Page 1
Dell PowerConnect W-
AirWave 7.4
Best Practices Guide
Page 2

Copyright
®
© 2011 Aruba Networks, Inc. Aruba Networks trademarks include , Aruba Networks
registered Aruba the Mobile Edge Company logo, and Aruba Mobility Management System
®
. Dell™, the DELL™ logo, and PowerConnect™ are
, Aruba Wireless Networks®, the
trademarks of Dell Inc.
All rights reserved. Specifications in this manual are subject to change without notice.
Originated in the USA. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Open Source Code
Certain Aruba products include Open Source software code developed by third parties, including software code subject to the GNU General
Public License (GPL), GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL), or other Open Source Licenses. The Open Source code used can be found at
this site:
www.arubanetworks.com/open_source
Legal Notice
The use of Aruba Networks, Inc. switching platforms and software, by all individuals or corporations, to terminate other vendors’ VPN client
devices constitutes complete acceptance of liability by that individual or corporation for this action and indemnifies, in full, Aruba Networks, Inc.
from any and all legal actions that might be taken against it with respect to infringement of copyright on behalf of those vendors.
Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave | Best Practices Guide 0510824-04 | November 2011
Page 3

Contents
Preface....................................................................................................................................................................... 5
Document Organization.....................................................................................................................5
Note, Caution, and Warning Icons ..................................................................................................6
Contacting Support ...........................................................................................................................6
Chapter 1 Overview ............................................................................................................................... 7
Prerequisites for Integrating Dell PowerConnect W-Series Infrastructure............................. 7
Chapter 2 Configuring AirWave for Global Dell PowerConnect W-Series Infrastructure ........ 9
Disabling Rate Limiting in AMP Setup > General .......................................................................... 9
Entering Credentials in Device Setup > Communication .............................................................9
Setting Up Recommended Timeout and Retries .........................................................................10
Setting Up Time Synchronization...................................................................................................11
Setting up NTP on AirWave.................................................................................................... 11
Manually Setting the Clock on a Controller ......................................................................... 11
Enabling Support for Channel Utilization and Statistics ............................................................ 11
AirWave Setup..........................................................................................................................12
Controller Setup (Master and Local)..................................................................................... 12
Chapter 3 Configuring a Dell PowerConnect W Group in AMP ................................................... 13
Basic Monitoring Configuration ..................................................................................................... 13
Advanced Configuration.................................................................................................................. 14
Chapter 4 Discovering Dell PowerConnect
W-Series Infrastructure ................................................................................................... 15
Discovering Master Controllers ..................................................................................................... 15
Local Controller Discovery..............................................................................................................17
Thin AP Discovery ............................................................................................................................17
Chapter 5 AMP and Dell PowerConnect W-Series Integration Strategies ............................... 19
Integration Goals .............................................................................................................................. 19
Example Use Cases .......................................................................................................................... 20
When to Use Enable Stats ...................................................................................................... 20
When to Use WMS Offload.....................................................................................................20
When to Use RTLS....................................................................................................................20
When to Define AMP as Trap Host ....................................................................................... 20
When to use Channel Utilization............................................................................................ 20
Prerequisites for Integration .......................................................................................................... 21
Enable Stats Utilizing AMP .............................................................................................................21
WMS Offload Utilizing AMP............................................................................................................22
Define AMP as Trap Host using ArubaOS CLI ............................................................................. 22
ArubaOS Traps Utilized by AMP ............................................................................................23
Auth Traps .........................................................................................................................23
IDS Traps ...........................................................................................................................23
ARM Traps.........................................................................................................................24
Dell PowerConnect W AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide | 3
Page 4

Ensuring That IDS and Auth Traps Display in AMP Using CLI..........................................24
Understanding WMS Offload Impact on Dell PowerConnect W-Series infrastructure.......26
Chapter 6 Dell PowerConnect W-Specific Capabilities in AMP.................................................. 29
Dell PowerConnect W Traps for RADIUS Auth and IDS Tracking ........................................... 29
Remote AP Monitoring .................................................................................................................... 30
ARM and Channel Utilization Information .................................................................................... 30
VisualRF and Channel Utilization ........................................................................................... 31
Configuring Channel Utilization Triggers ..............................................................................31
Viewing Channel Utilization Alerts ........................................................................................ 32
View Channel Utilization in RF Health Reports .................................................................... 32
Viewing Controller License Information .......................................................................................32
Rogue Device Classification ........................................................................................................... 33
Rules-Based Controller Classification ..........................................................................................34
Using RAPIDS Defaults for Controller Classification.......................................................... 34
Changing RAPIDS based on Controller Classification .......................................................35
Appendix A CLI ArubaOS and AMP Commands ................................................................................ 37
Enable Channel Utilization Events Utilizing ArubaOS CLI (Local and Master Controllers) .. 37
Enable Stats With the ArubaOS CLI (Local Controller in Master Local Environment) .......... 37
Offload WMS Utilizing ArubaOS CLI and AMP CLI (SNMP Walk)............................................ 38
ArubaOS CLI .............................................................................................................................. 38
AMP SNMP ...............................................................................................................................38
Ensuring Master Controller Pushes Config to Local Controllers Utilizing ArubaOS CLI....... 39
Disable Debugging Utilizing ArubaOS CLI....................................................................................39
Restart WMS on Local Controllers Utilizing ArubaOS CLI.........................................................39
Configure the ArubaOS CLI ............................................................................................................. 39
Enable Proper Traps With the ArubaOS CLI ................................................................................40
Appendix B How AMP Acquires Data from Dell PowerConnect W-Series devices................... 41
Appendix C WMS Offload Details ........................................................................................................ 43
State Correlation Process ............................................................................................................... 43
Benefits of using AMP as Master Device State Manager ........................................................ 44
Appendix D Increasing Location Accuracy........................................................................................ 45
Understand Band Steering's Impact on Location.......................................................................45
Leveraging RTLS to Increase Accuracy.......................................................................................45
Deployment Topology ..............................................................................................................45
Prerequisites .............................................................................................................................46
Enable RTLS service on the AMP server.............................................................................. 46
Enable RTLS on Controller ...................................................................................................... 47
Troubleshooting RTLS.............................................................................................................. 47
Wi-Fi Tag Setup Guidelines .................................................................................................... 48
4 | Dell PowerConnect W AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide
Page 5
Preface
This preface provides an overview of the best practices guide and contact information for Dell, and includes the
following sections:
“Document Organization” on page5
“Note, Caution, and Warning Icons” on page6
“Contacting Support” on page6
Document Organization
This best practices guide includes instructions and examples of optimal ways to use and integrate the AirWave
Management Platform (AMP) with Dell PowerConnect W-Series devices and infrastructure.
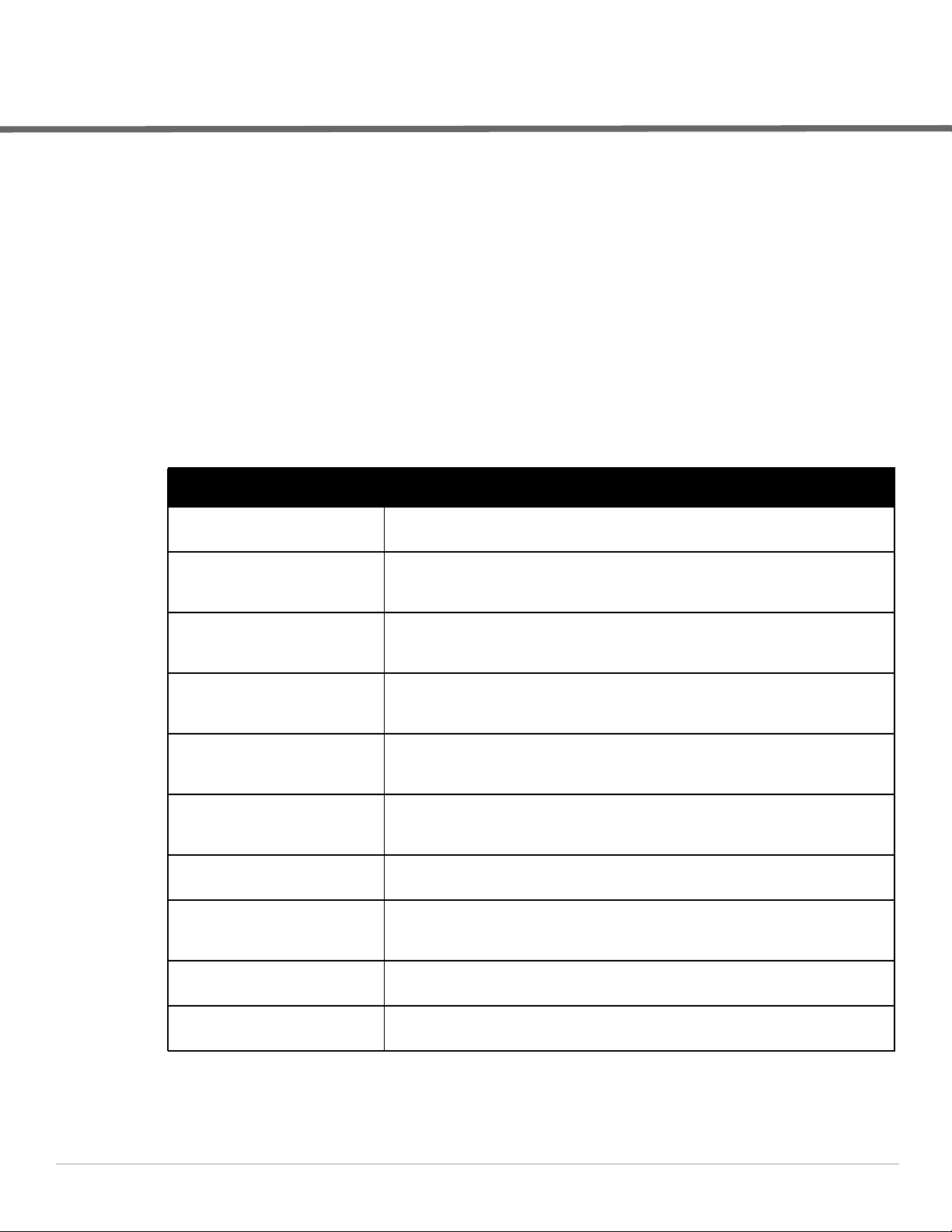
Table 1 Document Organization and Purposes
Chapter Description
Chapter 1, “Overview” on page 7 This chapter explains the minimum requirements, prerequisites, topology of an Dell
Chapter 2, “Configuring AirWave for
Global Dell PowerConnect W-Series
Infrastructure” on page 9
Chapter 3, “Configuring a Dell
PowerConnect W Group in AMP” on
page 13
Chapter 4, “Discovering Dell
PowerConnect W-Series
Infrastructure” on page 15
Chapter 5, “AMP and Dell
PowerConnect W-Series Integration
Strategies” on page 19
Chapter 6, “Dell PowerConnect WSpecific Capabilities in AMP” on
page 29
Appendix A, “CLI ArubaOS and AMP
Commands” on page 37
Appendix B, “How AMP Acquires
Data from Dell PowerConnect WSeries devices” on page 41
PowerConnect W-Series infrastructure integrated with AMP.
This chapter explains global configuration options in AMP.
This chapter explains how to create and monitor an Dell PowerConnect W group in AMP.
This chapter explains how to discover and manage your Dell PowerConnect W-Series
infrastructure.
This chapter highlights recommended integration strategies.
This chapter highlights AMP capabilities that are specific to Dell PowerConnect W-Series
devices.
This appendix explains command line interface (CLI) commands.
This appendix provides a table that explains how AMP acquires data from Dell
PowerConnect W-Series devices.
Appendix C, “WMS Offload Details”
on page 43
Appendix D, “Increasing Location
Accuracy” on page 45
Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide Preface | 5
This appendix explains WMS Offload in further detail.
This appendix explains ways to increase location accuracy in AMP.
Page 6

Note, Caution, and Warning Icons
This document uses the following note, caution, and warning icons to emphasize advisories for certain actions,
configurations, or concepts:
NOTE: Indicates helpful suggestions, pertinent information, and important things to remember.
CAUTION: Indicates a risk of damage to your hardware or loss of data.
WARNING: Indicates a risk of personal injury or death.
Contacting Support
Table 2 Website contact
Web Site
Main Website dell.com
Support Website support.dell.com
Documentation Website support.dell.com/manuals
6 | Preface Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide
Page 7
Chapter 1
Overview
This document provides best practices for leveraging Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 (AMP, Master Console
and Failover) to monitor and manage your Dell PowerConnect W-Series infrastructure. Dell PowerConnect WSeries wireless infrastructure provides a wealth of functionality such as firewall, VPN, remote AP, IDS, IPS, and
ARM, as well as an abundance of statistical information.
Follow the simple guidelines in this document to garner the full benefit of the Dell PowerConnect W-Series
infrastructure.
This overview chapter contains the following topics:
“Prerequisites for Integrating Dell PowerConnect W-Series Infrastructure” on page7
“Auth protocol” on page7
Prerequisites for Integrating Dell PowerConnect W-Series Infrastructure
You will need the following information to monitor and manage your Dell PowerConnect W infrastructure:
SNMP community string (monitoring and discovery)
Telnet/SSH credentials (configuration only)
enable password (configuration only)
NOTE: Without proper Telnet/SSH credentials AMP will not be able to acquire license and serial information from controllers.
SNMPv3 credentials are required for WMS Offload:
Username
Auth password
Privacy password
Auth protocol
Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide Overview | 7
Page 8

8 | Overview Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide
Page 9

Chapter 2
Configuring AirWave for Global Dell PowerConnect W-Series Infrastructure
This chapter explains how to optimally configure Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 to globally manage your
Dell PowerConnect W-Series infrastructure, and contains the following topics:
“Disabling Rate Limiting in AMP Setup > General” on page9
“Entering Credentials in Device Setup > Communication” on page9
“Setting Up Recommended Timeout and Retries” on page10
“Setting Up Time Synchronization” on page11
“Enabling Support for Channel Utilization and Statistics” on page11
Disabling Rate Limiting in AMP Setup > General
In AMP Setup > General, the SNMP Rate Limiting for Monitored Devices option adds a small delay between
each SNMP GET request, thus the actual polling intervals will be longer than what is configured. For example,
setting a 10-minute polling interval will result in an actual 12-minute polling interval. Disabling rate limiting is
recommended in most cases.
To disable rate limiting in AirWave, follow these steps:
1. Navigate to AMP Setup > General.
2. Locate the Performance section on this page.
3. In the SNMP Rate Limiting for Monitored Devices field, select No, as shown in Figure 1.
4. Select Save.
Figure 1 SNMP Rate Limiting in AMP Setup > General
Entering Credentials in Device Setup > Communication
AMP requires several credentials to properly interface with Dell PowerConnect W-Series infrastructure. To enter
these credentials, follow these steps:
1. Navigate to Device Setup > Communication.
2. In the Default Credentials section, select the Edit link next to Dell PowerConnect W. The page illustrated
in Figure 2 appears.
Best Practices GuideBest Practices GuideBest Practices Guide | Best Practices Guide Configuring AirWave for Global Dell PowerConnect W-Series
Page 10

3. Enter the SNMP Community String.
NOTE: Be sure to note the community string, because it must match the SNMP Trap community string which is configured later in
this document.
Figure 2 Dell PowerConnect W Credentials in Device Setup > Communication
4. Enter the required fields for configuration and basic monitoring:
Telnet/SSH Username
Telnet/SSH Password
“enable” Password
5. Enter the required fields for WMS Offload:
SNMPv3 Auth Protocol
SNMPv3 Privacy Protocol
SNMPv3 Username
Auth Password
Privacy Password
NOTE: The protocols should be SHA and DES in order for WMS Offload to work.
6. When finished, select Save.
Setting Up Recommended Timeout and Retries
To set recommended timeout and retries settings, follow these steps:
1. In the Device Setup > Communication page, locate the SNMP Setting section.
2. Change SNMP Timeout setting to 10.
3. Change SNMP Retries to 1.
Figure 3 Timeout settings in Device Setup > Communication
4. Select Save.
10 | Configuring AirWave for Global Dell PowerConnect W-Series Infrastructure Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide
Page 11
Setting Up Time Synchronization
Setting up NTP on AirWave
On the AMP Setup > Network page, locate the Network Time Protocol (NTP) section. The Network Time
Protocol is used to synchronize the time between AMP and your network reference NTP server. NTP servers
synchronize with external reference time sources, such as satellites, radios, or modems.
NOTE: Specifying NTP servers is optional. NTP servers synchronize the time on the AMP server, not on individual access points.
To disable NTP services, clear both the Primary and Secondary NTP server fields. Any problem related to
communication between AMP and the NTP servers creates an entry in the event log. For more information on
ensuring that AMP servers have the correct time, please see http://support.ntp.org/bin/view/Servers/
NTPPoolServers.
Table 3 AMP Setup > Network > Secondary Network Fields and Default Values
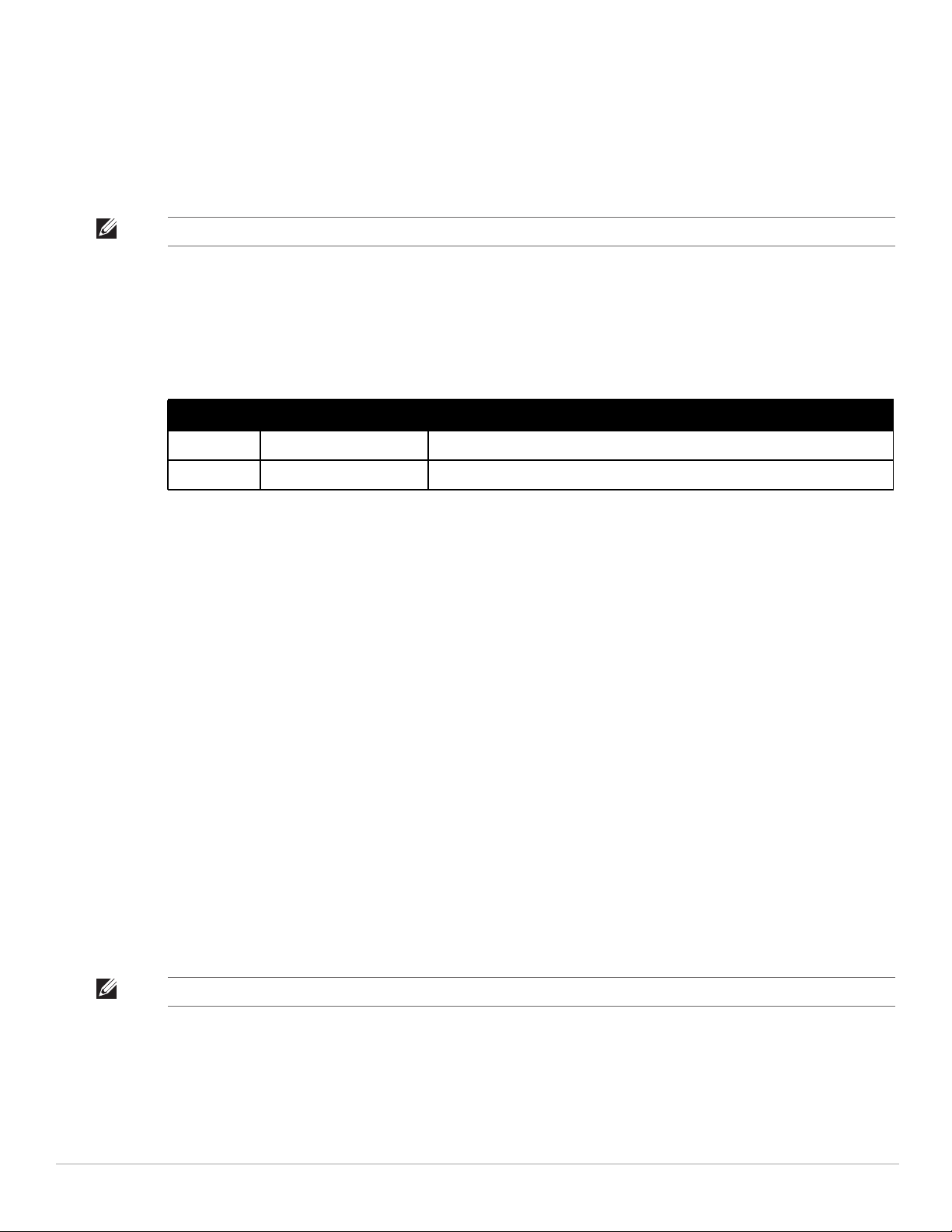
Setting Default Description
Primary ntp1.yourdomain.com Sets the IP address or DNS name for the primary NTP server.
Secondary ntp2.yourdomain.com Sets the IP address or DNS name for the secondary NTP server.
You can set the clock on a controller manually or by configuring the controller to use a Network Time Protocol
(NTP) server to synchronize its system clock with a central time source.
Manually Setting the Clock on a Controller
You can use either the WebUI or CLI to manually set the time on the controller’s clock.
1. Navigate to the Configuration > Management > Clock page.
2. Under Controller Date/Time, set the date and time for the clock.
3. Under Time Zone, enter the name of the time zone and the offset from Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
4. To adjust the clock for daylight savings time, click Enabled under Summer Time. Additional fields appear
that allow you to set the offset from UTC, and the start and end recurrences.
5. Click Apply.
Enabling Support for Channel Utilization and Statistics
In order to enable support for channel utilization statistics, you must have the following:
Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.2 or later
ArubaOS 6.0.1 or later
NOTE: AOS 6.0.1 can report RF utilization metrics, while AOS 6.1 is necessary to also obtain classified interferer information.
Access points - Dell PowerConnect W-AP105, W-AP92, W-AP93, W-AP125, W-AP124, and W-AP134
Controllers - Dell PowerConnect W-Series 6xx, 3xxx, or 6000
Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide Configuring AirWave for Global Dell PowerConnect W-Series Infrastructure | 11
Page 12

AirWave Setup
Follow these steps in AMP:
1. Navigate to AMP Setup > General.
2. In the Additional AMP Services section, set Enable AMON Data Collection to Yes, as shown in Figure 4:
Figure 4 AMON Data Collection setting in AMP Setup > General
3. Select Save.
Controller Setup (Master and Local)
CAUTION: Enabling these commands on AOS versions prior to 6.0.1.0 can result in performance issues on the controller. If you
are running previous firmware versions such as AOS 6.0.0.0, you should upgrade to AOS 6.0.1 (to obtain RF utilization metrics) or
6.1 (to obtain RF utilization and classified interferer information) before you enter this command.
SSH into the controller, enter “enable” mode, and issue the following commands:
(Controller-Name) # configure terminal
Enter Configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z
(Controller-Name) (config) # mgmt-server type amp primary-server <AMP IP>
(Controller-Name) (config) # write mem
12 | Configuring AirWave for Global Dell PowerConnect W-Series Infrastructure Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide
Page 13
Chapter 3
Configuring a Dell PowerConnect W Group in AMP
It is prudent to establish a Dell PowerConnect W Group within AMP. During the discovery process you will
move new discovered controllers into this group.
This chapter contains the following topics:
“Basic Monitoring Configuration” on page13
“Advanced Configuration” on page14
Basic Monitoring Configuration
1. Navigate to Groups > List.
2. Select Add.
3. Enter a Name that represents the Dell PowerConnect W-Series infrastructure from a security, geographical,
or departmental perspective and select Add.
4. You will be redirected to the Groups > Basic page for the Group you just created. On this page you will need
to tweak a few Dell PowerConnect W-specific settings.
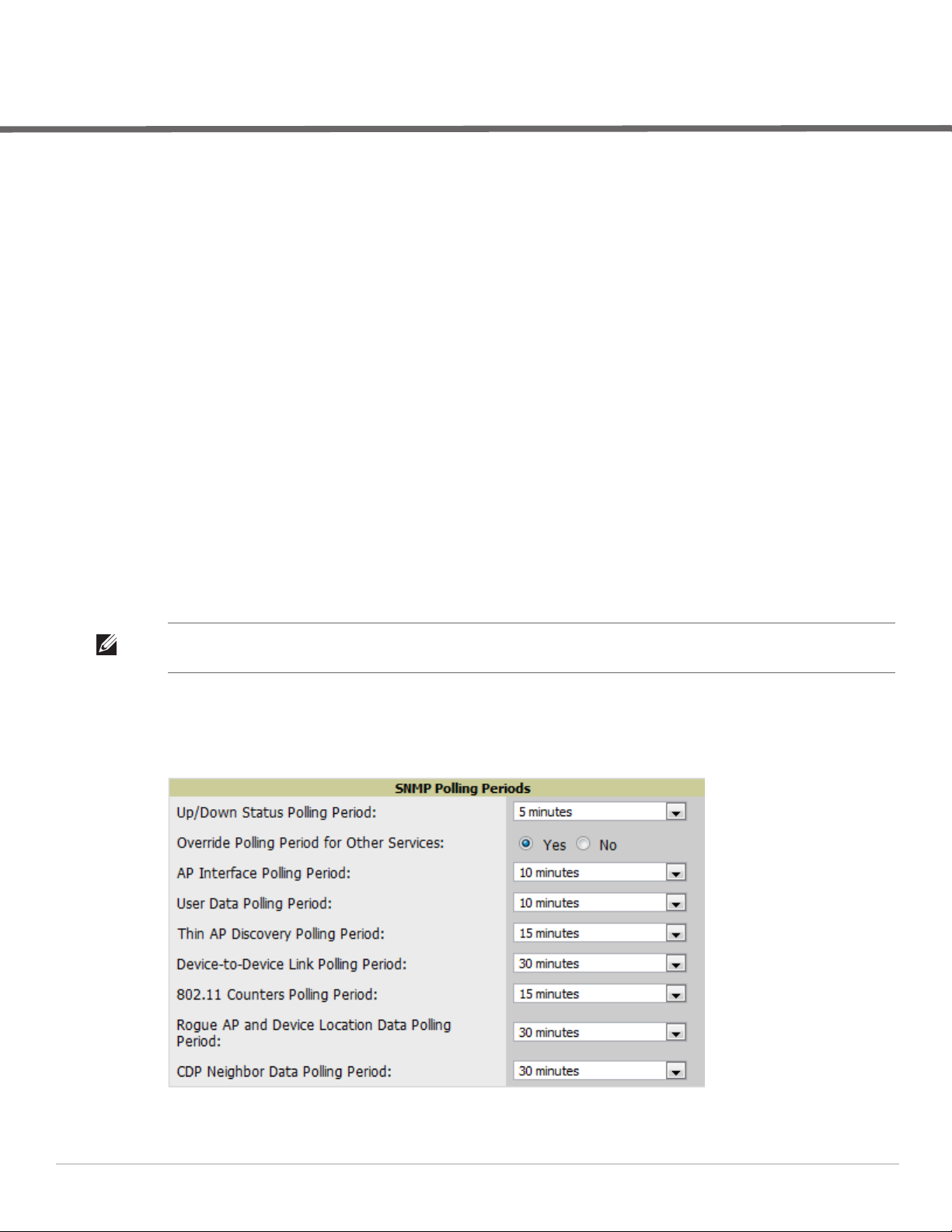
5. Find the SNMP Polling Periods section of the page, as illustrated in Figure 5.
6. Change Override Polling Period for Other Services to Yes.
7. Ensure User Data Polling Period is set to 10 minutes. Do not configure this interval lower than 5 minutes.
NOTE: Enabling the SNMP Rate Limiting for Monitored Devices option in the previous chapter adds a small delay between each
SNMP Get request, thus the actual polling interval is 12 minutes for 10 minute polling interval.
8. Change Device-to-Device Link Polling Period to 30 minutes.
9. Change Rogue AP and Device Location Data Polling Period to 30 minutes.
Figure 5 SNMP Polling Periods section of Groups > Basic
10. Locate the Aruba/Dell PowerConnect W section of this page, as illustrated in Figure 6.
11. Configure the proper SNMP Version for monitoring the Dell PowerConnect W-Series infrastructure.
Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide Configuring a Dell PowerConnect W Group in AMP | 13
Page 14

Figure 6 Group SNMP Version for Monitoring
12. Select Save and Apply.
Advanced Configuration
Refer to the Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave Configuration Guide at support.dell.com/manuals for detailed
instructions.
14 | Configuring a Dell PowerConnect W Group in AMP Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide
Page 15
Chapter 4
Discovering Dell PowerConnect W-Series Infrastructure
This chapter guides you through the process of discovering and managing your Dell PowerConnect W-Series
infrastructure.
AMP utilizes Dell PowerConnect W-Series topology to efficiently discover downstream infrastructure.
Refer to the following earlier chapters in this book before attempting discovery:
Chapter 2, “Configuring AirWave for Global Dell PowerConnect W-Series Infrastructure” on page9
Chapter 3, “Configuring a Dell PowerConnect W Group in AMP” on page13
The following topics in this chapter walk through the basic procedure for discovering and managing Dell
PowerConnect W-Series infrastructure:
“Discovering Master Controllers” on page15
“Local Controller Discovery” on page17
“Thin AP Discovery” on page17
NOTE: Always add one Controller and its affiliated Thin APs into management or monitoring mode in a serial fashion, one at a time.
Adding new devices is a very CPU intensive process for AMP and can quickly overwhelm all of the processing power of the server
if hundreds of Thin APs are added (migrated from New to Managed or Monitoring) simultaneously.
Discovering Master Controllers
Scan networks containing Dell PowerConnect W-Series Master controllers from Device Setup > Discover.
- or -
Manually enter the Master controller by following these steps in the Device Setup > Add page:
1. Select the Dell PowerConnect W-series controller type and select Add. The page illustrated on Figure 7
appears.
2. Enter the Name and the IP Address for the controller.
3. Enter SNMP Community String, which is required field for device discovery.
NOTE: Be sure to note the community string, because it must match the SNMP Trap community string which is configured later in
this document.
Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide Discovering Dell PowerConnect W-Series Infrastructure | 15
Page 16

Figure 7 Dell PowerConnect W Credentials in Device Setup > Add
4. Enter the required fields for configuration and basic monitoring:
Telnet/SSH Username
Telnet/SSH password
“enable” password
5. Enter the required fields for WMS Offload
SNMPv3 Auth Protocol
SNMPv3 Privacy Protocol
SNMPv3 Username
Auth Password
Privacy Password
NOTE: The protocols should be SHA and DES in order for WMS Offload to work.
16 | Discovering Dell PowerConnect W-Series Infrastructure Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide
Page 17

CAUTION: If you are using SNMPv3 and the controller's date/time is incorrect, the SNMP agent will not respond to SNMP
requests from AMP SNMP manager. This will result in the controller and all of its downstream access points showing as Down
in AMP.
6. Assign controller to a Group and Folder.
7. Ensure Monitor Only option is selected.
8. Select Add.
9. Navigate to APs/Devices > New page.
10. Select the Dell PowerConnect W Master controller you just added from the list of new devices.
11. Ensure Monitor Only option is selected.
12. Select Add.
Local Controller Discovery
Local controllers are added to AMP via the Master controller, by a discovery scan, or manually added in Device
Setup > Add. After waiting for the Thin AP Polling Period interval or executing a Poll Now command from the
APs/Devices > Monitor page, the Local controllers will appear on the APs/Devices > New page.
Add the Local controller to Group defined previously. Within AMP, Local controllers can be split away from the
Master controller's Group.
NOTE: Local Controller Discovery/monitoring may not work as expected if Airwave is unable to communicate directly with the
target device. Be sure and update any ACL/Firewall rules to allow AirWave to communicate with your network equipment.
Thin AP Discovery
Thin APs are discovered via the Local controller. After waiting for the Thin AP Polling Period or executing a Poll
Now command from the APs/Devices > Monitor page, thin APs will appear on the APs/Devices > New page.
Add the thin APs to the Group defined previously. Within Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave, thin APs can be split
away from the controller's Group. You can split thin APs into multiple Groups if required.
Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide Discovering Dell PowerConnect W-Series Infrastructure | 17
Page 18

18 | Discovering Dell PowerConnect W-Series Infrastructure Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide
Page 19

Chapter 5
AMP and Dell PowerConnect W-Series Integration Strategies
This chapter describes strategies for integrating AMP and Dell PowerConnect W-Series, and contains the
following topics:
“Integration Goals” on page19
“Example Use Cases” on page20
“Prerequisites for Integration” on page21
“Enable Stats Utilizing AMP” on page21
“WMS Offload Utilizing AMP” on page22
“Define AMP as Trap Host using ArubaOS CLI” on page22
“Understanding WMS Offload Impact on Dell PowerConnect W-Series infrastructure” on page26
Integration Goals
The following table summarizes the types of integration goals and strategies for meeting them in certain
architectural contexts:
Table 4 Integration Goals in All Masters or Master/Local Architectures
Integration Goals All Masters Architecture Master/ Local Architecture
Rogue and Client Info enable stats
Rogue containment only ssh access to controllers ssh access to controllers
Rogue and Client containment WMS Offload WMS Offload
Reduce Master Controller Load WMS Offload debugging off
IDS and Auth Tracking Define AMP as trap host Define AMP as trap host
Track Tag Location enable RTLS WMS Offload enable RTLS WMS Offload
Channel Utilization enable AMON enable AMON
Spectrum enable AMON enable AMON
Key integration points to consider include the following:
IDS Tracking does not require WMS Offload in an All-Master or Master/Local environment
IDS Tracking does require enable stats in a Master/Local environment
WMS Offload will hide the Security Summary tab on Master Controller's web interface
WMS Offload encompasses enable stats or enable stats is a subset of WMS Offload
Unless you enable stats on the Local Controllers in a Master/Local environment, the Local Controllers do not
populate their MIBs with any information about clients or rogue devices discovered/associated with their APs.
Instead the information is sent upstream to Master Controller.
Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide AMP and Dell PowerConnect W-Series Integration Strategies | 19
Page 20

Example Use Cases
The following are example use cases of integration strategies:
When to Use Enable Stats
You want to pilot Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave and doesn't want to make major configuration changes to
their infrastructure or manage configuration from AMP.
NOTE: Enable Stats still pushes a small subset of commands to the controllers via SSH.
See “Enable Stats Utilizing AMP” on page21.
When to Use WMS Offload
You have older Dell PowerConnect W-Series infrastructure in a Master/Local environment and their Master
controller is fully taxed. Offloading WMS will increase the capacity of the Master Controller by offloading
statistic gathering requirements and device classification coordination to AMP.
You want to use AMP to distribute client and rogue device classification amongst multiple Master Controllers
in a Master/Local environment or in an All-Masters environment.
See the following topics:
“WMS Offload Utilizing AMP” on page22
“Understanding WMS Offload Impact on Dell PowerConnect W-Series infrastructure” on page26
“WMS Offload Details” on page43
When to Use RTLS
A hospital wants to achieve very precise location accuracy (5 -15 feet) for their medical devices which are
associating to the WLAN.
You want to locate items utilizing Wi-Fi Tags.
NOTE: RTLS could negatively impact your AMP server's performance.
See “Leveraging RTLS to Increase Accuracy” on page45.
When to Define AMP as Trap Host
You want to track IDS events within the AMP UI.
You are in the process of converting their older third-party WLAN devices to Dell PowerConnect W and want
a unified IDS dashboard for all WLAN infrastructure.
You want to relate Auth failures to a client device, AP, Group of APs, and controller. AMP provides this
unique correlation capability.
See “Define AMP as Trap Host using ArubaOS CLI” on page22.
When to use Channel Utilization
You have a minimum version of AOS 6.1.0.0 and Dell PowerConnect W-AP105 or Dell PowerConnect W-
AP135
20 | AMP and Dell PowerConnect W-Series Integration Strategies Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide
Page 21

Prerequisites for Integration
If you have not discovered the Dell PowerConnect W-Series infrastructure or configured credentials, refer to the
previous chapters of this book:
Chapter 2, “Configuring AirWave for Global Dell PowerConnect W-Series Infrastructure” on page9
Chapter 3, “Configuring a Dell PowerConnect W Group in AMP” on page13
Chapter 4, “Discovering Dell PowerConnect W-Series Infrastructure” on page15
Enable Stats Utilizing AMP
To enable stats on the Dell PowerConnect W-series controllers, follow these steps:
1. Navigate to AMP Setup > General and locate the Device Configuration section.
2. Set the Allow WMS Offload Configuration in Monitor-Only Mode field to Yes, as shown in Figure 8:
Figure 8 WMS Offload Configuration in AMP Setup > General
3. Navigate to Groups > Basic for the group that contains your Dell PowerConnect W-series controllers.
4. Locate the Dell PowerConnect W section on the page.
5. Set the Offload WMS Database field to No, as shown in Figure 9:
Figure 9 Offload WMS Database field in Groups > Basic
6. Select Save and Apply.
7. Select Save.
This will push a set of commands via SSH to all Dell PowerConnect W local controllers. AMP must have read/
write access to the controllers in order to push these commands.
NOTE: This process will not reboot your controllers.
CAUTION: If you don't follow the above steps, local controllers will not be configured to populate statistics. This decreases
AMP's capability to trend client signal information and to properly locate devices. See Appendix A, “CLI ArubaOS and AMP
Commands” on page 37 on how to utilize ArubaOS CLI to enable stats on Dell PowerConnect W-Series infrastructure.
If your credentials are invalid or the changes are not applied to the controller, error messages will display on the
controller's APs/Devices > Monitor page under the Recent Events section. If the change fails, AMP does not
Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide AMP and Dell PowerConnect W-Series Integration Strategies | 21
Page 22

audit these setting (display mismatches) and you will need to apply to the controller by hand. See Appendix A,
“CLI ArubaOS and AMP Commands” on page37 for detailed instructions.
These are the commands pushed by AMP while enabling WMS Offload (do not enter these commands):
configure terminal
no mobility-manager <Active WMS IP Address>
wms
general collect-stats enable
stats-update-interval 120
show wms general
write mem
WMS Offload Utilizing AMP
To offload WMS on the Dell PowerConnect W-Series controllers using AMP:
1. In AMP Setup > General, locate the Device Configuration section and enable or disable Allow WMS
Offload Configuration in Monitor-Only Mode.
2. Select Save and Apply. This will push a set of commands via SSH to all Dell PowerConnect W Master
Controllers. If the controller does not have an SNMPv3 user that matches the AMP database it will
automatically create a new SNMPv3 user. AMP must have read/write access to the controllers in order to push
these commands
3. Navigate to Groups > Basic and locate the Dell PowerConnect W section.
4. Set the Offload WMS Database field to Yes, as shown in Figure 9.
NOTE: This process will not reboot your controllers. See Appendix A, “CLI ArubaOS and AMP Commands” on page 37 for
information on how to utilize ArubaOS CLI to enable stats or WMS Offload.
CAUTION: The SNMPv3 user's Auth Password and Privacy Password must be the same.
Do not enter these commands; these are pushed by AMP while enabling WMS Offload.
configure terminal
mobility-manager <AMP IP> user <AMP SNMPv3 User Name> <AMP Auth/Priv PW>
stats-update-interval 120
write mem
NOTE: AMP will configure SNMPv2 traps with the mobile manager command.
Define AMP as Trap Host using ArubaOS CLI
To ensure the AMP server is defined a trap host, SSH into each controller (Master and Local), enter “enable”
mode, and issue the following commands:
(Controller-Name) # configure terminal
Enter Configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z
22 | AMP and Dell PowerConnect W-Series Integration Strategies Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide
Page 23

(Controller-Name) (config) # snmp-server host <AMP IP ADDR> version 2c <SNMP COMMUNITY
STRING OF CONTROLLER>
NOTE: Ensure the SNMP community matches those that were configured in Chapter 2, “Configuring AirWave for Global Dell
PowerConnect W-Series Infrastructure” .
(Controller-Name) (config) # snmp-server trap source <CONTROLLER'S IP>
(Controller-Name) (config) # write mem
CAUTION: Do not configure the SNMP version to v3 because AMP does not support SNMPv3 traps/informs.
ArubaOS Traps Utilized by AMP
The following are Auth, IDS, and ARM traps utilized by AMP:
“Auth Traps” on page23
“IDS Traps” on page23
“ARM Traps” on page24
Auth Traps
wlsxNUserAuthenticationFailed
wlsxNAuthServerReqTimedOut
IDS Traps
wlsxwlsxSignatureMatchAP
wlsxSignatureMatchSta
wlsxSignAPNetstumbler
wlsxSignStaNetstumbler
wlsxSignAPAsleap
wlsxSignStaAsleap
wlsxSignAPAirjack
wlsxSignStaAirjack
wlsxSignAPNullProbeResp
wlsxSignStaNullProbeResp
wlsxSignAPDeauthBcast
wlsxSignStaDeauthBcastwlsxChannelFrameErrorRateExceeded
wlsxChannelFrameFragmentationRateExceeded
wlsxChannelFrameRetryRateExceeded
wlsxNIpSpoofingDetected
wlsxStaImpersonation
wlsxReservedChannelViolation
wlsxValidSSIDViolation
wlsxStaPolicyViolation
wlsxRepeatWEPIVViolation
wlsxWeakWEPIVViolation
wlsxFrameRetryRateExceeded
Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide AMP and Dell PowerConnect W-Series Integration Strategies | 23
Page 24

wlsxFrameReceiveErrorRateExceeded
wlsxFrameFragmentationRateExceeded
wlsxFrameBandWidthRateExceeded
wlsxFrameLowSpeedRateExceeded
wlsxFrameNonUnicastRateExceeded
wlsxChannelRateAnomaly
wlsxNodeRateAnomalyAP
wlsxNodeRateAnomalySta
wlsxEAPRateAnomaly
wlsxSignalAnomaly
wlsxSequenceNumberAnomalyAP
wlsxSequenceNumberAnomalySta
wlsxApFloodAttack
wlsxInvalidMacOUIAP
wlsxInvalidMacOUISta
wlsxStaRepeatWEPIVViolation
wlsxStaWeakWEPIVViolation
wlsxStaAssociatedToUnsecureAP
wlsxStaUnAssociatedFromUnsecureAP
wlsxAPImpersonation
wlsxDisconnectStationAttackAP
wlsxDisconnectStationAttackSta
ARM Traps
AP Power Change
AP Mode Change
AP Channel Change
Ensuring That IDS and Auth Traps Display in AMP Using CLI
Validate your ArubaOS configuration by exiting the configure terminal mode and issue the following command:
(Controller-Name) # show snmp trap-list
If any of the traps below don't show as enabled enter configure terminal mode and issue the following
command:
(Controller-Name) (config) # snmp-server trap enable <TRAPS FROM LIST ABOVE>
(Controller-Name) (config) # write mem
NOTE: See Appendix A, “CLI ArubaOS and AMP Commands” on page 37 for the full command that can be copied and pasted
directly into the ArubaOS CLI.
Ensure the source IP of the traps match the IP that AMP utilizes to manage the controller, as shown in Figure 10.
Navigate to APs/Devices > Monitor to validate the IP address in the Device Info section.
24 | AMP and Dell PowerConnect W-Series Integration Strategies Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide
Page 25

Figure 10 Verify IP Address on APs/Devices > Monitor Page
Verify that there is a SNMPv2 community string that matches the SNMP Trap community string on the
controller.
(Controller-Name) # show snmp community
SNMP COMMUNITIES
----------------
COMMUNITY ACCESS VERSION
--------- ------ -------
public READ_ONLY V1, V2c
(Controller-Name) # #show snmp trap-host
SNMP TRAP HOSTS
---------------
HOST VERSION SECURITY NAME PORT TYPE TIMEOUT RETRY
---- ------- ------------- ---- ---- ------- -----
10.2.32.4 SNMPv2c public 162 Trap N/A N/A
Verify firewall port 162 (default) is open between AMP and the controller.
Validate traps are making it into AMP by issuing the following commands from AMP command line.
[root@AMP ~]# qlog enable snmp_traps
[root@AMP ~]# tail -f /var/log/amp_diag/snmp_traps
1241627740.392536 handle_trap|2009-05-06 09:35:40 UDP: [10.2.32.65]->[10.51.5.118]:-
32737 sends trap: DISMAN-EVENT-MIB::sysUpTimeInstance = Timeticks: (127227800) 14 days,
17:24:38.00 SNMPv2-MIB::snmpTrapOID.0 = OID: SNMPv2SMI::enterprises.14823.2.3.1.11.1.2.1106 SNMPv2-SMI::enterprises.14823.2.3.1.11.1.1.60
= Hex-STRING: 07 D9 05 06 09 16 0F 00 2D 08 00 SNMPv2SMI::enterprises.14823.2.3.1.11.1.1.5.0 = Hex-STRING: 00 1A 1E 6F 82 D0 SNMPv2SMI::enterprises.14823.2.3.1.11.1.1.6.0 = STRING: aruba-apSNMPv2SMI::enterprises.14823.2.3.1.11.1.1.1.0 = Hex-STRING: 00 1A 1E C0 2B 32 SNMPv2SMI::enterprises.14823.2.3.1.11.1.1.56.0 = INTEGER: 2 SNMPv2SMI::enterprises.14823.2.3.1.11.1.1.17.0 = STRING: aruba-124-c0:2b:32 SNMPv2SMI::enterprises.14823.2.3.1.11.1.1.18.0 = INTEGER: 11 SNMPv2SMI::enterprises.14823.2.3.1.11.1.1.58.0 = STRING: http://10.51.5.118/screens/wmsi/
reports.html?mode=ap&bssid=00:1a:1e:6f:82:d0
NOTE: You will see many IDS and Auth Traps from this command. AMP only processes a small subset of these Traps which display
within AMP. The Traps that AMP does process are listed above.
Ensure you disable qlogging after testing as it could negatively impact AMP performance if left turned on:
[root@AMP ~]# qlog enable snmp_traps
Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide AMP and Dell PowerConnect W-Series Integration Strategies | 25
Page 26

Understanding WMS Offload Impact on Dell PowerConnect W-Series infrastructure
When offloading WMS, it is important to understand what functionality is migrated to AMP and what
functionality is deprecated.
The following ArubaOS tabs and sections are deprecated after offloading WMS:
Plan Tab - where floor plans are stored and heatmaps are generated. Prior to offloading WMS, ensure that you
have exported floor plans from ArubaOS and imported into AMP. All functionality within the Plan Tab is
incorporated with the VisualRF module in AMP.
Report Tab - All reports are incorporate within AMP.
Events Tab - the majority of functionality within this Tab is incorporate within AMP Reports and Alerts
sections with the exception of:
Interference Detected
Rogue AP
Station Failed
Suspected Rogue AP
The Security Summary section (Figure 11) disappears after offloading WMS. The data is still being processed by
the Master Controller, but the summary information is not available. AMP does provide the ability to view some
of this information in detail and summary form.
Figure 11 Security Summary on Master Controller
WLAN Attack Summary
DOS Attacks - no summary data available in AMP
Impersonation Attacks - no summary data available in AMP
Signature Pattern Matches - partial summary data available on Home and RAPIDS > Overview pages
Policy Violations - no summary data available in AMP
Unauthorized Devices Detected - no summary data available in AMP
Rogue AP Classification Summary
Rogue APs Detected - summary data available on RAPIDS > Overview
Rogue APs Disabled - no summary data available in AMP
Suspected Rogue APs - partial data is available in AMP on each APs/Devices > Manage page
Interfering APs Detected - partial data is available in AMP on each APs/Devices > Manage page
26 | AMP and Dell PowerConnect W-Series Integration Strategies Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide
Page 27

Known Interfering APs - partial data is available in AMP on each APs/Devices > Manage page
Router Summary
Routers Detected - no summary data available in AMP
Client Classification Summary
Valid Clients - summary data available on all pages in the dashboard
Interfering clients - no summary data available in AMP
Disabled Clients - no summary data available in AMP
See “Rogue Device Classification” on page33 for more information on security, IDS, WIPS, WIDS,
classification, and RAPIDS.
Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide AMP and Dell PowerConnect W-Series Integration Strategies | 27
Page 28

28 | AMP and Dell PowerConnect W-Series Integration Strategies Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide
Page 29

Chapter 6
Dell PowerConnect W-Specific Capabilities in AMP
This chapter discusses Dell PowerConnect W-specific capabilities in AMP, and contains the following topics:
“Dell PowerConnect W Traps for RADIUS Auth and IDS Tracking” on page29
“Remote AP Monitoring” on page30
“ARM and Channel Utilization Information” on page30
“Viewing Controller License Information” on page32
“Rogue Device Classification” on page33
“Rules-Based Controller Classification” on page34
Dell PowerConnect W Traps for RADIUS Auth and IDS Tracking
The authentication failure traps are received by the AMP server and correlated to the proper controller, AP, and
user. See Figure 12 showing all authentication failures related to a controller.
Figure 12 RADIUS Authentication Traps in AMP
The IDS traps are received by the AMP server and correlated to the proper controller, AP, and user. See Figure 13
showing all IDS traps related to a controller.
Figure 13 IDS Traps in AMP
Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide Dell PowerConnect W-Specific Capabilities in AMP | 29
Page 30

Remote AP Monitoring
To monitor remote APs, follow these steps:
1. From the APs/Devices > List page, filter on the Remote Device column to find remote devices.
2. To view detailed information on the remote device, select the device name. The page illustrated in Figure 14
appears.
Figure 14 Remote AP Detail Page
3. You can also see if there are users plugged into the wired interfaces in the Connected Users list.
NOTE: This feature is only available when the remote APs are in split tunnel and tunnel modes.
ARM and Channel Utilization Information
ARM statistics and Channel utilization are very powerful tools for diagnosing capacity and other issues in your
WLAN.
1. Navigate to an APs/Devices > Monitor page for any of the following Dell PowerConnect W models: Dell
PowerConnect W-AP105, W-AP92, W-AP93, W-AP124, W-AP125, W-AP134 or W-AP135.
2. In the Radios table, select a radio link under the Name column for a radio.
Figure 15 ARM and Channel Utilization Graphs
30 | Dell PowerConnect W-Specific Capabilities in AMP Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide
Page 31

See the Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 User Guide in Home > Documentation for more information on the
data displayed in the Radio Statistics page for these devices.
VisualRF and Channel Utilization
To view how channel utilization is impacting an area within a building, follow these steps:
1. Navigate to a floor plan by clicking on the thumbnail on a device’s APs/Devices > Monitor page or navigating
to VisualRF > Floor Plans page.
2. Select the Overlays menu.
3. Select Utilization overlay.
4. Select Current or Maximum (over last 24 hours).
5. Select total (default), receive, transmit, or interference (see Figure 16).
Figure 16 Channel Utilization in VisualRF (Interference)
Configuring Channel Utilization Triggers
1. Navigate to System > Triggers and select Add.
2. Select Channel Utilization from the Type drop-down menu as seen on Figure 17:
Figure 17 Channel Utilization Trigger
Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide Dell PowerConnect W-Specific Capabilities in AMP | 31
Page 32

3. Enter the duration evaluation period.
4. Select Add New Trigger Condition.
5. Create a trigger condition for Radio Type and select the frequency to evaluate.
6. Select total, receive, transmit, or interference trigger condition.
7. Set up any restrictions or notifications (refer to the Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 User Guide in Home >
Documentation for more details)
8. When finished, select Add.
Viewing Channel Utilization Alerts
1. Navigate to APs/Devices > Monitor or System > Alerts.
2. Sort the Trigger Type column and find Channel Utilization alerts.
View Channel Utilization in RF Health Reports
1. Navigate to Reports > Generated.
2. Find and select a Device Summary or RF Health report.
Figure 18 Channel Utilization in an RF Health Report
Viewing Controller License Information
Follow these steps to view your controller’s license information in AMP:
1. Navigate to the APs/Devices > Monitor page of a controller under AMP management.
2. Select the License link in the Device Info section. A pop-up window, shown on Figure 19, appears listing all
licenses.
Figure 19 License Popup from APs/Devices > Monitor
32 | Dell PowerConnect W-Specific Capabilities in AMP Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide
Page 33

Rogue Device Classification
Only complete this section if you have completed WMS Offload procedure above. After offloading WMS, AMP
maintains the primary ARM, WIPS, and WIDS state classification for all devices discovered over-the-air.
Table 5 WIPS/WIDS to AMP Controller Classification Matrix
AMP Controller Classification AOS (WIPS/WIDS)
Unclassified (default state) Unknown
Valid Valid
Suspected Neighbor Interfering
Neighbor Known Interfering
Suspected Rogue Suspected Rogue
Rogue Rogue
Contained Rogue DOS
To check and reclassify rogue devices, follow these steps:
1. Navigate to the Rogue > Detail page for the rogue device, as shown in Figure 20.
Figure 20 Rogue Detail Page Illustration
2. Select the proper classification from the RAPIDS Classification Override drop-down menu.
CAUTION: Changing the controller's classification within the AMP UI will push a reclassification message to all controllers
managed by the AMP server that are in Groups with Offloading the WMS database set to Yes. To reset the controller
classification of a rogue device on AMP, change the controller classification on the AMP UI to unclassified.
Controller classification can also be updated from RAPIDS > List via the Modify Devices link.
All rogue devices will be set to a default controller classification of unclassified when WMS is first offloaded
except for devices classified as valid. Rogue devices classified in AOS as valid will also be classified within AMP as
valid for their controller classification as well. As APs report subsequent classification information about rogues,
this classification will be reflected within AMP UI and propagated to controllers that AMP manages. The device
classification reflected in the Controller's UI and in the AMP UI will probably not match, because the Controller/
APs do not reclassify rogue devices frequently.
Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide Dell PowerConnect W-Specific Capabilities in AMP | 33
Page 34

To update a group of devices' controller classification to match the AOS device classification, navigate to
RAPIDS > List and utilize the Modify Devices checkbox combined with the multiple sorting a filtering features.
Table 6 ARM to AMP Classification Matrix
AMP ArubaOS (ARM)
Unclassified (default state) Unknown
Valid Valid
Contained DOS
1. Navigate to the Users > User Detail page for the user.
2. Select the proper classification from the Classification drop-down menu as seen in Figure 21:
Figure 21 User Classification
CAUTION: Changing User Classification within the AMP UI will push a user reclassification message to all controllers managed
by the AMP server that are in Groups with Offloading the WMS database set to Yes.
All users will be set to a default classification of unclassified when wms is first offloaded. As APs report
subsequent classification information about users, this classification will be reflected within AMP UI and
propagated to controllers that AMP manages. It is probable that the user's classification reflected in the
controller's UI and in the AMP UI will not match, because the controller/APs do not reclassify users frequently.
There is no method in the AMP UI to update user classification on mass to match the controller's classification.
Each client must be updated individually within the AMP UI.
Rules-Based Controller Classification
Using RAPIDS Defaults for Controller Classification
To use the controller's classification as RAPIDS classification, follow these steps:
1. Navigate to RAPIDS > Rules and select the pencil icon for a rule.
2. In the Classification drop-down menu, select Use Controller Classification as seen in Figure 22.
3. Select Save.
34 | Dell PowerConnect W-Specific Capabilities in AMP Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide
Page 35

Figure 22 Using Controller Classification
Changing RAPIDS based on Controller Classification
1. Navigate to RAPIDS > Rules.
2. In the Classification drop-down menu, select desired RAPIDS classification.
3. Select Controller Classification from drop-down menu, as shown in Figure 23.
Figure 23 Configure Rules for Classification
4. Select Add.
5. Select desired controller classification to use as an evaluation in RAPIDS.
6. Select Save.
Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide Dell PowerConnect W-Specific Capabilities in AMP | 35
Page 36

36 | Dell PowerConnect W-Specific Capabilities in AMP Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide
Page 37

Appendix A
CLI ArubaOS and AMP Commands
Enable Channel Utilization Events Utilizing ArubaOS CLI (Local and Master Controllers)
CAUTION: Enabling these commands on ArubaOS versions prior to 6.1 can result in performance issues on the controller.
SSH into the controller, and enter “enable” mode, and issue the following commands:
(Controller-Name) # configure terminal
Enter Configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z
(Controller-Name) (config) # mgmt-server type amp primary-server <AMP IP>
(Controller-Name) (config) # write mem
Enable Stats With the ArubaOS CLI (Local Controller in Master Local Environment)
NOTE: Do not use these commands if using AMP GUI.
CAUTION: Enabling these commands on ArubaOS versions prior to 6.1 can result in performance issues on the controller.
SSH into the controller, and enter “enable” mode, and issue the following commands:
(Controller-Name) # configure terminal
Enter Configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z
(Controller-Name) (config) # wms general collect-stats enable
(Controller-Name) (config) # write mem
Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide CLI ArubaOS and AMP Commands | 37
Page 38

Offload WMS Utilizing ArubaOS CLI and AMP CLI (SNMP Walk)
NOTE: Do not use these commands if using AMP GUI.
ArubaOS CLI
SSH into all controllers (local and master), and enter “enable” mode, and issue the following commands:
(Controller-Name) # configure terminal
Enter Configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z
(Controller-Name) (config) # mobility-manager <AMP IP> user <MMS-USER> <MMS-SNMPPASSWORD> trap-version 2c
NOTE: This command creates an SNMPv3 user on the controller with authentication protocol configured to 'sha' and privacy
protocol 'DES'. The user and password must be at least eight characters, because the Net-SNMP package in AMP adheres to this
IETF recommendation. ArubaOS automatically creates Auth and Privacy passwords from this single password. If mobilitymanager is already using a preconfigured SNMPv3 user ensure the Privacy and Authentication passwords are the same.
This command also creates the AMP server as an SNMPv3 Trap Host in the controller's running configuration.
Sample: mobility-manager 10.2.32.1 user airwave123 airwave123
(Controller-Name) (config) # write mem
AMP SNMP
Login into the Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave server with proper administrative access and issue the following
command for all controllers (master and locals):
NOTE: Do not use these commands if using AMP GUI.
[root@AMP ~]# snmpwalk -v3 -a SHA -l AuthPriv -u <MMS-USER> -A <MMS-SNMP-PASSWORD> -X
<MMS-SNMP-PASSWORD> <ARUBA CONTROLLER IP ADDRESS> wlsxSystemExtGroup
WLSX-SYSTEMEXT-MIB::wlsxSysExtSwitchIp.0 = IpAddress: 10.51.5.222
WLSX-SYSTEMEXT-MIB::wlsxSysExtHostname.0 = STRING: aruba-3600-2
.
..
WLSX-SYSTEMEXT-MIB::wlsxSysExtSwitchLastReload.0 = STRING: User reboot.
WLSX-SYSTEMEXT-MIB::wlsxSysExtLastStatsReset.0 = Timeticks: (0) 0:00:00.00 response
[root@AMP ~]#
NOTE: Unless this SNMP walk command is issued properly on all of the controllers, they will not properly populate client and
rogue statistics. Ensure the user and passwords match exactly to those entered in above sections.
Sample: snmpwalk -v3 -a SHA -l AuthPriv -u airwave123 -A airwave123 -X airwave123
10.51.3.222 wlsxSystemExtGroup
If you do not use AMP GUI to offload WMS, you must add a cronjob on the AMP server to ensure continued
statistical population. Because the MIB walk/touch does not persist through a controller reboot, a cronjob is
required to continually walk and touch the MIB.
38 | CLI ArubaOS and AMP Commands Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide
Page 39

Ensuring Master Controller Pushes Config to Local Controllers Utilizing ArubaOS CLI
NOTE: Do not use these commands if using AMP GUI.
(Controller-Name) (config) # cfgm mms config disable
NOTE: This command ensures configuration changes made on the master controller will propagate to all local controllers.
(Controller-Name) (config) # write mem
Disable Debugging Utilizing ArubaOS CLI
If you are experiencing performance issues on the Master Controller, ensure that debugging is disabled. It should
be disabled by default. Debugging coupled with gathering the enhanced statistics can put a strain on the
controllers CPU, so it is highly recommended to disable debugging.
To disable debugging, SSH into the controller, enter “enable” mode, and issue the following commands:
(Controller-Name) # show running-config | include logging level debugging
If there is output, then use the following commands to remove the debugging:
(Controller-Name) # configure terminal
Enter Configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z
(Controller-Name) (config) # no logging level debugging <module from above>
(Controller-Name) (config) # write mem
Restart WMS on Local Controllers Utilizing ArubaOS CLI
To ensure local controllers are populating rogue information properly, SSH into each local controller, enter
“enable” mode, and issue the following commands:
(Controller-Name) # configure terminal
Enter Configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z
(Controller-Name) (config) # process restart wms
NOTE: You will need to wait until the next Rogue Poll Period to execute a Poll Now for each local controller to see rogue devices
begin to appear in AMP after executing restart wms in ArubaOS.
Configure the ArubaOS CLI
Use the following procedure to configure the ArubaOS CLI when not Offloading WMS to AMP (AOS 6.0 and
GT). To ensure proper event correlation for IDS events when WMS if not offloaded to AMP, SSH into each
controller (Master and Local), enter “enable” mode, and issue the following commands:
(Controller-Name) # configure terminal
Enter Configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z
(Controller-Name) (config) # ids management-profile
(Controller-Name) (config) # ids general-profile <name>
(Controller-Name) (config) # ids-events logs-and-traps
(Controller-Name) (config) # write mem
Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide CLI ArubaOS and AMP Commands | 39
Page 40

Enable Proper Traps With the ArubaOS CLI
To ensure the proper traps are configured on Dell PowerConnect W-series controllers copy and paste the
following command after entering “enable” mode and issuing the configure terminal command:
snmp-server trap enable wlsxNUserAuthenticationFailed
snmp-server trap enable wlsxUserAuthenticationFailed
snmp-server trap enable wlsxNAuthServerReqTimedOut
snmp-server trap enable wlsxSignatureMatchAP
snmp-server trap enable wlsxSignatureMatchSta
snmp-server trap enable wlsxSignAPNetstumbler
snmp-server trap enable wlsxSignStaNetstumbler
snmp-server trap enable wlsxSignAPAsleap
snmp-server trap enable wlsxSignStaAsleap
snmp-server trap enable wlsxSignAPAirjack
snmp-server trap enable wlsxSignStaAirjack
snmp-server trap enable wlsxSignAPNullProbeResp
snmp-server trap enable wlsxSignStaNullProbeResp
snmp-server trap enable wlsxSignAPDeauthBcast
snmp-server trap enable wlsxSignStaDeauthBcastwlsxChannelFrameErrorRateExceeded
snmp-server trap enable wlsxChannelFrameFragmentationRateExceeded
snmp-server trap enable wlsxChannelFrameRetryRateExceeded
snmp-server trap enable wlsxNIpSpoofingDetected
snmp-server trap enable wlsxStaImpersonation
snmp-server trap enable wlsxReservedChannelViolation
snmp-server trap enable wlsxValidSSIDViolation
snmp-server trap enable wlsxStaPolicyViolation
snmp-server trap enable wlsxRepeatWEPIVViolation
snmp-server trap enable wlsxWeakWEPIVViolation
snmp-server trap enable wlsxFrameRetryRateExceeded
snmp-server trap enable wlsxFrameReceiveErrorRateExceeded
snmp-server trap enable wlsxFrameFragmentationRateExceeded
snmp-server trap enable wlsxFrameBandWidthRateExceeded
snmp-server trap enable wlsxFrameLowSpeedRateExceeded
snmp-server trap enable wlsxFrameNonUnicastRateExceeded
snmp-server trap enable wlsxChannelRateAnomaly
snmp-server trap enable wlsxNodeRateAnomalyAP
snmp-server trap enable wlsxNodeRateAnomalySta
snmp-server trap enable wlsxEAPRateAnomaly
snmp-server trap enable wlsxSignalAnomaly
snmp-server trap enable wlsxSequenceNumberAnomalyAP
snmp-server trap enable wlsxSequenceNumberAnomalySta
snmp-server trap enable wlsxApFloodAttack
snmp-server trap enable wlsxInvalidMacOUIAP
snmp-server trap enable wlsxInvalidMacOUISta
snmp-server trap enable wlsxStaRepeatWEPIVViolation
snmp-server trap enable wlsxStaWeakWEPIVViolation
snmp-server trap enable wlsxStaAssociatedToUnsecureAP
snmp-server trap enable wlsxStaUnAssociatedFromUnsecureAP
snmp-server trap enable wlsxAPImpersonation
snmp-server trap enable wlsxDisconnectStationAttackAP
snmp-server trap enable wlsxDisconnectStationAttackSta
NOTE: You will need to issue the write mem command.
40 | CLI ArubaOS and AMP Commands Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide
Page 41

Appendix B
How AMP Acquires Data from Dell PowerConnect W-Series devices
Table 7 How AMP Acquires Data from Dell PowerConnect W-Series devices
Data Elements Controller/Thin AP
SNMP MIB SNMP Traps AMON CLI/SSH WMS Offload RTLS
Configuration interface
Device configuration/audit X
User and client interfaces
Assoc/auth/roam XX
Bandwidth X
Signal quality XX
Auth failures X
AP/radio interfaces
CPU and memory utilization <--------------------------------N/A---------------------------------------->
Bandwidth X
Transmit Power X
Channel utilization X
Noise floor X
Frame rates X
Error counters X
Channel summary X
ARM events X
Active interferers X
Active BSSIDs/SSIDs X
Security
IDS events X
Neighbors/rogues XX
Neighbor re-classification XX
Client classification X
User de-auth X
Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide How AMP Acquires Data from Dell PowerConnect W-Series devices | 41
Page 42

42 | How AMP Acquires Data from Dell PowerConnect W-Series devices Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide
Page 43

Appendix C
WMS Offload Details
WMS Offload instructs the Master controller to stop correlating ARM, WIPS, and WIDS state information
amongst its Local controllers, because AMP will assume this responsibility. Figure 24 depicts how Dell
PowerConnect W-AirWave communicates state information with Local controllers.
Figure 24 ARM/WIPS/WIDS Classification Message Workflow
State Correlation Process
1. Dell PowerConnect W-Series AP hears rogue device A
2. Local controller 1-3 evaluates devices and does initial classification and sends a classification request to the
AMP
3. AMP receives message and re-classifies the device if necessary and reflects this within AMP GUI and via
SNMP traps, if configured
4. AMP sends a classification message back to all Local controllers managed by Master controller 1, (1-1, 1-2, and
1-3)
5. AMP sends a classification message back to all additional Local controllers managed by the Dell
PowerConnect W-AirWave server. In this example all Local controllers under Master controller 2, (2-1, 2-2,
and 2-3) would receive the classification messages.
6. If an administrative AMP user manually overrides the classification, then AMP will send a re-classification
message to all applicable local controllers
Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide WMS Offload Details | 43
Page 44

7. AMP periodically polls each Local controller's MIB to ensure state parity with the AMP database. If the Local
controller's device state does not comply with the AMP database, AMP will send a re-classification message to
bring it back into compliance.
NOTE: The Rogue Detail page displays a BSSID table for each rogue that displays the desired classification and the classification
on the device.
Benefits of using AMP as Master Device State Manager
Ability to correlate state among multiple Master controllers. This will reduce delays in containing a rogue
device or authorizing a valid device when devices roam across a large campus.
Ability to correlate state of third party access points with ARM. This will ensure Dell PowerConnect W-Series
infrastructure interoperates more efficiently in a mixed infrastructure environment.
Ability to better classify devices based on AMP wire-line information not currently available in ArubaOS.
AMP provides a near real-time event notification and classification of new devices entering air space.
RAPIDS gains additional wire-line discovery data from Dell PowerConnect W-Series controllers.
44 | WMS Offload Details Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide
Page 45

Appendix D
Increasing Location Accuracy
Understand Band Steering's Impact on Location
Band steering can negatively impact location accuracy when testing in highly mobile environment. The biggest
hurdle is scanning times in 5 GHz frequency.
Table 8 Location accuracy impact
Operating Frequency Total Channels Scanning Frequency Scanning Time Total Time One Pass
2.4 GHz 11 (US) 10 seconds 110 milliseconds 121.21 seconds
5 GHz 24 (US) 10 seconds 110 milliseconds 242.64 seconds
Leveraging RTLS to Increase Accuracy
This section provides instructions for integrating the AMP, Dell PowerConnect W-Series WLAN infrastructure
and RTLS feed for more accurately locating wireless clients and Wi-Fi Tags.
Deployment Topology
Figure 25 Typical Client Location
Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide Increasing Location Accuracy | 45
Page 46

Figure 26 Typical Tag Deployment
Prerequisites
You will need the following information to monitor and manage your Dell PowerConnect W-Series
infrastructure.
Ensure AMP server is already monitoring Dell PowerConnect W-Series infrastructure
Ensure WMS Offload process is complete
Ensure firewall configuration for port 5050 (default port) supports bidirectional UDP communication
between the AMP server's IP address and each access point's IP address
Enable RTLS service on the AMP server
To enable RTLS service on the AMP server, follow these steps:
1. Navigate to AMP Setup > General and locate the AMP Additional Services section
2. Select Yes to Enable RTLS Collector.
3. A new section will automatically appear with the following settings:
RTLS Port - match controller default is 5050
RTLS Username - match the SNMPv3 MMS username configured on controller
RTLS Password - match the SNMPv3 MMS password configured on controller
Figure 27 RTLS Fields in AMP Setup > General
4. Select Save at the bottom of the page.
46 | Increasing Location Accuracy Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide
Page 47

Enable RTLS on Controller
NOTE: RTLS can only be enabled on the master controller and it will automatically propagate to all local controllers.
SSH into master controller, enter “enable” mode, and issue the following commands:
(Controller-Name) # configure terminal
Enter Configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z
(Controller-Name) (config) # ap system-profile <PROFILE USED BY THIN APs>
(Controller-Name) (AP system profile default) # rtls-server ip-addr <IP OF AMP SERVER> port 5050
key <SNMPv3 MMS PASSWORD CONFIGURED ON CONTROLLER>
(Controller-Name) (AP system profile default) # write mem
To validate exit configuration mode:
(Controller-Name) # show ap monitor debug status ip-addr <IP ADDRESS OF ANY THIN ACCESS POINTS>
...
RTLS configuration
-------------------
Type Server IP Port Frequency Active
---- --------- ---- --------- ------
MMS 10.51.2.45 5070 120
Aeroscout N/A N/A N/A
RTLS 10.51.2.45 5050 60 *
Troubleshooting RTLS
Ensure the RTLS service is running on your AMP server. SSH into your AMP server.
[root@AMPServer]# daemons | grep RTLS
root 17859 12809 0 10:35 ? 00:00:00 Daemon::RTLS
or
Navigate to System > Status and look for the RTLS service, as shown in
Figure 28 RTLS System Status
Check the RTLS log file to ensure Tag chirps are making it to the AMP server. SSH into your AMP server.
[root@AMPServer]# logs
[root@AMPServer]# tail rtls
payload:
00147aaf01000020001a1ec02b3200000001000000137aae0100000c001a1ec02b320000001a1e82b32259
0006ddff02
1224534900.588245 - got 96 bytes from 10.51.1.39 on port 5050
Mon Oct 20 13:35:00 2008: 1224534900.588338 - got 96 bytes from 10.51.1.39 on port 5050
payload:
0014c9c90100003c001a1ec050780000000200000013c9c70100000c001a1ec050780000000d54a7a28054
0001ddff020013c9c80100000c001a1ec050780000000cdb8ae9a9000006c4ff02
1224534900.588245 - got 96 bytes from 10.51.1.39 on port 5050
Mon Oct 20 13:35:00 2008: 1224534900.588338 - got 96 bytes from 10.51.1.39 on port 5050
payload:
0014c9c90100003c001a1ec050780000000200000013c9c70100000c001a1ec050780000000d54a7a28054
0001ddff020013c9c80100000c001a1ec050780000000cdb8ae9a9000006c4ff02
Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide Increasing Location Accuracy | 47
Page 48

Ensure chirps are published to Airbus by snooping on proper topics
[root@AMP server]# airbus_snoop rtls_tag_report
Snooping on rtls_tag_report:
Mon Oct 20 13:49:03 2008 (1224535743.54077)
%
ap_mac => 00:1A:1E:C0:50:78
battery => 0
bssid => 00:1A:1E:85:07:80
channel => 1
data_rate => 2
noise_floor => 85
payload =>
rssi => -64
tag_mac => 00:14:7E:00:4C:E4
timestamp => 303139810
tx_power => 19
Verify external applications can see Wi-Fi Tag information by exercising the Tag XML API:
https://<AMP SERVER IP>/visualrf/rfid.xml
You should see the following XML output:
<visualrf:rfids version=1>
<rfid battery-level=0 chirp-interval= radio-mac=00:14:7E:00:4C:E0
vendor=>
<radio phy=g xmit-dbm=10.0/>
<discovering-radio ap=SC-MB-03-AP10 dBm=-91 id=811 index=1
timestamp=2008-10-21T12:23:30-04:00/>
<discovering-radio ap=SC-MB-03-AP06 dBm=-81 id=769 index=1
timestamp=2008-10-21T12:23:31-04:00/>
<discovering-radio ap=SC-MB-01-AP06 dBm=-63 id=708 index=1
timestamp=2008-10-21T12:23:31-04:00/>
<discovering-radio ap=SC-MB-02-AP04 dBm=-88 id=806 index=1
timestamp=2008-10-21T12:22:34-04:00/>
</rfid>
<rfid battery-level=0 chirp-interval= radio-mac=00:14:7E:00:4B:5C
vendor=>
<radio phy=g xmit-dbm=10.0/>
<discovering-radio ap=SC-MB-03-AP06 dBm=-74 id=769 index=1
timestamp=2008-10-21T12:23:20-04:00/>
<discovering-radio ap=SC-MB-01-AP06 dBm=-58 id=708 index=1
timestamp=2008-10-21T12:23:20-04:00/>
<discovering-radio ap=SC-MB-03-AP02 dBm=-91 id=734 index=1
timestamp=2008-10-21T12:23:20-04:00/>
</rfid>
<rfid battery-level=0 chirp-interval= radio-mac=00:14:7E:00:4D:06
vendor=>
<radio phy=g xmit-dbm=10.0/>
<discovering-radio ap=SC-SB-GR-AP04 dBm=-91 id=837 index=1
timestamp=2008-10-21T12:21:08-04:00/>
<discovering-radio ap=SC-MB-03-AP06 dBm=-79 id=769 index=1
timestamp=2008-10-21T12:22:08-04:00/>
<discovering-radio ap=SC-MB-01-AP06 dBm=-59 id=708 index=1
timestamp=2008-10-21T12:23:08-04:00/>
<discovering-radio ap=SC-MB-02-AP04 dBm=-90 id=806 index=1
timestamp=2008-10-21T12:22:08-04:00/>
</rfid>
</visualrf:rfids>
Wi-Fi Tag Setup Guidelines
Ensure that the tags can be heard by at least three (3) access points from any given location. The
recommended is 4 for best results.
Ensure that the tags chirp on all regulatory channels.
48 | Increasing Location Accuracy Dell PowerConnect W-AirWave 7.4 | Best Practices Guide
 Loading...
Loading...