Page 1

Server Administrator Storage Management
Page 2

Notes, Cautions, and Warnings
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your computer.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss of data and tells you
how to avoid the problem.
WARNING: A WARNING indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury, or death.
Copyright
Copyright © 2014 Dell Inc. All rights reserved. This product is protected by U.S. and international copyright and
intellectual property laws. Dell™ and the Dell logo are trademarks of Dell Inc. in the United States and/or other
jurisdictions. All other marks and names mentioned herein may be trademarks of their respective companies.
2014 - 03
Rev. A00
Page 3

Contents
1 Overview....................................................................................................................15
What Is New In This Release?..............................................................................................................15
Before Installing Storage Management.............................................................................................. 16
Version Requirements For Controller Firmware And Drivers...................................................... 16
Supported Controllers...................................................................................................................16
Supported Enclosures....................................................................................................................17
Support For Disk And Volume Management................................................................................ 17
2 Getting Started........................................................................................................ 19
Launching Storage Management........................................................................................................19
On Systems Running Microsoft Windows.................................................................................... 19
On A System Running Linux And Any Remote System................................................................19
User Privileges.....................................................................................................................................20
Using The Graphical User Interface................................................................................................... 20
Storage Object.............................................................................................................................. 20
Health............................................................................................................................................ 20
Information/Configuration........................................................................................................... 20
Using The Storage Management Command-Line Interface............................................................. 21
Displaying The Online Help.................................................................................................................21
Common Storage Tasks......................................................................................................................21
3 Understanding RAID Concepts........................................................................... 23
What Is RAID?...................................................................................................................................... 23
Hardware And Software RAID.......................................................................................................23
RAID Concepts.............................................................................................................................. 24
RAID Levels....................................................................................................................................24
Organizing Data Storage For Availability And Performance..............................................................24
Choosing RAID Levels And Concatenation........................................................................................25
Concatenation...............................................................................................................................25
RAID Level 0 (Striping)...................................................................................................................26
RAID Level 1 (Mirroring).................................................................................................................27
RAID Level 5 (Striping With Distributed Parity).............................................................................28
RAID Level 6 (Striping With Additional Distributed Parity)........................................................... 28
RAID Level 50 (Striping Over RAID 5 Sets)....................................................................................29
RAID Level 60 (Striping Over RAID 6 Sets)................................................................................... 30
RAID Level 10 (Striped-Mirrors).....................................................................................................31
RAID Level 1-Concatenated (Concatenated Mirror)....................................................................32
Comparing RAID Level And Concatenation Performance................................................................33
Page 4

No-RAID.............................................................................................................................................. 34
4 Quick Access To Storage Status And Tasks..................................................... 35
Storage Health.....................................................................................................................................35
Hot Spare Protection Policy............................................................................................................... 35
Storage Component Severity............................................................................................................. 36
Storage Properties And Current Activity............................................................................................ 36
Alerts Or Events................................................................................................................................... 37
Monitoring Disk Reliability On RAID Controllers................................................................................37
Using Alarms To Detect Failures.........................................................................................................37
Using Enclosure Temperature Probes................................................................................................37
Rescanning To Update Storage Configuration Changes...................................................................37
Time Delay In Displaying Configuration Changes.............................................................................38
5 PCI Express Solid-State Device Support...........................................................39
What Is PCIe SSD?...............................................................................................................................39
PCIe SSD Features...............................................................................................................................39
PCIe SSD SubSystem Properties.........................................................................................................39
PCIe Extender Cards...........................................................................................................................40
Physical Device Properties..................................................................................................................41
Physical Device Tasks......................................................................................................................... 43
Blinking And Unblinking A PCIe SSD............................................................................................ 43
Enabling Full Initialization On A Micron PCIe SSD.......................................................................43
Preparing To Remove A PCIe SSD................................................................................................44
Exporting The Log.........................................................................................................................44
Enabling Cryptographic Erase On An Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) PCIe SSD...........45
Adding PCIe SSDs To Fluid Cache Pool.............................................................................................46
Removing PCIeSSDs From Fluid Cache Pool.................................................................................... 46
PCIe SSD SubSystem Health...............................................................................................................47
Backplanes.....................................................................................................................................47
Backplane Firmware Version.........................................................................................................47
6 Fluid Cache For DAS ............................................................................................. 49
Fluid Cache Properties........................................................................................................................49
Fluid Cache Disks................................................................................................................................50
Fluid Cache Disk Properties..........................................................................................................50
Fluid Cache Pool..................................................................................................................................51
Fluid Cache Pool Properties..........................................................................................................51
Physical Device Properties............................................................................................................ 51
Cache I/O Statistics.............................................................................................................................53
Cache Pool Usage.........................................................................................................................53
Viewing The Performance Of The Fluid Cache Disk....................................................................53
Page 5

License Settings...................................................................................................................................54
7 Storage Information And Global Tasks............................................................. 57
Storage Properties...............................................................................................................................57
Global Tasks.........................................................................................................................................57
Performing A Global Rescan......................................................................................................... 57
Enabling Or Disabling A Smart Thermal Shutdown.....................................................................58
Storage Controller Properties.............................................................................................................58
Storage Components....................................................................................................................60
8 Controllers................................................................................................................61
What Is A Controller?.......................................................................................................................... 61
RAID Controller Technology: SCSI, SATA, ATA, And SAS...................................................................61
SAS RAID Controllers.....................................................................................................................61
RAID Controller Features....................................................................................................................62
Controller — Supported RAID Levels................................................................................................. 62
Controller — Supported Stripe Sizes..................................................................................................63
RAID Controller Read, Write, Cache, And Disk Cache Policy........................................................... 63
Read Policy.................................................................................................................................... 63
Write Policy....................................................................................................................................63
Cache Policy..................................................................................................................................64
Disk Cache Policy..........................................................................................................................64
Background Initialization On PERC Controllers................................................................................ 65
Non-RAID Controller Description...................................................................................................... 65
Non-RAID SCSI Controllers.......................................................................................................... 65
Non-RAID SAS Controllers............................................................................................................65
Firmware Or Driver Versions.............................................................................................................. 66
Firmware/Driver Properties...........................................................................................................66
Controller Health.................................................................................................................................67
Controller Components................................................................................................................67
Controllers Properties And Tasks....................................................................................................... 67
Controller Tasks...................................................................................................................................71
Rescanning The Controller........................................................................................................... 72
Creating A Virtual Disk...................................................................................................................72
Enabling The Controller Alarm......................................................................................................72
Disabling The Controller Alarm.....................................................................................................72
Turning Off The Controller Alarm.................................................................................................73
Testing The Controller Alarm........................................................................................................73
Setting The Rebuild Rate...............................................................................................................73
Resetting The Controller Configuration.......................................................................................74
Exporting The Controller Log File.................................................................................................74
Foreign Configuration Operations................................................................................................75
Page 6

Importing Foreign Configurations................................................................................................78
Importing Or Recovering Foreign Configurations.......................................................................78
Clearing Foreign Configuration.................................................................................................... 79
Physical Disks In Foreign Virtual Disks......................................................................................... 80
Setting Background Initialization Rate......................................................................................... 82
Setting The Check Consistency Rate........................................................................................... 83
Setting The Reconstruct Rate.......................................................................................................84
Setting The Redundant Path Configuration.................................................................................84
Setting The Patrol Read Mode......................................................................................................86
Starting And Stopping Patrol Read............................................................................................... 87
Changing The Controller Properties............................................................................................88
Managing The Physical Disk Power..............................................................................................89
Managing The Preserved Cache................................................................................................... 91
Encryption Key.............................................................................................................................. 92
Converting To Non-RAID Disks....................................................................................................94
Converting To RAID Capable Disks..............................................................................................94
Viewing Available Reports ..................................................................................................................95
Available Reports...........................................................................................................................95
Viewing Patrol Read Report..........................................................................................................95
Viewing Check Consistency Report............................................................................................. 95
Viewing Slot Occupancy Report.................................................................................................. 96
Viewing Physical Disk Firmware Version Report..........................................................................96
9 Support For PERC 9 Hardware Controllers..................................................... 99
Support For RAID Level 10 Virtual Disk Creation On PERC 9 Hardware Controller........................ 99
RAID Level 10 Virtual Disk Creation With Uneven Span.............................................................. 99
Support For Advanced Format 4K Sector Hard-Disk Drives........................................................... 100
Hot Spare Considerations — 4K Sector Hard-Disk Drives.........................................................101
Reconfiguration Considerations — 4K Sector Hard-Disk Drives...............................................101
T10 Standard Protection Information (PI) — Data Integrity Field.................................................... 101
Hot Spare Considerations — T10 Protection Information Capability....................................... 102
10 Enclosures And Backplanes............................................................................. 103
Backplanes.........................................................................................................................................103
Enclosures......................................................................................................................................... 103
SMART Thermal Shutdown.........................................................................................................104
Enclosure Physical Disks.............................................................................................................104
Enclosure Fans............................................................................................................................ 104
Enclosure Power Supplies...........................................................................................................105
Enclosure Temperature Probes..................................................................................................106
Enclosure Management Modules (EMMs)..................................................................................108
Enclosure And Backplane Health................................................................................................110
Page 7

Enclosure And Backplane Properties And Tasks........................................................................ 110
Changing The Mode On 220S And 221S Enclosures.......................................................................116
Enclosure Management.................................................................................................................... 116
Identifying An Open Connector On The Enclosure.........................................................................116
Enclosure Components.....................................................................................................................117
11 Connectors............................................................................................................119
Channel Redundancy And Thermal Shutdown................................................................................119
Creating A Channel-Redundant Virtual Disk....................................................................................119
Creating A Physical Disk For Channel Redundant Virtual Disks On PERC Controllers............ 120
Connector Health............................................................................................................................. 120
Controller Information................................................................................................................120
Connector Components.............................................................................................................120
Connector Properties And Tasks......................................................................................................120
Rescanning The Connector........................................................................................................ 121
Rescanning A Controller Connector.......................................................................................... 122
Logical Connector Properties And Tasks......................................................................................... 122
Path Health.................................................................................................................................. 123
Clearing The Connectors Redundant Path View....................................................................... 123
Connector Components.............................................................................................................123
12 Tape Drive.............................................................................................................125
Tape Drive Properties........................................................................................................................125
13 RAID Controller Batteries................................................................................. 127
Battery Properties And Tasks............................................................................................................ 127
Battery Properties........................................................................................................................ 127
Battery Tasks......................................................................................................................................128
Battery — Available Tasks..................................................................................................................128
Starting A Learn Cycle.................................................................................................................128
Battery Transparent Learn Cycle................................................................................................ 129
Initiating The Battery Delay Learn Cycle.................................................................................... 129
To Locate Delay Learn Cycle In Storage Management...................................................................130
14 Physical Disks Or Physical Devices.................................................................131
Guidelines To Replace A Physical Disk Or Physical Device............................................................. 131
Adding A New Disk To The System...................................................................................................131
For SCSI, SATA, And ATA Controllers..........................................................................................131
For SAS Controllers......................................................................................................................132
Replacing A Physical Disk Receiving SMART Alerts..........................................................................132
Disk Is Part Of A Redundant Virtual Disk.....................................................................................132
Disk Is Not Part Of A Redundant Virtual Disk............................................................................. 133
Page 8

Other Disk Procedures......................................................................................................................133
Physical Disk Or Physical Device Properties.................................................................................... 133
Physical Disk Or Physical Device Tasks............................................................................................138
Physical Disk Tasks............................................................................................................................138
Blinking And Unblinking A Physical Disk ....................................................................................138
Removing Dead Segments..........................................................................................................139
Preparing To Remove..................................................................................................................139
Rebuilding Data........................................................................................................................... 139
Canceling A Rebuild....................................................................................................................140
Assigning And Unassigning Global Hot Spare............................................................................140
Setting The Physical Disk Online Or Offline............................................................................... 141
Performing A Clear Physical Disk And Cancel Clear.................................................................. 141
Enabling Revertible Hot Spare.................................................................................................... 142
Enabling Instant Encrypt Erase................................................................................................... 142
Convert To RAID Capable Disk...................................................................................................143
Convert To Non-RAID Disk.........................................................................................................143
15 Virtual Disks..........................................................................................................145
Considerations Before Creating Virtual Disks.................................................................................. 145
Virtual Disk Considerations For Controllers............................................................................... 145
Virtual Disk Considerations For PERC S100, S110, And S300 Controllers................................ 147
Virtual Disk Considerations On Systems Running Linux............................................................147
Number Of Physical Disks Per Virtual Disk.................................................................................147
Number Of Virtual Disks Per Controller.....................................................................................148
Calculation For Maximum Virtual Disk Size................................................................................148
Channel-Redundant Virtual Disks.............................................................................................. 148
Creating Virtual Disks........................................................................................................................148
Reconfiguring Or Migrating Virtual Disks.........................................................................................149
Starting And Target RAID Levels For Virtual Disk Reconfiguration And Capacity Expansion........ 149
Maintaining The Integrity Of Redundant Virtual Disks..................................................................... 151
Rebuilding Redundant Information...................................................................................................151
Managing Virtual Disk Bad Block Management................................................................................151
Recommendations For Clearing Bad Blocks....................................................................................153
Virtual Disk Properties And Tasks......................................................................................................153
Virtual Disk Properties................................................................................................................. 153
Virtual Disk Tasks.........................................................................................................................156
Virtual Disk — Available Tasks...........................................................................................................156
Reconfiguring A Virtual Disk........................................................................................................157
Format, Initialize, Slow, And Fast Initialize.................................................................................. 157
Canceling Background Initialization........................................................................................... 157
Restoring Dead Segments...........................................................................................................157
Deleting Data On the Virtual Disk...............................................................................................158
Page 9

Performing A Check Consistency...............................................................................................158
Canceling A Check Consistency.................................................................................................158
Pausing A Check Consistency.................................................................................................... 158
Resuming A Check Consistency.................................................................................................158
Blinking And Unblinking A Virtual Disk....................................................................................... 158
Renaming A Virtual Disk..............................................................................................................158
Canceling A Rebuild.................................................................................................................... 159
Changing The Virtual Disk Policy................................................................................................159
Replacing A Member Disk........................................................................................................... 159
Clearing Virtual Disk Bad Blocks.................................................................................................159
Encrypting A Virtual Disk.............................................................................................................159
Create Virtual Disk Express Wizard...................................................................................................160
Create Virtual Disk Express Wizard (Step 2)......................................................................................161
Create Virtual Disk Advanced Wizard...............................................................................................162
Create Virtual Disk Advanced Wizard (Step 2)..................................................................................165
Create Virtual Disk Advanced Wizard (Step 3)................................................................................. 166
Span Edit............................................................................................................................................168
Virtual Disk Task: Reconfigure (Step 1 of 3)..................................................................................... 168
To Reconfigure A Virtual Disk: Step 1 of 3................................................................................. 169
Virtual Disk Task: Reconfigure (Step 2 of 3)..................................................................................... 170
To Reconfigure A Virtual Disk Expand Virtual Disk Capacity: Step 2 of 3..................................171
Virtual Disk Task: Reconfigure (Step 3 of 3)......................................................................................171
Slow And Fast Initialize......................................................................................................................172
Considerations For Slow Initialize...............................................................................................172
Formatting Or Initializing A Disk....................................................................................................... 173
To Locate Virtual Disks Task In Storage Management...............................................................173
Deleting A Virtual Disk.......................................................................................................................173
To Delete A Virtual Disk...............................................................................................................174
To Locate Delete In Storage Management................................................................................ 174
Renaming A Virtual Disk....................................................................................................................174
To Rename A Virtual Disk............................................................................................................174
To Locate Rename In Storage Management..............................................................................175
Changing The Policy Of A Virtual Disk............................................................................................. 175
Changing The Read, Write, Or Disk Cache Policy Of A Virtual Disk..........................................175
To Locate Change Policy In Storage Management .................................................................. 175
Split Mirror..........................................................................................................................................175
Splitting A Mirror.......................................................................................................................... 175
To Locate Split Mirror In Storage Management ........................................................................ 176
Unmirror............................................................................................................................................ 176
To Unmirror................................................................................................................................. 176
To Locate Unmirror In Storage Management............................................................................ 176
Assigning And Unassigning Dedicated Hot Spare............................................................................176
Page 10

Assigning A Dedicated Hot Spare................................................................................................177
Unassigning A Dedicated Hot Spare........................................................................................... 177
To Locate Assign Or Unassign Dedicated Hot Spare In Storage Management........................ 177
Virtual Disk Task: Replace Member Disk (Step 1 of 2)...................................................................... 177
Replacing A Member Disk: (Step 1 of 2)......................................................................................178
To Locate Replace Member Disk In Storage Management....................................................... 178
Virtual Disk Task: Replace Member Disk (Step 2 of 2)..................................................................... 178
Enabling Fluid Cache On Virtual Disks............................................................................................. 179
Disabling Fluid Cache On Virtual Disks............................................................................................ 179
Enabling Fluid Cache On Virtual Disk Partitions..............................................................................180
Disabling Fluid Cache On Virtual Disk Partitions............................................................................. 180
16 Moving Physical And Virtual Disks From One System To Another.........181
Required Conditions..........................................................................................................................181
SCSI And SAS Controllers............................................................................................................ 181
SAS Controller .............................................................................................................................181
Migrating SAS Virtual Disks To Another System............................................................................... 181
17 Protecting Your Virtual Disk With A Hot Spare........................................... 183
Understanding Hot Spares................................................................................................................183
Setting Hot Spare Protection Policy.................................................................................................183
Dedicated Hot Spare Protection Policy..................................................................................... 184
Global Hot Spare Protection Policy............................................................................................184
Considerations For Hot Spare Protection Policy.......................................................................184
Considerations For Enclosure Affinity........................................................................................ 185
Considerations For Hot Spares On PERC 5/E, PERC 5/i, PERC 6/E, And PERC 6/I Controllers.... 185
Dedicated Hot Spare Considerations.........................................................................................186
Considerations For Hot Spares On PERC S100 And PERC S300 Controllers................................ 186
Size Requirements For Global Hot Spares On S100 And S300 Controllers............................. 186
Global Hot Spare Considerations On A SAS 6/iR.............................................................................186
18 CacheCade Using Solid-State Drives............................................................ 189
Managing The CacheCade............................................................................................................... 189
CacheCade Properties................................................................................................................190
Creating A CacheCade............................................................................................................... 190
Resizing The CacheCade............................................................................................................ 191
Renaming The CacheCade......................................................................................................... 191
Blinking And Unblinking The CacheCade...................................................................................191
Deleting The CacheCade............................................................................................................ 191
19 Troubleshooting................................................................................................. 193
Common Troubleshooting Procedures...........................................................................................193
Page 11

Cables Attached Correctly..........................................................................................................193
System Requirements..................................................................................................................193
Drivers And Firmware..................................................................................................................194
Isolate Hardware Problems.........................................................................................................194
Rescan To Update Information On SCSI Controllers................................................................ 194
Replacing A Failed Disk............................................................................................................... 194
Using The Physical Disk Online Command On Select Controllers...........................................195
Recovering From Removing The Wrong Physical Disk............................................................. 196
Resolving Microsoft Windows Upgrade Problems.................................................................... 196
Virtual Disk Troubleshooting............................................................................................................ 196
A Rebuild Does Not Work........................................................................................................... 196
A Rebuild Completes With Errors............................................................................................... 197
Cannot Create A Virtual Disk.......................................................................................................197
A Virtual Disk Of Minimum Size Is Not Visible To Windows Disk Management....................... 197
Virtual Disk Errors On Systems Running Linux...........................................................................198
Problems Associated With Using The Same Physical Disks For Both Redundant And Non-
Redundant Virtual Disks.............................................................................................................. 198
Specific Problem Situations And Solutions...................................................................................... 198
Physical Disk Is Offline Or Displays An Error Status...................................................................199
Receive A Bad Block Alert With Replacement, Sense, Or Medium Error..................................199
Alerts 2146 Through 2150 Received During A Rebuild Or While A Virtual Disk Is Degraded...199
Alerts 2146 Through 2150 Received While Performing I/O, Consistency Check, Format,
Or Other Operation....................................................................................................................200
Read And Write Operations Experience Problems....................................................................200
A Task Menu Option Is Not Displayed....................................................................................... 200
A Corrupt Disk Or Drive Message Suggests Running Autocheck During A Reboot................ 200
Erroneous Status And Error Messages After A Windows Hibernation......................................200
Storage Management May Delay Before Updating Temperature Probe Status...................... 200
Storage Management May Delay Displaying Storage Devices After Reboot............................201
You Are Unable To Log Into A Remote System......................................................................... 201
Cannot Connect To Remote System Running Microsoft Windows Server 2003.................... 201
Reconfiguring A Virtual Disk Displays Error In Mozilla Browser................................................201
Physical Disks Are Displayed Under The Connector Object Instead Of The Enclosure
Object.......................................................................................................................................... 201
PCIe SSD Troubleshooting............................................................................................................... 201
Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) Solid-State Drive (SSD) Is Not Visible
In The Operating System............................................................................................................202
PCIe SSD Is Not Visible In Disk Management In The Operating System.................................. 202
Fluid Cache For DAS.........................................................................................................................202
Fluid Cache tree is not seen in OMSS........................................................................................ 202
Additional entries seen in the statistics chart.............................................................................202
Fluid Cache device is not seen in the operating system...........................................................202
Page 12

On H310 I do not see any option for Fluid Cache.....................................................................202
Cannot add more than 64 VDs for caching...............................................................................202
Configured mode vs operational mode troubleshooting in cases of Pass Through and
Write Through operational mode.............................................................................................. 203
When the Fluid Cache node is selected, Fluid Cache details is not displayed.........................203
Add PCIe SSD to Fluid Cache Pool fails..................................................................................... 203
Blank graph or graph with minimal data is plotted................................................................... 203
20 Frequently Asked Questions...........................................................................205
Why Is A Rebuild Not Working?....................................................................................................... 205
How To Avoid Removing The Wrong Disk...................................................................................... 205
How Can I Safely Remove Or Replace A Physical Disk...................................................................205
How Do I Recover From Removing The Wrong Physical Disk.......................................................206
How Do I Identify The Firmware Version That Is Installed..............................................................206
Which Controllers Do I Have?..........................................................................................................206
How Do I Turn Off An Alarm............................................................................................................206
Which RAID Level Is Best For Me?....................................................................................................207
21 Supported Features........................................................................................... 209
Supported Features On The PERC 5/ And PERC 6/ Controllers.................................................... 209
Controller Tasks Supported On The PERC 5/ And PERC 6/ Controllers..................................209
Battery Tasks Supported On The PERC 5/E And PERC 6/ Controllers......................................211
Connector Tasks Supported By The PERC 5/ And PERC 6/ Controllers.................................. 212
Physical Disk Tasks Supported By The PERC 5/E, And PERC 6/ Controllers............................ 212
Virtual Disk Tasks Supported By The PERC 5/ And PERC 6/ Controllers..................................213
Virtual Disk Specifications For The PERC 5/ And PERC 6/ Controllers.....................................214
RAID Levels Supported By The PERC 5/E And PERC 6 Controllers...........................................217
Read, Write, And Cache Policy Supported By The PERC 5/E And PERC 6 Controllers............217
Enclosure Support On The PERC 5/ And PERC 6/ Controllers.................................................218
Supported Features On The PERC Hardware Controllers...............................................................218
Controller Tasks Supported On The PERC Hardware Controllers............................................219
Battery Tasks Supported On The PERC Hardware Controllers.................................................222
Connector Tasks Supported By The PERC Hardware Controllers............................................222
Physical Disk Tasks Supported By The PERC Hardware Controllers........................................ 223
Virtual Disk Tasks Supported By The PERC Hardware Controllers...........................................224
Virtual Disk Specifications For The PERC Hardware Controllers..............................................226
RAID Levels Supported By The PERC Hardware Controllers.....................................................231
Read, Write, Cache And Disk Cache Policy Supported By The PERC Hardware Controllers.. 231
Enclosure Support On PERC Hardware Controllers..................................................................232
Supported Features On The SAS 5iR, SAS 6iR, And PERC H200 Controllers................................. 233
Controller Tasks Supported On The SAS 5/iR, SAS 6/iR, And H200 Controllers......................233
Battery Tasks Supported On The SAS 5/iR, SAS 6/iR, And H200 Controllers...........................234
Page 13

Connector Tasks Supported On The SAS 5/iR, SAS 6/iR, And H200 Controllers.................... 234
Physical Disk Tasks Supported On The SAS 5/iR, SAS 6/iR, And H200 Controllers................. 234
Virtual Disk Tasks Supported By The SAS 5/iR, SAS 6/iR, And H200 Controllers..................... 235
RAID Levels Supported By The SAS 5/iR, SAS 6/iR, And H200 Controllers.............................. 236
Virtual Disk Specifications For The SAS 5/iR, SAS 6/iR, And PERC H200 Controllers.............. 237
Read, Write, And Cache Policy Supported By The SAS 5/iR, SAS 6/iR, And H200
Controllers...................................................................................................................................238
Enclosure Support On The SAS 5/iR, SAS 6/iR, And H200 Controllers.................................... 239
Supported Features On The PERC S100, PERC S110, And S300 Controllers.................................239
Controller Tasks Supported On The PERC S100, PERC S110, And S300 Controllers..............239
Physical Disk Tasks Supported By The PERC S100, PERC S110, And S300 Controllers.......... 240
Virtual Disk Tasks Supported By The PERC S100, PERC S110, And S300 Controllers.............240
Virtual Disk Specifications For The PERC S100, PERC S110, And S300 Controllers.................241
RAID Levels Supported By The PERC S100, PERC S110, And S300 Controllers...................... 242
Read Write Cache And Disk Cache Policy Supported By The PERC S100, PERC S110, And
S300 Controllers.........................................................................................................................242
Enclosure Support On The PERC S100, PERC S110, And S300 Controllers............................ 243
Supported Features On The Non-RAID Controllers....................................................................... 243
Controller Tasks Supported On The Non-RAID Controllers.....................................................243
Battery Tasks Supported By Non-RAID Controllers..................................................................244
Connector Tasks Supported On The Non-RAID Controllers................................................... 244
Physical Disk Tasks Supported On The Non-RAID Controllers................................................ 244
Virtual Disk Tasks Supported By The Non-RAID Controllers.................................................... 245
Enclosure Support On The Non-RAID Controllers................................................................... 246
Enclosure And Backplane Features..................................................................................................246
Enclosure And Backplane Tasks.................................................................................................246
Maximum Supported Configuration For SAS Controllers............................................................... 247
22 Determining The Health Status For Storage Components..................... 249
Health Status Rollup: Battery Is Charging Or Dead.........................................................................249
Health Status Rollup: Physical Disks In A Virtual Disk Are Failed Or Removed.............................. 249
Health Status Rollup: Physical Disks In A Virtual Disk Are Unsupported, Partially, Or
Permanently Degraded.....................................................................................................................250
Health Status Rollup: All Physical Disks In A Virtual Disk Are In Foreign State...............................250
Health Status Rollup: Some Physical Disks In A Virtual Disk Are In Foreign State......................... 250
Health Status Rollup: Virtual Disk Is Degraded; Physical Disks Are Failed Or Rebuilding.............. 251
Health Status Rollup: Virtual Disk Is Failed....................................................................................... 251
Health Status Rollup: Unsupported Firmware Version.................................................................... 251
Health Status Rollup: Enclosure Power Supply Failed Or Power Connection Removed.............. 252
Health Status Rollup: One Enclosure Fan Is Failed..........................................................................252
Health Status Rollup: One Enclosure EMM Is Failed....................................................................... 252
Health Status Rollup: One Enclosure Temperature Probe Is Failed............................................... 253
Page 14

Health Status Rollup: Lost Both Power Connections To The Enclosure....................................... 253
Health Status Rollup: One Or More Physical Disks Are Failed........................................................ 253
Health Status Rollup: Physical Disk Is Rebuilding............................................................................254
Page 15

1
Overview
Server Administrator Storage Management provides enhanced features for configuring the locally
attached RAID and non-RAID disk storage on a system. Storage Management enables you to perform
controller and enclosure functions for all supported RAID and non-RAID controllers and enclosures from
a single graphical user interface (GUI) or command-line interface (CLI). The GUI is wizard-driven and
includes features for novice and advanced users. The CLI is fully featured and scriptable. Using Storage
Management, you can protect your data by configuring data-redundancy, assigning hot spares, or
rebuilding failed physical disks. All users of Storage Management should be familiar with their storage
environment and Storage Management.
Storage Management supports SCSI, SATA, ATA, and SAS but not Fibre Channel.
For information on Storage Management alerts, see the Server Administrator Messages Reference Guide.
What Is New In This Release?
This release of Storage Management provides the following new features:
• Added support for the following operating systems:
– Novell SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP3 (64–bit)
– VMware vSphere 5.0 U3 and 5.5
– Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.5
– Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2
* Foundation Edition
* Essential Edition
* Standard Edition
* Datacenter Edition
• Support for a new license format for Citrix XenServer 6.1
• Added support for web browsers:
– Mozilla Firefox version 22 and 23
– Internet Explorer version 8, 9, 10, and 11
– Google Chrome version 27, 28, 30, and 31
– Safari version 6.0
• Introduction of PowerEdge RAID Controller (PERC) 9 — PERC H730P Adapter
– Support For RAID Level 10 Virtual Disk Creation on PERC 9 Hardware Controller — Uneven Span
feature
– Support For Advanced Format 4K Sector Hard-Disk Drives
– T10 Standard Protection Information (PI) — Data Integrity Field
For more information, see Support For PERC 9 Hardware Controllers
15
Page 16
• Added support for Software RAID controllers (PERC S110) on systems running the Windows Server
2012 R2 operating system.
• Added support for Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) Peripheral Component Interconnect Express
(PCIe) solid-state drives (SSDs) — Cryptographic Erase. For more information on Cryptographic Erase,
see Enabling Cryptographic Erase On A Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) PCIe SSD
• Added support for the following LSI Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) Host Bus Adapters (HBAs):
– LSI SAS 9207–8e
– LSI SAS 9300–8e
– LSI SAS 9206–16e
Before Installing Storage Management
The following sections describe considerations for installing Storage Management.
Version Requirements For Controller Firmware And Drivers
For Storage Management to function properly, the controllers must have the minimum required version
of the firmware and drivers installed. The firmware and drivers listed in the Server Administrator Readme
refer to the minimum supported version for these controllers. Later versions of the firmware and drivers
are also supported. For the most recent driver and firmware requirements, contact your service provider.
NOTE: To download the latest storport driver, see the Microsoft Knowledge Base article KB943545
at support.microsoft.com.
If you install Storage Management without the minimum required firmware and drivers, Storage
Management may not be able to display the controllers or perform other functions. Storage Management
generates alerts 2131 and 2132 when it detects unsupported firmware or drivers on a controller.
For information on alert messages, see the Server Administrator Messages Reference Guide.
Supported Controllers
NOTE: The firmware and drivers listed in the Server Administrator Readme refer to the minimum
supported version for these controllers. Later versions of the firmware and drivers are also
supported. For the most recent driver and firmware requirements, contact your service provider.
This release of Storage Management supports the following controllers.
Supported RAID Controllers
Storage Management supports the following RAID controllers. For information on the technology used
by the supported RAID controllers, see RAID Controller Technology: SCSI, SATA, ATA, and SAS.
• PERC 5/E
• PERC 5/i Integrated and PERC 5/i Adapter
• SAS 5/iR Integrated and SAS 5/iR Adapter
• PERC 6/E
• PERC 6/I Integrated and PERC 6/I Adapter
• PERC 6/I Modular
• SAS 6/iR controller
• PERC S100, PERC S110, and PERC S300
16
Page 17

• PERC H200 Adapter, PERC H200 Integrated, and PERC H200 Modular
• PERC H800 Adapter, PERC H700 Adapter, PERC H700 Integrated, and PERC H700 Modular
• PERC H310 Adapter, PERC H310 Mini Monolithic, PERC H310 Mini Blades, PERC H710 Adapter, PERC
H710 Monolithic, PERC H710 Mini Monolithic, PERC H710P Adapter, PERC H710P Monolithic, PERC
H710P Mini Monolithic, and PERC H810 Adapter
• PERC H730P Adapter
NOTE: The PERC H200, PERC H7x0, and PERC H8x0 controllers support 3TB NL SAS hard drives,
3TB NL SATA hard drives, SATA SSDs, and SAS SSDs.
Supported Non-RAID Controllers
Storage Management supports the following non-RAID controllers:
• LSI PCI-e U320
• SAS 5/i Integrated
• SAS 5/E
• SAS 6 Gbps Adapter
• LSI SAS 9207-8e
• LSI SAS 9300-8e
• LSI SAS 9206-16e
Supported Enclosures
This release of Storage Management supports the following enclosures:
• 20xS and 21xS storage systems
• 220S and 221S storage systems
• MD1000 and MD1120 storage systems
• MD1200 and MD1220 storage systems
Support For Disk And Volume Management
Storage Management does not provide disk and volume management. To implement disk and volume
management, you must use the native disk and volume management utilities provided by your operating
system.
17
Page 18

18
Page 19

2
Getting Started
Server Administrator Storage Management is designed for system administrators who implement
hardware RAID solutions and understand corporate and small business storage environments.
Storage Management enables you to configure the storage components attached to your system. These
components include RAID and non-RAID controllers and the channels, ports, enclosures, and disks
attached to them. Using Storage Management, you can configure and manage the controller functions
without accessing the BIOS. These functions include configuring virtual disks and applying RAID levels
and hot spares for data protection. You can initiate many other controller functions like rebuilds,
troubleshooting, setting thresholds. Most functions can be configured and managed while the system
remains online and continues to process requests.
Storage Management reports the status of storage components. When the status for a component
changes, Storage Management updates the display for that component and sends an alert to the Alert
Log.
In addition to status changes, Storage Management generates alerts for user actions such as creating or
deleting a virtual disk and for many other events. Most alerts also generate SNMP traps.
Other than monitoring and reporting status, Storage Management does not automatically initiate actions
independent of user input. (Automatic shutdown of enclosures that have exceeded a critical temperature
is the only exception. For more information on automatic shutdown, see SMART Thermal Shutdown).
Storage Management actions are user-initiated using wizards and drop-down menus. Storage
Management does, however, report the actions taken by the controllers, which include generating alerts,
initiating tasks, such as a rebuild, and making state changes.
NOTE: Storage Management reports the change in state of disks and other storage components as
viewed by the controller.
Launching Storage Management
Storage Management is installed as a Server Administrator service. All Storage Management features are
accessible by selecting the Storage object in the Server Administrator tree view. For more information on
starting Server Administrator, see the Server Administrator User’s Guide
On Systems Running Microsoft Windows
To start a Server Administrator session on a local system running Microsoft Windows operating system,
click the Server Administrator icon on your desktop and log in using an account with Administrator
privileges.
NOTE: Administrative privileges are required for configuration purposes.
On A System Running Linux And Any Remote System
To start a Server Administrator session on a Linux or any remote system, click the Server Administrator
icon on your desktop and log in using an account with Administrator privileges.
Or, open a web browser and type one of the following in the address field and press <Enter>:
19
Page 20

https://<localhost>:1311
where <localhost> is the assigned name for the managed system and 1311 is the default port.
or
https://<IP address>:1311
where <IP address> is the IP address for the managed system and 1311 is the default port.
NOTE: Type https:// (not http://) in the address field to receive a valid response in your browser.
User Privileges
Server Administrator provides security through the User, Power User, and Administrator user groups. Each
user group is assigned a different level of access to the Server Administrator features.
The Administrator privileges are required to access all Storage Management features. Administrator
privilege allows you to execute the drop-down menu tasks, launch wizards, and use the omconfig
storage command-line interface commands. Without Administrator privileges, you cannot manage and
configure the storage component.
User and Power User privileges allow you to view storage status, but not manage or configure storage.
With User and Power User privileges, you can use the omreport storage command and not the omconfig
storage command.
For more information on user groups and other Server Administrator security features, see the Server
Administrator User’s Guide.
Using The Graphical User Interface
The following sections describe how to access the Storage Management features using the Server
Administrator graphical user interface (GUI).
Storage Object
The Server Administrator tree view displays a Storage object. The Storage Management features are
accessible by selecting the Storage object or expanding the Storage object and selecting a lower-level
object.
Related Links
Displaying The Online Help
Health
On the Properties page, click Health to view the status information for the storage components.
Related Links
Storage Health
Information/Configuration
On the Properties page, click Information/Configuration to view the property information for a storage
object. The Information/Configuration subtabs also have options for executing storage tasks or
launching wizards.
20
Page 21
Using The Storage Management Command-Line Interface
Storage Management has a fully featured command-line interface (CLI). For more information on CLI, see
the Server Administrator Command Line Interface User’s Guide.
Displaying The Online Help
Storage Management provides an extensive online Help. This Help is available from the Server
Administrator graphical user interface when the Storage or lower-level tree view object is selected.
The online Help is available as:
• Context-sensitive Help — Each Storage Management page has a icon. Click this icon to display
the context-sensitive online Help that describes the contents of the displayed page.
• Table of Contents — The table of contents is available in the page that displays the information when
you access the context-sensitive Help.
Related Links
Storage Object
Common Storage Tasks
This section provides information on commonly performed storage tasks:
• Create and configure virtual disks (RAID configuration). For more information, see:
– Create Virtual Disk Express Wizard — This topic provides information on using the Express Wizard
to create a virtual disk. Using the Express Wizard is the quickest method for creating a virtual disk.
The Express Wizard is appropriate for novice users.
– Create Virtual Disk Advanced Wizard — This topic provides information on using the Advanced
Wizard to create a virtual disk. The Advanced Wizard requires a good knowledge of RAID levels
and hardware and is appropriate for advanced users.
– Virtual Disks — This topic provides detailed information regarding the virtual disk management.
This information includes controller-specific considerations that affect virtual disk creation and
management.
• Assign a hot spare to the virtual disk — When a virtual disk uses a RAID level, you can assign a hot
spare (backup physical disk) to rebuild data if a physical disk in the virtual disk fails.
– Protecting Your Virtual Disk With A Hot Spare — This topic provides information on hot spares and
controller-specific information.
• Perform a Check Consistency — The Maintaining The Integrity Of Redundant Virtual Disks task verifies
the accuracy of the redundant data on a virtual disk.
• Reconfigure a Virtual Disk — To expand the capacity of a virtual disk you can add physical disks to the
virtual disk. You can also change the RAID levels. For more information, see Virtual Disk Task:
Reconfigure (Step 1 of 3).
21
Page 22

22
Page 23
3
Understanding RAID Concepts
Storage Management uses the Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) technology to provide
Storage Management capability. Understanding Storage Management requires an understanding of RAID
concepts, as well as some familiarity with how the RAID controllers and operating system view disk space
on your system.
Related Links
What Is RAID?
Organizing Data Storage For Availability And Performance
Choosing RAID Levels And Concatenation
Comparing RAID Level And Concatenation Performance
What Is RAID?
RAID is a technology for managing the storage of data on the physical disks that reside or are attached to
the system. A key aspect of RAID is the ability to span physical disks so that the combined storage
capacity of multiple physical disks can be treated as a single, extended disk space. Another key aspect of
RAID is the ability to maintain redundant data which can be used to restore data in the event of a disk
failure. RAID uses different techniques, such as striping, mirroring, and parity, to store and reconstruct
data. There are different RAID levels that use different methods for storing and reconstructing data. The
RAID levels have different characteristics in terms of read/write performance, data protection, and
storage capacity. Not all RAID levels maintain redundant data, which means for some RAID levels lost
data cannot be restored. The RAID level you choose depends on whether your priority is performance,
protection, or storage capacity.
NOTE: The RAID Advisory Board (RAB) defines the specifications used to implement RAID. Although
RAB defines the RAID levels, commercial implementation of RAID levels by different vendors may
vary from the actual RAID specifications. An implementation of a particular vendor may affect the
read and write performance and the degree of data redundancy.
Hardware And Software RAID
RAID can be implemented with either hardware or software. A system using hardware RAID has a RAID
controller that implements the RAID levels and processes data reads and writes to the physical disks.
When using software RAID provided by the operating system, the operating system implements the RAID
levels. For this reason, using software RAID by itself can slow the system performance. You can, however,
use software RAID along with hardware RAID volumes to provide better performance and variety in the
configuration of RAID volumes. For example, you can mirror a pair of hardware RAID 5 volumes across
two RAID controllers to provide RAID controller redundancy.
23
Page 24

RAID Concepts
RAID uses particular techniques for writing data to disks. These techniques enable RAID to provide data
redundancy or better performance. These techniques include:
• Mirroring — Duplicating data from one physical disk to another physical disk. Mirroring provides data
redundancy by maintaining two copies of the same data on different physical disks. If one of the disks
in the mirror fails, the system can continue to operate using the unaffected disk. Both sides of the
mirror contain the same data always. Either side of the mirror can act as the operational side. A
mirrored RAID disk group is comparable in performance to a RAID 5 disk group in read operations but
faster in write operations.
• Striping — Disk striping writes data across all physical disks in a virtual disk. Each stripe consists of
consecutive virtual disk data addresses that are mapped in fixed-size units to each physical disk in the
virtual disk using a sequential pattern. For example, if the virtual disk includes five physical disks, the
stripe writes data to physical disks one through five without repeating any of the physical disks. The
amount of space consumed by a stripe is the same on each physical disk. The portion of a stripe that
resides on a physical disk is a stripe element. Striping by itself does not provide data redundancy.
Striping in combination with parity does provide data redundancy.
• Stripe size — The total disk space consumed by a stripe not including a parity disk. For example,
consider a stripe that contains 64KB of disk space and has 16KB of data residing on each disk in the
stripe. In this case, the stripe size is 64KB and the stripe element size is 16KB.
• Stripe element — A stripe element is the portion of a stripe that resides on a single physical disk.
• Stripe element size — The amount of disk space consumed by a stripe element. For example, consider
a stripe that contains 64KB of disk space and has 16KB of data residing on each disk in the stripe. In
this case, the stripe element size is 16KB and the stripe size is 64KB.
• Parity — Parity refers to redundant data that is maintained using an algorithm in combination with
striping. When one of the striped disks fails, the data can be reconstructed from the parity information
using the algorithm.
• Span — A span is a RAID technique used to combine storage space from groups of physical disks into
a RAID 10, 50, or 60 virtual disk.
RAID Levels
Each RAID level uses some combination of mirroring, striping, and parity to provide data redundancy or
improved read and write performance. For specific information on each RAID level, see Choosing RAID
Levels And Concatenation.
Organizing Data Storage For Availability And Performance
RAID provides different methods or RAID levels for organizing the disk storage. Some RAID levels
maintain redundant data so that you can restore data after a disk failure. Different RAID levels also entail
an increase or decrease in the I/O (read and write) performance of a system.
Maintaining redundant data requires the use of additional physical disks. The possibility of a disk failure
increases with an increase in the number of disks. Since the differences in I/O performance and
redundancy, one RAID level may be more appropriate than another based on the applications in the
operating environment and the nature of the data being stored.
When choosing concatenation or a RAID level, the following performance and cost considerations apply:
• Availability or fault-tolerance — Availability or fault-tolerance refers to the ability of a system to
maintain operations and provide access to data even when one of its components has failed. In RAID
24
Page 25

volumes, availability or fault-tolerance is achieved by maintaining redundant data. Redundant data
includes mirrors (duplicate data) and parity information (reconstructing data using an algorithm).
• Performance — Read and write performance can be increased or decreased depending on the RAID
level you choose. Some RAID levels may be more appropriate for particular applications.
• Cost efficiency — Maintaining the redundant data or parity information associated with RAID volumes
requires additional disk space. In situations where the data is temporary, easily reproduced, or non-
essential, the increased cost of data redundancy may not be justified.
• Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF) — Using additional disks to maintain data redundancy also
increases the chance of disk failure at any given moment. Although this option cannot be avoided in
situations where redundant data is a requirement, it does have implications on the workload of the
system support staff within your organization.
• Volume — Volume refers to a single disk non-RAID virtual disk. You can create volumes using external
utilities like the O-ROM <Ctrl> <r>. Storage Management does not support the creation of volumes.
However, you can view volumes and use drives from these volumes for creation of new virtual disks
or Online Capacity Expansion (OCE) of existing virtual disks, provided free space is available. Storage
Management allows Rename and Delete operations on such volumes.
Choosing RAID Levels And Concatenation
You can use RAID or concatenation to control data storage on multiple disks. Each RAID level or
concatenation has different performance and data protection characteristics.
The following topics provide specific information on how each RAID level or concatenation store data as
well as their performance and protection characteristics:
• Concatenation
• RAID Level 0 (Striping)
• RAID Level 1 (Mirroring)
• RAID Level 5 (Striping With Distributed Parity)
• RAID Level 6 (Striping With Additional Distributed Parity)
• RAID Level 50 (Striping Over RAID 5 Sets)
• RAID Level 60 (Striping Over RAID 6 Sets)
• RAID Level 10 (Striping Over Mirror Sets)
• RAID Level 1-Concatenated (Concatenated Mirror)
• Comparing RAID Level And Concatenation Performance
• No-RAID
Related Links
Starting And Target RAID Levels For Virtual Disk Reconfiguration And Capacity Expansion
Concatenation
In Storage Management, concatenation refers to storing data on either one physical disk or on disk space
that spans multiple physical disks. When spanning more than one disk, concatenation enables the
operating system to view multiple physical disks as a single disk. Data stored on a single disk can be
considered a simple volume. This disk could also be defined as a virtual disk that comprises only a single
physical disk.
Data that spans more than one physical disk can be considered a spanned volume. Multiple concatenated
disks can also be defined as a virtual disk that comprises more than one physical disk.
A dynamic volume that spans to separate areas of the same disk is also considered concatenated.
25
Page 26
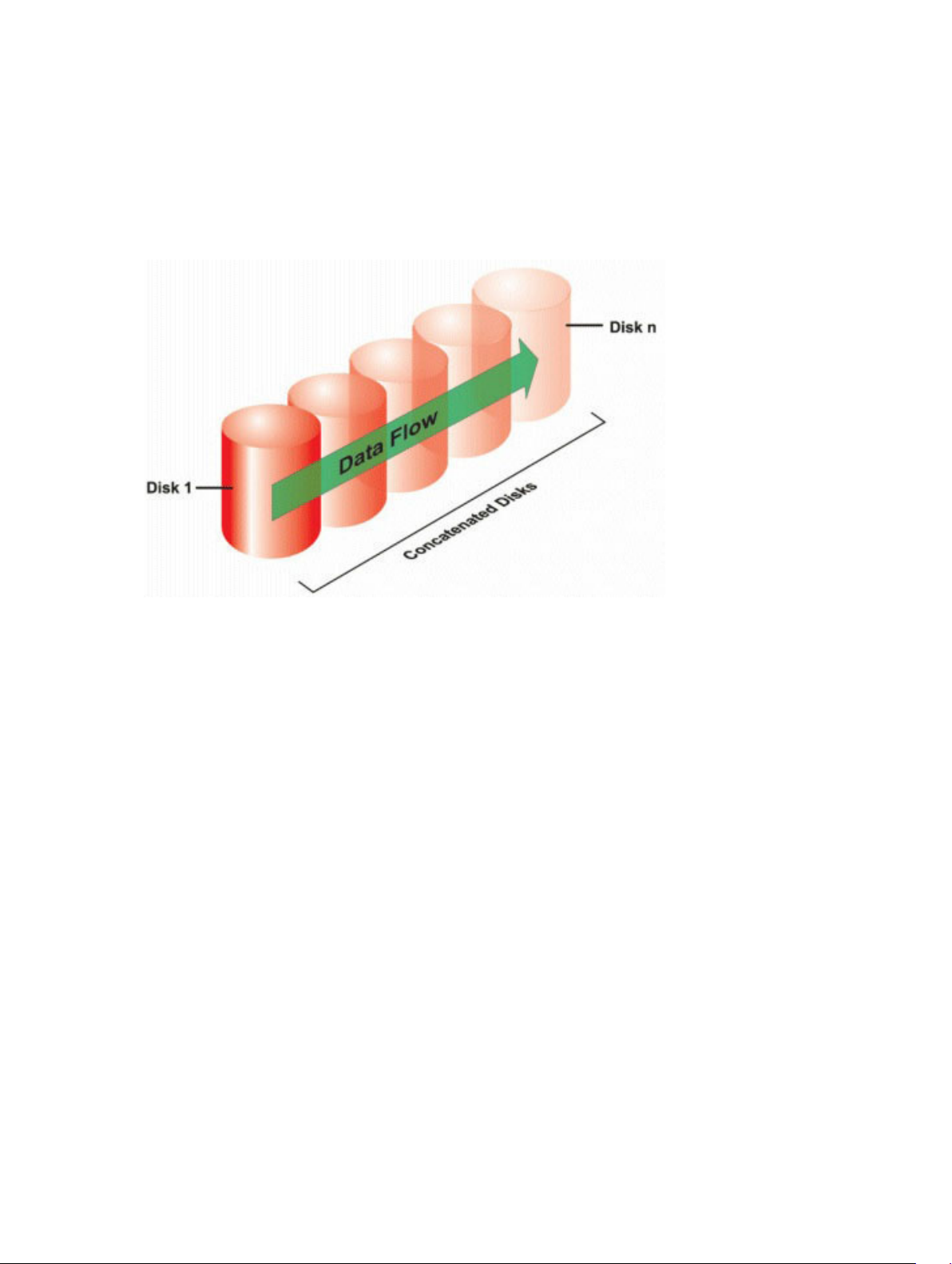
When a physical disk in a concatenated or spanned volume fails, the entire volume becomes unavailable.
Because the data is not redundant, it cannot be restored by rebuilding from a mirrored disk or parity
information. Restoring from a backup is the only option.
Because concatenated volumes do not use disk space to maintain redundant data, they are more costefficient than volumes that use mirrors or parity information. A concatenated volume may be a good
choice for data that is temporary, easily reproduced, or that does not justify the cost of data redundancy.
In addition, a concatenated volume can easily be expanded by adding an additional physical disk.
• Concatenates n disks as one large virtual disk with a capacity of n disks.
• Data fills up the first disk before it is written to the second disk.
• No redundant data is stored. When a disk fails, the large virtual disk fails.
• No performance gain.
• No redundancy.
RAID Level 0 (Striping)
RAID 0 uses data striping, which is writing data in equal-sized segments across the physical disks. RAID 0
does not provide data redundancy.
26
Page 27
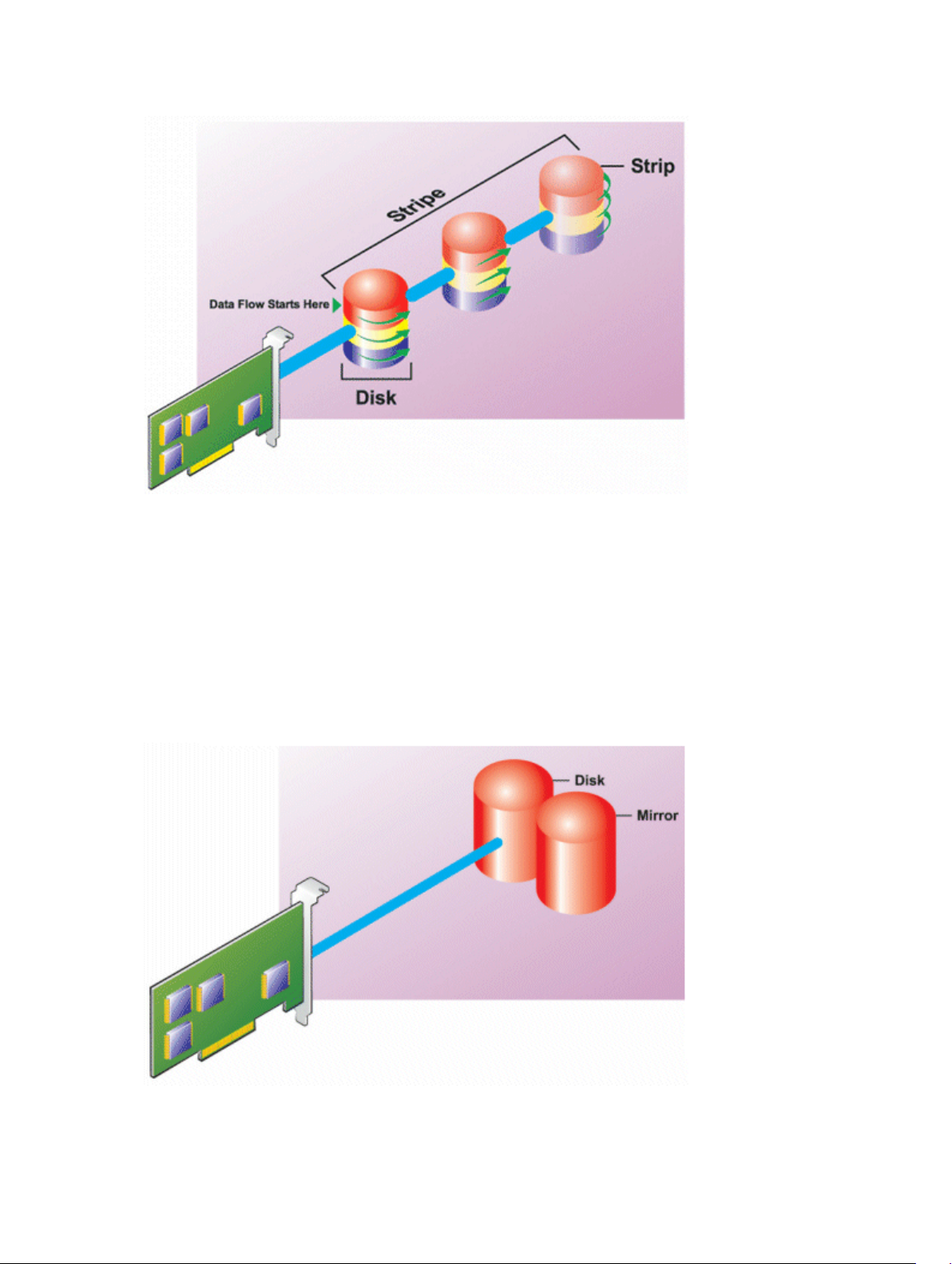
RAID 0 characteristics:
• Groups n disks as one large virtual disk with a capacity of (smallest disk size) *n disks.
• Data is stored to the disks alternately.
• No redundant data is stored. When a disk fails, the large virtual disk fails with no means of rebuilding
the data.
• Better read and write performance.
RAID Level 1 (Mirroring)
RAID 1 is the simplest form of maintaining redundant data. In RAID 1, data is mirrored or duplicated on
one or more physical disks. If a physical disk fails, data can be rebuilt using the data from the other side of
the mirror.
27
Page 28
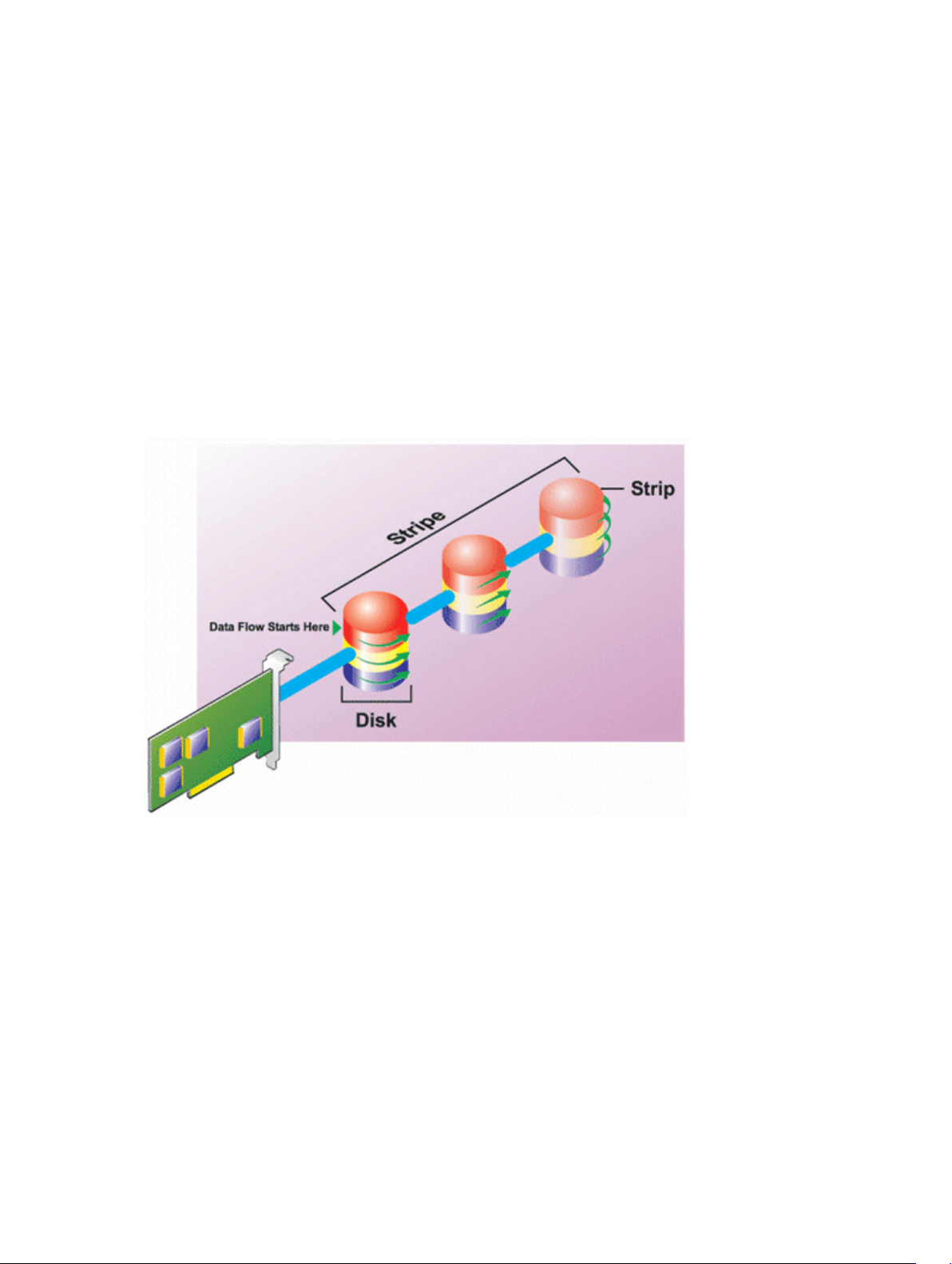
RAID 1 characteristics:
• Groups n + n disks as one virtual disk with the capacity of n disks. The controllers currently supported
by Storage Management allow the selection of two disks when creating a RAID 1. Because these disks
are mirrored, the total storage capacity is equal to one disk.
• Data is replicated on both the disks.
• When a disk fails, the virtual disk still works. The data is read from the mirror of the failed disk.
• Better read performance, but slightly slower write performance.
• Redundancy for protection of data.
• RAID 1 is more expensive in terms of disk space since twice the number of disks are used than
required to store the data without redundancy.
RAID Level 5 (Striping With Distributed Parity)
RAID 5 provides data redundancy by using data striping in combination with parity information. Rather
than dedicating a physical disk to parity, the parity information is striped across all physical disks in the
disk group.
RAID 5 characteristics:
• Groups n disks as one large virtual disk with a capacity of (n-1) disks.
• Redundant information (parity) is alternately stored on all disks.
• When a disk fails, the virtual disk still works, but it is operating in a degraded state. The data is
reconstructed from the surviving disks.
• Better read performance, but slower write performance.
• Redundancy for protection of data.
RAID Level 6 (Striping With Additional Distributed Parity)
RAID 6 provides data redundancy by using data striping in combination with parity information. Similar to
RAID 5, the parity is distributed within each stripe. RAID 6, however, uses an additional physical disk to
maintain parity, such that each stripe in the disk group maintains two disk blocks with parity information.
28
Page 29
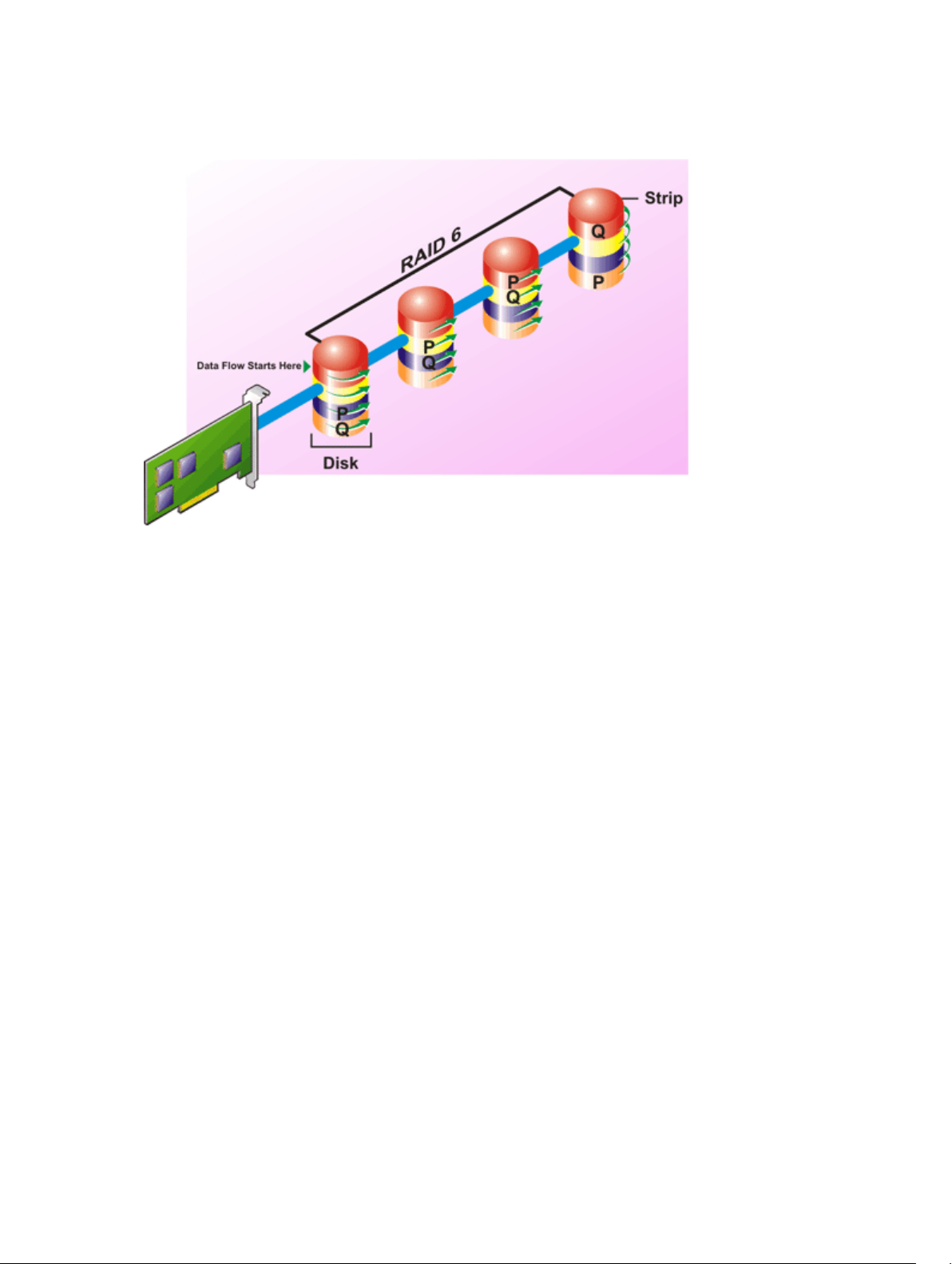
The additional parity provides data protection in the event of two disk failures. In the following image, the
two sets of parity information are identified as P and Q.
RAID 6 characteristics:
• Groups n disks as one large virtual disk with a capacity of (n-2) disks.
• Redundant information (parity) is alternately stored on all disks.
• The virtual disk remains functional with up to two disk failures. The data is reconstructed from the
surviving disks.
• Better read performance, but slower write performance.
• Increased redundancy for protection of data.
• Two disks per span are required for parity. RAID 6 is more expensive in terms of disk space.
RAID Level 50 (Striping Over RAID 5 Sets)
RAID 50 is striping over more than one span of physical disks. For example, a RAID 5 disk group that is
implemented with three physical disks and then continues on with a disk group of three more physical
disks would be a RAID 50.
It is possible to implement RAID 50 even when the hardware does not directly support it. In this case, you
can implement more than one RAID 5 virtual disks and then convert the RAID 5 disks to dynamic disks.
You can then create a dynamic volume that is spanned across all RAID 5 virtual disks.
29
Page 30
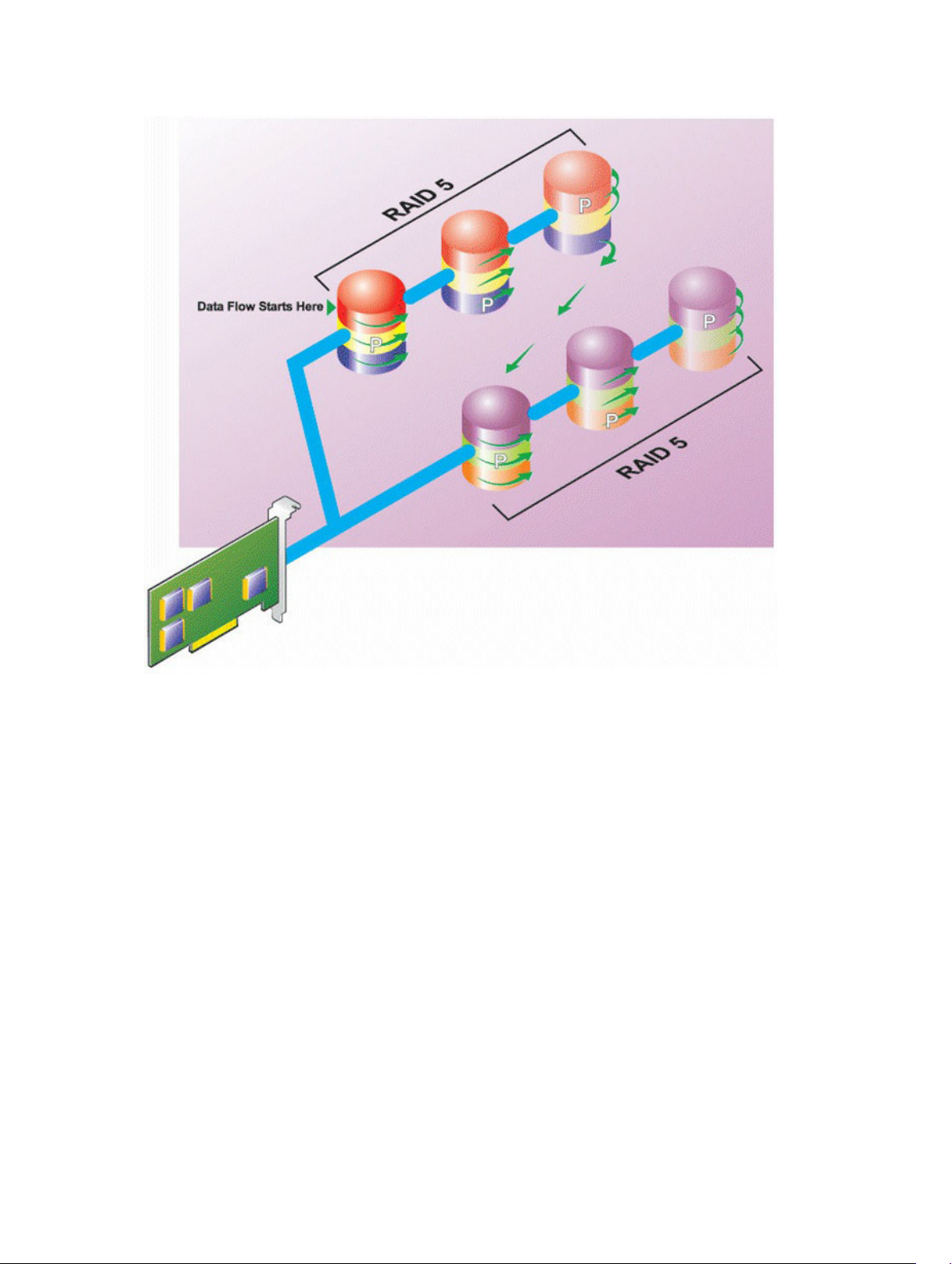
RAID 50 characteristics:
• Groups n*s disks as one large virtual disk with a capacity of s*(n-1) disks, where s is the number of
spans and n is the number of disks within each span.
• Redundant information (parity) is alternately stored on all disks of each RAID 5 span.
• Better read performance, but slower write performance.
• Requires as much parity information as standard RAID 5.
• Data is striped across all spans. RAID 50 is more expensive in terms of disk space.
RAID Level 60 (Striping Over RAID 6 Sets)
RAID 60 is striping over more than one span of physical disks that are configured as a RAID 6. For
example, a RAID 6 disk group that is implemented with four physical disks and then continues on with a
disk group of four more physical disks would be a RAID 60.
30
Page 31

RAID 60 characteristics:
• Groups n*s disks as one large virtual disk with a capacity of s*(n-2) disks, where s is the number of
spans and n is the number of disks within each span.
• Redundant information (parity) is alternately stored on all disks of each RAID 6 span.
• Better read performance, but slower write performance.
• Increased redundancy provides greater data protection than a RAID 50.
• Requires proportionally as much parity information as RAID 6.
• Two disks per span are required for parity. RAID 60 is more expensive in terms of disk space.
RAID Level 10 (Striped-Mirrors)
The RAB considers RAID level 10 to be an implementation of RAID level 1. RAID 10 combines mirrored
physical disks (RAID 1) with data striping (RAID 0). With RAID 10, data is striped across multiple physical
disks. The striped disk group is then mirrored onto another set of physical disks. RAID 10 can be
considered a mirror of stripes.
31
Page 32

RAID 10 characteristics:
• Groups n disks as one large virtual disk with a capacity of (n/2) disks, where n is an even integer.
• Mirror images of the data are striped across sets of physical disks. This level provides redundancy
through mirroring.
• When a disk fails, the virtual disk still works. The data is read from the surviving mirrored disk.
• Improved read performance and write performance.
• Redundancy for protection of data.
RAID Level 1-Concatenated (Concatenated Mirror)
RAID 1-concatenated is a RAID 1 disk group that spans across more than a single pair of physical disks.
This configuration combines the advantages of concatenation with the redundancy of RAID 1. No striping
is involved in this RAID type.
NOTE: You cannot create a RAID 1-concatenated virtual disk or reconfigure to RAID 1concatenated with Storage Management. You can only monitor a RAID 1- concatenated virtual disk
with Storage Management.
32
Page 33

Comparing RAID Level And Concatenation Performance
The following table compares the performance characteristics associated with the more common RAID
levels. This table provides general guidelines for choosing a RAID level. Evaluate your specific
environment requirements before choosing a RAID level.
NOTE: The following table does not show all supported RAID levels in Storage Management. For
information on all supported RAID levels in Storage Management, see Choosing RAID Levels And
Concatenation.
Table 1. RAID Level and Concatenation Performance Comparison
RAID Level Data
Availability
ConcatenationNo gain No gain No gain N/A 1 or 2
RAID 0 None Very Good Very Good N/A N Noncritical
RAID 1 Excellent Very Good Good Good 2N (N = 1) Small
Read
Performanc
e
Write
Performanc
e
Rebuild
Performanc
e
Minimum
Disks
Required
depending
on the
controller
Suggested
Uses
More cost
efficient than
redundant
RAID levels.
Use for
noncritical
data.
data.
databases,
database
logs, and
critical
information.
33
Page 34

RAID Level Data
Availability
Read
Performanc
e
Write
Performanc
e
Rebuild
Performanc
e
Minimum
Disks
Required
Suggested
Uses
RAID 5 Good Sequential
reads: good.
Transactiona
l reads: Very
good
RAID 10 Excellent Very Good Fair Good 2N x X Data
RAID 50 Good Very Good Fair Fair N + 2 (N = at
RAID 6 Excellent Sequential
reads: good.
Transactiona
l reads: Very
good
Fair, unless
using
writeback
cache
Fair, unless
using
writeback
cache
Fair N + 1 (N = at
least two
disks)
least 4)
Poor N + 2 (N = at
least two
disks)
Databases
and other
read
intensive
transactional
uses.
intensive
environment
s (large
records).
Medium
sized
transactional
or data
intensive
uses.
Critical
information.
Databases
and other
read
intensive
transactional
uses.
RAID 60 Excellent Very Good Fair Poor X x (N + 2) (N
= at least 2)
N = Number of physical disks
X = Number of RAID sets
Critical
information.
Medium
sized
transactional
or data
intensive
uses.
No-RAID
In Storage Management, a virtual disk of unknown metadata is considered a No-RAID volume. Storage
Management does not support this type of virtual disks. These must either be deleted or the physical disk
must be removed. Storage Management allows Delete and Rename operation on No-RAID volumes.
34
Page 35

4
Quick Access To Storage Status And Tasks
This section describes various methods to determine the status or health of the storage components on
your system and how to quickly launch the available controller tasks.
Related Links
Storage Health
Hot Spare Protection Policy
Storage Component Severity
Storage Properties And Current Activity
Alerts Or Events
Monitoring Disk Reliability On RAID Controllers
Using Alarms To Detect Failures
Using Enclosure Temperature Probes
Rescanning To Update Storage Configuration Changes
Time Delay In Displaying Configuration Changes
Storage Health
The Storage Dashboard displays the combined status for each controller and lower-level storage
components. For example, if the health of the storage system has been compromised due to a degraded
enclosure, both the enclosure Health and the controller severity on the Storage Dashboard display a
yellow exclamation mark to indicate a Warning severity. If a controller on the Storage Dashboard displays
a Warning or Critical status, perform the following actions to investigate the cause:
• Click Check Alert Log to display the Alerts Log. Review the Alert Log for alerts relating to the status of
the controller and its lower-level components. The Check Alert Log link is only displayed when the
controller displays a Warning or Critical status.
• Select the controller and investigate the status of the lower-level components. For more information,
see Storage Component Severity.
• Click the virtual disk that is in degraded state to display the Physical Disk Properties page.
NOTE: The virtual disk link is displayed only if the physical disks that are part of the virtual disk,
are in a Warning or Critical state.
For more information on how the status of lower-level components is rolled up into the status displayed
for the controller, see Determining The Health Status For Storage Components.
Related Links
Health
Hot Spare Protection Policy
The Set Hot Spare Protection Policy task allows you to set or modify the number of hot spares to be
assigned to the virtual disks.
35
Page 36

After you set the number of assigned hot spares, any deviation from the protection policy threshold
triggers an alert based on the severity level you set.
Related Links
Setting Hot Spare Protection Policy
Dedicated Hot Spare Protection Policy
Global Hot Spare Protection Policy
Storage Component Severity
Component status is indicated by the severity. A component with a Warning or Critical/Failure status
requires immediate attention to avoid data loss, if possible. The status of the component indicates the
combined status of the components and its lower-level objects.
It may be useful to review the Alert Log for events indicating why a component has a Warning or Critical
status.
Table 2. Component Severity
Severity Component Status
Normal/OK — The component is working as
expected.
Warning/Non-critical — A probe or other
monitoring device has detected a reading for the
component that is above or below the acceptable
level. The component may still be functioning, but
it could fail. The component may also be
functioning in an impaired state. Data loss is
possible.
Critical/Failure/Error/Fatal — The component has
either failed or failure is imminent. The component
requires immediate attention and may need to be
replaced. Data loss may have occurred.
Related Links
Determining The Health Status For Storage Components
Storage Properties And Current Activity
The Information/Configuration page displays information regarding the storage component. These
properties include details such as the number of connectors (channels or ports) on a controller or the
Enclosure Management Modules (EMM) firmware version.
The State and Progress properties display the current activity of a component. For example, an offline
physical disk displays the Offline status while the Progress property displays how close to completion an
operation (such as a rebuild) is.
The following sections describe the properties for each component:
• Storage Information And Global Tasks
• Battery Properties And Tasks
• Connector Properties And Tasks
• Enclosure And Backplane Properties And Tasks
36
Page 37

• Physical Disk Or Physical Device Properties
• Physical Disk Or Physical Device Tasks
• EMM Properties
• Fan Properties
• Power Supply Properties
• Temperature Probe Properties And Tasks
• Virtual Disk Properties And Tasks
Alerts Or Events
Storage activity generates alerts or events that are displayed in the Alert Log. Some alerts indicate normal
activity and are displayed for informational purposes only. Other alerts indicate abnormal activity which
must be addressed immediately. For more information about alerts and their corrective actions, see the
Server Administrator Messages Reference Guide.
Monitoring Disk Reliability On RAID Controllers
Storage Management supports Self Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology (SMART) on physical
disks that are SMART-enabled.
SMART performs predictive failure analysis on each disk and sends alerts if a disk failure is predicted. The
RAID controllers check physical disks for failure predictions and, if found, pass this information to Storage
Management. Storage Management immediately displays an alert icon on the disk. Storage Management
also sends an alert to the Alert Log and the Microsoft Windows application log.
NOTE: You may not receive SMART alerts when the I/O of a controller is paused.
Using Alarms To Detect Failures
Certain storage components have alarms which when enabled, alert you when the component fails.
Related Links
Enabling The Enclosure Alarm
Enabling The Controller Alarm
Using Enclosure Temperature Probes
Physical disk enclosures have temperature probes that warn you when the enclosure has exceeded an
acceptable temperature range.
Related Links
SMART Thermal Shutdown
Setting The Temperature Probe Values
Rescanning To Update Storage Configuration Changes
The Rescan task scans the storage device attached to the connectors on the controller (channels or
ports) to verify the currently connected devices or to recognize devices that have been added to or
removed from the connectors. When you rescan a controller object, object, all storage devices attached
to the controller are rescanned. Performing a rescan causes the controller to recognize changes in the
37
Page 38

storage configuration, such as adding or removing physical disks from a virtual disk or changing a RAID
level.
You can rescan a controller object to:
• View new disks attached to the controller.
• Enable the operating system to recognize a virtual disk.
• Enable Storage Management to display a new virtual disk.
• Allow the virtual disk to use the additional space after is it expanded.
• Update the status of an offline disk.
• Update information in a clustered configuration after a failover of cluster resources.
NOTE: For SCSI controller-based systems, if you want to rescan all controllers, perform the
procedures listed in the Performing A Global Rescan section. If you want to rescan only the
components attached to a particular controller, perform the procedures listed in the Rescanning
The Controller section.
NOTE: To view the new physical disk, click the system name displayed at the top of the left
pane, or select View → Refresh from the menu bar on the browser.
Related Links
Preparing To Remove
Time Delay In Displaying Configuration Changes
When you change the storage configuration, Storage Management quickly generates SNMP traps in
response to the configuration changes. The Storage Management, Management Information Base (MIB) is
also updated to reflect storage configuration changes. However, it may take up to five minutes to update
the MIB with the most recent storage configuration. For this reason, there is a time delay of up to five
minutes between the receipt of an SNMP trap and the ability to identify the configuration changes by
querying the Storage Management MIB. This time delay is particularly notable when creating a new virtual
disk or performing an unmirror or split mirror on a RAID 1-concatenated virtual disk. You can minimize
this time delay by performing a controller rescan.
Related Links
Rescanning The Controller
38
Page 39

5
PCI Express Solid-State Device Support
This section provides an overview of the Storage Management device management support for
Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) Solid-State Drive (SSD) and its associated devices like
the backplane and extender card.
In Storage Management, PCIe SSD appears under Storage in the tree view. Storage Management reports
the PCIe SSD devices and its various properties.
NOTE: Storage Management does not support RAID management or configuration on PCIe SSD sub
systems.
What Is PCIe SSD?
Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) solid-state device (SSD) is a high-performance
storage device designed for solutions requiring low latency, high Input Output Operations per Second
(IOPS), and enterprise class storage reliability and serviceability. The PCIe SSD is designed based on Single
Level Cell (SLC) NAND flash technology with a high-speed PCIe 2.0 compliant interface. The high-speed
PCIe 2.0 compliant interface helps improve performance for I/O bound solutions.
PCIe SSD Features
Following are the key features of PCIe SSD:
• Hot plug capability
• High-performance device
• Support for 2.5-inch HDD Form Factor
PCIe SSD SubSystem Properties
The PCIe SSD subsystem comprises of the following components:
• Backplane
• Extender Card
• PCIe Solid-State Device
Table 3. PCIe SSD Subsystem Properties
Properties Description
ID Displays the subsystem ID assigned to the PCIe
SSD subsystem by Storage Management. Storage
Management numbers the controllers and PCIe
SSD subsystems attached to the system starting
with zero. This number is the same as the PCIe
SSD subsystem ID number reported by the
39
Page 40

Properties Description
omreportcommand. For information on
Command Line Interface, see the Server
Administrator Command Line Interface User's
Guide.
NOTE: In CLI commands, the PCIe SSD
subsystem ID is displayed as the controller ID.
Name Displays the name of the subsystem.
State Displays the status of the subsystem. Possible
values are:
• Ready — The subsystem is functioning
normally.
• Degraded — The subsystem has encountered a
failure and is operating in a degraded state.
• Failed — The subsystem has encountered a
failure and is no longer functioning.
Number of Extender Cards Displays the number of extender cards in the
subsystem. Each extender card can be attached to
physical disks or an enclosure. The extender card
must be a PCIe SSD port.
Available Reports Allows you to view the Slot Occupancy report. For
more information, see Available Reports.
PCIe Extender Cards
The PCIe extender card is attached to the backplane of the system and provides PCIe connectivity for up
to four PCIe SSD devices at the front of the chassis.
NOTE: The PCIe extender card does not have any properties or tasks.
Table 4. PCIe Extender Card
Properties Description
Name Displays the name of the extender card.
State Displays the status of the extender card. Possible
values are:
Ready — The extender card is functioning
normally.
Degraded — The extender card has encountered a
failure and is operating in a degraded state.
Failed — The extender card has encountered a
failure and is no longer functioning.
Related Links
What Is PCIe SSD?
40
Page 41

Physical Device Properties
You can view information about PCIe SSDs and run PCIe SSD tasks on the Physical Device Properties
page. To view the complete PCIe SSD properties, click Full View on the top of the page.
The following table lists the physical device properties for PCIe SSD.
Table 5. Physical Device Properties
Properties Description
Name Displays the name of the PCIe SSD. The name
comprises the bay ID and the slot in which the
PCIe SSD is installed.
State Displays the health state of the PCIe SSD.
Bus Protocol Displays the technology that the PCIe SSD is using.
Media Displays the media type of the physical disk.
Device Life Status
Displays the life status of the PCIe SSD. The device
life status is determined by the following attributes:
Percent Lifetime Used — This attribute is
determined by the elapsed time since the start of
use (up to three years) or percentage of total bytes
written (TBW).
Write Protect Progress — This attribute is
determined by the reduction in number of
available spare sectors. If the available spare
sectors are less than 10 percent of the original
pool, the drive enters read-only mode.
Possible values for the device life status are:
Drive Health Good — The drive is used within the
TBW specification. The drive health is good as
sufficient spare blocks are available. The drive
health status is good if the values for percent
lifetime used and write protect progress is less
than 100 percent.
Approaching Warranty Coverage Expiry — The
drive is reaching the specified TBW, indicating that
it is close to the end of warranty coverage.
However, the drive will be functional as the
number of spare blocks available are still above the
threshold for entering the read-only mode. The
drive approaches the warranty coverage expiry if
the value for percent lifetime used is greater than
or equal to 90 percent and that for write protect
progress is less than the threshold value, which is
90 percent.
Warranty Coverage Expired — The drive has
reached the TBW threshold and met the life
expectancy specification. The drive is functional as
the number of spare blocks available are still above
the threshold for entering the read-only mode.
But, the specified data retention period (amount of
time that data can be read from the drive after
TBW is reached) drops, if TBW specification is
41
Page 42

Properties Description
exceeded and the warranty for the drive expires.
The warranty coverage for the drive expires if the
value for percent lifetime used is equal to 100
percent and that for write protect progress is less
than 100 percent.
Approaching Read Only — The drive is running out
of spare sectors and is reaching the read-only
mode. However, the health status of the drive is
good and data retention is unaffected. The drive is
stated to be approaching the read-only mode if
the value for percent lifetime used is less than 100
percent and that for write protect progress is
greater than or equal to 90 percent.
Read Only — The drive is in read-only mode. Users
must save open files, if any, to another device and
replace or remove the device. If this scenario
occurs within three years of the device installation,
this failure is covered under warranty. The drive is
in read-only mode if the value for percent lifetime
used is less than 100 percent and that for write
protect progress is equal to 90 percent.
Driver Version Displays the version of the driver that is installed
on the PCIe SSD sub-system.
NOTE: Storage Management displays Not
Applicable for sub system for which the driver
version cannot be obtained.
Remaining Rated Write Endurance
Firmware Revision Displays the firmware version of the physical
Model Number Displays the Piece Part Identification (PPID) of the
Capacity Displays the capacity of the device.
Vendor ID Displays the hardware vendor of the device.
Product ID Displays the product ID of the device.
Serial No. Displays the serial number of the device.
PCIe Negotiated Link Speed Displays the current negotiated transfer speed of
Displays information on the SSD renewal/
replacement based on the amount of write
workloads. This field indicates the total remaining
programs or erase-cycles available on the SSD,
based on the cumulative specification of the total
NAND (Negated AND or NOT AND) Flash chips in
the SSD.
NOTE: This option is applicable to Micron
PCIe SSDs, Non-Volatile Memory Express
(NVMe) PCIe SSDs, and SAS/SATA SSDs.
device.
PCIe SSD.
the physical device in GT/s.
42
Page 43

Properties Description
PCIe Maximum Link Speed Displays the capable transfer speed of the physical
device in GT/s.
Fluid Cache Pool Member Indicates whether the PCIe SSD is a part of a Fluid
Cache pool.
PCIe Maximum Link Width Displays the capable link width of the physical
device.
PCIe Negotiated Link Width Displays the current negotiated link width of the
physical device.
Physical Device Tasks
The physical device tasks for PCIeSSD are as follows:
• Blinking And Unblinking
• Performing A Full Initialization On A PCIeSSD
• Preparing To Remove A PCIeSSD
• Exporting The Log
• Adding PCIe SSDs to Fluid Cache Pool
• Removing PCIe SSDs from Fluid Cache Pool
To run a physical device task:
1. In the Server Administrator window, under the System tree, expand Storage tree object to display
the storage component objects.
2. Expand the PCIeSSD SubSystem object
3. Expand the Connector object.
4. Expand the Enclosure (Backplane) object.
5. Select the Physical Devices object.
6. Select a task from the Available Tasks drop-down menu.
7. Click Execute.
Blinking And Unblinking A PCIe SSD
The Blink task allows you to find a device within a system by blinking one of the LEDs on the device. You
can use this task to locate a failed device. Select Unblink to cancel the Blink task or to stop the LED on a
physical device that is blinking indefinitely.
Enabling Full Initialization On A Micron PCIe SSD
Does my controller support this feature? See Supported Features.
CAUTION: Full Initialization permanently erases all data present on the disk.
CAUTION: On VMware ESXi hosts, before performing Full Initialization on the Micron PCIe SSD it
is important to first delete any data stores on it. Failure to do so can result in system instability.
To erase an encrypted physical device, select the Full Initialization task. This task is available for:
43
Page 44

• Unconfigured SED drive
• Foreign configured encrypted drives
• Unconfigured and foreign SED drive even when an Encryption Key is not present in the controller
Performing A Full Initialization On A Micron PCIe SSD
Performing a Full Initialization on a Micron PCIe SSD overwrites all blocks and results in permanent loss of
all data on the Micron PCIe SSD. During Full Initialization, the host is unable to access the Micron PCIe
SSD.
NOTE: If the system reboots or experiences a power loss during Full Initialization, the operation is
canceled. You must reboot the system and restart the process.
To Locate Full Initialization In Storage Management
To locate this task in storage management:
1. In the Server Administrator window, under the system tree, expand Storage to display the controller
objects.
2. Expand a controller object.
3. Expand a connector object.
4. Expand the enclosure or backplane object.
5. Select the Physical Devices object.
6. Select Full Initialization from the Tasks drop-down menu of the physical device you want to clear.
7. Click Execute.
Preparing To Remove A PCIe SSD
PCIe SSDs support orderly hot swap allowing you to add or remove a device without halting or rebooting
the system in which the devices are installed.
CAUTION: The identify LED pattern (blink operation) is the same LED pattern as safe to remove.
When you initiate a prepare to remove operation, ensure that your PCIe SSD is no longer
accessible by the system before physically removing the PCIe SSD.
CAUTION: To prevent data loss, it is mandatory that you use the Prepare to Remove task before
physically removing a device.
NOTE: Orderly hot swap is only supported when PCIe SSDs are installed in a supported system
running a supported operating system. To ensure that you have the correct configuration for your
PCIe SSD, see the system-specific Owner's Manual.
NOTE: The Prepare to Remove task is not supported for PCIe SSDs on VMware vSphere (ESXi)
systems.
Select the Prepare to Remove task to safely remove a PCIe SSD from the system. This task causes the
status LEDs on the device to blink. You can safely remove the device from the system under the following
conditions after you initiate the Prepare to Remove task:
• The PCIe SSD is blinking the safe to remove LED pattern.
• The PCIe SSD is no longer accessible by the system.
Exporting The Log
The log contains debug information of the PCIe-SSD and can be useful for troubleshooting. You can
export the reliability log from the Physical Device Available Tasks drop-down list.
44
Page 45

Enabling Cryptographic Erase On An Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) PCIe SSD
Does my controller support this feature? See Supported Features.
NOTE: After you hot plug an NVMe PCIe SSD, the NVMe PCIe SSD may take several seconds to be
displayed on Storage Management.
CAUTION: Cryptographic Erase permanently erases all data present on the disk.
CAUTION: On VMware ESXi hosts, before performing Cryptographic Erase on the NVMe PCIe SSD
it is important to first delete any data stores on it. Failure to do so can result in system instability.
To erase an NVMe PCIe SSD, select the Cryptographic Erase task. This task is available for:
• Unconfigured SED drive
• Foreign configured encrypted drives
• Unconfigured and foreign SED drive even when an Encryption Key is not present in the controller
Related Links
Performing A Cryptographic Erase On An NVMe PCIe SSD
To Locate Cryptographic Erase In Storage Management
Performing A Cryptographic Erase On An NVMe PCIe SSD
Performing a Cryptographic Erase on an NVMe PCIe SSD overwrites all blocks and results in permanent
loss of all data on the NVMe PCIe SSD. During Cryptographic Erase, the host is unable to access the
NVMe PCIe SSD.
NOTE: If the system reboots or experiences a power loss during Cryptographic Erase, the operation
is canceled. You must reboot the system and restart the process.
Related Links
Enabling Cryptographic Erase On An Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) PCIe SSD
To Locate Cryptographic Erase In Storage Management
To Locate Cryptographic Erase In Storage Management
1. In the Server Administrator window, under the system tree, expand Storage to display the controller
objects.
2. Expand a controller object.
3. Expand a connector object.
4. Expand the enclosure or backplane object.
5. Select the Physical Devices object.
6. Select Cryptographic Erase from the Tasks drop-down menu of the physical device you want to
clear.
7. Click Execute.
Related Links
Enabling Cryptographic Erase On An Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) PCIe SSD
Performing A Cryptographic Erase On An NVMe PCIe SSD
45
Page 46

Adding PCIe SSDs To Fluid Cache Pool
You can configure or increase the capacity of the Fluid Cache pool by adding PCIe SSDs.
To add a PCIe SSD to a cache pool:
1. In the Server Administrator window, under the system tree, expand Storage to display the controller
objects.
2. Expand the PCIe SSD SubSystem object.
3. Expand the Enclosure (Backplane) object.
4. Expand the Physical Devices object.
The Physical devices on PCIe SSD SubSystem page is displayed with the available list of physical
disks.
5. From the list of Tasks corresponding to the physical disk to which you want to add the PCIe SSD,
select the
6. Click Execute to add the PCIe SSD. The following message is displayed:
Data present on the device will be lost. Are you sure you want to proceed?
7. Click OK.
After the device is added to the cache pool, the Part of Cache Pool displays Active.
Add to Cache Pool option.
NOTE: When the device is part of the cache pool, the tasks, Cryptographic Erase, Full
Initialization, and Prepare to Remove, are not displayed in the Tasks drop-down list.
NOTE: PCIe SSDs cannot be partitioned and must be used entirely as cache.
Removing PCIeSSDs From Fluid Cache Pool
To remove a PCIeSSD from a cache pool:
1. In the Server Administrator window, under the system tree, expand Storage to display the controller
objects.
2. Expand the PCIe SSD SubSystem object.
3. Expand the Enclosure (Backplane) object.
4. Expand the Physical Devices object.
The Physical devices on PCIe SSD SubSystem page is displayed with the available list of physical
disks.
5. From the list of Tasks corresponding to the physical disk to which you want to remove the PCIeSSD,
select the Remove from Cache Pool option.
6. Click Execute to remove the PCIeSSD. The following message is displayed:
Device will be removed from Fluid Cache Pool. Are you sure you want to
proceed?
46
Page 47

7. Click OK.
Once the device removal is initiated from the cache pool, any dirty data is moved to the back-end
disk. While the data migration is in progress, Storage Management displays a transient removal state.
After the device is removed from the cache pool, the Part of Cache Pool attribute is Not Enabled.
When the last but one PCIeSSD is removed from the Fluid Cache pool, the cache pool high
availability changes from True to False indicating that the cache pool is Write Through capable only
and the operational cache mode for any Fluid Cache disk configured for Write Back changes to
Write Through.
When the last PCIeSSD is removed from the Fluid Cache pool, the operational cache mode for all
Fluid Cache disk changes to Pass Through.
PCIe SSD SubSystem Health
Indicates the roll-up health status of physical devices. The individual health status of the physical devices
appears at the respective level.
Related Links
Backplanes
Backplane Firmware Version
Backplanes
PCIe SSDs are attached to the PCIe SSD backplane of the system. The number of supported PCIe SSDs
depend on the system.
NOTE: PCIe SSDs must be used with PCIe SSD backplanes. Do not plug in SAS/SATA devices to a
PCIe SSD backplane or vice versa.
Related Links
PCIe SSD SubSystem Health
Backplane Firmware Version
The backplane firmware version information is available in the Information/Configuration page of the
PCIe SSD sub system.
NOTE: The firmware version is the only backplane property supported for PCIe SSD.
Related Links
PCIe SSD SubSystem Health
47
Page 48

48
Page 49

6
Fluid Cache For DAS
Fluid Cache is a server-side caching accelerator that makes high-speed Express Flash (PCIeSSD) a shared,
distributed resource. Fluid Cache enables the caching of active data working sets from storage closer to
the compute tier to enable accelerated response times for latency sensitive customer workloads using
Direct Attached Storage (DAS) external storage architectures.
The Storage Management application facilitates addition of PCIe SSDs to the Fluid Cache pool. The
Storage Management support for Fluid Cache helps in:
• Managing Fluid Cache license.
• Configuring cache pool.
• Enabling cache for virtual disks behind a PERC controller. The supported PERC controllers are H710,
H710P, H810 and H730P.
• Monitoring cache pool usage and read/write performance of the Fluid Cache disks.
Fluid Cache for DAS technology uses the Express Flash PCIe SSDs in supported systems and provides
read and write flash cache.
Fluid Cache Pool comprises of the set of PCIe SSDs that forms the shared, distributed cache resource.
Fluid Cache Disks is a new logical device created as a result of enabling the Fluid Cache on virtual disk or
its partitions. The new Fluid Cache Disk must be used for all data access following Fluid Cache
enablement as opposed to accessing the Virtual Disk or its partitions directly. The new Fluid Cache
Disk /dev/fldcx created as a result of enabling Fluid Cache on the Virtual disk MUST be used for all data
access moving forward. Any additional data access to the corresponding Virtual Disk /dev/sdx or its
partitions being cached may lead to data corruption.
For more information, see the Fluid Cache For DAS User’s Guide.
On the left-hand side of the Storage Management page, click Storage → Fluid Cache.
From the Options menu:
Connect Fluid Cache: Click to refresh the Fluid Cache node information for Fluid Cache Disks and
License.
The Sub-System Information Fluid Cache page is displayed with the Fluid Cache and cache pool
properties.
Fluid Cache Properties
Table 6. Fluid Cache Properties
Properties Description
Status
Displays the status of the Fluid Cache. The possible options are:
• OK
• Non-critical
49
Page 50

Properties Description
• Critical
License State
Displays the status of the Fluid Cache license. The possible options
are:
• Valid License
• Expired
Fluid Cache Disks
NOTE: When caching is enabled on the virtual disk, partitioning of corresponding back-end virtual
disk is not supported.
For enabling caching on a virtual disk or partition, see Enabling Fluid Cache On Virtual Disks or Enabling
Fluid Cache On Virtual Disk Partitions. For disabling cache on virtual disk or partition, see Disabling Fluid
Cache On Virtual Disks or Disabling Fluid Cache On Virtual Disk Partitions.
Related Links
Fluid Cache Disk Properties
Fluid Cache Disk Properties
The following table lists the properties for Fluid Cache:
Table 7. Fluid Cache Disk Properties
Properties Description
Status
Displays the status of the Fluid Cache. The possible options are:
• OK
• Non-critical
• Critical
Name Displays the name of the Fluid Cache disk.
State
Tasks Allows you to disable and discard a particular Fluid Cache disk. Click
Type
Device Name Displays the device map name of the back-end disk.
Size Displays the total size of the Fluid Cache Disk.
Displays the state of the Fluid Cache. The possible options are:
• Active
• Failed
Execute to complete this operation.
Displays the type of device. The possible values are:
• Virtual Disk
• Partition
50
Page 51

Properties Description
Configured Cache Mode
Displays the configured cache mode for the Fluid Cache disk.
Possible values are:
• Write Back
• Write Through
Operational Cache Mode
Displays the operational cache mode for the Fluid Cache disk. If there
is a single PCIe-SSD in the Fluid Cache pool, this property is displayed
as Write Through irrespective of the Configured Cache mode. If
there is no PCIe-SSD in the Fluid Cache pool or the evaluation
license has expired, this property is displayed as Pass Through.
Possible values are:
• Write Back
• Write Through
• Pass Through
Fluid Cache Pool
To configure a Fluid Cache pool by adding PCIe-SSDs, see Add PCIe SSDs To Fluid Cache Pool. For
removing PCIe-SSDs from the Fluid Cache pool, see Remove PCIe SSDs From Fluid Cache Pool.
Related Links
Fluid Cache Pool Properties
Fluid Cache Pool Properties
The table below list the Fluid Cache Pool Properties:
Table 8. Fluid Cache Pool Properties
Properties Description
Cache Pool Size Displays the size of the cache pool in GiB.
Cache Pool High Availability
Cache Store Count Displays the number of PCIe SSDs that is part of the Fluid Cache
The possible options are:
• True — Indicates that the cache pool is write-back capable.
This option is set to True when more than one PCIe SSDs are
part of Fluid Cache pool.
• False — Indicates that the cache pool is writethrough capable.
This option is set to False when only one PCIe SSDs is part of
Fluid Cache pool.
pool.
Physical Device Properties
Table below list the Physical Device Properties
51
Page 52

Table 9. Physical Device Properties
Properties Description
ID Displays the physical device ID as reported by the omreport
CLI command.
Status Displays the status of the physical device.
Name Displays the name of the physical device.
State Indicates whether the physical device is ready or not.
Device Name Displays the operating system device name for the physical
device.
Bus Protocol Displays the bus protocol used with the physical device.
Part of Cache Pool Indicates whether the physical device is a part of the cache
pool or not.
Remaining Rated Write Endurance
Failure Predicted
Displays information on the SSD renewal/replacement based
on the amount of write workloads. This field indicates the
total remaining programs or erase-cycles available on the
SSD, based on the cumulative specification of the total
NAND (Negated AND or NOT AND) Flash chips in the SSD.
NOTE: This option is applicable to Micron PCIe SSDs,
Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) PCIe SSDs, and
SAS/SATA SSDs.
Displays whether the physical disk has received a SelfMonitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology (SMART) alert
and is therefore predicted to fail. For more information on
SMART predictive failure analysis, see Monitoring Disk
Reliability On RAID Controllers. For information on replacing
the physical disk, see Replacing A Physical Disk Receiving
SMART Alerts.
You may also want to review the Alert Log to see if the
physical disk has generated alerts pertaining to a SMART
predictive failure. These alerts can assist you in identifying
the cause of the SMART alert. The following alerts may be
generated in response to a SMART alert:
• 2094
• 2106
• 2107
• 2108
• 2109
• 2110
• 2111
For information on Alert Messages, see the Server
Administrator Messages Reference Guide.
Firmware Revision
Displays the firmware version of the physical device.
Driver Version Displays the version number of the driver.
Device Life Status Displays the health status of the physical device.
52
Page 53

Properties Description
Model Number Displays the model number of the physical device.
Capacity Displays the capacity of the physical device.
Vendor ID Displays the name of the physical device vendor
Product ID Displays the product ID of the device.
Serial No. Displays the serial number of the device.
PCIe Negotiated Link Speed Displays the current negotiated transfer speed of the
physical device in GT/s.
PCIe Maximum Link Speed Displays the capable transfer speed of the physical device in
GT/s.
PCIe Maximum Link Width Displays the capable link width of the physical device.
PCIe Negotiated Link Width Displays the current negotiated link width of the physical
device.
Cache I/O Statistics
The statistics page allows you to view:
• Cache usage of Fluid Cache disk
• Fluid Cache performance data in terms of bytes and IO operations
The Expand View option enables you to view the chart in a pop-up window.
Cache Pool Usage
The cache pool usage by each Fluid Cache disk and the available disk space in the Fluid Cache pool can
be viewed from the pie chart.
Viewing The Performance Of The Fluid Cache Disk
You can view the performance history and the average read/write performance of Fluid Cache disk as
listed.
Fluid Cache Disk Performance
The following table lists the fluid cache performance:
Table 10. Fluid Cache Disk Performance
Properties Description
Fluid Cache Disk Select the Fluid Cache disk from the drop-down option to view the
performance information. The drop-down list contains the list of all
Fluid Cache disks irrespective of the state (failed, active.)
Time Interval Type the time interval for which you want to view the performance
information. Time can be specified in Minutes, hours, days, weeks,
and months.
State Displays the state of the Fluid Cache Disk.
53
Page 54

In the Read/Write Bytes per Second for Fluid Cache Disk graph, the performance of cache read, cache
write, disk read and disk write for the specified Fluid Cache disk and time interval is plotted. You can click
the legend to compare the entries with one another. For example, you can gray-out the cache write and
disk write and compare the cache read and disk read performance. Hover the cursor over the line graph
to display the Read/Write performance details for a specific time. The legend also provides more
information about the average bytes read/written for the respective Fluid Cache Disk.
The I/O Operations per second for Fluid Cache Disk graph plots the I/O operations per second for the
chosen Fluid Cache disk and back-end disk in the specified time interval. Hovering the cursor over the
line graph provides the Read/Write performance details for specific time. The legend also provides more
information about the average read or write operation performed during a specific time.
License Settings
The License Settings page displays the digital license associated with the Fluid Cache.
Table 11. License Settings
Properties Description
License Type
Indicates the type of license. Possible values:
• Evaluation — License expires after being active for certain number
of days. The expiry time for this field is displayed in days.
• Node license — License applicable for a limited number of nodes
indicated by the Node Limit field.
License state
Software Service Tag
Duration Indicates the time line by which this license expires. This is applicable
Remaining Period Indicates the number of days for which the evaluation license is valid.
Vendor Indicates the license vendor.
Product ID Indicates the unique product ID.
License Generation Indicates the version of license for DAS solution.
License Node Limit
Feature ID Indicates the ID of the Fluid Cache products. The default ID for Direct
Feature Description Describes the features of the installed license.
To upgrade an existing license, use the Apply new license field. Click Browse to select the stored license
and click Apply to activate the license.
You can upgrade the license from evaluation to node.
Indicates the license state for the Fluid Cache:
• Valid — The license is valid.
• Expired — The license has expired.
Indicates the Service Tag of the license.
only for evaluation licenses.
Indicates the number of nodes on which a single Node license can
be installed.
NOTE: This field is applicable for a Node license.
Access Storage is 01
54
Page 55

Click Exit Wizard to go back to the Information Configuration page.
55
Page 56

56
Page 57

7
Storage Information And Global Tasks
Use the Storage information and Global Tasks window to view high-level information about the storage
components or devices on your system. These windows also allow you to launch global tasks that affect
all controllers attached to the system.
Related Links
Storage Properties
Global Tasks
Storage Controller Properties
Storage Properties
The Storage tree-view object has the following properties.
Table 12. Storage Properties
Property Definition
Status These icons represent the severity or health of the
storage component. For more information, see
Storage Component Severity.
— Normal/OK
— Warning/Non-critical
— Critical/Failure/Error
Smart Thermal Shutdown Displays whether thermal shutdown is enabled or
disabled. For more information, see Enabling Or
Disabling A Smart Thermal Shutdown.
Global Tasks
To execute a global task, select a task from the Global Tasks drop-down menu and click Execute.
The available tasks in the Global Tasks drop-down box are:
• Performing A Global Rescan
• Enabling Or Disabling A Smart Thermal Shutdown
• Setting Hot Spare Protection Policy
Performing A Global Rescan
A global rescan updates configuration changes (such as new or removed devices) for all SCSI controllers
and their attached components. For information on global rescan, see Rescanning To Update Storage
Configuration Changes.
57
Page 58

NOTE: Global Rescan is not supported on non-RAID controllers. You must reboot the system
before Storage Management can display the configuration changes on non-RAID SCSI controllers.
NOTE: The Global Rescan task updates the configuration changes in the Information/
Configuration page. To update the tree view, click the server name which is displayed above the
tree view.
To globally rescan:
1. In the Server Administrator window, under the System tree, expand Storage.
2. Click Information/Configuration on the Storage properties page.
3. Select Global Rescan from the Global Tasks drop-down list box.
4. Click Execute.
Enabling Or Disabling A Smart Thermal Shutdown
By default, the operating system and server turn off when the 220S and 221S enclosures reach a critical
temperature of 0 or 50 degrees celsius. You can change the setting to Enable Smart Thermal Shutdown
in Global Tasks, to ensure that only the enclosure and not the operating system or server is turned off
when the enclosure reaches a critical temperature.
If the enclosure has virtual disks that are channel-redundant, then the enclosure can be turned off while
redundant data continues to be available on another channel.
NOTE: Only SCSI controllers support Smart Thermal Shutdown.
To enable or disable thermal shut down:
1. In the Server Administrator window, under the System tree, expand Storage.
2. Click Information/Configuration on the Storage Properties page.
3. From the Global Tasks drop-down list box, select Enable Smart Thermal Shutdown or Disable
Smart Thermal Shutdown
4. Click Execute.
Related Links
Channel Redundancy And Thermal Shutdown
.
Storage Controller Properties
The information displayed for each controller can vary depending on the controller characteristics.
NOTE: The firmware and drivers listed in the Server Administrator Readme refer to the minimum
supported version for these controllers. Later versions of the firmware and drivers are also
supported. For the most recent driver and firmware requirements, contact your service provider.
Table 13. Controller Properties
Property Definition
Status Displays the status of the controller.
ID Displays the controller ID as reported by the
omreport CLI command.
58
Page 59

Property Definition
Name Displays the name of the controller. For more
detailed information on a controller, click its name
on the controller name.
Slot ID Displays the slot to which the controller is
attached. Storage Management displays Slot Not
Applicable for controllers for which it is unable to
display the slot ID and Embedded for embedded
controllers.
NOTE: If Slot Not Available is displayed, you
can identify the slot ID by selecting the
System → Main → System Chassis → Slots
object in the tree view and selecting the
Information tab. The Slot ID property on this
tab may display the correct information.
State Displays the state of the controller. Possible values
are:
• Ready — The controller is functioning
normally.
• Degraded — The controller has suffered a
failure of a component and is operating in a
degraded state.
• Failed — The controller has suffered a failure of
one or more components and is no longer
functioning.
Firmware Version Displays the version of the firmware available on
the controller.
Minimum Required Firmware Version Displays the minimum firmware version that is
required by Storage Management. This property is
displayed only if the controller firmware does not
meet the minimum requirement.
Driver Version Displays the version of the drivers installed on the
controller.
Minimum Required Driver Version Displays the minimum driver version that is
required by Storage Management. This property is
displayed only if the controller driver does not
meet the minimum requirement.
Number of Connector Displays the number of connectors available on
the controller. Each connector can be attached to
physical disks or an enclosure. Depending on the
controller type, the connector can be either a SCSI
channel or a SAS port.
Rebuild Rate The rebuild rate is the percentage of the resources
available on the system dedicated to rebuild a
59
Page 60

Property Definition
failed disk when a rebuild is necessary. For more
information on rebuild rate, see Setting The
Rebuild Rate.
Alarm State Displays whether the alarm on the controller is
enabled or disabled.
Cluster Mode Indicates whether the controller is part of a cluster
configuration.
SCSI Initiator ID Displays the SCSI ID of a SCSI controller. The
default value is 7. You can change the default
value in the BIOS. When controllers in a cluster
configuration display duplicate SCSI Initiator IDs,
refer to SCSI documentation.
Storage Management displays Not Applicable on
some controllers when this property is not
available.
Storage Components
For information on attached controllers, see Controllers.
60
Page 61

8
Controllers
This chapter provides information about the supported controllers and controller features in Storage
Management.
Related Links
RAID Controller Technology: SCSI, SATA, ATA, And SAS
Which Controllers Do I Have?
Non-RAID Controller Description
What Is A Controller?
Most operating systems do not read and write data directly from the disks, but instead send read and
write instructions to a controller. The controller is the hardware in your system that interacts directly with
the disks to write and retrieve data. A controller has connectors (channels or ports) which are attached to
one or more physical disks or an enclosure containing physical disks. RAID controllers can span the
boundaries of the disks to create an extended amount of storage space — or a virtual disk — using the
capacity of more than one disk.
Controllers also perform other tasks, such as initiating rebuilds, initializing disks, and more. To complete
their tasks, controllers require special software known as firmware and drivers. In order to function
properly, the controller must have the minimum required version of the firmware and drivers installed.
Storage Management supports different types of controllers. If your system has a supported controller,
the controller is displayed by expanding the Storage object in the System tree view in the GUI. You can
select the controller to display tabs for executing controller tasks and viewing controller properties.
Different controllers have different characteristics in the way they read and write data and execute tasks.
It is helpful to understand these features to most efficiently manage the storage. The following sections
describe the supported controllers and their features.
RAID Controller Technology: SCSI, SATA, ATA, And SAS
Storage Management supports RAID controllers using SCSI, SATA, ATA, and SAS technology. This section
indicates which technology the supported RAID controllers use. For more information on these
controllers, see Supported Features and the controller hardware documentation.
SAS RAID Controllers
The following RAID controllers use Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) technology.
• PERC 5/E
• PERC 5/i Integrated
• PERC 5/i Adapter
• SAS 5/iR Integrated
• SAS 5/iR Adapter
61
Page 62

• PERC 6/E
• PERC 6/I controller family
• SAS 6/iR controller family
• PERC S100, S110, and S300 controllers
• PERC H200, H700, and H800 controllers
• PERC H310 Adapter, PERC H310 Mini Monolithic, PERC H310 Mini Blades, PERC H710 Adapter, PERC
H710 Mini Blades, PERC H710 Mini Monolithic, PERC H710P Adapter, PERC H710P Mini Blades, PERC
H710P Mini Monolithic, and PERC H810 Adapter controllers
• PERC H730P Adapter
RAID Controller Features
Different controllers have different features. If you have more than one controller attached to your
system, you may notice that the tasks displayed on the Information/Configuration page of the controller
are different for each controller.
Controllers may also have differences in their read, write, and cache policies as well as how they handle
hot spares. You should be aware of these differences when creating virtual disks and assigning hot spares.
The following describes some of the RAID controller features and provides links to a more detailed
explanation. For information on the features supported by the controllers, see Supported Features.
• Hot spares — On RAID controllers, a hot spare is a backup for a disk that fails. See Protecting Your
Virtual Disk With A Hot Spare.
• Rebuilding data — You can rebuild data from a failed physical disk if the disk is a member of a
redundant virtual disk. See Rebuilding Redundant Information.
• Virtual disk expansion — Virtual disk expansion enables you to expand the capacity of a virtual disk
while it remains online by adding additional disks to the virtual disk. This feature is also known as
online capacity expansion (OLCE). See Virtual Disk Tasks.
• RAID migration — After creating a virtual disk, you can change the RAID level. See Reconfiguring Or
Migrating Virtual Disks.
• Moving physical and virtual disks to another controller — This feature enables you to move the
physical and virtual disks from one system to another. See Moving Physical And Virtual Disks From
One System To Another.
• Read, write, and cache policies — The manner in which a controller reads and writes data can vary.
The read, write, and cache policies have implications for data encryption and system performance.
See RAID Controller Read, Write, Cache, And Disk Cache Policy.
• Check consistency — A check consistency determines the integrity of the redundant data on a virtual
disk. When necessary, this feature rebuilds the redundant information. See Maintaining The Integrity
Of Redundant Virtual Disks.
• Patrol Read — Patrol read identifies disk errors to avoid disk failures, data loss, or corruption. For more
information, see Setting The Patrol Read Mode.
• Disk migration or foreign configurations — Some controllers enable you to move physical disks that
contain one or more virtual disks to another controller. The receiving controller is able to recognize
and import the foreign configuration (virtual disks). For more information, see Foreign Configuration
Operations.
Controller — Supported RAID Levels
RAID controllers may support different RAID levels. For information on supported RAID levels for a
controller, see Supported Features.
62
Page 63

Controller — Supported Stripe Sizes
When creating a virtual disk, you must specify the stripe size for the virtual disk. Different controllers have
different limitations on the stripe sizes they can support. For information on the supported stripe sizes for
a controller, see the virtual disk specifications section for the controller in Supported Features.
RAID Controller Read, Write, Cache, And Disk Cache Policy
When creating a virtual disk, you can specify the read, write, and cache policies for the virtual disk. The
following subsection describes these policies.
Related Links
Changing The Virtual Disk Policy
Read Policy
Does my controller support this feature? See Supported Features.
The read policies indicate whether the controller should read sequential sectors of the virtual disk when
seeking data.
• Read Ahead — The controller reads sequential sectors of the virtual disk when seeking data. Read
ahead policy may improve system performance if the data is written to the sequential sectors of the
virtual disk.
• No Read Ahead — Selecting no read ahead policy indicates that the controller should not use read
ahead policy.
• Adaptive Read Ahead — The controller initiates read ahead only if the two most recent read requests
accessed sequential sectors of the disk. If subsequent read requests access random sectors of the
disk, the controller reverts to no read ahead policy. The controller continues to evaluate whether read
requests are accessing sequential sectors of the disk, and initiates read ahead if necessary.
• Read Cache Enabled — The controller reads the cache information to verify if the requested data is
available in the cache before retrieving the data from the disk. Reading the cache information first can
provide faster read performance because the data (if available in the cache) can be retrieved more
quickly from the cache than from the disk.
• Read Cache Disabled — The controller retrieves data directly from the disk and not from the cache.
Write Policy
Does my controller support this feature? See Supported Features.
The write policies specify if the controller sends a write-request completion signal as soon as the data is
in the cache or after it has been written to the disk.
• Write Back — The controller sends a write-request completion signal as soon as the data is in the
controller cache but has not yet been written to disk. Write back caching may provide improved
performance since subsequent read requests can retrieve data quickly from the cache then from the
disk. However, data loss may occur in the event of a system failure which prevents that data from
being written on a disk. Other applications may also experience problems when actions assume that
the data is available on the disk.
63
Page 64

NOTE: Storage Management does not allow you to select the Write Back policy for controllers
that do not have a battery. The only exceptions are PERC S100 and PERC S300. This restriction
protects a controller without a battery from the loss of data that may occur in the event of a
power failure. On some controllers, the Write Back policy may be available in the controller
BIOS even though it is not available in Storage Management.
• Force Write Back — The write cache is enabled regardless of whether the controller has a battery. If
the controller does not have a battery and force write back caching is used, data loss may occur in the
event of a power failure.
• Write Back Enabled — The controller firmware disables the write cache if it does not detect the
presence of a charged battery over a specified period. For example, on some controllers, the write
cache is disabled if the firmware does not detect a charged battery within 72 hours.
• Write Through — The controller sends a write-request completion signal only after the data is written
to the disk. Write-through caching provides better data security than write-back caching, since the
system assumes the data is available only after it has been safely written to the disk.
NOTE: Write-through is the default write policy setting when cluster mode is enabled.
• Write Cache Enabled Protected — The controller writes data to the write cache before writing data to
the physical disk. Because it takes less time to write data to the write cache than it does to a disk,
enabling write cache can improve system performance. After data is written to the write cache, the
system is free to continue with other operations. The controller, in the meantime, completes the write
operation by writing the data from the write cache to the physical disk. The Write Cache Enabled
Protected policy is available only if the controller has a functional battery. The presence of a
functional battery ensures that data can be written from the write cache to the physical disk even
when there is power failure.
NOTE: Storage Management does not allow you to select the Write Cache Enabled Protected
policy for controllers that do not have a battery. This restriction protects a controller without a
battery from the data loss that may occur in the event of a power failure. When using the Create
Virtual Disk Advanced Wizard on a controller without a battery, the wizard either displays Write
Cache Disabled as the only available option or the wizard does not display any option for write
policy.
• Write Cache Disabled — This is the only option available when the controller does not have a
functional battery.
Cache Policy
Does my controller support this feature? See Supported Features.
The Direct I/O and Cache I/O policy apply to readings on a specific virtual disk. These settings do not
affect the read-ahead policy. The cache policies are:
• Cache I/O — Specifies that all reads are buffered in cache memory.
• Direct I/O — Specifies that reads are not buffered in cache memory. When using Direct I/O, data is
transferred to the controller cache and the host system simultaneously during a read request. If a
subsequent read request requires data from the same data block, it can be read directly from the
controller cache. The Direct I/O setting does not override the cache policy settings. Direct I/O is the
default setting.
NOTE: Cache policy is not supported on controllers that do not have a battery.
Disk Cache Policy
Does my controller support this feature? See Supported Features.
Set the physical disk caching policy of all members of a virtual disk by enabling the Disk Cache Policy.
When this feature is enabled, the physical disk writes data to the physical disk cache before writing it to
the physical disk. Because it is faster to write data to the cache than to a disk, enabling this feature
improves system performance.
64
Page 65

The cache policies are:
• Enabled — Disk Cache Policy is enabled.
• Disabled — Disk Cache Policy is disabled.
NOTE: The default setting for Disk Cache Policy for virtual disks based on SATA drives is Enabled;
and for virtual disks based on SAS drives is Disabled.
NOTE: For SAS 6i/R and PERC H200 family of controllers, the Disk Cache Policy setting is available
only after creating the virtual disk.
Background Initialization On PERC Controllers
On PERC controllers, background initialization of a redundant virtual disk begins automatically within 0 to
5 minutes after the virtual disk is created. The background initialization of a redundant virtual disk
prepares the virtual disk to maintain redundant data and improve write performance. For example, after
the background initialization of a RAID 5 virtual disk completes, the parity information is initialized. After
the background initialization of a RAID 1 virtual disk completes, the physical disks are mirrored.
The background initialization process helps the controller identify and correct problems that may occur
with the redundant data later. In this regard, the background initialization process is similar to a check
consistency.
The background initialization should be allowed to run to completion. If canceled, the background
initialization automatically restarts within 0 to 5 minutes. Some processes such as read and write
operations are possible while the background initialization is running. However, other processes such as
creating a virtual disk, cannot be run concurrently with background initialization. These processes cause
the background initialization to cancel.
Related Links
Canceling Background Initialization
Setting Background Initialization Rate
Non-RAID Controller Description
The non-RAID SCSI and SAS controllers are non-RAID controllers that support SCSI and SAS devices.
Because these controllers are non-RAID, they do not support virtual disks. You can manage these nonRAID controllers and their attached SCSI and SAS devices with Storage Management.
NOTE: Supported features may vary from controller to controller.
Non-RAID SCSI Controllers
The LSI PCI-e U320 non-RAID controllers use Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) technology.
Non-RAID SAS Controllers
The following non-RAID controllers use Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) technology:
• SAS 5/i Integrated
• SAS 5/E
• SAS 6 Gbps Adapter
• LSI SAS 9207-8e
65
Page 66

• LSI SAS 9300-8e
• LSI SAS 9206-16e
Firmware Or Driver Versions
Use the firmware or driver versions window to view information about the controller firmware and
drivers. For more information on firmware and drivers, see Before Installing Storage Management.
Related Links
Firmware/Driver Properties
Firmware/Driver Properties
The firmware and driver properties can vary depending on the model of the controller. The firmware and
driver properties are listed in the table below.
NOTE: The firmware and drivers listed in the Server Administrator Readme refer to the minimum
supported version for these controllers. Later versions of the firmware and drivers are also
supported. For most recent driver and firmware requirements, contact your service provider.
Table 14. Firmware/Driver Properties
Property Definition
Firmware Version Displays the version of the firmware that is installed on the
controller.
NOTE: Storage Management displays Not Applicable on
some controllers for which the firmware version cannot
be obtained.
Minimum Required Firmware Version Displays the minimum firmware version that is required by
Storage Management. This property is displayed only if the
controller firmware does not meet the minimum
requirement.
Driver Version Displays the version of the driver that is installed on the
controller.
NOTE: Storage Management displays Not Applicable on
some controllers for which the driver version cannot be
obtained.
Minimum Required Driver Version Displays the minimum driver version that is required by
Storage Management. This property is displayed only if the
controller driver does not meet the minimum requirement.
Storport Driver Version Displays the version of the storport driver that is installed on
the system.
Minimum Required Storport Driver
Version
Displays the minimum storport driver version required by
Storage Management. This property is displayed if the
operating system storport driver does not meet the minimum
requirement. This option is applicable only on systems
running Microsoft Windows operating system.
66
Page 67

Property Definition
NOTE: To download the latest storport driver, see the
Microsoft Knowledge Base article KB943545 at
support.microsoft.com.
Controller Health
The controller Health page displays the status of the controller and the components attached to the
controller.
Related Links
Storage Component Severity
Controller Information
Controller Components
Controller Components
For information on attached components, see:
• RAID Controller Batteries
• Firmware Or Driver Versions
• Connectors
NOTE: If you have connected the enclosure in Redundant path mode, the connectors are
represented as Logical Connector.
• Virtual Disks
Controllers Properties And Tasks
Use the controllers properties and tasks window to view information about the controller and execute
controller tasks.
NOTE: The firmware and drivers listed in the Server Administrator Readme refer to the minimum
supported version for these controllers. Later versions of the firmware and drivers are also
supported. For the most recent driver and firmware requirements, contact your service provider.
The controller properties can vary depending on the model of the controller. Controller properties may
include:
Table 15. Controller Properties
Property Definition
Status These icons represent the severity or health of the storage component.
For more information, see Storage Component Severity.
• — Normal/OK
• — Warning/Non-critical
67
Page 68

Property Definition
• — Critical/Failure/Error
ID Displays the ID assigned to the controller by Storage Management.
Storage Management numbers the controllers attached to the system
starting with zero. This number is the same as the controller ID
number reported by the omreport CLI Command. For information on
Command Line Interface, see the Server Administrator Command Line
Interface User’s Guide.
Name Displays the name of the controller.
State Displays the status of the controller. Possible values are:
• Ready — The controller is functioning normally.
• Degraded — The controller has encountered a failure and is
operating in a degraded state.
• Failed — The controller has encountered a failure and is no longer
functioning.
Firmware Version Displays the version of the firmware that is installed on the controller.
NOTE: Storage Management displays Not Applicable on some
controllers for which the firmware version cannot be obtained.
Minimum Required Firmware
Version
Driver Version Displays the version of the driver that is installed on the controller.
Minimum Required Driver
Version
Number of Connectors Displays the number of connectors on the controller. Each connector
Rebuild Rate Rebuild rate is the percentage of resources available on a system
BGI Rate The background initialization (BGI) rate is the percentage of resources
Displays the minimum firmware version that is required by Storage
Management. This property is displayed only if the controller firmware
does not meet the minimum requirement.
NOTE: Storage Management displays Not Applicable on some
controllers for which the driver version cannot be obtained.
Displays the minimum driver version that is required by Storage
Management. This property is displayed only if the controller driver
does not meet the minimum requirement.
can be attached to physical disks or an enclosure. Depending on the
controller type, the connector can be either a SCSI channel or a SAS
port.
dedicated to rebuild a failed disk when necessary. For more
information on rebuild rate, see Setting The Rebuild Rate.
NOTE: The value for the Revertible Hot Spare operation is the
same as the value set for the Rebuild Rate property.
available on a system dedicated to perform the background
68
Page 69

Property Definition
initialization of a virtual disk after it is created. For more information on
BGI rate, see Setting Background Initialization Rate.
Check Consistency Rate The check consistency rate is the percentage of resources available on
a system dedicated to perform check consistency on a redundant
virtual disk. For more information, see Performing A Check
Consistency.
Reconstruct Rate The reconstruct rate is the percentage of resources available on a
system dedicated to reconstruct a disk group after adding a physical
disk or changing the RAID level of a virtual disk residing on the disk
group. For more information on reconstruct rate, see Setting The
Reconstruct Rate.
Alarm State Displays whether the alarm on the controller is enabled or disabled.
NOTE: This property is displayed only for SCSI storage controllers.
Abort Check Consistency on
Error
Allow Revertible Hot Spare
and Replace Member
Loadbalance Provides the ability to automatically use both controller ports or
Auto Replace Member on
Predictive Failure
Redundant path view Indicates whether Storage Management has detected a redundant path
Encryption Capable Indicates whether the controller has the capability to support
Enables you to stop the Check Consistency operation on error. This
property is available only on controllers that have controller firmware
version 6.1 and later.
Enables the automatic copying of data from a physical disk to a hot
spare (in case of predictive failure) or from a hot spare to a physical
disk (in case of replacement of a degraded disk). For more information,
see Enabling Revertible Hot Spare.
connectors connected to the same enclosure to route I/O requests.
This property is available only on SAS controllers that have controller
firmware version 6.1 and later.
Enables the automatic copying of data from a physical disk to a hot
spare in case of predictive failure. Use this property in conjunction with
the Allow Revertible Hot Spare and Replace Member property.
configuration. Storage Management detects a redundant path
configuration when both controller ports are connected to the same
enclosure that is in a unified mode. For more information, see Setting
The Redundant Path Configuration.
encryption. Possible values are Yes and No.
Encryption Key Present Indicates whether the controller has an encryption key established.
Possible values are Yes and No.
Encryption Mode Indicates whether the controller is using Local Key Management (LKM)
or None. For more information, see Managing The Encryption Key.
T10 Protection Information
Capability
Indicates whether the controller supports data integrity. Possible values
are Yes and No.
69
Page 70

Property Definition
Cache Memory Size Displays the size of the cache memory on the controller.
Patrol Read Mode Displays the Patrol Read Mode setting for the controller. Possible
values are:
• Auto — Patrol read runs continuously on the system. When one
iteration of the patrol read is complete, the next patrol read is
scheduled to start within a period of time specified by the
controller. You do not have the option of manually starting or
stopping the Patrol Read in this mode.
• Manual — Allows you to manually start or stop the patrol read
process.
• Disabled — Indicates that the patrol read process is disabled.
For more information about patrol read, see Setting The Patrol Read
Mode and Starting And Stopping Patrol Read.
Patrol Read State Displays the current state of the patrol read process. Possible values
are:
• Ready — The patrol read process is enabled and runs when next
scheduled or when manually initiated.
• Active — The patrol read process is running.
• Stopped — The patrol read has been stopped.
For more information about patrol read, see Setting The Patrol Read
Mode.
Patrol Read Rate Displays the percentage of system resources dedicated for running the
Patrol Read operation. Patrol Read Rate changes the amount of
system resources assigned for the patrol read task. The Patrol Read
Rate can be configured between 0% and 100%, where:
• 0% — indicates the lowest priority for controllers and has the least
impact on the system performance.
• 100% — indicates the highest priority for controllers and has a
greater impact on the system performance.
Patrol Read Iterations Displays the number of Patrol Read Iterations. For more information
about patrol read, see Setting The Patrol Read Mode.
Cluster Mode Indicates whether the controller is part of a cluster configuration.
Persistent Hot Spare Displays if the hot spare is persistent. The possible values are:
• Enabled — The slot corresponding to the hot spare drive is
persistent. Any drive in the slot functions as a hot spare if the drive
is qualified to be a hot spare. If the drive contains foreign data, it is
overwritten.
• Disabled — The slot corresponding to the hot spare drive is not
persistent. If the drive is removed from the slot and any drive is
inserted, the slot stops functioning as a hot spare. You need to
manually assign the drive as a hot spare again.
Controller Tasks Enables you to configure and manage the controller. For more
information about controller tasks, see Controller Tasks.
70
Page 71

Property Definition
Available Reports Enables you to view patrol read report, check consistency report, slot
occupancy report, and physical disk firmware version report. For more
information on available reports, see Available Reports.
Related Links
How Do I Identify The Firmware Version That Is Installed
Controller Tasks
Available Reports
Controller Tasks
To execute a controller task:
1. In the Server Administrator window, under the system tree, expand Storage to display the controller
objects.
2. Select a controller object.
3. Click Information/Configuration on the controller Properties page.
4. Select a task from the Available Tasks drop-down menu.
5. Click Execute.
NOTE: Different controllers support different features. The tasks displayed on the Available Tasks
drop-down menu vary depending on the controller selected. The No Task Available option is
displayed when no tasks can be performed due to controller or system configuration limitations.
Controller Tasks
The following are the list of available tasks on a controller:
• Rescanning The Controller
• Creating A Virtual Disk
• Enabling The Controller Alarm
• Disabling The Controller Alarm
• Turning Off The Controller Alarm
• Testing The Controller Alarm
• Setting The Rebuild Rate
• Resetting Configuration
• Exporting The Controller Log File
• Foreign Configuration Operations
• Importing Foreign Configurations
• Importing Or Recovering Foreign Configurations
• Clearing Foreign Configuration
• Setting Background Initialization Rate
• Setting Check Consistency Rate
• Setting The Reconstruct Rate
• Setting The Patrol Read Mode
• Starting And Stopping Patrol Read
• Managing The Preserved Cache
71
Page 72

• Changing The Controller Properties
• Managing The Physical Disk Power
• Managing The Encryption Key
• Converting To RAID Capable Disks
• Converting To Non-RAID Disks
Rescanning The Controller
Does my controller support this feature? See Supported Features.
On SCSI controllers, a rescan updates configuration changes (such as new or removed devices) for all
components attached to the controller. For information on when to perform a rescan, see Rescanning To
Update Storage Configuration Changes.
NOTE: Rescan controller is not supported on non-RAID SCSI controllers. You must reboot the
system before Storage Management can display configuration changes on non-RAID SCSI
controllers. Otherwise, configuration changes are not reflected in the Storage Management
graphical user interface (GUI).
Related Links
Time Delay In Displaying Configuration Changes
To Rescan A Controller
1. In the Server Administrator window, under the system tree, expand Storage to display the controller
objects.
2. Select the controller object.
3. Click Information/Configuration on the controller Properties page.
4. Select Rescan from the Controller Tasks drop-down menu.
5. Click Execute.
You can also locate this task from the Change Controller Properties drop-down menu.
Related Links
Changing The Controller Properties
Creating A Virtual Disk
Does my controller support this feature? See Supported Features.
To launch the Create Virtual Disk Express Wizard, select the Create Virtual Disk task.
Related Links
Create Virtual Disk Express Wizard
Enabling The Controller Alarm
Does my controller support this feature? See Supported Features.
To enable the alarm on the controller, select the Enable Alarm task. When enabled, the alarm sounds in
the event of a device failure.
Related Links
Using Alarms To Detect Failures
Disabling The Controller Alarm
Does my controller support this feature? Supported Features.
72
Page 73

Select the Disable Alarm task to disable the alarm on the controller. When disabled, the alarm does not
sound in the event of a device failure.
Turning Off The Controller Alarm
Does my controller support this feature? See Supported Features.
Select the Quiet Alarm task to turn off the controller alarm. However, the controller alarm remains
enabled for future device failure.
Testing The Controller Alarm
Does my controller support this feature? See Supported Features.
Select the Test Alarm task to test whether the controller alarm is functional. The alarm sounds for about
2 seconds.
Setting The Rebuild Rate
Does my controller support this feature? See Supported Features.
The Set Rebuild Rate task allows you to change the rebuild rate for a controller.
During a rebuild, the complete contents of a physical disk are reconstructed. The rebuild rate,
configurable between 0% and 100%, represents the percentage of the system resources dedicated for
rebuilding failed physical disks. At 0%, the rebuild has the lowest priority for the controller, takes the
maximum time to complete, and is the setting with the least impact to system performance. A rebuild
rate of 0% does not mean that the rebuild is stopped or paused.
At 100%, the rebuild is the highest priority for the controller, minimizes the rebuild time, and is the setting
with the most impact to system performance.
On the PERC controllers, the controller firmware also uses the rebuild rate setting to control the system
resource allocation for the following tasks:
• Performing A Check Consistency
• Background Initialization. See Cancelling Background Initialization
• Full Initialization. A BIOS setting determines whether a full or fast initialization occurs. See Format,
Initialize, Slow And Fast Initialize
• Reconfigure. See Virtual Disk Task: Reconfigure (Step 1 of 3)
Related Links
Rebuilding Redundant Information
To Change The Rebuild Rate
To locate Set Rebuild Rate In Storage Management
To Change The Rebuild Rate
To change the rebuild rate:
1. Type a numerical value in the Set New Rebuild Rate (0-100) field. The value must be within the 0–
100 range.
2. Click Apply Changes.
To exit and cancel your changes, click Return to Previous Page.
73
Page 74

To locate Set Rebuild Rate In Storage Management
1. Expand the Storage tree object to display the controller objects.
2. Select a controller object.
3. Click Information/Configuration.
4. Select Set Rebuild Rate from the Available Tasks drop-down menu.
5. Click Execute.
You can also locate this task from the Change Controller Properties drop-down menu.
Resetting The Controller Configuration
Does my controller support this feature? See Supported Features.
The Reset Configuration task allows you to erase all the information on the controller so that you can
perform a fresh configuration. This operation destroys all data and virtual disks on the controller and
unassigns any hot spares.
You must completely reconfigure the storage after performing this reset operation.
CAUTION: Resetting a configuration permanently destroys all data on all virtual disks attached to
the controller. If the system or boot partition resides on these virtual disks, it is destroyed.
NOTE: Resetting the controller configuration does not remove a foreign configuration. To remove a
foreign configuration, select Clear Foreign Configuration task.
Related Links
Reset The Controller Configuration
To Locate Reset Configuration In Storage Management
Changing The Controller Properties
Reset The Controller Configuration
To reset the controller configuration:
1. Review the virtual disks that are destroyed by resetting the controller configuration. Make backups as
necessary. Click Blink at the bottom of the page to blink the physical disks included in the virtual
disks.
2. Click Reset Configuration when you are ready to erase all information on the controller.
To exit without resetting the controller configuration, click Go Back to Previous Page.
To Locate Reset Configuration In Storage Management
1. In the Server Administrator window, under the system tree, expand Storage to display the controller
objects.
2. Select a controller object.
3. Click Information/Configuration.
4. Select Reset Configuration from the Available Tasks drop-down menu.
5. Click Execute.
You can also locate this task from the Change Controller Properties drop-down menu.
Exporting The Controller Log File
Does my controller support this feature? See Supported Features.
74
Page 75

The Export Log task exports the controller log to a text file. This log provides detailed information on the
controller activities and can be useful for troubleshooting.
On a system running Microsoft Windows, the log file is exported to the windows or winnt directory. On a
system running Linux, the log file is exported to the /var/log directory.
Depending on the controller, the log file name is afa_<mmdd>.log or lsi_<mmdd>.log, where <mmdd> is
the month and date.
NOTE: In the VMware ESXi environment, only one log file is created (lsiexport.log). If the file exists,
exporting the log file overwrites the existing log file.
NOTE: Controllers without cache cannot store logs and export log files.
Related Links
What Is PCIe SSD?
Export The Controller Log File
To Locate Export Log In Storage Management
Changing The Controller Properties
Export The Controller Log File
1. Click Export Log File when ready.
2. To exit without exporting the controller log file, click Return to Previous Page.
To Locate Export Log In Storage Management
To locate this task in storage management:
1. Expand the Storage tree object to display the controller objects.
2. Select a controller object.
3. Click Information/Configuration.
4. Select Export Log from the Available Tasks drop-down menu.
5. Click Execute.
You can also locate this task from the Change Controller Properties drop-down menu.
Foreign Configuration Operations
Does my controller support this feature? See Supported Features.
The Foreign Configuration Operations task provides a preview of the foreign configurations that you can
import.
NOTE: Foreign Configuration Operations task is available only on PERC 6 and SAS controllers with
firmware versions 6.1 and later.
A foreign configuration is data residing on physical disks that have been moved from one controller to
another. Virtual disks residing on physical disks that have been moved are considered to be a foreign
configuration.
NOTE: It is not recommended to remove an external enclosure cable while the operating system is
running on the system. Removing the cable could result in a foreign configuration when the
connection is re-established.
The Foreign Configuration Operations task is displayed only when a controller detects a foreign
configuration. Select this option and click Execute to display the Foreign Configuration Preview page.
75
Page 76

The Foreign Configuration Preview page provides a preview of the foreign disks and enables you to
perform operations such as, importing, recovering, or clearing the foreign disks. You can also import or
clear a locked foreign configuration.
If any foreign configurations locked using Local Key manager (LKM) are detected, the associated
Encryption Key Identifier is displayed prompting you to provide the corresponding passphrase to unlock
the drives.
To avoid unlocking foreign configurations and to proceed to preview, import, or clear a foreign
configuration that has not been locked, click Skip or Continue.
If you do not want to import or clear the foreign configurations, or in case of loss of the associated
passphrase of the corresponding Encryption Key Identifier, execute the Instant Encrypt Erase task for
the physical disks.
CAUTION: Executing the Instant Encrypt Erase task erases all data on the physical disk.
Some conditions, such as an unsupported RAID level or an incomplete disk group, can prevent the import
or recovery of foreign virtual disks.
Related Links
Foreign Configuration Properties
To Locate Foreign Configuration Operations Task In Storage Management
Importing Foreign Configurations
Importing Or Recovering Foreign Configurations
Clearing Foreign Configuration
Managing The Encryption Key
Enabling Instant Encrypt Erase
Foreign Configuration Properties
The following table describes the properties that are displayed for the Foreign Disks and Global Hot
Spares.
Table 16. Foreign Configuration Properties
Property Definition
Status These icons represent the severity or health of the storage component.
• — Normal/OK
• — Warning/Non-critical
• — Critical/Failure/Error
For more information, see Storage Component Severity.
Name Displays the name of the foreign configuration and is available as a link.
This link enables you to access the physical disks that constitute the foreign
disk.
State Displays the current state of the foreign configuration. Possible values are:
• Ready — The foreign disk can be imported and functions normally after
import.
• Degraded — The foreign disk is in degraded state and rebuilds after
import.
76
Page 77

Property Definition
• Failed — The foreign disk has encountered a failure and is no longer
functioning. You cannot import the foreign configuration.
The foreign configuration may be in degraded or failed state due to any of
the following reasons:
• Missing physical disk — One of the physical disk(s) in the potential
virtual disk is missing or not available.
• Missing span — One or more spans of a hybrid virtual disk is missing.
• Stale physical disks — One or more physical disks in the configuration
may contain out-of-date data relating to other disks of that virtual disk.
Hence, the data integrity of the imported virtual disk is not intact.
• Unsupported configuration of the virtual disk — The virtual disk has an
unsupported RAID level.
• Import and Export — The virtual disks available for import exceed the
number of virtual disks available for export.
• Incompatible physical disks — Configuration on the physical disks is not
recognized by the RAID firmware.
• Orphan drive — A physical disk in the foreign configuration has
configuration information that matches another physical disk that is
already a part of an array (either a foreign or a native array).
NOTE: For other applicable physical disk tasks and properties, see
Physical Disk Or Physical Device Properties and Physical Disk Or
Physical Device Tasks.
Layout Displays the RAID level of the foreign configuration.
Remarks Provides information about the foreign virtual disk. If the virtual disk cannot
be imported, the reason for failure is displayed.
• Exceeded maximum — The number of virtual disks selected for import
has exceeded the maximum number of supported disks.
• Missing physical disk or Missing span — One or more physical disk(s) or
span(s) in the virtual disk to be imported is missing.
• Unsupported — The selected RAID level is not supported on this
controller.
• Orphan drive — The physical disk has been replaced and is no longer a
part of the RAID volume. The configuration should be cleared.
• Stale physical disk — The physical disk to be imported in the virtual disk
has outdated data.
• Partially foreign — The virtual disk is part of an already existing
configuration. Some physical disks in this virtual disk are foreign.
Dedicated Hot Spare Displays whether the foreign disk is a dedicated hot spare.
Based on the properties information, you can decide whether you want to import, recover, or clear the
foreign configuration.
To Locate Foreign Configuration Operations Task In Storage Management
For SAS controllers with firmware version 6.1:
1. In the Server Administrator window, under the system tree, expand Storage to display the controller
objects.
2. Select a controller object.
77
Page 78

3. Click Information/Configuration on the controller Properties page.
4. Select Foreign Configuration Operations from the Controller Tasks drop-down menu.
5. Click Execute.
Importing Foreign Configurations
Some controllers enable you to import a foreign configuration so that virtual disks are not lost after
moving the physical disks.
You can import a foreign configuration only if it contains a virtual disk that is either in a Ready or
Degraded state. In other words, all of the virtual disk data must be present, but if the virtual disk is using a
redundant RAID level, the additional redundant data is not required.
For example, if the foreign configuration contains only one side of a mirror in a RAID 1 virtual disk, then
the virtual disk is in a Degraded state and can be imported. On the other hand, if the foreign
configuration contains only one physical disk that was originally configured as a RAID 5 using three
physical disks, then the RAID 5 virtual disk is in a Failed state and cannot be imported.
In addition to virtual disks, a foreign configuration may consist of a physical disk that was assigned as a
hot spare on one controller and then moved to another controller. The Import Foreign Configuration
task imports the new physical disk as a hot spare. If the physical disk was set as a dedicated hot spare on
the previous controller, but the virtual disk to which the hot spare was assigned is no longer present in
the foreign configuration, then the physical disk is imported as a global hot spare.
The Import Foreign Configuration task is only displayed when the controller has detected a foreign
configuration. You can also identify whether a physical disk contains a foreign configuration (virtual disk
or hot spare) by checking the physical disk state. If the physical disk state is Foreign, then the physical
disk contains all or some portion of a virtual disk or has a hot spare assignment.
If you have an incomplete foreign configuration which cannot be imported, you can use the Clearing
Foreign Configuration option to erase the foreign data on the physical disks.
NOTE: The task of importing foreign configuration imports all virtual disks residing on physical disks
that have been added to the controller. If more than one foreign virtual disk is present, all the
configurations are imported.
Related Links
Foreign Configuration Properties
Importing Or Recovering Foreign Configurations
The recover operation attempts to restore degraded, failed, or missing virtual disks to a healthy state. A
virtual disk may be in a degraded, failed, or missing state after losing communication with the controller
due to a power loss, faulty cable connection, or other failure. A rebuild or background initialization may
automatically initiate after the recover operation completes.
The virtual disk data may be inconsistent after recovery. Verify the virtual disk data after the Import/
Recover Foreign Configuration task completes.
In some cases, the virtual disk data is incomplete and it is not possible to successfully recover the virtual
disk.
To import or recover a foreign configuration:
Click Import/Recover to import or recover all virtual disks residing on physical disks attached to the
controller.
To exit without importing or recovering the foreign configuration, click Cancel.
78
Page 79

To Locate Import Or Recover Foreign Configuration In Storage Management
For SAS controllers with firmware versions 6.1 and later:
1. In the Server Administrator window, under the system tree, expand Storage to display the controller
objects.
2. Select a controller object.
3. Click Information/Configuration on the controller Properties page.
4. Select Foreign Configuration Operations from the Controller Tasks drop-down menu.
5. Click Execute.
6. In the Foreign Configuration Preview page, click Import/Recover.
For SAS controllers with firmware version 6.0 and earlier, select Import/Recover Foreign Configuration
from the Controller tasks.
Clearing Foreign Configuration
Does my controller support this feature? See Supported Features.
After moving a physical disk from one controller to another, you may find that the physical disk contains
all or some portion of a virtual disk (foreign configuration). You can identify whether a previously used
physical disk contains a foreign configuration (virtual disk) by checking the physical disk state. If the
physical disk state is Foreign, then the physical disk contains all or some portion of a virtual disk. Use the
Clear Foreign Configuration task to clear or erase the virtual disk information from the newly attached
physical disks.
NOTE: The Clear Foreign Configuration task permanently destroys all data residing on the physical
disks that are added to the controller. If more than one foreign virtual disk is present, all the
configurations are erased. You may prefer to import the virtual disk rather than destroy the data.
To clear a foreign configuration:
Click Clear Foreign Configuration to clear or erase all virtual disks residing on physical disks is added to
the controller.
To exit without clearing the foreign configuration, click Cancel.
Related Links
To Locate Clear Foreign Configuration In Storage Management
Importing Foreign Configurations
Importing Or Recovering Foreign Configurations
To Locate Clear Foreign Configuration In Storage Management
For SAS controllers with firmware versions 6.1 and later:
1. In the Server Administrator window, under the system tree, expand Storage to display the controller
objects.
2. Select a controller object.
3. Click Information/Configuration on the controller Properties page.
4. Select Foreign Configuration Operations from the Controller Tasks drop-down menu.
5. Click Execute.
6. In the Foreign Configuration Preview page, click Clear.
79
Page 80

For SAS controllers with firmware version 6.0 and earlier, select Clear Foreign Configuration from the
Controller Tasks drop-down menu.
Physical Disks In Foreign Virtual Disks
The Physical Disks in Foreign Virtual Disks page displays the physical disks and the dedicated hot spare,
if any, included in the foreign configuration.
The following table describes the properties for physical disks in the foreign configuration.
Table 17. Physical Disk Properties
Property Definition
Status These icons represent the severity or health of the storage component.
• — Normal/OK
• — Warning / Non-critical
• — Critical/Failure/Error
For more information, see Storage Component Severity.
Name Displays the name of the physical disk. The name is comprised of the
connector number followed by the disk number.
State Displays the current state of the physical disk.
After Import State Displays the after-import state of the physical disk. The physical disk can be
imported in any of the following states:
• Online — The physical disk is part of the imported virtual disk and
functions normally.
• Offline — The physical disk is offline after import to the virtual disk.
• Foreign — The virtual disk containing the physical disk cannot be
imported and the physical disk remains in foreign state.
• Rebuild — After import of virtual disk, the physical disk rebuilds.
• Replacing — A Replace Member Disk task is performed on the physical
disk. For more information on replacing a member disk, see Replacing A
Member Disk and Enabling Revertible Hot Spare.
Capacity Displays the capacity of the disk.
Failure Predicted Displays whether the physical disk has received a Self-Monitoring Analysis
and Reporting Technology (SMART) alert and is therefore predicted to fail.
For more information on SMART predictive failure analysis, see Monitoring
Disk Reliability On RAID Controllers. For information on replacing the
physical disk, see Replacing A Physical Disk Receiving SMART Alerts.
You may also want to review the alert log to see whether the physical disk
has generated alerts pertaining to a SMART predictive failure. These alerts
can assist you in identifying the cause of the SMART alert. The following
alerts may be generated in response to a SMART alert:
• 2094
• 2106
• 2107
80
Page 81

Property Definition
• 2108
• 2109
• 2110
• 2111
For information on alert messages, see the Server Administrator Messages
Reference Guide.
Progress Displays the progress of an operation being performed on the physical disk.
Bus Protocol Displays the technology that the physical disk is using. Possible values are:
• SCSI — Small Computer System Interface
• SAS — Serial Attached SCSI
• SATA — Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA)
Certified Indicates that the drive has firmware which has been tested and fully
qualified by the service provider. Drives that are not certified by the service
provider may work but, are not supported and recommended for use in
servers.
Media Displays the media type of the physical disk. The possible values are:
• HDD — Hard Disk Drive. An HDD is a non-volatile storage device which
stores digitally-encoded data on rapidly rotating platters with magnetic
surfaces.
• SSD — Solid-State Drive. An SSD is a data storage device that uses
solid-state memory to store persistent data.
• Unknown — Storage Management is unable to determine the media
type of the physical disk.
Used RAID Disk Space Displays the amount of the physical disk space that is used by the virtual
disks on the controller. This property is not applicable for physical disks
attached to non-RAID controllers.
In certain circumstances, the Used RAID Disk Space displays a value of
zero (0) even though a portion of the physical disk is actually being used.
This occurs when the used space is 0.005GB or less. The algorithm for
calculating the used disk space rounds off a figure of 0.005GB or less than
zero. Used disk space that is between 0.006GB and 0.009GB is rounded
off to 0.01GB.
Available RAID Disk Space Displays the amount of available space on the disk. This property is not
applicable for physical disks attached to non-RAID controllers.
Hot Spare Indicates whether the disk has been assigned as a hot spare. This property
is not applicable for physical disks attached to non-RAID controllers.
Vendor ID Displays the hardware vendor of the disk.
Product ID Displays the product ID of the device.
Firmware Revision Displays the firmware version of the physical device.
Serial No. Displays the serial number of the disk.
81
Page 82

Property Definition
PCIe Negotiated Link
Speed
PCIe Maximum Link
Speed
Manufacture Day Displays the day of the month on which the physical disk was
Manufacture Week Displays the week of the year during which the physical disk was
Manufacture Year Displays the year in which the physical disk was manufactured.
SAS Address Displays the SAS address of the physical disk. The SAS address is unique to
After Import Status Displays the status of the physical disk after importing the foreign
Encryption Capable Displays whether the physical disk is a Self Encryption Disk (SED). The
Displays the current negotiated transfer speed of the physical device in
GT/s.
Displays the capable transfer speed of the physical device in GT/s.
manufactured.
manufactured.
each SAS disk.
configuration. Possible values are:
• Foreign
• Online
• Offline
• Replaced
• Rebuild
possible values are Yes and No.
Encrypted Displays whether the physical disk is encrypted to the controller. The
possible values are Yes and No. For a non-SED the value is N/A.
Part Number Displays the unique Bill Of Materials assignment number for a physical disk.
The numbers four through eight represent the service provider part
number for that model drive.
PCIe Maximum Link
Width
PCIe Negotiated Link
Width
Displays the capable link width of the physical device.
Displays the current negotiated link width of the physical device.
Setting Background Initialization Rate
Does my controller support this feature? See Supported Features.
The Set Background Initialization Rate task changes the amount of system resources dedicated to the
background initialization task.
The background initialization rate, configurable between 0% and 100%, represents the percentage of the
system resources dedicated for running the background initialization task. At 0%, the background
initialization has the lowest priority for the controller, takes maximum time to complete, and has the least
impact to system performance. A background initialization rate of 0% does not mean that the
background initialization is stopped or paused.
82
Page 83

At 100%, the background initialization is the highest priority for the controller. The background
initialization time is minimized and has the most impact to system performance.
Related Links
Background Initialization On PERC Controllers
To Change The Background Initialization Rate For A Controller
1. Type a numerical value in the Set New BGI Rate (0-100) field. The value must be within the 0–100
range.
2. Click Apply Changes. To exit and cancel your changes, click Return to Previous Page.
To Locate Background Initialization Rate In Storage Management
1. In the Server Administrator window, under the system tree, expand Storage to display the controller
objects.
2. Select a controller object.
3. Click Information/Configuration on the controller Properties page.
4. Select Set Background Initialization Rate from the Available Tasks drop-down menu.
5. Select Execute.
You can also locate this task from the Change Controller Properties drop-down menu.
Related Links
Changing The Controller Properties
Setting The Check Consistency Rate
Does my controller support this feature? See Supported Features.
The Set Check Consistency Rate task changes the amount of system resources dedicated to the check
the consistency rate.
The check consistency rate, configurable between 0% and 100%, represents the percentage of the
system resources dedicated for running the check consistency task. At 0%, the check consistency has the
lowest priority for the controller, takes maximum time to complete, and has least impact to system
performance. A check consistency rate of 0% does not mean that the check consistency is stopped or
paused.
At 100%, the check consistency is the highest priority for the controller. The check consistency time is
minimized and has most impact to system performance.
Related Links
Performing A Check Consistency
To Change The Check Consistency Rate For A Controller
1. Type a numerical value in the Set New Check Consistency Rate (0-100) field. The value must be
within the 0–100 range.
2. Click Apply Changes.
To exit and cancel your changes, click Return to Previous Page.
To Locate Set Check Consistency Rate In Storage Management
1. In the Server Administrator window, under the system tree, expand Storage to display the controller
objects.
2. Select a controller object.
83
Page 84

3. Click Information/Configuration on the controller Properties page.
4. Select Set Check Consistency Rate from the Available Tasks drop-down menu.
5. Click Execute.
You can also locate this task from the Change Controller Properties drop-down menu.
Related Links
Changing The Controller Properties
Setting The Reconstruct Rate
Does my controller support this feature? See Supported Features.
The Set Reconstruct Rate task changes the amount of system resources dedicated for the reconstruct
task.
The reconstruct task recreates the virtual disk after you have changed the RAID level or reconfigured the
virtual disk. The reconstruct rate, configurable between 0% and 100%, represents the percentage of the
system resources dedicated for running the reconstruct task. At 0%, the reconstruct has the lowest
priority for the controller, takes maximum time to complete, and has least impact to system performance.
A reconstruct rate of 0% does not mean that the reconstruct is stopped or paused.
At 100%, the reconstruct is the highest priority for the controller, the reconstruct time is minimized, and
has most impact to system performance.
Related Links
Reconfiguring Or Migrating Virtual Disks
To Change The Reconstruct Rate For A Controller
1. Type a numerical value in the Set New Reconstruct Rate (0-100) field. The value must be within the
0–100 range.
2. Click Apply Changes. To exit and cancel your changes, click Return to Previous Page.
To Locate Set Reconstruct Rate In Storage Management
1. In the Server Administrator window, under the system tree, expand Storage to display the controller
objects.
2. Select a controller object.
3. Click Information/Configuration on the controller Properties page.
4. Select Set Reconstruct Rate from the Available Tasks drop-down menu.
5. Select Execute.
You can also locate this task from the Change Controller Properties drop-down menu.
Related Links
Changing The Controller Properties
Setting The Redundant Path Configuration
Does my Controller Support This Feature? See Supported Features.
Redundant path is supported only on external PERC cards that use firmware version 6.1 and later. A
redundant path internal to the system is not supported. MD1xxx enclosures are supported.
For redundant paths, the enclosure must be in the Unified mode however specific port connections are
not required. A connection from either controller ports to either EMM In ports creates the redundant path
as long as two cables are used. But, Redundant Path continues to appear in the field even as the
84
Page 85

redundant path is removed. The redundant path ceases to appear only when it is cleared in the storage
management.
In a daisy-chain scenario, more than one enclosure can be connected to a controller in a redundant path
mode. You can connect up to three MD1000 and MD1120 to a PERC 6/E controller in a daisy-chain
enclosure. You can connect up to four MD1200 and MD1220 to a PERC H800 and PERC H810 controller
in a daisy-chain enclosure. For an example of a daisy-chain configuration (for PERC 6/E controller), see
the following image:
If the communication channel between the connector and the first enclosure is lost, the redundant path
configuration is lost. In this case, the health of the logical connector is displayed as critical. Navigate to
the Information/Configuration page of the logical connector to view details of the Path Health. For a
brief outline of this scenario, see the following table:
Table 18. Path between Controller and Enclosure 1
Health of Logical Connector Path between Controller and Enclosure 1
Connector 0 (C0) Connector 1 (C1)
Available Available
Available Disconnected
Disconnected Available
However, if the communication channel between any two enclosures is lost, the redundant path
configuration is degraded and the health of the logical connector is displayed as degraded. For a brief
outline of this scenario, see the following table.
85
Page 86

Table 19. Path between Enclosure n and Enclosure n +1
Health of Logical Connector Path between Enclosure n and Enclosure n +1
Connector 0 (C0) Connector 1 (C1)
Available Available
Available Disconnected
Disconnected Available
In the above scenario, the enclosure status is displayed in warning mode. Clicking Information/
Configuration in the Enclosures page displays all enclosure components (EMMs, Fans, Physical Disks,
Power Supplies, and Temperature) in normal condition. To view the Path Failure message to indicate that
the enclosure has lost a communication path to the controller, indicating that the enclosure is no longer
in redundant path mode.
Related Links
Path Health
Clearing The Connectors Redundant Path View
Clearing The Redundant Path View
Consider a case where you reboot your system and Storage Management, displays the logical connector
with a path failure message. It is possible that you may have intentionally unplugged the second
connector. In this case, the path failure message is not relevant. There could be a fault in the connected
cable or the cable may not be connected properly to the controller. In both cases, Storage Management
displays that the system was in redundant path configuration before reboot and is no longer in this
configuration. If you are sure you, do not want the redundant path mode, clear the existing redundant
path view using Clear Redundant Path View provided in the Changing The Controller Properties
controller task. Selecting this option clears the redundant path view and the connectors are represented
on the user interface as Connector 0 and Connector 1.
Related Links
Setting The Redundant Path Configuration
Logical Connector Properties And Tasks
Setting The Patrol Read Mode
Does my controller support this feature? See Supported Features.
Patrol read identifies disk errors in order to avoid disk failures and data loss or corruption. The Set Patrol
Read task is applicable only for disks used as virtual disks or hot spares.
The Set Patrol Read tasks run in the background and corrects, when possible. When the Set Patrol Read
mode is set to Auto, patrol read is initiated when the controller is idle for a period of time and when no
other background tasks are active. In this scenario, the patrol read enhances the system performance as
disk errors can be identified and corrected when there is not input/output activity on the disk.
The controller adjusts the amount of system resources dedicated for patrol read based on the amount of
controller activity that is competing with the Patrol Read task. When the controller activity is high, fewer
system resources are dedicated to the patrol read task.
Patrol Read does not run on a physical disk in the following circumstances:
• The physical disk is not included in a virtual disk or is assigned as a hot spare.
86
Page 87

• The physical disk is included in a virtual disk that is currently undergoing one of the following:
– Rebuild
– Reconfiguration or reconstruction
– Background initialization
– Check consistency
In addition, the Patrol Read suspends during heavy I/O activity and resumes when the I/O is finished.
Related Links
Starting And Stopping Patrol Read
To Set The Patrol Read Mode
Select the desired Patrol Read Mode option. The options available are:
• Auto — Initiates the Patrol Read task. After the task is complete, it automatically runs again within a
specified period. For example, on some controllers the Patrol Read runs every four hours and on
other controllers, the Patrol Read runs every seven days. The Patrol Read task runs continuously on
the system starting again within the specified period after each iteration of the task completes. If the
system reboots while the Patrol Read task is running in Auto mode, the Patrol Read restarts at zero
percent (0%). When the Patrol Read task is set to Auto mode, you cannot start or stop the task. Auto
mode is the default setting.
NOTE: For more information on how often the Patrol Read task runs when in Auto mode, see
your controller documentation.
• Manual — Enables you to start and stop the Patrol Read task using Start and Stop Patrol Read. Setting
the mode to Manual does not initiate the Patrol Read task. If the system reboots while Patrol Read is
running in Manual mode, Patrol Read does not restart.
• Disabled — Prevents the Patrol Read task from running on the system.
To Locate Set Patrol Read Mode In Storage Management
1. In the Server Administrator window, under the system tree, expand Storage to display the controller
objects.
2. Select a controller object.
3. Click Information/Configuration on the controller Properties page.
4. Select Set Patrol Read mode from the Available Tasks drop-down menu.
5. Click Execute.
You can also locate this task from the Change Controller Properties drop-down menu.
Related Links
Changing The Controller Properties
Starting And Stopping Patrol Read
Does my controller support this feature? See Supported Features.
NOTE: The Patrol Read operation is not supported on solid-state drives (SSD).
When the Set Patrol Read mode is set to Manual, you can start the Patrol Read task or stop the task when
it is running.
There are certain conditions under which the Patrol Read task cannot be run.
To start or stop the Patrol Read Task:
Click Start Patrol Read or Stop Patrol Read.
87
Page 88

To exit without starting or stopping the Patrol Read, click Go Back to Previous Page.
Related Links
Setting The Patrol Read Mode
Locate Start Stop Patrol Read In Storage Management
1. In the Server Administrator window, under the system tree, expand Storage to display the controller
objects.
2. Select a controller object.
3. Click Information/Configuration on the controller Properties page.
4. Select Start Patrol Read or Stop Patrol Read from the Available Tasks.
5. Click Execute.
You can also locate this task from the Change Controller Properties drop-down menu.
Related Links
Changing The Controller Properties
Changing The Controller Properties
Does my controller support this feature? See Supported Features.
The Change Controller Properties task provides you the option to change multiple controller properties
simultaneously. This task is available only on SAS controllers with firmware version 6.1 and later.
You can change any or all of the following properties using the Change Controller Properties task:
• Rebuild Rate
• BGI Rate
• Check Consistency Rate
• Reconstruct Rate
• Abort check consistency on error
• Revertible Hot Spare
• Loadbalance
• Auto replace member on predictive failure
• Redundant path view
• Persistent hot spare
NOTE: You can also set these properties using the command line interface. For more information,
see the Server Administrator Command-Line Interface User’s Guide.
Related Links
To Rescan A Controller
To Locate Change Controller Properties In Storage Management
1. In the Server Administrator window, under the system tree, select Storage.
2. On the Storage Dashboard page, Change Controller Properties from the Available Tasks drop-
down menu.
3. Click Execute.
88
Page 89

To Locate Change Controller Properties In Storage Management: Method 2
1. In the Server Administrator window, under the system tree, expand Storage to display the controller
objects.
2. Select a controller object.
3. Click Information/Configuration on the controller Properties page.
4. Select Change Controller Properties ... from the Controller Tasks drop-down menu.
5. Click Execute.
Managing The Physical Disk Power
Does my controller support this feature? See Supported Features.
The Manage Physical Disk Power task allows you to manage the power consumed by the physical disks.
NOTE: The Manage Physical Disk Power task is provided with PERC H700, H800, and H310 cards
by spinning down the hot spares and unconfigured disks. PERC H710, H710P, H810, and H730P
cards also support the Manage Physical Disk Power task with additional power-saving modes, Spin
Down Configured Drives, and Automatic Disk Power Saving (Idle C) options.
You can enable one of the following modes to manage the power consumed:
• No Power Savings Mode — This is the default mode for the controller. In this mode, all power-saving
features are disabled.
• Balanced Power Savings Mode — Provides good power savings while limiting I/O latency.
• Maximum Power Savings Mode — Provides maximum power savings for all drives.
• Customized Power Savings Mode — Allows you to customize the power-saving settings. The default
values are populated when you select this power mode. You can select or clear the features you want
to enable. You can select Quality of Service (QoS) to customize power saving on configured drives by
setting the Start Time and Time interval to spin up.
To enable the Quality of Service (QoS) feature:
1. Select Customized Power Savings Mode.
2. Select Enable for the Spin Down Configured Drives option
Related Links
Properties In Manage Physical Disk Power Option
Physical Disk Power On Unconfigured Drives And Hot Spares
Managing Physical Disk Power Using The Customized Power Savings Mode
Managing Physical Disk Power Using The QoS Option
Managing The Time Interval For The QoS Option
Properties In Manage Physical Disk Power Option
The following table displays the properties in the Manage Physical Disk Power option:
89
Page 90

Table 20. Manage Physical Disk Power Properties
Property Definition
Spin Down Unconfigured Drives The Enabled option spins down the unconfigured
disks if they are unattended for a specified interval
of time.
Spin Down Hot Spares The Enabled option spins down the hot spares if
no read‑write operation takes place on the hot
spare in a specified interval of time.
Spin Down Configured Drives The Enabled option spins down the configured
disks if they are unattended for a specified interval
of time.
Automatic Disk Power Saving (Idle C) Enables or disables the Automatic Disk Power
Saving (Idle C) feature for additional power saving.
When enabled, it enables the new generation
power savings without affecting the legacy drives.
Time Interval for Spin Down Sets the time interval after which the hot spares
and unconfigured drives spins down.
Quality Of Service (QOS)
Enable Quality Of Service Settings Select to set the start time and the time interval for
spin up activity at the virtual disk level.
NOTE: This option is available only if the Spin
Down Configured Drives option is selected.
Start Time (HH:MM) Displays the start time of the battery learn cycle.
This option is enabled only if Enable Quality Of
Service Settings is selected.
Time Interval for Spin Up (in Hours) Displays the spin up time interval for the battery
learn cycle. The time interval can range from 1-24
hours.
Related Links
Managing The Physical Disk Power
Physical Disk Power On Unconfigured Drives And Hot Spares
1. Select Enabled for the Spin Down Unconfigured Drives and Spin Down Hot Spares options.
2. Click Apply Changes. To exit and cancel your changes, click Go Back to Previous Page.
Related Links
Managing The Physical Disk Power
Managing Physical Disk Power Using The Customized Power Savings Mode
To manage physical disk power through the Customized Power Savings Mode:
1. Select the Customized Power Save Mode option.
2. Edit the remaining parameters on the Manage Physical Disk Power page. You can also configure the
options in the QoS section as described in the following section.
Related Links
90
Page 91

Managing The Physical Disk Power
Managing Physical Disk Power Using The QoS Option
To manage physical disk power through the QoS option:
1. Select the Customized Power Save Mode option.
2. In the Spin Down Configured Drives drop-down menu, select Enabled.
3. The Quality of Service (QoS) option is enabled.
Enter the Start Time and Time Interval to spin up.
4. Click Apply.
Related Links
Managing The Physical Disk Power
Managing The Time Interval For The QoS Option
To manage the time interval for the QoS option at the virtual disk level:
1. In the Quality Of Service (QoS) page, select Enable Quality of Service Settings.
2. Set the Start Time.
The start time can range from 1 to 24 hours.
3. Click Apply Changes.
NOTE: The Enable Quality of Service Settings option is enabled only if the Spin Down
Configured Drives option is enabled.
Related Links
Managing The Physical Disk Power
To Locate Manage Physical Disk Power In Storage Management
1. In the Server Administrator window, under the system tree, expand Storage to display the controller
objects.
2. Select a controller object.
3. Click Information/Configuration on the controller Properties page.
4. Select Manage Physical Disk Power from the Available Tasks drop-down menu.
5. Click Execute.
Managing The Preserved Cache
The Managed Preserved Cache feature provides you the option to ignore or restore the controller cache
data.
In the write-back policy, data is written to the cache before being written to the physical disk. If the virtual
disk goes offline or is deleted for any reason, the data in the cache is lost.
Data in the cache may also be lost in case of unintended cable or power failure. If such a failure, Storage
Management preserves the data written on the preserved or dirty cache until you recover the virtual disk
or clear the cache.
This feature is available only on SAS controllers with firmware version 6.1 and later.
The status of the controller is affected by the preserved cache. The controller status is displayed as
degraded if the controller has preserved cache.
91
Page 92

CAUTION: You may not be able to use Storage Management to manage the preserved cache in
some cases. As an example, consider you have a RAID 1 level with two disks — D1 and D2. If you
now remove D2, the virtual disk is degraded and the data in the controller cache is written to D1.
So, D1 has the latest data. Now, if you re-insert D2 and pull out D1, the virtual disk is still
degraded and does not have the latest data.
You can discard the preserved cache only if all of the following conditions are met:
• The controller does not have any foreign configuration. Select Click for Preview to view details of the
foreign configuration. See Foreign Configuration Operations.
• The controller does not have any offline or missing virtual disks. If there are offline or missing virtual
disks, ensure that you have a backup of these virtual disks.
• Cables to any virtual disk are not disconnected.
Encryption Key
The controller uses the encryption key to lock or unlock access to SED. You can create only one
encryption key for each encryption-capable controller.
If you are using LKM, you must create the encryption key by providing the Encryption Key Identifier and
the Passphrase.
Encryption Key Identifier
An Encryption Key Identifier is a user-supplied text label for the Passphrase. The identifier helps you
determine which Passphrase to provide while authenticating import of foreign encrypted SED drives.
Passphrase
A Passphrase is a user supplied string that the controller uses to create the encryption key.
NOTE: For more information on Encryption Key and Passphrase guidelines, click the icon on
the Manage Encryption Key page.
Related Links
Managing The Encryption Key
Creating An Encryption Key And Enabling LKM
To create an encryption key on the selected controller:
1. Select the Enable Local Key Management (LKM) option.
2. Type Encryption Key Identifier.
An Encryption Key Identifier can contain numerals, alphabets both lower and upper case are
allowed, non-alphanumeric characters, or a combination of any of these.
NOTE: For the Encryption Key Identifier and Passphrase guidelines, click the icon on the
page.
3. Type a Passphrase.
A Passphrase must contain at least one numeral, alphabets both lower and upper case are allowed,
and one non-alphanumeric character (except space).
NOTE: Server Administrator Storage Management provides a suggested passphrase below the
Passphrase text box.
92
Page 93

4. If you want to save the Encryption Key credentials in a file on the system where Distributed Web
Server is running, select the Escrow check box.
The Path field is displayed. Provide the path where you want to save the file. The path should contain
a filename with an .xml extension. The saved file contains the information: SAS address, Encryption
Key Identifier, Passphrase, and modified date. You can use this file for future reference.
CAUTION: It is important to understand that if you lose the Passphrase, you cannot recover
it. If you move the physical disks associated with the lost Passphrase to another controller or
if the controller fails or is replaced, you cannot access data from that disk.
NOTE: If Encryption Key Identifier or Passphrase contain special characters such as & , " , <,
and >, in the file, they are written as & , ", < and > respectively.
NOTE: If the system crashes while saving the file, the backup file is saved in the specified
location.
5. Select the check-box indicating that you understand the implications of using a passphrase and click
Apply Changes.
In the controller Information/Configuration page, the Encryption Key Present is set to Yes and the
Encryption mode is set to LKM.
Changing Or Deleting The Encryption Key
You can change an encryption key of a controller if the controller already has a configured encryption
key. You can delete an encryption key for encrypted controllers only if there are no encrypted virtual
disks.
To change the encryption key, type the New Encryption Key Identifier and Passphrase. You are
prompted to authenticate the current Passphrase. Ensure that you read the note on the importance of
passphrase and consequences of not saving the same, before applying the changes.
When you change the encryption key, the existing configuration on the controller is updated to use the
new encryption key. If you have removed any of the encrypted drives previously, you must authenticate
with the old passphrase to import the encrypted drives.
When changing the encryption key, you can also save or update the new encryption key credentials to a
file in the system where Distributed Web Service is running. Select the Escrow check box. If you have
already saved the encryption key credentials for a controller, providing the path of the file updates the
credentials for that controller. If the credentials are for a new controller, the details are appended in the
same file.
If you have not saved the credentials to a file, you can provide the path on which the file must be saved.
The path must contain a filename with an .xml extension. On applying changes, this file is created with
the credentials.
If you delete the encryption key, you cannot create encrypted virtual disks and all encrypted
unconfigured self-encrypting drives are erased. However, deleting an encryption key does not affect
encryption or data in foreign disks. If you have saved the encryption key credentials to a file, deleting the
encryption key does not delete the file. Managing the file is the responsibility of the administrator.
Managing The Encryption Key
NOTE: To configure encryption, SED is not required. The encryption settings are used to configure
the virtual disk and the SED.
NOTE: On controller when encryption is disabled, manually enable encryption for virtual disks
created using SED drives. If the virtual disk is created after encryption is enabled on a controller, the
virtual disk is automatically encrypted, it will automatically be configured as an encrypted virtual disk
unless the enabled encryption option is disabled during the advance configuration virtual disk
creation.
93
Page 94

On an encryption-capable controller, the Manage Encryption Key task allows you to enable encryption
in LKM mode. If you enable LKM, you can create an encryption key on an encryption-capable controller
and save it locally. You can also change or delete the encryption key.
NOTE: This task is available only on PERC H7x0 and H8x0 controllers.
Related Links
Passphrase
Manage Encryption Key Task In Storage Management
To go to the Manage Encryption Key task in Storage Management:
1. In the Server Administrator window, under the system tree, select Storage.
2. Go to Storage Dashboard → Available Tasks drop-down menu → Manage Encryption Key....
3. Click Execute.
Manage Encryption Key Task In Storage Management — Method 2
Alternatively to go to Manage Encryption Key task in Storage Management
1. Expand the Storage tree object to display the controller objects.
2. Select an encryption-capable controller object.
3. Click Information/Configuration.
4. Select Manage Encryption Key.... from the Controller Tasks drop-down menu.
5. Click Execute.
If the controller is encryption-capable and an encryption key is not present, then the Create Encryption
page is displayed. Else, the Change or Delete Encryption Key page is displayed.
Key
Converting To Non-RAID Disks
On PERC H310 adapters:
1. In the Server Administrator window, under the system tree, expand Storage to display the controller
objects.
2. Select the Controller object.
3. Click Information/Configuration on the controller Properties page.
4. In the controller tasks drop-down menu select the task Convert to Non-RAID disks.
The disks in Ready state are displayed.
5. Select the drives that you want to convert.
6. Click Apply.
An acknowledgement that the disks have been converted is displayed.
Related Links
Converting To RAID Capable Disks
Converting To RAID Capable Disks
On PERC H310 adapters:
1. In the Server Administrator window, under the system tree, expand Storage to display the controller
objects.
2. Select the Controller object.
94
Page 95

3. Click Information/Configuration on the controller Properties page.
4. In the controller tasks drop-down menu select the task Convert to RAID Capable disks
The non-RAID disks are displayed.
5. Select the drives that you want to convert.
6. Click Apply.
An acknowledgement that the disks have been converted is displayed.
Related Links
Converting To Non-RAID Disks
Viewing Available Reports
To view a report:
1. Expand the Storage tree object to display the controller objects.
2. Select a controller object.
3. Click Information/Configuration.
4. Select a report from the Select Report drop-down menu.
5. Click Execute.
Available Reports
• Viewing Patrol Read Report
• Viewing Check Consistency Report
• Viewing Slot Occupancy Report
• Viewing Physical Disk Firmware Version Report
Viewing Patrol Read Report
Does my controller support this feature? See Supported Features.
The patrol read report provides information on all the patrol reads performed on the controller in the
chronological order. It provides information such as last run time and result. If a patrol read fails, the
reason for the failure is displayed.
Related Links
Setting The Patrol Read Mode
To Locate View Patrol Read Report In Storage Management
1. In the Server Administrator window, under the system tree, click Storage.
2. Select View Patrol Read Report from the Select Report drop-down menu.
3. Click Execute.
Viewing Check Consistency Report
Does my controller support this feature? See Supported Features.
The check consistency report provides information on all the consistency checks performed on the
controller in a chronological order. It provides information such as last run time and result. If the
consistency check fails, it provides the reason for the failure.
Related Links
95
Page 96

Performing A Check Consistency
To Locate View Check Consistency Report In Storage Management
1. In the Server Administrator window, under the system tree, click Storage.
2. Select View Check Consistency Report from the Select Report drop-down menu.
3. Click Execute.
Viewing Slot Occupancy Report
Does my controller support this feature? See Supported Features.
The View Slot Occupancy Report allows you to view empty and occupied slot details of all enclosures
and back planes. It provides a diagram that represents the occupancy of physical drive slots. Move the
mouse over each slot to view details, such as physical disk ID, state, and size.
Viewing Physical Disk Firmware Version Report
Does my controller support this feature? See Supported Features
The Physical Disk Firmware Version Report compares the current firmware against a list of currently
available firmware and legacy driver models.
NOTE: To generate the HDD firmware version report, negotiable speed and the model number of
the drives are used as keys for indexing entries in the hddfwver.csv file. If the negotiable speed of
the drive is not available from the controller, then the model number of the drive is used as the key
for indexing entries in the hddfwver.csv file.
You can run the report on each controller basis or for the storage system.
For each controller report, click Storage → Controller → Information/Configuration → Available
Reports
For a storage system report, select Storage → Information/Configuration → Global Tasks → View
Physical Disk Firmware Version Report → Execute.
If you do not have the latest compare file (hddfwver.csv), contact your service provider to download the
latest compare file. Replace the existing hddfwver.csv file with the new file at the following location:
On systems running Windows:
C:\<Program Files (x86)>\Dell\SysMgt\sm
where C:\Program files may vary based on the system.
On systems running Linux:
/opt/dell/srvadmin/etc/srvadmin-storage/hddfwver.csv
On systems running ESXi:
/etc/cim/dell/srvadmin/srvadmin-storage/hddfwver.csv
If the existing firmware(s) for all physical disks is the latest, the following message is displayed:
There are no physical disks available that require firmware update.
Related Links
→ View Physical Disk Firmware Version Report → Execute.
Physical Disk Firmware Version Report Properties
Physical Disk Firmware Version Report Properties
The report displays information for the drives that require a firmware upgrade as listed in the table below:
96
Page 97

Table 21. Physical Disk Firmware Version Report Properties
Property Definition
Name Displays the nexus or location of each drive that has to be
updated. This nexus is represented as a two or three-digit
mapping of the drive location. Example:
Two-digit mapping: 0:1 = Controller 0: Slot 1 Three-digit
mapping: 1:0:4 = Controller 1: Connector 0: Slot 4
Model Number Displays the unique number associated with a specific OEM
vendor's drives and drive capacity.
Firmware Version Displays the current running version of the firmware on the
specific drive in the system.
Latest Available Firmware Version Displays the firmware version that is compared against the
firmware version in the comparison file.
Nautilus EFI Nautilus is the tool that is used for offline firmware updates.
Nautilus EFI is the version of the tool that works on 11th
generation of supported servers. This tool updates multiple
drive types with a single scan and updates procedure boot
and runs from a USB key. If the Nautilus EFI column has a
part number, then that drive is shipped on an 11th generation
server. When downloaded, this tool appears under the Drive
Firmware Downloads with a filename of the format
NautilusEFIAxx_ZPE.exe.
Nautilus DOS Nautilus is the tool that is used for offline firmware updates.
Nautilus DOS is the version of the tool that works on 9th —
11th generation of supported servers with SAS and SATA
drives. This tool updates multiple drive types with a single
scan and updates procedure boot and runs from a USB key,
preboot execution environment (PXE), or CD-ROM. If the
Nautilus DOS column has a part number, then that drive is
shipped on a 9th — 11th generation server. When
downloaded, this tool appears under the Drive Firmware
Downloads with a filename of the format
NautilusAxx_ZPE.exe.
DUP Reboot Required If this field is set to Yes, then the Update Package (DUP) field
is not blank. It indicates the availability of an online DUP. The
DUP allows to be sent to the firmware payload through an
online executable, but the firmware will not be committed to
the disk until the next system reboot. Hence, you can
perform one-to-many online deployments using
applications or scripts that can launch the online executable.
DUP It is a single executable that runs on a single family of drives.
Unlike Nautilus, to update different drives you have to use
different DUP packages. A single DUP package updates all
drives applicable to that DUP package in an execution. You
can run the DUP online without a reboot. It is recommended
97
Page 98

Property Definition
to stop or at least slow I/O operations during a DUP online
firmware upgrade.
Part Number In the event of a drive failure, you can run the View Physical
Disk Firmware Version Report to find out the part number of
the failed drive and to check if any of the drives require an
update.
98
Page 99

9
Support For PERC 9 Hardware Controllers
The Dell PowerEdge RAID Controller (PERC) family of enterprise-class controllers is designed for
enhanced performance, increased reliability and fault tolerance, and simplified management — providing
a powerful, easy-to-manage way to create a robust infrastructure and help maximize server uptime. The
introduction of the new PERC H730P Adapter, also bring about improvements in storage solutions.
The PERC H730P Adapter supports the following storage enhancements:
• Support For RAID Level 10 Virtual Disk On PERC 9 Hardware Controller
• Support For Advanced Format 4K Sector Hard-Disk Drives
• T10 Standard Protection Information (PI) - Data Integrity Field
Support For RAID Level 10 Virtual Disk Creation On PERC 9 Hardware Controller
RAID Level 10 is a solution for users who require high performance and redundancy with quickest
recovery during drive failure. Though a RAID Level 10 setup is more expensive to maintain, it has several
benefits as it combines the properties of RAID Level 1 and RAID Level 0.
RAID Level 10 virtual disk creations with PERC H730P Adapter supports Uneven Span feature. When you
create RAID Level 10 virtual disks with PERC H730P Adapter and if you have selected mismatched number
of physical disks, in this situation the PERC 9 firmware reevaluates and suggests the preferred span layout.
NOTE: A minimum of 4 physical disks and a maximum of 256 physical disks are allowed for a RAID
Level 10 virtual disk setup with PERC H730P Adapter.
You can create RAID Level 10 Virtual Disk on PERC H730P Adapter using the following Wizards :
• Express Wizard
• Advanced Wizard
NOTE:
The procedure for creating virtual disks on PERC 9 hardware controllers is the same as other
PERC hardware controllers.
Related Tasks
• Create Virtual Disk Express Wizard
• Create Virtual Disk Advanced Wizard
RAID Level 10 Virtual Disk Creation With Uneven Span
RAID Level 10 virtual disk creation with uneven span feature is available on Storage Management User
Interface (UI) and Command Line Interface (CLI). For information on Storage Management CLI, see Dell
OpenManage Server Administrator Command Line Interface Guide.
99
Page 100

• Based on the minimum (and even) number of physical disks selection the firmware on the PERC 9
hardware controller recommends the preferred span layout.
NOTE: RAID Level 10 virtual disk creation command from Storage Management CLI does not
support optional parameter [spanlength=<n>] on PERC 9 hardware controllers.
• The Advanced Wizard does not provide the option to select span length for RAID Level 10 virtual disk
creation on PERC 9 hardware controllers.
• The span layout for RAID Level 10 virtual disk created from the Express Wizard on PERC 9 hardware
controllers uses the span layout as recommended by the firmware of the PERC 9 hardware controller.
NOTE: Storage Management uses the PERC 9 hardware controller-firmware suggested span
layout for RAID Level 10 virtual disk creation.
• The PERC 9 hardware controller firmware suggested span layout is same for the same set of physical
disks.
• Intelligent Mirroring feature is supported on PERC 9 hardware controllers.
• When you create a virtual disk using the Advanced Wizard on PERC 9 hardware controllers the span
layout information under Selected Physical Disks will not be displayed.
• Sliced RAID Level 10 virtual disk creation on PERC 9 hardware controllers support uneven span.
• Grouping of selected physical disks for RAID Level 10 virtual disk through the Advanced Wizard is not
supported on PERC 9 hardware controllers.
• When you import a foreign configuration from hardware controllers prior to PERC 9 hardware
controllers to PERC 9 hardware controllers, the span layout for RAID Level 10 virtual disk remains the
same.
• When you import a foreign configuration for RAID Level 10 virtual disks from PERC 9 hardware
controllers to other PERC 9 hardware controllers the span layout does not change.
NOTE: Importing a foreign configuration (other than RAID Level 10 virtual disks) from PERC 9
hardware controllers to hardware controllers prior to PERC 9 is not supported.
Related Tasks
• Create Virtual Disk Express Wizard
• Create Virtual Disk Advanced Wizard
Support For Advanced Format 4K Sector Hard-Disk Drives
From the introduction of PERC 9 hardware controller support in Storage Management, users using legacy
512B sector hard-disk drives can now transition to Advanced Format 4K sector hard-disk drives. 4K sector
hard-disk drives utilize the storage-surface media more efficiently by combining data that would have
been stored in eight 512B sector hard-disk drives into one sector of 4096B (4KB). This data-combining
feature in 4K sector hard-disk drives results in improved data efficiency and error correction capabilities.
Storage Management supports virtual disk creation on 4K sector hard-disk drives connected to PERC 9
controllers.
NOTE: 4K sector hard-disk drives are not supported on controllers (including Software RAID
controllers) prior to PERC 9 hardware controllers. If the 4K sector hard-disk drive is connected to
hardware controller prior to PERC 9 hardware controller, the 4K sector hard-disk drive is displayed
as Unsupported.
100
 Loading...
Loading...