Datto OM2P User Manual

Wireless 802.11b/g/n
Mesh Router
Long Range Wireless N
Client Bridge/Access Point
Model: OM2P
User Manual
Version : 1.0

Table of Contents
CHAPTER 1 PRODUCT OVERVIEW............................................................................................................................. 7
1.1 F
EATURE
....................................................................................................................................................................... 7
1.2 B
ENEFITS
....................................................................................................................................................................... 8
1.3 P
ACKAGE CONTENTS
1.3 S
YSTEM REQUIREMENT
CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE OVERVIEW........................................................................................................................10
CHAPTER 3 INSTALLATION .......................................................................................................................................11
CHAPTER 4 CONFIGURING YOUR COMPUTER FOR TCP/IP .................................................................................14
4.1 C
ONFIGURING MICROSOFT WINDOWS
4.2 C
ONFIGURING MICROSOFT WINDOWS VISTA
4.3 C
ONFIGURING MICROSOFT WINDOWS
4.4 C
ONFIGURING MICROSOFT WINDOWS
4.5 C
ONFIGURING AN APPLE MACINTOSH COMPUTER
CHAPTER 5 INTRODUCING THE WEB CONFIGURATOR.....................................................................................................23
...................................................................................................................................................... 9
.................................................................................................................................................. 9
7 ............................................................................................................................ 15
....................................................................................................................... 17
XP .......................................................................................................................... 19
2000 ...................................................................................................................... 20
................................................................................................................ 22
5.1 L
OGGING IN TO THE WEB CONFIGURATOR
CHAPTER 6 STATUS ....................................................................................................................................................25
6.1 S
AVE/LOAD
6.2 M
AIN
6.3 W
IRELESS CLIENT LIST
6.4 S
YSTEM LOG
6.5 C
ONNECTION STATUS
6.6 DHCP C
CHAPTER 7 SYSTEM....................................................................................................................................................31
7.1 C
HANGING OPERATING MODES
CHAPTER 8 WIRELESS CONFIGURATION ................................................................................................................33
8.1 W
IRELESS SETTINGS
8.1.1 Access Point Mode ........ ..... .... .... .... .... ..... .... .... .... .... .................... .... .... .... .... ..... .... .... ................... ..... .... .... .... . 33
8.1.2 Client Bridge Mode ....................................................................................................................................... 37
8.1.3 WDS Bridge Mode......................................................................................................................................... 39
................................................................................................................................................................. 25
......................................................................................................................................................................... 26
................................................................................................................................................. 27
............................................................................................................................................................... 28
.................................................................................................................................................. 29
LIENT TABLE
................................................................................................................................................... 30
..................................................................................................................................................... 33
........................................................................................................................... 23
................................................................................................................................... 31
8.1.4 Client Router Mode ....................................................................................................................................... 41
8.2 W
IRELESS SECURITY SETTINGS
8.2.1 WEP................................................................................................................................................................ 43
8.2.2 WPA-PSK ....................................................................................................................................................... 44
8.2.3 WPA2-PSK ............................................................................................ ..... .... ................... .... ..... .... .... .... .... .... 45
...................................................................................................................................... 43

8.2.4 WPA-PSK Mixed............................................................................................................................................ 46
8.2.5 WPA................................................................................................................................................................ 47
8.2.6 WPA2 ............................................................................................................................................................. 48
8.2.7 WPA Mixed .................................................................................................................................................... 49
8.4 W
IRELESS ADVANCED SETTINGS
8.5 W
IRELESS
MAC F
ILTER
................................................................................................................................................ 52
8.6 WDS L
CHAPTER 9 LAN SETUP ..............................................................................................................................................54
9.1 IP S
9.2 S
CHAPTER 10 ROUTER SETTINGS ..............................................................................................................................56
10.1 WAN S
INK SETTINGS
ETTINGS
PANNING TREE SETTINGS
10.1.1 Static IP........................................................................................................................................................ 56
10.1.2 DHCP (Dynamic IP) .................................................................................................................................... 58
10.1.3 PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) ..................................................................... .... ..... .... .... .. 60
10.1.4 PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) ........................................................................................ .... .... 62
................................................................................................................................................................ 54
ETTINGS
................................................................................................................................................... 53
........................................................................................................................................................ 56
................................................................................................................................... 50
........................................................................................................................................... 55
10.2 LAN S
10.3 VPN P
10.4 P
10.5 DMZ ....................................................................................................................................................................... 68
CHAPTER 11 MANAGEMENT SETTINGS..................................................................................................................69
11.1 A
11.2 M
11.3 SNMP S
11.4 B
11.5 F
11.6 T
11.7 LOG.......................................................................................................................................................................... 76
11.8 D
CHAPTER 12 NETWORK CONFIGURATION EXAMPLES.........................................................................................78
12.1 A
ETTINGS (ROUTER MODE
ASS THROUGH
ORT FORWARDING
DMINISTRATION
ANAGEMENT
ETTINGS
ACKUP/RESTORE SETTINGS
IRMWARE UPGRADE
IME SETTINGS
IAGNOSTICS
CCESS POINT
............................................................................................................................................................ 77
................................................................................................................................................ 65
.................................................................................................................................................. 66
...................................................................................................................................................... 69
VLAN............................................................................................................................................... 71
...................................................................................................................................................... 72
................................................................................................................................................. 74
.......................................................................................................................................................... 75
.......................................................................................................................................................... 78
) ............................................................................................................................... 64
...................................................................................................................................... 73
12.2 C
LIENT BRIDGE MODE
12.3 WDS B
12.4 C
CHAPTER 13 BUILDING A WIRELESS NETWORK ...................................................................................................81
13.1 A
13.2 A
RIDGE MODE
LIENT ROUTER
CCESS POINT MODE
CCESS POINT MODE WITH
............................................................................................................................................... 79
................................................................................................................................................. 80
......................................................................................................................................................... 81
................................................................................................................................................ 82
WDS F
UNCTION
............................................................................................................. 82

13.3 C
LIENT BRIDGE MODE
............................................................................................................................................... 83
13.4 WDS B
13.5 C
13.6 RADIUS C
APPENDIX A – TROUBLESHOOTING .................................................................................................................................85
A.1 P
A.2 C
APPENDIX B – SPECIFICATIONS .......................................................................................................................................87
APPENDIX C – GLOSSARY ................................................................................................................................................88
APPENDIX D – FCC INTERFERENCE STATEMENT ...............................................................................................................93
RIDGE MODE
LIENT ROUTER MODE
ONNECTIONS
ROBLEM SOLVING
ONTACTING TECHNICAL SUPPORT
................................................................................................................................................. 83
.............................................................................................................................................. 84
........................................................................................................................................... 84
......................................................................................................................................................... 85
.................................................................................................................................... 86

About This Document
Audience
This document is written for networking professionals responsible for installing and managing
the EnGenius ENH Series Outdoor Access Point/Bridge. To use this guide, you should have
knowledge about TCP/IP and IEEE 802.11 standards, and be familiar with the concepts and
terminology associated with wireless local-area networks (WLANs).
This document provides the information you need to install and configure your Access
Point/bridge.
Convention
This publication uses these conventions/symbols to convey instructions and information
and highlight special message.
Caution: This symbol represents the important message on incorrect device
operation that might damage the device
Note: This symbol represents the important message for the settings.
Tip: This symbol represents the alternative choice that can save time or
resources.
Icons used
__________________________________________________
Figures in this document may use the following generic icons.
EHN device
Internet
Power adapter
WLAN signal
Client computer desktop
Client computer laptop
PoE injector

Chapter 1
Thank you for choosing OM2P. The OM2P is a long range, high-performance IEEE 802.11b/g/n network solution that
provides Access Point, Client Bridge, WDS, and Client Router functions in a single device.
In addition to providing the latest wireless technology, the OM2P supports Power over Ethernet and Power by Adapter
capabilities, which allow the device to be installed easily in nearly any indoor or outdoor location. Advanced features
include power level control, narrow bandwidth selection, traffic shaping, and Real-time RSSI indication.
A variety of security features help to protect your data and privacy while you are online. Security features include Wi-Fi
Protected Access (WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK), 64/128/152-bit WEP Encryption, and IEEE 802.1x with RADIUS.
1.1 Feature
The following list summarizes the key features of the OM2P:
Product Overview
-
High-speed data rates up to 150 Mbps make the OM2P ideally suited for handling heavy data payloads
such as MPEG video streaming
- Fully Interoperable with IEEE 802.11b/IEEE 802.11g/IEEE 802.11n-compliant devices
- Multi-function capabilities enable users to use different modes in various environments
- Point-to-point and point-to-multipoint wireless connectivity enable data transfers between two or more
buildings
- Channel bandwidth selection allows the appropriate bandwidth to be used to reach various distances
- RSSI indicator makes it easy to select the best signal for Access Point connections
- Power-over-Ethernet capabilities allow for flexible installation locations and cost savings
- Four SSIDs let clients access different networks through a single Access Point, and assign different policies
and functions for each SSID
- WPA2/WPA/ WEP/ IEEE 802.1x support and MAC address filtering ensure secure network connections
- PPPoE/PPTP function support make it easy to access the Internet via Internet Service Provider (ISP) service
authentication
- SNMP Remote Configuration Management helps administrators remotely configure or manage the Access
Point
- QoS (WMM) support enhances performance and user experiences

1.2 Benefits
The OM2P is the ideal product around which you can build your WLAN. The following list summarizes
a few key advantages that WLANs have over wired networks:
Ideal for hard-to-wire environments
There are many scenarios where cables cannot be used to connect networking devices.
Historic and older buildings, open areas, and busy streets, for example, make wired LAN
installations difficult, expensive, or impossible.
Temporary workgroups
WLANs make it easy to provide connectivity to temporary workgroups that will later be
removed. Examples include parks, athletic arenas, exhibition centers, disaster-recovery
shelters, temporary offices, and construction sites.
Ability to access real-time information
With a WLAN, workers who rely on access to real-time information, such as doctors and
nurses, point-of-sale employees, mobile workers, and warehouse personnel, can access
the data they need and increase productivity, without having to look for a place to plug
into the network.
Frequently changed environments
WLANs are well suited for showrooms, meeting rooms, retail stores, and manufacturing
sites where workplaces are rearranged frequently.
Wireless extensions to Ethernet networks
WLANs enable network managers in dynamic environments to minimize overhead caused
by moves, extensions to networks, and other changes.
Wired LAN backup
Network managers can implement WLANs to provide backup for mission-critical
applications running on wired networks.
Mobility within training/educational facilities
Training sites at corporations and students at universities are a few examples where
wireless connectivity can be used to facilitate access to information, information
exchanges, and learning.

1.3 Package Contents
Open the package carefully and make sure it contains all of the items listed below.
- One EnGenius Wireless Access Point / Client Bridge (OM2P)
- One 24V/0.6A power adapter
- One PoE injector (EPE-24R)
- One mast strap
- One quick-installation guide
- One CD containing the user manual
If any item is missing or damaged, contact your place of purchase immediately.
Keep all packing materials in case you need to return the OM2P. The OM2P must be returned with its
original packing materials.
Use only the power adapter supplied with your OM2P. Using a different power adapter
can damage the OM2P.
1.3 System Requirement
To install the OM2P, you need an Ethernet cable and a computer equipped with:
- An Ethernet interface
- One of the following operating systems: Microsoft Windows XP, Vista, or 7; or Linux
- An Internet browser that supports HTTP and JavaScript

Chapter 2
The following figures show the key components on the OM2P.
Hardware Overview
2.1 Bottom View
The bottom panel of the OM2P contains two RJ-45 ports, a PoE interface, and a Reset button. A
removable cover covers these components.
- The RJ-45 port connects to an Ethernet adapter in a computer you use to configure the OM2P. For
more information, see Chapter 4.
- The PoE interface allows the OM2P to be powered using the supplied PoE injector.
- The Reset button can be used to reboot the OM2P and return the device to its default factory
configuration, erasing any overrides you may have made to the device’s default settings. The
Reset button is recessed to prevent accidental resets. To reboot the OM2P, use a flat object such
as a pencil to press the Reset button for approximately 10 seconds and then stop pressing the
Reset button.
2.2 Back Panel
The back panel of the OM2P contains the LED indicators that show the link quality and status of the
OM2P.

Chapter 3
This chapter describes how to install the OM2P. It also describes the OM2P LEDs.
codes and, wherever applicable, are licensed by the appropriate government regulatory authorities
should install the OM2P.
Installation
Only experienced installation professionals who are familiar with local building and safety
3.1 Pre-installation Guidelines
Select the optimal locations for the equipment using the following guidelines:
-
T
he OM2P should be mounted on a 1"-4" pole. Its location should enable easy access to the unit
and its connectors for installation and testing.
- The higher the placement of the antenna, the better the achievable link quality.
- The antenna should be installed to provide a direct, or near line of sight with the Base Station
antenna. The antenna should be aligned to face the general direction of the Base Station.
3.2 Installing the OM2P
To install the OM2P, use the following procedure to mount the device on a pole and refer to the
figure below.
1. The bottom of the OM2P is a movable cover. Grab the cover and pull it back hard to
remove the cover.
2. Insert a standard Ethernet cable into the RJ-45 port labeled MAIN LAN.
3. Slide the cover back to seal the bottom of the OM2P.
4. Remove the power cord and PoE injector from the box and plug the power cord into the
DC port of the PoE injector.
Only use the power adapter supplied with the OM2P. Using a different power adapter
might damage the OM2P.
5. Plug the other side of the Ethernet cable in step 3 into the PoE port of the PoE injector.
When you finish step 5, the installation will resemble the following picture.
6. Turn over the OM2P. Then insert the mast strap through the middle hole of the OM2P.
Use a screwdriver to unlock the pole-mounting ring putting it through the OM2P.
7. Mount the EOA200 securely to the pole by locking the strap tightly.
This completes the installation procedure.

3.2 Understanding the OM2P LEDs
The rear of the OM2P has two groups of LEDs. One group, labeled INDICATORS, shows the status of
the device. The second group, LINK QUALITY, shows the strength of the link between the OM2P and
the network. The following table describes the OM2P LEDs.
LED Color Mode Status
Power Green OFF= OM2P is not receiving power.
ON= OM2P is receiving power.
LAN Green OFF = OM2P is not connected to the network.
ON = OM2P is connected to the network, but not sending or
receiving data.
Blink = OM2P is sending or receiving data.
WLAN Green Access Point
or Client
Bridge Mode
Link Quality See Status
column
Access Point
or Client
Bridge Mode
OFF = OM2P radio is off and the device is not sending
or receiving data over the wireless LAN.
ON = OM2P radio is on, and the device is not sending
or receiving data over the wireless LAN.
Blink = OM2P radio is on, and the device is sending
or receiving data over the wireless LAN.
Shows the strength of the link between the OM2P
and the network.
G = good quality (green).
Y = medium quality (yellow).
R = poor or no link (red).

Chapter 4 Configuring Your Computer for TCP/IP
To configure the OM2P, use a computer that is configured for TCP/IP. This chapter describes how to
configure the TCP/IP settings on a computer that will be used to configure the OM2P.
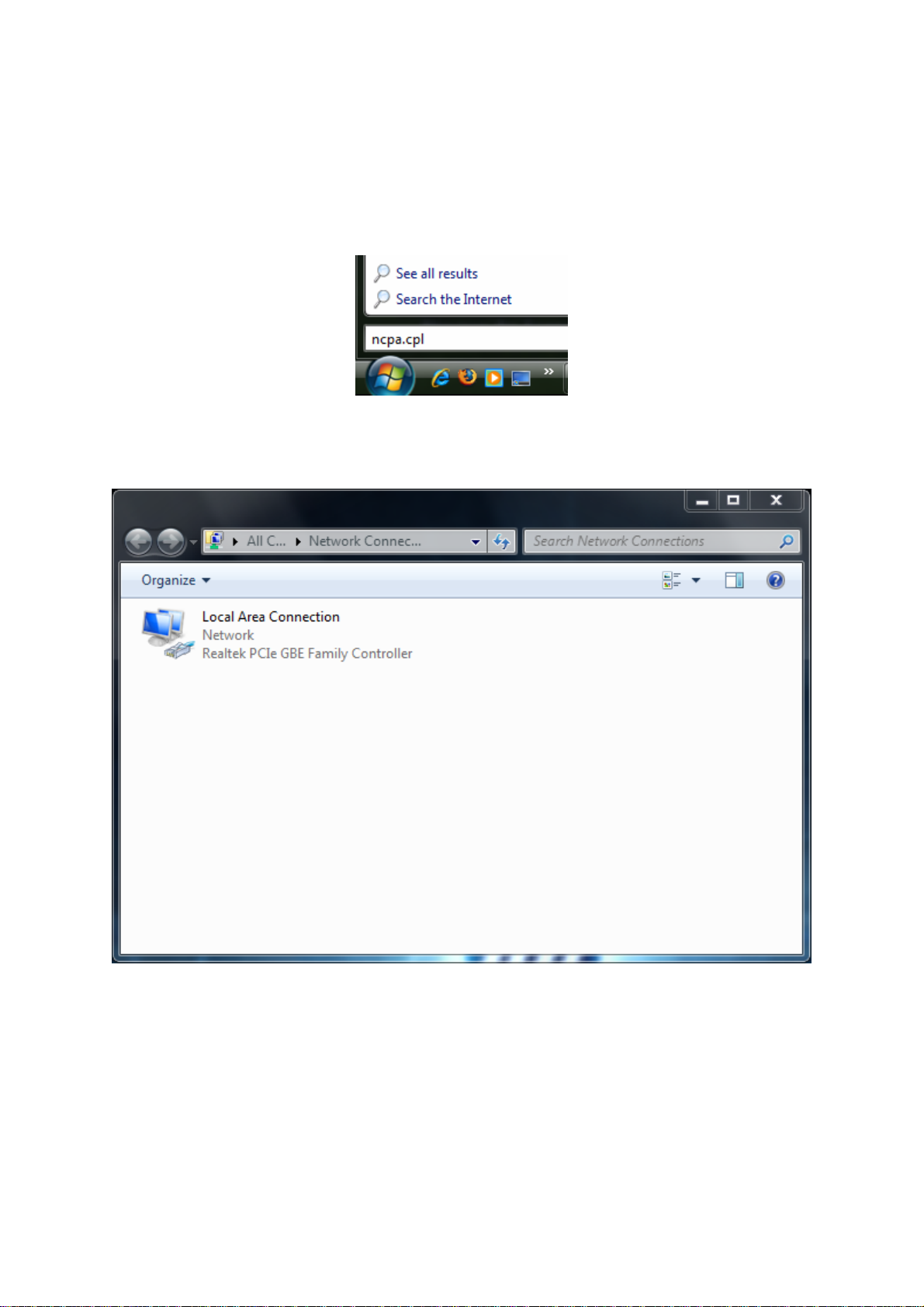
4.1 Configuring Microsoft Windows 7
Use the following procedure to configure a computer running Microsoft Windows 7.
1. In the Start menu search box, type: ncpa.cpl
2. When the Network Connections List appears, right-click the Local Area Connection icon
and click Properties.
3. In the Networking tab, click either Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) or Internet
Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6), and then click Properties.
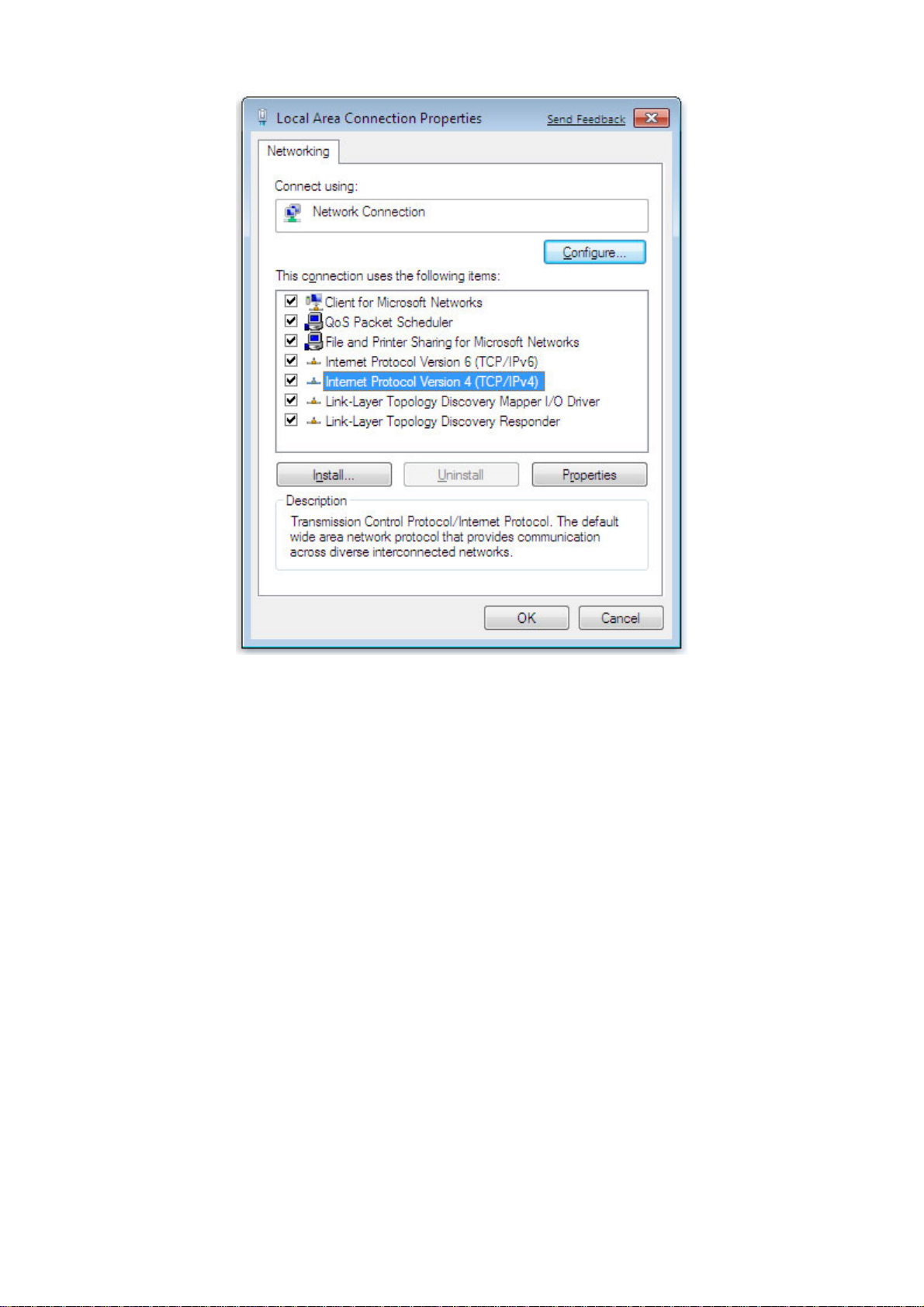
4. In the properties dialog box, click Obtain an IP address automatically to configure your
computer for DHCP.
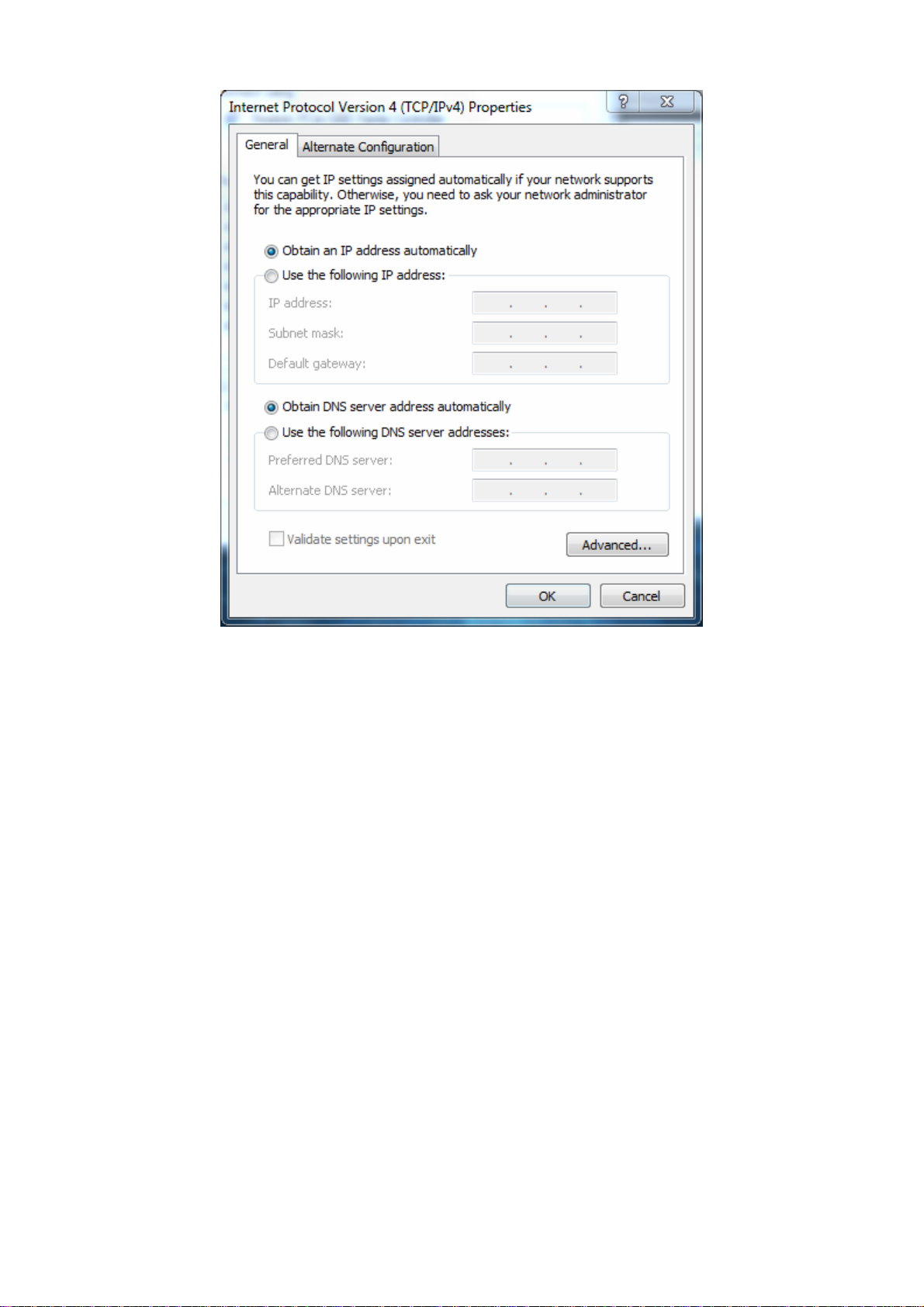
5. Click the OK button to save your changes and close the dialog box.
6. Click the OK button again to save your changes.
4.2 Configuring Microsoft Windows Vista
Use the following procedure to configure a computer running Microsoft Windows Vista with the
default interface. If you use the Classic interface, where the icons and menus resemble previous
Windows versions, perform the procedure in section 4.4.
1. On the Windows taskbar, click Start, click Control Panel, and then select the Network
and Internet icon.
2. Click View Networks Status and tasks and then click Management Networks
Connections.
3. Right-click the Local Area Connection icon and click Properties.
4. Click Continue. The Local Area Connection Properties dialog box appears.
5. In the Local Area Connection Properties dialog box, verify that Internet Protocol
(TCP/IPv4) is checked. Then select Internet Protocol (TCP/IPv4) and click the Properties
button. The Internet Protocol Version 4 Properties dialog box appears.
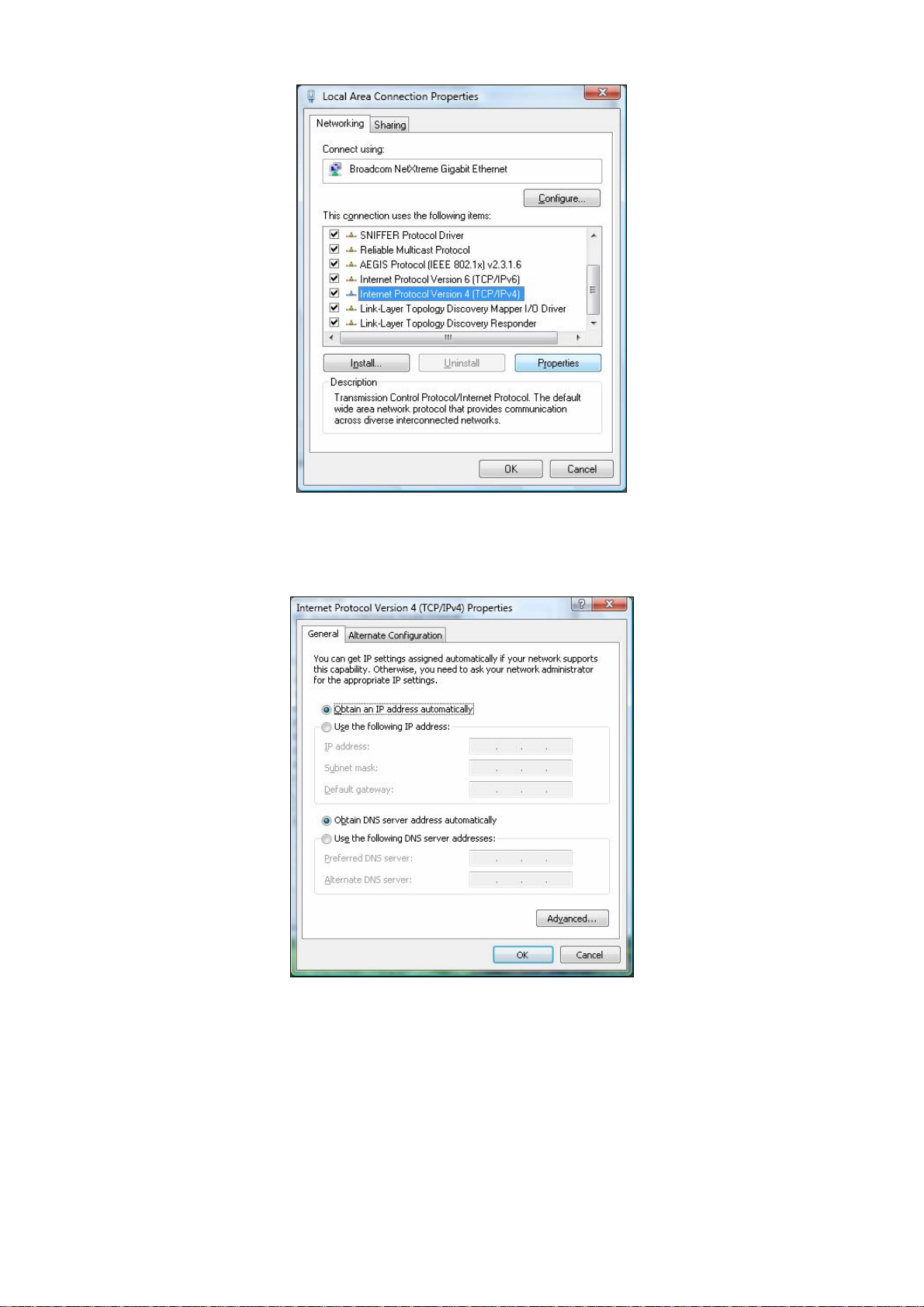
6. In the Internet Protocol Version 4 Properties dialog box, click Obtain an IP address
automatically to configure your computer for DHCP.
7. Click the OK button to save your changes and close the dialog box.
8. Click the OK button again to save your changes.
4.3 Configuring Microsoft Windows XP
Use the following procedure to configure a computer running Microsoft Windows XP with the default
interface. If you use the Classic interface, where the icons and menus resemble previous Windows
versions, perform the procedure in section 4.4.
1. On the Windows taskbar, click Start, click Control Panel, and then click Network and
Internet Connections.
2. Click the Network Connections icon.
3. Click Local Area Connection for the Ethernet adapter connected to the OM2P. The Local
Area Connection Status dialog box appears.
4. In the Local Area Connection Status dialog box, click the Properties button. The Local
Area Connection Properties dialog box appears.
5. In the Local Area Connection Properties dialog box, verify that Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
is checked. Then select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click the Properties button. The
Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box appears.
6. In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, click Obtain an IP address
automatically to configure your computer for DHCP. Click the OK button to save this
change and close the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box.
7. Click the OK button again to save your changes.
8. Restart your computer.
4.4 Configuring Microsoft Windows 2000
Use the following procedure to configure your computer if your computer has Microsoft Windows
2000 installed.
1. On the Windows taskbar, click Start, point to Settings, and then click Control Panel.
2. In the Control Panel window, double-click the Network and Dial-up Connections icon. If
the Ethernet adapter in your computer is installed correctly, the Local Area Connection
icon appears.
3. Double-click the Local Area Connection icon for the Ethernet adapter connected to the
OM2P. The Local Area Connection Status dialog box appears.

4. In the Local Area Connection Status dialog box, click the Properties button. The Local
Area Connection Properties dialog box appears.
5. In the Local Area Connection Properties dialog box, verify that Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
is checked. Then select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click the Properties button.
6. Click Obtain an IP address automatically to configure your computer for DHCP.
7. Click the OK button to save this change and close the Local Area Connection Properties
dialog box.
8. Click OK button again to save these new changes.
9. Restart your computer.
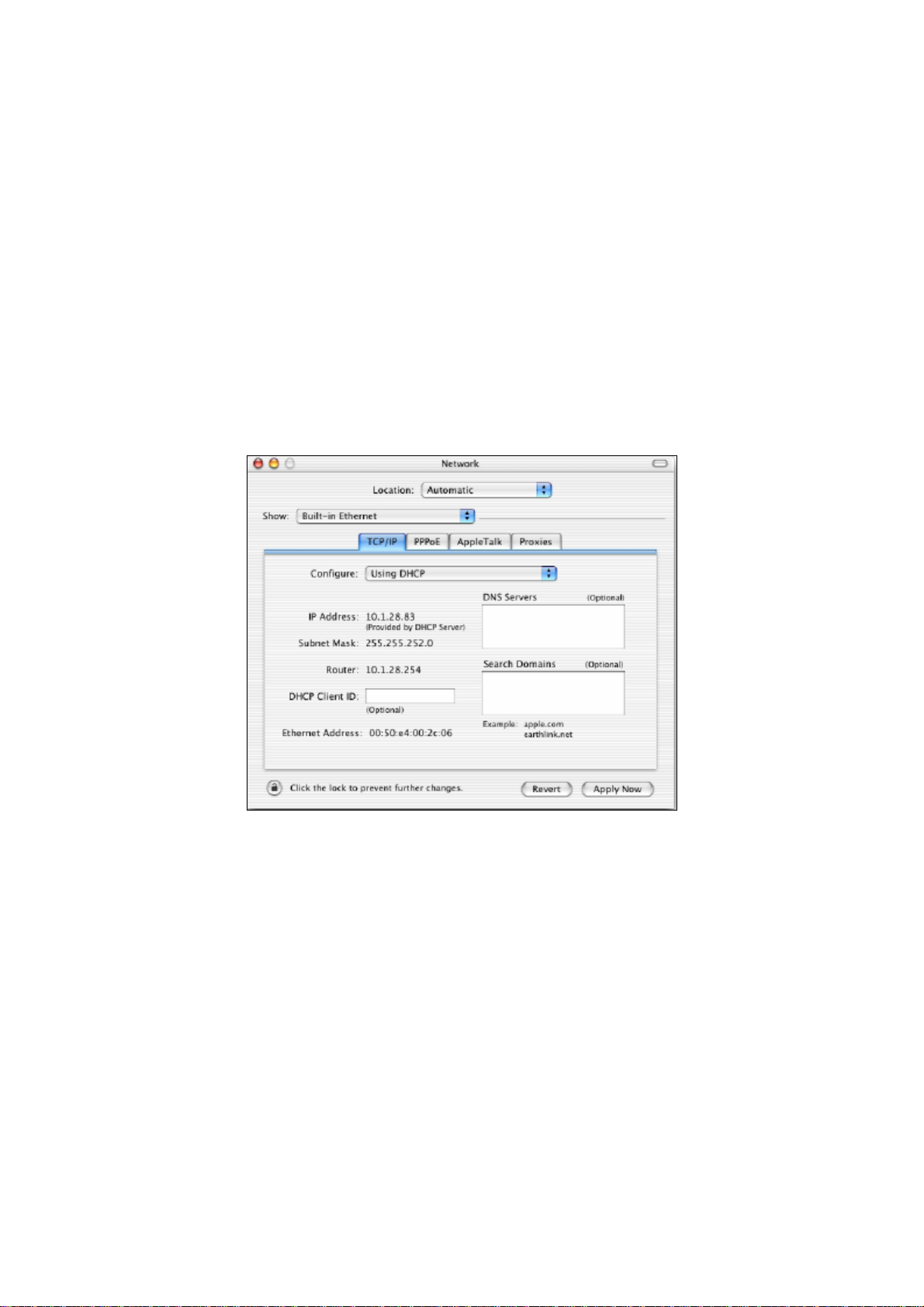
4.5 Configuring an Apple Macintosh Computer
The following procedure describes how to configure TCP/IP on an Apple Macintosh running Mac OS
10.2. If your Apple Macintosh is running Mac OS 7.x or later, the steps you perform and the screens
you see may differ slightly from the following. However, you should still be able to use this procedure
as a guide to configuring your Apple Macintosh for TCP/IP.
1. Pull down the Apple Menu, click System Preferences, and select Network.
2. Verify that the NIC connected to the OM2P is selected in the Show field.
3. In the Configure field on the TCP/IP tab, select Using DHCP.
4. Click Apply Now to apply your settings and close the TCP/IP dialog box.
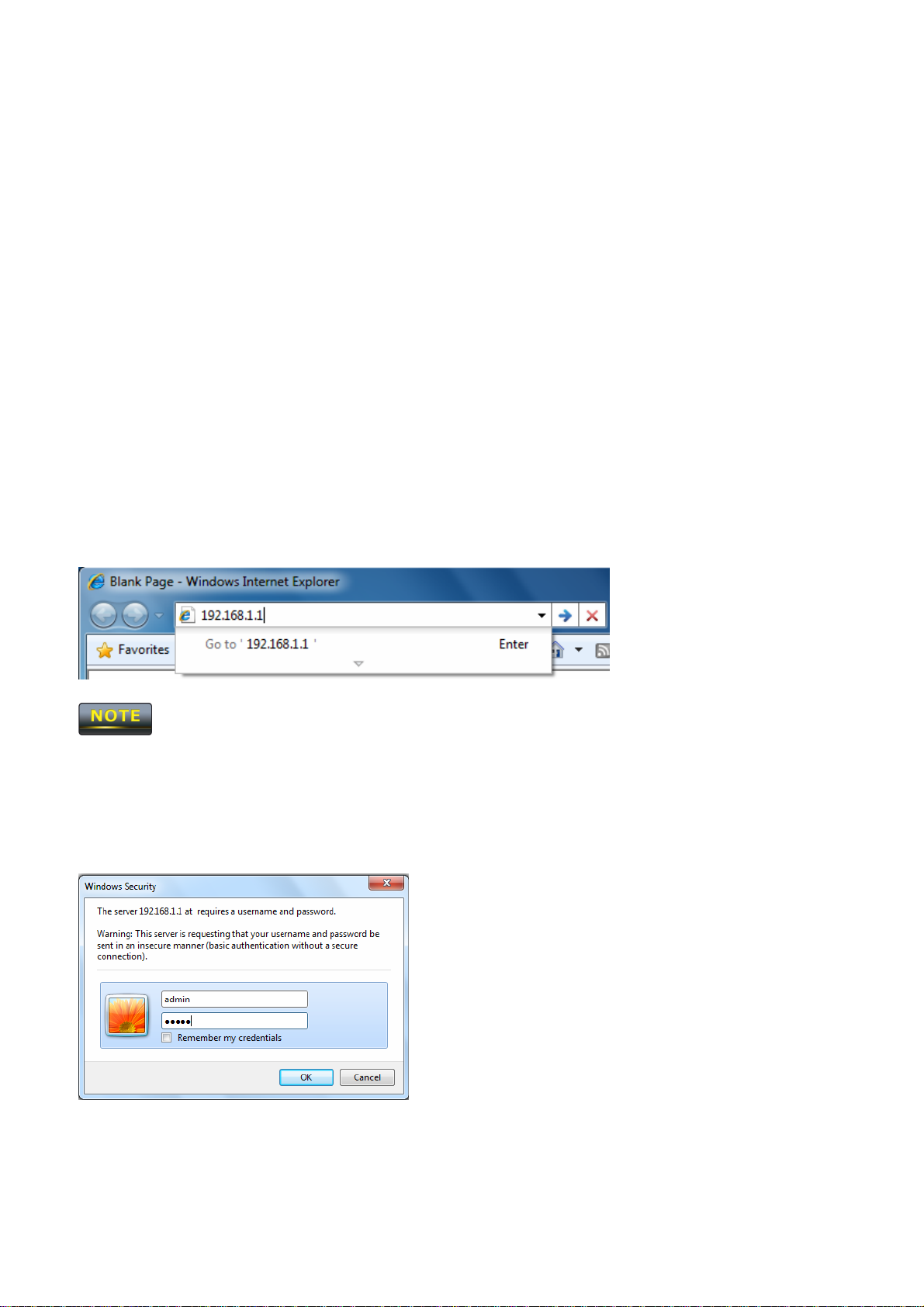
Chapter 5 Introducing the Web Configurator
The OM2P has a built-in Web Configurator that lets you manage the unit from any location using a
Web browser that supports HTTP and has JavaScript installed.
5.1 Logging in to the Web Configurator
After configuring the computer for TCP/IP using the procedure appropriate for your operating system,
use that computer’s Web browser to log in to the OM2P Web Configurator.
1. Launch your Web browser.
2. In the browser address bar, type 192.168.1.1 and press the Enter key.
If you changed the OM2P LAN IP address, enter the correct IP address.
3. When the Windows Security window appears, type admin as the username in the top field and
type admin as the password in the bottom field.
4. Click OK
You are now ready to use the instructions in the following chapters to configure the OM2P.

5.2 Best Practices
Perform the following procedures regularly to make the OM2P more secure and manage the OM2P
more effectively.
- Change the default password. Use a password that is not easy to guess and that contains
different characters, such as numbers and letters. The OM2P username cannot be changed. For
more information, see page 69.
- Back up the configuration and be sure you know how to restore it. Restoring an earlier working
configuration can be useful if the OM2P becomes unstable or crashes. If you forget your password,
you will have to reset the OM2P to its factory default settings and lose any customized override
settings you configured. However, if you back up an earlier configuration, you will not have to
completely reconfigure the OM2P. You can simply restore your last configuration. For more
information, see page 73.
Chapter 6 Status
The Status section on the navigation drop-down menu contains the following options:
- Main
- Wireless Client List
- System Log
- Connection Status
The following sections describe these options.
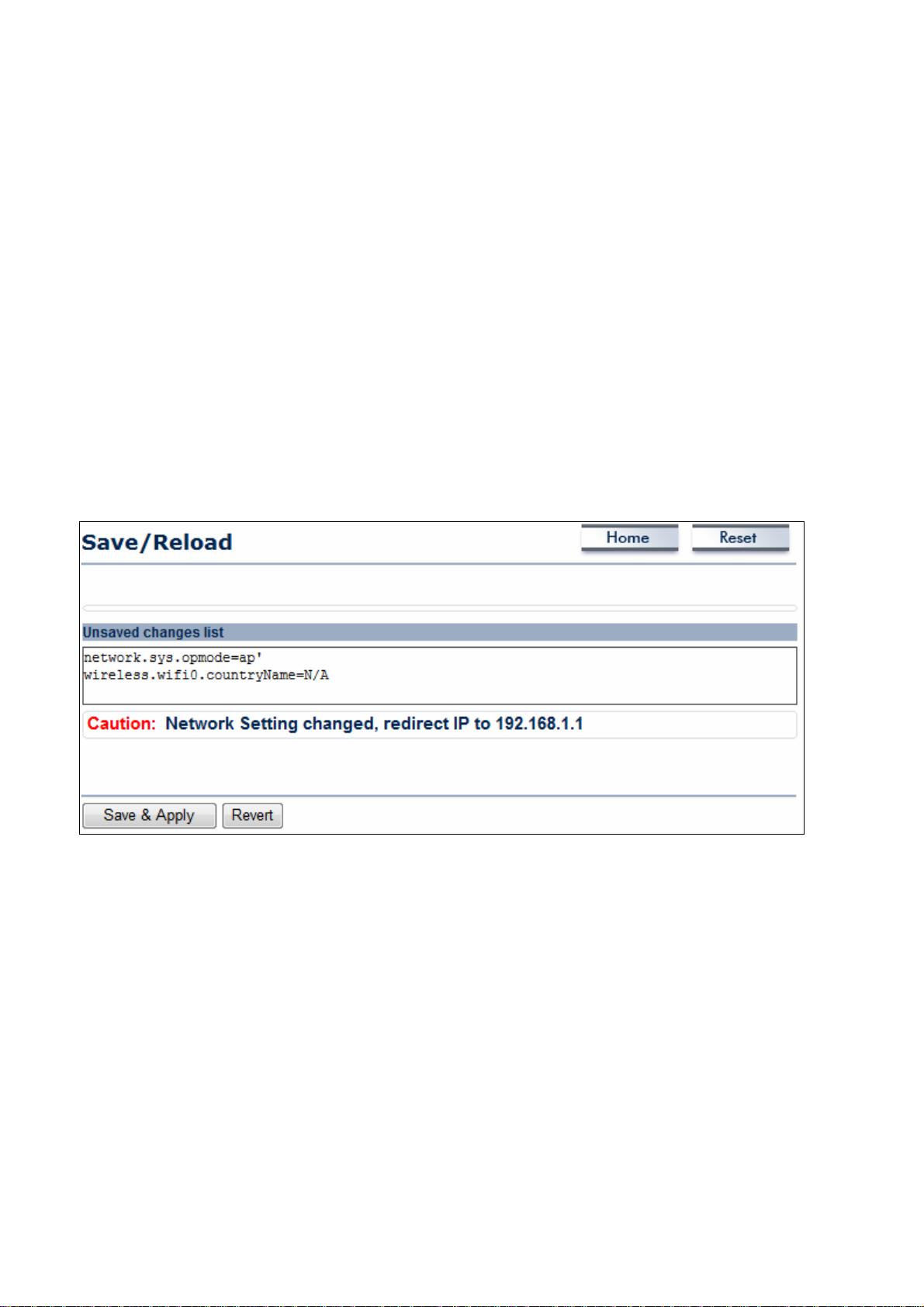
6.1 Save/Load
This page lets you save and apply the settings shown under Unsaved changes list, or cancel
the unsaved changes and revert to the previous settings that were in effect.
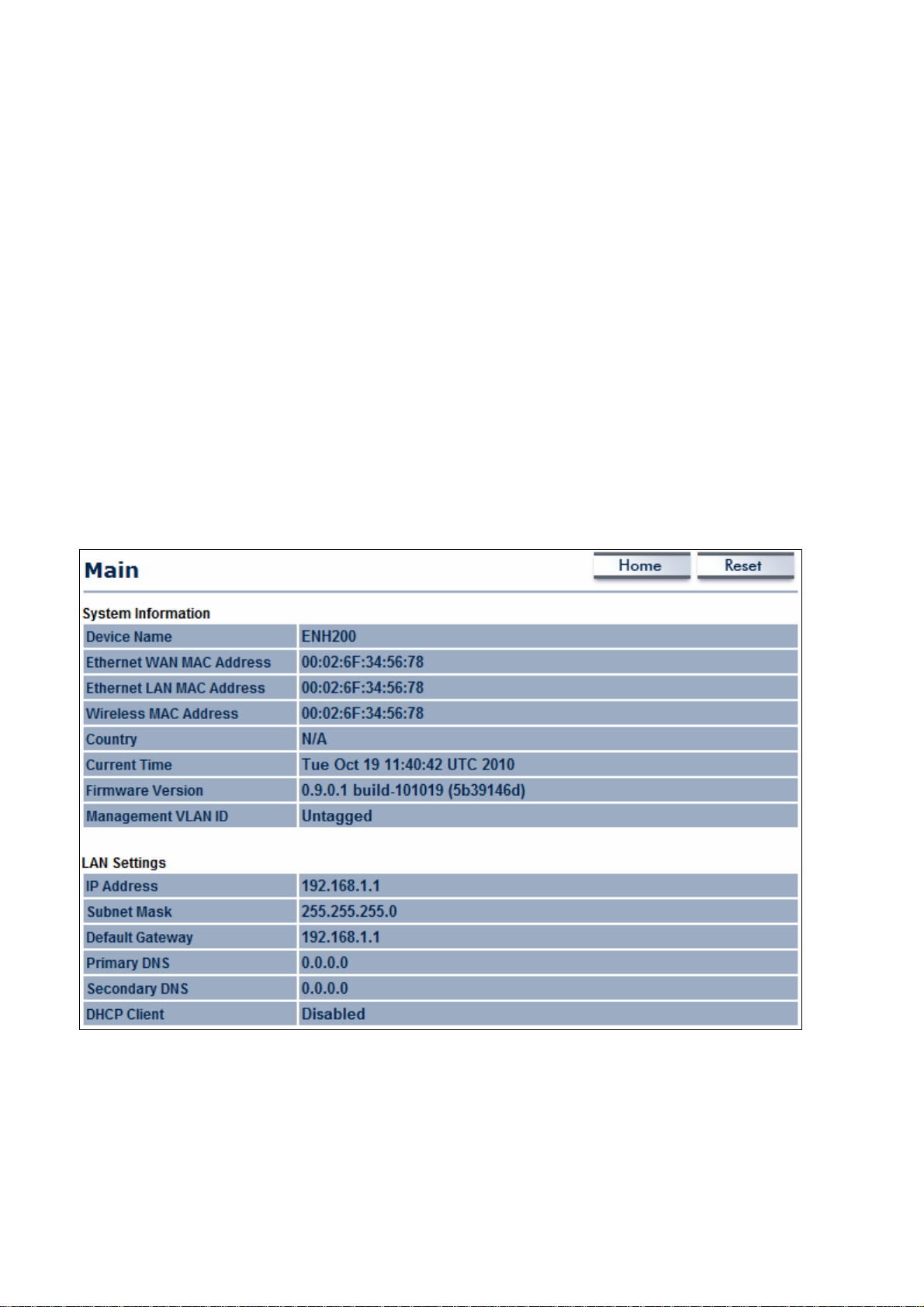
6.2 Main
Clicking the Main link under the Status drop-down menu or clicking Home at the top-right
of the Web Configurator shows status information about the current operating mode.
- The System Information section shows general system information such as operating
mode, system up time, firmware version, serial number, kernel version, and application
version.
- The LAN Settings section shows Local Area Network setting such as the LAN IP address,
subnet mask, and MAC address.
- The Current Wireless Settings section shows wireless information such as frequency and
channel. Since the OM2P supports multiple-SSIDs, information about each SSID, such as
its ESSID and security settings, are displayed.
6.3 Wireless Client List
Clicking the Wireless Client List link under the Status drop-down menu displays the list of
clients associated to the OM2P, along with the MAC addresses and signal strength for each
client. Clicking the Refresh button updates (refreshes) the client list.
6.4 System Log
The OM2P automatically logs (records) events of possible interest in its internal memory. To
view the logged information, click the System Log link under the Status drop-down menu. If
there is not enough internal memory to log all events, older events are deleted from the log.

6.5 Connection Status
Clicking the Connection Status link under the Status drop-down menu displays the current
status of the network. The information shown includes network type, SSID, BSSID, connection
status, wireless mode, current channel, security, data rate, noise level, and signal strength.
6.6 DHCP Client Table
Clicking the DHCP Client List link under the Status drop-down menu displays the clients that
are associated to the OM2P through DHCP. The MAC addresses and signal strength for each
client are also shown. Clicking the Refresh button updates (refreshes) the client list.
 Loading...
Loading...