Page 1

DATA SH EET
Product specification
Supersedes data of 1995 May 08
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
1996 Feb 21
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
TDA8790
8-bit, 40 Msps 2.7 to 5.5 V universal
analog-to-digital converter
Page 2

1996 Feb 21 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit, 40 Msps 2.7 to 5.5 V universal
analog-to-digital converter
TDA8790
FEATURES
• 8-bit resolution
• Operation between 2.7 and 5.5 V
• Sampling rate up to 40 MHz
• DC sampling allowed
• High signal-to-noise ratio over a large analog input
frequency range (7.3 effective bits at 4.43 MHz
full-scale input at f
clk
= 40 MHz)
• CMOS/TTL compatible digital inputs and outputs
• External reference voltage regulator
• Power dissipation only 30 mW (typical)
• Low analog input capacitance, no buffer amplifier
required
• Sleep mode (4 mW)
• No sample-and-hold circuit required.
APPLICATIONS
High-speed analog-to-digital conversion for:
• Video data digitizing
• Camera
• Camcorder
• Radio communication.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA8790 is an 8-bit universal analog-to-digital
converter (ADC) for video and general purpose
applications. It converts the analog input signal from
2.7 to 5.5 V into 8-bit binary-coded digital words at a
maximum sampling rate of 40 MHz. All digital inputs and
outputs are CMOS/TTL compatible. A sleep mode allows
reduction of the device power consumption down to 4 mW.
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
ORDERING INFORMATION
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
DDA
analog supply voltage 2.7 3.3 5.5 V
V
DDD
digital supply voltage 2.7 3.3 5.5 V
V
DDO
output stages supply voltage 2.5 3.3 5.5 V
∆V
DD
supply voltage difference
V
DDA
− V
DDD
−0.2 − +0.2 V
V
DDD
− V
DDO
−0.2 − +2.25 V
I
DDA
analog supply current − 46mA
I
DDD
digital supply current − 58mA
I
DDO
output stages supply current f
clk
= 40 MHz; CL= 20 pF;
ramp input
− 12mA
INL integral non-linearity f
clk
= 40 MHz; ramp input −±0.5 ±0.75 LSB
DNL differential non-linearity f
clk
= 40 MHz; ramp input −±0.25 ±0.5 LSB
f
clk(max)
maximum clock frequency 40 −−MHz
P
tot
total power dissipation V
DDA=VDDD=VDDO
= 3.3 V − 30 53 mW
TYPE
NUMBER
PACKAGE
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
TDA8790M SSOP20 plastic shrink small outline package; 20 leads; body width 4.4 mm SOT266-1
Page 3

1996 Feb 21 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit, 40 Msps 2.7 to 5.5 V universal
analog-to-digital converter
TDA8790
BLOCK DIAGRAM
Fig.1 Block diagram.
handbook, full pagewidth
7
9
8
10
V
RB
V
SSA
V
SSOVSSD1
V
RM
V
RT
V
R
LAD
I
3
V
DDD
5
V
DDA
17
18
19
16 D4
D5
D6
D7
15
14
2
D3
D2
13 D1
12
D0
CMOS
OUTPUTS
LATCHES
ANALOG -TO - DIGITAL
CONVERTER
CLOCK DRIVER
MBE502
1
CLK
SLEEP
TDA8790
20
V
DDO
6
analog
ground
411
output
ground
digital
ground
analog
voltage input
data outputs
LSB
MSB
Page 4
1996 Feb 21 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit, 40 Msps 2.7 to 5.5 V universal
analog-to-digital converter
TDA8790
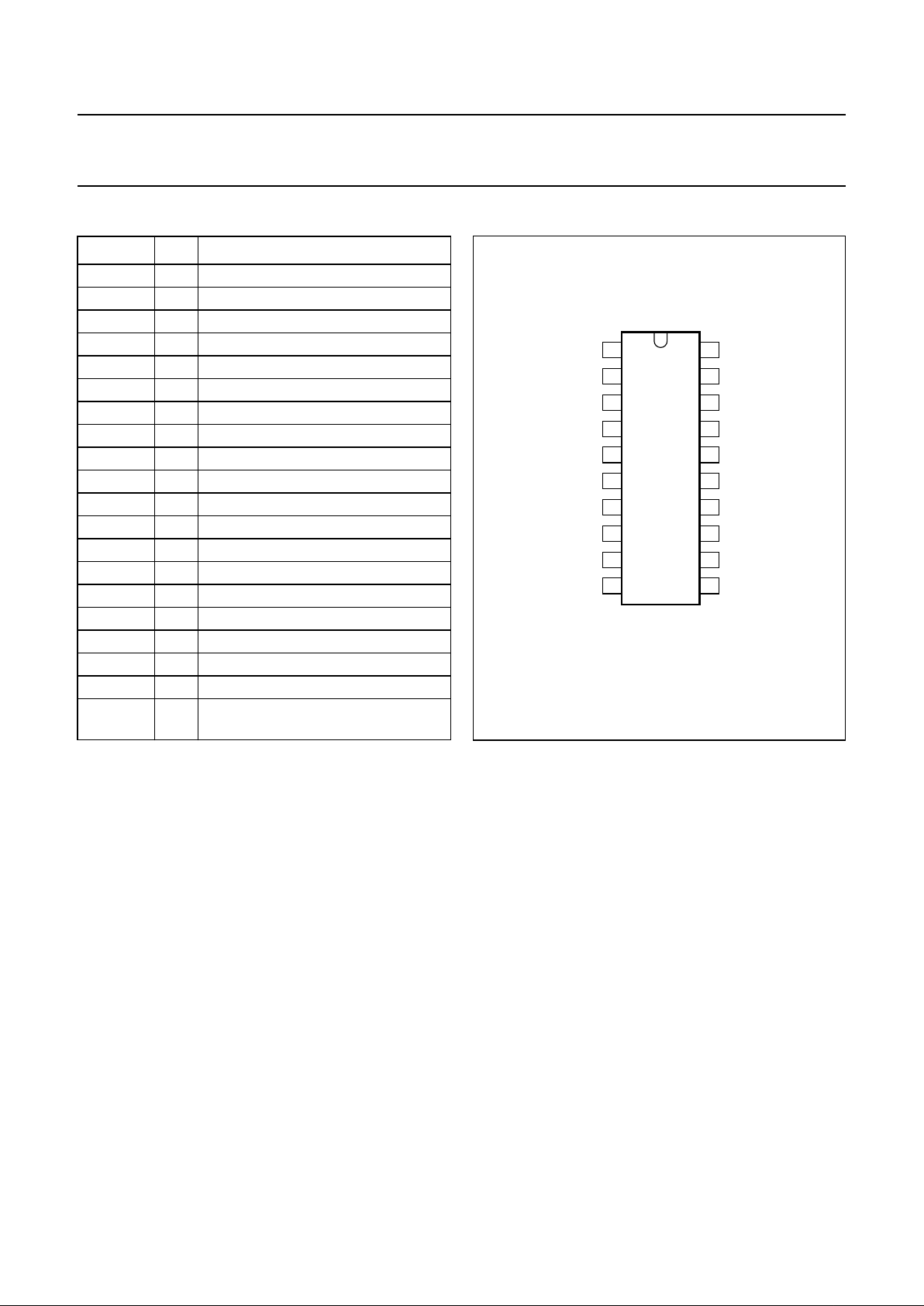
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
CLK 1 clock input
SLEEP 2 sleep mode input
V
DDD
3 digital supply voltage (2.7 to 5.5 V)
V
SSD
4 digital ground
V
DDA
5 analog supply voltage (2.7 to 5.5 V)
V
SSA
6 analog ground
V
RB
7 reference voltage BOTTOM input
V
RM
8 reference voltage MIDDLE
V
I
9 analog input voltage
V
RT
10 reference voltage TOP input
V
SSO
11 digital output ground
D0 12 data output; bit 0 (LSB)
D1 13 data output; bit 1
D2 14 data output; bit 2
D3 15 data output; bit 3
D4 16 data output; bit 4
D5 17 data output; bit 5
D6 18 data output; bit 6
D7 19 data output; bit 7 (MSB)
V
DDO
20 positive supply voltage for output
stage (2.7 to 5.5 V)
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
TDA8790
MBE501
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
CLK
V
DDO
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
V
SSO
SLEEP
V
DDD
V
SSD
V
DDA
V
SSA
V
RB
V
RM
V
I
V
RT
Page 5

1996 Feb 21 5
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit, 40 Msps 2.7 to 5.5 V universal
analog-to-digital converter
TDA8790
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134).
Note
1. The supply voltages V
DDA
, V
DDD
and V
DDO
may have any value between −0.3 V and +7.0 V provided that the supply
voltage ∆VDD remains as indicated.
HANDLING
Inputs and outputs are protected against electrostatic discharges in normal handling. However, to be totally safe, it is
desirable to take normal precautions appropriate to handling integrated circuits.
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
DDA
analog supply voltage note 1 −0.3 +7.0 V
V
DDD
digital supply voltage note 1 −0.3 +7.0 V
V
DDO
output stages supply voltage note 1 −0.3 +7.0 V
∆V
DD
supply voltage difference
V
DDA
− V
DDD
−1.0 +4.0 V
V
DDA
− V
DDO
−1.0 +4.0 V
V
DDD
− V
DDO
−1.0 +4.0 V
V
I
input voltage referenced to V
SSA
−0.3 +7.0 V
V
clk(p-p)
AC input voltage for switching
(peak-to-peak value)
referenced to V
SSD
− V
DDD
V
I
O
output current − 10 mA
T
stg
storage temperature −55 +150 °C
T
amb
operating ambient temperature −20 +75 °C
T
j
junction temperature − +150 °C
SYMBOL PARAMETER VALUE UNIT
R
th j-a
thermal resistance from junction to ambient in free air 120 K/W
Page 6

1996 Feb 21 6
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit, 40 Msps 2.7 to 5.5 V universal
analog-to-digital converter
TDA8790
CHARACTERISTICS
V
DDA=V5
to V6= 3.3 V; V
DDD=V3
to V4= 3.3 V; V
DDO=V20
to V11= 3.3 V; V
SSA,VSSD
and V
SSO
shorted together;
V
i(p-p)
= 1.84 V; CL= 20 pF; T
amb
=0to+70°C; typical values measured at T
amb
=25°C; unless otherwise specified.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supply
V
DDA
analog supply voltage 2.7 3.3 5.5 V
V
DDD
digital supply voltage 2.7 3.3 5.5 V
V
DDO
output stages supply voltage 2.5 3.3 5.5 V
∆V
DD
supply voltage difference
V
DDA
− V
DDD
−0.2 − +0.2 V
V
DDD
− V
DDO
−0.2 − +2.25 V
I
DDA
analog supply current − 46 mA
I
DDD
digital supply current − 58 mA
I
DDO
output stages supply current f
clk
= 40 MHz; ramp input;
CL=20pF
− 12 mA
Inputs
C
LOCK INPUT CLK (REFERENCED TO V
SSD
); see note 1
V
IL
LOW level input voltage 0 − 0.3V
DDD
V
V
IH
HIGH level input voltage 0.7V
DDD
− V
DDD
V
V
DDD
≤ 3.6 V 0.6V
DDD
− V
DDD
V
I
IL
LOW level input current V
clk
= 0.3V
DDD
−10+1µA
I
IH
HIGH level input current V
clk
= 0.7V
DDD
−−5µA
Z
I
input impedance f
clk
= 40 MHz − 4 − kΩ
C
I
input capacitance f
clk
= 40 MHz − 3 − pF
INPUT SLEEP (REFERENCED TO V
SSD
); see Table 2
V
IL
LOW level input voltage 0 − 0.3V
DDD
V
V
IH
HIGH level input voltage 0.7V
DDD
− V
DDD
V
V
DDD
≤ 3.6 V 0.6V
DDD
− V
DDD
V
I
IL
LOW level input current VIL= 0.3V
DDD
−1 −− µA
I
IH
HIGH level input current VIH= 0.7V
DDD
−−+1 µA
VI(ANALOG INPUT VOLTAGE REFERENCED TO V
SSA
)
I
IL
LOW level input current VI=V
RB
− 0 −µA
I
IH
HIGH level input current VI=V
RT
− 9 −µA
Z
I
input impedance fi= 1 MHz − 20 − kΩ
C
I
input capacitance fi= 1 MHz − 2 − pF
Reference voltages for the resistor ladder; see Table 1
V
RB
reference voltage BOTTOM 1.1 1.2 − V
V
RT
reference voltage TOP V
TOP
≤ V
DDA
2.7 3.3 V
DDA
V
V
diff
differential reference voltage
VRT− V
RB
1.5 2.1 2.7 V
I
ref
reference current − 0.95 − mA
Page 7

1996 Feb 21 7
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit, 40 Msps 2.7 to 5.5 V universal
analog-to-digital converter
TDA8790
R
LAD
resistor ladder − 2.2 − kΩ
TC
RLAD
temperature coefficient of the
resistor ladder
− 1860 − ppm
− 4092 − mΩ/K
V
osB
offset voltage BOTTOM note 2 − 170 − mV
V
osT
offset voltage TOP note 2 − 170 − mV
V
i(p-p)
analog input voltage (peak-to-peak
value)
note 3 1.4 1.76 2.4 V
Outputs
D
IGITAL OUTPUTS D7 TO D0 (REFERENCED TO V
SSD
)
V
OL
LOW level output voltage IO=1mA 0 − 0.5 V
V
OH
HIGH level output voltage IO= −1mA V
DDO
− 0.5 − V
DDO
V
I
OZ
output current in 3-state mode 0.4V<VO<V
DDO
−20 − +20 µA
Switching characteristics
C
LOCK INPUT CLK; see Fig.4; note 1
f
clk(max)
maximum clock frequency 40 −− MHz
t
CPH
clock pulse width HIGH 9 −− ns
t
CPL
clock pulse width LOW 9 −− ns
Analog signal processing
L
INEARITY
INL integral non-linearity f
clk
= 40 MHz; ramp input;
see Fig.6
−±0.5 ±0.75 LSB
DNL differential non-linearity f
clk
= 40 MHz; ramp input;
see Fig.7
−±0.25 ±0.5 LSB
BANDWIDTH (f
clk
= 40 MHz)
B analog bandwidth full-scale sine wave;
note 4
− 10 − MHz
75% full-scale sine wave;
note 4
− 13 − MHz
50% full-scale sine wave;
note 4
− 20 − MHz
small signal at mid scale;
V
i
= ±10 LSB at
code 128; note 4
− 350 − MHz
INPUT SET RESPONSE (f
clk
= 40 MHz; see Fig.8; note 5)
t
STLH
analog input settling time
LOW-to-HIGH
full-scale square wave − 35 ns
t
STHL
analog input settling time
HIGH-to-LOW
full-scale square wave − 35 ns
HARMONICS;(f
clk
=40MHZ; see Fig.9; note 6)
THD total harmonic distortion f
i
= 4.43 MHz −−50 − dB
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Page 8

1996 Feb 21 8
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit, 40 Msps 2.7 to 5.5 V universal
analog-to-digital converter
TDA8790
Notes
1. In addition to a good layout of the digital and analog ground, it is recommended that the rise and fall times of the clock
must not be less than 1 ns.
2. Analog input voltages producing code 0 up to and including 256:
a) V
osB
(voltage offset BOTTOM) is the difference between the analog input which produces data equal to 00 and
the reference voltage BOTTOM (VRB) at T
amb
=25°C.
b) V
osT
(voltage offset TOP) is the difference between VRT (reference voltage TOP) and the analog input which
produces data outputs equal to 256 at T
amb
=25°C.
S
IGNAL-TO-NOISE RATIO; see Fig.9; note 6
S/N signal-to-noise ratio (full scale) without harmonics;
f
clk
= 40 MHz;
fi= 4.43 MHz
− 47 − dB
EFFECTIVE BITS; see Fig.9; note 6
EB effective bits f
clk
= 40 MHz
f
i
= 300 kHz − 7.8 − bits
f
i
= 4.43 MHz − 7.3 − bits
DIFFERENTIAL GAIN; see note 7
G
diff
differential gain f
clk
= 40 MHz;
PAL modulated ramp
− 1.5 − %
DIFFERENTIAL PHASE; see note 7
ϕ
diff
differential phase f
clk
= 40 MHz;
PAL modulated ramp
− 0.25 − deg
Timing (f
clk
= 40 MHz; CL= 20 pF); see Fig.4; note 8
t
ds
sampling delay time −−5ns
t
h
output hold time 5 −− ns
t
d
output delay time V
DDO
= 4.75 V 8 12 15 ns
V
DDO
= 3.15 V 8 17 20 ns
V
DDO
= 2.7 V 8 18 21 ns
3-state sleep mode delay times; see Fig.5
t
dZH
enable HIGH − 14 18 ns
t
dZL
enable LOW − 16 20 ns
t
dHZ
disable HIGH − 16 20 ns
t
dLZ
disable LOW − 14 18 ns
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Page 9

1996 Feb 21 9
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit, 40 Msps 2.7 to 5.5 V universal
analog-to-digital converter
TDA8790
3. In order to ensure the optimum linearity performance of such converter architecture the lower and upper extremities
of the converter reference resistor ladder (corresponding to output codes 0 and 255 respectively) are connected to
pins VRB and VRT via offset resistors ROB and ROT as shown in Fig.3.
a) The current flowing into the resistor ladder is and the full-scale input range at the converter,
to cover code 0 to code 255, is
b) Since R
L
, ROB and ROT have similar behaviour with respect to process and temperature variation, the ratio
will be kept reasonably constant from part to part. Consequently variation of the output codes
at a given input voltage depends mainly on the difference V
RT
− VRB and its variation with temperature and supply
voltage. When several ADCs are connected in parallel and fed with the same reference source, the matching
between each of them is then optimized.
4. The analog bandwidth is defined as the maximum input sine wave frequency which can be applied to the device.
No glitches greater than 2 LSBs, nor any significant attenuation is observed in the reconstructed signal.
5. The analog input settling time is the minimum time required for the input signal to be stabilized after a sharp full-scale
input (square-wave signal) in order to sample the signal and obtain correct output data.
6. Effective bits are obtained via a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) treatment taking 8 K acquisition points per equivalent
fundamental period. The calculation takes into account all harmonics and noise up to half of the clock frequency
(NYQUIST frequency). Conversion to signal-to-noise ratio: S/N = EB × 6.02 + 1.76 dB.
7. Measurement carried out using video analyser VM700A, where video analog signal is reconstructed through a DAC.
8. Output data acquisition: the output data is available after the maximum delay time of t
d
.
I
L
VRTVRB–
R
OBRLROT
++
------------------------------------------
=
V
iRLIL
×
R
L
R
OBRLROT
++
------------------------------------------
== V
RTVRB
)– 0.838 VRTVRB–(×=()×
R
L
R
OBRLROT
++
------------------------------------------
Fig.3 Explanation of note 3.
handbook, halfpage
R
LAD
R
OT
V
RT
V
RM
V
RB
R
OB
code 255
code 0
7
6
9
MGD284
I
L
R
L
Page 10

1996 Feb 21 10
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit, 40 Msps 2.7 to 5.5 V universal
analog-to-digital converter
TDA8790
Table 1 Output coding and input voltage (typical values; referenced to V
SSA
)
Table 2 Sleep mode selection
STEP
V
I(p-p)
(V)
BINARY OUTPUT BITS
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Underflow <1.37 0 0 0 0 0000
0 1.37 0 0 0 0 0000
1 . 00000001
. . ........
. . ........
254 . 11111110
255 3.13 1 1 1 1 1111
Overflow >3.13 1 1 1 1 1111
SLEEP D7 TO D0 I
DDA+IDDD
(typ.)
1 high impedance 1.2 mA
0 active 9 mA
Fig.4 Timing diagram.
handbook, full pagewidth
ds
t
sample N + 1
sample N
CLK
MSA670
sample N + 2
50 %
V
l
DATA
D0 to D7
t
d
t
h
CPH
t
CPL
t
V
DDO
0 V
50 %
DATA
N + 1
DATA
N
DATA
N - 1
DATA
N - 2
Page 11

1996 Feb 21 11
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit, 40 Msps 2.7 to 5.5 V universal
analog-to-digital converter
TDA8790
Fig.5 Timing diagram and test conditions of 3-state output delay time.
f
SLEEP
= 100 kHz.
handbook, full pagewidth
MBE503
50 %
50 %
HIGH
LOW
dZH
t
dHZ
t
50 %
HIGH
LOW
dZL
t
dLZ
t
10 %
90 %
output
data
V
DDD
output
data
3.3 kΩ
20 pF
S1
V
DDD
TDA8790
SLEEP
SLEEP
TEST
dLZ
t
dZL
t
dHZ
t
dZH
S1
DDD
V
DDD
V
GND
GND
t
Page 12

1996 Feb 21 12
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit, 40 Msps 2.7 to 5.5 V universal
analog-to-digital converter
TDA8790
Fig.6 Typical integral non-linearity (INL) performance.
handbook, full pagewidth
255
0.291
0 68 102 136 204 23834 170
MBE548
0.065
−0.160
−0.272
−0.047
0.178
A
(LSB)
codes
Fig.7 Typical differential non-linearity (DNL) performance.
handbook, full pagewidth
255
0.150
0 68 102 136 204 23834 170
MBE549
0.032
−0.84
−0.143
−0.025
0.091
A
(LSB)
codes
Page 13

1996 Feb 21 13
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit, 40 Msps 2.7 to 5.5 V universal
analog-to-digital converter
TDA8790
Fig.8 Analog input settling-time diagram.
handbook, full pagewidth
MBE504
50 %
STLH
t
5 ns
code 0
code 255
I
50 %
2 ns
50 %
5 ns
STHL
t
50 %
2 ns
CLK
V
Fig.9 Typical Fast Fourier Transform (f
clk
= 40 MHz; fi= 4.43 MHz).
Effective bits: 7.32; THD = 51.08 dB.
Harmonic levels (dB): 2nd = −68.99; 3rd = −51.62; 4th = −66.05; 5th = −63.23; 6th = −72.79.
20
0
120
0 5.0 7.5 10.0 15.0 17.52.5 12.5
MBE550
40
80
100
60
20
A
(dB)
f (MHz)
Page 14

1996 Feb 21 14
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit, 40 Msps 2.7 to 5.5 V universal
analog-to-digital converter
TDA8790
INTERNAL PIN CONFIGURATIONS
Fig.10 CMOS data outputs.
h
andbook, halfpage
MBE505
V
DDO
V
D7 to D0
SSO
Fig.11 Analog inputs.
ndbook, halfpage
MLC857
V
DDA
V
SSA
V
I
Fig.12 SLEEP 3-state input.
MBE506
V
DDO
V
SSO
SLEEP
Fig.13 VRB, VRM and VRT.
handbook, halfpage
R
MLC859
V
RB
V
RM
V
DDA
V
SSA
V
RT
LAD
Page 15

1996 Feb 21 15
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit, 40 Msps 2.7 to 5.5 V universal
analog-to-digital converter
TDA8790
Fig.14 CLK input.
handbook, halfpage
V
DDD
V
SSD
CLK
MLC860
1
/2V
DDD
APPLICATION INFORMATION
Fig.15 Application diagram.
The analog and digital supplies should be separated and decoupled.
The external voltage generator must be built such that a good supply voltage ripple rejection is achieved with respect to the LSB value. Eventually, the
reference ladder voltages can be derived from a well regulated V
DDA
supply through a resistor bridge and a decoupled capacitor.
(1) VRB, VRM and VRT are decoupled to V
SSA
.
MBE507
CLK
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
SLEEP
V
DDD
V
DDO
V
SSD
V
DDA
V
SSA
V
SSA
V
RB
D2
D1
D0
V
SSO
(1)
V
RM
V
I
(1)
V
RT
(1)
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
100
nF
V
SSA
100
nF
V
SSA
100
nF
TDA8790
Page 16

1996 Feb 21 16
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit, 40 Msps 2.7 to 5.5 V universal
analog-to-digital converter
TDA8790
PACKAGE OUTLINE
UNIT A1A2A
3
b
p
cD
(1)E(1)
(1)
eHELLpQZywv θ
REFERENCES
OUTLINE
VERSION
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
ISSUE DATE
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
mm
0.1501.4
1.2
0.32
0.20
0.20
0.13
6.6
6.4
4.5
4.3
0.65 1.0 0.2
6.6
6.2
0.65
0.45
0.48
0.18
10
0
o
o
0.13 0.1
DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions)
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.20 mm maximum per side are not included.
0.75
0.45
SOT266-1
90-04-05
95-02-25
w M
θ
A
A
1
A
2
b
p
D
H
E
L
p
Q
detail X
E
Z
e
c
L
v M
A
X
(A )
3
A
y
0.25
110
20
11
pin 1 index
0 2.5 5 mm
scale
SSOP20: plastic shrink small outline package; 20 leads; body width 4.4 mm
SOT266-1
A
max.
1.5
Page 17

1996 Feb 21 17
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit, 40 Msps 2.7 to 5.5 V universal
analog-to-digital converter
TDA8790
SOLDERING
Introduction
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all IC
packages. Wave soldering is often preferred when
through-hole and surface mounted components are mixed
on one printed-circuit board. However, wave soldering is
not always suitable for surface mounted ICs, or for
printed-circuits with high population densities. In these
cases reflow soldering is often used.
This text gives a very brief insight to a complex technology.
A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in
our
“IC Package Databook”
(order code 9398 652 90011).
Reflow soldering SSOP
Reflow soldering techniques are suitable for all SSOP
packages.
Reflow soldering requires solder paste (a suspension of
fine solder particles, flux and binding agent) to be applied
to the printed-circuit board by screen printing, stencilling or
pressure-syringe dispensing before package placement.
Several techniques exist for reflowing; for example,
thermal conduction by heated belt. Dwell times vary
between 50 and 300 seconds depending on heating
method. Typical reflow temperatures range from
215 to 250 °C.
Preheating is necessary to dry the paste and evaporate
the binding agent. Preheating duration:
45 minutes at 45 °C.
Wave soldering SSOP
Wave soldering is not recommended for SSOP packages.
This is because of the likelihood of solder bridging due to
closely-spaced leads and the possibility of incomplete
solder penetration in multi-lead devices.
If wave soldering cannot be avoided, the following
conditions must be observed:
• A double-wave (a turbulent wave with high upward
pressure followed by a smooth laminar wave)
soldering technique should be used.
• The longitudinal axis of the package footprint must
be parallel to the solder flow and must incorporate
solder thieves at the downstream end.
Even with these conditions, only consider wave
soldering SSOP packages that have a body width of
4.4 mm, that is SSOP16 (SOT369-1) or
SSOP20 (SOT266-1).
During placement and before soldering, the package must
be fixed with a droplet of adhesive. The adhesive can be
applied by screen printing, pin transfer or syringe
dispensing. The package can be soldered after the
adhesive is cured.
Maximum permissible solder temperature is 260 °C, and
maximum duration of package immersion in solder is
10 seconds, if cooled to less than 150 °C within
6 seconds. Typical dwell time is 4 seconds at 250 °C.
A mildly-activated flux will eliminate the need for removal
of corrosive residues in most applications.
Repairing soldered joints
Fix the component by first soldering two diagonallyopposite end leads. Use only a low voltage soldering iron
(less than 24 V) applied to the flat part of the lead. Contact
time must be limited to 10 seconds at up to 300 °C. When
using a dedicated tool, all other leads can be soldered in
one operation within 2 to 5 seconds at between 270 and
320 °C.
Page 18

1996 Feb 21 18
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit, 40 Msps 2.7 to 5.5 V universal
analog-to-digital converter
TDA8790
DEFINITIONS
LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or systems where malfunction of these
products can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips customers using or selling these products for
use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips for any damages resulting from such
improper use or sale.
Data sheet status
Objective specification This data sheet contains target or goal specifications for product development.
Preliminary specification This data sheet contains preliminary data; supplementary data may be published later.
Product specification This data sheet contains final product specifications.
Limiting values
Limiting values given are in accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134). Stress above one or
more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation
of the device at these or at any other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the specification
is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Application information
Where application information is given, it is advisory and does not form part of the specification.
Page 19

1996 Feb 21 19
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit, 40 Msps 2.7 to 5.5 V universal
analog-to-digital converter
TDA8790
NOTES
Page 20

Philips Semiconductors – a worldwide company
Argentina: IEROD, Av. Juramento 1992 - 14.b, (1428)
BUENOS AIRES, Tel. (541)786 7633, Fax. (541)786 9367
Australia: 34 Waterloo Road, NORTH RYDE, NSW 2113,
Tel. (02)805 4455, Fax. (02)805 4466
Austria: Triester Str. 64, A-1101 WIEN, P.O. Box 213,
Tel. (01)60 101-1236, Fax. (01)60 101-1211
Belgium: Postbus 90050, 5600 PB EINDHOVEN, The Netherlands,
Tel. (31)40-2783749, Fax. (31)40-2788399
Brazil: Rua do Rocio 220 - 5
th
floor, Suite 51,
CEP: 04552-903-SÃO PAULO-SP, Brazil,
P.O. Box 7383 (01064-970),
Tel. (011)821-2333, Fax. (011)829-1849
Canada: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS/COMPONENTS:
Tel. (800) 234-7381, Fax. (708) 296-8556
Chile: Av. Santa Maria 0760, SANTIAGO,
Tel. (02)773 816, Fax. (02)777 6730
China/Hong Kong: 501 Hong Kong Industrial Technology Centre,
72 Tat Chee Avenue, Kowloon Tong, HONG KONG,
Tel. (852)2319 7888, Fax. (852)2319 7700
Colombia: IPRELENSO LTDA, Carrera 21 No. 56-17,
77621 BOGOTA, Tel. (571)249 7624/(571)217 4609,
Fax. (571)217 4549
Denmark: Prags Boulevard 80, PB 1919, DK-2300
COPENHAGEN S, Tel. (45)32 88 26 36, Fax. (45)31 57 19 49
Finland: Sinikalliontie 3, FIN-02630 ESPOO,
Tel. (358)0-615 800, Fax. (358)0-61580 920
France: 4 Rue du Port-aux-Vins, BP317,
92156 SURESNES Cedex,
Tel. (01)4099 6161, Fax. (01)4099 6427
Germany: P.O. Box 10 51 40, 20035 HAMBURG,
Tel. (040)23 53 60, Fax. (040)23 53 63 00
Greece: No. 15, 25th March Street, GR 17778 TAVROS,
Tel. (01)4894 339/4894 911, Fax. (01)4814 240
India: Philips INDIA Ltd, Shivsagar Estate, A Block,
Dr. Annie Besant Rd. Worli, Bombay 400 018
Tel. (022)4938 541, Fax. (022)4938 722
Indonesia: Philips House, Jalan H.R. Rasuna Said Kav. 3-4,
P.O. Box 4252, JAKARTA 12950,
Tel. (021)5201 122, Fax. (021)5205 189
Ireland: Newstead, Clonskeagh, DUBLIN 14,
Tel. (01)7640 000, Fax. (01)7640 200
Italy: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS S.r.l.,
Piazza IV Novembre 3, 20124 MILANO,
Tel. (0039)2 6752 2531, Fax. (0039)2 6752 2557
Japan: Philips Bldg 13-37, Kohnan 2-chome, Minato-ku, TOKYO 108,
Tel. (03)3740 5130, Fax. (03)3740 5077
Korea: Philips House, 260-199 Itaewon-dong,
Yongsan-ku, SEOUL, Tel. (02)709-1412, Fax. (02)709-1415
Malaysia: No. 76 Jalan Universiti, 46200 PETALING JAYA,
SELANGOR, Tel. (03)750 5214, Fax. (03)757 4880
Mexico: 5900 Gateway East, Suite 200, EL PASO, TX 79905,
Tel. 9-5(800)234-7381, Fax. (708)296-8556
Netherlands: Postbus 90050, 5600 PB EINDHOVEN, Bldg. VB,
Tel. (040)2783749, Fax. (040)2788399
New Zealand: 2 Wagener Place, C.P.O. Box 1041, AUCKLAND,
Tel. (09)849-4160, Fax. (09)849-7811
Norway: Box 1, Manglerud 0612, OSLO,
Tel. (022)74 8000, Fax. (022)74 8341
Pakistan: Philips Electrical Industries of Pakistan Ltd.,
Exchange Bldg. ST-2/A, Block 9, KDA Scheme 5, Clifton,
KARACHI 75600, Tel. (021)587 4641-49,
Fax. (021)577035/5874546
Philippines: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS PHILIPPINES Inc.,
106 Valero St. Salcedo Village, P.O. Box 2108 MCC, MAKATI,
Metro MANILA, Tel. (63) 2 816 6380, Fax. (63) 2 817 3474
Portugal: PHILIPS PORTUGUESA, S.A.,
Rua dr. António Loureiro Borges 5, Arquiparque - Miraflores,
Apartado 300, 2795 LINDA-A-VELHA,
Tel. (01)4163160/4163333, Fax. (01)4163174/4163366
Singapore: Lorong 1, Toa Payoh, SINGAPORE 1231,
Tel. (65)350 2000, Fax. (65)251 6500
South Africa: S.A. PHILIPS Pty Ltd.,
195-215 Main Road Martindale, 2092 JOHANNESBURG,
P.O. Box 7430, Johannesburg 2000,
Tel. (011)470-5911, Fax. (011)470-5494
Spain: Balmes 22, 08007 BARCELONA,
Tel. (03)301 6312, Fax. (03)301 42 43
Sweden: Kottbygatan 7, Akalla. S-164 85 STOCKHOLM,
Tel. (0)8-632 2000, Fax. (0)8-632 2745
Switzerland: Allmendstrasse 140, CH-8027 ZÜRICH,
Tel. (01)488 2211, Fax. (01)481 77 30
Taiwan: PHILIPS TAIWAN Ltd., 23-30F, 66, Chung Hsiao West
Road, Sec. 1. Taipeh, Taiwan ROC, P.O. Box 22978,
TAIPEI 100, Tel. (886) 2 382 4443, Fax. (886) 2 382 4444
Thailand: PHILIPS ELECTRONICS (THAILAND) Ltd.,
209/2 Sanpavuth-Bangna Road Prakanong,
Bangkok 10260, THAILAND,
Tel. (66) 2 745-4090, Fax. (66) 2 398-0793
Turkey:Talatpasa Cad. No. 5, 80640 GÜLTEPE/ISTANBUL,
Tel. (0212)279 27 70, Fax. (0212)282 67 07
Ukraine: Philips UKRAINE, 2A Akademika Koroleva str., Office 165,
252148 KIEV, Tel.380-44-4760297, Fax. 380-44-4766991
United Kingdom: Philips Semiconductors LTD.,
276 Bath Road, Hayes, MIDDLESEX UB3 5BX,
Tel. (0181)730-5000, Fax. (0181)754-8421
United States:811 East Arques Avenue, SUNNYVALE,
CA 94088-3409, Tel. (800)234-7381, Fax. (708)296-8556
Uruguay: Coronel Mora 433, MONTEVIDEO,
Tel. (02)70-4044, Fax. (02)92 0601
Internet: http://www.semiconductors.philips.com/ps/
For all other countries apply to: Philips Semiconductors,
International Marketing and Sales, Building BE-p,
P.O. Box 218, 5600 MD EINDHOVEN, The Netherlands,
Telex 35000 phtcnl, Fax. +31-40-2724825
SCDS47 © Philips Electronics N.V. 1996
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the
prior written consent of the copyright owner.
The information presented in this document does not form part of any quotation
or contract, is believed to be accurate and reliable and may be changed without
notice. No liability will be accepted by the publisher for any consequence of its
use. Publication thereof does not convey nor imply any license under patent- or
other industrial or intellectual property rights.
Printed in The Netherlands
537021/1100/03/pp20 Date of release: 1996 Feb 21
Document order number: 9397 750 00677
 Loading...
Loading...