Page 1

Dell™ Remote Console
Switch
User's Guide
Page 2

Notes, Cautions, and Warnings
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you
make better use of your computer.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates potential damage to hardware or
loss of data if instructions are not followed.
WARNING: A WARNING indicates a potential for property damage,
personal injury, or death.
____________________
Information in this document is subject t o change without notice.
© 2012 Dell Inc. All rights reserved.
Reproduction of these materials in any manner whatsoever without the written
permission of Dell I nc. is strictly forbidden.
Trademarks used in this text: Dell, the DELL logo, and PowerEdge are trademarks
of Dell Inc.; Avocent is a trademark or registered trademark of Avocent Corporation
or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries.
Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this document to refer to either the
entities claiming the mar ks and names or their products. Dell Inc. disclaims any
proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names other than its own.
590-1021-501B
July2012
Model 1082DS/2162DS/4322DS Remote Console Switch
Page 3

Contents
Product Overview 1
Features and Benefits 1
Sample Configurat ion 7
Safety Precautions 8
General 9
Reduce Cable Bulk 2
KVMSwitching Capabilities 2
Multiplatform Support 2
True Serial Capabilities 3
Local and Remote User Interfaces 3
Virtual Media and Smart Card-capable Switches 3
On-board Web Interface 4
Access the Switch Using a Standard TCP/IP Network 4
Encryption 4
Video 4
Flash Upgradeable 5
Tier Expansion 5
Avocent Management Software Plug-in 5
FIPS cryptographic module 5
LAN Options 10
Installation 13
RCS Quick Setup 13
Getting Start ed 15
Setting up Your Network 16
Rack Mounting the RCS 16
Rack Mounting Safety Considerations 16
Installing the Dell ReadyRails™ System 17
Contentsxxx | xxxi
Page 4

Installing the RCS 22
Connecting the RCS Hardware 25
Connecting a SIP 29
Adding a Tiered Switch 31
Cascading with Legacy Switches 34
Adding a PEM (Optional) 36
Configuring the Remote Console Switch 38
Setting up the Built-in Web Server 38
Connecting to the OBWI Through a Firewall 38
Verifying the Connections 41
Rear Panel Ethernet Connection LEDs 41
Rear Panel Power Status LEDs 41
Adjusting Mouse Settings on Target Devices 42
Local and Remote Configuration 43
Local User I nterface (UI) 43
Filtering 44
OBWI 45
Using the User Interfaces 47
Launching a Session 49
Scan Mode 50
Viewing System Information 51
RCS Tools 52
Network Settings 55
DNSSet tings 56
Contentsxxx | xxxii
Rebooting the RCS 52
Upgrading RCS Firmware 52
Saving and Restoring RCS Configurations and RCS User
Databases 53
Page 5

NTP Settings 57
SNMP Settings 57
Auditing Event Set tings 58
Setting Event Destinations 58
Ports - Configuring SIPs 59
Upgrading SIPs 59
Power Device Sett ings 60
Associated Target Servers and Power Outlets 61
Grouping Power Outlets 63
Default Outlet Names 64
Assigning an Outlet Name 65
Local Session Page on the Local Port 69
Local Port UI Sett ings 70
Modem Settings 71
Setup Set tings - Port Security 72
Sessions 72
Configuring General Sessions 72
Configuring KVM Sessions 73
Configuring Local Virtual Media Sessions 73
Configuring Serial Sessions 77
Setting Up User Accounts 77
Managing Local Accounts 77
Access Levels 77
Avocent Management Software Device IP Addresses 79
LDAP 79
Override Admin 79
Active Sessions 80
Closing a Session 80
Contentsxxx | xxxiii
Page 6

The Video Viewer Window 81
Changing the Toolbar 83
Launching a Session 84
Session Time-out 84
Window Size 85
Adjusting the View 85
Refreshing the I mage 87
Video Settings 87
Additional Video Adjustment 87
Target Video Settings 89
Automatic Video Adjustment 89
Video Test Pattern 90
Vendor-specific Video Settings 90
Color Settings 90
Adjusting Color Depth 90
Contrast and Brightness 91
Noise Settings 91
Detection Thresholds 91
Mouse Settings 92
Virtual Media 96
Smart Cards 102
Contentsxxx | xxxiv
Adjusting Mouse Options 92
Cursor Type 92
Mouse Scaling 95
Mouse Alignment and Synchronization 95
Requirements 96
Sharing and Preemption Considerations 97
Virtual Media Dialog Box 97
Opening a Virtual Media Session 98
Closing a Virtual Media Session 101
Page 7

Keyboard Pass-t hrough 103
Macros 104
Saving the View 104
Closing a Session 104
LDAP Feature for the RCS 105
The Structure of Active Directory 105
Domain Controller Computers 105
Object Classes 106
Attributes 107
Schema Extensions 107
Standard Schema versus Dell Extended Schema 108
Standard Installation 109
Configure the O verride Admin Account 110
Configuring DNS Settings 110
Configuring the Network Time Protocol (NTP) Settings 112
Configuring the LDAP Authentication Paramet ers 112
Enabling LDAP Authentication 112
Entering Authentication Parameters - Operational Modes 115
Entering Extension Options - Active Directory LDAP 116
Entering Authentication Parameters - Standard LDAP 116
Entering Authentication Parameters - Custom IP Port
Assignments 117
Completing LDAP Configuration 118
Secondary LDAPSettings - Standard Configuration 119
Setting up the RCS for performing Standard LDAP
queries 119
Search Configuration Settings 120
Query Mode Selection Settings 121
Group Configuration Parameters 122
Secondary LDAP Settings - Active Directory Configuration124
Contentsxxx | xxxv
Page 8

LDAP SSL Certificates 127
Enabling SSL on a Domain Controller 128
Login Timeout 132
CA Certif icate I nformation Display 133
Configuring Group Objects 134
Active Directory Object Overview for Standard Schema 137
Dell Extended Schema Active Directory Object Overview 139
Configuring Active Directory with Dell Schema Extensions to
Access Your RCS 143
Extending the Active Directory Schema (Optional) 143
Installing the Dell Extension to the Active Directory Users
and Computers Snap-In (Optional) 144
Opening the Active Directory Users and Computers SnapIn 145
Adding Users and Privileges to Active Directory with Dell
Schema Extensions 145
Creating a SIP Object 145
Creating a Privilege Object 146
Using Dell Association Objects Synt ax 147
Creating an Association Object 148
Adding Objects to an Association Object 148
Console Redirection Access Security 149
Using Active Directory t o Log In to the RCS 150
Target Device Naming Requirement s for LDAP
Implementation 151
Frequently Asked Questions 152
Appendix A: Terminal Operations 155
Console Boot Menu Options 155
Console Main Menu Options 156
Contentsxxx | xxxvi
Page 9

Appendix B: Using SIPs 157
ACS Console Server Port Pinouts 157
Cisco Port Pinout s 158
Appendix C: MIB and SNMP Traps 159
Appendix D: Cable Pinouts Information 165
Modem Pinout s 165
Console/ Setup Pinouts 166
Appendix E: UTP Cabling 167
UTP Copper Cabling 167
Wiring Standards 167
Cabling Inst allation, Maintenance, and Safety Tips 168
Appendix F: Sun Advanced Key Emulation 171
Appendix G: Technical Specifications 173
Appendix H: Technical Support 177
Contentsxxx | xxxvii
Page 10

Contentsxxx | xxxviii
Page 11

1
Product Overview
The Dell 1082DS/2162DS/4322DS Remote Console Switch (RCS) digital
keyboard, video and mouse (KVM) over IP and serial console switches combine
analog and digital technology to provide flexible, centralized control of data
center servers, and to facilitate the operations, activation, and maintenance of
remote branch offices where trained operators may be unavailable. The IP-based
RCS gives you flexible target device management control and secure remote
access from anywhere at anytime through the RCS software or on-board web
interface (OBWI).
Features and Benefits
The RCS provides enterprise customers with the following features and options:
• significant reduction of cable volume
• Virtual Media (VM) capabilites, configurable for analog (local) or digital
(remote) connectivity
• smart card/Common Access Card (CAC) capability
• true serial capability through Secure Shell (SSH) and Telnet
• enhanced video resolution support, up to 1600 x 1200 or 1680 x 1050
(widescreen) native from target to remote
• optional dual power models for redundancy
• optional support for managing intelligent power devices
• dual independent local port video paths (dedicated to ACI)
Product Overviewxxx | xxx1
Page 12

• dual stack IPv4 (DHCP) and IPv6 (DHCPv6 and stateless autoconfiguration) for simultaneous access
• accessibility to target devices across 10/100/1000BaseT LAN ports.
• a MODEM port that supports V.34, V.90 or V.92-compatible modems that
may be used to access the switch when an Ethernet connection is not
available
• FIPS support
Reduce Cable Bulk
With server densities continually increasing, cable bulk remains a major concern
for network administrators. The RCS significantly reduces KVM cable volume in
the rack by utilizing the innovative Server Interface Pod (SIP) modules and
single, industry-standard Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) cabling. This allows a
higher server density while providing greater airflow and cooling capacity.
KVMSwitching Capabilities
The RCS supports SIPs that are powered directly from the target device and
provide Keep Alive functionality when the switch is not powered. The SIPs with
CAT 5 design dramatically reduce cable clutter while providing optimal
resolution and video settings. The built-in memory of the SIPs simplifies
configuration by assigning and retaining unique device names and Electronic ID
(EID) numbers for each attached device.
PS/2 and USB SIPs are available allowing direct KVM connectivity to devices.
The USB2+CAC SIP is also available. The RCS is offered with 8, 16, or 32
Analog Rack Interface (ARI) ports for connecting SIPs. Utilizing the SIP, you
can attach additional switches to expand your RCS system. This flexibility
allows you to add capacity as your data center grows.
Multiplatform Support
The Dell SIPs are available for use with the RCS to support PS/2, USB, USB2,
and USB2+CAC device environments. Using the OBWI in conjunction with
these modules allows you to switch easily across platforms.
2xxx | Product Overviewxxx
Page 13

Interoperability with Avocent® IQ Module Intelligent Cabling may also be used
to connect devices to the RCS. PS/2, USB, Sun®, and serial module options are
available. For more information, please refer to the appropriate Avocent
installer/user guide for your product or visit avocent.com/manuals for more
information..
True Serial Capabilities
The RCS supports SIPs that provide true serial capabilities through Telnet.
With a SIP, you can launch an SSH session or launch a serial viewer from the
OBWI to connect to serial targets that are connected to an RCS.
Local and Remote User Interfaces
You can use the local user interface (local UI) by connecting directly to the local
port to manage the RCS. You can also use the remote OBWI to manage your
switch. The OBWI is web browser based and is launched directly from the
switch, and any devices connected to the switch are automatically detected.
Virtual Media and Smart Card-capable Switches
The RCS allows you to view, move, or copy data located on virtual media to and
from any target device. You can manage remote systems more efficiently by
allowing operating system installation, operating system recovery, hard drive
recovery or duplication, BIOS updating, and target device backup.
The RCS also allows you to use smart cards in conjunction with your switch
system. Smart cards are pocket-sized cards that store and process information.
Smart cards such as the CAC can be used to store identification and
authentication to enable access to computers, networks, and secure rooms or
buildings.
Virtual media and a smart card reader can be connected directly to the USB
ports on the switch. In addition, virtual media and smart card readers may be
connected to any remote workstation that is running the remote OBWI, Dell
RCS software, or Avocent management software and is connected to the switch
using an Ethernet connection.
Product Overviewxxx | xxx3
Page 14

NOTE: To open a virtual media or smart card session with a target device,
you must first connect the target device to a switch using a SIP.
On-board Web Interface
The OBWI provides similar management functions as the RCS software, but
does not require a software server or any installation. The OBWI is launched
directly from the switch, and any servers connected to the RCS are
automatically detected. You can use the OBWI to configure the RCS from a
web browser. Launch the Viewer from the OBWI to establish KVM and virtual
media sessions to target devices. The OBWI also supports LDAP
authentication, which allows permissions for multiple RCSs to be managed
through a single interface.
Access the Switch Using a Standard TCP/IP Network
The switch provides agentless remote control and access. No special software or
drivers are required on the attached servers or client.
NOTE: The client connects to the switch using an Internet browser.
You can access the switch and all attached systems via Ethernet or using a V.34,
V.90, or V.92 modem from a client. The clients can be located anywhere a valid
network connection exists.
Encryption
The RCS supports 128-bit SSL(ARCFOUR), as well as AES, DES, and 3DES
encryption of keyboard/mouse, video, and virtual media sessions.
Video
The RCS provides optimal resolution for analog VGA, SVGA, and XGA video.
You can achieve resolutions up to 1600 x 1200 or 1680 x 1050 (widescreen),
depending on the length of cable separating your switch and servers.
4xxx | Product Overviewxxx
Page 15

Flash Upgradeable
Upgrade your RCS and SIPs at any time to ensure you are always running the
most current firmware version available. Flash Upgrades can be initiated through
the OBWI or the serial console. The RCS can be configured to perform
automatic firmware upgrades of SIPs. See "Upgrading RCS Firmware" on page
52 for more information.
Tier Expansion
The RCS features allow you to tier additional Dell RCSs from each of the
Analog Rack Interface (ARI) port on the switch. The tiered switches are
attached in the same manner as any device. This additional tier of units allows
you to attach up to 1024 servers in one system. See "Adding a Tiered Switch" on
page 31.
Avocent Management Software Plug-in
Avocent management software may be used with the switch to allow IT
administrators to remotely access, monitor, and control target devices on
multiple platforms through a single, web-based user interface. For more
information, see the Technical Bulletin for the Avocent management software.
FIPS cryptographic module
The RCS switches support FIPS 140-2 Level 1 cryptographic security
requirements. The FIPS mode of operation can be enabled or disabled via the
OBWI or local port and executed after a reboot. When FIPS is enabled, a reboot
of the switch requires approximately two additional minutes to complete a FIPS
mode integrity check. Also, when FIPS is enabled, if the keyboard, mouse or
video encryption is set to 128-bit SSL (ARCFOUR) or DES, the encryption
level is automatically changed to the encryption level AES.
NOTE: The FIPS mode of operation is initially disabled and must be enabled
to operate.
NOTE: The Setup port factory default setting will automatically disable the
FIPS module.
Product Overviewxxx | xxx5
Page 16

NOTE: The FIPS mode can be changed via the DSView software plug-in.
RCS switches use an embedded FIPS 140-2 validated cryptographic module
(Certificate #1051) running on a Linux PPC platform per FIPS 140-2
Implementation Guidance section G.5 guidelines.
The FIPS mode can be enabled/disabled via the OBWI, Local Port, or DSView
plug-in. A reboot is required to enable or disable FIPS mode. A firmware upgrade
to this version or setting the state to the default state (Setup Port menu) will
disable FIPS mode.
In FIPS mode, encryption ciphers are restricted to AES or 3DES. When FIPS is
enabled, if the Keyboard/Mouse or Video encryption is set to 128-bit SSL or
DES, the encryption level is automatically changed to AES. With FIPS enabled,
these files are saved (or restored) using a FIPS compatible algorithm, AES.
When FIPS is disabled, the User Database and Appliance Configuration files
saved from or restored to the appliance as external files are encrypted (or
decrypted) using DES.
This is true even when the user does not fill in the Password parameter in the
Save (or Load) dialog on the OBWI, in which case a default OEM password is
used for encryption or decryption.
One result of enabling the FIPS module is to render previously saved User
Database and Appliance Configuration files incompatible. In this case, you may
temporarily disable the FIPS module, reboot the appliance, restore the previously
saved database or configuration file, re-enable the FIPS module, reboot, and then
save the file externally again while the FIPS module is enabled. The new saved
external file will be compatible with the appliance as long as the appliance is
running with FIPS mode enabled.
The opposite situation is also true, in that database and configuration files
saved with FIPS module enabled are not compatible for restoring to an
appliance without the FIPS module enabled or an appliance with older firmware
not supporting the FIPS module.
6xxx | Product Overviewxxx
Page 17
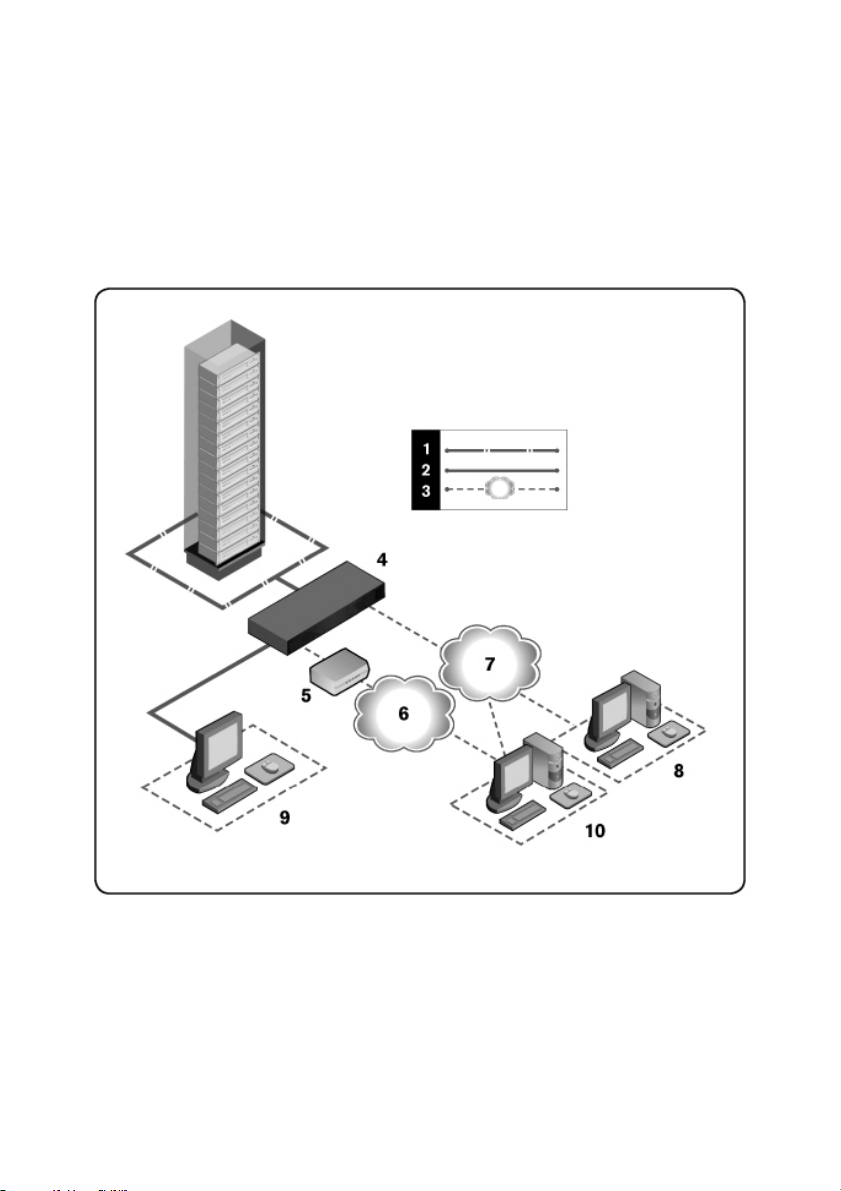
Sample Configuration
Figure 1.1: Example RCS Con figuration
Table 1.1: Descriptions for Figure 1.1
Product Overviewxxx | xxx7
Page 18

Number Descript ion Number Descript ion
1 UTP connection 6
2 KVM connection to the RCS 7 Ethernet
3 Remote IP connection 8
4 RCS 9
5 Modem 10
Telephone
network
Avocent
Management
Software Server
Analog User
(local UI)
Digital user
(computer with
Internet browser
for a remote
OBWI or Dell
RCS software)
Safety Precautions
Use the following safety guidelines to help ensure your own personal safety and
to help protect your system and working environment from potential damage.
CAUTION: The power supplies in your system may produce high voltages and energy
hazards, which can cause bodily harm. Only trained service technicians are
authorized to remove the covers and access any of the components inside the system.
This warning applies to Dell™ Remote Console Switch, Dell™ PowerEdge™ servers,
and Dell PowerVault™ storage systems.
This document pertains only to the Dell 1082DS/2162DS/4322DS Remote
Console Switch. You should also read and follow the additional safety
instructions.
• Dell Remote Console Switch User's Guide
• Dell Safety Sheet
8xxx | Product Overviewxxx
Page 19

• Dell RTF Regulatory Tech Bulletin
General
• Observe and follow service markings.
• Do not service any product except as explained in your system
documentation.
• Opening or removing covers that are marked with the triangular symbol with
a lightning bolt may expose you to electrical shock.
• Components inside these compartments should be serviced only by a
trained service technician.
• This product contains no serviceable components. Do not attempt to open.
If any of the following conditions occur, unplug the product from the electrical
outlet and replace the part or contact your trained service provider:
- The power cable, extension cable, or plug is damaged.
- An object has fallen into the product.
- The product has been exposed to water.
- The product has been dropped or damaged.
- The product does not operate correctly when you follow the
operating instructions.
• Keep your system away from radiators and heat sources. Also, do not block
cooling vents.
• Do not spill food or liquids on your system components, and never operate
the product in a wet environment. If the system gets wet, see the
appropriate section in your troubleshooting guide or contact your trained
service provider.
• Use the product only with approved equipment.
• Allow the product to cool before removing covers or touching internal
components.
Product Overviewxxx | xxx9
Page 20

• Operate the product only from the type of external power source indicated
on the electrical ratings label. If you are not sure of the type of power source
required, consult your service provider or local power company.
NOTE: To help avoid damaging your system, be sure the voltage selection
switch (if provided) on the power supply is set for the voltage that most closely
matches the AC power available in your location. Also be sure that your
monitor and attached devices are electrically rated to operate.
• Be sure that your monitor and attached devices are electrically rated to
operate with the power available in your location.
• Use only power cables provided with this product.
• To help prevent electric shock, plug the system and peripheral power cables
into properly grounded electrical outlets. These cables are equipped with
three-prong plugs to help ensure proper grounding. Do not use adaptor plugs
or remove the grounding prong from a cable.
• Observe extension cable and power strip ratings. Make sure that the total
ampere rating of all products plugged into the power strip does not exceed
80 percent of the ampere ratings limit for the power strip.
• To help protect your system from sudden, transient increases and decreases
in electrical power, use a surge suppressor, line conditioner, or
uninterruptible power supply (UPS).
• Position system cables and power cables carefully. Route cables so that they
cannot be stepped on or tripped over. Be sure that nothing rests on any
cables.
• Do not modify power cables or plugs. Consult a licensed electrician or your
power company for site modifications. Always follow your local/national
wiring rules.
LAN Options
• Do not connect or use during a lightning storm. There may be a risk of
electrical shock from lightning.
10xxx | Product Overviewxxx
Page 21

• Never connect or use in a wet environment.
Product Overviewxxx | xxx11
Page 22

12xxx | Product Overviewxxx
Page 23

2
Installation
The RCS transmits KVM and serial information between operators and target
devices connected to the switch over a network using either an Ethernet or
modem connection. The RCS uses TCP/IP for communication over Ethernet.
For the best system performance, use a dedicated, switched 100BaseT or
1000BaseT network. You can also use 10BaseT Ethernet.
The RCS uses the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) for communication over a
V.34, V.90, or V.92 modem. You can perform KVM and serial switching tasks by
using the OBWI or the Avocent management software. For more information on
the Avocent management software, visit http://www.avocent.com.
The RCS box includes the RCS, RCS software, and the OBWI. You may choose
to use either the RCS software or the OBWI to manage your system. The
OBWI manages a single RCS and its connections, while the RCS software can
manage multiple switches and their connections. If you plan to use only the
OBWI, you do not need to install the RCS software.
NOTE: The RCS software can be used to manage some switches. For more
information, please refer to the appropriate installer/user guide for your
product.
NOTE: Please ensure that all your RCSs have been upgraded to their most
recent version of Firmware. For information on upgrading an RCS through the
OBWI, refer to "RCS Tools" on page 52.
RCS Quick Setup
The following is a quick setup list. To begin by mounting the RCS in a rack and
for detailed installation instructions, see "Getting Started" on page 15.
Installationxxx | xxx13
Page 24

1 Adjust mouse acceleration on each server to Slow or None.
2 Install the RCS hardware, and connect a Server Interface Pod (SIP) or
Avocent® IQ module to each server or tiered switch. Connect each SIP or
Avocent IQ module to the RCS with CAT 5 cabling and connect the
keyboard, monitor, and mouse connectors to the analog port of the RCS.
3 Connect the local port peripherals to the appropriate ports on the back
panel of the RCS and set up the network configuration. The IP address can
be set here or from the RCS software. Dell recommends using a static IP
address for ease of configuration.
4 Using the local port, input all server names using the OBWI interface.
To set up the RCS software (see the RCS Software User's Guide):
1 Install the RCS software on each client workstation.
2 From one client workstation, launch the RCS software.
3 Click the New RCS task button to add the new switch to the RCS software
database. If you configured the IP address as described above, select Yes,
the product already has an IP address, otherwise select No, the product does
not have an IP address.
RCS software will find the RCS and all SIPs connected to it and display the
names in the Explorer.
NOTE: In addition to adding and managing Dell RCSs using the RCS
software, you can add and manage some Avocent switches.
4 Set properties and group servers as desired into locations, sites, or folders
through the Explorer.
5 Create user accounts through the OBWI. See "Setting Up User Accounts"
on page 77 for more information.
6 Once one client workstation is set up, select File - Database - Save to save a
copy of the database with all the settings.
7 From the second client workstation, click File - Database - Load and browse
to find the file you have saved. Select the file and click Load.
14xxx | Installationxxx
Page 25

8 If the local user adds, deletes, or renames any SIPs after you have loaded this
file, you can resynchronize your local switch by selecting the RCS and
clicking Resync. To control a connected server, select it in the Explorer and
click the Connect Video task button to launch a server session in the
Viewer.
9 Adjust the resolution (select View - Scaling) and quality (select View -
Color) of the server video in the Viewer.
Getting Started
The following items are supplied with the Remote Console Switch. Before
installing your RCS, locate the necessary items for proper installation.
• Remote Console Switch
• Jumper Cord(s)
• 0U Mounting Bracket
• 1U Mounting Bracket Hardware Kit (two additional rails that are premounted to the RCS are included in the kit assembly)
• Cable and Adaptors for SETUP and MODEM
• Remote Console Switch System User's Guide on CD
• Dell Safety Sheet
• Dell RTF Regulatory Tech Bulletin
Additional Items Needed:
• One Dell SIP or Avocent IQ module per attached device
• One CAT 5 patch cable per attached device (up to 45 meters)
Optional Items:
• V.34, V.90, Or V.92-compatible Modem and cables
• Power Control Device(s)
• Port Expansion Module (PEM)
Installationxxx | xxx15
Page 26

NOTE: You cannot open a virtual media session or a CAC session if the
server is connected via a PEM.
Setting up Your Network
The switch uses IP addresses to uniquely identify the switch and the target
devices. The RCS supports both Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
(DHCP) and static IP addressing. Make sure that an IP address is reserved for
each switch and that each IP address remains static while the switch is
connected to the network.
Keyboards
A USB keyboard and mouse may be connected to the analog port of the RCS.
NOTE: The RCS also supports the use of multiple keyboards and multiple
mice on the analog port. The use of more than one input device
simultaneously, however, may produce unpredictable results.
Rack Mounting the RCS
You may either place the RCS on the rack shelf or mount the switch directly
into a 19" wide, EIA-310-E compliant rack (four-post, two-post, or threaded
methods). The Dell ReadyRails™ system is provided for 1U front-rack, 1U rearrack, and two-post installations. The ReadyRails system includes two separately
packaged rail assemblies and two rails that are shipped attached to the sides of
the RCS. In addition, one mounting bracket is provided for 0U configurations,
and one blanking panel is provided for rear-rack installations.
WARNING: This is a condensed reference. Read the safety instructions in your
Safety, Environmental, and Regulatory Information booklet before you begin.
NOTE: The illustrations in this document are not intended to represent a
specific switch.
Rack Mounting Safety Considerations
• Rack Loading: Overloading or uneven loading of racks may result in shelf or
rack failure, causing damage to equipment and possible personal injury.
16xxx | Installationxxx
Page 27

Stabilize racks in a permanent location before loading begins. Mount
components beginning at the bottom of the rack, then work to the top. Do
not exceed your rack load rating.
• Power considerations: Connect only to the power source specified on the
unit. When multiple electrical components are installed in a rack, ensure
that the total component power ratings do not exceed circuit capabilities.
Overloaded power sources and extension cords present fire and shock
hazards.
• Elevated ambient temperature: If installed in a closed rack assembly, the
operating temperature of the rack environment may be greater than room
ambient. Use care not to exceed the 50°C maximum ambient temperature
of the switch.
• Reduced air flow: Install the equipment in the rack so that the amount of
airflow required for safe operation of the equipment is not compromised.
• Reliable earthing: Maintain reliable earthing of rack-mounted equipment.
Pay particular attention to supply connections other than direct
connections to the branch circuit (for example, use of power strips).
• Product should not be mounted with the rear panel facing in the downward
position.
Installing the Dell ReadyRails™ System
The ReadyRails system is provided to easily configure your rack for installation
of your RCS. The ReadyRails system can be installed using the 1U tool-less
method or one of three possible 1U tooled methods (two-post flush mount, twopost center mount, or four-post threaded).
1U Tool-less Configuration (Four-post Square Hole or Unthreaded
Round Hole)
1 With the ReadyRails flange ears facing outward, place one rail between the
left and right vertical posts. Align and seat the rear flange rail pegs in the
rear vertical post flange. In Figure 2.1, item 1 and its extractions illustrate
how the pegs appear in both the square and unthreaded round holes.
Installationxxx | xxx17
Page 28
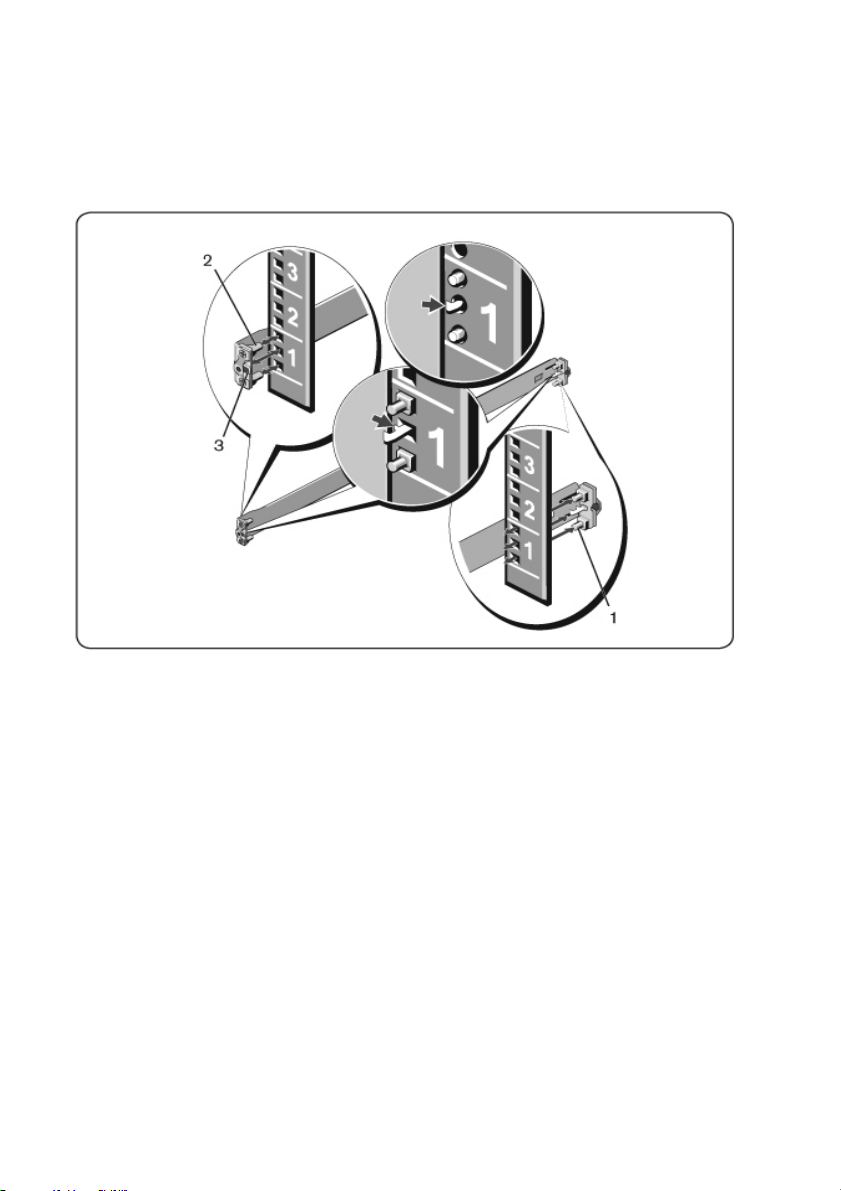
Figure 2.1: 1U Tool-less Configuration
2 Align and seat the front flange pegs in the holes on the front side of the
vertical post (item 2).
3 Repeat this procedure for the second rail.
4 To remove each rail, pull on the latch release button on each flange ear
(item 3) and unseat each rail.
Two-post Flush-mount Configuration
1 For this configuration, the castings must be removed from the front side of
each ReadyRails assembly (Figure 2.2, item 1). Use a Torx™ driver to
remove the two screws from each front flange ear (on the device side of the
rail) and remove each casting. Retain castings for future rack requirements.
It is not necessary to remove the rear flange castings.
Figure 2.2: Two-post Flush-mou nt Configuratio n
18xxx | Installationxxx
Page 29
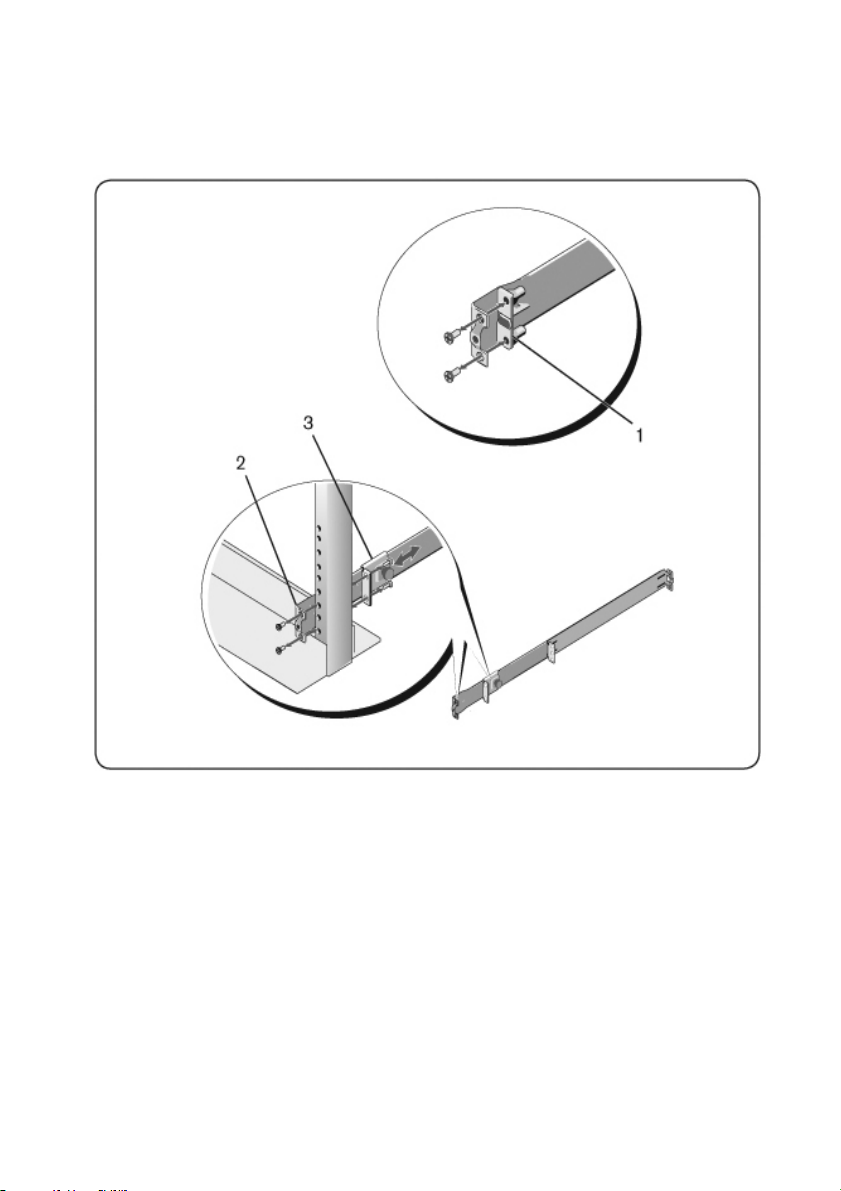
2 Attach one rail to the front post flange with two user-supplied screws (item
2).
3 Slide the plunger bracket forward against the vertical post and secure the
plunger bracket to the post flange with two user-supplied screws (item 3).
4 Repeat this procedure for the second rail.
Installationxxx | xxx19
Page 30
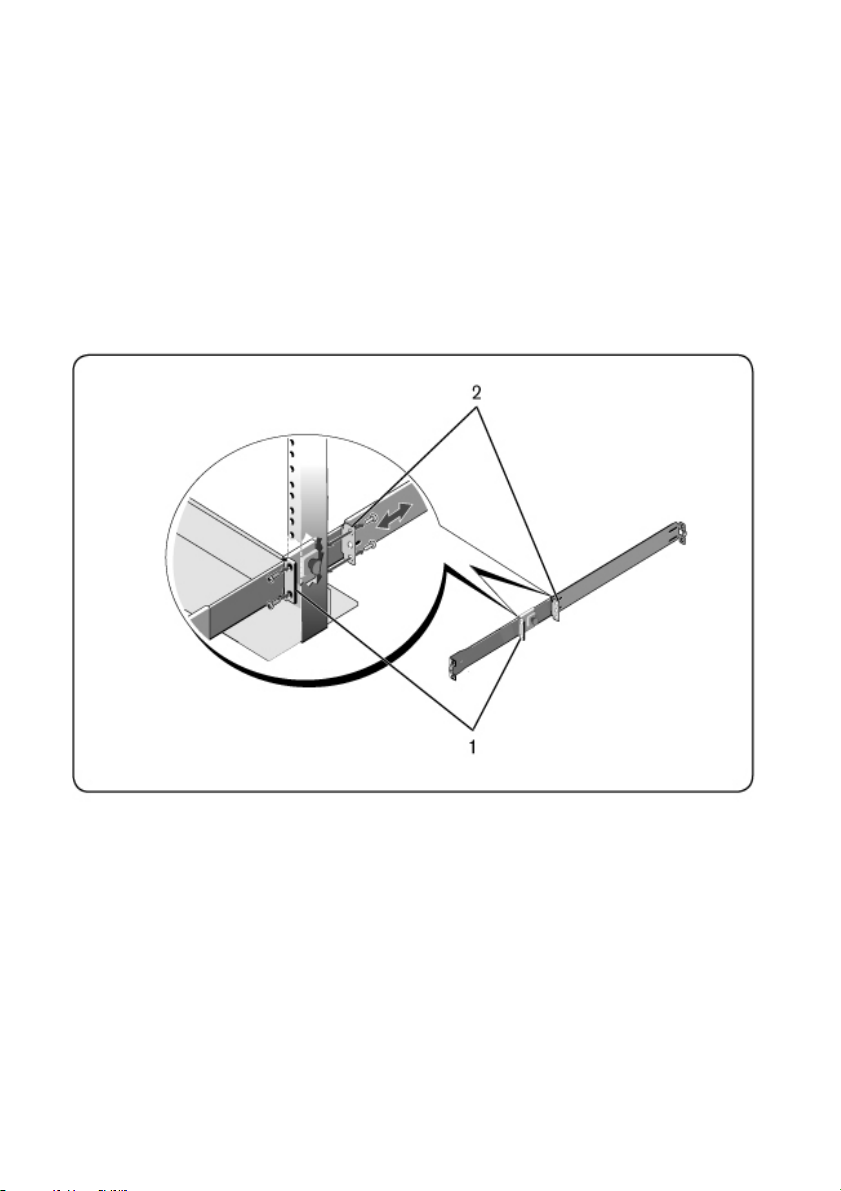
Two-post Center-mount Configuration
1 Slide the plunger bracket rearward until it clicks into place and secure the
bracket to the front post flange with two user-supplied screws (Figure 2.3,
item 1).
Figure 2.3: Two-post Center-mount Configuration
2 Slide the back bracket towards the post and secure it to the post flange with
two user-supplied screws (item 2).
3 Repeat this procedure for the second rail.
Four-post Threaded Configuration
1 For this configuration, the flange ear castings must be removed from each
end of the ReadyRails assemblies. Use a Torx™ driver to remove the two
20xxx | Installationxxx
Page 31

screws from each flange ear and remove each casting (Figure 2.4, item 1).
Retain castings for future rack requirements.
2 For each rail, attach the front and rear flanges to the post flanges with two
user-supplied screws at each end (item 2).
Figure 2.4: Four-post Threaded Configuration
Installationxxx | xxx21
Page 32

Installing the RCS
The switch may be mounted in the 1U rear-rack, 1U front-rack, 1U two-post
(flush and center), and 0U configurations. The following are examples of 1U rearrack, 1U front-rack, and 0U configurations. For 1U two-post (flush and center)
configurations, you can slide the switch into the rails in the same manner as the
four-post configurations.
1U Rear-rack Installation
1 Insert the ends of the rails that are attached to the switch into the
ReadyRails assembly and push the switch into the rack (Figure 2.5, item 1).
Figure 2.5: 1U Rear-rack In stallation
22xxx | Installationxxx
Page 33

2 Secure each switch rail with the thumbscrew (item 2).
3 (Optional) Assemble the blanking panel to the rails on the front side of the
rack and tighten the thumbscrews (item 3).
To remove the switch from the rack:
1 Unscrew the thumbscrews and pull the switch assembly out of the rack until
the travel stops are reached. The travel stop position is intended to provide
the opportunity to reposition the rail grip; it is not intended for service.
2 Locate the blue tabs on the sides of the switch rails (item 4).
3 Push the tabs inward and continue pulling the assembly until the switch
rails are clear of the ReadyRails assemblies.
1U Front-rack Installation
Before installation, the rails that are attached to the switch must be reconfigured.
1 On each switch rail, lift the tab under the front standoff and slide the rail
forward as you lift the rail from the switch (Figure 2.6, item 1).
Figure 2.6: Rotating the Switch Rails
Installationxxx | xxx23
Page 34

2 Rotate each rail 180° (item 2) and then reassemble each rail to the switch
(item 3).
3 Refer to the 1U rear-rack instructions to insert and remove the switch
assembly from the ReadyRails system.
NOTE: No blanking panel is required for this configuration.
0U RCS Installation
1 Align and assemble the 0U mounting bracket to the switch rails (Figure 2.7,
item 1). Tighten the thumbscrews (item 2).
2 Insert the mounting bracket hooks into the rack holes and push down until
the blue button pops out and locks the bracket into place.
Figure 2.7: 0U Installation
24xxx | Installationxxx
Page 35

To remove the switch assembly, press the blue button (item 3) to unseat the
bracket and then lift the assembly from the posts.
Connecting the RCS Hardware
The following diagram illustrates one possible configuration for your RCS
hardware.
Figure 2.8: Basic RCS Configuration
Installationxxx | xxx25
Page 36

Table 2.1: Basic RCS Co nfiguration Descriptions
Number Description Number Descript ion
1 Jumper cord 7 External virtual media
2 Analog user 8 Power control device
26xxx | Installationxxx
Page 37

Number Description Number Descript ion
3 Modem 9 SIPs
4
5 Network 11
6 Digital user
Telephone
network
10 Target devices
RCS (32-port model
shown)
To connect and turn on your switch:
CAUTION: To reduce the risk of electric shock or damage to your equipment, do not
disable the jumper cord grounding plug. The grounding plug is an important safety
feature. Plug the jumper cord into a grounded (earthed) outlet that is easily accessible
at all times. Disconnect the power from the unit by unplugging the jumper cord from
either the power source or the unit.
NOTE: If the building has 3-phase AV power, ensure that the computer and
monitor are on the same phase to avoid potential phase-related video and/or
keyboard problems.
NOTE: The maximum supported cable length from switch to device is 30
meters.
• Do not disable the power grounding plug. The grounding plug is an
important safety feature.
• Connect the jumper cord into a grounded (earthed) outlet that is easily
accessible at all times.
• Disconnect the power from the product by unplugging the jumper cord
from either the power source or the product.
• The AC inlet is the main disconnect for removing power to this
product. For products that have more than one AC inlet, to remove
power completely, all AC line cords must be disconnected.
Installationxxx | xxx27
Page 38

• This product has no user serviceable parts inside the product enclosure.
Do not open or remove product cover.
1 Connect your VGA monitor and USB keyboard and mouse cables to the
appropriately labeled ports.
2 Connect one end of a UTP cable (4-pair, up to 150 ft/45 m) to an available
numbered port. Connect the other end to an RJ-45 connector of a SIP.
3 Connect a SIP to the appropriate port on the back of a target device.
Repeat steps 2 and 3 for all target devices you want to connect.
NOTE: When connecting to a Sun Microsystems target device, you must use
a multi-sync monitor in the local port to accommodate Sun computers that
support both VGA and sync-on-green or composite sync.
4 Connect a user-supplied UTP cable from the Ethernet network to a LAN
port on the back of the RCS. Network users will access the RCS through
this port. Plugging the redundant LAN ports to separate Ethernet switches
provides additional redundancy in the event one Ethernet switch fails.
5 (Optional) The switch may also be accessed using an ITU V.92, V.90, or
V.24-compatible modem. Connect one end of an RJ-45 cable to the
MODEM port on the switch. Connect the other end to the supplied RJ-45
to DB-9 (male) adaptor, which then connects to the appropriate port on the
back of the modem.
NOTE: Using a modem connection instead of a LAN connection will limit the
performance capability of your switch.
6 (Optional) Connect a supported PDU to the RCS by connecting one end of
a CAT 5 cable to the PDU1 port on the switch. Connect the other end to
the PDU. Connect the power cords from the target devices to the PDU.
Connect the PDU to a power source. Repeat this procedure for the PDU2
port to connect a second PDU, if desired.
7 Turn on each target device, then locate the jumper cord(s) that came with
the switch. Connect one end to the power socket on the rear of the switch.
Connect the other end into an appropriate power source. If using an RCS
equipped with dual power, use the second jumper cord to connect to the
28xxx | Installationxxx
Page 39

second power socket on the rear of the RCS, and plug the other end into a
different power source.
NOTE: Plug the redundant power supplies into separate branch circuits to
provide additional redundancy in the event one external AC power source
should go away.
8 (Optional) Connect the virtual media devices or smart card readers to any
of the USB ports on the switch.
NOTE: For all virtual media sessions, you must use a USB2 or USB2+CAC
SIP.
Connecting a SIP
To connect a SIP to each server:
1 Locate the SIPs for your RCS.
2 If you are using a PS/2 SIP connection, attach the color-coded ends of the
SIP cable to the appropriate keyboard, monitor, and mouse ports on the
first server you will be connecting to this RCS. If you are using a USB
connection, attach the plug from the SIP to the USB port on the first server
you will be connecting to this RCS.
3 To the RJ-45 connector on the SIP, attach one end of the CAT 5 cabling
that will run from your SIP to the RCS. See Figure 2.9.
4 Connect the other end of the CAT 5 cable to the desired Avocent Rack
Interface (ARI) port on the back of your RCS.
5 Repeat steps 2-4 for all servers you wish to attach.
NOTE: Power down the RCS before servicing. Always disconnect the jumper
cord from the power source.
NOTE: In addition to Dell SIPs, the RCS may also be connected to devices
using Avocent IQ modules, including Sun and Serial IQ modules.
Figure 2.9: SIP Connection
Installationxxx | xxx29
Page 40

Table 2.2: Descriptions for Figure 2.9
Number Descript ion
1 CAT 5
2 USB Connection
3 VGA Connection
To connect a SIP to a serial device using a UTP connector:
1 Connect the SIP RJ-45 connector to the serial device.
-or-
30xxx | Installationxxx
Page 41

Connect the SIP to an RJ-45 to 9-pin female adaptor. Connect the
adaptor to the serial port of the serial device.
2 Connect one end of a UTP cable (4-pair, up to 150 ft/45 m) into an
available numbered port on the rear of the switch. Connect the other end
into the RJ-45 connector of the SIP.
3 Connect a USB-to-barrel power cord to the power connector on your SIP.
Connect the USB connector on the USB-to-barrel power cord into any
available USB port on the serial target device.
Adding a Tiered Switch
NOTE: The RCS does not support the EL80-DT.
NOTE: The M1000e Modular Enclosure is supported in a tiered
configuration. Attach one end of a CAT5 cable to target port on RCS switch.
Attach the other end to the Analog Console Interface (ACI) compatible RJ45
port on the iKVM module on the back of the M1000e chassis.Firmware
upgrades to the components of the M1000e Modular Enclosure are not
possible via this tiered configuration.
You can tier up to two levels of switches, enabling users to connect to up to
1024 servers. In a tiered system, each target port on the main switch will
connect to the ACI port on each tiered switch. Each tiered switch can then be
connected to a device with a SIP or Avocent IQ module.
To tier multiple switches:
1 Attach one end of a UTP cable to a target port on the switch.
2 Connect the other end of the UTP cable to the ACI port on the back of
your tiered switch.
3 Connect the devices to your tiered switch.
4 Repeat these steps for all the tiered switches you wish to attach to your
system.
NOTE: The system will automatically “merge” the two switches. All switches
connected to the tiered switch will display on the main switch list in the local
UI.
Installationxxx | xxx31
Page 42

NOTE: The switch supports one tiered switch per target port of the main
switch. You cannot attach a switch to the tiered switch.
NOTE: When cascading with an RCS, an 8-port or 16-port analog console
switch is not supported as the primary unit in a tiered configuration. The RCS
must be the primary unit.
32xxx | Installationxxx
Page 43

Figure 2.10: Tiering the RCS With a UTP Analog Switch
Table 2.3: Descriptions for Figure 2.10
Number Description
1 Local User
2 ARI Connection
3 UTP Connection
4 ACI Connection
Installationxxx | xxx33
Page 44

Cascading with Legacy Switches
To add a legacy switch (optional):
1 Mount the switch into your rack. Locate a UTP cable to connect your RCS
to the legacy switch.
2 Attach one end of the UTP cabling to the ARI port on the Console Switch.
3 Connect the other end of the UTP cable to a PS/2 SIP.
4 Connect the SIP to your legacy switch according to the switch
manufacturer's recommendations.
5 Repeat steps 1-4 for all the legacy switches you wish to attach to your
switch.
NOTE: The RCS supports only one switch per ARI port. You cannot cascade
another switch under this first switch.
NOTE: When cascading with an RCS, an 8-port or 16-port analog console
switch is not supported as the primary unit. The RCS must be the primary unit.
34xxx | Installationxxx
Page 45

Figure 2.11: Cascadin g Legacy Switches
Table 2.4: Descriptions for Figure 2.11
Number Descript ion
1 Local User
2 ARI Connection
Installationxxx | xxx35
Page 46

Number Descript ion
3 PS2 Connection
4 Target Connection
Adding a PEM (Optional)
A Port Expansion Module (PEM) allows you to expand each ARI port to
accommodate up to eight devices instead of one. See the following figure and
figure description table.
NOTE: The PEM operates passively. Therefore, once a user accesses a
device attached to a PEM, any subsequent users attempting to access any of
the devices attached to that PEM will be blocked.
NOTE: The use of VM or CAC SIPs behind a PEM is not supported.
NOTE: True Serial SIP does not work behind PEM.
To add a PEM (optional):
1 Mount the PEM into your rack. Using up to nine UTP cables, one connects
your RCS to the PEM, and the other eight connect the PEM to the SIP
attached to each device.
2 Attach one end of the UTP cabling that will run between your PEM and the
RCS to the RJ-45 connector slightly separated from the other connectors on
the PEM. Connect the remaining end of the UTP cable to the desired ARI
port on the back of your RCS.
3 To one of the eight RJ-45 connectors grouped on the back of the PEM,
attach the UTP cabling that will run between your PEM and each device’s
SIP.
4 Connect the other end of the UTP cable to the first SIP.
5 Repeat steps 3-4 for all devices you wish to attach.
Figure 2.12: RCS Config uration With a PEM
36xxx | Installationxxx
Page 47

Table 2.5: Descriptions for Figure 2.12
Number Description
1 ARI Port
2 UTP
3 PEM
4 SIP or Avocent IQ Module
5 Server
Installationxxx | xxx37
Page 48

Configuring the Remote Console Switch
Once all physical connections have been made, you will need to configure the
switch for use in the overall switch system. This can be accomplished in two
ways.
To configure the switch using Avocent management software, see the applicable
Avocent Installer/User Guide for detailed instructions.
To configure the switch using the local UI:
See "Network Settings" on page 55 for detailed instructions on using the local UI
to configure initial network setup.
Setting up the Built-in Web Server
You can access the switch using the embedded web server that handles most
day-to-day switch tasks. Before using the web server to access the switch, first
specify an IP address through the SETUP port on the back panel of the switch
or local UI. See Chapter 3 for detailed instructions on using the switch user
interface.
Connecting to the OBWI Through a Firewall
For switch installations that use the OBWI for access, the following ports must
be opened in a firewall if outside access is desired.
Table 2.6: OBWI Ports With a F irewall
Port
Number
TCP 22 Used for SSH for serial sessions to a SIP.
TCP 23 Used for Telnet (when Telnet is enabled).
TCP 80
38xxx | Installationxxx
Function
Used for the initial downloading of the Video Viewer. The
RCS Admin can change this value.
Page 49

Port
Number
TCP 443
Function
Used by the web browser interface for managing the
switch and launching KVM sessions. The RCS Admin can
change this value.
TCP
2068
TCP/UDP
3211
TCP 389
TCP 636
TCP
3268
TCP
3269
Transmission of KVM session data (mouse & keyboard) or
transmission of video on switches.
Discovery.
(Optional) Used by LDAP Directory Services; standard
access port
(Optional) Used by LDAPDirectory Services; Secure/SSL
port
(Optional) Used by Microsoft Active Directory Services;
standard access port
(Optional) Used by Microsoft Active Directory Services;
Secure/SSL access port
The following figure and table provide a typical configuration, where the user’s
computer is located outside of the firewall and the switch resides inside the
firewall.
Figure 2.13: Typical RCS Firewall Configuration
Installationxxx | xxx39
Page 50

Table 2.7: Descriptions for Figure 2.13
Number Descript ion
1 RCS
2 Firewall
3 User’s computer
4
5 User browses to firewall’s external IP address
Firewall forwards HTTP requests and KVM traffic to the
switch
To configure the firewall:
To access the switch from outside a firewall, configure your firewall to forward
ports 22, 23 (if telnet is enabled), 80, 443, 2068, and 3211 from its external
interface to the KVM switch through the firewall’s internal interface. Consult
the manual for your firewall for specific port forwarding instructions.
NOTE: Ports 80 and 443 can be reconfigured by an administrator.
40xxx | Installationxxx
Page 51

For information on launching the OBWI, see "OBWI" on page 45.
Verifying the Connections
Rear Panel Ethernet Connection LEDs
On the RCS, the rear panel features two LEDs indicating the Ethernet LAN1
connection status and two LEDs indicating the Ethernet LAN2 connection
status.
• The green LEDs illuminate when a valid connection to the network is
established and blink when there is activity on the port.
• The bi-color LEDs may illuminate either green or amber.
• They illuminate green when the communication speed is 1000M.
• They illuminate amber when the communication speed is 100M.
• They are not illuminated when the communication speed is 10M.
Rear Panel Power Status LEDs
The rear panel of each RCS has one for each power supply. There are two Power
LEDs for dual power models (16-port and 32-port) and only one LED for the 8port model. The LED(s) illuminate green when the switch is turned on and
operating normally.
• The LED is off if the power supply does not have power or has failed.
• The LED illuminates when the unit is ready.
• The LED blinks when the switch is booting or an upgrade is in progress.
• The LED blinks "SOS" if a fault condition occurs, such as power supply
failure, elevated ambient temperature, or fan failure. The LED will continue
to blink "SOS" as long as the failure persists.
The switch prevents a serial break from the attached device if the module loses
power. However, a user can generate a serial break with the attached device by
pressing Serial Break on the serial session viewer.
Installationxxx | xxx41
Page 52

Adjusting Mouse Settings on Target Devices
Before a computer connected to the switch can be used for remote user control,
you must set the target mouse speed and turn off acceleration. For machines
running Microsoft®Windows®(Windows NT®, 2000, XP, Server 2003), use
the default PS/2 mouse driver.
To ensure that the local mouse movement and remote cursor display remain in
sync, mouse acceleration must be set to “none” for all user accounts accessing a
remote system through a KVM switch. Mouse acceleration must also be set to
“none” on every remote system. Special cursors should not be used and cursor
visibility options, such as pointer trails, Ctrl key cursor location animations,
cursor shadowing, and cursor hiding, should also be turned off.
NOTE: If you are not able to disable mouse acceleration from within a
Windows operating system, or if you do not wish to adjust the settings of all
your target devices, you may use the Tools - Single Cursor Mode command
available in the Video Viewer window. This command places the Video
Viewer window into an “invisible mouse” mode, which allows you to manually
toggle control between the mouse pointer on the target system being viewed
and the mouse pointer on the client computer.
42xxx | Installationxxx
Page 53

3
Local and Remote Configuration
The RCS comes equipped with two “point-and-click” interfaces: a local user
interface (local UI) and a remote OBWI. Using the configuration options
provided by these interfaces, you can tailor the switch to your specific
application, control any attached devices, and handle all basic KVM or serial
switch needs.
NOTE: The local UI and remote OBWI are almost identical. Unless specified,
all information in this chapter applies to both interfaces.
From either interface, you can launch two different kinds of sessions:
• The Video Viewer window allows you to control the keyboard, monitor, and
mouse functions of individual target devices connected to the switch in real
time. You may also use predefined global macros to perform actions within
the Video Viewer window. For instructions on how to use the Video
Viewer, see Chapter 4.
• The serial viewer window allows you to manage individual serial target
devices either by using commands or scripts.
Local User Interface (UI)
The switch includes a local port on the back. This port enables you to connect a
keyboard, monitor and mouse directly to the switch and use the local UI.
You can choose any of the following keystrokes to be configured to open the
local UI or to switch between the local UI and an active session: <Print
Local and Remote Configurationxxx | xxx43
Page 54

Screen>, <Ctrl +Ctrl>, <Shift +Shift>, and <Alt +Alt>. The defaults are
<PrintScreen> and <Ctrl-Ctrl>.
To launch the local UI:
1 Connect your monitor, keyboard and mouse cables to the switch. For more
information,see "Connecting the RCS Hardware" on page 25.
2 Press any of the enabled keystrokes to launch the local UI.
3 If local UI authentication has been enabled, enter your username and
password.
NOTE: If the switch has been added to an Avocent management software
server, then the Avocent management software server will be accessed to
authenticate the user. If the switch has not been added to an Avocent
management software server, or if the Avocent management software server
cannot be reached, then the switch local user database will be accessed to
authenticate the user. The default local username is Admin, and there is no
password. Usernames in the local user database are case-sensitive.
Attached target devices in the Local Port User Interface can be viewed and
managed from two individual screens that are selected from the left navigational
toolbar. For less than 20 targets, the Target List-Basic screen is recommended
for navigation. For more than 20 attached target devices, the Target List-Full
screen provides additional navigation tools. At the Target List-Full screen you
can navigate by entering the page number, using the page navigation buttons, or
using the filter. Either the Basic or Full screens can be set as the default screen
for selecting target devices.
Filtering
You may filter the list of target devices by providing a text string that will be
used to retrieve matching items. Filtering can provide a shorter, more exact list
of items. When filtering is performed, the Name column is searched for the
specified text string. The search is not case sensitive. When filtering, you may
use an asterisk (*) before or after text strings as a wildcard. For example, typing
emailserver* and clicking Filter will display items with emailserver at the
beginning (such as emailserver, emailserverbackup).
44xxx | Local and Remote Configurationxxx
Page 55

OBWI
The switch OBWI is a remote, web browser based user interface. For details on
setting up your system, see "Connecting the RCS Hardware" on page 25. The
following table lists the operating systems and browsers that are supported by
the OBWI. Make sure that you are using the latest version of your Web browser.
Table 3.1: Operating Systems Supported by the OBWI
Browser
Operating System
Microsoft Windows 2000
Workstation or Server
with Service Pack 2
Microsoft Windows
Server®2003 Standard,
Enterprise, or Web
Edition
Microsoft Windows
Server®2008 Standard,
Enterprise, or Web
Edition
Microsoft®Internet
Explorer version 6.0
SP1 and lat er
Yes Yes
Yes Yes
Yes Yes
Firefox version 2.0 and lat er
Windows XP
Professional with
Service Pack 3
Windows Vista
Business with Service
Pack 1
®
Yes Yes
Yes Yes
Local and Remote Configurationxxx | xxx45
Page 56

Operating System
Red Hat Enterprise
Linux®4 and 5
Standard, Enterprise or
Web Edition (Smart card
may not be supported by
the operating system)
Sun Solaris®9 and 10
(Smart card may not be
supported by the
operating system)
Novell SUSE Linux
Enterprise 10 and 11
(Smart card may not be
supported by the
operating system)
Ubuntu 8 Workstation
(Smart card may not be
supported by the
operating system)
Browser
Microsoft®Internet
Explorer version 6.0
SP1 and lat er
No Yes
No Yes
No Yes
No Yes
Firefox version 2.0 and lat er
To log in to the switch OBWI:
1 Launch a web browser.
2 In the address field of the browser, enter the IP address or host name
assigned to the switch you wish to access. Use https://xxx.xx.xx.xx or
https://hostname as the format.
NOTE: If using IPv6 mode, you must include square brackets around the IP
address. Use https://[<ipaddress-] as the format.
46xxx | Local and Remote Configurationxxx
Page 57

3 When the browser makes contact with the switch, enter your username and
password, then click Login. The switch OBWI will appear.
NOTE: The default username is Admin with no password.
To log in to the switch OBWI from outside a firewall, repeat the above
procedure, entering the external IP address of the firewall instead.
NOTE: The RCS will attempt to detect if Java is already installed on your PC.
If it is not, in order to use the on-board web interface, you will need to install it.
You may also need to associate the JNLP file with Java WebStart.
NOTE: Using the on-board web interface requires using Java Runtime
Environment (JRE) version 1.6.0_11 or higher.
NOTE: Once you have logged in to the on-board web interface, you will not
have to log in again when launching new sessions unless you have logged
out or your session has exceeded the inactivity timeout specified by the
administrator.
Using the User Interfaces
After you have been authenticated, the user interface appears. You may view,
access, and manage your switch, as well as specify system settings and change
profile settings. The following figure shows the user interface window areas.
Screen descriptions are provided in the following table.
Figure 3.1: User In terface Window
Local and Remote Configurationxxx | xxx47
Page 58

Table 3.2: User Interface Descriptions
Number Descript ion
Top option bar: Use the top option bar to contact Technical
1
Support, view the software general information, or log out of
an OBWI session.
2
Second option bar: Use this bar to print a web page, refresh
the current web page or access the Help tool.
Version block: The firmware version of the product and the
3
username of the user currently logged in appears on the left
side of the top option bar.
48xxx | Local and Remote Configurationxxx
Page 59

Number Descript ion
Side navigation bar: Use the side navigation bar to select
4
5
the information to be displayed. You can use the side
navigation bar to display windows in which you can specify
settings or perform operations.
Navigation tabs: The selected tab displays the system
information in the content area. Some tabs provide sub tabs
that can be clicked to display and revise details within a
category.
6
Content area: Use the content area to display or make
changes to the switch OBWI system.
Launching a Session
NOTE: Java 1.6.0_11 or later is required to launch a session.
To launch a session:
1 From the side navigation bar, select Target List. A list of available devices
will appear.
2 The applicable action, KVM Session or Serial Session, will be displayed in
the Action column, and will depend on the target device that was selected
to launch the session. If more than one action is available for a given target
device, click the drop-down arrow and select the applicable action from the
list.
If the target device is currently in use, you may be able to gain access by forcing
a connection to the device if your preemption level is equal to or higher than
the current user’s.
The RCS also allows serial sessions to Serial SIPs via an external Telnet or SSH
application such as PuTTY. Telnet and SSH sessions are only used to connect to
Serial SIPs and cannot be used to access or manage RCS or KVM target devices.
To launch a serial session from a Telnet or SSH application:
Local and Remote Configurationxxx | xxx49
Page 60

1 Enter the RCS host IP address that the Serial SIP is connected to.
2 Enter <RCS-username>:<Serial-SIP-name>, for example, jsmith:router.
3 Enter the password for the RCS user.
NOTE: The Telnet feature default is disabled. To enable Telnet support, refer
to "Configuring Serial Sessions" on page 77.
To switch to the active session from the local UI (local users only):
1 From the side navigation bar, select Local Session.
2 Select the Resume Active Session checkbox. The Video Viewer window will
appear.
Scan Mode
In Scan mode, the switch scans multiple target devices. The scanning order is
determined by placement of the target device in the list. You can also configure
the amount of time before the scan moves to the next target device in the
sequence.
NOTE: The Scan button is disabled if you are connected via modem.
To add target devices to the Scan list:
1 From the side navigation bar, select Unit View - Target List to open the
Target Devices screen.
2 Select the checkboxes next to the names of the target devices you wish to
scan.
3 Click Scan.
To configure Scan Time:
1 From the side navigation bar, select Ports - Local Port UI to open the
Local Port UISettings screen.
2 Under the Scan Mode heading, enter an amount of time in seconds (from 3-
255) in the Scan Time field.
50xxx | Local and Remote Configurationxxx
Page 61

3 Click Save.
Viewing System Information
You can view switch and target device information from the following screens in
the user interface.
Table 3.3: System Information
Category Select This: To View This:
RCS name and type, and the
RCS
Unit View - RCS Tools
RCS tools (Maintenance,
Diagnostics, Certificates and
Trap MIB)
Target
Device
Unit View - RCS Files
Unit View - RCS Properties - Identity
Unit View - RCS Properties - Location
Unit View - RCS
Settings - Versions
Unit View - Target List
RCS Configuration, User
Database, and Target Device
Part Number, Serial Number,
and EID
Site, Department, and Location
Current Application and Boot
versions
List of connected target
devices, as well as the Name,
Type, Status, and Action of
each device
Click on a target device to view
the following additional
information: Name, Type, EID,
available session option, and
the connection path
Local and Remote Configurationxxx | xxx51
Page 62

RCS Tools
From the Tools - Maintenance - Overview screen, you can view the appliance
name and type. You can also perform basic appliance tasks.
Rebooting the RCS
To reboot the RCS:
1 From the side navigation bar, select the Unit View - RCS - Tools -
Maintenance - Overview tab to open the Unit Maintenance screen.
2 Click Reboot.
3 A dialog box appears, warning you that all active sessions will be
disconnected. Click OK.
NOTE: If you are using the local UI, the screen will be blank while the switch
reboots. If you are using the remote OBWI, a message will appear to let you
know that the interface is waiting on the appliance to complete the reboot.
Upgrading RCS Firmware
You can update your RCS with the latest firmware available.
After the Flash memory is reprogrammed with the upgrade, the switch performs
a soft reset, which terminates all SIP sessions. A target device experiencing a SIP
firmware update may not display, or may display as disconnected. The target
device will appear normally when the Flash update is completed.
Attention: Disconnecting a SIP during a firmware update or cycling power to
the target device will render the module inoperable and require the SIP to be
returned to the factory for repair.
To upgrade the switch firmware:
1 From the side navigation bar, select the Unit View - RCS - Tools -
Maintenance - Upgrade tab to open the Upgrade RCS Firmware window.
2 Click Upgrade to open the Upgrade Appliance Firmware.
52xxx | Local and Remote Configurationxxx
Page 63

3 Select one of the following methods from which to load the firmware
file:Filesystem, TFTP, FTP, or HTTP.
NOTE: The Filesystem option is only available on the remote OBWI.
4 If you selected Filesystem, select Browse to specify the location of the
firmware upgrade file.
-orIf you selected TFTP, enter the Server IP Address and Firmware File
you wish to load.
-orIf you selected FTP or HTTP, enter the Server IP Address and
Firmware File you wish to load, as well as the User Name and User
Password.
5 Click Upgrade.
Saving and Restoring RCS Configurations and RCS User Databases
You may save the switch configuration to a file. The configuration file will
contain information about the managed appliance. You may also save the local
user database on the switch. After saving either file, you may also restore a
previously saved configuration file or local user database file to the switch.
To save a managed appliance configuration or user database of a managed
appliance:
1 From the side navigation bar, click the Unit View - RCS - Files tab.
2 Click either the RCS Configuration tab or the User Database tab, then
click the Save tab.
3 Select the file save method: Filesystem, TFTP, FTP, or HTTP PUT.
4 If you selected TFTP, enter the Server IP Address and Firmware Filename
you wish to load.
-or-
Local and Remote Configurationxxx | xxx53
Page 64

If you selected FTP or HTTP, enter the Server IP Address, Username,
User Password, and Firmware Filename you wish to load.
5 Enter an encryption password if you wish to encrypt the data before
download.
6 Click Download. The Save As dialog box will open.
7 Navigate to the desired location and enter a name for the file. Click Save.
To restore a managed appliance configuration or user database of a managed
appliance:
1 From the side navigation bar, click the Unit View - RCS - Files tab.
2 Click either the RCS Configuration tab or the User Database tab, then
click the Restore tab.
3 Select the file save method: Filesystem, TFTP, FTP, or HTTP.
4 If you selected Filesystem, select Browse to specify the location of the
firmware upgrade file.
-orIf you selected TFTP, enter the Server IP Address and Firmware
Filename you wish to load.
-orIf you selected FTP or HTTP, enter the Server IP Address, User Name,
User Password, and Firmware Filename you wish to load.
5 Click Browse. Navigate to the desired location and select the file name.
Click Upload.
6 Enter the decryption password if the original file was encrypted.
7 After the success screen appears, reboot the managed appliance to enable
the restored configuration. See "Rebooting the RCS" on page 52.
To recover from a Flash update failure:
If after a Flash procedure, the RCS does not boot into the new firmware version,
you may use the following steps to revert to the previous firmware version.
54xxx | Local and Remote Configurationxxx
Page 65

1 Connect a serial cable to the SETUP port on the rear panel of the RCS.
2 Run a terminal program on the PC connected to the Setup port. The serial
port settings should be: 9600 baud, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, no parity, and no
flow control.
3 Turn on the RCS.
4 In the terminal program, when the prompt "Hit any key to stop autoboot"
appears, press any key. A menu will be displayed.
5 Enter <1> (Boot Alternate) and press <Enter>. The RCS will
automatically reboot to the previous firmware version.
6 After the RCS reboots, you can attempt the Flash upgrade.
Network Settings
NOTE: Only switch administrators can make changes to the network dialog
box settings. Other users will have view only access.
From the side navigation bar, click Network to display the General, IPv4, and
IPv6 tabs.
To configure general network settings:
1 Click the Network tab, then click the General tab to display the RCS
General Network Settings screen.
2 Select one of the following options from the LAN Speed drop-down menu:
Auto-Detect, 10 Mbps Half Duplex, 10 Mbps Full Duplex, 100 Mbps Half
Duplex, 100 Mbps Full Duplex, or 1 Gbps Full Duplex.
NOTE: You must reboot if you change the Ethernet mode.
3 Select either Enabled or Disabled in the ICMP Ping Reply drop-down
menu.
4 Verify or modify the HTTP or HTTPS ports. The settings will default to
HTTP 80 and HTTPS 443.
5 Click Save.
Local and Remote Configurationxxx | xxx55
Page 66

To configure IPv4 network settings:
1 Click the IPv4 tab to display the IPv4 Settings screen.
2 Click to fill or clear the Enable IPv4 checkbox.
3 Enter the desired information in the Address, Subnet, and Gateway fields.
IPv4 addresses are entered as the xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx dot notation.
4 Select either Enabled or Disabled from the DHCP drop-down menu.
NOTE: If you enable DHCP, any information that you enter in the Address,
Subnet, and Gateway fields will be ignored.
5 Click Save.
To configure IPv6 network settings:
1 Click the IPv6 tab to display the IPv6 Settings screen.
2 Click to fill or clear the Enable IPv6 checkbox.
3 Enter the desired information in the Address, Subnet, and Prefix Length
fields. IPv6 addresses are entered as the FD00:172:12:0:0:0:0:33 or
abbreviated FD00:172:12::33 hex notation.
4 Select either Enabled or Disabled from the DHCP drop-down menu
NOTE: If you enable DHCPv6, any information that you enter in the Address,
Gateway, and Prefix length fields will be ignored.
5 Click Save.
DNSSettings
You can choose to either manually assign theDNS server or to use the addresses
obtained using DHCP or DHCPv6.
To manually configure DNSsettings:
1 From the side navigation bar, select DNS to display the RCS DNS Settings
screen.
2 Select Manual, DHCP (if IPv4 is enabled) or DHCPv6 (if IPv6 is enabled).
56xxx | Local and Remote Configurationxxx
Page 67

3 If you selected Manual, enter the DNS Server numbers in the Primary,
Secondary, and Tertiary fields.
4 Click Save.
NTP Settings
The switch must have access to the current time to verify that certificates have
not expired. You can configure the switch to request time updates from the
NTP. Refer to Configuring the Network Time Protocol (NTP) Settings in
Chapter 5.
SNMP Settings
SNMP is a protocol used to communicate management information between
network management applications and the switch. Other SNMP managers can
communicate with your switch by accessing MIB-II. When you open the SNMP
screen, the OBWI will retrieve the SNMP parameters from the unit.
From the SNMP screen, you can enter system information and community
strings. You may also designate which stations can manage the switch as well as
receive SNMP traps from the switch. If you select Enable SNMP, the unit will
respond to SNMP requests over UDP port 161.
To configure general SNMP settings:
1 Click SNMP to open the SNMPscreen.
2 Click to enable the Enable SNMP checkbox to allow the switch to respond
to SNMP requests over UDP port 161.
3 Enter the system’s fully qualified domain name in the Name field, as well as
a node contact person in the Contact field.
4 Enter the Read, Write, and Trap community names. These specify the
community strings that must be used in SNMP actions. The Read and
Write strings only apply to SNMP over UDP port 161 and act as passwords
Local and Remote Configurationxxx | xxx57
Page 68

that protect access to the switch. The values can be up to 64 characters in
length. These fields may not be left blank.
5 Type the address of up to four management workstations that are allowed to
manage this switch in the Allowable Managers fields. Alternatively, you may
leave these fields blank to allow any station to manage the RCS.
6 Click Save.
Auditing Event Settings
An event is a notification sent by the switch to a management station
indicating that something has occurred that may require further attention.
To enable individual events:
1 Click Auditing to open the Events screen.
2 Specify the events that will generate notifications by clicking the
appropriate checkboxes in the list.
-orSelect or clear the checkbox next to Event Name to select or deselect
the entire list.
3 Click Save.
Setting Event Destinations
You can configure audit events to be sent to SNMPtrap destinations and Syslog
servers. The events enabled on the Events screen are sent to all the servers listed
on the Event Destination screen.
1 Click Auditingand the Destinations tab to open the Event Destinations
screen.
2 Type the address of up to four management workstations to which this
switch will send events in the SNMP Trap Destination fields, as well as up
to four Syslog servers.
58xxx | Local and Remote Configurationxxx
Page 69

3 Click Save.
Ports - Configuring SIPs
From the switch, you can display a list of the attached SIPs, as well as the
following information about each SIP: EID (electronic ID), Port, Status,
Application, Interface Type, and USB Speed. You can click on one of the SIPs
to view the following additional information: Switch Type, Boot Version,
Application Version, Hardware Version, FPGA Version, Version Available, and
Upgrade Status.
You can also perform the following tasks: delete offline SIPs, upgrade the SIP
firmware, set the USB speed, or decommission the cables.
To delete offline SIPs:
1 From the side navigation bar, click Ports - SIPs to open the SIP screen.
2 Click Delete Offline.
Upgrading SIPs
The SIP Flash upgrade feature allows RCS Administrators to update the SIP
with the latest firmware available. This update can be performed using the
switch user interface or Avocent management software.
After the Flash memory is reprogrammed with the upgrade, the switch performs
a soft reset, which terminates all SIP sessions. A target device experiencing a SIP
firmware update may or may not display as disconnected. The target device will
appear normally when the Flash update is completed.
If the RCS is configured to Auto-Upgrade SIPs, the SIPs will automatically
update when the switch is updated. To update your switch firmware, see "RCS
Tools" on page 52 or the Avocent management software Online Help. If issues
occur during the normal upgrade process, SIPs may also be force-upgraded when
needed.
NOTE: Check http://www.dell.com for firmware upgrade files.
Local and Remote Configurationxxx | xxx59
Page 70

To change the SIP Auto-Upgrade feature:
1 From the side navigation bar, click Ports - SIPs to open the SIPs screen.
2 Select the checkbox(es) next to the SIP(s) that you wish to upgrade and
click Enable Auto-Upgrade.
Attention: Disconnecting a SIP during a firmware update or cycling power to
the target device will render the module inoperable and require the SIP to be
returned to the factory for repair.
To upgrade the SIP firmware:
1 From the side navigation bar, click Ports - SIPs to open the SIPs screen.
2 Select the checkbox(es) next to the SIP(s) that you wish to modify.
3 Select Choose an operation and select Upgrade.
4 If the settings are correct, click Upgrade.
To set the USB Speed:
NOTE: This section only applies to the USB2 SIP.
1 From the side navigation bar, click Ports - SIPs to open the SIPs screen.
2 Select the checkbox(es) next to the SIP(s) that you wish to modify.
3 Select Choose an operation and select either Set USB 1.1 Speed or Set
USB 2.0 Speed.
Power Device Settings
NOTE: You must have Administrator privileges to change power control
device settings.
NOTE: Refer to www.dellkvm.com for a list of supported PDUs.
From the RCS Power Devices screen, you can view a list of connected power
devices, as well as the following information about each power device: Name,
Port, Status, Version, Model, Buzzer, Alarm, and Temperature. You can also
select a power device, then select Settings to view the following details about
60xxx | Local and Remote Configurationxxx
Page 71

that power device: Name, Description, Status, Version, Sockets, Vendor Name,
Model, and Input Feeds.
If a target device is connected to a power control device outlet, you can turn on,
turn off or cycle (turn off, then turn on) the target device.
To turn on, turn off or power cycle a target device:
1 From the side navigation bar, click Ports - Power Devices to open the
Power Devices screen.
2 Click the name of the unit you wish to configure and select Outlet List.
3 Select the checkbox to the left of the outlet(s) that you wish to configure.
4 Click On, Off, or Cycle, as desired.
To delete offline power devices:
1 From the side navigation bar, click Ports - Power Devices to open the
Power Devices screen.
2 Click Delete Offline.
To change the minimum on time, off time or wake up state:
1 From the side navigation bar, click Ports - Power Devices to open the
Power Devices screen.
2 Click the name of the unit you wish to configure and select Outlets.
3 Click the outlet name that you wish to modify.
4 Use the drop-down windows to alter the desired settings and click Save.
Associated Target Servers and Power Outlets
In the OBWI Target List page, power control actions are selectable for a target
with linked outlets. Selecting the Ports - Power Devices tabs, and then clicking
on a device name will display the Device Settings, Device Firmware Upgrade,
and Outlet List tabs. Click the Outlet List tab to display the outlets linked with
a target device.
Local and Remote Configurationxxx | xxx61
Page 72

In the following figure, the target device named Server2 has linked power outlets.
Clicking on the drop-down menu arrow in the Action column shows the
additional power actions available.
Figure 3.2: Target List
In the following figure, the target Unit Overview page for Server2 shows the Wall
Outlet Power, where outlet 1 and outlet 9 from PDU 1 are linked to Server2.
Figure 3.3: Target Overview Server2
62xxx | Local and Remote Configurationxxx
Page 73

Grouping Power Outlets
The outlets can be linked or associated with the target server for easier control.
To group outlets (or outlets to servers), the first device to be named must use
the Manual name field. The second and subsequent devices must use the Link
to Target Device menu, and then select the target name for the first device from
the drop down list.
Power actions performed on the Target List page are applied to all applicable
outlets. Power control actions for specific power outlets of a target may be
performed on the Unit Overview page. In the following figure, the target named
Group2 is composed of power outlets 4 and 5 from PDU 1.
To group sockets 4 and 5:
1 Select outlet 4 to display the Power Devices Outlet Settings page.
2 Select Manual and enter Group2.
3 Click Save.
Local and Remote Configurationxxx | xxx63
Page 74

4 Select outlet 5 to display the Power Devices Outlet Settings page.
5 Select Link to Target Device, select Group2 from the drop down menu.
6 Click Save. After returning to the Outlet List, outlets 4 and 5 will have the
same name.
Figure 3.4: Target Overview for Group2
Default Outlet Names
On the Power Devices page, the checkbox “Assign Default Names to Outlets”
controls whether or not power outlets are given default names for a power
device, as shown in the following figure. Only power outlets with names are
listed on the Target page. Default assigned power outlet names may be removed
by clearing the "Assign Default Names to Outlets" checkbox and saving. Power
outlets without names are assigned default names by turning on “Assign Default
Names to Outlets” and saving.
Figure 3.5: RCS Power Devices Page
64xxx | Local and Remote Configurationxxx
Page 75

Assigning an Outlet Name
On the Power Device Outlet Settings page, three options are available for
assigning the name of a outlet as shown in the following figure. The options are
Manual Name assignment, Link to Target Device and Do Not Display as Target
Device.
Figure 3.6: Power Device Outlet Settings Page
Local and Remote Configurationxxx | xxx65
Page 76

• The Manual Name assignment gives a unique name to an outlet. The name
must be unique for all the SIPs and power outlet names. An attempt to
specify a manual name which is not unique will result in an error and the
name will not be saved.
• The Link to Target List assignment links the outlet to another target name
(either an outlet or SIP) for power control of the named target. When an
outlet is linked to a SIP target name, typically the outlet physically provides
power to the server attached to the SIP.
• The Do Not Display as Target Device option gives the outlet a blank name,
which prevents it from being displayed on the Target List page. This option
may be used for spare outlets to remove them from the Target List page.
Access Control Inheritance
When a power outlet name is changed by linking it to a target, the outlet
inherits the access control already configured for that target name. When a SIP
is added, if the name retrieved from the SIP matches the name of an existing
66xxx | Local and Remote Configurationxxx
Page 77

target, the new SIP inherits the access control from that target. When a target
device is renamed, all the SIPs and outlets of that target are renamed, and they
carry forward the access control previously configured for the old target name.
Renaming of a Target Device
On the Target List - Overview page, the name for that target may be changed to
any unique target name. The name must be unique for the set of all targets,
including SIPs and power outlets. When a target is renamed, all outlets linked to
that target are also given the new target name.
Prioritized Status of Target Devices
On the Target List page, a target with linked power outlets controls multiple
devices. The Status value displayed for a target is chosen as the highest priority
of all the status values of the devices. The following table shows the possible
status values in priority order (highest to lowest) and the applicable target
device types.
Table 3.4: Target Status Valu es
Status Value Applicable for: Stat us Descript ion
SIP
In Use x N/A A session is active
Path Blocked x N/A
Upgrading x N/A SIP is being upgraded
Turning On N/A x
Turning Off N/A x
Power
Outlet
Path to Target is in use by
another session
One or more outlets are turning
on
One or more outlets are turning
off
Local and Remote Configurationxxx | xxx67
Page 78

Status Value Applicable for: Stat us Descript ion
SIP
No Power x N/A No power detected on SIP
Partial Power N/A x
Locked-Off N/A x
Turned Off N/A x
Locked-On N/A x
Idle x N/A
Turned On N/A x Outlets are turned on
Power
Outlet
Target has outlets in both on
and off states
One or more outlets are locked
on
One or more outlets are turned
off
One or more outlets are locked
off
No session active; SIP has
power
When a target device has multiple power outlets linked by name and they do
not have a common power state, the RCS may consider the Locked-Off outlet
status as Off, and the Locked-On outlet status as On. The following table lists
the resulting Status values for combinations of two outlet status values.
Table 3.5: Multiple Outlet Status Values and Displayed Status
Outlet 1 Stat us
Off Off Off
Off On Partial Power
On On Powered On
68xxx | Local and Remote Configurationxxx
Outlet 2
Status
Resulting Status
Page 79

Outlet 1 Stat us
Locked-On On Powered On
Locked-On Locked-On Locked-On
Locked-On Off Partial Power
Locked-Off On Partial Power
Locked-Off Locked-Off Locked-Off
Locked-Off Off Powered Off
Locked-On Locked-Off Partial Power
Outlet 2
Status
Resulting Status
Local Session Page on the Local Port
On the local port's Local Session page, when the target of the active session has
power outlets linked, three power controls are displayed on the page under the
Active session. The following figure illustrates the power controls displayed for
an active local port session for a target named Server2.
Figure 3.7: Local Session Page With Power Controls
Local and Remote Configurationxxx | xxx69
Page 80

Local Port UI Settings
To change how the local UI is invoked:
1 From the side navigation bar, select Ports - Local Port UI to open the
Local Port UI Settings screen.
2 Under the Invoke Local Port UI heading, select the checkbox next to one or
more of the listed methods.
3 Click Save.
You can turn on or turn off local port user interface authentication and choose a
user access level. If you turn on local port user interface authentication, you will
be required to log in to use the interface.
You can also select the keyboard language for the local port, scan mode time,
enable/disable the local port password and select a user preemption level. The
70xxx | Local and Remote Configurationxxx
Page 81

preemption level of users determines whether they may disconnect another user’s
serial or KVM session with a target device. Preemption levels range from 1 - 4,
with 4 being the highest level. For example, a user with a preemption level of 4
may preempt other level 4 users, as well as those with a level 1, 2, or 3 setting.
To change the Local Port User Authentication (Administrator only):
1 From the side navigation bar, select Ports - Local Port UI to open the
Local Port UI Settings screen.
2 Select or deselect the Disable Local Port User Authentication checkbox.
3 If Disable Local Port User Authentication is checked, select one of the
following options from the User Access Level drop-down menu:User, User
Administrator, or RCS Administrator.
4 Click Save.
Modem Settings
From the RCS Modem Settings screen, you can configure several modem
settings, as well as view the following modem settings:Local Address, Remote
Address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway.
For information on connecting your switch to a modem, see "Connecting the
RCS Hardware" on page 25.
To configure modem settings:
1 From the side navigation bar, select Ports - Modem to open the Modem
Settings screen.
2 Either enable or disable the Modem sessions can preempt digital sessions
checkbox.
3 Select an Authentication Timeout time from 30 to 300 seconds, and an
Inactivity Timeout time from 1 to 60 minutes.
4 Select Save.
Local and Remote Configurationxxx | xxx71
Page 82

Setup Settings - Port Security
From the serial setup port, you can change the appliance network configuration,
enable debug information, and reset the appliance.
To enable a password to restrict access the serial setup port:
1 From the side navigation bar, select RCS Settings - Ports - Setup to display
the Setup Port Settings page.
2 Click to enable the Enable Setup Port Security box.
3 Enter and confirm your password.
4 Click Save.
Sessions
From the Active Sessions screen, you can view a list of active sessions and the
following information about each session: Target Device, Owner, Remote Host,
Duration, and Type.
Configuring General Sessions
To configure general session settings:
1 From the side navigation bar, select Sessions - General. The General
Session Settings screen appears.
2 Select or deselect the Enable Inactivity Timeout checkbox.
3 In the Inactivity Timeout field, enter the amount of inactive time you want
to pass before the session closes (from 1 to 90 minutes).
4 In the Login Timeout field, enter the amount of inactive time you want to
pass before you must log in again (from 21 to 120 seconds).
5 Select or deselect the Enable Preemption Timeout checkbox.
72xxx | Local and Remote Configurationxxx
Page 83

6 In the Preemption Timeout field, enter the amount of time (from 1 to 120
seconds) that a prompt will be displayed to inform you that your session is
going to be preempted.
7 Select the applicable session sharing options (Enabled, Automatic,
Exclusive, or Stealth).
8 Select the Input Control Timeout from 1 to 50, with 1 representing one
tenth of a second.
9 Click Save.
Configuring KVM Sessions
To configure KVM session settings:
1 From the side navigation bar, select Sessions - KVM. The KVM Session
Settings screen appears.
2 Select an encryption level for keyboard and mouse signals (128-bit SSL
(ARCFOUR), DES, 3DES, or AES) and for video signals (128-bit SSL
(ARCFOUR), DES, 3DES, AES, or None).
3 Select a language from the Keyboard drop-down menu.
4 If your hardware includes the USB2+CAC SIP, select the video resolution.
5 Click Save.
Configuring Local Virtual Media Sessions
To set virtual media options:
1 From the side navigation bar, select Sessions - Virtual Media to open the
Virtual Media Session Settings screen.
2 Either enable or disable the Virtual Media locked to KVM Sessions
checkbox.
3 Either enable or disable the Allow Reserved Sessions checkbox.
4 Select one of the following options from the Virtual Media Access Mode
from the drop-down menu: Read-Only or Read-Write.
Local and Remote Configurationxxx | xxx73
Page 84

5 Select one of the Encryption Levels that you wish to be supported.
6 Click Save.
7 Select the checkbox next to each SIP for which you want to enable virtual
media and click Enable VM.
-orSelect the checkbox next to each SIP for which you want to disable
virtual media and click Disable VM.
Virtual Media Options
You can determine the behavior of the switch during a virtual media session
using the options provided in the Virtual Media Session Settings screen. Table
3.4 outlines the options that can be set for virtual media sessions.
For information about using virtual media in a KVMsession, see "Virtual Media"
on page 96.
Table 3.6: Virtu al Media Session Settings
Setting Description
The locking option specifies whether a virtual
media session is locked to the KVM session on
Session Settings:
Virtual Media
locked to KVM
Session
the target device. When locking is enabled
(default) and the KVM session is closed, the
virtual media session will also be closed. When
locking is disabled and the KVM session is
closed, the virtual media session will remain
active.
74xxx | Local and Remote Configurationxxx
Page 85

Setting Description
Ensures that a virtual media connection can only
Session
Settings:Allow
Reserved
Sessions
Drive Mappings:
Virtual Media
Access Mode
be accessed with your username and that no
other user can create a KVM connection to that
target device. When the associated KVM session
is disconnected, the virtual media session may
be disconnected according to the Locked setting
in the Virtual Media dialog box.
You may set the access mode for mapped drives
to read-only or read-write. When the access
mode is read-only, the user will not be able to
write data to the mapped drive on the client
server. When the access mode is read-write, the
user will be able to read and write data from/to
the mapped drive. If the mapped drive is readonly by design (for example, a CD-ROM drive,
DVD-ROM drive or ISO images), the configured
read-write access mode will be ignored. Setting
the read-only mode can be helpful when a readwrite drive such as a mass storage device or a
USB removable media is mapped, and you wish
to prevent the user from writing data to it.
Encryption Level
You can have one DVD drive and one mass
storage device mapped concurrently. A CD drive,
DVD drive, or ISO disk image file is mapped as a
virtual CD/DVD drive.
You may configure encryption levels for virtual
media sessions. The choices are: None (default),
128-bit SSL (ARCFOUR), DES, 3DES, and AES.
Local and Remote Configurationxxx | xxx75
Page 86

Setting Description
Virtual Media
Access per
SIP:Enable
VM/Disable VM
The Virtual Media Access per the SIP section lists
all virtual media SIPs. The list includes details
about each cable, including the option to enable
or disable virtual media for each cable.
Local Users
Local users can also determine the behavior of virtual media from the Local
Session screen. In addition to connecting and disconnecting a virtual media
session, you can configure the settings in the following table.
Table 3.7: Local Virtual Media Session Settings
Setting Description
Allows virtual media sessions to the first detected
CD ROM/
DVD ROM
Mass Storage
CD-ROM or DVD-ROM (read-only) drives. Enable
this checkbox to establish a virtual media CD-ROM
or DVD-ROM connection to a target device.
Disable to end a virtual media CD-ROM or DVDROM connection to a target device.
Allows virtual media sessions to the first detected
mass storage drive. Enable this checkbox to
establish a virtual media mass storage connection
to a target device. Disable to end a virtual media
mass storage connection to a target device.
Ensures that a virtual media connection can only
Reserved
76xxx | Local and Remote Configurationxxx
be accessed with your username and that no other
user can create a KVM connection to that target
device.
Page 87

Configuring Serial Sessions
To configure serial session settings:
1 From the side navigation bar, click Sessions - Serial to display the Serial
Session Settings screen.
2 Either enable or disable the Telnet Access Enabled checkbox.
3 Click Save.
Setting Up User Accounts
Managing Local Accounts
The switch OBWI provides local and login security through administratordefined user accounts. By selecting User Accounts on the side navigation bar,
administrators may add and delete users, define user preemption, and access
levels and change passwords.
Access Levels
When a user account is added, the user may be assigned to any of the following
access levels: RCS Administrators, User Administrators, and Users.
Table 3.8: Allowed Operations by Access Level
Operation RCS Administrator User Administ rator Users
Configure interface
system-level settings
Configure access rights Yes Yes No
Add, change and delete
user accounts
Yes No No
Yes, for all access
levels
Local and Remote Configurationxxx | xxx77
Yes, for Users and
User Administrators
only
No
Page 88

Operation RCS Administrator User Administ rator Users
Change your own
password
Access target device
Yes Yes Yes
Yes, all target
devices
Yes, all target
devices
Yes, if
allowed
To add a new user account (User Administrator or RCS Administrator only):
1 On the side navigation bar, select User Accounts - Local User Accounts to
open the Local User Accounts screen.
2 Click the Add button.
3 Enter the name and password of the new user in the blanks provided.
4 Select the access level for the new user.
5 Select any of the available target devices that you wish to assign to the user
account and click Add.
NOTE: User Administrators and RCS Administrators can access all target
devices.
6 Click Save.
To delete a user account (User Administrator or RCS Administrator only):
1 On the side navigation bar, select User Accounts - Local Accounts to open
the Local User Accounts screen.
2 Click the checkbox to the left of each account that you wish to delete, then
click Delete.
To edit a user account (Administrator or active user only):
1 On the side navigation bar, select User Accounts - Local Accounts. The
Local User Accounts screen is displayed.
2 Click the name of the user you wish to edit. The user profile will appear.
78xxx | Local and Remote Configurationxxx
Page 89

3 Fill out the user information on the screen, then click Save.
Avocent Management Software Device IP Addresses
You can contact and register an unmanaged switch with an Avocent
management software server by specifying the IP address of the management
software server.
To configure the server IP address:
1 On the side navigation bar, select User Accounts - Avocent. The Avocent
Management Software Settings screen is displayed.
2 Enter the server IP addresses that you want to contact. Up to four addresses
are allowed.
3 Use the scroll bar to select the desired retry interval.
4 To disassociate an RCS that has been registered with the server, click the
Disassociate button.
5 Click Save.
LDAP
The Dell 1082DS/2162DS/4322D RCS can authenticate and authorize users via
a local database or by an external scalable distributed directory service using the
Dell RCS software or OBWI with LDAP (Lightweight Directory Assistance
Protocol) support. Refer to the LDAP section for additional information on
configuring and using LDAP on the RCS.
Override Admin
Should a network failure occur, an account is provided that may be used
regardless of the unit’s ability to authenticate against an LDAP server. Refer to
Configure the Override Admin Account in Chapter 5.
Local and Remote Configurationxxx | xxx79
Page 90

Active Sessions
From the Active Sessions screen, you can view a list of active sessions and the
following information about each session: Target Device, Owner, Remote Host,
Duration, and Type.
Closing a Session
To close a session:
1 From the side navigation bar, select Active Sessions to display the RCS
Active Sessions screen.
2 Click the checkbox next to the desired target device(s).
3 Click Disconnect.
NOTE: If there is an associated locked virtual media session, it will be
disconnected.
To close a session (local users only):
1 From the side navigation bar, select Local Session.
2 Select the Disconnect Active Session checkbox.
80xxx | Local and Remote Configurationxxx
Page 91

4
The Video Viewer Window
The Video Viewer is used to conduct a KVM session with the target devices
attached to an switch using the OBWI. When you connect to a device using the
Video Viewer, the target device desktop appears in a separate window
containing both the local and the target device cursors.
The switch OBWI software uses a Java-based program to display the Video
Viewer window. The switch OBWI automatically downloads and installs the
Video Viewer the first time it is opened.
NOTE: Java 1.6.0_11 or later is required to launch a session.
NOTE: The switch OBWI does not install the Java Resource Engine (JRE).
The JRE is available as a free download from http://www.sun.com.
NOTE: The switch OBWI uses system memory to store and display images
within Video Viewer windows. Each opened Video Viewer window requires
additional system memory. An 8-bit color setting on the client server requires
1.4 MB of memory per Video Viewer window, a 16-bit color setting requires
2.4 MB and a 32-bit color setting requires 6.8 MB. If you attempt to open more
Video Viewer windows than your system memory allows (usually four), you
will receive an out-of-memory error and the requested Video Viewer window
will not open.
If the device you are attempting to access is currently being viewed by another
user, you will be prompted to preempt the other user if your preemption level is
equal to or greater than the other user's preemption level. An RCS Administrator
can also disconnect an active user via the Active Session page. For more
information, see "Active Sessions" on page 80.
Figure 4.1: Video Viewer Window (normal windo w mode)
The Video Viewer Windowxxx | xxx81
Page 92

Table 4.1: Video Viewer Description s
Number
Description
Title Bar: Displays the name of the target device being viewed. When
1
in Full Screen mode, the title bar disappears and the target device
name appears between the menu and toolbar.
2
Thumbtack icon: Locks the display of the menu and toolbar so that it is
visible at all times.
82xxx | The Video Viewer Windowxxx
Page 93

Number
3
Description
Menu and toolbar: Enables you to access many of the features in the
Video Viewer window. The menu and toolbar is in a show/hide state if
the thumbtack has not been used. Place your cursor over the toolbar to
display the menu and toolbar. Up to ten commands and/or macro
group buttons can be displayed on the toolbar. By default, the Single
Cursor Mode, Refresh, Automatic Video Adjust and Align Local Cursor
buttons appear on the toolbar. For more information, see "Changing
the Toolbar" on page 83 and "Macros" on page 104.
4
5
6
7 Display area: Accesses the server desktop.
8
Macro buttons: Commonly used keyboard sequences that can be sent
to the target device.
Connection Status Indicator: Indicates the status of the user that is
connected to the RCS for this server. The modes are exclusive, basic
active connection, primary active sharing, secondary active sharing,
passive sharing, stealth, and scanning.
Smart Card Status Indicators: Indicate whether or not a smart card is in
the smart card reader. The Video Viewer screen smart card icon is
greyed out and indicates that the smart card option is unavailable or
disabled. The icon is green if the smart card is mapped.
Frame: Resizes the Video Viewer window by clicking and holding on
the frame.
Changing the Toolbar
You can choose the amount of elapsed time before the toolbar hides in the
Video Viewer window when it is in show/hide state (that is, not locked in place
by the thumbtack).
To specify a toolbar hide time:
1 Select Tools - Session Options from the Video Viewer window menu.
The Video Viewer Windowxxx | xxx83
Page 94

-orClick the Session Options button.
The Session Options dialog box appears.
2 Click the Toolbar tab.
3 Use the arrow keys to specify the number of elapsed seconds prior to hiding
the toolbar.
4 Click OK to save your changes and close the dialog box.
Launching a Session
NOTE: When using a non-proxied connection, video performance over a
slower network connection may be less than optimal. Since certain color
settings (such as Grayscale) use less network bandwidth than others (such
as Best Color), changing the color settings can increase video performance.
For optimal video performance over a slower network connection, use a color
setting such as Grayscale/Best Compression or Low Color/High
Compression. See "Adjusting the View" on page 85 for more information.
NOTE: If a user connects to a target device with a higher screen resolution
than the local computer, the Video Viewer window will display a portion of the
target device screen, with scroll bars for viewing the remainder of the screen.
The user may view the entire screen by adjusting the resolution on the target
device, the local computer or both.
To launch a KVM session from the switch Explorer window:
1 Click on a device listed on the Target List screen to open the unit overview
window.
2 Click the KVM Session link to open the Video Viewer in a new window.
Session Time-out
A remote session can time-out when no activity occurs in a Session window for
a specified time. The session time-out value can be configured in the RCS KVM
Session Settings window. The specified time-out value will be used the next
time the switch OBWI is accessed.
84xxx | The Video Viewer Windowxxx
Page 95

To enable, disable, or configure the session time-out:
1 In the side menu, select Unit View - RCS - RCS Settings - Sessions -
General.
2 Select the desired setting for the Enable Activity Timeout box.
3 If necessary, select the time limit for the inactivity time-out.
4 Click Save.
Window Size
NOTE: The View - Scaling command is not available if the Video Viewer
window is in Full Screen mode or to non-primary users of a shared session.
When the switch OBWI is used for the first time, any open Video Viewer
windows display at a resolution of 1024 x 768 until the user changes the value.
Each Video Viewer window can be set to a different resolution.
The switch OBWI automatically adjusts the display if the window size changes
during a session as long as autoscaling is enabled. If the target device resolution
changes any time during a session, the display adjusts automatically.
To change the Video Viewer window resolution:
1 Select the View - Scaling command.
2 Select the desired resolution.
Adjusting the View
Using menus or task buttons in the Video Viewer window, you can do the
following:
• Align the mouse cursors.
• Refresh the screen.
The Video Viewer Windowxxx | xxx85
Page 96

• Enable or disable Full Screen mode. When Full Screen mode is enabled, the
image adjusts to fit the desktop up to a size of 1600 x 1200 or 1680 x 1050
(widescreen). If the desktop has a higher resolution, the following occurs:
• The full-screen image is centered in the desktop, and the areas
surrounding the Video Viewer window are black.
• The menu and toolbar are locked so that they are visible at all times.
• Enable automatic, full or manual scaling of the session image:
• With full scaling, the desktop window remains fixed and the device
image scales to fit the window.
• With automatic scaling, the desktop window is sized to match the
resolution of the target device being viewed.
• With manual scaling, a drop-down menu of supported image scaling
resolutions is displayed.
• Change the color depth of the session image.
To align the mouse cursors:
Click the Align Local Cursor button in the Video Viewer window toolbar. The
local cursor should align with the cursor on the remote device.
NOTE: If cursors drift out of alignment, turn off mouse acceleration in the
attached device.
To refresh the screen, click the Refresh Image button in the Video Viewer
window, or select View - Refresh from the Video Viewer window menu. The
digitized video image is completely regenerated.
To enable Full Screen mode, click the Maximize button, or select View - Full
Screen from the Video Viewer window menu. The desktop window disappears
and only the accessed device desktop is visible. The screen resizes up to a
maximum of 1600 x 1200 or 1680 x 1050 (widescreen). If the desktop has a
higher resolution, then a black background surrounds the full screen image. The
floating toolbar appears.
86xxx | The Video Viewer Windowxxx
Page 97

To disable Full Screen mode, click the Full Screen Mode button on the floating
toolbar to return to the desktop window.
To enable full scaling, select View - Scaling from the Video Viewer window
menu and select Full Scale. The device image scales automatically to the
resolution of the target device being viewed.
To enable manual scaling, select View - Scaling from the Video Viewer window
menu. Choose the dimension to scale the window. The available manual scaling
sizes will vary according to your system.
Refreshing the Image
Clicking the Refresh Image button in the Manual Video Adjust dialog box
completely regenerates the digitized video image.
NOTE: You can also select View - Refresh from the Video Viewer window
menu to refresh the image.
Video Settings
Additional Video Adjustment
Generally, the Video Viewer window automatic adjustment features optimize
the video for the best possible view. However, users can fine-tune the video with
the help of Dell Technical Support by selecting the Tools - Manual Video
Adjust command in the Video Viewer window menu or clicking the Manual
Video Adjust button. This displays the Manual Video Adjust dialog box. Video
adjustment is a per target setting.
Users can also verify the level of packets per second required to support a static
screen by observing the packet rate located in the lower left-hand corner of the
dialog box.
To manually adjust the video quality of the window:
NOTE: The following video adjustments should be made only with the help of
Dell Technical Support.
The Video Viewer Windowxxx | xxx87
Page 98

1 Select Tools - Manual Video Adjust from the Video Viewer window menu.
-orClick the Manual Video Adjustbutton.
The Manual Video Adjust dialog box appears.
Figure 4.2: Manual Video Ad just Dialog Box
Table 4.2: Descriptions for Figure 4.2
Number Description Number Description
1 Image Capture Width 9
2 Pixel Sampling/Fine Adjust 10 Refresh Image
3
88xxx | The Video Viewer Windowxxx
Image Capture Horizontal
Position
11 Adjustment bar
Automatic Video
Adjustment
Page 99

Number Description Number Description
4
5 Contrast 13 Help
6 Brightness 14 Performance Monitor
7 Noise Threshold 15 Close button
8 Priority Threshold
Image Capture Vertical
Position
12 Video Test Pattern
2 Click the icon corresponding to the feature you wish to adjust.
3 Move the Contrast slider bar and then fine-tune the setting by clicking the
Min (-) or Max (+) buttons to adjust the parameter for each icon pressed.
The adjustments display immediately in the Video Viewer window.
4 When finished, click Close to exit the Manual Video Adjust dialog box.
Target Video Settings
The Image Capture Width, Pixel Sampling/Fine Adjust, Image Capture
Horizontal Position and Image Capture Vertical Position adjustments affect
how the target video is captured and digitized. They are seldom changed.
The image capture parameters are automatically changed by the Automatic
Adjustment function. A special image is required on the target in order to make
accurate adjustments independently.
Automatic Video Adjustment
In most cases, you do not need to alter the Video Settings from the default
settings. The system automatically adjusts and uses the optimal video
parameters. The switch OBWI performs best when the video parameters are set
such that no (0) video packets are transmitted for a static screen.
The Video Viewer Windowxxx | xxx89
Page 100

You can easily adjust your video parameters to ideal settings by clicking on the
Auto Adjust Video button in the Manual Video Adjust dialog box.
NOTE: You can also select Tools - Automatic Video Adjust from the Video
Viewer window menu or click the Aut omatic Video Adjust toolbar icon to
automatically adjust the video.
Video Test Pattern
Clicking the Video Test Pattern button in the Manual Video Adjust dialog box
toggles a display of a video test pattern. Click the Video Test Pattern button
again to toggle back to a normal video image.
Vendor-specific Video Settings
Video settings vary significantly among manufacturers. Dell maintains an online
database of optimized video settings for various video cards, particularly Sunspecific ones. This information can be obtained from the Dell online knowledge
base or by calling Dell technical support.
Color Settings
Adjusting Color Depth
The Dambrackas Video Compression® (DVC) algorithm enables users to adjust
the number of viewable colors in a remote session window. You can choose to
display more colors for the best fidelity or fewer colors to reduce the volume of
data transferred on the network.
Video Viewer windows can be viewed using the Best Color Available (slower
updates), Best Compression (fastest updates), a combination of Best Color and
Best Compression or in Grayscale.
You can specify the color depths of individual ports and channels by selecting
the View Color command in a remote session window. These settings are saved
individually per channel.
90xxx | The Video Viewer Windowxxx
 Loading...
Loading...