
Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point
Installation Guide
The Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 is a resilient, environmentally hardened, outdoor rated, dual-radio, dual-band
IEEE 802.11 a/b/g/n wireless access point. This outdoor access point is part of Dell’s comprehensive wireless
network solution. The W-AP175 works only in conjunction with an Dell PowerConnect W-Series controller and
each AP can be centrally managed, configured, and upgraded through the controller.
NOTE: The W-AP175P requires ArubaOS 5.0.2.1 or later. The W-AP175AC and W-AP175DC require ArubaOS 6.1.2.3 or later.
There are three versions of the W-AP175, which mainly differ in the way they receive power.
W-AP175P: PoE+ powered (802.3at)
W-AP175AC: AC powered (100-240 V AC)
W-AP175DC: DC powered (12-48 V DC)
NOTE: The W-AP175AC/DC can function as a Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE) device by providing power through its ethernet
port in compliance with the IEEE 802.3af standard.
Guide Overview
“W-AP175 Hardware Overview” on page3 provides a detailed hardware overview of the three W-AP175
models.
“Outdoor Planning and Deployment Considerations” on page7 provides key questions to ask and items to
consider when deploying an outdoor wireless network.
“Installing Antennas” on page11 describes how to installing antennas.
“Weatherproofing Connections” on page12 provides instructions on weatherproofing the AP’s connectors.
“Installing the W-AP175” on page20 describes the multi-step process for a successful installation and
deployment of an W-AP175.
“Safety and Regulatory Compliance” on page30 provides an overview of safety and regulatory compliance
information.
W-AP175 Operations
Wireless access point (IEEE 802.11 a/b/g/n)
Wireless air monitor (IEEE 802.11 a/b/g/n)
Enterprise mesh point
Enterprise mesh portal
Protocol-independent networking functionality
W-AP175P: IEEE 802.3at Power over Ethernet+ (PoE+) compatible
W-AP175AC and W-AP175DC: IEEE 802.3af Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE) device
0511047-01 | January 2012 1

Package Contents
W-AP175 Access Point
W-AP175 Mounting Bracket
Solar Shield
Pole Anchors x 2
M4 x 16 bolts, flat washers, and spring washers x4 (These bolts are attached to the solar shield)
M6 x 30 bolts, flat washers, and spring washers x2
M4 x 12 bolt, external-tooth washer, and OT copper lug x1
M8 x 110 bolt, flat washers, spring washers, and nuts x4
Metal Weatherproof Caps x2 for use on unused antenna interfaces
RJ-45 Connector Kit with plastic RJ-45 connector (W-AP175P only)
RJ-45 Connector Kit with metal RJ-45 connector (W-AP175AC/DC only)
USB Console Cable
Installation Guide
NOTE: Inform your supplier if there are any incorrect, missing, or damaged parts. If possible, retain the carton, including the
original packing materials. Use these materials to repack and return the unit to the supplier if needed.
2 Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide
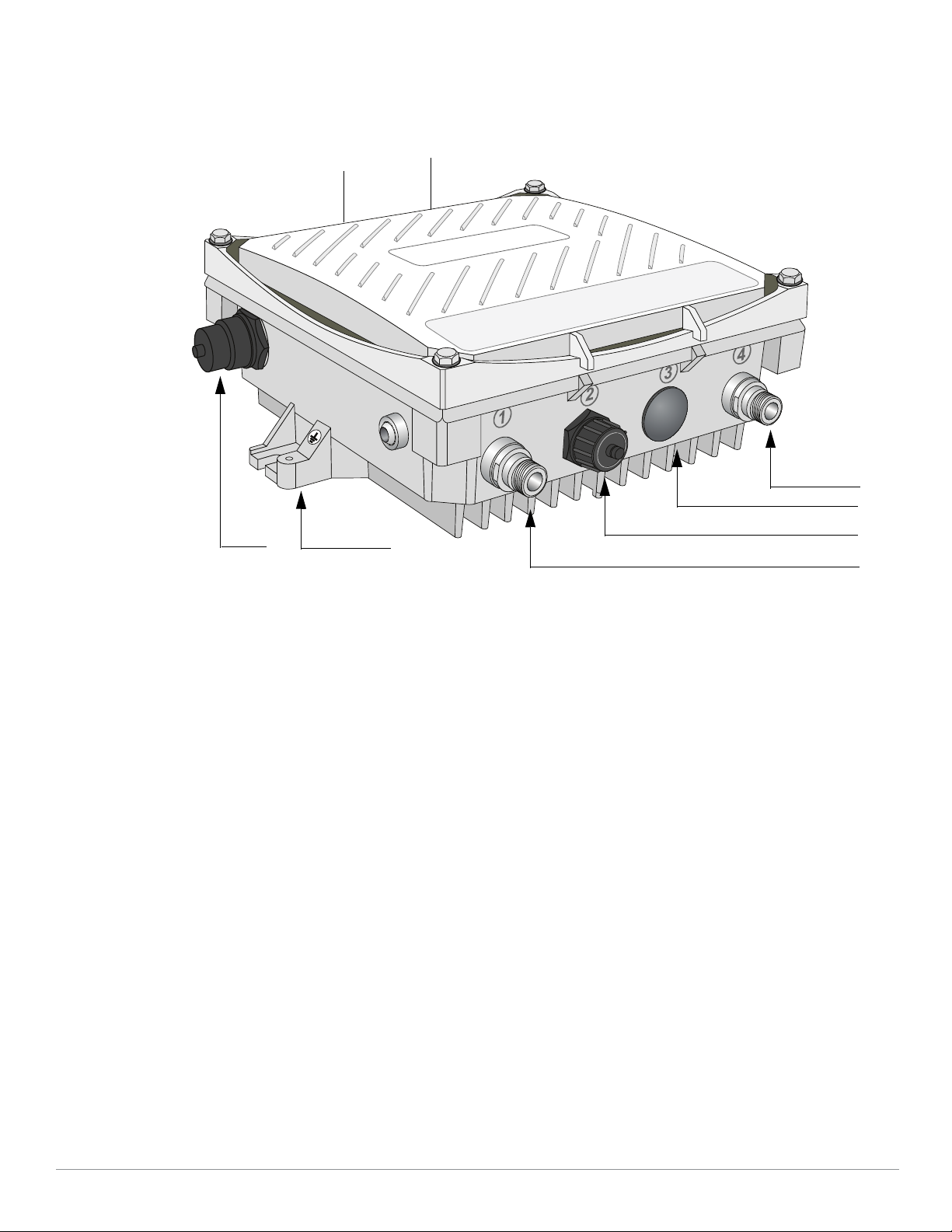
W-AP175 Hardware Overview
2
1
3
4
8
7
6
5
The following section describes the hardware features of the W-AP175.
Figure 1
W-AP175 Overview (W-AP175P shown)
1 Antenna Interface (Radio 1) 5 Antenna Interface (Radio 0)
2 USB Console Interface 6 Antenna Interface (Radio 1)
3 Reserved (W-AP175P) or
Power Interface (W-AP175AC and W-AP175DC)
4 Antenna Interface (Radio 0) 8 Grounding Point
Antenna Interface
The W-AP175 requires the use of detachable outdoor-rated antennas. Select the correct antenna type to support
7 Ethernet Interface (PoE)
the required frequency band (2.4 or 5 GHz) and the desired coverage pattern.
The W-AP175 is equipped with four, female N-type antenna interfaces; two on the top of the AP and two on the
bottom. The interfaces are grouped into diversity pairs, one pair is marked R0 (Radio 0) and the other pair
marked as R1 (Radio 1). R0 supports the 5 GHz frequency band and R1 supports the 2.4 GHz radio band.
Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide 3

USB Console Interface
A USB serial console port is provided for connection to a terminal, allowing direct local management. Use the
included USB console cable to connect to the AP. You can download the necessary driver for USB-UART adapter
from download.dell-pcw.com under Tools & Resources.
Use the following setting to access the terminal:
Table 1
Console Settings
Baud Rate Data Bits Parity Stop Bits Flow Control
9600 8 None 1 None
Power Interface
The type of power interface on your W-AP175 depends on which model you have purchased.
W-AP175P: This version does not include a power interface since it is only powered by PoE+ (802.3at).
W-AP175AC: 1x AC power connector
W-AP175DC: 1x DC power connector
CAUTION: Do not connect a DC power cable to an W-AP175AC or an AC power cable to a W-AP175DC.
CAUTION:
For the W-AP175AC, only use the AC power cord with model number CBL-AC-INTL.
For the W-AP175DC, only use DC power cord with model number CBL-DC-WW.
Ethernet Interface
The W-AP175 is equipped with a 10/100/1000Base-T Gigabit Ethernet port for wired network connectivity. On
the W-AP175P, this port also supports IEEE 802.3at Power over Ethernet (PoE), accepting 48 VDC as a
standards-defined powered device (PD) from a power sourcing equipment (PSE) device, such as a PoE midspan
injector. Inversely, the W-AP175AC and W-AP175DC can act as a PSE device to provide IEEE802.3af PoE
power to devices connected to the ethernet port.
Grounding Point
Always remember to protect your W-AP175 by installing grounding lines. The ground connection must be
complete before connecting power to the W-AP175 enclosure. Ensure that the resistance is less than 5 ohm
between the ground termination point and the grounding tier.
4 Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide
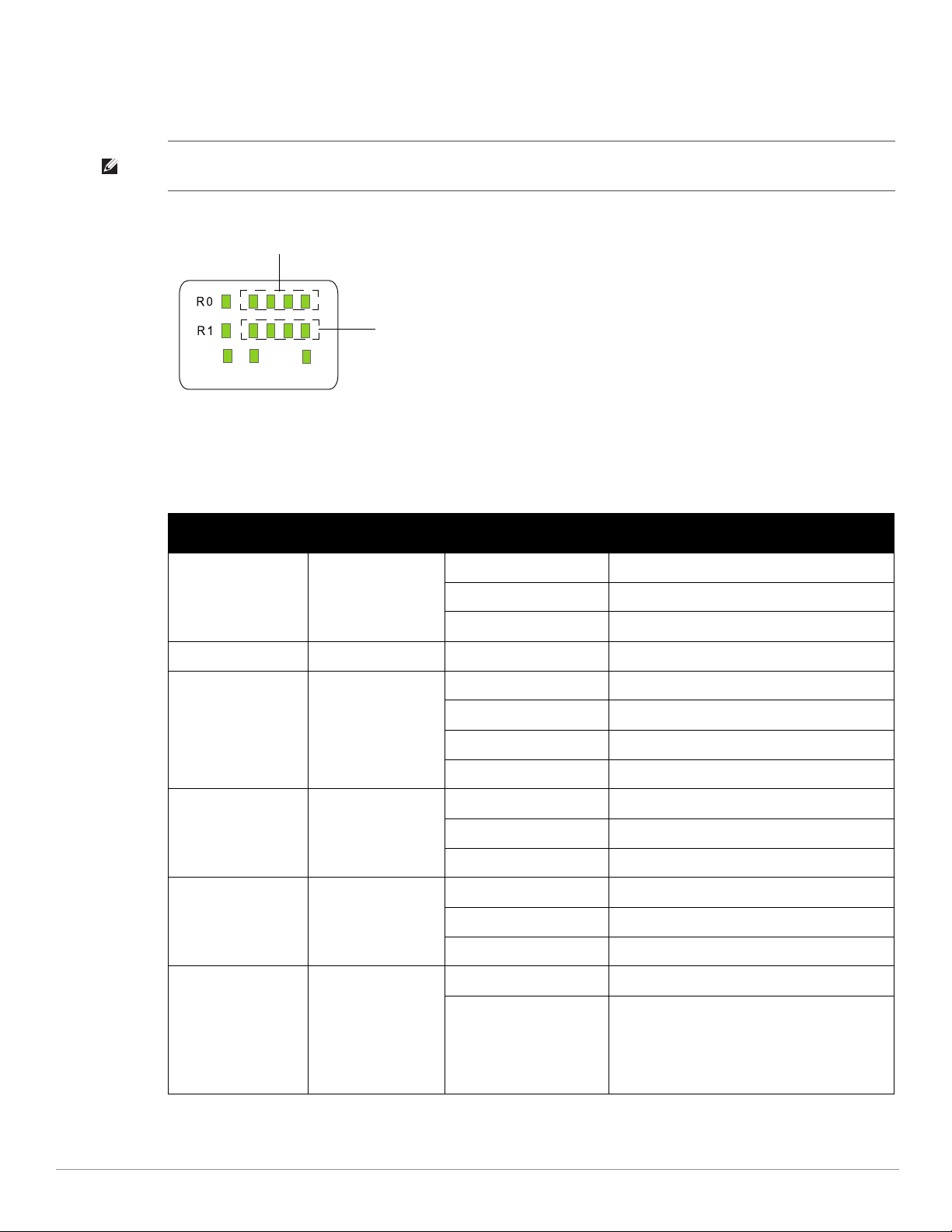
W-AP175P LED Status Indicators
P/S
ENT
POE
RSSI for Radio 1
RSSI for Radio 0
The W-AP175 include visual indicators for power, link, and radio status. Additionally, each radio has a four-LED
array that indicates received signal strength (RSSI).
NOTE: The RSSI LED indicators represent varying degrees in the RSSI level. The absence of a signal is indicated by no LED
response, and full signal strength is indicated when all four LEDs are active and lit.
Figure 2
LED Layout
Table 2 lists the meanings of the LEDs on the W-AP175P outdoor access point.
Table 2
W-AP175P LED Status Indicators
LED Function Indicator Status
P/S AP Power/Ready
Status
POE N/A N/A Not currently used
Off No power to AP
Blinking Device booting, not ready
On Device ready
ENT LAN/Network Link
Status
R0 Radio 0 Status Off Radio 0 disabled
R1 Radio 1 Status Off Radio 1disabled
RSSI (Radio 0) RSSI Level for Radio 0 Off RSSI disabled/no signal
Off Ethernet link unavailable
On (Amber) 10/100 Mbs ethernet link negotiated
On (Green) 1000 Mbs ethernet link negotiated
Blinking Traffic on ethernet link
On (Amber) Radio 0 enabled in WLAN mode
Blinking Air Monitor (AM) mode
On (Blue) Radio 1 enabled in WLAN mode
Blinking Air Monitor (AM) mode
4 Step Progressive Bars
(Red)
25/50/75/100%
Each bar represents a progressive increase in
signal strength, with 4 bars representing
maximum signal strength (100%).
Minimum data rate: One lit LEDs
Maximum data rate: Four lit LEDs
Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide 5
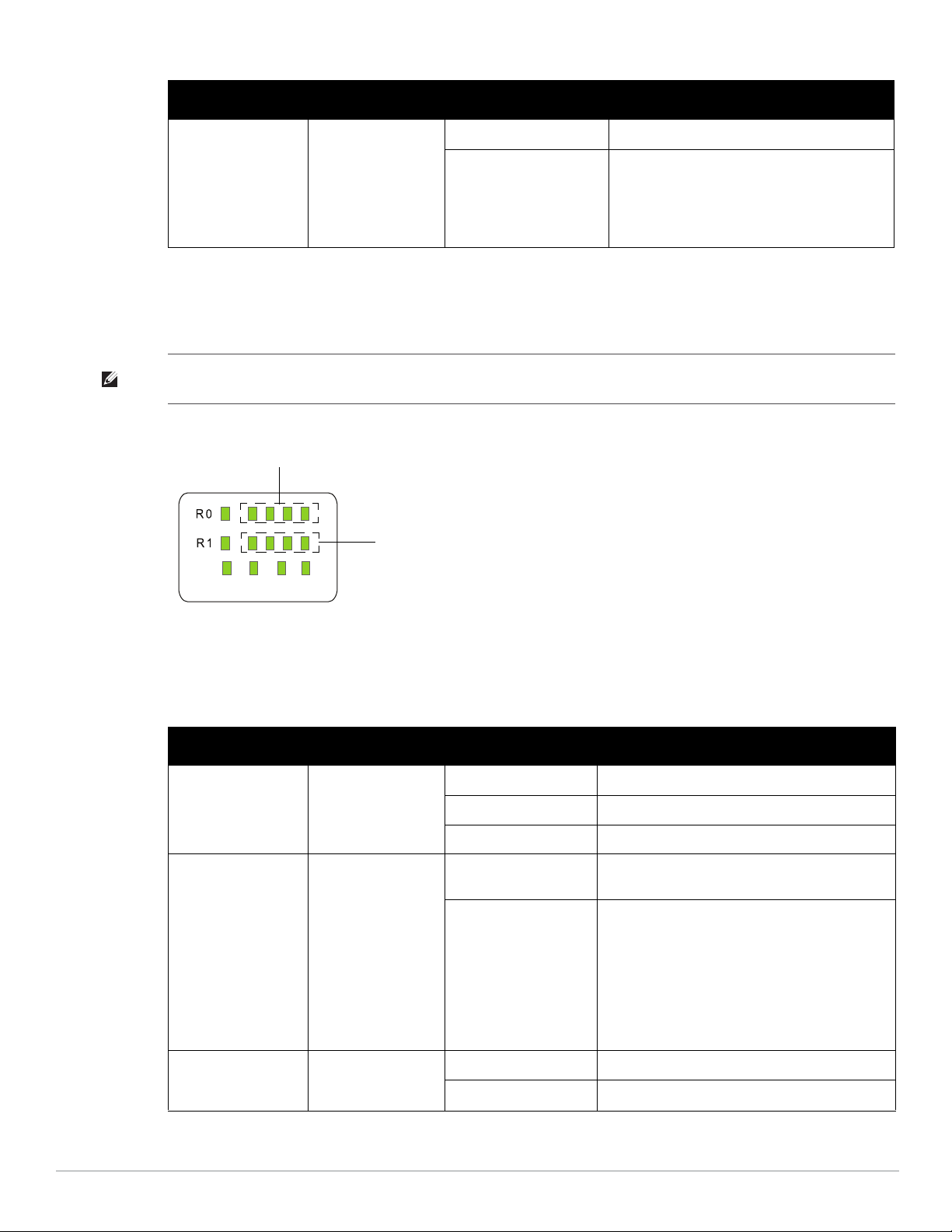
Table 2
P/S
ENT
POE
HEAT
RSSI for Radio 1
RSSI for Radio 0
W-AP175P LED Status Indicators (Continued)
LED Function Indicator Status
RSSI (Radio 1) RSSI Level for Radio 1 Off RSSI disabled/no signal
4 Step Progressive Bars
(Blue)
25/50/75/100%
Each bar represents a progressive increase in
signal strength, with 4 bars representing
maximum signal strength (100%).
Minimum data rate: One lit LEDs
Maximum data rate: Four lit LEDs
W-AP175AC/DC LED Status Indicators
The W-AP175 include visual indicators for power, link, heat and radio status. Additionally, each radio has a fourLED array that indicates received signal strength (RSSI).
NOTE: The RSSI LED indicators represent varying degrees in the RSSI level. The absence of a signal is indicated by no LED
response, and full signal strength is indicated when all four LEDs are active and lit.
Figure 3
LED Layout
Table 3 lists the meanings of the LEDs on the W-AP175AC/DC outdoor access points.
Table 3
W-AP175AC/DC LED Status Indicators
LED Function Indicator Status
P/S AP Power/Ready
Status
POE Displays PSE power
output status
Heat Displays the heating
status of low
temperature
Off No power to AP
Blinking Device booting, not ready
On Device ready
Off Non-powered device (0Ω<Rport<200Ω) or Port
open (Rport>1MΩ)
Green Port on (25kΩ)
1 Flash: Low signature resistance
(300Ω<Rport<15kΩ)
2 Flashes: High signature resistance
(33kΩ<Rport<500kΩ)
5 Flashes: Port overload fault
9 Flashes: Power management allocation
exceeded
Off Unit is not in heating status
Blinking (Blue) Unit is pre-heating
6 Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide
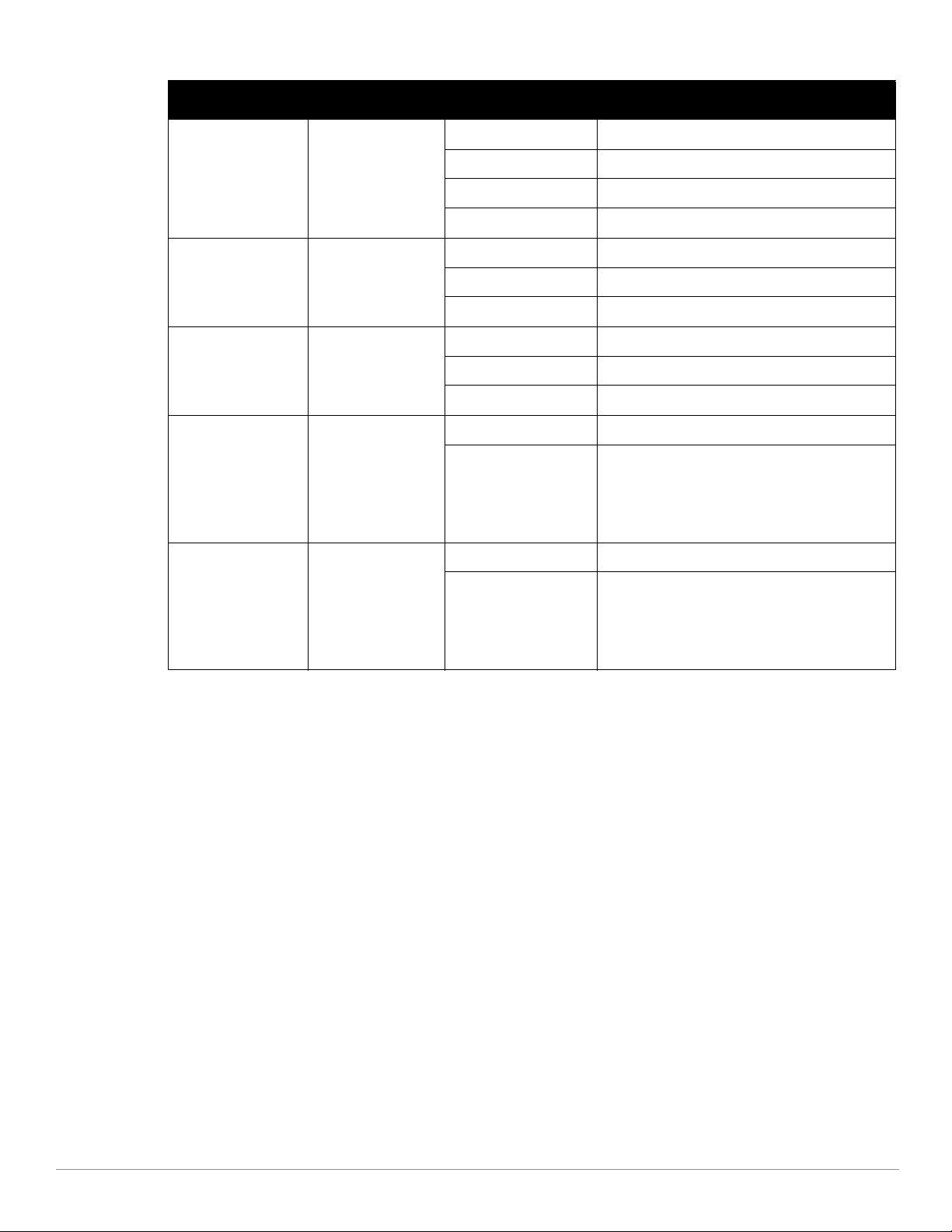
Table 3
W-AP175AC/DC LED Status Indicators (Continued)
LED Function Indicator Status
ENT LAN/Network Link
Status
R0 Radio 0 Status Off Radio 0 disabled
R1 Radio 1 Status Off Radio 1disabled
RSSI (Radio 0) RSSI Level for Radio 0 Off RSSI disabled/no signal
RSSI (Radio 1) RSSI Level for Radio 1 Off RSSI disabled/no signal
Off Ethernet link unavailable
On (Amber) 10/100 Mbs ethernet link negotiated
On (Green) 1000 Mbs ethernet link negotiated
Blinking Traffic on ethernet link
On (Amber) Radio 0 enabled in WLAN mode
Blinking Air Monitor (AM) mode
On (Blue) Radio 1 enabled in WLAN mode
Blinking Air Monitor (AM) mode
4 Step Progressive Bars
(Red)
25/50/75/100%
Each bar represents a progressive increase in
signal strength, with 4 bars representing maximum
signal strength (100%).
Minimum data rate: One lit LEDs
Maximum data rate: Four lit LEDs
4 Step Progressive Bars
(Blue)
25/50/75/100%
Each bar represents a progressive increase in
signal strength, with 4 bars representing maximum
signal strength (100%).
Minimum data rate: One lit LEDs
Maximum data rate: Four lit LEDs
Outdoor Planning and Deployment Considerations
Prior to deploying an outdoor wireless network, the environment must be evaluated to plan for a successful Dell
WLAN deployment. Successfully evaluating the environment enables the proper selection of Dell APs and
antennas and assists in the determination of their placement for optimal RF coverage. This process is considered
WLAN or RF planning.
Scale Requirements
The potentially immense scale of outdoor deployments requires consideration of factors that may not be as
important in a typical indoor deployment:
Range (distance): Range or distance between APs must be taken into account during the planning phase.
Available AP mounting locations are often far less flexible in an outdoor environment. Regardless of these
outdoor restrictions, the desired goal is to achieve results similar to an indoor deployment: a “dense” RF
deployment that supports advanced Aruba features, such as ARM, efficient client roaming, and failover.
Elevation: Proper consideration and planning for elevation differences between APs (AP to AP) and AP to
Client can be critical to success. To plan for these differences in elevation, it is important to understand the
3D coverage pattern provided by the antennas that will be deployed in the environment.
Non-Fixed Considerations: The RF environment might change on a day to day basis. Keep non-fixed items,
such as shipping containers, vehicles, and future building construction, in mind when planning for an outdoor
deployment.
Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide 7

Identifying Known RF Absorbers/Reflectors/Interferences Sources
Radio Line of Sight
Visual Line of Sight
Identifying known RF absorbers/reflectors/interference sources while out in the field during the installation phase
is critical. Even though outdoor environments consist of fewer RF absorbers/reflectors/interference sources
compared to indoor environments, ensure that these sources are identified and taken into consideration when
installing and mounting an AP to its fixed outdoor location.
RF Absorbers
Cement/Concrete
Natural Items: Trees/vegetation
Brick
RF Reflectors
Metal Objects: Roof-installed air-conditioning equipment, chain link fences (depending on aperture size),
other wire fences, or water pipes
RF Interference Sources
Other 802.11a/b/g/n or broadband access equipment operating nearby
Industrial RF welding equipment or other Industrial, Scientific and Medical (ISM) equipment that utilizes
RF to heat or alter the physical properties of materials
Military, Commercial Aviation or Weather Radar Systems
Line of Sight (Radio Path Planning)
A wireless bridge or mesh link requires a “radio line of sight” between the two antennas for optimum
performance. The concept of radio line of sight involves the area along a link through which the bulk of the radio
signal power travels. This area is known as the first Fresnel Zone of the radio link. For a radio link, no object
(including the ground) must intrude within 60% of the first Fresnel Zone.
Figure 4 illustrates the concept of a good radio line of sight.
Figure 4
If there are obstacles in the radio path, there may still be a radio link but the quality and strength of the signal will
be affected. Calculating the maximum clearance from objects on a path is important as it directly affects the
decision on antenna placement and height. It is especially critical for long-distance links, where the radio signal
could easily be lost.
Line of Sight
When planning the radio path for a wireless bridge or mesh link, consider these factors:
Avoid any partial line of sight between the antennas
Be cautious of trees or other foliage that may be near the path, or may grow and obstruct the path.
8 Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide

Be sure there is enough clearance from buildings and that no building construction may eventually block the
path.
For very long distance links, the curvature of the earth (20 cm per km) may need to be considered in the
calculation of relative heights.
Check the topology of the land between the antennas using topographical maps, aerial photos, or even
satellite image data (software packages are available that may include this information for your area)
Avoid a path that may incur temporary blockage due to the movement of cars, trains, or aircraft.
Antenna Height
A reliable wireless bridge or mesh link is usually best achieved by mounting the antennas at each end high enough
for a clear radio line of sight between them. The minimum height required depends on the distance of the link,
obstacles that may be in the path, topology of the terrain, and the curvature of the earth (for links over 3 miles).
For long-distance links, the AP may have to be mounted on masts or poles that are tall enough to attain the
minimum required clearance. Use the following table to estimate the required minimum clearance above the
ground or path obstruction (for 5 GHz bridge links).
Table 4
Total Link Distance
0.25 mile (0.402 km) 4.6 ft (1.4 m) 0.007 ft (0.002 m) 4.6 ft (1.4 m)
0.5 mile (0.805 km) 6.2 ft (1.9 m) 0.03 ft (0.010 m) 6.2 ft (1.9 m)
1 mile (1.6 km) 8.9 ft (2.7 m) 0.13 ft (0.04 m) 8.9 ft (2.7 m)
2 miles (3.2 km) 12.5 ft (3.8 m) 0.5 ft (0.15 m) 13.1 ft (4.0 m)
3 miles (4.8 km) 15.4 ft (4.7 m) 1.0 ft (0.3 m) 16.4 ft (5.0 m)
4 miles (6.4 km) 17.7 ft (5.4 m) 2.0 ft (0.6 m) 19.7 ft (6.0 m)
5 miles (8 km) 20 ft (6.1 m) 3.0 ft (0.9 m) 23 ft (7.0 m)
7 miles (11.3 km) 23.6 ft (7.2 m) 6.2 ft (1.9 m) 30 ft (9.1 m)
9 miles (14.5 km) 27 ft (8.2 m) 10.2 ft (3.1 m) 37 ft (11.3 m)
12 miles (19.3 km) 30.8 ft (9.4 m) 18.0 ft (5.5 m) 49 ft (14.9 m)
15 miles (24.1 km) 34.4 ft (10.5 m) 28.0 ft (8.5 m) 62.7 ft (19.1 m)
Antenna Minimum Height and Clearance Requirements
Max Clearance for
60% of First Fresnel
Zone at 5.8 GHz
Approximate Clearance
for Earth Curvature
Total Clearance
Required at
Mid-point of Link
NOTE: To avoid any obstruction along the path, the height of the object must be added to the minimum clearance required for a
clear radio line of sight. Consider the following simple example, illustrated in Figure 5.
Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide 9
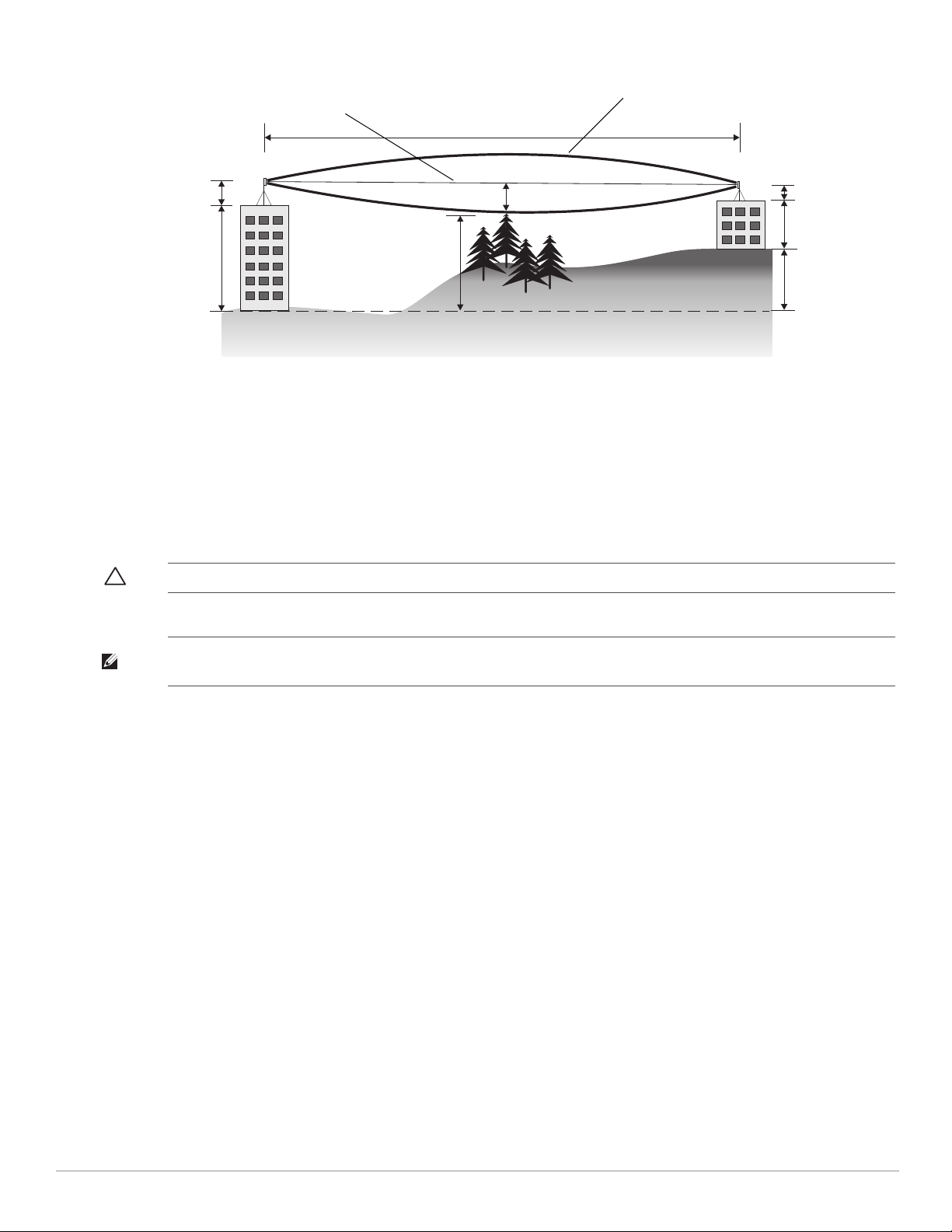
Figure 5
A
B
3 miles (4.8 km)
5.4 m
17 m
20 m
2.4 m
12 m
9m
1.4 m
Radio Line of Sight
Visual Line of Sight
Antenna Height and Line of Sight
A wireless bridge or mesh link is deployed to connect building A to building B, which is located three miles (4.8
km) away. Mid-way between the two buildings is a small tree-covered hill. From the above table it can be seen
that for a three-mile link, the object clearance required at the mid-point is 5.3 m (17.4 ft). The tree tops on the
hill are at an elevation of 17 m (56 ft), so the antennas at each end of the link need to be at least 22.3 m (73 ft)
high. Building A is six stories high, or 20 m (66 ft), so a 2.3 m (7.5 ft) mast or pole must be constructed on its roof
to achieve the required antenna height. Building B is only three stories high, or 9 m (30 ft), but is located at an
elevation that is 12 m (39 ft) higher than building A. To mount an antenna at the required height on building B,
a mast or pole of 1.3 m (4.3 ft) is needed.
CAUTION: Never construct a radio mast, pole, or tower near overhead power lines.
NOTE: Local regulations may limit or prevent construction of a high radio mast or tower. If your wireless bridge or mesh link
requires a high radio mast or tower, consult a professional contractor for advice.
Antenna Position and Orientation
Once the required antenna height has been determined, other factors affecting the precise position of the wireless
bridge or mesh link must be considered:
Be sure there are no other radio antennas within 2 m (6 ft) of the wireless bridge or mesh link. These include
other WiFi radio antennas.
Place the wireless bridge or mesh link away from power and telephone lines.
Avoid placing the wireless bridge or mesh link too close to any metallic reflective surfaces, such as roof-
installed air-conditioning equipment, tinted windows, wire fences, or water pipes. Ensure that there is at least
5 feet clearance from such objects.
The wireless bridge or mesh link antennas at both ends of the link must be positioned with the same
polarization direction, either horizontal or vertical. Proper alignment helps to maximize throughput.
Radio Interference
The avoidance of radio interference is an important part of wireless link planning. Interference is caused by other
radio transmissions using the same or an adjacent channel frequency. You should first scan your proposed site
using a spectrum analyzer to determine if there are any strong radio signals using the 802.11a/b/g channel
frequencies. Always use a channel frequency that is furthest away from another signal.
If radio interference is still a problem with your wireless bridge or mesh link, changing the antenna direction may
improve the situation.
10 Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide

Weather Conditions
When planning wireless bridge or mesh links, you must take into account any extreme weather conditions that
are known to affect your location. Consider these factors:
Temperature: The wireless bridge or mesh link is tested for normal operation in temperatures from -30ºC to
55ºC. Operating in temperatures outside of this range may cause the unit to fail.
Wind Velocity: The wireless bridge or mesh link can operate in winds up to 165 miles per hour. You must
consider the known maximum wind velocity and direction at the site and be sure that any supporting
structure, such as a pole, mast, or tower, is built to withstand this force.
Lightning: To protect against lightning induced surges, the W-AP175 requires lightning protection on the
radio interface ports.
CAUTION: A Dell Lightning Arrestor, AP-LAR-1, must be installed on each antenna port for protection against lightning induced
surges. Failure to use an AP-LAR-1 can void the warranty of an Dell outdoor AP model and renders the AP susceptible to failure
from lightning induced surges
Rain: The wireless bridge or mesh link is weatherproofed against rain. However, it is recommended to apply
weatherproof sealing tape around the ethernet port and antenna connectors for extra protection. If moisture
enters a connector, it may cause a degradation in performance or even a complete failure of the link.
Snow and Ice: Falling snow, like rain, has no significant effect on the radio signal. However, a buildup of snow
or ice on antennas may cause the link to fail. In this case, the snow or ice has to be cleared from the antennas
to restore operation of the link.
Ethernet Cabling
When a suitable antenna location has been determined, you must plan a cable route from the wireless bridge or
mesh link outdoors to a suitable power and/or network source.
Consider these points:
The ethernet cable length should never be longer than 90 m (295 ft).
Determine a building entry point for the cable (if applicable).
Determine if conduits, bracing, or other structures are required for safety or protection of the cable.
For lightning protection at the power injector end of the cable, consider using a lightning arrestor
immediately before the cable enters the building
Grounding
It is important that the wireless bridge or mesh link, cables, and any supporting structures are properly grounded.
Each W-AP175 access point includes a grounding screw for attaching a ground wire.
CAUTION: Be sure that grounding is available and that it meets local and national electrical codes. Ground the access point first
using the external ground stud on the unit before making any other connection.
Installing Antennas
1. Before connecting the antennas, identify which of your antennas are 2.4 GHz and which are 5 GHz. On the
W-AP175, the 2.4 GHz antennas must be installed the R1 radio interfaces and the 5.0 GHz must be installed
on the R0 radio interfaces.
2. After identifying which antennas will go where, install them by placing the antenna connector over the
corresponding connector and the AP and turning the connector clockwise until hand tight. Repeat this
process for each antenna.
Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide 11

3. Place the included metal weatherproof caps over any unused antenna interfaces by turning them clockwise
until hand tight.
Weatherproofing Connections
Weatherproofing your antenna and/or cable connections on your outdoor AP is essential to reliability and
longevity of your product. This process prevents water from entering the AP or antennas through the connectors.
A good weatherproofing job consists of three wrappings:
1. electrical tape
2. butyl rubber
3. electrical tape
The first wrapping of tape should be at least two layers, followed by a single wrap of butyl rubber, and four-layer
wrap of electrical tape. This provides good protection from water, heat, and other potential hazards that could
damage your AP or antennas.
Additionally, wrap your connections such that water is always directed down and away from connections.
Required Items and Tools
3/4” (19 mm) Vinyl Electrical Tape
Butyl Rubber Tape
Knife or Box Cutter
Types of Connections
The following sections provide guidance on weatherproofing directly connected antennas (Figure 6) and cable
connections (Figure 7). The same materials are needed for weatherproofing both types of connections but the
procedure is slightly different. For weatherproofing directly connected antennas, see “Weatherproofing Directly
Connected Antennas” on page15. For weatherproofing cable connections, see “Weatherproofing Cable
Connections” on page18.
12 Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide

Figure 6
AP175_11
Weep holes
Directly Connected Antennas
Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide 13

Figure 7
AP175_16
Connectors on bottom of antenna
N-type connector
on an RF cable
N-type
connector
on a pigtail
Cable Connections
Important Points to Remember
Do not cover the weep holes on the antennas. Doing so can restrict the release of condensation from the
antennas.
Proper weatherproofing is not a fast process. Set aside ample time to complete the steps outlined below.
When wrapping, make the each layer of tape as flat as possible. Wrinkles and folds in the tape create places
for water and moisture to gather.
14 Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide

Weatherproofing Directly Connected Antennas
Wrap tape from
just above knurled
section to base of
antenna mount
Pieces of tape as needed
Leave
weep holes
uncovered
AP175_12
First Wrapping of Tape
1. Before wrapping the antennas, locate the weep holes (Figure 6). Weep holes allow condensation that has built
up inside the antenna to escape.
2. Prepare the antenna connector by cleaning and drying it.
3. Cut a 4” (100 mm) strip of electrical tape from the roll. Pre-cutting the tape into strips makes in easier to
maneuver the tape around the antennas and other components of the AP’s case.
4. Beginning just below the weep holes, tightly wrap the connection with a layer of the 3/4” (19mm) electrical
tape. Overlap the tape to a half-width.
5. Repeat steps 3 and 4 until the wrapping extends all the way to the AP’s case.
Figure 8
First Wrapping of Tape
Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide 15

Wrapping of Butyl Rubber
Cut 3/4” strip
of rubber
Squeeze thinner
& wider
Wrap rubber
around base
of antenna
mount
AP175_13
Wrap rubber
around base
of antenna
mount
Squeeze to
bond rubber
to itself
Rubber will
be wrapped
with 4 layers
of tape
AP175_14
1. Cut a 3/4” (19 mm) strip of butyl rubber.
2. Wrap the strip of rubber around the taped connector (Figure 9)
3. Join the two ends by pushing them together until there is no longer a seam (Figure 10).
Figure 9
Butyl Rubber Placement
Figure 10
Butyl Rubber Wrap
16 Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide

Second Wrapping of Tape
First and third layers wrap
top to bottom
AP175_15
Rubber will
be wrapped
with 4 layers
of tape
Second and final layers wrap
bottom to top
Pieces of tape as needed
1. Cut a 4” (100 mm) strip of electrical tape from the roll.
2. Where you begin wrapping depends on the orientation of the antenna. Water should flow in the opposite
direction of the wrapping to prevent water from entering the connector between the layers of tape.
Therefore, if the antenna is facing up, you should begin wrapping at the AP end of the connector. This will
ensure that your fourth and final layer will be layered correctly. Conversely, if your antenna is facing down, you
should begin wrapping on the antenna end of the connector.
3. After completing the fourth layer of tape, check your work to ensure there are no places where water can
collect. If there are, you must smooth out those areas with additional layers of tape or remove the
weatherproofing and begin again.
Figure 11
Completed Wrapping (Antenna on Top of AP)
4. Repeat this process for all connectors.
Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide 17

Weatherproofing Cable Connections
Wrap tape
from antenna
connector base
to cable
Pieces of tape as needed
AP175_17
First Wrapping of Tape
1. Prepare the antenna connector by cleaning and drying it.
2. Cut a 4” (100 mm) strip of electrical tape from the roll. Pre-cutting the tape into strips makes in easier to
maneuver the tape around the connectors and other components but is not required.
3. Beginning at the top of the connector, tightly wrap the connection with a layer of the 3/4” (19mm) electrical
tape. Overlap the tape to a half-width.
4. Repeat steps 3 and 4 until the wrapping extends all the way to the cable’s insulation.
Figure 12
First Wrapping of Tape
18 Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide

Wrapping of Butyl Rubber
Stretch thinner
& wider
AP175_18
Wrap rubber
around connector
and cable
Squeeze to
bond rubber
to itself
Rubber will
be wrapped
with 4 layers
of tape
AP175_19
Wrap rubber
around connector
and cable
1. Cut a piece of butyl rubber large enough to wrap around the connector and extended past the first layer of
tape.
2. Wrap the strip of rubber around the taped connector (Figure 13)
3. Join the two ends by pushing them together until there is no longer a seam (Figure 14).
Figure 13
Figure 14
Butyl Rubber Placement
Butyl Rubber Wrap
Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide 19

Second Wrapping of Tape
First and third layers wrap
top to bottom
AP175_20
Pieces of tape as needed
Rubber will be wrapped
with 4 layers of tape
Second and final layers wrap
bottom to top
1. Cut a 4” (100 mm) strip of electrical tape from the roll.
2. Using 3/4” (19mm) electrical tape, begin wrapping at the connector and create four layers.
3. After completing the fourth layer of tape, check your work to ensure there are no places where water can
collect. If there are, you must smooth out those areas with additional layers of tape or remove the
weatherproofing and begin again.
Figure 15
Completed Wrapping
4. Repeat this process for all connectors.
Installing the W-AP175
The W-AP175 can be installed on a wall or attached to a pole. The following section describes how to attach the
necessary hardware to the AP and how to mount the AP in the selected location.
Selecting the Installation Site
The site should be located within at least a 60% range of the 1st fresnel zone without obstacles to provide line
of sight (LOS) transmission, increase coverage capacity, and minimize the number of necessary sites.
If no LOS is secured, areas in non-line-of-sight (NLOS) areas could be covered as well, but the distance of
coverage and area of coverage are decreased; more sites are needed to provide coverage for same area than in
the LOS scenario.
Interference must be considered in site selection. The new site should avoid known interference, unless the
interference is controllable.
Keep the W-AP175 away from places that are susceptible to high temperature, dust, harmful gas,
inflammable, explosive, electromagnetic interference (high power radar, radio station and transformer),
unstable voltage, heavy vibration, or loud noise. In engineering design, the site should be selected according to
the network planning and technical requirements of communications equipment, as well as the
considerations such as climate, hydrology, geology, earthquake, electric power, and transportation.
20 Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide

Installing the W-AP175 on a Pole
AP175_03
1. Attach the W-AP175 on the mounting bracket using the two M6 x30 bolts (with flat and spring washers) on
each side of the mounting bracket.
Figure 16
Attaching the mounting bracket to the AP
2. Attach the mounting bracket (with W-AP175) on the pole using four M8 x110 bolts (with flat washers, spring
washers and nuts) and the pair of pole anchors.
Figure 17
Attaching the mounting bracket to the pole
Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide 21

Installing the W-AP175 on a Wall
1. Begin by marking the screw points on the wall in the location you have selected.
a. Put the mounting bracket on the installation position against the wall.
b. Mark four expansion screw holes on the wall.
Figure 18
2. Use a drill to create four holes on the four markings you created in the previous step.
3. Install wall (masonry) anchors.
a. Insert a masonry anchor into each drilled hole.
Position of the screw holes
b. Tap the flat end of the anchor with a rubber hammer until the anchor is flush with the wall surface.
4. Attach the mounting bracket to the wall.
a. Align the four holes in the mounting bracket with the anchors and insert four expansion screws through
the installation holes into the anchors.
b. Adjust the position of the mounting bracket and tighten the expansion screws.
5. Attach the W-AP175 to the mounting bracket by inserting the two M6 x30 bolts (with flat and spring
washers) through the installation holes, and tighten the bolts.
22 Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide

Figure 19
Front
Front
AP175_04
Attaching the AP to the Mounting Bracket
Grounding the W-AP175
The grounding must be completed before powering up the W-AP175. The resistance of grounding wire should be
less than 5 ohm and the grounding cable’s cross-section area should be no less than 6 mm.The grounding hole is
at the right side of the W-AP175.
Figure 20
Grounding the W-AP175
1. Peel the cover of one end of the grounding cable (green or yellow and green grounding cable with 6 mm crosssection area) and place the bare grounding cable into the copper lug, and press firmly with the crimping pliers.
2. Fasten the copper lug to the grounding hole on the W-AP175 with the M4 x12 bolt and external-tooth
washer.
Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide 23

Connecting the Ethernet Cable (W-AP175P)
To ensure that your outdoor access point (AP) maintains ethernet connectivity and Power over Ethernet (PoE),
you must use the included weatherproof connector kit and install it using the steps below.
WARNING: Failure to use the included weatherproof connector kit can lead to connectivity and PoE issues.
Figure 21
1 Shielded RJ45 connector 4 Locknut
2 Gasket Mat 5 Seal Ring
3 Waterproof Connector Socket 6 Sealing Nut
Waterproof Ethernet Connector Cover
1. Remove the cover from the adhesive side of the gasket mat and place it over the weatherproof connector
socket.
2. Place the locknut over the weatherproof connector socket.
3. Place the sealing nut over an ethernet cable (without a connector attached to the end).
4. Place the seal ring over the ethernet cable.
5. Insert the ethernet cable into the narrow end of the weatherproof connector socket and pass it through the
opening on the wide end.
6. Using a crimping tool, attach the included shielded RJ45 connector.
7. Slide the seal ring up the ethernet cable and insert it into the narrow end of the weatherproof connector
socket.
8. Pull the ethernet cable so the shielded RJ45 connector fits into the RJ45 shaped opening in the wide end of
the weatherproof connector socket.
9. Slide the sealing nut over the narrow end of the weatherproof connector socket and hand tighten it.
10. Insert the ethernet cable connector into the ethernet interface and hand-tighten the locknut.
11. Water-proof the ethernet cable connection with electrical tape and butyl rubber.
24 Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide

Connecting the Ethernet Cable (W-AP175AC/DC)
To ensure that your outdoor access point (AP) maintains ethernet connectivity and Power over Ethernet (PoE),
you must use the included weatherproof connector kit and install it using the steps below.
WARNING: Failure to use the included weatherproof connector kit can lead to connectivity and PoE issues.
Figure 22
1 Shielded RJ45 connector 5 Shield rings
2 Waterproof Connector Socket 6 Sealing Bolt
3 Locknut 7 Sealing Nut
4 Clamp ring
Waterproof Ethernet Connector Cover
1. Hold the clamp ring (4) vertically, with the wide end facing up, and place the locknut (3) over it.
2. Drop the waterproof connector socket (2) into the locknut/clamp ring items (3,4), with the RJ45 connector
opening facing up, and screw the socket into the threads on the clamp ring.
3. Place the sealing nut (7) over an ethernet cable (without a connector attached to the end).
4. Place the seal bolt (6) over the ethernet cable.
5. Strip off about 55mm (2 inches) of the outer ethernet cable sheath to expose the ground wire and other pair
wires.
6. Insert all pair wires into the two shield rings (5).
7. Make the ground wire attach to the narrow end of the inner ring and place the outer ring over the narrow end
of the inner ring.
8. Insert the ethernet cable into the narrow end of the clamp ring and pass it through the opening end of
waterproof connector socket.
9. Using a crimping tool, attach the included shielded RJ45 connector.
10. Slide the shield rings up the ethernet cable and insert it into the narrow end of the clamp ring.
11. Pull the ethernet cable so the shielded RJ45 connector fits into the RJ45 shaped opening in the wide end of
the weatherproof connector socket.
12. Slide the sealing bolt over the narrow end of the clamp ring and hand tighten it.
13. Thread the sealing nut onto the sealing bolt.
14. Insert the ethernet cable connector into the ethernet interface and hand-tighten the locknut.
15. Water-proof the ethernet cable connection with electrical tape and butyl rubber.
Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide 25

Figure 23
Connecting the Ethernet cable
Connecting the Power Cable (W-AP175 AC/DC)
CAUTION: Installation and service of Dell products should be performed by Professional Installers.
The W-AP175AC and W-AP175DC versions need an outdoor rated power cable to connect to a compatible AC
or DC power source.
NOTE: The W-AP175 does not ship with any power cables; these are available as accessories and should be ordered separately.
In addition to completed power cables, Dell also offers an outdoor rated AC and DC connector kit that can be used to connect a
compatible power cable to the W-AP175.
AC power source specifications (at W-AP175 interface): 100-240Vac, 100W
DC power source specifications (at W-AP175 interface): 12-48Vdc, 100W
AC power cable specifications (when using AC connector kit and custom cable): minimum voltage/current
rating 250V/1A, diameter 6-12mm, rated for outdoor use
DC power cable specifications (when using DC connector kit and custom cable): minimum voltage/current
rating 60V/10A, diameter 6-12mm, rated for outdoor use
Cable Connection Steps
1. Remove the protective cap on the power interface.
2. Insert the power cable connector into the power interface and hand-fasten the waterproof cover.
3. Water-proof the power cable connection with PVC insulation tape, adhesive insulation tape and strap.
26 Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide

Attaching the Solar Shield to the W-AP175
AP175_07
AP175_08
Attach the solar shield to the W-AP175 by using the four M4 x16 (with flat and spring washers).
Figure 24
Attaching the Solar Shield to the AP
Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide 27

Product Specifications
Mechanical
Dimensions (H x W x D)
10.2 inches x 9.4 inches x 4.1 inches
26 cm x 24 cm x 10.5 cm
Weight: 7 lbs/3.25 kg
Shipping Dimensions (H x W x D)
12.9 inches x 12.6 inches x 11.8 inches
33 cm x 32 cm x 30 cm
Shipping Weight: 16.6 lbs/7.5 kg
Temperature
Operating (W-AP175P): -30ºC to 60ºC (-22ºF to 140ºF)
Operating (W-AP175AC/DC): -40ºC to 55ºC (-40ºF to 131ºF)
Storage: –40ºC to 70ºC (-40ºF to 158ºF)
Relative Humidity: 5% to 95% non-condensing
Altitude: Up to 9,850ft (3,000 meters)
Mounting: wall or pole mountable
Antennas:
Quad, N-type female interfaces (2 x 2.4 GHz, 2 x 5GHz) for external antenna support (supports MIMO)
Feeder cable may be used for external antenna deployments
Visual Status Indicators (LEDs): See Table 2
Electrical
Power In
W-AP175P: 48-volt DC 802.3at power over Ethernet (PoE+)
W-AP175AC: 100-240 volt AC from external AC power source
W-AP175DC: 12-48 volt DC from external DC power source
Maximum power consumption: 18 watts (excludes power consumed by any POE device connected to and
powered by the W-AP175AC or W-AP175DC)
Power Out
The AC and DC powered models provide an 802.3af POE power source (PSE) on the ethernet interface.
Interfaces
Network:
1 x 10/100/1000BASE-T Ethernet (RJ-45), auto-sensing link speed and MDI/MDX
Power:
1 x DC power connector (in W-AP175DC model only)
1 x AC power connector (in W-AP175AC model only)
Antenna:
4 x N-Type female antenna interfaces
28 Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide

Other:
1 x USB console interface
Wireless LAN
AP type: Dual-radio, dual-band 802.11n outdoor
Supported frequency bands (country-specific restrictions apply):
2.400 to 2.4835 GHz
5.150 to 5.250 GHz
5.250 to 5.350 GHz
5.470 to 5.725 GHz
5.725 to 5.850 GHz
Available channels: Controller-managed, dependent upon configured regulatory domain
Supported radio technologies:
802.11b: Direct-sequence spread-spectrum (DSSS)
802.11a/g/n: Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM)
802.11n: 2x2 MIMO with two spatial streams
Supported modulation types:
802.11b: BPSK, QPSK, CCK
802.11a/g/n: BPSK, QPSK, 16-QAM, 64-QAM
Transmit power: Configurable in increments of 0.5 dBm
Maximum transmit power:
2.4 GHz: 25 dBm (limited by local regulatory requirements)
5 GHz: 25 dBm (limited by local regulatory requirements)
Maximum ratio combining (MRC) for improved receiver performance
Association rates (Mbps):
802.11b: 1, 2, 5.5, 11
802.11a/g: 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, 54
802.11n: MCS0 - MCS15 (6.5 Mbps to 300 Mbps)
802.11n high-throughput (HT) support: HT 20/40
802.11n packet aggregation: A-MPDU, A-MSDU
Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide 29

Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Dell provides a multi-language document containing country specific restrictions and additional safety and
regulatory information for all Dell hardware products. The Dell PowerConnect W-Series Safety, Environmental,
and Regulatory Information document is included with this product.
CAUTION: RF Radiation Exposure Statement: This equipment complies with FCC RF radiation exposure limits. This equipment
should be installed and operated with a minimum distance of 13.78 inches (35 cm) between the radiator and your body for 2.4
GHz and 5 GHz operations. This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or
transmitter. When operated in the 5.15 to 5.25 GHz frequency range, this device is restricted to indoor use to reduce the potential
for harmful interference with co-channel Mobile Satellite Systems.
CAUTION: Dell Access Points and the AP-LAR-1 lightning arrestor are required to be installed by a professional installer. The
professional installer is responsible for ensuring that grounding is available and it meets applicable local and national electrical
codes.
WARNING: Do not work on an AP and do not connect or disconnect cables during periods of lightning activity.
FCC Class B Device
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to part
15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a
residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does
cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment
off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/ TV technician for help.
For a complete list of Country Specific Regulations please speak with your Dell Representative.
30 Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide

Proper Disposal of Dell Equipment
TRA
REGISTERED No:
DEALER No:
DA0039425/10
ER0055290/11
200202320G
For the most current information about Global Environmental Compliance and Dell products, see dell.com.
Waste of Electrical and Electronic Equipment
Dell products at end of life are subject to separate collection and treatment in the EU
Member States, Norway, and Switzerland and therefore are marked with the symbol shown at
the left (crossed-out wheelie bin). The treatment applied at end of life of these products in
these countries shall comply with the applicable national laws of countries implementing
Directive 2002/96EC on Waste of Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE).
European Union RoHS
Dell products also comply with the EU Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive
2002/95/EC (RoHS). EU RoHS restricts the use of specific hazardous materials in the
manufacture of electrical and electronic equipment. Specifically, restricted materials
under the RoHS Directive are Lead (including Solder used in printed circuit assemblies),
Cadmium, Mercury, Hexavalent Chromium, and Bromine. Some Dell products are subject to the exemptions
listed in RoHS Directive Annex 7 (Lead in solder used in printed circuit assemblies). Products and packaging will
be marked with the “RoHS” label shown at the left indicating conformance to this Directive.
China RoHS
Dell products also comply with China environmental declaration requirements and are labeled
with the “EFUP 25” label shown at the left.
Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide 31

Contacting Support
Website Support
Main Website dell.com
Support Website support.dell.com
Dell Documentation support.dell.com/manuals
Copyright
© 2011 Aruba Networks, Inc. Aruba Networks trademarks include , Aruba Networks
Edge Company logo, and Aruba Mobility Management System
All rights reserved. Specifications in this manual are subject to change without notice.
Originated in the USA. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Open Source Code
Certain Aruba products include Open Source software code developed by third parties, including software code subject to the GNU General Public License (GPL), GNU
Lesser General Public License (LGPL), or other Open Source Licenses. The Open Source code used can be found at this site:
®
. Dell™, the DELL™ logo, and PowerConnect™ are trademarks of Dell Inc.
®
, Aruba Wireless Networks®, the registered Aruba the Mobile
http://www.arubanetworks.com/open_source
Legal Notice
The use of Aruba Networks, Inc. switching platforms and software, by all individuals or corporations, to terminate other vendors’ VPN client devices constitutes complete
acceptance of liability by that individual or corporation for this action and indemnifies, in full, Aruba Networks, Inc. from any and all legal actions that might be taken against it
with respect to infringement of copyright on behalf of those vendors.
Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 Outdoor Access Point | Installation Guide
Part Number 0511047-01 | January 2012
 Loading...
Loading...