Page 1

Dell™ PowerEdge™ 2950 Systems
Hardware Owner’s Manual
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Page 2
Notes, Notices, and Cautions
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your computer.
NOTICE: A NOTICE indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss of data and tells you how to avoid the
problem.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury, or death.
____________________
Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
© 2006 Dell Inc. All rights reserved.
Reproduction in any manner whatsoever without the written permission of Dell Inc. is strictly forbidden.
Trademarks used in this text: Dell, the DELL logo, Inspiron, Dell Precision, Dimension, OptiPlex, Latitude, PowerEdge, P owerV ault, P owerApp,
PowerConnect, XPS, and Dell OpenManage are trademarks of Dell Inc.; Intel, Pentium, and Celeron are registered trademarks, and Xeon is a
trademark of Intel Corporation; Microsoft and Windows are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation; EMC is a registered trademark of
EMC Corporation.
Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this document to refer to either the entities claiming the marks and names or their products.
Dell Inc. disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names other than its own.
Model EMS01
January 2006
Page 3

Contents
1 About Your System. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Other Information You May Need . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Accessing System Features During Startup
Front-Panel Features and Indicators
Hard-Drive Indicator Codes
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Back-Panel Features and Indicators
Connecting External Devices
Power Indicator Codes
NIC Indicator Codes
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
LCD Status Messages
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Solving Problems Described by LCD Status Messages
Removing LCD Status Messages
System Messages
Warning Messages
Diagnostics Messages
Alert Messages
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
. . . . . . . . . . 27
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
2 Using the System Setup Program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Entering the System Setup Program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Responding to Error Messages
Using the System Setup Program
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
System Setup Options
Main Screen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
CPU Information Screen
Integrated Devices Screen
Serial Communication Screen
System Security Screen
Exit Screen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Contents 3
Page 4

System and Setup Password Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Using the System Password
Using the Setup Password
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Disabling a Forgotten Password
Baseboard Management Controller Configuration
Entering the BMC Setup Module
BMC Setup Module Options
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
3 Installing System Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Recommended Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Inside the System
Front Bezel
Removing the Front Bezel
Replacing the Front Bezel
Opening and Closing the System
Opening the System
Closing the System
Hard Drives
Before You Begin
Removing a Drive Blank
Installing a Drive Blank
Removing a Hot-Plug Hard Drive
Installing a Hot-Plug Hard Drive
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
4 Contents
Replacing a Hard-Drive Carrier
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Removing a Hard Drive From a Hard-Drive Carrier
Installing a SAS Hard Drive Into a SATAu Drive Carrier
Installing a SATA Hard Drive Into a SATA Drive Carrier
Installing a SATA Hard Drive and Interposer Card Into a
SATAu Hard-Drive Carrier
Power Supplies
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Removing a Power Supply
Replacing a Power Supply
Removing the Power Supply Blank
Installing the Power Supply Blank
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
. . . . . . . . . . 59
. . . . . . . . . . 60
Page 5

System Fans . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Removing a System Fan
Replacing a Cooling Fan
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Cooling Shroud
Removing the Cooling Shroud
Installing the Cooling Shroud
Fan Brackets
Removing the Fan Bracket
Replacing the Fan Bracket
SAS Controller Daughter Card
Installing a SAS Controller Daughter Card
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
SAS and SAS RAID Controller Daughter Card Cabling Guidelines
Removing a SAS Controller Daughter Card
RAID Battery
Configuring the Boot Device
Expansion Cards
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Installing a RAID Battery
Removing a RAID Battery
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Expansion Card Installation Guidelines
Installing an Expansion Card
Removing an Expansion Card
Expansion-Card Cage
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Removing the Expansion-Card Cage
Replacing the Expansion-Card Cage
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
. . . . . 72
Installing a RAC Card
Optical Drive
Removing the Optical Drive
Installing the Optical Drive
Diskette Drive
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Removing the Diskette Drive From the System
Installing the Diskette Drive Into the System
Removing the Diskette Drive From the Drive Carrier
Installing the Diskette Drive Into the Drive Carrier
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
. . . . . . . . . . . . 85
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Contents 5
Page 6

SCSI Tape Drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Removing and Installing an Internal SCSI Tape Drive
Removing and Replacing the Tape Drive Cable Retention Bracket
. . . . . . . . . . . 86
. . . . 88
System Memory
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
General Memory Module Installation Guidelines
Non-Optimal Memory Configurations
Memory Sparing Support
Memory Mirroring Support
Installing Memory Modules
Removing Memory Modules
Activating the Integrated NIC TOE
Processors
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Removing a Processor
Installing a Processor
System Battery
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Replacing the System Battery
Expansion-Card Riser Boards
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Removing the Left Expansion-Card Riser Board
Installing the Left Riser Board
Removing the Central Riser Board
Installing the Central Riser Board
Sideplane Board
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Removing the Sideplane Board
Installing the Sideplane Board
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
6 Contents
SAS Backplane Board
Removing the SAS Backplane Board
Installing the SAS Backplane Board
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Control Panel Assembly (Service-only Procedure)
Removing the Control Panel Assembly
Installing the Control Panel Assembly
System Board (Service-only Procedure)
Removing the System Board
Installing the System Board
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Page 7

4 Troubleshooting Your System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Safety First—For You and Your System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Start-Up Routine
Checking the Equipment
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Troubleshooting IRQ Assignment Conflicts
Troubleshooting External Connections
Troubleshooting the Video Subsystem
Troubleshooting the Keyboard
Troubleshooting the Mouse
Troubleshooting Basic I/O Functions
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Troubleshooting a Serial I/O Device
Troubleshooting a USB Device
Troubleshooting a NIC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Troubleshooting a Wet System
Troubleshooting a Damaged System
Troubleshooting the System Battery
Troubleshooting Power Supplies
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Troubleshooting System Cooling Problems
Troubleshooting a Fan
Troubleshooting System Memory
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Troubleshooting a Diskette Drive
Troubleshooting an Optical Drive
Troubleshooting an External SCSI Tape Drive
Troubleshooting a Hard Drive
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Troubleshooting a SAS or SAS RAID Controller Daughter Card
Troubleshooting Expansion Cards
Troubleshooting the Microprocessors
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
. . . . . . . 126
Contents 7
Page 8

5 Running the System Diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Using Server Administrator Diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
System Diagnostics Features
When to Use the System Diagnostics
Running the System Diagnostics
System Diagnostics Testing Options
Using the Custom Test Options
Selecting Devices for Testing
Selecting Diagnostics Options
Viewing Information and Results
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
6 Jumpers and Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
System Board Jumpers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
System Board Connectors
SAS Backplane Board Connectors
Sideplane Board Connectors
Expansion-Card Riser-Board Components and PCI Buses
Disabling a Forgotten Password
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
. . . . . . . . . . 142
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
7 Getting Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
8 Contents
Technical Assistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Online Services
AutoTech Service
Automated Order-Status Service
Technical Support Service
Dell Enterprise Training and Certification
Problems With Your Order
Product Information
Returning Items for Warranty Repair or Credit
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Page 9

Before You Call. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Contacting Dell
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
Index
Contents 9
Page 10

10 Contents
Page 11

About Your System
This section describes the physical, firmware, and software interface features that provide and ensure
the essential functioning of your system. The physical connectors on your system’s front and back
panels provide convenient connectivity and system expansion capability. The system firmware,
applications, and operating systems monitor the system and component status and alert you when a
problem arises. System conditions can be reported by any of the following:
• Front or back panel indicators
• System messages
• Warning messages
• Diagnostics messages
• Alert messages
This section describes each type of message, lists the possible causes, and provides steps to resolve
any problems indicated by a message. The system indicators and features are illustrated in this
section.
Other Information You May Need
CAUTION: The Product Information Guide provides important safety and regulatory information. Warranty
information may be included within this document or as a separate document.
• The
• The
• CDs included with your system provide documentation and tools for configuring and managing
• Systems management software documentation describes the features, requirements, installation,
• Operating system documentation describes how to install (if necessary), configure, and use the
• Documentation for any components you purchased separately provides information to configure
Rack Installation Guide
describes how to install your system into a rack.
Getting Started Guide
technical specifications.
your system.
and basic operation of the software.
operating system software.
and install these options.
or
Rack Installation Instructions
provides an overview of system features, setting up your system, and
included with your rack solution
About Your System 11
Page 12
• Updates are sometimes included with the system to describe changes to the system, software, and/or
documentation.
NOTE: Always check for updates on support.dell.com and read the updates first because they often
supersede information in other documents.
• Release notes or readme files may be included to provide last-minute updates to the system or
documentation or advanced technical reference material intended for experienced users or
technicians.
Accessing System Features During Startup
Table 1-1 describes keystrokes that may be entered during startup to access system features. If your
operating system begins to load before you enter the keystroke, allow the system to finish booting, and
then restart your system and try again.
Table 1-1. Keystrokes for Accessing System Features
Keystroke Description
<F2> Enters the System Setup program. See "Using the System Setup Program" on page 38.
<F10> Opens the utility partition, allowing you to run the system diagnostics. See "Running the
System Diagnostics" on page 131
<Ctrl+E> Enters the Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) Management Utility, which allows
access to the system event log (SEL). See the BMC User’s Guide for more information on
setup and use of BMC.
<Ctrl+C> Enters the SAS Configuration Utility. See your SAS adapter User’s Guide for more
information.
<Ctrl+R> Enters the RAID configuration utility, which allows you to configure an optional RAID card.
For more information, see the documentation for your RAID card.
<Ctrl+S> Option is displayed only if you have PXE support enabled through the System Setup Program
(see "Integrated Devices Screen" on page 42). This keystroke allows you to configure NIC
settings for PXE boot. For more information, see the documentation for your integrated NIC.
<Ctrl+D> If you have the optional Dell Remote Access Controller (DRAC), this keystroke allows access
to selected DRAC configuration settings. See the DRAC User’s Guide for more information
on setup and use of DRAC.
12 About Your System
Page 13
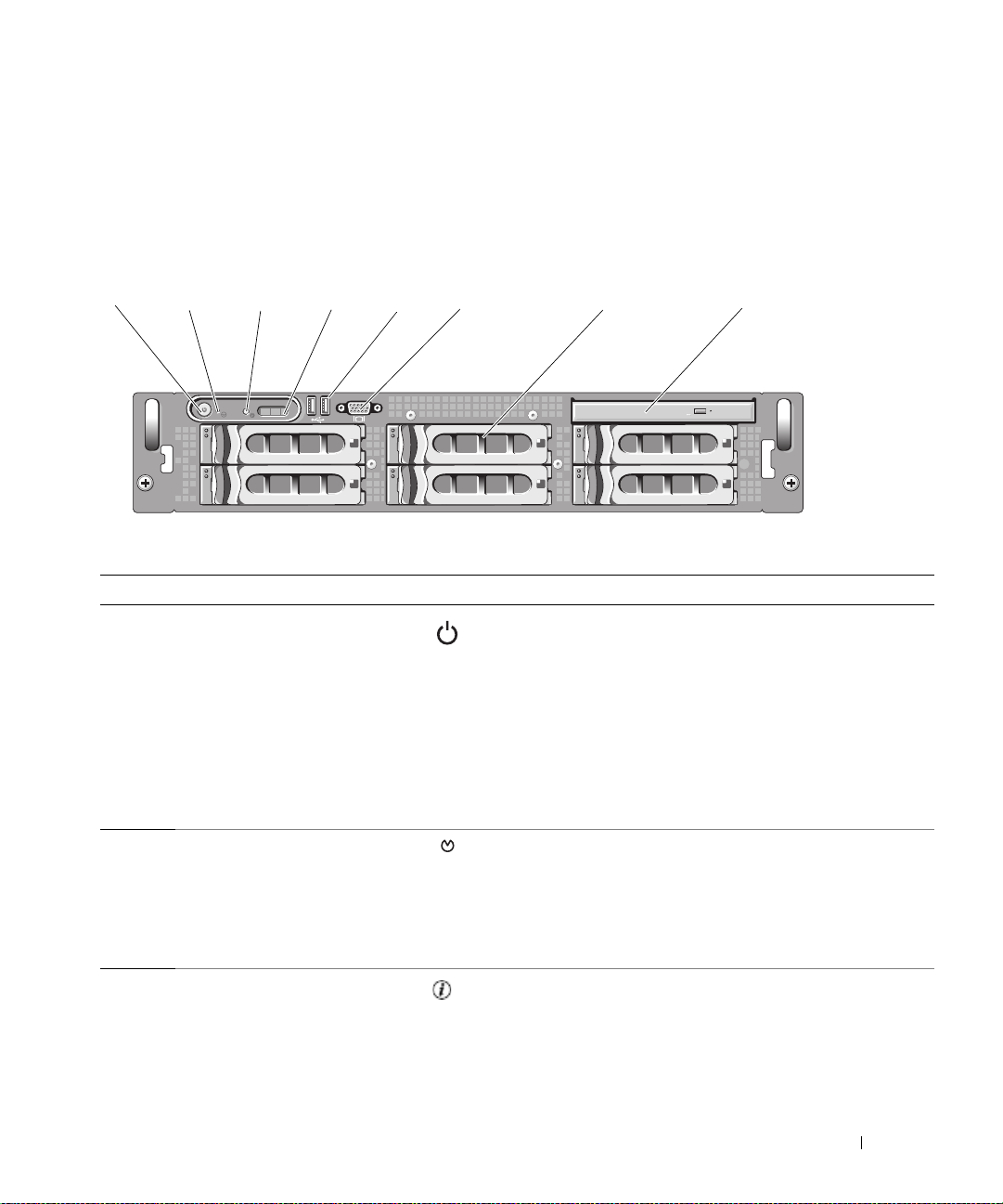
Front-Panel Features and Indicators
Figure 1-1 shows the controls, indicators, and connectors located behind the optional rack bezel on the
system's front panel.
Figure 1-1. Front-Panel Features and Indicators
654321 87
0 2
31
4
5
Table 1-2. Front-Panel LED Indicators, Buttons, and Connectors
Item Indicator, Button, or Connector Icon Description
1 Power-on indicator, power
button
The power-on indicator lights when the system power
is on.
The power button controls the DC power supply output
to the system.
NOTE: If you turn off the system using the power button
and the system is running an ACPI-compliant operating
system, the system performs a graceful shutdown before
the power is turned off. If the system is not running an
ACPI-compliant operating system, the power is turned off
immediately after the power button is pressed.
2 NMI button Used to troubleshoot software and device driver errors
when using certain operating systems. This button can
be pressed using the end of a paper clip.
Use this button only if directed to do so by qualified
support personnel or by the operating system's
documentation.
3 System identification button The identification buttons on the front and back panels
can be used to locate a particular system within a rack.
When one of these buttons is pushed, the LCD panel
on the front and the blue system status indicator on the
back blink until one of the buttons is pushed again.
About Your System 13
Page 14

Table 1-2. Front-Panel LED Indicators, Buttons, and Connectors (continued)
Item Indicator, Button, or Connector Icon Description
4 LCD panel Provides system ID, status information, and system error
messages.
The LCD lights during normal system operation. Both
the systems management software and the
identification buttons located on the front and back of
the system can cause the LCD to flash blue to identify a
particular system.
The LCD lights amber when the system needs
attention, and the LCD panel displays an error code
followed by descriptive text.
NOTE: If the system is connected to AC power and an
error has been detected, the LCD lights amber regardless
of whether the system has been powered on.
5 USB connectors (2) Connects USB 2.0-compliant devices to the system.
6 Video connector Connects a monitor to the system.
7 Hard drives (8) Eight 2.5-inch hot plug
OR
Six 3.5-inch hot plug
OR
Four 3.5-inch hot-plug
8 Optical drive (optional) One optional slimline IDE or DVD drive.
14 About Your System
Page 15

Hard-Drive Indicator Codes
The hard-drive carriers have two indicators—the drive-activity indicator and the drive-status indicator. See
Figure 1-2. In RAID configurations, the drive-status indicator lights to indicate the status of the drive. In
non-RAID configurations, only the drive-activity indicator lights; the drive-status indicator is off.
Figure 1-2. Hard-Drive Indicators
1
2
1 drive-status indicator (green
and amber)
2 green drive-activity indicator
About Your System 15
Page 16

Table 1-3 lists the drive indicator patterns for RAID hard drives. Different patterns are displayed as drive
events occur in the system. For example, if a hard drive fails, the "drive failed" pattern appears. After the
drive is selected for removal, the "drive being prepared for removal" pattern appears, followed by the "drive
ready for insertion or removal" pattern. After the replacement drive is installed, the "drive being prepared for
operation" pattern appears, followed by the "drive online" pattern.
NOTE: For non-RAID configurations, only the drive-activity indicator is active. The drive-status indicator is off.
Table 1-3. Hard-Drive Indicator Patterns for RAID
Condition Drive-Status Indicator Pattern
Identify drive/preparing for
removal
Drive ready for insertion or
removal
Drive predicted failure Blinks green, amber, and off.
Drive failed Blinks amber four times per second.
Drive rebuilding Blinks green slowly.
Drive online Steady green.
Rebuild aborted Blinks green three seconds, amber three seconds, and off six seconds.
Blinks green two times per second
Off
16 About Your System
Page 17

Back-Panel Features and Indicators
Figure 1-3 shows the controls, indicators, and connectors located on the system's back panel.
Figure 1-3. Back-Panel Features and Indicators
3
13 12
1 center PCI riser (slot 1) 2 left PCI riser (slot 2) 3 left PCI riser (slot 3)
4 power supplies (2) 5 system identification button 6 system status indicator
7 system status indicator
connector
10 USB connectors (2) 11 video connector 12 serial connector
13 remote access controller
(optional)
11 10 9 8 7 56
8 NIC2 connector 9 NIC1 connector
41 2
Connecting External Devices
When connecting external devices to your system, follow these guidelines:
• Most devices must be connected to a specific connector and device drivers must be installed before the
device operates properly. (Device drivers are normally included with your operating system software or
with the device itself.) See the documentation that accompanied the device for specific installation
and configuration instructions.
• Always attach external devices while your system and the device are turned off. Next, turn on any
external devices before turning on the system (unless the documentation for the device specifies
otherwise).
For information about individual connectors, see "Jumpers and Connectors" on page 135. For information
about enabling, disabling, and configuring I/O ports and connectors, see "Using the System Setup Program"
on page 37.
About Your System 17
Page 18

Power Indicator Codes
The power button on the front panel controls the power input to the system's power supplies. The power
indicator lights green when the system is on.
The indicators on the redundant power supplies show whether power is present or whether a power fault
has occurred (see Figure 1-4). Table 1-4 lists the power supply indicator codes.
Table 1-4. Redundant Power Supply Indicators
Indicator Function
Power supply status Green indicates that the power supply is operational.
Power supply fault Amber indicates a problem with the power supply.
AC line status Green indicates that a valid AC source is connected to the power supply.
Figure 1-4. Redundant Power Supply Indicators
1
2
3
1 power supply status 2 power supply fault 3 AC line status
18 About Your System
Page 19
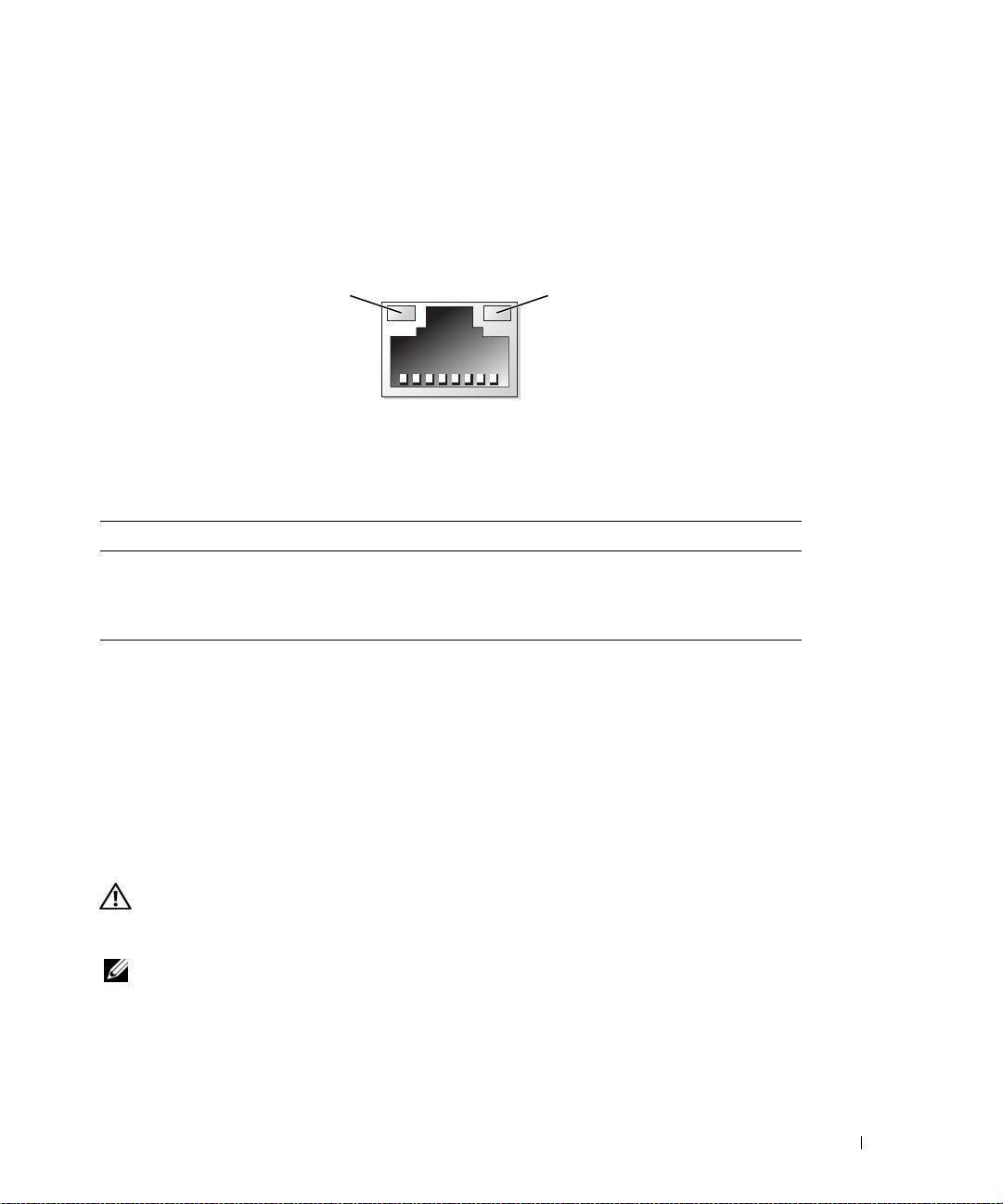
NIC Indicator Codes
Each NIC on the back panel has an indicator that provides information on network activity and link status.
See Figure 1-5. Table 1-5 lists the NIC indicator codes.
Figure 1-5. NIC Indicators
1
1 link indicator 2 activity indicator
Table 1-5. NIC Indicator Codes
Indicator Indicator Code
Link and activity indicators are off The NIC is not connected to the network.
Link indicator is green The NIC is connected to a valid link partner on the network.
Activity indicator is amber blinking Network data is being sent or received.
2
LCD Status Messages
The system's control panel LCD provides status messages to signify when the system is operating
correctly or when the system needs attention.
The LCD lights blue to indicate a normal operating condition, and lights amber to indicate an error
condition. The LCD scrolls a message that includes a status code followed by descriptive text. Table 1-6
lists the LCD status messages that can occur and the probable cause for each message. The LCD
messages refer to events recorded in the System Event Log (SEL). For information on the SEL and
configuring system management settings, see the systems management software documentation.
CAUTION: Only trained service technicians are authorized to remove the system cover and access any of the
components inside the system. See your Product Information Guide for complete information about safety
precautions, working inside the computer, and protecting against electrostatic discharge.
NOTE: If your system fails to boot, press the System ID button for at least five seconds until an error code appears
on the LCD. Record the code, then see "Getting Help" on page 147.
About Your System 19
Page 20

Table 1-6. LCD Status Messages
Code Text Causes Corrective Actions
N/A
E1000 FAILSAFE, Call
E1114 Temp Ambient Ambient system temperature is
E1116 Temp Memory Memory has exceeded acceptable
E12
E1210 CMOS Batt CMOS battery is missing, or the
E1211 ROMB Batt RAID battery is either missing,
E1229 CPU # VCORE Processor # VCORE voltage
E1310 RPM Fan ## RPM of specified cooling fan is
E1313 Fan Redundancy The system is no longer fan-
SYSTEM NAME
Support
nn xx
A 62-character string that can be
defined by the user in the System
Setup program.
SYSTEM NAME
The
under the following conditions:
• The system is powered on.
• The power is off and active
POST errors are displayed.
out of acceptable range.
temperature and has been
disabled to prevent damage to the
components.
PwrGd Specified voltage regulator has
failed.
voltage is out of acceptable range.
bad, or unable to recharge due to
thermal issues.
regulator has failed.
out of acceptable operating range.
redundant. Another fan failure
will put the system at risk of overheating.
displays
This message is for information
only.
You can change the system ID
and name in the System Setup
program. See "Using the System
Setup Program" on page 37.
See "Getting Help" on page 147.
See "Troubleshooting System
Cooling Problems" on page 119.
See "Troubleshooting System
Cooling Problems" on page 119.
See "Getting Help" on page 147.
See "Troubleshooting the System
Battery" on page 118.
Reseat the RAID battery
connector. See "RAID Battery" on
page 74, and "Troubleshooting
System Cooling Problems" on
page 119.
See "Getting Help" on page 147.
See "Troubleshooting System
Cooling Problems" on page 119.
Check control panel LCD for
additional scrolling messages. See
"Troubleshooting System Cooling
Problems" on page 119.
20 About Your System
Page 21

Table 1-6. LCD Status Messages (continued)
Code Text Causes Corrective Actions
E1410 CPU # IERR Specified microprocessor is
reporting an internal error.
E1414 CPU # Thermtrip Specified microprocessor is out of
acceptable temperature range and
has halted operation.
See your system’s Information
Update Tech Sheet located on
support.dell.com for the most
current system information. If
problem persists, see "Getting
Help" on page 147.
See "Troubleshooting System
Cooling Problems" on page 119.
If the problem persists, ensure
that the microprocessor heat
sinks are properly installed. See
"Troubleshooting the
Microprocessors" on page 128.
NOTE: The LCD continues to
display this message until the
system’s power cord is
disconnected and reconnected to
the AC power source, or the SEL is
cleared using either Server
Assistant or the BMC Management
Utility. See the Dell OpenManage
Baseboard Management
Controller User’s Guide for
information about these utilities.
E1418 CPU # Presence Specified processor is missing or
bad, and the system is in an
unsupported configuration.
E141C CPU Mismatch Processors are in a configuration
unsupported by Dell.
E141F CPU Protocol The system BIOS has reported a
processor protocol error.
E1420 CPU Bus PERR The system BIOS has reported a
processor bus parity error.
E1421 CPU Init The system BIOS has reported a
processor initialization error.
See "Troubleshooting the
Microprocessors" on page 128.
Ensure that your processors
match and conform to the type
described in the Microprocessor
Technical Specifications outlined
in your system’s Getting Started
Guide.
See "Getting Help" on page 147.
See "Getting Help" on page 147.
See "Getting Help" on page 147.
About Your System 21
Page 22

Table 1-6. LCD Status Messages (continued)
Code Text Causes Corrective Actions
E1422 CPU Machine Chk The system BIOS has reported a
machine check error.
E1610 PS # Missing No power is available from the
specified power supply; specified
power supply is improperly
installed or faulty.
E1614 PS # Status No power is available from the
specified power supply; specified
power supply is improperly
installed or faulty.
E1618 PS # Predictive Power supply voltage is out of
acceptable range; specified power
supply is improperly installed or
faulty.
E161C PS # Input Lost Power source for specified power
supply is unavailable, or out of
acceptable range.
E1620 PS # Input Range Power source for specified power
supply is unavailable, or out of
acceptable range.
E1624 PS Redundancy The power supply subsystem is no
longer redundant. If the last
supply fails, the system will go
down.
E1710 I/O Channel Chk The system BIOS has reported an
I/O channel check.
See "Getting Help" on page 147.
See "Troubleshooting Power
Supplies" on page 118.
See "Troubleshooting Power
Supplies" on page 118.
See "Troubleshooting Power
Supplies" on page 118.
Check the AC power source for
the specified power supply. If
problem persists, see
"Troubleshooting Power Supplies"
on page 118.
Check the AC power source for
the specified power supply. If
problem persists, see
"Troubleshooting Power Supplies"
on page 118.
See "Troubleshooting Power
Supplies" on page 118.
See "Getting Help" on page 147.
22 About Your System
Page 23

Table 1-6. LCD Status Messages (continued)
Code Text Causes Corrective Actions
E1711 PCI PERR B## D##
F##
PCI PERR Slot #
The system BIOS has reported a
PCI parity error on a component
that resides in PCI configuration
space at bus ##, device ##,
function ##.
The system BIOS has reported a
PCI parity error on a component
that resides in the specified PCI
slot.
Remove and reseat the PCI
expansion cards. If the problem
persists, see "Troubleshooting
Expansion Cards" on page 127.
Reinstall the expansion-card cage.
See "Expansion-Card Cage" on
page 78.
If the problem persists, the riser
card or system board is faulty. See
"Getting Help" on page 147.
E1712 PCI SERR B## D##
F##
PCI SERR Slot #
The system BIOS has reported a
PCI system error on a component
that resides in PCI configuration
space at bus ##, device ##,
function ##.
The system BIOS has reported a
PCI system error on a component
that resides in the specified slot.
Remove and reseat the PCI
expansion cards. If the problem
persists, see "Troubleshooting
Expansion Cards" on page 127.
Reinstall the expansion-card cage.
See "Expansion-Card Cage" on
page 78.
If the problem persists, the riser
card or system board is faulty. See
"Getting Help" on page 147.
E1714 Unknown Err The system BIOS has determined
See "Getting Help" on page 147.
that there has been an error in the
system, but is unable to
determine its origin.
E171F PCIE Fatal Err
B## D## F##
PCIE Fatal Err
Slot #
The system BIOS has reported a
PCIe fatal error on a component
that resides in PCI configuration
space at bus ##, device ##,
function ##.
The system BIOS has reported a
PCIe fatal error on a component
that resides in the specified slot.
Remove and reseat the PCI
expansion cards. If the problem
persists, see "Troubleshooting
Expansion Cards" on page 127.
Reinstall the expansion-card cage.
See "Expansion-Card Cage" on
page 78.
If the problem persists, the riser
card or system board is faulty. See
"Getting Help" on page 147.
E1810 HDD ## Fault The SAS subsystem has
determined that hard drive ##
has experienced a fault.
See "Troubleshooting a Hard
Drive" on page 124.
About Your System 23
Page 24

Table 1-6. LCD Status Messages (continued)
Code Text Causes Corrective Actions
E1811 HDD ## Rbld Abrt The specified hard drive has
experienced a rebuild abort.
E1812 HDD ## Removed The specified hard drive has been
removed from the system.
E1913 CPU & Firmware
Mismatch
E1A11 PCI Rsr Config PCI risers are not configured
E1A12 PCI Rsr Missing One or all of the PCI risers is
E1A14 SAS Cable A SAS cable A is missing or bad. Reseat the cable. If problem
E1A15 SAS Cable B SAS cable B is missing or bad. Reseat the cable. If problem
E2010 No Memory No memory is installed in the
E2011 Mem Config Err Memory detected, but is not
E2012 Unusable Memory Memory is configured, but not
E2013 Shadow BIOS Fail The system BIOS failed to copy
E2014 CMOS Fail CMOS failure. CMOS RAM not
E2015 DMA Controller DMA controller failure. See "Getting Help" on page 147.
The BMC firmware does not
support the CPU.
correctly; some invalid
configurations may prevent the
system from powering on.
missing, preventing the system
from powering on.
system.
configurable. Error detected
during memory configuration.
usable. Memory subsystem
failure.
its flash image into memory.
functioning properly.
See "Troubleshooting a Hard
Drive" on page 124. If the
problem persists, see your RAID
documentation.
Information only.
Update to the latest BMC
firmware. See the BMC User’s
Guide for more information on
setup and use of BMC.
See "Expansion-Card Riser
Boards" on page 98.
Information only.
persists, replace cable. See "SAS
Controller Daughter Card" on
page 69.
persists, replace cable. See "SAS
Controller Daughter Card" on
page 69.
Install memory. See "Installing
Memory Modules" on page 90.
See "Troubleshooting System
Memory" on page 120.
See "Troubleshooting System
Memory" on page 120.
See "Troubleshooting System
Memory" on page 120.
See "Getting Help" on page 147.
24 About Your System
Page 25

Table 1-6. LCD Status Messages (continued)
Code Text Causes Corrective Actions
E2016 Int Controller Interrupt controller failure. See "Getting Help" on page 147.
E2017 Timer Fail Timer refresh failure. See "Getting Help" on page 147.
E2018 Prog Timer Programmable interval timer
error.
E2019 Parity Error Parity error. See "Getting Help" on page 147.
E201A SIO Err SIO failure. See "Getting Help" on page 147.
E201B Kybd Controller Keyboard controller failure. See "Getting Help" on page 147.
E201C SMI Init System management interrupt
(SMI) initialization failure.
E201D Shutdown Test BIOS shutdown test failure. See "Getting Help" on page 147.
E201E POST Mem Test BIOS POST memory test failure. See "Troubleshooting System
E201F DRAC Config Dell remote access controller
(DRAC) configuration failure.
E2020 CPU Config CPU configuration failure. Check screen for specific error
E2021 Memory
Population
E2022 POST Fail General failure after video. Check screen for specific error
E2110 MBE Crd # DIMM ##
& ##
Incorrect memory configuration.
Memory population order
incorrect.
One of the DIMMs in the set
implicated by "## & ##" has
had a memory multi-bit error
(MBE). If no memory card is
present, the "Crd #" string is left
out of the message.
See "Getting Help" on page 147.
See "Getting Help" on page 147.
Memory" on page 120. If problem
persists, see "Getting Help" on
page 147.
Check screen for specific error
messages.
Ensure that DRAC cables and
connectors are properly seated. If
problem persists, see your DRAC
documentation.
messages.
Check screen for specific error
messages. See "Troubleshooting
System Memory" on page 120.
messages.
See "Troubleshooting System
Memory" on page 120.
About Your System 25
Page 26

Table 1-6. LCD Status Messages (continued)
Code Text Causes Corrective Actions
E2111 SBE Log Disable
Crd # DIMM ##
E2112 Mem Spare Crd #
DIMM ##
E2113 Mem Mirror Crd #
DIMM ## & ##
E2118 Fatal NB Mem CRC One of the connections in the
E2119 Fatal SB Mem CRC One of the connections in the
I1910 Intrusion System cover has been removed. Information only.
I1911 >3 ERRs Chk Log LCD overflow message.
The system BIOS has disabled
memory single-bit error (SBE)
logging, and will not resume
logging further SBEs until the
system is rebooted. "##"
represents the DIMM implicated
by the BIOS. If no memory riser
card is present, the "Crd #" string
is left out of the message.
The system BIOS has spared the
memory because it has
determined that the memory had
too many errors. "## & ##"
represents the DIMM pair
implicated by the BIOS. If no
memory card is present, the "Crd
#" string is left out of the
message.
The system BIOS has disabled
memory mirroring because it has
determined that one half of the
mirror has had too many errors.
"## & ##" represents the
DIMM pair implicated by the
BIOS. If no memory card is
present, the "Crd #" string is left
out of the message.
Fully Buffered DIMM (FBD)
memory subsystem link on the
Northbound side has failed.
FBD memory subsystem link on
the Southbound side has failed.
A maximum of three error
messages can display sequentially
on the LCD. The fourth message
displays as the standard overflow
message.
See "Troubleshooting System
Memory" on page 120.
See "Troubleshooting System
Memory" on page 120.
See "Troubleshooting System
Memory" on page 120.
See "Troubleshooting System
Memory" on page 120.
See "Troubleshooting System
Memory" on page 120.
Check the SEL for details on the
events.
26 About Your System
Page 27

Table 1-6. LCD Status Messages (continued)
Code Text Causes Corrective Actions
I1912 SEL Full System Event Log is full of
events, and is unable to log any
more events.
W1228 ROMB Batt < 24hr Warns predictively that the RAID
battery has less than 24 hours of
charge left.
Clear the log by deleting event
entries.
Replace RAID battery. See "RAID
Battery" on page 74.
NOTE: For the full name of an abbreviation or acronym used in this table, see the "Glossary" on page 169.
Solving Problems Described by LCD Status Messages
The code and text on the LCD can often specify a very precise fault condition that is easily corrected. For
example, if the code
E1418 CPU_1_Presence appears, you know that a microprocessor is not installed
in socket 1.
In contrast, you might be able to determine the problem if multiple related errors occur. For example, if
you receive a series of messages indicating multiple voltage faults, you might determine that the problem
is a failing power supply.
Removing LCD Status Messages
For faults associated with sensors, such as temperature, voltage, fans, and so on, the LCD message is
automatically removed when that sensor returns to a normal state. For example, if temperature for a
component goes out of range, the LCD displays the fault; when the temperature returns to the
acceptable range, the message is removed from the LCD. For other faults, you must take action to
remove the message from the display:
• Clear the SEL — You can perform this task remotely, but you will lose the event history for the
system.
• Power cycle — Turn off the system and disconnect it from the electrical outlet; wait approximately
ten seconds, reconnect the power cable, and restart the system.
Any of these actions will remove fault messages, and return the status indicators and LCD colors to the
normal state. Messages will reappear under the following conditions:
• The sensor returns to a normal state but fails again, resulting in a new SEL entry.
• The system is reset and new error events are detected.
• A failure is recorded from another source that maps to the same display entry.
About Your System 27
Page 28

System Messages
System messages appear on the screen to notify you of a possible problem with the system. Table 1-3 lists
the system messages that can occur and the probable cause and corrective action for each message.
NOTE: If you receive a system message that is not listed in Table 1-3, check the documentation for the application
that is running when the message appears or the operating system's documentation for an explanation of the
message and recommended action.
CAUTION: Only trained service technicians are authorized to remove the system cover and access any of the
components inside the system. See your Product Information Guide for complete information about safety
precautions, working inside the computer, and protecting against electrostatic discharge.
Table 1-7. System Messages
Message Causes Corrective Actions
Alert! Redundant memory
disabled! Memory
configuration does not
support redundant memory.
Attempting to update
Remote Configuration.
Please wait...
BIOS Update Attempt
Failed!
Caution! NVRAM_CLR jumper
is installed on system
board.
CPUs with different cache
sizes detected!
Decreasing available
memory
DIMM pairs must be matched
in size, speed, and
technology. The following
DIMM pair is mismatched:
DIMM x and DIMM y.
Installed memory modules are not the
same type and size; faulty memory
module(s).
Remote Configuration request has
been detected and is being processed.
Remote BIOS update attempt failed. Retry the BIOS update. If problem
NVRAM_CLR jumper is installed.
CMOS has been cleared.
Microprocessors with different cache
sizes are installed.
Faulty or improperly installed memory
modules.
Mismatched or unmatched DIMMs
installed; faulty or improperly seated
memory module(s).
Ensure that all memory modules are of
the same type and size and that they are
properly installed. If the problem
persists, see "Troubleshooting System
Memory" on page 120.
Wait until the process is complete.
persists, see "Getting Help" on page 147.
Remove NVRAM_CLR jumper. See
Figure 6-1 for jumper location.
Ensure that all microprocessors have the
same cache size and that they are
properly installed. See "Processors" on
page 93.
See "Troubleshooting System Memory"
on page 120.
Ensure that all pairs of memory modules
are of the same type and size and that
they are properly installed. See "System
Memory" on page 89. If the problem
persists, see "Troubleshooting System
Memory" on page 120.
28 About Your System
Page 29

Table 1-7. System Messages (continued)
Message Causes Corrective Actions
DIMMs must be populated in
sequential order beginning
with slot 1. The following
DIMM is electrically
isolated: DIMM x.
DIMMs should be installed
in pairs. Pairs must be
matched in size, speed,
and technology.
Dual-rank DIMM paired with
Single-rank DIMM - The
following DIMM/rank has
been disabled by BIOS:
DIMM x Rank y
n
Diskette drive
failure
Diskette read failure Faulty or improperly inserted diskette
Diskette subsystem reset
failed
Drive not ready Diskette missing from or improperly
seek
The specified DIMM is inaccessible to
the system due to its location. DIMMs
must be populated in sequential order,
beginning with slot 1.
Mismatched or unmatched DIMMs
installed; faulty or improperly seated
memory module(s). The system will
operate in a degraded mode with
reduced ECC protection. Only
memory installed in channel 0 will be
accessible.
Mismatched DIMMs installed; faulty
memory module(s). The system has
detected a dual-rank DIMM paired
with a single-rank DIMM. The second
rank of the dual-rank DIMM will be
disabled.
Incorrect configuration settings in the
System Setup program.
Faulty or improperly installed diskette
drive.
Loose tape drive interface cable, or
loose power cable.
or tape drive.
Faulty or improperly installed diskette
or tape drive.
inserted in diskette drive.
Populate 2, 4, or 8 DIMMs sequentially
beginning with slot 1. See "System
Memory" on page 89.
Ensure that all pairs of memory modules
are of the same type and size and that
they are properly installed. See "System
Memory" on page 89. If the problem
persists, see "Troubleshooting System
Memory" on page 120.
Ensure that all pairs of memory modules
are of the same type and size and that
they are properly installed. See "System
Memory" on page 89. If the problem
persists, see "Troubleshooting System
Memory" on page 120.
Run the System Setup program to
correct the settings. See "Using the
System Setup Program" on page 37.
Replace the diskette. If the problem
persists, see "Troubleshooting a Diskette
Drive" on page 121.
Reseat tape drive interface cable, or
power cable. If the problem persists, see
"Troubleshooting a Diskette Drive" on
page 121.
Replace the diskette. See
"Troubleshooting a Diskette Drive" on
page 121.
Replace the diskette or tape. If the
problem persists, see "Troubleshooting a
Diskette Drive" on page 121.
Replace the diskette. If the problem
persists, see "Troubleshooting a Diskette
Drive" on page 121.
About Your System 29
Page 30

Table 1-7. System Messages (continued)
Message Causes Corrective Actions
Error: Incorrect memory
configuration. DIMMs must
be installed in pairs of
matched memory size,
speed, and technology.
Error: Memory failure
detected. Memory size
reduced. Replace the
faulty DIMM as soon as
possible.
!!*** Error: Remote Access
Controller initialization
failure*** RAC virtual USB
devices may not be
available...
FBD training error: The
following branch has been
disabled: Branch x
Gate A20 failure Faulty keyboard controller; faulty
General failure The operating system is unable to
Invalid NVRAM
configuration, Resource
Re-allocated
Keyboard Controller
failure
Manufacturing mode
detected
MEMBIST failure - The
following DIMM/rank has
been disabled by BIOS:
DIMM x Rank y
Mismatched or unmatched DIMMs
installed; faulty or improperly seated
memory module(s).
Faulty or improperly seated memory
module(s).
Remote Access Controller
initialization failure
The specified branch (channel pair)
contains DIMMs that are
incompatible with each other.
system board.
carry out the command.
System detected and corrected a
resource conflict.
Faulty keyboard controller; faulty
system board
System is in manufacturing mode. Reboot to take the system out of
Faulty memory module(s). See "Troubleshooting System Memory"
Ensure that all pairs of memory modules
are of the same type and size and that
they are properly installed. See "System
Memory" on page 89. If the problem
persists, see "Troubleshooting System
Memory" on page 120.
See "Troubleshooting System Memory"
on page 120.
Ensure that the Remote Access
Controller is properly installed. See
"Installing a RAC Card" on page 80.
Ensure that only Dell-qualified memory
is used. Dell recommends purchasing
memory upgrade kits directly from
www.dell.com or your Dell sales agent to
ensure compatibility.
See "Getting Help" on page 147.
This message is usually followed by
specific information. Note the
information, and take the appropriate
action to resolve the problem.
No action is required.
See "Getting Help" on page 147.
manufacturing mode.
on page 120.
30 About Your System
Page 31

Table 1-7. System Messages (continued)
Message Causes Corrective Actions
Memory address line
failure at
value
expecting
Memory double word logic
failure at
value
expecting
Memory odd/even logic
failure at
value
expecting
Memory write/read failure
address
at
expecting
Memory tests terminated by
keystroke.
No boot device available Faulty or missing optical/diskette
No boot sector on hard
drive
No timer tick interrupt Faulty system board. See “"Getting Help" on page 147."
Northbound merge error -
The following DIMM has
been disabled by BIOS:
DIMM x
Not a boot diskette No operating system on diskette. Use a bootable diskette.
address
address
address,
, read
value
, read
value
, read
value
read
value
value
Faulty or improperly installed memory
modules.
POST memory test terminated by
pressing the spacebar.
drive subsystem, hard drive, or harddrive subsystem, or no boot disk in
drive A.
Incorrect configuration settings in
System Setup program, or no
operating system on hard drive.
The specified DIMM was unable to
establish a successful data link with
the memory controller.
See "Troubleshooting System Memory"
on page 120.
Information only.
Use a bootable diskette, CD, or hard
drive. If the problem persists, see
"Troubleshooting a Diskette Drive" on
page 121, "Troubleshooting an Optical
Drive" on page 123, and
"Troubleshooting a Hard Drive" on
page 124. See "Using the System Setup
Program" on page 37 for information on
setting the order of boot devices.
Check the hard-drive configuration
settings in the System Setup program.
See "Using the System Setup Program"
on page 37. If necessary, install the
operating system on your hard drive. See
your operating system documentation.
See "Troubleshooting System Memory"
on page 120.
About Your System 31
Page 32

Table 1-7. System Messages (continued)
Message Causes Corrective Actions
PCIe Degraded Link Width
Error: Embedded
nn
Bus#
Expected Link Width is
Actual Link Width is
PCIe Degraded Link Width
Error: Slot
Expected Link Width is
Actual Link Width is
PCIe Training Error:
Embedded
Bus#
PCIe Training Error:
Slot
PCI BIOS failed to install PCI device BIOS (Option ROM)
Plug & Play Configuration
Error
Read fault
Requested sector not found
Remote configuration
update attempt failed
/Dev#nn/Func
n
nn
/Dev#nn/Funcn
n
n
n
n
Faulty or improperly installed PCIe
card in the specified slot.
n
Faulty or improperly installed PCIe
card in the specified slot.
n
Faulty or improperly installed PCIe
card in the specified slot.
checksum failure is detected during
shadowing.
Loose cables to expansion card(s);
faulty or improperly installed
expansion card(s).
Error encountered in initializing PCI
device; faulty system board.
The operating system cannot read
from the diskette or hard drive, the
system could not find a particular
sector on the disk, or the requested
sector is defective.
System unable to process Remote
Configuration request
Reseat the PCIe card in the specified
slot number. See "Expansion Cards" on
page 76. If the problem persists, see
"Getting Help" on page 147.
Reseat the PCIe card in the specified
slot number. See "Expansion Cards" on
page 76. If the problem persists, see
"Getting Help" on page 147.
Reseat the PCIe card in the specified
slot number. See "Expansion Cards" on
page 76. If the problem persists, see
"Getting Help" on page 147.
Reseat the expansion card(s). Ensure
that all appropriate cables are securely
connected to the expansion card(s). If
the problem persists, see
"Troubleshooting Expansion Cards" on
page 127.
Install the NVRAM_CLR jumper and
reboot the system. See Figure 6-1 for
jumper location. If the problem persists,
see "Troubleshooting Expansion Cards"
on page 127.
Replace the diskette. Ensure that the
diskette and hard drive cables are
properly connected. See
"Troubleshooting a USB Device" on
page 115, or "Troubleshooting a Hard
Drive" on page 124 for the appropriate
drive(s) installed in your system.
Retry Remote Configuration.
32 About Your System
Page 33

Table 1-7. System Messages (continued)
Message Causes Corrective Actions
ROM bad checksum = address Expansion card improperly installed or
faulty.
Sector not found
Seek error
Seek operation failed
Shutdown failure Shutdown test failure. See "Troubleshooting System Memory"
The amount of system
memory has changed
Time-of-day clock stopped Faulty battery or faulty chip. See "Troubleshooting the System
The following DIMM pair is
not compatible with the
memory controller: DIMM x
and DIMM y
The following DIMMs are
not compatible: DIMM x and
DIMM y
Time-of-day not set please run SETUP program
Faulty diskette or hard drive. See "Troubleshooting a Diskette Drive"
Memory has been added or removed
or a memory module may be faulty.
The specified DIMM(s) are
incompatible with the system.
The specified DIMM(s) are
incompatible with the system.
Incorrect Time or Date settings; faulty
system battery.
Reseat the expansion card(s). Ensure
that all appropriate cables are securely
connected to the expansion card(s). If
the problem persists, see
"Troubleshooting Expansion Cards" on
page 127.
on page 121, "Troubleshooting a USB
Device" on page 115, or
"Troubleshooting a Hard Drive" on
page 124 for the appropriate drive(s)
installed in your system.
on page 120.
If memory has been added or removed,
this message is informative and can be
ignored. If memory has not been added
or removed, check the SEL to determine
if single-bit or multi-bit errors were
detected and replace the faulty memory
module. See "Troubleshooting System
Memory" on page 120.
Battery" on page 118.
Ensure that only Dell-qualified memory
is used. Dell recommends purchasing
memory upgrade kits directly from
www.dell.com or your Dell sales agent to
ensure compatibility.
Ensure that only ECC FBD1 memory is
used. Dell recommends purchasing
memory upgrade kits directly from
www.dell.com or your Dell sales agent to
ensure compatibility.
Check the Time and Date settings. See
"Using the System Setup Program" on
page 37. If the problem persists, replace
the system battery. See "System Battery"
on page 96.
About Your System 33
Page 34

Table 1-7. System Messages (continued)
Message Causes Corrective Actions
Timer chip counter 2
failed
Unsupported CPU
combination
Unsupported CPU stepping
detected
Utility partition not
available
Warning! No micro code
update loaded for
processor 0
Warning: Embedded RAID
firmware is not present.
Warning: Embedded RAID
error.
Warning: The current
memory configuration is
not optimal. Dell
recommends a population of
2, 4, or 8 DIMMs. DIMMs
should be populated
sequentially starting in
slot 1.
Write fault Faulty diskette, optical/diskette drive
Write fault on selected
drive
Faulty system board. See "Getting Help" on page 147.
Microprocessor(s) is not supported by
the system.
The <F10> key was pressed during
POST, but no utility partition exists
on the boot hard drive.
Micro code update failed. Update the BIOS firmware. See "Getting
Embedded RAID firmware does not
respond.
Embedded RAID firmware responds
with an error.
System has detected a legal but nonoptimal population of DIMMs (for
example, 1 DIMM, 6 DIMMs,
4 DIMMs in slots 1, 2, 5, and 6, etc.).
The system will run with all memory
accessible but will experience suboptimal performance.
assembly, hard drive, or hard-drive
subsystem.
Install a supported microprocessor or
microprocessor combination. See
"Processors" on page 93.
Create a utility partition on the boot
hard drive. See the CDs that came with
your system.
Help" on page 147.
See the RAID controller documentation
for information about installing or
updating the RAID firmware.
See "Troubleshooting a SAS or SAS
RAID Controller Daughter Card" on
page 126. See the RAID controller
documentation for information about
installing or updating the RAID
firmware.
Populate 2, 4, or 8 DIMMs sequentially
beginning with slot 1. See "System
Memory" on page 89.
See "Troubleshooting a Diskette Drive"
on page 121, "Troubleshooting an
Optical Drive" on page 123, and
"Troubleshooting a Hard Drive" on
page 124.
NOTE: For the full name of an abbreviation or acronym used in this table, see the "Glossary" on page 169.
34 About Your System
Page 35

Warning Messages
A warning message alerts you to a possible problem and prompts you to respond before the system
continues a task. For example, before you format a diskette, a message will warn you that you may lose all
data on the diskette. Warning messages usually interrupt the task and require you to respond by typing
(yes) or
n (no).
NOTE: Warning messages are generated by either the application or the operating system. For more information,
see the documentation that accompanied the operating system or application.
Diagnostics Messages
When you run system diagnostics, an error message may result. Diagnostic error messages are not
covered in this section. Record the message on a copy of the Diagnostics Checklist in "Getting Help" on
page 147, and then follow the instructions in that section for obtaining technical assistance.
Alert Messages
Systems management software generates alert messages for your system. Alert messages include
information, status, warning, and failure messages for drive, temperature, fan, and power conditions. For
more information, see the systems management software documentation.
y
About Your System 35
Page 36

36 About Your System
Page 37

Using the System Setup Program
After you set up your system, run the System Setup program to familiarize yourself with your system
configuration and optional settings. Record the information for future reference.
You can use the System Setup program to:
• Change the system configuration stored in NVRAM after you add, change, or remove hardware
• Set or change user-selectable options—for example, the time or date
• Enable or disable integrated devices
• Correct discrepancies between the installed hardware and configuration settings
Entering the System Setup Program
1
Turn on or restart your system.
2
Press <F2> immediately after you see the following message:
<F2> = System Setup
If your operating system begins to load before you press <F2>, allow the system to finish booting,
and then restart your system and try again.
NOTE: To ensure an orderly system shutdown, see the documentation that accompanied your operating
system.
Responding to Error Messages
You can enter the System Setup program by responding to certain error messages. If an error message
appears while the system is booting, make a note of the message. Before entering the System Setup
program, see "System Messages" on page 28 for an explanation of the message and suggestions for
correcting errors.
NOTE: After installing a memory upgrade, it is normal for your system to send a message the first time you
start your system.
Using the System Setup Program 37
Page 38

Using the System Setup Program
Table 2-1 lists the keys that you use to view or change information on the System Setup program screens
and to exit the program.
Table 2-1. System Setup Program Navigation Keys
Keys Action
Up arrow or <Shift><Tab> Moves to the previous field.
Down arrow or <Tab> Moves to the next field.
Spacebar, <+>, <
right arrows
<Esc> Exits the System Setup program and restarts the
<F1> Displays the System Setup program
NOTE: For most of the options, any changes that you make are recorded but do not take effect until you restart the
system.
–>, left and
Cycles through the settings in a field. In many fields,
you can also type the appropriate value.
system if any changes were made.
's help file.
System Setup Options
Main Screen
When you enter the System Setup program, the main System Setup program screen appears (see
Figure 2-1).
38 Using the System Setup Program
Page 39

Figure 2-1. Main System Setup Program Screen
Table 2-2 lists the options and descriptions for the information fields that appear on the main System
Setup program screen.
NOTE: The options for the System Setup program change based on the system configuration.
NOTE: The System Setup program defaults are listed under their respective options, where applicable.
Table 2-2. System Setup Program Options
Option Description
System Time Resets the time on the system's internal clock.
System Date Resets the date on the system's internal calendar.
Memory Information Displays information related to installed system, video, and redundant memory,
including size, type, and speed.
CPU Information Displays information related to microprocessors (speed, cache size, and so on).
Enable or disable Hyper-Threading technology by changing the setting of the
Logical Processor option. See Table 2-3.
SATA Port X Displays type and capacity of SATA drive attached to Port X.
Using the System Setup Program 39
Page 40

Table 2-2. System Setup Program Options (continued)
Option Description
Boot Sequence Determines the order in which the system searches for boot devices during system
startup. Available options can include the diskette drive, CD drive, hard drives, and
network. If you have installed a RAC, additional options such as virtual floppy and
virtual CD-ROM may be present.
NOTE: System boot is not supported from an external device attached to a SAS or
SCSI adapter. See support.dell.com for the latest support information about booting
from external devices
USB Flash Drive Type
Auto
default)
(
Integrated Devices See Table 2-4.
PCI IRQ Assignment Displays a screen to change the IRQ assigned to each of the integrated devices on
Serial Communication Displays a screen to configure serial communication, external serial connector, fail-
Embedded Server
Management
System Security Displays a screen to configure the system password and setup password features.
Keyboard NumLock
(
On
default)
Report Keyboard Errors
Report
default)
(
Asset Tag Displays the customer-programmable asset tag number for the system if an asset
Determines the emulation type for a USB flash drive. Hard disk allows the USB
flash drive to act as a hard drive. Floppy allows the USB flash drive to act as a
removal diskette drive. Auto automatically chooses an emulation type.
the PCI bus, and any installed expansion cards that require an IRQ.
safe baud rate, remote terminal type, and redirection after boot.
Displays a screen to configure the front-panel LCD options and to set a userdefined LCD string.
See Table 2-6. For further information, see "Using the System Password" on page 45
and "Using the Setup Password" on page 47.
Determines whether your system starts up with the NumLock mode activated on
101- or 102-key keyboards (does not apply to 84-key keyboards).
Enables or disables reporting of keyboard errors during the POST. Select Report for
host systems that have keyboards attached. Select Do Not Report to suppress all
error messages relating to the keyboard or keyboard controller during POST. This
setting does not affect the operation of the keyboard itself if a keyboard is attached
to the system.
tag number has been assigned.
40 Using the System Setup Program
Page 41

CPU Information Screen
Table 2-3 lists the options and descriptions for the information fields that appear on the
screen.
Table 2-3. CPU Information Screen
Option Description
Bus Speed Displays the bus speed of the processors.
Logical Processor
(Enabled default)
Adjacent Cache Line
Prefetch
(Enabled default)
Virtualization Technology
(Disabled default)
Hardware Prefetcher
(Enabled default)
Demand-Based Power
Management
(Disabled default)
Processor X ID Displays the family and model number of each processor. A
Displays when the processors support HyperThreading. Enabled
permits all logical processors to be used by the operating system.
Only the first logical processor of each processor installed in the
system is used by the operating system if Disabled is selected.
Enables or disables optimal use of sequential memory access.
Disable this option for applications that require high use of random
memory access.
Displays when the processor(s) support Virtualization Technology.
Enabled permits virtualization software to utilize Virtualization
Technology functions incorporated in the processor design. This
feature can only be used by software that supports Virtualization
Technology.
Enables or disables the hardware prefetcher.
Enables or disables demand-based power management. When
enabled, the CPU Performance State tables will be reported to the
operating system; when disabled, the CPU Performance State
tables will not be reported to the operating system. If any of the
CPUs do not support demand-based power management, the field
will become read-only, and automatically set to Disabled.
submenu displays processor core speed, amount of level 2 cache,
and number of cores.
CPU Information
Using the System Setup Program 41
Page 42

Integrated Devices Screen
Table 2-4 lists the options and descriptions for the information fields that appear on the Integrated
Devices screen.
Table 2-4. Integrated Devices Screen Options
Option Description
Integrated SAS Controller
(Enabled default)
Embedded SATA (Off
default)
IDE CD-ROM Controller
(Auto default)
User Accessible USB Ports
(All Ports On default)
Embedded Gb NIC1
(Enabled with PXE
default)
MAC Address Displays the MAC address for the integrated 10/100/1000 NIC. This field does not
TOE Capability Displays the TCP/IP offload engine (TOE) feature status of the onboard NIC.
Embedded Gb NIC2
(Enabled with PXE
default)
MAC Address Displays the MAC address for the integrated 10/100/1000 NIC. This field does not
TOE Capability Displays the TCP/IP offload engine (TOE) feature status of the onboard NIC.
Diskette Controller
(Auto default)
Enables or disables the integrated SAS controller.
Allows the integrated SATA controller to be set to Off or ATA Mode.
Enables the integrated IDE controller. When set to Auto, each channel of the
integrated IDE controller is enabled if IDE devices are attached to the channel and
the external IDE controller is not detected.
NOTE: This CD-ROM option will not appear on this menu screen if your system does
not include this optional device.
Enables or disables the system’s user accessible USB ports. Options are All Ports
On, Only Back Ports On, and All Ports Off.
Enables or disables the system's integrated NIC. Options are Enabled without
PXE, Enabled with PXE, and Disabled. PXE support allows the system to boot
from the network. Changes take effect after the system reboots.
have user-selectable settings.
Enables or disables the system's integrated NIC. Options are Enabled without
PXE, Enabled with PXE, and Disabled. PXE support allows the system to boot
from the network. Changes take effect after the system reboots.
have user-selectable settings.
Enables or disables the system's diskette drive controller. When Auto is selected,
the system turns off the controller when necessary to accommodate a controller
card installed in an expansion slot. You can also configure the drive as Read-Only,
or Off. When using the Read-Only setting, the drive cannot be used to write to a
disk.
42 Using the System Setup Program
Page 43

Serial Communication Screen
Table 2-5 lists the options and descriptions for the information fields that appear on the Serial
Communication screen.
Table 2-5. Serial Communication Screen Options
Option Description
Serial Communication
(Off default)
Failsafe Baud Rate
(57600 default)
Remote Terminal Type
(VT 100/VT 220 default)
Redirection After Boot
(Enabled default)
Options are On with Console Redirection via COM2, and Off.
Displays the failsafe baud rate used for console redirection when
the baud rate cannot be negotiated automatically with the remote
terminal. This rate should not be adjusted.
Select either VT 100/VT 220 or ANSI.
Enables or disables BIOS console redirection after your system
boots to the operating system.
System Security Screen
Table 2-6 lists the options and descriptions for the information fields that appear on the System Security
screen.
Table 2-6. System Security Screen Options
Option Description
System Password Displays the current status of your system's password security feature and allows
you to assign and verify a new system password.
NOTE: See "Using the System Password" on page 45 for instructions on assigning a
system password and using or changing an existing system password.
Setup Password Restricts access to the System Setup program in the same way that you restrict
access to your system using the system password feature.
NOTE: See "Using the Setup Password" on page 47 for instructions on assigning a
setup password and using or changing an existing setup password.
Using the System Setup Program 43
Page 44

Table 2-6. System Security Screen Options (continued)
Option Description
Password Status Setting the Setup Password option to Enabled prevents the system password from
being changed or disabled at system start-up.
To lock the system password, assign a setup password in the Setup Password option
and then change the Password Status option to Locked. In this state, you cannot
change the system password using the System Password option and cannot be
disabled at system start-up by pressing <Ctrl><Enter>.
To unlock the system password, enter the setup password in the Setup Password
field and then change the Password Status option to Unlocked. In this state, you
can disable the system password at system start-up by pressing <Ctrl><Enter>
and then change the password using the System Password option.
Power Button
(
Enabled
default)
Turns system's power off and on.
• If you turn off the system using the power button and the system is running an
ACPI-compliant operating system, the system can perform an orderly shutdown
before power is turned off.
• If the system is not running an ACPI-compliant operating system, power is turned
off immediately after the power button is pressed.
The button is enabled in the System Setup program. When disabled, the button
can only turn on system power.
NOTE: You can still turn on the system by using the power button, even if the Power
Button option is set to Disabled.
NMI Button
(Disabled default)
AC Power Recovery
(Last default)
NOTICE: Use the NMI button only if directed to do so by qualified support
personnel or by the operating system's documentation. Pressing this button
halts the operating system and displays a diagnostic screen.
Sets the NMI feature On or Off.
Determines how the system reacts when power is restored to the system. If system
is set to Last, the system returns to the last power state. On turns on the system
after power is restored. When set to Off, the system remains off after power is
restored.
Exit Screen
After you press <Esc> to exit the System Setup program, the Exit screen displays the following options:
• Save Changes and Exit
• Discard Changes and Exit
• Return to Setup
44 Using the System Setup Program
Page 45

System and Setup Password Features
NOTICE: The password features provide a basic level of security for the data on your system. If your data requires
more security, use additional forms of protection, such as data encryption programs.
NOTICE: Anyone can access the data stored on your system if you leave the system running and unattended
without having a system password assigned or if you leave your system unlocked so that someone can disable the
password by changing a jumper setting.
Your system is shipped to you without the system password feature enabled. If system security is a
concern, operate your system only with system password protection.
To change or delete an existing password, you must know the password (see "Deleting or Changing an
Existing System Password" on page 47). If you forget your password, you cannot operate your system or
change settings in the System Setup program until a trained service technician changes the password
jumper setting to disable the passwords, and erases the existing passwords. This procedure is described in
"Disabling a Forgotten Password" on page 144.
Using the System Password
After a system password is assigned, only those who know the password have full use of the system.
When the System Password option is set to Enabled, the system prompts you for the system password
after the system starts.
Assigning a System Password
Before you assign a system password, enter the System Setup program and check the System Password
option.
When a system password is assigned, the setting shown for the System Password option is Enabled. If
the setting shown for the Password Status is Unlocked, you can change the system password. If the
Password Status option is Locked, you cannot change the system password. When the system password
feature is disabled by a jumper setting, the system password is Disabled, and you cannot change or enter
a new system password.
When a system password is not assigned and the password jumper on the system board is in the enabled
(default) position, the setting shown for the System Password option is Not Enabled and the Password
Status field is Unlocked. To assign a system password:
1
Verify that the
2
Highlight the
3
Type your new system password.
You can use up to 32 characters in your password.
Password Status
System Password
option is set to
option and press <Enter>.
Unlocked
.
As you press each character key (or the spacebar for a blank space), a placeholder appears in the field.
Using the System Setup Program 45
Page 46

The password assignment is not case-sensitive. However, certain key combinations are not valid. If you
enter one of these combinations, the system beeps. To erase a character when entering your password,
press <Backspace> or the left-arrow key.
NOTE: To escape from the field without assigning a system password, press <Enter> to move to another field,
or press <Esc> at any time prior to completing step 5.
4
Press <Enter>.
5
To confirm your password, type it a second time and press <Enter>.
The setting shown for the
System Password
changes to
Enabled
. Exit the System Setup program and
begin using your system.
6
Either reboot your system now for your password protection to take effect or continue working.
NOTE: Password protection does not take effect until you reboot the system.
Using Your System Password to Secure Your System
NOTE: If you have assigned a setup password (see "Using the Setup Password" on page 47), the system accepts
your setup password as an alternate system password.
When the Password Status option is set to Unlocked, you have the option to leave the password security
enabled or to disable the password security.
To leave the password security enabled:
1
Turn on or reboot your system by pressing <Ctrl><Alt><Del>.
2
Type your password and press <Enter>.
To disable the password security:
1
Turn on or reboot your system by pressing <Ctrl><Alt><Del>.
2
Type your password and press <Ctrl><Enter>.
When the Password Status option is set to Locked whenever you turn on your system or reboot your
system by pressing <Ctrl><Alt><Del>, type your password and press <Enter> at the prompt.
After you type the correct system password and press <Enter>, your system operates as usual.
If an incorrect system password is entered, the system displays a message and prompts you to re-enter
your password. You have three attempts to enter the correct password. After the third unsuccessful
attempt, the system displays an error message showing the number of unsuccessful attempts and that
the system has halted and will shut down. This message can alert you to an unauthorized person
attempting to use your system.
Even after you shut down and restart the system, the error message continues to be displayed until the
correct password is entered.
NOTE: You can use the Password Status option in conjunction with the System Password and Setup Password
options to further protect your system from unauthorized changes.
46 Using the System Setup Program
Page 47

Deleting or Changing an Existing System Password
1
When prompted, press <Ctrl><Enter> to disable the existing system password.
If you are asked to enter your setup password, contact your network administrator.
2
Enter the System Setup program by pressing <F2> during POST.
3
Select the
4
When prompted, type the system password.
5
Confirm that
Not Enabled
If
Enabled
System Security
screen field to verify that the
Not Enabled
is displayed for the
is displayed for the
is displayed for the
System Password
System Password
option, press the <Alt><b> key combination to restart
Password Status
System Password
option.
option is set to
option, the system password has been deleted. If
Unlocked
.
the system, and then repeat steps 2 through 5.
Using the Setup Password
Assigning a Setup Password
You can assign (or change) a setup password only when the Setup Password option is set to Not Enabled.
To assign a setup password, highlight the Setup Password option and press the <+> or <–> key. The
system prompts you to enter and verify the password. If a character is illegal for password use, the system
beeps.
NOTE: The setup password can be the same as the system password. If the two passwords are different, the setup
password can be used as an alternate system password. However, the system password cannot be used in place of
the setup password.
You can use up to 32 characters in your password.
As you press each character key (or the spacebar for a blank space), a placeholder appears in the field.
The password assignment is not case-sensitive. However, certain key combinations are not valid. If you
enter one of these combinations, the system beeps. To erase a character when entering your password,
press <Backspace> or the left-arrow key.
After you verify the password, the Setup Password setting changes to Enabled. The next time you enter
the System Setup program, the system prompts you for the setup password.
A change to the Setup Password option becomes effective immediately (restarting the system is not
required).
Operating With a Setup Password Enabled
If Setup Password is set to Enabled, you must enter the correct setup password before you can modify
most of the System Setup options. When you start the System Setup program, the program prompts you
to enter a password.
Using the System Setup Program 47
Page 48

If you do not enter the correct password in three attempts, the system lets you view, but not modify, the
System Setup screens—with the following exception: If System Password is not set to Enabled and is not
locked through the Password Status option, you can assign a system password (however, you cannot
disable or change an existing system password).
NOTE: You can use the Password Status option in conjunction with the Setup Password option to protect the
system password from unauthorized changes.
Deleting or Changing an Existing Setup Password
1
Enter the System Setup program and select the
2
Highlight the
<Enter> twice to clear the existing setup password.
The setting changes to
3
If you want to assign a new setup password, perform the steps in "Assigning a Setup Password" on
page 47.
Setup Password
Not Enabled
option, press <Enter> to access the setup password window, and press
.
System Security
option.
Disabling a Forgotten Password
See "Disabling a Forgotten Password" on page 144.
Baseboard Management Controller Configuration
The Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) enables configuring, monitoring, and recovery of systems
remotely. BMC provides the following features:
• Uses the system’s integrated NIC
• Fault logging and SNMP alerting
• Access to system event log and sensor status
• Control of system functions including power on and off
• Support is independent of the system’s power or operating state
• Provides text console redirection for system setup, text-based utilities, and operating system consoles
NOTE: To remotely access the BMC through the integrated NIC, you must connect the network connection to
integrated NIC1.
For additional information on using BMC, see the documentation for the BMC and systems management
applications.
48 Using the System Setup Program
Page 49

Entering the BMC Setup Module
1
Turn on or restart your system.
2
Press <
If your operating system begins to load before you press <
booting, and then restart your system and try again.
Ctrl-E
> when prompted after POST.
Crtl-E
>, allow the system to finish
BMC Setup Module Options
For information about the BMC Setup Module options and how to configure the emergency management
port (EMP), see the
BMC User’s Guide
.
Using the System Setup Program 49
Page 50

50 Using the System Setup Program
Page 51

Installing System Components
This section describes how to install the following system components:
• Hard drives
• Power supplies
• System fans
• Cooling shroud
• Fan brackets
• SAS controller daughter card
• RAID battery
• Expansion cards
• Expansion card cage
• RAC card
• Optical, diskette, and tape drives
• System memory
• Processors
• System battery
• Expansion-card riser boards
• Sideplane board
• SAS Backplane board
• Control panel assembly
• System board
Recommended Tools
You may need the following items to perform the procedures in this section:
• Key to the system keylock
• #1 and #2 Phillips screwdrivers
• T-10 Torx driver
• Wrist grounding strap
Installing System Components 51
Page 52

Inside the System
CAUTION: Only trained service technicians are authorized to remove the system cover and access any of the
components inside the system. See your Product Information Guide for complete information about safety
precautions, working inside the computer, and protecting against electrostatic discharge.
In Figure 3-1, the bezel and system cover are removed to provide an interior view of the system.
Figure 3-1. Inside the System
4
3
2
1
14
9
10
13
1 RAID battery (optional) 2 SAS controller daughter card
or SAS RAID controller
daughter card (optional)
4 power supply bay 5 power supplies (2) 6 left riser
7 central riser 8 memory modules (8) 9 heatsinks and
10 hot-pluggable fans (4) 11 SAS backplane 12 slimline optical drive (optional)
13 SAS or SATA hard drives (up to
8, depending on configuration)
14 control panel
11
12
3 sideplane
5
6
7
8
microprocessors (2)
52 Installing System Components
Page 53

The system board holds the system's control circuitry and other electronic components. Several hardware
options, such as the microprocessors and memory, are installed directly on the system board. The expansioncard cage containing the left riser accommodates up to two full-length PCIe or PCI-X expansion cards, while
the central riser accommodates one half-length PCIe expansion card.
The system provides space for an optional optical drive. The optical drive connects to the controllers on the
system board through the sideplane board. For more information, see "Optical Drive" on page 81.
Depending on the hard drive configuration you ordered, an optional 3.5-inch diskette drive, and an
optional tape drive may also be available for installation into a media bay. See Table 3-1 for configuration
options.
Table 3-1. Hard Drive and Media Bay Configurations
Number of Hard Drives on Backplane Hard-Drive Size Media Bay
63.5-inchNo
4 3.5-inch Yes
8 2.5-inch Yes
The hard-drive bays provide space for up to eight 2.5-inch SAS drives or six 3.5-inch SAS or SATA hard
drives. The hard drives connect to a RAID controller card through the SAS backplane board. For more
information, see "Hard Drives" on page 55 and "SAS Controller Daughter Card" on page 69.
During an installation or troubleshooting procedure, you may be required to change a jumper setting. For
more information, see "System Board Jumpers" on page 135.
Front Bezel
A lock on the bezel restricts access to the power button, diskette drive, optical drive, and hard drive(s). A
control panel LCD located on the front panel and accessible through the front bezel displays the system’s
status.
Removing the Front Bezel
1
Using the system key, unlock the bezel.
2
Press the tab at the left end of the bezel.
3
Rotate the left end of the bezel away from the system to release the right end of the bezel.
4
Pull the bezel away from the system. See Figure 3-2.
Installing System Components 53
Page 54

Figure 3-2. Removing the Front Bezel
1
1 bezel lock 2 control panel LCD
Replacing the Front Bezel
To replace the front bezel, perform the above steps in reverse.
2
Opening and Closing the System
CAUTION: Only trained service technicians are authorized to remove the system cover and access any of the
components inside the system. See your Product Information Guide for complete information about safety
precautions, working inside the computer, and protecting against electrostatic discharge.
Opening the System
To upgrade or troubleshoot the system, remove the system cover to gain access to internal components.
1
Unless you are installing a hot-plug component such as a cooling fan or power supply, turn off the
system and attached peripherals, and disconnect the system from the electrical outlet and peripherals.
2
To remove the system cover, turn the latch release lock counter-clockwise to the unlocked position. See
Figure 3-3.
3
Lift up on the latch on top of the system. See Figure 3-3.
4
Grasp the cover on both sides and carefully lift the cover away from the system.
54 Installing System Components
Page 55

Closing the System
1
Lift up the latch on the cover.
2
Place the cover on top of the system and offset the cover slightly back so that it clears the chassis J
hooks and lays flush on the system chassis. See Figure 3-3.
3
Push down the latch to lever the cover into the closed position.
4
Rotate the latch release lock in a clockwise direction to secure the cover.
Figure 3-3. Removing the Cover
1
2
3
1 latch 2 latch release lock 3 alignment J hooks
Hard Drives
This subsection describes how to install and configure SAS or SATA hard drives in the system's internal
hard-drive bays.
connect to the system board through one of three optional SAS backplane boards. See "SAS Backplane
Board Connectors" on page 139 for information on these backplane options.
NOTE: Depending on the hard drive configuration you ordered, your hard drive(s) may come with a drive interposer
that allows your SATA drive to attach to the SAS connector on the backplane.
Your system features up to six 3.5-inch hard drives, or eight 2.5-inch hard drives. All drives
Installing System Components 55
Page 56

Before You Begin
Hard drives are supplied in special hot-pluggable drive carriers that fit in the hard-drive bays. Depending
on your configuration, you received one of the following two drive carrier types:
• SATA drive carrier — Usable only with a SATA hard drive.
• SATAu drive carrier — Usable with either a SAS hard drive or a SATA hard drive with a universal
interposer card. The interposer card provides enhanced functionality that makes the SATA hard drive
usable in some storage systems.
NOTICE: Before attempting to remove or install a drive while the system is running, see the documentation for the
optional SAS RAID controller daughter card to ensure that the host adapter is configured correctly to support hotplug drive removal and insertion.
NOTE: It is recommended that you use only drives that have been tested and approved for use with the SAS
backplane board.
You may need to use different programs than those provided with the operating system to partition and
format SAS or SATA hard drives.
NOTICE: Do not turn off or reboot your system while the drive is being formatted. Doing so can cause a drive
failure.
When you format a high-capacity hard drive, allow enough time for the formatting to be completed.
Long format times for these drives are normal. A 9-GB hard drive, for example, can take up to 2.5 hours
to format.
Removing a Drive Blank
NOTICE: To maintain proper system cooling, all empty hard-drive bays must have drive blanks installed. If you
remove a hard-drive carrier from the system and do not reinstall it, you must replace the carrier with a drive blank.
The process for removing a drive blank depends on whether your system is configured with 3.5-inch or
2.5-inch hard drives.
For 3.5-inch hard drive configurations:
1
Remove the front bezel, if attached. See "Removing the Front Bezel" on page 53.
2
Insert your finger under the shrouded end of the blank and press in on the latch to eject the blank
outward from the bay.
3
Pry the ends of the blank outward until the blank is free.
For 2.5-inch hard drive configurations, remove the blank as you would the 2.5-inch hard drive carrier:
1 Remove the front bezel, if attached. See
2 Open the drive blank release handle to release the blank. See
Slide the drive blank out until it is free of the drive bay.
3
"Removing the Front Bezel" on page 53
Figure 3-4
.
.
56 Installing System Components
Page 57

Installing a Drive Blank
The process for installing a drive blank depends on whether your system is configured with 3.5-inch or
2.5-inch hard drives.
For 3.5-inch hard drive configurations, the drive blank is keyed to ensure correct insertion into the drive
bay. To install a 3.5-inch drive blank, insert and rotate in the keyed side of the blank into the drive bay
and press evenly on the other end of the blank until it is fully inserted and latched.
For 2.5-inch hard drive configurations, install the hard drive blank as a 2.5-inch hard drive carrier:
1 Remove the front bezel, if attached. See
2
Open the handle on the drive blank.
3
Insert the drive blank into the drive bay until the blank is fully seated.
4
Close the handle to lock the blank in place.
5 Replace the front bezel, if it was removed in
"Removing the Front Bezel" on page 53
step 1.
.
Removing a Hot-Plug Hard Drive
1 Remove the front bezel, if attached. See
2
From the RAID management software, prepare the drive for removal a
indicators on the drive carrier signal that the drive can be removed safely.
controller documentation for information about hot-plug drive removal.
If the drive has been online, the green
When both drive indicators are off, the drive is ready for removal.
"Removing the Front Bezel" on page 53
nd wait until the hard-drive
activity/
fault indicator will flash as the drive is powered down.
.
See your SAS RAID
3 Open the drive carrier release handle to release the drive. See
4
Slide the hard drive out until it is free of the drive bay.
5
If you do not replace the hard drive, insert a drive blank in the vacated drive bay. See "Installing a Drive
Figure 3-4
.
Blank" on page 57.
NOTICE: To maintain proper system cooling, all empty hard-drive bays must have drive blanks installed.
Installing a Hot-Plug Hard Drive
NOTICE: When installing a hard drive, ensure that the adjacent drives are fully installed. Inserting a hard-drive
carrier and attempting to lock its handle next to a partially installed carrier can damage the partially installed
carrier's shield spring and make it unusable.
NOTICE: Not all operating systems support hot-plug drive installation. See the documentation supplied with your
operating system.
1 Remove the front bezel, if attached. See
2
If a drive blank is present in the bay, remove it. See "Removing a Drive Blank" on page 56.
3
Install the hot-plug hard drive.
a
Open the handle on the hard-drive carrier.
"Removing the Front Bezel" on page 53
Installing System Components 57
.
Page 58

Figure 3-4. Installing a Hot-Plug Hard Drive
1
2
3
1 hard drive 2 drive carrier 3 drive carrier release handle
b
Insert the hard-drive carrier into the drive bay until the carrier contacts the backplane.
c
Close the handle to lock the drive in place.
4 Replace the front bezel, if it was removed in
step 1.
Replacing a Hard-Drive Carrier
Removing a Hard Drive From a Hard-Drive Carrier
1
If you are removing a SATA hard drive from a SATAu drive carrier, remove the interposer card:
a
Viewing the hard drive carrier from the rear, locate the release lever on the left end of the
interposer card.
b
Push the lever away from the carrier rail to release the left end of the card.
c
Rotate the left end away from the hard drive to release the connector.
d
Pull the right end of the interposer card clear of the slots in the carrier rail.
2
Remove the four screws from the slide rails on the hard-drive carrier and separate the hard drive from
the carrier.
58 Installing System Components
Page 59

Installing a SAS Hard Drive Into a SATAu Drive Carrier
NOTE: SAS hard drives must be installed only in SATAu drive carriers. The SATAu drive carrier is labeled "SATAu"
and also has marks indicating the SAS and SATA mounting screws.
1 Insert the SAS hard drive into the hard-drive carrier with the connector end of the drive at the rear.
See
Figure 3-5
2 Viewing the assembly as shown in
with the hole labeled "SAS" on the hard drive carrier.
When aligned correctly, the rear of the hard drive will be flush with the rear of the hard-drive carrier.
.
Figure 3-5, a
lign the bottom rear screw hole on the hard drive
3 Attach the four screws to secure the hard drive to the hard-drive carrier. See
Figure 3-5. Installing a SAS Hard Drive Into a SATAu Drive Carrier
1
2
SATAu SAS
Figure 3-5
3
.
1 screws (4) 2 SATAu drive carrier 3 SAS hard drive
Installing System Components 59
Page 60

Installing a SATA Hard Drive Into a SATA Drive Carrier
NOTE: SATA hard drives that connect directly to the SAS backplane must be installed in SATA drive carriers
(labeled "SATA"). Only SATA hard drives with interposer cards can be installed in SATAu drive carriers.
1 Insert the SATA hard drive into the hard-drive carrier with the connector end of the drive at the
rear. See
2 Align the screw holes on the hard drive with the holes on the hard-drive carrier. See
3 Attach the four screws to secure the hard drive to the hard-drive carrier. See
Figure 3-6. Installing a SATA Hard Drive Into a SATA Drive Carrier
Figure 3-6
.
Figure 3-6
Figure 3-6
.
.
1
2
3
1 screws (4) 2 SATA drive carrier 3 SATA hard drive
60 Installing System Components
Page 61

Installing a SATA Hard Drive and Interposer Card Into a SATAu Hard-Drive Carrier
NOTE: When you install a SATA hard drive into a SATAu drive carrier, you must install an interposer card onto the
back of the hard drive. The SATAu drive carrier is labeled "SATAu" and also has marks indicating the SAS and SATA
mounting screws.
1 Insert the SATA hard drive into the SATAu hard-drive carrier with the connector end of the drive at
the rear. See
2 Viewing the assembly as shown in
with the hole labeled "SATAu" on the hard drive carrier.
When aligned correctly, the rear of the interposer will be flush with the rear of the hard-drive carrier.
Figure 3-7
.
Figure 3-7, a
lign the bottom rear screw hole on the hard drive
3 Attach the four screws to secure the hard drive to the hard-drive carrier. See
4
Attach the interposer card to the rear of the SATA hard drive:
a
Angle the top of the interposer card into the inside top carrier rail so that the tabs on the
interposer card bracket attach to the slots on the inside of the carrier rail.
b
Rotate the bottom end of the card toward the hard drive to seat the connector.
c
Push the bottom end of the card to the hard drive until the latch on the card bracket clicks into
place.
Figure 3-7.
See
Figure 3-7.
See
Figure 3-7.
Installing System Components 61
Page 62

Figure 3-7. Installing a SATA Hard Drive and Interposer Card Into a SATAu Drive Carrier
1
SATAu SAS
2
3
4
5
1 screws (4) 2 SATAu drive carrier 3 interposer card (SATA only)
4 SATA hard-drive 5 hole labels
Power Supplies
Your system supports one or two power supplies rated at an output of 750 W. If only one power supply is
installed, it must be installed in the left power supply bay (1). If two power supplies are installed, the
second power supply serves as a redundant, hot-plug power source.
NOTICE: To ensure proper system cooling, the power supply blank must be installed on the unoccupied power
supply bay in a non-redundant configuration. See "Installing the Power Supply Blank" on page 65.
62 Installing System Components
Page 63

Removing a Power Supply
NOTICE: The system requires one power supply for the system to operate normally. The system is in the redundant
mode when two power supplies are installed and both power supplies are connected to an AC power source.
Remove and replace only one power supply at a time in a system that is powered on. Operating the system with only
one power supply installed and without a power supply blank installed for extended periods of time can cause the
system to overheat.
NOTICE: If only one power supply is installed, it must be installed in the left power supply bay (1).
NOTICE: If you connect the system to a power source in the range of 120 to 220 VAC, and if two power supplies are
installed, the second power supply serves as a redundant, hot-plug power source.
NOTE: On your rack system, you may have to unlatch and lift the cable management arm if it interferes with power
supply removal. For information about the cable management arm, see the system’s Rack Installation Guide.
1
If your system has a single power supply, turn off the system and all attached peripherals. For a
redundant system, you can leave the system running and proceed to the next step.
2
Disconnect the power cable from the power source.
3
Disconnect the power cable from the power supply and remove the cable from the cable retention
bracket.
4
Release the locking tab on the left side of the power supply by pressing in toward the right, and rotate
the power-supply handle up until the power supply is released from the chassis. See Figure 3-8.
5
Pull the power supply straight out to clear the chassis.
Installing System Components 63
Page 64

Figure 3-8. Removing and Installing a Power Supply
3
1 locking tab 2 cable retention bracket 3 power-supply handle
1
2
Replacing a Power Supply
1
With the power-supply handle in the extended position, slide the new power supply into the chassis.
See Figure 3-8.
2
Rotate the handle down until it is completely flush with the power-supply faceplate and the orange
snap engages. See Figure 3-8.
3
Insert the power cable through the cable retention bracket, connect the power cable to the power
supply, and plug the cable into a power outlet.
NOTE: After installing a new power supply, allow several seconds for the system to recognize the power supply
and determine whether it is working properly. The power supply status indicator will turn green to signify that the
power supply is functioning properly. See Figure 1-4.
Removing the Power Supply Blank
Using a Phillips screwdriver, remove the screw on the left side of the blank, rotate the blank slightly to
clear the bay, and remove from the chassis.
NOTICE: To ensure proper system cooling, the power supply blank must be installed on the unoccupied power
supply bay in a non-redundant configuration. Remove the power supply blank only if you are installing a second
power supply.
64 Installing System Components
Page 65

Installing the Power Supply Blank
To install the power supply blank, insert the tab on the right edge of the blank into the slot in the power
supply bay wall. Rotate the blank into the power supply bay and secure with the Phillips screw.
System Fans
The system includes four hot-pluggable cooling fans.
Removing a System Fan
CAUTION: Only trained service technicians are authorized to remove the system cover and access any of the
components inside the system. See your Product Information Guide for complete information about safety
precautions, working inside the computer, and protecting against electrostatic discharge.
NOTICE: The system fans are hot-pluggable. To maintain proper cooling while the system is on, replace only one
fan at a time.
1
Open the system. See "Opening the System" on page 54.
CAUTION: Use caution when handling the fan until the fan blades stop spinning.
2
Raise the fan handle and pull the fan straight up from the fan cage to clear the chassis. See Figure 3-9.
Installing System Components 65
Page 66

Figure 3-9. Removing and Installing a Cooling Fan
2
1
3
1 fan bracket 2 fan handle 3 fan
Replacing a Cooling Fan
1
Ensure that the fan handle is upright and lower the fan into its fan cage until the fan is fully seated.
Then lower the fan handle until it snaps into place. See Figure 3-9.
2
Close the system. See "Closing the System" on page 55.
Cooling Shroud
The cooling shroud produces and directs airflow over the system memory modules.
CAUTION: The DIMMs are hot to the touch for some time after the system has been powered down. Allow the
DIMMs to cool before handling them.
NOTICE: Never operate your system with the memory cooling shroud removed. Overheating of the system can
develop quickly resulting in a shutdown of the system and the loss of data.
66 Installing System Components
Page 67

Removing the Cooling Shroud
1
The cooling shroud is secured with a latch at the end of the shroud. Release the latch by pulling it
towards the outside wall of the chassis. See Figure 3-10.
2
Rotate the shroud upward and toward the front of the system on its hinges, and then lift the shroud
out of the system.
Figure 3-10. Removing and Installing the Cooling Shroud
2
1
5
1 shroud pivots (2) 2 cooling shroud 3 release latch
4 shroud hinges (2) 5 fan bracket
3
4
Installing the Cooling Shroud
1
Align the hinges on the shroud pivots located on either end of the fan bracket. See Figure 3-10.
2
Slowly lower the shroud straight down into the system until the fan connector engages and the latches
snap into place.
Installing System Components 67
Page 68

Fan Brackets
Removing the Fan Bracket
CAUTION: Only trained service technicians are authorized to remove the system cover and access any of the
components inside the system. See your Product Information Guide for complete information about safety
precautions, working inside the computer, and protecting against electrostatic discharge.
1
Turn off the system, including any attached peripherals, and disconnect the system from the electrical
outlet.
2
Open the system. See "Opening the System" on page 54.
3
Remove the cooling shroud. See "Removing the Cooling Shroud" on page 67.
4
Remove the SAS controller daughter card. See "Removing a SAS Controller Daughter Card" on
page 74
5
Remove the fans from the fan bracket. See "Removing a System Fan" on page 65.
6
Remove the fan bracket from the system:
a
Press down on the release latch on the left side of the fan bracket. See Figure 3-11.
If the bracket does not disengage completely, push down slightly on the bracket when releasing the
latch.
b
Rotate the left side of the bracket upward, releasing the plastic clip from its slot in the power
supply cage.
c
Draw the bracket out of the system.
68 Installing System Components
Page 69

Figure 3-11. Removing and Installing the Fan Bracket
3
2
1
1 release latch 2 fan bracket 3 plastic clip
4 fan bracket slot in power
supply cage
5tabs (2)
4
5
Replacing the Fan Bracket
1
Insert the two tabs on the right side of the fan bracket into the two slots on the system board tray.
2
Gently rotate the left end of the fan bracket downward into the system until the release latch and
plastic clip fully engage.
3
Reinstall the SAS controller daughter card. See "Installing a SAS Controller Daughter Card" on
page 70.
4
Replace the fans in the fan bracket. See "Replacing a Cooling Fan" on page 66.
5
Close the system. See "Closing the System" on page 55.
6
Reconnect the system to the electrical outlet and turn on the system and attached peripherals.
SAS Controller Daughter Card
Your system includes a dedicated slot on the sideplane for a SAS controller daughter card. The SAS
controller daughter card provides the SAS storage subsystem for your system’s internal hard drives. The
optional SAS RAID controller daughter card allows you to set up any internal hard drives in a RAID
Installing System Components 69
Page 70

configuration. Although the cabling for the two types of daughter cards is different (the SAS controller
daughter card has only one connector, while the SAS RAID controller daughter card has two), both cards
install into the sideplane as described below. The SAS RAID controller daughter card is shown in
Figure 3-12.
Installing a SAS Controller Daughter Card
NOTICE: Do not press on the RAID card DIMM while installing the RAID card into the sideplane board.
NOTE: If you are installing a replacement RAID card, do not remove the plastic cover protecting the card until after
installation of the card is complete.
1
Turn off the system, including any attached peripherals, and disconnect the system from the electrical
outlet.
2
Open the system. See "Opening the System" on page 54.
3
Disconnect the control panel cable from the sideplane board. See "Removing the Control Panel
Assembly" on page 105.
4
Hold the SAS daughter card by its edges with the card connector facing the sideplane board.
5
Aligning the chassis slots on the SAS daughter card tray with the corresponding hooks on the chassis,
insert the card connector into the SAS daughter card connector on the sideplane board. See
Figure 3-12.
Ensure that the card is aligned with the mid-section standoff on the SAS controller daughter card and
fully seat the card in the sideplane board.
70 Installing System Components
Page 71

Figure 3-12. Installing a SAS Controller Daughter Card
3
2
1
7
1 SAS controller daughter card 2 SAS controller daughter card
slot
4 SAS controller daughter card
battery connector
7 SAS controller daughter card
tray
5 SAS connectors 0 and 1 (for
RAID card only) out to
backplane SAS_A or SAS_B
(for RAID card only) connector
6
4
5
3 release tab
6 chassis slots (2)
6
Attach any cables from the SAS controller daughter card to the backplane, referring to Figure 3-13,
Figure 3-14, Figure 3-15, or Figure 3-16 for the cabling guidelines for your system’s card and backplane
configuration.
Installing System Components 71
Page 72

SAS and SAS RAID Controller Daughter Card Cabling Guidelines
Figure 3-13. SAS Controller Daughter Card Cabling With all Backplanes
2
1
3
4
1 SAS controller daughter card 2 SAS controller 0 3 SAS backplane A
4 backplane
Figure 3-14. SAS RAID Controller Daughter Card Cabling With 3.5-inch x6 Backplane
2
1
1 SAS controller 0 2 SAS RAID controller daughter
card
4 SAS backplane A 5 3.5-inch x6 backplane 6 SAS backplane B
3 SAS controller 1
72 Installing System Components
3
4
5
6
Page 73

Figure 3-15. SAS RAID Controller Daughter Card Cabling With 3.5-inch x4 Backplane
2
1
3
4
5
1 SAS controller 0 2 SAS RAID controller daughter
card
4 SAS backplane A 5 3.5-inch x4 backplane
Figure 3-16. SAS RAID Controller Daughter Card Cabling With 2.5-inch x8 Backplane
2
1
1 SAS controller 0 2 SAS RAID controller daughter
card
4 SAS controller 1 5 SAS backplane B 6 2.5-inch x8 backplane
3 SAS controller 1
3
4
5
6
3 SAS backplane A
Installing System Components 73
Page 74

Removing a SAS Controller Daughter Card
1
Disconnect any battery connectors if applicable.
2
Disconnect the control panel cable. See "Removing the Control Panel Assembly" on page 105
3
Disconnect any SAS cables from the card.
4
Gently press down on the release tab while sliding the SAS controller daughter card in its tray away
from the sideplane connector, freeing the chassis slots on the tray from the chassis hooks, and lifting
the card from the system. See Figure 3-12.
RAID Battery
Installing a RAID Battery
1
Insert the RAID battery into the battery carrier. See Figure 3-17.
2
Locate the battery bay to the right of the SAS daughter card on top of the hard drive bays.
3
Insert the battery carrier and RAID battery into the chassis battery carrier slots and connect the battery
cable to the storage daughter card, ensuring that the battery carrier is aligned and fully seated in the
slots.
74 Installing System Components
Page 75

Figure 3-17. Installing a RAID Battery
2
1
3
4
1 chassis battery carrier slot (2) 2 battery cable 3 battery carrier
4 SAS RAID controller daughter
card battery
Removing a RAID Battery
1
Disconnect the cable between the RAID battery and the SAS RAID controller daughter card. See
Figure 3-17.
2
Press down and to the left on the battery carrier to disengage the carrier from the chassis battery carrier
slots.
3
Gently pulling back the two guides holding the RAID battery into the battery carrier, draw out the
RAID battery from the battery carrier.
Installing System Components 75
Page 76

Configuring the Boot Device
NOTE: System boot is not supported from an external device attached to a SAS or SCSI adapter. See
support.dell.com for the latest support information about booting from external devices.
If you plan to boot the system from a hard drive, the drive must be attached to the primary (or boot)
controller. The device that the system boots from is determined by the boot order specified in the System
Setup program
The System Setup program provides options that the system uses to scan for installed boot devices. See
"Using the System Setup Program" on page 37 for information about the System Setup program.
.
Expansion Cards
The system is available with either a PCI-X or a PCI Express (PCIe) left riser board option. The PCI-X left
riser board provides two PCI-X 64-bit/133-MHz expansion slots, while the PCIe left riser board provides one
PCIe x8-lane expansion slot and one PCIe x4-lane expansion slot. The half-height center riser board
provided with both PCI-X and PCIe left riser board options features one PCIe x8-lane expansion slot. The
three expansion card slots are on separate buses.
Expansion Card Installation Guidelines
To identify expansion slots, see "Expansion-Card Riser-Board Components and PCI Buses" on page 142.
NOTE: The expansion-card slots are not hot-pluggable.
NOTE: Although the PCIe x4-lane expansion slot on the PCIe left riser option is physically a PCIe x8 connector, it
functions only as a PCIe x4-lane slot.
NOTE: Slot 1 on the central riser supports half-length expansion cards only. Slots 2 and 3 on the left riser support
full-length expansion cards.
NOTE: Your system supports up to two RAID expansion cards to manage external storage.
Installing an Expansion Card
CAUTION: Only trained service technicians are authorized to remove the system cover and access any of the
components inside the system. See your Product Information Guide for complete information about safety
precautions, working inside the computer, and protecting against electrostatic discharge.
NOTE: The procedure for installing expansion cards into the left and central risers is the same except that there is
no card guide for cards installing into the central riser, and only half-height cards are supported on the central
riser. Full-length expansion card installation is illustrated in Figure 3-18.
1
Unpack the expansion card and prepare it for installation.
For instructions, see the documentation accompanying the card.
2
Turn off the system, including any attached peripherals, and disconnect the system from the electrical
outlet.
3
Open the system. See "Opening the System" on page 54.
76 Installing System Components
Page 77

4
Open the expansion-card guide latch and remove the filler bracket. See Figure 3-18.
5
Install the expansion card:
a
If the expansion card is full length, align its front edge with the front card guide. See Figure 3-18.
b
Position the expansion card so that the card-edge connector aligns with the expansion-card
connector on the expansion-card riser board.
c
Insert the card-edge connector firmly into the PCI card connector until the card is fully seated.
d
When the card is seated in the connector, close the expansion-card latch. See Figure 3-18.
Figure 3-18. Installing an Expansion Card
3
2
1
1 front card guide 2 expansion-card connector 3 card-edge connector
4 expansion card 5 expansion-card guide latch
4
5
6
Connect any expansion-card cables for the new card.
See the documentation that came with the card for information about its cable connections.
7
Close the system. See "Closing the System" on page 55.
Installing System Components 77
Page 78

Removing an Expansion Card
CAUTION: Only trained service technicians are authorized to remove the system cover and access any of the
components inside the system. See your Product Information Guide for complete information about safety
precautions, working inside the computer, and protecting against electrostatic discharge.
1
Turn off the system, including any attached peripherals, and disconnect the system from the electrical
outlet.
2
Open the system. See "Opening the System" on page 54.
3
Disconnect all expansion-card cables.
4
Release the expansion card:
a
Open the expansion-card latch. See Figure 3-18.
b
Grasp the expansion card by its top corners, and carefully remove it from the expansion-card
connector.
5
If you are removing the card permanently, install a metal filler bracket over the empty expansion slot
opening and close the expansion-card latch.
NOTE: You must install a filler bracket over an empty expansion slot to maintain Federal Communications
Commission (FCC) certification of the system. The brackets also keep dust and dirt out of the system and aid in
proper cooling and airflow inside the system.
6
Reconnect all expansion-card cables.
7
Close the system. See "Closing the System" on page 55.
Expansion-Card Cage
Removing the Expansion-Card Cage
CAUTION: Only trained service technicians are authorized to remove the system cover and access any of the
components inside the system. See your Product Information Guide for complete information about safety
precautions, working inside the computer, and protecting against electrostatic discharge.
NOTE: You must remove all expansion cards from the expansion-card cage before removing the expansion-card
cage from the system.
1
Turn off the system, including any attached peripherals, and disconnect the system from the electrical
outlet.
2
Open the system. See "Opening the System" on page 54.
3
Disconnect all expansion-card cables.
4
Remove any expansion cards from the expansion-card cage. See "Removing an Expansion Card" on
page 78.
5
Press the two blue release latches on the expansion-card cage. See Figure 3-19.
78 Installing System Components
Page 79

Figure 3-19. Installing and Removing the Expansion-Card Cage
1
2
3
1 expansion-card cage 2 chassis pins (2) 3 release latches (2)
6
Lift the cage straight up to clear the chassis. See Figure 3-19.
Replacing the Expansion-Card Cage
CAUTION: Only trained service technicians are authorized to remove the system cover and access any of the
components inside the system. See your Product Information Guide for complete information about safety
precautions, working inside the computer, and protecting against electrostatic discharge.
1
Align the guides on each end of the expansion-card cage with the pins on the system board, and lower
the cage. See Figure 3-19.
2
Install any expansion cards.
3
Reconnect all expansion-card cables.
4
Close the system. See "Closing the System" on page 55.
Installing System Components 79
Page 80

Installing a RAC Card
CAUTION: Only trained service technicians are authorized to remove the system cover and access any of the
components inside the system. See your Product Information Guide for complete information about safety
precautions, working inside the computer, and protecting against electrostatic discharge.
The optional Remote Access Controller (RAC) provides a set of advanced features for managing the
server remotely. The following procedure describes the steps for installing the optional RAC card.
1
Turn off the system, including any attached peripherals, and disconnect the system from the electrical
outlet.
2
Open the system. See "Opening the System" on page 54.
3
Remove the plastic filler plug from the system back panel. See Figure 3-20.
4
Remove the central riser board. See "Removing the Central Riser Board" on page 100.
5
Angle the RAC card so that its NIC connector inserts through the back-panel RAC card opening, and
then straighten the card.
Figure 3-20. Installing a RAC Card
2
3
4
1
6
1 RAC-card connectors (2) 2 RAC-card cables (2) 3 retention standoff hole
4 RAC card 5 filler plug 6 support standoffs holes(2)
80 Installing System Components
5
Page 81

6
Align the front edge of the RAC card with the two front plastic retention standoffs adjacent to the
RAC system board connector, and press down the side of the card until it is fully seated. See
Figure 3-20.
When the front of the card is fully seated, the plastic standoff snaps over the edge of the card.
7
Connect the two short ribbon cables to the RAC card and the system board. See Figure 6-2 for the
connector locations
NOTICE: Be careful when attaching cables to the system board that you do not damage the surrounding system
board components.
Connect one cable to connector 1 on the RAC card and to RAC_CONN1 on the system board.
a
b Connect the second cable to connector 2 on the RAC card and to RAC_CONN2 on the system
board.
Reinstall the central riser board. See "Installing the Central Riser Board" on page 100.
NOTICE: When detaching the RAC cables from the system board, squeeze the metal ends of the cable connectors
and gently work the connector out of the socket. Do not pull on the cable to unseat the connector. Doing so can
damage the cable.
8
Close the system. See "Closing the System" on page 55.
9
Reconnect the system and peripherals to their power sources, and turn them on.
See the RAC card documentation for information on configuring and using the RAC card.
Optical Drive
An optional slimline optical drive is mounted on a tray that slides in the front panel and connects to the
controllers on the system board through the SAS backplane board.
Removing the Optical Drive
CAUTION: Only trained service technicians are authorized to remove the system cover and access any of the
components inside the system. See your Product Information Guide for complete information about safety
precautions, working inside the computer, and protecting against electrostatic discharge.
1
Turn off the system, including any attached peripherals, and disconnect the system from its electrical
outlet.
2
Remove the bezel. See "Removing the Front Bezel" on page 53.
3
Open the system. See "Opening the System" on page 54
4
Disconnect the optical drive cable from the back of the drive.
5
To remove the optical drive, press down and forward on the blue tray release tab and slide the drive tray
out of the system. See Figure 3-21.
Installing System Components 81
Page 82

Figure 3-21. Removing and Installing the Optical Drive Tray
1
2
4
1 optical-drive cable 2 optical-drive release tab 3 optical -drive tray
4 optical drive
3
Installing the Optical Drive
1
Align the optical drive tray with its opening in the front panel.
The optical drive opening is above the hard-drive slots on the far right, or the flex bay, depending on
your system’s drive configuration (the hard-drives slots are identified by labels on the front panel of the
system).
2
Slide in the drive tray until the tray snaps into place. See Figure 3-21.
3
Connect the optical drive cable to the connector on the back of the drive.
4
Close the system. See "Closing the System" on page 55.
5
Replace the bezel. See "Replacing the Front Bezel" on page 54.
6
Reconnect your system and peripherals to their electrical outlets, and turn on the system.
82 Installing System Components
Page 83

Diskette Drive
Removing the Diskette Drive From the System
CAUTION: Only trained service technicians are authorized to remove the system cover and access any of the
components inside the system. See your Product Information Guide for complete information about safety
precautions, working inside the computer, and protecting against electrostatic discharge.
1
Turn off the system, including any attached peripherals, and disconnect the system from the electrical
outlet.
2
Remove the front bezel, if attached. See "Removing the Front Bezel" on page 53.
3
Open the system. See "Opening the System" on page 54.
4
If your system configuration includes a tape backup device installed in the optional media bay, remove
the tape backup device’s strain relief bracket. See "Removing and Replacing the Tape Drive Cable
Retention Bracket" on page 88.
5
Disconnect the cable from the back of the diskette drive.
6
Release the diskette drive carrier from its slot in the media bay:
a
Gently squeeze down on the plastic tabs on the side of the carrier while pushing toward the front
of the system until you feel the carrier sliding freely forward.
b
Slide the carrier forward and out of the chassis. See
Figure 3-23.
Installing System Components 83
Page 84

Figure 3-22. Installing and Removing the Diskette Drive From the System
2
1
3
1 diskette drive carrier 2 release tabs (2) 3 media bay
Installing the Diskette Drive Into the System
CAUTION: Only trained service technicians are authorized to remove the system cover and access any of the
components inside the system. See your Product Information Guide for complete information about safety
precautions, working inside the computer, and protecting against electrostatic discharge.
1
Turn off the system, including any attached peripherals, and disconnect the system from the electrical
outlet.
2
Remove the front bezel, if attached. See "Removing the Front Bezel" on page 53.
3
Open the system. See "Opening the System" on page 54.
4
Install the diskette drive carrier into the system:
a
Align the slots on the bottom of the diskette drive carrier with the drive bay rails in the media bay.
b
Push the carrier toward the system front plate until the plastic latch on the carrier locks into
position.
5
Attach one end of the ribbon cable to the floppy connector (FLOPPY) on the system board and the
other end to the connector on the rear of the diskette drive. See Figure 6-2 for the location of the
floppy cable connector on the system board.
6
Close the system. See "Closing the System" on page 55.
84 Installing System Components
Page 85

7
Replace the front bezel if removed in step 2. See "Replacing the Front Bezel" on page 54.
8
Reconnect the system and peripherals to their electrical outlets.
Removing the Diskette Drive From the Drive Carrier
1
Remove the diskette drive from the system. See "Removing the Diskette Drive From the System" on
page 83.
2
Gently draw one side of the carrier away from the diskette drive until the drive pops from the tray. See
Figure 3-23.
Figure 3-23. Installing and Removing the Diskette Drive Into and From the Drive Carrier
2
3
1
1 diskette drive tray 2 shim 3 diskette drive
4 diskette drive release tabs (2)
Installing the Diskette Drive Into the Drive Carrier
1
Align the back of the diskette drive with the back of the carrier.
2
Add the shim to the drive.
3
Gently push the drive into the carrier until it pops in securely. See Figure 3-23.
Installing System Components 85
4
Page 86

SCSI Tape Drive
This section describes how to configure and install an internal SCSI tape drive.
NOTE: Installing a SCSI tape drive requires an optional SCSI controller card.
Removing and Installing an Internal SCSI Tape Drive
NOTICE: See "Protecting Against Electrostatic Discharge" in the safety instructions in your Product Information
Guide.
1
Turn off the system, including any attached peripherals, and disconnect the system from the electrical
outlet.
2
Remove the tape drive carrier from the media bay by squeezing the release tabs on either side of the
carrier down and forward, sliding the carrier gently from the bay. See Figure 3-24.
Figure 3-24. Removing and Installing the Tape Drive Carrier
1
2
1 tape drive blank 2 tape drive rails 3 release tab (2)
4 media bay
3
Remove the four screws affixing the tape drive blank to the rails, and set the rails aside for installation
onto the drive. See Figure 3-25.
86 Installing System Components
4
3
Page 87

4
Prepare the tape drive for installation.
Ground yourself by touching an unpainted metal surface on the back of the system, unpack the drive
(and controller card, if applicable), and compare the jumper and switch settings with those in the drive
documentation.
5
Aligning the four holes on the tape drive with the four screw holes on the tape drive rails, affix the rails
to the drive.
6
Insert the tape drive along the rails in the media bay. See Figure 3-25.
Figure 3-25. Removing and Installing an Internal SCSI Tape Drive
1
1 screws (4) 2 tape drive rails (2) 3 rail release tabs (2)
4 tape drive
7
Route the tape drive's SCSI interface cable through the tape drive cable retention bracket and connect
2
3
4
it to the connector on the SCSI controller card. See "Removing and Replacing the Tape Drive Cable
Retention Bracket" on page 88.
8
Connect the tape drive power cable to the tape drive power connector on the backplane. See Figure 6-4
or Figure 6-5 for the connector location.
9
Reconnect the system to its electrical outlet and turn the system on, including any attached
peripherals.
10
Perform a tape backup and verification test with the drive as instructed in the software documentation
that came with the drive.
Installing System Components 87
Page 88

Removing and Replacing the Tape Drive Cable Retention Bracket
The optional tape drive available with the 3.5" x4 and 2.5" x8 backplane configurations connects to the
system board through an expansion card plugged into one of the PCI expansion card slots. The tape drive
cable is routed along the right side of the chassis and behind the tape drive cable retention bracket.
To remove the tape drive cable retention bracket, gently draw the blue release latch toward the center of
the system while sliding the cable retention bracket toward the front of the system and disengaging the
bracket from the chassis wall. See Figure 3-26.
To replace the bracket, align the bracket clips with their slots on the chassis wall, then slide the bracket
toward the back of the system until all the clips and the blue release latch are fully engaged.
Figure 3-26. Installing and Removing the Tape Drive Cable Retention Bracket
2
1
1 tape drive cable 2 SCSI controller card 3 release latch
4 bracket clips (6) 5 tape drive cable retention
bracket
3
4
5
88 Installing System Components
Page 89

System Memory
You can upgrade your system memory to a maximum of 32 GB by installing 533MHz or 667MHz fully
buffered (FB) DDR II memory modules in sets of 256-MB, 512-MB, 1-GB, 2-GB, or 4-GB. The eight
memory sockets are located on the system board under the cooling shroud adjacent to the power supply
bays. See Figure 6-2. You can purchase memory upgrade kits from Dell.
NOTICE: If you remove your original memory modules from the system during a memory upgrade, keep them
separate from any new memory modules that you may have, even if you purchased the new memory modules from
Dell. Use only 533 MHz or 667 MHz DDR II FB-DIMMs.
The memory module sockets are divided into two equal branches (0 and 1). Each branch consists of two
channels:
• Channel 0 and channel 1 are in branch 0.
• Channel 2 and channel 3 are in branch 1.
Each channel consists of two DIMM sockets:
• Channel 0 contains DIMM_1, DIMM_5.
• Channel 1 contains DIMM _2, DIMM_6.
• Channel 2 contains DIMM_3, DIMM_7.
• Channel 3 contains DIMM _4, DIMM _8.
The first DIMM socket of each channel has white release tabs.
General Memory Module Installation Guidelines
To ensure optimal performance of your system, observe the following guidelines when configuring your
system memory.
• Use only qualified Fully-Buffered DIMMs (FBDs). FBDs can be either s
FBDs m
• A minimum of two identical FBDs must installed.
• DIMM sockets must be populated by lowest number first.
• FBDs m
number of FBDs in the configuration must total two, four, or eight. For best system performance, all
four, or eight FBDs should be identical memory size, speed, and technology.
•Memory sp
memory size, speed, and technology.
• Memory sparing and memory mirroring cannot be implemented at the same time.
arked with a 1R are single-ranked and modules marked with a 2R are dual-ranked.
ust be installed in pairs of matched memory size, speed, and technology
aring and
memory m
irroring require eight FBDs, and all FBDs must be of identical
ingle-ranked
, and the total
or d
ual-ranked
.
Installing System Components 89
Page 90

Non-Optimal Memory Configurations
System performance can be affected if your memory configuration does not conform to the preceding
installation guidelines. Your system may issue an error message during startup stating that your memory
configuration is non-optimal.
Memory Sparing Support
The system supports memory sparing if eight identical memory modules are installed in the system. The
memory sparing feature must be enabled in the System Setup program and can be used only if memory
mirroring is not enabled.
Memory sparing allocates four ranks of DIMM memory to the spare bank. These four ranks consist of the
first rank of memory in DIMM sockets 1 through 4. For single-rank DIMMs, the entire capacity of the
four DIMMs is allocated to sparing whereas for dual-rank DIMMs, only half of the four-DIMM capacity
is allocated to sparing. Table 3-2 shows how memory sparing splits the available and spared memory in
each of the single- and dual-ranked memory module combinations.
Table 3-2. Memory Sparing Configurations
DIMMs Size/Type Total Memory Available Spare
8 256-MB single-rank 2 GB 1 GB 1 GB
512-MB single-rank 4 GB 2 GB 2 GB
1-GB single-rank 8 GB 4 GB 4 GB
2-GB single-rank 16 GB 8 GB 8 GB
2-GB dual-rank 16 GB 12 GB 4 GB
4-GB dual-rank 32 GB 24 GB 8 GB
Memory Mirroring Support
The system supports memory mirroring if eight identical memory modules are installed in the system.
Mirroring must be enabled in the System Setup program and can be used only if memory sparing is not
enabled. In a mirrored configuration, the total available system memory is one-half of the total installed
memory.
Installing Memory Modules
CAUTION: Only trained service technicians are authorized to remove the system cover and access any of the
components inside the system. See your Product Information Guide for complete information about safety
precautions, working inside the computer, and protecting against electrostatic discharge.
1
Turn off the system, including any attached peripherals, and disconnect the system from the electrical
outlet.
2
Open the system. See "Opening the System" on page 54.
3
Remove the memory cooling shroud. See "Removing the Cooling Shroud" on page 67.
90 Installing System Components
Page 91

NOTICE: Never remove the memory cooling shroud without first powering down the system. Overheating of the
system can develop quickly resulting in a shutdown of the system and the loss of data.
4
Locate the memory module sockets on the system board. See Figure 6-2.
CAUTION: The DIMMs are hot to the touch for some time after the system has been powered down. Allow time
for the DIMMs to cool before handling them. Handle the DIMMs by the card edges and avoid touching the DIMM
components.
5
Press the ejectors on the memory module socket down and out, as shown in Figure 3-27, to allow the
memory module to be inserted into the socket.
Figure 3-27. Installing and Removing a Memory Module
1
2
3
4
1 memory module 2 memory module socket
ejectors (2)
4 alignment key
6
Align the memory module's edge connector with the alignment key on the memory module socket, and
3 socket
insert the memory module in the socket.
NOTE: The memory module socket has an alignment key that allows you to install the memory module in the
socket in only one way.
7
Press down on the memory module with your thumbs while pulling up on the ejectors with your index
fingers to lock the memory module into the socket.
When the memory module is properly seated in the socket, the ejectors on the memory module socket
align with the ejectors on the other sockets that have memory modules installed.
8
Repeat step 3 through step 7 of this procedure to install the remaining memory modules.
Installing System Components 91
Page 92

9
Replace the memory cooling shroud. See "Installing the Cooling Shroud" on page 67.
NOTICE: Never operate your system with the memory cooling shroud removed. Overheating of the system can
develop quickly resulting in a shutdown of the system and the loss of data.
10
Close the system. See "Opening the System" on page 54.
11
(Optional) Enter the System Setup program, and check the
System Setup
screen. See "Entering the System Setup Program" on page 37.
System Memory
setting on the main
The system should have already changed the value to reflect the newly installed memory.
12
If the value is incorrect, one or more of the memory modules may not be installed properly. Repeat
step 2 through step 11 of this procedure, checking to ensure that the memory modules are firmly
seated in their sockets.
13
Run the system memory test in the system diagnostics. See "Running the System Diagnostics" on
page 132.
Removing Memory Modules
CAUTION: Only trained service technicians are authorized to remove the system cover and access any of the
components inside the system. See your Product Information Guide for complete information about safety
precautions, working inside the computer, and protecting against electrostatic discharge.
1
Turn off the system, including any attached peripherals, and disconnect the system from the electrical
outlet.
2
Open the system. See "Opening the System" on page 54.
3
Remove the memory cooling shroud. See "Removing the Cooling Shroud" on page 67.
NOTICE: Never remove the memory cooling shroud without first powering down the system. Overheating of the
system can develop quickly resulting in a shutdown of the system and the loss of data.
4
Locate the memory module sockets on the system board. See Figure 6-2.
CAUTION: The DIMMs are hot to the touch for some time after the system has been powered down. Allow the
DIMMs to cool before handling them. Handle the DIMMs by the card edges, and avoid touching the DIMM
components.
5
Press down and out on the ejectors on each end of the socket until the memory module pops out of the
socket. See Figure 3-27.
6
Replace the memory cooling shroud. See "Installing the Cooling Shroud" on page 67.
NOTICE: Never operate your system with the memory cooling shroud removed. Overheating of the system can
develop quickly resulting in a shutdown of the system and the loss of data.
7
Close the system. See "Closing the System" on page 55.
92 Installing System Components
Page 93

Activating the Integrated NIC TOE
To add TCP/IP Offload Engine (TOE) functionality to the system’s integrated NIC, install the TOE
NIC hardware key in the TOE_KEY socket on the system board (
see Figure 6-2.)
Processors
You can upgrade your processor(s) to take advantage of future options in speed and functionality. Each
processor and its associated internal cache memory are contained in a land grid array (LGA) package that is
installed in a ZIF socket on the system board.
Removing a Processor
CAUTION: Only trained service technicians are authorized to remove the system cover and access any of the
components inside the system. See your Product Information Guide for complete information about safety
precautions, working inside the computer, and protecting against electrostatic discharge.
1 Prior to upgrading your system, download the latest system BIOS version on support.dell.com.
2
Turn off the system, including any attached peripherals, and disconnect the system from the electrical
outlet.
3
Open the system. See "Opening the System" on page 54.
4
Remove the fans. See "Removing a System Fan" on page 65
5
Remove the fan bracket. See "Removing the Fan Bracket" on page 68.
NOTICE: When you remove the heat sink, the possibility exists that the processor might adhere to the heat sink
and be removed from the socket. It is recommended that you remove the heat sink while the processor is still
warm.
NOTICE: Never remove the heat sink from a processor unless you intend to remove the processor. The heat sink is
necessary to maintain proper thermal conditions.
6
Press the blue tab on the end of one of the heat-sink retention levers to disengage the lever, then lift
the lever 90 degrees. See Figure 3-28.
Installing System Components 93
Page 94

Figure 3-28. Installing and Removing the Heat Sink
1
2
3
1 heat sink 2 heat-sink retention levers (2) 3 retention lever latch
7
Wait 30 seconds for the heat sink to loosen from the processor.
8
Open the other heat sink retention lever.
9
If the heat sink has not separated from the processor, carefully rotate the heat sink in a clockwise, then
counterclockwise direction until it releases from the processor. Do not pry the heat sink from the
processor.
10
Lift the heat sink off of the processor and set the heat sink aside.
11
Pull the socket-release lever 90 degrees upward until the processor is released from the socket. See
Figure 3-29.
12
Rotate the processor shield upward and out of the way.
94 Installing System Components
Page 95

Figure 3-29. Installing and Removing a Processor
1
6
1 notch in processor (2) 2 processor 3 socket-release lever
4 processor shield 5 ZIF socket 6 socket key (2)
13
Lift the processor out of the socket and leave the release lever up so that the socket is ready for the new
2
5
4
3
processor.
NOTICE: Be careful not to bend any of the pins on the ZIF socket when removing the processor. Bending the pins
can permanently damage the system board.
Installing a Processor
1
Unpack the new processor.
2 Align the processor with the
3Install the processor in the socket.
socket keys on t
he ZIF socket. See
Figure 3-29.
NOTICE: Positioning the processor incorrectly can permanently damage the system board or the processor when
you turn it on. When placing the processor in the socket, be careful not to bend the pins in the socket.
If the release lever on the processor socket is not positioned all the way up, move it to that
a
position.
b With the
NOTICE: Do not use force to seat the processor. When the processor is positioned correctly, it engages easily into
the socket.
Close the processor shield. See Figure 3-29.
c
d
W
hen the processor is fully seated in the socket, rotate the socket release lever back down until
it snaps into place, securing the processor.
p
rocessor and
the
socket
keys
aligned, set the processor lightly in the socket.
See Figure 3-29.
Installing System Components 95
Page 96

4
Install the heat sink.
NOTE: If you did not receive a replacement heat sink, use the heat sink that you removed in step 10.
a
If you receive a heat sink and pre-applied thermal grease with your processor kit, remove the
protective sheet from the thermal grease layer on top of the heat sink.
If you did not receive a replacement heat sink with your processor kit, do the following:
• Using a clean lint-free cloth, remove the existing thermal grease from the heat sink you
removed in step 10.
• Open the grease packet included with your processor kit and apply thermal grease evenly to
the top of the processor.
b Place the heat sink on the processor. See
c Close one of the two heat sink retention levers until it locks. See
d
Repeat for the other heat sink retention lever.
5
Reinstall the fan bracket. See "Replacing the Fan Bracket" on page 69.
6
Close the system. See "Closing the System" on page 55.
Figure 3-28
.
Figure 3-28
.
As the system boots, it detects the presence of the new processor and automatically changes the system
configuration information in the System Setup program.
7
Press <F2> to enter the System Setup program, and check that the processor information matches the
new system configuration. See "Entering the System Setup Program" on page 37.
8
Run the system diagnostics to verify that the new processor operates correctly.
See "Running the System Diagnostics" on page 132 for information about running the diagnostics.
System Battery
The system battery is a 3.0-volt (V), coin-cell battery.
Replacing the System Battery
CAUTION: Only trained service technicians are authorized to remove the system cover and access any of the
components inside the system. See your Product Information Guide for complete information about safety
precautions, working inside the computer, and protecting against electrostatic discharge.
CAUTION: There is a danger of a new battery exploding if it is incorrectly installed. Replace the battery only
with the same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer. Discard used batteries according to the
manufacturer's instructions. See your System Information Guide for additional information.
1
Turn off the system, including any attached peripherals, and disconnect the system from the electrical
outlet.
2
Open the system. See "Opening the System" on page 54
96 Installing System Components
Page 97

3
Locate the battery socket. See "System Board Connectors" on page 137.
NOTICE: If you pry the battery out of its socket with a blunt object, be careful not to touch the system board with
the object. Ensure that the object is inserted between the battery and the socket before you attempt to pry out the
battery. Otherwise, you may damage the system board by prying off the socket or by breaking circuit traces on the
system board.
NOTICE: To avoid damage to the battery connector, you must firmly support the connector while installing or
removing a battery.
4
Remove the system battery.
a
Support the battery connector by pressing down firmly on the positive side of the connector.
b
While supporting the battery connector, press the battery toward the positive side of the
connector and pry it up out of the securing tabs at the negative side of the connector.
Figure 3-30. Replacing the System Battery
1
2
3
1 positive side of battery
connector
NOTICE: To avoid damage to the battery connector, you must firmly support the connector while installing or
removing a battery.
5
Install the new system battery.
a
Support the battery connector by pressing down firmly on the positive side of the connector.
b
Hold the battery with the "+" facing up, and slide it under the securing tabs at the positive side of
2 system battery 3 negative side of battery
connector
the connector.
c
Press the battery straight down into the connector until it snaps into place.
6
Close the system. See "Closing the System" on page 55.
7
Reconnect the system to its electrical outlet and turn the system on, including any attached
peripherals.
Installing System Components 97
Page 98

8
Enter the System Setup program to confirm that the battery is operating properly. See "Entering the
System Setup Program" on page 37.
9
Enter the correct time and date in the System Setup program's
10
Exit the System Setup program.
11
To test the newly installed battery, turn off the system and disconnect it from the electrical outlet for
at least an hour.
12
After an hour, reconnect the system to its electrical outlet and turn it on.
13
Enter the System Setup program and if the time and date are still incorrect, see "Getting Help" on
page 147 for instructions on obtaining technical assistance.
Time
and
Date
fields.
Expansion-Card Riser Boards
Removing the Left Expansion-Card Riser Board
CAUTION: Only trained service technicians are authorized to remove the system cover and access any of the
components inside the system. See your Product Information Guide for complete information about safety
precautions, working inside the computer, and protecting against electrostatic discharge.
1
Turn off the system and attached peripherals, and disconnect the system from the electrical outlet.
2
Open the system. See "Opening the System" on page 54.
3
Remove any expansion cards from the left riser expansion-card slots. See "Removing an Expansion
Card" on page 78.
4
Remove the expansion-card cage. See "Removing the Expansion-Card Cage" on page 78.
5
Remove the expansion-card riser board:
a
Pull the expansion-card riser release pin. See Figure 3-31.
b
While pulling the release pin, slide the riser board away from the expansion card openings.
c
Lift the riser board from the six securing tabs.
98 Installing System Components
Page 99

Figure 3-31. Replacing the Left Riser Board
3
2
1
1 riser release pin 2 expansion-card rails 3 expansion-card cage
4 riser securing tabs (6) 5 riser securing slots (6)
4
Installing the Left Riser Board
5
CAUTION: Only trained service technicians are authorized to remove the system cover and access any of the
components inside the system. See your Product Information Guide for complete information about safety
precautions, working inside the computer, and protecting against electrostatic discharge.
1
Place the riser board in the expansion-card cage so that the six securing tabs are fully inserted in the six
securing slots on the riser board. See Figure 3-31.
2
Slide the riser board toward the expansion card openings until you feel the riser-board release pin snap
into place.
3
Replace the expansion-card cage. See "Replacing the Expansion-Card Cage" on page 79.
4
Install all expansion cards in the expansion-card slots. See "Installing an Expansion Card" on page 76.
5
Close the system. See "Closing the System" on page 55.
Installing System Components 99
Page 100

Removing the Central Riser Board
CAUTION: Only trained service technicians are authorized to remove the system cover and access any of the
components inside the system. See your Product Information Guide for complete information about safety
precautions, working inside the computer, and protecting against electrostatic discharge.
1
Press the blue release tab in the center of the central riser to release the board from the system board
socket while easing both ends of the riser upward.
2
Lift the central riser board from the two guide pins on either end, and draw the riser away from the
system board.
Figure 3-32. Replacing the Central Riser Board
2
1
1 card guide (2) 2 release tab 3 central riser board
4 guide pins (2) 5 system board socket
3
4
5
Installing the Central Riser Board
1
Fitting the two guides over the guide pins on the system board, gently lower the central riser board
until the board connector is firmly seated into the system board socket. See Figure 3-32.
100 Installing System Components
 Loading...
Loading...