Datasheet Z8932120FSC, Z8932120PSC, Z8932120VSC, Z8939120VSC, Z8937116FSC Datasheet (ZILOG)
...Page 1

1
0 °
m
FEATURES
DSP ROM
Device
Z89321 4 512 24
Z89371 4 512 16
Z89391 64* 512 24
Note: *External
C to +70 ° C Standard Temperature Range
■
-40 ° C to +85 ° C Extended Temperature Range
4.5- to 5.5-Volt Operating Range
■
(KW)
OTP
(KW)
DSP RAM
Lines
MIPS
(Max)
P
RELIMINARY
P
RODUCT
S
PECIFICATION
Z89321/371/391
16-B
IT
D
IGITAL
40-Pin
Device
Z89321 X X X
Z89371 X X X
Z89391 X
Note: *General-Purpose
DIP
S
IGNAL
44-Pin
PLCC
P
ROCESSORS
44-Pin
QFP
On-Board Peripherals
■
Dual 8/16-Bit CODEC Interface Capable of up to
10 Mbps
1
84-Pin
PLCC
DSP Core
24 MIPS @ 24 MHz Maximum, 16-Bit Fixed Point DSP
■
■
41.7 ns Minimum Instruction Cycle Time
■
Six-Level Hardware Stack
Six Register Address Pointers
■
■
Optimized Instruction Set (30 Instructions)
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The Z893XX products are high-performance Digital Signal
Processors (DSPs) with a modified Harvard-type architecture featuring separate program and data memory. The design has been optimized for processing power while minimizing silicon space.
The single-cycle instruction execution and bus structure
promotes efficient algorithm execution, while the six register pointers provide circular buffering capabilities and dual
operand fetching.
■
-Law Compression Option
(Decompression is Performed in Software)
16-Bit I/O Bus (Tri-Stated)
■
■
Three I/O Address Pins (Latched Outputs)
Wait-State Generator
■
■
Three Vectored Interrupts
13-Bit General-Purpose Timer
■
Three vectored interrupts are complemented by a six-level
stack, and the CODEC interface allows high-speed transfer rates to accommodate digital audio and voice data.
A dedicated Counter/Timer provides the necessary timing
signals for the CODEC interface, and an additional 13-bit
timer is available for general-purpose use.
DS97DSP0100
P R E L I M I N A R Y
1
Page 2
2
Z89321/371/391
16-Bit Digital Signal Processors Zilog
The Z893XX DSPs are optimized to accommodate advanced signal processing algorithms. The 24 MIPS (maximum) operating performance and efficient architecture
provides real-time instruction execution. Compression, filtering, frequency detection, audio, voice detection/synthesis, and other vital algorithms can all be accommodated.
The Z89321/371/391 devices feature an on-board CODEC interface, compatible with 8-bit PCM and 16-bit CODECs for digital audio applications. Additionally, an onboard wait-state generator is provided to accommodate
slow external peripherals.
For prototypes, as well as production purposes, the
Z89371 member of the DSP product family is a one-time
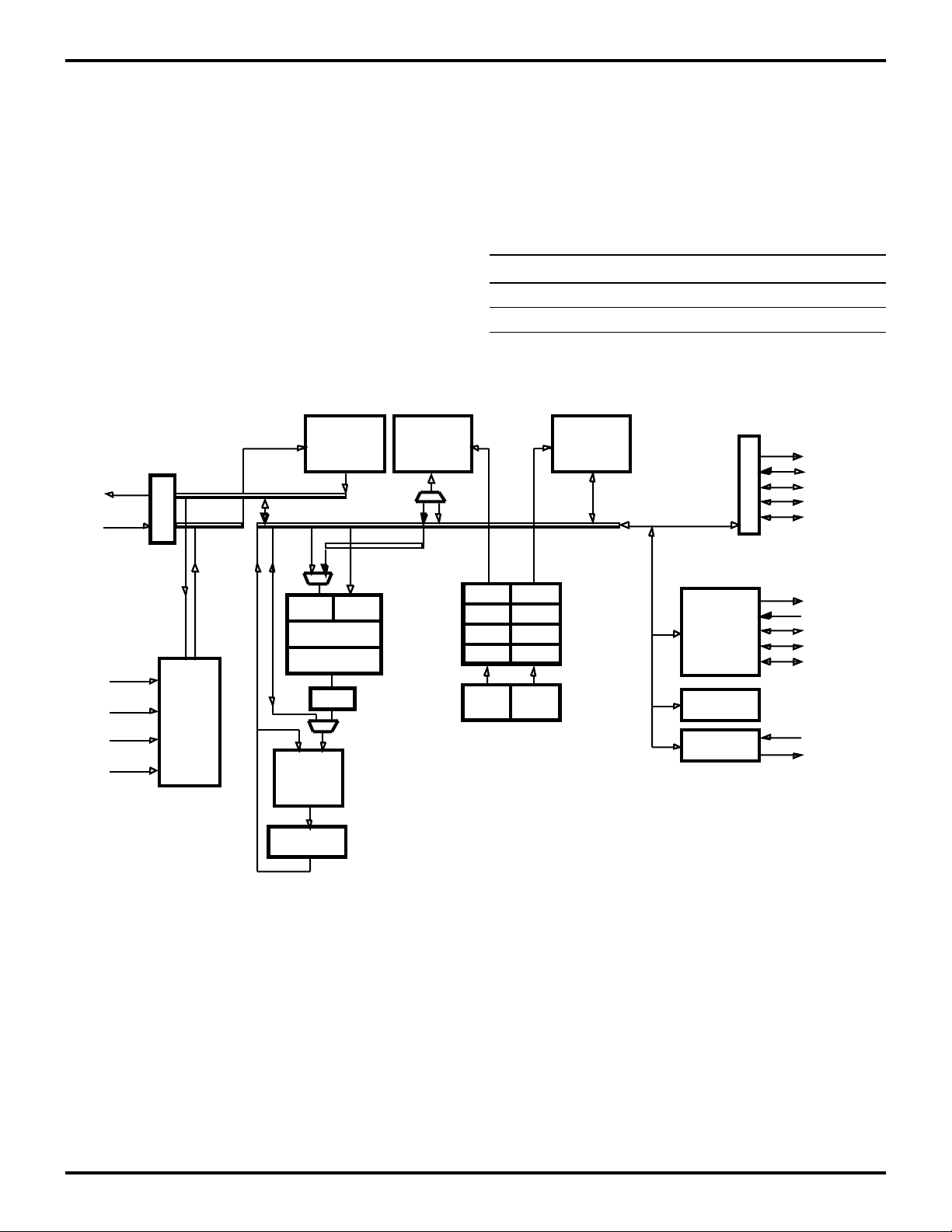
PA0-15
PD0-15
Program
ROM/OTP
4096x16
PDATA
PADDR
Data RAM0
256x16
DDATA
pro-grammable (OTP) device with a 16 MHz maximum operating frequency.
Notes: All signals with a preceding front slash, "/", are
active Low. For example, B//W (WORD is active Low);
/B/W (BYTE is active Low, only).
Power connections follow conventional descriptions below:
Connection Circuit Device
Power V
CC
Ground GND V
Data RAM1
256x16
V
DD
SS
EA0-2
EXT0-15
/DS
WAIT
RD//WR
INT0-2
HALT
/RESET
CLK
Program
Control
Unit
XDATA
P0 P0
XY
Multiplier
P
Shifter
Arithmetic
Logic Unit
(ALU)
Accumulator
P1 P1
P2 P2
DP0-3 DP4-6
ADDR
GEN0
ADDR
GEN1
Figure 1. Z89321/371/391 Functional Block Diagram
8/16-Bit,
Full Duplex,
10 MBPS
Serial Port
13-Bit Timer
User I/O
TXD
RXD
SCLK
FS0
FS1
UI1-0
UO1-0
P R E L I M I N A R Y
DS97DSP0100
Page 3
1
Z89321/371/391
Zilog 16-Bit Digital Signal Processors
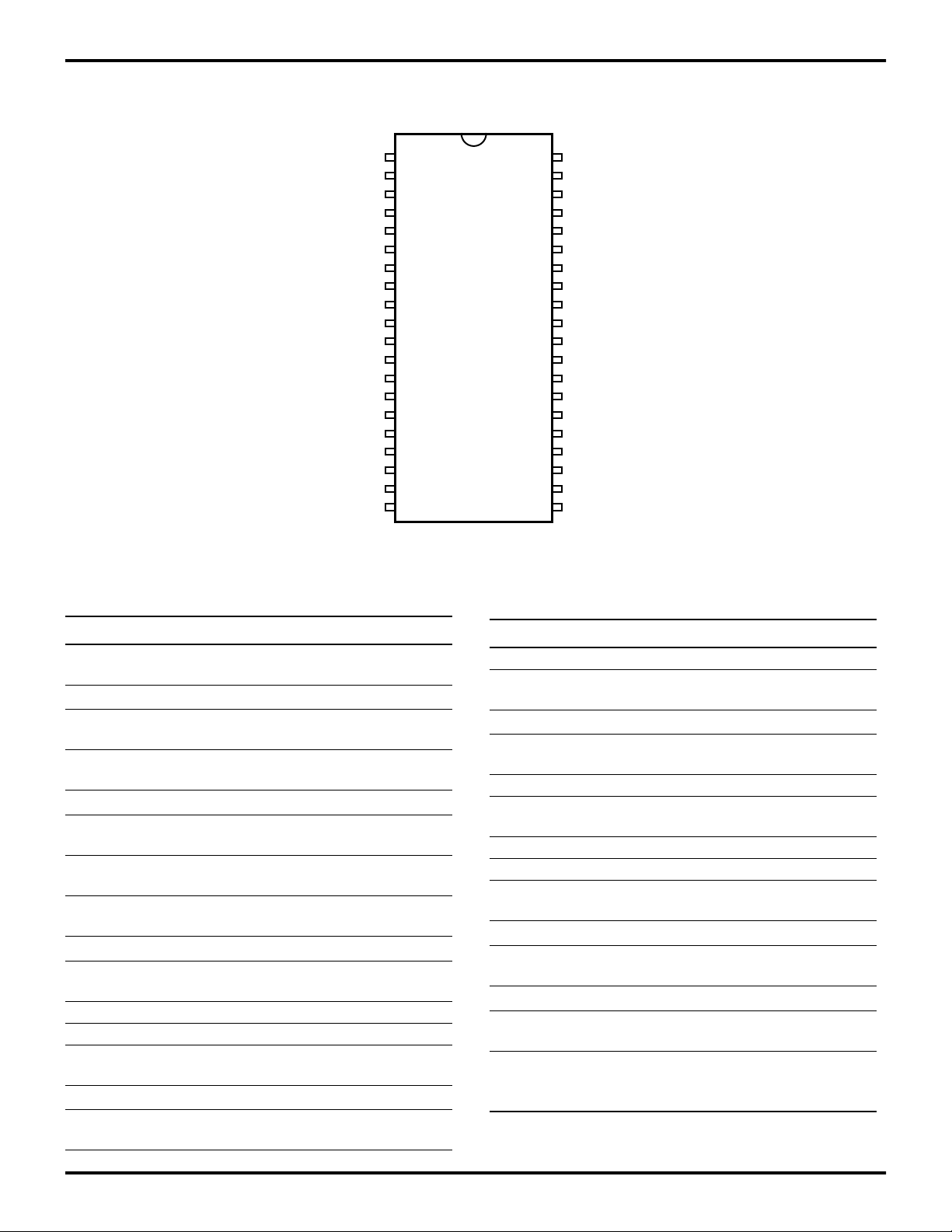
PIN DESCRIPTION
EXT12
EXT13
EXT14
VSS
EXT15
EXT3
EXT4
VSS
EXT5
EXT6
EXT7
TXD
EXT8
EXT9
VSS
EXT10
EXT11
SCLK
1
UI1
UI0
20 21
Figure 2. Z89321/371 40-Pin DIP Pin Assignments
Table 1. Z89321/371 40-Pin DIP Pin IdentiÞcation
DIP 40 - Pin
Table 1. Z89321/371 40-Pin DIP Pin IdentiÞcation
40
RXD
VSS
EXT2
EXT1
EXT0
VSS
FS1
U01
U00
/INT0
FS0
CLK
/DS
VDD
EA2
EA1
EA0
/RESET
RD//WR
VDD
No. Symbol Function Direction
1-3 EXT12-
EXT14
4V
SS
5 EXT15 External Data
External Data
Bus
Ground
Input/Output
Input/Output
Bus
6-7 EXT3-EXT4 External Data
Input/Output
Bus
8V
SS
9-11 EXT5-EXT7 External Data
Ground
Input/Output
Bus
12 TXD Serial Output to
Output
CODECs
13-14 EXT8-EXT9 External Data
Input/Output
Bus
15 V
SS
16-17 EXT10-
EXT11
Ground
External Data
Bus
Input/Output
18 UI1 User Input Input
19 UI0 User Input Input
20 SCLK CODEC Serial
Input/Output*
Clock
21 V
DD
22 RD//WR Strobes for
Power Supply Input
Output
External Bus
No. Symbol Function Direction
23 /RESET Reset Input
24-26 EA0-EA2 External Address
Output
Bus
27 V
DD
28 /DS Data Strobe for
Power Supply Input
Output
External Bus
29 CLK Clock Input
30 FS0 CODEC 0 Frame
Input/Output*
Sync
31 /INT0 Interrrupt Input
32-33 UO0-UO1 User Output Output
34 FS1 CODEC 1 Frame
Input/Output*
Sync
35 V
SS
36-38 EXT0-EXT2 External Data
Ground
Input/Output
Bus
39 V
SS
40 RXD Serial Input from
Ground
Input
CODECs
Notes:
*Input/Output is defined by interface mode selection.
HALT/WAIT pins not available on 40-pin DIP package.
DS97DSP0100
P R E L I M I N A R Y
3
Page 4
4
Z89321/371/391
16-Bit Digital Signal Processors Zilog
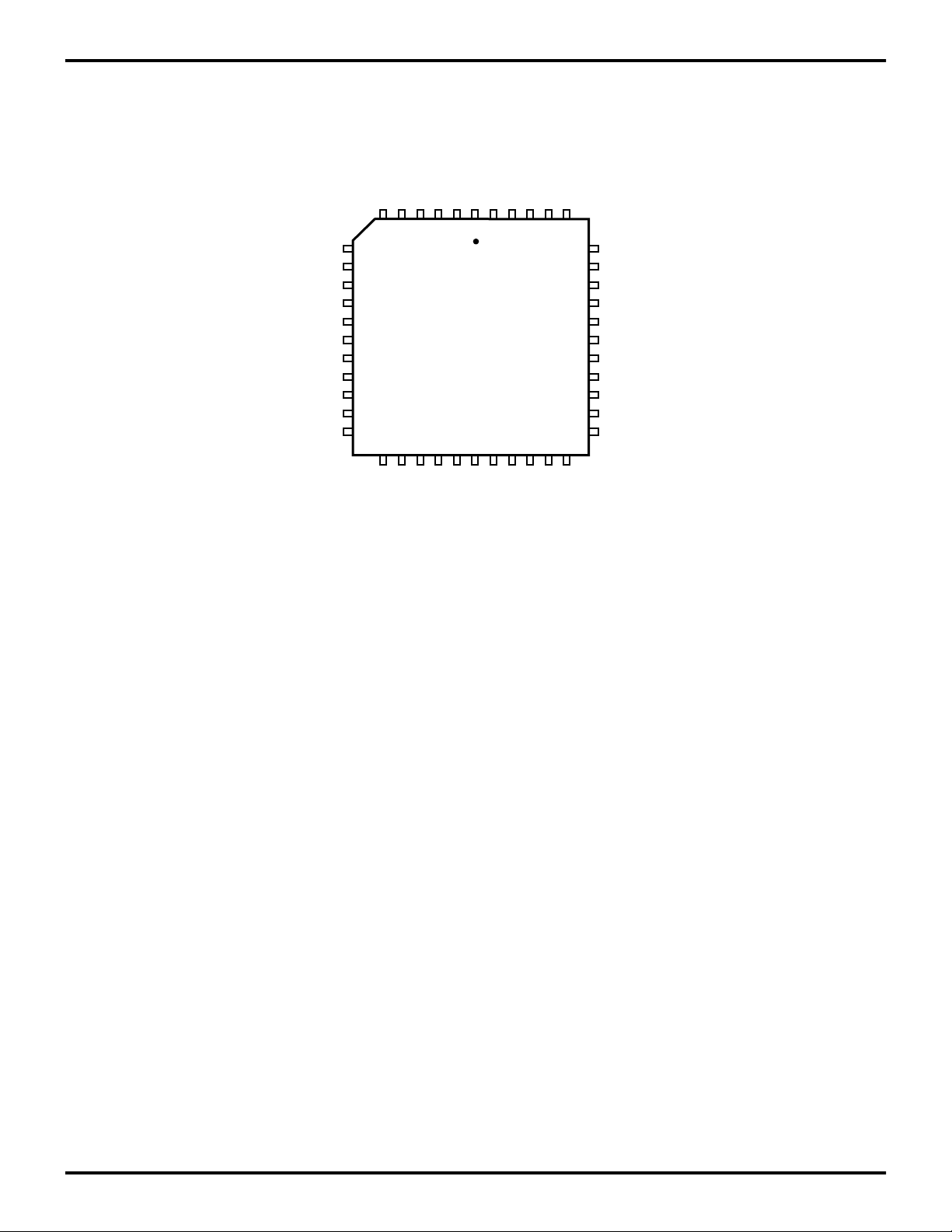
PIN DESCRIPTION (Continued)
FS1
UO1
UO0
/INT0
FSO
HALT
CLK
/DS
VDD
EA2
EA1
VSS
EXT0
EXT1
EXT2
VSS
RXD
EXT12
EXT13
EXT14
VSS
EXT15
7
17
6
EXT3
VSS
EXT4
1
PLCC 44 -Pin
EXT6
EXT7
TXD
EXT5
EXT8
EXT9
40
29
2818
VSS
39
EXT10
EA0
/RESET
WAIT
RD//WR
VDD
SCLK
UI0
UI1
INT1
INT2
EXT11
Figure 3. Z89321/371 44-Pin PLCC Pin Assignments
P R E L I M I N A R Y
DS97DSP0100
Page 5

1
Z89321/371/391
Zilog 16-Bit Digital Signal Processors
Table 2. Z89321/371 44-Pin PLCC Pin IdentiÞcation
No. Symbol Function Direction
1 HALT Stop Execution Input
2 FS0 CODEC 0 Frame Sync Input/Output*
3 /INT0 Interrupt Input
4-5 O0-UO1 User Output Output
6 FS1 CODEC 1 frame sync Input/Output*
7V
SS
Ground
8-10 EXT0-EXT2 External data bus Input/Output
11 V
SS
Ground
12 RXD Serial input from CODECs Input
13-15 EXT12-EXT14 External data bus Input/Output
16 V
SS
Ground
17 EXT15 External data bus Input/Output
18-19 EXT3-EXT4 External data bus Input/Output
20 V
SS
Ground
21-23 EXT5-EXT7 External data bus Input/Output
24 TXD Serial output to CODECs Output
25-26 EXT8-EXT9 External data bus Input/Output
27 V
SS
Ground
28-29 EXT10-EXT11 External data bus Input/Output
30 /INT2 Interrupt Input
31 /INT1 Interrupt Input
32 UI1 User input Input
33 UI0 User input Input
34 SCLK CODEC serial clock Input/Output*
35 V
DD
Power supply Input
36 RD//WR RD//WR strobe for EXT bus Output
37 WAIT WAIT state Input
38 /RESET Reset Input
39-41 EA0-EA2 External Address bus Output
42 V
DD
Power Supply Input
43 /DS Data strobe for external bus Output
44 CLK Clock Input
Note: * Input or output is defined by interface mode selection.
DS97DSP0100
P R E L I M I N A R Y
5
Page 6
6
Z89321/371/391
16-Bit Digital Signal Processors Zilog
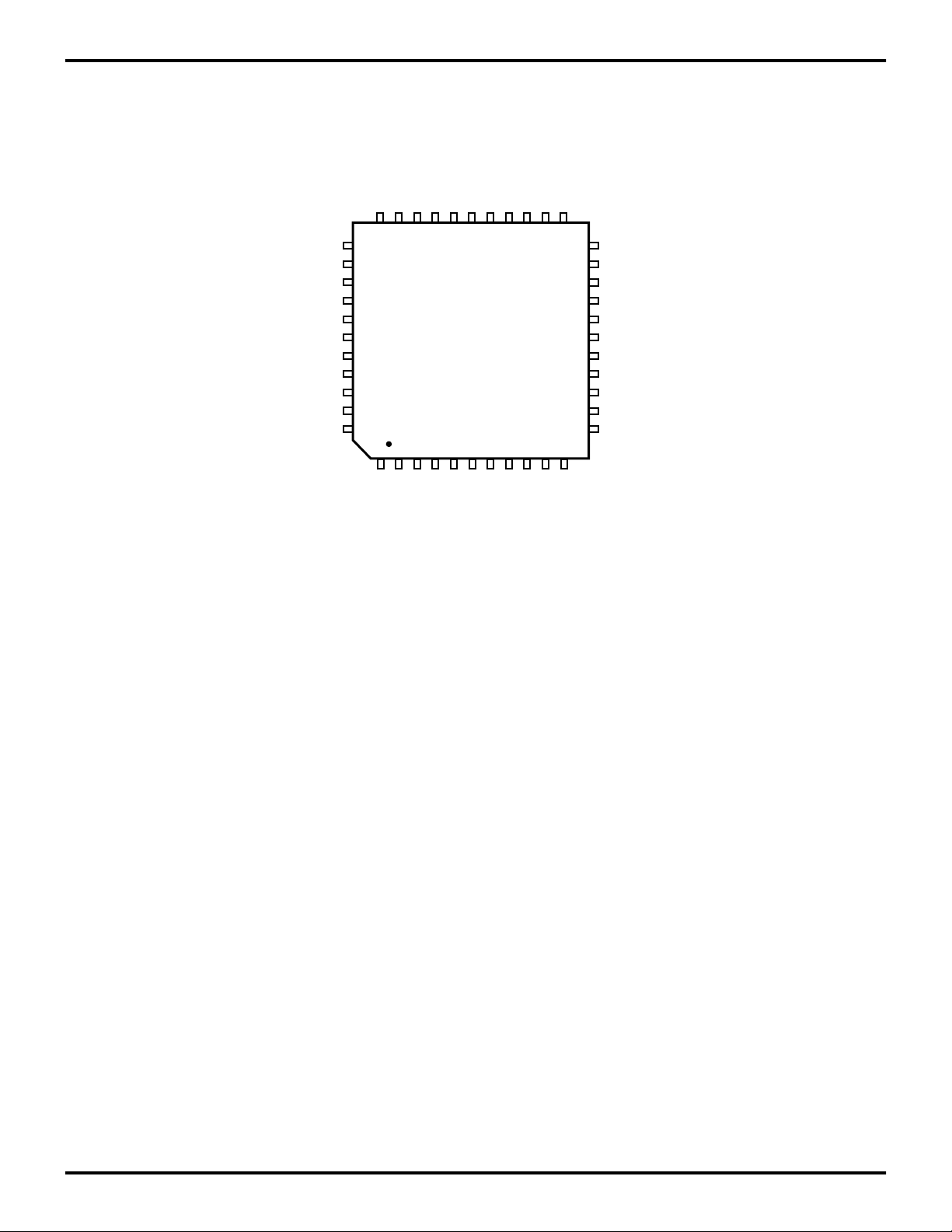
PIN DESCRIPTION (Continued)
FS1
UO1
UO0
/INT0
FSO
HALT
CLK
/DS
VDD
EA2
EA1
2333
11
22
12
EA0
/RESET
WAIT
RD//WR
VDD
SCLK
UI0
UI1
INT1
INT2
EXT11
VSS
EXT0
EXT1
EXT2
VSS
RXD
EXT12
EXT13
EXT14
VSS
EXT15
34
Z89321/371
QFP
44
1
EXT3
EXT4
VSS
EXT5
EXT6
EXT7
TXD
EXT8
EXT9
VSS
EXT10
Figure 4. Z89321/371 44-Pin QFP Pin Assignments
P R E L I M I N A R Y
DS97DSP0100
Page 7

1
Z89321/371/391
Zilog 16-Bit Digital Signal Processors
Table 3. Z89321/371 44-Pin QFP Pin IdentiÞcation
No. Symbol Function Direction
1-2 EXT3-EXT4 External data bus Input/Output
3V
SS
Ground
4-6 EXT5-EXT7 External data bus Input/Output
7 TXD Serial output to CODECs Output
8-9 EXT8-EXT9 External data bus Input/Output
10 V
SS
Ground
11-12 EXT10-EXT1 External data bus Input/Output
13 /INT2 Interrupt Input
14 /INT1 Interrupt Input
15 UI1 User input Input
16 UI0 User input Input
17 SCLK CODEC serial clock Input/Output*
18 V
DD
Power supply Input
19 RD//WR RD//WR strobe EXT bus Output
20 WAIT WAIT state Input
21 /RESET Reset Input
22-24 EA0-EA2 External address bus Output
25 V
DD
Power supply Input
26 /DS Data strobe for external bus Output
27 CLK Clock Input
28 HALT Stop execution Input
29 FS0 CODEC 0 frame sync Input/Output*
30 /INT0 Interrupt Input
31-32 UO0-UO1 User output Output
33 FS1 CODEC 1 frame sync Input/Output*
34 V
SS
Ground
35-37 EXT0-EXT2 External data bus Input/Output
38 V
SS
Ground
39 RXD Serial input to CODECs Input
40-42 EXT12-EXT14 External data bus Input/Output
43 V
SS
Ground
44 EXT15 External data bus Input/Output
Note: *Input or output is defined by interface mode selection.
DS97DSP0100
P R E L I M I N A R Y
7
Page 8
8
Z89321/371/391
16-Bit Digital Signal Processors Zilog
PIN DESCRIPTION (Continued)
/PA_EN
EXT15
PA 7
VSS
PA 6
EXT14
PA 5
EXT13
PA 4
EXT12
RXD
VSS
PA 3
EXT2
PA 2
EXT1
PA 1
EXT0
VSS
PA 0
VDD
/EXTEN
EXT3
PA 8
EXT4
PA 9
VSS
EXT5
PA10
EXT6
PA11
EXT7
TXD
PA12
EXT8
PA13
EXT9
VSS
PA14
EXT10
PA15
VDD
12
32
11
1
Z89391
84-Pin PLCC
75
5333
74
54
VSS
PD15
FS1
PD14
UO1
PD13
UO0
PD12
INTO
FS0
HALT
PD11
CLK
/DS
PD10
VDD
PD9
EA2
PD8
EA1
/ROMEN
VSS
PD0
PD1
EXT11
INT2
PD2
INT1
PD3
UI0
VDD
SCLK
PD4
WAIT
RD//WR
PD5
EA0
PD6
/RESET
UI1
Figure 5. Z89391 84-Pin PLCC Pin Assignments
PD7
VDD
P R E L I M I N A R Y
DS97DSP0100
Page 9

1
Z89321/371/391
Zilog 16-Bit Digital Signal Processors
Table 4. Z89391 84-Pin PLCC Pin IdentiÞcation
No. Symbol Function Direction
1 RXD Serial Input from CODEC Input
2 EXT12 External Data 12 In/Output
3 PA4 Program Address 4 Output
4 EXT13 External Data 13 In/Output
5 PA5 Program Address 5 Output
6 EXT14 External Data 14 In/Output
7 PA6 Program Address 6 Output
8V
SS
Ground
9 PA7 Program Address 7 Output
10 EXT15 External Data 15 In/Output
11 /PA_EN Prog. Mem. Address Enable Input
12 /EXTEN Ext. Bus Enable Input
13 EXT3 External Data 3 In/Output
14 PA8 Program Address 8 Output
15 EXT4 External Data 4 In/Output
16 PA9 Program Address 9 Output
17 V
SS
Ground
18 EXT5 External Data 5 In/Output
19 PA10 Program Address 10 Output
20 EXT6 External Data 6 In/Output
21 PA11 Program Address 11 Output
22 EXT7 External Data 7 In/Output
23 TXD Serial Output to CODEC Output
24 PA12 Program Address 12 Output
25 EXT8 External Data 8 In/Output
26 PA13 Program Address 13 Output
27 EXT9 External Data 9 In/Output
28 V
SS
Ground
29 PA14 Program Address 14 Output
30 EXT10 External Data 10 In/Output
31 PA15 Program Address 15 Output
32 V
33 V
DD
SS
Power Supply Input
Ground
34 PD0 Program Data 0 Input
35 EXT11 External Data 11 In/Output
36 PD1 Program Data 1 Input
37 INT2 User Interrupt 2 Input
38 PD2 Program Data 2 Input
39 INT1 User Interrupt 1 Input
40 PD3 Program Data 3 Input
41 UI1 User Input 1 Input
42 UI0 User Input 0 Input
Table 4. Z89391 84-Pin PLCC Pin IdentiÞcation
No. Symbol Function Direction
43 SCLK CODEC Interface Clock In/Output
44 V
DD
Power Supply Input
45 RD//WR R/W External Bus Output
46 PD4 Program Data 4 Input
47 WAIT Wait State Input Input
48 PD5 Program Data 5 Input
49 /RESET Reset Input
50 PD6 Program Data 6 Input
51 EA0 External Address 0 Output
52 PD7 Program Data 7 Input
53 V
DD
Power Supply Input
54 /ROMEN ROM Enable Input
55 EA1 External Address 1 Output
56 PD8 Program Data 8 Input
57 EA2 External Address 2 Output
58 PD9 Program Data 9 Input
59 V
DD
Power Supply Input
60 PD10 Program Data 10 Input
61 /DS External Data Strobe Output
62 CLK Clock Input
63 PD11 Program Data 11 Input
64 HALT Stop Execution Input
65 FS0 Frame Synch for CODEC
In/Output
Interface 0
66 INT0 User Interrupt 0 Input
67 PD12 Program Data 12 Input
68 UO0 User Output 0 Input
69 PD13 Program Data 13 Input
70 UO1 User Output 1 Input
71 PD14 Program Data 14 Input
72 FS1 Frame Synch for CODEC
In/Output
Interface 1
73 PD15 Program Data 15 Input
74 V
75 V
SS
DD
Ground
Power Supply Input
76 PA0 Program Address 0 Output
77 V
SS
Ground
78 EXT0 External Data 0 In/Output
79 PA1 Program Address 1 Output
80 EXT1 External Data 1 In/Output
81 PA2 Program Address 2 Output
82 EXT2 External Data 2 In/Output
83 PA3 Program Address 3 Output
84 V
Note: *Input or output is defined by interface mode selection.
SS
Ground
DS97DSP0100
P R E L I M I N A R Y
9
Page 10
Z89321/371/391
16-Bit Digital Signal Processors Zilog
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Symbol Description Min. Max. Units
V
T
Note:
* Voltage on all pins with respect to GND.
See Ordering Information.
Supply voltage (*) Ð0.3 +7.0 V
CC
Storage Temp. Ð65° +150 °C
STG
T
Oper. Ambient Temp. °C
A
STANDARD TEST CONDITIONS
The characteristics listed below apply for standard test
conditions as noted. All voltages are referenced to
Ground. Positive current flows into the referenced pin (Figure 6).
Stresses greater than those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; operation of the device at
any condition above those indicated in the operational sections of these specifications is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods
may affect device reliability.
+5V
2.1 K W
From Output
Under Test
30 pF 9.1 K W
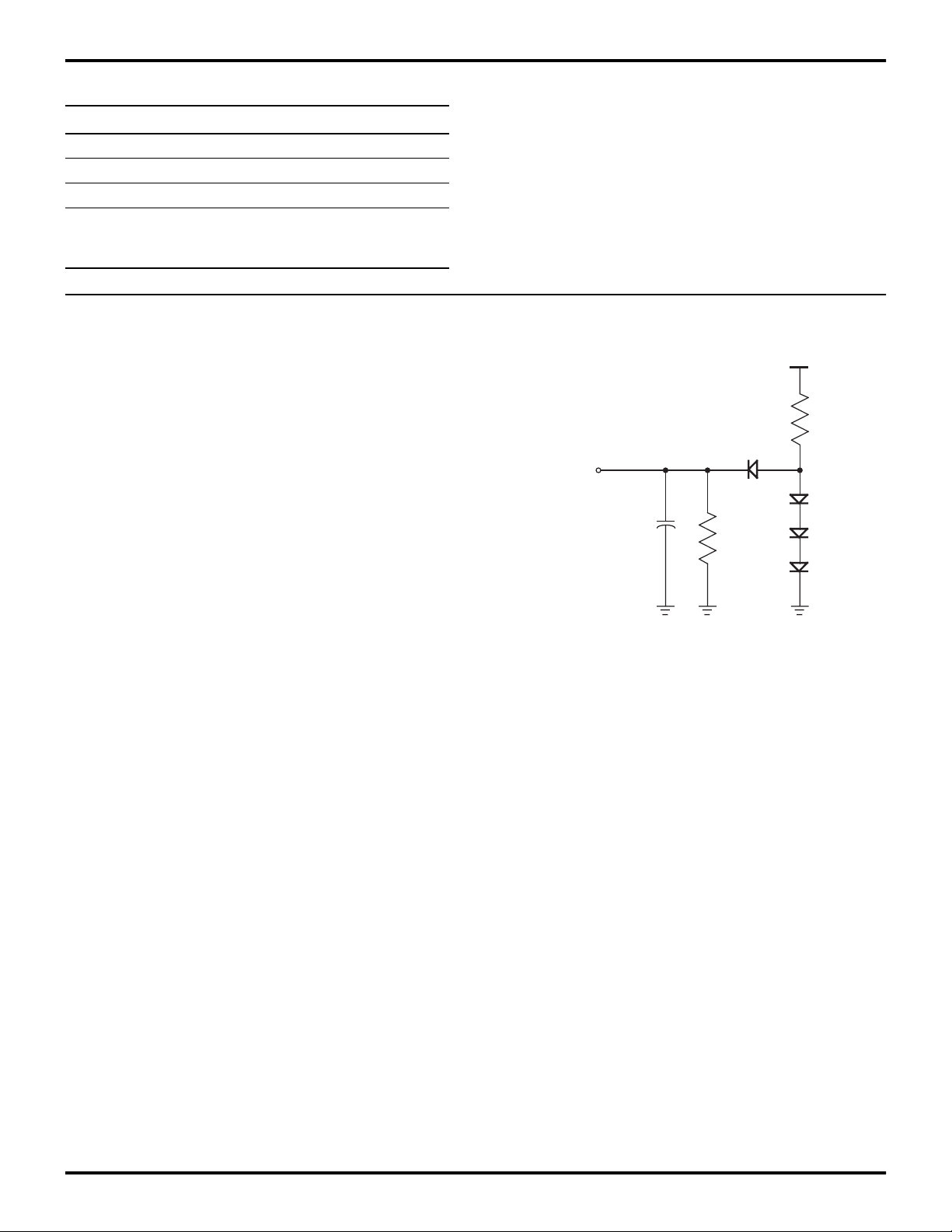
Figure 6. Test Load Diagram
10 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS97DSP0100
Page 11

Z89321/371/391
1
Zilog 16-Bit Digital Signal Processors
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
= 5V ±10%, TA = 0°C to +70°C, unless otherwise noted.)
(V
DD
fclock=20 MHz
1
fclock=16 MHz
2
fclock=24 MHz
3
Sym Parameter Condition Min Typ Max. Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Units
IDD Supply Current V
I
DC Power Consumption 5 5 5 5 mA
DC
V
Input High Level 2.7 2.7 2.7 V
IH
V
Input Low Level .8 .8 .8 V
IL
I
Input Leakage 10 10 10 mA
L
V
Output High Voltage I
OH
V
Input Low Voltage I
OL
I
Output Floating
FL
= 5.5V 70 55 85 mA
DD
=100 mAVDD-0.2 V VDD-0.2 VDD-0.2 V
OH
=2.0 mA .5 .5 .5 V
OL
10 10 10 mA
Leakage Current
Notes:
1. Z89321 and Z89391 only
2. Z89371 only. V
3. Z89321 only. Limited availability. Contact Zilog sales office.
= 5V, ± 5% for 16 MHz operation. VDD = 5V, ± 10% for 10 MHz operation.
DD
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
= 5V 10%, TA = Ð40°C to +85°C, unless otherwise specified)
(V
DD
Sym Parameter Condition Min Typ Max
I
DD
I
DC
V
IH
V
IL
IL Input Leakage 10
V
OH
V
OL
I
FL
Notes:
1. Z89321 only
fclock = 20 MHz
1
Supply Current VDD=5.5V 70
DC Power Consumption 5
Input High Level 2.7
Input Low Level .8
Output High Voltage IOH=100 mAV
Input Low Voltage I
=2.0 mA .5
OL
Output Floating
DD
-0.2
10
Leakage Current
DS97DSP0100 P R E L I M I N A R Y 11
Page 12

Z89321/371/391
16-Bit Digital Signal Processors Zilog
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
= 5V ±10%, TA = 0°C to +70°C, unless otherwise specified.)
(V
DD
fclock = 20
1
MHz
fclock = 16 MHz
fclock = 24
2
MHz
3
Symbol Parameter Min Max Min Max Min Max Units
Clock ns
TCY Clock Cycle Time 50 6.25 41.7 ns
Tr Clock Rise Time 2 2 2 ns
Tf Clock Fall Time 2 2 2 ns
CPW Clock Pulse Width 23 29 19 ns
I/O
DSVALID /DS Valid Time from CLOCK Fall 0 15 0 15 0 15 ns
DSHOLD /DS Hold Time from CLOCK Rise 4 15 4 15 4 15 ns
EASET EA Setup Time to /DS Fall 12 12 12 ns
EAHOLD EA Hold Time from /DS Rise 4 4 4 ns
RDSET Data Read Setup Time to /DS Rise 14 14 14 ns
RDHOLD Data Read Hold Time from /DS Rise 6 6 6 ns
WRVALID Data Write Valid Time from /DS Fall 18 18 18 ns
WRHOLD Data Write Hold Time from /DS Rise 5 5 5 ns
Interrupt
INTSET Interrupt Setup Time to CLOCK Fall 7 7 7 ns
INTWIDTH Interrupt Low Pulse Width 1 TCY 1 TCY 1 TCY ns
CODEC Interface
SSET SCLK Setup Time from Clock Rise 15 15 15 ns
FSSET FSYNC Setup Time from SCLK Rise 6 6 6 ns
TXSET TXD Setup Time from SCLK Rise 7 7 7 ns
RXSET RXD Setup Time to SCLK Fall 7 7 7 ns
RXHOLD RXD Hold Time from SCLK Fall 0 0 0 ns
Reset
RRISE Reset Rise Time 1000 10000 1000 ns
RSET Reset Setup Time to CLOCK Rise 15 15 15 ns
RWIDTH Reset Low Pulse Width 2 TCY 2 TCY 2 TCY ns
External Program Memory
PAVALID PA Valid Time from CLOCK Rise 20 20 20 ns
PDSET PD Setup Time to CLOCK Rise 10 10 10 ns
PDHOLD PD Hold Time from CLOCK Rise 10 10 10 ns
Wait State
WSET WAIT Setup Time to CLOCK Rise 23 23 23 ns
WHOLD WAIT Hold Time from CLOCK Rise 1 1 1 ns
Halt
HSET Halt Setup Time to CLOCK Rise 3 3 3 ns
HHOLD Halt Hold Time from CLOCK Rise 10 10 10 ns
Notes:
1. Z89321 and Z89391 only
2. Z89371 only (V
3. Z89321 only. Limited availability. Contact Zilog sales office.
= 5V ± 5%)
DD
12 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS97DSP0100
Page 13

Z89321/371/391
1
Zilog 16-Bit Digital Signal Processors
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
= 5V ±10%, TA = Ð40°C to +85°C, unless otherwise specified.)
(V
DD
Symbol Parameter Min Max
Clock
TCY Clock Cycle Time 50
Tr Clock Rise Time 5
Tf Clock Fall Time 5
CPW Clock Pulse Width 20
I/O
DSVALID /DS Valid Time from CLOCK Fall 0 18
DSHOLD /DS Hold Time from CLOCK Rise 5 18
EASET EA Setup Time to /DS Fall 15
EAHOLD EA Hold Time from /DS Rise 5
RDSET Data Read Setup Time to /DS Rise 17
RDHOLD Data Read Hold Time from /DS Rise 8
WRVALID Data Write Valid Time from /DS Fall 20
WRHOLD Data Write Hold Time from /DS Rise 6
Interrupt
INTSET Interrupt Setup Time to CLOCK Fall 9
INTWIDTH Interrupt Low Pulse Width 1 TCY
CODEC Interface
SSET SCLK Setup Time from Clock Rise 18
FSSET FSYNC Setup Time from SCLK Rise 8
TXSET TXD Setup Time from SCLK Rise 9
RXSET RXD Setup Time to SCLK Fall 9
RXHOLD RXD Hold Time from SCLK Fall 0
Reset
RRISE Reset Rise Time 1000
RSET Reset Setup Time to CLOCK Rise 18
RWIDTH Reset Low Pulse Width 2 TCY
External Program Memory
PAVALID PA Valid Time from CLOCK Rise 25
PDSET PD Setup Time to CLOCK Rise 12
PDHOLD PD Hold Time from CLOCK Rise 12
Wait State
WSET WAIT Setup Time to CLOCK Rise 28
WHOLD WAIT Hold Time from CLOCK Rise 2
Halt
HSET Halt Setup Time to CLOCK Rise 4
HHOLD Halt Hold Time from CLOCK Rise 12
Note:
1. Z89321 only
fclock = 20 MHz
1
DS97DSP0100 P R E L I M I N A R Y 13
Page 14

Z89321/371/391
16-Bit Digital Signal Processors Zilog
TIMING DIAGRAMS
TCY Tr Tf
CLOCK
/DS
EA(2:0)
RD//WR
EXT(15:0)
DSHOLD
DSVALID
EASET EAHOLD
Valid Address Out
RDHOLD
RDSET
Data In
Figure 7. Read Timing
TCY
CPW
CLOCK
WAIT
/DS
EA(2:0)
RD//WR
EXT(15:0)
WHOLD
WSET
Valid Address Out
Data In
Figure 8. External (EXT) Bus Read Timing Using WAIT Pin
14 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS97DSP0100
Page 15

Z89321/371/391
16-Bit Digital Signal Processors Zilog
TIMING DIAGRAMS (Continued)
TCY
CLOCK
DSHOLD
DSVALID
/DS
EASET EAHOLD
EA(2:0)
RD//WR
EXT(15:0)
Valid Address Out
EASET
EAHOLD
WRHOLD
WRVALID
Data Out
Figure 9. Write Timing
15 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS97DSP0100
Page 16

Z89321/371/391
16-Bit Digital Signal Processors Zilog
TCY
CLOCK
SSET
SCLK
FS0, FS1
TXD
RXD
CLOCK
FSSET
TXSET
RXHOLD
RXSET
1
01 0 1
Figure 10. CODEC Interface Timing
TCY
FSSET
10101
INTSET
INT 0,1,2
INTWidth
PROGRAM
ADDRESS
EXECUTE
Fetch N –1 Fetch N Fetch N +1 Fetch Int_Addr Fetch I Fetch I +1
Execute N –1 Execute N CALL Int Routine Execute Int Routine
Figure 11. Interrupt Timing
16 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS97DSP0100
Page 17

Z89321/371/391
16-Bit Digital Signal Processors Zilog
TIMING DIAGRAMS (Continued)
TCY
CLOCK
HHOLD
HSET
HALT
Figure 12. HALT Timing
TCY
CLOCK
RSET RRISE
/RESET
RWIDTH
INTERNAL
RESET
EXECUTE
RD/WR
/DS
UO0-1
EA0-2
EXT0-15
PA0-15
RAM/
REGISTERS
Cycle 0
Cycle 1 Cycle 2 Cycle 3 Cycle 4 Cycle 5 Code Execution
Tri-Stated
Tri-Stated Access Reset Vector
Intact*
* The RAM and hardware registers are left intact
during a warm reset. A cold reset will produce
random data in these locations. The status
register is set to zeroes in both cases.
Figure 13. RESET Timing
17 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS97DSP0100
Page 18

Z89321/371/391
16-Bit Digital Signal Processors Zilog
TCY
CLOCK
PASET
PROGRAM
ADDRESS
PROGRAM
DATA
Valid Valid Valid
PDSET
Valid
Figure 14. External Program Memory Port Timing
ADDRESS SPACE
Program Memory. Programs of up to 4 K words can be
masked into internal ROM (OTP for Z89371). Four locations are dedicated to the vector address for the three interrupts (0FFDH-0FFFH) and the starting address following a Reset (0FFCH). Internal ROM is mapped from 0000H
to 0FFFH, and the highest location for program is 0FFBH.
A 64 K word External Program Memory Space is available
on the Z89391. The vector addresses for the Z89391 reside at FFFCH-FFFFH (Figure 15).
Internal Data RAM. The Z89321, 371 and 391 all have internal 512 x 16-bit word data RAM organized as two banks
of 256 x 16-bit words each: RAM0 and RAM1. Each data
RAM bank is addressed by three pointers: Pn:0 (n = 0-2)
for RAM0 and Pn:1 (n = 0-2) for RAM1. The RAM addresses for RAM0 and RAM1 are arranged from 0-255 and 256511, respectively. The address pointers, which may be
written to, or read from, are 8-bit registers connected to the
PDHOLD
Valid
Valid
lower byte of the internal 16-bit D-Bus and are used to perform modulo addressing.
Three addressing modes are available to access the Data
RAM: register indirect, direct addressing, and short form
direct. The contents of the RAM can be read to, or written
from, in one machine cycle per word, without disturbing
any internal registers or status other than the RAM address pointer used for each RAM. The contents of each
RAM can be loaded simultaneously into the X and Y inputs
of the multiplier.
Registers. The Z89321 has 19 internal registers and up to
an additional eight external registers. The external registers are user-definable for peripherals, such as A/D or D/A,
or to DMA, or other addressing peripherals. Both external
and internal registers are accessed in one machine cycle.
Program Memory
FFFF
FFFC
Or
0FFF
0FFC
0000
INT0-INT2 Vect.
64 Kwords
RESET Vector
512 words
Data Memory
Not Used
DRAM1
DRAM0
FFFF
01FF
0100
00FF
0000
4 Kwords
Not Used
INT0-INT2 Vect.
RESET Vector
On-Chip Memory Off-Chip Memory
Figure 15. Memory Map
18 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS97DSP0100
Page 19

Z89321/371/391
1
Zilog 16-Bit Digital Signal Processors
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Instruction Timing. Most instructions are executed in one
machine cycle. Long immediate instructions and Jump or
Call instructions are executed in two machine cycles. A
multiplication or multiplication/accumulate instruction requires a single cycle. Specific instruction cycle times are
described in the Condition Code section.
Multiply/Accumulate. The multiplier can perform a 16-bit
x 16-bit multiply, or multiply accumulate, in one machine
cycle using the Accumulator and/or both the X and Y inputs. The multiplier produces a 32-bit result, however, only
the 24 most significant bits are saved for the next instruction or accumulation. For operations on very small numbers where the least significant bits are important, the data
should first be scaled by eight bits (or the multiplier and
multiplicand by four bits each) to avoid truncation errors.
DDATA
XDATA
1616
X Register (16) Y Register (16)
Multiplier
P Register (24)
24
Note that all inputs to the multiplier should be fractional
twoÕs-complement, 16-bit binary numbers (Figure 16). This
puts them in the range [Ð1 to 0.9999695], and the result is
in 24 bits so that the range is [Ð1 to 0.9999999]. In addition,
if 8000H is loaded into both X and Y registers, the resulting
multiplication is considered an illegal operation as an overflow would result. Positive one cannot be represented in
fractional notation, and the multiplier will actually yield the
result 8000H x 8000H = 8000H (Ð1 x Ð1 = Ð1).
ALU. The ALU has two input ports, one of which is connected to the output of the 24-bit Accumulator. The other
input is connected to the 24-bit P-Bus, the upper 16 bits of
which are connected to the 16-bit D-Bus. A shifter between
the P-Bus and the ALU input port can shift the data by
three bits right, one bit right, one bit left or no shift (Figure
17).
DDATA
Mult. (24) Shift Unit *
16
2424
MUX
24
* Options:
2424
1 Bit Right
3 Bits Right
No Shift
1 Bit Left
MUX
Shift Unit *
24
24
* Options:
1 Bit Right
3 Bits Right
No Shift
1 Bit Left
24
Figure 16. Multiplier Block Diagram
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
24
Accumulator (24)
Figure 17. ALU Block Diagram
DS97DSP0100 P R E L I M I N A R Y 19
Page 20

Z89321/371/391
16-Bit Digital Signal Processors Zilog
Hardware Stack. A six-level hardware stack is connected
to the D-Bus to hold subroutine return addresses or data.
The Call instruction pushes PC+2 onto the stack, and the
RET instruction pops the contents of the stack to the PC.
User Inputs. The Z89321 has two inputs, UI0 and UI1,
which may be used by Jump and Call instructions. The
Jump or Call tests one of these pins and if appropriate,
jumps to a new location. Otherwise, the instruction behaves like a NOP. These inputs are also connected to the
status register bits S10 and S11, which may be read by the
appropriate instruction (Figure 8).
User Outputs. The status register bits S5 and S6 connect
directly to UO0 and UO1 pins and may be written to by the
appropriate instruction. Note: The user output value is the
opposite of the status register content.
Interrupts. The Z89321 has three positive edge-triggered
interrupt inputs. An interrupt is acknowledged at the end of
an instruction execution. It takes two machine cycles to enter an interrupt instruction sequence. The PC is pushed
onto the stack. A RET instruction transfers the contents of
the stack to the PC and decrements the stack pointer by
one word. The priority of the interrupts is INT0 = highest,
INT2 = lowest. INT1 is dedicated to the CODEC interface
and INT2 is dedicated to the 13-bit timer if both peripherals
are enabled. Note: The SIEF instruction enables the interrupts. The SIEF instruction must be used before exiting an
interrupt routine since the interrupts are automatically disabled when entering the routine.
Registers. The Z89321 has 19 physical internal registers
and up to eight user-defined external registers. The EA2EA0 determines the address of the external registers. The
signals are used to read from or write to the external registers /DS, WAIT, RD//WR.
I/O Bus. The processor provides a 16-bit, CMOS-compatible bus. I/O Control pins provide convenient communication capabilities with external peripherals, and single-cycle
access is possible. For slower communications, an onboard hardware wait-state generator can be used to accommodate timing conflicts. Three latched I/O address
pins are used to access external registers. The EXT 4, 5,
6, 7 pins are used by the internal peripherals. Disabling a
peripheral allows access to these addresses for generalpurpose use.
CODEC Interface. The multi-compatible, dual CODEC interface provides the necessary control signals for transmission of CODEC information to the DSP processor. The
interface accommodates 8-bit PCM or 16-bit Linear CODECs. Special compatibility with Crystal Semiconductor's
4215/4216 CODECs provides the necessary interface for
audio applications. Many general-purpose 8-, 16-bit A/Ds,
D/As are adaptable. The interface can also be used as a
high-speed serial port.
m-Law Compression. The 8-bit CODEC interface mode
provides m-law compression from 13-bit format to 8-bit for-
mat. Decompression is performed in software by use of a
128-word lookup table.
Timer. Two programmable timers are available. One is
dedicated to the CODEC interface, the other for generalpurpose use. When a time-out event occurs, an interrupt
request is generated. Single pass and/or continuous
modes are available. If the CODEC interface is not used,
both timers can be used for general-purpose.
Note: Wait-State Generator. An internal wait-state
generator is provided to accommodate slow external
peripherals. A single wait-state can be implemented
through control registers EXT7-2. For additional states, a
dedicated pin (WAIT) can be held High. The WAIT pin is
monitored only during execution of a read or write
instruction to external peripherals (EXT bus).
Note: A WAIT pin is not available on the 40-pin DIP
package.
20 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS97DSP0100
Page 21

Z89321/371/391
1
Zilog 16-Bit Digital Signal Processors
REGISTERS
The internal registers are defined below:
Register Register DeÞnition
P Output of Multiplier, 24-bit
X X Multiplier Input, 16-bit
Y Y Multiplier Input, 16-bit
A Accumulator, 24-bit
SR Status Register, 16-bit
Pn:b Six Ram Address Pointers, 8-bit each
PC Program Counter, 16-bit
EXT4 13-Bit Timer ConÞguration Register
EXT5-1 CODEC Interface Channel 0 Data
EXT5-2 CODEC Interface Channel 0 Data
EXT6-1 CODEC Interface Channel 1 Data
EXT6-2 CODEC Interface Channel 1 Data
EXT7-1 CODEC Interface ConÞguration Register
EXT7-2 Wait-State Generator/CODEC Interface
ConÞguration Register
The following are virtual registers as physical RAM does
not exist on the chip.
Register Register DeÞnition
EXTn External Registers, 16-bit
BUS D-Bus
Dn:b Eight Data Pointers*
Note: * These occupy the first four locations in RAM bank.
P holds the result of multiplications and is read-only.
X and Y are two 16-bit input registers for the multiplier.
These registers can be utilized as temporary registers
when the multiplier is not being used.
A is a 24-bit Accumulator. The output of the ALU is sent to
this register. When 16-bit data is transferred into this register, it is placed into the 16 MSBs and the least significant
eight bits are set to zero. Only the upper 16 bits are transferred to the destination register when the Accumulator is
selected as a source register in transfer instructions.
Pn:b are the pointer registers for accessing data RAM, (n
= 0,1,2 refer to the pointer number) (b = 0,1 refers to RAM
Bank 0 or 1). They can be directly read from or written to,
and can point to locations in data RAM or Program Memory.
EXTn are external registers (n = 0 to 7). There are eight
16-bit registers provided here for mapping external devices into the address space of the processor. Note that the
actual register RAM does not exist on the chip, but would
exist as part of the external device, such as an ADC result
latch. Use of the CODEC interface and 13-bit timer reduces the number of external registers to four.
BUS is a read-only register which, when accessed, returns
the contents of the D-Bus. Bus is used for emulation only.
Dn:b refers to locations in RAM that can be used as a
pointer to locations in program memory which is efficient
for coefficient addressing. The programmer decides which
location to choose from two bits in the status register and
two bits in the operand. Thus, only the lower 16 possible
locations in RAM can be specified. At any one time, there
are eight usable pointers, four per bank, and the four pointers are in consecutive locations in RAM.
For example, if S3/S4 = 01 in the status register, then
D0:0/D1:0/D2:0/D3:0 refer to register locations 4/5/6/7 in
RAM Bank 0. Note that when the data pointers are being
written to, a number is actually being loaded to Data RAM,
so they can be used as a limited method for writing to
RAM.
SR is the status register, which contains the ALU status
and certain control bits (Table 5).
Table 5. Status Register Bit Functions
Status Register Bit Function
S15 (N) ALU Negative
S14 (OV) ALU Overßow
S13 (Z) ALU Zero
S12 (L) Carry
S11 (UI1) User Input 1
S10 (UI0) User Input 0
S9 (SH3) MPY Output Arithmetically
Shifted Right by Three Bits
S8 (OP) Overßow Protection
S7 (IE) Interrupt Enable
S6 (UO1) User Output 1
S5 (UO0) User Output 0
S4-S3 ÒShort Form DirectÓ bits
S2-S0 (RPL) RAM Pointer Loop Size
DS97DSP0100 P R E L I M I N A R Y 21
Page 22

Z89321/371/391
16-Bit Digital Signal Processors Zilog
The status register can always be read in its entirety. S15S10 are set/reset by hardware and can only be read by
software. S9-S0 control hardware looping and can be written by software (Table 6).
Table 6. RPL Description
S2 S1 S0 Loop Size
0 0 0 256
0012
0104
0118
10016
10132
11064
1 1 1 128
NOVZ C
S15 S14 S13 S12 S11 S10 S9 S8
UI1 UI0 SH3 OP IE UO1 UO0 RPL
S7 S6 S5 S4 S3 S2 S1 S0
S15-S12 are set/reset by the ALU after an operation. S11S10 are set/reset by the user inputs. S6-S0 are control bits
described in Table 5. S7 enables interrupts. If S8 is set, the
hardware clamps at maximum positive or negative values
instead of overflowing. If S9 is set and a multiple/shift option is used, then the shifter shifts the result three bits right.
This feature allows the data to be scaled and prevents
overflows.
PC is the Program Counter. When this register is assigned
as a destination register, one NOP machine cycle is added
automatically to adjust the pipeline timing.
External Register, EXT4-EXT7, are used by the CODEC
interface and 13-bit timer, the registers are reviewed in the
CODEC interface section.
Ram Pointer Loop Size
0 0 0
0 0 1
0 1 0
0 1 1
1 0 0
1 0 1
1 1 0
1 1 1
"Short Form Direct" bits
User Output 0-1*
Interrupt Enable
Overflow protection
256
2
4
8
16
32
64
128
* The output value is the opposite of the status register content.
Figure 18. Status Register
MPY output arithmetically shifted
right by three bits
User Input 0-1 (Read Only)
Carry
Zero
Overflow
Negative
22 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS97DSP0100
Page 23

Z89321/371/391
1
Zilog 16-Bit Digital Signal Processors
PERIPHERAL OPERATION
Disabling Peripherals
Disabling a peripheral (CODEC Interface, Counter) allows
general-purpose use of the EXT address for the disabled
peripheral. If the peripheral is not disabled, the EXT control
signals and EXT data are still provided, but transfer of data
on the EXT pins is not available (because internal transfers
are being processed on the internal bus). Care must be
taken to ensure that control of the EXT bus does not cause
bus conflicts.
Reading Data from CODEC Interface*
External data is serially transferred into the CODEC interface registers from an external CODEC. This serial data is
loaded into EXT5-2 (8- or 16-bit modes). Because the interface is double-buffered, data must be transferred to
Internal 16-Bit Bus
16
EXT5-1 before being transferred along the internal data
bus of the processor. This is accomplished by writing data
to EXT5-2.
Writing Data to CODEC Interface
Internal data is transferred from the internal data bus of the
processor to the EXT5-2 register. The CODEC interface
constantly transfers and receives data during normal operation. Data to be transferred is loaded to EXT5-2 and is automatically serially transferred.
Note: EXT5-1 and EXT5-2 are used in the example, but
this information applies equally to EXT6-1 and EXT6-2.
(Refer to Figure 20, CODEC Block Diagram.)
16
EXT7-1
CODEC Timer RegisterEXT7-1
EXT7-2
Figure 19. EXT7 Register ConÞguration
Wait-State Register
LOADING EXT7
Because EXT7 is double-buffered, a pair of writes are performed when loading the EXT7 registers (Figure 19).
LD EXT7, #%54F4 Loads CODEC Timer Register
LD EXT7, #%6CDA Loads Wait-State Register
LD @P0:0, EXT7 Reads EXT7-1 and places
data in RAM
EXT7-2
Interrupts
The Z89321 features three interrupts:
INT0 General-Purpose
INT1 CODEC Interface
INT2 13-Bit Timer
If all peripherals are enabled, INT0 (general-purpose) can
be used.
DS97DSP0100 P R E L I M I N A R Y 23
Page 24

Z89321/371/391
16-Bit Digital Signal Processors Zilog
CODEC Interface
The CODEC Interface provides direct-connect capabilities
for standard 8-, 16-bit CODECs. The interface also supports 8-bit PCM, 8-bit PCM with hardware m-law conversion (m-law expansion is done in software), 16-bit Linear
and Crystal's Sigma-Delta Stereo CODEC modes. Registers are used to accommodate the CODEC Interface
(EXT5, EXT6 and EXT7). The CODEC interface provides
two Frame Sync signals, which allows two channels of
data for transmission/receiving.
CODEC Interface Hardware
The CODEC Interface hardware uses six 16-bit registers,
m-law compression logic and general-purpose logic to control transfers to the appropriate register (Figure 20).
Data Bus
16 16
CODEC Interface Control Signals
SCLK (Serial Clock)
The Serial Clock provides a clock signal for operating the
external CODEC. A 4-bit prescaler is used to determine
the frequency of the output signal.
SCLK = (0.5* CLK)/PS where: CLK = System Clock
PS = 4-bit Prescaler*
* The Prescaler is an up-counter.
Note: An internal divide-by-two is performed before the
clock signal is passed to the Serial Clock prescaler.
16
m-Law
Compression
CLKIN
TXD
EXT5-1 EXT6-1
CLKIN
16
EXT5-2
CLKIN CLKIN
CONTROL
LOGIC
CLKIN
EXT6-2
Figure 20. CODEC Interface Block Diagram
16
RXD
16
EXT7-1
16
EXT7-2
24 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS97DSP0100
Page 25

Z89321/371/391
1
Zilog 16-Bit Digital Signal Processors
TXD (Serial Output to CODEC)
The TXD line provides 8-, 16-, and 64-bit data transfers.
Each bit is clocked out of the processor by the rising edge
of the SCLK, with the MSB transmitted first.
RXD (Serial Input from CODEC)
The RXD line provides 8-, 16-, and 64-bit data transfers.
Each bit is clocked into the processor by the falling edge of
the SCLK, with the MSB received first.
int1_
fs1
fs0
sclk
txd
FS0, FS1 (Frame Sync)
The Frame Sync is used for enabling data transfer/receive.
The rising and falling edge of the Frame Sync encloses the
serial data transmission.
Interrupt
Once the transmission of serial data is completed an internal interrupt signal is initiated. A single-cycle Low pulse allows an interrupt on INT1. When this occurs, the processor
will jump to the defined Interrupt 1 vector location (Figure
21).
rxd
Figure 21. CODEC Interface Timing (8-Bit Mode)
CODEC INTERFACE TIMING
Figure 21 depicts a typical 8-bit serial data transfer using
both of the CODEC Interface Channels. The transmitting
data is clocked out on the rising edge of the SCLK signal.
An external CODEC clocks data in on the falling edge of
the SCLK signal. Once the serial data is transmitted, an interrupt is given. The CODEC interface signals are not initiated if the CODEC interface is not enabled.
The following modes are available for FSYNC and SCLK
signals:
SCLK FSYNC
Internal Internal
External External
External Internal
Internal External
The CODEC interface timing is independent of the processor clock when external mode is chosen. This feature provides the capability for an external device to control the
transfer of data to the Z89321. The Frame Sync signal envelopes the transmitted data, therefore care must be taken
to ensure proper sync signal timing (Figure 21).
Full Duplex Operation
The Transmit and Receive lines are used for transfer of serial data to or from the CODEC interface. The CODEC interface performs both data transmit and receive simultaneously.
Control Registers
The CODEC interface is double-buffered, therefore, four
registers are provided for CODEC interface data storage.
EXT5-1 and EXT5-2 operate with the Frame Sync 0 while
EXT6-1 and EXT6-2 operate with Frame Sync 1. In 8- or
16-bit mode, the CODEC interface uses EXT5-1 and
EXT6-1. For Stereo mode, all four registers are used (Figures 22 and 23).
The CODEC Interface Control Register (EXT7-1) is shown
in Figure 14. Setting of the CODEC mode, FSYNC, and
Enable/Disable of CODEC 0 is done through this register.
The Wait-State Generator, SCLK, and CODEC 1 are controlled from EXT7-2 (Figure 24).
DS97DSP0100 P R E L I M I N A R Y 25
Page 26

Z89321/371/391
16-Bit Digital Signal Processors Zilog
5-1
D5
D15 D14 D13 D11 D10 D9
5-2
D15 D14 D13 D11 D10 D9
D12 D7
D12 D7
Figure 22. CODEC Interface Data Registers (Channel 0)
D8
D8
D6
D6
D5
D4
D4
D3
D3
D2
D2
D1
D1
D0
Data Bits 15-0
D0
Data Bits 15-0
6-1
D15 D14 D13 D11 D10 D9
D12 D7
6-2
D15 D14 D13 D11 D10 D9
D12 D7
Figure 23. CODEC Interface Data Registers (Channel 1)
D8
D8
D6
D6
D5
D5
D4
D4
D3
D3
D2
D2
D1
D1
D0
Data Bits 15-0
D0
Data Bits 15-0
26 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS97DSP0100
Page 27

Z89321/371/391
1
Zilog 16-Bit Digital Signal Processors
REGISTERS
EXT7-1
D14
D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8
Note: The timer is an up-counter.
Example: EXT7-1 = #%x00D OSC = 12.288 MHz, SCLK = 2.048 MHz, FSYNC = 8 kHz
EXT7-1 = #%x80F OSC = 12.288 MHz, SCLK = 6.144 MHz, FSYNC = 48 kHz
EXT7-1 = #%xFFx No interrupt
EXT7-1 = #%x000 Max interrupt period (667 ms for OSC = 12.288 MHz)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0D15
Figure 24. CODEC Interface Control Register
SCLK Prescaler (up-counter)
SCLK/FSYNC Ratio Prescaler (up-counter)
CODEC Mode
00 8-bit with hardware m-law
01 8-bit without hardware m-law
10 16-bit linear
11 Crystal CS4215 / CS4216
FSYNC
0 External Source*
1 Internal Source
CODEC 0 Disable/Enable
0 = Disable*
1 = Enable
* Default
DS97DSP0100 P R E L I M I N A R Y 27
Page 28

Z89321/371/391
16-Bit Digital Signal Processors Zilog
EXT7-2
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8
Wait State EXT0
Wait State EXT1
Wait State EXT2
Wait State EXT3
Wait State EXT4
Wait State EXT5
Wait State EXT6
SCLK
0 External Source*
1 Internal Source
CODEC 1 Disable/Enable
0 = Disable*
1 = Enable
*Default
Figure 25. WSG, SCLK and CODEC Interface Control Register
nws - no wait states
ws - one wait states
00 no wait states (nws)
01 read (nws), write (ws)
10 read (ws), write (nws)
11 read (ws), write (ws)
28 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS97DSP0100
Page 29

Z89321/371/391
1
Zilog 16-Bit Digital Signal Processors
A/D Accommodation
The CODEC interface can be used for serial A/D or serial
D/A transmission. The interface provides the necessary
control signals to adapt to many standard serial converters. The low-pass and smoothing filters are necessary for
systems with converters.
Z89321/371/391
Serial A/D
SCLK
FSO
FS1
CLKIN
Communicate
Data
Serial
Data Out
High-Speed Serial Port
The Z89321 CODEC interface can be used as a highspeed serial port. The necessary control signals are provided for adaptation to standard processors or external peripherals. Byte, word, or 64-bit data can be transmitted at
speeds up to 10 Mbps. (Condition includes a 20 MHz oscillator. Data can be transferred with single-cycle instructions to an internal register file.)
Low-Pass
Filter
Analog
In
RXD
TXD
Serial A/D
CLKIN
Serial
Data In
Communicate
Data
Figure 26. A/D, D/A Implementation Block Diagram
Table 7. Tabulated Transmission Rates*
Transmission Rate
Maximum SCLK 10 Mbps
Maximum Frame Sync
8-bit 769.2 kHz
16-bit 476.2 kHz
Stereo (64-bit) 263.2 kHz
Note: Calculations consider the interrupt access time (typically
four cycles), transfer of data, loading of new data, and latency periods between CODEC transfers. During the interrupt cycle, developers often execute additional software, affecting the
maximum transfer rate. Calculations are for single-channel transfers only.
Smoothing
Filter
Analog
Out
8-Bit CODEC Interface
The Z89321 provides an option for a standard 8-bit CODEC interface. Hardware m-law compression is available
(expansion performed by software lookup table). The CODEC interface transmits data consisting of 8-bit or compounded 8-bit information. Figure 27 shows a typical schematic arrangement.
The timing for this type of arrangement is presented in Figure 28. The flexible design provides adaptation for 16-bit
linear CODEC.
DS97DSP0100 P R E L I M I N A R Y 29
Page 30

Z89321/371/391
16-Bit Digital Signal Processors Zilog
Z89321
/371
/391
TXD
RXD
SCLK
FS1
VCC
VDD
RDD 15
DC
CCI
TDD
TDE
VLS 9
MC145505p
16
14RCE
13
12
11
10
Analog
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
VAG
Rx0
+Tx
Txl
–Tx
Mu/A
PDI
VSS
5k10k
VCC
Out
Analog
In
int1_
fs1
fs0
sclk
txd
rxd
GND
–5V
Figure 27. 8-Bit CODEC Schematic
Figure 28. 8-Bit Mode Timing Diagram
30 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS97DSP0100
Page 31

Z89321/371/391
1
Zilog 16-Bit Digital Signal Processors
16-Bit Linear CODEC Interface
For higher precision transmissions, a 16-bit linear CODEC
is used, however, data is not compressed in this mode of
transmission. The Z89321 provides accommodation for
two channels of 16-bit transmission (Figure 29).
int1_
fs1
fs0
sclk
txd
rxd
Figure 29. 16-Bit Mode Timing Diagram
For data acquisition systems, designers may opt for a 16bit serial A/D. A block diagram of the Z89321 with the
AD1876 16-bit 100 Kbps sampling ADC is shown in Figure
30.
Z89321/371/391
SCLK
Figure 30. 16-Bit Mode Timing Diagram
UO0
RxD
FS1
AD 1876
Sample
CLK
Dout
Busy
16-Bit A/D
Anti-Alias
Filtered
Analog
Signal
Vin
DS97DSP0100 P R E L I M I N A R Y 31
Page 32

Z89321/371/391
16-Bit Digital Signal Processors Zilog
Stereo CODEC Interface
The Z893XX DSP product family CODEC interface provides direct connection to other CODECs for master or
slave modes, supporting 64 bits of transmission data (16
bits right channel, 16 bits left channel, and 32 bits of configuration information). This configuration information consists of input gain, input MUX, output attenuation, ADC
clipping, and mute and error functions of the CODECs.
Audio
Z89321
/371/391
Out
(Right)
Audio
Out
(Left)
10mF
³ 1.0 mF
³ 1.0 mF
+
40k
0.0022mF
NPO
40k
0.0022mF
NPO
+
+
0.1mF
A key feature of the Z893XX DSP product family is that it
adapts easily to other stereo CODECs, including Crystal
Semiconductor's CS4215 and CS4216 devices (Figure
31).
The 64 bits of data transferred from the CODEC are placed
in four registers, EXT5-1, 5-2, 6-1, and 6-2 (Figure 32 ).
1 mF
Ferrite Bead
+
150
0.01mF
NPO
150
0.01mF
NPO
150
+5V
Supply
Channel 2
Input
Channel 2
Input
Channel 1
Input
600
600
16
21
22
15
0.1 mF
24
VA
ROUT
LOUT
REFBYP
REFGND
+
1 mF
CS4216
2.0
VD
RIN2
LIN2
RIN1
0.1 mF
4
0.47mF
26
0.47mF
28
0.47mF
27
SCLK
FS0
TxD
RxD
43
SCLK
42
SSYNC
44
SDIN
1
Mode
Setting
32
31
30
29
SDOUT
SMODE2
SFS1
SFS2
SMODE1
LIN1
Figure 31. Z893XX and CS4216 CODEC Interface
0.47mF
27
0.01mF
NPO
150
0.01mF
NPO
Channel 1
Input
32 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS97DSP0100
Page 33

Z89321/371/391
1
Zilog 16-Bit Digital Signal Processors
int1_
fs1
fs0
64 bits transferred
sclk
txd
rxd
Figure 32. CODEC Stereo Mode Timing Diagram
16-Bit General-Purpose Timer
The 13-bit counter/timer is available for general-purpose
use. When the counter counts down to the zero state, an
interrupt is received on INT2. If the counter is disabled,
EXT4 can be used as a general-purpose address. The
counting operation of the counter can be disabled by resetting bit 14. Selection of the clock source allows the ability
to extend the counter value past the 13 bits available in the
control register. Use of the CODEC counter output can extend the counter to 26 bits (see Figure 33).
Note: Placing zeroes into the count value register does
not generate an interrupt. Therefore, it is possible to have
a single-pass option by loading the counter with zeroes
after the start of count.
The counter is defaulted to the enable state, but if it is not
needed, it can be disabled. However, once disabled, the
counter cannot be enabled unless a reset of the processor
is performed.
Example:
LD EXT, #%C008 ;1100 0000 0000 1000
; Enable Counter
; Enable Counting
; Clock Source = OSC/2
; Count Value = 1000 = 8
; Interrupt will occur every
16 clock cycles
DS97DSP0100 P R E L I M I N A R Y 33
Page 34

Z89321/371/391
16-Bit Digital Signal Processors Zilog
ADDRESSING MODES (Continued)
EXT4
D14
D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8
* Default State
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0D15
Figure 33. CODEC Timer Register
ADDRESSING MODES
This section discusses the syntax of the addressing
modes supported by the DSP assembler.
Count Value (Down-Counter)
Clock Source
0 Oscillator/2*
1 CODEC Counter Output
Count Operation
0 = Disable*
1 = Enable
Counter
0 = Disable
1 = Enable*
Table 8. Addressing Modes
Symbolic Name Syntax Description
<pregs> Pn:b Pointer Register
<dregs> (Points to RAM) Dn:b Data Register
<hwregs> X,Y,PC,SR,P , EXTn, A, BUS Hardware Registers
<accind> (Points to Program Memory @A Accumulator Memory Indirect
<direct> <expression> Direct Address Expression
<limm> #<const exp> Long (16-bit) Immediate Value
<simm> #<const exp> Short (8-bit) Immediate Value
<regind> (Points to RAM) @Pn:b Pointer Register Indirect
@Pn:b+ Pointer Register Indirect with Increment
@Pn:bÐLOOP Pointer Register Indirect with Loop Decrement
@Pn:b+LOOP Pointer register Indirect with Loop Increment
<memind> (Points to Program Memory) @@Pn:b Pointer Register Memory Indirect
@Dn:b Data Register Memory Indirect
@@Pn:bÐLOOP Pointer Register Memory Indirect with Loop
Decrement
@@Pn:b+LOOP Pointer Register Memory Indirect with Loop
Increment
@@Pn:b+ Pointer Register Memory Indirect with Increment
34 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS97DSP0100
Page 35

Z89321/371/391
1
Zilog 16-Bit Digital Signal Processors
There are eight distinct addressing modes for data transfer.
<pregs>, <hwregs> These two modes are used for simple loads to and from registers within the chip, such as
loading to the Accumulator, or loading from a pointer register. The names of the registers need only be specified in
the operand field (destination first, then source).
<regind> This mode is used for indirect accesses to the
data RAM. The address of the RAM location is stored in
the pointer. The Ò@Ó symbol indicates ÒindirectÓ and precedes the pointer, therefore @P1:1 instructs the processor
to read or write to a location in RAM1, which is specified by
the value in the pointer.
<dregs> This mode is also used for accesses to the data
RAM, but only the lower 16 addresses in either bank. The
4-bit address comes from the status register and the operand field of the data pointer. Note that data registers are
typically used not for addressing RAM, but loading data
from program memory space.
<memind> This mode is used for indirect accesses to the
program memory. The address of the memory is located in
a RAM location, which is specified by the value in a pointer. Therefore, @@P1:1 instructs the processor to read
(write is not possible) from a location in memory, which is
specified by a value in RAM, and the location of the RAM
is in turn specified by the value in the pointer. Note that the
data pointer can also be used for a memory access in this
manner, but only one Ò@Ó precedes the pointer. In both
cases, the memory address stored in RAM is incremented
by one, each time the addressing mode is used, to allow
easy transfer of sequential data from program memory.
<accind> Similar to the previous mode, the address for
the program memory read is stored in the Accumulator.
@A in the second operand field loads the number in memory specified by the address in A.
<direct> The direct mode allows read or write to data
RAM from the Accumulator by specifying the absolute address of the RAM in the operand of the instruction. A number between 0 and 255 indicates a location in RAM0, and
a number between 256 and 511 indicates a location in
RAM1.
<limm> This address mode indicates a long immediate
load. A 16-bit word can be copied directly from the operand
into the specified register or memory.
<simm> This address mode can only be used for immediate transfer of 8-bit data in the operand to the specified
RAM pointer.
CONDITION CODES
The following Instruction Description defines the condition
codes supported by the DSP assembler.
Code Description
C Carry
EQ Equal (same as Z)
F False
IE Interrupts Enabled
MI Minus
NC No Carry
NE Not Equal (same as NZ)
NIE Not Interrupts Enabled
NOV Not Overßow
NU0 Not User Zero
If the instruction description refers to the <cc> (condition
code) symbol in one of its addressing modes, the instruction will only execute if the condition is true.
Code Description
NU1 Not User One
NZ Not zero
OV Overßow
PL Plus (Positive)
U0 User Zero
U1 User One
UGE Unsigned Greater Than or
Equal (Same as NC)
ULT Unsigned Less Than (Same as C)
Z Zero
DS97DSP0100 P R E L I M I N A R Y 35
Page 36

Z89321/371/391
16-Bit Digital Signal Processors Zilog
PACKAGE INFORMATION
Figure 34. 40-Pin Package Diagram
Figure 35. 44-Pin PLCC Package Diagram
36 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS97DSP0100
Page 37

Z89321/371/391
1
Zilog 16-Bit Digital Signal Processors
Figure 36. 44-Pin QFP Package Diagram
Figure 37. 84-Pin PLCC Package Diagram
DS97DSP0100 P R E L I M I N A R Y 37
Page 38

Z89321/371/391
16-Bit Digital Signal Processors Zilog
ORDERING INFORMATION
Z89321 Z89371 Z89391
20 MHz 16 MHz 20 MHz
44-Pin PLCC 44-pin PLCC 84-Pin PLCC
Z8932120VSC Z8937116VSC Z8939120VSC
20 MHz 16 MHz
40-Pin DIP 40-Pin DIP
Z8932120PSC Z8937116PSC
20 MHz 16 MHz
44-Pin QFP 44-Pin QFP
Z8932120FSC Z8937116FSC
For fast results, contact your local Zilog sales office for assistance in ordering the part desired.
CODES
Package
P= Plastic DIP
V = Plastic PLCC
F = Plastic QFP
Temperature
S = 0°C to +70°C
E = -40°C to 85°C
Example:
Z 89321 20 V S C
Speed
20 = 20 MHz
16 = 16 MHz
Environmental
C = Plastic Standard
is a Z89321, 20 MHz, PLCC, 0°C to +70°C, Plastic Standard Flow
Environmental Flow
Temperature
Package
Speed
Product Number
Zilog Prefix
38 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS97DSP0100
Page 39

Z89321/371/391
1
Zilog 16-Bit Digital Signal Processors
© 1997 by Zilog, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this
document may be copied or reproduced in any form or by
any means without the prior written consent of Zilog, Inc.
The information in this document is subject to change
without notice. Devices sold by Zilog, Inc. are covered by
warranty and patent indemnification provisions appearing
in Zilog, Inc. Terms and Conditions of Sale only. Zilog, Inc.
makes no warranty, express, statutory, implied or by
description, regarding the information set forth herein or
regarding the freedom of the described devices from
intellectual property infringement. Zilog, Inc. makes no
warranty of merchantability or fitness for any purpose.
Zilog, Inc. shall not be responsible for any errors that may
appear in this document. Zilog, Inc. makes no commitment
to update or keep current the information contained in this
document.
DS97DSP0100 P R E L I M I N A R Y 39
ZilogÕs products are not authorized for use as critical
components in life support devices or systems unless a
specific written agreement pertaining to such intended use
is executed between the customer and Zilog prior to use.
Life support devices or systems are those which are
intended for surgical implantation into the body, or which
sustains life whose failure to perform, when properly used
in accordance with instructions for use provided in the
labeling, can be reasonably expected to result in
significant injury to the user.
Zilog, Inc. 210 East Hacienda Ave.
Campbell, CA 95008-6600
Telephone (408) 370-8000
FAX 408 370-8056
Internet: http://www.zilog.com
Page 40

Z89321/371/391
16-Bit Digital Signal Processors Zilog
40 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS97DSP0100
 Loading...
Loading...