Page 1

OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter for
Desktop Client
User's Guide Version 2.3
Page 2

Notes, Cautions, and Warnings
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your computer.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss of data and tells you how to avoid the
problem.
WARNING: A WARNING indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury, or death.
Copyright © 2014 Dell Inc. All rights reserved. This product is protected by U.S. and international copyright and intellectual property
laws. Dell™ and the Dell logo are trademarks of Dell Inc. in the United States and/or other jurisdictions. All other marks and names
mentioned herein may be trademarks of their respective companies.
2015
Rev. A00
Page 3

Contents
1 Overview.......................................................................................................................................9
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter .......................................................................................................9
Key Features............................................................................................................................................................. 9
How Does the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter Help With vCenter Administration......................... 9
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter Features.......................................................................................10
2 OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter Configuration..........................................11
Security Roles and Permissions............................................................................................................................. 11
Data Integrity....................................................................................................................................................11
Access Control Authentication, Authorization, And Roles...............................................................................12
Dell Operation Role.......................................................................................................................................... 12
Dell Infrastructure Deployment Role................................................................................................................12
Understanding Privileges.................................................................................................................................13
3 Understanding How To Configure or Edit the OpenManage Integration for
VMware vCenter.......................................................................................................................... 16
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter Home Page.................................................................................. 17
Configuration Wizard Welcome Page.................................................................................................................... 17
Creating A New Connection Profile [Wizard]......................................................................................................... 17
Configuring Events And Alarms [Wizard]............................................................................................................... 18
Setting Up A Proxy Server [Wizard]........................................................................................................................19
Scheduling Inventory Jobs [Wizard]...................................................................................................................... 19
Running A Warranty Retrieval Job [Wizard].......................................................................................................... 20
Configuring the Deployment Credentials [Wizard]................................................................................................. 20
Setting The Default Firmware Update Repository [Wizard]................................................................................... 21
Enabling The OMSA Link [Wizard]..........................................................................................................................21
Configuring NFS Shares..........................................................................................................................................22
Settings Overview...................................................................................................................................................22
General Settings Overview...............................................................................................................................22
Creating A New Connection Profile................................................................................................................. 23
Configuring Events And Alarms .......................................................................................................................25
About Proxy Configuration............................................................................................................................... 26
Running Inventory Jobs................................................................................................................................... 27
Running A Warranty Retrieval Job...................................................................................................................27
Viewing or Editing Deployment Credentials.....................................................................................................28
Setting Up The Firmware Repository ...............................................................................................................28
Server Security Settings For Deployment........................................................................................................29
About Host, Bare Metal, and iDRAC Compliance Issues........................................................................................30
Page 4

Running The Fix Non-Compliant vSphere Hosts Wizard..................................................................................30
Running The Fix Non-Compliant Bare Metal Server Wizard............................................................................31
iDRAC License Compliance..............................................................................................................................32
Upgrading OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter....................................................................................33
Upgrading From a Trial Version To a Full Product Version.............................................................................. 33
About OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter Licensing...........................................................................33
4 End-To-End Hardware Management.....................................................................................34
Monitoring the Datacenter And Host System.........................................................................................................34
Understanding Events And Alarms.................................................................................................................. 34
vSphere Client Host Overview................................................................................................................................ 37
Resetting iDRAC............................................................................................................................................... 39
About Inventory Schedule...................................................................................................................................... 39
Modifying An Inventory Job Schedule.............................................................................................................39
Displaying The Inventory For A Single Host System in vCenter.......................................................................40
Inventory And Licensing...................................................................................................................................41
Viewing Storage Inventory..................................................................................................................................... 42
Viewing Host Power Monitoring.............................................................................................................................42
Displaying The Entire Datacenter Hardware Configuration And Status................................................................ 43
Managing Connection Profiles............................................................................................................................... 43
Viewing Or Editing An Existing Connection Profile.......................................................................................... 44
Deleting A Connection Profile..........................................................................................................................45
Testing A Connection Profile............................................................................................................................45
Refreshing A Connection Profile......................................................................................................................46
Understanding System Event Logs In vSphere Client Host View........................................................................... 46
Displaying Logs in Dell Management Center................................................................................................... 46
Displaying The Event Logs For An Individual Host...........................................................................................47
About Firmware Updates........................................................................................................................................47
Running The Firmware Update Wizard............................................................................................................ 48
Updating Older Firmware Versions ................................................................................................................. 49
Running the Update Firmware Wizard for Clusters and Datacenters..............................................................49
Advanced Host Management Using vCenter......................................................................................................... 51
Setting Up Physical Server Front Indicator Light.............................................................................................52
Server Based Management Tools....................................................................................................................52
Warranty Retrieval........................................................................................................................................... 52
5 Hardware Management...........................................................................................................54
Provisioning Overview............................................................................................................................................55
Understanding Deployment Job Times...................................................................................................................55
Server States Within The Deployment Sequence.................................................................................................. 55
Downloading Custom Dell ISO Images...................................................................................................................56
Understanding How To Configure A Hardware Profile.......................................................................................... 56
Page 5

Creating A New Hardware Profile................................................................................................................... 57
Cloning A Hardware Profile..............................................................................................................................59
About Managing Hardware Profiles.......................................................................................................................60
Viewing Or Editing A Hardware Profile............................................................................................................ 60
Duplicating A Hardware Profile....................................................................................................................... 60
Renaming A Hardware Profile..........................................................................................................................60
Deleting A Hardware Profile............................................................................................................................ 60
Refreshing An Updated Hardware Profile........................................................................................................61
Creating A New Hypervisor Profile.........................................................................................................................61
Managing Hypervisor Profiles................................................................................................................................ 62
VLAN Support...................................................................................................................................................62
Viewing Or Editing Hypervisor Profiles............................................................................................................ 63
Duplicating a Hypervisor Profiles.....................................................................................................................63
Renaming Hypervisor Profile............................................................................................................................64
Deleting A Hypervisor Profile...........................................................................................................................64
Refreshing Hypervisor Profiles........................................................................................................................ 64
Building A New Deployment Template...................................................................................................................64
Managing Deployment Templates................................................................................................................... 64
Running The Deployment Wizard........................................................................................................................... 65
Deployment Wizard - Step 1: Select Servers .................................................................................................. 66
Deployment Wizard Step 2: Deployment Templates........................................................................................66
Deployment Wizard Step 3: Global Settings.....................................................................................................66
Deployment Wizard Step 4: Server Identification............................................................................................ 67
Deployment Wizard Step 5: Connection Profile............................................................................................... 68
Deployment Wizard Step 6: Scheduling Jobs.................................................................................................. 68
Understanding Job Queue............................................................................................................................... 68
Adding A Server Manually............................................................................................................................... 69
Removing A Bare Metal Server........................................................................................................................70
6 Console Administration............................................................................................................ 71
Web-based Administration Console.......................................................................................................................71
Managing vCenter Server Connections................................................................................................................. 71
Registering a vCenter Server........................................................................................................................... 71
Uploading A OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter License To The Administration Console...........73
Virtual Appliance Management..............................................................................................................................74
Restarting The Virtual Appliance..................................................................................................................... 74
Updating A Repository Location And Virtual Appliance.................................................................................. 74
Updating the Virtual Appliance Software Version........................................................................................... 75
Downloading the Troubleshooting Bundle.......................................................................................................75
Setting Up The HTTP Proxy.............................................................................................................................. 75
Setting Up the NTP Servers............................................................................................................................. 75
Generating a Certificate Signing Request........................................................................................................76
Page 6

Setting up Global Alerts..........................................................................................................................................77
Managing Backup And Restore..............................................................................................................................77
Configuring Backup And Restore.....................................................................................................................77
Scheduling Automatic Backups.......................................................................................................................78
Performing An Immediate Backup................................................................................................................... 78
Restoring The Database From A Backup......................................................................................................... 78
Understanding the vSphere Client Console ...........................................................................................................79
Configuring Network Settings..........................................................................................................................79
Changing The Virtual Appliance Password......................................................................................................79
Setting The Local Time Zone............................................................................................................................80
Rebooting Virtual Appliance.............................................................................................................................80
Resetting The Virtual Appliance To Factory Settings...................................................................................... 80
Refreshing the Console View........................................................................................................................... 80
Read-only User Role.........................................................................................................................................80
Migration Path to migrate from 1.6/1.7 to 2.3....................................................................................................81
7 Troubleshooting.........................................................................................................................82
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)......................................................................................................................... 82
Using OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter to update an Intel Network card with the
firmware version of 13.5.2 is not supported..................................................................................................... 82
On trying a firmware update with an invalid DUP, the hardware update job status on the vCenter
console neither fails nor times-out for hours, though the job status in LC says ‘FAILED’. Why is this
happening?.......................................................................................................................................................82
Administration Portal is still showing the unreachable Update Repository location.......................................82
Why is the DNS configuration settings restored to original settings after appliance reboot if using
DHCP for appliance IP and DNS settings overwritten..................................................................................... 83
Why did my system not enter maintenance mode when I performed a one-to-many firmware update?....... 83
Even if my repository has bundles for selected 11G system, why is firmware update showing that I
have no bundles for Firmware Update?........................................................................................................... 83
Why Does My ESX / ESXi Deployment Fail on Servers Having a PERC S300 Boot Controller?....................... 83
How Come I See An Error Message Displayed After Clicking The Firmware Link?.........................................83
What generation of Dell servers does the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter configure
and support for SNMP traps?.......................................................................................................................... 84
How does the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter support more than three vCenters in
Linked Mode?...................................................................................................................................................84
Does OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter support vCenter in linked mode?................................. 84
What are the Required Port Settings for the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter?...................... 85
What are the Minimum requirements for successful installation and operation of the virtual appliance?.... 86
Why is the password not changed for the user used for bare-metal discovery after successfully
applying the hardware profile that has the same user with new changed credentials in the iDRAC
user list?........................................................................................................................................................... 86
Why is the processor version “Not Applicable” in Processor view in the System overview page?...............87
Page 7

Why is the DNS configuration settings restored to original settings after appliance reboot if using
DHCP for appliance IP and DNS settings overwritten..................................................................................... 87
How come I do not see my new iDRAC version details listed on the vCenter Hosts & Clusters page?.......... 87
How Do I Test Event Settings by Using OMSA to Simulate a Temperature Hardware Fault?.........................87
I Have the OMSA Agent Installed on a Dell Host System, But I Still Get an Error Message That OMSA
is Not Installed. What Should I Do?
Can the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter Support ESX/ESXI with Lockdown Mode
Enabled?...........................................................................................................................................................88
Inventory is Failing on Hosts ESXi 4.0 Update2 and ESXi Update 3 in Lockdown Mode After a Reboot..........88
When I tried to use lockdown mode, it failed...................................................................................................88
On trying a firmware update with an invalid DUP, the hardware update job status on the vCenter
console neither fails nor times-out for hours, though the job status in LC says ‘FAILED’. Why is this
happening?.......................................................................................................................................................88
What Setting Should I Use For UserVars.CIMoeMProviderEnable With ESXi 4.1 U1?....................................89
I Am Using A Reference Server to Create a Hardware Profile But it Failed. What Should I Do?....................89
I Am Attempting To Deploy ESX/ESXi On A Blade Server And It Failed. What Should I Do?...........................89
Why Are My Hypervisor Deployments Failing On R210 II Machines?............................................................. 89
Why Do I See Auto-discovered Systems Without Model Information in the Deployment Wizard..................89
The NFS Share is Set Up With the ESX/ESXI ISO, but Deployment Fails with Errors Mounting the
Share Location................................................................................................................................................. 89
How Do I Force Removal of the Virtual Appliance?......................................................................................... 89
Entering a Password in the Backup Now Screen Receives an Error Message.............................................. 90
My Firmware Update Failed. What Do I Do?....................................................................................................90
My vCenter Registration Failed. What Can I Do?.............................................................................................90
Performance during Connection Profile Test Credentials is extremely slow or unresponsive....................... 90
Does the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter support the VMware vCenter Server
appliance?........................................................................................................................................................91
Does the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter support the vSphere Web Client?..........................91
In the Administration Console, why the Update Repository Path is not set to default path after I reset
the appliance to factory settings?....................................................................................................................91
After backup and restore of OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter, why alarm settings are
not restored? ................................................................................................................................................... 91
Bare Metal Deployment Issues.............................................................................................................................. 91
Enabling Auto-Discovery On A Newly Purchased System.............................................................................. 91
Contacting Dell....................................................................................................................................................... 92
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter Related Information.....................................................................92
................................................................................................................. 88
8 Virtualization-related Events For Dell PowerEdge Servers................................................93
A Understanding Auto-Discovery............................................................................................101
Auto-Discovery Prerequisites...............................................................................................................................101
Page 8

Enabling or Disabling Administrative Accounts on iDRAC Servers......................................................................102
Manually Configuring a Server For Auto-Discovery (11th Generation of PowerEdge Servers)...........................102
Manually Configuring a Server for Auto–Discovery (12th Generation of PowerEdge Servers)...........................104
Page 9

1
Overview
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter
VMware vCenter is the primary console used by IT administrators to manage and monitor VMware vSphere ESX/ESXi
hosts. In a standard virtualized environment, VMware alerts and monitoring are used to prompt an administrator to
launch a separate console to resolve hardware issues. Today, using the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter,
administrators have new capabilities to manage and monitor Dell hardware within the virtualized environment, such as:
• Alerting and environment monitoring
• Single server monitoring and reporting
• Firmware updates
• Enhanced deployment options
Key Features
Dell customers can use the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter to perform:
Inventory Inventory key assets, perform configuration tasks, and provide cluster and datacenter views of
Dell platforms.
Monitoring and
Alerting
Firmware
Updates
Deployment and
Provisioning
Service
Information
Detect key hardware faults and perform virtualization-aware actions (for example, migrate
workloads or place host in maintenance mode).
Update Dell hardware to the most recent version of BIOS and firmware.
Create hardware profiles, hypervisor profiles, and deploy any combination of the two on baremetal Dell PowerEdge servers, remotely and without PXE using vCenter.
Retrieve warranty information from Dell online.
How Does the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter Help With vCenter Administration
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter provides additional virtualization functionality that supplements the
current vCenter administration functions:
• Compresses tasks and adds management processes, such as firmware updates and bare-metal deployment, to the
vCenter Server Administration Console.
• Organizes deployment of multiple bare-metal servers without requiring Preboot Execution Environment (PXE).
• Provides additional intelligence (inventory, events, alarms) to diagnose server problems.
9
Page 10

• Integrates with standard vCenter authentication, rules, and permissions.
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter Features
The following are high-level features of the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter:
• Monitor Dell servers using the standard vCenter event and alarm subsystem
• Perform advanced hardware management and configuration
• Perform zero touch deployment of VMware ESX / ESXi hypervisors on bare-metal systems without using PXE
• Build hardware and VMware ESX / ESXi hypervisor profiles
• Perform firmware updates
• Troubleshoot infrastructure issues
• Generate at report at the Datacenter and Cluster view—export to CSV file
• Integrate OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter capabilities with standard vCenter roles and permissions
10
Page 11
2
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter Configuration
The following sections provide step-by-step instructions for the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter initial
configuration. Upgrade, uninstallation, and security role information are also covered in the following sections.
Security Roles and Permissions
The OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter stores user credentials in an encrypted format. It does not provide
any passwords to client applications to avoid any improper requests that could lead to issues. The Backup Database are
fully encrypted using custom security phrases, and therefore the data cannot be misused.
By default, users in the Administrators group have all the privileges. Administrators can use all the functions of the
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter within VMware vSphere Client or Web Client. If you want a nonadmin
user to manage the product, then create a role including both the Dell roles and then assign permission on the root/top
node in the inventory and propagate permissions, as needed, on the child nodes to which you want to give access to the
user. For example, if you want a user to manage only Cluster A, then keep the permissions on Cluster A and remove
permissions from other clusters.
Data Integrity
Communication between the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter virtual appliance, Administration Console,
and vCenter is accomplished using SSL/HTTPS. The OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter generates an SSL
certificate used for trusted communication between vCenter and the appliance. It also verifies and trusts the vCenter
server's certificate before communication and the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter registration. The
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter Console tab (in VMware vCenter) uses security procedures to avoid
improper requests while the keys are transferred back and forth from the Administration Console and back-end
services. This type of security causes cross-site request forgeries to fail.
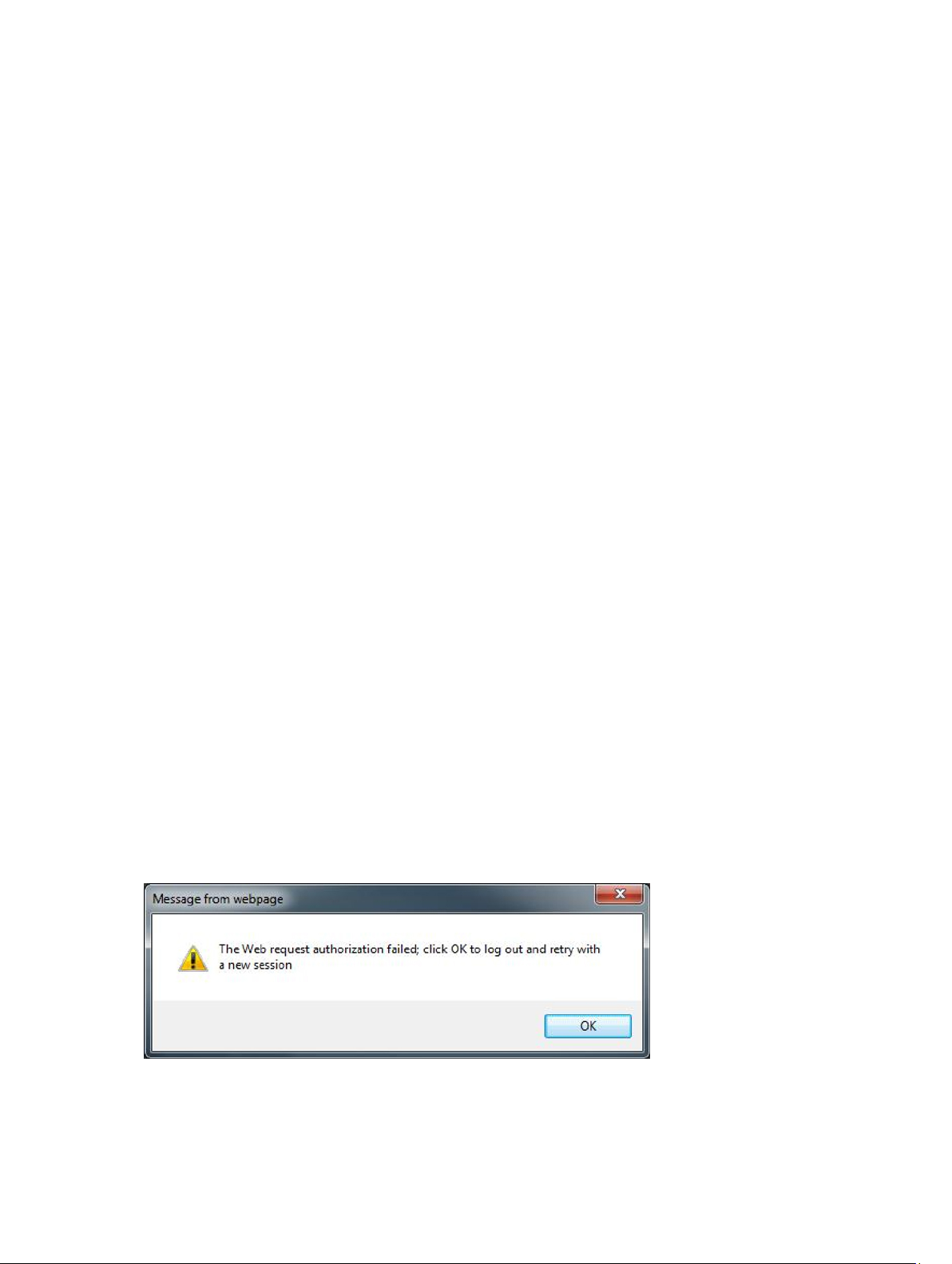
A secure Administration Console session has a five-minute idle timeout, and the session is only valid in the current
browser window and/or tab. If the user tries to open the session in a new window or tab, a security error is created that
asks for a valid session. This action also prevents the user from clicking any malicious URL that could try to attack the
Administration Console session.
Figure 1. Error Message
11
Page 12
Access Control Authentication, Authorization, And Roles
The OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter uses the vSphere Client's current user session and the stored
administration credentials for the virtual appliance to perform vCenter operations. The OpenManage Integration for
VMware vCenter uses the vCenter server's built-in roles and privileges model to authorize user actions with the virtual
appliance and the vCenter managed objects (hosts and clusters).
Figure 2. vCenter vSphere Client Roles and Privileges
Dell Operation Role
Contains the privileges/groups to accomplish appliance and vCenter server tasks including firmware updates, hardware
inventory, restarting a host, placing a host in maintenance mode, or creating a vCenter Server task
This role contains the following privilege groups.
Privilege Group Dell.Configuration
Privilege Group Dell.Inventory
Privilege Group Dell.Monitoring
Privilege Group Dell.Reporting
(Not used)
Privilege - Perform Host-Related Tasks, Perform vCenter-Related Tasks, Configure SelLog,
Configure ConnectionProfile, Configure ClearLed, Firmware Update
Privilege - Configure Inventory, Configure Warranty Retrieval, Configure ReadOnly
Privilege - Configure Monitoring, Monitor
Privilege - Create a Report, Run a Report
Dell Infrastructure Deployment Role
This role contains the privileges specifically related to the hypervisor deployment features.
12
Page 13
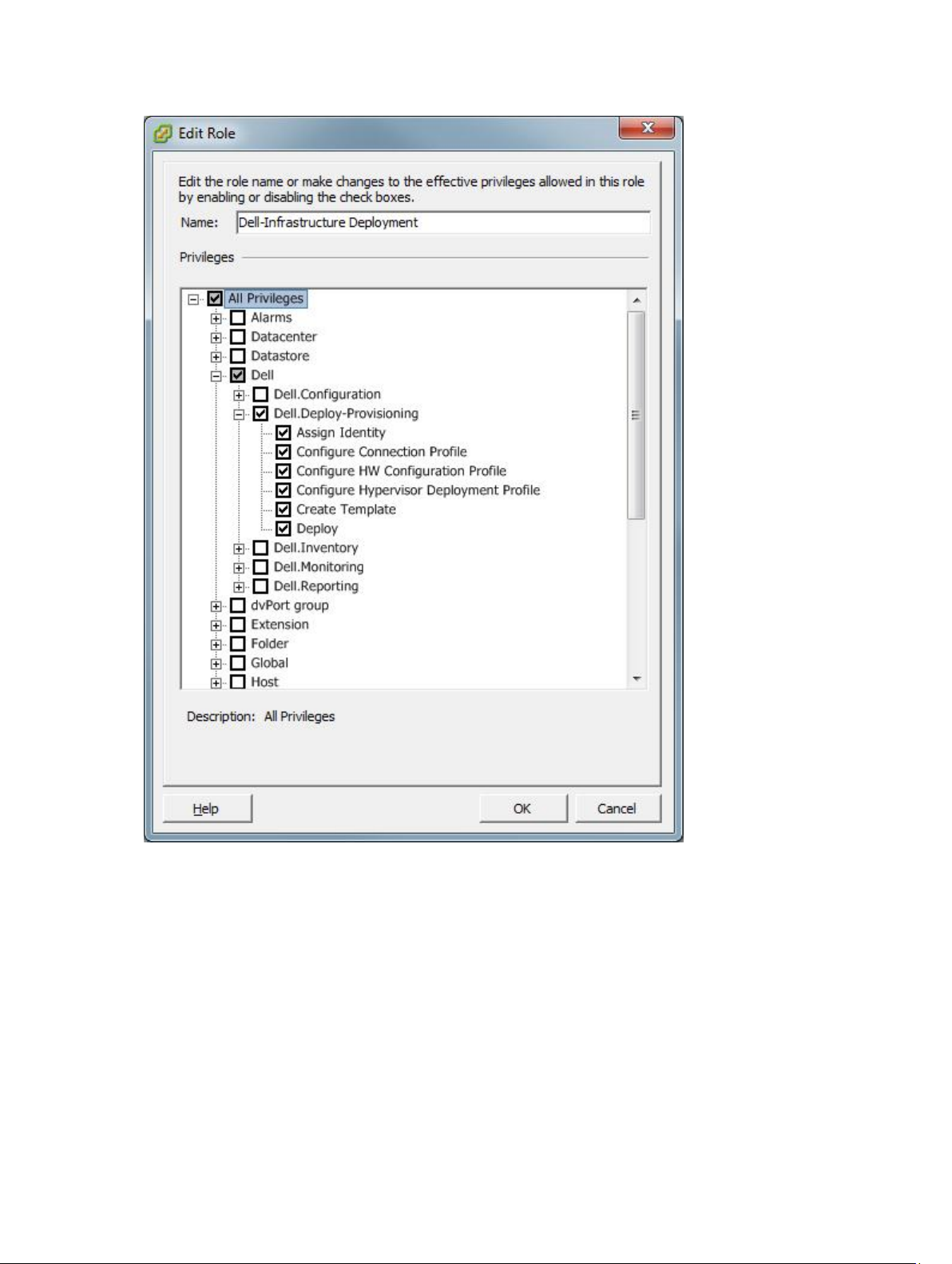
Figure 3. Dell Infrastructure Deployment Role
The privileges that his role provides are Create Template, Configure HW Configuration Profile, Configure Hypervisor
Deployment Profile, Configure Connection Profile, Assign Identity, and Deploy.
Dell.Deploy —
Provisioning
Create Template, Configure HW Configuration Profile, Configure Hypervisor Deployment
Profile, Configure Connection Profile, Assign Identity, Deploy
Understanding Privileges
Every action performed by the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter is associated with a privilege. The
following sections list the available actions and the associated privileges:
13
Page 14

• Dell.Configuration.Perform vCenter-Related Tasks
– Exit and enter maintenance mode
– Get the vCenter user group to query the permissions
– Register and configure alerts, for example enable/disable alerts on the event settings page
– Post events/alerts to vCenter
– Configure event settings on the event settings page
– Restore default alerts on the event settings page
– Check DRS status on clusters while configuring alerts/events settings
– Reboot host after performing update or any other configuration action
– Monitor vCenter tasks status/progress
– Create vCenter tasks, for example firmware update task, host configuration task, and inventory task
– Update vCenter task status/progress
– Get host profiles
– Add host to data center
– Add host to cluster
– Apply profile to host
– Get CIM credentials
– Configure hosts for compliance
– Get the compliance tasks status
• Dell.Inventory.Configure ReadOnly
– Get all vCenter hosts to construct the vCenter tree while configuring connection profiles
– Check if the host is a Dell server when the tab is selected
– Get the vCenter's Address/IP
– Get host IP/Address
– Get the current vCenter session user based on the vSphere client session ID
– Get the vCenter inventory tree to display the vCenter inventory in a tree structure.
• Dell.Monitoring.Monitor
– Get host name for posting the event
– Perform the event log operations, for example get the event count, or change the event log settings
– Register, unregister, and configure events/alerts – Receive SNMP traps and post events
• Dell.Configuration.Firmware Update
– Perform firmware update
– Load firmware repository and DUP file information on the firmware update wizard page
– Query firmware inventory
– Configure firmware repository settings
– Configure staging folder and perform update using the staging feature
– Test the network and repository connections
• Dell.Deploy-Provisioning.Create Template
– Create, display, delete, and edit deployment templates
• Dell.Configuration.Perform Host-Related Tasks
14
Page 15

– Blink LED, Clear LED, Configure OMSA URL from the Dell Server Management tab
– Launch OMSA Console
– Launch iDRAC Console
– Display and clear SEL log
• Dell.Inventory.Configure Inventory
– Display system inventory in the Dell Server Management tab
– Get storage details
– Get power monitoring details
– Create, display, edit, delete, and test connection profiles on the connection profiles page
– Schedule, update, and delete inventory schedule
– Run inventory on hosts
15
Page 16

Understanding How To Configure or Edit the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter
After you complete the basic installation of the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter, you can proceed to
configure the appliance using one of the following methods described later in this section:
• Configuration Tasks Using the Configuration Wizard
• Configuration Tasks Using the Settings Options
Although using the Configuration Wizard is the most common method used, you can also accomplish this through the
appliance's Settings page in the Dell Management Center.
The user interface in both areas is similar except in the wizard you click
options you click
Configuration Tasks Using the Configuration Wizard
Use these tasks when configuring the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter using the Configuration Wizard:
1. Configuration Wizard Welcome Page
2. Creating A New Connection Profile
3. Configuring Events And Alarms
4. Setting Up A Proxy Server
5. Scheduling Inventory Jobs
6. Running A Warranty Retrieval Job
7. Configuring The Deployment Credentials
8. Setting The Default Firmware Update Repository
9. Enabling The OMSA Link
Apply
.
Save and Continue
, whereas in the Settings
3
Configuration Tasks Using the Settings Options
Use these tasks to set up or edit the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter configuration tasks:
• Creating A New Connection Profile
• Configuring Events And Alarms
• Setting Up A Proxy Server
• Modifying An Inventory Job Schedule
• Warranty Retrieval
• Viewing Or Editing Deployment Credentials
• Setting Up The Firmware Repository And Credentials
• Enabling The OMSA Link
16
Page 17
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter Home Page
When you log in to the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter home page, the navigation buttons are in the left
pane, and the right pane provides useful links and information. This design provides key links into the tasks you do most
often. While all these tasks are found under the left-pane navigation, you can also find them on the home page for ease
of use. The tasks provided on this page belong to the following categories:
• Hosts and Server Deployment
This section provides more information on hosts and server deployment.
• vSphere Host and Bare Metal Server Compliance
This section provides more information and lets you view details about non-compliant hosts or bare metal servers or
run the wizards to fix them.
• Inventory Schedule
In this section, you can learn more about inventory scheduling.
• Warranty Data Retrieval Schedule
This section lets you learn more or view/change warranty schedules.
• Licensing
This section lets you learn more about licensing. Use the links to go to the licensing tasks.
• Events and Alarms Settings
Learn more about event and alarm settings or take the link that lets you configure them.
• Host Connection Licenses
Here you can view the host connection licenses in real time. In addition, you can use the Buy Now link to purchase a
full version license to manage more than one host. The Buy Now link only appears if you are using a demo license.
• vCenter Connection Licenses. Here you can view the VMware vCenter connection license related information. For
more information on vCenter connection license, see About OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter Licensing
Configuration Wizard Welcome Page
After you install the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter, it must be configured.
1. In the vSphere Client, from Home page, under Management tab, click the Dell Management Center icon.
2. The first time you click on the Dell Management Center icon, it opens the Configuration Wizard. You can also
access this wizard on the Dell Management Center → Settings page.
3. In the Welcome tab, review the steps you will step through, and then click Next.
Creating A New Connection Profile [Wizard]
A connection profile stores the credentials that the virtual appliance uses to communicate with Dell servers. Each Dell
server must be associated with a connection profile to be managed by the Dell Management Plug-in. You may assign
multiple servers to a single connection profile. Creating the Connection Profile is similar between the Configuration
Wizard and from the Dell Management Center, Settings option.
NOTE: With installations on hosts that are using 12th or later generation of the Dell PowerEdge servers, the OMSA
agent installation is not required. For installations on 11th generation servers, OMSA agent is now automatically
installed during the deployment process.
17
Page 18
To create a new connection profile using the wizard:
1. From the Connection Profiles tab, click Create New.
2. In the Profile Name and Description panel, enter the Profile Name and an optional Description that are used to help
manage custom connection profiles, and then click Next.
3. In the Associated Hosts panel, select the host(s) associated with the Connection Profile, and click Next.
4. View the information about credentials and connection protocols and click Next.
5. In the iDRAC panel, enter the iDRAC credential information.
a. Enter the User Name, Password, and Verify Password. The user name can contain up to 16 characters
including white space..The passwords must match and use ASCII-printable characters only.
NOTE: Passwords can contain up to 20 printable ASCII characters. The domain name can contain
alphanumeric characters, - (dash), or . (period) only.
b. For Certificate Check, select Enable to download and store the iDRAC certificate and validate it during all future
connections, or select
You need to select Enable if you are using Active Directory.
6. Click Next.
7. In the Host Root Credentials panel, do the following:
a. Enter the User Name, Password, and Verify Password. The passwords must match.
NOTE: Passwords cannot exceed 127 characters and cannot contain any special characters.
NOTE: For servers that do not have either an iDRAC Express or iDRAC Enterprise, when the iDRAC test
connection is run,
NOTE: The OMSA credentials are the same credentials used for ESX and ESXi hosts.
b. For Certificate Check, select Enable to download and store the OMSA certificate and validate it during all future
connections, or select Disable to perform no check and not store the certificate. Select Enable if you use Active
Directory.
8. Click Next.
9. The Test Connection window tests the entered iDRAC and Host Root Credentials on the selected servers. Do one of
the following:
Disable to perform no check and not store the certificate.
Not Applicable for this system
message is displayed.
• To begin the test, click Test Selected. The other options are inactive.
• To stop the tests click Abort All Tests.
10. To complete the profile, click Save.
11. To continue on to configure Events and Alarms, click Save and Continue.
Configuring Events And Alarms [Wizard]
Configure events and alarms using the Configuration Wizard or from the Dell Management Center, Settings option for
Events and Alarms.
NOTE: On hosts prior to 12th generation, this feature requires that the virtual appliance is configured as a trap
destination in OMSA to display host events in vCenter.
To configure events and alarms:
1. In the Configuration Wizard, under Event Posting Levels, select one of the following:
• Do not post any events - Block hardware events.
• Post All Events - Post all hardware events.
• Post only Critical and Warning Events - Post only critical or warning level hardware events.
18
Page 19

• Post only Virtualization-Related Critical and Warning Events - Post only virtualization-related critical and
warning events; this is the default event posting level.
2. To enable all hardware alarms and events, select the Enable Alarms for Dell Hosts check box.
NOTE: Dell hosts that have alarms enabled respond to critical events by entering maintenance mode.
3. In the dialog box that displays, click Continue to accept this change, or click Cancel.
NOTE: This step is only seen if Enable Alarms For Dell Hosts is selected.
4. To restore the default vCenter alarm settings for all managed Dell servers, click Restore Default Alarms.
It may take up to a minute before the change takes effect.
5. To continue the wizard, click Save and Continue.
Restoring the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter appliance backup does not restore all the Alarm settings.
However, in the OpenManage Integration for VMware GUI, the Alarms and Events field displays the restored settings. To
resolve this issue, in the OpenManage Integration for VMware GUI, in the Manage → Settings tab, manually change the
Events and Alarms settings.
NOTE: After restoring the appliance the Events and Alarms settings are not enabled even if the Graphic User
Interface shows it as enabled. You need to enable the Events and Alarms settings again from the Settings page
Setting Up A Proxy Server [Wizard]
Set the proxy server in the Configuration Wizard or later using the Dell Management Center, Settings → Proxy page.
To set up a proxy server:
1. In the Configure HTTP Proxy window, do one of the following:
• To not use a proxy server, click Save and Continue.
• To use a proxy server, under Settings enter a Proxy Server Address.
2. Enter the Proxy Port number.
3. Select the Credentials Required check box, if needed.
4. If you selected Credentials Required, do the following:
a. In the Proxy User Name text box, type the proxy user name.
b. In the Proxy Password text box, type the proxy password.
c. In the Verify Password text box, re-type the proxy password.
5. Under Proxy, select the Use Proxy check box.
6. To save these options and continue, click Save and Continue.
Scheduling Inventory Jobs [Wizard]
The inventory schedule configuration is similar between the Configuration Wizard and from the Dell Management Center
→ Settings option. The only difference is that the wizard supplies an option to select if you want to run the inventory
immediately.
NOTE: To make sure that the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter continues to display updated
information, it is recommended that you schedule a periodic inventory job. The inventory job consumes minimal
resources and will not degrade host performance.
To schedule an inventory job:
1. In the Configuration Wizard, in the Inventory Schedule window, do one of the following:
• To run inventory schedules, click On Selected Days.
19
Page 20

• To not run inventory schedules, select Do not run inventory on Dell hosts.
2. If you select On Selected Days, then do the following:
a. Select the check box next to each day of the week that you want to run the inventory.
b. In the text box, enter the time in HH:MM format.
The time you enter is your local time. Therefore, if you want to run the inventory at the virtual appliance time
zone, calculate the time difference between your local and virtual appliance time zone, and then enter the time
appropriately.
3. To apply the changes and continue, click Save and Continue.
Running A Warranty Retrieval Job [Wizard]
The warranty retrieval job configuration is similar between the wizard and from the Dell Management Center → Settings
option. In addition, you can run the Warranty Retrieval Job now, from Job Queue.
To run a warranty retrieval job:
1. In the Configuration Wizard, on the Warranty Schedule window, do one of the following:
• To run warranty schedules, click On Selected Days.
• To not run warranty schedules, select Do not retrieve Warranty Data.
2. If you selected On Selected Days, then do the following:
a. Select the text box next to each day of the week that you want to run the warranty jobs.
b. In the text box, enter the time in HH:MM format.
The time you enter is your local time. Therefore, if you want to run the inventory at the virtual appliance time
zone, calculate the time difference between your local and virtual appliance time zone, and then enter the time
appropriately.
3. To apply the changes and continue, click Save and Continue.
Configuring the Deployment Credentials [Wizard]
Deployment credentials are used to communicate securely with a bare-metal system that is discovered using
AutoDiscovery. For secure communication, it uses iDRAC from initial discovery until the end of the deployment process.
Once deployment completes, the credentials are changed to those in the connection profile matched to the bare-metal
system from the Deployment wizard. If the deployment credentials are changed, all newly discovered systems from that
point on are provisioned with the new credentials; however, the credentials on servers discovered prior to the change
are not affected.
NOTE: OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter acts as a provisioning server. The Deployment credentials
are set on the iDRAC that uses the plug-in as a provisioning server in the Auto Discovery process.
To configure the deployment credentials:
1. In the Deployment Credential window you can view or change the credentials. The bare— metal server switches
from these credentials to those specified in the Connection Profile.
2. To change these credentials, under Credentials for Bare Metal Server Deployment, do the following:
a. In the User name text box, edit the user name.
b. In the Password text box, edit the password.
c. In the Verify Password, text box, confirm the password.
3. To save the specified credentials and continue with the Configuration Wizard, click Save and Continue.
20
Page 21

Setting The Default Firmware Update Repository [Wizard]
Firmware repository settings contain the firmware catalog location used to update deployed servers. You can set up
firmware repository initially here in the wizard or later from the Dell Management Center → Settings option. In addition,
you can run the firmware update later from the OpenManage Integration tab.
To set the default firmware update repository:
1. In the Configuration Wizard, on the Firmware Repository page, to choose the default repository for firmware
updates, select one of the following:
• Dell Online
Default firmware repository (ftp.dell.com) with a staging folder. The OpenManage Integration for VMware
vCenter downloads selected firmware updates and stores them in the staging folder, and then they are applied
as necessary.
• Local/shared repository:
These are created with the Dell Repository Manager application. These local repositories should be located on
file shares.
2. If you selected Local/shared repository, do the following:
a. Enter the Catalog File Location using the following format:
• NFS share for xml file: host:/share/filename.xml
• NFS share for gz file: host:/share/filename.gz
• CIFS share for xml file: \\host\share\filename.xml
• CIFS share for gz file: \\host\share\filename.gz
b. If using a CIFS share, enter the User Name, Password, and Verify Password; the passwords must match. These
fields are only active when entering a CIFS share.
NOTE: The @ character is not supported for use in shared network folder user names/passwords.
c. To validate your entries click Begin Test.
3. To save this selection and continue the Configuration Wizard, click Save and Continue.
Enabling The OMSA Link [Wizard]
To launch OpenManage Server Administator (OMSA) within the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter virtual
appliance, the OMSA Web Server must be installed and configured. See the
Installation Guide
NOTE: OMSA is only required on Dell servers prior to 12th generation of Dell PowerEdge servers.
You can use OMSA to:
• Manage vCenter elements (detailed sensor/component-level health information).
• Clear command logs and system event logs (SELs).
• Obtain NIC statistics.
• Make sure that the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter captures events from a selected host.
1. In the Configuration Wizard, on the OpenManage Server Admin page, use the OMSA Web Server URL text box to
enter the OMSA URL. You must include the full URL including the HTTPS and the port number. For example,
https:\\<OMSA_Server_IP_or_hostname>:1311.
2. To save this URL and finish the Configuration Wizard, click Finish.
for instructions on how to install and configure the Web Server.
OpenManage Server Administrator
21
Page 22

Configuring NFS Shares
To use NFS shares with the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter for backup and restore operations, firmware
updates, and as a staging folder, there are certain configuration items that you must complete. CIFS shares do not
require additional configuration.
To configure NFS shares:
1. On the Linux or Unix OS machine hosting the NFS shares, edit /etc/exports to add: /share/path <appliance IP> (rw)
*(ro).
This allows the virtual appliance full read and write access to the share, but limits all other users to read only.
2. Start nfs services:
service portmap start
service nfs start
service nfslock status
NOTE: The steps above may vary depending on the Linux distribution in use.
3. If any of the services were already running:
exportfs -ra
Settings Overview
You can perform the following tasks from the Settings section:
• General: Set the OMSA URL that displays on the Dell Hosts tab in vCenter. You can also enable or disable Warranty
Expiration Notification.
• Events And Alarms: Enables or disables all hardware alarms (current alert status is displayed on the Alarms tab).
Also configures incoming event and alert filtering.
• HTTP Proxy: Enable or disable HTTP proxy usage during communication with Internet sites.
• Inventory Schedule: Sets vCenter Host Inventory Schedule.
• Warranty Schedule: Sets warranty information retrieval schedule for Dell hosts from Dell Online.
• Deployment Credentials: Sets up credentials to be used for communication with Dell servers during initial discovery
and bare metal server deployment.
• Firmware Repository: Lets you edit where your firmware updates are stored.
• Security: Provides a server white list that limits the servers that are deployed.
General Settings Overview
General settings are used to:
• Define the OpenManage Server Administrator (OMSA) URL.
• Enable or Disable Warranty Expiration Notification.
The OMSA software can be used to:
• Manage vCenter elements (detailed sensor, component-level health information).
• Clear command logs and system event logs (SELs).
• Obtain NIC statistics.
• Make sure that the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter captures events from a selected host.
22
Page 23
NOTE: OMSA software is only required on Dell servers prior to 12th generation of Dell PowerEdge servers.
Warranty Expiration Notification can be used to:
• Monitor the warranty expiration date.
• Set a minimum number of warranty days left threshold beyond which either a warning or critical alert is generated.
The alert appears as an icon on the host's OpenManage Integration tab.
Related Tasks:
• Enabling The OMSA Link
• Enable or Disable Warranty Expiration Notification
Enabling The OMSA Link Outside the Configuration Wizard
To launch OpenManage Server Administrator (OMSA) within the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter virtual
appliance, the OMSA Web Server must be installed and configured. See the
Installation Guide
NOTE: OMSA is only required on Dell servers prior to 12th generation of Dell PowerEdge servers.
To enable the OMSA link:
1. In the Dell Management Center, Settings → General under OMSA Launcher, click Edit.
2. Use the OMSA Web Server URL text box to enter the URL for OMSA. You must include the full URL including the
HTTPS and the port number 1311.
3. To save this URL, click Apply.
For information about setting up an OMSA trap destination, see Setting Up An OMSA Trap Destination.
for the version of OMSA in use for instructions on how to install and configure the Web Server.
Dell OpenManage Server Administrator
Enable or Disable Server Warranty Expiration Notification
Warranty settings control when server warranty information is retrieved from Dell online by enabling or disabling the
warranty schedule and then setting the Minimum Days Threshold alert. Use this page to enable or disable server
warranty expiration notifications for hosts and clusters. Set or edit this feature in the Dell Management Center on the
Settings, General Page.
To enable or disable server warranty expiration notification:
1. In the Dell Management Center, click Settings → General.
2. In the General page, to enable notifications, select the Enable Warranty Status Notifications check box.
3. To set the Minimum Days Threshold Alert do the following:
a. To set warnings, in the Warnings drop-down list select the number of days for warnings about server warranty
status.
b. To set critical license status, in the Critical drop-down list set the number of days for warning of critical server
warranty status.
4. To apply the changes, click Apply.
Creating A New Connection Profile
A connection profile stores the credentials that the virtual appliance uses to communicate with Dell servers. Each Dell
server must be associated with only one connection profile to be managed by the
vCenter. You may assign multiple servers to a single connection profile. Creating the Connection Profile is similar
between the Configuration Wizard and from the Dell Management Center → Settings. You can run the Configuration
Wizard when you first access the Dell Management Console, or run it later on the Settings window.
OpenManage Integration for VMware
23
Page 24

NOTE: With installations on hosts that are 12th and later generation of Dell PowerEdge servers, the OMSA agent
installation is not required. For installations on 11th generation of Dell PowerEdge servers, the OMSA agent is now
automatically installed during the deployment process.
NOTE: Refer the About OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter Licensing for more information about
licensing.
NOTE: You are not allowed to create a connection profile if the number of hosts added exceeds the license limit.
To create a new connection profile:
1. In the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter , in the left pane, click Connection Profiles.
2. In the Profile Name and Description page, enter the Connection Profile Name and an optional Connection Profile
Description that are used to help manage custom connection profiles.
3. In the Associated Hosts page, select the hosts for the connection profile and click Next.
4. In the Credentials page, read the information and click Next.
5. In the iDRAC page, under Credentials, do one of the following:
NOTE: The iDRAC account requires administrative privileges for updating firmware, applying hardware
profiles, and deploying hypervisor.
• For iDRACs already configured and enabled for Active Directory on which you want to use Active Directory,
select the Use Active Directory check box; otherwise skip down to configure the iDRAC credentials.
– In the Active Directory User Name text box, type the user name. Type the username in one of these formats:
domain\username or domain/username or username@domain. The user name is limited to 256 characters.
Refer to Microsoft Active Directory documentation for user name restrictions.
– In the Active Directory Password text box, type the password. The password is limited to 127 characters.
– In the Verify Password text box, type the password again.
– In the Certificate Check drop-down list, select one of the following:
* To download and store the iDRAC certificate and validate it during all future connections, select
Enable .
* To perform no check and not store the certificate, select Disabled.
• To configure iDRAC credentials without Active Directory, do the following:
– In the User Name text box, type the user name. The user name is limited to 16 characters. Refer to the
iDRAC documentation for information about user name restrictions for your version of iDRAC.
NOTE: The local iDRAC account requires administrative privileges for updating firmware, applying
hardware profiles, and deploying hypervisor.
– In the Password text box type the password. The password is limited to 20 characters.
– In the Verify Password text box, type the password again.
– In the Certificate Check drop-down list, select one of the following:
* To download and store the iDRAC certificate and validate it during all future connections, select Enable.
* To perform no check and not store the iDRAC certificate, select Disabled.
6. Click Next.
7. In the Host Credentials page, under Credentials, do one of the following:
24
Page 25
• For hosts already configured and enabled for Active Directory on which you want to use Active Directory,
select the Use Active Directory check box; otherwise skip down to configure your Host Credentials.
– In the Active Directory User Name text box, type the user name. Type the username in one of these formats:
domain\username or domain/username or username@domain. The user name is limited to 256 characters.
Refer to Microsoft Active Directory documentation for user name restrictions.
– In the Active Directory Password text box, type the password. The password is limited to 127 characters.
– In the Verify Password text box, type the password again.
– In the Certificate Check drop-down list, select one of the following:
* To download and store the Host certificate and validate it during all future connections, select Enable .
* To perform no check and not store the Host certificate, select Disabled.
• To configure Host Credentials without Active Directory, do the following:
– In the User Name text box, type the user name. The read only default user name is root. If you select Use
Active Directory the user name can be different from root.
– In the Password text box type the password. The password is limited to 127 characters.
NOTE: The OMSA credentials are the same credentials used for ESX and ESXi hosts.
– In the Verify Password text box, type the password again.
– In the Certificate Check drop-down list, select one of the following:
* To download and store the Host certificate and validate it during all future connections, select Enable .
* To perform no check and not store the Host certificate, select Disabled.
8. Click Next.
9. The Test Connection link is used to validate the provided iDRAC and Host Credentials for the selected servers. Do
one of the following:
• To begin the test, click Test Selected. The other options are inactive.
• To stop the tests click Abort Tests.
NOTE: For servers that do not have either an iDRAC Express or iDRAC Enterprise, the iDRAC test connection
result states Not Applicable for this system.
10. To complete the profile, click Save.
To manage connection profiles, see Managing Connection Profiles.
Configuring Events And Alarms
The Dell Management Center Events and Alarms page enables or disables all hardware alarms. The current alert status
is displayed on the vCenter Alarms tab. A critical event indicates actual or imminent data loss or system malfunction. A
warning event is not necessarily significant, but may indicate a possible future problem. Events and alarms can also be
enabled using the VMware Alarm Manager. Events are displayed on the vCenter Tasks & Events tab in the Hosts and
Clusters view.
NOTE: On hosts prior to 12th generation of Dell PowerEdge servers, this feature requires that the virtual appliance
is configured as a trap destination in OMSA to display host events in vCenter. For more information on OMSA, see
Setting Up An OMSA Trap Destination.
You can configure events and alarms using in the Dell Management Center under the Settings option for Events and
Alarms.
25
Page 26
To configure events and alarms:
1. In the Dell Management Center, under Settings → Events and Alarms , click Edit.
2. Under Event Posting Levels, select one of the following:
• Do not post any events - Block hardware events.
• Post All Events - Post all hardware events.
• Post only Critical and Warning Events - Post only critical or warning level hardware events.
• Post only Virtualization-Related Critical and Warning Events - Post only virtualization-related critical and
warning events; this is the default event posting level.
3. To enable all hardware alarms and events, select the Enable Alarms for Dell Hosts check box.
NOTE: Dell hosts that have alarms enabled respond to critical events by entering maintenance mode.
4. In the dialog box that displays, click Continue to accept this change, or click Cancel.
5. To restore the default vCenter alarm settings for all managed Dell servers, click Restore Default Alarms.
It may take up to a minute before the change takes effect.
6. To save, click Save.
About Proxy Configuration
The proxy settings define the HTTP proxy and any required credentials used to retrieve information from the Web
(including from Dell online), such as:
• Enable or disable the proxy server
• Enter the proxy server and port number needed
• Define any required credentials - user name and password
Related Tasks:
• Setting Up A Proxy Server
• Using The HTTP Proxy For Retrieving Web Based Data
• Setting Up The HTTP Proxy Using The Administration Console
Setting Up A Proxy Server
Set up the proxy server in the Configuration Wizard or later using the Settings option, Proxy.
NOTE: Proxy passwords cannot exceed 31 characters.
To set up a proxy server:
1. In the Dell Management Center, select Settings → HTTP Proxy, and then click Edit.
2. In the HTTP Proxy window, do one of the following:
• To not use a proxy server, click Save and Continue.
• To use a proxy server, under Settings enter a Proxy Server Address.
3. Enter the Proxy Port number.
4. Select the Credentials Required check box, if needed.
5. If you selected Credentials Required, do the following:
a. In the Proxy User Name text box, enter the proxy user name.
b. In the Proxy Password text box, enter the proxy password.
c. In the Verify Password text box, re-enter the proxy password you just typed.
26
Page 27

6. Under Proxy, select the Use Proxy check box.
7. To save these options, click, Save.
Using The HTTP Proxy For Retrieving Web Based Data
To use the HTTP proxy for retrieving Web based data:
1. In the Dell Management Center, select Settings → HTTP Proxy, and then click Edit.
2. Select the Use Proxy check box.
3. Click Apply.
4. To validate settings, click Test Connection.
Running Inventory Jobs
To run the inventory job:
1. Once the Configuration Wizard is complete, click Job Queue → Inventory → Run Now to immediately run an
inventory job.
2. To see the status of the inventory job, click Refresh.
3. Navigate to the Host and Cluster view, click on any Dell host, then click the OpenManage Integration tab. The
following info should be available:
• Overview Page
• System Event Log
• Hardware Inventory
• Storage
• Firmware
• Power Monitoring
• Warranty Status
NOTE: Inventory job for hosts exceeding the license limit will be skipped and marked as Failed.
The following host commands work within the OpenManage Integration tab:
• Blink Indicator Light
• Run Firmware Update Wizard
• Launch Remote Access
• Launch OMSA
• Launch CMC
Running A Warranty Retrieval Job
The warranty retrieval job configuration is similar between the wizard and from the Dell Management Center → Settings
option. After running the wizard you can edit at anytime from the Dell Management Center → Settings → Warranty
Schedule page. You can run the Warranty Retrieval job now from the Job Queue → Warranty History page.
To schedule a warranty retrieval job:
1. In the Dell Management Center, select Settings → Warranty Schedule.
2. In the Warranty Schedule window, click Edit.
3. To configure the schedule, do one of the following:
a. To run Warranty Schedules, click On Selected Days.
b. To not run Warranty Schedules, select Do not run inventory on Dell hosts.
27
Page 28

4. If you selected On Selected Days, then do the following:
a. Select the check box next to each day of the week that you want to run the warranty jobs.
b. In the text box, enter the time in HH:MM format.
The time you enter is your local time. Calculate the time difference you need to run the warranty jobs at the
proper time.
5. To run the warranty jobs now, navigate to Job Queue → Warranty History and then click Run Now.
Viewing or Editing Deployment Credentials
In Dell Management Center, you can edit the deployment credentials. Deployment credentials are used to securely
communicate with a bare-metal system using the iDRAC from initial discovery, until the end of the deployment process.
Once deployment completes, the credentials are changed to those in the connection profile matched to the bare-metal
system from the deployment wizard. If the deployment credentials are changed, all newly discovered systems from that
point on will be provisioned with the new credentials - the credentials on servers discovered prior to the change of
credentials are not affected by this change. The user name should be 16 characters or less (only ASCII printable
characters). The password should be 20 characters or less (only ASCII printable characters).
To view or edit deployment credentials:
1. In Dell Management Center → Settings → Deployment Credentials, click Edit.
2. In the Credentials for Bare Metal Server Deployment, under Credentials, do the following:
• In the User Name text box, enter the user name.
The user name should be 16 characters or less (only ASCII printable characters).
• In the Password text box, enter the password.
The password should be 20 characters or less (only ASCII printable characters).
• In the Verify Password text box, enter the password again.
The passwords must match.
3. Click Apply.
Setting Up The Firmware Repository
To set up the firmware repository and credentials:
1. In the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter , select Settings → Firmware Repository and then click Edit.
2. On the Firmware Repository page, to choose the default repository for firmware updates, select one of the
following:
• Dell Online
This uses the default firmware update repository of Dell online (ftp.dell.com) with a required staging folder. The
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter downloads selected firmware updates and stores them in the
staging folder, and then they are applied as necessary.
• Shared Network Folder
Hosts using Lifecycle Controller can update from a custom repository which is hosted on a accessible network
shared folder. To create a custom repository, Dell recommends using Dell Repository Manager to create it and
then save it to a shared location where the hosts and OpenManage Integration can access it. Enter the location
of the repository's catalog file below.
3. If you select Shared Network Folderenter the full the of catalog file in the Catalog File Location field
4. Click Begin Test.
5. Click Apply.
28
Page 29
Server Security Settings For Deployment
Restrict the set of deployable servers using a white list. If a server is in the white list, it is provided with credentials
during the Auto-Discovery and handshake process and is displayed in the list of servers that are used for deployment.
The white list is maintained by manually adding server service tags, deleting service tags, or importing a list of service
tags from a CSV file.
NOTE: Use a CSV-delimited file to import servers. This contains multiple records on different lines where each
record has one or more service tags separated by commas.
To set up and manage white lists choose from the following:
• Enabling A Server White List
• Adding Servers To A White List
• Deleting Servers From A WhiteList
Enabling A Deployable Server White List
For information about security settings for deployable servers, see Server Security Settings For Deployment.
To enable a server white list:
1. In the Dell Management Center, in the left pane, select Settings.
2. In the right-pane, select Security.
3. In the Security window, click Edit.
4. To use the white list to restrict server deployment, select the Enforce Server White List check box.
5. Click Apply, and the server white setting changes to ENABLED.
Adding Deployable Servers To A White List
For information about security settings for deployable servers, see Server Security Settings For Deployment. When
enforced, only Dell servers on the Server White List are available for deployment using the OpenManage Integration for
VMware vCenter. You can add deployable servers to a white list manually or import using a list.
To add deployable servers to a white list:
1. In the Dell Management Center, in the left pane, select Settings → Security.
2. In the Server White List window, click Edit, then do one of the following:
• To add servers to the white list manually, click Add Server.
– In the Add Service Tags, dialog , enter the service tags.
– To add the tags, click Continue.
• To import a list of service tags, click Import White List.
– When the Select File to Upload dialog box displays, navigate to the CSV file and click Open.
For an example white list:
ASDFG12
SDCNRD0
TESCVD3
AS243AS, ASWERF3, FGVCSD9
– When the We found these service tags in your file dialog displays, click Apply.
The service tags are now displayed in the Service Tag list.
29
Page 30

Deleting Deployable Servers From A White List
For information about security settings for deployable servers, see Server Security Settings For Deployment.
To delete deployable servers from a white list:
1. In the Dell Management Center, in the left pane, select Settings.
2. In the right-pane, select Security.
3. In the Security window, click Edit.
4. Do one of the following:
• To delete an individual server, click the Service Tag check box, and then click Delete Selected.
• To delete all servers, click the Service Tag check box, and then click Delete Selected.
5. When the Are you sure you want to delete the selected service tags dialog displays, click Apply , or click Cancel to
cancel.
6. To complete the changes, click Apply.
About Host, Bare Metal, and iDRAC Compliance Issues
To manage hosts, bare metal servers, and iDRAC with the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter each must
meet certain minimum criteria. If not compliant, then they are not managed properly by the OpenManage Integration for
VMware vCenter. Use the Fix Non-Compliant Hosts, Bare Metal Server, and iDRAC compliance links to see which host/
bare metal servers/iDRACs in your configuration are not compliant and fix them. This wizard displays hosts/bare metal
servers/iDRACs where:
• Hosts have not been assigned to a connection profile.
If a connection profile is not assigned to a host, a dialog box is offered to take you to the Connection Profile screen.
This configuration is outside this wizard. Return later to run this wizard.
• Collect System Inventory on Reboot (CSIOR) is disabled or has not been run, which requires a manual reboot.
• The OMSA agent (Host Root credentials ) is not installed, is out of date, or not configured properly.
• Bare metal servers have outdated Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller (iDRAC) firmware, Lifecycle Controller
(LC) firmware, or BIOS versions.
CAUTION: Hosts in Lockdown Mode will not appear in compliance checks even if they are non-compliant. They do
not display because their compliance status cannot be determined. Make sure to check the compliance of these
systems manually. When this is the case a warning displays.
In each case, you need to fix the compliance issues by running one of the following:
• To fix vSphere host compliance issues, see Running The Fix Non-Compliant vSphere Hosts Wizard
• To fix bare metal servers that have compliance issues, see Running The Fix Non-Compliant Bare Metal Server
Wizard
• To fix iDRAC compliance issues: iDRAC License Compliance
Related Information:
• Re-Checking Bare Metal Server Compliance
• Downloading An ISO For Manual Firmware Updates
Running The Fix Non-Compliant vSphere Hosts Wizard
Run the Fix Non-Compliant vSphere Hosts Wizard to fix non-compliant hosts. For information about compliance, see
About Host And Bare Metal Compliance Issues. Some non-compliant ESXi hosts require reboots. An ESXi host reboot is
30
Page 31

required if OpenManage Server Administrator (OMSA) must be installed or updated. In addition, a reboot is required on
any host that has never run CSIOR. If you select to automatically reboot an ESXi host, the following actions take place:
• For a CSIOR status fix:
If CSIOR is not enabled on the host, then CSIOR is set to ON on the host, and then the host is set into maintenance
mode and rebooted.
• For an OMSA status fix:
a. OMSA is installed on the host.
b. The host is set to maintenance mode and rebooted.
c. After the reboot completes, OMSA is configured for the changes to take effect.
d. The host comes out of maintenance mode.
e. Inventory is run to refresh data.
To run the Fix Non-Compliant vSphere Hosts Wizard:
1. In the Dell Management Center, in the left pane, click Compliance → vSphere Hosts.
2. In the vSphere Host Compliance window, view the noncompliant hosts, then click Fix Non-Compliant vSphere
.
Hosts
3. In the Fix Non-Compliant vSphere Hosts wizard, select the check boxes for the hosts you want to fix.
4. Click Next.
5. If there is a server without a connection profile, you are given the option to exit the wizard and fix these systems
from the Connection Profile page, or continue with this wizard. See, Creating A New Connection Profile. When
done, return to this wizard.
6. In the Turn On CSIOR window, select the check boxes to turn on CSIOR for the selected hosts.
7. Click Next.
8. In the Fixing OMSA window, select the check boxes to fix OMSA for the selected hosts.
9. Click Next.
10. In the Reboot Hosts window, view the ESXi hosts that must be rebooted. An ESXi host reboot is required if OMSA
must be installed or updated. In addition, a reboot is required on any host that has never run CSIOR. Do one of the
following:
• If you want to automatically put hosts in maintenance mode and reboot when required, select the Automatically
put hots in maintenance mode and reboot whenever required check box.
• If you want to reboot manually, you must do the following:
1. Once the
2. Once the host is up and if OMSA is not configured, configure OMSA manually or use the Compliance
Wizard.
3. Re-run inventory, see Running Inventory Jobs.
11. Click Next.
12. In the Summary window, review the actions that take place on the non-compliant hosts. Manual reboots are
required for these to take effect.
13. Click Finish.
Install OMSA
task is completed for a host, reboot the host.
Running The Fix Non-Compliant Bare Metal Server Wizard
Run the Fix Non-Compliant Bare Metal Server Wizard to fix non-compliant bare metal servers. For information about
compliance, see About Host And Bare Metal Compliance Issues.
31
Page 32

To run the Fix Non-Compliant Bare Metal Server Wizard:
1. In the Dell Management Center, in the left pane, click Compliance → Bare Metal Servers.
2. In the Bare Metal Servers window, view the non-compliant hosts, then click Fix Non-Compliant Bare Metal Servers.
3. In the Fix Bare Metal Servers wizard, select the check boxes for the hosts you want to fix.
4. Click Next.
5. In the Summary window, review the actions that take place on the non-compliant bare metal servers.
6. Click Finish.
Re-checking Bare Metal Server Compliance
For servers you have fixed outside of the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter, you must run this manual server
compliance re-check. You can find this on the Dell Management Center, Compliance, Bare Metal Servers page.
To re-check bare metal server compliance:
1. In the Dell Management Center → Compliance → Bare Metal Servers page, click Re-check Compliance.
2. In the Non-Compliant Servers window, to refresh the list, click Refresh.
3. To run the re-check, click Check Compliance.
4. To abort the re-check, click Abort All Tests.
5. If you successfully fixed your system, the list refreshes and your system is removed from the list. If not, the noncompliant system remains on the list.
6. When finished, click Done.
Downloading An ISO For Manual Firmware Updates
The OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter automatically fixes most compliance issues. Sometimes, a manual
ISO installation is required. .You can download the required ISO to manually fix compliance using the following steps:
1. In the Dell Management Center → Compliance → Bare Metal Servers page, to download an ISO, click Download
ISO.
2. In the Download ISO dialog box, to find the location of the ISO, click Download.
NOTE: The external browser may open behind this application window.
3. Navigate to the ISO file you need to make your bare metal server compliant.
4. Burn that ISO, boot the host through that ISO and then update the FW components to the required level.
iDRAC License Compliance
When you select the iDRAC License Compliance page, it runs a compliance test. This test lasts for a few minutes. The
vSphere hosts and bare metal servers listed on this page are non-compliant because they do not have a compatible
iDRAC license. The table displays the status of the iDRAC license. On this page you can see how many days remain on
your license and update it as required. If your
that are non-compliant due to the iDRAC license. If the
means there are no bare metal servers that are non-compliant due to the iDRAC license.
1. In Dell Management Center, in the left pane, click Compliance.
2. Expand Compliance, and click iDRAC License.
Once you arrive to this page the compliance test runs. This is the same test that runs when you click Refresh.
3. If your license is out of date, click Purchase/Renew iDRAC License.
4. Log into the Dell License Management page and update or purchase a new iDRAC license.
Use the information on this page to identify and update your iDRAC.
5. After you install an iDRAC license, run an inventory job for vSphere hosts and return to this page after the inventory
job completes. For bare metal servers, recheck licensed bare metal server compliance.
Run inventory job
Recheck Bare Metal Server Compliance
link is disabled, that means there are no vSphere hosts
link is disabled, that
32
Page 33

Upgrading OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter
The following is the upgrade scenario for the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter:
• Upgrading From Trial Version To Full Product Version
NOTE: Perform an appliance backup before you begin the upgrade. See Performing An Immediate Backup.
Upgrading From a Trial Version To a Full Product Version
To upgrade from trial version to a full product versions:
1. Go to the Dell Web site and purchase the full product version.
You may also access the Dell Web site in the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter using one of the Buy
Now links, like the one located in the Administration Portal on the Licensing window. This is applicable only when
you are using evaluation license.
2. The download includes the new full version product, and a new license file.
3. Launch a browser window and enter the Administration Console URL displayed in the vSphere vCenter Console tab
for the virtual machine you want to configure or use the link from the
The URL uses the following format and is case insensitive: https://<ApplianceIPAddress>
4. In the Administration Console login window, enter the password and click Login.
5. To upload the license file, click Upload.
6. In the Upload License window, click Browse to navigate to the license file.
7. Select the license file and then click Upload.
Dell Management Console → Settings page.
About OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter Licensing
The OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenterhas two types of licenses:
Evaluation
license
Standard license The full product version contains a standard license for up to ten vCenters and you can
When you upgrade from a evaluation license to a full standard license, a new license XML file along with the Zip file that
contains the license file to be uploaded is sent to you by e-mail. Save the file to your local system and upload the new
license file using the Administration Console. Licensing presents the following information:
• Maximum vCenter Connection Licenses - up to ten registered and in use vCenter connections are allowed.
• Maximum Host Connection Licenses - the number of host connections that were purchased.
• In Use - the number of vCenter connection or host connection licenses in use. For host connection, this number
represents the number of hosts (or servers) that have been discovered and inventoried.
• Available - the number of vCenter connection or host connection licenses available for future use.
• Unlicensed Hosts - The number of host connections that exceeded the licensed amount. The OpenManage
Integration for VMware vCenter continues to function normally, but a new license must be purchased and installed
to resolve this warning
The trial version contains a evaluation license for five hosts (servers) that are managed by the
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter.This is applicable only for 11th and later
generations. This is a default license and is for a 90 days trial period only.
purchase any number of host connections that are managed by the OpenManage Integration
for VMware vCenter.
33
Page 34

End-To-End Hardware Management
The goal of end-to-end hardware management is to provide the system health status and up-to-date infrastructure
information that an administrator needs to respond to critical hardware events without leaving the Dell Management
Center or vCenter. End-to-end hardware management within the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter is
divided into four separate parts:
• Monitoring
• Inventory
• Advanced host management
• Warranty retrieval
Monitoring the Datacenter And Host System
Datacenter and host system monitoring lets an administrator monitor infrastructure health by displaying hardware
(server and storage) and virtualization-related events on the Tasks & Events tab in vCenter. Additionally, critical
hardware alerts can trigger the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter alarms. Few alarms defined for Dell
virtualization-related events can move the managed host system to maintenance mode.
To perform monitoring:
4
1. Configure the Event and Alarm settings.
2. Configure SNMP OMSA trap destinations, if needed.
3. Use the Tasks & Events tab in vCenter to review event information.
Understanding Events And Alarms
You can edit events and alarms from the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter within Manage → Settings tab.
From here you can select the Event Posting Level, enable Alarms for Dell Hosts, or Restore Default Alarms. You can
configure events and alarms for each vCenter or all at once for all registered vCenters.
There are four event posting levels.
Table 1. Event Posting Level Descriptions
Event Description
Do not post any Events Do not have the OpenManage Integration for VMware
vCenter forward any events or alerts into related vCenters.
Post all Events Post all events, including informal events, that the
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter receives
from managed Dell hosts into related vCenters.
Post only Critical and Warning Events Posts only events with either Critical or Warning criticality
into related vCenters.
34
Page 35

Post only Virtualization-Related Critical and Warning
Events
When you configure your events and alarms, you can enable them. When enabled, critical hardware alarms can trigger
the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter to put the host system into a maintenance mode, and in certain cases,
migrate the virtual machines to another host system. The OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter forwards events
received from managed Dell hosts, and creates alarms for those events. Use these alarms to trigger actions from
vCenter, like a reboot, maintenance mode, or migrate. For example, when a dual power supply fails and an alarm is
created, the resulting action is to migrate the virtual machine on that machine to a new one.
A host enters or leaves maintenance mode only as when you request it. If the host is in a cluster when it enters
maintenance mode, you are given the option to evacuate powered-off virtual machines. If this option is selected, each
powered-off virtual machine is migrated to another host, unless there is no compatible host available for the virtual
machine in the cluster. While in maintenance mode, the host does not allow deployment or
machine. Virtual machines that are running on a host entering maintenance mode need to be either migrated to another
host or shut down, either manually or automatically by VMware Distributed Resource Scheduling (DRS).
Any hosts outside of clusters, or in clusters without VMware Distributed Resource Scheduling (DRS) enabled, could see
virtual machines being shut down due to a critical event. DRS continuously monitors usage across a resource pool and
intelligently allocates available resources among virtual machines according to business needs. Use clusters with DRS
configured in conjunction with Dell Alarms to make sure that virtual machines are automatically migrated on critical
hardware events. Listed in the details of the on screen message are any clusters on this vCenter instance that may be
impacted. Confirm that the clusters are impacted before enabling Events and Alarms.
If you ever need to restore the default alarm settings, you can do so with the Reset Default Alarm button. This button is a
convenience to restore the default alarm configuration without uninstalling and reinstalling the product. If any Dell alarm
configurations have been changed since install, those changes are reverted using this button.
Post Virtualization related events received from hosts into
related vCenters. Virtualization related events are those
that Dell has selected to be most critical to hosts running
virtual machines.
power-on
of a virtual
NOTE: To receive Dell events, you must enable the events.
NOTE: The OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter pre-selects the virtualization-related events that are the
essential to hosts successfully running virtual machines. Dell host alarms are disabled by default. If Dell alarms
are enabled, the clusters should use the VMware Distributed Resource Scheduler to make sure that the virtual
machines that send critical events are automatically migrated.
Understanding OMSA For 11th Generation Dell PowerEdge Hosts
On PowerEdge servers earlier than 12th generation, it is mandatory to install OMSA to work with the OpenManage
Integration for VMware vCenter. OMSA is installed automatically on 11th generation Dell PowerEdge hosts during
deployment, or if you want to install it manually, you may still do so.
NOTE: When deploying the OMSA agent using the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter starts the
httpClient service and enables port 8080 on and releases after ESXi 5.0 to download OMSA VIB and install it. Once
the OMSA installation is completed, the service automatically stops and the port is closed.
To configure OMSA on 11th generation Dell PowerEdge servers, choose from the following:
• Deploying an OMSA Agent Onto ESXi System
• Deploying an OMSA Agent Onto ESX System
• Setting Up An OMSA Trap Destination
Deploying the OMSA Agent onto an ESX System
Install the OMSA tar.gz on an ESX system to gather inventory and alert information from the systems.
35
Page 36

NOTE: OpenManage agents are required on Dell hosts earlier than Dell PowerEdge 12th generation servers. Install
OMSA using the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter or install manually to hosts prior to installing the
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter. Details on manually installing the agents are at http://
en.community.dell.com/techcenter/systems-management/w/wiki/1760.openmanage-server-administratoromsa.aspx.
To deploy the OMSA agent tar.gz on an ESX system with the required remote enablement setting (-c) option:
1. Run the OMSA agent installation script:
srvadmin-install.sh -x -c
2. Start OMSA services:
srvadmin-services.sh start
3. If the OMSA agent is already installed, make sure that it has remote enablement configuration (-c) option or
theOpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter installation will not complete successfully. Reinstall it with the -c
option and restart the service:
srvadmin-install.sh -c
srvadmin-services.sh restart
Deploying The OMSA Agent Onto An ESXi System
Install the OMSA VIB on an ESXi system to gather inventory and alert information from the systems.
NOTE: OpenManage agents are required on Dell hosts earlier than Dell PowerEdge 12th generation servers. Install
OMSA using the
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter. Details on manually installing the agents are at http://
en.community.dell.com/techcenter/systems-management/w/wiki/1760.openmanage-server-administratoromsa.aspx.
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter or install manually to hosts prior to installing the
1. If not already installed, install the vSphere command line tool (vSphere CLI) from http://www.vmware.com.
2. Enter the following command:
Vihostupdate.pl -server <IP Address of ESXi host> -i -b OM-SrvAdmin-DellWeb-6.3.0-2075.VIB-ESX41i_A00.8.zip
NOTE: It can take a few minutes for OMSA to install. This command requires a reboot of the host after it
completes.
Setting Up An OMSA Trap Destination
All 11th generation of hosts must have OMSA configured.
NOTE: OMSA is only required on Dell servers earlier than 12th generation Dell PowerEdge servers.
To set up an OMSA trap destination:
1. Either use the link to the OMSA user interface found in Settings → General, or navigate to the OMSA agent from a
Web browser (
2. Log in to the interface, and select the Alert Management tab.
3. Select Alert Actions and make sure that any events to be monitored have the Broadcast Message option set, so
that the events will be sent out.
4. Select the Platform Events option at the top of the tab.
5. Click the grey Configure Destinations button, and click the Destination link.
6. Select the Enable Destination check box.
7. Enter the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter appliance IP address in the Destination IP Address field.
8. Click Apply Changes.
9. Repeat step 1 to step 8 to configure additional events.
https://<HostIP>:1311/).
36
Page 37

Viewing Events
To view events, do one of the following:
• Navigate to the virtual machine and right-click to display the vCenter → Tasks & Events tab and click Events so that
the selected level of events is displayed.
• Click on the parent node (cluster or datacenter) of the host or the root folder of the vCenter.
Events appear only on those nodes in the vSphere tree.
vSphere Client Host Overview
The Overview provides information on key host server attributes, including individual component health, identification,
hypervisor, and firmware information.
HARDWARE COMPONENT HEALTH
Component health is a graphical representation of the status of all major host server components: system chassis,
power supply, temperature, fans, voltage, processors, batteries, intrusion, hardware log, power management, and
memory. The available status states are:
• Healthy (green check mark) - component operating normally
• Warning (yellow triangle with exclamation point) - component has a non-critical error
• Critical (red X) - component has a critical failure
• Unknown (question mark) - status is unknown for the component
A global health status is displayed in the upper-right header bar.
SERVER INFORMATION
Server information provides identification, hypervisor, and firmware information, such as:
• Host name, power state, iDRAC IP, Management IP, connection profile in use, model, service tag and asset tag
numbers, number of days left on the warranty, and when the last inventory scan was performed.
• Hypervisor, BIOS firmware, and iDRAC firmware versions.
• Ten most recent system event log entries. Click Details to launch the System Event Log window that displays
additional log details.
Host Information
In the left pane of the Host Overview, you can find the links to the following types of Host information:
• System Event Log
Displays hardware system event log information. See, Understanding System Event Logs.
• Hardware Inventory
Displays information about the following hardware devices:
– Field Replaceable Units (FRUs) such as DIMMs, system planar, power supplies, backplanes, controller cards,
etc.
– Memory - Number of slots available and in use, maximum capacity and amount of memory in use, and details on
individual DIMMs.
– Network Interface Cards (NICs) - Number of installed cards and details on individual NICs.
– PCI Slots - Total available and number in use and details on individual slots.
– Power Supplies - Number present and details on individual PSUs.
– Processors - Number present and details on individual CPUs.
37
Page 38

– Remote Access Card - IP address information and RAC type and Web interface URL.
See, About Inventory Jobs.
• Storage
The host system storage provides a graphical and detailed view of the capacity and type of physical and logical
storage for storage connected to a host-based storage controller, including:
– Host system total storage, unconfigured, configured, and both global and dedicated hot spare disks capacity
– List of how many of each storage component is present in the system component data table that contains
detailed information on that component
• Firmware
Run the Firmware Update Wizard or view your firmware version. See, Firmware Updates.
• Power Monitoring
The host system power monitoring provides general power information, energy statistics, and reserve power
information, including:
– Current power budget, profile, warning and failure thresholds
– Energy consumption, system peak power, and amperage statistics
– Reserve power and peak reserve capacity
NOTE: Not all power supplies support this feature and blade enclosure power supplies are not supported.
• Warranty
Warranty retrieval provides the following information for Dell servers:
– Updated service warranty information, while only transmitting the host service tag
– Warranty information updated at scheduled intervals
– Secure transmission using a proxy server and credentials
– Information through a tested, secure connection
See, Warranty Retrieval.
Host Actions
The Host actions are commands you performed on the current host server, such as:
• Use the Blink Indicator Light to blink the LCD front indicator light. See, Setting Up Physical Server Front Indicator
Lights.
• Use the Run Firmware Update Wizard to display the Firmware Update wizard and update the host server firmware.
See, Running the Firmware Update Wizard.
• Use the iDRAC Reset to reset iDRAC without rebooting the host.
See, Resetting iDRAC.
Management Consoles
The management consoles are used to launch external system management consoles, such as:
• Click Remote Access Console to launch the Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller (iDRAC) Web user interface.
• Click OMSA Console to launch the OpenManage Server Administrator (OMSA) user interface if it has been
configured. See, Enabling The OMSA Link
• Click Blade Chassis Console to launch the Chassis Management Controller (CMC) Web user interface.
Dell Online Services
38
Page 39

Resetting iDRAC
Sometimes iDRAC may become nonresponsive to requests and this results in unexpected behavior within the
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter. The only way to recover from this state is to reset iDRAC. An iDRAC reset
performs a normal reboot of the iDRAC. This reboot does not reboot the host. After you perform a reset, it takes 1 or 2
minutes for iDRAC to return to a usable state.
While iDRAC is rebooting, you may see:
• Some delay or a communication error while the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter obtains its health
status.
• All open sessions with iDRAC close.
• DHCP address for iDRAC may change. If iDRAC uses DHCP for its IP address, then there is a chance that the IP
address will change. If this happens, rerun the host inventory job to capture the new iDRAC IP in the inventory data
NOTE: A soft reset of iDRAC may not always work to get iDRAC back to reusable state. You may need a hard reset.
To do a hard reset, on the server, power off server, remove the power cable for 2 minutes and connect it back. For
more information on resetting iDRAC, refer to your version of iDRAC User’s Guide.
NOTE: Dell recommends that you place the host in maintenance mode before resetting iDRAC.
1. In vSphere Client, under the Inventory heading, select Hosts and Clusters.
2. From Hosts and Clusters, select the host system in the tree view and select the OpenManage Integration tab.
3. Under Host Actions, select iDRAC Reset.
4. On the iDRAC Rest dialog box, select the Continue iDRAC Reset, and click OK.
About Inventory Schedule
The inventory schedule sets the time/day for running inventory jobs, such as:
• Weekly at a specific time and on selected days
• At a set time interval
Most of the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter features require that an inventory is completed first to gather
required data. An inventory of all host systems must be collected to display this information. To perform an inventory on
host systems, create a connection profile that provides communication and authentication information. Once the
inventory is complete, you can view the inventory results for an individual host system.
NOTE: To make sure that the inventory contains up-to-date information, schedule the inventory job to run a
minimum of once a week. The inventory job consumes minimal resources and does not degrade host
performance.
Related Tasks:
• Running Inventory Jobs
• Modifying An Inventory Job Schedule
• Displaying The Inventory For A Single Host System
• Displaying The Datacenter Hardware Configuration And Status
Modifying An Inventory Job Schedule
The Inventory Schedule sets the time/day for running inventory jobs, such as:
39
Page 40

• Weekly at a specific time and on selected days.
• At a set time interval a completed inventory is required to gather the data needed by the majority of the
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter features.
NOTE: To make sure that the inventory contains up-to-date information, the inventory job should run a minimum of
once a week. The inventory job consumes minimal resources and does not degrade host performance.
To modify the inventory job schedule:
1. From the Dell Management Center, select Settings → Inventory Schedule.
2. To change the current schedule, click Edit.
3. Select the On Selected Days option button, and then select the check box for the day of the week and enter the
time. Click
4. To change the inventory schedule, click Apply, or to cancel the inventory schedule, click Cancel.
5. To run the job now, from the management center, select Job Queue and the Inventory History tab.
6. Click Run Now.
7. To update the Details of Last Inventory Job, click Refresh.
Clear to clear the entries.
Displaying The Inventory For A Single Host System in vCenter
To display the inventory for a single host system:
1. From the vSphere client, under the Inventory heading select Hosts and Clusters.
2. From Hosts and Clusters, in the left pane, select the host system, and then select the OpenManage Integration tab.
3. An overview of the selected host is displayed.
The overview provides information on key host server attributes, including individual component health,
identification, hypervisor, and firmware information.
• Hardware Component Health is a graphical representation of the status of all major host server components:
system chassis, power supply, temperature, fans, voltage, processors, batteries, intrusion, hardware log, power
management, and memory. The available status states are:
– Healthy (green check mark) - component operating normally
– Warning (yellow triangle with exclamation point) - component has a non-critical error
– Critical (red X) - component has a critical failure
– Unknown (question mark) - status is unknown for the component
A global health status is displayed in the upper-right header bar.
• Server Information provides identification, hypervisor, and firmware information, such as:
– Host name, power state, iDRAC IP address, Management IP address, connection profile in use, model,
service tag and asset tag numbers, number of days left on the warranty, and when the last inventory scan
was performed
– Hypervisor, BIOS firmware, and iDRAC firmware versions
– Fault Resilient Memory (FRM): This is a BIOS attribute and is enabled in the BIOS during initial setup of the
sever and displays the memory operational mode of the server. You need to restart your system when you
change memory operational mode value. This is applicable for R620, R720, T620, M620 and 13th generation
servers with ESXi 5.5 or later version. The four different values are:
* Enabled and Protected: This value indicates that the system is supported and the operating system
version is ESXi 5.5 or later, and the memory operational mode in BIOS is set to FRM.
* Enabled and Not Protected: This value indicates that the memory operational mode in BIOS is set to
FRM, but the operating system does not have support for this feature.
40
Page 41

* Disabled: This value indicates that it supports valid systems with any operating system version and here
memory operational mode in BIOS is not set to FRM.
* Blank: If memory operational mode in BIOS is not supported the FRM attribute is not displayed.
• Recent System Log Entries provide the 10 most recent system event log entries. To launch the System Event
Log window that displays additional log details, click Details.
4. Under Host Information, click Hardware Inventory to display a list and further details on all components installed in
host system, including:
• Field-replaceable units (FRUs) - DIMMS, system planar, power supplies, backplanes, controller cards, and so
on.
• Memory - Number of slots available and in use, maximum capacity and amount of memory in use, and details
on individual DIMMs.
• Network Interface Cards (NICs) - Number of installed cards and details on individual NICs.
• PCI Slots - Total available and number in use, and details on individual slots.
• Power Supplies - Number present and details on individual PSUs.
• Processors - Number present and details on individual CPUs.
• Remote Access Card - IP address information, RAC type, and Web interface URL.
5. Under Host Information, click Storage to display a graphic and detailed view of the capacity and type of physical
and virtual storage, including:
• Host system total storage, unconfigured, configured, and global hot spare disk capacity.
• List of how many of each storage component is present in the system.
• Component data table that contains detailed information on that component.
6. Under Host Information, click Firmware to display all Dell Lifecycle Controller firmware information including:
• Update name - BIOS, Dell Lifecycle Controller, power supply, and so on.
• Update type - BIOS, firmware, or application.
• Individual update details - Version, installation time, if an update is in progress or the update status, and the
update version. The update status and version only have data when an update is scheduled, and the update
version is the firmware version to which the system will be updated.
7. Under Host Information, click Power Monitoring to display general power information, energy statistics, and
reserve power information, including:
• Current power budget, profile, warning and failure thresholds.
• Energy consumption, system peak power, and amperage statistics.
• Reserve power and peak reserve capacity.
8. Under Host Information, click Warranty to display system warranty information including:
• Warranty provider name and description of the warranty.
• Start and end dates and how many days are left on the warranty.
• Status of the warranty (Active, Expired) and when the warranty information was last updated.
Inventory And Licensing
If server data cannot be retrieved and displayed, there are several possible causes:
• The server was not associated with a connection profile, and therefore an inventory task cannot be completed.
• An inventory task was not run on the server to collect the data, therefore there is nothing to display.
• The number of host licenses is exceeded, and you must have additional licenses available in order for the inventory
task to complete.
41
Page 42

• The server does not have the correct iDRAC license required for 12th and later generation servers and you must
purchase the correct iDRAC license.
The Buy Now link is for purchasing the product for the first time and not for upgrades. The Buy Now link only appears if
you are using a evaluation license.
Related Tasks:
• Viewing And Editing An Existing Connection Profile
• Modifying An Inventory Job Schedule
The OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter has two types of licenses:
• Evaluation license: The trial version contains a demo license for five hosts (servers) that are managed by the
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter.
• Standard license: The full product version contains a product license for ten vCenters and the purchased number of
host connections that are managed by the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter.
Related Tasks:
• About OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter Licensing
• Uploading OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter License To The Administration Console
Viewing Storage Inventory
The host system storage provides a graphical and detailed view of the capacity and type of physical and logical storage
for storage connected to a host-based storage controller, including:
• Host system total storage, unconfigured, configured, and global hot spare disks capacity
• List of how many of each storage component is present in the system
• Component data table that contains detailed information on that component
To view storage data:
1. In vSphere Client, select a host and then select the OpenManage Integration Tab.
2. In the Host Overview page, in the left pane, click Storage.
3. In the Storage page, view the graphical summary or use the table and View and Filter drop-down lists to sort your
inventory information.
Viewing Host Power Monitoring
The host system power monitoring provides general power information, energy statistics, and reserve power
information, including:
• Current power budget, profile, warning and failure thresholds
• Energy consumption, system peak power, and amperage statistics
• Reserve power and peak reserve capacity
To view host power monitoring:
1. In vSphere Client, select your host, then select the OpenManage Integration tab.
2. In the left pane, under Host Information, click Power Monitoring.
3. In the Power Monitoring page, view the power for this host.
42
Page 43

Displaying The Entire Datacenter Hardware Configuration And Status
You must complete an inventory job prior to displaying the entire datacenter hardware configuration and status. Once
the inventory is run, you can view any of the following:
• Hardware: Field Replaceable Units
• Hardware: Processors
• Hardware: Power Supplies
• Hardware: Memory
• Hardware: NICs
• Hardware: PCI Slots
• Hardware: Remote Access Card
• Storage: Physical Disks
• Storage: Virtual Disks
• Firmware
• Power Monitoring
• Warranty
To display the entire datacenter hardware configuration and status:
1. From the vSphere Client , under the Inventory heading select Hosts and Clusters.
2. In Hosts and Clusters, select a datacenter in the tree view and select the OpenManage Integration tab.
3. An overview of all hosts in the datacenter is displayed. Use the View drop-down list to view an inventory category.
4. Use the Filter text box to enter a filter for the inventory data.
5. To refresh the displayed inventory, click Refresh.
6. In the download location window, browse to the location to save the inventory and click Save.
Managing Connection Profiles
Connection profiles associate access and deployment credentials with a set of host systems and typically contain:
• Profile name and unique description (to help with profile management)
• A list of hosts associated with the connection profile
• iDRAC credentials
• Host credentials
• Date Created
• Date Modified
• Last Modified User
After you run the Configuration Wizard, you manage credential profiles from the OpenManage Integration for VMware
vCenter Manage tab → Templates & Profiles using the following:
• Creating A Connection Profile
• Viewing And Editing An Existing Connection Profile
• Deleting A Connection Profile
• Testing A Connection Profile
43
Page 44

• Refreshing A Connection Profile
Viewing Or Editing An Existing Connection Profile
After you have configured a connection profile, you can edit the profile name, description, associated hosts, and iDRAC
and OMSA Agent credentials.
To view or edit an existing connection profile:
1. From the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter, select Connection Profiles.
2. Under Available Profiles, select the profile to view or edit and then click Edit/View.
3. In the Profile Name and Description page, enter the Connection Profile Name and an optional Connection Profile
Description that are used to help manage custom connection profiles.
4. In the Associated Hosts page, select the hosts for the connection profile and click Next.
5. In the Credentials page, read the information and click Next.
6. In the iDRAC page, under Credentials, do one of the following:
NOTE: The iDRAC account requires administrative privileges for updating firmware, applying hardware
profiles, and deploying hypervisor.
• For iDRACs already configured and enabled for Active Directory on which you want to use Active Directory,
select the Use Active Directory check box; otherwise skip down to configure the iDRAC credentials.
– In the Active Directory User Name text box, type the user name. Type the username in one of these formats:
domain\username or domain/username or username@domain. The user name is limited to 256 characters.
Refer to Microsoft Active Directory documentation for user name restrictions.
– In the Active Directory Password text box, type the password. The password is limited to 127 characters.
– In the Verify Password text box, type the password again.
– In the Certificate Check drop-down list, select one of the following:
* To download and store the iDRAC certificate and validate it during all future connections, select
Enable .
* To perform no check and not store the certificate, select Disabled.
• To configure iDRAC credentials without Active Directory, do the following:
– In the User Name text box, type the user name. The user name is limited to 16 characters. Refer to the
iDRAC documentation for information about user name restrictions for your version of iDRAC.
NOTE: The local iDRAC account requires administrative privileges for updating firmware, applying
hardware profiles, and deploying hypervisor.
– In the Password text box type the password. The password is limited to 20 characters.
– In the Verify Password text box, type the password again.
– In the Certificate Check drop-down list, select one of the following:
* To download and store the iDRAC certificate and validate it during all future connections, select Enable.
* To perform no check and not store the iDRAC certificate, select Disabled.
7. Click Next.
8. In the Host Credentials page, under Credentials, do one of the following:
44
Page 45

• For hosts already configured and enabled for Active Directory on which you want to use Active Directory,
select the Use Active Directory check box; otherwise skip down to configure your Host Credentials.
– In the Active Directory User Name text box, type the user name. Type the username in one of these formats:
domain\username or domain/username or username@domain. The user name is limited to 256 characters.
Refer to Microsoft Active Directory documentation for user name restrictions.
– In the Active Directory Password text box, type the password. The password is limited to 127 characters.
– In the Verify Password text box, type the password again.
– In the Certificate Check drop-down list, select one of the following:
* To download and store the Host certificate and validate it during all future connections, select Enable .
* To perform no check and not store the Host certificate, select Disabled.
• To configure Host Credentials without Active Directory, do the following:
– In the User Name text box, type the user name. The user name must be root.
– In the Password text box type the password. The password is limited to 127 characters.
NOTE: For servers that do not have either an iDRAC Express or iDRAC Enterprise, the iDRAC test
connection result states Not Applicable for this system.
NOTE: The OMSA credentials are the same credentials used for ESX and ESXi hosts.
– In the Verify Password text box, type the password again.
– In the Certificate Check drop-down list, select one of the following:
* To download and store the Host certificate and validate it during all future connections, select Enable .
* To perform no check and not store the Host certificate, select Disabled.
9. Click Save.
10. To close the window, click X (upper-right corner).
Deleting A Connection Profile
You can remove a connection profile from the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter.
To delete a connection profile:
1. From the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter , click Connection Profiles.
2. Under Available Profiles, select the profile to delete and then click Delete.
3. On the message that displays, to remove the profile, click Delete, or click Cancel to cancel the delete action.
Testing A Connection Profile
To test a connection profile:
1. In the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter , select Connection Profiles.
2. Under Available Profiles, to test the entered iDRAC and host root credentials on the selected servers, select the
connection profile and then click Test Connection.
3. Use the check boxes to select the hosts you want tested, and then click Test Selected.
4. To abort all selected tests and cancel the testing, click Abort All Tests.
5. To exit, click Done.
45
Page 46

Refreshing A Connection Profile
To refresh a connection profile:
Click Refresh.
NOTE: If a host is removed from vCenter, then it is removed from the connection profile.
Understanding System Event Logs In vSphere Client Host View
The System Event Log provides status information for hardware discovered by the OpenManage Integration for VMware
vCenter.
System Event Logs provide information based on the following criteria:
Status There are several status icons: Informational (blue exclamation point), Warning (yellow triangle
with exclamation point), Error (red X).
Time (Server
Time)
Search this page Displays the specific message, server names, configuration settings, and so on.
The severity levels are defined as:
Info The OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter operation completed successfully.
Warning The OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter operation partially failed, and was partially
Indicates the time and date the event occurred.
successful.
Error The OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter operation failed.
Security Contains information on system security.
You can save the log as an external CSV file.
Related Information:
• Displaying The System Event Logs For An Individual Host
Displaying Logs in Dell Management Center
Dell Management Center logs include status information for discovered hardware and a history of user actions.
To display logs in Dell Management Center:
1. From the Dell Management Center, in the left pane, select Log.
2. To update the log with the most recent data, click Refresh.
3. To select a severity category to filter the log data, in the All Categories drop-down list select one of the following:
All Categories, Info, Warning, Error, or Security.
4. To select a date range for filtering log data, click the Last Week drop-down list and select one of the following: Last
week, Last Month, Last Year, or Custom Range.
If Custom Range is selected, then the Start Date and Stop Date drop-down lists are displayed.
5. If you selected custom date range:
a. Click the calendar to populate the Start date.
b. Click the calendar to populate End date.
c. To save your configuration, click Apply.
46
Page 47

6. To control how the log is displayed, use the display controls to set the Records per screen, go to a desired Page,
and use the forward and backward page controls.
7. To export the Log contents to a comma-separated value (CSV) file, click Export.
8. In the download location window, browse to the location to save the log and click Save.
Displaying The Event Logs For An Individual Host
System HardwareEvent Logs provide information based on the following criteria:
• Status
There are several status icons: Informational (blue exclamation point), Warning (yellow triangle with exclamation
point), Error (red X).
• Time (Server Time)
Displays the time and date the event occurred.
• Search this page
Displays the specific message, server names, configuration settings, and so on.
To display the system event log for an individual host:
1. From the vSphere Client, under the Inventory heading select Hosts and Clusters.
2. In the tree view, select the host system.
3. Select the OpenManage Integration tab.
4. From Recent System Log Entries, to launch the System Event Log window, click Details.
5. To update the System Event Log, click Refresh Log.
6. To limit (filter) the number of event log entries, choose one of the following:
• In the search filter text box, and enter a text string to dynamically filter the log entries.
• To clear the filter text box, click X and all the event log entries display.
7. To clear all event log entries, click Clear Log. A message displays stating that all log entries are deleted after they
are cleared and select one of the following:
• To agree to clear log entries, click OK.
• To cancel, click Cancel.
8. To export the event log to a CSV file, click Export.
9. Browse to the location to save the system event log and click Save.
About Firmware Updates
The location where servers receive firmware updates is a global setting that is available in the OpenManage Integration
for VMware vCenter on the Settings tab.
Firmware repository settings contain the firmware catalog location used to update deployed servers. There are two
location types:
Dell (ftp.dell.com) Uses the firmware update repository of Dell (ftp.dell.com). The OpenManage Integration for
VMware vCenter downloads selected firmware updates from Dell repository.
Shared Network
Folder
Created with Dell Repository Manager™. These local repositories are located on CIFS or NFS
file share.
47
Page 48

NOTE: Once the repository is created, save it to a location that the registered hosts can access. Repository
passwords cannot exceed 31 characters. Do not use any of the following characters in a password: @, &, %, ', ", ,
(comma), < >
The Firmware Update Wizard always checks for the minimum firmware levels for iDRAC, BIOS, and Lifecycle Controller,
and attempts to update them to required minimum versions. Once iDRAC, Lifecycle Controller, and BIOS firmware
versions meet minimum requirements, the Firmware Update wizard allows updates for all firmware including: iDRAC,
Lifecycle Controller, RAID, NIC/LOM, Power Supply, BIOS, and so on.
NOTE: For 9th and 10th generation servers, BIOS/BMC/DRAC firmware versions are viewable only at the Cluster
View level in vCenter or on the Overview page of the individual host view. Firmware version information is not
active in the individual host view under Firmware, and remote firmware updates are not available.
Firmware Versions After October 14, 2010
For Firmware updated on or after October 14th, 2010, the Firmware Update Wizard runs.
Firmware Versions Newer Than July 29, 2009 and Prior to October 14th
If your firmware was updated on or after July 29, 2009 and prior to October 14, 2010, you still will not see the Firmware
Update Wizard, but you are delivered an ISO bundle to update your firmware. After this update, you may not have the
latest firmware. After you run the bundle, it is recommended that you run the update again.
Firmware Versions Older than July 29, 2009
If your firmware is older than July 29, 2009, you may have to download and run the ISO file to update your machines.
After you run the ISO, it is recommended that you run the Firmware Update Wizard again.
Related Information:
• Setting Up The Firmware Repository
Running The Firmware Update Wizard
This functionality is only available for 11th and later generations Dell servers that have either an iDRAC Express or
iDRAC Enterprise. When your firmware was installed on or after October 14th, 2010, you can automatically update your
firmware versions using the Firmware Update Wizard.
NOTE: To safeguard against browser timeout issues, change the default timeout to 30 seconds. For information on
changing the default timeout setting, see How Come I see an Error Message Displayed After Clicking the Firmware
Update Link in the Troubleshooting section of the
NOTE: For trial/evaluation license, you can use Firmware wizard as long as license is not expired.
To run the Firmware Update Wizard:
1. In vSphere Client → OpenManage Integration tab → Host Information, click Firmware → Run Firmware Update
Wizard.
2. To use the Load a single firmware update from a file option:
a. Enter the file path in the following format:
CIFS: \\<host accessible share path>\<FileName>.exe or
NFS: host:/share/filename.exe
b. If you have NFS, skip to step 7. Otherwise enter the User Name and Password in a domain format that has
access to the share drive.
c. Continue to step 7.
Alternatively, to use the Update from repository option:
a. Select Update from repository.
b. Make sure you have a network connection to ftp.dell.com.
c. Click Next.
User’s Guide
.
48
Page 49

3. Select the bundle for your host and click Next.
4. Select the desired firmware updates and click Next. Components that are either a downgrade, already up-to-date,
or currently scheduled for update are not selectable. If you select the Allow Components to be Downgraded check
box, select the options that are listed as Downgrade. Selecting this option is only recommended to advanced users
who understand the implications of downgrading firmware.
5. Select the desired restart option.
• Enter maintenance mode, apply updates, and restart.
Host goes into maintenance mode. If the host cannot enter maintenance mode, then the host is not restarted
and the update is applied during the next reboot. Select the Exit maintenance mode after firmware update
completes check box, to exit maintenance mode after the update.
• Apply updates on next reboot.
To avoid a service interruption, it is recommended that the host enters maintenance mode before the reboot.
• Apply updates and force reboot without entering maintenance mode.
The update is applied, and a reboot occurs even if the host is not in maintenance mode. This method is not
recommended.
6. Click Finish.
7. To verify that the update was successful, in Dell Management Center, select Job Queue → Inventory History →
Run Now, and to see the new versions, go to vSphere Client → OpenManage Integration tab and click Firmware.
Updating Older Firmware Versions
Firmware must be at a minimum level for the Firmware Update Wizard to run. When it is not, you are offered options to
help update your firmware, prior to running the Firmware Update Wizard. Typically, firmware installed earlier than July
29, 2009 requires you to download and run an ISO file, see Firmware Updates. For firmware installed between July 29,
2009 and prior to Oct. 14, 2010, you are offered an ISO bundle to automatically install from the OpenManage Integration
for VMware vCenter. Firmware updated after October 14th, 2010 runs the Firmware Update Wizard. Firmware updates
are run from vSphere Client on the host OpenManage Integration tab. To set up the repository, see Setting Up The
Firmware Repository .
To update older firmware versions:
1. In vSphere Client, on the OpenManage Integration tab, under Host Actions, click Run Firmware Update Wizard.
The Update Required dialog displays when your host is at a lower level of firmware than the wizard supports. You
will either be asked to download and run an ISO file or be given a bundle of updates to run.
2. In the Update Required dialog box, do one of the following:
• To automatically exit maintenance mode after the firmware update, select the Exit maintenance mode after
firmware update completes check box.
• To enter maintenance mode to examine and/or test the machine before adding it back to the cluster, do not
check the check box.
3. Click Update.
4. The Success dialog box tells you that an update is now in progress.
If you chose to Exit maintenance mode after firmware update completes, the firmware update puts the host into
maintenance mode and then reboots automatically. Otherwise, it stays in maintenance mode.
5. Refer to the Recent Tasks area of the vSphere Client to watch the update progress.
After this procedure, run the Firmware Update Wizard again to make sure your firmware is completely updated.
Running the Update Firmware Wizard for Clusters and Datacenters
This functionality is only available for 11th and later generations of Dell servers that have either an iDRAC Express or
iDRAC Enterprise. If your firmware was installed on or after October 14th, 2010, you can automatically update your
49
Page 50

firmware versions using the Firmware Update Wizard. This wizard only updates hosts that are part of a connection
profile and compliant in terms of firmware, CSIOR status, hypervisor, and OMSA status (11th generation servers only). If
your host is not listed, run the Compliance Wizard for vSphere Hosts from the OpenManage Integration for VMware
vCenter or select the host that is not listed from the Hosts and Clusters view and use the Firmware Update Wizard. It
typically takes from 30 to 60 minutes to update firmware components for each host. Enable DRS on a cluster so that
virtual machines can be migrated when a host enters/exits maintenance mode during the firmware update process. You
can only schedule or run one firmware update task at a time.
If you want to export from the wizard, use the Export to CSV button. Search is available for locating a specific cluster,
datacenter, host, or any topic item from the datagrid except for Date Applied.
NOTE: Always update firmware together as part of the repository bundle: BIOS, iDRAC, and Lifecycle Controller.
NOTE: For information on changing the default timeout setting, see How Come I see an Error Message Displayed
After Clicking the Firmware Update Link in the Troubleshooting section of the
You can view the status and manage Firmware update jobs from the Job Queue page. See, Viewing Firmware Update
Status for Clusters and Datacenters.
1. In the vSphere Client, under the Inventory heading select Hosts and Clusters.
2. In Hosts and Clusters, in the tree view, select a datacenter or a cluster and then select the OpenManage
Integration tab.
3. Click Update Firmware.
If this link is not enabled or if you get an popup message when you click this option, then there is a firmware update
job in progress or scheduled, close the dialog box, wait and try this again later. View the status of all jobs on the
Firmware Update Jobs tab in Job Queues.
4. In the Welcome page, review the information about the update before proceeding with the wizard.
5. Click Next.
6. In the Firmware Inventory page, review the components that are already installed on the systems.
7. Click Next.
8. In the Select Updated Bundles page, select the update bundles using the check boxes.
9. Click Next.
10. In the Select the Systems/Components to Update page, use the check boxes to select the components to upgrade
or downgrade. If you want to downgrade, select the
Allow components to be downgraded check box.
User’s Guide
.
NOTE: If you select all components and some remain unselected, that means that there are no upgrades
available for those components. You may select those components for a downgrade.
11. Click Next.
12. In the Firmware Update Information page, review the components you have selected for an upgrade or downgrade.
13. Click Next.
14. In the Schedule Firmware Updates page, under Job Name, do the following:
a. In the Firmware Update Job Name text box, type the firmware update job name.
This is a mandatory field. If this is not filled in, this upgrade is not scheduled. Do not use a name that is already
in use. If your purge this name, you may reuse it again.
b. In the Firmware Update Description, type the description.
15. Under Job Schedule, do one of the following:
NOTE: Selecting an option is mandatory. If one is not selected, the upgrade is blocked.
• If you want to run the update job now, click Update Now, and then click Finish.
• If you want to run the update job later, click Schedule Update, and then do the following:
1. In the Calendar box, select the month and day.
50
Page 51

2. In the Time text box, type the time in HH:MM, and then click Finish.
NOTE: The time is the local timezone where your client is physically located. Invalid time values
result in a blocked update.
Viewing Firmware Update Status for Clusters and Datacenters
For information to display on this page, run a firmware update for a cluster or a datacenter. This page only displays
information about firmware updates for clusters and datacenters. See, Running the Update Firmware Wizard for Clusters
and Datacenters.
On this page you can refresh, purge, or abort your firmware update jobs.
1. From the Dell Management Center, select Job Queue → Firmware Update Jobs.
2. To display the most recent information, click Refresh.
3. View the status in the datagrid. This grid offers the following information about firmware update jobs:
• Status
• Scheduled Time
• Name
• Description
• Collection Size
The collection size is the number of servers on this firmware inventory job.
• Progress Summary
The progress summary lists the progress details of this firmware update.
4. To see more details about a particular job, in the datagrid for a particular job, click Details.
Here you can find the following details:
• Service Tag
• iDRAC IP
• Status
• Warnings
• Firmware Update Job Details
• Start Time
• End Time.
5. If you want to abort a scheduled firmware update that is not running, in the same line as the job you want to abort,
Abort.
click
6. If you want to purge scheduled firmware updates, click Purge Job Queue.
You can only purge jobs that are completed or scheduled.
7. Select the Older than date and job Status, and click Apply. The selected jobs are then cleared from the queue.
Advanced Host Management Using vCenter
The advanced host management tasks are host system-based actions that let an administrator identify a physical server
in the datacenter environment, launch server-based management tools, and display server warranty information. All of
these actions are initiated from the OpenManage Integration tab in vCenter or by right-clicking the host in
Clusters
view for an individual host system.
Host &
51
Page 52

Setting Up Physical Server Front Indicator Light
To assist in locating a physical server in a large datacenter environment, you can set the front indicator light to blink for
a set time period.
To set up a physical server's front indicator light:
1. In vSphere Client, under the Inventory heading, select Hosts and Clusters.
2. From Hosts and Clusters, select the host system in the tree view and select the OpenManage Integration tab.
3. Under Host Actions, select Blink Indicator Light.
4. Choose one of the following:
• To turn the blink on and set the time period, in the Indicator Light dialog box, click Blink On, and use the Timeout
drop-down list to select the timeout increment, and then click OK.
• To turn the blink off, in the Indicator Light dialog box, click Blink Off, and then click OK.
Server Based Management Tools
There are two server-based management tools, iDRAC and OMSA, that can be launched from the vSphere Client →
OpenManage Integration tab. Under the Management Consoles link in the left pane you can access:
• Launch Remote Access.
Use this option to launch the iDRAC user interface
• Launch OMSA
Use this option to launch the OpenManage Server Administrator user interface URL that was entered into the
management center either during the initial Configuration Wizard or using Settings → General. You must install the
URL for the server administrator Web server on a Windows-based management station.
• If you are on a blade system, launch the CMC to launch the Chassis Management Controller user interface. If you
are not on a blade system, this does not display.
Warranty Retrieval
Warranty retrieval provides the following information for Dell servers:
• Updated service warranty information, while only transmitting the host service tag
• Warranty information updated at scheduled intervals
• Secure transmission using a proxy server and credentials
NOTE: Dell does not store transmitted service tag information.
Related Tasks:
• Running A Warranty Retrieval Job
• Viewing Server Warranty Information For A Single Host
• Viewing Warranty Information For An Entire Data Center
Viewing Server Warranty Information For An Entire Data Center
Once the warranty job completes, you can view server warranty information in vSphere Client, on the Datacenter View
page.
52
Page 53

To view the server warranty information for an entire datacenter:
1. From the vSphere Client, under the Inventory heading select Hosts and Clusters.
2. From Hosts and Clusters, select the datacenter in the tree view and select the OpenManage Integration tab.
3. An overview of all hosts in the datacenter is displayed. In the View drop-down list select Warranty.
4. In the Filter text box, enter a filter for the warranty data.
5. To refresh the displayed inventory, click Refresh.
6. To export the inventory as a CSV file, click Export. In the Download Location window, browse to the location to save
the inventory and click Save.
Viewing Server Warranty Information For A Single Host
Once a warranty job completes you can view the warranty information for a single host in vSphere Client on the Hosts
View page.
To view the server warranty information for a single host:
1. From the vSphere client, under the Inventory heading select Hosts and Clusters.
2. From Hosts and Clusters, select the host system in the tree view and select the OpenManage Integration tab.
3. To display system warranty information, select Warranty. The information on the Warranty Status page includes:
• Warranty provider name and description of the warranty
• The start and end dates and how many days are left on the warranty
• The warranty status (active or inactive) and when warranty information was last updated
53
Page 54

Hardware Management
Prerequisites:
To successfully perform hardware provisioning and deployment, the physical servers must appear in the Deployment
Wizard. All physical servers must meet the following prerequisites:
5
• See the
• The server must have the minimum supported versions of iDRAC firmware, Lifecycle controller and BIOS. See the
• The OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter supports deployment using only embedded/integrated LOMs. You
• The OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter allows deployment onto Internal Dual SD Module (hypervisor
• If the iDRAC is in dedicated mode, its NIC must be enabled to communicate with the OpenManage Integration for
• CSIOR must be enabled. Additionally, before initiating Auto Discovery, to make sure that retrieved data is current,
• Dell servers can be ordered with Auto Discovery and handshake options pre-configured by the factory. If a server is
• If the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter is not used for hardware configuration, then make sure the
• If the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter is used for hardware configuration, the BIOS setting for VT is
• If your servers are from versions prior to Dell PowerEdge 12th generation servers, then the deployment process
• Custom ESXi images that contain
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter Release Notes
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter Release Notes
NOTE: If the firmware versions are outdated, a two step upgrade process could be required. See the firmware
documentation for detailed upgrade instructions.
can configure NICs in PCI slots manually after the deployment. If using add-on NICs, the system must have the host
LOMs enabled.
only) or local hard drives. The Internal Dual SD Module must be enabled from BIOS before you deploy the hypervisor
with the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter. You can change the management NIC manually, and add the
system to vCenter.
NOTE: For the supported Dual SD Module, see the respective server product documentation.
VMware vCenter.
the system must be completely powered off and then back on (hard reboot).
not pre-configured with these options, you must manually enter the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter IP
address or configure your local network to provide this information.
following conditions are met prior to initiating hypervisor deployment:
– Enable the VT (Virtualization Technology) flag in the BIOS.
– Set the system's boot order to either a bootable Virtual Disk or an Internal Dual SD Module for operating system
installation.
automatically enabled, even if BIOS configuration is not part of the hardware profile. Express/Clone RAID
configuration is required if a virtual disk is not already present on the target system.
installs the OpenManage Server Administrator package on the target system, and automatically configures the
SNMP trap destination to point to the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter.
all
the Dell drivers are required for deployment. You can find the correct images by
going to the Dell Drivers & Downloads page and saving the custom images to a location you can access during the
deployment process. For the most up-to date list of supported ESXi versions for this release, see the Release Notes.
for specific hardware support information.
for specific hardware support information.
•
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter
server. Make sure that you have BIOS mode selected in the reference hardware profile prior to applying the
Hypervisor profile. If there is no hardware profile selected, then make sure to manually configure the boot mode as
BIOS and reboot the server prior to applying the hypervisor profile.
54
only supports BIOS mode to auto-deploy hypervisor on the target
Page 55

NOTE: Operating system deployment from OpenManage Integration for VMware and vCenter ( OMIVV ) fails if the
BOOT mode in the target machine is set to UEFI
Provisioning Overview
Once a physical inventory of the datacenter is complete, all auto-discovered bare-metal systems are available to the
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter for zero touch hardware provisioning and hypervisor deployment. To
prepare for provisioning and deployment, you must:
Create a
Hardware Profile
Create a
Hypervisor Profile
Create a
Deployment
Template
Once the deployment template is created, use the Deployment Wizard to gather the information necessary to create a
scheduled job that provisions server hardware and deploys new hosts in vCenter. For information about running the
Deployment Wizard, see Running The Deployment Wizard . Lastly, use the Job Queue to view job status and make
changes to pending deployment jobs.
NOTE: No more than two deployment jobs should be scheduled to run consecutively. Multiple jobs should use the
scheduling feature to stagger deployment execution.
Contains the hardware settings gathered from a reference server that is used to deploy new
servers. See Creating A New Hardware Profile.
Contains the hypervisor installation information needed for ESX/ESXi deployment. See Creating
A New Hypervisor Profile.
Optionally contains a hardware profile, a hypervisor profile, or both. You can save and reuse
these profiles as needed for all available datacenter servers. See Building Deployment
Templates.
Understanding Deployment Job Times
Provisioning and deploying bare-metal servers can take between 30 minutes to several hours to complete, depending on
certain factors. When starting a deployment job, it is recommended that you plan your deployment time according to the
guidelines provided. The amount of time it takes to complete provisioning and deployment varies with deployment type,
complexity, and number of deployment jobs running simultaneously. The table below gives guidelines of the approximate
time a deployment job may take. Deployment jobs are run in batches of up to five concurrent servers, to improve time for
the overall deployment job. The exact number of concurrent jobs depends on resources available.
Table 2. Approximate Deployment Time Scenarios
Deployment Type Approximate Time Per Deployment
Hypervisor only Between 30 minutes to 130 minutes
Hardware only Up to 2 hours depending on the complexity and the RAID,
BIOS, and boot options to configure
Hypervisor and Hardware profiles 1 to 4 hours
Server States Within The Deployment Sequence
When an inventory job is run, auto-discovered bare-metal systems are classified in different states to help determine if
the server is new to the datacenter or has a pending deployment job scheduled. Administrators can use these states to
determine if a server should be included in a deployment job. The states are:
55
Page 56

Unconfigured The server has contacted the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter and is waiting to
be configured. See Understanding Deployment Job Times.
Configured The server is configured with all hardware information required for a successful hypervisor
deployment.
Downloading Custom Dell ISO Images
Custom ESXi images that contain
images. For deployments to work
date list of supported ESXi versions for this release, see the Release Notes.
NOTE: The OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter ISO does not contain the required ESXi ISO images for
deployment. You must download these images to a location that is accessible during deployment or your
deployment may fail.
1. Navigate to support.dell.com.
2. Browse to the Drivers & Downloads page in your language, and then do one of the following:
• To select the drivers using the Service Tag or Express Service Code, under Yes, in the text box enter the service
tag or express service code, and then click Submit.
• To select the drivers using another option, under No, select one of the following:
– Automatically detect my Service Tag for me
– Choose from My Products and Services List
– Choose from a list of all Dell products
Then click Continue and follow the directions for the option selected.
3. On the page for the server selected, scroll down to Refine your results and under Operating System, use the dropdown list to select the ESX or ESXi system you want.
4. Click Enterprise Solutions.
5. In the Enterprise Solutions list, select the version of ISO required, and then click Download File.
NOTE: Embedded ISOs are used for hypervisor installs on to Dual Internal SD Modules. Installable ISOs are
for installs on to hard disks.
6. In the dialog box, select For Single File Download via Browser, and then click Download Now.
7. In the dialog box, browse to the location to store the ISO images for deployment.
all
Dell drivers are required for deployment. Dell cannot produce custom ESX 4.1
all
drivers must be present natively in the ISO VMware produces. For the most up-to
Understanding How To Configure A Hardware Profile
To configure server hardware settings, you must create a hardware profile. A hardware profile is a configuration
template you can apply to newly-discovered infrastructure components and it requires the following information:
Boot Order The boot order is the boot device sequence and hard drive sequence, which you can edit only
if the boot mode is set to BIOS.
BIOS Settings The BIOS settings include: memory, processor, SATA, integrated devices, serial
communications, embedded server management, power management, system security, and
miscellaneous settings.
iDRAC Settings iDRAC settings include: Network, user list, and user configuration (IPMI/iDRAC privileges).
56
Page 57

NOTE: For systems that have iDRAC Express, the iDRAC configuration cannot be
extracted; therefore, the server should not be used as a reference server. If it is used as a
target system, then no iDRAC configuration from the reference server is applied.
RAID
Configuration
The RAID configuration displays the current RAID topology on the reference server at the time
the hardware profile was extracted.
NOTE: There are two RAID configuration options configured in the Hardware Profile: 1.
Apply RAID1 + create a dedicated hot spare, applicable
apply default RAID configuration settings to the target server. The RAID configuration
task defaults to RAID1 on the first two drives of the integrated controller that are RAID1
capable. Additionally, a dedicated hot-spare for the RAID1 array is created if a candidate
drive meeting the criteria exists. 2.
shown below
Creating A New Hardware Profile.
NOTE: The OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter enables certain BIOS settings
under the Processor group in the BIOS on all deployed servers, regardless of the settings
on the reference server. Before using a reference server to create a new hardware
profile, it must have the Collect System Inventory On Reboot (CSIOR) setting enabled and
be rebooted to provide accurate inventory and configuration information.
The tasks for creating hardware profiles include:
• Enabling CSIOR On A Reference Server
• Creating A New Hardware Profile
• Cloning A New Hardware Profile
• About Managing Hardware Profiles
. Use this option if you want to clone the reference server setting. See
Creating A New Hardware Profile
. Use this option if you want to
Clone RAID configuration from the reference Server as
To create a new hardware profile:
1. In the Dell Management Center, select Deployment → Deployment Templates → Hardware Profiles.
2. Click Create New.
3. In the New Hardware Profile page, do the following:
• In the Profile Name text box, enter the profile name.
• In the Description text box, type an optional description.
4. Click Save.
5. To continue, in the left pane, click Reference Server.
6. In the Reference Server window, click Edit.
7. To find a reference server that is compliant, managed by vCenter, and successfully inventoried by the OpenManage
Integration for VMware vCenter
8. In the Servers dialog box, scroll down the list to find the right reference server, and click Select.
9. To customize the reference server settings as defaults, click Customize Settings from Reference Server , and then
click Save.
10. A dialog box that states extracting the settings takes several minutes is displayed. To populate settings, click
Continue. The selected server’s name, iDRAC IP address, and service tag are displayed in the Reference Server
window.
11. In the left pane, select Boot Order. To include boot order information in the profile, select the Include Boot Order in
this Hardware Profile check box.
, click Browse.
57
Page 58

12. To display the boot order options, expand Boot Order, and then click Edit to make updates:
NOTE: For Dell 13th generation PowerEdge Servers, only the current boot mode details are displayed for the
hardware profiles.
NOTE: Operating system deployment from OpenManage Integration for VMware and vCenter fails if the BOOT
mode in the target machine is set to UEFI
a. In the Boot Mode drop-down list to select either BIOS or UEFI.
b. In the View/Configure drop-down list, under Boot Device Sequence, to make changes to the boot device
sequence displayed, select the device and click either Move Up or Move Down.
c. In the Boot Retry Sequence drop-down list, select Enabled so that the server automatically retries the boot
sequence, or select Disabled to not retry the sequence.
d. Click Save to save the changes, or Cancel to cancel the changes.
13. If the BIOS boot mode was selected, you can expand Hard Drive Sequence to display the hard drive sequence
options, and click
• To make changes to the hard drive sequence displayed, select the device and click either Move Up or Move
Down.
• Click Save to save the changes, or Cancel to cancel the changes.
14. In the left pane, select BIOS Settings. To include BIOS setting information in the profile, select the Include BIOS
Settings in this Hardware Profile check box. Expand a category to display the setting options, and click Edit to make
updates to one of the following:
• Memory Settings
• Processor Settings
• SATA Settings
• Integrated Devices
• Serial Communication
• Embedded Server Management
• Power Management
• System Security
• Miscellaneous Settings
Edit to make updates:
Once all updates are made for a category, click Apply to save the changes or click Cancel to cancel the changes.
NOTE: For detailed BIOS information, including setting options and explanations, refer to the
Owner’s Manual
15. In the left pane, select iDRAC Settings and then select Network.
16. To include network setting information in the profile, select the Include Network Settings in this Hardware Profile
check box. Expand a category to display the setting options, and click Edit to make updates to one of the following:
• Network
• Network Settings
• Virtual Media
Once all updates are made for a category, click Apply to save the changes or click Cancel to cancel the changes.
NOTE: For detailed iDRAC information, including setting options and explanations, refer to the
Guide
for the selected server.
17. In the left pane, select iDRAC Settings → User List. To include user list information in the profile, select the Include
User List in this Hardware Profile check box. Under iDRAC Local User List, do one of the following:
58
for the selected server.
Hardware
iDRAC User’s
Page 59

a. Add User: Manually enter an iDRAC user and the required information. When finished, click Save to save your
changes or Cancel to cancel.
b. Delete User: Delete the selected user. Select the check box for the user and click Delete, or click Cancel to
cancel.
c. Edit User: Manually edit an iDRAC user’s information. When finished, click Save to save your changes or Cancel
to cancel.
NOTE: For detailed iDRAC information, including setting options and explanations, refer to the
Guide
for the selected server.
18. In the left pane, select RAID Configuration. To include RAID configuration information in the profile, select the
Include RAID Configuration in this Hardware Profilecheck box. Then select one of the following:
• Apply RAID1 + create a dedicated hot spare, applicable.
Use this option if you want to apply default RAID configuration settings to the target server. The RAID
configuration task defaults to RAID1 on the first two drives of the integrated controller that are RAID1 capable.
Additionally, a dedicated hot-spare for the RAID1 array is created if a candidate drive meeting the criteria
exists.
• Clone RAID configuration from the reference Server .
Use this option if you want to clone the reference server setting.
The profile is automatically saved, and displays in the Hardware Profiles window under Available Profiles
iDRAC User’s
Enabling CSIOR On A Reference Server
Before creating a hardware profile using a reference server, enable the Collect System Inventory On Reboot (CSIOR)
setting and reboot the server to provide accurate inventory and configuration information. There are two methods for
enabling CSIOR:
Locally This uses an individual host using the Dell Lifecycle Controller United Server Configurator
(USC) user interface.
Remotely This uses a WS-Man script. For more information on scripting this functionality, see the
Tech Center
To enable CSIOR locally on a reference server:
and the
DCIM Lifecycle Controller Management Profile
.
Dell
1. Power on the system, and during POST press <F10> to launch USC.
2. Select Hardware Congfiguration → Part Replacement Configuration.
3. Enable the Collect System Inventory on Reboot setting, and exit USC.
Cloning A Hardware Profile
To clone a new hardware profile:
1. In the Dell Management Center, select Deployment → Deployment Templates → Hardware Profiles.
2. Click Create New.
3. In the New Hardware Profile page, do the following:
• In the Profile Name text box, enter the profile name
• In the Description text box, enter an optional description.
4. Click Save.
5. In the left pane, click Reference Server.
6. In the Reference Server window, click Edit.
7. To extract all hardware settings from the reference server, click the Clone Reference Server Settings option button.
59
Page 60

8. Click Save.
9. A dialog box that states extracting the settings will take several minutes is displayed, then click Continue. The
settings are populated, and the selected server’s name, iDRAC IP address, and service tag are displayed in the
Reference Server window.
The profile is saved, and displays in the Hardware Profiles window under Available Profiles.
About Managing Hardware Profiles
Hardware profiles define a server's hardware configuration using a reference server. From the Dell Management
Center, there are several management actions you can perform on existing hardware profiles, including:
• Viewing or Editing A Hardware Profile
• Duplicating Hardware Profiles
• Renaming A Hardware Profile
• Deleting A Hardware Profile
• Refreshing Hardware Profiles
Viewing Or Editing A Hardware Profile
To view or edit a hardware profile:
1. In the Dell Management Center, select Deployment → Deployment Templates → Hardware Profiles.
2. Select a profile and click View/Edit.
3. In the Hardware Profile window, to make any changes, click Edit.
4. Click Save to apply changes, or click Cancel to cancel changes.
Duplicating A Hardware Profile
To duplicate a hardware profile:
1. In the Dell Management Center, select Deployment → Deployment Templates → Hardware Profiles.
2. On the Hardware Profile page, select a profile, and then click Duplicate.
3. In the Duplicate dialog box, enter a unique hardware profile name.
4. Click Apply to create a copy of the profile with the new name, or click Cancel to cancel.
Renaming A Hardware Profile
To rename a hardware profile:
1. In the Dell Management Center, select Deployment → Deployment Template → Hardware Profiles.
2. On the Hardware Profile page, select a profile and click Rename.
3. In the Rename dialog box, enter a unique hardware profile name.
4. Click Apply to use the new name, or click Cancel to cancel.
Deleting A Hardware Profile
To delete a hardware profile:
60
Page 61

NOTE: Deleting a hardware profile that is part of a running deployment task can cause the task to fail.
1. In the Dell Management Center, select Deployment → Deployment Templates → Hardware Profiles.
2. Select a profile and click Delete.
3. In the message dialog box, to remove the profile click Delete , or click Cancel to cancel.
Refreshing An Updated Hardware Profile
To refresh an updated hardware profile:
1. In the Dell Management Center, select Deployment → Deployment Templates → Hardware Profiles.
2. Click Refresh.
The updated hardware profile information displays.
Creating A New Hypervisor Profile
To deploy and configure ESX/ESXi to a server, a hypervisor profile must be created. A hypervisor profile requires the
following information:
• The scriptable Reference ISO software media location on an NFS or CIFS share
• vCenter instance that manages the deployed hosts, plus an optional host profile
• The destination cluster or datacenter where the plug-in deploys servers in vCenter
NOTE: Use one of the following naming conventions for the Reference ISO file name:
NFS format: host:/share/hypervisor_image.iso
CIFS format: \\host\share\hypervisor.iso
NOTE: A successful deployment requires an ESX ISO that has the correct drivers. Deployment on newer Dell
systems may require using Dell custom ISO images that contain all the required Dell drivers. ESX 4.1 may not work
on newer Dell systems and may not have a custom ISO available from Dell.
To create a new hypervisor profile:
1. In the Dell Management Center, select Deployment → Deployment Templates → Hypervisor Profile.
2. In the Hypervisor Profiles page, click Create New.
3. In the New Hypervisor Profile page, do the following:
• In the Profile Name text box, enter the profile name.
• In the Description text box, enter an optional description.
4. In the left pane, click Reference ISO, and then click Edit, and on the Hypervisor Installation Source dialog box, enter
the following information:
• In the Installation Source ISO text box, type the path to your hypervisor share location. A copy of this hypervisor
image is modified to permit a scripted installation. The reference ISO location must be in one of the following
format:
NFS format: host:/share/hypervisor_image.iso
CIFS format: \\ host\share\hypervisor.iso
• In the Select a Version drop-down list, select an ESX or ESXi version.
All servers deployed using this Hypervisor Profile will have this image, and if the servers are versions prior to 12G,
the latest recommended version of OpenManage Server Administrator is installed.
5. If using a CIFS share, enter the User Name, Password, and Verify Password. The passwords must match.
61
Page 62

6. To add the settings to the profile, click Save.
7. In the left pane, click vCenter Settings, and then edit where required:
• vCenter Instance: Displays the server instance that manages a host after deployment.
• vCenter Version: Displays the current version.
• vCenter Destination Container: Datacenter or cluster that hosts the new physical servers; click Browse to
search for vCenter destinations.
• vCenter Host Profile: Select a profile that encapsulates host configuration and helps to manage host
configuration.
8. To add the information to the profile, click Save.
For information on Managing Hypervisor Profiles, see Managing Hypervisor Profiles.
Managing Hypervisor Profiles
There are several management actions you can perform on existing hypervisor profiles, including:
• Understanding VLAN Support
• Viewing Or Editing Hypervisor Profiles
• Duplicating Hypervisor Profiles
• Renaming Hypervisor Profiles
• Deleting A Hypervisor Profile
• Refreshing Hypervisor Profiles
VLAN Support
The OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter supports hypervisor deployment to a routable VLAN. Configure VLAN
support in the Deployment Wizard. In this portion of the Deployment Wizard, there is an option to specify use of VLANs
and to specify a VLAN ID. When a VLAN ID is provided, it is applied to the hypervisor's management interface during
deployment and tags all traffic with the VLAN ID.
Make sure that the VLAN provided during deployment communicates with both the virtual appliance and the vCenter
server. The deployment of a hypervisor to a VLAN that cannot communicate to one or both of these destinations causes
the deployment to fail.
If you have selected multiple bare-metal servers in a single deployment job and want to apply the same VLAN ID to all
the servers then on the Server Identification portion of the Deployment Wizard, under Default Settings, use the
settings to all selected servers
settings to all the servers in that deployment job.
NOTE: The OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter does not support a multi-homed configuration. Adding a
second network interface to the appliance for communication with a second network causes problems for the
work flows involving hypervisor deployment, server compliance, and firmware updates.
button. This option lets you apply the same VLAN ID along with the other network
Apply
62
Page 63

Figure 4. Example VLAN network.
In this example network, the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter is on VLAN 5, while the vCenter and the
VMkernal of the ESXi hosts being deployed are on VLAN 10. Because the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter
does not support multi-VLAN homing, VLAN 5 must route to VLAN 10 for all systems to communicate to each other
correctly. If routing is not enabled between these VLANs, then the deployment fails.
Viewing Or Editing Hypervisor Profiles
To view or edit hypervisor profiles:
1. In the Dell Management Center, select Deployment → Deployment Template → Hypervisor Profiles window.
2. Select a profile and click View/Edit.
3. In the Hypervisor Profiles: Profile Name window, select the profile section to display or change, and make any
necessary changes.
4. Click Save to apply changes, or click Cancel to cancel changes.
Duplicating a Hypervisor Profiles
To duplicate a hypervisor profile:
1. In the Dell Management Center, select Deployment → Deployment Template → Hypervisor Profiles.
2. On the Hypervisor Profiles page, select a profile and click Duplicate.
3. In the Duplicate dialog box, enter a unique hypervisor profile name.
4. Click Apply to create a copy of the profile with the new name, or click Cancel to cancel.
63
Page 64

Renaming Hypervisor Profile
To rename a hypervisor profile:
1. In the Dell Management Center, select Deployment → Deployment Templates → Hypervisor Profiles.
2. On the Hypervisor Profiles page, select a profile and click Rename.
3. In the Rename dialog box, enter a unique hypervisor profile name.
4. Click Apply to use the new name, or click Cancel to cancel.
Deleting A Hypervisor Profile
To delete a hypervisor profile:
NOTE: Deleting a hypervisor profile that is part of a running deployment task can cause the task to fail.
1. In the Dell Management Center, select Deployment → Deployment Templates → Hypervisor Profiles.
2. Select a profile and click Delete.
3. In the message dialog box, click Delete to remove the profile, or click Cancel to cancel.
Refreshing Hypervisor Profiles
To refresh an updated hypervisor profile:
1. In the Dell Management Center, select Deployment → Deployment Templates → Hypervisor Profiles.
2. Click Refresh.
The updated hypervisor profile information displays.
Building A New Deployment Template
A deployment template contains either a hardware profile, a hypervisor profile, or both. The Deployment Wizard uses
this template to provision server hardware and deploy hosts within vCenter.
To build a new deployment template:
1. In the Dell Management Center, select Deployment → Deployment Templates.
2. Under Available Profiles, click Create New.
3. In the Create New window, enter a name for the template, and then click Save.
4. To complete the template, click Edit.
5. In the right pane, in the Profile drop-down list, choose a profile, and then do one of the following:
• To display the hardware/hypervisor profile settings for the selected profile, click View.
• To create a new hardware/hypervisor profile, click Create New.
6. Enter an optional Description for the deployment template that is helpful for managing the template.
7. To apply profile selections and save changes, click Save. To cancel, click Cancel.
Managing Deployment Templates
From the Dell Management Center, there are several management actions you can perform on existing deployment
templates, including:
64
Page 65

• Building Deployment Templates
• Duplicating Deployment Templates
• Renaming Deployment Templates
• Deleting A Deployment Template
Duplicating Deployment Templates
To duplicate a deployment template:
1. In the Dell Management Center, select Deployment → Deployment Templates.
2. On the Deployment Templates page, select a template, and then click Duplicate.
3. Enter the template's new name and click Apply. The template must have a unique name.
Deleting A Deployment Template
To delete a deployment template:
1. In the Dell Management Center, select Deployment → Deployment Templates.
2. On the Deployment Templates page, select a template and click Delete.
3. Click Delete on the message box to delete the template, or click Cancel to cancel.
Renaming a Deployment Template
To rename deployment template:
1. In the Dell Management Center, select Deployment → Deployment Templates.
2. On the Deployment Templates page, select a template, click Rename.
3. Enter the template's new name and click Apply. The template must have a unique name.
4. To display all deployment templates, from the Dell Management Center select Deployment → Deployment
Templates and click Refresh.
Running The Deployment Wizard
The Deployment Wizard steps you through the bare metal server deployment process of:
• Selecting undeployed servers.
When you deploy hypervisor, you can deploy to an Internal Dual SD Module with a minimum of 1 GB of storage. The
Internal Dual SD Module must be enabled from the BIOS before you deploy the hypervisor with the OpenManage
Integration for VMware vCenter.
• Using a deployment template (hardware and hypervisor profiles combination).
• Setting up global settings. This page lets you choose to deploy hypervisor to a hard disk or Internal Dual SD Module.
• Assigning identification to the deployed servers.
• Matching a desired connection profile to each server.
• Scheduling the server deployment jobs to run.
• Displaying the Job Queue where you can manage deployment jobs.
NOTE: If you’re deploying a hardware profile only, then the new Global Settings, Server Identification, and
Connection Profile pages are skipped and you go directly to the Schedule Job page.
NOTE: For trial/evaluation license, you can use Deployment wizard as long as license is not expired.
Related Tasks:
• Deployment Wizard Step 1: Selecting Servers
65
Page 66

• Deployment Wizard Step 2: Deployment Templates
• Deployment Wizard Step 3: Global Settings
• Deployment Wizard Step 4: Server Identification
• Deployment Wizard Step 5: Connection Profile
• Deployment Wizard Step 6: Schedule Jobs
Deployment Wizard - Step 1: Select Servers
This page covers server deployment. If you want to deploy hypervisor to an Internal Dual SD Module, this page displays
whether that option is available or unavailable. For more information about Internal Dual SD Modules see, Running The
Deployment Wizard. If the server you want to deploy does not display in the list for step 2, you can manually add a server
to have it display in the list for this step, see Adding A Server Manually.
To select servers:
1. In the Dell Management Center, select Deployment → Deployment Wizard.
2. In the Select Servers window, to assign non-deployed servers to this deployment job, use the check boxes to select
Servers.
3. Click Next.
To continue with the task to step two, click Deployment Wizard Step 2.
Deployment Wizard Step 2: Deployment Templates
Deployments to a hardware profile differ from hypervisor deployments. If you are deploying to a hardware profile, click
Deployment Wizard Step 6.
NOTE: A successful deployment requires an ESX ISO that has the correct drivers. Deployment on newer Dell
systems may require using Dell custom ISO images that contain all the required Dell drivers. ESX 4.1 may not work
on newer Dell systems and may not have a custom ISO available from Dell.
To select a deployment template:
1. Deployment Template selects/creates a deployment template in one of several ways:
• Select an existing deployment template under Available Templates. Information for the selected template
populates the right pane.
• Select an existing deployment template, and then click Edit to change one or both associated profiles.
• Click Create New to define a new template.
2. Select one of the following:
• If you are deploying to a hardware profile, click Next, which jumps you to Deployment Wizard Step 6.
• If you are deploying to a hypervisor profile, click Next, which takes you to Deployment Wizard Step 3.
Deployment Wizard Step 3: Global Settings
You can deploy hypervisor to either a hard drive or an Internal Dual SD Module. If an Internal Dual SD Module is
available on at least one of the servers selected, the Internal Dual SD Module option is enabled by default. If not, both
Hard Disk and Internal Dual SD Module options are not selected.
the
To deploy the hypervisor, perform the following steps:
1. In the Global Settings page, select one of the following options:
• Hard Disk — Deploys the hypervisor on the hard disk drive.
66
Page 67

• Internal Dual SD Module — Deploys the hypervisor on the Internal Dual SD Module.
2. If any of the selected servers do not support an Internal Dual SD Module, or an Internal Dual SD Module is not
present during deployment, perform one of the following actions:
• Select the Deploy the hypervisor to the first hard disk for servers that do not have an available Internal Dual SD
Module check box if you want to deploy the hypervisor on the first hard disk of the servers.
CAUTION: If you select this option and deploy the hypervisor on the first hard disk drive of the servers, all
the data on the disk drives will be erased.
• Clear the Deploy the hypervisor to the first hard disk for servers that do not have an available Internal Dual SD
Module check box to skip the deployment on those servers and continue hypervisor deployment on the next
server.
3. Click Next.
To continue with the task to Step 4, click Deployment Wizard Step 4: Server Identity.
Deployment Wizard Step 4: Server Identification
Server identification can be provided in two ways:
• Enter networking information (IP address, subnet mask and gateway); a fully-qualified domain name for the
hostname is mandatory. The use of
to vCenter.
• Use the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to configure IP addresses, subnet mask, gateway IP, hostname
and preferred/alternate DNS servers. The DHCP assigned IP address will be used when adding the host to vCenter.
When using DHCP, it is highly recommended that an IP reservation for selected NIC MAC addresses be used.
localhost
for the FQDN is not supported. The FQDN is used when adding the host
NOTE: Use a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) for hostname instead of localhost. Starting with ESXi 5.1, a value
of localhost impairs Dell Management Plug-in from processing events sent from the host. Create a DNS record
that resolves the IP address to the FQDN. For SNMP alerts from ESXi 5.1 to be identified correctly, configure the
DNS server to support reverse lookup requests. The DHCP reservations and DNS host names must be in place and
verified before the deployment job is scheduled to run.
This screen provides the option to specify a VLAN ID. When a VLAN ID is provided, it is applied to the hypervisor’s
management interface during deployment and tags all traffic with the VLAN ID.
To identify your server:
1. Server Identification assigns deployed servers new names and network identification. To display a list of servers
that do not meet the minimum requirements for firmware, BIOS, or have other issues, click Non-Compliant Servers.
2. For additional information, click Details.
3. Once the systems are updated, click Check Compliance to retest and verify fixes. To refresh the list, click Refresh,
and click Abort All Test to cancel the testing.
4. Click ^ to expand and view individual server information.
5. Under Host Name and NIC, enter a Fully Qualified Host Name for the server.
6. In the NIC Management Tasks drop-down list, select the NIC that will be used for managing the server.
7. Enter IP addresses, subnet mask, and other network information, or select the Obtain using DHCP check box.
8. If deploying to a network that requires a VLAN ID, select the VLAN check box and then enter the VLAN ID.
For the VLAN ID, use the numbers 1 through 4094. VLAN ID 0 is reserved for tagging the priority of frames.
9. Repeat for all servers to deploy, or select the Apply settings to all selected servers check box.
10. Click Next.
To continue with the task to Step 5, click Deployment Wizard Step 5.
67
Page 68

Deployment Wizard Step 5: Connection Profile
Connection profiles are used to establish connection credentials for hosts by associating them with iDRAC or Host Root
Credentials. The Connection Profiles window allows you to:
• Display or edit a current connection profile
• Delete a connection profile
• Refresh the connection profile list to reflect vCenter host changes
To create a connection profile:
1. Connection Profile automatically assigns servers to connection profiles after the deployment job completes.
Once a connection profile is selected, click Next.
2. Select the Assign all servers to the same connection profile option button, and select the connection profile from
the drop-down list to assign all servers to the same existing profile.
3. To create a new profile, click New and to view or edit the selected profile click View/Edit.
4. To display the selected connection profile settings, click View.
5. Select the Select a Connection Profile for each Server option button, and then select an individual connection
profile for each server from the drop-down list.
6. Once a connection profile is selected, click Next.
To continue with the task to Step 6, click Deployment Wizard Step 6.
Deployment Wizard Step 6: Scheduling Jobs
Schedule sets the schedule for the deployment job. There are several options of when to run the deployment job:
immediately, schedule the deployment job to run on a selected date and time, hold deployment job and manually start it.
To set up scheduling:
1. Determine when to run a deployment job by entering a date and time:
a. Click Schedule server(s) for deployment.
b. Use the calendar control to select the date.
c. Enter the time of day:
• Immediately: Click Deploy server(s) now.
• Postpone job: Click Create deployment job.
• Put on hold: With this option, only the schedule can be modified and all other deployment job options
cannot be changed.
2. Enter a Job Name and Job Description.
3. Click Finish.
4. Now that the deployment wizard is complete, you can manage deployment jobs using the Job Queue.
5. To display a list of non-compliant servers that must have a firmware update before the wizard can be completed,
click Non-Compliant Servers.
Related Tasks:
• Managing Deployment Jobs Using Deployment JobQueue
Understanding Job Queue
The Job Queue manages server deployment and inventory retrieval jobs, such as:
68
Page 69

• Displaying the submitted server deployment jobs.
• Refreshing the Deployment Jobs or Inventory/Warranty History queues.
• Scheduling an inventory job to update the Dell server attributes found in the current vCenter.
• Purging the deployment job queue entries.
• Managing firmware updates for clusters and databases.
NOTE: To make sure the inventory/warranty contains up-to-date information, schedule the inventory/warranty job
to run a minimum of once a week. The inventory/warranty job consumes minimal resources and does not degrade
host performance.
Tasks on this page include:
• Managing Deployment Jobs Using Deployment Job Queue
• Running Inventory Jobs
• Modifying An Inventory Job Schedule
• Viewing Firmware Update Status for Clusters and Datacenters
Managing Deployment Jobs Using The Deployment Job Queue
To manage deployment jobs using the deployment job queue:
1. From the Dell Management Center, select Job Queue → Deployment Jobs.
2. To update Deployment Jobs Details, click Refresh.
3. To display a Deployment Job Details dialog, which contains detailed information on the servers included in the
deployment job, click Details. This displays the following details:
• Service tag
• iDRAC IP address
• Server status
• If any warnings occurred
• Deployment job details
• Start and End time
To display full information for each item in the dialog’s table, hover over the item and an additional text pop-up is
displayed.
4. To either put a selected job on hold or to enter an updated schedule, click Modify.
5. Click Abort to abort the deployment job.
6. When the message displays, click Abort Job to abort, or click Do Not Abort Job to cancel.
NOTE: Any deployment jobs that are in progress cannot be aborted.
7. To display the Purge Deployment Job Queue window, click Purge Job Queue. Select the Older than date and job
, and click Apply. The select jobs are then cleared from the queue.
Status
Adding A Server Manually
You can manually add a server that has not been added by the discovery process. Once it is added, the server shows up
in the list of servers in the Deployment Wizard.
1. In the Dell Management Center, Deployment, and then click Deployment Wizard.
2. On the Select Server tab, click Add Server.
3. In the Add Server dialog box, do the following:
a. In the iDRAC IP Address text box, enter the iDRAC IP Address.
69
Page 70

b. In the User Name text box, enter the user name.
c. In the Password text box, enter the password.
4. Click Add Server. This could take a few minutes.
Removing A Bare Metal Server
You can manually remove a server that has been automatically discovered or manually added.
1. In Dell Management Center, under Deployment click Deployment Wizard.
2. On the Select Servers tab, click Remove Servers.
3. In the Remove Servers dialog box, select the check box of the server to remove.
4. Click Remove Selected Servers.
5. On the Select Servers tab, view the servers listed in the table to confirm it was removed.
70
Page 71

6
Console Administration
Administration of the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter and its virtual environment is achieved by using two
additional administration portals:
• Web-based Administration Console
• Console view for an individual server (the appliance virtual machine console).
Through the use of these two portals, global settings for vCenter management, OpenManage Integration for VMware
vCenter database backup and restore, and reset/restart actions can be entered and used across all vCenter instances.
Web-based Administration Console
The Web-based Administration Console provides several key pieces of functionality: vCenter server registration and
management, virtual appliance management, global vCenter alert settings, and backup and restore settings.
Managing vCenter Server Connections
From the vCenter Registration window in the Administration Console, you can register a vCenter server, and upload or
buy a license. If you are using a demo license, a Buy Now link displays from which you can purchase a full-version
license for managing multiple hosts. In this section, you can also modify, update, and unregister a server.
Related Tasks:
• Registering A vCenter Server
– Modifying The Administrator vCenter Login
– Updating The SSL Certificates For Registered vCenters
– Uninstalling OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter From vCenter
• Uploading OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter License Using The Administration Console
Registering a vCenter Server
You can register the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter after the OpenManage Integration for VMware
vCenter is installed. OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter uses the admin user account for vCenter operations.
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter supports 10 vCenters per appliance.
1. In OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter, on the Summary tab, use the link to open the Administration
Console.
2. In the Login dialog box, type your password.
3. To register a new server, in the left pane, click VCENTER REGISTRATION, and then click Register New vCenter
Server.
4. In the Register a New vCenter dialog box, under vCenter Name do the following:
a. In the vCenter Server IP or Hostname text box, enter the vCenter IP address or a FQDN of the host.
71
Page 72

b. In the Description text box, enter an optional description.
5. Under Admin User Account, do the following:
a. In the Admin User Name text box, enter the administrator's user name.
b. In the Password text box, enter the password.
c. In the Verify Password text box, enter the password again.
6. Click Register.
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter Requirements
The OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter (OMIVV) requires information from OpenManage on older generation
servers, and more current platforms are restricted to start at the version of vSphere that understands the newer
chipset. Due to this, there are limits on the version of vSphere that a given version of OMIVV will work with.
Versions of ESXi that should be supported on hosts managed:
ESX/ESXi version
support
v4.1 (ESX/ESXi)
v4.1 U1 (ESX/ESXi)
v4.1 U2 (ESX/ESXi)
v4.1 U3 (ESX/ESXi)
v5.0
v5.0 U1
v5.0 U2
v5.0 U3
v5.1
v5.1 U1
v5.1 U2
v5.5
v5.5 U1
v5.5 U2
Platform Generation Support
9G 10G 11G 12G 13G
Y Y Y N N
Y Y Y N N
Y Y Y Y N
Y Y Y Y N
Y Y Y Y N
Y Y Y Y N
Y Y Y Y N
Y Y Y Y N
Y Y Y Y N
Y Y Y Y N
Y Y Y Y N
N y Y Y N
N N N N Y
N N N Y Y
vCenter sSupport
Currently, support for v5.5 U1 is only available with 12th generation servers through iDRAC with Lifecycle Controller
support. OpenManage support for v5.5 U1 with the older generation servers is forthcoming. vSphere v5.5 U1 is not
supported with the latest chipset, so is not supported on 13th generation platforms.
Support for vSphere v5.5 U2
With iDRAC with Lifecycle Controller support, v5.5 U2 is supported vSphere for the 12th and 13th generation platforms.
Supported vCenter Server versions for release 2.3
The OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter will work with any of these vCenter Server versions:
vCenter version
v5.0 U3
72
Desktop Client Support Web Client Support
Y N
Page 73

v5.1 U2
Y N
v5.5
v5.5 U1
v5.5 U2
With any given vCenter version, the ESX / ESXi hosts it administrates must be equal or lower in version. To administrate
a vSphere v4.1 or v5.0 environment with OMIVV, you must have at least a v5.0 U3 vCenter administrating it.
Y Y
Y Y
Y Y
Modifying The vCenter Administrator Login
1. In OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter, on the Summary tab, use the link to open the Administration
Console.
2. In the Login dialog box, type your password.
3. In the left pane, click VCENTER REGISTRATION. The registered vCenters are displayed in the right pane. To open
the Modify Admin Acct window, under Credentials, click Modify.
4. Enter the vCenter Administrator User Name, Password, and Verify Password; the passwords must match.
5. To change the password, click Apply, or to cancel the change click Cancel.
Updating The SSL Certificates For Registered vCenter Servers
If the SSL certificate is changed on a vCenter server, then use the following steps to import the new certificate for the
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter. The OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter uses this certificate to
make sure the vCenter server it is talking to is the correct vCenter server and not an impersonator.
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter uses the openssl API to create the Certificate Signing Request (CSR)
using the RSA encryption standard with a 2048 bit key length. The CSR generated by the OpenManage Integration for
VMware vCenter is used to get a digitally signed certificate from a trusted Certification Authority. The OpenManage
Integration for VMware vCenter uses the digital certificate to enable SSL on the Web server for secure communication.
1. Launch a web Browser then enter https://<ApplianceIPAdrdress>
2. In the left pane, click VCENTER REGISTRATION. The registered vCenters are displayed in the right pane. To update
the certificates, click Update.
Uninstalling the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter From VMware vCenter
To remove the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter, it must be unregistered from the vCenter server using the
Administration Console.
1. Launch a web browser then enter https://<ApplianceIPAdrdress>
2. In the vCenter Registration page, under the vCenter server table, unregister the OpenManage Integration for
VMware vCenter by clicking Unregister.
You may have more than one vCenter, so be sure select the right one.
3. In the Unregister vCenter dialog box that asks if you really want to unregister this server, click Unregister.
Uploading A OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter License To The Administration Console
To upload a OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter license to the Administration Portal:
1. Launch a web Browser then enter https://<ApplianceIPAddress>
2. In the left pane, click VCENTER REGISTRATION. The registered vCenters are displayed in the right pane. To display
the upload license dialog box, click Upload License.
73
Page 74

3. To navigate to the license file, click the Browse button , and then click Upload.
NOTE: If the license file is modified or edited in any way, the appliance views it as corrupted and the file will
not work.
Virtual Appliance Management
Virtual appliance management contains the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter network, version, NTP, and
HTTPS information, and lets an administrator:
• Restart the virtual appliance
• Update the virtual appliance, and configure an update repository location
• Generate a troubleshooting bundle that contains appliance logging information.
• Enter Network Time Protocol (NTP) settings
• Upload and manage HTTPS certificates
Related Tasks:
• Restarting The Virtual Appliance
• Updating A Repository Location And Updating An Appliance
• Downloading Troubleshooting Bundle
• Setting Up The NTP Servers
Restarting The Virtual Appliance
To restart the virtual appliance:
NOTE: Restarting the virtual appliance logs you out from the Administration Console, and the OpenManage
Integration for VMware vCenter is unavailable until the virtual appliance and its services are active.
1. Launch a web Browser then enter https://<ApplianceIPAddress>
2. In the left pane, click APPLIANCE MANAGEMENT.
3. To restart the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter, click Restart the Virtual Appliance.
4. On the Restart Virtual Appliance dialog box, to restart the virtual appliance click Apply or click Cancel to cancel.
Updating A Repository Location And Virtual Appliance
Perform a backup prior to an update of the virtual appliance to make sure all data is protected.
1. Launch a web Browser then enter https://<ApplianceIPAddress>.
2. In the left pane, click APPLIANCE MANAGEMENT.
3. Next to Appliance Update, click Edit.
4. In the Appliance Update window, enter the Repository Location URL, and then click Apply.
NOTE: If the update location is on an external network, such as the Dell FTP site, then a proxy must be
entered below in the HTTP Proxy area.
74
Page 75

Updating the Virtual Appliance Software Version
To prevent data loss, perform an appliance backup prior to beginning the software update.
1. Launch a web Browser then enter https://<ApplianceIPAddress>.
2. In the left pane, click APPLIANCE MAINTENANCE.
3. To update the virtual appliance to the software version listed under Appliance Update, click Update Virtual
Appliance.
4. In the Update Appliance dialog box, the current and available versions are listed. To begin the update, click Update.
5. The system is locked down and put into maintenance mode. When the update is complete, the Appliance page
displays showing the newly installed version.
Downloading the Troubleshooting Bundle
Use this information to assist in troubleshooting issues, or send to Technical Support.
1. Launch a web Browser then enter https://<ApplianceIPAddress>.
2. In the left pane, click APPLIANCE MANAGEMENT.
3. To display the troubleshooting bundle dialog box, click Generate Troubleshooting Bundle.
4. To either open or save a zip file that contains the virtual appliance logging information, click the Download
Troubleshooting Bundle link.
5. To exit, click Close.
Setting Up The HTTP Proxy
You can set up the HTTP proxy settings using the Administration Console or the Dell Management Console.
1. In OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter, on the Summary tab, use the link to open the Administration
Console.
2. In the Login dialog box, type your password.
3. In the left pane, click APPLIANCE MANAGEMENT.
4. In the Appliance Management page, scroll down to the HTTP Proxy Settings, and then click Edit.
5. In the Edit page, do the following:
a. To enable the use of HTTP Proxy Settings, next to Use HTTP Proxy Settings, select Enable.
b. In the Proxy Server Address text box, enter the proxy server address.
c. In the Proxy Server Port text box, enter the proxy server port.
d. To use proxy credentials, next to Use Proxy Credentials, select Yes.
e. If you are using credentials, in the User Name text box, enter the user name.
f. In the Password text box, type the password.
6. Click Apply.
Setting Up the NTP Servers
Use the Network Time Protocol (NTP) to synchronize the virtual appliance clocks to that of a NTP server.
1. In OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter, on the Summary tab, use the link to open the Administration
Console.
2. In the Login dialog box, type your password.
3. In the left pane, click APPLIANCE MANAGEMENT.
75
Page 76

4. Click Edit for NTP.
5. Select the Enabled check box. Enter the host name or IP address for a Preferred and Secondary NTP Server and
click Apply.
6. To exit, click Cancel.
Generating a Certificate Signing Request
NOTE: You must upload the certificate before registering the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter with
the vCenter.
Generating a new Certificate Signing Request prevents certificates that are created with the previously generated CSR
from being uploaded to the appliance.
1. In OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter, on the Summary tab, use the link to open the Administration
Console.
2. In the Login dialog box, type your password.
3. In the left pane, click APPLIANCE MANAGEMENT.
4. Click Generate Certificate Signing Request for HTTPS Certificates. A message displays stating that if a new request
is generated, then certificates created using the previous CSR can no longer be uploaded to the appliance. To
continue with the request, click Continue, or Cancel to cancel.
5. Enter the Common Name, Organizational Name, Organizational Unit, Locality, State Name, Country and Email for the
request. Click
6. Click Download, and then save the resulting HTTPS certificate to an accessible location.
Uploading an HTTPS Certificate
You can use HTTPS Certificates for secure communication between the virtual appliance and host systems. To set up
this type of secure communication, a certificate signing request must be sent to a certificate authority and then the
resulting certificate is uploaded using the Administration Console. There is also a default certificate that is self-signed
and can be used for secure communication; this certificate is unique to every installation.
NOTE: You can use Microsoft Internet Explorer , Firefox, Crome to upload certificates.
Continue.
1. In OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter, on the Summary tab, use the link to open the Administration
Console.
2. In the Login dialog box, type your password.
3. In the left pane, click APPLIANCE MANAGEMENT.
4. Click Upload Certificate for HTTPS Certificates.
5. In the Upload Certificates dialog box, click OK.
6. To select the certificate to upload, click Browse, and then click Upload.
7. If you want to abort the upload, click Cancel.
NOTE: The certificate must use PEM format.
Restoring the Default HTTPS Certificate
1. In OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter, on the Summary tab, use the link to open the Administration
Console.
2. In the Login dialog box, type your password.
3. In the left pane, click APPLIANCE MANAGEMENT.
4. Click Restore Default Certificate for HTTPS Certificates.
5. In the restore default certificate dialog box, click Apply.
76
Page 77

Setting up Global Alerts
Alert management lets you enter global settings for how alerts are stored for all vCenter instances.
1. In OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter, on the Summary tab, use the link to open the Administration
Console.
2. In the Login dialog box, type your password.
3. In the left pane, click ALERT MANAGEMENT. To enter new vCenter alert settings, click Edit.
4. Enter numeric values for the following items:
• Maximum number of alerts
• Number of days to retain alerts
• Timeout for duplicate alerts (seconds)
5. To save your settings, click Apply, or click Cancel to cancel.
Managing Backup And Restore
Managing backup and restore is accomplished from the Administrative Console. Tasks on this page include:
• Configuring Backup And Restore
• Scheduling Atomatic Backups
• Performing An Immediate Backup
• Restoring The Database From Backup
Configuring Backup And Restore
The backup and restore function backs up the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter database to a remote
location from which it can be restored at a later date. Profiles, templates, and host information are included in the
backup. It is recommended that you schedule automatic backups to guard against data loss. After this procedure, you
must configure a backup schedule.
To configure backup and restore:
1. Launch a web Browser then enter https://<ApplianceIPAddress>.
2. In the left pane, click BACKUP AND RESTORE.
3. To edit the current backup and restore settings, click Edit.
4. In the Settings and Details page, do the following:
a. In the Backup Location text box, type the path to the backup files.
b. In the User Name text box, type the user name.
c. In the Password text box, type the password.
d. Under Enter the password used to encrypt backups, type the encrypted password in the text box.
The encryption password can contain alpha numeric characters and the following special characters: !@#$%*.
There is no length restriction.
e. In the Verify Password text box, retype the encrypted password.
5. To save these settings, click Apply.
6. Configure the backup schedule. For more information see, Scheduling Automatic Backups.
77
Page 78

Scheduling Automatic Backups
This is the second part of configuring backup and restore. For detailed information on configuring the backup location
and credentials, see Configuring Backup And Restore.
To schedule an automatic backup:
1. Launch a web Browser then enter https://<ApplianceIPAddress>.
2. In the left pane, click BACKUP AND RESTORE.
3. To edit the backup and restore settings, click Edit Automatic Scheduled Backup (this makes fields active).
4. To enable the backups, click Enabled.
5. Select the check boxes for the days of the week for which you want to run the backup.
6. In the Time for Backup (24 Hour Time Format, HH:mm) text box, enter the time in HH:mm format.
The Next Backup populates with the date and time of the next scheduled backup.
7. Click Apply.
Performing An Immediate Backup
To perform an immediate backup:
1. Launch a web Browser then enter https://<ApplianceIPAddress>.
2. In the left pane, click BACKUP AND RESTORE.
3. Click Backup Now.
4. To use location and encryption password from the Backup settings, in the Backup Now dialog box, select that
check box.
5. Enter a Backup Location, User Name, Password, and Encryption Password.
The encryption password can contain alpha numeric characters and the following special characters: !@#$%*.
There is no length restriction.
6. Click Backup.
Restoring The Database From A Backup
NOTE: The restore operation causes the virtual appliance to reboot after it has completed.
To restore the database from backup:
1. Launch a web Browser then enter https://<ApplianceIPAddress>.
2. In the left pane, click BACKUP AND RESTORE and the current backup and restore settings are displayed.
3. Click Restore Now.
4. In the Restore Now dialog box, enter a File Location (CIFS/NFS Format).
5. Enter the User Name, Password, and Encryption Password for the backup file.
The encryption password can contain alpha numeric characters and the following special characters: !@#$%*.
There is no length restriction.
6. To save your changes, click Apply
The appliance reboots or restarts once Apply is clicked.
78
Page 79

Understanding the vSphere Client Console
The Console is found within the vSphere Client on a virtual machine. The Console works hand and hand with the
Administration Console. The Console provides the ability to:
• Configure network settings
• Change the virtual appliance password
• Set the local timezone
• Reboot the virtual appliance
• Reset the virtual appliance to factory settings
• Refresh Console
• Logout option
Use the arrow keys to navigate up or down. Once you have selected the option you want, press <ENTER>. After you
access the Console screen, VMware vSphere Client takes control of your cursor. To escape from that control, press
<CTRL> + <ALT>.
Configuring Network Settings
Changes to the network settings are done in the vSphere Client on the Console tab.
To configure network settings:
1. In the vSphere Client, select the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter, and then click the Console tab.
2. In the Console window, select Configure Network, then press <ENTER>.
3. Enter the desired network settings under Edit Devices or under Edit DNS configuration, then click Save & Quit. To
abort any changes, click
Quit.
Changing The Virtual Appliance Password
The virtual appliance password is changed in the vSphere Client using the Console tab.
To change the virtual appliance password:
1. In the vSphere Client, select the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter virtual machine and click the
Console tab.
2. In the Console tab, use the arrow keys to select Change Admin Password and press <ENTER>.
3. Enter the Current Admin Password and press <ENTER>.
Admin passwords include one special character, one number, one uppercase, one lowercase, and at least 8
letters.
4. Enter a new password for Enter new Admin Password and press <ENTER>.
5. Type the new password again in Please Confirm Admin Password text box , and then press <ENTER>. The
administration password is changed.
79
Page 80

Setting The Local Time Zone
To set the local time zone:
NOTE: You can only edit the timezone and not the current time and date.
1. In vSphere Client, select the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter virtual machine, and then click the
Console tab.
2. Select Set Time Zone and press <ENTER>.
3. In the Timezone Selection window, select the desired time zone and click OK. To cancel changes click Cancel. The
time zone is updated.
Rebooting Virtual Appliance
To reboot the virtual appliance:
1. In vSphere Client, select the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter virtual machine, and then click the
Console tab.
2. Select Reboot this Virtual Appliance and press <ENTER>.
3. The following message is displayed:
If there are any processes running on this appliance they will be
terminated by this action. Are you sure you wish to do this?
4. Enter y to reboot or n to cancel. The appliance is rebooted.
Resetting The Virtual Appliance To Factory Settings
To reset the virtual appliance to factory settings:
1. In vSphere Client, select the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter virtual machine, and click the Console
tab.
2. Select Reset this Virtual Appliance to Factory Settings and press <ENTER>.
3. The following notice is displayed:
This operation is completely Irreversible if you continue you will
completely reset *this* appliance to its original settings. All changes you
have made to this appliance will be Lost. Are you sure you wish to Reset
this Appliance to Factory Settings?
4. Enter y to reset or n to cancel.
The appliance is reset to the original factory settings and all the all others settings and saved data will be lost.
NOTE: When the virtual appliance is reset to factory settings, any updates made to the Network Configuration
are preserved; these settings are not reset.
Refreshing the Console View
To refresh the Console view, select Refresh and press <ENTER>.
Read-only User Role
There is an unprivileged user role called readonly with shell access for diagnostic purposes. The read-only user has
limited privileges to run the mount. The read-only user's password is set to the same as the admin.
80
Page 81

Migration Path to migrate from 1.6/1.7 to 2.3
There is no RPM update support to this version from 1.7 or lower versions. You can migrate from older version (1.6 or 1.7)
to the version 2.3 release using the Backup and Restore path. Also, the migration path is only supported from version 1.6
and 1.7. If you are at a lower version than 1.6, you will have to upgrade your appliance to the supported version before
you perform the migration to OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter version 2.3.
Do the following to migrate from older version to the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter 2.3 version:
1. Take a Backup of the database for the older release. For more information, See the section, Managing Backup and
Restore in this guide.
2. Power off the older appliance from the vCenter.
NOTE: Do not unregister the Plug-in from the vCenter. Unregistering the plug-in from the vCenter will remove
all the Alarms registered on the vCenter by the plug-in and remove all the customizing performed on the
alarms like actions and so on, on the vCenter. For more information, see the section How to recover if I have
unregistered the older plugin after the backup in this guide if you have already unregistered the Plug-ins after
the backup.
3. Deploy the new OpenManage Integration version 2.3 OVF. For more information, see the section Deploying the
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter OVF Using the vSphere Client in this guide to deploy the OVF.
4. Power on the OpenManage Integration version 2.3 appliance.
5. Setup the network, time zone and so on to the appliance. It is recommended that the new OpenManage Integration
version 2.3 appliance has the same IP address as the old appliance. To setup the network details, see the section,
Registering OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter And Importing The License File in this guide.
6. Restore the database to the new appliance. For more information, see the section, Restoring The Database From A
in this guide.
Backup
7. Upload the new license file. For more information, see the section, Registering OpenManage Integration for
VMware vCenter And Importing The License File in OpenManage Integration Version 2.3 Quick Install Guide.
8. Verify the appliance. For more information, see the section Installation Verification in this guide to ensure the
database migration is successful.
9. Run the Inventory on all the registered vCenters.
NOTE:
It is recommended that you run the inventory on all the hosts managed by the plug-in again after the upgrade.
For more information, see the section Running Inventory Jobs for steps to run the inventory on demand.
If the IP address of the new OpenManage Integration version 2.3 appliance has changed from that of the old
appliance, the trap destination for the SNMP traps must be configured to point to the new appliance. For 12th
generation and higher generation servers, this will be fixed by running the Inventory on these hosts. For all
11th generation or lower generation hosts that were earlier complaint, this IP change will show up as noncomplaint and will require configuring OMSA. For more information, see the section, Running the Fix NonCompliant vSphere hosts Wizard to fix the host compliance in the this guide.
81
Page 82

7
Troubleshooting
Use this section to find answers to troubleshooting questions. This section includes:
• Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
• Bare metal deployment issues
• Contacting Dell
• Related product information
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
This section contains some common questions and solutions.
Using OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter to update an Intel Network card with the firmware version of 13.5.2 is not supported.
There is a known issue with Dell PowerEdge 12th generation servers and some Intel Network cards with the firmware
version of 13.5.2. Updating some models of Intel network cards at this version of firmware fails when the firmware
update is applied using the Lifecycle Controller. Customers with this version of firmware must update the network driver
software using an operating system. If the Intel Network card has a version of firmware other than 13.5.2, you can
update using OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter. For more information, see http://en.community.dell.com/
techcenter/b/techcenter/archive/2013/03/20/intel-network-controller-card-with-v13-5-2-firmware-cannot-be-upgradedusing-lifecycle-controller-to-v13-5-6.aspx
NOTE: Note: When using the one-to-many firmware update, avoid selecting Intel network adapters that are at
version 13.5.2, as the update will fail and stop the update task from updating remaining servers.
On trying a firmware update with an invalid DUP, the hardware update job status on the vCenter console neither fails nor times-out for hours, though the job status in LC says ‘FAILED’. Why is this happening?
When the invalid DUP is picked for firmware update, the status of the task in the vCenter console window remains ‘In
Progress’ but the message is changed to the reason of failure. This is a known VMWare defect and will be fixed in the
future releases of VMWare vCenter.
Resolution: The task has to be cancelled manually.
Version Affected: All
Administration Portal is still showing the unreachable Update Repository location.
If the user provided a unreachable Update Repository path, the error message “Failed: Error while connecting to the URL
…. ” is displayed on the top of the Appliance Update view, however the Update Repository Path is not cleared out to the
value before update.
Resolution: Move out of this page to another page and make sure the page is refreshed.
82
Page 83

Version Affected: All
Why is the DNS configuration settings restored to original settings after appliance reboot if using DHCP for appliance IP and DNS settings overwritten
There is a known defect where statically assigned DNS settings are replaced by values from DHCP. This can happen
when DHCP is used to obtain IP settings, and DNS values are assigned statically. When the DHCP lease is renewed or
the appliance is restarted the statically assigned DNS settings are removed. Resolution: Statically assign IP settings
when the DNS server settings will be different from DHCP.
Version Affected: All
Why did my system not enter maintenance mode when I performed a one-to-many firmware update?
Some firmware updates do not require rebooting the host. In that case, the firmware update is performed without
putting the host into maintenance mode.
Even if my repository has bundles for selected 11G system, why is firmware update showing that I have no bundles for Firmware Update?
When I added a host to the connection profile in lockdown mode, the inventory kicked off but failed stating that “No
Remote Access Controller was found or Inventory is not supported on this host.” Inventory is supposed to work for a
host in lockdown mode, right?
If you put the host in lockdown mode or remove a host from lockdown mode, you must wait 30–minutes before
performing the next operation on the If I pick a 11G host for firmware update, the firmware update wizard will not show
any bundles even if the repository provided has bundles for that system. This will happen because the 11G host might
not configured for OMSA to send traps to OpenManage Integration.
Resolution: Ensure that the host is compliant using the host Compliance screen of OpenManage Integration desktop
client. If it is not compliant, use the fix Host Compliance to get it compliant.
Version Affected: 2.2 and 2.3
Why Does My ESX / ESXi Deployment Fail on Servers Having a PERC S300 Boot Controller?
Deployments of OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter using different ESX/ESXi versions on Dell PowerEdge
servers with the PERC S300 boot controller failed. The Dell customized ESX/ESXi operating systems do not carry the
driver for the PERC S300 boot controller, which causes the boot controller/HDD not to be recognized during operating
system installation. Servers with PERC S300 boot controllers are not supported for OpenManage Integration for VMware
vCenter deployments.
How Come I See An Error Message Displayed After Clicking The Firmware Link?
If you have a slow network speed (9600BPS), you may get a Communication Error Message. This error message may
display when you click the Firmware link in the vSphere Client for the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter. It
happens when the connection times out while trying to obtain the Software Inventory list. Microsoft Internet Explorer
initiates this timeout. For Microsoft Internet Explorer versions 9/10, the default “Receive Time out” value is set to 10
seconds. Fix this issue by using the following steps.
83
Page 84

Figure 5. Firmware link communication error
1. Open Microsoft Registry Editor (Regedit).
2. Navigate to the following location:
KHEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings
3. Add a DWORD value for ReceiveTimeout.
4. Set the value to 30 seconds (30000) [This value may need to be a higher value in your environment].
5. Exit Regedit.
6. Restart Internet Explorer.
NOTE: Just opening a new Internet Explorer window is not enough. Restart the Internet Explorer browser.
What generation of Dell servers does the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter configure and support for SNMP traps?
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter supports OMSA SNMP traps on pre-12th generation servers and iDRAC
traps on 12th generation servers.
How does the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter support more than three vCenters in Linked Mode?
Each virtual appliance supports a maximum of three vCenters in Linked Mode. If you have more than ten vCenters, you
need a new instance of the appliance for every ten vCenters with associated licensing.
Does OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter support vCenter in linked mode?
Yes , OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter supports up to 10 vCenters in linked mode. For more information on
how OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter works in linked mode, see the white paper,
for VMware vCenter: Working in Linked Mode
84
on www.Dell.com.
Dell Management Plug-in
Page 85

What are the Required Port Settings for the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter?
NOTE: When deploying the OMSA agent using the
Compliance window in the
httpClient service and enables port 8080 on releases after ESXI 5.0 to download OMSA VIB and install it. Once the
OMSA installation is completed the service automatically stops and the port is closed.
Use these port settings for the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter.
Table 3. Virtual Appliance Ports
Port Number Protocols Port Type Max.
21 FTP TCP None Out FTP command
53 DNS TCP None Out DNS client No
80 HTTP TCP None Out Dell Online
80 HTTP TCP None In Administration
162 SNMP Agent UDP None In SNMP Agent
11620 SNMP Agent UDP None In SNMP Agent
443 HTTPS TCP 128–bit In HTTPS server No
443 WSMAN TCP 128–bit In/Out iDRAC/OMSA
4433 HTTPS TCP 128–bit In Auto Discovery No
2049 NFS UDP None All Public Share No
4001–4004 NFS UDP None All Public Share No
11620 SNMP Agent UDP None Om SNMP Agent
Dell Management Center, the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter starts the
Fix non-complient vSphere hosts
Direction Usage Configurable
Encryption
Level
link available from the
No
client
No
Data Access
No
Console
No
(server)
No
(server)
No
communication
No
(server)
Table 4. Managed Nodes
Port Number Protocols Port Type Max.
Encryption
Level
162, 11620 SNMP UDP None Out Hardware
443 WSMAN TCP 128–bit In iDRAC/OMSA
4433 HTTPS TCP 128–bit Out Auto Discovery No
2049 NFS UDP None All Public Share No
4001–4004 NFS UDP None All Public Share No
Direction Usage Configurable
events
communication
No
No
85
Page 86

Port Number Protocols Port Type Max.
Encryption
Level
443 HTTPS TCP 128–bit In HTTPS server No
8080 HTTP TCP In HTTP server;
50 RMCP UDP/TCP 128–bit Out Remote Mail
51 IMP UDP/TCP N/A N/A IMP Logical
5353 mDNS UDP/TCP All Multicast DNS No
631 IPP UDP/TCP None Out Internet
69 TFTP UDP 128–bit All Trivial File
111 NFS UDP/TCP 128–bit In SUN Remote
68 BOOTP UDP None Out Bootstrap
Direction Usage Configurable
No
downloads the
OMSA VIB and
fixes noncompliant
vSphere hosts
No
Check Protocol
No
Address
Maintenance
No
Printing
Protocol (IPP)
No
Transfer
No
Procedure Call
(Portmap)
No
Protocol Client
What are the Minimum requirements for successful installation and operation of the virtual appliance?
The following settings outline the minimum appliance requirements:
• Physical RAM: 3 GB.
• Reserved Memory: 1 GB
NOTE: For optimal performance Dell recommends 3 GB.
• Disk: 32.5 GB.
• CPU: 2 virtual CPUs.
Why is the password not changed for the user used for bare-metal discovery after successfully applying the hardware profile that has the same user with new changed credentials in the iDRAC user list?
The password of the user used from discovery is not changed to the new credential if only hardware profile template is
selected for deployment. This is done intentionally so that the plugin is able to communicate with the iDRAC future use in
deployment needs.
86
Page 87

Why is the processor version “Not Applicable” in Processor view in the System overview page?
In case of PowerEdge 12th Generation Dell Servers and higher generations, the processor version is in the Brand
column. In case of lower generation servers processor version is shown in the Version column.
Why is the DNS configuration settings restored to original settings after appliance reboot if using DHCP for appliance IP and DNS settings overwritten
There is a known defect where statically assigned DNS settings are replaced by values from DHCP. This can happen
when DHCP is used to obtain IP settings, and DNS values are assigned statically. When the DHCP lease is renewed or
the appliance is restarted the statically assigned DNS settings are removed. Resolution: Statically assign IP settings
when the DNS server settings will be different from DHCP.
Version Affected: All
How come I do not see my new iDRAC version details listed on the vCenter Hosts & Clusters page?
After the successful completion of a firmware update task in the vSphere Desktop client’s recent tasks pane, refresh the
Firmware Update page and verify the firmware versions. If the page shows the old versions, then go to Host Compliance
page in OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter and check the CISOR status of that host. If CISOR is not enabled,
then enable CISOR and reboot host. If the CISOR was already enabled, then login to the iDRAC console, reset iDRAC,
wait for few minutes, and then refresh the Firmware Update page in vSphere Desktop client.
How Do I Test Event Settings by Using OMSA to Simulate a Temperature Hardware Fault?
To make sure that events are functioning correctly:
1. In the OMSA user interface, navigate to Alert Management → Platform Events.
2. Select the Enable Platform Event Filter Alerts check box.
3. Scroll down to the bottom, and click Apply Changes.
4. To make sure that a specific event is enabled, such as temperature warning, from the tree on the left, select Main
System Chassis.
5. Under Main System Chassis, select Temperatures.
6. Select the Alert Management tab, and select Temperature Probe Warning.
7. Select the Broadcast a Message check box, and select Apply Changes.
8. To cause the temperature warning event, from the tree view on the left, select Main System Chassis.
9. Select Temperatures under Main System Chassis.
10. Select the System Board Ambient Temp link, and select the Set to Values option button.
11. Set the Maximum Warning Threshold to below the current listed reading; for example if the current reading is 27,
set the threshold to
12. Select Apply Changes, and the temperature warning event is generated. To cause another event, restore the
original settings using the same Set to Values option. Events are generated as warnings, and then to a normal state.
If everything is working properly, navigate to the vCenter Tasks & Events view; a temperature probe warning event
should be displayed.
NOTE: There is a filter for duplicate events; if you try to trigger the same event too many times in a row, you
will only receive one event. Allow at least 30 seconds between events to see all events.
25.
87
Page 88

I Have the OMSA Agent Installed on a Dell Host System, But I Still Get an Error Message That OMSA is Not Installed. What Should I Do?
To resolve this issue on an 11th generation server:
1. Install OMSA with the Remote Enablement component on the host system.
2. If you are using the command line to install OMSA, make sure to specify the -c option. If OMSA is already installed,
reinstall it with the -c option and restart the service:
srvadmin-install.sh -c
srvadmin-services.sh restart
For an ESXi host, you must install OMSA VIB using the VMware Remote CLI tool, and reboot the system.
Can the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter Support ESX/ESXI with Lockdown Mode Enabled?
Yes. Lockdown Mode is supported in this release on hosts ESXi 4.1 and above.
Inventory is Failing on Hosts ESXi 4.0 Update2 and ESXi Update 3 in Lockdown Mode After a Reboot.
Lockdown Mode requires ESXi 4.1 or later. If you are using an earlier ESXi version, when a host is rebooted for any
reason during Lockdown Mode, inventory continues failing unless you perform the following steps on host after a
reboot.
The workaround steps for ESXi 4.0 Update2 and Update3 are:
1. In vSphere Client, select Hosts and Clusters, then in the left pane, select the host and then click the Configuration
tab.
2. In the left pane, under Software click Security Profile.
3. Scroll down to Lockdown Mode, and then click Edit.
4. In the Lockdown Mode dialog box, to disable Lockdown Mode, clear the Enable check box, and then click OK.
5. Log in to the host console and select Restart Management Agents, press <ENTER>, and to confirm, press <F11>.
6. To enable Lockdown Mode, repeat steps 1 through 4, except this time select the Enable check box, and then click
OK.
When I tried to use lockdown mode, it failed.
When I added a host to the connection profile in lockdown mode, the inventory kicked off but failed stating that “No
Remote Access Controller was found or Inventory is not supported on this host.” Inventory is supposed to work for a
host in lockdown mode, right?
If you put the host in lockdown mode or remove a host from lockdown mode, you must wait 30–minutes before
performing the next operation on the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter.
On trying a firmware update with an invalid DUP, the hardware update job status on the vCenter console neither fails nor times-out for hours, though the job status in LC says ‘FAILED’. Why is this happening?
When the invalid DUP is picked for firmware update, the status of the task in the vCenter console window remains ‘In
Progress’ but the message is changed to the reason of failure. This is a known VMWare defect and will be fixed in the
future releases of VMWare vCenter.
88
Page 89

Resolution: The task has to be cancelled manually.
Version Affected: All
What Setting Should I Use For UserVars.CIMoeMProviderEnable With ESXi 4.1 U1?
Set UserVars.CIMoemProviderEnabled to 1.
I Am Using A Reference Server to Create a Hardware Profile But it Failed. What Should I Do?
Check to make sure that minimum recommended versions of iDRAC firmware, Lifecycle Controller firmware, and BIOS
are installed.
To make sure that the data retrieved from the reference server is current, enable Collect System Inventory On Restart
(CSIOR), and restart the reference server prior to extraction of data. See Setting CSIOR on a Reference Server.
I Am Attempting To Deploy ESX/ESXi On A Blade Server And It Failed. What Should I Do?
To resolve this issue, do the following:
1. Make sure the ISO location (NFS path) and staging folder paths are accurate.
2. Make sure the NIC selected during assignment of server identity is on the same network as the virtual appliance.
3. If using static IP address, make sure the network information provided (including subnet mask and default gateway)
is accurate. In addition, , make sure the IPaddress is not already assigned on the network.
4. Make sure at least one Virtual Disk is seen by the system. ESXi also installs to an internal RIPS SD card.
Why Are My Hypervisor Deployments Failing On R210 II Machines?
A timeout issue on R210 II systems produces a hypervisor deployments failure error due to the failure of the BIOS to boot
from attached ISO. To resolve this issue, manually install hypervisor on the machine.
Why Do I See Auto-discovered Systems Without Model Information in the Deployment Wizard
This usually indicates that the firmware version installed on the system does not meet recommended minimum
requirements. In some cases, a firmware update may not have registered on the system. Cold booting the system or
reseating the blade fixes this problem. The newly enabled account on the iDRAC must be disabled and auto-discovery
reinitiated to provide model information and NIC information to the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter.
The NFS Share is Set Up With the ESX/ESXI ISO, but Deployment Fails with Errors Mounting the Share Location.
To find the solution:
1. Make sure the iDRAC is able to ping the appliance.
2. Make sure your network is not running too slow.
How Do I Force Removal of the Virtual Appliance?
1. Go to https://<vcenter_serverIPAddress>/mob
2. Enter the VMware vCenter admin credentials.
89
Page 90

3. Click Content.
4. Click ExtensionManager.
5. Click UnregisterExtension.
6. Enter the extension key com.dell.plugin.openManage_integration_for_VMware_vCenter, and
then click Invoke method.
7. Turn off the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter virtual appliance and delete it.
Entering a Password in the Backup Now Screen Receives an Error Message
If you are using a low resolution monitor, the Encryption Password field is not visible from the BACKUP NOW window.
You must scroll down the page to enter the encryption password.
My Firmware Update Failed. What Do I Do?
Check the virtual appliance logs to see if the tasks timed out. If so, iDRAC needs to be reset by performing a cold reboot.
Once the system is up and running, check to see if the update was successful by either running an inventory or using the
Firmware tab.
My vCenter Registration Failed. What Can I Do?
vCenter registration can fail due to communication issues, therefore if you are experiencing these issues one solution is
to use a static IP address. To use a static IP address, in the Console tab of the OpenManage Integration for VMware
vCenter and select Configure Network → Edit Devices and enter the correct gateway and FQDN (Fully Qualified Domain
Name). Enter the DNS server name under Edit DNS Config.
NOTE: Make sure that the virtual appliance can resolve the DNS server you entered.
Performance during Connection Profile Test Credentials is extremely slow or unresponsive.
The iDRAC on a server has only one user (for example, only
disabled state. Communicating to a server in a disabled state causes delays. To fix this issue, you can either fix the
disable state of the server, or reset iDRAC on the server to re-enable the root user to default setting.
To fix a server in a disabled state:
1. Open the Chassis Management Controller console and select the disabled server.
2. To automatically open the iDRAC console, click Launch iDRAC GUI.
3. Navigate to the user list in iDRAC console, and choose one of the following:
• iDRAC 6 : Select iDRAC settings → Network/Security tab → Users tab.
• iDRAC 7 : Select iDRAC settings → Users tab.
• iDRAC 8 : Select iDRAC settings → Users tab.
4. To edit the settings, in the User ID column, click the link for the admin (root) user.
5. Click Configure User, and then click Next.
6. In the User Configuration page for the selected user, select the check box next to Enable user, and then and click
Apply.
root
) and the user is in a disabled state, or all users are in a
90
Page 91

Does the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter support the VMware vCenter Server appliance?
Yes, the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter supports the VMware vCenter Server appliance.
Does the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter support the vSphere Web Client?
Yes, the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter supports the VMware vSphere Web client.
In the Administration Console, why the Update Repository Path is not set to default path after I reset the appliance to factory settings?
After you reset the appliance, go to the Administration Console, and then click APPLIANCE MANAGEMENT in the left
pane. In the Appliance Settings page, the Update Repository Path is not changed to default path.
Resolution: In the Administration Console, manually copy the path in the Default Update Repository field to Update
Repository Path field.
After backup and restore of OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter, why alarm settings are not restored?
Restoring the OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter appliance backup does not restore all the Alarm settings.
However, in the OpenManage Integration for VMware GUI, the Alarms and Events field displays the restored settings.
Resolution: In the OpenManage Integration for VMware GUI, in the Manage → Settings tab, manually change the Events
and Alarms settings.
Bare Metal Deployment Issues
This section deals with issues found during the deployment process.
Auto-Discovery and Handshake Prerequisites
• Prior to running auto-discovery and handshake, make sure that iDRAC and Lifecycle Controller firmware and BIOS
versions meet the minimum recommendations.
• CSIOR must have run at least once on the system or iDRAC.
Hardware Configuration Failure
• Before initiating a deployment task, make sure the system has completed CSIOR and is not in the process of
rebooting.
• It is highly recommended that BIOS configuration be run in Clone mode, so that the reference server is an identical
system.
• Some controllers do not allow creation of a RAID 0 array with one drive. This feature is supported only on high-end
controllers, and the application of such a hardware profile can cause failures.
Enabling Auto-Discovery On A Newly Purchased System
The auto-discovery feature of a host system is not enabled by default; instead, enablement must be requested at the
time of purchase. If auto-discovery enablement is requested at the time of purchase, DHCP is enabled on the iDRAC and
admin accounts are disabled. It is not necessary to configure a static IP address for the iDRAC. It gets one from a DHCP
server on the network. To make use of the auto-discovery feature, a DHCP server or a DNS server (or both) must be
configured to support the discovery process. CSIOR has already been run by factory process. For more information on
91
Page 92

how to set up a network to support auto-discovery, see the Dell Auto-Discovery Network Setup Specification at http://
attachments.wetpaintserv.us/xBUlrs4t%2B2TzbrwqYkblvQ%3D%3D2 62254
If auto-discovery was not requested at the time of purchase, it can be enabled as follows:
1. During the boot process, press <Ctrl-E>.
2. In the iDRAC setup window, enable the NIC (blade servers only).
3. Enable Auto-Discovery.
4. Enable DHCP.
5. Disable admin accounts.
6. Enable Get DNS server address from DHCP.
7. Enable Get DNS domain name from DHCP.
8. In the Provisioning Server field, enter:
<OpenManage Integration virtual appliance IPaddress>:4433
Contacting Dell
NOTE: If you do not have an active Internet connection, you can find contact information on your purchase
invoice, packing slip, bill, or Dell product catalog.
Dell provides several online and telephone-based support and service options. Availability varies by country and
product, and some services may not be available in your area. To contact Dell for sales, technical support, or customer
service issues:
1. Visit dell.com/support
2. Select your support category.
3. Verify your country or region in the Choose a Country/Region drop-down menu at the top of page.
4. Select the appropriate service or support link based on your need.
OpenManage Integration for VMware vCenter Related Information
• View or download Dell server documentation for PowerEdge™ Servers at:
http://www.dell.com/poweredgemanuals
• Dell OpenManage System Administrator documents
http:// www.delltechcenter.com/omsa
• Dell Lifecycle Controller documentation
http://www.dell.com/enterprisemanagement
92
Page 93

8
Virtualization-related Events For Dell PowerEdge Servers
The following table contains virtualization-related critical and warning events, including event name, description and
severity level for 11th, 12th, and 13th generation of PowerEdge servers.
Table 5. Virtualization-related Events of 11th, 12th, and 13th Generation PowerEdge Servers
Event Name Description Severity Recommended Action
Dell-Current sensor
detected a warning value
Dell-Current sensor
detected a failure value
Dell-Current sensor
detected a non-recoverable
value
Dell-Redundancy regained Sensor Returned to Normal
Dell-Redundancy degraded A redundancy sensor in the
Dell - Redundancy lost A redundancy sensor in the
A current sensor in the
specified system exceeded
its warning threshold.
A current sensor in the
specified system exceeded
its failure threshold.
A current sensor in the
specified system detected
an error from which it
cannot recover
Value
specified system detected
that one of the components
of the redundancy unit has
failed but the unit is still
redundant.
specified system detected
that one of the components
in the redundant unit has
been disconnected, has
failed, or is not present.
Warning No action
Error Put the system into
maintenance mode
Error No action
Info No action
Warning No action
Error Put the system into
maintenance mode
Dell - Power supply
returned to normal
Dell - Power supply
detected a warning
Sensor Returned to Normal
Value
A power supply sensor
reading in the specified
system exceeded a user
definable warning
threshold.
Info No action
Warning No action
93
Page 94

Dell - Power supply
detected a failure
A power supply has been
disconnected or has failed.
Error Put the system into
maintenance mode
Dell - Power supply sensor
detected a non-recoverable
value
Dell - Memory Device
Status warning
Dell - Memory Device error A memory device correction
Dell - Fan enclosure
inserted into system
Dell - Fan enclosure
removed from system
Dell - Fan enclosure
removed from system for an
extended amount of time
A power supply sensor in
the specified system
detected an error from
which it cannot recover.
A memory device correction
rate exceeded an
acceptable value.
rate exceeded an
acceptable value, a memory
spare bank was activated,
or a multibit ECC error
occurred.
Sensor returned to normal
value.
A fan enclosure has been
removed from the specified
system.
A fan enclosure has been
removed from the specified
system for a user-definable
length of time.
Error No action
Warning No action
Error Put the system into
maintenance mode
Info No action
Warning No action
Error No action
Dell - Fan enclosure sensor
detected a non-recoverable
value
Dell - AC power has been
restored
Dell - AC power has been
lost warning
Dell - An AC power cord has
lost its power
Dell - Processor sensor
returned to a normal value
Dell - Processor sensor
detected a warning value
A fan enclosure sensor in
the specified system
detected an error from
which it cannot recover.
Sensor Returned to Normal
Value.
An AC power cord has lost
its power, but there is
sufficient redundancy to
classify this as a warning.
An AC power cord has lost
its power, and lack of
redundancy requires this to
be classified as an error.
Sensor Returned to Normal
Value
A processor sensor in the
specified system is in a
throttled state.
Error No action
Info No action
Warning No action
Error No action
Info No action
Warning No action
94
Page 95

Dell - Processor sensor
detected a failure value
A processor sensor in the
specified system is
disabled, has a
configuration error, or
experienced a thermal trip.
Error No action
Dell - Processor sensor
detected a non-recoverable
value
Dell - Device configuration
error
Dell - Battery sensor
returned to a normal value
Dell - Battery sensor
detected a warning value
Dell - Battery sensor
detected a failure value
Dell - Battery sensor
detected a nonrecoverable
value
Dell - Thermal shutdown
protection has been
initiated
A processor sensor in the
specified system has failed.
A configuration error was
detected for a pluggable
device in the specified
system.
Sensor Returned to Normal
Value
A battery sensor in the
specified system detected
that a battery is in a
predictive failure state.
A battery sensor in the
specified system detected
that a battery has failed.
A battery sensor in the
specified system detected
that a battery has failed.
This message is generated
when a system is
configured for thermal
shutdown due to an error
event. If a temperature
sensor reading exceeds the
error threshold for which
the system is configured,
the operating system shuts
down and the system
powers off. This event may
also be initiated on certain
systems when a fan
enclosure is removed from
the system for an extended
period of time.
Error No action
Error No action
Info No action
Warning No action
Error No action
Error No Action
Error No action
Dell - Temperature sensor
returned to a normal value
Dell - Temperature sensor
detected a warning value
Sensor Returned to Normal
Value.
A temperature sensor on
the backplane board,
system board, CPU, or drive
Info No action
Warning No action
95
Page 96

carrier in the specified
system exceeded its
warning threshold.
Dell - Temperature sensor
detected a failure value
Dell - Temperature sensor
detected a non-recoverable
value
Dell - Fan sensor returned
to a normal value
Dell - Fan sensor detected a
warning value
Dell - Fan sensor detected a
failure value
A temperature sensor on
the backplane board,
system board, or drive
carrier in the specified
system exceeded its failure
threshold value.
A temperature sensor on
the backplane board,
system board, or drive
carrier in the specified
system detected an error
from which it cannot
recover.
Sensor Returned to Normal
Value
Fan Sensor reading in the
host <x> exceeded a
warning threshold value.
A fan sensor in the
specified system detected
the failure of one or more
fans.
Error Put the system into
maintenance mode
Error No action
Info No action
Warning No Action
Error Put the system into
maintenance mode
Dell - Fan sensor detected a
nonrecoverable value
Dell - Voltage sensor
returned to a normal value
Dell - Voltage sensor
detected a warning value
Dell - Voltage sensor
detected a failure value
Dell - Voltage sensor
detected a nonrecoverable
value
Dell - Current sensor
returned to a normal value
Dell - Storage: storage
management error
A fan sensor detected an
error from which it cannot
recover.
Sensor Returned to Normal
Value
A voltage sensor in the
specified system exceeded
its warning threshold
A voltage sensor in the
specified system exceeded
its failure threshold.
A voltage sensor in the
specified system detected
an error from which it
cannot recover.
Sensor Returned to Normal
Value.
Storage management has
detected a device
Error No action
Info No action
Warning No action
Error Put the system into
maintenance mode
Error No action
Info No action
Error Put the system into
maintenance mode
96
Page 97

independent error
condition.
Dell - Storage: Controller
warning
Dell - Storage: Controller
failure
Dell - Storage: Channel
Failure
Dell - Storage: Enclosure
hardware information
Dell - Storage: Enclosure
hardware warning
Dell - Storage: Enclosure
hardware failure
Dell - Storage: Array disk
failure
Dell - Storage: EMM failure EMM failure. Error Put the system into
Dell - Storage: power supply
failure
Controller warning. Refer to
the Tasks & Events tab on
the vSphere client for
details.
Controller failure. Refer to
the Tasks & Events tab on
the vSphere client for
details.
Channel failure. Error Put the system into
Enclosure hardware
information.
Enclosure hardware
warning.
Enclosure hardware error. Error Put the system into
Array disk failure. Error Put the system into
Power supply failure. Error Put the system into
Warning No action
Error Put the system into
maintenance mode
maintenance mode
Info No action
Warning No action
maintenance mode
maintenance mode
maintenance mode
maintenance mode
Dell - Storage: temperature
probe warning
Dell - Storage: temperature
probe failure
Dell - Storage: Fan failure Fan failure. Error Put the system into
Dell - Storage: Battery
warning
Dell - Storage: Virtual disk
degraded warning
Dell - Storage: Virtual disk
degraded failure
Dell - Storage: Temperature
probe information
Physical disk temperature
probe warning, too cold or
too hot
Physical disk temperature
probe error, too cold or too
hot.
Battery warning. Warning No action
Virtual disk degraded
warning.
Virtual disk degraded failure Error Put the system into
Temperature probe
information
Warning No action
Error Put the system into
maintenance mode
maintenance mode
Warning No action
maintenance mode
Info No action
97
Page 98

Dell - Storage: Array disk
warning
Array disk warning. Warning No action
Dell - Storage: Array disk
information
Dell - Storage: Power
supply warning
Dell - Chassis Intrusion Physical Security Violation
Dell - Chassis
Intrusion( Physical Security
Violation) Event Cleared
Dell - CPU Presence
(Processor Presence
detected)
Dell - System Event Log
(SEL) Full (Logging Disabled)
Dell - System Event Log
(SEL) Cleared
Dell - SD Card redundancy
Has Returned to Normal
Dell - SD Card Redundancy
has been Lost
Array disk information. Info No action
Power supply warning. Warning No action
Chassis Intrusion - Physical
Security Violation
Chassis Intrusion ( Physical
Security Violation) Event
Cleared
CPU Presence (Processor
Presence detected)
System Event Log (SEL) Full
(Logging Disabled)
System Event Log (SEL)
Cleared
SD Card redundancy Has
Returned to Normal
SD Card Redundancy has
been Lost
error No Action
info No Action
info No Action
error No Action
info No Action
info No Action
error No Action
Dell - SD Card Redundancy
Degraded
Dell - Module SD Card
Present (SD Card Presence
Detected)
Dell - Module SD Card
Failed (Error)
Dell - Module SD Card Write
Protect(Warning)
Dell - Module SD Card not
Present
Dell - Watchdog Timer
Expired
Dell - Watchdog Reset Watchdog Reset error No Action
Dell - Watchdog Power
Down
98
SD Card Redundancy
Degraded
Module SD Card Present
(SD Card Presence
Detected)
Module SD Card Failed
(Error)
Module SD Card Write
Protect (Warning)
Module SD Card not
Present
Watchdog Timer Expired error No Action
Watchdog Power Down error No Action
warning No Action
info No Action
error No Action
warning No Action
info No Action
Page 99

Dell - Watchdog Power
cycle
Watchdog Power cycle error No Action
Dell - System Power
Exceeds PSU Wattage
Dell - System Power
Exceeds Error Cleared
Dell - Power Supply
Inserted
Dell - Internal Dual SD
Module is present
Dell - Internal Dual SD
Module is online
Dell - Internal Dual SD
Module is operating
normally
Dell - Internal Dual SD
Module is write protected
Dell - Internal Dual SD
Module is writable
Dell - Integrated Dual SD
Module is absent
Dell - Integrated Dual SD
Module redundancy is lost
System Power Exceeds PSU
Wattage
System Power Exceeds
Error Cleared
Power Supply Inserted info No Action
Internal Dual SD Module is
present
Internal Dual SD Module is
online
Internal Dual SD Module is
operating normally
Internal Dual SD Module is
write protected
Internal Dual SD Module is
writable
Integrated Dual SD Module
is absent
Integrated Dual SD Module
redundancy is lost
error No Action
info No Action
info No Action
info No Action
info No Action
warning No Action
info No Action
error No Action
error No Action
Dell - Internal Dual SD
Module is redundant
Dell - Internal Dual SD
Module is not redundant
Dell - Integrated Dual SD
Module failure
Dell - Internal Dual SD
Module is offline
Dell - Integrated Dual SD
Module redundancy is
degraded
Dell - SD card device has
detected a warning
Dell - SD card device has
detected a failure
Dell - Integrated Dual SD
Module warning
Internal Dual SD Module is
redundant
Internal Dual SD Module is
not redundant
Integrated Dual SD Module
failure
Internal Dual SD Module is
offline
Integrated Dual SD Module
redundancy is degraded
SD card device has
detected a warning
SD card device has
detected a failure
Integrated Dual SD Module
warning
info No Action
info No Action
error No Action
warning No Action
warning No Action
warning No Action
error No Action
warning No Action
99
Page 100

Dell - Integrated Dual SD
Module information
Integrated Dual SD Module
information
info No Action
Dell - Integrated Dual SD
Module redundancy
information
Dell - Network failure or
critical event
Dell - Network warning Network warning warning No Action
Dell - Network information Network information info No Action
Dell - Physical disk failure Physical disk failure error No Action
Dell - Physical disk warning Physical disk warning warning No Action
Dell - Physical disk
information
Dell - An error was detected
for a PCI device
Dell - A warning event was
detected for a PCI device
Dell - An informational
event was detected for a
PCI device
Integrated Dual SD Module
redundancy information
Network failure or critical
event
Physical disk information info No Action
An error was detected for a
PCI device
A warning event was
detected for a PCI device
An informational event was
detected for a PCI device
info No Action
error No Action
error No Action
warning No Action
info No Action
100
 Loading...
Loading...