Page 1

DATA SH EET
Product specification
Supersedes data of 1999 Aug 30
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
1999 Nov 11
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
TDA8060TS
Satellite ZERO-IF QPSK
down-converter
Page 2
1999 Nov 11 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Satellite ZERO-IF QPSK down-converter TDA8060TS
FEATURES
• Direct conversion QPSK demodulation (Zero IF)
• 920 to 2200 MHz range
• On-chip loop-controlled 0 or 90° phase shifter
• Variable gain on RF input
• 60 MHz, at −1 dB, bandwidth for baseband
I and Q amplifiers
• Local oscillator output to PLL satellite or terrestrial
• 5 V supply voltage.
APPLICATIONS
• Direct Broadcasting Satellite (DBS) QPSK
demodulation
• Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) QPSK demodulation.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The direct conversion QPSKdemodulator is the front-end
receiver dedicated to digital TV broadcasting, satisfying
both DVB and DBS TV standards.
The 920 to 2200 MHz wide range oscillator covers
American, European and Asian satellite bands as well as
the future SMA-TV US standard.
Accurate QPSK demodulation is ensured by the on-chip
loop-controlled phase shifter. The Zero-IF concept
discardstraditionalIFfilteringandintermediateconversion
techniques. It also simplifies the signal path.
The baseband I and Q signal bandwidth only depends, to
a certain extent, on the external filter used in the
application.
Optimum signal level is guaranteed by a gain-controlled
amplifier at the RF input. The GAIN pin sets the gain for
both I and Q channels, providing a 30 dB range.
The chip also offers a selectable internal LO prescaler
(divide-by-2) and buffer that has been designed to be
compatible with the input of a terrestrial or satellite
frequency synthesizer.
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
ORDERING INFORMATION
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
CC
supply voltage 4.75 5.00 5.25 V
∆Φ quadrature error −−3 deg
f
osc
oscillator frequency 920 − 2200 MHz
V
o(p-p)
output voltage (peak-to-peak value) − 0.75 − V
T
amb
ambient temperature −20 − +85 °C
TYPE
NUMBER
PACKAGE
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
TDA8060TS SSOP24 plastic shrink small outline package; 24 leads; body width 5.3 mm SOT340-1
Page 3
1999 Nov 11 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Satellite ZERO-IF QPSK down-converter TDA8060TS
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
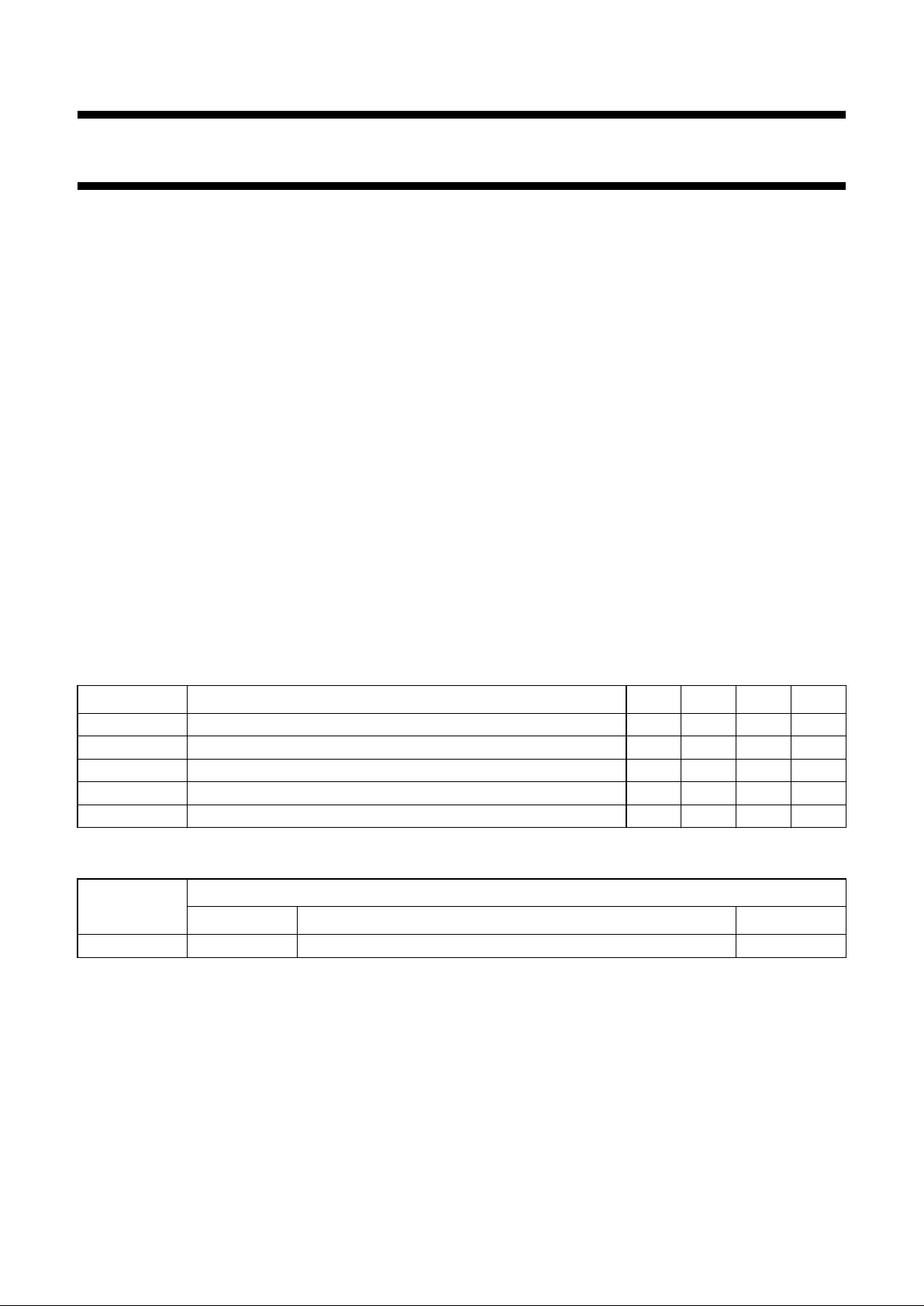
BLOCK DIAGRAM
Fig.1 Block diagram.
handbook, full pagewidth
MGM318
ASYM AMP
AMP
SYM
LNA
BASEBAND
STAGE
I CONVERTER
×
100 MHz
ASYMSYM
Q CONVERTER
×
100 MHz
CONVERSION STAGE
RFA 8
IBBOUT23
QBBOUT14
V
CC(BB1)
1
BBGND13
V
CC(BB2)
12
BBGND210
RFB 7
COMGAIN 4
PEN 5
QUADRATURE
GENERATOR
STABILIZED LO
PLL AND
AMPLIFIER
OSCILLATORDIVIDE-BY-2
TDA8060TS
11
QOUT
20
LOOUT21LOOUTC18TKA17TKB
V
CC(RF)
6
RFGND
9
V
CC(LO1)
16
LOGND1
15
V
CC(LO2)
19
LOGND2
22
13
QBBIN
IOUT2IBBIN
24
LOW-PASS
FILTER
LOW-PASS
FILTER
Page 4
1999 Nov 11 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Satellite ZERO-IF QPSK down-converter TDA8060TS
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
V
CC(BB1)
1 supply voltage 1 for baseband
circuit (+5 V)
IOUT 2 ‘I’ output from demodulator
BBGND1 3 ground 1 for baseband circuit
COMGAIN 4 RF amplifier gain control input
PEN 5 prescaler enable
V
CC(RF)
6 supply voltage for RF circuit (+5 V)
RFB 7 RF signal input B
RFA 8 RF signal input A
RFGND 9 ground for RF circuit
BBGND2 10 ground 2 for baseband circuit
QOUT 11 ‘Q’ output from demodulator
V
CC(BB2)
12 supply voltage 2 for baseband
circuit (+5 V)
QBBIN 13 ‘Q’ baseband amplifier input
QBBOUT 14 ‘Q’ baseband amplifier output
LOGND1 15 ground 1 for local oscillator circuit
V
CC(LO1)
16 supply voltage 1 for local oscillator
circuit (+5 V)
TKB 17 tank circuit input B
TKA 18 tank circuit input A
V
CC(LO2)
19 supply voltage 2 for local oscillator
circuit (+5 V)
LOOUT 20 local oscillator output to
synthesizer divided or not
according to PEN voltage
LOOUTC 21
LOGND2 22 ground 2 for local oscillator circuit
IBBOUT 23 ‘I’ baseband amplifier output
IBBIN 24 ‘I’ baseband amplifier input
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
handbook, halfpage
V
CC(BB1)
IOUT
BBGND1
COMGAIN
PEN
V
CC(RF)
RFB
RFA
RFGND
BBGND2
QOUT
V
CC(BB2)
IBBIN
IBBOUT
LOGND2
LOOUTC
V
CC(LO2)
TKA
LOOUT
TKB
V
CC(LO1)
LOGND1
QBBOUT
QBBIN
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
TDA8060TS
MGM317
Page 5
1999 Nov 11 5
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Satellite ZERO-IF QPSK down-converter TDA8060TS
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134).
HANDLING
Inputs and outputs are protected against electrostatic discharge in normal handling. However, to be totally safe, it is
desirable to take normal precautions appropriate to handling MOS devices.
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
DC CHARACTERISTICS
T
amb
=25°C; VCC= 5 V; unless otherwise specified.
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
CC
supply voltage −0.3 +6.0 V
V
i(max)
maximum input voltage on all pins −0.3 V
CC
V
t
sc(max)
maximum short-circuit time − 10 s
T
amb
ambient temperature −20 +85 °C
T
stg
storage temperature −55 +150 °C
T
j
junction temperature − 150 °C
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS VALUE UNIT
R
th(j-a)
thermal resistance from junction to ambient in free air 120 K/W
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
CC
supply voltage 4.75 5.00 5.25 V
I
CC
supply current PEN = 5 V 63 73 83 mA
PEN=0V 607080mA
Conversion stage
V
I(RFA)
DC input voltage on pin RFA − 0.9 − V
V
I(RFB)
DC input voltage on pin RFB − 0.9 − V
V
O(IOUT)
DC output voltage on pin IOUT − 2.0 − V
V
O(QOUT)
DC output voltage on pin QOUT − 2.0 − V
Quadrature generator
V
O(LOOUT)
DC output voltage on pin LOOUT − 4.7 − V
V
O(LOOUTC)
DC output voltage on pin LOOUTC − 4.7 − V
Baseband stage
V
I(IBBIN)
DC input voltage on pin IBBIN − 2.5 − V
V
I(QBBIN)
DC input voltage on pin QBBIN − 2.5 − V
V
O(IBBOUT)
DC output voltage on pin IBBOUT − 2.5 − V
V
O(QBBOUT)
DC output voltage on pin QBBOUT − 2.5 − V
Page 6

1999 Nov 11 6
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Satellite ZERO-IF QPSK down-converter TDA8060TS
AC CHARACTERISTICS
T
amb
=25°C; VCC= 5 V; unless otherwise specified.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Quadrature generator
f
osc
oscillator frequency range 920 − 2200 MHz
ΦN
osc
oscillator phase noise at 10 kHz offset;
note 1
−−80 −75 dBc/Hz
∆Φ absolute quadrature error note 2 − 0 3 deg
f
LOOUT
output frequency V
PEN
=0V − f
osc
− MHz
V
PEN=VCC
−
1
⁄2f
osc
− MHz
V
o(diff)(LOOUT)
differential output voltage at pin LOOUT RL= 100 Ω
differential
−30 −22 − dBm
Z
o(diff)(LOOUT)
differential output impedance at pin LOOUT − 60 −Ω
Conversion stage
R
i(diff)
series real part of differential input
impedance at pins RFA and RFB
note 3 − 34 −Ω
L
i(diff)
series inductance of differential input
impedance at pins RFA and RFB
note 3 − 5 − nH
P
i(max)
maximum input power per channel −−22 − dBm
P
i(min)
minimum input power per channel −−52 − dBm
∆G
v/∆V(slope)
AGC slope at G
v(RF-IOUT)(min)
− 30 43 dB/V
∆G
v(I-Q)
voltage gain mismatch between I and Q −−1dB
∆t
d(g)(RF-IOUT)
group delay variation per channel (40 MHz)
from RF input to pin IOUT
− 0.5 2 ns
∆t
d(g)(RF-QOUT)
group delay variation per channel (40 MHz)
from RF input to pin QOUT
− 0.5 2 ns
t
d(g)(I-Q)(40)
group delay mismatch per channel (40 MHz)
between I and Q
− 0 0.5 ns
B
(−1dB)(RF-IOUT)
channel −1 dB bandwidth from RF input to
pin IOUT
40 50 − MHz
B
(−1dB)(RF-QOUT)
channel −1 dB bandwidth from RF input to
pin QOUT
40 50 − MHz
B
(−3dB)(RF-IOUT)
channel −3 dB bandwidth from RF input to
pin IOUT
70 80 − MHz
B
(−3dB)(RF-QOUT)
channel −3 dB bandwidth from RF input to
pin QOUT
70 80 − MHz
Z
o(IOUT)
output impedance at pin IOUT − 65 −Ω
Z
o(QOUT)
output impedance at pin QOUT − 65 −Ω
V
o(IOUT)
nominal output voltage level at pin IOUT per channel − 25 − dBmV
V
o(QOUT)
nominal output voltage level at pin QOUT per channel − 25 − dBmV
R
oL(IOUT)
resistive load at pin IOUT 400 −−Ω
R
oL(QOUT)
resistive load at pin QOUT 400 −−Ω
Page 7

1999 Nov 11 7
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Satellite ZERO-IF QPSK down-converter TDA8060TS
SYMMETRICAL RF INPUT (Fig.3)
G
v(RF-IOUT)(min)
minimum voltage gain from RF input to
pin IOUT
V
AGC
= 0.1 x VCC;
note 4
−−−1dB
G
v(RF-IOUT)(max)
maximum voltage gain from RF input to
pin IOUT
V
AGC
= 0.9 x VCC;
note 4
28 29 − dB
G
v(RF-QOUT)(min)
minimum voltage gain from RF input to
pin QOUT
V
AGC
= 0.1 x VCC;
note 4
−−−1dB
G
v(RF-QOUT)(max)
maximum voltage gain from RF input to
pin QOUT
V
AGC
= 0.9 x VCC;
note 4
28 29 − dB
IP
3i(I)
I 3rd-order interception point at RF input 1 4 − dBm
IP
2i(I)
I 2nd-order interception point at RF input 12 15 − dBm
IP
3i(Q)
Q 3rd-order interception point at RF input 1 4 − dBm
IP
2i(Q)
Q 2nd-order interception point at RF input 12 15 − dBm
F
i
noise figure at maximum gain V
AGC
= 0.9 x VCC;
Z
source
=50Ω
− 12 15 dB
ASYMMETRICAL RF INPUT (Fig.4)
G
v(RF-IOUT)(min)
minimum voltage gain from RF input to
pin IOUT
V
AGC
= 0.1 x VCC;
note 5
−−−1dB
G
v(RF-IOUT)(max)
maximum voltage gain from RF input to
pin IOUT
V
AGC
= 0.9 x VCC;
note 5
− 29 − dB
G
v(RF-QOUT)(min)
minimum voltage gain from RF input to
pin QOUT
V
AGC
= 0.1 x VCC;
note 5
−−−1dB
G
v(RF-QOUT)(max)
maximum voltage gain from RF input to
pin QOUT
V
AGC
= 0.9 x VCC;
note 5
− 29 − dB
IP
3i(I)
I 3rd-order interception point at RF input − 3 − dBm
IP
2i(I)
I 2nd-order interception point at RF input − 15 − dBm
IP
3i(Q)
Q 3rd-order interception point at RF input − 3 − dBm
IP
2i(Q)
Q 2nd-order interception point at RF input − 15 − dBm
F
i
noise figure at maximum gain V
AGC
= 0.9 x VCC;
Z
source
=50Ω
− 13 − dB
Baseband stages
Z
i
input impedance − 10 − kΩ
V
i
nominal input voltage level per channel − 25 − dBmV
NTX
i
number of channels at input − 2 −−
G
v(IBBIN-IBBOUT)
voltage gain from pin IBBIN to pin IBBOUT 19 20 22 dB
G
v(QBBIN-QBBOUT)
voltage gain from pin QBBIN to pin QBBOUT 19 20 22 dB
G
v(I-Q)
voltage gain mismatch between I and Q − 01dB
IP
3i
3rd-order interception point at IQBBIN input 54 59 − dBmV
IP
2i
2nd-order interception point at IQBBIN input 72 79 − dBmV
∆t
d(g)(40)
group delay variation in 40 MHz bandwidth − 0.5 2 ns
t
d(g)(I-Q)(40)
group delay mismatch in 40 MHz band
between I and Q
− 0.5 2 ns
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Page 8

1999 Nov 11 8
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Satellite ZERO-IF QPSK down-converter TDA8060TS
Notes
1. Measured in baseband (at pin IOUT or pin QOUT) on a carrier at 2 MHz and 25 dBmV.
2. Quadrature error with respect to 90°.
3. The differential input impedance of the IC is 34 Ω in series with the IC pins which give an inductance of 5 nH.
For optimum performance, this inductance should be cancelled by a matching network. Coupling capacitors of 1 pF
give an acceptable result.
4. Gain = V
o(dB)
− V
i(dB)
(see Fig.3). Gain for symmetrical RF input
5. Gain = V
o(dB)
− V
i(dB)
(see Fig.3). Gain for asymmetrical RF input
B
(−1dB)
channel −1 dB bandwidth 40 65 − MHz
B
(−3dB)
channel −3 dB bandwidth 70 100 − MHz
Z
o
output impedance − 50 −Ω
V
o(p-p)
nominal output voltage level − 750 − mV
R
o(L)
resistive load at output 400 −−Ω
Overall with a 100 nF capacitor instead of LP1 and LP2
t
d(g)(I-Q)(40)
group delay mismatch in 40 MHz band
between I and Q
− 0.5 2 ns
t
d(g)(I-Q)(R40)
group delay ripple in 40 MHz band for I or Q − 0.5 1 ns
G
v(I-Q)(40)
voltage gain mismatch in 40 MHz band
between I and Q
−−1dB
G
R(I-Q)(40)
voltage gain ripple in 40 MHz band for I or Q −−1dB
SYMMETRICAL RF INPUT
G
v(RF-IBBOUT)(min)
minimum voltage gain from RF input to
pin IBBOUT
V
AGC
= 0.1 x V
CC
−−19 dB
G
v(RF-IBBOUT)(max)
maximum voltage gain from RF input to
pin IBBOUT
V
AGC
= 0.9 x V
CC
48 49 − dB
G
v(RF-QBBOUT)(min)
minimum voltage gain from RF input to
pin QBBOUT
V
AGC
= 0.1 x V
CC
−−19 dB
G
v(RF-QBBOUT)(max)
maximum voltage gain from RF input to
pin QBBOUT
V
AGC
= 0.9 x V
CC
48 49 − dB
F
i
noise figure at maximum gain V
AGC
= 0.9 x VCC;
Z
source
=50Ω
− 13 16 dB
ASYMMETRICAL RF INPUT
G
v(RF-IBBOUT)(min)
minimum voltage gain from RF input to
pin IBBOUT
V
AGC
= 0.1 x V
CC
−−19 dB
G
v(RF-IBBOUT)(max)
maximum voltage gain from RF input to
pin IBBOUT
V
AGC
= 0.9 x V
CC
− 49 − dB
G
v(RF-QBBOUT)(min)
minimum voltage gain from RF input to
pin QBBOUT
V
AGC
= 0.1 x V
CC
−−19 dB
G
v(RF-QBBOUT)(max)
maximum voltage gain from RF input to
pin QBBOUT
V
AGC
= 0.9 x V
CC
− 49 − dB
F
i
noise figure at maximum gain V
AGC
= 0.9 x VCC;
Z
source
=50Ω
− 14 − dB
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Page 9

1999 Nov 11 9
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Satellite ZERO-IF QPSK down-converter TDA8060TS
Fig.3 Gain control diagram for symmetrical RF input.
handbook, full pagewidth
MGM319
RF
SOURCE
Vi (dB)
Vo (dB)
50 Ω
50 Ω
RF
SOURCE
50 Ω
50 Ω
100 Ω
1 pF
1 pF
RFA
TDA8060TS
RFB
IOUT
QOUT
high
impedance
probe
IOUT
QOUT
Fig.4 Gain control diagram for asymmetrical RF input
handbook, full pagewidth
FCE406
RF
SOURCE
Vi (dB)
50 Ω
50 Ω
RF
SOURCE
50 Ω
1.5 pF
1.5 pF
RFB
RFA
TDA8060TS
IOUT
QOUT
IOUT
QOUT
Vo (dB)
high
impedance
probe
Page 10

1999 Nov 11 10
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Satellite ZERO-IF QPSK down-converter TDA8060TS
APPLICATION INFORMATION
Closeattentionshould be paid to the design of theexternal
tank circuit of the VCO so that it covers the
920 to 2200 MHz frequency range. Both series 6 Ω
resistors kill all parasitic oscillations that could alter this
frequency range. The BB835 Siemens varicap diodes are
mentioned because they provide the highest C
max/Cmin
ratio as well as the least parasitic elements in our
frequencyrange.The U-shaped inductance can be printed
with a total length of approximately 20 mm.
Filters LP1 and LP2 are not detailed in this data sheet
because their design only depends on the global system.
As the TDA8060 has been designed to be compatible with
DVB, DSS and Asian DVB, the cut-off frequencies and the
tolerance in group delay, the orders of the filters cannot be
globally established.
Nevertheless, TDA8060 internally filters the baseband at
100 MHz and the nominal levels at inputs and outputs
mentioned in the specification table should be respected.
The input impedance of LP1 and LP2 must exceed 400 Ω
to avoid signal distortion.
The converter outputs (pin IOUT and pin QOUT) must be
AC-coupled via the low-pass filter to the baseband
amplifiers inputs (pin IBBIN and pin QBBIN). Because of
the high impedance at pin IQBBIN, a 100 nF capacitor
gives a high-pass frequency of 160 Hz.
Page 11

1999 Nov 11 11
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Satellite ZERO-IF QPSK down-converter TDA8060TS
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
pagewidth
to PLL
synthesizer IC
V
tune
from PLL synthesizer IC
100 nF
MGM320
ASYM
100 nF
1 pF
100 nF
AMP
AMP
SYM
1 pF
LNA
BASEBAND
STAGE
I CONVERTER
×
100 MHz
ASYMSYM
Q CONVERTER
×
100 MHz
CONVERSION STAGE
RFA 8
IBBOUT23
QBBOUT
to
I channel
ADC
to
Q channel
ADC
14
V
CC(BB1)
1
BBGND13
V
CC(BB2)
12
BBGND210
RFB
RF
(2)
RF
7
COMGAIN
gain
(1)
4
PEN
0 to 5 V
5
QUADRATURE
GENERATOR
STABILIZED LO
PLL AND
AMPLIFIER
OSCILLATORDIVIDE-BY-2
TDA8060TS
11
QOUT
20
LOOUT21LOOUTC18TKA17TKB
V
CC(RF)
6
RFGND
9
V
CC(LO1)
16
LOGND1
15
V
CC(LO2)
19
LOGND2
22
13
QBBIN
IOUT2IBBIN
24
6 Ω 6 Ω
20
kΩ
20
kΩ
1 pF
BB835
(2×)
LOW-PASS
FILTER
(3)
LOW-PASS
FILTER
(3)
LOW-PASS
FILTER
(3)
LOW-PASS
FILTER
(3)
Fig.5 Application diagram.
(1) Gain control voltage; minimum gain at 0.1 x VCC, maximum gain at 0.9 x VCC; 30 dB range.
(2) Differential RF input 950 to 2200 MHz; level = −22 to −52 dBm per channel.
(3) The filter input impedance is 400 Ω minimum.
Page 12

1999 Nov 11 12
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Satellite ZERO-IF QPSK down-converter TDA8060TS
PACKAGE OUTLINE
UNIT A1A2A
3
b
p
cD
(1)E(1) (1)
eHELLpQZywv θ
REFERENCES
OUTLINE
VERSION
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
ISSUE DATE
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
mm
0.21
0.05
1.80
1.65
0.38
0.25
0.20
0.09
8.4
8.0
5.4
5.2
0.65 1.25
7.9
7.6
0.9
0.7
0.8
0.4
8
0
o
o
0.13 0.10.2
DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions)
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.20 mm maximum per side are not included.
1.03
0.63
SOT340-1 MO-150AG
93-09-08
95-02-04
X
w M
θ
A
A
1
A
2
b
p
D
H
E
L
p
Q
detail X
E
Z
e
c
L
v M
A
(A )
3
A
112
24 13
0.25
y
pin 1 index
0 2.5 5 mm
scale
SSOP24: plastic shrink small outline package; 24 leads; body width 5.3 mm
SOT340-1
A
max.
2.0
Page 13

1999 Nov 11 13
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Satellite ZERO-IF QPSK down-converter TDA8060TS
SOLDERING
Introduction to soldering surface mount packages
Thistextgivesaverybriefinsight to a complex technology.
A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in
our
“Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit Packages”
(document order number 9398 652 90011).
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all surface
mount IC packages. Wave soldering is not alwayssuitable
for surface mount ICs, or for printed-circuit boards with
high population densities. In these situations reflow
soldering is often used.
Reflow soldering
Reflow soldering requires solder paste (a suspension of
fine solder particles, flux and binding agent) to be applied
tothe printed-circuit board by screen printing, stencilling or
pressure-syringe dispensing before package placement.
Several methods exist for reflowing; for example,
infrared/convection heating in a conveyor type oven.
Throughput times (preheating, soldering and cooling) vary
between 100 and 200 seconds depending on heating
method.
Typical reflow peak temperatures range from
215 to 250 °C. The top-surface temperature of the
packages should preferable be kept below 230 °C.
Wave soldering
Conventional single wave soldering is not recommended
forsurfacemountdevices(SMDs)orprinted-circuitboards
with a high component density, as solder bridging and
non-wetting can present major problems.
To overcome these problems the double-wave soldering
method was specifically developed.
If wave soldering is used the following conditions must be
observed for optimal results:
• Use a double-wave soldering method comprising a
turbulent wave with high upward pressure followed by a
smooth laminar wave.
• For packages with leads on two sides and a pitch (e):
– larger than or equal to 1.27 mm, the footprint
longitudinal axis is preferred to be parallel to the
transport direction of the printed-circuit board;
– smaller than 1.27 mm, the footprint longitudinal axis
must be parallel to the transport direction of the
printed-circuit board.
The footprint must incorporate solder thieves at the
downstream end.
• Forpackageswithleadsonfoursides,thefootprintmust
be placed at a 45° angle to the transport direction of the
printed-circuit board. The footprint must incorporate
solder thieves downstream and at the side corners.
During placement and before soldering, the package must
be fixed with a droplet of adhesive. The adhesive can be
applied by screen printing, pin transfer or syringe
dispensing. The package can be soldered after the
adhesive is cured.
Typical dwell time is 4 seconds at 250 °C.
A mildly-activated flux will eliminate the need for removal
of corrosive residues in most applications.
Manual soldering
Fix the component by first soldering two
diagonally-opposite end leads. Use a low voltage (24 V or
less) soldering iron applied to the flat part of the lead.
Contact time must be limited to 10 seconds at up to
300 °C.
When using a dedicated tool, all other leads can be
soldered in one operation within 2 to 5 seconds between
270 and 320 °C.
Page 14

1999 Nov 11 14
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Satellite ZERO-IF QPSK down-converter TDA8060TS
Suitability of surface mount IC packages for wave and reflow soldering methods
Notes
1. All surface mount (SMD) packages are moisture sensitive. Depending upon the moisture content, the maximum
temperature (with respect to time) and body size of the package, there is a risk that internal or external package
cracks may occur due to vaporization of the moisture in them (the so called popcorn effect). For details, refer to the
Drypack information in the
“Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit Packages; Section: Packing Methods”
.
2. Thesepackages are not suitable for wave soldering as a solder joint between the printed-circuit board and heatsink
(at bottom version) can not be achieved, and as solder may stick to the heatsink (on top version).
3. If wave soldering is considered, then the package must be placed at a 45° angle to the solder wave direction.
The package footprint must incorporate solder thieves downstream and at the side corners.
4. Wavesoldering is only suitable for LQFP, TQFP and QFP packages with a pitch (e) equal to or larger than 0.8 mm;
it is definitely not suitable for packages with a pitch (e) equal to or smaller than 0.65 mm.
5. Wavesoldering is only suitable for SSOP and TSSOP packages with a pitch (e) equal to or larger than 0.65 mm; it is
definitely not suitable for packages with a pitch (e) equal to or smaller than 0.5 mm.
DEFINITIONS
LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or systems where malfunction of these
products can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips customers using or selling these products for
use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips for any damages resulting from such
improper use or sale.
PACKAGE
SOLDERING METHOD
WAVE REFLOW
(1)
BGA, SQFP not suitable suitable
HLQFP, HSQFP, HSOP, HTSSOP, SMS not suitable
(2)
suitable
PLCC
(3)
, SO, SOJ suitable suitable
LQFP, QFP, TQFP not recommended
(3)(4)
suitable
SSOP, TSSOP, VSO not recommended
(5)
suitable
Data sheet status
Objective specification This data sheet contains target or goal specifications for product development.
Preliminary specification This data sheet contains preliminary data; supplementary data may be published later.
Product specification This data sheet contains final product specifications.
Limiting values
Limiting values given are in accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134). Stress above one or
more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation
of the device at these or at any other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the specification
is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Application information
Where application information is given, it is advisory and does not form part of the specification.
Page 15

1999 Nov 11 15
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Satellite ZERO-IF QPSK down-converter TDA8060TS
NOTES
Page 16

© Philips Electronics N.V. SCA
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior written consent of the copyright owner.
The information presented in this document does not form part of any quotation or contract, is believed to be accurate and reliable and may be changed
without notice. No liability will be accepted by the publisher for any consequence of its use. Publication thereof does not convey nor imply any license
under patent- or other industrial or intellectual property rights.
Internet: http://www.semiconductors.philips.com
1999
68
Philips Semiconductors – a w orldwide compan y
For all other countries apply to: Philips Semiconductors,
International Marketing & Sales Communications, Building BE-p, P.O. Box 218,
5600 MD EINDHOVEN, The Netherlands, Fax. +31 40 27 24825
Argentina: see South America
Australia: 3 Figtree Drive, HOMEBUSH, NSW 2140,
Tel. +61 2 9704 8141, Fax. +61 2 9704 8139
Austria: Computerstr. 6, A-1101 WIEN, P.O. Box 213,
Tel. +43 1 60 101 1248, Fax. +43 1 60 101 1210
Belarus: Hotel Minsk Business Center, Bld. 3, r. 1211, Volodarski Str. 6,
220050 MINSK, Tel. +375 172 20 0733, Fax. +375 172 20 0773
Belgium: see The Netherlands
Brazil: see South America
Bulgaria: Philips Bulgaria Ltd., Energoproject, 15th floor,
51 James Bourchier Blvd., 1407 SOFIA,
Tel. +359 2 68 9211, Fax. +359 2 68 9102
Canada: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS/COMPONENTS,
Tel. +1 800 234 7381, Fax. +1 800 943 0087
China/Hong Kong: 501 Hong Kong Industrial Technology Centre,
72 Tat Chee Avenue, Kowloon Tong, HONG KONG,
Tel. +852 2319 7888, Fax. +852 2319 7700
Colombia: see South America
Czech Republic: see Austria
Denmark: Sydhavnsgade 23, 1780 COPENHAGEN V,
Tel. +45 33 29 3333, Fax. +45 33 29 3905
Finland: Sinikalliontie 3, FIN-02630 ESPOO,
Tel. +358 9 615 800, Fax. +358 9 6158 0920
France: 51 Rue Carnot, BP317, 92156 SURESNES Cedex,
Tel. +33 1 4099 6161, Fax. +33 1 4099 6427
Germany: Hammerbrookstraße 69, D-20097 HAMBURG,
Tel. +49 40 2353 60, Fax. +49 40 2353 6300
Hungary: see Austria
India: Philips INDIA Ltd, Band Box Building, 2nd floor,
254-D, Dr. Annie Besant Road, Worli, MUMBAI 400 025,
Tel. +91 22 493 8541, Fax. +91 22 493 0966
Indonesia: PT Philips DevelopmentCorporation, SemiconductorsDivision,
Gedung Philips, Jl. Buncit Raya Kav.99-100, JAKARTA 12510,
Tel. +62 21 794 0040 ext. 2501, Fax. +62 21 794 0080
Ireland: Newstead, Clonskeagh, DUBLIN 14,
Tel. +353 1 7640 000, Fax. +353 1 7640 200
Israel: RAPAC Electronics, 7 Kehilat Saloniki St, PO Box 18053,
TEL AVIV 61180, Tel. +972 3 645 0444, Fax. +972 3 649 1007
Italy: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS,Via Casati, 23 - 20052 MONZA(MI),
Tel. +39 039 203 6838, Fax +39 039 203 6800
Japan: Philips Bldg 13-37, Kohnan 2-chome, Minato-ku,
TOKYO 108-8507, Tel. +81 3 3740 5130, Fax. +81 3 3740 5057
Korea: Philips House, 260-199 Itaewon-dong, Yongsan-ku, SEOUL,
Tel. +82 2 709 1412, Fax. +82 2 709 1415
Malaysia: No. 76 Jalan Universiti, 46200 PETALING JAYA, SELANGOR,
Tel. +60 3 750 5214, Fax. +60 3 757 4880
Mexico: 5900 Gateway East, Suite 200, EL PASO, TEXAS 79905,
Tel. +9-5 800 234 7381, Fax +9-5 800 943 0087
Middle East: see Italy
Netherlands: Postbus 90050, 5600 PB EINDHOVEN, Bldg. VB,
Tel. +31 40 27 82785, Fax. +31 40 27 88399
New Zealand: 2 Wagener Place, C.P.O. Box 1041, AUCKLAND,
Tel. +64 9 849 4160, Fax. +64 9 849 7811
Norway: Box 1, Manglerud 0612, OSLO,
Tel. +47 22 74 8000, Fax. +47 22 74 8341
Pakistan: see Singapore
Philippines: Philips Semiconductors Philippines Inc.,
106 Valero St. Salcedo Village, P.O. Box 2108 MCC, MAKATI,
Metro MANILA, Tel. +63 2 816 6380, Fax. +63 2 817 3474
Poland: Al.Jerozolimskie 195 B, 02-222 WARSAW,
Tel. +48 22 5710 000, Fax. +48 22 5710 001
Portugal: see Spain
Romania: see Italy
Russia: Philips Russia, Ul. Usatcheva 35A, 119048 MOSCOW,
Tel. +7 095 755 6918, Fax. +7 095 755 6919
Singapore: Lorong 1, Toa Payoh, SINGAPORE 319762,
Tel. +65 350 2538, Fax. +65 251 6500
Slovakia: see Austria
Slovenia: see Italy
South Africa: S.A. PHILIPS Pty Ltd., 195-215 Main Road Martindale,
2092 JOHANNESBURG, P.O. Box 58088 Newville 2114,
Tel. +27 11 471 5401, Fax. +27 11 471 5398
South America: Al. Vicente Pinzon, 173, 6th floor,
04547-130 SÃO PAULO, SP, Brazil,
Tel. +55 11 821 2333, Fax. +55 11 821 2382
Spain: Balmes 22, 08007 BARCELONA,
Tel. +34 93 301 6312, Fax. +34 93 301 4107
Sweden: Kottbygatan 7, Akalla, S-16485 STOCKHOLM,
Tel. +46 8 5985 2000, Fax. +46 8 5985 2745
Switzerland: Allmendstrasse 140, CH-8027 ZÜRICH,
Tel. +41 1 488 2741 Fax. +41 1 488 3263
Taiwan: Philips Semiconductors, 6F, No. 96, Chien Kuo N. Rd., Sec. 1,
TAIPEI, Taiwan Tel. +886 2 2134 2886, Fax. +886 2 2134 2874
Thailand: PHILIPS ELECTRONICS (THAILAND) Ltd.,
209/2 Sanpavuth-Bangna Road Prakanong, BANGKOK 10260,
Tel. +66 2 745 4090, Fax. +66 2 398 0793
Turkey: Yukari Dudullu, Org. San. Blg., 2.Cad. Nr. 28 81260 Umraniye,
ISTANBUL, Tel. +90 216 522 1500, Fax. +90 216 522 1813
Ukraine: PHILIPS UKRAINE, 4 Patrice Lumumba str., Building B, Floor 7,
252042 KIEV, Tel. +380 44 264 2776, Fax. +380 44 268 0461
United Kingdom: Philips Semiconductors Ltd., 276 Bath Road, Hayes,
MIDDLESEX UB3 5BX, Tel. +44 208 730 5000, Fax. +44 208 754 8421
United States: 811 East Arques Avenue, SUNNYVALE, CA 94088-3409,
Tel. +1 800 234 7381, Fax. +1 800 943 0087
Uruguay: see South America
Vietnam: see Singapore
Yugoslavia: PHILIPS, Trg N. Pasica 5/v, 11000 BEOGRAD,
Tel. +381 11 62 5344, Fax.+381 11 63 5777
Printed in The Netherlands 545004/25/04/pp16 Date of release: 1999 Nov 11 Document order number: 9397 750 06554
 Loading...
Loading...