Page 1

Dell OpenManage™
Server Administrator
CIM Reference Guide
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Page 2

Notes and Notices
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your computer.
NOTICE: A NOTICE indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss of data and tells you how to avoid the problem.
COMMENT
____________________
Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
© 2003–2006 Dell Inc. All rights reserved.
Reproduction in any manner whatsoever without the written permission of Dell Inc. is strictly forbidden.
Trademarks used in this text: Dell, the DELL logo, and Dell OpenManage are trademarks of Dell Inc.; Microsoft is a registered trademark of
Microsoft Corporation; Intel, Pentium, Xeon, and Celeron are registered trademarks, and i960, MMX, Itanium, i386, and i486 are trademarks
of Intel Corporation.
Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this document to refer to either the entities claiming the marks and names or their products.
Dell Inc. disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names other than its own.
March 2006
Page 3

Contents
1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Server Administrator. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Documenting CIM Classes and Their Properties
Base Classes
Parent Classes
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Classes That Describe Relationships
Dell-defined Classes
Typographical Conventions
Common Properties of Classes
Other Documents You May Need
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2 CIM_PhysicalElement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
CIM_PhysicalElement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
CIM_PhysicalPackage
CIM_PhysicalFrame
CIM_Chassis
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
DELL_Chassis
CIM_PhysicalComponent
CIM_Chip
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
CIM_PhysicalMemory
CIM_PhysicalConnector
CIM_Slot
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
3 CIM_LogicalElement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
CIM_LogicalElement. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
CIM_System
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Contents 3
Page 4

CIM_ComputerSystem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
DELL_System
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_FRU
CIM_LogicalPort
CIM_LogicalPort
CIM_NetworkPort
DELL_NetworkPort
CIM_Sensor
CIM_DiscreteSensor
CIM_NumericSensor
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
CIM_TemperatureSensor
CIM_CurrentSensor
CIM_VoltageSensor
CIM_Tachometer
CIM_WatchDog
CIM_CoolingDevice
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
4 Contents
CIM_Fan
CIM_UserDevice
CIM_PointingDevice
CIM_Keyboard
CIM_PowerSupply
CIM_Controller
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
CIM_ParallelController
CIM_SerialController
CIM_PCIController
CIM_PCIDevice
CIM_PCIBridge
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Page 5

CIM_Processor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
CIM_StorageExtent
CIM_Memory
CIM_CacheMemory
CIM_SoftwareElement
CIM_BIOSElement
CIM_SoftwareFeature
DELL_SoftwareFeature
CIM_SystemResource
CIM_IRQ
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
CIM_MemoryMappedIO
CIM_DMA
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
CIM_RedundancyGroup
CIM_ExtraCapacityGroup
DELL_PSRedundancyGroup
DELL_FanRedundancyGroup
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
CIM_EnabledLogicalElement Group
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
CIM_ServiceAccessPoint
CIM_RemoteServiceAccessPoint
DELL_RemoteServiceAccessPort
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
4 Dell-defined Classes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
DELL_EsmLog. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
DELL_PostLog
DELL_CMApplication
DELL_CMDevice
DELL_CMDeviceApplication
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Contents 5
Page 6

DELL_CMInventory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
DELL_CMOS
DELL_CMProductInfo
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
5 CIM_Dependency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
DELL_FanSensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
CIM_PackageTempSensor
CIM_PackageVoltSensor
CIM_PackageCurrentSensor
CIM_PackageFanSensor
CIM_PackagePowerSupplySensor
DELL_PackagePSRedundancy
DELL_PSRedundancy
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Index
6 Contents
Page 7

Introduction
This reference guide documents the Dell OpenManage™ Server Administrator Common Information
Model (CIM) provider contained in the Management Object File (MOF) dccim32.mof.
CIM provides a conceptual model for describing manageable objects in a systems management
environment. CIM is a modeling tool rather than a programming language. CIM provides the
structure for organizing objects into a model of a managed environment. For modeling a managed
environment, CIM makes available a set of abstract and concrete classes of objects. These classes
model the basic characteristics of systems, networks, and applications, as well as groupings of
management-related data.
For more information about CIM, see the Distributed Management Task Force (DMTF) website at
www.dmtf.org and the Microsoft
Server Administrator
Server Administrator 1.0 or later provides a suite of systems management information for keeping
track of your networked systems. In addition to providing systems management agents that are
independent of the management console, Server Administrator supports these systems management
standards: CIM and Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
In addition to supporting systems management industry standards, Server Administrator provides
additional systems management information about the specific components of your Dell™ system.
Documenting CIM Classes and Their Properties
®
website at www.microsoft.com.
The Dell CIM provider extends support to Dell-specific software and hardware components. The
Dell MOF defines the classes for the Dell CIM provider. All of the supported classes and properties
in the MOF are documented in this guide.
The following subsections define some of the basic building blocks of CIM classes that are used in
describing the dccim32 provider name. These subsections also explain how the elements used in
describing these classes are organized. This section does not document the entire CIM schema, but
only those classes and properties supported by the dccim32 provider. The list of properties for each
supported class varies greatly.
Introduction 7
Page 8

Base Classes
The classes listed in the Server Administrator CIM provider class hierarchy do not have a parent property.
These base classes do not derive from another class. The base classes are:
• CIM_ManagedSystemElement
• CIM_Dependency
• DELL_Esm Log
• DELL_PostLog
• DELL_CMApplication
• DELL_CMDevice
• DELL_CMDeviceApplications
• DELL_CMInventory
• DELL_CMOS
• DELL_CMProductInfo
The CIM_ManagedSystemElement class is the base class for the system element hierarchy from which
all other CIM classes are derived. As a result, CIM_ManagedSystemElement has no parent. Examples of
managed system elements include software components such as files, devices such as hard drives and
controllers, and physical subcomponents of devices such as chip sets and cards. For the
CIM_ManagedSystemElement properties, see Caption, CreationClassName, Description, Name, and
Status in Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes."
The Dell-defined classes are not defined in the official schema by the DMTF, the industry group that
defines the standards for CIM, and hence do not have parent classes. CIM_Dependency does not have a
parent class because it is a relationship or association between two managed system elements.
Parent Classes
Most classes in the dccim32 provider document both a Class Name and a Parent Class property. The
parent class is the class from which any given class inherits its core properties. For example, the
CIM_Controller class has the CIM_LogicalDevice class as its parent, and has various types of controllers
(CIM_ParallelController, CIM_SerialController) as its children.
Classes That Describe Relationships
Classes that derive from CIM_Dependency have CIM_Dependency as their parent class, but they are
documented in terms of antecedent and dependent elements in a relationship rather than in terms of
common properties. Consider the following relationship between two CIM_ManagedSystemElements:
Antecedent CIM_PackageCurrentSensor
Dependent CIM_PhysicalPackage
8 Introduction
Page 9

The CIM_PackageCurrentSensor monitors an entire physical package, such as all the components
contained in a given system chassis. The CIM_PhysicalPackage is dependent on the
CIM_PackageCurrentSensor for this monitoring function.
Dell-defined Classes
Server Administrator has extended some CIM classes and has created new classes to assist in managing
systems and their components. In the diagrams that appear in the documentation for each class, those
classes created and populated by Dell are designated by the gold (lighter gray) triangle icon.
Typographical Conventions
The following example shows how most of the classes in the Dell CIM provider are documented.
Table 1-1 shows a partial class description for the DELL_DMA class. (For a full class description, see
Table 3-41, "CIM_DMA Properties.")
Class Name appears in
Parent Class appears in
class is derived.
Property denotes the name of the attribute that is being defined for this class.
Description includes text that defines the property.
Data Type stipulates the format that the values of this property must take. Common data types include
Boolean, string, and various types of integer. Boolean indicates that the property must be expressed as
one of two alternatives.
Table 1-1. CIM_DMA Properties
Courier typeface and provides the string that names the class in the MOF.
Courier typeface and provides the name of the class from which the present
Class Name: CIM_DMA
Parent Class: CIM_SystemResource
Property Description Data Type
DMAChannel A part of the object’s key value, the DMA channel number. uint32
Availability Availability of the DMA. Availability values are defined as follows:
1
Other
2
Unknown
3
Available
4
In Use/Not Available
5
In Use and Available/Shareable
uint16
Introduction 9
Page 10

Common Properties of Classes
Many classes have properties such as Caption, Description, and CreationClassName. Table 1-2 defines
properties that have the same meaning in every class that has this property and are defined more than
once in this guide.
Table 1-2. Common Properties of Classes
Property Description Data Type
Caption Describes the object using a short textual
description (one-line string).
CreationClassName Indicates the name of the class or the subclass
used in the creation of an instance. When used
with the other key properties of this class, this
property allows all instances of this class and its
subclasses to be uniquely identified.
CSCreationClassName Indicates the computer system’s creation class
name.
CSName Indicates the computer system’s name. string
CurrentReading Indicates the actual current value indicated by the
sensor in amperes.
Description Provides a textual description of the object. string
LowerThresholdNonCritical If current reading is between lower threshold
noncritical and upper threshold noncritical, the
current state is normal. See Figure 3-2.
LowerThresholdCritical If the current reading is between upper threshold
critical and upper threshold fatal, the current state
is critical. See Figure 3-2.
IsLinear Indicates that the sensor is linear over its
dynamic range.
Manufacturer Provides the name of the organization responsible
for producing the CIM_PhysicalElement or
CIM_SoftwareElement. This may be the entity
from whom the element is purchased, but not
necessarily. Purchase information is contained in
the Vendor property of CIM_Product.
Name Defines the label by which the object is known.
When subclassed, the Name property can be
overridden to be a Key property.
string
string
string
sint32
sint32
sint32
Boolean
string
string
10 Introduction
Page 11

Table 1-2. Common Properties of Classes (continued)
Property Description Data Type
Status Provides a string indicating how well the
component is functioning—comparable to
"health." Status values for operational and
nonoperational conditions include:
Operational Status Values:
OK indicates that the object is
functioning normally.
Degraded means that the item is functioning, but
not optimally.
Stressed indicates that the element is functioning,
but needs attention. Examples of Stressed states
are overloaded, overheated, and so on.
Nonoperational Status Values:
Non-recover means that a nonrecoverable error
has occurred.
Error means that an element has encountered an
operational condition that is severe as compared to
its normal mode of operation.
SystemCreationClassName Indicates the system’s creation class name. string
UnitModifier Provides the unit multiplier for the values returned
by this sensor. All the values returned by this
sensor are represented in units of 10 raised to the
power of the unit modifier. If the unit modifier is
–6, then the units of the values returned are
microvolts. The units apply to all numeric
properties of the sensor, unless explicitly
overridden by the units’ qualifier.
UpperThresholdCritical If the current reading is between upper threshold
critical and upper threshold fatal, the current
status is critical. See Figure 3-2.
UpperThresholdNonCritical If the current reading is between lower threshold
noncritical and lower threshold critical, the current
status is noncritical. See Figure 3-2.
Version Version should be in the form
<major>.<minor>.<revision> or
<major>.<minor><letter><revision>; for
example, 1.2.3 or 1.2a3.
string
sint32
sint32
sint32
string
Introduction 11
Page 12

Other Documents You May Need
Besides this Dell OpenManage Server Administrator CIM Reference Guide, you can find the following
guides either on the Dell Support website at support.dell.com or on the documentation CD:
•
Server Administrator Online Help
Administrator. Help screens provide step-by-step instructions on how to perform systems management
tasks using Server Administrator.
•
Dell OpenManage Server Administrator User’s Guide
uninstallation of Server Administrator.
•
Dell OpenManage Installation and Security User’s Guide
procedures and step-by-step instructions for installing, upgrading, and uninstalling Server
Administrator for each operating system.
•
Dell OpenManage Server Administrator Command Line Interface User’s Guide
tasks using the text-based command line interface.
•
Dell OpenManage Server Administrator Messages Reference Guide
receive on your systems management console or on your operating system’s event viewer. This guide
explains the text, severity, and cause of each message that the Server Administrator issues.
•
Dell OpenManage Server Administrator SNMP Reference Guide
information base (MIB). The SNMP MIB defines variables that cover the capabilities of Server
Administrator systems management agents.
is context-sensitive help that you can access while running Server
documents the features, installation, and
provides complete information on installation
explains how to perform
lists the messages that you can
documents the SNMP management
12 Introduction
Page 13
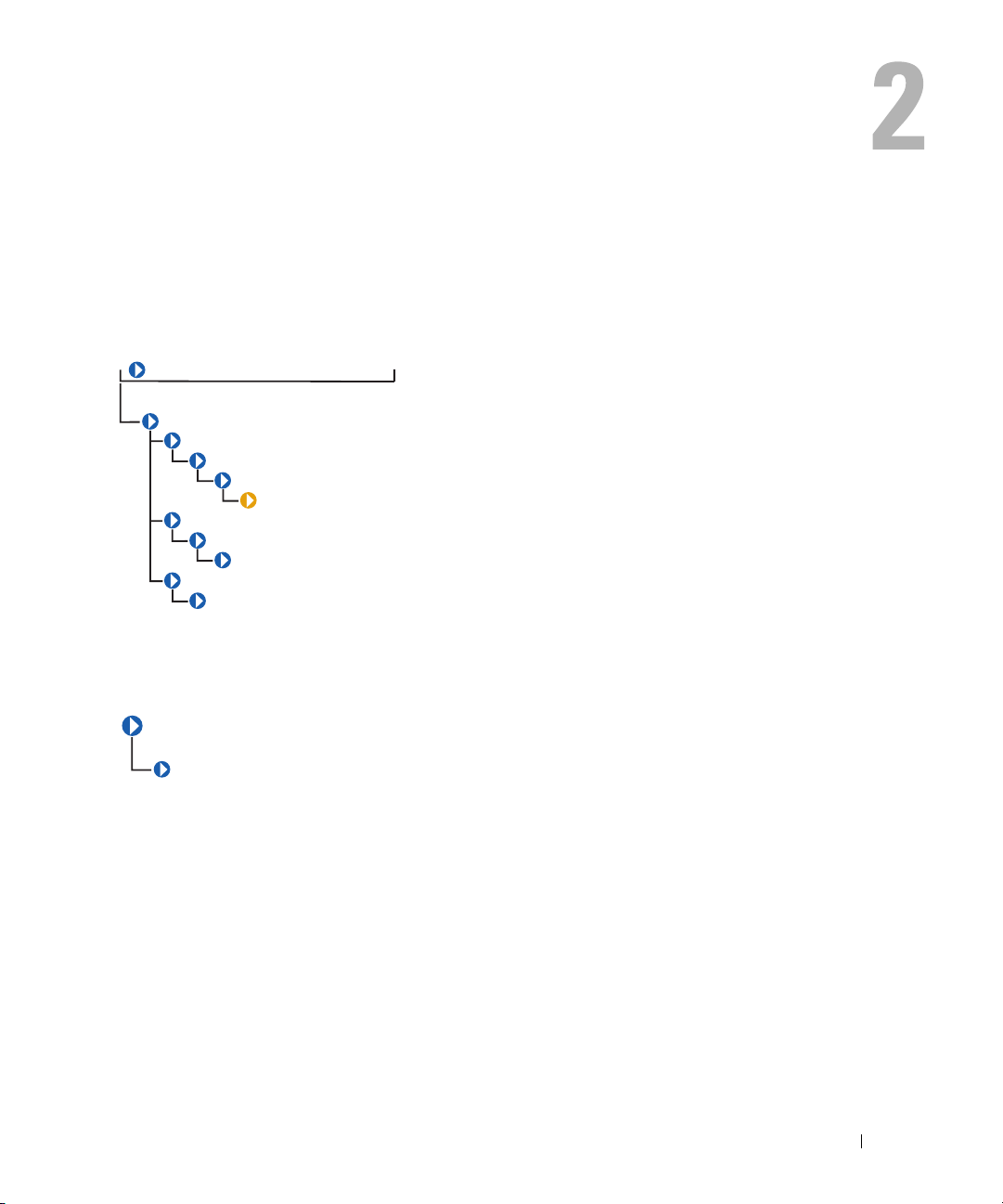
CIM_PhysicalElement
CIM_PhysicalElement is a CIM-defined class. The CIM_PhysicalElement class contains the
subclasses shown in Figure 2-1.
Figure 2-1. CIM_PhysicalElement Class Structure
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_PhysicalElement
CIM_PhysicalPackage
CIM_PhysicalFrame
CIM_Chassis
DELL_Chassis
CIM_PhysicalComponent
CIM_Chip
CIM_PhysicalMemory
CIM_PhysicalConnector
CIM_Slot
CIM_PhysicalElement
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_PhysicalElement
Subclasses of the CIM_PhysicalElement class listed in Table 2-1 define any component of a system
that has a distinct physical identity. Physical elements are tangible managed system elements
(usually actual hardware items) that have a physical manifestation of some sort. By contrast,
processes, files, and logical devices are not classified as physical elements. A managed system
element is not necessarily a discrete component. A single card (which is a type of physical element)
can host more than one logical device. One card, for example, could implement both a modem and a
local area network (LAN) adapter. In this case, the card would be represented by a single physical
element associated with multiple logical devices.
CIM_PhysicalElement 13
Page 14

Table 2-1. CIM_PhysicalElement Properties
Class Name: CIM_PhysicalElement
Parent Class: CIM_ManagedSystemElement
Property Description Data Type
CreationClassName See Table 1-2, “Common Properties of Classes.”
Manufacturer See Table 1-2, “Common Properties of Classes.”
Model The name by which the physical element is generally known. string
SerialNumber A manufacturer-allocated number used to identify the
physical element.
Tag Uniquely identifies the physical element and serves as the
element’s key. The Ta g property can contain information
such as asset tag or serial number data. The key for physical
element is placed very high in the object hierarchy in order
to identify the hardware/entity independently, regardless of
physical placement in or on cabinets, adapters, and so on.
For example, a hot-swappable or removable component can
be taken from its containing (scoping) package and
temporarily unused. The object still continues to exist and
may even be inserted into a different scoping container.
Therefore, the key for physical element is an arbitrary string
that is defined independently of any placement or
location-oriented hierarchy.
string
string
CIM_PhysicalPackage
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_PhysicalElement
CIM_PhysicalPackage
The CIM_PhysicalPackage class listed in Table 2-2 represents physical elements that contain or host
other components. Examples are a rack enclosure or an adapter card with multiple functions.
14 CIM_PhysicalElement
Page 15
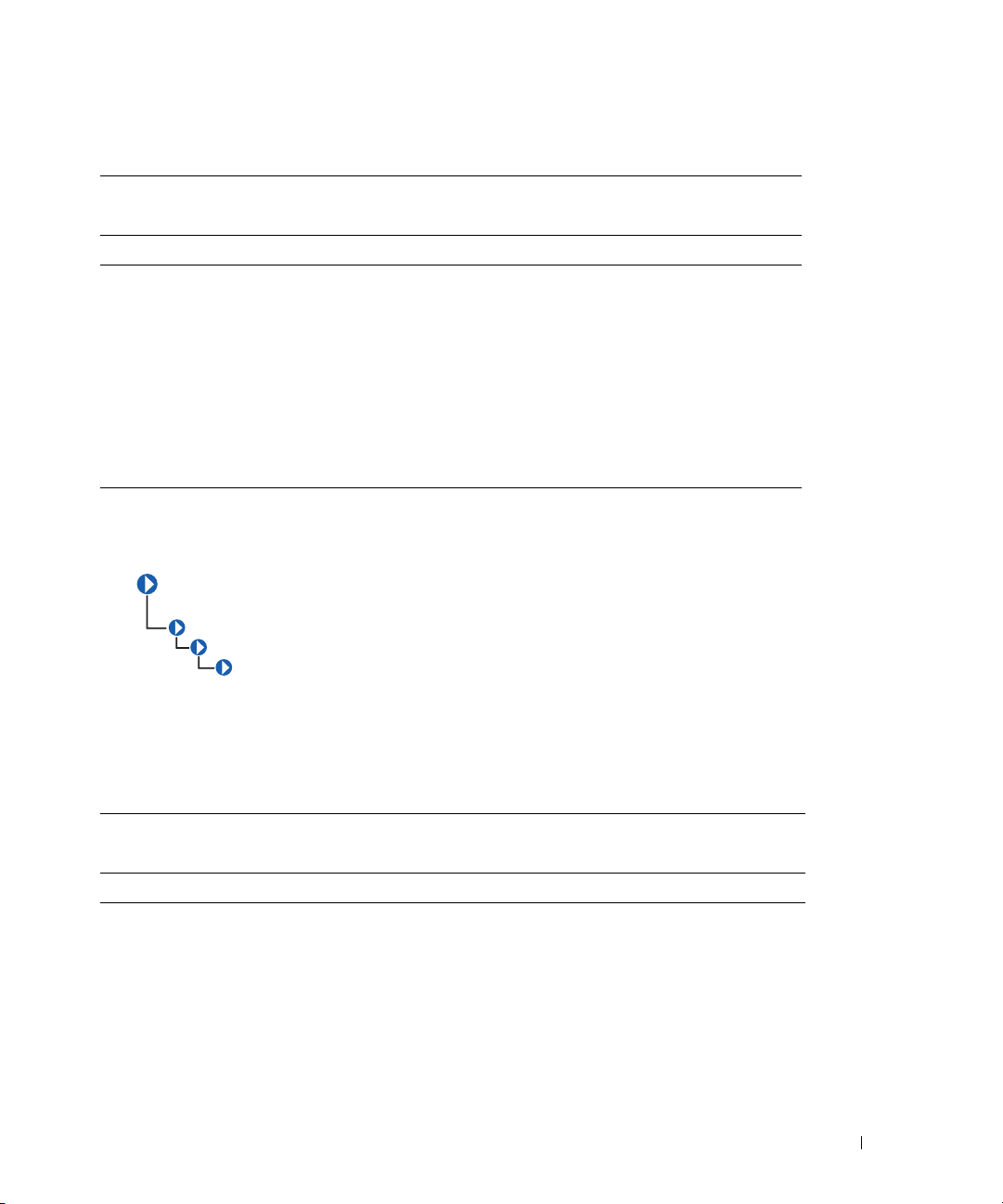
Table 2-2. CIM_PhysicalPackage Properties
Class Name: CIM_PhysicalPackage
Parent Class: CIM_PhysicalElement
Property Description Data Type
Removable A CIM_PhysicalPackage is removable if it is designed to be
taken in and out of the physical container in which it is
normally found without impairing the function of the
overall package.
Replaceable A CIM_PhysicalPackage is replaceable if it is possible to
substitute a physically different element for the original
element, as in a field replaceable unit (FRU). For example,
some computer systems allow the microprocessor to be
upgraded to one of a higher clock rating. In this case, the
microprocessor is said to be replaceable.
Boolean
Boolean
CIM_PhysicalFrame
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_PhysicalElement
CIM_PhysicalPackage
CIM_PhysicalFrame
The CIM_PhysicalFrame class described in Table 2-3 contains other frame enclosures such as racks and
chassis. Properties like VisibleAlarm or AudibleAlarm, and data related to security breaches are also
members of this class.
Table 2-3. CIM_Physical Frame Properties
Class Name: CIM_PhysicalFrame
Parent Class: CIM_PhysicalPackage
Property Description Data Type
LockPresent Indicates whether the frame is protected with a lock. Boolean
AudibleAlarm Indicates whether the frame is equipped with an
audible alarm.
VisibleAlarm Indicates that the equipment includes a
visible alarm.
Boolean
Boolean
CIM_PhysicalElement 15
Page 16

Table 2-3. CIM_Physical Frame Properties (continued)
Class Name: CIM_PhysicalFrame
Parent Class: CIM_PhysicalPackage
Property Description Data Type
SecurityBreach An enumerated, integer-valued property indicating
uint16
that a physical breach of the frame is in progress.
Values for the SecurityBreach property are as follows:
1
Other
2
Unknown
3
No breach
4
Breach attempted
5
Breach successful
IsLocked Indicates that the frame is currently locked. Boolean
CIM_Chassis
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_PhysicalElement
CIM_PhysicalPackage
CIM_PhysicalFrame
CIM_Chassis
The CIM_Chassis class described in Table 2-4 represents the physical elements that enclose physical
elements such as power supplies, fans, and processors.
16 CIM_PhysicalElement
Page 17

Table 2-4. CIM_Chassis Parent Properties
Class Name: CIM_Chassis
Parent Class: CIM_PhysicalFrame
Property Description Data Type
ChassisTypes Values for the ChassisTypes property are as follows:
1
Other
2
Unknown
3
Mini-tower
4
To we r
5
Space-saving
6
Main system chassis
7
Expansion chassis
8
Subchassis
9
Space-saving
10
Main system chassis
11
Expansion chassis
12
Subchassis
13
Bus expansion chassis
14
Peripheral chassis
15
Storage chassis
16
Rack-mount chassis
uint16
DELL_Chassis
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_PhysicalElement
CIM_PhysicalPackage
CIM_PhysicalFrame
CIM_Chassis
DELL_Chassis
The DELL_Chassis class explained in Table 2-5 defines the identifying and status properties of the
chassis. DELL_Chassis inherits from CIM-defined classes, but is populated by Dell™ properties.
CIM_PhysicalElement 17
Page 18

Table 2-5. DELL_Chassis Properties
Class Name: DELL_Chassis
Parent Class: CIM_Chassis
Property Description Data Type
AssetTag Indicates the container AssetTag string. This asset tag
string
string is writable by the system administrator.
SystemClass Refers to the system type that is installed and
uint16
running the instrumentation. Values for the
SystemClass property are as follows:
1
Other
2
Unknown
3
Workstation
4
Server
5
Desktop
6
Portable
7
Net PC
SystemID Indicates the system identifier code uint16
LogFormat Defines whether the event log data is unicode
uint16
formatted or binary (raw). Values for the event
LogFormat property are as follows:
1
Formatted (event log only)
2
Unformatted
3
Events_and_POST_Formatted (both the event log
and the power-on self-test (POST) log are unicode
formatted)
FanStatus Indicates the global status of fan sensors. string
TempStatus Indicates the global status of temperature sensors. string
VoltStatus Indicates the global status of voltage sensors. string
AmpStatus Indicates the global status of current sensors. string
PsStatus Indicates the global status of power supplies. string
MemStatus Indicates the global status of memory devices. string
ProcStatus Indicates the global status of processor devices. string
FanRedStatus Indicates the global status of the cooling unit. string
PsRedStatus Indicates the global status of the power unit. string
IsDefaultThrSupported Indicates whether resetting default thresholds
Boolean
are supported.
18 CIM_PhysicalElement
Page 19
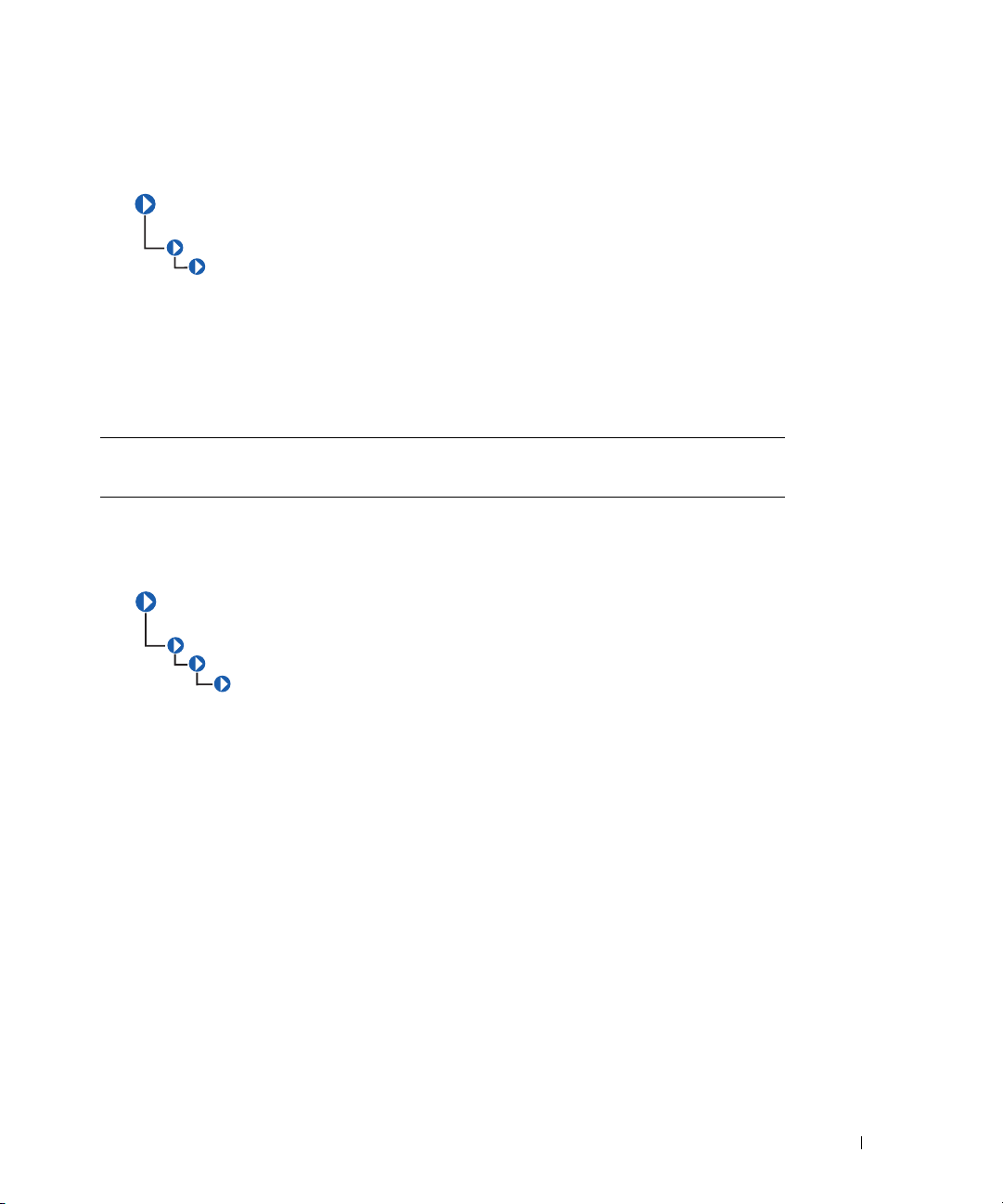
CIM_PhysicalComponent
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_PhysicalElement
CIM_PhysicalComponent
The CIM_PhysicalComponent class listed in Table 2-6 represents any low-level or basic component
within a package. A component object either cannot or does not need to be broken down into its
constituent parts. For example, an application specific integrated circuit (ASIC) cannot be broken down
into smaller discrete parts.
Table 2-6. CIM_PhysicalComponent Properties
Class Name: CIM_PhysicalComponent
Parent Class: CIM_PhysicalElement
CIM_Chip
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_PhysicalElement
CIM_PhysicalComponent
CIM_Chip
The CIM_Chip class listed in Table 2-7 represents any type of integrated circuit hardware, including
ASICs, processors, memory chips, and so on.
CIM_PhysicalElement 19
Page 20

Table 2-7. CIM_Chip Properties
Class Name: CIM_Chip
Parent Class: CIM_PhysicalComponent
Property Description Data Type
Form Fac to r
Form Fac to r
0 Unknown
1
Other
2
SIP
3
DIP
4
ZIP
5
SOJ
6
Proprietary
7
SIMM
8
DIMM
9
TSOP
10
PGA
11
RIMM
12
SODIMM
13
SRIMM
14
SMD
15
SSMP
16
QFP
17
TQFP
18
SOIC
19
LCC
20
PLCC
21
BGA
22
FPBGA
23
LGA
24
FB-DIMM
uint16
uint16
20 CIM_PhysicalElement
Page 21

CIM_PhysicalMemory
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_PhysicalElement
CIM_PhysicalComponent
CIM_Chip
CIM_PhysicalMemory
The CIM_PhysicalMemory class described in Table 2-8 is a subclass of CIM_Chip, representing low-level
memory devices, such as SIMMS, DIMMs, and so on.
Table 2-8. CIM_PhysicalMemory Properties
Class Name: CIM_PhysicalMemory
Parent Class: CIM_Chip
Property Description Data Type
FormFactor See Table 2-7, “CIM_Chip Properties." uint16
CIM_PhysicalElement 21
Page 22

Table 2-8. CIM_PhysicalMemory Properties (continued)
Class Name: CIM_PhysicalMemory
Parent Class: CIM_Chip
Property Description Data Type
MemoryType Indicates the type of physical memory. Values for the
uint16
MemoryType property are as follows:
0 Unknown
1
Other
2
DRAM
3
Synchronous DRAM
4
Cache DRAM
5
EDO
6
EDRAM
7
VRAM
8
SRAM
9
RAM
10
ROM
11
Flash
12
EEPROM
13
FEPROM
14
EPROM
15
CDRAM
16
3DRAM
17
SDRAM
18
SGRAM
19
RDRAM
20
DDR
21
DDR2
22
DDR2 FB-DIMM
TotalWidth Indicates the total width, in bits, of the physical memory,
uint16
including check or error correction bits. If there are no
error correction bits, the value in this property should
match that specified for the DataWidth property.
DataWidth Indicates the data width, in bits, of the physical memory.
uint16
A data width of 0 and a total width of 8 would indicate
that the memory is solely used to provide error
correction bits.
Speed Indicates the speed of the physical memory, in
uint32
nanoseconds.
22 CIM_PhysicalElement
Page 23

Table 2-8. CIM_PhysicalMemory Properties (continued)
Class Name: CIM_PhysicalMemory
Parent Class: CIM_Chip
Property Description Data Type
SpeedAsString Indicates the accurate speed of the physical memory, in
string format (with units).
Capacity Indicates the total capacity of this physical memory, in
bytes.
BankLabel A string identifying the physically labeled bank where the
memory is located, for example, "Bank 0" or "Bank A."
PositionInRow Specifies the position of the physical memory in a “row.”
For example, if it takes two 8-bit memory devices to form
a 16-bit row, then a value of 2 means that this memory is
the second device. 0 is an invalid value for this property.
InterleavePosition Indicates the position of this physical memory in an
interleave. 0 indicates noninterleaved. 1 indicates the
first position, 2 the second position and so on. For
example, in a 2:1 interleave, a value of 1 indicates that
the memory is in the “even” position.
string
uint64
string
uint32
uint32
CIM_PhysicalConnector
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_PhysicalElement
CIM_PhysicalConnector
The CIM_PhysicalConnector class explained in Table 2-9 includes physical elements such as plugs,
jacks, or buses that connect physical elements. Any object that can be used to connect and transmit
signals or power between two or more physical elements is a member of this class. For example, slots and
D-shell connectors are types of physical connectors. See Table 2-10 for a list of valid connector
type values.
CIM_PhysicalElement 23
Page 24

Table 2-9. CIM_PhysicalConnector Properties
Class Name: CIM_PhysicalConnector
Parent Class: CIM_PhysicalElement
Property Description Data Type
ConnectorPinout A free-form string describing the pin configuration
string
and signal usage of a physical connector.
ConnectorType An array of integers defining the type of physical
uint16
connector. An array is specified to allow the
description of “combinations” of connector
information. For example, one array entry could
specify RS-232, another DB-25, and a third entry
could define the connector as male. See Table 2-10 for
the values of the ConnectorType property.
Table 2-10. Connector Type Values
0 Unknown 30
1
Other
2
Male
3
Fema le
4
Shielded
5
Unshielded
6
SCSI (A)
High-Density
(50 pins)
7
SCSI (A)
Low-Density
(50 pins)
8
SCSI (P)
High-Density (68 pins)
9
SCSI SCA-I (80 pins)39RJ45
10
SCSI SCA-II
(80 pins)
11
Fibre Channel
(DB-9 Copper)
12
Fibre Channel
(Fiber Optical)
unused
31
unused
32
IEEE-48
33
AUI
34
UTP Category 3
35
UTP Category 4
36
UTP Category 5
37
BNC
38
RJ11
40
Fiber MIC
41
unused
42
unused
60
Micro-DIN
61
PS/2
62
Infrared
63
unused
64
Access. bus
65
unused
66
Centronics
67
Mini-Centronics
68
Mini-Centronics
Ty p e - 1 4
69
Mini-Centronics
Ty p e - 2 0
70
Mini-Centronics
Ty p e - 2 6
71
Bus Mouse
72
ADB
90
On Board IDE
Connector
91
On Board Floppy
Connector
92
9 Pin Dual Inline
93
25 Pin Dual Inline
94
50 Pin Dual Inline
95
68 Pin Dual Inline
96
On Board Sound
Connector
97
Mini-jack
98
PCI-X
99
Sbus IEEE 1396-1993
32-bit
100
Sbus IEEE 1396-1993
64-bit
101
unused
102
GIO
24 CIM_PhysicalElement
Page 25

Table 2-10. Connector Type Values (continued)
13
Fibre Channel SCA-II
43
PCI
(40 pins)
14
Fibre Channel SCA-II
44
ISA
(20 pins)
15
Fibre Channel BNC45unused
16
ATA 3-1/2 Inch
46
VESA
(40 pins)
17
ATA 2-1/2 Inch
47
unused
(44 pins)
18
ATA-2
19
ATA-3
20
ATA/66
21
DB-9
22
DB-15
23
DB-25
24
DB-36
25
RS-232C
26
RS-422
27
RS-423
28
RS-485
29
RS-449
48
unused
49
unused
50
unused
51
unused
52
unused
53
USB
54
IEEE 1394
55
HIPPI
56
HSSDC (6 pins)
57
GBIC
58
DIN
59
Mini-DIN
73
AGP
74
VME Bus
75
VME64
76
Proprietary
77
Proprietary Processor
Card Slot
78
Proprietary Memory
Card Slot
79
Proprietary I/O
Riser Slot
80
PCI-66 MHz
81
AGP2X
82
AGP4X
83
PC-98
84
PC-98-Hireso
85
PC-H98
86
PC-98Note
87
PC-98Full
88
SSA SCSI
89
Circular
103
XIO
104
HIO
105
NGIO
106
PMC
107
MTRJ
108
VF-45
109
Future I/O
110
SC
111
SG
112
Electrical
113
Optical
114
Ribbon
115
GLM
116
1x9
117
Mini SG
118
LC
119
HSSC
CIM_Slot
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_PhysicalElement
CIM_PhysicalConnector
CIM_Slot
The CIM_Slot class described in Table 2-11 represents connectors into which packages are inserted. For
example, a physical package that is a hard drive can be inserted into an small computer system interfacesingle connector attachment (SCSI-SCA) slot. As another example, a card can be inserted into a 16-, 32, or 64-bit expansion slot on a host board.
CIM_PhysicalElement 25
Page 26

Table 2-11. CIM_Slot Properties
Class Name: class CIM_Slot
Parent Class: CIM_PhysicalConnector
Property Description Data Type
ConnectorType See Table 2-10 uint16
SupportsHotPlug Indicates whether the slot supports hot-plug adapter cards. Boolean
MaxDataWidth Indicates the maximum bus width in bits of adapter cards
uint16
that can be inserted into this slot. Values for the
MaxDataWidth property are as follows:
0 Unknown
1
Other
8
Bits
16
Bits
32
Bits
64
Bits
128
Bits
26 CIM_PhysicalElement
Page 27
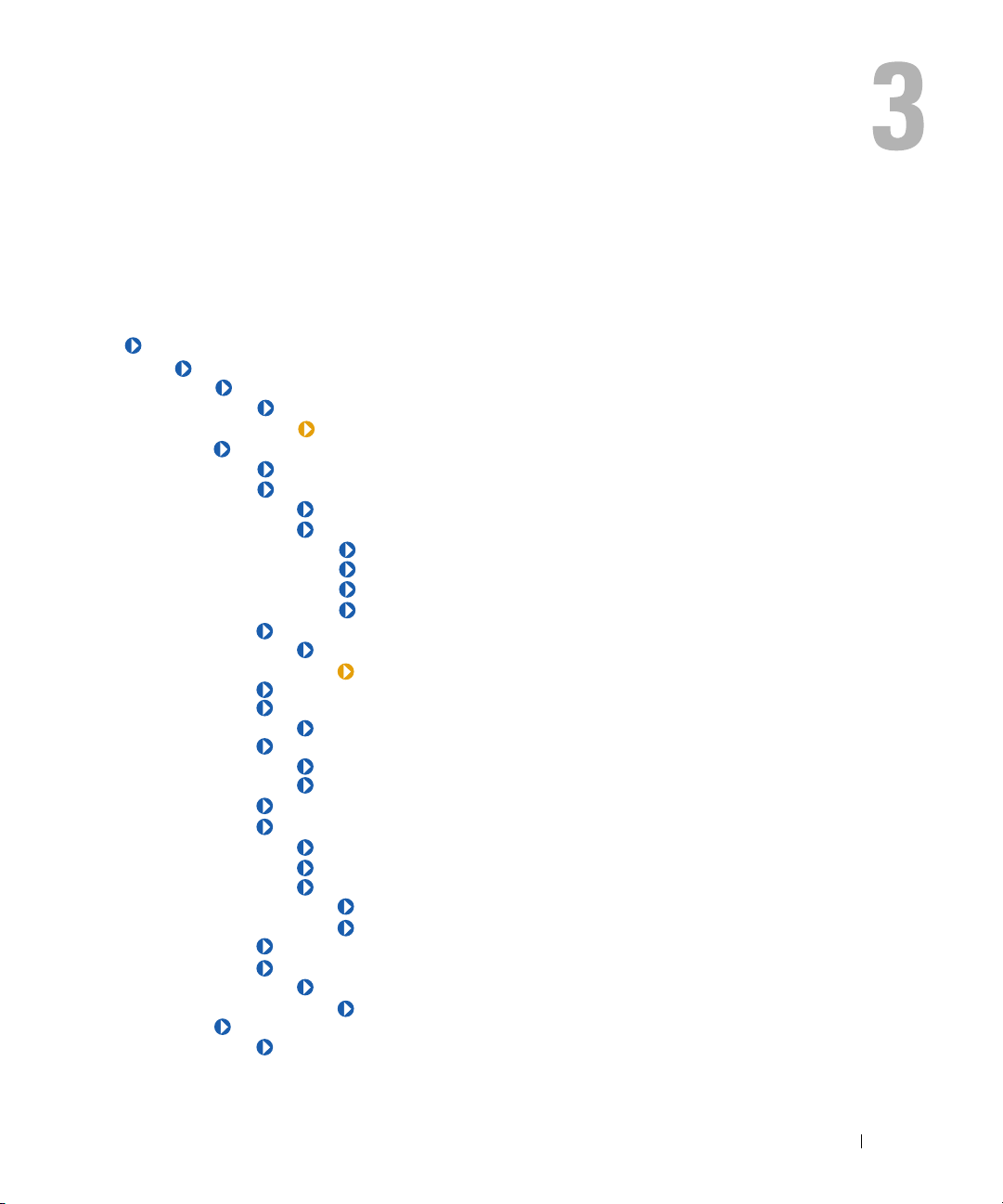
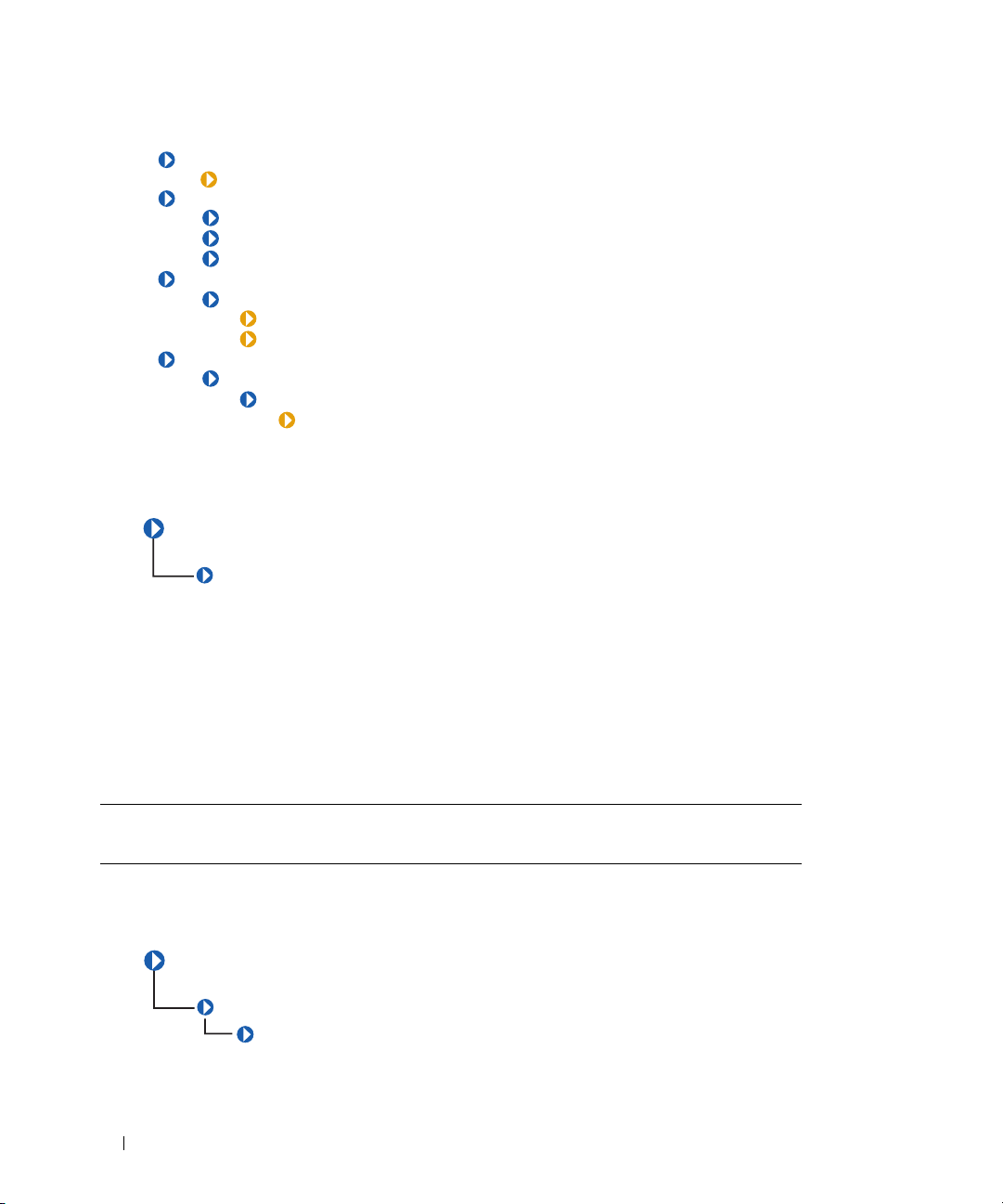
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalElement is a CIM-defined class containing the subclasses shown in Figure 3-1.
Figure 3-1. CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_System
CIM_ComputerSystem
DELL_Chassis
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_FRU
CIM_Sensor
CIM_DiscreteSensor
CIM_NumericSensor
CIM_TemperatureSensor
CIM_CurrentSensor
CIM_VoltageSensor
CIM_Tachometer
CIM_LogicalPort
CIM_NetworkPort
CIM_Watchdog
CIM_CoolingDevice
CIM_UserDevice
CIM_PowerSupply
CIM_Controller
CIM_Processor
CIM_StorageExtent
CIM_SoftwareElement
CIM_BIOSElement
DELL_NetworkPort
CIM_Fan
CIM_PointingDevice
CIM_Keyboard
CIM_ParallelController
CIM_SerialController
CIM_PCIController
CMI_PCIDevice
CMI_PCIBridge
CIM_Memory
CIM_CacheMemory
CIM_LogicalElement 27
Page 28
CIM_SoftwareFeature
DELL_SoftwareFeature
CIM_SystemResource
CIM_IRQ
CIM_MemoryMappedIO
CIM_DMA
CIM_RedundancyGroup
CIM_ExtraCapacityGroup
DELL_PSRedundancyGroup
DELL_FanRedundancyGroup
CIM_EnabledLogicalElement
CIM_ServiceAccessPoint
CIM_RemoteServiceAccessPoint
DELL_RemoteServiceAccessPort
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
The Distributed Management Task Force (DMTF) identified in Table 3-1 lists the following
characteristics for members of the CIM_LogicalElement class:
• Represent abstractions used to manage and coordinate aspects of a physical environment such as files,
processes, systems, system capabilities, and network components in the form of logical devices
• Represent devices, where devices are abstractions of hardware entities that may or may not be realized
in physical hardware
Table 3-1. CIM_LogicalElement Properties
Class Name: CIM_LogicalElement
Parent Class: CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_System
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_System
28 CIM_LogicalElement
Page 29

The CIM_System class shown in Table 3-2 defines a collection of managed system elements that
operates as a functional whole. An instance of the CIM_System class contains a well-defined list of
components that work together to perform a specific function.
Table 3-2. CIM_System Properties
Class Name: CIM_System
Parent Class: CIM_LogicalElement
Property Description Data Type
CreationClassName See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." string
Name Indicates the name of a specific system, such as a
particular storage system or server.
PrimaryOwnerContact Provides information on how the primary system
owner can be reached, for example, a phone number
or e-mail address.
PrimaryOwnerName Indicates the name of the primary system owner. string
Roles An array of strings that specifies the roles this
system plays in the IT environment. For example,
for an instance of a network system, the Roles
property might contain the string "storage system."
string
string
string
CIM_ComputerSystem
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_System
CIM_ComputerSystem
The CIM_ComputerSystem class listed in Table 3-3 contains some or all of the following
CIM_ManagedSystemElements: file system, operating system, processor and memory (volatile and/or
nonvolatile storage). For properties, see Table 3-2, "CIM_System Properties."
Table 3-3. CIM_ComputerSystem Properties
Class Name: CIM_ComputerSystem
Parent Class: CIM_System
CIM_LogicalElement 29
Page 30

DELL_System
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_System
CIM_ComputerSystem
DELL_System
The DELL_System class listed in Table 3-4 is the set of all Dell™ instrumented systems, including server
and storage systems. For properties, see Table 3-2, "CIM_System Properties."
Table 3-4. DELL_System Properties
Class Name: DELL_System
Parent Class: CIM_ComputerSystem
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
The CIM_LogicalDevice class described in Table 3-5 models a hardware entity that may be realized in
physical hardware. CIM_LogicalDevice includes any characteristics of a logical device that manages its
operation or configuration. An example of a logical device is a temperature sensor’s reading of actual
temperature.
Table 3-5. CIM_Logical Device Properties
Class Name: CIM_LogicalDevice
Parent Class: CIM_LogicalElement
Property Description Data Type
SystemCreationClassName See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." string
SystemName Indicates the scoping system’s name. string
CreationClassName See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." string
DeviceID Identifies an address or other identifying information
to uniquely name the logical device.
string
30 CIM_LogicalElement
Page 31

CIM_FRU
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_FRU
The CIM_FRU class described in Table 3-6 contains manufacturing information related to the Field
Replaceable Units (FRU) of a system such as system planar, I/O riser card.
Table 3-6. CIM_FRU Properties
Class Name: CIM_FRU
Parent Class: CIM_LogicalDevice
Property Description Data Type
FRUInformationState Indicates the state and availability of FRU
information.
FRUDeviceName Indicates the device name of the FRU String
FRUManufacturingDateName Indicates the manufacturing date of the FRU in
ticks.
FRUManufacturerName Indicates the name of the manufacturer. String
FRUPartNumberName Indicates the FRU part number. String
FRUSerialNumberName Indicates the FRU serial number. String
FRURevisionName Indicates the FRU Revision number. String
Uint 16
Integer
CIM_LogicalPort
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_LogicalPort
The CIM_LogicalPort class listed in Table 3-14 represents the abstraction of a port or connection point
of a device. For example, a USB port can be abstracted to represent a port. This feature is used when the
abstracted port has independent management characteristics from the device that includes it.
CIM_LogicalElement 31
Page 32

Table 3-7. CIM_LogicalPort Properties
Class Name: CIM_LogicalPort
Parent Class: CIM_LogicalDevice
Property Description Data Type
Speed Indicates the bandwidth of the port in bits per
second.
MaxSpeed Indicates the maximum bandwidth of the port in
bits per second.
RequestedSpeed Indicates the requested bandwidth of the port in
bits per second.
UsageRestriction Indicates usage parameters for the port. For
example, a storage array may have backend ports
to communicate with disk drives and front end
ports to communicate with hosts.
Uint64
Uint64
Unit64
Unit16
CIM_NetworkPort
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_LogicalPort
CIM_NetworkPort
The CIM_NetworkPort class listed in Table 3-8 describes the logical representation of a network.
Table 3-8. CIM_NetworkPort Properties
Class Name: CIM_NetworkPort
Parent Class: CIM_LogicalPort
Property Description Data Type
Speed Indicates the bandwidth of the port in bits per
second.
PortType Identifies port type and whether it is DMTF
reserved or vendor reserved. When this property is
set to 1 (Other), the OtherPropertyType property
contains a string description of the port type.
Uint64
Uint16
32 CIM_LogicalElement
Page 33

Table 3-8. CIM_NetworkPort Properties (continued)
Class Name: CIM_NetworkPort
Parent Class: CIM_LogicalPort
Property Description Data Type
OtherPortType When used in conjunction with PortType, this
String
property identifies port type.
LinkTechnology Enumerates the types of links to the device.
Uint16
When this property is set to 1, the
OtherLinktechnology property displays relevant
links to the device.
OtherLinkTechnology When used in conjunction with Link Technology,
String
this property displays relevant links to the device.
PermanentAddress Defines the network address hardcoded into a
String
port.
NetworkAddresses Indicates the network addresses for a port. String
FullDuplex Indicates whether the port is operating in a full
Boolean
duplex mode.
AutoSense Indicates whether the Network Port is capable of
Boolean
automatically determining the speed or other
characteristics of network attached media.
SupportedMaximumTransmission
Unit
ActiveMaximumTransmissionUnit Indicates the active or negotiated maximum
Indicates the maximum transmission unit
supported.
Uint64
Uint64
transmission unit supported.
DELL_NetworkPort
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_LogicalPort
CIM_NetworkPort
DELL_NetworkPort
The DELL_NetworkPort class listed in Table 3-9 represents the abstraction of a port or connection point
of a device. For example, a USB port can be abstracted to represent a port. This feature is used when the
abstracted port has independent management characteristics from the device that includes it.
CIM_LogicalElement 33
Page 34

Table 3-9. DELL_NetworkPort Properties
Class Name: Dell_NetworkPort
Parent Class: CIM_NetworkPort
Property Description Data Type
NicTOECapability Defines NIC TOE capability. The following
values, with explanations, are possible for this
property:
0 - NIC/driver does not support querying for
capability.
1 - NIC/driver supports querying for capability but
query returned an error.
2 - NIC/driver supports querying for capability and
query says it is capable.
4- NIC/driver supports querying for capability and
query says it is not capable.
8 - NIC/driver supports querying for capability but
error prevented querying NIC/driver.
16 - NIC/driver supports querying for capability
but NIC/driver did not respond to query.
NicRDMACapability Defines NIC RDMA capability. The following
values, with explanations, are possible for this
property:
0 - NIC/driver does not support querying for
capability.
1 - NIC/driver supports querying for capability but
query returned an error.
2 - NIC/driver supports querying for capability and
query says it is capable.
4- NIC/driver supports querying for capability and
query says it is not capable.
8 - NIC/driver supports querying for capability but
error prevented querying NIC/driver.
16 - NIC/driver supports querying for capability
but NIC/driver did not respond to query.
Uint32
Uint32
34 CIM_LogicalElement
Page 35

Table 3-9. DELL_NetworkPort Properties (continued)
Class Name: Dell_NetworkPort
Parent Class: CIM_NetworkPort
Property Description Data Type
NiciSCSICapability Defines NIC iSCSI Capability. The following
values, with explanations, are possible for this
property:
0 - NIC/driver does not support querying for
capability.
1 - NIC/driver supports querying for capability but
query returned an error.
2 - NIC/driver supports querying for capability and
query says it is capable.
4- NIC/driver supports querying for capability and
query says it is not capable.
8 - NIC/driver supports querying for capability but
error prevented querying NIC/driver.
16 - NIC/driver supports querying for capability
but NIC/driver did not respond to query.
IsTOEEnable Indicates whether TOE is enabled. Boolean
IsRDMAEnable Indicates whether RDMA is enabled. Boolean
IsiSCSIEnable Indicates whether SCSI is enabled. Boolean
NicStatus Indicates NIC /driver status. The following values
are possible:
0 - Unknown
1 - Connected
2 - Disconnected
3 - Driver Bad
4 - Driver Disabled
10 - Hardware initializing
11 - Hardware resetting
12 - Hardware closing
13 - Hardware not ready
BusNumber Indicates the PCI bus number. uint8
FunctionNumber Indicates the PCI Function number. uint8
Driver version Indicates the NIC driver version. string
Uint32
unit32
CIM_LogicalElement 35
Page 36

Table 3-9. DELL_NetworkPort Properties (continued)
Class Name: Dell_NetworkPort
Parent Class: CIM_NetworkPort
Property Description Data Type
IPAddress Indicates the NIC IP Address. String
SubnetMask Indicates the NIC subnet mask. String
DHCPServer Indicates the NIC DHCP Server. String
DefaultGateway Indicates the NIC default gateway. String
CurrentMACAddress Indicates the NIC current MAC address. String
OSAdapterDescription Describes the OS Adapter. String
OSAdapterVendor Provides OS Adapter vendor details. String
OSAdapterProductName Identifies the OS Adapter name. String
ServiceName Identifies the Service Name. String
CIM_Sensor
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_Sensor
CIM_NumericSensor
CIM_CurrentSensor
The CIM_Sensor class explained in Table 3-10 contains hardware devices capable of measuring the
characteristics of some physical property, for example, the temperature or voltage characteristics of a
computer system.
36 CIM_LogicalElement
Page 37

Table 3-10. CIM_Sensor Properties
Class Name: CIM_Sensor
Parent Class: CIM_LogicalDevice
Property Description Data Type
SensorType The type of the sensor, for example, voltage or
uint16
temperature sensor.
Values for the SensorType property are as follows:
0 Unknown
1
Other
2
Temperature sensors measure the environmental temperature.
3
Voltage sensors measure electrical voltage.
4
Current sensors measure current readings.
5
Tachometers measure speed/revolutions of a device. For example,
a fan device can have an associated tachometer that measures
its speed.
6
Batteries maintain the time and date and save the system’s BIOS
configuration when switched off.
OtherSensorType
The type of sensor when the SensorType property is set to Other. String
Description
PossibleStates Enumerates the string outputs of the sensor. For example, a
String
NumericSensor can report states based on threshold readings.
CurrentState Indicates the current state of the sensor. This value is always one
String
of the Possible States.
PollingInterval Indicates the polling interval, in nanoseconds, that the sensor
uint64
hardware or instrumentation uses to determine the current state
of the sensor.
CIM_LogicalElement 37
Page 38

CIM_DiscreteSensor
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_Sensor
CIM_DiscreteSensor
The CIM_DiscreteSensor class described in Table 3-11 has a set of legal string values that it can report.
The CIM_DiscreteSensor will always have a "current reading" that corresponds to one of the
enumerated values.
Table 3-11. CIM_DiscreteSensor Properties
Class Name: CIM_DiscreteSensor
Parent Class: CIM_Sensor
Property Description Data Type
CurrentReading See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
PossibleValues Enumerates the string outputs that can be reported by the sensor. sint32
CIM_NumericSensor
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_Sensor
CIM_NumericSensor
The CIM_NumericSensor class described in Table 3-12 returns numerical settings and may also support
threshold settings. Figure 3-2 shows the relationship among upper and lower critical and upper and lower
noncritical threshold values. The normal range falls between upper and lower noncritical thresholds.
38 CIM_LogicalElement
Page 39

Figure 3-2. Ranges for Threshold Values
FATAL
UPPER
CRITICAL
WARNIN G
UPPER
User Definable
NORMAL
LOWER
User Definable
WARNIN G
LOWER
CRITICAL
FATAL
Table 3-12 provides definitions for NumericSensor properties.
Table 3-12. CIM_NumericSensor Properties
NONCRITICAL
NONCRITICAL
Class Name: CIM_NumericSensor
Parent Class: CIM_Sensor
Property Description Data Type
UnitModifier See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
CurrentReading See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
IsLinear See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." Boolean
LowerThresholdNonCritical See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
UpperThresholdNonCritical See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
LowerThresholdCritical See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
CIM_LogicalElement 39
Page 40

Table 3-12. CIM_NumericSensor Properties (continued)
Class Name: CIM_NumericSensor
Parent Class: CIM_Sensor
Property Description Data Type
UpperThresholdCritical See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
SupportedThresholds An array representing the thresholds supported
uint16
by this sensor. The supported values are
as follows:
1
LowerThresholdNonCritical
2
UpperThresholdNonCritical
3
LowerThresholdCritical
4
UpperThresholdCritical
EnabledThresholds An array representing the thresholds that are
uint16
currently enabled for this sensor.
Enabled threshold values are as follows:
1
LowerThresholdNonCritical
2
UpperThresholdNonCritical
3
LowerThresholdCritical
4
UpperThresholdCritical
SettableThresholds An array representing the writable thresholds
uint16
supported by sensor.
Settable threshold values are as follows:
1
LowerThresholdNonCritical
2
UpperThresholdNonCritical
CIM_TemperatureSensor
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_Sensor
CIM_NumericSensor
CIM_TemperatureSensor
The CIM_TemperatureSensor class listed in Table 3-13 contains sensors that sample ambient
temperature and return a value in degrees Celsius.
40 CIM_LogicalElement
Page 41

Table 3-13. CIM_TemperatureSensor Properties
Class Name: CIM_TemperatureSensor
Parent Class: CIM_NumericSensor
Property Description Data Type
UnitModifier See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
CurrentReading See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
IsLinear See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." Boolean
LowerThresholdNonCritical See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
UpperThresholdNonCritical See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
LowerThresholdCritical See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
UpperThresholdCritical See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
CIM_CurrentSensor
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_Sensor
CIM_NumericSensor
CIM_CurrentSensor
The CIM_CurrentSensor class listed in Table 3-14 contains sensors that measure amperage and returns a
value in amperes.
Table 3-14. CIM_CurrentSensor Properties
Class Name: CIM_CurrentSensor
Parent Class: CIM_NumericSensor
Property Description Data Type
UnitModifier See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
CurrentReading See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
IsLinear See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." Boolean
LowerThresholdNonCritical See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
UpperThresholdNonCritical See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
LowerThresholdCritical See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
CIM_LogicalElement 41
Page 42

Table 3-14. CIM_CurrentSensor Properties (continued)
Class Name: CIM_CurrentSensor
Parent Class: CIM_NumericSensor
Property Description Data Type
UpperThresholdCritical See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
CIM_VoltageSensor
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_Sensor
CIM_NumericSensor
CIM_VoltageSensor
The CIM_VoltageSensor class shown in Table 3-15 contains sensors that measure voltage and return a
value in volts.
Table 3-15. CIM_VoltageSensor Properties
Class Name: CIM_VoltageSensor
Parent Class: CIM_NumericSensor
Property Description Data Type
UnitModifier See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
CurrentReading See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
IsLinear See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." Boolean
LowerThresholdNonCritical See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
UpperThresholdNonCritical See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
LowerThresholdCritical See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
UpperThresholdCritical See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
42 CIM_LogicalElement
Page 43

CIM_Tachometer
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_Sensor
CIM_NumericSensor
CIM_Tachometer
The CIM_Tachometer class listed in Table 3-16 contains devices that measure revolutions per minute
(RPM) of a fan and return the value in RPMs.
Table 3-16. CIM_Tachometer Properties
Class Name: CIM_Tachometer
Parent Class: CIM_NumericSensor
Property Description Data Type
SensorType See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." uint16
UnitModifier See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
CurrentReading See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
IsLinear See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." Boolean
LowerThresholdNonCritical See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
UpperThresholdNonCritical See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." sint32
CIM_WatchDog
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_Watchdog
The CIM_WatchDog class described in Table 3-17 represents a timer that is implemented in system
hardware. The watchdog feature allows the hardware to monitor the state of the operating system, BIOS,
or a software component installed on the system. If the monitored component fails to rearm the timer
before its expiration, the hardware assumes that the system is in a critical state and could reset the
system. This feature can also be used as an application watchdog timer for a mission-critical application.
In this case, the application would assume responsibility for rearming the timer before expiration.
CIM_LogicalElement 43
Page 44

Table 3-17. CIM_WatchDog Properties
Class Name: CIM_WatchDog
Parent Class: CIM_LogicalDevice
Property Description Data Type
MonitoredEntity Indicates the entity that is currently being
uint16
monitored by the watchdog feature. This
property is used to identify the module that is
responsible for rearming the watchdog at
periodic intervals. Values for the
MonitoredEntity property are as follows:
1
Unknown
2
Other
3
Operating System
MonitoredEntity Description A string describing additional textual
string
information about the monitored entity.
TimeoutInterval Indicates the time-out interval used by the
uint32
watchdog, in microseconds.
TimerResolution Indicates the resolution of the watchdog timer.
uint32
For example, if this value is 100, then the timer
can expire anytime between –100 microseconds
and +100 microseconds.
CIM_CoolingDevice
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_CoolingDevice
The CIM_CoolingDevice class described in Table 3-18 contains a set of devices that work to keep the
ambient internal temperature of the system at a safe value.
44 CIM_LogicalElement
Page 45

Table 3-18. CIM_CoolingDevice Properties
Class Name: CIM_CoolingDevice
Parent Class: CIM_LogicalDevice
Property Description Data Type
ActiveCooling Specifies whether the device provides active (as opposed to
Boolean
passive) cooling.
CIM_Fan
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_CoolingDevice
CIM_Fan
The CIM_Fan class explained in Table 3-19 contains a set of devices that work to keep the ambient
internal temperature of the system at a safe value by circulating air.
Table 3-19. CIM_Fan Properties
Class Name: CIM_Fan
Parent Class: CIM_CoolingDevice
Property Description Data Type
VariableSpeed Specifies whether the fan supports variable speeds. Boolean
DesiredSpeed Indicates the currently requested fan speed, defined in RPM.
When the value = TRUE, the fan supports variable speeds.
When a variable speed fan is supported (VariableSpeed
Boolean = TRUE), the actual speed is determined using a
sensor (CIM_Tachometer) that is associated with the fan.
uint64
CIM_UserDevice
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_UserDevice
CIM_LogicalElement 45
Page 46

The CIM_UserDevice class shown in Table 3-20 contains logical devices that allow a computer system’s
users to input, view, or hear data. Classes derived from CIM_UserDevice include CIM_Keyboard and
CIM_PointingDevice.
Table 3-20. CIM_UserDevice Properties
Class Name: CIM_UserDevice
Parent Class: CIM_LogicalDevice
Property Description Data Type
IsLocked Indicates whether the device is locked, preventing user input
Boolean
or output.
CIM_PointingDevice
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_UserDevice
CIM_PointingDevice
The CIM_PointingDevice class described in Table 3-21 includes those devices used to point to regions of
a display. Examples are a mouse or a trackball.
Table 3-21. CIM_PointingDevice Properties
Class Name: CIM_PointingDevice
Parent Class: CIM_UserDevice
Property Description Data Type
PointingType Indicates the type of pointing device. Values for the
Boolean
PointingType property are as follows:
1
Other
2
Unknown
3
Mouse
4
Trackball
5
Trackpoint
6
Glidepoint
7
Touch pad
8
Touch screen
9
Mouse—optical sensor
46 CIM_LogicalElement
Page 47

Table 3-21. CIM_PointingDevice Properties (continued)
Class Name: CIM_PointingDevice
Parent Class: CIM_UserDevice
Property Description Data Type
NumberOfButtons Indicates the number of buttons. If the CIM_PointingDevice
uint8
has no buttons, a value of 0 is returned.
Handedness Integer indicating whether the CIM_PointingDevice is
uint16
configured for right- or left-handed operation. Values for
the Handedness property are as follows:
0 Unknown
1
Not applicable
2
Right-handed operation
3
Left-handed operation
CIM_Keyboard
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_UserDevice
CIM_Keyboard
The CIM_Keyboard class explained in Table 3-22 includes devices that allow users to enter data.
Table 3-22. CIM_Keyboard Properties
Class Name: CIM_Keyboard
Parent Class: CIM_UserDevice
Property Description Data Type
NumberOfFunctionKeys Indicates the number of function keys on the
keyboard.
Layout A free-form string indicating the format and layout
of the keyboard.
uint16
string
CIM_LogicalElement 47
Page 48

Table 3-22. CIM_Keyboard Properties (continued)
Class Name: CIM_Keyboard
Parent Class: CIM_UserDevice
Property Description Data Type
Password An integer indicating whether a hardware-level
uint16
password is enabled at the keyboard, preventing local
input. Values for the Password property are as follows:
1
Other
2
Unknown
3
Disabled
4
Enabled
5
Not implemented
CIM_PowerSupply
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_PowerSupply
The CIM_PowerSupply class described in Table 3-23 contains devices that provide current and voltage
for the operation of the system and its components.
Table 3-23. CIM_PowerSupply Properties
Class Name: CIM_PowerSupply
Parent Class: CIM_LogicalDevice
Property Description Data Type
IsSwitchingSupply Indicates that the power supply is a switching power
Boolean
supply and not a linear power supply.
Range1InputVoltageLow Indicates the low voltage in millivolts of input
uint32
voltage range 1 for this power supply. A value of 0
denotes unknown.
Range1InputVoltageHigh Indicates the high voltage in millivolts of input
uint32
voltage range 1 for this power supply. A value of 0
denotes unknown.
48 CIM_LogicalElement
Page 49

Table 3-23. CIM_PowerSupply Properties (continued)
Class Name: CIM_PowerSupply
Parent Class: CIM_LogicalDevice
Property Description Data Type
ActiveInputVoltage Indicates which input voltage range is currently in
uint16
use. Range 1, 2, or both can be specified using the
values 3, 4, or 5, respectively. If the supply is not
drawing power, a value of 6 (neither) can be
specified. This information is necessary in the case
of an uninterruptible power supply (UPS), a subclass
of power supply. Values for the ActiveInputVoltage
property are as follows:
1
Other
2
Unknown
3
Range 1
4
Range 2
5
Both range 1 and range 2
6
Neither range 1 nor range 2
TotalOutputPower Represents the total output power of the power
uint32
supply in milliwatts. A value of 0 denotes that the
power output is unknown.
CIM_Controller
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_Controller
The CIM_Controller class shown in Table 3-24 groups miscellaneous control-related devices. Examples
of controllers are small computer system interface (SCSI) controllers, Universal Serial Bus (USB)
controllers, and serial controllers.
CIM_LogicalElement 49
Page 50
Table 3-24. CIM_Controller Properties
Class Name: CIM_Controller
Parent Class: CIM_LogicalDevice
Property Description Data Type
ProtocolSupported The protocol used by the controller to access controlled
uint16
devices. Values for the ProtocolSupported property are
as follows:
1
Other
2
Unknown
3
PCI
4
Parallel protocol
CIM_ParallelController
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_Controller
CIM_ParallelController
The CIM_ParallelController class identified in Table 3-25 contains a set of objects that control parallel
devices. Parallel controllers transfer 8 or 16 bits of data at a time to the devices they control, for example,
a parallel port controlling a printer.
Table 3-25. CIM_ParallelController Properties
Class Name: CIM_ParallelController
Parent Class: CIM_Controller
Property Description Data Type
DMASupport Set to TRUE if the parallel controller supports DMA. Boolean
Security An enumeration indicating the operational security for the
uint16
controller. Values for the Security property are as follows:
1
Other
2
Unknown
3
None
4
External interface locked out
5
External interface enabled
6
Boot bypass
50 CIM_LogicalElement
Page 51

CIM_SerialController
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_Controller
CIM_SerialController
The CIM_SerialController class explained in Table 3-26 contains controllers that transfer data one bit at
a time to the devices they control, for example, a serial port controlling a modem.
Table 3-26. CIM_SerialController Properties
Class Name: CIM_SerialController
Parent Class: CIM_Controller
Property Description Data Type
MaxBaudRate Indicates the maximum baud rate in bits per second
supported by the serial controller.
Security An enumeration indicating the operational security for the
controller. Values for the Security property are as follows:
1
Other
2
Unknown
3
None
4
External interface locked out
5
External interface enabled
6
Boot bypass
uint32
uint16
CIM_PCIController
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_Controller
CIM_PCIController
The CIM_PCIController class listed in Table 3-27 contains a set of devices that follow the Peripheral
Component Interconnect (PCI) protocol defined by the Personal Computer Memory Card International
Association (PCMCIA). The PCI protocol defines how data is transferred between devices. The
CIM_PCIController class contains PCI adapters and bridges.
CIM_LogicalElement 51
Page 52

Table 3-27. CIM_PCIController Properties
Class Name: CIM_PCIController
Parent Class: CIM_Controller
Property Description Data Type
CommandRegister The current contents of the register that provides basic
uint16
control over the device’s ability to respond to, and/or
perform PCI accesses. The data in the capabilities array is
gathered from the PCI status register and the PCI
capabilities list as defined in the PCI specification.
Values for the CommandRegister property are as follows:
0 Unknown
1
Other
2
Supports 66 MHz
3
Supports user-definable features
4
Supports fast back-to-back transactions
5
PCI-X capable
6
PCI power management supported
7
Message signaled interrupts supported
8
Parity error recovery capable
9
AGP supported
10
Vital product data supported
11
Provides slot identification
12
Hot swap supported
CIM_PCIDevice
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_Controller
CIM_PCIController
CIM_PCIDevice
The CIM_PCIDevice class shown in Table 3-28 describes the capabilities and management of a PCI
device controller on an adapter card.
52 CIM_LogicalElement
Page 53

Table 3-28. CIM_PCIDevice Properties
Class Name: CIM_PCIDevice
Parent Class: CIM_PCIController
Property Description Data Type
BaseAddress Identifies an array of up to six double-word base
uint32
memory addresses.
SubsystemID Identifies a subsystem identifier code. uint16
SubsystemVendorID Identifies a subsystem vendor ID. ID information
uint16
is reported from a PCI device via protocol-specific
requests. This information is also present in the
CIM_PhysicalElement class (the manufacturer
property) for hardware, and the CIM_Product
class (the vendor property) for information related
to product acquisition.
ExpansionROMBaseAddress Identifies a double-word expansion ROM base
uint32
memory address.
CIM_PCIBridge
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_Controller
CIM_PCIController
CIM_PCIBridge
The CIM_PCIBridge class shown in Table 3-29 describes the capabilities and management of a PCI
controller providing bridge-to-bridge capability. An example is a PCI to Industry-Standard Architecture
(ISA) bus bridge.
CIM_LogicalElement 53
Page 54

Table 3-29. CIM_PCIBridge Properties
Class Name: CIM_PCIBridge
Parent Class: CIM_PCIController
Property Description Data Type
BaseAddress Identifies an array of double-word base memory addresses. uint32
BridgeType Indicates the type of bridge. A bridge is PCI to <value>,
uint16
except for the Host, which is a host-to-PCI bridge. Values for
the BridgeType property are as follows:
0 Host
1
ISA
128
Other
BaseAddress Identifies an array of double-word base memory addresses. uint32
CIM_Processor
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_Processor
The CIM_Processor class described in Table 3-30 contains devices that interpret and execute demands,
for example, the Intel
®
Xeon® microprocessor.
54 CIM_LogicalElement
Page 55

Table 3-30. CIM_Processor Properties
Class Name: CIM_Processor
Parent Class: CIM_LogicalDevice
Property Description Data Type
Role A string describing the role of the microprocessor, for example,
string
central microprocessor or math processor.
UpgradeMethod Provides microprocessor socket information including data on
uint16
how this microprocessor can be upgraded (if upgrades are
supported). This property is an integer enumeration. Values for
the UpgradeMethod property are as follows:
1
Other
2
Unknown
3
Daughter board
4
ZIF socket
5
Replacement/piggy back
6
None
7
LIF socket
8
Slot 1
9
Slot 2
10
370-pin socket
19
Socket mPGA604
20
Socket LGA771
21
Socket LGA775
MaxClockSpeed Indicates the maximum speed (in MHz) of this microprocessor. uint32
Core count Indicates the number of processors core detected. uint16
CoreEnabledCount Indicates the number of processors core enabled. uint16
CurrentClockSpeed Indicates the current speed (in MHz) of this microprocessor. uint32
DataWidth Indicates the processor data width in bits. uint16
AddressWidth Indicates the processor address width in bits. uint16
Stepping Indicates the revision level of the processor within the
string
microprocessor family.
UniqueID Identifies a globally unique identifier for the microprocessor. This
string
identifier may only be unique within a microprocessor family.
Brand Indicates the brand name of the processor. string
Model Indicates the model name of the processor. string
CIM_LogicalElement 55
Page 56

Table 3-30. CIM_Processor Properties (continued)
Class Name: CIM_Processor
Parent Class: CIM_LogicalDevice
Property Description Data Type
ExtendedCharacteristics Indicates the extended capabilities of the processor. This attribute
unit16
is a bit field. The following are the definitions of a bit when set
to one:
Bit 0 — Virtualization Technology (VT) supported
Bit 1 — Demand-Based Switching (DBS) supported
Bit 2 — eXecute Disable (XD) supported
Bit 3 — Hyper Threading (HT) supported
ExtendedStates Indicates the setting of the extended capabilities of the processor.
unit16
This attribute is a bit field. The following are the definitions of a
bit when set to one:
Bit 0 — Virtualization Technology (VT) enabled
Bit 1 — Demand-Based Switching (DBS) enabled
Bit 2 — eXecute Disable (XD) enabled
Bit 3 — Hyper Threading (HT) enabled
CPUStatus Indicates the current status of the microprocessor. For example, it
uint16
may be disabled by the user via the BIOS or disabled due to a
POST error. Values for the CPUStatus property are as follows:
0 Unknown
1
Microprocessor enabled
2
Microprocessor disabled by user via BIOS setup
3
Microprocessor disabled by BIOS (POST error)
4
Microprocessor is idle
5
Other
56 CIM_LogicalElement
Page 57

Table 3-30. CIM_Processor Properties (continued)
Class Name: CIM_Processor
Parent Class: CIM_LogicalDevice
Property Description Data Type
Family Refers to the processor family type. Values for the Family property
uint16
are as follows:
1
Other
2
Unknown
3
8086
4
80286
5
80386
6
80486
7
8087
8
80287
9
80387
10
80487
11
Pentium® family
12
Pentium PRO
13
Pentium II
14
Pentium MMX™
15
16
17
18
19
24
25
26
27
®
Celeron
Xeon (Pentium II)
Pentium III
M1 family
M2 family
5 family
K6 family
K6-2
K6-3
CIM_LogicalElement 57
Page 58

Table 3-30. CIM_Processor Properties (continued)
Class Name: CIM_Processor
Parent Class: CIM_LogicalDevice
Property Description Data Type
28
AMD Athlon family
29
AMD Duron
30
AMD29000 family
31
K6-2+
32
Power PC family
33
Power PC 601
34
Power PC 603
35
Power PC 603+
36
Power PC 604
37
Power PC 620
38
Power PC X704
39
Power PC 750
48
Alpha family
49
Alpha 21064
50
Alpha 21066
51
Alpha 21164
52
Alpha 21164PC
53
Alpha 21164a
54
Alpha 21264
55
Alpha 21364
64
MIPS family
65
MIPS R4000
66
MIPS R4200
67
MIPS R4400
68
MIPS R4600
69
MIPS R10000
80
SPARC family
81
SuperSPARC
82
MicroSPARC II
83
MicroSPARC IIep
84
UltraSPARC
85
UltraSPARC II
86
UltraSPARC Iii
87
UltraSPARC III
58 CIM_LogicalElement
Page 59

Table 3-30. CIM_Processor Properties (continued)
Class Name: CIM_Processor
Parent Class: CIM_LogicalDevice
Property Description Data Type
88
UltraSPARC IIIi
96
68040
97
68xx family
98
68000
99
68010
100
68020
101
68030
112
Hobbit family
120
Crusoe TM5000 family
121
Crusoe TM3000 family
122
Efficeon TM8000 family
128
We it ek
130
Itanium™
131
AMD Athlon 64-bit family
132
AMD Opteron family
133
AMD Sempron family
134
AMD Turion 64 Mobile Technology
135
Dual Core AMD Opteron family
136
AMD Athlon 64 X2 Dual Core family
144
PA-RISC family
145
PA-RISC 8500
146
PA-RISC 8000
147
PA-RISC 7300LC
148
PA-RISC 7200
149
PA-RISC 7100LC
150
PA-RISC 7100
160
V30 family
176
Xeon (Pentium II)
177
960™
178
Pentium 4
179
Intel Xeon
180
AS400 family
181
Intel Xeon processor MP
182
AMD Athlon XP family
183
AMD Athlon MP family
CIM_LogicalElement 59
Page 60

Table 3-30. CIM_Processor Properties (continued)
Class Name: CIM_Processor
Parent Class: CIM_LogicalDevice
Property Description Data Type
184
Intel Itanium 2
185
Pentium M
186
Celeron Dual Core
187
Pentium Dual Core
188
Pentium Extreme edition
190
K7
200
S/390 and zSeries family
201
ESA/390 G4, ESA/390 G5
202
ESA/390 G6
203
z/Architecture base
250
i860
251
i960
260
SH-3
261
SH-4
280
ARM
281
StrongARM
300
6x86
301
MediaGX
302
MII
320
WinChip
350
DSP
500
Video processor
60 CIM_LogicalElement
Page 61

CIM_StorageExtent
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_StorageExtent
CIM_StorageExtent identified in Table 3-31 contains devices that manage data storage, for example,
hard drives or microprocessor memory.
Table 3-31. CIM_StorageExtent Properties
Class Name: CIM_StorageExtent
Parent Class: CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_Memory
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_StorageExtent
CIM_Memory
The CIM_Memory class identified in Table 3-32 describes the capabilities and management of storage
extent devices, for example, cache memory or system memory.
Table 3-32. CIM_Memory Properties
Class Name: CIM_Memory
Parent Class: CIM_StorageExtent
CIM_LogicalElement 61
Page 62

CIM_CacheMemory
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalDevice
CIM_StorageExtent
CIM_Memory
CIM_CacheMemory
The CIM_CacheMemory class explained in Table 3-33 describes the capabilities and management of
cache memory. Cache memory allows a microprocessor to access data and instructions faster than normal
system memory.
Table 3-33. CIM_CacheMemory Properties
Class Name: CIM_CacheMemory
Parent Class: CIM_Memory
Property Description Data Type
Level Defines whether this is the primary, secondary, or tertiary cache.
Values for the Level property are as follows:
1
Other
2
Unknown
3
Primary
4
Secondary
5
Tertiary
6
Not applicable
WritePolicy Either defines whether this cache is a write-back or write-
through cache or whether this information varies with address or
is defined individually for each input/output (I/O). Values for the
WritePolicy property are as follows:
1
Other
2
Unknown
3
Write-back
4
Write-through
5
Varies with address
6
Determination per I/O
uint16
uint16
62 CIM_LogicalElement
Page 63

Table 3-33. CIM_CacheMemory Properties (continued)
Class Name: CIM_CacheMemory
Parent Class: CIM_Memory
Property Description Data Type
CacheType Defines whether this cache is for instruction caching, data
uint16
caching, or both (unified). Values for the CacheType property
are as follows:
1
Other
2
Unknown
3
Instruction
4
Data
5
Unified
LineSize Indicates the size, in bytes, of a single cache bucket or line. uint32
ReadPolicy Defines the policy used by the cache for handling read requests.
uint16
Values for the ReadPolicy property are as follows:
1
Other
2
Unknown
3
Read
4
Read-ahead
5
Read and read-ahead
6
Determination per I/O
CIM_SoftwareElement
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_SoftwareElement
The CIM_SoftwareElement class described in Table 3-34 is used to define a CIM_SoftwareFeature. The
CIM_SoftwareElement class consists of individually manageable or deployable parts for a particular
platform. A software element’s platform is uniquely identified by its underlying hardware architecture
and operating system (for example, a system running Microsoft
microprocessor). A software element’s implementation on a particular platform depends on the
platform’s operating system.
®
Windows NT® on an Intel
CIM_LogicalElement 63
Page 64

Table 3-34. CIM_SoftwareElement Properties
Class Name: CIM_SoftwareElement
Parent Class: CIM_LogicalElement
Property Description Data Type
Name Indicates the name that identifies this software element. string
Version Provides the version in the form
<major>.<minor>.<revision> or
<major>.<minor><letter><revision>; for example, 1.2.3 or
1.2a3.
Manufacturer See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." string
BuildNumber Indicates the internal identifier for this build of the software
element.
IdentificationCode Provides the manufacturer’s identifier for this software element.
Often this will be a stock keeping unit (SKU) or a part number.
string
string
string
CIM_BIOSElement
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_SoftwareElement
CIM_BIOSElement
The CIM_BIOSElement class listed in Table 3-35 describes the BIOS for the system. The BIOS controls
the following:
• Communications between the microprocessor and peripheral devices, such as the keyboard and the
video adapter
• Miscellaneous functions, such as system messages
Table 3-35. CIM_BIOSElement Properties
Class Name: CIM_BIOSElement
Parent Class: CIM_SoftwareElement
Property Description Data Type
Version Provides the product version information. string
Manufacturer See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." string
PrimaryBIOS Specifies whether a given BIOS is the primary BIOS for the system.
When the value = TRUE, the BIOS is the primary BIOS.
Boolean
64 CIM_LogicalElement
Page 65

CIM_SoftwareFeature
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_SoftwareFeature
The CIM_SoftwareFeature class shown in Table 3-36 defines a particular function or capability of a
product or application system. This class is intended to be meaningful to a consumer, or user of a
product, rather than to explain how the product is built or packaged. When a software feature can exist
on multiple platforms or operating systems (for example, a client component of a three-tiered
client/server application might run on Windows NT), a software feature is a collection of all the software
elements for these different platforms. The users of the model must be aware of this situation because
typically they will be interested in a subcollection of the software elements required for a
particular platform.
Table 3-36. CIM_SoftwareFeature Properties
Class Name: CIM_SoftwareFeature
Parent Class: CIM_LogicalElement
Property Description Data Type
IdentifyingNumber Provides product identification such as a serial number
on software.
ProductName Identifies the commonly used product name. string
Vendor Identifies the name of the product’s supplier.
Corresponds to the vendor property in the product object
in the DMTF solution exchange standard.
Version Identifies the product version information. Corresponds
to the version property in the product object in the
DMTF solution exchange standard.
Name Defines the label by which the object is known to the
users. This label is a user-defined name that uniquely
identifies the element.
string
string
string
string
CIM_LogicalElement 65
Page 66

DELL_SoftwareFeature
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_SoftwareFeature
DELL_SoftwareFeature
DELL_SoftwareFeature described in Table 3-37 defines the universal resource locator (URL) of the
systems management software and the language in which systems management information displays.
Defining these properties enables users to manage a system using an Internet browser. You can access
Server Administrator using the secure hypertext transfer protocol (https) and a preassigned port number
of 1311, or you can specify a port number of your own choosing.
Table 3-37. DELL_SoftwareFeature Properties
Class Name: DELL_SoftwareFeature
Parent Class: CIM_SoftwareFeature
Property Description Data Type
OmsaURL Defines the URL for Server Administrator. string
Language Sets the language for systems management information. string
CIM_SystemResource
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_SystemResource
The CIM_SystemResource class listed in Table 3-38 provides access to system resources from an
operating system. SystemResources consist of interrupt requests (IRQs) and direct memory access
(DMA) capabilities.
Table 3-38. CIM_SystemResource Properties
Class Name: CIM_SystemResource
Parent Class: CIM_LogicalElement
66 CIM_LogicalElement
Page 67

CIM_IRQ
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_SystemResource
CIM_IRQ
The CIM_IRQ class described in Table 3-39 contains IRQ information. An IRQ is a signal that data is
about to be sent to or received by a peripheral device. The signal travels by an IRQ line to the
microprocessor. Each peripheral connection must be assigned an IRQ number. For example, the first
serial port in your computer (COM1) is assigned to IRQ4 by default.
Table 3-39. CIM_IRQ Properties
Class Name: CIM_IRQ
Parent Class: CIM_SystemResource
Property Description Data Type
CSCreationClassName See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." string
CSName See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." string
CreationClassName See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." string
IRQNumber Identifies the interrupt request number. uint32
Availability Indicates the availability of the IRQ. Values for the
Availability property are as follows:
1
Other
2
Unknown
3
Available
4
In use/not available
5
In use and available
TriggerLevel Indicates whether the interrupt is triggered by the
hardware signal going high or low. Values for the
TriggerLevel property are as follows:
1
Other
2
Unknown
3
Active low
4
Active high
uint16
uint16
CIM_LogicalElement 67
Page 68

Table 3-39. CIM_IRQ Properties (continued)
Class Name: CIM_IRQ
Parent Class: CIM_SystemResource
Property Description Data Type
TriggerType Indicates whether edge (value=4) or level triggered
uint16
(value=3) interrupts occur.
1
Other
2
Unknown
3
Level
4
Edge
Shareable Indicates whether the IRQ can be shared. A value of
Boolean
TRUE indicates that the IRQ can be shared.
Hardware Indicates whether the interrupt is hardware- or
Boolean
software-based. (A value of TRUE indicates that the
interrupt is hardware based.) On a personal computer,
a hardware IRQ is a physical wire to a programmable
interrupt controller (PIC) chip set through which the
microprocessor can be notified of time critical events.
Some IRQ lines are reserved for standard devices such
as the keyboard, diskette drive, and the system clock.
A software interrupt is a programmatic mechanism to
allow an application to get the attention of
the processor.
CIM_MemoryMappedIO
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_SystemResource
CIM_MemoryMappedIO
The CIM_MemoryMappedIO class explained in Table 3-40 addresses both memory and port I/O
resources for personal computer architecture memory mapped I/O.
68 CIM_LogicalElement
Page 69

Table 3-40. CIM_MemoryMappedIO Properties
Class Name: CIM_MemoryMappedIO
Parent Class: CIM_SystemResource
Property Description Data Type
CSCreationClassName See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." string
CSName See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." string
CreationClassName See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." string
StartingAddress Identifies the starting address of memory mapped I/O. uint64
EndingAddress Identifies the ending address of memory mapped I/O. uint64
MappedResource
Indicates the type of memory mapped I/O.
uint16
MappedResource defines whether memory or I/O
is mapped, and for I/O, whether the mapping is to a
memory or a port space. Memory mapped
I/O values are as follows:
1
Other
2
Mapped memory
3
I/O mapped to memory space
4
I/O mapped to port space
CIM_DMA
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_SystemResource
CIM_DMA
The CIM_DMA class explained in Table 3-41 contains DMA information. A DMA channel allows
certain types of data transfer between RAM and a device to bypass the microprocessor.
CIM_LogicalElement 69
Page 70

Table 3-41. CIM_DMA Properties
Class Name: CIM_DMA
Parent Class: CIM_SystemResource
Property Description Data Type
CSCreationClassName See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." string
CSName See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." string
CreationClassName See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." string
DMAChannel Identifies a part of the object’s key value, the DMA
channel number.
Availability Indicates the availability of the DMA. Values for the
Availability property are as follows:
1
Other
2
Unknown
3
Available
4
In use/not available
5
In use and available/shareable
uint32
uint16
CIM_RedundancyGroup
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_RedundancyGroup
The CIM_RedundancyGroup class explained in Table 3-42 is a set of components that provide more
instances of a critical component than are required for the system’s operation. The extra components are
used in case of critical component failure. For example, multiple power supplies allow a working power
supply to take over when another power supply has failed.
Table 3-42. CIM_RedundancyGroup Properties
Class Name: CIM_RedundancyGroup
Parent Class: CIM_LogicalElement
Property Description Data Type
CreationClassName See Table 1-2, "Common Properties of Classes." string
Name Serves as the key for the redundancy group’s instance in an
enterprise environment.
string
70 CIM_LogicalElement
Page 71

Table 3-42. CIM_RedundancyGroup Properties (continued)
Class Name: CIM_RedundancyGroup
Parent Class: CIM_LogicalElement
Property Description Data Type
RedundancyStatus Provides information on the state of the redundancy group.
uint16
Values for the RedundancyStatus property are as follows:
0 Unknown
1
Other
2
Fully redundant. Fully redundant means that all of the
configured redundancy is still available.
3
Degraded redundancy. Degraded redundancy means that
some failures have been experienced but some reduced
amount of redundancy is still available.
4
Redundancy lost. Redundancy lost means that a sufficient
number of failures have occurred so that no redundancy is
available and the next failure experienced will cause
overall failure.
CIM_ExtraCapacityGroup
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_RedundancyGroup
CIM_ExtraCapacityGroup
The CIM_ExtraCapacityGroup class explained in Table 3-43 applies to systems that have more
capability and components than are required for normal operation, for example, systems that have extra
fans or power supplies.
Table 3-43. CIM_ExtraCapacityGroup Properties
Class Name: CIM_ExtraCapacityGroup
Parent Class: CIM_RedundancyGroup
Property Description Data Type
MinNumberNeeded Specifies the smallest number of elements that must be
operational in order to have redundancy. For example, in an
N+1 redundancy relationship, the MinNumberNeeded
property should be set to N.
uint32
CIM_LogicalElement 71
Page 72

DELL_PSRedundancyGroup
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_RedundancyGroup
CIM_ExtraCapacityGroup
DELL_PSRedundancyGroup
The DELL_PSRedundancyGroup described in Table 3-44 is a Dell-specific extension of the
CIM_PowerSupply class. The DELL_PSRedundancyGroup class defines what constitutes power supply
redundancy in a system.
Table 3-44. DELL_PSRedundancyGroup Properties
Class Name: DELL_PSRedundancyGroup
Parent Class: CIM_ExtraCapacityGroup
DELL_FanRedundancyGroup
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_RedundancyGroup
CIM_ExtraCapacityGroup
DELL_FanRedundancyGroup
The DELL_FanRedundancyGroup described in Table 3-45 defines what constitutes fan redundancy in a
system.
Table 3-45. DELL_FanRedundancyGroup Properties
Class Name: DELL_FanRedundancyGroup
Parent Class: CIM_ExtraCapacityGroup
72 CIM_LogicalElement
Page 73

CIM_EnabledLogicalElement Group
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_EnabledLogicalElement
The CIM_EnabledLogicalElementGroup class described in Table 3-46 extends the
CIM_LogicalElementGroup class to abstract the concept of an element that is enabled or disabled, such
as a LogicalDevice or ServiceAccessPoint.
Table 3-46. CIM_EnabledLogicalElementGroup Properties
Class Name: CIM_EnabledLogicalElementGroup
Parent Class: CIM_LogicalElementGroup
CIM_ServiceAccessPoint
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_EnabledLogicalElement
CIM_ServiceAccessPoint
The CIM_ServiceAccessPointGroup class described in Table 3-47 represents the ability to utilize or
invoke a service. Access points indicate that a service is available to other entities for use.
Table 3-47. CIM_ServiceAccessPointGroup Properties
Class Name: CIM_ServiceAccessPointGroup
Parent Class: CIM_EnabledLogicalElement
CIM_RemoteServiceAccessPoint
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_EnabledLogicalElement
CIM_ServiceAccessPoint
CIM_RemoteServiceAccessPoint
CIM_LogicalElement 73
Page 74

The CIM_RemoteServiceAccessPointGroup class identified in Table 3-48 describes the accessing and
addressing of information for a remote connection that is known to a "local" network element. This
information is contained in the "local" network element since this is the context in which it is "remote".
The relevance of the remote service access point and information on its use are described by subclassing
or associating to the CIM_RemoteServiceAccessPointGroup class.
Table 3-48. CIM_RemoteServiceAccessPointGroup Properties
Class Name: CIM_RemoteServiceAccessPointGroup
Parent Class: CIM_ServiceAccessPointGroup
Property Description Data Type
AccessInfo Describes accessing or addressing of information for a
remote connection. This can be a host name, network
address, and other similar information.
InfoFormat Indicates an enumerated integer describing the format and
interpretation of the AccessInfo property. This property can
have the following values:
•"Other"
•"Host Name"
• "Ipv4 Address"
• "Ipv6 Address"
• "IPX Address"
• "DECnet Address"
• "SNA Address"
• "Autonomous System Number"
• "MPLS Label"
• "DMTF Reserved"
• "Dial String"
• "Ethernet Address"
• "Token Ring Address"
• "ATM Address"
• "Frame Relay Address"
• "DMTF Reserved"
•"URL"
• "Vendor Specific"
string
uint16
74 CIM_LogicalElement
Page 75

DELL_RemoteServiceAccessPort
CIM_
ManagedSystemElement
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_EnabledLogicalElement
CIM_ServiceAccessPoint
CIM_RemoteServiceAccessPoint
DELL_RemoteServiceAccessPort
The DELL_RemoteServiceAccessPortGroup class described in Table 3-49 is an extended class of the
CIM_RemoteServiceAccessPointGroup class. The DELL_RemoteServiceAccessPortGroup class provides
information about Dell implementation-specific attributes.
Table 3-49. DELL_RemoteServiceAccessPortGroup Properties
Class Name: DELL_RemoteServiceAccessPortGroup
Parent Class: CIM_RemoteServiceAccessPointGroup
Property Description Data Type
PortName Displays the name of the service access port. string
VersionString Indicates the version of the access point service. string
CIM_LogicalElement 75
Page 76

76 CIM_LogicalElement
Page 77

Dell-defined Classes
The Dell-defined classes are defined and populated by Dell rather than by CIM. None of these
classes have a parent class and are on the same level as CIM_ManagedSystemElement. For
information on how the logs are formatted, see Table 2-5, “DELL_Chassis Properties.”
DELL_EsmLog
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
DELL_EsmLog
The DELL_EsmLog class described in Table 4-1 records failure threshold violations collected by
Server Administrator’s embedded server management (ESM) capabilities.
Table 4-1. DELL_EsmLog Properties
Class Name: DELL_EsmLog
Parent Class: None
Property Description Data Type
RecordNumber Provides an index to the ESM table. uint32
LogRecord Provides the ESM message content. string
EventTime Indicates the time that the message is generated. datetime
Status Indicates the severity of the event that caused the log to
be generated.
string
Dell-defined Classes 77
Page 78

DELL_PostLog
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
DELL_PostLog
The DELL_PostLog identified in Table 4-2 is a record of the system’s power-on self-test (POST). When
you turn on a system, the POST tests various system components, such as random-access memory
(RAM), the hard drives, and the keyboard.
Table 4-2. DELL_PostLog Properties
Class Name: DELL_PostLog
Parent Class: None
DELL_CMApplication
NOTE: Dell-updateable components, such as BIOS and FW, are considered applications.
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
DELL_CMApplication
The DELL_CMApplication class identified in Table 4-3 contains information related to the Dell Change
Management applications.
Table 4-3. DELL_CMApplication Properties
Class Name: DELL_CMApplications
Parent Class: None
Property Description Data Type
Product ID Indicates the product ID number string
Name Indicates the name of the product string
Description Provides a short description of the product string
Vendor Indicates the name of the product
manufacturer
Version Indicates the current version of the product string
string
78 Dell-defined Classes
Page 79

DELL_CMDevice
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
DELL_CMDevice
The DELL_CMDevice identified in Table 4-4 contains information related to the Dell Change
Management device.
Table 4-4. DELL_CMDevice Properties
Class Name: DELL_CMDevice
Parent Class: None
Property Description Data Type
Component ID Defines a component string string
Name Indicates the name of the device string
VendorID Defines an ID for vendor supplying the
device
DeviceID Indicates the ID of the device string
SubDevice ID Indicates the ID for additional device string
Bus Indicates the PCI bus number string
Device Indicates the PCI device number string
Function Indicates the PCI Function number string
string
Dell-defined Classes 79
Page 80

DELL_CMDeviceApplication
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
DELL_CMDeviceApplications
The DELL_CMDeviceApplication class identified in Table 4-5 contains information related to the Dell
Change Management association between the device and application.
Table 4-5. DELL_CMDeviceApplication Properties
Class Name: DELL_CMDeviceApplication
Parent Class: None
Property Description Data Type
Antecedent Refers to the device string
Dependent Refers to the application string
DELL_CMInventory
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
DELL_CMInventory
The DELL_CMInventory identified in Table 4-6 contains information related to the Dell Change
Management inventory.
..
Table 4-6. DELL _CMInventory Properties
Class Name: DELL_CMInventory
Parent Class: None
Property Description Data Type
Local Indicates the locale of the system string
SchemaVersion Indicates the Inventory schema
implemented by the system
SystemID Defines the System ID string
string
80 Dell-defined Classes
Page 81

DELL_CMOS
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
DELL_CMOS
The DELL_CMOS class identified in Table 4-7 contains information related to the Dell Change
Management operating system.
Table 4-7. DELL_CMOS Properties
Class Name: DELL_CMOS
Parent Class: None
Property Description Data Type
Vendor Indicates the vendor of the operating system string
MajorVersion Indicates the major version of the operating system string
MinorVersion Indicates the minor version of the operating system string
spMajorVersion Indicates the current service pack number for the
operating system’s major version
spMinorVersion Indicates the current service pack number for the
operating system’s minor version
string
string
Dell-defined Classes 81
Page 82

DELL_CMProductInfo
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
DELL_CMProductInfo
The DELL_CMProductInfo identified in Table 4-8 contains information related to the Dell Change
Management product.
Table 4-8. DELL_CMProductInfo Properties
Class Name: DELL_CMProductInfo
Parent Class: None
Property Description Data Type
ProductID Indicates the product ID number string
Name Indicates the name of the product string
Description Provides a short description of the product string
Vendor Indicates the name of the product manufacturer string
Version Indicates the current version number of the product string
82 Dell-defined Classes
Page 83

CIM_Dependency
The CIM_Dependency class is an association used to establish dependency relationships between
two managed system elements. CIM_Dependency shown in Figure 5-1 does not have a parent class
because it is a relationship or association between two elements.
Figure 5-1. CIM_Dependency Class Structure
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_Dependency
DELL_FanSensor
CIM_PackageTempSensor
CIM_PackageVoltSensor
CIM_PackageCurrentSensor
CIM_PackageFanSensor
CIM_PackagePowerSupplySensor
DELL_PackagePSRedundancy
DELL_PS Redundancy
Each class derived from CIM_Dependency has an element called an antecedent that represents the
independent object in this association, and another element called a dependent that represents the
object that is dependent on the antecedent. For example, consider two managed system elements:
Chassis1 and PowerSupply3. Chassis1 is the antecedent element because a managed power supply
would always be either contained in, or grouped with, a chassis.
DELL_FanSensor
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_Dependency
DELL_FanSensor
The DELL_FanSensor class described in Table 5-1 defines a Dell-specific association between a fan
and a sensor. The CIM_PackageFanSensor class contains fans that assist in cooling the entire
package as opposed to a fan that is dedicated to cooling only some of the components in
the package.
CIM_Dependency 83
Page 84

Table 5-1. DELL_FanSensor Properties
Class Name: DELL_FanSensor
Parent Class: CIM_Dependency
Property Description
Antecedent CIM_Tachometer refers to the tachometer (fan sensor) that measures the
RPM of the fan.
Dependent CIM_Fan refers to the fan whose revolutions are measured by the
tachometer.
CIM_PackageTempSensor
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_Dependency
CIM_PackageTempSensor
The CIM_PackageTempSensor class listed in Table 5-2 contains temperature sensors that are often
installed in a package such as a chassis or a rack to assist in the monitoring of the package in general. This
relationship is described by the CIM_PackageTempSensor association.
Table 5-2. CIM_PackageTempSensor Properties
Class Name: CIM_PackageTempSensor
Parent Class: CIM_Dependency
Property Description
Antecedent CIM_TempSensor refers to the temperature sensor for the package.
Dependent CIM_PhysicalPackage refers to the physical package whose environment is
being monitored.
84 CIM_Dependency
Page 85

CIM_PackageVoltSensor
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_Dependency
CIM_PackageVoltSensor
The CIM_PackageVoltSensor identified in Table 5-3 contains voltage sensors that are often installed in a
package such as a chassis or a rack to assist in the monitoring of the package in general. This relationship
is described by the CIM_PackageVoltSensor association.
Table 5-3. CIM_PackageVoltage Properties
Class Name: CIM_PackageVoltSensor
Parent Class: CIM_Dependency
Property Description
Antecedent CIM_PackageVoltSensor refers to the voltage sensor for the package.
Dependent CIM_PhysicalPackage refers to the physical package whose voltages are
being monitored.
CIM_PackageCurrentSensor
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_Dependency
CIM_PackageCurrentSensor
The CIM_PackageCurrentSensor shown in Table 5-4 contains amperage sensors that are often installed
in a package such as a chassis or a rack to assist in the monitoring of the package in general. This
relationship is described by the CIM_PackageCurrentSensor association.
Table 5-4. CIM_PackageCurrentSensor Properties
Class Name: CIM_PackageCurrentSensor
Parent Class: CIM_Dependency
Property Description
Antecedent CIM_CurrentSensor refers to the amperage sensor for the package.
Dependent CIM_PhysicalPackage refers to the physical package whose amperage is
being monitored.
CIM_Dependency 85
Page 86

CIM_PackageFanSensor
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_Dependency
CIM_PackageFanSensor
The CIM_PackageFanSensor class described in Table 5-5 contains fan sensors that monitor the
whole package.
Table 5-5. CIM_PackageFanSensor Properties
Class Name: CIM_PackageFanSensor
Parent Class: CIM_Dependency
Property Description
Antecedent CIM_Fan refers to the cooling device for the package.
Dependent CIM_PhysicalPackage refers to the physical package whose environment is
being monitored.
CIM_PackagePowerSupplySensor
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_Dependency
CIM_PackagePowerSupplySensor
The CIM_PackagePowerSupplySensor class described in Table 5-6 contains power supplies that provide
power to the whole package.
Table 5-6. CIM_PackagePowerSupplySensor Properties
Class Name: CIM_PackagePowerSupplySensor
Parent Class: CIM_Dependency
Property Description
Antecedent CIM_PowerSupplySensor refers to the power supply sensor that monitors
wattage for the entire package.
Dependent CIM_PhysicalPackage refers to the package whose wattage is being monitored.
86 CIM_Dependency
Page 87

DELL_PackagePSRedundancy
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_Dependency
DELL_PackagePSRedundancy
The DELL_PackagePSRedundancy class listed in Table 5-7 defines what constitutes power supply
redundancy for an entire package.
Table 5-7. DELL_PackagePSRedundancy Properties
Class Name: DELL_PackagePSRedundancy
Parent Class: CIM_Dependency
Property Description
Antecedent DELL_PSRedundancyGroup refers to power supplies that deliver wattage
for the entire package.
Dependent CIM_PhysicalPackage refers to the package to which the wattage is
being supplied.
CIM_Dependency 87
Page 88

DELL_PSRedundancy
CIM_ManagedSystemElement
CIM_Dependency
DELL_PSRedundancy
The DELL_PSRedundancy class shown in Table 5-8 defines what constitutes power supply redundancy
for Dell™ systems.
Table 5-8. DELL_PSRedundancy Properties
Class Name: DELL_PSRedundancy
Parent Class: CIM_Dependency
Property Description
Antecedent CIM_PowerSupplySensor refers to the power supply sensor that monitors
wattage for the entire package.
Dependent CIM_PhysicalPackage refers to the package whose wattage is
being monitored.
88 CIM_Dependency
Page 89

Glossary
The following list defines or identifies technical terms, abbreviations, and acronyms used in user documents.
Array Manager
A systems management application that allows you to
manage and configure SCSI and Fibre Channel RAID
controllers through a common user interface.
asset tag code
An individual code assigned to a computer, usually by
a system administrator, for security or
tracking purposes.
attribute
An attribute, or property, contains a specific piece of
information about a manageable component. For
example, a component can have attributes for settings,
capabilities, and status.
CIM
Acronym for Common Information Model, which is a
model for describing management information from
the DMTF. CIM is implementation independent,
allowing different management applications to collect
the required data from a variety of sources. CIM
includes schemas for systems, networks, applications,
and devices. It provides mapping techniques for
interchange of CIM data with MIB data from
SNMP agents.
CIMOM
Acronym for common information model object
manager.
CI/O
Acronym for comprehensive input/output.
class
For the purposes of the Dell CIM provider, a class is a
set of managed system elements that can be monitored
and managed using a systems management console
capable of receiving CIM information. Managed
system elements can have various levels of complexity,
from rack systems containing multiple servers and
storage systems, to individual fans, power supplies,
processors, and chips. Physical objects that contain
systems can be associated with the
CIM_PhysicalPackage class. Managed objects of
intermediate complexity can be represented by such
classes as CIM_SoftwareElement or
CIM_PowerSupplyRedundancy. Simple managed
system elements can be represented by classes such
as CIM_Processor.
component
Manageable components are operating systems,
computer systems, expansion cards, or peripherals that
are compatible with a systems management standard
such as CIM and SNMP. Each component is made up
of groups and attributes that are defined as relevant to
that component.
controller
A chip that controls the transfer of data between the
microprocessor and memory or between the
microprocessor and a peripheral device such as a disk
drive or the keyboard.
DMTF
Abbreviation for Distributed Management Task Force,
a consortium of companies representing hardware and
software providers.
ix86
Variable used to represent microprocessors such as
®
i386™, i486™, and so forth.
Intel
Glossary 89
Page 90

IHV
Acronym for independent hardware vendor. IHVs often
develop their own SNMP MIBs for components that
they manufacture.
IT Assistant
A comprehensive systems management application
that integrates event management, configuration
management, and asset management for systems
distributed throughout an enterprise.
MIB
Acronym for management information base. A MIB is
used to send detailed status/commands from or to an
SNMP managed device.
MOF
Acronym for managed object format, which is an ASCII file
that contains the formal definition of a CIM schema.
NIC
Acronym for network interface controller.
property
A property is a capability or characteristic of a CIM
class. The temperature probe class, for example, has a
property that describes its thresholds for normal, lower
critical, and upper critical ranges of operation. Defining
where normal operation ends and where critical
temperatures begin determines when warnings should
be sent to the systems manager for corrective action.
.
Every property has a Description and a Data Type
The
Description provides a brief explanation of what a particular
managed object does. The Data Type specifies the form
that the values of a property must take. For example, some
values are bit fields and others are integers or strings.
provider
A provider is an extension of a CIM schema that
communicates with managed objects. The provider
accesses data and generates event notifications from a
variety of sources. The Dell CIM provider extends the
standard CIM schema to make it easier to
manage systems.
MOF
A MOF is a management object file that models objects
in a systems management environment. The MOF
models the relationships between different managed
objects. For example, the CIM_RedundancyGroup is
a parent class for components that are so critical to the
proper functioning of a system that the system is
designed to have additional critical components.
When a critical component fails, redundancy allows
the system to continue operation because there are
other components that can compensate for the loss.
The DELL_PowerSupply and DELL_FanRedundancy
classes are derived from the CIM redundancy group.
The relationship is one of child to parent.
RAID
Acronym for redundant array of independent disks.
response file
The file that records the features that an administrator
wants to incorporate into an unattended installation is
called a “response file” or an “answer file.”
set operation
An operation used to write or “set” data to MIB
variables maintained by the SNMP agent.
SNMP
Abbreviation for Simple Network Management Protocol.
SNMP is an industry-standard interface that allows a
network manager to remotely monitor and manage
workstations.
unattended installation
An unattended installation requires far less operator
involvement than an interactive installation. Also
called a “silent installation,” unattended installation
programs record the administrator’s preferences about
which features of an application program to install. The
file that records these installation feature preferences
is called a “response file” or an “answer file.” System
administrators typically create packages that include
the response file and any other files needed to install
the program, distribute the package to multiple
systems, and activate the unattended installation.
90 Glossary
Page 91

Index
C
CIM classes and properties, 7
base classes, 8
classes that describe
relationships, 8
common properties of
classes, 10
conventions, 9
parent classes, 8
CIM_Chip, 19
CIM_Dependency
CIM_PackageCurrentSensor, 85
CIM_PackageFanSensor, 86
CIM_PackagePowerSupplySen
sor, 86
CIM_PackageTempSensor, 84
CIM_PackageVoltSensor, 85
DELL_FanSensor, 83
DELL_PackagePSRedundancy,
87
DELL_PSRedundancy, 88
CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_BIOSElement, 63
CIM_CacheMemory, 62
CIM_ComputerSystem, 29
CIM_Controller, 49
CIM_CoolingDevice, 44
CIM_CurrentSensor, 41
CIM_DiscreteSensor, 38
CIM_DMA, 69
CIM_ExtraCapacityGroup, 71
CIM_Fan, 45
CIM_FRU, 31
CIM_LogicalElement (continued)
CIM_IRQ, 67
CIM_Keyboard, 47
CIM_LogicalDevice, 30
CIM_LogicalPort, 31
CIM_Memory, 61
CIM_MemoryMappedIO, 68
CIM_NumericSensor, 38
CIM_ParallelController, 50
CIM_PCIBridge, 53
CIM_PCIController, 51
CIM_PointingDevice, 46
CIM_PowerSupply, 48
CIM_Processor, 54
CIM_RedundancyGroup, 70
CIM_Sensor, 31, 36
CIM_SerialController, 51
CIM_SoftwareElement, 63
CIM_SoftwareFeature, 65-66
CIM_System, 28
CIM_SystemResource, 66
CIM_Tachometer, 43
CIM_TemperatureSensor, 40
CIM_UserDevice, 45
CIM_VoltageSensor, 42
CIM_Watchdog, 43
DELL_FanExtraCapacityGrou
p, 72
DELL_NetworkPort, 33
DELL_PSRedundancyGroup,
72
DELL_System, 30
CIM_LogicalElement Class
structure of, 27
CIM_PhysicalComponent, 19
CIM_PhysicalElememt
CIM_PhysicalConnector, 23
CIM_PhysicalMemory, 21
CIM_PhysicalElement, 13
CIM_Chassis, 16
CIM_Chip, 19
CIM_PhysicalComponent, 19
CIM_PhysicalFrame, 15
CIM_PhysicalPackage, 14
CIM_Slot, 25
DELL_Chassis, 17
structure of, 13
CIM_PhysicalElementClass
structure of, 13
CIM_SoftwareElement, 63
class name, 9
common properties of
classes, 10
current reading, 10
D
data type, 9
Dell OpenManage Server
Agent, 7
DELL_CMApplication, 78
DELL_CMDevice, 79
DELL_CMDeviceApplication, 80
DELL_CMInventory, 80
Index 91
Page 92

DELL_CMOS, 81
DELL_CMProductInfo, 82
DELL_EsmLog, 77
DELL_PostLog, 78
DELL_PSRedundancy, 88
description, 9
P
parent class, 9
property, 9
S
Server Administrator 1.0, 7
V
version, 11
92 Index
 Loading...
Loading...