Enter the total number of switches and wireless access points that will
be installed on the BBSM internal network. You can also enter a larger
number than the current amount of network devices in anticipation of
additional devices in the future.
SNMP Password Enter the SNMP password that is used to access network devices.
BBSM Hotspot needs this information to run switch discovery. Note
that on Cisco Catalyst switches, the SNMP password is also known as
the SNMP community read/write string.
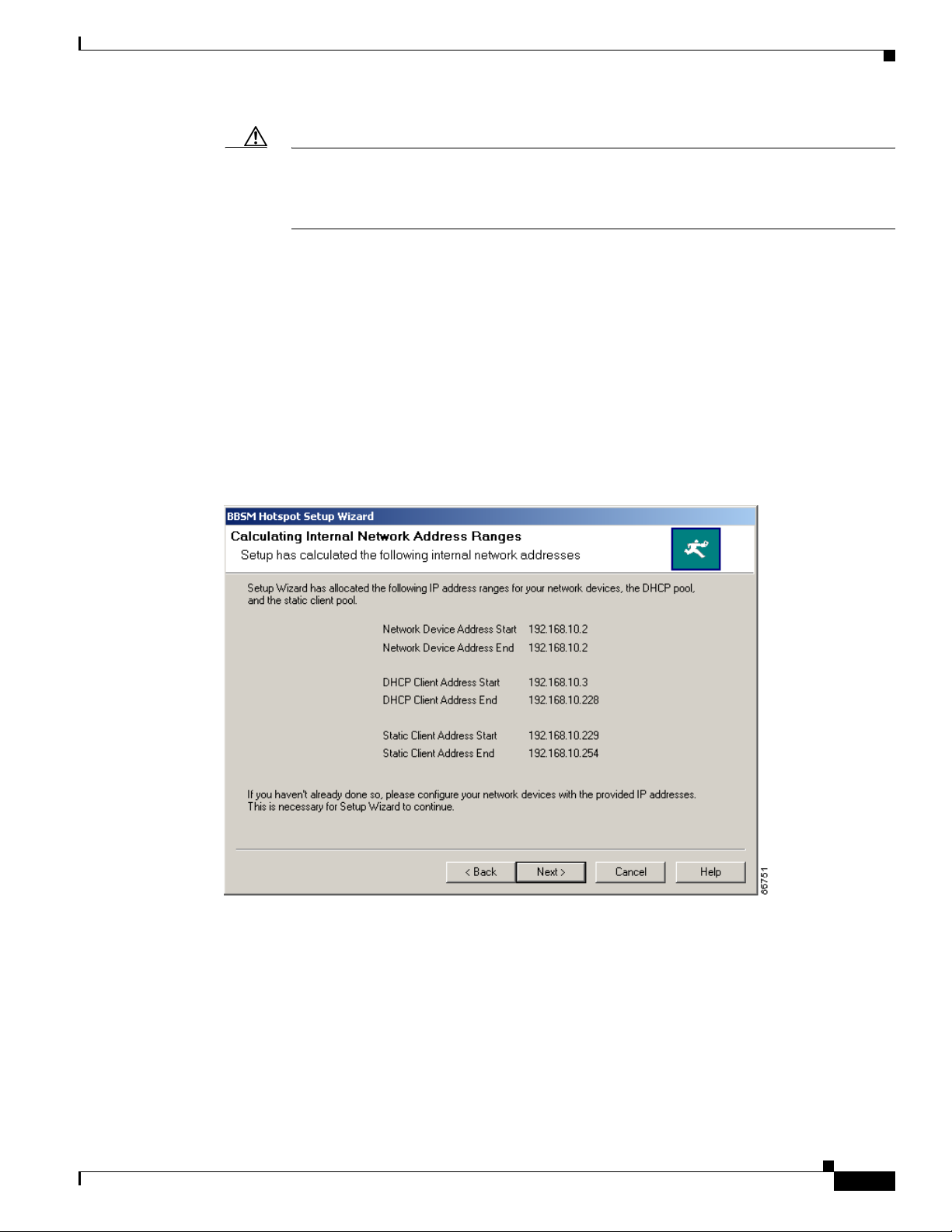
Step 13 Click Next. The Calculating Internal Network Address Ranges window appears, providing you with a
list of the internal IP address ranges that have been calculated and assigned by the BBSM Hotspot server.
These include the following:
• Network Device Addresses—These addresses are allocated to the network devices. This address
range is allocated from the “Number of Network Devices” number entered in Step 12.
2-12
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
78-15293-01
Page 13
Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Caution The IP addresses of your switches and access points must be set to addresses that are within
• DHCP Client Addresses—These addresses are allocated to the DHCP client address pool. Because
most network devices are configured as DHCP, after the BBSM NIC and the network device
addresses have been allocated, BBSM Hotspot allocates 90 percent of the available end-user
addresses to the DHCP pool. You can modify this address range in the Hotspot Configuration tool
on the Dashboard or by using the Address Change Wizard.
• Static Client Addresses—These addresses are allocated to the statically configured client address
pool. Because static configurations are not common, this range is allocated by BBSM Hotspot to
10 percent of the total remaining pool after the BBSM NIC and the Network Device addresses have
been allocated.
(See Figure 2-11.)
Figure 2-11 Calculating Internal Network Address Ranges Window
Running the Setup Wizard
this Network Devices Address range. To increase performance, we recommend using the
numbers in this range consecutively so that any unused IP addresses are at the end of the
range.
78-15293-01
Step 14
Click Next. The Discovering Network Devices window appears, showing that BBSM Hotspot is running
switch discovery to find network devices connected to the BBSM Hotspot internal network.
(See Figure 2-12.) As each device is discovered, BBSM Hotspot is automatically configured to work
with the device. The progress bar shows the number of devices found based on the number entered in
Step 12. The Back and Next buttons are disabled until the process is complete.
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
2-13
Page 14

Running the Setup Wizard
Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Figure 2-12 Discovering Network Devices Window
When discovery is complete, two scenarios are possible:
• If all of the network devices were found, a dialog box appears, telling you that network discovery is
complete. (See Figure 2-13.) Go to Step 16.
Figure 2-13 Network Discovery Complete Window
If some of the network devices were not found, a dialog box appears, telling you that not all of the
•
devices could be found. (See Figure 2-14.) Go to Step 15.
Figure 2-14 Devices Not Found Window
2-14
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
78-15293-01
Page 15

Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Step 15 Click OK. The Discovering Network Devices Results window appears, listing discovery results and a
summary of devices found. If the wizard located less devices than you entered in the “Number of
Network Devices” field in Step 12, BBSM Hotspot shows the reduced number that were found. The
reasons for the discrepancy can include the following:
–
–
–
–
You are asked if you want to change the network device configuration parameters:
–
–
–
–
(See Figure 2-15.)
Running the Setup Wizard
Intentional discrepancies may exist, because addresses were included for future system growth.
The physical connections may be faulty.
The IP address and SNMP password may not be configured correctly.
The correct network device cannot be found for each IP address.
Click Back to make corrections, such as reconnecting a cable, then retest the server. Then
continue with the setup.
To change your network device data, click Ye s. Then click Next to continue. You are returned
to the Enter Network Device Configuration Parameters window where you can change the
network device data. Then continue with the setup.
If you choose not to change your network device data; for example, if you assigned additional
addresses for future system growth, click No to ignore the discrepancy and continue with the
setup.
Click Cancel to stop the setup.
Step 16
Figure 2-15 Discovering Network Devices Results Window
Click Next. The Create Custom Web Page window appears. The wizard prompts you to decide if you
want to create a custom web page now or use the default web pages that ship with BBSM Hotspot:
78-15293-01
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
2-15
Page 16

Running the Setup Wizard
–
Click No to use the BBSM Hotspot default web pages. The Setup Wizard generates a generic
FreeAccess web page to all ports. If you do not want to create a custom web page at this time,
you can create one later by using the Custom Web Page Wizard. The custom web page can then
be enabled on a per-port basis by using the Port Configuration tool on the Dashboard.
Note The first time you run Setup Wizard, it sets all ports to free Internet access. If you run
the Setup Wizard again at a later time, it will not change the port settings.
–
Click Ye s to complete the Setup Wizard, then launch the Custom Web Page Wizard to create a
custom web page at this time. Creating a custom web page allows you to provide a welcome
message, instructions, and branding information to your end users.
(See Figure 2-16.)
Figure 2-16 Create Custom Web Page Window
Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
2-16
Step 17
Click Next. The Congratulations window appears, showing the configurations that you set. The Setup
Wizard saves these settings to a text file named “BBSMHotspotSettings.txt on the Windows desktop.
(See Figure 2-17.)
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
78-15293-01
Page 17

Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Figure 2-17 Congratulations! Window
Understanding the BBSM Hotspot Dashboard
Step 18
Click Finish:
• If you chose to create a custom web page, the Setup Wizard launches the Custom Web Page Wizard.
• If you chose to use the default web page that the Setup Wizard creates, the Setup Wizard closes.
Understanding the BBSM Hotspot Dashboard
The BBSM Hotspot Dashboard comprises two primary components—Configuration and Operations,
from which an administrator can perform all system functions. These functions include configuring the
system, performing all system operations, managing and updating the system, and reporting. The
Dashboard and the two components are described in the sections that follow.
78-15293-01
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
2-17
Page 18

Understanding the BBSM Hotspot Dashboard
Dashboard Access
The Dashboard is the BBSM Hotspot home page for accessing BBSM Hotspot options. (See
Figure 2-18.)
Figure 2-18 Dashboard
Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
You can access the Dashboard locally or remotely:
• To access the Dashboard locally, at the BBSM Hotspot console, double-click the Dashboard icon on
the desktop. The Dashboard appears. You can also choose Start > BBSM Hotspot Dashboard.
• To access the Dashboard remotely, launch Internet Explorer to access the BBSM Hotspot server on
port 9488 instead of through the default web server port 80, as shown below. Use one of the
following IP addresses:
–
If you are accessing BBSM Hotspot from a remote location, enter BBSM Hotspot’s external IP
address: http://<external_NIC_address>:9488/www, where <external_NIC_address> is the
external NIC address of the BBSM Hotspot server you want to access; for example, type
http://192.168.38.1:9488/www, and press Enter. The Enter Network Password dialog box
appears. (See Figure 2-19.)
–
If you are accessing the BBSM Hotspot server within BBSM Hotspot’s subnet, enter the BBSM
Hotspot server’s internal IP address: http://<internal_IP_address>:9488/www, where
<internal_IP_address> is the internal IP address of the BBSM Hotspot server you want to
access; for example, type http://192.168.10.1:9488/www, and press Enter. The Enter Network
Password dialog box appears. (See Figure 2-19.)
Note To access the Dashboard from BBSM Hotspot’s internal subnet, the end user’s client
must have either an IP address in the Network Devices address range or an active BBSM
Hotspot session. If neither of these is true, the end user will be redirected to the Start
page for the port that they are connected to.
2-18
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
78-15293-01
Page 19

Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Figure 2-19 Enter Network Password Dialog Box
–
Understanding the BBSM Hotspot Dashboard
When you access the Dashboard remotely, you are prompted for a username and password.
(Leave the domain name blank.)
Configuration
The following three Administration options allow an administrator to perform all configuration tasks:
• Hotspot Configuration—Use this tool to configure the BBSM Hotspot server. Figure 2-20 shows the
functionality accessed through the Hotspot Configuration navigation bar (NavBar).
Figure 2-20 Hotspot Configuration NavBar
Port Configuration—Use this tool to change port settings.
•
• Custom Web Page Wizard—Use this wizard to create a customized end-user web pages.
78-15293-01
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
2-19
Page 20

Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Understanding the BBSM Hotspot Dashboard
The Hotspot Configuration web page options are described in Tab le 2-6.
Table 2-6 Hotspot Configuration Web Page Options
Web Page Description
Server
Settings
IP Addresses Configures the IP address ranges for the BBSM Hotspot server and the network devices.
Routers Sets router interface parameters. Configures routes to the switches and to the clients attached to these
Network
Devices
Billing Expands to the RADIUS and Credit Card web pages, which define the billing features:
Configures server-wide settings such as bandwidth throttling and the e-mail server IP address.
switches. (This feature is for routed networks and is not related to WAN activities.)
Expands to the Access Points and Switches web pages:
• Access Points—Sets the access point parameters, such as access point IP address and access point type.
• Switches—For a particular cluster and switch number, sets the switch parameters, such as number of
client ports, cluster IP address, router IP address, and Cisco switch type. Note that each cluster can
support up to 16 cluster-capable switches.
• Credit Card—Configures the credit card server parameters and the merchant ID number.
• RADIUS—Configures the RADIUS server parameters and the ability to have multiple concurrent
RADIUS sessions.
Security/SSL Configures the domain name for SSL web pages and enables changes to the MSDE ‘sa’ password.
Custom Web
Pages
Walled
Garden
Adds your new custom web pages and sets the associated Start page. The web page then appears in the Web
Page drop-down menu when configuring port settings from the Access Points or Switches web page.
Configures the desired walled garden web sites, which let the end user view the web sites that you specify
free of charge.
Operations
The following are the options available under the Operations section of the Dashboard:
• Reports—Use this tool to view and print reports about the BBSM Hotspot server.
• Access Code Management—Use this tool to generate, edit, and delete access codes for connecting
to the Internet.
• Client Deactivation—Use this option to remotely terminate active client sessions.
• Updates—Use this option to install maintenance releases (service packs) and patches.
Using Navigation Buttons
2-20
BBSM Hotspot web pages use navigation buttons to help you locate information. Use the navigation
buttons to locate the correct record before making changes. (See Tab le 2-7.)
When no records exist for that function, the button is disabled. For example, the First and Previous
buttons are grayed out when you are viewing the first record.
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
78-15293-01
Page 21

Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Table 2-7 Navigation Button Descriptions
Button Description
Returns the user to the first record or page.
Returns the user to the previous record or page.
Takes the user to the next record or page.
Takes the user to the last record or page.
Connecting a Client to BBSM Hotspot
To connect a client to BBSM Hotspot, the client should meet minimum requirements. This section
provides those requirements and tells how an end user connects to the BBSM Hotspot server. Ta ble 2-8
shows the operating system and browser versions that have been tested and are supported for the BBSM
Hotspot software release 1.0.
Connecting a Client to BBSM Hotspot
Table 2-8 Minimum End-User Client Connection Requirements
Component Tested and Supported for BBSM Hotspot 1.0
Operating system Windows 98, 2000 Professional, and XP Professional
Linux Red Hat 7.1
Macintosh OS9.0 and OS10.0
Browser Internet Explorer 5.0 or higher
Netscape Navigator 4.7x or higher
Colors, depth 256 (65,000 recommended)
Screen Area, pixels 800 by 600—For Compaq H3635 and H3760 iPAQ pocket PCs: 240 by 320
limitation.
Note that the Setup Wizard sets all ports to the FreeAccess web page the first time the wizard is run. You
can change the Start page by using the Custom Web Page Wizard or the Port Settings option in Hotspot
Configuration. Figure 2-21 shows the FreeAccess Start page. (For instructions on how to use the Setup
Wizard, refer to the “Running the Setup Wizard” section on page 2-2.)
78-15293-01
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
2-21
Page 22

Connecting a Client to BBSM Hotspot
Figure 2-21 FreeAccess Start Page
Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
The following example shows how an end user using a wireless NIC connects to the Internet using
BBSM Hotspot. In the example, a coffee shop has purchased a BBSM Hotspot server, set it up, and
selected the FreeAccess web page. The end user does the following:
Step 1 Turn on your laptop and open your web browser. The FreeAccess web page should appear.
Step 2 If the Start page does not appear, contact property staff for information on configuring your wireless
NIC.
Step 3 After verifying the configuration of the wireless NIC, open the web browser. The FreeAccess Start page
appears.
Note If the Start page does not appear, refer to the troubleshooting section, “No Start Page Received
by End User” section on page 4-31, for probable causes and corrective action.
Step 4 The end user is then redirected to a “Connecting...” window and then to the end user’s configured initial
page.
2-22
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
78-15293-01
Page 23

Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Changing the Default Security Passwords
This section describes how to change the default security passwords that come with your BBSM Hotspot
server. Table 2-9 lists these passwords.
Caution For security reasons, we strongly recommend that you change these default passwords immediately.
Failing to change them could compromise network security. Do not use any blank passwords.
Table 2-9 BBSM Hotspot Default Passwords
Default
Account Username
Windows 2000
Administrator
MSDE System
Administrator
Cisco cisco The Windows 2000 Administrator has full system
sa cisco The MSDE system administrator (‘sa’) login is a
Password Description
permissions and rights, can alter any BBSM Hotspot
configuration setting, and has access to any Dashboard
option.
default system administrator login that is included
with every MSDE installation.
Changing the Default Security Passwords
Changing the Windows 2000 Administrator Password
Use the following procedure to change the Windows 2000 Administrator default password.
Step 1 Choose Start > Programs > Administrative Tools > Computer Management. The Computer
Management window appears. (See Figure 2-22.)
78-15293-01
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
2-23
Page 24

Changing the Default Security Passwords
Figure 2-22 Computer Management Window
Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Step 2 In the left pane, double-click Local Users and Groups. The folder opens, showing the Users and Groups
folders.
Step 3 Double-click Users. The folder opens, showing the user accounts. (See Figure 2-23.)
Figure 2-23 Computer Management Window, showing User Accounts
2-24
Step 4
Step 5 In the New password field, enter the new password.
Step 6 In the Confirm password field, enter the new password again.
Step 7 Click OK. A confirmation dialog box appears, notifying you that the password has been changed.
In the right pane, right-click Cisco, and from the drop-down menu, choose Set Password.
(See Figure 2-24.)
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
78-15293-01
Page 25

Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Figure 2-24 Password Changed Confirmation Dialog Box
Changing the Default Security Passwords
Step 8
Step 9 Close the Computer Management window.
Click OK to close the dialog box. The Computer Management window reappears.
Changing the MSDE ‘sa’ Password
The system administrator (‘sa’) login is a default system administrator login that is included with every
MSDE installation. Use the following procedure to change the default MSDE ‘sa’ password.
Step 1 From the Dashboard, click Hotspot Configuration. The Server Settings web page appears.
Step 2 In the NavBar, click Security/SSL. The Security/SSL web page appears.
Step 3 Next to Change MSDE ‘sa’ Password, click Change. The MSDE ‘sa’ Password Form appears.
(See Figure 2-25.)
Note You cannot change this password without knowing the current password. Save this password in
a secure location.
Figure 2-25 MSDE ‘sa’ Password Form
78-15293-01
Step 4
Step 5 In the Enter new password field, enter the new password.
Step 6 In the Confirm new password field, reenter the new password again.
In the Enter current password field, enter the current ‘sa’ password.
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
2-25
Page 26

Configuring Windows for Multinet
Step 7 Click Submit. A confirmation window appears.
Step 8 Click Close.
Configuring Windows for Multinet
This section describes how to configure the Windows operating system to support multiple networks
(multinets), on the BBSM Hotspot server. You only need to perform this procedure if you are using a
multinet. BBSM Hotspot servers are initially configured as single networks, or singlenets.
Note For more information on multinets, refer to the “Private and Public IP Addresses (Multinet)” section on
page 2-40.
Caution Although you use the Network and Dial-up Connections window to add multinet 2, do not delete
multinet 2 through this window, because although it is deleted from the GUI, it does not actually get
removed from the BBSM Hotspot databases. Use the Address Change Wizard to remove multinet 2.
Refer to the “Running the Address Change Wizard” section on page A-1.
Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Use the following procedure to reconfigure the internal NIC on your BBSM Hotspot server.
Step 1 Right-click My Network Places.
Step 2 From the pop-up menu, select Properties. The Network and Dial-up Connections window appears.
(See Figure 2-26.)
Figure 2-26 Network and Dial-up Connections Window
2-26
Step 3 Right-click AtNatMP, and select Properties. The AtNatMP Properties window appears.
(See Figure 2-27.)
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
78-15293-01
Page 27

Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Figure 2-27 AtNatMP Properties Window
Configuring Windows for Multinet
Step 4
Highlight Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and select Properties. The Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
Properties window appears. (See Figure 2-28.)
78-15293-01
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
2-27
Page 28

Configuring Windows for Multinet
Figure 2-28 Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties Window
Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Step 5
Click Advanced. The Advanced TCP/IP Settings window appears, showing the IP addresses tab.
(See Figure 2-29.)
2-28
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
78-15293-01
Page 29

Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Figure 2-29 Advanced TCP/IP Settings Window
Configuring Windows for Multinet
Step 6
Step 7
From the IP addresses area, click Add. The TCP/IP Address window appears. (See Figure 2-30.)
Figure 2-30 Advanced TCP/IP Settings Window
In the IP address and Subnet mask fields, enter the second IP address and subnet mask, and then
click Add. You are returned to the Advanced TCP/IP Settings window, which now shows the added
TCP/IP address, and you are finished with the configuration. (See Figure 2-31.) No gateways are
configured for the internal NIC.
78-15293-01
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
2-29
Page 30

Configuring DNS Forwarding
Figure 2-31 Advanced TCP/IP Settings Window with Added TCP/IP Address
Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Step 8
Step 9 To close the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window, click OK.
Step 10 To close the AtNatMP Properties window, click OK.
Step 11 Close the Network and Dialup Connections window.
To close the Advanced TCP/IP Settings window, click OK.
Configuring DNS Forwarding
This section describes how to configure DNS forwarding if you did not configure your server by using
the Setup Wizard. If you used the Setup Wizard, it configured DNS forwarding automatically.
The Domain Name System (DNS) forwarding feature is enabled on BBSM Hotspot to allow DNS
requests to be relayed to a remote DNS server. BBSM Hotspot is not configured as a DNS server; it acts
as a DNS forwarder for its clients and its own DNS requests. These DNS requests, such as
www.cisco.com, are resolved into IP addresses so the Internet routers can locate the web server with the
content.
Note You must obtain the IP address for your DNS servers from your ISP before you can perform the
following procedure. Refer to the BBSM Hotspot Configuration Requirements Checklist.
2-30
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
78-15293-01
Page 31

Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Use the following procedure to configure DNS forwarding for each IP address.
Step 1 Choose Start > Programs > Administrative Tools > DNS. The DNS window appears.
(See Figure 2-32.)
Figure 2-32 DNS Window
Configuring DNS Forwarding
Step 2
From the left pane, right-click BBSMHS10 and choose Properties. The BBSMHS10 Properties window
appears, showing the Interfaces tab. (See Figure 2-33.)
Figure 2-33 BBSM Hotspot Properties Window, Interfaces Tab
78-15293-01
Step 3
Click the Forwarders tab. (See Figure 2-34.)
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
2-31
Page 32

Feature Considerations
Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Figure 2-34 BBSMHS10 Properties Window, Forwarders Tab
Step 4
Step 5 In the IP address field, enter your DNS server IP address that is provided by your ISP, and click Add.
Step 6 To save the changes, click OK.
Step 7 Close the DNS window.
Check the Enable forwarders check box.
Feature Considerations
The following sections describe BBSM Hotspot features that may need some background and
explanation. For information on configuring these features, refer to the “Running the Setup Wizard”
section on page 2-2.
Using Web Pages
A web page set is a set of active server page (ASP) files written in Microsoft JScript, JavaScript, and
HTML. They are executed on both the BBSM Hotspot server and the end user’s browser when the end
user starts the browser. BBSM Hotspot ships with a set of default web page sets shown in Table 2-1 0.
You can use these default web pages without making changes.
If you want to create custom web page sets, the simplest way to create a custom web page set is to use
the Custom Web Page Wizard. Refer to the “Using the Custom Web Page Wizard” section on page 3-32.
2-32
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
78-15293-01
Page 33

Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
If you want to customize your web page beyond what is offered by the Custom Web Page Wizard, refer
to the Cisco BBSM 5.2 SDK Developer Guide for instructions on manually customizing web page sets.
This guide can also be used to create a custom web page for pocket PCs.
Note SDK software is provided with Cisco’s BBSM software product so customers can create custom web
page sets and web page policies. Although the Cisco BBSM 5.2 SDK Developer Guide was written to be
used with the BBSM software, the appropriate sections of the guide can be used to manually create
custom web page sets for BBSM Hotspot, if you choose not to use BBSM Hotspot’s Custom Web Page
Wizard. The SDK software, however, cannot be used with BBSM Hotspot. Using this software will
corrupt the BBSM Hotspot server.
You add the new custom web page to the list of web pages on the BBSM Hotspot server by using the
Custom Web Pages option in the Hotspot Configuration tool. Refer to the Adding Custom Web Pages to
BBSM Hotspot, page 3-24.
If a web page requires the end user to enter sensitive information, such as credit card information, an
SSL certificate should be used. When using the SSL web pages, you must buy and install an SSL
certificate. For complete details on installing the certificate, refer to Appendix B, “Installing an SSL
Certificate.”
Feature Considerations
Caution Because web page sets whose name ends in “Clear” do not use SSL security to transmit data to the
BBSM Hotspot server, Cisco does not recommend using them in production. Without SSL, the end user’s
browser transmits RADIUS and credit card information to BBSM Hotspot in clear text. BBSM Hotspot
provides these web pages for demonstration and testing situations in which installing a server certificate
is not feasible.
78-15293-01
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
2-33
Page 34

Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Feature Considerations
Table 2-10 BBSM Hotspot Default Web Page Descriptions
Web Page Set Uses SSL? Description
AccessCode No Prompts the end user to enter an access code to access the Internet for the time period
configured by the BBSM Hotspot administrator. Only one user at a time is able to access
the Internet using the access code.
BlockICS
BlockICSClear
DailyICS
DailyICSClear
FreeAccess No Allows the end user to connect to the Internet for an indefinite time period without
Hotspot
HotspotClear
MinuteICS
MinuteICSClear
RADIUS
RADIUSClear
RADIUSUBand
RADIUSUBandClear
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
No
Prompts the end user to enter credit card information to access the Internet for a block of
minutes. When the end user disconnects, they forfeit any unused time. The time does not
carry over to their next session.
Prompts the end user to enter credit card information to access the Internet for a 24-hour
period.
charges.
Allows the end user to select the desired access option—RADIUS, access codes, or a
specified time period.
Prompts the end user to enter credit card information to access the Internet per minute.
Prompts the end user to enter a RADIUS username and password to access the Internet.
Prompts the end user to enter a RADIUS username and password to access the Internet.
It also permits the end user to select their desired bandwidth at a specified price. For this
web page, the disconnect web page presents the end user with an estimated summary for
the time of the active session and the charges accrued at the selected bandwidth.
Using RADIUS with BBSM Hotspot
RADIUS is the industry-standard client/server protocol for user authentication, authorization, and
accounting, which enables users to access the Internet. It is designed to enable a RADIUS client to
communicate with a RADIUS server by using secure communication methods. You can implement one
or more RADIUS servers and a distributed network of RADIUS clients to manage security and retrieve
accounting information across various broadband building sites. This strategy benefits you by providing
greater security, a more scalable architecture, the ability to implement an open standards protocol, and
the ability to leverage future RADIUS enhancements.
The BBSM Hotspot system has a built-in RADIUS client that supports RADIUS and is compliant with
RFCs 2865 and 2866, which are the standards for RADIUS and RADIUS authentication.
Note Because this section explains only the BBSM Hotspot implementation and configuration of a RADIUS
server, the customer is expected to be familiar with RADIUS protocols, as documented in RFC 2865 and
RFC 2866, and how to configure their specific RADIUS server. Configuration of RADIUS servers is
outside the scope of this text.
For detailed information on configuring BBSM Hotspot for RADIUS, refer to the “Configuring
RADIUS Billing” section on page 3-19.
2-34
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
78-15293-01
Page 35

Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Although BBSM Hotspot officially supports the Cisco ACS, Microsoft IAS, and Navis RADIUS server
protocols, it is compatible with any RADIUS server that complies with RFCs 2865 and 2866 and allows
configuration of vendor-specific attributes.
BBSM Hotspot stores accounting and activation/deactivation information in the
RADIUS_SessionHistory table in the BBSM Hotspot database. This table provides independent auditing
of end-user sessions. Session data can be viewed in the RADIUS Session History report or by direct SQL
query.
The RADIUS Session History report shows session activation and deactivation entries:
• Session activation entries—When the end user authenticates through the RADIUS authentication
server and gains Internet access
• Session deactivation entries—When the end user’s Internet access is terminated
The report shows Start and Stop accounting requests and whether or not an accounting response was
received. If BBSM Hotspot is configured to send Interim-Update packets, the report displays the first
Interim-Update accounting request made for each session. Subsequent Interim-Update requests are
reported only if an error occurs during the packet transmission.
RADIUS Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting
Feature Considerations
Each time the end user connects to the BBSM Hotspot service, BBSM Hotspot prompts the user for a
username and password. These values are sent in the Access-Request packet to the RADIUS
authentication server. These authentication servers can be configured by administrators by order of rank
using the RADIUS Server web page in Hotspot Configuration. (Servers are ranked in ascending order,
so the primary RADIUS server is rank = 1, secondary server is rank = 2, and so on.) When sending the
Access-Request packets, BBSM Hotspot begins authenticating servers in ascending order by using all
configured RADIUS authentication servers until an Access-Accept packet is received:
• If a server does not respond within the specified time, BBSM Hotspot attempts to contact that server
up to three times before moving to the next highest ranked server.
• If a server responds with an Access-Reject packet, BBSM Hotspot immediately attempts to
authenticate using the next highest ranked server. (A RADIUS user can have a session active on
more than one computer on the BBSM Hotspot network at the same time if this option is
configured.)
When a RADIUS server sends a vendor-specific attribute that contains a bandwidth kbps value, BBSM
Hotspot throttles the bandwidth of the end-user session to the specified kbps value (if bandwidth throttle
is configured on BBSM Hotspot). To use this feature, administrators need to configure their RADIUS
server to send the vendor-specific attribute to transmit the following:
• A vendor ID of 5263
• A vendor type of 1
• The integer value of the bandwidth kbps desired for the user account
RADIUS accounting provides administrators with end-user session information when Internet access is
granted and terminated. This end-user information can then be retrieved from RADIUS accounting
servers, and independent billing can be performed. Administrators can choose flat-rate or per-minute
billing by using the information that BBSM Hotspot sends to the RADIUS accounting server in Start and
Stop Accounting-Request packets. If configured, BBSM Hotspot also sends Interim-Update packets to
the RADIUS accounting server at intervals set by the administrator.
78-15293-01
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
2-35
Page 36

Feature Considerations
Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Administrators can configure multiple RADIUS accounting servers, which provides redundancy in case
the primary RADIUS server is not responding. As with RADIUS authentication servers, each server is
configured with a ranking. BBSM Hotspot attempts to send accounting packets to accounting servers
until an accounting response packet is successfully received. For each server, BBSM Hotspot attempts
to send accounting request packets up to three times if the server fails to respond.
Table 2-11 shows the RADIUS attributes and the packets in which they are sent from the BBSM Hotspot
server to the RADIUS server. Tabl e 2-12 describes these attributes.
Table 2-11 RADIUS Access-Request and Accounting-Request Packets
Accounting-Request
Attribute No. Access-Request
User-Name 1X XXX
User-Password 2X
NAS-IP-Address 4X XXX
NAS-Port 5X XXX
Service-Type 6X XXX
Framed-Protocol 7X XXX
Framed-IP-Address 8X XXX
Vendor-Specific 26 XXX
Called-Station-ID 30X XXX
Calling-Station-ID 31X XXX
NAS-Identifier 32X XXX
Acct-Status-Type 40 XXX
Acct-Input-Octets 42 X
Acct-Output-Octets 43 X
Acct-Session-ID 44X XXX
Acct-Session-Time 46 X
Acct-Input-Packets 47 X
Start Interim-Update Stop
2-36
Acct-Output-Packets 48 X
Acct-Terminate-Cause 49 X
NAS-Port-Type 61X XXX
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
78-15293-01
Page 37

Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Feature Considerations
Table 2-12 RADIUS Attribute Descriptions
Attribute Description
User-Name The end user enters this name to authenticate against the RADIUS server and access the Internet
through BBSM Hotspot.
User-Password The end user enters this password to authenticate against the RADIUS server and access the Internet
through BBSM Hotspot.
NAS-IP-Address Contains either the IP address of the BBSM Hotspot external NIC or the IP address entered in the
WEBconfig RADIUS Server web page as the NAT IP address.
NAS-Port The NAS-Port value is a numeric value (therefore the leading zeros of the site number are dropped).
BBSM Hotspot maps the NAS-Port attribute as the following: aaabbccddd, where aaa = site number,
bb = cluster, cc = switch, and ddd = port.
For example, if the site number = 1, the cluster number = 2, the switch number = 3, and the port
number = 5, the NAS-Port number = 10203005.
Service-Type 2 indicates Framed.
Framed-Protocol 1 indicates PPP.
Framed-IP-Address IP address of client computer (PC) connecting to the Internet through BBSM Hotspot.
Called-Station-Id Contains the MAC address of the BBSM Hotspot internal NIC.
Calling-Station-Id Contains the MAC address of the client (end-user) NIC.
Vendor-Specific Contains the bandwidth kbps value that the end user selects when requesting Internet access. This
attribute is only sent to RADIUS accounting servers if the UBand feature is enabled. See Tab le 2-13
for the vendor-specific attribute formatting.
NAS-Identifier Contains the NAS Identifier value entered in the WEBconfig RADIUS Server web page. If no value
is entered in this field, BBSM Hotspot will not include this attribute in the RADIUS Access-Request
packet.
Acct-Status-Type 1: Start Accounting-Request packet—Requests that a message be sent when the user gains access.
2: Interim-Update Accounting-Request packet—Requests that a message be sent at regular
intervals, as configured.
3: Stop Accounting-Request packet—Requests that a message be sent when the user disconnects.
Acct-Input-Octets The number of octets (bytes) that BBSM Hotspot received from the end user during their session.
Acct-Output-Octets The number of octets (bytes) that BBSM Hotspot transmitted to the end user during their session.
Acct-Session-Id The unique Session ID assigned to each BBSM Hotspot end-user session used to identify all
authentication and accounting messages generated for a single user session.
Acct-Session-Time Indicates how many seconds the user has received service for and can only be present in
Accounting-Request records where the Acct-Status-Type is set to Stop.
Acct-Input-Packets The number of packets that BBSM Hotspot received from the end user during the user’s session.
Acct-Output-Packets The number of packets that BBSM Hotspot transmitted to the end user during the user’s session.
Acct-Terminate-Cause Indicates how the session was terminated and can only be present in Accounting-Request records
where the Acct- Status-Type is set to Stop.
NAS-Port-Type 5 = Virtual.
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
78-15293-01
2-37
Page 38

Feature Considerations
Table 2-13 RADIUS Cisco BBSM Hotspot-Bandwidth Vendor-Specific Attribute Format
Byte Value Description
1 26 Vendor-specific attribute type in accordance with RFC 2865
2 (4 * sizeof (BYTE)) +
(2 * sizeof (DWORD))
The length in bytes of the full attribute specification beginning with
attribute type (byte 1); should come out to 12 if each byte size = 1.
3–6 5263 The vendor-ID value.
7 1 The vendor data type; 1 indicates bandwidth kbps value.
8 (2 * sizeof (BYTE)) +
sizeof (DWORD)
The length in bytes of the vendor-specific portion of the attribute
specification starting with vendor-specific attribute data type. If each
byte size = 1, should come out to 6.
9–12 A bandwidth specified
Actual bandwidth kbps value (ulong).
in kbps; such as 256
User-Selected Bandwidth (UBand) Web Pages
Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
User-selected bandwidth (UBand) web pages support a user-specified bandwidth. This feature allows the
administrator to define the service offerings and allows the end user to select from the tiered services
offered directly from the Start page, such as the following:
• 64K for $0.15/minute
• 128K for $0.25/minute
• Unlimited for $0.30/minute
When a UBand web page is used, BBSM Hotspot throttles the session bandwidth at the kbps value that
the end user selects. This bandwidth value is transmitted to the RADIUS accounting servers in the Start,
Stop, and Interim-Update Accounting-Request packets and BBSM Hotspot ignores any bandwidth value
that the RADIUS authentication servers return in the Access-Accept packets.
The two BBSM Hotspot-provided sample web pages that implement this feature are RADIUSUBand and
RADIUSUBandClear. These web pages can be used as templates to customize the tiered services that
you want to offer.
Note Note that the administrators must make sure that the RADIUS accounting servers are configured to
accept the bandwidth that BBSM passes in the vendor-specific attribute and to record this attribute value
so the data can be retrieved for billing. The RADIUS provider is responsible for charging the end user
for the selected bandwidth.
When the user disconnects from the session, the Disconnect web page appears and displays the session
summary information: username, session duration (in minutes), and estimated session charge.
Port Hopping
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
2-38
The port hopping feature allows users to move from port to port without interrupting BBSM Hotspot
service. Within a BBSM Hotspot network, users can move between like types of hardware, such as
wireless access points or switch ports. Users cannot hop between wireless access points and wired
switches. Also, mobility across subnets or cells operated by different customers is not allowed.
78-15293-01
Page 39

Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Port hopping is disabled by default and can only be enabled on a per-port basis by an administrator. For
procedures on different ways to configure port hopping, refer to the following sections:
• “Configuring Your Server (Hotspot Configuration)” section on page 3-1
• “Configuring Ports (Port Configuration)” section on page 3-27
When port hopping is enabled, BBSM Hotspot keeps the session active when the user moves to another
port or temporarily disassociates. For example, disassociation might occur when the signal is weak or an
object comes between the wireless access point and the end user, which causes the user to associate
suddenly with a secondary access point that might be configured to another aggregation switch port.
When a user dissociates from the BBSM Hotspot network, BBSM Hotspot searches for the user until one
of the following occurs:
• The user’s MAC address reappears back on the network within the configured port hop delay time
period. The session then continues without interruption.
• The port hop delay time period expires. BBSM Hotspot then deactivates the session, and the user
must reauthenticate to regain Internet access.
Note the following about port hopping:
• Searching for end user—When port hopping is enabled and an end user disappears from the network,
BBSM Hotspot begins searching for the end user. BBSM Hotspot searches all configured network
elements. It first searches the last known network element that the end user was connected to or
associated with. If the user is not found, BBSM Hotspot then searches all other configured network
elements until the end user is found or the port hop delay time period expires.
• Session duration—The reported duration of an active session varies depending on how the session
terminates:
–
Feature Considerations
If the search succeeds, BBSM Hotspot includes the time that it searched for the user in the
session duration.
–
If the search fails to find the user before the port hop delay time period expires, BBSM Hotspot
does not include the search time in the session duration. In this way, the user that terminates a
session by turning off the computer is not charged for the time that BBSM Hotspot spends
searching for the user on other ports.
• Port hopping from a port hop disabled port—Port hopping is enabled on a per-port basis. The end
user is allowed to hop from a port hop enabled port to any port on the same site and continue the
session even if the port hop status of the destination port is disabled. However, the user is not
allowed to hop from a port hop disabled port at all. If this is attempted, BBSM Hotspot deactivates
the session.
• Port policy—As the user hops from port to port, the port policy that BBSM Hotspot associates with
the user session follows the user to each new port:
–
BBSM Hotspot applies the bandwidth limit (in kbps) specified at session activation to the
session as the user moves from port to port.
–
If a user has selected a dynamic bandwidth boost from a BBSM Hotspot web page, when the
user moves to another port, the bandwidth boost settings follow the session to the new port.
• Active Ports report—While the system is searching for a user, the user session remains active and
appears in the Active Ports report as associated with the last used port.
78-15293-01
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
2-39
Page 40

Feature Considerations
Private and Public IP Addresses (Multinet)
You can offer end users the choice of using individually assigned private or public DHCP IP addresses:
• Public IP addresses can be accessed by other devices on the Internet.
• Private IP addresses cannot be accessed by other Internet devices.
To explain the difference between private and public IP addresses, we can compare the IP address to a
phone number. A public IP address is equivalent to a full 10-digit telephone number (619-555-1234),
and a private address is equivalent to an office extension number.
The advantage of using one type of IP address over the other depends on the end user’s needs:
• The advantage of using public IP addresses is that some virtual private network (VPN) systems
require their clients to have public IP addresses to operate correctly.
• The advantage of using private IP addresses is many security threats are eliminated, because other
Internet devices cannot access private IP addresses. Because the local network automatically maps
each private IP address to a different public IP address for data going to and from the Internet, a
private IP address is never visible on the Internet. In addition, because private IP addresses are free,
they of course cost less than public IP addresses.
Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
BBSM Hotspot servers are configured initially as singlenet. If you want to use a multinet configuration,
you must reconfigure the server for multinet. Singlenet and multinet BBSM Hotspot servers are defined
as follows:
• Singlenet—A singlenet BBSM Hotspot server is configured as a single logical subnet and only
supports one logical subnet of IP address.
• Multinet—A multinet BBSM Hotspot server is configured with two distinct logical subnets and
supports both public and private IP addresses.
To change your BBSM Hotspot server to a multinet configuration, you must configure Windows for
multinet. Refer to the “Configuring Windows for Multinet” section on page 2-26.
To configure public or private IP addresses, refer to the “Running the Address Change Wizard” section
on page A-1. To add, change, or delete public-private IP addresses after the initial configuration, refer
to the “Configuring IP Addresses” section on page 3-3.
The per-port default IP type, which can be overridden by web page sets, can only be changed by the
BBSM Hotspot administrator. To add this functionality to your custom web page sets, refer to the
Cisco BBSM 5.2 SDK Developer Guide.
Cisco Switch Clustering
The BBSM Hotspot software supports the Cisco switch clustering technology that allows up to
16 switches (Catalyst 2950, 3500, and 3550 XL switches) to be clustered together and managed using
just one IP address for the entire cluster. It allows the administrator to update the Network Devices page
in the Hotspot Configuration tool, by using only the master switch IP address and a unique SNMP
password for each switch in the cluster.
The switch clustering feature also continues to support cluster configurations in which each
cluster/switch has a unique IP address.
2-40
Note Before running the Setup Wizard, the administrator must enable the switch clustering capability for all
cluster-capable switches. For detailed information, refer to your switch documentation.
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
78-15293-01
Page 41

Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
Feature Considerations
78-15293-01
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
2-41
Page 42

Feature Considerations
Chapter 2 Setting Up BBSM Hotspot
2-42
Cisco BBSM Hotspot 1.0 User Guide
78-15293-01
 Loading...
Loading...