Page 1

Link Aggregation Interoperability
of the Dell™ PowerConnect™
5316M with Cisco IOS or Cisco
CatOS based Switches
By Bruce Holmes
August 2005
Page 2

Contents
Introduction................................................................................................................................................3
Link Aggregation with Gigabit Ethernet Cisco Switches.................................................................. 5
Configuring the PowerConnect 5316M external ports for Dynamic Link Aggregation...............6
Configuring a Cisco IOS Gigabit Ethernet Switch for Dynamic Link Aggregation.....................6
Configuring a Cisco CATOS Gigabit Ethernet Switch for Dynamic Link Aggregation .............7
Confirming a successful Dynamic Link Aggregation connection with the PowerConnect
5316M...........................................................................................................................................................7
Confirming a successful Dynamic Link Aggregation connection with Cisco IOS.......................7
Confirming a successful Dynamic Link Aggregation connection with CISCO CATOS............. 8
Configuring the PowerConnect 5316M external ports for Static Link Aggregation..................... 9
Configuring a CISCO IOS Switch for Static Link Aggregation.......................................................9
Configuring a Cisco CATOS Switch for Static Link Aggregation...................................................9
Confirming a successful Static Link Aggregation connection........................................................10
Link aggregation with Cisco Fast Ethernet Switches........................................................................11
Configuration Limitations..................................................................................................................... 12
Port configuration differences with Dell and CISCO ......................................................................13
August 2005 Page 2 Dell Enterprise Product Group
Page 3
Introduction
The Dell PowerConnect 5316M is a fully managed Layer 2 switch that helps organizations reduce
the price and cable sprawl traditionally associated with the networking of servers. This robust
networking switch is based on the same technology as the PowerConnect 5324, but is housed in a
different form factor that is specifically designed for the Dell Modular Server Enclosure.
Many IT organizations have great investments in a standardized core network infrastructure as
well as the human resources to maintain that network. With this investment in mind, Dell has
designed the PowerConnect 5316M based on industry standard network protocols to ensure
interoperability whenever possible.
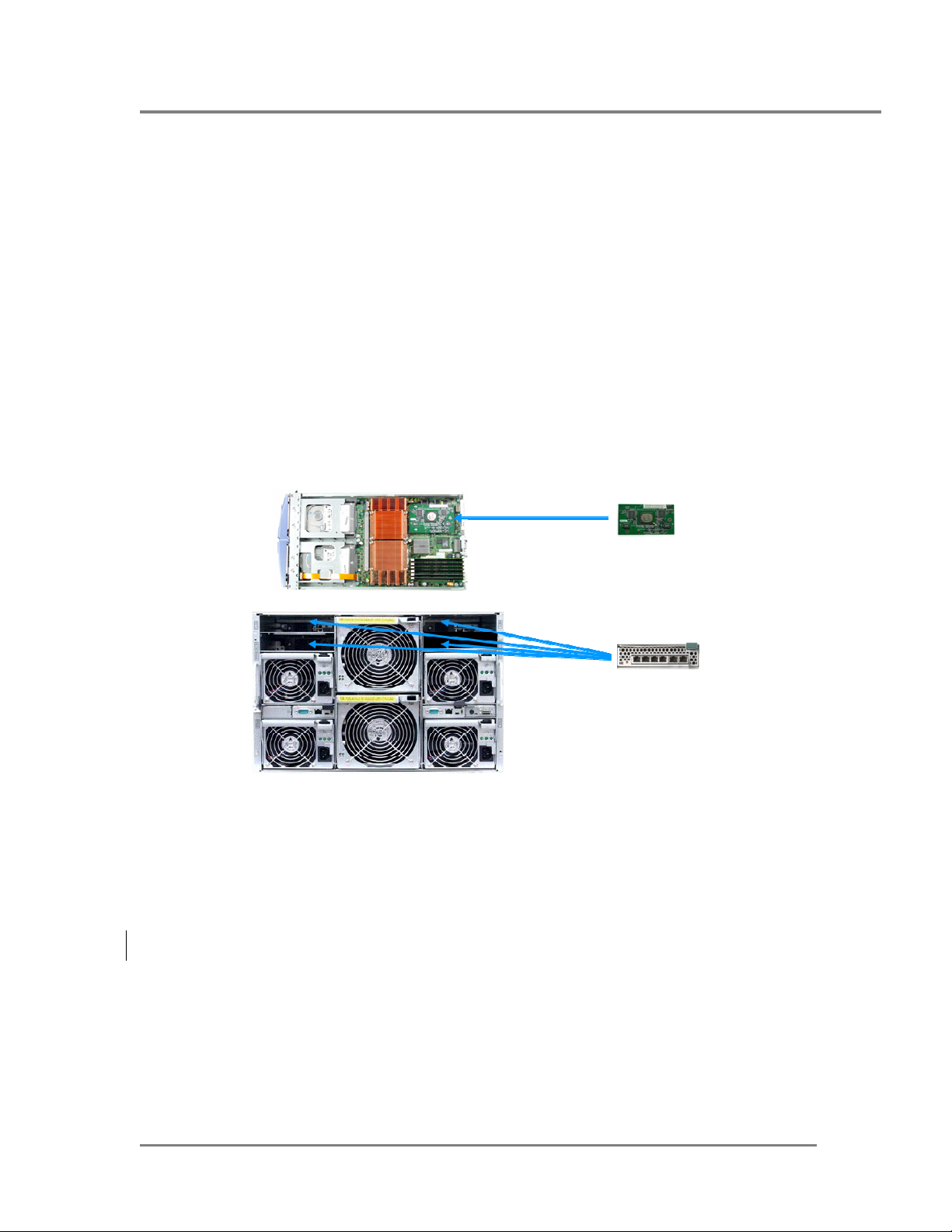
Figure 1 – PowerConnect 5316M configuration options
Dell PowerEdge 1855
Blade Server (top view)
Optional Intel Gigabit
Ethernet daughtercard
PowerConnect 5316M
The Dell Modular Server Enclosure can support one to four PowerConnect 5316M switch modules.
Modules in chassis I/O bays 1 and 2 connect to the embedded Ethernet controllers on the blade
(population of I/O bay 1 is required; population of I/O bay 2 is optional). Additionally, chassis I/O
bays 3 and 4 can also be populated if optional dual port GbE daughtercards are installed in the
blade servers.
This paper describes how to configure the Dell PowerConnect™ 5316M Gigabit Ethernet switch to
interoperate and connect with Cisco IOS
standard link aggregation groups (LAGs) that adhere to the IEE 802.3ad standard. Both static and
dynamic LAGs are discussed.
The table below shows some of the terms used to refer to LAGs in Dell and Cisco documentation.
This paper will use the term LAG.
Dell Modular Server Enclosure
(rear view)
2
and CatOS3 based switches when using industry
August 2005 Page 3 Dell Enterprise Product Group
Page 4
Dell PowerConnect Cisco IOS/Cat OS
Link Aggregation
Groups (LAGs)
EtherChannel
Fast EtherChannel (FEC)
Gigabit EtherChannel
(GEC)
port-channel Channeling
channel-group channel-group
The primary purpose of LAGs is to increase the overall bandwidth between two switches. This is
accomplished by effectively aggregating multiple ports together that act as a single, logical
connection between the two switches.
The IEEE 802.3ad standard based link aggregation implemented on the PowerConnect 5316M is
interoperable with Cisco Ether Channel using both static and dynamic configuration (dynamic via
LACP not the Cisco proprietary PAgP). Dell is a member of the University of New Hampshire
Interoperability Lab, where all PowerConnect products are tested to confirm interoperability with
other Consortium members. Included in these tests is link aggregation interoperability with other
Consortium members. Additional information regarding UNH’s link aggregation testing can be
found at:
ftp://ftp.iol.unh.edu/pub/bfc/testsuites/la.io.test.suite.pdf
Link aggregation can be configured as either dynamic or static. Dynamic configuration is
supported using the IEEE 802.3ad standard, which is known as Link Aggregation Control Protocol
(LACP). Static configuration is used when connecting the Dell PowerConnect 5316M Gigabit
Ethernet switch to an external Gigabit Ethernet switch that does not support LACP. One advantage
of LACP is that the protocol enables the Gigabit Ethernet switch to confirm that the external switch
is also configured for link aggregation. When using static configuration, a cabling or configuration
mistake involving the Dell PowerConnect 5316M or the external switch could go undetected and
thus can cause undesirable network behavior. Both static and dynamic LAGs (via LACP) can
detect physical link failures within the LAG and continue forwarding traffic through the other
connected links within that same LAG. LACP can also detect switch or port failures that do not
result in loss of link. This provides a more resilient LAG. Best practices suggest using dynamic
link aggregation instead of static link aggregation.
The examples shown below use the switches’ command line interfaces to configure the switches.
See the Dell™ PowerConnect™ 5316M Command Line Interface (CLI) Guide for more detailed
information. See the section “Port Channel Commands” for information on configuring LAGs via
the CLI.
August 2005 Page 4 Dell Enterprise Product Group
Page 5

If desired, any of the example configurations can be performed on the Dell PowerConnect 5316M
via the web based interface (WBI) as well. See the Dell PowerConnect 5316M Ethernet Switch Module
Userʹs Guide for a description of the Dell WBI. See the section “Defining LAG Parameters” for
information on configuring LAGs via the WBI. The Dell™ PowerConnect™ 5316M Command Line
Interface (CLI) Guide and the Dell PowerConnect 5316M Ethernet Switch Module Userʹs Guide are
located on the dell support website:
http://support.dell.com/support/edocs/network/PC5316M/en/index.htm.
Link Aggregation with Gigabit Ethernet Cisco Switches
The following examples show minimal configurations necessary to establish a LAG between a
Cisco IOS Gigabit Ethernet switch (Catalyst 3750), Cisco CatOS Ethernet switch (Catalyst 6509) and
the Dell PowerConnect 5316M. These commands work without issue when starting from a default
configuration of the switches.
To set the Dell PowerConnect 5316M to default configuration, use the following commands:
NOTE: This will erase any configuration data previously configured and reboot the switch.
5316M# delete startup-config
5316M# reload
To set a Cisco IOS based switch to default configuration, use the following commands:
NOTE: This will erase any configuration data previously configured and reboot the switch.
3750# delete flash:/config.text
3750# reload
To set a Cisco CatOS based switch (e.g. Catalyst 6509) to default configuration, use the following
commands:
NOTE: This will erase any configuration data previously configured and reboot the switch.
Cat_6509 (enable) clear config all
Please see other sections of this paper for cases when it is impractical to reset the switches to factory
defaults.
The Dell PowerConnect 5316M can support up to 8 different LAGs. A port channel can have from
zero to six of the external ports as members. Internal ports can not be members of a LAG. The
examples in this document show different numbers of ports in a LAG.
It is recommended that the ports to be aggregated on both the Cisco and Dell switches be
disconnected during configuration. This will avoid any network loops being formed before the
LAGs are set up.
August 2005 Page 5 Dell Enterprise Product Group
Page 6

Configuring the PowerConnect 5316M external ports for
Dynamic Link Aggregation
The following example shows the Dell PowerConnect 5316M Gigabit Ethernet switch commandline interface (CLI) commands for configuring the six external ports on the Gigabit Ethernet switch
for LACP.
5316M(config)# interface range ethernet g11-16
5316M(config-if)# channel-group 1 mode auto
The first command sets the CLI mode to configure the six external Gigabit Ethernet ports (referred
to in the command as g11-16, which stands for Gigabit Ethernet ports 11 through 16).
NOTE: All 6 ports do not have to be selected; a LAG can have 0-6 ports depending on the
requirements of the network network (i.e the more ports in the LAG, the more bandwidth and
more redundancy that is available). A LAG can even be configured without any member ports.
When ports are added to the LAG, they will be set to the configuration of the LAG.
The second command aggregates the six ports into a LAG (referred to in the command as
channel-group), which will use LACP (referred to in the command as mode auto). The ‘1’ for
the channel-group number only has meaning within the switch and is used to differentiate up to
eight unique channel-groups. For each LAG created, the user will need to choose a number
between one and eight, for up to the maximum of eight groups. Only the external ports (11-16) can
be part of a LAG
Configuring a Cisco IOS Gigabit Ethernet Switch for
Dynamic Link Aggregation
The following example shows the Cisco IOS switch CLI commands for configuring six ports for
LACP.
3750(config)# interface range GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 - 6
3750(config-if)# channel-protocol lacp
3750(config-if)# channel-group 1 mode active
The first command sets the CLI mode to configure six Gigabit Ethernet ports (referred to in the
command as Gigabit Ethernet 1/0/1 – 6, which stands for Gigabit Ethernet ports 1 through 6).
The second command sets ports to use LACP as the LAG protocol (and not PAgP). The third
command aggregates the six ports into a LAG (referred to in the command as channel-group),
which will use LACP (referred to in the command as mode active). The ‘1’ for the channelgroup number only has meaning within the switch and is used to differentiate unique channelgroups
August 2005 Page 6 Dell Enterprise Product Group
Page 7

Configuring a Cisco CatOS Gigabit Ethernet Switch for
Dynamic Link Aggregation
The following example shows the Cisco CatOS switch CLI commands for configuring six ports for
LACP.
Cat_6509(enable) set channelprotocol lacp 2
Cat_6509(enable) set port lacp-channel 2/1-6 mode active
The first command sets the LAG dynamic protocol to LACP on module 2 (module 2 just happens to
be the module that is in the switch used to validate the examples in this paper. Your switch may be
configured differently). The second command aggregates six ports on module 2 (referred to in the
command as 2/1–6, which stands for ports 1 through 6 on module 2) into a LAG (referred to in
the command as lacp-channel), which will use LACP (referred to in the command as mode
active).
NOTE: Only the Cisco “mode active” is supported for LACP interoperability with the
PowerConnect 5316M. The other modes (passive, auto, on, desirable) should not be
used when using LACP between a Cisco switch and the PowerConnect 5316M. This is a common
mis-configuration error.
Confirming a successful Dynamic Link Aggregation
connection with the PowerConnect 5316M
The following example shows how the PowerConnect 5316M ‘show interfaces port-channel 1’
command can be used to assure that the 5316M has established a LAG and that the LAG is
connected.
5316M# show interface port-channel 1
Channel Ports
....... .....
ch1 Active: g(11-16)
The output of the command shows the ports g11-16 are ‘Active’. This confirms that there is
physical link on all ports in the LAG and that the 5316M has communicated with the Cisco switch
to successfully establish an aggregated link on ports g11-16 with LACP.
Confirming a successful Dynamic Link Aggregation
connection with Cisco IOS
The following example shows how the Cisco IOS ‘show interfaces port-channel 1
etherchannel’ command can be used to assure that the Cisco has established a LAG and that the
LAG is connected.
3750# show interfaces port-channel 1 etherchannel
August 2005 Page 7 Dell Enterprise Product Group
Page 8

Port-channel1 (Primary aggregator)
Age of the Port-channel = 00d:01h:11m:34s
Logical slot/port = 10/1 Number of ports = 6
HotStandBy port = null
Port state = Port-channel Ag-Inuse
Protocol = LACP
Ports in the Port-channel:
Index Load Port EC state No of bits
------+------+------+------------------+---------- 0 00 Gi1/0/1 Active 0
0 00 Gi1/0/2 Active 0
0 00 Gi1/0/3 Active 0
0 00 Gi1/0/4 Active 0
0 00 Gi1/0/5 Active 0
0 00 Gi1/0/6 Active 0
The output of the command shows the ports Gi1/0/1 through Gi1/0/6 are ‘Active’. This confirms
that there is physical link on all ports in the LAG and that the Cisco switch has communicated with
the PowerConnect 5316M switch to successfully establish an aggregated link on ports 1/0/1 through
1/0/6 with LACP.
Confirming a successful Dynamic Link Aggregation
connection with CISCO CatOS
The following example shows how the Cisco CatOS ‘show interfaces lacp-channel info’ command
can be used to assure that the Cisco switch has established a LAG and that the LAG is connected.
Cat_6509> (enable) show lacp-channel info
Chan Port Status Channel Admin Speed Duplex Vlan
id mode group
---- ----- ---------- -------------------- ----- ----- ------ --- 801 2/1 connected active 395 a-1Gb a-full 1
801 2/2 connected active 395 a-1Gb a-full 1
801 2/3 connected active 395 a-1Gb a-full 1
801 2/4 connected active 395 a-1Gb a-full 1
801 2/5 connected active 395 a-1Gb a-full 1
801 2/6 connected active 395 a-1Gb a-full 1
. . .
August 2005 Page 8 Dell Enterprise Product Group
Page 9

The output of the command shows the ports 2/1 through 2/6 Status is ‘connected’ and a
Channel mode of ‘active’. This confirms that there is physical link on all ports in the LAG and
that the Cisco switch has communicated with the PowerConnect 5316M switch to successfully
establish an aggregated link on ports 2/1 through 2/6 with LACP.
Configuring the PowerConnect 5316M external ports for
Static Link Aggregation
The following example shows the PowerConnect 5316M Gigabit Ethernet switch CLI commands
for configuring three external ports of the Gigabit Ethernet switch for static aggregation. Note that
a LAG can be configured with 0-6 ports (example is using 3), a port may only be part of a single
LAG:
5316M(config)# interface range ethernet g13-15
5316M(config-if)# channel-group 1 mode on
The first command sets the CLI mode to configure three external Gigabit Ethernet ports (g13-15).
The second command aggregates the three ports into a static LAG. Static LAGs do not use LACP
and are defined in the CLI by setting the channel-group mode to ‘mode on’. The ‘1’ for the
channel-group number only has meaning within the switch and is used to differentiate up to eight
unique channel-groups. For each LAG created, you will need to choose a number between one and
eight, for up to the maximum of eight groups. The internal ports that connect to the servers do not
support link aggregation groups.
Configuring a CISCO IOS Switch for Static Link
Aggregation
The following example shows the Cisco IOS CLI commands for configuring three ports of the Cisco
switch for static link aggregation.
3750(config)# interface range GigabitEthernet 1/0/9 - 11
3750(config-if)# channel-group 1 mode on
The first command sets the CLI mode to configure three Gigabit Ethernet ports (1/0/9 through
1/0/11). The second command aggregates the three ports into a static LAG. Static LAGs do not
use LACP and are defined in the Cisco CLI by setting the channel-group mode to ‘on’. The ‘1’ for
the channel-group number only has meaning within the switch and is used to differentiate channelgroups. The number of channel-groups supported by Cisco switches depends on the switch model.
Configuring a Cisco CatOS Switch for Static Link
Aggregation
August 2005 Page 9 Dell Enterprise Product Group
Page 10

Cisco CatOS CLI allows the configuration of static LAGs via the LACP or the PAgP CLI commands.
Both commands are shown below.
The following example shows the Cisco CatOS CLI LACP channelprotocol commands for
configuring three ports of the Cisco switch for static link aggregation.
Cat_6509(enable) set channelprotocol lacp 2
Cat_6509(enable) set port lacp-channel 2/1-6 mode on
The first command sets module 2 to use the LACP commands to configure LAGs. Since we are
defining a static LAG, the setting for the ‘channelprotocol’ does not matter (more on this below).
The second command configures the three Ethernet ports (2/9 through 2/11) into a static LAG.
Static LAGs do not use LACP and are defined in the Cisco CLI by setting the lacp-channel mode to
‘on’.
The following example shows the Cisco CatOS CLI PAgP channelprotocol commands for
configuring three ports of the Cisco switch for static link aggregation using the PAgP command.
Cat_6509(enable) set channelprotocol pagp 2
Cat_6509(enable) set port channel 2/1-6 mode on
The first command sets module 2 to use the PaGP commands to configure LAGs. As we mentioned
before, since we are defining a static LAG, the setting for the ‘channelprotocol’ does not
matter. The second command configures the three Ethernet ports (2/9 through 2/11) into a
static LAG. Static LAGs do not use PAgP and are defined in the Cisco CLI by setting the channel
mode to ‘on’.
The number of channel-groups supported by Cisco switches depends on the switch model.
Confirming a successful Static Link Aggregation
connection
Since LACP is not being used, only careful inspection of the Cisco and PowerConnect 5316M
configurations can confirm that a static LAG has been established. The following steps may be
helpful:
o Check cabling is to correct ports on both switches
o Check that all LAG ports have link
o Confirm via the Dell and Cisco switches’ “show running-config” commands, that the desired
ports are in the LAG
5316M# show running-config
3750# show running-config
August 2005 Page 10 Dell Enterprise Product Group
Page 11

Cat_6509(enable) show running-config
Link aggregation with Cisco Fast Ethernet Switches
Some customers have an investment in a Cisco Fast Ethernet (100Mbps) network. In this case the
customer may not want to incur the expense to replace their Cisco Fast Ethernet switches to match
the highest speed of the Dell PowerConnect 5316M, but they still want to have the most bandwidth
possible. Since the Dell PowerConnect 5316M supports auto-negotiation, there is nothing
additional that a customer has to do to connect aggregated links to a Cisco Fast Ethernet switch if
the Cisco switch’s link aggregation ports are also set to auto negotiation.
The ports in a Dell PowerConnect 5316M LAG are set to auto-negotiation by default. If the
negotiation setting of the LAG has been changed due to a previous configuration of the switch, use
the following command to set the LAG ports back to auto-negotiation:
5316M(config)# interface port-channel 1
5316M(config-if)# negotiation
To set the ports on a Cisco IOS switch to auto-negotiation, use the following commands:
2950(config)# interface range FastEthernet 0/1 - 3
2950(config-if)# speed auto
2950(config-if)# duplex auto
To set the ports on a Cisco CatOS switch to auto-negotiation, use the following command:
Cat_6509> (enable) set port speed 2/9-11 auto
If auto negotiation cannot be used, both the Dell PowerConnect LAG and the Cisco switch ports in
the LAG must be set to the same speed and duplex. One switch cannot be left in auto-negotiation
mode and the other forced to a certain speed and duplex or intermittent link failures may occur.
The Dell PowerConnect 5316M LAG can be forced to 100 Mbps with the following commands.
5316M(config)# interface port-channel 1
5316M(config-if)# no negotiation
5316M(config-if)# speed 100
In the example the LAG is referred to as “port-channel 1”. “no negotiation” means that there is no
auto negotiation on the ports in the LAG. “speed 100” sets all the ports in the LAG to 100Mbps.
Since this is a LAG configuration, and the 802.3ad standard requires all ports in a LAG to be full
duplex, it is not required (or allowed via the PowerConnect 5316M CLI) to set the duplex to full.
Duplex is set to full by default on LAG ports.
August 2005 Page 11 Dell Enterprise Product Group
Page 12

NOTE: This is different from the Cisco IOS and CatOS methods which would require that all the
ports in the LAG be configured to 100 Mbps and full duplex rather than setting the LAG to
100Mbps. Configuring all ports in a LAG to 100 Mbps and full duplex on the Dell PowerConnect
5316M would have no effect since the LAG configuration takes precedence. It is important to note
this distinction between the Dell CLI and the Cisco IOS and CatOS commands.
Use the following commands to set the ports on the Cisco IOS switch to 100Mbps and full duplex:
2950(config)# interface range FastEthernet 0/1 - 3
2950(config-if)# speed 100
2950(config-if)# duplex full
Use the following commands to set the ports on the Cisco CatOS switch to 100Mbps and full
duplex:
Cat_6509> (enable) set port speed 2/9-11 100
Cat_6509> (enable) set port duplex 2/9-11 full
Configuration Limitations
Ports to be aggregated must be configured so that they are compatible with the link aggregation
feature and with the partner switch they are to be connected to.
For the Dell PowerConnect 5316M the following limitations apply to aggregated ports. The
commands to remove the configuration are shown below each limitation.
• The port cannot have an IP address defined on it
5316M(config)# interface Ethernet g11
5316M(config-if)# no ip address
• The port cannot belong to another LAG
5316M(config)# interface Ethernet g11
5316M(config-if)# no channel-group
• The port cannot be a mirrored port
5316M(config)# interface Ethernet g11
5316M(config-if)# no port monitor gxx
• The port cannot have GVRP enabled
5316M(config)# interface Ethernet g11
5316M(config-if)# no gvrp enable
• The port cannot belong to an
5316M(config)# interface Ethernet g11
5316M(config-if)# no switchport access vlan
• The port cannot belong to a trunk VLAN (other than the default VLAN 1)
5316M(config)# interface Ethernet g11
5316M(config-if)# no switchport trunk native vlan
• The internal switch ports (g1-g10) cannot be part of a LAG
August 2005 Page 12 Dell Enterprise Product Group
access VLAN (other than the default VLAN, 1)
Page 13

CLI will prevent adding internal ports to a LAG
To check the configuration of the ports on the Dell PowerConnect 5316M use the ‘show runningconfig’ command and look at the “interface Ethernet gxx” configurations, where the “xx” indicates
the port number. In the following example, the “no gvrp enable” command would have to be
issued on port g11 before it could be added to a LAG.
5316M(config-if)# exit
5316M(config)# exit
5316M# show running-config
interface range ethernet g(13-16)
channel-group 1 mode on
exit
interface ethernet g11
gvrp enable
exit
Port configuration differences with Dell and CISCO
On the Dell PowerConnect 5316M, configurations for the LAG take precedence over the
configuration of the port. In the following example, port g11 is actually set to 100 Mbps (and not
set at 10 Mbps) because the LAG is set to 100 Mbps. If g11 is removed from the LAG, the port
configuration will be applied (g11 would be set to 10Mbps)
5316M# show running-config
interface port-channel 1
speed 100
no negotiation
exit
interface ethernet g11
speed 10
no negotiation
exit
interface range ethernet g(11,13-16)
channel-group 1 mode on
exit
On Cisco IOS and CatOS based switches, ports must be configured identically to be included in a
LAG.
August 2005 Page 13 Dell Enterprise Product Group
Page 14

Cisco IOS based switches may have the ‘desirable’ and ‘passive’ mode options for the LAG setting.
The PowerConnect 5316M does not support this implementation. Do not use the ‘desirable’ or
‘passive’ modes when configuring a LAG with a Dell PowerConnect switch. Only use the ‘active’
(for LACP) or ‘on’ (for static) modes.
Switches can only control the distribution of outgoing traffic on LAG ports. The PowerConnect
5316M has static distribution method based on source and destination MAC addresses to decide
which port or a LAG a packet will travel. For an in-depth discussion of this algorithm and network
design considerations, see the following article:
http://www.dell.com/downloads/global/power/ps2q05-20040286-Holmes-OE.pdf.
Cisco IOS and CatOS switches provide configuration options for changing the distribution of traffic
on LAG ports.
One of the following Cisco IOS command may be useful if poor performance on the LAG from the
Cisco IOS switch is observed. In the order listed, the commands will allow the user to configure the
switch to distribute packets to ports in a LAG based on: destination IP address, destination
Ethernet address, a combination of source and destination IP addresses, a combination of source
and destination Ethernet addresses, source IP address, or source Ethernet address.
3750(config)#port-channel load-balance dst-ip
3750(config)#port-channel load-balance dst-mac
3750(config)#port-channel load-balance src-dst-ip
3750(config)#port-channel load-balance src-dst-mac
3750(config)#port-channel load-balance src-ip
3750(config)#port-channel load-balance src-mac
One of the following Cisco CatOS command may be useful if poor performance on the LAG from
the Cisco CatOS switch is observed. In the order listed, the commands will allow the user to
configure the switch to distribute packets to ports in a LAG based on: destination IP address,
destination Ethernet address, a combination of source and destination IP addresses, a combination
of source and destination Ethernet addresses, source IP address, or source Ethernet address.
Cat_6509> (enable) set port channel all distribution ip destination
Cat_6509> (enable) set port channel all distribution mac destination
Cat_6509> (enable) set port channel all distribution ip both
Cat_6509> (enable) set port channel all distribution mac both
Cat_6509> (enable) set port channel all distribution ip source
Cat_6509> (enable) set port channel all distribution mac source
August 2005 Page 14 Dell Enterprise Product Group
Page 15

1
IOS:
Switch Ports Model SW Version SW Image
* 1 28 WS-C3750G-24TS 12.2(18)SE1 C3750-I5-M
2
CatOS:
WS-C6509 Software, Version NmpSW: 7.6(10)
Copyright (c) 1995-2004 by Cisco Systems
NMP S/W compiled on Oct 27 2004, 17:59:09
THIS WHITE PAPER IS FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY, AND MAY CONTAIN TYPOGRAPHICAL ERRORS
AND TECHNICAL INACCURACIES. THE CONTENT IS PROVIDED AS IS, WITHOUT EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND.
Dell, PowerEdge, and PowerConnect are trademarks of Dell Inc. Intel and Xeon are registered trademarks of Intel Corp.
Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this document to refer to either the entities claiming the marks and
names or their products. Dell disclaims proprietary interest in the marks and names of others.
©Copyright 2005 Dell Inc. All rights reserved. Reproduction in any manner whatsoever without the express written
permission of Dell Inc. is strictly forbidden. For more information, contact Dell.
Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
August 2005 Page 15 Dell Enterprise Product Group
 Loading...
Loading...