Page 1

Septe m ber 2002 1/15
VIPer22ADI P
VIPer22AS
LOW POWER OFF LINE SMPS PRIMARY SWITCHER
®
TYPICAL POWER CA PABILITY
n
FIXED 60 KHZ SWI TCHING FREQUENCY
n
9V TO 38V WIDE RANGE VDD VOLTAGE
n
CURRENT MODE CONTROL
n
AUXILIARY UNDERVOLTAGE LOCKOUT
WITH HYSTERESIS
n
HIGH VOLTAGE START UP CURRENT
SOURCE
n
OVERTEMPERA TURE, OVERCURRENT AN D
OVERVOLTAGE PROTECTION WITH
AUTORESTAR T
DESCRIPTION
The VIPer22A combines a dedicated current mode
PWM controller with a high voltage Power
MOSFET on the same silicon chip. Typical
applications cover off line power supplies for
battery charg er adapter s, stan dby pow er suppl ies
for TV or monitors, auxiliary supplies for motor
control, etc. The i nternal control circuit offers the
following benefits:
– Large input voltage range on the VDD pin
accommodates changes in auxiliary supply
voltage. This fe ature is well adapted to battery
charger adapter configurations.
– Automatic burst mode in low load condition.
– Overvoltage protection in hiccup mode.
Main s t y pe SO-8 DIP- 8
European
(195 - 265 Vac)
12 W 20 W
US / Wide range
(85 - 265 Vac)
7 W 12 W
ORDER CODE S
PACKAGE TUBE T&R
SO-8 VIPer22AS VIPer22AS13TR
DIP-8 VIPer22ADIP -
SO-8 DIP-8
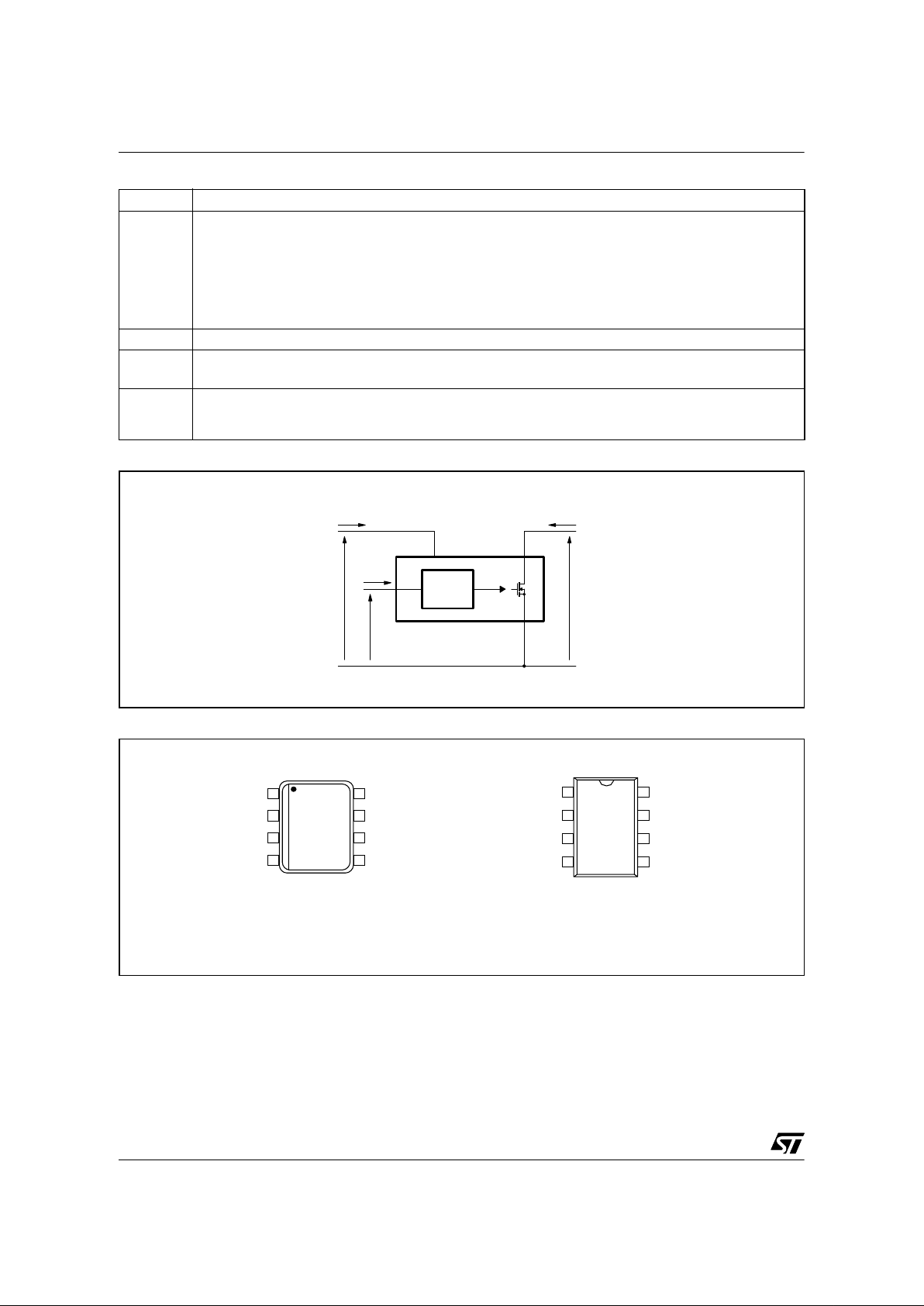
BLO C K DIAGRA M
ON/OFF
0.23 V
DRAIN
SOURCE
VDD
PWM
LATCH
60kHz
OSCILLATOR
BLANKING
+
_
8/14.5V
_
+
FF
S
R1
R4QR3
FB
REGULATOR
INTERNAL
SUPPLY
OVERVOLTAGE
LATCH
OVERTEMP.
DETECTOR
1 k
Ω
42V
_
+
R2
FF
S
R
Q
230
Ω
Page 2
VIPer22ADIP / VIPer22AS
2/15
PIN FUNCTION
CURRENT AND VOLTAGE CONVENTIONS
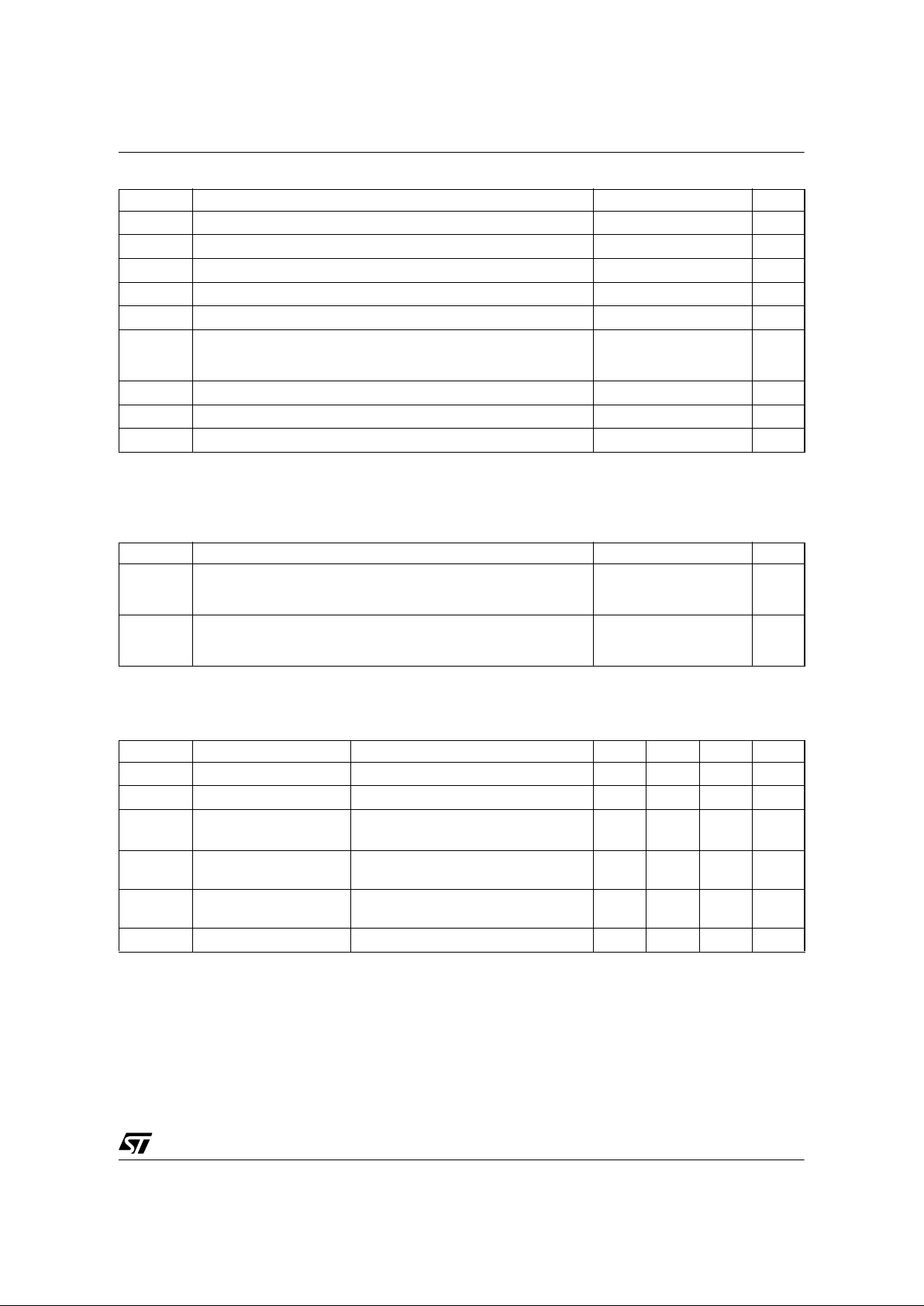
CONNECTION DIAGRAM
Name Function
V
DD
Power supply of the control circuits. Also provides a charging current during start up thanks to a high
voltage current sour ce connected to the drai n. For this p urpose, an hysteresis comparator mo nitors the
V
DD
voltage and provides two thres holds:
- V
DDon
: Voltage value (typically 14.5V) at whi ch the device starts switching and tur ns off the start up
curre nt source.
- V
DDoff
: Voltage value (typically 8V) at which the device stops switching and turns on the start up current
source.
SOURCE Power MOSFET source and circuit ground reference.
DRAIN
Power MOSFET drain. Al so used by the internal high voltage cu rrent source during start up phase for
charging the extern al V
DD
capacitor.
FB
Feedbac k input. The useful voltage range extends from 0V to 1V, and defines the pea k drain MOSFET
current. The current limitation, which corresponds to the maximum drain current, is obtained for a FB pin
shorted to the SOURCE pin.
I
DD
I
D
I
FB
V
DD
V
FB
V
D
FB
VDD DRAIN
SOURCE
CONTROL
VIPer22A
1
2
3
4
DRAIN
DRAIN
DRAIN
DRAIN
8
7
6
5
DRAIN
DRAIN
DRAIN
DRAIN
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
FB
VDD
SOURCE
FB
VDD
SOURCE
SOURCE SOURCE
SO-8 DIP8
Page 3
VIPer22ADIP / VIPer22AS
3/15
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATI NGS
Note: 1. This parameter applies when the start up current source is off. This is the case when the VDD voltage has reached V
DDon
and
remains ab ov e V
DDoff
.
2. This parameter applies when the s tart up current source is on. This is the case when the V
DD
voltage has not yet reached V
DDon
or has fallen below V
DDoff
.
THERMAL DATA
Note: 1. When mounted on a standard single-sided FR4 board with 200 mm² of Cu (at least 35 µm thick) connected to all DRAIN pins.
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (Tj=25°C, VDD=18V, unless otherwise specified)
POWER SECTION
Note: 1. On clamped inductiv e load
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
DS(sw)
Switchin g Drain Source Voltage (Tj=25 ... 125 ° C) (See note 1)
-0.3 ... 730 V
V
DS(st)
Start Up Drain Source Voltage (Tj=25 ... 12 5°C) (See note 2)
-0.3 ... 400 V
I
D
Continuous Drain Current Internally limited A
V
DD
Supply V o ltage 0 ... 50 V
I
FB
Feedbac k Current 3 mA
V
ESD
Electrostatic Discharge:
Machine Model (R=0Ω; C=200pF)
Charged Device Model
200
1.5
V
kV
T
j
Junction Operating Temperature Internally limited °C
T
c
Case Oper ating Temperature -40 to 150 °C
T
stg
Storage Temperature -55 to 150 °C
Symbol Parameter Max Value Unit
Rthj-case
Thermal Resistance Junction-P ins for :
SO-8
DIP-8
25
15
°C/W
Rthj-amb
Thermal Resistance Junction-A m bient for :
SO-8 (See note 1)
DIP-8 (See note 1)
55
45
°C/W
Symbol Parameter Test Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
BV
DSS
Drain-Source Voltage
I
D
=1mA; VFB=2V
730 V
I
DSS
Off State Drain Current
V
DS
=500V; VFB=2V; Tj=125°C
0.1 mA
R
DSon
Static Drain-Source
On State Resistance
I
D
=0.4A
I
D
=0.4A; Tj=100°C
15 17
31
Ω
t
f
Fall Time
I
D
=0.2A; VIN=300V (See fig.1)
(See note 1)
100 ns
t
r
Rise Time
I
D
=0.4A; VIN=300V (See fig.1)
(See note 1)
50 ns
C
oss
Drain Capaci tance
V
DS
=25V
40 pF
Page 4
VIPer22ADIP / VIPer22AS
4/15
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (Tj=25°C, VDD=18V, unless otherwise specified)
SUPPLY SECTION
Note: 1. These test condit ions obtained with a resist iv e load are lead ing to the maxim um c onduction time of the device.
OSCILLATOR SECTION
PWM COMPARATOR SECTION
OVERTEMPERATURE SECTION
Symbol Parameter Test Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
I
DDch
S ta r t Up Ch arging
Current
V
DS=100V; V
DD
=0V ...V
DDon
(See fig. 2)
-1 mA
I
DDoff
S ta r t Up Ch arging
Current
in Thermal Shutdown
V
DD
=5V; VDS=100V
T
j
> TSD - T
HYST
0mA
I
DD0
Oper ating Supply Current
Not Switching
I
FB
=2mA
35mA
I
DD1
Oper ating Supply Current
Switching
I
FB
=0.5mA; ID=50mA (Note 1)
4.5 mA
D
RST
Restart Duty Cycle (See fig. 3) 16 %
V
DDoff
V
DD
Undervoltage
Shut do w n Th reshold
(See fig. 2 & 3) 7 8 9 V
V
DDon
VDD Start Up Threshold
(See fig. 2 & 3) 13 14.5 16 V
V
DDhyst
VDD Threshold
Hysteresis
(See fig. 2) 5.8 6.5 7.2 V
V
DDovp
VDD Overvo ltage
Threshold
38 42 46 V
Symbol Parameter Test Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
F
OSC
Oscillator Frequency
Total Variation
V
DD=VDDoff
... 35V; Tj=0 ... 100°C
54 60 66 kHz
Symbol Parameter Test Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
G
ID
IFB to ID Current Gain
(See fig. 4) 560
I
Dlim
Peak Current Limitation
V
FB
=0V (See fig. 4)
0.56 0.7 0.84 A
I
FBsd
IFB Shutdown Cur rent
(See fig. 4) 0.9 mA
R
FB
FB Pin Input Impedance
I
D
=0mA (See fig. 4)
1.2 kΩ
t
d
Current Sense Delay to
Turn-Off
I
D
=0.4A
200 ns
t
b
Blanking Time 500 ns
t
ONmin
Minimum Turn On Time 700 ns
Symbol Parameter Test Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
T
SD
Thermal Shutdown
Temperature
(See fig. 5) 140 170 °C
T
HYST
Thermal Shutdown
Hysteresis
(See fig. 5) 40 °C
Page 5
VIPer22ADIP / VIPer22AS
5/15
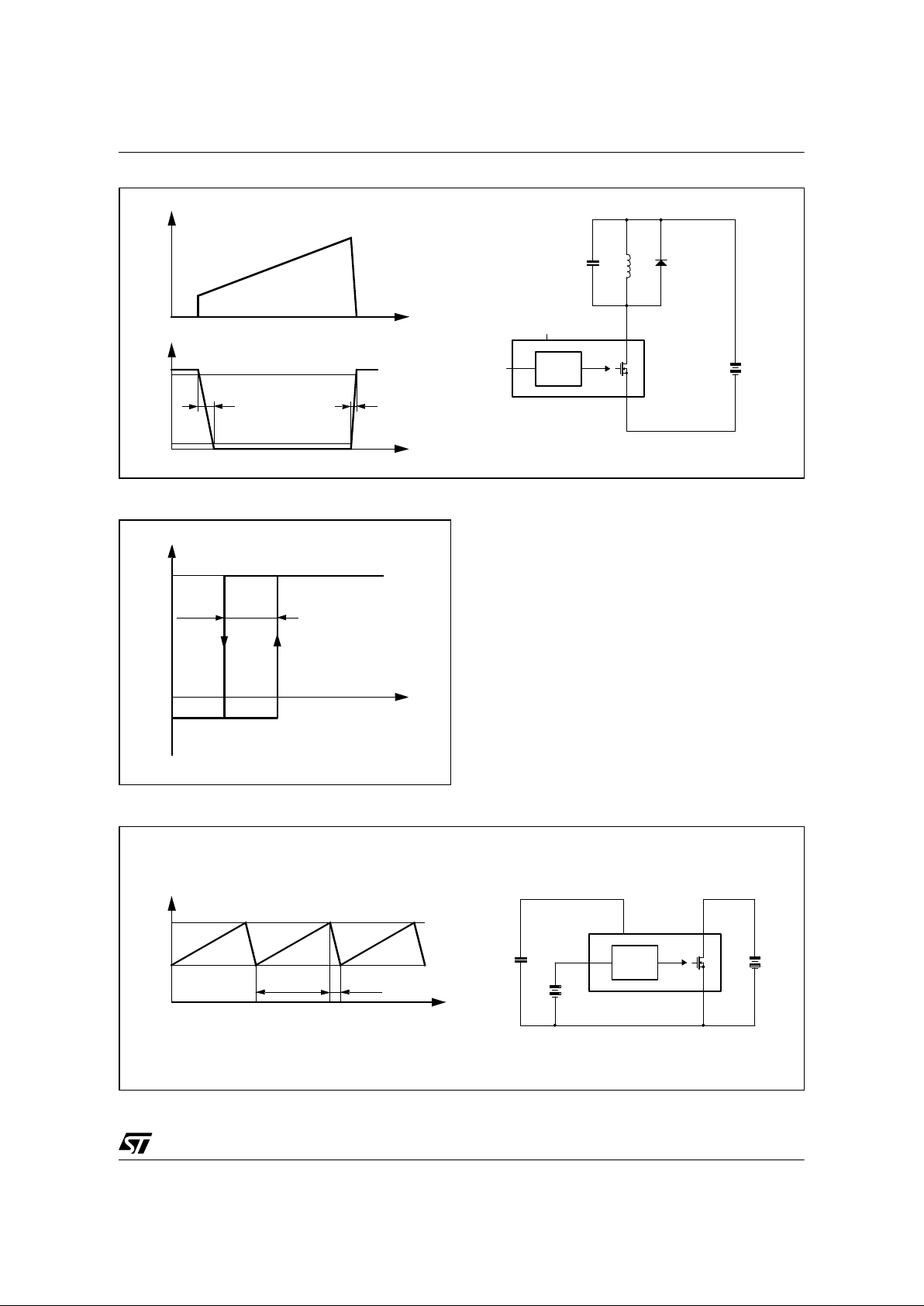
Figur e 1 : Rise and Fall Time
Figur e 2 : Start Up VDD Current
Figur e 3 : Restart Duty Cycle
I
D
V
DS
90%
10%
t
fv
t
rv
t
t
L D
300V
C
FB
VDD DRAIN
SOURCE
CONTROL
VIPer22A
C << Coss
V
DD
V
DDhyst
V
DDoff
V
DDon
I
DD0
I
DDch
VDS = 100 V
F
sw
= 0 kHz
I
DD
t
V
DD
V
DDoff
V
DDon
t
CH
t
ST
D
RST
t
ST
tSTtCH+
-------------------------=
100V
10µF
FB
VDD DRAIN
SOURCE
CONTROL
VIPer22A
2V
Page 6

VIPer22ADIP / VIPer22AS
6/15
Figur e 4 : Peak Drain Current vs. Feedback Current
Figur e 5 : Thermal Shutdown
I
FB
4mH
100V
100V
18V
FB
VDD DRAIN
SOURCE
CONTROL
VIPer22A
47nF
G
ID
I
Dpeak
∆
I
FB
∆
---------------------- -–=
I
D
I
Dpeak
t
1/F
OSC
I
FB
I
Dpeak
I
Dlim
I
FB
I
FBsdRFB
⋅
V
FB
The drain current limitation is
obtained for VFB = 0 V, and a
negative current is drawn from
the FB pin. See the Application
section for further details.
0
I
FBsd
t
t
V
DD
T
j
V
DDon
T
SD
T
HYST
Automatic
start up
Page 7

VIPer22ADIP / VIPer22AS
7/15
Figur e 6 : Switching Frequency vs Tempera ture
Figur e 7 : Current Limitation vs Temperature
-20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
Temperature (°C)
0.97
0.98
0.99
1
1.01
Normalized Frequency
Vdd = 10V ... 35V
-20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
Temperature (°C)
0.94
0.95
0.96
0.97
0.98
0.99
1
1.01
1.02
1.03
1.04
Normalized Current Limitation
Vin = 100V
Vdd = 20V
Page 8

VIPer22ADIP / VIPer22AS
8/15
Figur e 8 : Rectangular U-I output characteristics for battery charger
RECTANGULAR U-I OUTPUT
CHARACTERISTIC
A complete regulation scheme can achieve
combined and accurate output characteristics.
Figure 8 presents a seco ndary feedback through
an optocoupl er driven by a TSM101. This dev ice
offers two operational amplifiers and a voltage
reference, thus allowing the regulation of both
output voltage and current. An integrated OR
function performs the combination of the two
resulting error signals, leading to a dual voltage
and current limitation, known as a rectangular
output characteri stic .
This type of pow er supply is especial ly useful for
battery chargers where the output is mainly used in
current mode, in order to deliver a defined charging
rate. The accurate voltage regulation is also
convenien t for Li-ion batterie s which require both
modes of operation.
WIDE RANGE OF VDD VOLTAGE
The VDD pin voltage range extends from 9V to 38V.
This feature offers a great flexibility in design to
achieve various behaviors. In figure 8 a forward
configuration has been chosen to supply the
device with two benefits:
– as soon as the device starts switching, it
immediately receives some energy from the
auxiliary winding. C5 can be therefore reduced
and a small ceramic chip (100 nF) is sufficient to
insure the filtering function. The total start up
time from the switch on of input voltage to output
voltage presence is dramatically decreased.
– the output current characteristic can be
maintained even with very low or zero output
voltage. Since the TSM101 is also supplied in
forward mode, it keeps the current regulation up
whatever the output voltage is.The VDD pin
voltage may vary as m uch a s the input voltag e,
that is to say with a ratio of about 4 for a wide
range application.
T1
D3
C5
C4
-+
D4
C3
T2
F1
C1
C10
-
+
-
+
Vref
Vcc
GND
U2
TSM101
R6
R9
R10
R4
C9
R7R5R8
C8
R3
ISO1
D2
D5
R2
C7
R1
C2
D1
FB
VDD DRAIN
SOURCE
CONTRO L
U1
VIPerX2A
C6
AC IN
DCOUT
GND
Page 9

VIPer22ADIP / VIPer22AS
9/15
FEEDBACK PIN PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION
A feedback pin controls the operation of the
device. Unli ke conventional PWM control circuits
which use a voltage input (the inverted inp ut of an
operational amplifier), the FB pin is sensitive to
current. Figure 9 presents the internal current
mode structure.
The Power MOS FET delivers a sense current I
s
which is proportional to the main current Id. R2
receives this cu rrent and the current coming from
the FB pin. The voltage across R2 is then
compared to a fixed reference voltage of about
0.23 V. The MOSFET is switched off when the
following equation is reached:
By extracting IS:
Using the current sense ratio of the MOSFET GID:
The curren t limitation is obt ained with the FB pin
shorted to ground (VFB = 0 V). This leads to a
negative current sourced by this pin, and
expressed by:
By reporting this expression in the previous one, it
is possible to obtain the drain current limitation
I
Dlim
:
In a real applicat ion, the FB pin is driven w ith an
optocoupler as sho w n o n figu re 9 wh ich act s as a
pull up. So, it is not possible to really short this pin
to ground and the above drain current value is not
achievable. Nevertheless, the capacitor C is
averaging the voltage on the FB pin, and when the
optocoupler is off (start up or short circuit), it can be
assumed that the corresponding voltage is very
close to 0 V.
For low dr ain curre nts, the form ula (1) is valid as
long as IFB satisfies IFB< I
FBsd
, where I
FBsd
is an
internal threshol d of the VIPer22A. If IFB exceeds
this threshold the d evice will sto p switchin g. T his is
represented on figure 4, and I
FBsd
value is
specified in the PWM COMPARATOR SECTION.
Actually, as soon as the drain current is about 12%
of Idlim, that is to say 85 mA, the device will enter
a burst mode operation by missing switching
cycles. This is especially important when the
converter is lightly loaded.
It is then possible to build the total DC transfer
function between ID and IFB as shown on figure 10.
This figure also takes into account the internal
blanking time and it s associated minimum tur n on
time. This imposes a minimum drain current under
which the device is no more able to control it in a
linear way. This drain current depends on the
primary inductance value of the transformer and
the input voltage. Two cases may occur,
depending on the val ue of this curr ent versus the
fixed 85 mA value, as described above.
START UP SEQUENCE
This device includes a high voltage start up current
source connecte d on the drain of the device. As
soon as a voltage is applied on the input of the
converter, this start up cur rent source is activat ed
as long as VDD is lower than V
DDon
. When
reaching V
DDon
, the start up current source is
switched off and the device begins to o perate by
turning on and off its main power MOSFET. As the
FB pin does not receive any current from the
optocoupler, the device operates at full current
capacity and the output voltage rises until reaching
Fi
gure 9 : Internal Current Control Structure
60kHz
OSCILLATOR
PWM
LATCH
S
Q
R
0.23V
Id
DRAIN
SOURCE
FB
R1
R2
C
+Vdd
Secondary
feedback
I
FB
Is
1 kΩ
230 Ω
R2ISIFB+()⋅ 0.23V=
I
S
0.23V
R
2
-------------- IFB–=
I
D
GIDIS⋅ G
ID
0.23V
R
2
-------------- IFB–
⋅==
I
FB
0.23V
R
1
--------------–=
I
Dlim
GID0.23V
1
R
2
------
1
R
1
----- -+
⋅⋅=
Fi
gure 10 :
I
FB
Transfer function
I
FBsd
I
Dlim
I
FB
t
ONmin
V
2
⋅
IN
L
---------------------------------------
t
ONmin
V
1
⋅
IN
L
---------------------------------------
85mA
I
Dpeak
0
Part masked by the
I
FBsd
threshold
Page 10

VIPer22ADIP / VIPer22AS
10/15
the regulation point where the secondary loop
begins to send a current in the optocoupler. At this
point, the converter ent ers a regulated operation
where the F B pin receives the amount of current
needed to deliver the right power on secondary
side.
This sequence is shown in figure 11. Note that
during the real starting phase tss, the device
consumes some energy from the VDD capacitor,
waiting for the auxiliary winding to provide a
continuous s upply. If th e value of this c apacitor i s
too low, th e start up phase is terminated before
receiving any energy from the auxiliary winding
and the converter never starts up. This is illustrated
also in the same figure in dashed lines.
OVERVOLTAGE THRESHOLD
An overvoltage dete c tor on the VDD pin allows the
VIPer22A to reset itself when VDD exceeds
V
DDovp
. This is illustrated in figure 12, which shows
the whole sequence of an overvoltage event. Note
that this event i s only latche d for the time needed
by VDD to reach V
DDoff
, and then the device
resumes normal operati on autom atic ally .
Fi
gure 11 : Start Up Sequence
t
t
I
FB
V
DDon
t
V
OUT
V
DD
V
DDoff
tss
Fi
gure 12 : Overvoltage Sequence
t
t
V
DS
V
DDon
V
DD
V
DDoff
V
DDovp
Page 11

VIPer22ADIP / VIPer22AS
11/15
DIM.
mm. inch
MIN. TYP MAX. MIN. TYP. MAX.
A 1.75 0.068
a1 0.1 0.25 0.003 0.009
a2 1.65 0.064
a3 0.65 0.85 0.025 0.033
b 0.35 0.48 0.013 0.018
b1 0.19 0.25 0.007 0.010
C 0.25 0.5 0.010 0.019
c1 45 (typ .)
D 4 .8 5 0.188 0.196
E
5.8
6.2 0.228 0.244
e 1.27 0.050
e3 3.81 0.150
F 3.8 4 0.14 0.157
L 0.4 1.27 0.01 5 0. 050
M 0.6 0.023
S 8 (max.)
L1 0.8 1.2 0.031 0.047
1
SO-8 MECHANICAL DATA
Page 12

VIPer22ADIP / VIPer22AS
12/15
DIM.
mm.
MIN. TYP MAX.
A 5.33
A1 0.38
A2 2.92 3.30 4.95
b 0.36 0.46 0.56
b2 1.14 1.52 1.78
c 0.20 0.25 0.36
D 9.02 9.27 10.16
E 7.62 7.87 8.26
E1 6.10 6.35 7.11
e2.54
eA 7.62
eB 10.92
L 2.92 3.30 3.81
Packag e W eight Gr. 470
P001
Plastic DIP-8 MECHANI CAL DATA
Page 13

VIPer22ADIP / VIPer22AS
13/15
1
SO-8 TUBE SHIPMENT (no suffix)
All dimensions are i n m m .
Base Q.ty 100
Bulk Q.ty 2000
Tube length (± 0.5) 532
A 3.2
B 6
C (± 0.1) 0.6
TAPE AND REEL SHIPMENT (suffix “13TR”)
All dimensions are i n m m .
Base Q.ty 2500
Bulk Q.ty 2500
A (max) 330
B (min) 1.5
C (± 0.2) 13
F 20.2
G (+ 2 / -0) 12.4
N (min) 60
T (max) 18.4
TAPE DIMENSIONS
According to Electronic Industries Asso ciation
(EIA) S tanda rd 481 re v. A, Feb 1 9 86
All dimensions are i n m m .
Tape width W 12
Tape Hole Spacing P0 (± 0.1) 4
Component Spacing P 8
Hole Diameter D (± 0.1/-0) 1.5
Hole Diameter D1 (min) 1.5
Hole Position F (± 0.05) 5.5
Compartment Depth K (max) 4.5
Hole Spacing P1 (± 0.1) 2
Top
cover
tape
End
Start
No componentsNo components Components
500mm min
500mm min
Empty components pockets
saled with cover tape.
User direction of feed
REEL DIMENSIONS
C
B
A
Page 14

VIPer22ADIP / VIPer22AS
14/15
11
DIP-8 TUBE SHIPMENT (no suffix)
All dimensions are in mm.
Base Q.ty 20
Bulk Q.ty 1000
Tube length (± 0.5) 532
A 8.4
B 11.2
C (± 0.1) 0.8
A
B
C
Page 15

VIPer22ADIP / VIPer22AS
15/15
Information furnish ed is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, STMic r oelectroni c s as s um es no respons ibility for the cons equences
of use of such information nor for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties which may results from its use. No license is
granted by implication or otherwise unde r any patent or pat ent rights of STMicroelectronics. Spe c ifications m entioned in thi s publication are
subject to c hange without notice. This public ation supers edes and replaces all information previously s upplied. STMicroel ec tronics pr oducts
are not authorized for use as critical components in life support devices or systems without express written approval of STMicroelectronics.
The ST logo is a trademark of STMicroelectronics
2002 STMicroelectronics - Printed in ITALY- All Rights Reserved.
STMicroelectronics GROUP OF COMPANIES
Australia - Brazil - Canada - Ch ina - Finland - Fr anc e - Germany - Ho ng K ong - India - Israel - Italy - J apan - Malaysia -
Malta - Morocco - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - U.S.A.
http://www.st.com
 Loading...
Loading...