Page 1

Dell OpenManage Network Manager version 5.1
Web Client Guide
Page 2

Notes, and Cautions
A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your computer or software.
A CAUTION indicates potential harm to your data or hardware if you proceed as indicated.
____________________
Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
© 2012 Dell Inc. All rights reserved.
Reproduction of these materials in any manner whatsoever without the written permission of Dell Inc. is strictly forbidden.
Trademarks used in this text: Dell™, the DELL logo, PowerEdge™, PowerVault™, PowerConnect™, OpenManage™, EqualLogic™,
KACE™, FlexAddress™ and Vostro™ are trademarks of Dell Inc. Microsoft
®
are either trademarks or registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries. Red Hat Enterprise
Vista
®
and Enterprise Linux® are registered trademarks of Red Hat, Inc. in the United States and/or other countries. Verizon® is a registered
Linux
trademark of Verizon Wireless.
Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this publication to refer to either the entities claiming the marks and names or their products.
Dell Inc. disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names other than its own.
®
, Windows®, Windows Server®, MS-DOS® and Windows
2012-7 Rev. A01
Page 3

Contents
1 Preface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2 Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager .15
Why Dell OpenManage Network Manager?. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Key Features
Networks with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
Additional Products
Online Help / Filter
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
11
11
12
How to: Use “How To” . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Feedback. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
A Note About Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
System Basics
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
15
Single Server Sizing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Sizing for Standalone Installations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Network Basics
Authentication
Supported PowerConnect Models
Windows Management Interface
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
22
24
24
24
Getting Started. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Installation and Startup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
How to: Set Linux Permissions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Perl
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Starting Web Client
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
32
33
Control Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Search Indexes
[My Account]
RCSynergy / [Domain]
Portal > Users and Organizations
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
34
35
35
36
How to: Add Users and connect them to Roles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
How to: Configure Organizations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Public / Private Page Behavior
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
40
How to: Add and Configure User Roles / Permissions . . . . . . . . . . 40
Portal > Roles
Portal > Portal Settings
Portal > [Other]
Redcell > Permission Manager
Redcell > Data Configuration
Redcell > Mediation
Redcell > Filter Management
Server
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
41
41
42
42
45
46
48
49
Redcell > Database Aging Policies (DAP). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
9
3
Page 4

How to: DAP Workflow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Aging Policies Editor
Aging Policies Options
Sub-Policies
Repositories
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Portlet Level Permissions
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
How to: Configure Portlet Permissions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
How to: Configure Resource Level Permissions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Quick Navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
License Viewer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
How to: Register a License . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Discovery Profiles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
How to: Discover Your Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Discovery Profile Editor
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Managed Resources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Common Setup Tasks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
SMTP Configuration
Netrestore File Servers
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 Portal Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Tooltips
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Refresh
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
The Back Button
Show Versions
The Dock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Status Bar Alerts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Chat / Conferencing
Menu Bar
Site Map
Graphs
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Portlets
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Expanded Portlets
How to: Show / Hide / Reorder Columns . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
How to: Filter Expanded Portlet Displays . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Common Menu Items . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Import / Export
Sharing
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
How to: Share a Resource . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Edit Custom Attributes
View as PDF
Ta g
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Audit Trail / Jobs Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Audit Trail Viewer
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
52
54
55
57
58
65
69
70
72
72
72
72
76
77
77
77
78
82
86
87
89
90
90
92
4
Page 5

Audit Trail Portlet. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Schedules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Schedules Portlet
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4 Key Portlets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Alarms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Expanded Alarm Portlet
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
101
Event History. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Event Processing Rules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
How to: Create Event Processing Rules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Rule Editor
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
111
Event Definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Event Definition Editor
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
128
Contacts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Locations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Ta g
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
138
Vendors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
5 Resource Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
Authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
Container Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
Container Manager Expanded
Container View. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
How to: Use Containers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Container Editor
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Map Context. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Resource Discovery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
How to: Discover Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
Discovery Profiles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Discovery Profile Editor
How to: Edit Discovery Profiles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Managed Resource Groups. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
Static Group
Dynamic Group
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Managed Resources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
New Link
Link Discovery
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Equipment Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
Performance Indicators
Interfaces
Alarms
Ports
Details
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
146
148
154
164
165
175
176
179
180
181
181
185
95
5
Page 6

How to: Schedule Actions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 186
Direct Access. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 188
MIB Browser
Te rm in a l
Ping (ICMP)
HTTP / HTTPS
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
188
190
191
191
Ports. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
Port Editor
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
194
Report Templates. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
How to: Create a Report Template . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
Report Template Editors
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
196
Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200
How to: Generate a Report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 204
Report Editor
Branding Reports
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
204
206
6 Visualize My Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .207
How to: Create a Visualization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207
Configuring Views
Control and Styles
Data / Node Finder
Layout
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
OVERVIEW
Alarms in Visualizations / Topologies. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 219
Links in Visualization. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 220
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
208
210
213
216
219
7 File Servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 221
File Server Editor
File Management. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 223
How to: Backup Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 225
How to: Restore Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 227
Configuration Files
Image Repository. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
Firmware Image Editor
Configuration Image Editor
Deploy Firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 238
How to: Deploy Firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 239
Deploy Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 240
How to: Restore a single configuration to many target devices . 241
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
222
229
235
236
8 Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 243
How to’s. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 243
OpenManage Network Manager Server Statistics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 244
6
Page 7

Resource Monitors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 245
Retention Policies
Monitor Editor
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
248
251
How to: Create an SNMP Interface Monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 262
How to: Create an ICMP Monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 263
How to: Create a Key Metrics Monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 264
How to: Create a Monitor Report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 265
Monitor Options Type-Specific Panels
Scheduling Refresh Monitor Targets
. . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
266
276
Top [Asset] Monitors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 276
Top Configuration Backups
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
277
Dashboard Views. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 277
How to: Create a Simple Dashboard View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 279
Performance Dashboard
Dashboard Editor
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
279
281
How to: Create a Custom Dashboard View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 282
Show Performance Templates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 286
How to: Create A Performance Template . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 286
Key Metric Editor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 289
9 Traffic Flow Analyzer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .293
How does it work?. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 294
Setup
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
How to: Use Traffic Flow Analyzer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 295
Exporter Registration
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Traffic Flow Portlet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 296
Drill Down
Search
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Traffic Flow Analyzer - Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 301
294
296
299
301
10 Change Management – ProScan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .303
How to: Use ProScan / Change Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 303
How to: Configure ProScan Groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 304
How to: Do Change Management (Example) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 305
ProScan Portlet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 306
Compliance Policy Summary
Creating or Modifying a ProScan Policy
How to: Create Source Group Criteria . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 316
Creating or Modifying ProScan Policy Groups
Change Determination Process . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 326
Change Determination Process Workflow
How to: Run Change Determination . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 329
Change Determination Defaults
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
308
310
325
327
329
7
Page 8

Compliance and Change Reporting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 329
How to: Report on Change Determination . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 331
11 Storage Arrays . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 333
Introducing Storage Arrays . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 333
Storage Array Portlet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 333
Storage Array Portlet Expanded
General
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
334
337
12 Actions and Adaptive CLI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 341
Using Adaptive CLI
Actions Portlet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 343
Adaptive CLI Editor
General
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Attributes
Scripts
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Comparison
External Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 360
Seeded Scripts
How to: Create a Monitor for an External Script . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 364
Adaptive CLI Script Language Syntax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 366
Attributes
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Conditional Blocks
Perl Scripts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 368
How to: Create Adaptive CLI Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 369
Scheduling Actions
Active Performance Monitor Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 371
Adaptive CLI Records Archiving Policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 373
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
341
348
349
350
355
360
362
366
367
369
Glossary. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 375
Index
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
381
8
Page 9

Preface
Dell OpenManage Network Manager can give you automated, consolidated configuration and
control of your network’s resources. It is customizable, unifying multiple systems while still
communicating with other software systems (like billing) in generic WSDL, XML and SOAP.
OpenManage Network Manager’s
runtime features supporting these applications. The OpenManage Network Manager
Administration Section of the User Guide and
Release Notes for information about changes not covered in this
Administration Section
Administration Section
describes security and some of the
discuss licensing. Consult
Synergy User Guide
.
Why Dell OpenManage Network Manager?
Dell OpenManage Network Manager’s benefits:
Productive
Discovery and wizard-driven configuration features within minutes of installing Dell OpenManage
Network Manager, you can monitor your network.
Easy
Dell OpenManage Network Manager provides the network information you need, and offers
advanced capabilities with minimal configuration overhead.
Valuable
Dell OpenManage Network Manager often costs less to use and maintain than most other
solutions.
Scalability
You can scale Dell OpenManage Network Manager to almost any size.
Key Features
The following are some key features of Dell OpenManage Network Manager:
Customizable and Flexible Web Portal
You can customize the web portal, even providing custom designed views of your data assigned to
individual users. You can even create web portal accounts for departments, geographic areas, or
other criteria.
Why Dell OpenManage Network Manager? | Preface
9
Page 10

Automate and Schedule Device Discovery
Device discovery populates Dell OpenManage Network Manager’s database and begins network
analysis. You can also create network discovery schedules to automatically run Discovery whenever
you need them.
Dell OpenManage Network Manager Administration
You can now conduct administrative tasks—adding devices, user accounts, and web portal
displays—from a secure console on your network.
Open Integration
Dell OpenManage Network Manager supports industry standards. It comes with an open-source
MySQL database. It also uses industry-standard MIBs and protocols, and even lets you install opensource screen elements like Google gadgets to the web portal.
Topology
The OpenManage Network Manager topology screen lets you create multi-layered, fully
customizable, web-based maps of your network to track devices wherever they are in your network.
Alarms
You can configure custom alarms to respond to hundreds of possible network scenarios, including
multiple condition checks. Dell OpenManage Network Manager’s alarms help you recognize issues
before your network users experience productivity losses. Alarms can also trigger actions like email,
executing Perl
®
scripts, paging, SNMP traps, Syslog messaging, and external application execution.
10
Traps and Syslog
Dell OpenManage Network Manager lets you investigate network issues with traps and Syslog
messages. You can use Dell OpenManage Network Manager to set up events / alarms and then
receive, process, forward, and send syslog and trap messages.
Reports and Graphs
Dell OpenManage Network Manager comes with many pre-configured reports and graphs to
display data from its database. You can archive and compare reports, or automate creating them
with Dell OpenManage Network Manager’s scheduler.
Modularity
With additional modules, Dell OpenManage Network Manager can analyze network traffic,
manage services and IP address and subnet allocations. OpenManage Network Manager modules
save time adding to existing Dell OpenManage Network Manager deployments to add feature
functionality without requiring additional standalone software.
Why Dell OpenManage Network Manager? | Preface
Page 11

Networks with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
Tip
The beginning of network management with Dell OpenManage Network Manager is Discovery
Profiles of the resources on a network. After that occurs, you can configure Visualize (topology
views), Resource Monitors and Performance Dashboards.
Once you have done these initial steps, Dell OpenManage Network Manager helps you understand
and troubleshoot your network. For example: Suppose a OpenManage Network Manager
Performance Dashboard displays something you want to troubleshoot. You can right-click the
impacted device in the Visualize topology view to access configuration and actions. The color of
the icon in this view indicates the highest severity alarm on the device or its sub-components. For
example, red indicates a
Displays include right-click access to the Details screen (see Equipment Details on page 178),
where you can examine each section of device information and right-click to see further applicable
actions. For example right-click to Show Performance, and edit and/or save that view of
performance as another Performance Dashboard. Performance can also display portlets that Show
Top Talkers (the busiest devices) or Show Key Metrics.
From looking at Performance Dashboards or Top [Asset] Monitors you may conclude some
configuration changes made memory consumption spike. Right-click to access resource actions
under File Management that let you see the current configuration files on devices, and compare
current to previous. You can also back up devices (see Backup Configurations on page 225) and
restore previously backed up files (see Restore Configurations on page 227). Finally, you may simply
want to Resync (another right-click menu item) to insure the device and your management system
are up-to-date.
Critical
alarm.
Alternatively, the Alarms portlet also lets you right-click to expose Alarm Actions.
You can right click for Direct Access – Telnet or Direct Access – MIB Browser to display a command
line telnetting to the device, or an SNMP MIB browser to examine SNMP possibilities for it.
The Managed Resources portlet can display the anatomy of a Resource with its right-click actions
(see Equipment Details on page 178). Click the plus in the upper right corner to see Managed
Resources Expanded. This displays detail or “Snap-in” panels with additional information about a
selected resource.
Reports let you take snapshots of network conditions to aid in analysis of trends, and Audit Trail
Portlets track message traffic between Dell OpenManage Network Manager and devices.
Additional Products
The following describes how to increase the power of your Dell OpenManage Network Manager
installation. While the documents mentioned above describe everything available with Dell
OpenManage Network Manager, your installation may provide only a limited subset of those
features.
Why Dell OpenManage Network Manager? | Preface
11
Page 12

Updating Your License
NOTE:
Tip
How To:
If you have a limited license — for example OpenManage Network Manager may limit discovery to
a certain number of devices— then your application does not function outside those licensed
limits.
You can purchase additional capabilities, and can update your license for OpenManage Network
Manager by putting the updated license file in a convenient directory. Then click
Management
browser (
button. Your updated license should be visible in the
63
for details.)
If you update your installation from a previous one where you upgraded license, you must also reregister those licenses.
You must restart application server or wait up to 15 minutes before a license modification takes
effect. (see Installation and Startup on page 28). Licenses now support three expiration formats:
Never, Date certain, and a format that indicates the license will be valid for a number of days after
registration.
in the Quick Navigation portlet item to open a screen with a button leading to a file
Register License: Select File
). Locate the license file, and click the
License Viewer
(See
License
Register License
License Viewer on page
Online Help / Filter
Access general online help by clicking
appropriate to each portlet appears when you click question mark icon on the portlet title bar.
By default, this opens a separate browser window which is not necessarily always in front of the
screen that calls it. Because it is separate, you can arrange the display so the help screen does not
conceal the portlet it describes. Click the
tabs (
moves to different topics within the helpset.
Use “How To”
Several sections of what follows contain the “How to” instructions for use. These are typically steps
to follow to produce the desired result. For a look at all such steps available, refer to the
section of the Index.
12
Why Dell OpenManage Network Manager? | Preface
Help
in the The Dock at the top of the screen. Help
Show
button to display the contents, index and search
Hide
conceals them again), and the
Sometimes your browser’s cache may interfere with help’s correct appearance. If you see a table of
contents node without contents, you can often repair it by refreshing the panel or whole screen.
Prev / Next
buttons, or clicking table of contents topics
How to
Page 13

Feedback
Tip
To provide your input about this software click the
OpenManage Network Manager screen. Provide your contact information, enter
New Idea
Dorado Software responds, and often uses customer suggestions in future versions of the software.
s, or a
Problem,
in the screen that appears next, then click
Fee dba ck
link in the lower left corner of the Dell
Questions, Likes,
Send.
A Note About Performance
Dell OpenManage Network Manager is designed to help you manage your network with alacrity.
Unfortunately, the devices managed or the networks that communicate with those devices are not
always as fast as this software. If discovery takes a long time (it can), often network and device
latency is the culprit. You can also optimize installations to be faster (see the recommendations in
the Administration Section of the User Guide and
queries with filters, but device and network latency limit how quickly your system can respond.
If you use management systems other than this one, you must perform a device level resync before
performing configuration actions. Best practice is to use a single management tool whenever possible.
Administration Section
s), and limit device
Feedback | Preface
13
Page 14

14
A Note About Performance | Preface
Page 15
Getting Started with Dell OpenManage
Tip
Network Manager
Overview
This chapter describes how to install and start Dell OpenManage Network Manager for basic
network monitoring and management. For more detailed descriptions of all this software’s features,
consult its other manuals (the OpenManage Network Manager Administration Section of the User
Guide,
Synergy User Guide, Administration Section
If you want to find something but are unsure about which manual it is in, you can search all text in the
Acrobat files in a single directory. You can also click on the blue cross-references to go to the target
destination of cross-references in Acrobat, however for such electronic cross-references to the other
documents to work, they must be in the same directory. Cross-document links do not work between
documents for different versions of this software, but may provide an approximate location to consult.
If you are sure your hardware, software and network is correct and just want to get started
immediately, go to Getting Started on page 27.
The Dell OpenManage Network Manager portal delivers powerful solutions to network problems,
and, in addition to the OpenManage Network Manager technology documented in the following
pages, Dell OpenManage Network Manager offers the following capabilities:
• Message Boards, Blogs, Wikis
• Shared Calendars
• Enterprise Chat / Messaging
• RSS Feeds
• Tagging, Ratings, Comments
The section Server on page 49 describes how to set up some of these features.
and
User Guide
) or the online help.
1
System Basics
System requirements depend on how you use the application and the operational environment.
Your specific network and devices may require something different from the recommendations for
typical installations.
Overview | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
15
Page 16

Generally, base the minimum configuration of any system on its expected peak load. Your
NOTE:
CAUTION:
installation should spend 95% of its time idle and 5% of its time trying to keep pace with the
resource demands.
Upgrading from a Previous Version
When you upgrade your OpenManage Network Manager installation from a previous version, keep
the following in mind:
• Upgrading requires a new license to activate new features.
• Performance capabilities have been completely reconfigured. When upgrading from previous
versions, you must (re-)create dashboards from scratch.
• The following require manual migration (export, then import) from previous versions: SMTP
settings. Some scheduled items.
• You must re-create topologies as Visualizations. (suggestion: take a screenshot)
• Group Operations have been deprecated, replaced by Adaptive CLIs.
• Command monitors must be recreated, and monitors must be re-configured to monitor
Adaptive CLIs that run external scripts.
• User Names / Passwords, and User Groups (Roles) are not automatically reassigned and must
be created manually.
Supported Operating System Versions
The following are supported operating system versions:
Microsoft Windows
and Web) and Windows Server 2008 (including R2 and Enterprise Edition). This is a 64-bit
application, it has been tested for Windows on 64-bit operating system versions.
—The supported operating systems are: Windows 2003 (Standard,Enterprise
16
Windows Terminal Server is not supported. The installer becomes non-responsive with Data Execution
Prevention enabled. This option is disabled by default on Windows Server 2008, but is enabled on a
Windows Server 2008 machine running Terminal Server.
• You must disable User Account Control if you are installing Windows Server 2008.
Alternatively, you can run application server as service. Another option is to run as
administrator on startappserver. In Vista, right click the startappserver icon and select run as
administrator.
• Installer may halt when pre-existing bash sessions or cmd sessions are left open. Close all such
sessions.
Linux
—This application supports Red Hat (Enterprise version 5.5 or 6.0) Linux, 64-bit only. (See
32-bit Linux Libraries on page 18 for additional requirements)
For Linux, you must install no more than a single instance of MySQL—the one installed with this
software. Before you install, remove any MySQL if it exists on your Linux machine.
Overview | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
Page 17

Linux Installation Best Practices
How you install Linux has an impact on Dell OpenManage Network Manager’s installation. Here
are some tested best practices:
• You can install Linux in its Desktop option, or if you select Basic Server (default) - choose
additional packages: XWindows, Basic / Core Gnome Desktop without Gnome utilities,
although we suspect any Gnome will work).
• Turn off SE Linux in /etc/selinux/config. Change SELINUX=disabled. This typically requires
a reboot.
• You must install compatibility library from installation media (so it is compatible with
installation)
compat-libstdc++-33.x86_64 3.2.3-69.el6 @InstallMedia.
Also: verify that
/etc/hosts
points to new name-use the following command and you
should see similar output.
[qa@rh6Test Desktop]$ cat /etc/hosts
10.18.0.241rh6Test.localrh6Test# Added by NetworkManager
127.0.0.1localhost.localdomainlocalhost
::1 rh6Test.localrh6Testlocalhost6.localdomain6localhost6
Upgrading on Linux
The following are best practices for upgrading from a previous OpenManage Network Manager
version on a Linux machine:
1
Make sure Red Hat is not installed with a MySql database option (or remove the Linux MySql
first).
2
Ensure you have installed the 32-bit Linux Libraries, as described below.
3
Verify your previous version’s installation application server starts without excpetions
4
Back up the database, and any other resources that need manual installation. Consult Release
notes for a list of these.
5
Proceed with the upgrade.
Disable Firewalls
System->Administration->Firewall - You may be prompted to enter the root password; the
password dialog may be hidden behind the Firewall Configuration Startup dialog.
Directories and Permissions
Create the directory for the installation:
1
Open a terminal.
2
Change to Super User: su <enter> password: []
3
Create directory and configure its ownership and permissions:
Overview | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
17
Page 18

mkdir /opt/
NOTE:
NOTE:
chown [your login name] /opt/[your installation directory]
chmod 775 /opt/[your installation directory]
[your login name] is the original non-root user available when you imported the machine. Replace [your
login name] with whichever user you are logged in as or will be installing as.
You may need to change the permissions on the installer in our package in order to give it execute
rights. If you have used the shared folder method from above, you can give the Linux installer
rights as follows:
chmod uga+x /[Install Media Path]/install/linux_install
Make sure that there is no other
mv /etc/my.cnf /etc/my.cnf.original
my.cnf
file under the
/etc
directory. If there is, do the following:
32-bit Linux Libraries
For Red Hat Enterprise 64 bit installations, you must identify the appropriate package containing
32-bit libtcl8.4.so (for the example below: tcl-8.4.13-3.fc6.i386.rpm for Red Hat).
Do not use any x86_x64 rpms; these would not install the 32-bit libraries.
Any 32-bit tcl rpm that is of version 8.4 and provides libtcl8.4.so works. You can download them
from Sourceforge:
rpm -ivh --force tcl-8.4.13-3.fc6.i386.rpm
sourceforge.net
. Download these, then issue the command:
This forces the installation of the 32-bit libraries on a 64-bit system. Ensure that your expect
executable in your installation directory is properly linked by issuing the following commands:
[someone@RHEL5-64bit ~]$ which expect
/opt/dorado/oware3rd/expect/linux/bin/expect
[someone@RHEL5-64bit ~]$ ldd /opt/dorado/oware3rd/expect/linux/bin/expect
linux-gate.so.1 => (0xffffe000)
libexpect5.38.so => /opt/dorado/oware3rd/expect/linux/bin/
libexpect5.38.so (0xf7fd2000)
libtcl8.4.so => /usr/lib/libtcl8.4.so (0x0094c000)
libdl.so.2 => /lib/libdl.so.2 (0x0033e000)
libm.so.6 => /lib/libm.so.6 (0x00315000)
libutil.so.1 => /lib/libutil.so.1 (0x00b8d000)
libc.so.6 => /lib/libc.so.6 (0x001ba000)
/lib/ld-linux.so.2 (0x0019d000)
18
Overview | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
Page 19

Make sure that
NOTE:
Tip
CAUTION:
libtcl8.4.so
maps to
/lib/libtcl8.4.so
An Alternative for Red Hat
Linux:
1
Copy
/usr/lib/libtcl8.4.so
from a 32-bit RH system to
/usr/local/lib/32bit
on your 64-bit Red Hat system
2
As root, execute:
ln –s /usr/local/lib/32bit/libtcl8.4.so /usr/lib/
libtcl8.4.so
Supported Web Browsers
Supported web browsers include:
• Chrome (v 6 and above)
• Safari (v 5 and above)
• Firefox (v 3.6 and above)
• Internet Explorer (v 9 and above)
Screen resolution should equal or exceed 1280 x N pixels. Users running Safari on an Apple
machine must modify Java preference to run applets as their own process. Java Preferences are
under Applications > Utilities on OSX.
Internet Explorer versions 8 and older display alignment issues, have slower JavaScript and Flash
processing, and some transparencies do not work. Other anomalies include non-rounded corners, no
alpha rendering, scroll bars in performance indicators, non-working multi-level menus, a too-large OS
Images schedule form, and others. To fix these anomalies, install the Chrome plug-in at code.google.com/
chrome/chromeframe/. After it installs, close IE and re-open it. The look and feel should improve.
You can often resolve problems by refreshing the browser’s display.
Opening Dell OpenManage Network Manager, or links originating within it in multiple tabs on multi-tab
browsers is not supported. To see “multiple” screens, configure Dell OpenManage Network Manager’s
Menu Bar.
You can download and install updates if your browser or version varies from those supported. To
have all Dell OpenManage Network Manager functionality, you must also install the latest version
of Java (v.1.6 or later) Adobe’s Flash and Adobe’s Acrobat that works with these browsers. Flash for
Overview | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
19
Page 20

64-bit browsers is currently a preliminary version, but you can typically run a 32-bit browser even in
NOTE:
Tip
a 64-bit operating system, so Flash features will still be available even if you do not want to run
Adobe’s beta software.
If Flash is installed, but the screen still requests it, reload the page in the browser. Also: Your screen must
be at least 1250 pixels wide.
When no cursor or focus is onscreen, some browsers interpret backspace as the Previous button.
Single Server Sizing
The following describes hardware and sizing configuration for common Dell OpenManage
Network Manager deployments. Before any deployment, administrators should review and
understand the different deployment options and requirements. Consider future growth of the
network when estimating hardware sizing. You can generally expand modern systems running Dell
OpenManage Network Manager by adding more RAM to the host server(s). Selecting expandable
hardware may also be critical to future growth. For ease of management, deployments selection
best practice is to use the fewest possible servers. Standalone (single server) deployment offer the
simplest and easiest management solution. Where high availability (HA) is required, you can
produce the simplest deployment with as few as two servers.
20
Minimum Hardware
The minimum hardware specification describes what Dell OpenManage Network Manager needs
at a minimum. In such minimum installations, traffic flowing from the network to OpenManage
Network Manager may exceed the capacity of the hardware. When estimating the size of a
deployment, it is important to understand the applications configurations in the target
environment. Applications that are typically the most demanding of resources are Traffic Flow
Analyzer (TFA), Event Management and Performance Monitoring.
REQUIRED Minimum hardware
Supports
• Standalone installations (Single Server) is supported when high-resource demand
RECOMMENDED Minimum hardware:
Supports:
• Standalone installations (non-distributed).
Single Server Sizing | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
:
applications are used minimally.
—6GB RAM, dual core CPU, 200 GB 7200 RPM Disk.
8GB RAM, quad core CPU, 400 GB 10,000 RPM Disk
Page 21
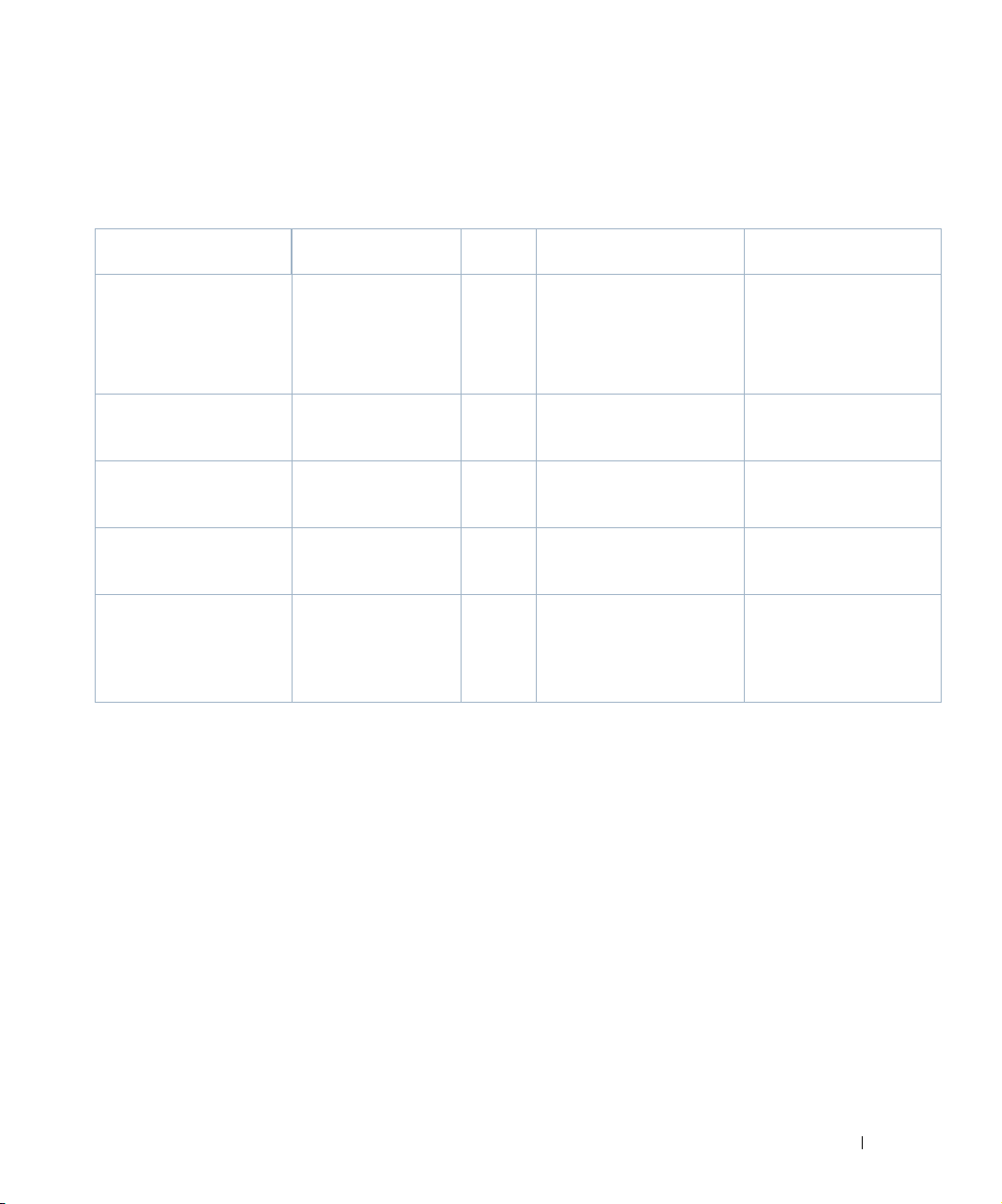
Sizing for Standalone Installations
The following are suggested sizing guidelines for your Dell OpenManage Network Manager system.
Operating System / Disks /
Network Size Devices
2
Application Constraints
3
RAM / Hardware
64-bit OS with 6GB RAM
or 32-bit OS with 4GB
<5 Users <20 <2Mbs Internet egress and a
1:1000 sample rate
RAM
All below are 64-bit OS’s:
8GB RAM, single disk,
consumer level PC
12GB RAM, single disk,
business level PC
16GB RAM, multi-disk,
server level PC
Single-site, less than 10
concurrent users
Single-site, less than 25
concurrent users.
Medium-large network,
up to 50 concurrent
<100 <2Mbs Internet egress and a
1:1000 sample rate
< 500 < 10Gbs Internet egress and
a sample rate of 1:1000
< 1,000 < 50Gbs Internet egress and
a sample rate of 1:1000
users
32GB RAM, multi-disk,
server level PC,
Large network, up to
100 concurrent users
< 2,000 < 200Gbs Internet egress
and a sample rate of 1:1000
recommend fast disk array
or SSD drive array for the
many database actions
1
Assumptions: Servers have at least four cores and are no more than four years old. As memory and
usage increases, the number of CPU cores increase. Two cores can work for the most basic installations,
but are not recommended.
2
Each device is equivalent to a L2 or L3 switch with a total of 48 interfaces per device being monitored.
For each of devices not being monitored for 48 interfaces, one can add another 50 devices to the overall
inventory for ICMP-only monitoring.
3
Application Constraints are most relevent to Traffic Flow Analysis, Peformance Management, and Event
Management.
Traffic Flow Analysis ratings map to constant throughput divided by sample rate, as in bandwidth /
sample rate. 20G / 2000 is easier to manage than 20G / 1000. 20G / 1 is a thousand times more demanding
than 20G / 1000. Best practice is to avoid such high sample rates. The bandwidth the hardware your Dell
OpenManage Network Manager installation can support is dramatically lower in such cases. Best
Installation Changes to
Heap (RAM) Settings
Use defaults: (1 or 2GB
application server heap (32
v. 64-bit) 512M database
4
768M Synergy
3GB application server
heap, 2GB database, 1G
Synergy
4GB application server
heap, 3GB database, 3G
Synergy
5G application server heap,
4G database, 4.5G Synergy
10G application server
heap, 8G database, 9G
Synergy
,
Sizing for Standalone Installations | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
21
Page 22
practice is to sample a maximum of one traffic flow for every 1000 (1:1000). Higher sampling rates
NOTE:
degrade database performance and increase network traffic without adding any significant statistical
information.
Performance Management can support 600 inserts per second using a single disk (SSD) Drive. 1 insert =
1 monitored attribute. Expect better performance as you add more drives (and worse performance with
slower drives).
Event Management can support a sustained 1200 traps /sec using a single (SSD) drive. Expect better
performance as you add more drives (and worse performance with slower drives).
4
Database memory settings increase as the number of database hits increases. At the 32GB level best
practice is to use an SSD drive or fast disk array because of the large number of database actions
possible.
You can start and stop the client portion of the software without impacting the application server.
Device monitoring stops when you stop the application server or turn off its host machine. The
client can also be on a different machine than the application server.
See Starting Web Client on page 33 for more information about using web access to this software.
64-bit
Since Dell OpenManage Network Manager has a web server, demands on 32-bit system resources
are near their limits. A standalone 32-bit system with Application server, Web server, and database
requires nearly all addressable memory, and is therefore not supported. Applications like Traffic
Flow Analyzer and Performance Monitoring require even more memory. For these reasons, and for
future scalability, do not install this software on 32-bit systems.
22
Tablets, phones and iPads
Dell OpenManage Network Manager detects mobile devices and pads. For smaller screens, the
Navigation bar collapses to the left hand side and the page only displays a single column. Some
limits apply:
• Since touch devices do not support right click, the first time clicking on a row selects it. A
repeat click launches a menu displaying the available actions. Click the one you want.
• Charts that require flash may not work (some have HTML5 backup).
• Visualize / Topology is unavailable.
• Phones may limit views further
Network Basics
OpenManage Network Manager communicates over a network. In fact, the machine where you
install it must be connected to a network for the application to start successfully. Firewalls, or even
SNMP management programs using the same port on the same machine where this software is
installed can interfere with communication with your equipment.
Sizing for Standalone Installations | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
Page 23

Dealing with any network barriers to communicating with OpenManage Network Manager, any
Tip
required initial device configuration to accept management, and managing security measures or
firewalls—all are outside the scope of these instructions. Consult with your network administrator
to ensure this software has access to the devices you want to manage with the Protocols described
below.
One simple way to check connectivity from a Windows machine to a device is to open a command shell
cmd
with Start > Run
device responds, it is connected to the network. If not, consult your network administrator to correct this.
No useful information comes from disconnected or powered-down devices.
. Then, type
ping [device IP address]
at the command line. If the
Name Resolution
OpenManage Network Manager server requires resolution of equipment names to work completely,
whether by host files or domain name system (DNS). The application server cannot respond to
hosts with IP addresses alone. The application server might not even be in the same network and
therefore the host would be unable to connect.
If your network does not have DNS, you can also assign hostnames in
%windir%\System32\drivers\etc\hosts
you must assign a hostname in addition to an IP address somewhere in the system. Here are some
example hosts file contents (including two commented lines where you would have to remove the
# sign to make them effective):
# 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server
# 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host
127.0.0.1 localhost
on Windows (
/etc/hosts
in Linux). Here,
Protocols
OpenManage Network Manager uses the following protocols: TCP/IP, SNMP, HTTP/S, UDP
Multicast.
Overriding Properties
Dell OpenManage Network Manager lets you fine-tune various features of the application. Rather
than lose those changes if and when you upgrade your application, best practice is to override
changes. To do this, first change the provided file
overrides.properties.sample
to
server-overrides.properties
properties within it by uncommenting them, and altering them to fit your needs. The comments in
this file provide more information.
You can also override application server-related properties in
\owareapps\installprops\lib\installed.properties
Sizing for Standalone Installations | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
\oware\synergy\conf\server-
, and enable the
.
23
Page 24

Fixed IP Address
NOTE:
OpenManage Network Manager includes a web server and application server which must be
installed to hosts with fixed IP addresses or permanently assigned Dynamic Host Control Protocol
(DHCP) leases.
If you do change your host’s IP address
To accommodate a changed IP address, first delete the contents of
local IP address anywhere it appears in
\owareapps\installprops\lib\installed.properties
oware
Alternatively, in a shell, after running
ipaddresschange -n
If you change your host’s IP address, you must also change the Virtual host IP to the new IP address in
Manage > Control Panel > Portal.
If you do change your server’s IP address, you must also change the URL for web client access in
your browser.
followed by the new IP address.
to set the environment, you can run
\oware\temp
. Then restart your machine.
. Change your
Authentication
For successful discovery of the resources on your network, this software requires authenticated
management access to the device. To get this access, you must provide the correct SNMP
community strings, WMI login credentials, and any other command-line (Telnet / SSH) or browser
(HTTP/HTTPS) authentication, and SNMP must be turned on, if that is not the device’s default.
Some devices require pre-configuration to recognize this management software. Consult your
network administrator or the device’s manuals for instructions about how to enable those. See
Authentication on page 143 for more.
24
Supported PowerConnect Models
Refer to release notes for a list of supported devices. You can also look at the HTML files in the
SupportedDevices directory of your installation source for information about supported devices
and operating systems.
Windows Management Interface
The Windows Management driver currently supports any Windows based operating system that
supports the Windows Management Interface (WMI).
Windows Management is always installed on the following operating systems (or later):
• Windows XP Professional (with a browser other than Internet Explorer)
Sizing for Standalone Installations | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
Page 25
• Windows 2003 All Editions
NOTE:
•Windows Vista
The login credentials must be for an administrator on the installation host for complete
functionality. Both this and .NET installation are requirements for any installation managing
devices supported by this driver.
This driver supports global group operations.
Discovery may display benign retry warning messages in the application server shell or log. You can
safely ignore these.
Prerequisites
Before installing this software to manage other computers with a Windows Management Interface
driver (assuming you are installing that driver), if you do not already have it installed, you must
download and install the Microsoft .Net framework version 3.0 or later on the application server.
For complete functionality, the WMI login for this software must be a login for a domain user who
also belongs to the administrator group on the WMI device. Both are requirements for any
installation managing WMI devices.
The following are common Windows Base prerequisites:
Credentials
Firewall
License
—You must use administrative credentials to manage the computer system.
— Some firewalls installed on the computer may block Windows Management requests.
Allow those you want to manage. (See Firewall Issues below.)
—Make sure you have the proper Windows Base driver license installed. If you have a Dellonly license and are discovering a non-Dell computer, discovery does not work. Or if you have
a Dell license for desktop discover you cannot discover a server.
License come in the following types:
• Major Vendor by Name—For example: Dell, Compaq, HP, Gateway
• Server/Desktop individual license support
• Generic computers—Non-major vendors
• ALL—This gives the driver all capabilities for any computer system
Firewall Issues
Configure the firewall between your server and the Internet as follows:
• Deny all incoming traffic from the Internet to your server.
• Permit incoming traffic from all clients to TCP port 135 (and UDP port 135, if necessary) on
your server.
• Open Port 445 (WMI)
Sizing for Standalone Installations | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
25
Page 26

• Permit incoming traffic from all clients to the TCP ports (and UDP ports, if necessary) on
NOTE:
your server in the Ports range(s) specified above.
• If you are using callbacks, permit incoming traffic on all ports where the TCP connection was
initiated by your server.”
WMI queries will succeed only if you add the User account to local admin group. Refer to the
Microsoft knowledgebase articles for the way to do this. For example: Leverage Group Policies with
WMI Filters: support.microsoft.com/kb/555253/en-us
For user rights for WMI access, see: www.mcse.ms/archive68-2005541196.html
See also:
Service overview and network port requirements for the Windows Server system
(support.microsoft.com/kb/832017/)
Web-Based Enterprise Management (WBEM) Driver
The Web-Based Enterprise Management driver currently supports operating systems supporting
the Web-Based Enterprise Management interface (WBEM).
WBEM is always installed on the following operating systems versions (and later):
• Red Hat Linux 5.5 or 6.0
• VM Ware (ESX) with WBEM installed.
You can install Web-Based Enterprise Management on some other systems if they do not already
use it, but monitored devices must have this installed.
26
To verify WBEM is running on your system, run the following command:
should see a process labelled
Installing WBEM on Red Hat
cimserver
.
For Red Hat 5, the latest supported release for WBEM is
2.el5_2.1.i386.rpm
and this is what you need to download once you have logged into the
tog-pegasus-2.7.0-
ps-e | grep cim
Red Hat network.
Install this as follows:
rpm -ih tog-pegasus-2.7.0-2.el5_2.1.i386.rpm
Install:
Upgrade:
To determine if wbem is running, run
rpm -Uh tog-pegasus-2.7.0-2.el5_2.1.i386.rpm
ps -ef | grep cimserver
in a shell.
To start | stop | get status of the WBEM service:
tog-pegasus start | stop | status"
If the system is running Fedora, then you can access tog-pegasus updates at this site:
admin.fedoraproject.org/pkgdb/packages/name/tog-pegasus
Sizing for Standalone Installations | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
. You
Page 27

WBEM Prerequisites
NOTE:
CAUTION:
The following are common prerequisites:
Credentials
Firewall
License
• Major Vendor by Name - Such as Dell, Compaq, HP, Gateway.
• Server/Desktop individual license support.
• Generic computers - non-major vendors.
• ALL - this gives the driver all capabilities for any computer system.
—WBEM credentials have a role in discovering the device. Your system must have
access to the computer using Administrative only credentials. These are the same credentials
as the user installing WBEM on the device.
Telnet / SSH credentials are necessary for other supported applications.
For full functionality, this WBEM device driver requires administrative (root) access. Many
devices may only allow root logins on a local console.
In such cases, configure the Telnet/SSH authentication for these devices to login as a nonroot user—and, in Authentication Manager, enter
the root user’s password in
full device management functionality with root access.
Credentials for Telnet / SSH should have a privilege level sufficient to stop services and to restart the
computer system.
— Some firewalls installed on the computer may block Web-Based Enterprise
Management requests. Allow those you want to manage.
—Make sure you have the correct WBEM driver license installed. Licenses come in the
following types:
Enable User Password
su
in the
Enable User ID
in that same authentication. This enables
field and enter
If you discover an Amigopod host that does not have its SNMP agent turned on, Dell OpenManage
Network Manager labels it a WMI or WBEM host rather than an Amigopod host.
Getting Started
The following section outlines the steps in a typical installation and subsequent first use. Because
the software described here is both flexible and powerful, this section does not exhaustively
describe all the details of available installations. Instead, this Guide refers to those descriptions
elsewhere in the OpenManage Network Manager
A typical installation means doing the following:
Getting Started | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
User Guide
or online help.
27
Page 28

Installation and Startup
network, or anticipate a large number of web clients, then best practice is to install Dell
OpenManage Network Manager as the Administration Section of the User Guide guide
instructs.
Administering User Permissions
for users, as you begin to use it. See Control Panel on page 34.
Discovering Resources
want to manage, and model it in the Dell OpenManage Network Manager database. See
Discovery Profiles on page 65.
Resource Management
Management in this Guide.
Configuration Management
compare configuration files. See Top Configuration Backups on page 277.
Problem Diagnosis
Network Troubleshooting
OpenManage Network Manager’s performance management capabilities.
Reports
Real-time Diagnosis through Collaboration
Unified View
Finally do not neglect what Common Setup Tasks on page 68 describes.
—Run reports to clarify the state of your network and devices. See Reports on page 200 for
details.
both by sending them messages that display the device conditions of concern, and with online
chat within Dell OpenManage Network Manager. See Sharing on page 87, and Status Bar
Alerts on page 75 for details.
—You can scale your Dell OpenManage Network Manager installation to handle the
largest, most complex environments with distributed deployment.
below includes instructions for a basic installation. If you have a large
—You can also set up users, device access passwords, and groups
—After you install the application, you must discover the equipment you
—See Managed Resources on page 68, and Chapter 4, Resource
—Use Dell OpenManage Network Manager to backup, restore, and
—See Alarms on page 99 for information about Fault Management.
—See Alarms on page 99, and Chapter 7, Monitoring for details of Dell
—Collaborate with others about network issues,
28
Installation and Startup
Application server produces the Dell OpenManage Network Manager information for web clients.
It monitors devices, and produces the output which the web server then makes available for those
web clients. See Linux Prerequisites on page 30 for advice about installing to Linux.
Initiate installation by executing
Click through the installation wizard, accepting the license and making the appropriate entries.
During some installations, one screen lets you select the application’s memory size. Best practice is
to select the largest available on your hardware while leaving sufficient memory for the operating
system.
Installation and Startup | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
win_install.exe
(Windows) or
linux_install
(Linux).
Page 29

Heap
CAUTION:
Memory on a single machine installation serves the operating system, database and web server. You
can configure the selected application server heap memory size any time, with the following
properties in \owareapps\installprops\lib\installed.properties:
oware.server.min.heap.size=8192m
oware.server.max.heap.size=8192m
To manually change Dell OpenManage Network Manager web portal heap settings, change the
setenv.sh
JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Dfile.encoding=UTF8 -Xmx1024m -XX:MaxPermSize=256m"
The file is in
directive in front of the line and change the
file:
/opt/dorado/oware/synergy/tomcat-x.x.x/bin
-Xmx[max memory]
setting as appropriate. For
. Add the
export
example, for 8G:
export JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Dfile.encoding=UTF8 -Xmx8192m -
XX:MaxPermSize=256m"
To manage Windows systems—in single server deployments, you must install this application on a
Windows host. In distributed deployments, a mediation server that supports WMI must communicate to
managed Windows systems.
Windows installation also installs Internet Information Services (IIS)—formerly called Internet
Information Server. That installation does not turn IIS on by default. Do not enable IIS on the host(s)
running Dell OpenManage Network Manager.
Also: Do not install if you are logged in as user “admin.”
Installation and startup include:
• Running the installer, responding to its prompts.
•
Starting application server
OpenManage Network Manager
command shell, or right-click the server manager tray icon and select
installed Dell OpenManage Network Manager as a service
•
Starting web server
OpenManage Network Manager
to start it. You can also double-click this icon and automate web server startup.
On Linux start (or stop) the web server with scripts
startportal.sh stop
. In Windows, you can use the
> Start application server
. If this does not auto-start, you can use the
> Synergy Manager
), or right click the web server’s tray icon
startportal.sh start
Start
), or type
button (
startappserver
Start (
Start >
if you have
and that icon is red, not green
Start
button (
Start >
(or
in a
).
) located in the oware/synergy/tomcat-x.x.x/bin directory.
Installation and Startup | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
29
Page 30

•
CAUTION:
NOTE:
CAUTION:
NOTE:
Starting the Client
OpenManage Network Manager
and go to the web address
. The client provides the user interface. In Windows, click
> Synergy
hostname:8080
, or after starting the web server, open a browser
where
hostname
is the name of the machine
Start >
running application server (or it’s IP address). See Starting Web Client on page 33 for more
information.
If you are using Dell OpenManage Network Manager in an environment with a firewall, ports 8080 and 80
must be open for it to function correctly. If you want to use cut-through outside of your network then
ports 8082 – 8089 must be open. Dell OpenManage Network Manager uses the first one available, so
typically 8082, but if another application uses 8082, Dell OpenManage Network Manager uses 8083 and
so on.
• Start using Dell OpenManage Network Manager as outlined in Getting Started on page 27, or
below.
Linux Prerequisites
If you are installing on Linux, you must log in as a non-root user. Linux installation prompts you to
run some additional scripts as root.
When installing to Linux, ensure you are installing as a user with the correct permissions, and are
in the correct group. You must configure the installation directory so this user and group have all
permissions (770, at least). You may install without any universal (“world”) permissions. However,
you must create a home directory for the installing user.
30
All files created during installation respect a umask of 007. All files from setup.jar are 770. Files from
ocpinstall -x are set for 660. Bin scripts from ocpinstall -x are 770.
Best practice is to install as the user designated as DBA and admin of the system (
not
root user). If
necessary, create the appropriate user and login as this user for running the install program. The
installing user must have create privileges for the target directory. By default, this directory is
dell/openmanage/networkmanager
Linux sometimes installs a MySQL database with the operating system. Before you install this application,
remove any MySQL if it exists on your Linux machine.
To set the environment correctly for command line functions, after installation, type
etc/.dsienv
Also: This application can run on any Linux desktop environment (CDE, KDE, Gnome, and so on) but the
installer will only install shortcuts for CDE.
Installation and Startup | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
in UNIX—[dot][space]/etc/[dot]dsienv) before running the specified command.
.
oware
(or
/
. /
Page 31

File Handles
How To:
CAUTION:
Best practice is to modify file handles for Linux. If you do not do this, exceptions appear in
application server log every fifth minute. To prevent this, alter
limits.conf.
Here, administrators can set hard and soft limits for the file handles for users and
/etc/security/
user groups. These settings take effect on reboot. Best practice is to set the following for
OpenManage Network Manager on a single machine:
<Installing User> soft nofile 65536
<Installing User> hard nofile 65536
<Installing User>
You can also check/set file handles temporarily using the
is the installing user login. Set these higher for more heavily used systems.
ulimit -H/Sn
command. Like the
following:
$ ulimit -Hn
$ ulimit -Sn
Set Linux Permissions
These following ensures appropriate permissions exist so that the install succeeds on Linux. Your
steps may vary slightly depending on the version on which you install.
1
Create a user, for example “redcell.”
2
Ty pi ca ll y t he
3
In any case, ensure that user
redcell
4
Create
owns
/dell/openmanage/networkmanager
/dell/openmanage/networkmanager
installation root.
redcell
user’s home directory resembles
redcell
owns its home directory (the
directory).
/dell/openmanage/networkmanager
is Dell OpenManage Network Manager’s
/export/home/redcell
/export/home/
, and ensure that your user (
.
redcell
)
5
If necessary, unzip the downloaded installation package into a subdirectory under user
redcell
6
Ensure the unzipped script file
7
Log in as user
Do not install root. During the installation a prompt appears to execute a script as root. This means you
need root password and must open another shell where you act as root.
8
Execute
’s home directory.
redcell
linux_install
Installation and Startup | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
linux_install
has execute permissions.
, this begins the installation process, and follow the prompts.
31
Page 32

Uninstalling
NOTE:
Use Control Panel to uninstall in Windows. Uninstall by running the following on Linux:
$OWARE_USER_ROOT/_uninst/uninstall.sh
You must uninstall from Linux as root. No graphic wizard appears, and you must respond to the
command-line prompts as they appear.
SNMP in Multi-Homed Environment
Trap listener, Inform listener and all outbound SNMP requests must bind to a specific interface in
a multi-homed environment. This interface is considered appropriate to use for all network-facing
SNMP activity. By default, this is localhost, interpreted as the application's local IP value (the NIC
selected at installation time). The following text in installed.properties provides a specific IP
address to control outbound SNMP interface binding on the local machine:
# specific interface used for all NMS initated
# communications to the network
com.dorado.mediation.outbound.address=localhost
Include the following text and provide a specific IP address to control inbound (listener) interface
binding on the local machine:
#
# specific interface used for binding mediation
# listeners such as SNMP trap listener
com.dorado.mediation.listener.address=localhost
Events with no corresponding definition appear as alarms of indeterminate severity. The only way
to change behavior of an unknown event in this version would be to locate the missing MIB and
load it into the system. This creates the missing event definition(s) needed to specify explicit
behaviors.
32
Perl
If you install Perl to take advantage of this application’s use of Perl Scripting capabilities, you must
install it on the path on the application server and mediation server host. Best practice is to use Perl
version 5.10 or later because some applications also require Perl as well as the Perl module
Net::Telnet.
This application does not package Perl. If you want to use the Perl scripting features, you must
make sure your system has Perl installed. You can find information about Perl at
Follow the downloads link to find the recommended distribution for your specific platform. (See
Adaptive CLI Script Language Syntax on page 366)
Installation and Startup | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
www.perl.com.
Page 33

One of the recommended Perl packages is from ActiveState which can be found at:
CAUTION:
www.activestate.com/activeperl/
Starting Web Client
You can also open the client user interface in a browser. See Supported Web Browsers on page 19.
The URL is
http://[application server hostname or IP address]:8080
The default login user is
a password reminder. If you have forgotten your password, click the
admin
, with a password of
admin
. The first time you log in, you can select
Forgot Password
link in the
initial screen to begin a sequence that concludes by mailing your user’s e-mail address a password.
For this forgotten password sequence to work, you must configure users’ e-mails correctly. Click the link
that is your user name in the upper right corner of the portal to configure your account’s settings for this
and other things. The same configuration settings are available in Control Panel’s tabs labeled as your
login.
The
application server hostname
is the name of the system where OpenManage Network Manager
is installed.
HTTPS
You can connect to application server securely by configuring the included Apache Tomcat server
for secure access. Consult your favorite search engine for more detailed information about setting
up SSL with Tomcat web servers.
The following sections discuss typical administrative steps in getting started, once you have
installed OpenManage Network Manager. See Getting Started on page 27 for a list of, and links to,
other initial tasks once you have installed Dell OpenManage Network Manager.
Changing the Session Timeout Period
The timeout for the web portal extends automatically if data is changing onscreen. Nevertheless,
you can change the timeout period with (non-override-able) properties in some files, as follows:
You must modify two
controls the overall server and the other is the push servers for Async-based views. These
files are in the following directories:
/dorado/oware/synergy/tomcat-XX/webapps/ROOT/WEB-INF/web.xml
And
/dorado/oware/synergy/tomcat-xx/webapps/netview/WEB-INF/web.xml
The xml element that contains the session timeout is
<session-config>
web.xml
files with the same values to alter the session timeout. One
web.xml
Installation and Startup | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
33
Page 34

<session-timeout>30</session-timeout>
</session-config>
The
portal.properties
containing the session timeout (in minutes) is:
session.timeout=30
file is in
/portal/portal-impl/classes
. The property
Control Panel
To configure access to Dell OpenManage Network Manager, you must be signed in as a user with
the permissions. (The default
item opens a screen with the following tabs of interest:
• [My Account]
•RCSynergy / [Domain]
• Portal > Users and Organizations
•Portal > Roles
•Portal > Portal Settings
•Portal > [Other]
• Redcell > Permission Manager
• Redcell > Database Aging Policies (DAP))
• Redcell > Data Configuration
• Redcell > Mediation
• Redcell > Filter Management
•Server
Tips describing these screens and fields appear
when you hover the cursor over fields, or click the
blue circle around a question mark next to them.
This blue circle can also toggle the appearance /
disappearance of the tip.
Users with less-than-Administrator permissions may not see all of the features described in this
guide.
admin
user has such permissions.) The
Go to > Control Panel
menu
34
Search Indexes
Sometimes Dell OpenManage Network Manager may display Control Panel objects like users,
roles, and organizations inaccurately. This occurs because search Indexes need to be re-indexed
every so often, especially when changes to roles, users and organizations are frequent.
To re-index go to Control Panel > Server Administration and then click on the
indexes
. This takes little time.
Control Panel | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
Reindex all search
Page 35

[My Account]
Tip
To configure information for your login, look for the bar titled with your account login’s name. It
has the following lines beneath it:
My Account
and so on.
My Pages
that appears on the left of this screen to drag and drop pages in the order you want. Notice
that you can also configure the look and feel, the logo that appears and other settings with the
editor screens on the right.
Contacts Center
are following. Click the
Yo u m us t c li c k
button to explore other possibilities.
The contact has to approve you in their requests. To
followed person’s activity stream, blog postings, and so on.
see your activity and you can see theirs. They have to accept any
You can export vCards for all contacts in the system to use with other software that uses contacts. For
example: e-mail clients.
—This configures your information as a user, including your e-mail address, password,
—This manages public and private pages visible to you as a user. Use the tree of pages
—This configures contacts, in other words, people within your system that you
Find People
Action > Follow
link to see a list of potential contacts within your system.
to see them listed in the
Contacts Home.
Follow
means you want to receive the
Friend
ing means your friends can
Friend
Use the
request.
Action
RCSynergy / [Domain]
RCSynergy appears as a default domain name in
configurations appear as additional items to configure when you click the down arrow to the right
of RCSynergy.
The items under this label configure the overall look and feel of the portal, reference information,
and so on. See the tooltips for more complete descriptions. This also configures pages, documents,
calendars, blogs, wikis, polls and so on.
Social equity
determine the reward value of an action; equity lifespans determine when to age the reward of
action.
lets you alter measurements for user participation in organizations. Equity values
Control Panel | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
Control Panel. Global
and
[My Login’s] Site
35
Page 36

Portal > Users and Organizations
NOTE:
How To:
Create organizations and locations in addition to groups with the appropriate permissions
(operators, administrators, and so on) in these screens. Users are individuals who performs tasks
using the portal. Administrators can create new users or deactivate existing users. Users can be
organized in a hierarchy of organizations and delegate its administration.
After creating them, add Users to roles which configure their permissions for access and action.
By default, every user is assigned to the role User. To assign a new user to specific permissions only,
remove all rights on the User role, or confine its permissions to those that are universal first. Even though
you don't see that user assigned to the User role, Best practice to spend some time designing your
system’s security before creating users, organizations and roles.
When you are signed in, edit your user information by clicking the link with your username in the
top right corner of the screen. Your user name does not appear in this screen.
Notice that if you select
component locations, groups and users.
Add Users and connect them to Roles
Add Users with the following steps:
1
Click
Go to > Control Panel
36
Control Panel | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
View > Hierarchy
and navigate to Portal > Users and Organizations
you can see organizations, grouped together with their
.
Page 37

2
Tip
Tip
Click the
3
Enter the details of the new user. If you are editing an existing user, more fields appear.
Name,
4
After you click
Make sure you specify a
5
Notice that if you are editing an existing user, or creating a new one, you can use the links on
the right to configure connections with
Add > User
and
Email Address
Save
menu item at the top of the
are required. Optionally, you can enter
Users and Organizations
Name, Job Title
screen.
notice that the right panel expands to include additional information.
Pas sw or d
.
Roles.
Roles, in particular, configure the OpenManage
Network Manager functional permissions for that user. For example the group of
would likely have more limited capabilities than
6
Click
Save
again, and the user you just configured should appear listed in the
Organizations
7
To assign a user to a role, click
screen when you select
Action > Permissions
View > All Users
Administrators
.
Users and
.
and check the appropriate box next to
the role. Configure OpenManage Network Manager functional permissions for these roles in
Roles (see Redcell > Permission Manager on page 42).
You can Export Users to a comma-separated value (CSV) file.
Once you have configured a user, you can click
Edit
—Re-configure the selected user. Select the user’s Role in the editor, too. Roles configure
Action
and to do the following:
access and action permissions.
Permissions
Manage Pages—
—Manage the user’s access to and control over various parts of the portal.
Configure the
Public
or
Private
pages for a user, depending on the selected tab.
Possible actions here include changing the look and feel of pages (for computers and mobile
browsers), adding pages and child pages, and importing or exporting page configurations.
Notice that you can configure meta tags, and javascript on these pages too.
Exports are in
.lar
format, and go to the download location configured in the browser you
are using. The export screen lets you select specific features, and the date range of pages to
export.
Screen
, and so on.
Operators
If you want to set up several pages already configured elsewhere for another user, or even for an entire
community of users, export those pages from their origin, then Manage > Pages menu for the user or
community.
Impersonate User
Impersonate User (Opens New Window)
—Open a web client with the same permissions as the user configured here.
—This allows you to see the effect of any configuration
changes you have made on a user. The new window (typically a new tab) also lets you click the
Sign Out
link in the upper right corner where you can return to your original identity
impersonation concealed.
Control Panel | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
37
Page 38

Deactivate
Tip
NOTE:
How To:
—Retires a user configured on your system. You can also check users and click the
Deactivate
state. You can do an Advanced search for inactive users and
button above the listed users. Such users are not deleted, but are in a disabled
Activate
them or permanently
delete them.
Your organization has a number of geographic locations and you plan to manage the network
infrastructure for all these locations using RC7 Synergy. You can define the geographic locations to
which devices can be associated. This will help you manage and view your network, grouped by
location or branches. See Locations on page 135 for the specifics about the portlet where you can
set up locations.
To edit your own information as a signed-in user, simply click your login name in the upper right corner of
the portal screen.
Organizations
Create Organizations just as you would create Users. You can create a
Regular
or
Location
type of
organization.
You must first create a Regular organization to be the parent for a Location.
Configure Organizations
Follow these steps to configure organizations. Associating organizational roles with organization
members empowers them to exercise the associated permissions within the organization’s site(s).
1
2
3
4
38
Control Panel | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
Create a new
Regular
organization (
Add > Regular Organization
named MyCorp) as the
parent of location organizations.
Notice that you can add much more identifying information once you have saved the basics
(
Name
and
Description
) for the organization. This includes an
Organization Site
(a
checkbox) that would create a separate portal for the organization, to which you can add and
configure pages, portlets, and so on.
Create two
Location
organizations (
Add > Location
, for example Admin and Headquarters).
Select MyCorp as the parent when you create the organization.
Create users in MyCorp. TestUserA, TestUserB, and TestUserBoss.
Page 39
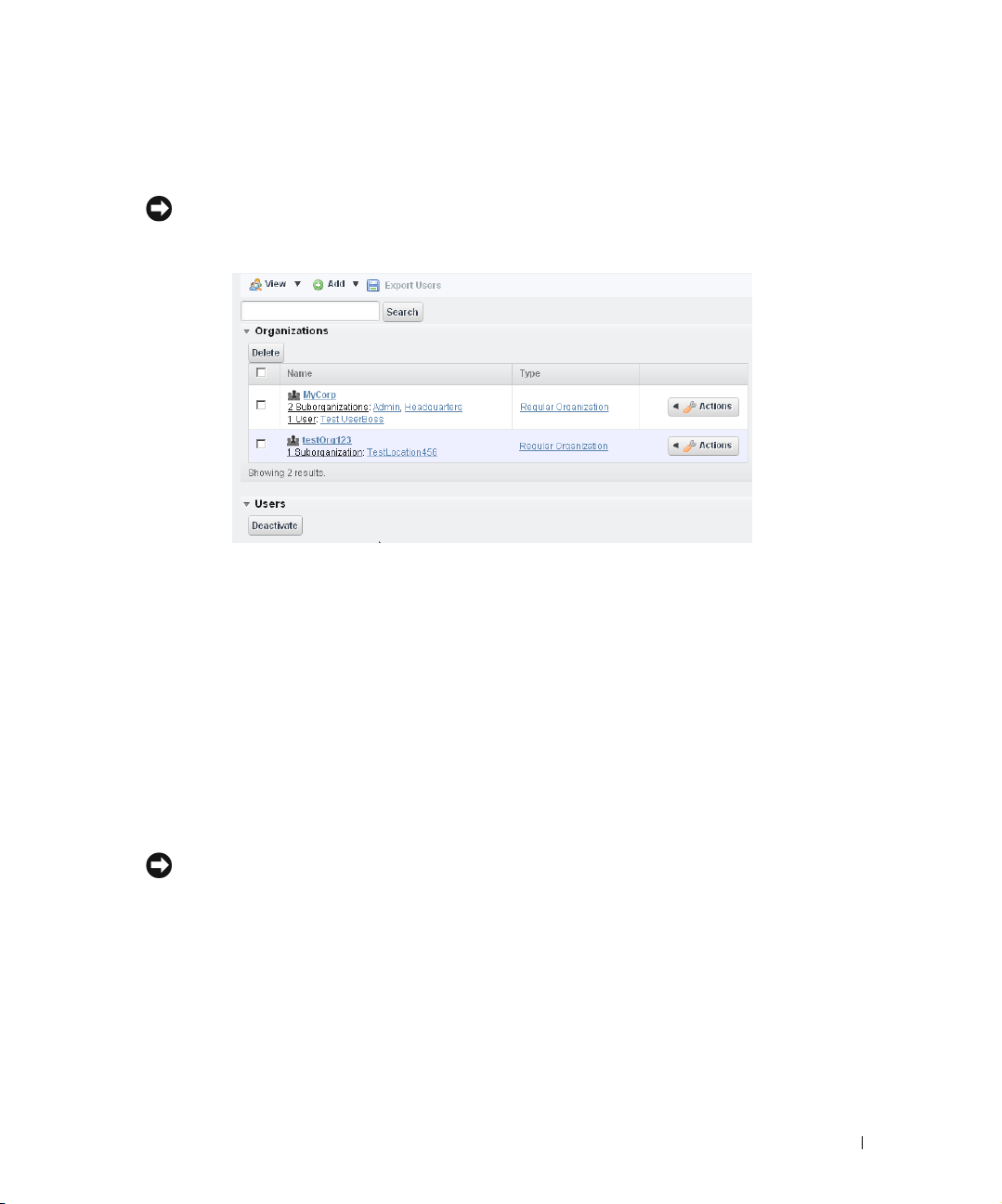
5
Tip
Tip
As you create these users, add each to one of the MyCorp organizational children, Admin or
Headquarters.
Notice that you can View > Hierarchy to see the parent / child relationships between organizations.
Users unassigned to organizations also appear below this portion of the screen.
Click MyCorp, and a screen appears displaying its components and a management menu
6
where you can add additional properties.
7
Click
8
Assign Organization Roles
Select
Organization Administrator
in the MyCorp menu.
from the default roles available.
If you need permissions other than this administrative user provides, you can create an
organization role with the correct permissions in Portal > Roles.
9
Click the
10
Click
11
You can click the Admin location, and similarly configure its user as associated with an
Available
tab, and select TestUserBoss as the organization’s administrator.
Update Associations.
organizational role. Do the same for Headquarters.
You are a member of the organization you created, because you created it. By creating an organization,
you become both a member and have the Organization Owner role, which gives you full rights to the
organization.
Control Panel | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
39
Page 40

Public / Private Page Behavior
Tip
How To:
Public pages are visible to everyone; private pages are only visible to the user who created them, and
are not vulnerable to others changing their arrangement. Page Standard settings are
Default Filter, Max Items per Page
for users who have the portlet on their Public or Private pages (which makes them the owner of that
instance).
Some portlets provide extra settings—for example Alarms portlet’s the charting options, or the
portlets number of Top Items. These persist too.
N
Max Items, Max Items Per Page and Columns persist for both the summary and maximized portlets
independently. For example: If Max Items is 50 in minimized mode it does not affect the Max Items in the
Maximized window state. This lets you configure modes independently.
Dell OpenManage Network Manager remembers the default sort column and order per user,
whether the user has Admin rights or not. The Sort Column/Order (Descending/Ascending) is
also shared between both summary and maximized portlets. A sort on IP Address in Resources
persists if you expand the summary portlet to maximized mode.
Add and Configure User Roles / Permissions
Add and configure User Roles with the following steps:
1
Click
Go to > Control Panel
2
Click the
that you can also add roles that configure permissions for sites and organizations.
3
Enter the details of the new role (
4
Click Portal > Roles’
added.
5
By clicking the
permissions to alter web portal access in a subsequent screen.
6
Click
7
To do more with Dell OpenManage Network Manager’s functional permissions, go to the
Redcell > Permission Manager, and click to open this screen.
8
The Role to Permission mapping screen appears. Click the
Roles to see and configure available permissions.
9
Click
actions.
Add
tab under the heading at the top of the page, and select Regular
View All
Action
icon to the right of any listed Role, you can also select the role’s
Add
to add permissions. Click the checkboxes to enable the type of permission desired.
Advanced
to see available permissions organized by
Max Items
, and
Column Configuration
and navigate to Portal > Roles
Name, Title, Description
. These persist for Admin users or
.
Roles
. Notice
), then
Save
it.
button to see a list of available roles, including the one you
Edit
button to the right of listed
Read, Write, Execute, Add
or
,
To p
Delete
40
Control Panel | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
Page 41

10
NOTE:
CAUTION:
After you have selected permissions, click
Notice that you can revisit this role, manage it and its membership with the
the right of the role. You can also add users to the group by selecting and editing that user.
Apply
to accept them and add them to the role.
Action
button to
Portal > Roles
Roles determine the applications permissions available to users assigned them; manage them in
this screen. To configure functional permissions for the application, see Redcell > Permission
Manager on page 42.
Click
Add
to create a
permissions to its members. A
organization to which you can assign users.
Click the
(this last works to see and assign users)
Organizations
Notice also that when you
Sites, Organizations
collective designations, then assign the collection to a role.
Notice also that you can view both
even
Click
their
Action
Owner Roles do not have an Action button. Owner implies something you have added or created and so
actions do not apply.
Search
for members.
Back
(in the upper right corner) or the
Action
buttons.
Regular Role, Site Role,
Site
or
Organizational Role
button to the right of a role to
. Y
ou can also assign role members in the Portal > Users and
user editor
.
Assign Members,
and
User Roles.
Typical best practice is to assign users to one of these
Current
or
Organizational Role.
assigns its permissions to a site or
Edit,
view or alter
a screen appears with tabs where you can assign
and
Available
View All
members with those sub-tabs. You can
tab to return to the screen listing roles and
A
Regular Role
Permissions, Assign Members
assigns its
Users,
Portal > Portal Settings
The
Settings
about Dell OpenManage Network Manager. These include the following:
•Mail hosts
• Email notifications, who sends them, what the contents are for account creation notices, or
• Identification, including address, phone, email and web sites.
• Display settings
• Google Apps login / password.
screens are where users who are administrators can configure the most basic things
password change / reset notices.
Checking Allow Strangers to create accounts may produce a defective login screen.
Control Panel | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
41
Page 42

Portal > [Other]
Some of the remaining portal labels permit the following:
Sites
—Configure sites. Sites are a set of pages that display content and provide access to specific
applications. Sites can have members, which are given exclusive access to specific pages or
content.
Site Template
Page Templat e
Password Policy
expiration, and assign them to users.
Custom Fields
Folders, Calendar Events, and so on.
Monitoring
is usually turned off in production for performance reasons.
Plugins Configuration
administrators can add portlets / plugins to their pages.
—Configures pages and web content for organizations.
—Configures a page and portlets, as well as permissions.
—Configure the security policies you want, including user lockout and password
—Lets you configure custom fields for Blog entries, Bookmarks or Bookmark
—Lets you see all the live sessions on the portal. Click a session to see its details. This
—Configure role access to portlets and features. By default, only
Redcell > Permission Manager
Manage Permissions to manage user access to different features. These are configured as part of
Roles, which aggregate users regardless of community affiliation. Create Roles with Portal > Roles.
The
Users
editor screen accessible from the
Organizations lets you manage groups to which Users are assigned.
Action
menu for users listed in Portal > Users and
42
Control Panel | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
Page 43
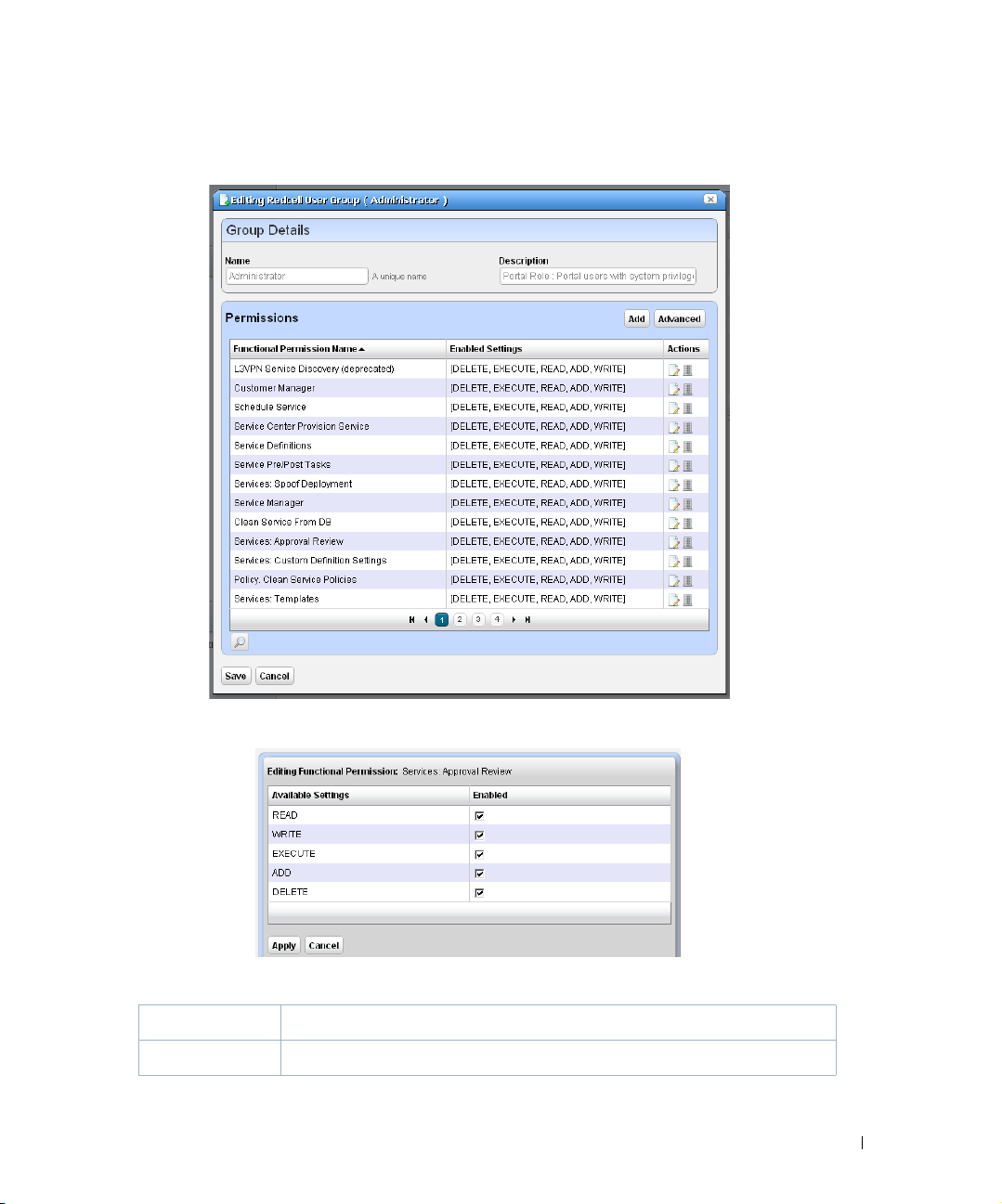
Click the
Edit
permissions.
button (the pencil and paper) to the right of a listed group to see and configure its
Edit permissions with the
Edit
button to the right of the listed permission.
The following describes the actions of the permissions, when checked:
Action Default Behavior
read Enables Details, Visualize and View as PDF
Control Panel | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
43
Page 44

Tip
Action Default Behavior
write Enables the Edit, Save, and Import / Export.
execute Lets you see the view altogether, launch from a portlet and query for
elements. Alternatively this action can control a specific application function,
(typically described by the permission name) like provisioning a policy.
add Enables the New menu item, and Save. If you do not check this action, then
the New menu item does not appear.
delete Enables the Delete menu item.
The
Add
and the
READ
button on the
Advanced
permissions.
Per mis sio ns
button lets you configure permissions by type. For example, if you want to see all of the
panel lets you add permissions previously deleted, if they are available,
44
When you hover the cursor over a functional permission, tooltips provide a description. You can also
click on the Search button at the bottom to find a phrase within the functional permissions.
Control Panel | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
Page 45

Redcell > Data Configuration
This panel configures custom attributes for Dell OpenManage Network Manager. Click the
button next to the
which you want to create custom attributes.
This opens an editor listing the available custom attributes for the entity type. Edit Custom
Attributes on page 89 describes right-clicking to access this directly from the portlet menu, and the
details of how to edit custom attributes.
Entity Type
(Managed Equipment, Port, Contact, Vendor, or Location) for
Edit
Control Panel | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
45
Page 46

Redcell > Mediation
NOTE:
This panel monitors mediation servers in your system, appearing only when such servers exist.
Mediation servers appear listed in the
connected to application server(s).
Mediation server, routing entries and partition entries appear automatically when mediation server
connects for the first time. You can test connectivity from appserver cluster and medserver/
partition.
You can export or import both server and partition configurations. Use the button on the right
above the listed servers or partitions to do this. Importing Partitions/MedServers overwrites those in
the database with the same names. Exporting a partition exports contained medservers too.
Importing a partition looks for overlapping routing entries and saves the partition with only its
unique entries. If no entries are unique, the partition is not saved.
Servers
tab of this manager if mediation servers are
46
This panel does not appear if you install Dell OpenManage Network Manager in stand-alone mode,
without a separate mediation server. To make it appear, add
portal-ext.properties
Overriding Properties on page 23.
Control Panel | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
. Remember, best practice is to override properties as described in
medserver.support=true
to the
Page 47
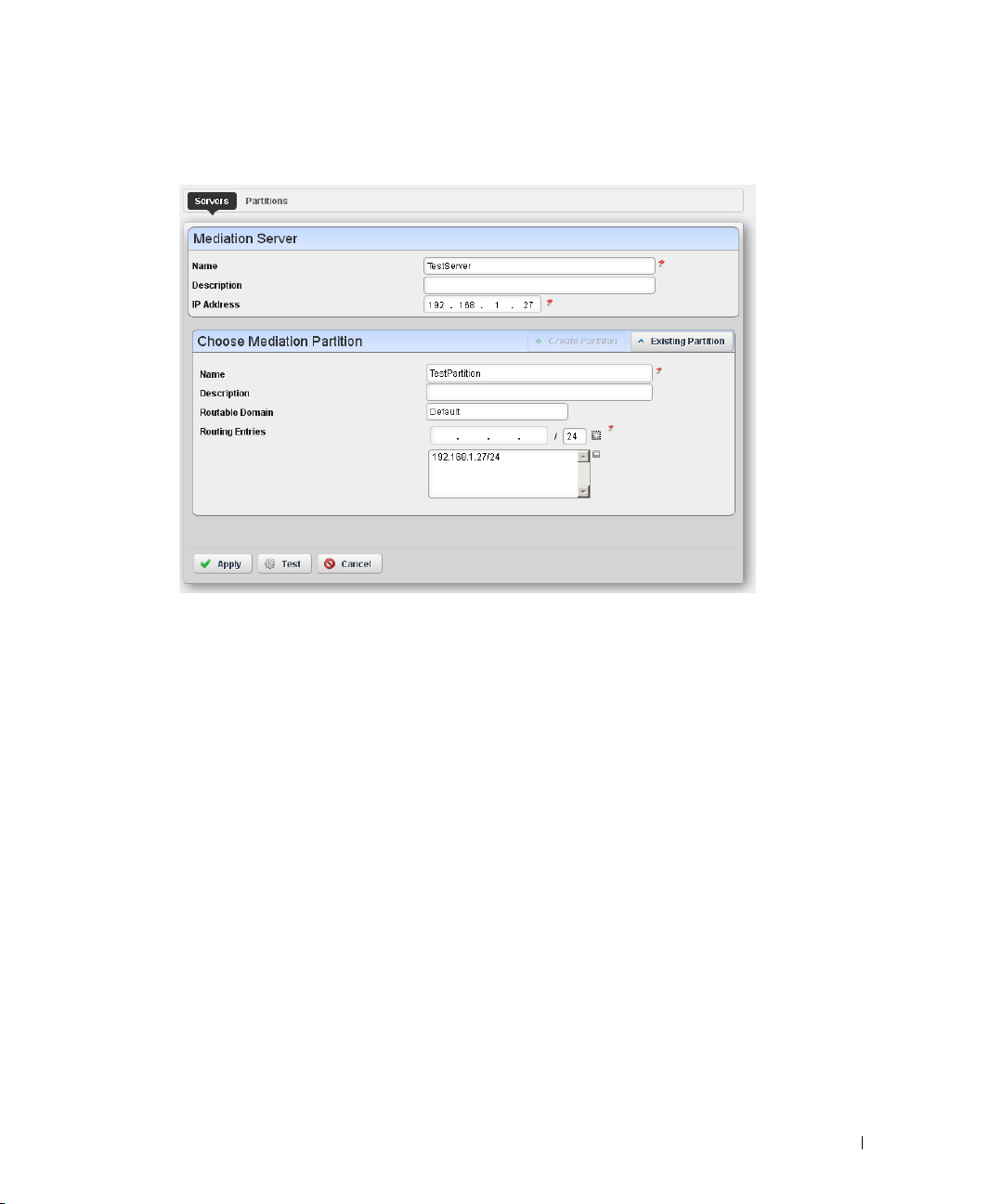
In addition to automatically detecting mediation servers, you can click
additional mediation servers.
Add Server
to configure
When creating a new server, enter a
(or select from
Entries
(click the ‘+’ to add your entries to the list).
Te s t
The
Existing Partition
s), choosing a
button scanning the ports in the proposed application server / mediation server link,
Name, Description
Name, Description, Routable Domain,
and
IP Address
. You can also
Add Partitions
and
Routing
validating the installed versions of Dell OpenManage Network Manager in both locations are the
same, and validating the connection between application server and mediation server. A job screen
like those described in
The
Par ti ti on s
tab of the Mediation monitor displays already-configured partitions, and lets you
edit them with an
Test listed partitions with the gear icon to the right of the partition, or delete it with the
entry
icon.
Audit Trail / Jobs Screen on page 91
Edit this entry
icon. The editor screen is like the one that adds new partitions.
Control Panel | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
appears to track the progress of testing.
Delete this
47
Page 48
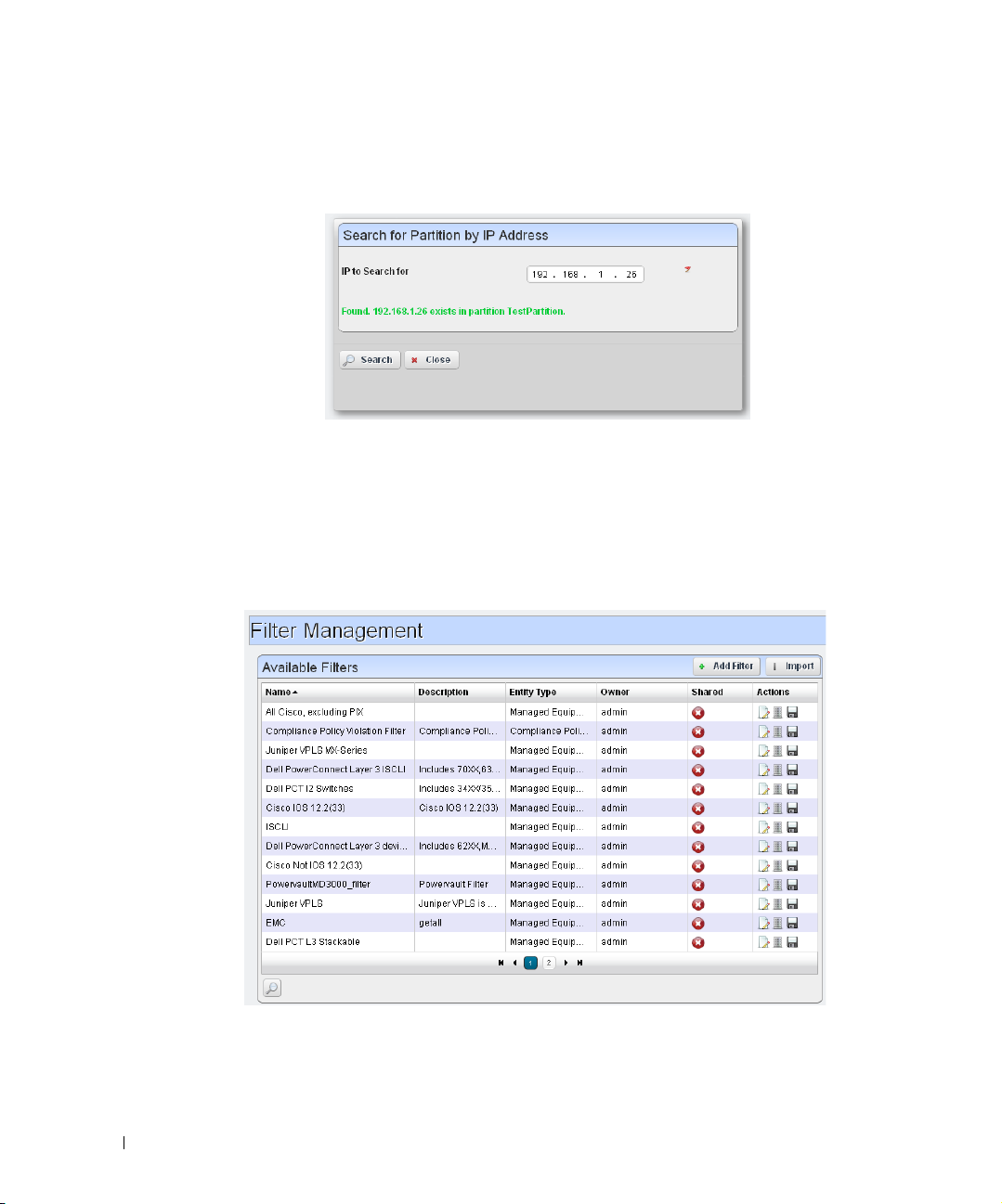
Search for Mediation Server
The
Search
button in the
enter an address in
Par ti ti on s
IP to Search for
tab of the Mediation monitor opens a screen where you can
.
Clicking
does not determine whether that partition is up and running).
Search
locates the mediation partition that services the entered IP address (although it
Redcell > Filter Management
This screen, accessible from
Network Manager.
Go to > Control Panel
lets you manage the filters in OpenManage
48
Control Panel | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
Page 49

Click the
Tip
to export the filter. Clicking the
exported filters.
Clicking the
editor.
Delete
icon to the right of a listed filter to remove it from the system. Click the disk icon
Import
button at the top of the screen lets you import previously
To find a particular filter, click the Search (magnifying glass) icon in the lower left corner of this screen.
Edit
icon to the right of a listed filter, or clicking the
Add Filter
button opens the filter
Use this editor to configure filters. Enter a
select an entity type. If you check
groups of filter criteria (click
filter in the
page 85. Delete filters with the
Criteria Group
Shared
to make the filter available to all users. You can add
Add Group
panel as described in the How to: Filter Expanded Portlet Displays on
Delete this entry
) that logical
Description
AND
icon next to the edit icon.
, and use the green plus (+) to
or OR with each other. Configure the
Name
and
Server
This portion of the
screens appear when you hover the cursor over fields, or click the blue circle surrounding a question
mark in the title bar. Here are some of its functions:
Control Panel
lets you manage the portal’s web server. Tooltips describing these
Control Panel | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
49
Page 50

Server > Server Administration
Tip
NOTE:
caching, search indexes, file upload maximums, e-mail settings, and so on. See Search Indexes
on page 34 for a description of a particularly important function.
This panel is visible to administrators only, and contains helpful settings and resource information related
to the server.
Server > Portal Instance
Server > Plugins Installation
you add portlets besides those available from Dell OpenManage Network Manager. You can
install free portlets for Google, Youtube, Collab and more. For Dell OpenManage Network
Manager, we include Wikis, Journals, Blogs so, in addition to the collaborative features within
Dell OpenManage Network Manager itself (as in Sharing on page 87, and Status Bar Alerts on
page 75). This means you can collect the knowledge and advice of those managing your
network as it expands or changes. To experiment with this screen’s capabilities, click the
Install More Portlets
Server > Updates Manager
As long as portlets adhere to open source portlet specifications, you can install them.
—Monitor resources and administer settings like logging,
—Lets you configure more than one portal instance on your server.
—Configure portlet theme and layout plugins here. This panel lets
button near the top and explore the subsequent screens.
—Plug-in versioning, uninstalling, and updating.
Redcell > Database Aging Policies (DAP)
50
Database Aging Policies prevent the Dell OpenManage Network Manager database from filling up
by filling up by deleting old records. You can also save designated contents to an archive file on a
specified cycle. Database Aging Policies configure which contents to archive, the archive location,
and the configuration of that archive file.
Redcell > Database Aging Policies (DAP) | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
Page 51

To view and manage such policies, right click an item with them (for example, an alarm), or click
How To:
Manage > Control Panel
, and under Redcell click
Database Aging Policies.
Policies appear in the
policy is
three
you
Enabled,
Actions (Edit, Delete
Enable / Disable / Execute All
Aging Policies
the
Policy Name, Details
and
Execute
tab of this screen, with columns that indicate whether the
). Notice that the bottom right corner of this page also lets
policies listed.
DAP Workflow
The following are steps typical for implementing DAP:
1
From the screen listing Database Aging Policies (DAP), click
from the displayed list of alternatives.
2
This opens Aging Policies Editor.
3
In the
Aging Policies > General
is
Enabled
4
Specify the
You can manage those on that tab.
, and so on.
Archive Location
Redcell > Database Aging Policies (DAP) | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
tab, specify the name, schedule interval, whether this policy
. Those listed are the
(description),
Repositories
Scheduled Intervals
Add Policy
listed on the Repositories tab.
and icons triggering
, and select a policy
51
Page 52

5
In the Aging Policies Options tab, specify either the archiving and retention you want, or
further specify Sub-Policies that refine the items archived, and specify archiving and retention
for those sub-policy elements. Which one you can specify depends on the type of DAP you
are configuring.
6
Click
Apply
until the displayed screen is the DAP manager.
Aging Policies Editor
When you click
(DAP) screen, first a selector appears where you can click on the kind of policy you want to create,
then the editor appears. If you click the
Editor appears with that policy’s information already filled out, ready to modify.
The
General
Name
—An identifier for the policy
Description
Enabled
Schedule Interval
here, you can re-configure it in the Schedules Portlet.
Base Archive Name
Compress Archive
Archive Location
Add Policy
screen has the following fields:
—A text description of the policy
—Check to enable the policy.
—Use the pick list to select an interval. Once you have configured an interval
—Check to compress the archive file.
—Select from the available Repositories in the pick list.
in the upper right corner of the Redcell > Database Aging Policies
—The prefix for the archived file.
Edit
icon to the right of a listed policy, the Aging Policies
52
Redcell > Database Aging Policies (DAP) | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
Page 53

The contents of the
Options
tab depend on the type of DAP you are configuring. Typically, this tab
is where you set the retention thresholds.
DAP SubPolicies
Some Options tabs include sub-policies for individual attribute retention.
Add SubPolicy
Click
or click the
Edit
button to the right of listed policies to access the editor.
Editing Tips
Archiving options that appear in the Aging Policies Editor vary, based on type of policy
selected. Inventory Change Tracking DAPs ask how long you would like to keep Config
reports, Inventory Report DAPs ask how long you would like to keep your Historical Reports
based on number of instances, days, and weeks, months or years.
Set these thresholds in the
Check the
Enabled
checkbox to enable the policy.
DAPs run on a schedule. If the record threshold number is greater than or equal to the
configured threshold then the DAP runs at the scheduled time. You may also manually click
the gear icon to the right of a listed policy, and execute a DAP at any time to check that
threshold figure. In either case, if the threshold is not crossed Dell OpenManage Network
Manager creates no archives.
To verify when current DAPs are scheduled to run, open the Schedules portlet, and select the
schedule on which it runs. For most DAPs, this is the Daily (recommended) DAP. Right-click
to edit it. The Scheduled Aging Policies list should include all DAPs that have selected that
schedule.
Options
tab. All DAPs require a Name and a record threshold.
Redcell > Database Aging Policies (DAP) | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
53
Page 54

Aging Policies Options
The
Options
Typical fields can include the following:
Keep [Aged Item] for this many days
archiving it.
Archive [Aged Item]
tab in this editor can vary, depending on the type of policy.
—Check this to activated archiving according to this policy.
—The number of days to keep the aged item before
54
Redcell > Database Aging Policies (DAP) | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
Page 55
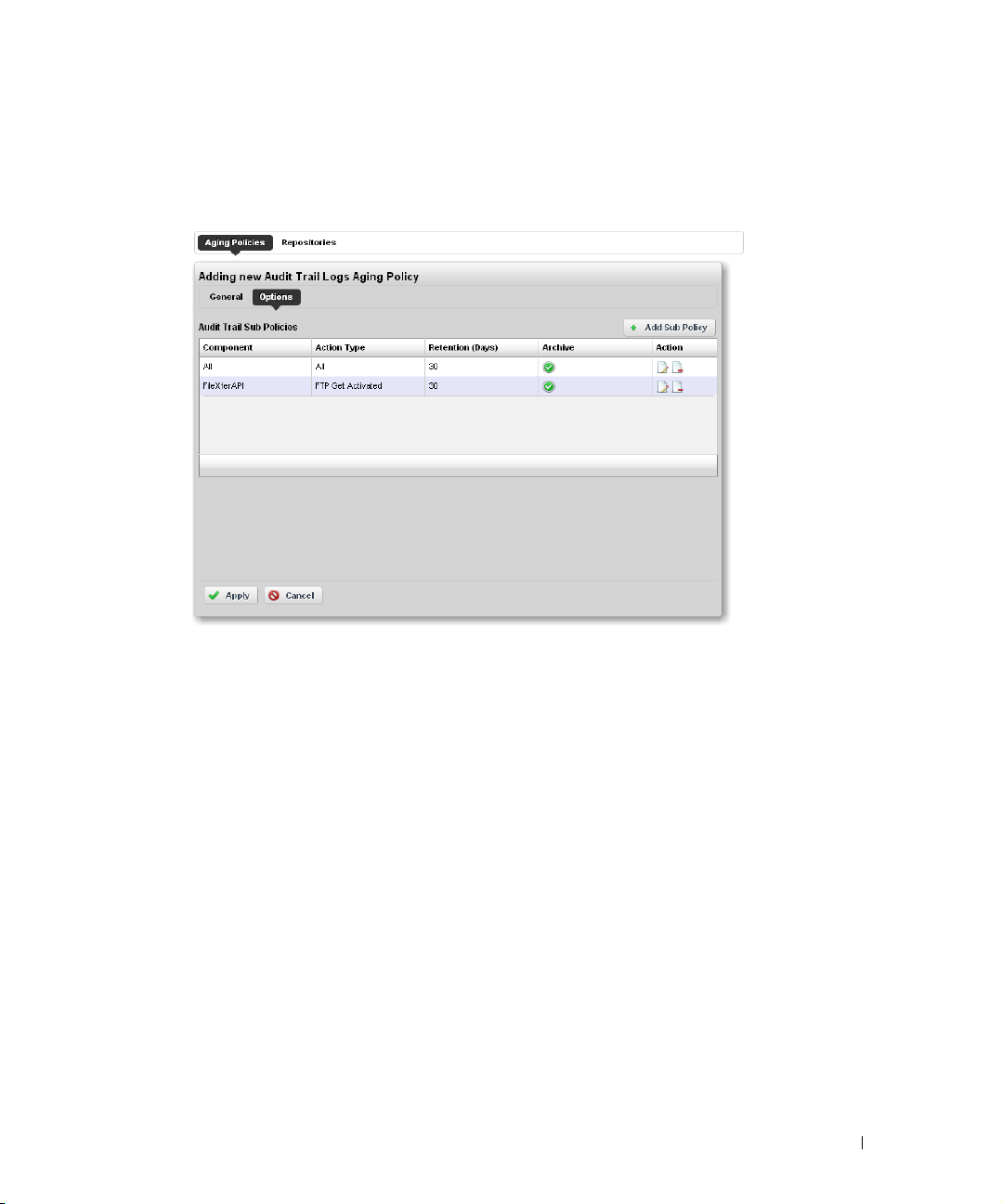
Sub-Policies
Some types of Database Aging Policies can have sub-policies that further refine the aging for their
type of contents.
Redcell > Database Aging Policies (DAP) | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
55
Page 56

These appear listed in the Aging Policies Options tab. Click
that you can
Edit
or
Delete
listed policies with the icons in the far-right
Such sub-policies contain the following types of fields:
Component
Action Type
Retention (Days)
Archive
—Select the component for the sub-policy from the pick list.
—This further sub-classifies the
Component
.
—The number of days to keep the aged item before archiving it.
—Check this to activated archiving according to this policy.
Add Sub Policy
Action
to create them. Notice
column in this list.
56
Redcell > Database Aging Policies (DAP) | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
Page 57

Repositories
When you select a repository in the Aging Policies Editor, the available policies come from what is
configured in this tab of the editor.
Redcell > Database Aging Policies (DAP) | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
57
Page 58

Available repositories appear listed in the initial screen. Like the Aging Policies Editor, you can click
Tip
Add Repository
in the
Action
Online
with a green icon (this is red, when the destination is offline).
to create a new repository, and
column. Notice the listed policies indicated whether the archiving destination is
Edit
or
Delete
selected, listed policies with the icons
58
When you
Repository Name
Description
Virtual Path
Online
Dell OpenManage Network Manager automatically writes to any configured failover repository if
the primary repository is full or not writable.
Add Repository
—An identifier for the archiving destination.
—A text comment.
—This is the path relative to the installation root directory. Any user with
administrator permissions can specify or change the default archive path here.
—Check this to put this repository online.
To view any archived DAP file, use
[Enter], type
dapviewer
or
Edit
an existing one, the following fields appear in the editor:
dapviewer
to use this utility.
. Type
oware
in a command shell, then, after pressing
Portlet Level Permissions
You can also provide permission for a user/group/role/organization on a defined portlet.
Redcell > Database Aging Policies (DAP) | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
Page 59
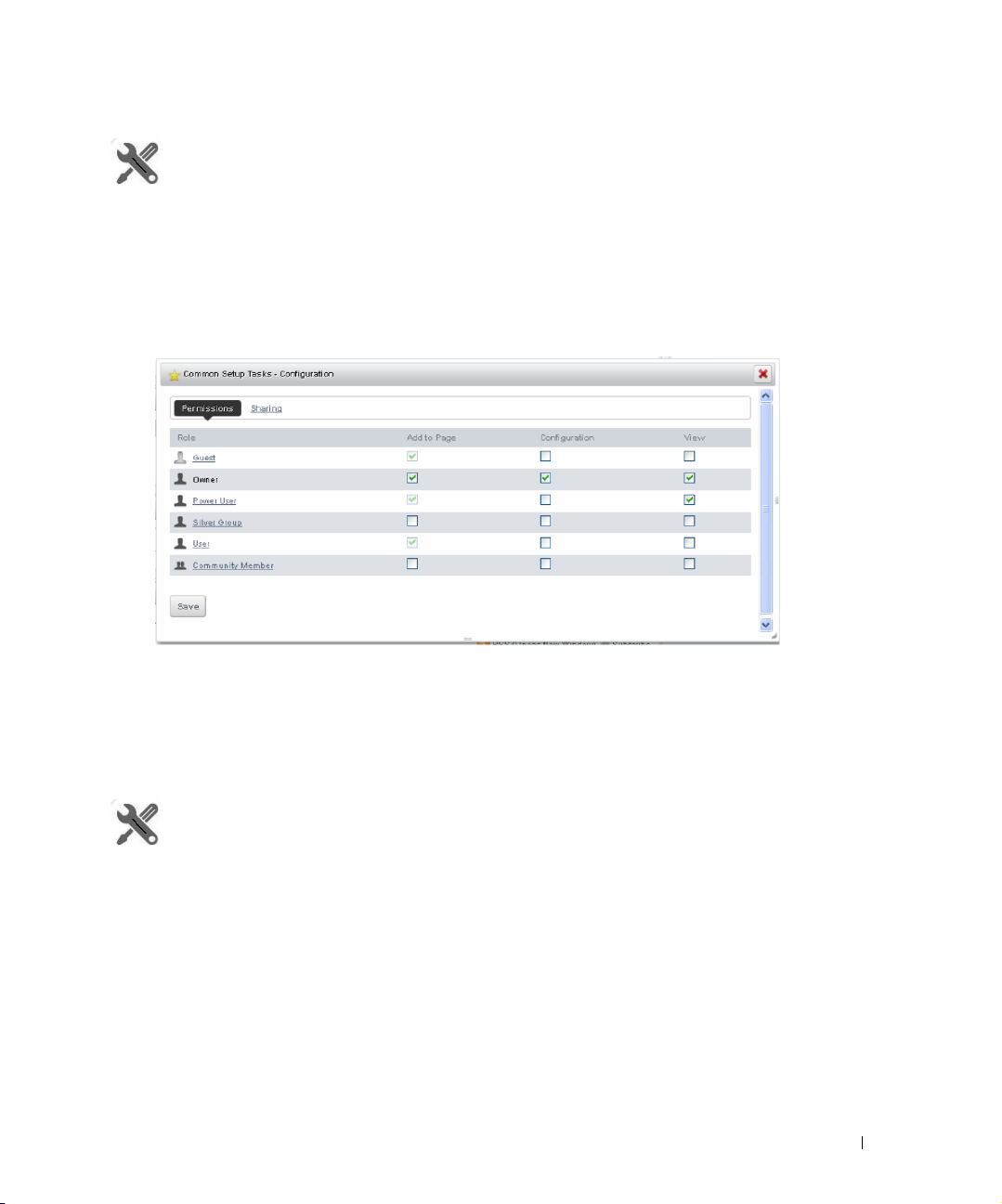
How To:
Configure Portlet Permissions
How To:
1
As an admin user, click on the Configuration icon (the wrench) in the top right corner of the
portlet of interest.
2
Click on the
3
Uncheck the View permission for Guest and Community members. Make sure Owner and
PowerUser still have View permissions.
4
Now check View for the relevant roles (for example,
5
Click
6
You should now be able to log out as admin, and log in as Guest or other community
members and confirm you cannot view the portlet you just configured.
Save.
Configuration
and go to the Permissions tab in the next screen.
Silver
Group).
Configure Resource Level Permissions
You can provide permission for a user/group/role/organization on a defined resource. The following
outlines the steps:
• Create a Container for each Customer
• Configure Membership for Container (resources that customer can access)
• Set Authorization for User Container
• Set up a Page for Device Level View
Redcell > Database Aging Policies (DAP) | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
59
Page 60

Create a Container for each Customer
1
In Container Manager Portlet, right-click to select
2
Create a container for the desired customer, naming and describing it.
3
In the
Authorizations
tab for this container, delete authorization for ALL (non-portal), Add
New.
authorization for Synergy Admin, Add authorization for Power User Role, and delete the
Ven do rs
Child Container.
60
Configure Membership for Container
4
Create Gold Customer as a Top Level Container.
5
Make it Shared, and configure its membership (Select and Add a group of devices)
Set Authorization for User Container
6
In the Authorizations tab, Add Gold Customer (with limited permission), and User Synergy
Admin (with full permission).
7
Delete Group: User
8
Create a Gold Customer user as described above.
Set up a Page for Device Level View
9
Add a Container View to the page of interest with portlets for which you want to restrict
access. Currently Container View is enabled for the following portlets: Managed Resources,
Alarms, Ports, Audit Trails, Printers.
Redcell > Database Aging Policies (DAP) | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
Page 61

10
NOTE:
Tip
Log out as admin, and log back in as a user with Gold Customer permissions.
11
Confirm your permission configuration is operating on this page.
Database Backup
To back up your database, open a command shell (
the following at the prompt replacing USERNAME and owbusdb. By default, the database is
owbusdb
.
mysqldump -a -u USERNAME --password=[name] owbusdb > FILENAME.mysql
For ex amp le :
mysqldump -a -u oware --password=dorado owmetadb > owmetadb.mysql
If you have Performance monitors or Traffic Analyzer, you must also back up your stored procedures
otherwise they do not get restored when you restore the database. The command line here adds
routines
mysqldump -a -u oware --password=dorado --routines owbusdb > owbusdb.mysql
. For example:
This writes the owbusdb to a plain-text file called
examples). This file is a full backup with which you can fully restore your database in case of
problems.
Defaults for the database are oware (login) and dorado (password). These are typically different from the
login / password for the application.
Start > Run cmd
, in Windows), and then type
FILENAME.mysql (owbusdb.mysql
--
in our
To get a rough estimate of database size, looking at the size of the directory
\oware3rd\mysql\data.
Restoring Databases
Restoring from
1
Drop the database:
mysqladmin -u USERNAME -p drop owbusdb
or
mysqadmin -u USERNAME --password=[password] drop owbusdb
2
Recreate the database
mysqladmin -u USERNAME -p create owbusdb
or
mysqadmin -u USERNAME --password=[password] create owbusdb
3
Import the backup data
FILENAME.mysql
Redcell > Database Aging Policies (DAP) | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
is a three step process. This occurs, again, in a command shell:
61
Page 62

mysql -u USERNAME -p owbusdb < FILENAME.mysql
or
mysql -u USERNAME --password=[password] owbusdb < FILENAME.mysql
Portal Database Backup / Restore
The web portal itself has a MySQL database. Back it up as follows:
1
Open a command shell and type
2
Then type the following command:
mysqldump –uroot -–password=dorado lportal > mybackup.sql
3
The
mybackup.sql
To restore the database, use another
1
Drop the database:
mysqladmin -uroot --password=dorado drop lportal
2
Recreate the database
mysqladmin -uroot --password=dorado create lportal
3
Import the backup data
mysql -uroot --password=dorado lportal < mybackup.sql
file is the backup.
oware.
oware
shell:
Quick Navigation
62
The Quick Navigation portlet lets you quickly perform some basic tasks:
Resource Discovery
you construct a Quick Discovery profile if none exists. See Resource Discovery on page 152
for details.
Link Discovery
Discovery on page 176.
Backup Config Files
can use this feature, you must have servers configured as described in Netrestore File Servers
on page 70 and/or File Servers on page 221. See also File Management on page 223.
OS Image Upload
235 for more about these capabilities.
Deploy OS Image
configured, as described above for Backup. See Deploy Firmware on page 238.
Quick Navigation | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
—Discover devices in your network with the Quick Discovery defaults, or lets
—After you have discovered resources, this discovers their connections. See Link
—This lets you back up discovered devices’ configuration files. Before you
—Upload firmware updates for devices. See Firmware Image Editor on page
—This deploys firmware updates. To deploy images, you must have File Servers
Page 63
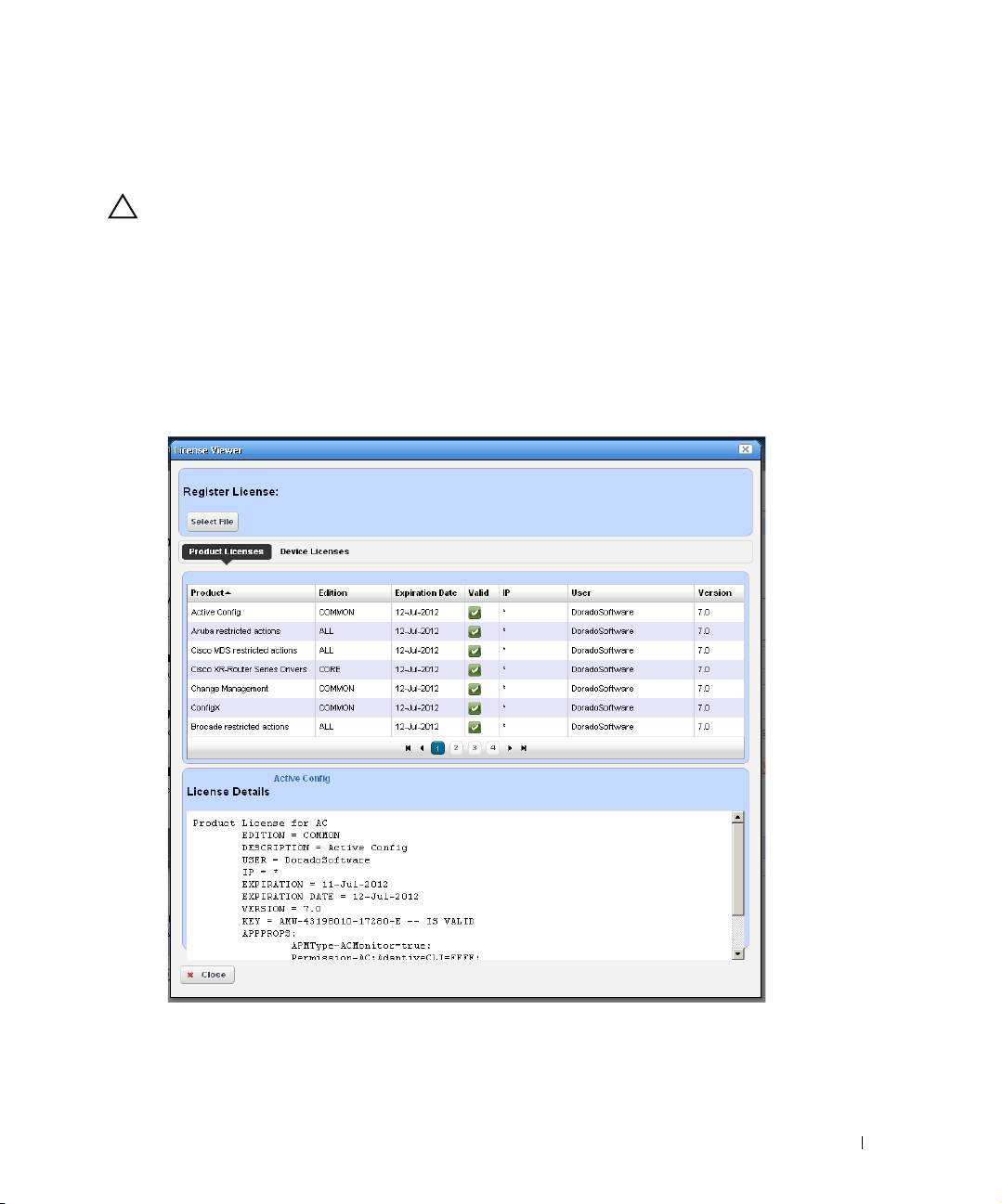
License Management
CAUTION:
OpenManage Network Manager. See License Viewer below for details.
Do not remove this portlet. You cannot re-enable it once it is removed.
Admin user and Power User can see all the above menu items. The User role sees only sees four.
Link discovery and OS image upload do not appear by default. To see them, you must give User
'write' permission.
—This lets you see and manage the licensed capabilities of Dell
License Viewer
This screen appears when you click
License Management
in the Quick Navigation portlet.
Click
Close
to return to Dell OpenManage Network Manager. You may find Licenses in a name
slightly different from the one you expect. For example, the
the Inventory Manager product.
License Viewer | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
Reports
portlet is licensed as part of
63
Page 64

How To:
Register a License
Tip
To register a license click the
a license file.
Select File
button at the top, and use the subsequent screen to select
To import a license when application server is not running, type
file name]
You must restart application server or wait up to 15 minutes before a license modification takes
effect.
Product Licenses
This portion of the License Viewer lists the products for which you have licenses already, displaying
the
Product, Edition, Expire Date,
installed the product and/or license, and the
License Details: [Product]
This portion of the screen displays the details of a license selected in the
Licenses
list above this panel.
Device Licenses
This tab displays the
Va ri a nc e
and count managed.
portion of the License Viewer screen. It is blank if you have not selected a license in the
between maximum and managed, and
on a command line.
whether the license is
Maximum Allowed
Ve rs io n
number of licenses for devices, the
of product for which the license is valid.
Ty p e
of license along with sums of the maximum
licenseimporter [license
Va li d ,
any IP restrictions, the
Registered Product
Count Managed
User
who
the
64
License Viewer | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
Page 65

Discovery Profiles
How To:
Discovery profiles configure
equipment discovery for Dell
OpenManage Network Manager.
The summary view displays the
Name, Description, Default
green check indicates the default
profile), whether the profile is
Scheduled
Date
The Expanded portlet adds a
Reference Tree snap panel that
displays a tree of associations
between selected profiles and
authentication and tasks that they execute. See Discovery Profiles on page 153 for more about this
portlet.
and
Next Execution
for scheduled discovery
Discover Your Network
1
Right click the Discovery Profiles list and select
2
The Discovery Profile Editor appears, with a step-by-step set of screens to configure resource
discovery. You can navigate through it by clicking the screen tab names at the top, or by
clicking the
Next
(the
.
New.
button at the bottom of the page.
Discovery Profile Editor
Use this editor to configure discovery once you have started Discover Your Network. Baseline
discovery is the initial discovery to compare to later discoveries. Follow these steps to discover
equipment on your network:
General
3
General Parameters
default.
4
Profile Options
discovered), whether to
Hostname(s), ICMP Ping Device(s), Manage ICMP-only Device(s),
Device(s).
This last checkbox determines whether Dell OpenManage Network Manager
—Set the
—Select the
Manage by
Discovery Profiles | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
Name, Description
Device Naming Format
IP address or hostname, and check whether to
and whether this profile is the baseline
(how the device appears in lists, once
or
Manage Unclassified
Resolve
65
Page 66

attempts to manage devices that have no device driver installed. Management may be
Tip
possible, but more limited than for devices with drivers installed, provided this capability is
one you have licensed.
The Filters (by
Location, Vendor,
or
Device Type
) let you narrow the list of devices discovered
by the selected item(s). As the screen says, this filtering will not have any impact on the
processing that occurs during the Inspection step.
Network
5
After you click
Network Type and Addresses
CIDR Address, Hostname, SNMP Broadcast, Subnet
You can specify an IP Address range by separating the beginning and end with a dash. For example:
192.168.1.1 - 192.168.1.240.
Next,
the
Network
screen appears.
—Select the type of entry in the pick list (
).
IP Address(es),
The tooltips in the data entry field describe what valid entries look like.
6
Authentication
Profiles on page 153 for details.) Notice that authentications appear with
and
Up / Down
—You can
Create new
, or
arrows on their right. The
Choose existing
authentications. (See Discovery
Edit / Delete
Edit
icon opens the authentication editor. Click the
arrows to arrange the order in which credentials are tried (top first). Ordering only applies
when two credentials are of the same type.
icons
66
Actions
7
You can configure Actions to run as part of discovery. By default, the actions screen includes
the
Resync
action. Use
Add Action
to select others to enter here. You can also edit parameters
(if available), delete and re-order the actions listed here by clicking the icons to the right of
them. Dell OpenManage Network Manager executes them in top-to-bottom order.
Inspection
8
Inspect Network using your current settings
—This screen lets you preview the discovery
profile’s actions and access to devices. If you clicked
the previous screen, click
Start Inspection
to begin the inspection process for selected
authentications that validates the device’s credentials.
Notice that the
Inspection Status
fields below listed authentications indicates the success or
failure of Ping, Hostname resolution, and the listed Authentications.
If the device does not match all required authentications, you can click the
wrench with a red or yellow dot) to edit them for the selected device. You can also click
Device
,
Create New,
Discovery Profiles | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
or
Choose Existing
authentications while in the editor clicking the
Next
rather than
Inspect
at the bottom of
Fix it
icon (a
Te s t
Fix it
Page 67

icon displays the authentication selection panel. The yellow dot on the
Tip
Fix it
icon means an
optional authentication is missing. A red dot means a required one is missing.
When authentications are unsuccessful, you can remove or edit them in this editor too. Click
the icons to the right of listed authentications to do this.
When they test successfully, the authentications appear in a nested tree under the
checkbox (checked when they test successfully).
9
Save—
begin discovery
Click
Save
to preserve the profile. You can then right-click it to select
.
If you select
Execute
from the profile editor, Dell OpenManage Network
Execute
Manager does not save the profile to execute later.
Results
10
Execute
—Clicking
Execute
begins discovery, confirm you do not mind waiting, and the
message traffic between Dell OpenManage Network Manager and the device appears on the
Results
This is a standard
11
A message (
screen.
Audit
screen. See
Audit Trail / Jobs Screen on page 91
Discovery Profile Execute is complete
) appears in the
for more about it.
Messages
at the bottom left
of the status bar.
You can also schedule discovery profiles to run periodically, updating your Dell OpenManage Network
Manager database with any network changes. For more, see Schedules on page 95.
12
The devices in your network now appear in the Managed Resources portlet, and elsewhere (in
Topology, for example).
See Discovery Profiles on page 153 for more about these capabilities.
Discover
and
Discovery Profiles | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
67
Page 68

Managed Resources
This portlet displays all the devices
you have discovered.
See Managed Resources on page
166 for the details of this screen’s
capabilities.
See also Managed Resource Groups
on page 162.
Common Setup Tasks
If you install it (
the Common Setup Tasks portlet can
appear on the page of your choice. It
reminds you of the following common
tasks:
• SMTP Configuration
• Netrestore File Servers
• Netrestore Image Repository
A red flag appears with the “Setup required” message in the
configured. Configuring them displays a green flag with the “Setup complete” message. Click the
edit
link in the
Add > Applications
Action
column to open editors for each of these.
),
Status
column when these are not
68
Managed Resources | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
Page 69

SMTP Configuration
You can use Dell OpenManage Network Manager’s messaging capabilities to communicate with
other users, but if you want to receive e-mails automated by actions like configuration file backups,
Dell OpenManage Network Manager must have a mail account. This screen configures the e-mail
server so Dell OpenManage Network Manager can send such automated e-mails.
The
Apply
button accepts your edits.
OpenManage Network Manager. This screen contains the following fields:
SMTP Server Host
SMTP Server Port
Authentication Enabled
the next two fields.
User Name
Password
Use SSL
Return Address
Default Subject
Connection / Send Timeout
Max Per Minute
SMTP Server Host
—The login ID for the SMTP server, if authentication is enabled.
—The password for the SMTP server, if authentication is enabled.
—Enable Secure Sockets Layer protocol to interact with your SMTP server.
OpenManage Network Manager.
Manager.
send per minute.
—The IP address or hostname of your SMTP server.
—The port for your SMTP server (110 is typical).
—Check this to enable authentication for this server. Checking enables
—The return address for mail sent from Dell OpenManage Network Manager.
—Text that appears by default in the subject line of mail sent by Dell
—The time-outs for mail sent by Dell OpenManage Network
—The maximum number of e-mails Dell OpenManage Network Manager can
—The IP address or hostname of your SMTP server.
Te s t
tries them.
Cancel
abandons them and returns to Dell
Common Setup Tasks | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
69
Page 70
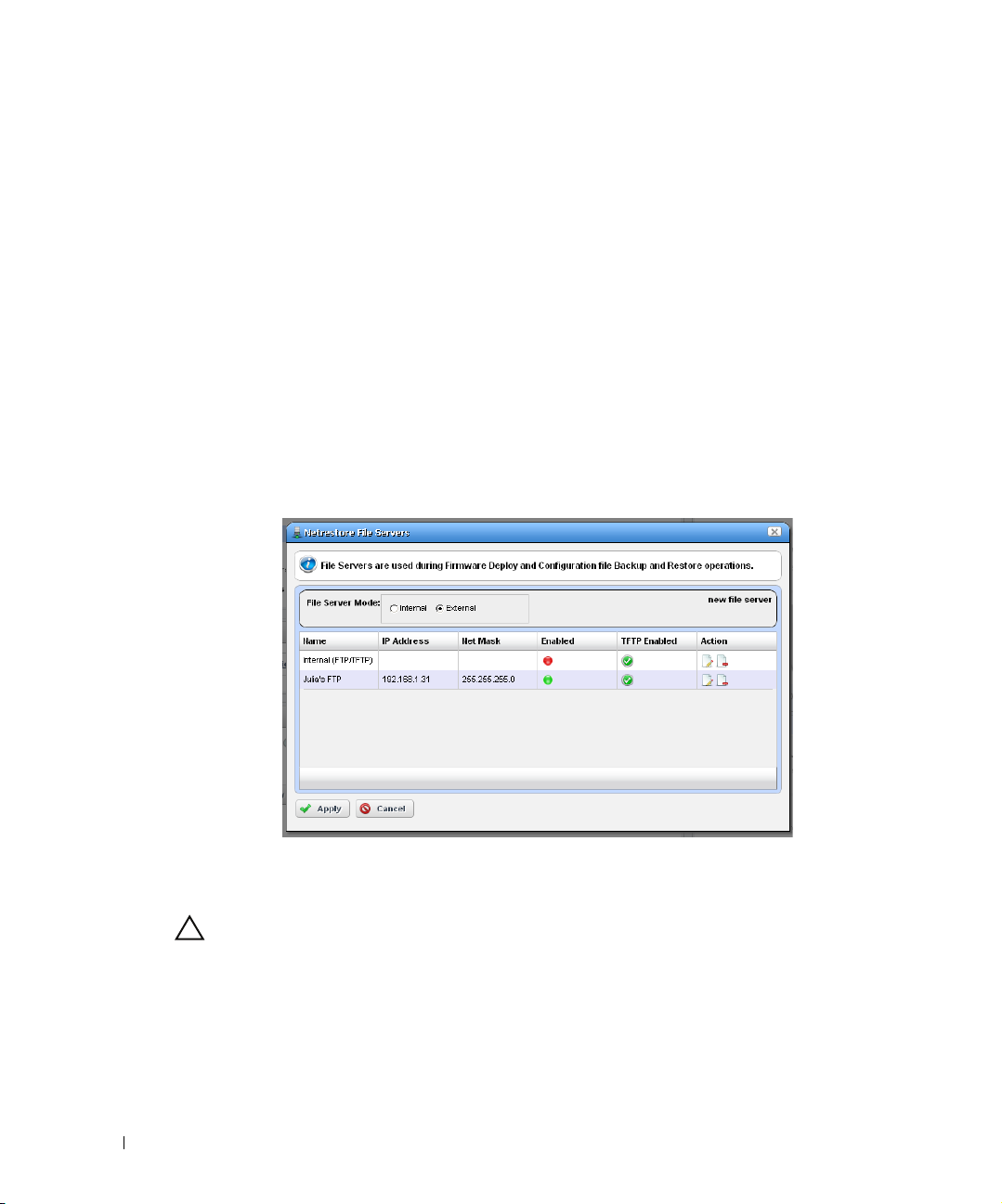
SMTP Server Port
CAUTION:
Two settings for e-mail servers appear in Control Panel, one in the Control Panel > Portal >
Settings Mail Host Names edit screen, and another in Control Panel > Server Administration >
Mail. The Portal-based e-mail settings help Administrators limit signups to e-mails only existing in
their organization. The screen in that panel provides a list of allowed domain names, if that feature
is enabled.
Control Panel > Server Administration > Mail is where to configure the Main server and
authentication for routing mail
—The port used by your SMTP server.
Netrestore File Servers
The Netrestore file servers provide FTP connections for retrieving and deploying devices’
configuration files, and for deploying firmware updates to devices on your network. See File Servers
on page 221 for a description of the portlet that manages file servers. If you want to configure
servers from the
Edit.
Common Setup Tasks
portlet, a slightly different screen appears when you click
70
This displays configured file servers. Configure new servers by clicking the
upper right corner. The editing process after that is as described in File Server Editor on page 222.
If you select the internal file server, make sure no external file server is running on the same host. A port
conflict prevents correct operation. Either turn off the external file server, or use it as the FTP server.
Dell OpenManage Network Manager selects the file server protocol for backup, restore or deploy
based on the most secure protocol the device supports.
Common Setup Tasks | Getting Started with Dell OpenManage Network Manager
new file server
link in the
Page 71

Portal Conventions
Tip
Tip
This section explains how to navigate and configure the Dell OpenManage Network Manager web
portal. Because this portal is based on open source features, and can be so flexible, this is not a
comprehensive catalog of all its features. The following discusses only features significant for using
Dell OpenManage Network Manager.
The application’s web Portal contains the following common elements:
•The Dock
• Status Bar Alerts
• Menu Bar
•Portlets
Because the elements that manage the Web portal are so flexible, and can be very detailed, only
Dell OpenManage Network Manager’s most important, or most-frequently-used features appear
documented below.
Clicking Go to in the Dock and selecting My Private Pages to open pages not shared with others, unless
you configure sharing. (See Sharing on page 87.)
Because they are so fundamental to Dell OpenManage Network Manager’s functioning, this
section also describes the following portlets:
• Audit Trail Portlet
• Schedules
2
You can rename any portlet by clicking its title. You can also configure portlets’ default filters to work in
concert with the title. See Filtering / Settings on page 112.
| Portal Conventions
71
Page 72

Tooltips
NOTE:
Dell OpenManage Network Manager has extensive tooltips that appear when you click the blue
circle with a question mark (one help icon—see also Online Help / Filter on page 12), or when you
hover the cursor over a field.
Tooltips also display the content most fields in portlets. If the screen does not allow a full field to
appear, you can still find out what is in a field by letting the tooltip re-state what it contains.
Refresh
You may have to refresh your browser to see screen updates. One way to refresh without re-loading
the entire window, however, is to click the
Settings on page 80)
Refresh
button at the top of an individual portlet. (See
The Back Button
72
Although browsers have a
way to return to a previous screen within the portal. For example,
clicking
that trail. If it is available, the
upper right corner of a screen provides the most dependable way to return to a previous screen.
Back
within a breadcrumb trail of links returns to the root of
Back
button, this is not always the best
Return to previous
button in the
Show Versions
To see which products are installed, and what versions, select the
item.
This can be critical information if you request support for your Dell OpenManage Network
Manager installation. The
listed in the bottom. Device drivers list supported devices and their operating systems. This can be
important for troubleshooting, and is vital information for support.
Tabs can display more information about supported devices.
| Portal Conventions
Application Software Versions
screen appears with the product versions
Manage > Show Versions
menu
Page 73

Custom Debug
Tip
For more advanced users, any component under owareapps can define a
component matching the following pattern:
owareapps\<component-dir>\server\conf\*log4j.xml
Consult these files for categories you want to change, and copy those (altered) properties to the file
you created in owareapps\installprops. The categories altered in this file override any others.
Changing such properties can produce enhanced error output in server logs.
log4j.xml
file for each
The Dock
This menu bar appears at the top of portal pages. Its exact appearance depends on your package.
With it, you can open online help, add, edit, and navigate to portal pages and content.
Click the down arrow to see menus for items on the dock. Here are its functions
Help
—Opens the online help.
Add—
This menu lets you add
The “breadcrumb” trail that appears near the top of pages lets you navigate directly through the
hierarchy of parent / child pages directly by clicking links displayed there.
The
More...
menu item contains Dell OpenManage Network Manager’s content. Click a node
to see available portlets. See Portlets on page 78.
Pa ge s ,
or
Applications
.
Manage
—This menu lets you alter the following:
The Dock | Portal Conventions
73
Page 74

Pa ge (page order [note that you can drag-and-drop pages within the Page s tab] permissions,
Tip
Tip
appearance and so on). You can create Children pages, and can Import / Export page
configurations as described below.
Use the screen that appears after selecting Manage > Page to configure add or delete
pages and to manage their appearance and permissions. You must refresh any altered
page before edits take effect.
74
You can create a new page, then Copy Portlets from Page you can duplicate another page’s portlets on
the selected page.
Pag e La you t —Configure the page’s columns. This menu item does not appear if you have
an expanded portlet open, because the focus is not in the context of a page.
The Freeform page layout may stack portlets on top of one another. Toggle the Fullscreen icon in the
upper right corner to see portlets so you can re-arrange them.
Site Settings—Configures page behavior, look and feel. See also Import / Export on page 86.
Show Versions—See Show Versions on page 72.
The Dock | Portal Conventions
Page 75
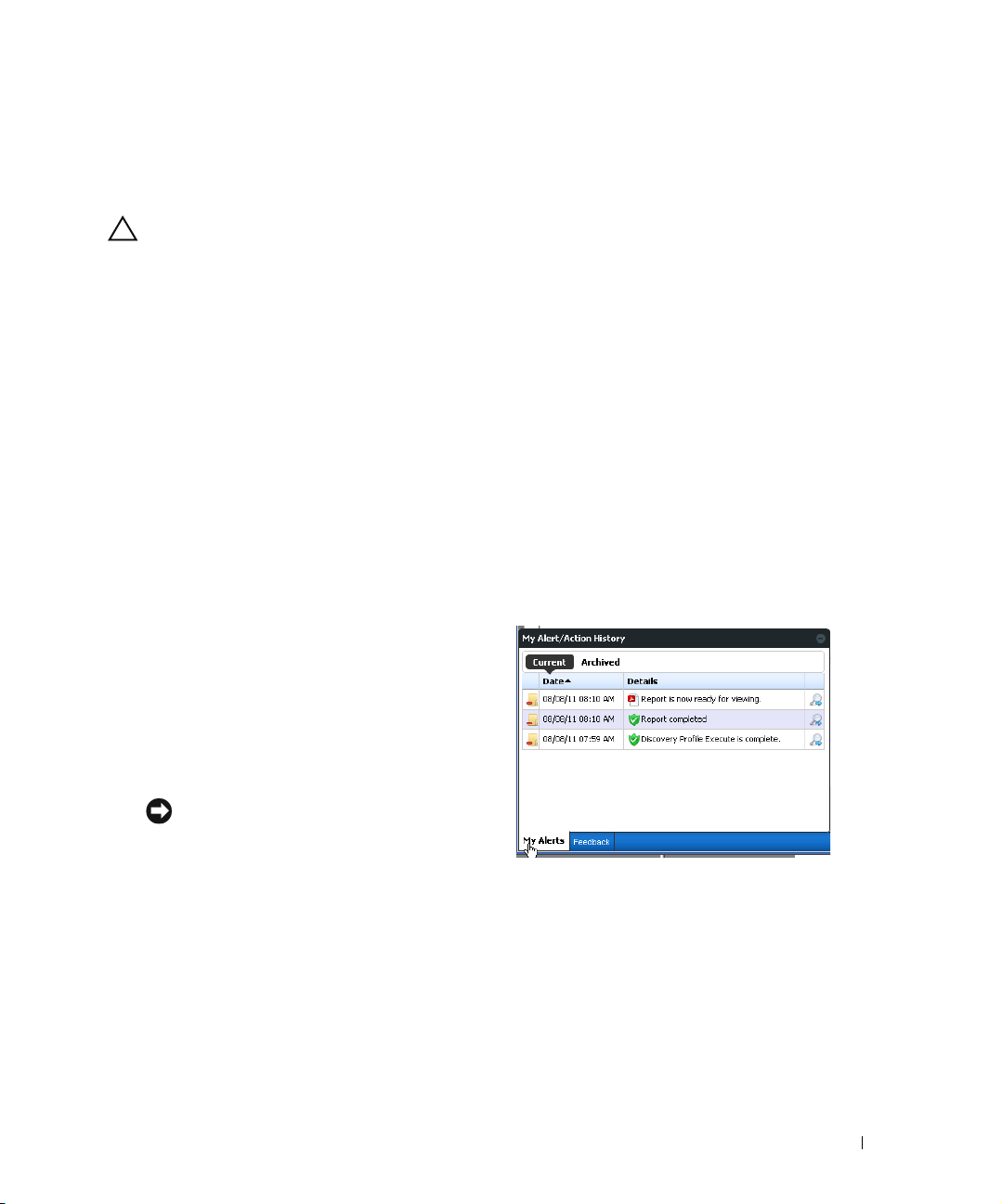
Go To
CAUTION:
Tip
—Makes the selected screen type appear. Select
example. When you add a new Community, its configured pages appear in this menu too.
This also provides access to
Dell OpenManage Network Manager does not support multiple tab browsing as a reliable way to see its
screens. Pages overcome that limitation.
Administrators can permanently configure
configure their
have the rights to make changes on a page. See Public / Private Page Behavior on page 40 for
the details.
Private
Control Panel
pages. Any page changes persist after you make them, provided you
My Public Pages
(see Control Panel on page 34)
Public
pages, while users with fewer rights can only
or
My Private Pages
.
, for
[User Name]
name, job title, image, e-mail and so on. The
OpenManage Network Manager.
Toggle Full Screen
you can use more screen area for portlets if you need it. This toggle also impacts the Menu
Bar.
(sign out)—Opens the
—The icon on the far right of this bar toggles its appearance / disappearance so
Manage My Account
Sign out
screen, where you can configure your
link lets you log out of Dell
Status Bar Alerts
The Status bar appears at the bottom of the portal.
On the left, it catalogs messages and notifications you
have received, including generated reports in
Alerts
. Click the magnifying glass to the right of
reports and Job Status notifications to open a separate
viewing window. The panel includes
Archived
messages tabs.
You can see the portal when web server is up, but
application server is not. When application server runs
after web server has started, and you have already
started the portal, an alert appears letting you know it is up.
Current
My
and
Status Bar Alerts | Portal Conventions
75
Page 76

Chat / Conferencing
Tip
This portion of the message bar lets you send and receive messages to colleagues who are online at
the same time you are.
76
This has the following fields and other possibilities for you to configure:
[Saying]
Status Bar Alerts | Portal Conventions
—Configure this text in the menu produced by the
(Settings)
including the saying, whether your online presence appears, and whether to play a sound
when messages arrive.
When you have a message from another user, that user’s name appears on the status bar to the left of
this icon.
(Conferences)
colleagues. The
and check to make a private conference that only invites can attend. The
active when you are invited to a conference. An online chat window appears after you join.
Settings
—This configures your user settings for any online chat with your colleagues,
—This configures your user settings for any online chat with multiple
Create
tab lets you
edit
to invite colleagues, configure an invitation message
icon (the next item).
Join
tab becomes
Page 77

Colleagues (n)
Tip
the number of colleagues online. Click to open the chat screen. Click on a colleague and enter
text at the bottom of the popup that appears to send messages. Previous chat history also
appears above any current text on that chat popup.
Click the minus icon in the top right corner of these screens to close them.
— A green dot indicates others are online (it is red when you are alone), and n is
Menu Bar
The Menu Bar appears on the left side of the screen. It consists of Menu items that lead to separate
pages configured with
The pages that appear on this bar can vary, depending on which Dell OpenManage Network
Manager package you have installed. The toggle on the right side of the The Dock makes this menu
bar appear or disappear.
You can drag and drop the menu bar labels to different positions, and can click a label to rename the
page, or delete it (with the “x”).
Manage > Page
.
Site Map
To see where pages and sub-pages are within your installation
look at the Site Map portlet.
Click the listed link(s) to go to the location(s).
Graphs
Graphs can appear in alarm and performance portlets. These
display the real-time division of total alarms or performance
metrics, and you can change their appearance, or associated
data lists display. See Alarms on page 99 for more graphs / charts
in that portlet.
Status Bar Alerts | Portal Conventions
77
Page 78

Hovering the cursor over a listed
NOTE:
item in the column where a
question mark appears indicates a
“tooltip” with more information is
available for this item. An
informational popup screen
appears after a brief wait to query
the application server. These popups can include graphs of recent
activity too.
Graphs can appear as lines, bars or
pie graphs, depending on the portlet, device and activity monitored.
Install the latest Adobe Flash for graph functionality.
Portlets
Portlets are the elements of any page within the Dell OpenManage Network Manager web client.
Initially, they appear in a small, summary screen format. Click
page you have created. See Portlet Instances on page 81 below for the distinction between portlets
that display the same data, and portlets that can exist in more than one instance, displaying
different data.
For a more specific look at available portlets, see the chapters following this one. The following
describe common portlet features.
One of the first portlets typical
users see is Discovery Profiles.
To act on listed items, right-click.
A menu appropriate to the
portlet appears.
The title bar for the portlet
displays its name. To rename it,
click on the name, and the field
becomes editable. You can make
changes, then click the green
checkbox to accept them (or the
red “X” to abandon them). The
right portion of the title bar
Add > More...
to add a portlet to a
78
Status Bar Alerts | Portal Conventions
Page 79

contains several editing controls. Clicking on the wrench icon produces a menu that leads to
Tip
Tip
NOTE:
editors for the
Configuration
of this portlet (user permissions to view and configure, Sharing, and
so on).
Some portlets, like Site Map, let you import or export .lar files of their setup and user preferences.
The plus or minus (+ or -) icons
Expanded Portlets, and X removes the portlet from the page
To see information about listed items in a portlet, hover your cursor over the row until a question mark
appears. A mini-query about the selected item appears in a large tooltip. See Portlet Toolbar below for a
description of the buttons at the top of portlets.
Portlet summary screens support displaying up to 200 rows, the expanded portlet supports 1000. Using
the portlets’ filtering capability makes more sense than trying to see more rows. (See How to: Filter
Expanded Portlet Displays on page 85.)
Portlet Toolbar
Minimize,
displaying only the title bar, or
.
Maximize,
displaying an
Buttons on portlet toolbars let you do the following:
?
—The Question Mark icon accesses online Help, opening the page appropriate for the portlet.
Refresh
Settings
—Isolates the browser’s page refresh to the selected portlet
—Configures the portlet’s filter, size, and so on. In portlets like Alarms, this also can
configure whether charts / graphs appear.
Search—
Locates an item in the portlet. When you click this, the columns filtered in the database
appear indented. For example,
Name
and
Model
appear indented in the Managed Resource
portal.
Similar functionality is available in Expanded Portlets when you click these buttons in the upper
right corner. The
Settings
button also lets you configure the columns displayed and their order. See
How to Show / Hide / Reorder Columns on page 84.
Status Bar Alerts | Portal Conventions
79
Page 80

Settings
Tip
The
Settings
Filter
applied to the summary portlet with an
The
Settings
button opens a screen where you can configure the
screen also includes a tab where you can Show / Hide / Reorder Columns.
Max Items
Apply
button to activate any changes you make there.
that appear in, and the
80
For performance reasons, Max Items are set to relatively low defaults.
Settings
on page 85
in expanded portlet does not include the
for information about the alternative.
As an Administrator, you can configure a portlet’s default display filter, then click the portlet name and rename it. For example, make the default filter in Managed Resources display only Powerconnect, then
click Managed Resources in the upper left corner of the portlet to rename it Powerconnect Routers.
If you are not an administrator, you must make a personal page for such portlets if you want the
filter settings to persist.
Status Bar Alerts | Portal Conventions
Filter
item. See
Filter Expanded Portlet Displays
Page 81

Search
Tip
NOTE:
You can search by clicking
Search
at the top of portlets. This opens a search field where you can
enter search terms for all the fields that appear in the list at the top of the portlet. The search is for
what you enter, no wildcards are supported. To clear a search, clear the field.
This searches all available items in the database, whether they appear listed or not.
Sort on a column by clicking on that column’s heading. Reverse the sort order by clicking it again. This
only sorts what appears in the portlet, whether expanded or not. The application remembers each user’s
choice saving the last Sort Column and Order on any page. Most portlets also “remember” settings for
Max Items and the selected Filter.
Portlet Instances
When you add content to a page, some portlets
(for example, the OpenManage Network
Manager Container View portlet) appear with a
purple icon and others (for example, the
Authentication or Container Manager portlets)
have green icons. The green-icon portlets are
instanceable and the purple-icon portlets are non-instanceable.
In other words, you can add only one instance of the (purple-icon) Container View portlet to a
community; and it displays the same data, even if it appears on more than one screen.
Once you have added a non-instanceable portlet to a page, its entry in the Add menu appears grayed out
and disabled. You can add more than one non-instanceable portlets to different pages, but they display
the same data. Instanceable portlets can appear multiple times on the same page, and can display
different data.
The Authentication portlet, for one example, is different. You can add it many times to pages in the
community, and can configure each instance of the portlet to display different authentication data.
Mandatory Fields
Some portlets include
editors. These appear after
you select an item, rightclick, and select either
New
or
Open.
Mandatory fields in these editors appear with a red flag icon to their right.
Status Bar Alerts | Portal Conventions
81
Page 82

Sorting Portlet Lists
Tip
NOTE:
Sorting tables that list items occurs when you click a
column heading. The arrow to the right of that heading’s
text displays the direction of the sort (ascending or
descending). When the arrow appears in a heading, the
selected column is the basis for sorting.
Expanded Portlets
Some portlets appear with a plus (+) icon in their upper-right corner, and can expand to display
more information and permit multi-selection of listed items. Return to the smaller portlet by
clicking
User permissions may limit access to the expanded portlets. For example, OpenManage Network
Manager can have many communities and limit users’ memberships. Such users can lightly browse
other Communities’ screens without full privileges.
Return to Previous
If you want to multi-select within listed items in a portlet, you must expand it. The one exception to this
rule: the File Management portlet.
Screen size limitations may require you to expand the browser to see expanded screens correctly. You
must have at least 1250 pixels in width.
in the expanded portlet’s upper right corner.
82
Status Bar Alerts | Portal Conventions
Page 83

See Control Panel on page 34 for more about setting up user privileges for portlets.
You can right-click to act on listed elements as in the basic, smaller portlet, but here you can also
see details about a selected row in the Snap Panels
below the table list items in an expanded
portlet.
Snap Panels
The snap panels that appear below the expanded portlet’s list
can “stack” on top of each other, so several can appear
simultaneously in each slot for Snap Panels. Click the title bar
of the panel to toggle its expansion or collapse. In the
Reference Tree snap panel, click the plus (+) to expand the
tree of connections.
You can collapse the entire snap panel area with a
Close
button at the bottom right of expanded portlets. These
panels re-appear when you click the
Open
button.
Status Bar Alerts | Portal Conventions
83
Page 84

How To:
Show / Hide / Reorder Columns
Click the
expanded portlet, and screen
appears with a
you elect to show or hide columns.
Click the appropriate buttons
(they change color) to display the
columns you want. You can also
drag-and-drop the order in which
columns appear to re-arrange the
display. Click
columns that appear on screen by
default. Abandon any changes and
Close
appear instantaneously when you
return to the expanded portlet.
Pages
Most portlets use the “recorder” icons to page through a list that occupies more
than one screen. The right/left arrows go forward and back one page. The icons at
either end go to the beginning or end of the pages.
Exports
Excel and Acrobat icons appear at the top right corner of the expanded portlet. Click
these to export the list contents as either an Excel spreadsheet (.xls), or a pdf file. These
download to the default download location you have configured on your browser. Some
browsers display the pdf before you can save it.
Settings
Columns
Apply
this screen. The changes
button in an
tab where
to change the
84
Status Bar Alerts | Portal Conventions
Page 85

Snap Panels (Reference Tree)
How To:
These vary, depending on the portlet, but the convention of
displaying a
items related to the selected list item in tree form. Click the
plus (+) to expand a node on the tree.
Click
expanded portlet to return to the page where you started, with
the smaller portlet. If the page you are on has a “breadcrumb
trail” of intervening detail pages (for example), you can click an
intervening page’s breadcrumb if you do not want to return to
the previous screen
Reference Tree
Return to previous
panel is common. This displays
in the upper right corner of the
Filter Expanded Portlet Displays
Among other places, filters appear at the top of expanded portlets. Many pre-installed filters come
from drivers your installed package. Filters match entity types, but may not necessarily be sensible
in the context of a particular portlet.
You can pick from already-configured filters with the drop-down on the left, or you can click
Advanced Filter
to create one of your own.
After you click the green plus (+), select
Click
Apply Filter
state.
Save As
Click
corner of this filter panel is where you would select it.
to see the list after the filter acts on it. Click
to preserve a filter you have configured for future use. The pick list in the upper left
and
or or on the left to combine more than one filter.
Reset
to return the list to its original
Status Bar Alerts | Portal Conventions
85
Page 86

Create a name and description, then click
Tip
NOTE:
NOTE:
configuration. See Redcell > Filter Management on page 48 for the screen that lists all such filters.
You can also filter what appears on a page with the Container View portlet. Select a container, and the
rest of the portlets on that page confine displayed data to reflect the selected container’s contents.
When using a filter you must click the refresh icon to the right of the drop down list to populate it.
Save
on the next screen to preserve your filter
Common Menu Items
Several menu items appear in multiple portlets. In addition to editing commands (
such menus let you:
•
Import / Export
Share with User
•
• Edit Custom Attributes
• View as PDF
•
Ta g
items with a location.
You can also export or import page configurations as well as items Dell OpenManage Network Manager
manages like equipment, discovery profiles, locations and so on.
Aging Policy
configuring these.
—See Redcell > Database Aging Policies (DAP) on page 50 for instructions about
[All]
—See Sharing, below.
New, Open
Import / Export
Menus often contain these options:
Import
Export Selection
— Retrieve a file with an XML description of the listed items in the manager. Some imports
can come from a URL.
— Export a file with a text or XML description of the selected item(s) in the
manager
),
86
Common Menu Items | Portal Conventions
Page 87

Export All
Tip
CAUTION:
— Export a file with a text or XML descriptions of all listed items in the manager.
Printing manager contents: You can Export a full size manager into PDF or Excel format and print from
there.
You must import into the correct portlet. You cannot import event processing rules into the Actions
portlet, for example. You must import event processing rules into the Event Processing Rule portlet.
Sharing
You can share elements within Dell OpenManage Network Manager with colleagues when more
than one user exists on your Dell OpenManage Network Manager system, and consult with them
using the texting described in Status Bar Alerts on page 75.
Common Menu Items | Portal Conventions
87
Page 88

How To:
Share a Resource
To share an something, first select it where it appears listed in the appropriate portlet. Right click
and select
Share Asset
.
88
In the subsequent screen, select a user with whom you want to share, type any message you want to
include and click
that opens to display the Snap Panels for the selected item.
Common Menu Items | Portal Conventions
Share Asset.
The chat message to the selected user includes your text and a link
Cancel
aborts sharing.
Page 89

Edit Custom Attributes
In several right-click menus (Managed Equipment, Port, Contact, Vendor, or Location), the
Custom Attributes
type listed in the portlet. See Redcell > Data Configuration on page 45 for another way to get to
this editor.
menu item lets you open the custom attribute editor appropriate for the device
Edit
Selecting a row in the editor lets you edit rows describing custom fields directly. The following are
the custom attribute properties you can alter:
Enabled
Label
To ol ti p
Click
— Check Enabled to activate the selected custom field.
— This is a label for the tooltip identified in the
portlets appropriate for the entity type you have selected. The
describes the data type of the custom attribute (String, Integer, Date, Boolean–read only).
When you select Boolean the field is a checkbox.
— The tip that appears when you hover the cursor over the custom field.
Save
to preserve any changes you have made, or
Name
. The Label is what you see in the
Ty p e
column in the attribute
Cancel
to abandon them.
Common Menu Items | Portal Conventions
89
Page 90
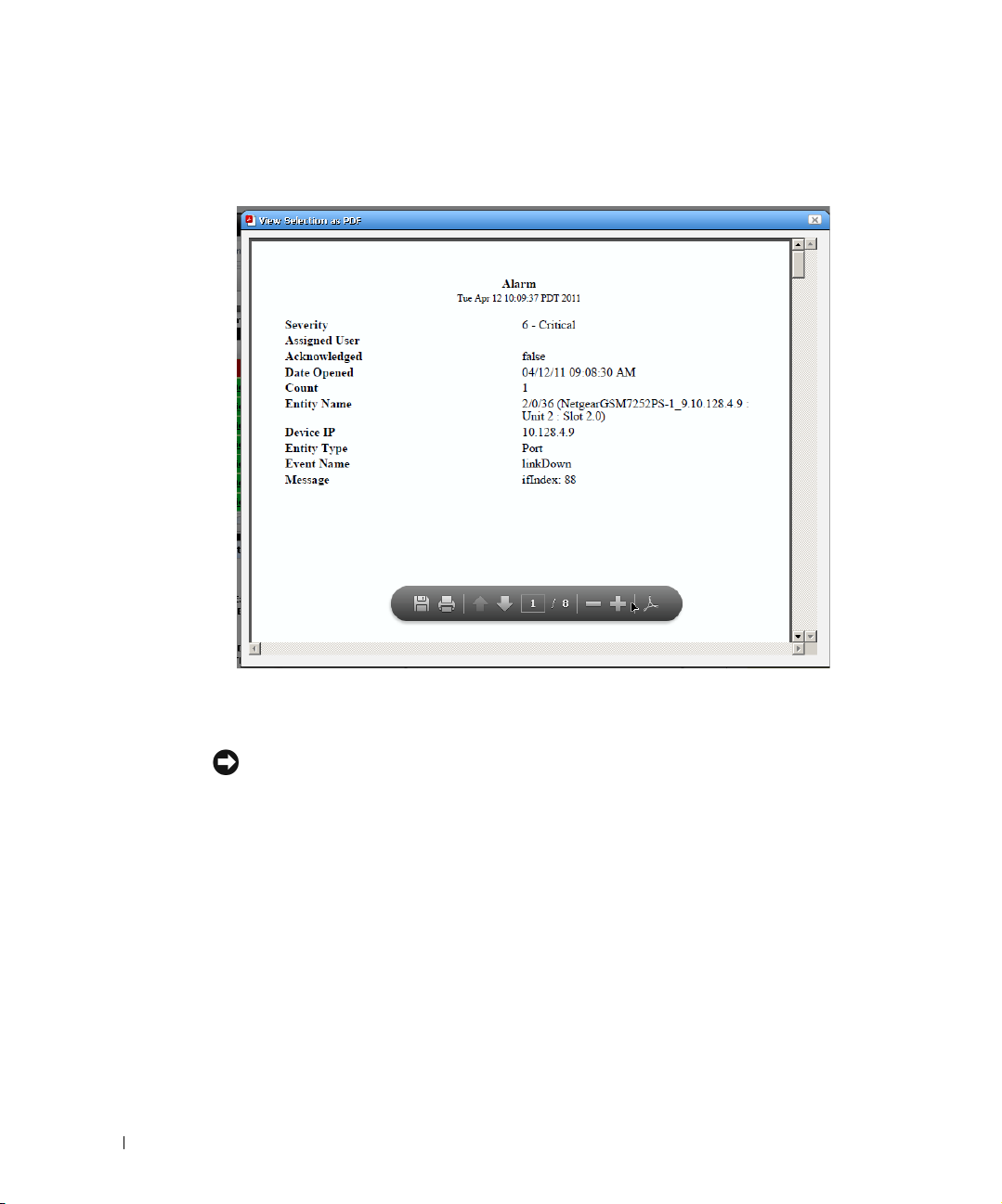
View as PDF
Tip
This displays the selected asset’s information as a PDF.
90
You can search, print or save this to file, and use any of the other Acrobat capabilities. Clicking the
acrobat logo docks the floating / disappearing Acrobat toolbar within this screen.
To search the PDF produced, click the binocular icon in the docked toolbar.
You can also create PDF reports containing descriptions of multiple selected assets, but you must
open an expanded portlet to multi-select.
Tag
The right-click menu of many items lets you tag them, for example Managed Resources, Locations,
Contacts, Customers, Services and Containers. When you select the
Coordinates
click on the map to specify its coordinates. See Map Context on page 151 for more information
about the uses of tagging.
Common Menu Items | Portal Conventions
, a new Map popup appears (see Tag on page 138) and you can search for an address or
Ta g
menu item, and
Page 91
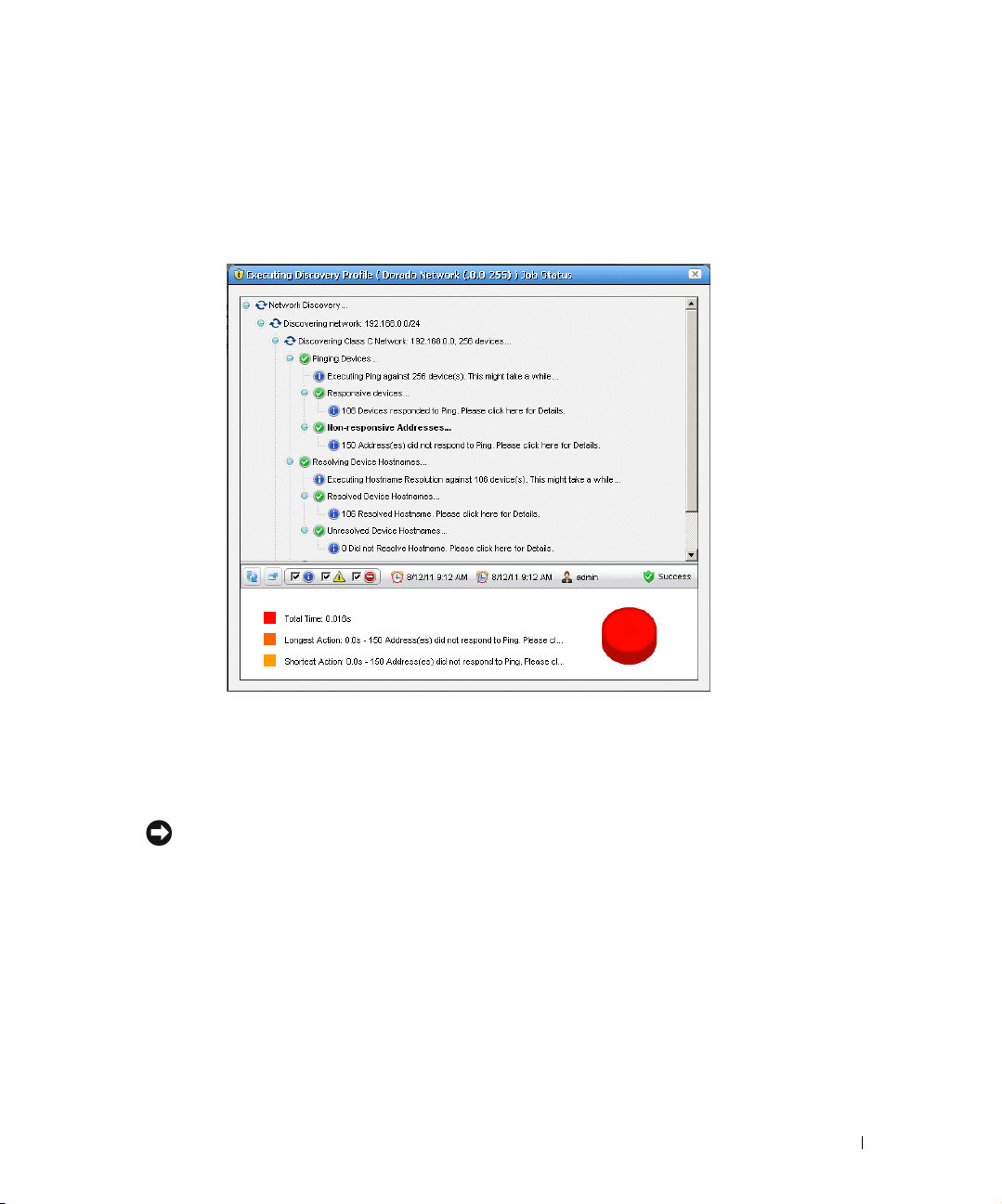
Audit Trail / Jobs Screen
Tip
When you execute an action, for example discovering network resources, an audit trail screen
appears with a tree displaying the message traffic between Dell OpenManage Network Manager
and the device(s) the action addresses.
To see the details of any message, click on it, and those details appear in the lowest panel of this
screen. If you click on a summary message (not a “leaf” on the tree), a graph appears displaying the
duration for its component messages. Hover your cursor over each portion of the graph for more
details.
The time for messages and logged in user initiating the action appear on the bar between the upper and
lower screen, and an icon summarizing the action appears on its right. Click the second icon from the left
to configure the amount of detail displayed in audit messages. Click the first (Refresh) icon to re-display
messages if you re-configure the type(s) displayed.
Close the audit trail viewer any time, and the action continues in the background. The the audit
trail is archived in the portlet described in Audit Trail Portlet on page 93.
Audit Trail / Jobs Screen | Portal Conventions
91
Page 92

Audit Trail Viewer
Some portlets also offer an Audit Trail menu item that displays Audit Trail / Jobs Screens for the
selected item.
92
The top of this screen contains a list of Audit Records. Click one of this list to see the Job details as
you would in the Audit Trail / Jobs Screen.
Audit Trail / Jobs Screen | Portal Conventions
Page 93

Audit Trail Portlet
Tip
The audit trail summary portlet displays an archive of the message traffic between Dell
OpenManage Network Manager and monitored devices, as well as OpenManage Network
Manager’s reaction to failed message transmission.
Creation Date, Subject, Action
The
ID of the user whose actions resulted in this trail)
(hover the cursor over the icon for a text message describing status). Right click to
message, manage its
page 50 for more about such policies.
To see the audit trail for recently completed processing, open the My Alerts tab in the lower left corner of
the portal, and click the magnifying glass to the right of the appropriate message.
Aging Policy
(the summary message of the audit trail)
,
and
Status
of the messages appear in the table
or
View as PDF.
See Redcell > Database Aging Policies (DAP) on
, User ID
Delete
(the login
a
Audit Trail Portlet | Portal Conventions
93
Page 94
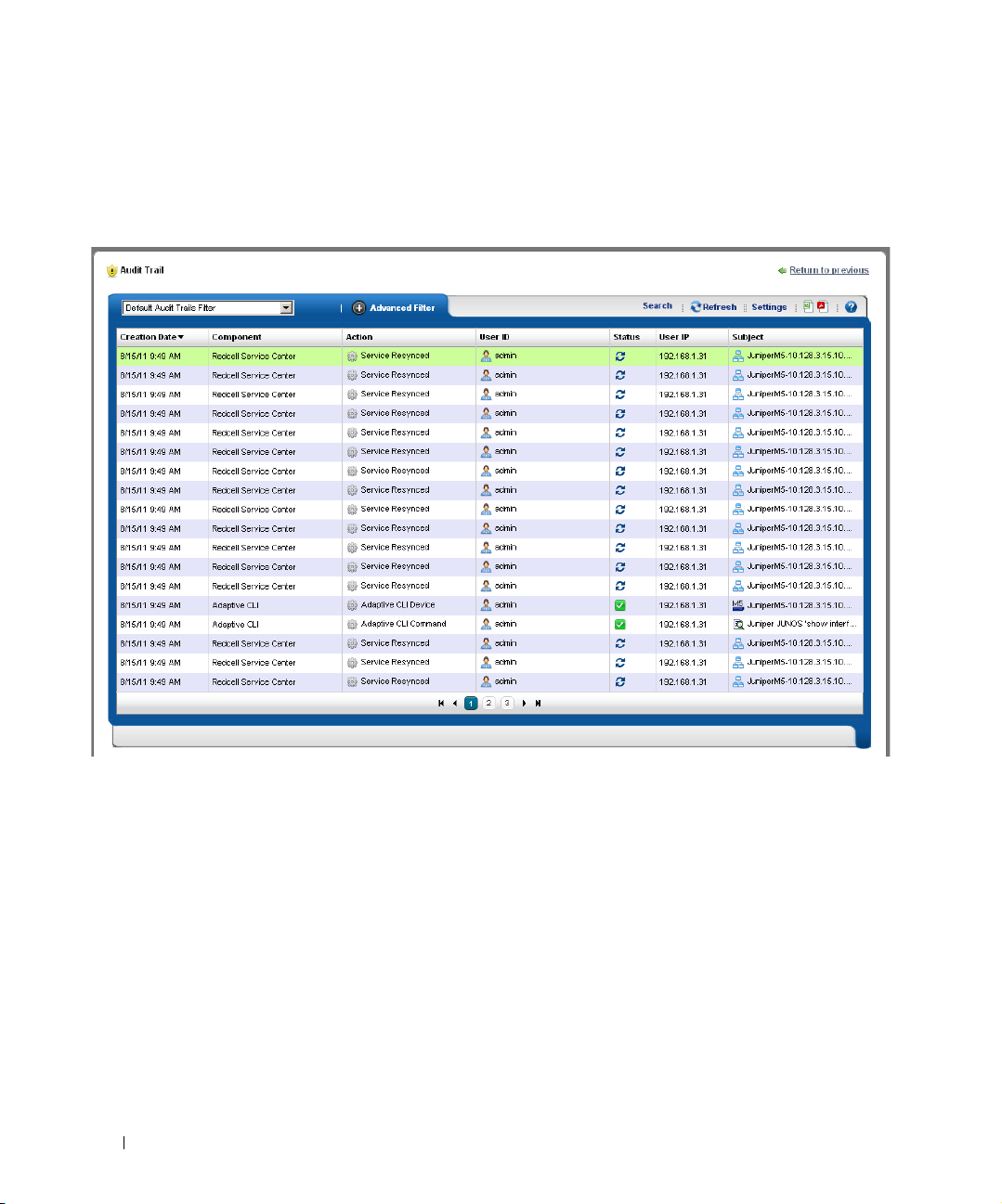
Expanded Audit Trail Portlet
When you click the plus (+) in the upper right corner of the summary screen, the expanded portlet
appears. Click the
order. Filter the appearance of the screen with the
Settings
button to configure the columns that appear in this screen and their
Advanced Filter
capabilities at its top.
94
In addition to the summary screen’s columns, the following are available in this screen:
User IP
Subject
—The IP address of the user who created this audit trail.
—The equipment at the origin of the message traffic with Dell OpenManage Network
Manager.
You can right-click a selected item and either
Delete
it, or
View Job.
This last option displays a
screen with the details of the job itself.
View Job
The
Audit Job Viewer
displays the audit trail messages in tree form. To see the contents of an
individual message that appears in the upper panel, select it and view its contents in the bottom
panel. The divider has the binoculars in the left corner, and the
Refresh
to clear an old message so you can view a new one.
Audit Trail Portlet | Portal Conventions
Refresh
icon in the right. Click
Page 95

Click the binocular icon to
check (info, warning,
error) filters that limit the
types of visible messages.
Notice that the date and time of the message appears to the right of the binocular icon.
Schedules
To schedule an action, for example using a
discovery profile, right click and select
Schedule
where you can create a new schedule,
entering a
Stopping On
number. You can also configure recurrence
in this screen.
Once you save the schedule, the action (for
example Discovery Profile) it also appears in
the Schedules Portlet as a scheduled item.
Schedules Portlet
. The Schedule panel appears,
Starting On
date and time or occurrence
date and time, and
You can view and modify schedules in the
This displays the
Recurrence
the appropriate menu item:
Delete
—Deletes the selected scheduled item, displaying a confirming dialog box.
Enable Schedule
enable the schedule, you can also edit it and check the
Enabled
in columns. You can do the following by right-clicking a scheduled item, and selecting
—Appears on an already disabled scheduled item so you can change its status. To
status, a
Schedules
Description,
portlet, or the Expanded Schedules Portlet
the
Ty p e
of schedule, its
Enabled
Next Execution
check box.
Schedules | Portal Conventions
and
95
Page 96

Disable Schedule
Tip
Execute
—Executes the scheduled item. If the
—Appears on an already enabled scheduled item.
scheduled item is an activity-based or discoveryprofile based scheduled item, an audit viewer
appears progress of the selected item.
For other types of scheduled actions, a dialog
appears saying
The scheduled item(s) has been sent
to the application server for immediate execution.
You can monitor its progress in the audit trail
portlet. (see
New
—This lets you initiate new schedules for a variety of actions, selected from a sub-menu. The
Audit Trail / Jobs Screen on page 91
)
subsequent screen’s appearance depends on the action selected. See Managed Resources on
page 166 for more about available actions. See Scheduling Actions on page 369 for the details
of scheduling actions that require parameters.
Open
—This appears for an activity-based scheduled items. It opens the activity editor, and lets
you modify the activity’s data/properties and schedule parameters.
To edit an existing schedule for an already scheduled action like a Discovery Profile, just right
click the item in its portlet and select
Schedule
. This displays the schedule information for the
discovery profile and lets you make modifications.
Schedule new actions from the portlet that ordinarily executes them, for example Resource Discovery on
page 152.
If you have Dell OpenManage Network Manager’s Change Management / Proscan capabilities
installed, you can use Schedules to initiate the Change Determination process. See Change
Determination Process on page 326. It is disabled by default.
96
Schedules | Portal Conventions
Page 97

Expanded Schedules Portlet
When you expand this portlet, the additional columns that appear include
Date,
whether the schedule is still active (
Scheduled
), and the
Execution Count.
Submission Date, Start
If a green icon appears in the
Scheduled
column, it means the schedule will be executed on next
start date. If the schedule has exceeded execution count or passed stop date (if specified), then a
red icon appears there.
Schedules | Portal Conventions
97
Page 98

98
Schedules | Portal Conventions
Page 99

Key Portlets
Tip
This section describes some of the key Dell OpenManage Network Manager portlets. You may not
have access to all of these in your installation, or you may not be able to use them with the user
permissions you have been assigned by the portal administrator.
To see all available Dell OpenManage Network Manager portlets, click
the field at the top of the menu to search for the portlet functionality you want to add. This limits
the display to Dell OpenManage Network Manager portlets. The previous chapter discussed the
Schedules Portlet on page 95.
Filter what appears on a page with the Container View portlet. Select a container, and the rest of the
portlets on that page filter their data reporting to reflect that container’s contents. The only caveat for this
advice is that Container View is non-instanceable. In other words, you can only add one of them.
Add > Applications
and use
Alarms
In its summary form, this portlet displays alarms
3
Alarms | Key Portlets
99
Page 100

The chart can act as a filter, too. For example, clicking the
Tip
Critical
alarms slice means only
Critical
alarms appear listed. Notice also that the chart “explodes” to highlight the selected slice. Hover the
cursor over a portion of the chart and a tooltip with information about that slice also appears.
By default, the chart appears only when there are alarms. See Configuring the Alarms Chart below
for options available in configuring the display. See Menu on page 102 for details about menu items
available when you right-click in the summary and expanded portlets. The following columns
appear in this screen by default:
Severity
—The alarm severity indicated by the color of the leftmost icon. The severity only has
meaning for Alarms and Security Alarms. Informational Alarms get a severity level of
Indeterminate. Closed alarms appear without color.
Date Opened
Entity Name
DeviceIP
Event Name
If you hover the cursor over a row in the portlet
display, a tooltip appears with information
about the alarm. This can include the alarm’s
Date Opened, the Entity Name, any alarm
Message, Event Name, Alarm and Entity Type,
its status as Service Effecting, Notification OID,
Equipment, Severity, whether the alarm was
Suppressed, or Acknowledged and the Device
IP.
If an alarm is
—The date the alarm appeared.
—The entity emitting this alarm (often within the Equipment).
—The IP address of the equipment where the alarm appeared.
—The event associated with the alarm.
Service Effecting,
(reflect an
impact on a service) it can propagate to appear
as components of service- and link-related
alarms. Service-effecting alarms are of
indeterminate or greater severity.
See Alarms in Visualizations / Topologies on page 219 for a description of how alarms appear in the
topology portlet. The next section (Expanded Alarm Portlet) describes alarm actions and
additional alarm capabilities.
100
Alarms | Key Portlets
 Loading...
Loading...