Page 1
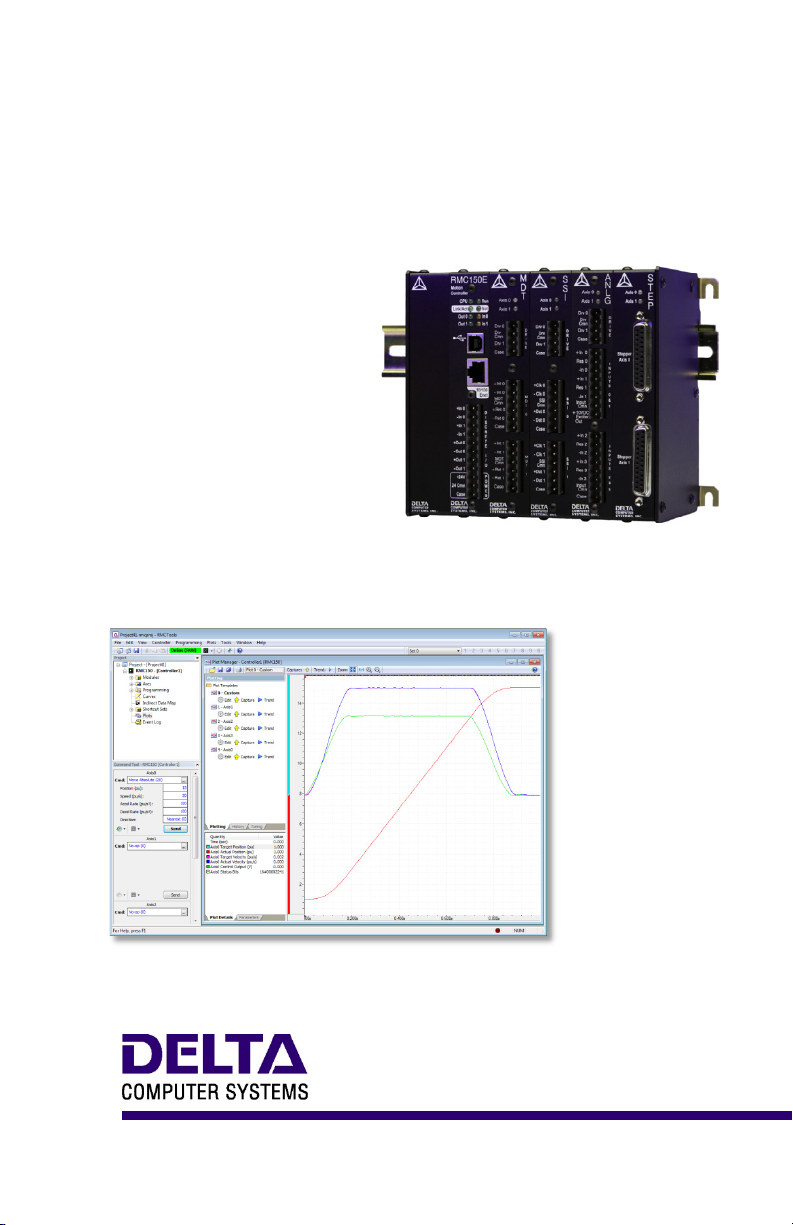
RMC150 MOTION CONTROLLER
STARTUP
GUIDE
With wiring diagrams
Motion Control and More
Page 2

RMC150 Startup Guide
Where to Get Help
Video Tutorials
In RMCTools, on the Help menu, click Video Tutorials.
RMCTools Help
In RMCTools, on the Help menu, click Help Topics.
Forum
forum.deltamotion.com
Delta Technical Support
Phone: +1-360-254-8688
support@deltamotion.com
Email:
deltamotion.com ii
Page 3

Contents
Contents
Step 1: Mounting ............................................................. 2
Step 2: Wiring ................................................................. 3
Step 3: Install RMCTools ................................................ 4
Step 4: Connect RMC to PC ........................................... 5
Step 5: Start a New Project ............................................ 6
Step 6: Define the Axes ................................................ 10
Step 7: Test an Actuator ............................................... 12
Step 8: Connect Feedback Device ............................... 15
Step 9: Scale and Offset ............................................... 19
Step 10: Set the Output Polarity ................................... 20
Step 11: Tuning ............................................................ 21
Continuing the Motion Application ................................ 23
Diagnostic Tools ........................................................... 25
Appendix A: W iring ....................................................... 26
Appendix B: Mounting Dimensions ............................... 39
Appendix C: Agency Compliance ................................. 40
Version 2.03, June 28, 2013
Copyright © 2013, Delta Computer Systems, Inc.
deltamotion.com 1
Page 4
RMC150 Startup Guide
Ambient Temperature
Clearance
122 - 140°F (50 - 60°C)
3 in. (7.6 cm)
86 - 122°F (30 - 50°C)
2 in. (5.1 cm)
Less than 86°F (30°C)
1 in. (2.5 cm)
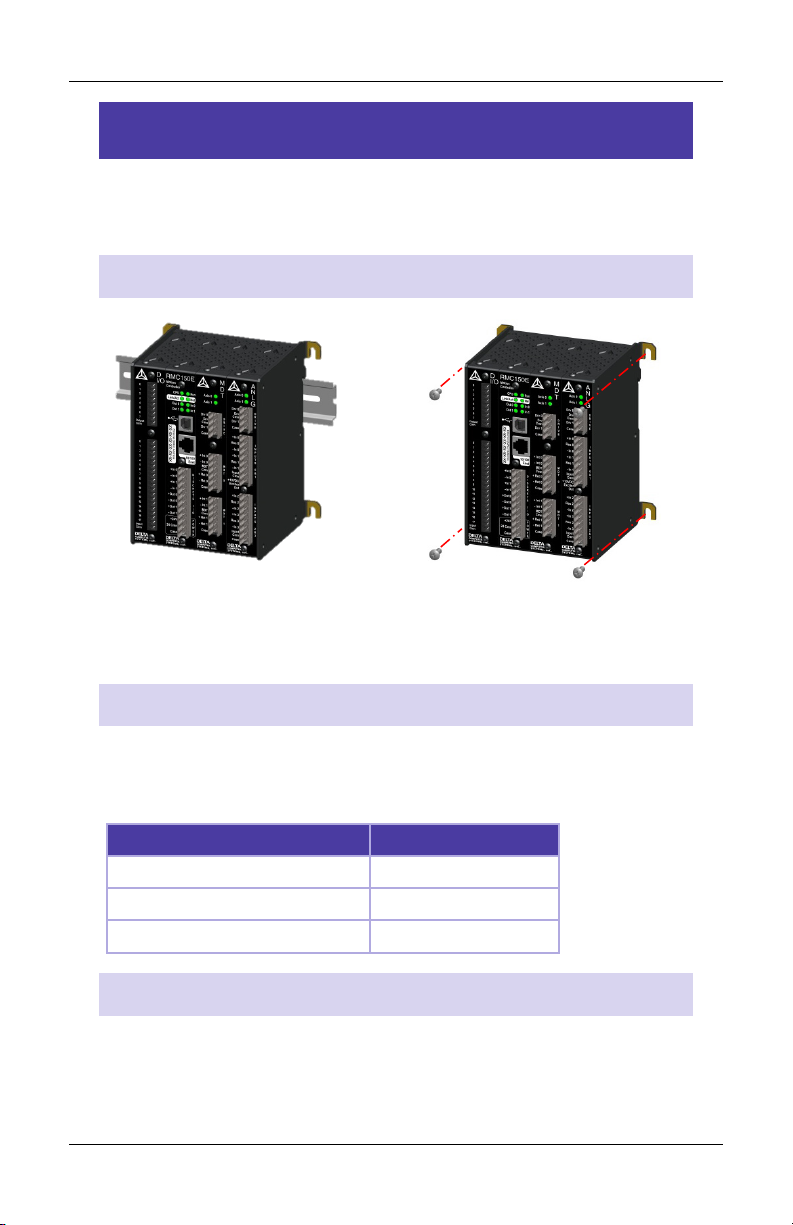
Step 1: Mounting
The RMC should be mounted upright on a vertical surface, such that
the ventilation holes are on the top and bottom.
Mounting Options
Symmetrical DIN 3 Panel-mount
See Appendix B: Mounting Dimensions for dimensions.
Clearance
The amount of clearance above and below depends on the maximum
ambient temperature:
Grounding
Make sure to properly ground the RMC. If mounted on a DIN rail, the
RMC will conduct to the DIN rail. The RMC shell is electrically
connected to its Case pins.
2 Delta Computer Systems, Inc.
Page 5
Step 2: Wiring
Wiring Topic
Page
General Wiring Information
27
Power
28
Control Output (Drive)
28
Start/Stop and PWM Inputs (Magnetostrictive)
29
SSI Inputs
31
Voltage Transducer
33
Potentiometer
34
Current Transducer
34
Resolver Inputs
36
Discrete Outputs
37
Discrete Inputs
38
Step 2: Wiring
Wire the power, actuators and feedback devices to the RMC according
to the instructions in Appendix A: Wiring on page 26.
Note: Remove power from the RMC before connecting any wires.
Analog Inputs
Discrete
Inputs/Outputs
deltamotion.com 3
Page 6

RMC150 Startup Guide
PC Requirements for RMCTools
Operating System*
Windows® XP/Vista/7/8
Memory
Minimum OS requirement
Hard Disk Space
20MB of available hard disk space
Display
1024x768 resolution with 16-bit color or
better
Accessories
Mouse or pointing device
Step 3: Install RMCTools
From CD
1. Insert the CD and wait for the splash screen to appear.
2. Click Install RMCTools and follow the instructions. If the splash
screen does not automatically open, run the autorun.exe file.
Download
1. Go to http://www.deltamotion.com/dloads/
2. Choose the RMC70 or RMC150 category, then choose the
Software category.
3. Choose the RMCTools 32-bit or 64-bit version as required for your
computer.
4. Run the rmctoolsinstall32.exe or rmctoolsinstall64.exe file and
follow the instructions.
Start RMCTools
On the Windows Start menu, choose All Programs and then
RMCTools.
*Windows XP requires Service Pack 2 or newer. Versions 3.37.1 (June 2010) and older
support Windows 2000 and Windows XP without SP2.
4 Delta Computer Systems, Inc.
Page 7

Step 4: Connect RMC to PC
Step 4: Connect RMC to PC
USB Cable
Connect a standard A to B USB cable to the
PC and to the RMC150E USB port .
This type of USB cable is used for PC
peripherals such as printers, and is available
at any store that sells electronics.
Or, use Ethernet Cable
Connect an Ethernet cable to the PC and the
RMC150E. The RMC150E supports both straight
through and crossover cables.
deltamotion.com 5
Page 8

RMC150 Startup Guide
Step 5: Start a New Project
1. Start RMCTools.
2. In the Startup dialog,
choose Create a New
Project and click OK.
3. Enter the Project Name,
then click Finish.
4. In the New Controller
Wizard, choose
Automatically Detect the
Controller Information,
then click Next.
6 Delta Computer Systems, Inc.
Page 9
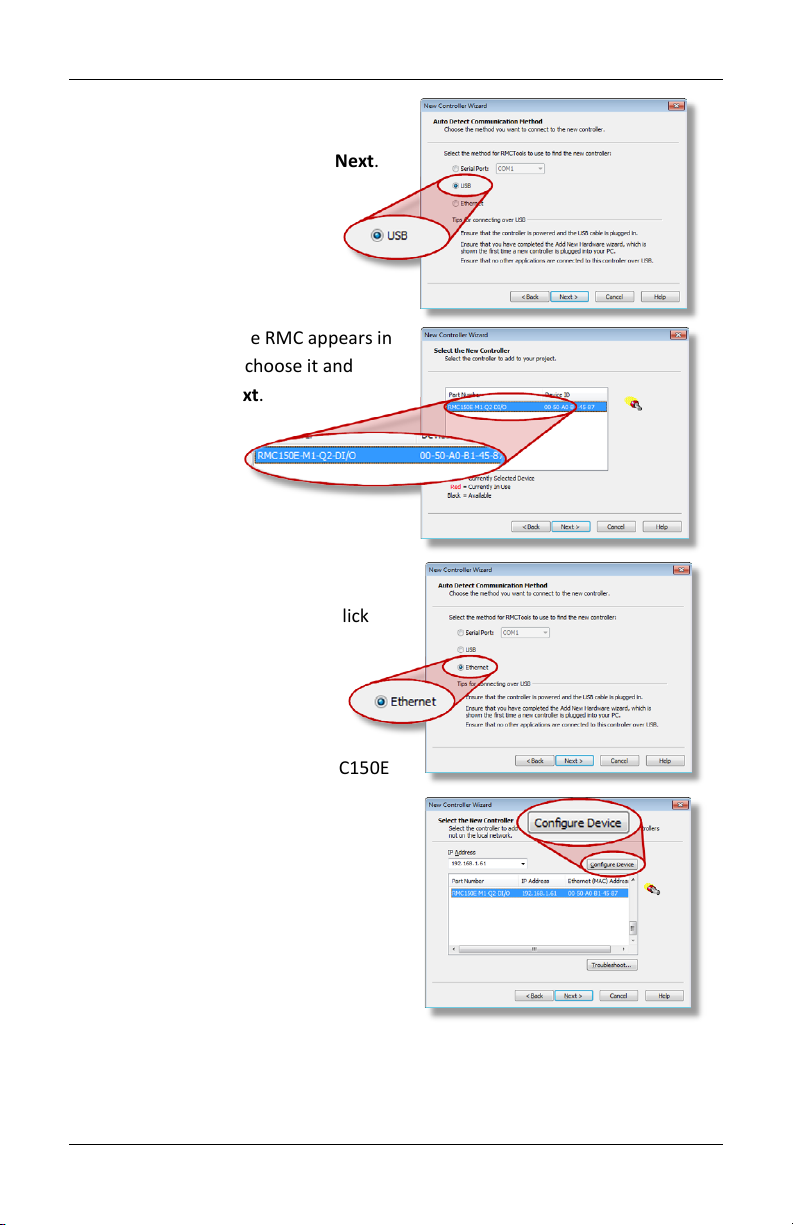
Step 5: Start a New Project
5. RMC150E via USB:
A. Click USB and click Next.
B. When the RMC appears in
the list, choose it and
click Next.
RMC150E via Ethernet:
A. Click Ethernet and click
Next.
B. Use the MAC
address (on the RMC150E
label) to identify the RMC
in the list, then click the
RMC.
C. If the RMC does not have
an IP address (0.0.0.0),
click Configure Device,
choose Use the following
IP address, set the IP
Address and Subnet Mask, then click OK.
D. Click Next.
deltamotion.com 7
Page 10

RMC150 Startup Guide
6. RMCTools will connect to the
RMC and display it.
Verify it is correct, then click
Finish.
7. The toolbar now displays . This means RMCTools is
communicating with the controller.
Project Pane
The project pane contains all
the items in the project. Use
the Project pane to navigate
through the entire project.
8 Delta Computer Systems, Inc.
Page 11

Step 5: Start a New Project
Set Up Universal I/O Channels
If your RMC includes a Universal I/O module, you must first set up the
high-speed channels before using them as part of an axis.
1. In the Project pane, expand the Modules folder and double-click
the UI/O module.
2. On the Quad/SSI page, choose the desired Mode for each
channel. Typically, this will be Quadrature Input or SSI Axis Input.
For more details, refer to the UI/O module topic in the RMCTools
help.
Saving Settings
Throughout the startup procedure, make sure to save the
configuration changes you make or they may be lost!
1. Save RMCTools Project
On the File menu, click Save.
2. Update Flash
On the Controller menu, click Update Flash.
IF YOU DO NOT UPDATE FLASH, CHANGES TO THE
RMC WILL BE LOST WHEN POWER IS REMOVED!
3. Repeat Often
Make sure to save often to prevent loss of data.
deltamotion.com 9
Page 12
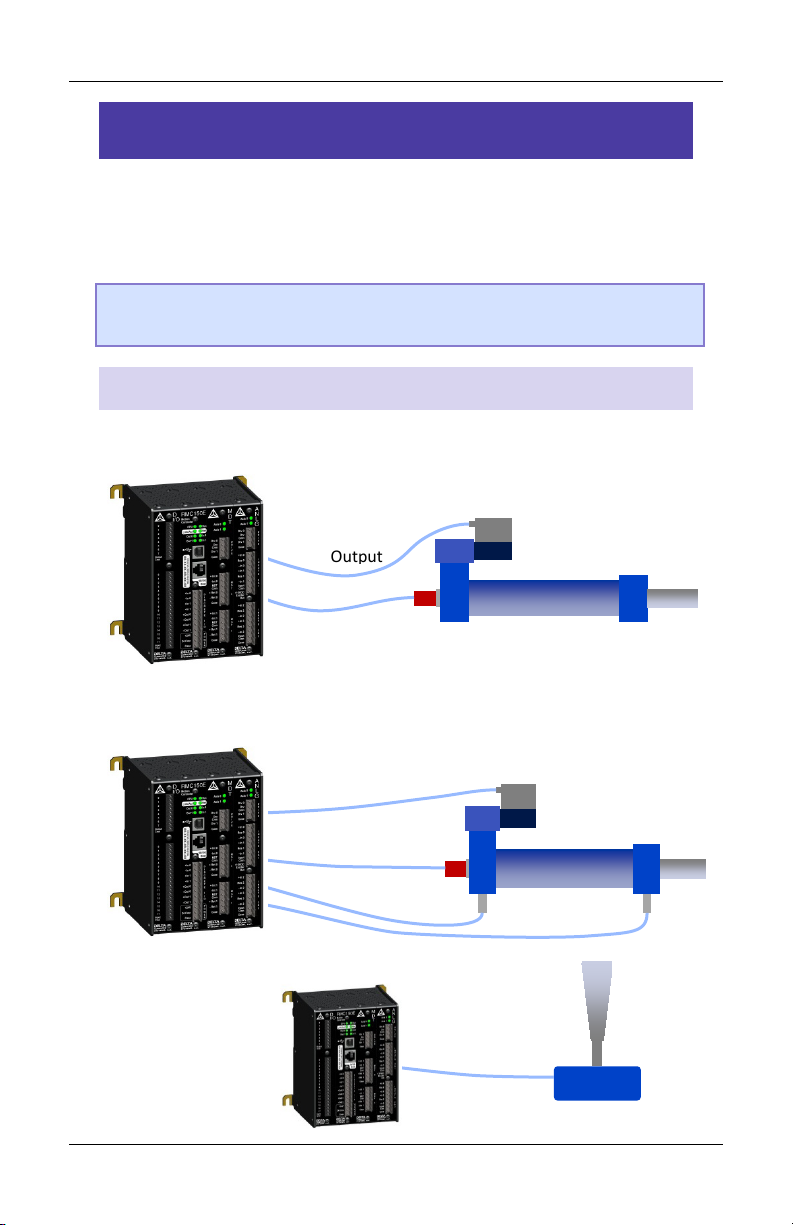
RMC150 Startup Guide
Control
Output
Position
Feedback
Dual-input Force Feedback
Valve
Hydraulic Cylinder
Analog
Position
Control
Output
Position
Feedback
Valve
Hydraulic Cylinder
Step 6: Define the Axes
To use a physical input or output, it must be assigned to an internal
software axis. The RMC starts with default axis assignments which you
will likely need to change.
Note: It is important to define the axes at the start of the project.
Major changes to axes later may result in lost axis parameters.
Example Axis Definitions
Position Control Axis
One Control Output, one position input.
Position-Force Control Axis (all part of a single axis)
One Control Output, one position input, dual-input force
Reference Axis
One position input.
Feedback
10 Delta Computer Systems, Inc.
Joystick
Page 13
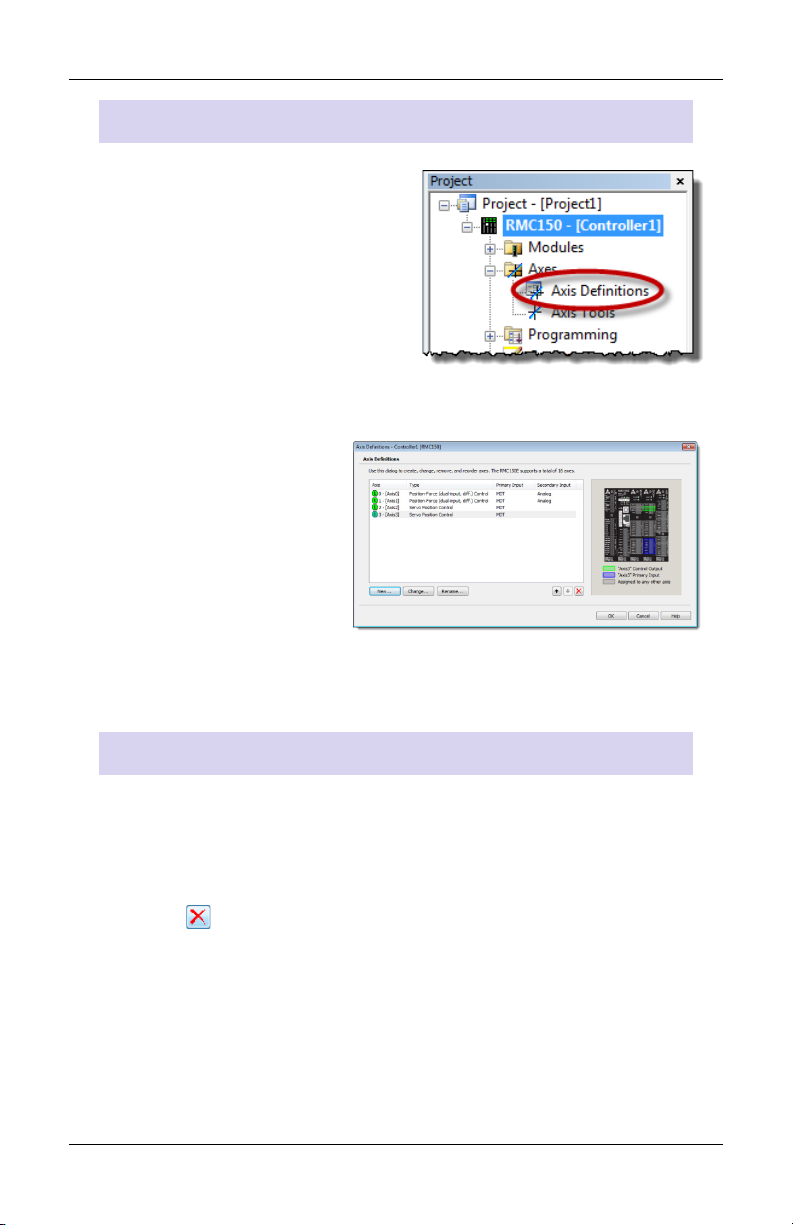
Step 6: Define the Axes
View Axis Definitions
1. In the Project tree, expand the
Axes folder and double-click
Axis Definitions.
2. The Axis Definitions dialog
opens:
The list displays the
software axes. To see
the assigned hardware,
click an axis in the list.
The hardware assigned
to that axis will be
highlighted in the
image.
Edit Axis Definitions
Use the Axis Definitions dialog to change the axis definitions:
• Click New to add an axis.
• Click Change to edit the selected axis.
• Click to remove an axis.
If you need to make significant changes to the axis definitions, first
delete all the axes, then create new ones.
For more details, click the Help button.
deltamotion.com 11
Page 14

RMC150 Startup Guide
Step 7: Test an Actuator
You will now test an actuator such as a hydraulic valve or a motor. You
will use the Direct Output command to send a voltage to the actuator.
The actuator must already have been wired to the RMC.
1. Check the machine and make sure that the axis may safely move
in both directions.
2. In the Project tree, double-click
Axis Tools.
3. In the Axis Status Registers, on
the Basic tab, look at the
Control Output.
It should be 0.
5. In the Command Tool, in the axis the actuator is connected to,
click the button.
12 Delta Computer Systems, Inc.
Page 15

Step 7: Test an Actuator
6. Browse to Motion Commands,
then Open Loop.
Choose the Direct Output
command and click OK.
7. For the Direct Output command
parameters, enter the following:
• Output: 0.1
• Ramp Rate: 100
When you send the command in the
next step, the Control Output voltage
will ramp to 0.1 V at a rate of 100
V/sec.
USE THE DIRECT OUTPUT COMMAND WITH CAUTION!
IT DISABLES THE SAFETY FEATURES OF THE RMC!
Fault Controller
Button
If the motion
causes problems,
be prepared to quickly stop the axis by clicking the Fault
Controller button on the toolbar, or pressing Ctrl + K on the
keyboard.
deltamotion.com 13
Page 16

RMC150 Startup Guide
8. In the Command Tool, click Send.
The axis should move, and the Control
Output (in the Axis Status Registers)
should be 0.100.
9. If the axis did not move, resend the command with a larger
Output until the axis moves.
Note: For the Quad module, if you are using the Enable
Output for enabling the actuator, such as a motor
drive, then you first need to set the Enable Output
before trying to move the actuator. For details, see the
Set Enable Output (67) Command topic in the
RMCTools help.
10. Now stop the axis:
In the Command tool, enter 0 in the
Output box and click Send.
11. Repeat these steps to move the axis in the other direction. In the
Direct Output command, use a negative Output.
Move the axis back and forth through the entire travel range to
make sure the machine is operating properly.
14 Delta Computer Systems, Inc.
Page 17

Step 8: Connect Feedback Device
Transducer Type
Module
Page
Start/Stop or PWM
(Magnetostrictive)
MDT (M)
16
SSI
(linear or rotary)
SSI (S),
Universal I/O (UI/O)
16
Analog
ANLG (H), ANALOG INPUTS (A),
Universal I/O (UI/O)
17
Quadrature Encoder
(A, B, Z)
QUAD (Q),
Universal I/O (UI/O)
17
Resolver
RESOLVER (R)
17
Step 8: Connect Feedback Device
Now that you have connected and tested an actuator, you will connect
and verify a feedback device. The device must already have been
wired to the RMC.
Configure Feedback
In Axis Tools, in the Axis Parameters pane, on the Setup tab, you will
configure certain parameters depending on the type of input you are
using.
Refer to the procedure for your transducer type and module:
(Voltage or Current)
deltamotion.com 15
ANLG2 (G),
Page 18

RMC150 Startup Guide
Start/Stop or PWM (Magnetostrictive) Feedback
1. In the Axis Parameters, on
the Setup tab, set the MDT
Type register to the type of
magnetostrictive transducer
you have.
This information is available
from your transducer
datasheet.
2. Click the Download button to apply the changes to the RMC.
3. Continue to the Verify Feedback section on page 18.
SSI Feedback
1. In the Axis Parameters pane,
on the Setup tab, set the
following cells.
• SSI Format
• SSI Data bits (e.g. 24)
• Linear/Rotary
This information is available
from your SSI device data
sheet.
Note: For help on a parameter, click the cell and press F1.
2. Click the Download button to apply the changes to the RMC.
3. Continue to the Verify Feedback section on page 18.
16 Delta Computer Systems, Inc.
Page 19

Step 8: Connect Feedback Device
Analog Feedback
1. In the Axis Parameters, on the
Setup tab, set the Input Type to
Voltage (±10V), Voltage (±5V) or
Current (4-20mA).
If the input is the primary input of
the axis, the Input Type is under
the Primary Control Setup section
in the Axis Parameters.
For pressure or force inputs on a dual-loop axis, the Input Type is
in the Secondary Control Setup section in the Axis Parameters.
2. Click the Download button to apply the changes to the RMC.
3. Continue to the Verify Feedback section on page 18.
Quadrature Encoder Feedback
The QUAD module does not require any configuration. Continue to the
Verify Feedback section on page 18.
Resolver Feedback
1. In the Axis Parameters pane, on the Setup tab, under Primary
Control Setup, set each register listed below, for each axis.
• Resolver Resolution – 14 bits or 16 bits
• Reference Frequency
• Reference Amplitude
Note: For help on these parameters, click the cell and press F1.
2. Click the Download button to apply the changes to the RMC.
3. Continue to the Verify Feedback section on page 18.
deltamotion.com 17
Page 20

RMC150 Startup Guide
Verify Feedback
1. In the Axis Status Registers
pane, on the All tab, expand the
Feedback section.
For secondary inputs, expand the
Pressure/Force/Accel Feedback
section.
2. Look at the Counts register (for analog feedback, look at Volts or
Current).
It may be changing slightly.
3. Use the Direct Output command to move the axis back and forth
(as described in the Testing an Actuator section).
4. As the axis moves, look for a corresponding change in the Counts,
Volts or Current. If it does not change smoothly, recheck the
wiring, verify that the parameters on the Setup tab are correct,
and check for smoothly changing Counts, Volts or Current again.
5. Save the project and update Flash.
18 Delta Computer Systems, Inc.
Page 21

Step 9: Scale and Offset
Step 9: Scale and Offset
The Scale and Offset parameters convert the Counts, Volts or Current
from the transducer into meaningful measurement units, such as
inches, millimeters, pounds, Newtons, etc. RMCTools provides
Scale/Offset wizards to help you calculate these parameters.
Before starting, determine approximately what the positions should
be at either end of travel. This will help you verify later that you
performed the Scaling and Offset procedure correctly.
To set the Scale and Offset:
1. Go to the Axes Parameters
pane, Setup tab, Tools and
Wizards section.
2. Click Launch in the desired
axis.
3. In the wizard, follow the directions. For help, press the Help
button.
4. After completing the wizard, click the Download button to
apply the changes to the RMC.
5. Remember to save your project and update Flash.
Tip: If the wizard does not work for your system, you can manually
determine the Scale and Offset parameters. See the Scaling topic
in the RMCTools help for details.
deltamotion.com 19
Page 22

RMC150 Startup Guide
Step 10: Set the Output Polarity
The Actual Position, Pressure, Force or Velocity must increase when
the RMC applies a positive output voltage. If this condition is not met,
you will not be able to perform closed-loop control.
1. Send the Direct Output command with a positive Output value
that is large enough to move the axis.
2. On the Basic tab of the Axis Status Registers pane, observe the
Actual Position and note whether it is increasing or decreasing:
Increasing
The Output Polarity is correct. Go to Enable the Axes below.
Decreasing
You must invert the Output Polarity:
A. In the Axis Parameters pane, on the Setup tab, double-click
the Invert Output Polarity parameter to set it.
B. Click the Download button to apply the change to the
RMC.
Enable the Axes
In order to send motion commands other than Direct Output, the axes
must be enabled after the RMC starts up.
1. In the Command Tool, in the Cmd box,
type Enable, and choose
Enable Controller (7) from the list.
2. Click Send. All axes will be enabled.
Entering RUN Mode will also enable the
axes.
20 Delta Computer Systems, Inc.
Page 23

Step 11: Tuning
Step 11: Tuning
In order to control an axis in closed-loop, it must first be tuned. You
can use autotuning or manually tune the axis.
Autotuning – Position Axes Only
Autotuning can be used for most
position control axes.
1. Open Tuning Tools
On the Tools menu, click
Tuning Tools.
2. Set Up Tuning Tools
Set up the buttons that you will use
to move the axis back and forth
after autotuning is complete.
• Click the first button labeled
[Click to set up].
• Enter a Move Absolute
command with position, speeds,
and acceleration values that will
work for your system.
• Repeat for the other button,
with a different position.
3. Start the Tuning Wizard
In the Tuning Tools, click Tuning
Wizard.
4. Complete the Autotuning Wizard
During the autotuning, the wizard
will move the axis a short distance when you prompt it to.
deltamotion.com 21
Page 24

RMC150 Startup Guide
5. When the wizard is complete, the Gain Calculator will open. Use
the slider bar to choose gains. Begin by pulling the slider close to
the bottom, then click Apply Gains.
6. Use the buttons you previously set up to move the axis back and
forth. The plot will automatically be displayed.
Tip: To halt the axis, click the Fault Controller button on the
toolbar, or press Ctrl+K.
7. If the Actual Position is not following the Target Position very well,
pull the slider bar up, apply gains, and move the axis again.
Repeat until the Actual Position tracks the Target Position very
well.
Manual Tuning– Position, Pressure, or Force Axes
You can manually tune systems for which autotuning does not work.
For instructions:
1. On the help menu, choose Help Topics.
2. On the Index tab, type tuning and double-click about.
3. The Tuning Overview topic describes tuning.
In the Manual Tuning section, choose a procedure. For most
position control applications, choose Tuning a Hydraulic Position
Axis or Motor in Velocity Mode. For pressure or force, choose the
procedure that applies to your axis.
After tuning, save the project and update Flash.
22 Delta Computer Systems, Inc.
Page 25

Continuing the Motion Application
Continuing the Motion Application
After setting up and tuning the RMC, it is ready to perform motion and
be integrated into the rest of your application. The RMC has numerous
features to assist you. The major components are listed here to guide
you when continuing your motion application.
Commands
The RMC has a rich set of pre-programmed commands that perform
anything from simple moves to complex motion to system control. For
a list of all the commands, see the Command List topic in the
RMCTools help.
User Programs
A User Program carries out simple or advanced sequences of
commands on the RMC. This allows the RMC to respond to events
within its control-loop time rather than the scan rate of a PLC or other
host controller. It also reduces the PLC programming required.
A User Program consists of multiple steps linked together in
sequences. Each step can issue any RMC command to one or several
axes. The link types allow branching and looping, waiting for
conditions and many other features. Simple and complex
mathematical operations are also possible in the user program.
A User Program runs on a task. Each task can run one user program at
a time. The RMC150 has ten tasks. Therefore, an RMC150 controller
may run up to ten User Programs simultaneously.
For details on creating and running User Programs, see the User
Programs topic in the help.
deltamotion.com 23
Page 26

RMC150 Startup Guide
Communications
Most PLCs or other host controllers can communicate with the RMC,
which includes reading status, writing values, and sending commands
to the RMC. The RMC150E supports Ethernet and PROFIBUS-DP.
See the Communications section of the RMCTools help for more
detailed information.
Discrete I/O
Discrete I/O augments the communications of the RMC. Discrete I/O is
often faster than the communications, and is therefore well-suited for
starting a sequence in the RMC at a specific time. See the Discrete I/O
topic in the RMCTools help for details.
Variables
Variables help make the User Programs very flexible and easy to
maintain. Variables can be used to effortlessly change programs and
easily modify User Program parameters via a PLC. Variables can also
be used to store data.
For details on using variables, see the Variables topic in the help.
Program Triggers
Use the Program Triggers to start User Programs based on conditions
defined by the user. For example,
• Start a User Program by writing to an RMC variable from a PLC.
• Start a User Program when a discrete input turns on.
• Automatically start a User Program when the RMC starts up.
• When an error condition occurs, automatically start a User
Program to handle it.
See the Program Triggers topic in the RMCTools help for details.
24 Delta Computer Systems, Inc.
Page 27

Diagnostic Tools
Diagnostic Tools
This section describes the main diagnostic tools of RMCTools that will
aid you in monitoring and troubleshooting your system.
Plots
The RMC provides very flexible plotting capabilities. Virtually any
register in the RMC can be plotted, and multiple registers may be
plotted simultaneously. You can easily capture events with the plot
trigger. For details on using plots, see the Plots topics in the help.
Event Log
The Event Log Monitor displays all events that have occurred in the
controller, such as issued commands, changed parameters and errors.
The Event Log Monitor is an important aid in troubleshooting.
The Event Log can help you:
• Determine if a command was successfully issued. The entire
command, with parameters, is displayed.
• Find out which, if any, error occurred.
• See where a command was issued from, for example, from a PLC,
from a User Program or from the Command Tool.
To open the Event Log:
• In the Project Pane, expand the controller, and double-click Event
Log .
Note: The Event Log is very useful! When you don’t know what
happened, or why something did not happen, look at the
Event Log.
deltamotion.com 25
Page 28

RMC150 Startup Guide
Wiring Topic
Page
General Wiring Information
27
Power
28
Control Output (Drive)
28
Start/Stop and PWM Inputs (Magnetostrictive)
29
SSI Inputs
31
Voltage Transducer
33
Potentiometer
34
Current Transducer
34
Resolver Inputs
36
Discrete Outputs
37
Discrete Inputs
38
Appendix A: Wiring
This appendix describes how to wire the RMC. Use the table below to
find the wiring diagram you need. For communications wiring, consult
the RMCTools help.
Note: Remove power from the RMC before connecting any wires.
Analog Inputs
Discrete
Inputs/Outputs
26 Delta Computer Systems, Inc.
Page 29

Appendix A: Wiring
Module
Gauge
Torque
RMC150E, MDT (M), SSI (S),
Analog (H, A, G), RES (R)
26-12 AWG
( 0.13 - 3.3 mm2)
4.5 lb-in
(0.51 Nm)
DI/O, UI/O
28-16 AWG
( 0.08 - 1.3 mm2)
2.2 lb-in
(0.25 Nm)
General Wiring Information
For CE compliance and to minimize electrical interference:
• Use twisted pairs for all wiring where possible.
• Use shielded cables for all wiring.
• Keep RMC wiring separate from AC mains or conductors carrying
high currents, especially high frequency switching power such as
conductors between servo drives and motors or amplifiers and
proportional valves.
For UL and CUL compliance:
• Power supply must be Class 2.
• All RMC inputs and outputs must be connected to Class 2 circuits
only.
For products labeled Class I, Division 2:
• Conductors must be copper only. Follow wire gauge and clamp
screw torque as listed below.
Wire Gauge and Clamp Screw Torque
Use the table below to determine proper wire gauge and torque for
the clamp screws on the terminal blocks.
deltamotion.com 27
Page 30

RMC150 Startup Guide
Drive or Amplifier4-pin Drive
Connector
Drv 0 or Drv 1
Drv Cmn
Case
Shield
+ Ref In
- Ref In
Cmn
To machine common
RMC
150E
Power Supply
+24 VDC
Cmn
Protective Earth
Ground
+24V
24 Cmn
Case
AC
Line
Backplane Slots
3 4 5 6 Max Current (mA)
375
500
625
750
Wiring Power
Voltage: +24VDC ( 20.4 – 27.6VDC)
Current rating:
UL and CUL Requirements
For UL and C-UL compliance, the power supply must be Class 2. Class 2
power supplies are limited to 100W output. No additional fusing is
required if a class 2 power supply is used.
Power Wiring Diagram
Note: For optimum power stability, do not power high-current-draw
Control Output for all Axis Modules
28 Delta Computer Systems, Inc.
devices with the same 24V power supply used for the RMC.
The RMC may restart if it experiences a momentary power
drop.
Page 31

Appendix A: Wiring
6-pin MDT
Connector
Interrogate +
Interrogate -
Return +
Return -
Power Supply
+Pwr
Cmn
Int+
Int-
Cmn
Ret+
Ret-
Case
Pwr+
DC Ground
Notes:
MDT Module Start/Stop or PWM Transducer Wiring
For magnetostrictive transducers with Start/Stop or PWM outputs.
Tip: See next page for manufacturer-specific wiring diagrams.
• The MDT module interfaces to 5V differential (RS-422) signals.
Single-ended (TTL) signals are strongly discouraged. See the
deltamotion.com 29
RMCTools help for single-ended wiring diagrams.
• The user must supply power to the transducer.
• Do NOT connect the transducer ground or common to the shield,
case, or protective earth ground.
Page 32

RMC150 Startup Guide
6-pin MDT
Connector
(+) Interrogation
(-) Interrogation
(+) Gate Out, (+) Start/Stop
+Pwr
Cmn
Int+
Int-
Cmn
Ret+
Ret-
Case
+ VDC
DC Ground
Yellow
Green
Pink
Gray
Red
White
(-) Gate Out, (-) Start/Stop
or
or
or
or
or
or
Wh/Gy
Gy/Wh
Or/Wh
Wh/Or
Wh/Gr
Wh/Bu
- VDC
Frame
-Pwr
Blue
or Gr/Wh
Brown
or Bu/Wh
6-pin MDT
Connector
(+) Interrogation or Start
(-) Interrogation or Start
(+) Gate or (+) Stop
+Pwr
Cmn
Int+
Int-
Cmn
Ret+
Ret-
Case
Customer Supplied Power (+Vdc)
DC Ground
Yellow
Green
Pink
Gray
Red or Brn
White
(-) Gate or (-) Stop
6-pin MDT
Connector
Interrogate + Input
Interrogate - Input
Pulse + Output
Pulse - Output
+PwrCmn
Int+
Int-
Cmn
Ret+
Ret-
Case
Pwr+
GND
Yellow
Pink
Gray
Green
Brown
Blue
White
GND
White wire must remain unconnected.
MDT Manufacturer-Specific Wiring Labels and Colors
These diagrams provide transducer manufacturer labels and colors.
Follow all MDT wiring instructions on page 29.
Balluff Micropulse BTL-5, digital RS-485 output
Styles: Z, W, K, E, P, R, AT
MTS Temposonics with digital output (Start/Stop or PWM)
Models: LH, LS, LD, LF, LPS, LPR, G, EP2, ER
MTS Temposonics II with DPM or RPM personality module
30 Delta Computer Systems, Inc.
Page 33

Appendix A: Wiring
Input
Connector
Clock+
Clock-
Data+
Data-
Power Supply
+Pwr
Cmn
Clk+
Clk-
Cmn
Dat+
Dat-
Case
Pwr+
DC Ground
Universal I/O Module:
Notes:
SSI Transducer Wiring
For Synchronous Serial Interface (SSI) transducers and encoders.
If the SSI transducer is linear, make sure to choose the synchronized
type.
Tip: See next page for manufacturer-specific wiring diagrams.
The Universal I/O SSI input wiring is identical to the diagram shown
above, with the exception of the pin order. For details, see the
UI/O Module Wiring topic in the RMCTools help.
• The user must supply power to the transducer.
• Do NOT connect the transducer ground or common to the shield,
case, or protective earth ground
deltamotion.com 31
Page 34

RMC150 Startup Guide
Input
Connector
+ Clk
- Clk
+Data
-Data
+PwrCmn
Clk+
Clk-
Cmn
Dat+
Dat-
Case
+24 V
GND
Yellow
Pink
Gray
Green
Brown
Blue
Input
Connector
(+) Clock
(-) Clock
(+) Data
+PwrCmn
Clk+
Clk-
Cmn
Dat+
Dat-
Case
+24 Vdc, Customer Supplied
DC Ground
Yellow
Green
Pink
Gray
Red or Brn
White
(-) Data
SSI Manufacturer-Specific Wiring Labels and Colors
These diagrams provide transducer manufacturer labels and colors.
Follow all SSI wiring instructions on page 31.
Balluff Micropulse BTL-5 with SSI output
Styles: Z, W, K, P
MTS Temposonics with SSI output
Models: R, RP, RH
32 Delta Computer Systems, Inc.
Page 35

Appendix A: Wiring
Input
Connector
+Analog Out
-Analog Out
Pwr Common
+Pwr
Power Supply
+Pwr
Cmn
+ In
Res or Jmpr
- In
Cmn
Case
Signal Common
Input
Connector
+Analog Out
Common
Power Supply
+24 VDC
Cmn
+ In
Res or Jmpr
- In
Cmn
Case
+Pwr
To reduce electrical interference:
connection at the transducer.
Analog Voltage Transducer Wiring
Voltage Transducer, 4- or 5-Wire
• -In and Cmn must be connected,
Voltage Transducer, 3-Wire
either internal to the transducer
or externally as close as possible
to the transducer.
• Use individually shielded
twisted-pair wire.
• Connect cable shield to earth
ground on one end only.
• If transducer has only one
common, connect Pwr Supply
Common and RMC Cmn to it. For
best results, make this
deltamotion.com 33
Page 36

RMC150 Startup Guide
Input
Connector
+ In
Res
- In
Cmn
+10VDC Exciter
Case
Potentiometer
Wiper
Input
Connector
+Analog Out
Power Supply
+24 VDC
Cmn
+ In
Res or Jmpr
- In
Cmn
Case
+Pwr
To reduce electrical interference:
• Connect cable shield to ground on one end only.
The Res and -In pins are
twisted-pair wire.
Potentiometer with Exciter Pin
Note: Use the Exciter pin to increase the measurement accuracy of
the potentiometer. Not available on the UI/O module.
• The connection of -Analog In to Cmn should be
made as close as possible to the transducer.
• Use individually shielded twisted-pair wire.
Analog 4-20 mA
Note: The Analog (G) module does not support 4-20 mA.
34 Delta Computer Systems, Inc.
internally connected via
a 250 Ω resistor.
To reduce noise, use
individually shielded
Page 37

Appendix A: Wiring
25-
pin Axis
Connector
A-
A+
B+
Z-
Power Supply
+
Pwr
Cmn
Pin 1: A-
Pin 2: A+
Pin 3: B-
Pin 4: B+
Pin 14: Z-
Cmn
Z+
B-
Pin 15: Z+
25
-pin Axis
Connector
Pin 6: RegY/NegLim-
Pin 7: RegY/NegLim+
Pin 8: RegX/PosLim-
Pin 9: RegX/PosLim+
Pin 18: Home-
Pin 19: Home+
Pwr+
Common
Drive or Amplifier
Pin 21: Flt In+
Pin 20: Flt In-
Enable or Inhibit
Pin 25: EnOut+
Pin 24: EnOut-
+VCC (12-24 VDC)
Apply 12-24 VDC across input to turn on
Apply 12-24 VDC across input to turn on
Apply 12-24 VDC across input to turn on
Apply 12-24 VDC across input to turn on
Important!
Reg/Lim and Home Inputs
Universal I/O Module
Quadrature Encoder Wiring
Pin-out table is available in the RMCTools help.
The A, B and Z signals accept 5 V
differential (RS-422) signals. Singleended (TTL) are strongly discouraged. If
absolutely necessary, see the RMCTools
help for single-ended wiring.
The Universal I/O encoder wiring is identical to the diagram shown
above, with the exception of the pin order. For details, see the UI/O
Module Wiring topic in the RMCTools help.
Compatible with 5-24 VDC. They draw 3.5 mA min, 10 mA max.
deltamotion.com 35
Page 38

RMC150 Startup Guide
8-pin Resolver
Connector
Ref Winding +
Ref Winding -
Sin Winding -
Cos Winding +
R1
Ref In
R3
S1
S3
S4
Cos Winding -
Sin Winding +
S2
Case
Pin
Function
R1
Reference Output +
Ref In
Reference In (normally not used)
R3
Reference Output -
S1
Sine Input +
S3
Sine Input -
S2
Cosine Input +
S4
Cosine Input -
Case
Controller Chassis Ground (shield)
Resolver Module Transducer Wiring
The wiring diagram below is for resolvers that fall within the Resolver
module’s signal specifications (800 Hz to 5 kHz and 1.41 to 4.8 VRMS).
The Ref In input is only used for reference signals outside of these
specifications, and requires contacting Delta for assistance.
36 Delta Computer Systems, Inc.
Page 39

Appendix A: Wiring
RMC150E
DI/O
UI/O
On Impedance
50Ω max, 25Ω typical
Max Current
75 mA
(50 mA for Class I Div 2)
75 mA
(Class I Div 2 not available)
Max Voltage
30 V
RMC150E
Resistive
load
+VCC (12-24 VDC)
Output +
Output -
RMC150E
+VCC (12-24 VDC)
Output +
Output -
Resistive
load
RMC Module
+VCC (12-24 VDC)
Output
Output
Resistive
Load
…
Output Cmn
RMC Module
+VCC (12-24 VDC)
Output
Output
Resistive
Load
…
Output Cmn
Discrete Output Wiring
The RMC150E, DI/O and UI/O outputs are solid state relays. When off,
they have high impedance, and when on, they have low impedance.
When switching inductive loads, place a diode or tranzorb across the
load to protect the switch when it turns off. Otherwise, a voltage spike
in excess of the 30 V rating of the SSR may occur. See the RMC150E
Discrete I/O Wiring topic in the RMCTools help for more details.
DI/O and UI/O Module
Outputs can be wired in either a high-side or low-side configuration.
Because all the outputs share a common, all outputs on the same
module must be wired the same.
RMC150E Module
Each output has a “+” and “–” connection. Outputs can be wired in
either a high-side or low-side configuration.
deltamotion.com 37
Page 40

RMC150 Startup Guide
PLC
RMC Module
Input
b
Input Common
Power
Output
Input a
Output
RMC150E
DI/O
UI/O
Signal Levels
12-24 VDC
5-24 VDC
12-24 VDC
Max Current
Draw
3 mA max
6 mA at 5V
10 mA at 24V
3 mA max
RMC Module
Input +
Input -
Apply 12-24 VDC across
input to turn on
PLC
RMC Module
Input +
Input -
Power
Output
Discrete Input Wiring
To turn on a discrete input, apply a voltage of the correct level. The
polarity is unimportant.
DI/O and UI/O Module
Because all the inputs share a common, all inputs on the same module
must be wired the same.
Example
38 Delta Computer Systems, Inc.
RMC150E Module
Each input has a “+” and “–” connection.
Example
Page 41

Appendix B: Mounting Dimensions
Backplane Slots
3 4 5
6
Total Width
4.10 in.
(104.1 mm)
5.10 in.
(129.5 mm)
6.10 in.
(154.9 mm)
7.10 in.
(180.3 mm)
Note: Allow space for
Appendix B: Mounting Dimensions
deltamotion.com 39
the connectors on the
front of the RMC.
Page 42

RMC150 Startup Guide
Appendix C: Agency Compliance
CE
For CE compliance and to minimize electrical interference:
• Use twisted pairs for all wiring where possible.
• Use shielded cables for all wiring.
• Keep RMC wiring separate from AC mains or conductors carrying
high currents, especially high frequency switching power such as
conductors between servo drives and motors or amplifiers and
proportional valves.
UL and CUL
For UL and CUL compliance:
• Power supply must be Class 2.
• All RMC inputs and outputs must be connected to Class 2 circuits
only.
Class I Div 2
Products marked “Class I Division 2, Group A, B, C, D” are suitable for
use in Class I Division 2, Groups A, B, C, and D hazardous locations and
nonhazardous locations only.
WARNING – EXPLOSION HAZARD – DO NOT DISCONNECT EQUIPMENT
WHILE THE CIRCUIT IS LIVE OR UNLESS THE AREA IS KNOWN TO BE
FREE OF IGNITABLE CONCENTRATIONS.
WARNING – EXPLOSION HAZARD – SUBSTITUTION OF ANY
COMPONENT MAY IMPAIR SUITABILITY FOR CLASS I, DIVISION 2.
Surrounding air temperature of 60° C.
The RMC150E USB port is intended for configuration, programming,
and troubleshooting purposes only. It should not be connected during
normal operation.
See page 27 for wire gauge, screw clamp torque and wire type
requirements.
40 Delta Computer Systems, Inc.
Page 43

deltamotion.com 41
Page 44

 Loading...
Loading...